Если вы забыли пароль root для базы данных MySQL или хотите его поменять в целях безопасности, нужно выполнить сброс пароля. В статье расскажем, как это сделать с помощью командной строки Windows.
1.Остановите сервер MySQL
- Проверьте, вошли ли вы в систему как администратор.
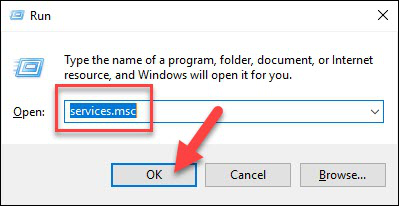
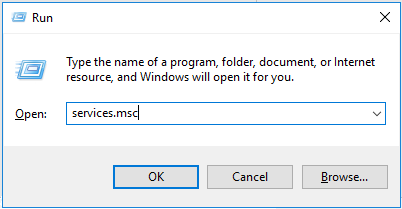
- Нажмите Win + R. Когда откроется окно «Выполнить», введите:
services.msc
- Нажмите ОК.
- В списке служб найдите MySQL. Кликните правой кнопкой мыши по ней, после чего левой кликните Stop.
2. Измените пароль в текстовом редакторе
- В меню найдите «Блокнот», либо используйте путь: Меню > Стандартные Windows > Блокнот.
- Создайте новый текстовый документ с помощью команды пароля
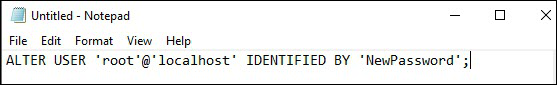
- В текстовом редакторе введите строку:
ALTER USER ‘root’@’localhost’, IDENTIFIED BY ‘NewPassword’;
- Проверьте, на месте ли кавычки и точка с запятой. Замените NewPassword своим новым паролем. «Файл» > «Сохранить как», чтобы сохранить файл в корень жесткого диска (C:). Придумайте осмысленное имя файлу.
Команда localhost изменит пароль в вашей локальной системе. Если вы пытаетесь изменить пароль по сети, замените текущее имя хоста на localhost.
3. Запустите cmd
- Откройте командную строку и нажмите Ctrl+Shift+Esc.
- В меню выберите «Файл» > «Запустить новую задачу».
- Введите cmd.exe и установите флажок для запуска от имени администратора.
- Нажмите ОК.
Бесплатный тестовый доступ к облаку на 30 днейПолучить
4. Перезапустите сервер MySQL с обновлённым файлом конфигурации.
Чтобы перейти в каталог MySQL используйте командную строку:
cd «C:Program FilesMySQLMySQL Server 8.0bin»
mysqld —init-file=C:\ИМЯ_ФАЙЛА.txt
Вместо ИМЯ_ФАЙЛА вы вводите своё название, которое использовали в пункте 2.
5. Теперь можете зайти на свой сервер MySQL как root, введя новый пароль.
- Повторите вход с новым паролем, чтобы убедиться, что всё работает. Если у вас есть уникальные параметры конфигурации (например, запуск MySQL с параметром -defaults-file ), делайте всё, что нужно.
- После запуска MySQL и подтверждения смены пароля удалите файл C:ИМЯ_ФАЙЛА.txt .
Вот и всё, вы благополучно сбросили пароль root для базы данных MySQL.
Если у вас Linux, то смотрите статью «Как сбросить пароль root для MySQL или MariaDB».
Пароль пользователя root спрашивается во время установки СУБД. Если установка делалась вручную, то есть без инстолятора, как это описано, например, в этой статье, то пароль может быть не установлен вовсе.
Если вы используете какие-то готовые сборки, которые включают в себя MySQL/MariaDB, то обратитесь за паролем на официальные сайты этих сборок. Также попробуйте такие учётные данные:
- Пользователь: root
- Пароль: root
Если вы действительно забыли пароль MySQL/MariaDB и вам нужно сбросить пароль root в MySQL на Windows, то данная статья расскажет, как это сделать.
Шаг 1 — Определяем версию системы управления базой данных
Найдите, в какой папке у вас расположен файл mysqld.exe. При установке по данной инструкции, этот файл расположен в папке C:Serverbinmysql-8.0bin.
