Table of Contents
- Introduction
- The RPC Server
- The RPC Client
- RPC Quick Fixes
- Unable to resolve DNS or NetBIOS names in an Active Directory environment.
- The RPC service or related services may not be started
- Network Connectivity
- Verify ports needed by RPC are open
- File and Printer Sharing is not enabled
- Name Resolution
- DNS Name Resolution
- NetBIOS Name Resolution
- TCP Session Establishment
- Firewall/Network
- RPC Discovery
- Discovery — RPC Over TCPIP
- Discovery — RPC Over SMB
- RPC Communication
- How to identify the RPC traffic in a trace
- RPC over TCPIP
- RPC over HTTP Port 80
- RPC over HTTP Port 443
- RPC over SMB aka “Named Pipes”
- Kerberos Authentication
- NTLM Authentication
- Troubleshooting Authentication
- Active Directory Symptoms:
- Troubleshooting Tools and Methods
- Methods to generate RPC Traffic
- Tools for Testing RPC
- Tools for monitoring RPC
- Using PortQry
- Resources
- RPC Blogs
- External TechNet Magazine article
- KB Article
Introduction
Remote Procedure Call (RPC) is an inter-process communication technique to allow client and server software to communicate on a network. The RPC protocol is based on a client/server model. The client makes a procedure call that appears to be local but is
actually run on a remote computer. During this process, the procedure call arguments are bundled and passed through the network to the server. The arguments are then unpacked and run on the server. The result is again bundled and passed back to the client,
where it is converted to a return value for the client’s procedure call.
RPC is used by several components in Windows Server, such as the File Replication Service (FRS), Active Directory Replication, Certificate services, DCOM, domain join, DCPromo and RDP, NLB and Cluster, Microsoft Operations Master, Exchange and SQL.
The RPC Server
An RPC server is a communications interface provided by an application or service that allows remote clients to connect, pass commands, and transfer data using the RPC protocol. A typical example of an RPC server is Microsoft Exchange Server. Microsoft Exchange
Server is an application running on a computer that supplies an RPC communications interface for an RPC client.
An application will register its RPC server with the operating system’s End Point Mapper (EPM) service so that the remote client can locate the RPC server. When the application registers with the EPM it will indicate the IP address and TCP port that it is
listening on.
The RPC Client
An RPC client is an application running on any given computer that uses the RPC protocol to communicate with an RPC server. An example of a typical RPC client is the Microsoft Outlook application.
NOTE: In this document the terms RPC server and
RPC client refer to the application running at both ends of an RPC communication.
↑
Back to top
RPC Quick Fixes
Common causes of RPC errors include:
- Errors resolving a DNS or NetBIOS name.
- The RPC service or related services may not be running.
- number of connectivity Problems with network connectivity.
- File and printer sharing is not enabled.
Use the following procedures to diagnose and repair common causes of RPC errors.
Unable to resolve DNS or NetBIOS names in an Active Directory environment.
- Use the following commands to verify DNS is working for all DC’s or specific DC’s:
- To get a DNS status for all DCs in forest, run the following command:
- DCDIAG /TEST:DNS /V /E /F:<filename.log>
- The «/e» switch runs the DNS test against all DCs in an Active Directory Forest
- To get DNS health on a single DC, run the command below.
- DCDIAG /TEST:DNS /V /S:<DCNAME> /F:<filename.log>
- The «/s:» switch runs the DNS test against a specified domain controller.
- To verify that a domain controller can be located for a specific domain, run the command below.
- NLTEST /DSGETDC:<NetBIOS or DNS domain name>
- Servers and clients that are receiving the error should be checked to verify that they are configured with the appropriate DNS server. Servers should not be pointing to their ISP’s DNS servers in the preferred or alternate DNS server portion of the TCP/IP
settings. The ISP’s DNS servers should only be used as forwarders in DNS.
- Ensure that at least one correct DNS record is registered on each domain controller.
- To ensure that a correct DNS record is registered on each domain controller, find this server’s Active Directory replication partners that run DNS.
- Open DNSManager and connect in turn to each of these replication partners.