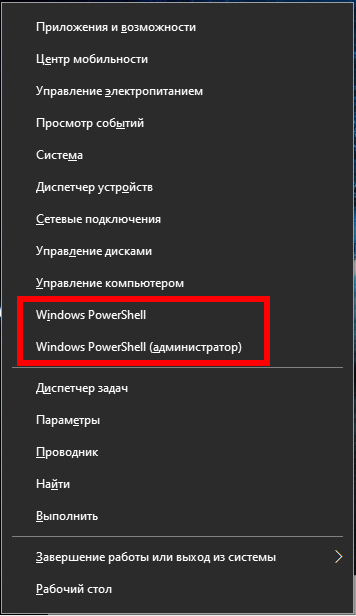
Откройте командную строку. Нам понадобятся права администратора, поэтому делаем следующее: нажмите Win+x и там выберите Windows PowerShell (администратор):
Теперь перейдите в командной строке в директорию с файлом mysqld.exe, для этого используйте команду вида:
cd путьдопапки
Например, у меня это папка C:Serverbinmysql-8.0bin, тогда команда такая:
cd C:Serverbinmysql-8.0bin
Нужно определить версию MySQL/MariaDB, для этого выполните команду:
.mysql --version
Пример вывода:
C:Serverbinmysql-8.0binmysqld.exe Ver 8.0.19 for Win64 on x86_64 (MySQL Community Server - GPL)
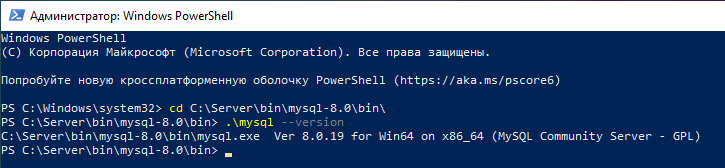
Шаг 2 — Остановка сервера базы данных
Для изменения пароля root вы должны заранее отключить сервер базы данных. Для MySQL и MariaDB вы можете сделать это командой:
net stop mysql
После того, как сервер остановлен, вы вручную получите к нему доступ для сброса пароля рута.
Шаг 3 — Перезапуск сервера базы данных без проверки разрешений
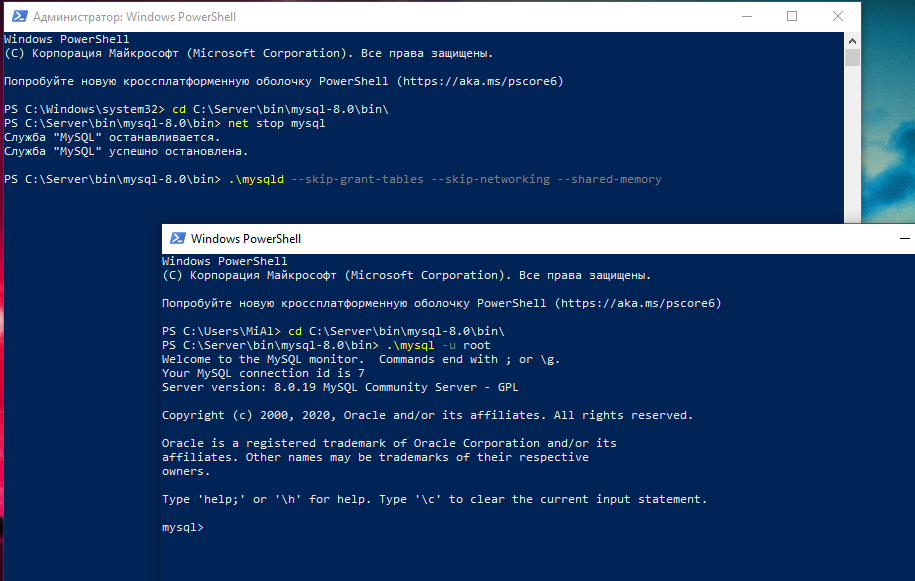
Если вы запускаете MySQL и MariaDB без загрузки информации о привилегиях пользователя, она позволит вам без ввода пароля получить доступ к командной строке базы данных с привилегиями рута. Это позволит вам получить доступ к базе данных без знания парольной фразы. Чтобы это сделать, вам нужно не дать базе данных загрузить таблицы привилегий, которые содержат информацию о привилегиях пользователя. Поскольку это несёт риск безопасности, вы также должны избежать сетевой активности, чтобы не допустить подключения других клиентов.
Запустите базу данных без загрузки таблиц привилегий и без доступа к сети:
.mysqld --skip-grant-tables --skip-networking --shared-memory
Программа НЕ должна завершить работу, то есть теперь в это окно командной строки ничего нельзя ввести.
Шаг 4 — Смена пароля рута
Теперь вы можете подключиться к базе данных как пользователь рут, у которого не спросят пароль.
Открываем новое окно командной строки, можно без прав администратора.
Опять переходим в нужную папку
cd C:Serverbinmysql-8.0bin
И подключаемся к серверу MySQL/MariaDB
.mysql -u root
Вы сразу же увидите приглашение оболочки базы данных. Приглашение командной строки MySQL:
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or g. Your MySQL connection id is 8 Server version: 8.0.19 MySQL Community Server - GPL Copyright (c) 2000, 2020, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective owners. Type 'help;' or 'h' for help. Type 'c' to clear the current input statement.
Теперь, когда у вас имеется рут доступ, вы можете изменить пароль рута.
Простым способом смены пароля рута для современных версий MySQL является использование запроса ALTER USER. Тем не менее эта команда не будет работать прямо сейчас, поскольку таблицы привилегий не загружены. Давайте скажем серверу баз данных перегрузить таблицы привилегий введя команду:
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
Теперь действительно мы можем поменять пароль рута.
Для MySQL 5.7.6 и новее, а также для MariaDB 10.1.20 и новее используйте следующую команду:
ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'новый_пароль';
Для MySQL 5.7.5 и старее, а также для MariaDB 10.1.20 и старее используйте:
SET PASSWORD FOR 'root'@'localhost' = PASSWORD('новый_пароль');
Не забудьте поменять новый_пароль на выбранный вами новый пароль.
Примечание: если команда ALTER USER не работает, то это обычно является признаком более серьёзной проблемы. Тем не менее вместо этой вы можете попробовать UPDATE … SET для сброса root пароля:
UPDATE mysql.user SET authentication_string = PASSWORD('новый_пароль') WHERE User = 'root' AND Host = 'localhost';
После этого не забудьте перегрузить таблицы привилегий:
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
В любом случае вы должны видеть подтверждение, что команда успешно выполнена. Вывод:
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec)
Выходим из сессии:
exit;
Пароль изменён, вы можете остановить запущенный вручную экземпляр сервера базы данных и перезапустить его как это было раньше.
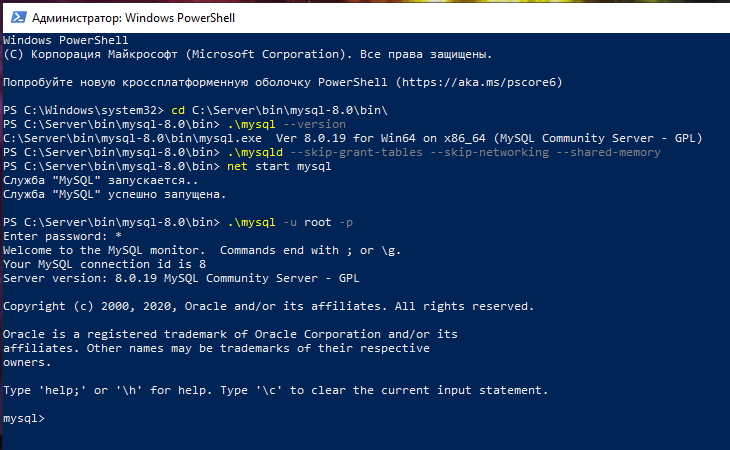
Шаг 5 — Обычный перезапуск сервера базы данных
Для начала, остановите экземпляр сервера базы данных, который вы запустили вручную на Шаге 3. Для этого перейдите в окно с запущенной mysqld и нажмите Ctrl+c.
Затем перезапустите сервис обычным образом:
net start mysql
Теперь вы можете подтвердить, что новый пароль работает, запустите:
.mysql -u root -p
Эта команда должна вызвать приглашение в который нужно ввести новый пароль. Введите его, вы должны получить доступ к интерфейсу командной строки базы данных, как это обычно и происходит.
Заключение
Теперь вы восстановили административный доступ к серверу MySQL или MariaDB. Убедитесь, что новый пароль рута, который вы выбрали, безопасный и храните его в надёжном месте.
Ошибка «—shared-memory, or —named-pipe should be configured on NT OS»
Если при запуске mysqld вы столкнулись со следующей ошибкой:
[ERROR] [MY-010131] [Server] TCP/IP, --shared-memory, or --named-pipe should be configured on NT OS
то вам необходимо к команде запуска mysqld добавить флаг —shared-memory.
Связанные статьи:
- MariaDB для Windows (100%)
- Как обновить MySQL (100%)
- Как обновить MariaDB в Windows (100%)
- Как сделать резервную копию баз данных MySQL (MariaDB) в Windows без phpMyAdmin (100%)
- Как в phpMyAdmin поменять настройки экспорта по умолчанию (100%)
- Как исправить «Configuration File (php.ini) Path» no value (RANDOM — 50%)
Introduction
MySQL is a popular database management system for web application software. Like many web services, MySQL has an administrator-level or root password. The root password allows a user to perform all top-level functions in the database.