- Find the host (A) resource record registration for this server on each of the other replication partner domain controllers.
- Delete those host (A) records that do not have IP addresses corresponding to any of this server’s IP addresses.
- If a domain controller has no host (A) records for this server, add at least one that corresponds to an IP address on this server. (If there are multiple IP addresses for this server, add at least one that is on the same network as the domain controller
you are updating.)
- Name resolution may also fail with the RPC Server is unavailable error if NetBIOS over TCP/IP is disabled on the WINS tab in the advanced section of the TCP/IP properties. The NetBIOS over TCP/IP setting should be either enabled or default (use DHCP).
- Verify that a single label domain name is not being configured. DNS names that do not contain a suffix such as .com, .corp, .net, .org or .local are considered to be single-label DNS names. Microsoft doesn’t recommend using single label domain names because
they cannot be registered with an Internet registrar and domain members do not perform dynamic updates to single-label DNS zones. Knowledge base article
826743 — «Clients cannot dynamically register DNS records in a single-label domain» provides instructions on how to configure your domain to allow dynamic registration of DNS records in a single label domain.
The RPC service or related services may not be started
Verify the status and startup type for the RPC and RPC locator services on the server that gets the error:
- By default, Windows server 2003 domain controllers and member servers all should have the RPC service started and set to Automatic startup and the RPC Locator service stopped and set to Manual Startup.
- Windows 2000 domain controllers should have the RPC and RPC Locator services both set to started and automatic startup, while Windows 2000 member servers should have the RPC service started and set to automatic startup while the RPC locator service should
be started and set to manual startup. - If you make any changes to the RPC service or to the RPC Locator service settings, restart the computer, and then test for the problem again.
- Additional Services that may result in «The RPC Server is Unavailable» errors are the TCP/IP NetBIOS helper service, Distributed File System service and Remote Registry service. These services should both be set to automatic and started. The Kerberos Key
Distribution Center (KDC) should be Started and Automatic on Windows 2000 and Windows 2003 DCs. It should not be started and set to Disabled in all other cases.
↑
Back to top
Network Connectivity
Verify ports needed by RPC are open
Verify that ports greater than 1024 are not blocked. Clients connect to RPC Endpoint Mapper on port 135. RPC Endpoint Mapper then tells the client which randomly assigned port between 1024-65535 a requested service is listening on.
Ports may be blocked by a hardware firewall or a software firewall. Software firewalls include Internet Connection Firewall on computers running Windows Server 2003 or Windows XP, and Windows Firewall on computers running Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows
Server 2008 and Windows Server 2008 R2. A computer might also have third-party firewall software installed, or antivirus software with built-in firewall functionality. By default, port 135 TCP/UDP and ports 1024-65535 TCP must be open for RPC to work. You
can restrict the ports greater than 1024 that RPC uses. However, RPC Endpoint Mapper is always on port 135.
File and Printer Sharing is not enabled
File and Printer sharing for Microsoft Networks will produce the error RPC Server is unavailable” when you try to view or manage services on a remote computer using the Services snap-in. See the following example:
Unable to open service control manager database on \<computer>.
Error 1722: The RPC server is unavailable.
This error message may occur if the File and Printer Sharing for Microsoft Networks component is not enabled on the remote computer.
Troubleshooting RPC
The process of an RPC client connecting to an RPC server can be broken down into four phases. This troubleshooting guide will discuss the events that occur at each phase, how to test these events, and how to identify if the phase completed successfully.
Phase 1: Name Resolution: Name resolution is the act of resolving a name to an IP address. This normally takes two forms: NetBIOS Name Resolution or the more common DNS Name Resolution.
Phase 2: TCP session establishment: TCP session establishment is the act of establishing a TCP connection between the RPC client and the RPC server. TCP sessions will be initiated by the RPC client via a TCP 3-way handshake with the RPC
server.
Phase 3: RPC Discovery: When a client wants to connect to the RPC server supplied by the application it will contact the computer that hosts the RPC Server and discover how to connect to the RPC Server.
Phase 4: RPC Communication: RPC Communication is the act of making RPC requests to the application endpoint and receiving RPC responses from this application.