If you’ve never set a root password on your MySQL database, you should be able to connect to it. However, this is not a good security practice as anyone can access your database.
If your database has a root password, but you lost track of it, this guide will help you reset a MySQL Root password on Linux and Windows.
Prerequisites
- An existing MySQL database
- Access to a Linux or Windows server running MySQL
- Administrator privileges on the computer that hosts the MySQL database
- A text editor. Notepad is included by default in Window. Vim is installed by default in Linux.
- Access to a command-line interface (or terminal)
Step 1: Log in as the MySQL User
When you boot into your Linux installation, make sure you’re logged in as the same user that normally runs MySQL. Although you can log in as root, once you start the MySQL server, make sure you start it with the --user=mysql option.
Otherwise, the system may create files owned by the root user, which can cause problems.
Step 2: Find the .pid File for the MySQL Service
The next step is to find the .pid file for the MySQL service.
Most systems store them in /var/lib/mysql/, /var/run/mysqld/, or /usr/local/mysql/data/ path. The filename usually starts with mysqld (or your system’s hostname) and ends with the .pid extension.
Step 3: Kill the mysqld Process
Before you create a new root password, stop the MySQL server. To kill the mysqld process, open a command line, and run the following:
kill `cat /mysql-data-directory/host_name.pid`Replace mysql-data-directory/host_name.pid with the filename you found in the previous step. Ensure to specify the whole path to the file. Also, make sure to use the back-tick key (usually above the tab key) and not a single-quote mark in the beginning of the command.
Step 4: Create the Password File
1. Open your favorite text editor. In this example, we use vim:
sudo vim2. Next, add the following line in the file:
ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'NewPassword';
Bear in mind to include the single-quote marks and the semicolon. Replace NewPassword with the password you want to use. Finally, make sure to use a strong secure password, like these examples.
The command will work for the machine you’re currently using. If you’re connecting to a different system, replace localhost with the appropriate hostname.
3. Save the file to home/me/mysql-init.
Step 5: Restart the MySQL Server and Apply the New Password
To apply the changes to the password, restart the MySQL server by running the following command in the terminal:
mysqld --init-file=/home/me/mysql-init &This launches MySQL, and apply the text-file password change. Depending on how you start your server, you may need to add other options (such as --defaults-file before the init command.)
Step 6: Cleaning Up
Lastly, log into your MySQL server using the root account, and verify the new password works. Then, delete the file you created in Step 4.
How to Reset MySQL Root Password in Windows
Step 1: Stop the MySQL server
1. Begin by checking if you’re logged in as an administrator.
2. Press Win+R (hold the Windows/Super key, and press “r”.) Once the “Run” box appears type:
services.msc3. Click OK.
4. Scroll down the list of services to find the MySQL service. Right-click that entry, then left-click Stop.
Step 2: Launch a Text Editor
Click on the menu and search for Notepad.
Alternatively, you can use the path: menu > Windows Accessories > Notepad.
Step 3: Create a New Text File with the Password Command
1. Enter the following line into the text editor:
ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'NewPassword';Make sure you keep the quote marks and semicolon. Replace NewPassword with the password of your choice.
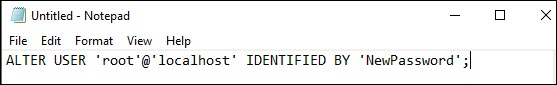
2. Use the File > Save As menu to save the file to the root of your hard drive (C: ). Choose a filename, such as mysql-init.txt.
Consequently, the localhost command makes the password change on your local system. If you’re changing the password on a system over the network, substitute the hostname for localhost.
Step 4: Open a Command Prompt
1. Press Ctrl+Shift+Esc.
2. Then, click on the File menu > Run new task.
3. Type cmd.exe, and check the box to run as administrator.
4. Click OK.
Step 5: Restart the MySQL Server with Your New Config File
1. Navigate to the MySQL directory using the command prompt:
cd "C:Program FilesMySQLMySQL Server 8.0bin"2. Then, enter the following:
mysqld --init-file=C:\mysql-init.txtNote that there are two slashes after the C: prompt.
Also, if you chose a different filename in Step 2, use that name after the double slash.
Step 6: Clean up
Now, you can log into your MySQL server as root using the new password.
Double-check to make sure it works. If you have unique configuration options (such as launching MySQL with a --defaults-file option), go ahead and do so.
Once MySQL launches, and you’ve confirmed the password change, delete the C:mysql-init.txt file.
Conclusion
After reading this guide, you should be ready to reset the root password on MySQL in Linux and Windows. Granted, it is not too challenging, yet it is a secure way to change a sensitive password.
Если Вы только установили службу Mysql сервера то вам просто необходимо сменить пароль так как он вообще не задан. Открываем консоль (пуск>выполнить>cmd) и сразу вводим:
mysqladmin -u root password ‘newpassword’
где newpassword – новый пароль
Если же у Вас уже существует пароль то сменить его можно командой
mysqladmin -u root -pcurrentpassword password ‘newpassword’
где currentpassword – старый пароль,
newpassword – новый пароль
более сложный метод без команды mysqladmin (может и не стоило это писать но для информации пригодится)
установка пароля:
mysql -u root
mysql> SET PASSWORD FOR ‘root’@’localhost’ = PASSWORD(‘newpassword’);
смена пароля:
mysql -u root
mysql> use mysql;
mysql> UPDATE user SET Password = PASSWORD(‘newpassword’) WHERE User = ‘root’;
mysql> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
А как сменить пароль если его не помнит никто?
для особо одаренных (у кого в голове много паролей или кто их не запоминает )
пишу по шагам
1) нужно остановить службу mysql сервера в большинстве случаев service mysqld stop или service mysql stop
2) выполнить команду
mysqld_safe –skip-grant-tables
3) после успешного старта mysqld
mysql –user=root mysql
там вводим команды
update user set Password=PASSWORD(‘new-password’) where user=’root’;
flush privileges;
exit;
4) перегружаем mysqld (обычно service mysqld restart)
I have a little problem with my phpmyadmin, in fact I accidentally delete multiple user accounts.
Since it is impossible to connect without the error:
# 1045 - Access denied for user 'root' @ 'localhost' (using password: NO)
I have search a little on the net before, and even the technic:
UPDATE mysql.user SET Password = PASSWORD ('') WHERE User = 'root';
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
does not work, or I didn’t understood how it worked.
I’m on FreeBSD 8.1, my version of PhpMyadmin is 2.11.
Thank you in advance for your answers.
OMG Ponies
321k79 gold badges517 silver badges499 bronze badges
asked Nov 23, 2010 at 16:11
I summarised my solution here: http://snippets.dzone.com/posts/show/13267
sudo stop mysql
sudo mysqld --skip-grant-tables --skip-networking
mysql
mysql> update mysql.user set password = password('your_new_password') where user = 'root';
mysql> flush privileges;
mysql> exit;
sudo mysqladmin shutdown
sudo start mysql
answered Jun 19, 2011 at 10:57
AlexeyAlexey
9,0774 gold badges62 silver badges76 bronze badges
2
For mysql 5.7.16 or later I found this (from mysql.com) to be the working solution. Below are some points which are different compared to previous older versions
1) I used the below command to run mysql in safe mode as per some other references which actually worked fine for me (mysql 5.7.16 ubuntu 16.04).
mysqld_safe --skip-grant-tables --skip-networking
2) The below update stmt is NOT working for later version (ie. 5.7 and above)
-- NOT Working for 5.7 and later
UPDATE mysql.user SET Password = PASSWORD ('') WHERE User = 'root';
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
INSTEAD use below for 5.7.6 and later
UPDATE mysql.user
SET authentication_string = PASSWORD('MyNewPass'), password_expired = 'N'
WHERE User = 'root' AND Host = 'localhost';
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
OR user below for 5.7.5 or earlier versions.
SET PASSWORD FOR 'root'@'localhost' = PASSWORD('MyNewPass');
answered Oct 29, 2016 at 21:40
user1941390user1941390
5106 silver badges17 bronze badges
1
I am Using MySQL Server 8 and this is how I solved this problem.
create a file and name it accordingly. I’ve named it as reset.txt. put below content in the file but change MyNewPass. This will be your new SQL password
ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'MyNewPass';
Stop my SQL server (Go to services and search MYSQL and right-click on it and stop )
Now open a cmd in your bin folder of My SQLserver directory. in my case it’s
C:Program FilesMySQLMySQL Server 8.0bin
execute the following command.
mysqld.exe --defaults-file="C:ProgramDataMySQLMySQL Server 8.0my.ini" --init-file="C:reset.txt'
NOTE: my reset.txt file is in the c drive. Give the correct path. Check my.ini file is in the directory. In my case, it is in
C:ProgramDataMySQLMySQL Server 8.0my.ini
Finally, restart the SQL Server. Check with your new password.
answered Feb 10, 2020 at 11:54
3
Please follow the instruction from the below link to reset your root password.You have to do it from outside mysql.
Resetting MySql Password
Forgetting your MySQL password can be a real headache for you.Here are some easy steps that you can follow to recover MySql password under Windows
Stop MySql
You have to stop MySql service before you proceed.In Windows environment, go to ‘Task Manager’ and Under ‘Service’ tab find MySQL and stop it.
Write Sql to change your password
All you need to do is to create a text file and put the below two lines into that. UPDATE mysql.user SET Password=PASSWORD(‘MyNewPass’) WHERE User=’root’; FLUSH PRIVILEGES; Save it under C: drive and give it a name ‘mysql-init.txt’
Time to restart MySQL by your own.
Now it’s time to restart your MySQl which you stopped in before but this time from command line. C:> C:mysqlbinmysqld-nt —init-file=C:mysql-init.txt
Finishing up!
Now you can log in with your new password. When you finish remove the file that you created in the previous stage.
Also there is a link (http://kaziprogrammingblog.osinweb.com/article/showarticle/Resetting-MySql-Password) where I have explained the same thing.
Hope this will help..:)
answered Nov 4, 2013 at 11:39
ktakta
19k7 gold badges65 silver badges46 bronze badges
Answer for XAMPP on Windows:
- Edit C:xamppmysqlbinmy.ini and insert skip-grant-tables below [mysqld]
- Restart MySQL from Control Panel interface
- In the phpMyAdmin window, select SQL tab from the top panel. This will open the SQL tab where we can run the SQL queries. Now type the following query in the text area and click Go
UPDATE mysql.user SET Password=PASSWORD(‘password’) WHERE User=’root’; FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
- Remove the skip-grant-tables in the my.ini file
- Restart MySQL from Control Panel interface
DONE!
Be awared that mysql root user password does not have to be the same as password for phpmyadmin.
answered May 9, 2017 at 19:11
DungDung
18.4k9 gold badges57 silver badges52 bronze badges
here is what I did and it worked:
After you install (rpm installation), do a vi /etc/my.cnf.
This will give you a path where your datadir is set. For me it was datadir=/var/lib/mysql.
Add a line there user=root, and remove all the content inside the datadir path: rm -rf /var/lib/mysql/*.
Now hit the command: mysqld --initialize.
A temporary password is generated at a location. For this:
grep "A temporary password" /var/log/*.
You will get a line that says:
/var/log/mysqld.log:2018-05-01T15:13:47.937449Z 5 [Note] [MY-010454] [Server] A temporary password is generated for root@localhost: &uosjoGfi9:K. So for me &uosjoGfi9:K was my temporary password.
Now do a mysql -u root -p. Paste your temporary password from what you got from above.
You will be in your mysql cli mode. Now do:
mysql> use mysql;
You will be asked to reset your password:
ERROR 1820 (HY000): You must reset your password using ALTER USER statement before executing this statement.
Run your ALTER command:
mysql> ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'MyNewPswd';
And you are done.
answered May 1, 2018 at 14:41
aimanaiman
1,01719 silver badges55 bronze badges
in my case its a frustrating Windows Server installation (iis/php/mysql) so this is what i did:
PART 1: remove the old MYSQL :
NOTE: if you already have data you should back it up!
Step 1
Uninstall MySQL from Control Panel. (you should know how to do this)
Step 2
Run Command Prompt as Admini and execute the following commands to stop and remove MySQL service.
Net stop MySQL
Sc delete MySQL
Step 3
Delete these folders:
C:Program FilesMySQL
C:Program Files (x86)MySQL
C:ProgramDataMySQL
And if it exists:
C:Users[User-Name]AppDataRoamingMySQL
PART 2: Install MYSQL
Download installer from https://dev.mysql.com/downloads/installer/ and install
-MySQL Server 8.0.23
open cmd as admin and go to
c:Program FilesMySQLMySQL Server 8.0bin
run
mysqld --initialize --console
mysqld --install
now start the service (type services.msc in run panel)
now back to console run:
mysql -u root -p
ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'MyNewPass';
that’s it
answered Feb 14, 2021 at 6:13
Jaxx0rrJaxx0rr
4974 silver badges7 bronze badges
mysql80:
update user SET authentication_string='your password after encode to sha256' where User='root';
answered Feb 28, 2022 at 11:01
I have a little problem with my phpmyadmin, in fact I accidentally delete multiple user accounts.
Since it is impossible to connect without the error:
# 1045 - Access denied for user 'root' @ 'localhost' (using password: NO)
I have search a little on the net before, and even the technic:
UPDATE mysql.user SET Password = PASSWORD ('') WHERE User = 'root';
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
does not work, or I didn’t understood how it worked.
I’m on FreeBSD 8.1, my version of PhpMyadmin is 2.11.
Thank you in advance for your answers.
OMG Ponies
321k79 gold badges517 silver badges499 bronze badges
asked Nov 23, 2010 at 16:11
I summarised my solution here: http://snippets.dzone.com/posts/show/13267
sudo stop mysql
sudo mysqld --skip-grant-tables --skip-networking
mysql
mysql> update mysql.user set password = password('your_new_password') where user = 'root';
mysql> flush privileges;
mysql> exit;
sudo mysqladmin shutdown
sudo start mysql
answered Jun 19, 2011 at 10:57
AlexeyAlexey
9,0774 gold badges62 silver badges76 bronze badges
2
For mysql 5.7.16 or later I found this (from mysql.com) to be the working solution. Below are some points which are different compared to previous older versions
1) I used the below command to run mysql in safe mode as per some other references which actually worked fine for me (mysql 5.7.16 ubuntu 16.04).
mysqld_safe --skip-grant-tables --skip-networking
2) The below update stmt is NOT working for later version (ie. 5.7 and above)
-- NOT Working for 5.7 and later
UPDATE mysql.user SET Password = PASSWORD ('') WHERE User = 'root';
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
INSTEAD use below for 5.7.6 and later
UPDATE mysql.user
SET authentication_string = PASSWORD('MyNewPass'), password_expired = 'N'
WHERE User = 'root' AND Host = 'localhost';
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
OR user below for 5.7.5 or earlier versions.
SET PASSWORD FOR 'root'@'localhost' = PASSWORD('MyNewPass');
answered Oct 29, 2016 at 21:40
user1941390user1941390
5106 silver badges17 bronze badges
1
I am Using MySQL Server 8 and this is how I solved this problem.
create a file and name it accordingly. I’ve named it as reset.txt. put below content in the file but change MyNewPass. This will be your new SQL password
ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'MyNewPass';
Stop my SQL server (Go to services and search MYSQL and right-click on it and stop )
Now open a cmd in your bin folder of My SQLserver directory. in my case it’s
C:Program FilesMySQLMySQL Server 8.0bin
execute the following command.
mysqld.exe --defaults-file="C:ProgramDataMySQLMySQL Server 8.0my.ini" --init-file="C:reset.txt'
NOTE: my reset.txt file is in the c drive. Give the correct path. Check my.ini file is in the directory. In my case, it is in
C:ProgramDataMySQLMySQL Server 8.0my.ini
Finally, restart the SQL Server. Check with your new password.
answered Feb 10, 2020 at 11:54
3
Please follow the instruction from the below link to reset your root password.You have to do it from outside mysql.
Resetting MySql Password
Forgetting your MySQL password can be a real headache for you.Here are some easy steps that you can follow to recover MySql password under Windows
Stop MySql
You have to stop MySql service before you proceed.In Windows environment, go to ‘Task Manager’ and Under ‘Service’ tab find MySQL and stop it.
Write Sql to change your password
All you need to do is to create a text file and put the below two lines into that. UPDATE mysql.user SET Password=PASSWORD(‘MyNewPass’) WHERE User=’root’; FLUSH PRIVILEGES; Save it under C: drive and give it a name ‘mysql-init.txt’
Time to restart MySQL by your own.
Now it’s time to restart your MySQl which you stopped in before but this time from command line. C:> C:mysqlbinmysqld-nt —init-file=C:mysql-init.txt
Finishing up!
Now you can log in with your new password. When you finish remove the file that you created in the previous stage.
Also there is a link (http://kaziprogrammingblog.osinweb.com/article/showarticle/Resetting-MySql-Password) where I have explained the same thing.
Hope this will help..:)
answered Nov 4, 2013 at 11:39
ktakta
19k7 gold badges65 silver badges46 bronze badges
Answer for XAMPP on Windows:
- Edit C:xamppmysqlbinmy.ini and insert skip-grant-tables below [mysqld]
- Restart MySQL from Control Panel interface
- In the phpMyAdmin window, select SQL tab from the top panel. This will open the SQL tab where we can run the SQL queries. Now type the following query in the text area and click Go
UPDATE mysql.user SET Password=PASSWORD(‘password’) WHERE User=’root’; FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
- Remove the skip-grant-tables in the my.ini file
- Restart MySQL from Control Panel interface
DONE!
Be awared that mysql root user password does not have to be the same as password for phpmyadmin.
answered May 9, 2017 at 19:11
DungDung
18.4k9 gold badges57 silver badges52 bronze badges
here is what I did and it worked:
After you install (rpm installation), do a vi /etc/my.cnf.
This will give you a path where your datadir is set. For me it was datadir=/var/lib/mysql.
Add a line there user=root, and remove all the content inside the datadir path: rm -rf /var/lib/mysql/*.
Now hit the command: mysqld --initialize.
A temporary password is generated at a location. For this:
grep "A temporary password" /var/log/*.
You will get a line that says:
/var/log/mysqld.log:2018-05-01T15:13:47.937449Z 5 [Note] [MY-010454] [Server] A temporary password is generated for root@localhost: &uosjoGfi9:K. So for me &uosjoGfi9:K was my temporary password.
Now do a mysql -u root -p. Paste your temporary password from what you got from above.
You will be in your mysql cli mode. Now do:
mysql> use mysql;
You will be asked to reset your password:
ERROR 1820 (HY000): You must reset your password using ALTER USER statement before executing this statement.
Run your ALTER command:
mysql> ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'MyNewPswd';
And you are done.
answered May 1, 2018 at 14:41
aimanaiman
1,01719 silver badges55 bronze badges
in my case its a frustrating Windows Server installation (iis/php/mysql) so this is what i did:
PART 1: remove the old MYSQL :
NOTE: if you already have data you should back it up!
Step 1
Uninstall MySQL from Control Panel. (you should know how to do this)
Step 2
Run Command Prompt as Admini and execute the following commands to stop and remove MySQL service.
Net stop MySQL
Sc delete MySQL
Step 3
Delete these folders:
C:Program FilesMySQL
C:Program Files (x86)MySQL
C:ProgramDataMySQL
And if it exists:
C:Users[User-Name]AppDataRoamingMySQL
PART 2: Install MYSQL
Download installer from https://dev.mysql.com/downloads/installer/ and install
-MySQL Server 8.0.23
open cmd as admin and go to
c:Program FilesMySQLMySQL Server 8.0bin
run
mysqld --initialize --console
mysqld --install
now start the service (type services.msc in run panel)
now back to console run:
mysql -u root -p
ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'MyNewPass';
that’s it
answered Feb 14, 2021 at 6:13
Jaxx0rrJaxx0rr
4974 silver badges7 bronze badges
mysql80:
update user SET authentication_string='your password after encode to sha256' where User='root';
answered Feb 28, 2022 at 11:01
There might arise a situation where you need to reset the root password for your MySQL database. It can be because you forgot your password or you need to change the password for security reasons.
In this article, we will look into the process of resetting the MySQL password using Windows cmd. To do so follow the below steps:
Step 1: Stop the MySQL server
- Begin by checking if you’re logged in as an administrator.
- Press Win+R (hold the Windows/Super key, and press “r”.) Once the “Run” box appears type:
services.msc
- Click OK.
- Scroll down the list of services to find the MySQL service. Right-click that entry then left-clicks Stop.
Step 2: Launch a Text Editor
- Click on the menu and search for Notepad.
- Alternatively, you can use the path: Menu > Windows Accessories > Notepad.
Step 3: Create a New Text File with the Password Command
- Enter the following line into the text editor:
ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'NewPassword';
- Make sure you keep the quote marks and semicolon. Replace NewPassword with the password of your choice.
- Use the File > Save As menu to save the file to the root of your hard drive (C: ). Choose a filename that makes sense, such as mysql-init.txt.
Consequently, the localhost command will make the password change on your local system. If you’re trying to change the password on a system over the network, substitute the hostname for localhost.
Step 4: Open a Command Prompt
- Press Ctrl+Shift+Esc.
- Then, click on the File menu > Run new task.
- Type cmd.exe, and check the box to run as administrator.
- Click OK.
Step 5: Restart the MySQL Server with Your New Config File
- Navigate to the MySQL directory using the command prompt:
cd "C:Program FilesMySQLMySQL Server 8.0bin"
Accordingly, the command line will show that you’re working in this folder.
- Enter the following:
mysqld --init-file=C:\mysql-init.txt
Note that there are two slashes after the C: prompt.
Also, if you choose a different name in Step 2, use the same name after the double slash.
Step 6: Clean up
Now, you can log into your MySQL server as root using the new password.
- Double-check to make sure it works. If you have unique configuration options (such as launching MySQL with a -defaults-file option), go ahead and do so.
Once MySQL launches, and you’ve confirmed the password change, delete the C:myswl-init.txt file.
At this stage, you have successfully reset the root password for your MySQL database.