Data needed to troubleshoot the issue:
- Identify the client and server computers reporting the RPC error. Identify the DNS and WINS servers used by these computers. To do this:
- On each machine, open a command prompt and run ipconfig /all.
- Determine the IP address of both machines. If the server is part of a cluster get the cluster resource IP address as well. Identify the DNS servers and WINS servers that the RPC client is configured to use.
Note: You can also obtain this information by opening Control PanelNetwork and Sharing Center, clicking Local Area Connection and selecting Properties.
- Identify the application(s) reporting RPC Server Unavailable
- Simultaneous network traces (using Wireshark, Netmon, or a comparable network sniffer) from the machines hosting the RPC client and RPC Server while reproducing the task that results in a “RPC Server Unavailable” error.
- The network captures on both hosts should be started first.
- From a command prompt on the client run ipconfig /flushdns and nbtstat –R to clear the name resolution caches.
- Reproduce the error.
- Stop the traces and save them.
↑
Back to top
Name Resolution
Name Resolution consists of one or possibly more NetBIOS or DNS queries to locate the IP address for the RPC Server. Troubleshooting this phase requires verifying that a response is received to the name resolution request and that the response contains the
correct IP address for the RPC server. Compare the IP address reported by DNS or NetBIOS in the network trace for the server with the IP addresses you noted earlier. If it does not match then check DNS and WINS and note if there is a difference.
DNS Name Resolution
To identify DNS Name Resolution in a network trace use the following filter in Network Monitor or Wireshark: dns. DNS resolution will be occurring at the client so open the network trace taken from the RPC client machine. You will be looking for one packet
that is the query from the client to the DNS server and then the response packet from the DNS server. It will look similar to this:
If the trace shows the correct IP address for the RPC server was returned by the DNS server proceed to TCP Session Establishment.
If the trace does not show a correct IP address returned or you do not see any answer from the DNS server then reference the following resources to help with DNS name resolution troubleshooting.
For details on troubleshooting Active Directory related DNS issues go
here.
For general DNS troubleshooting:
http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;EN-US;330511
NetBIOS Name Resolution
NetBIOS queries come in two forms, WINS or NetBIOS Broadcasts. WINS will consist of a unicast query to a WINS server and a response from the WINS server.
NetBIOS broadcasts are queries broadcast to all hosts on the local subnet so name resolution is limited to only hosts on the subnet. The host with the name listed in the NetBIOS Broadcast will respond with its IP address.
To identify NetBIOS Name Resolution in a network trace, use the following filter in Network Monitor — “nbtns”. For Wireshark, use the following filter — nbns”. If the trace shows a successful resolution using WINS or NetBIOS queries proceed to TCP Session
Establishment.
For details on troubleshooting this NetBIOS Name Resolution further:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc940110.aspx
TCP Session Establishment
TCP Sessions always begin with a TCP 3-way handshake. The handshake should look similar to what is shown below. The RPC Client will send the first packet, known as the SYN packet. The computer hosting the RPC Server will send a SYN/ACK response, and then
the RPC Client will send an ACK packet.
Scenarios that may cause the TCP session to fail
Firewall/Network
If a firewall or network problem is the culprit, it is likely a failure will occur during this phase. To diagnose this you will want to look at the network traces taken from the RPC Client and RPC Server. If a firewall or other network device is causing a problem
it will usually manifest as a retransmit of the TCP SYN packet by the RPC Client about 3 seconds after the first TCP SYN is sent. This can be seen in a Netmon network trace using the display filter specification of “tcpsynretransmit==1”. In other cases, firewalls
will allow the 3-way handshake to succeed but may block the RPC packets due to the contents of the packet at a higher level. In these cases it is possible to see the retransmit of the RPC packet within half a second of the original packet being sent. To identify
this condition in a Netmon network trace use the display filter specification of “tcpretransmit==1”. To see either of these retransmit conditions in a trace taken using Wireshark use the display filter specification of “tcp.analysis.retransmission”.
The RPC Server is not actively listening.
It was noted earlier that an RPC Server will register itself and listen on a particular port and IP address of the host computer. If for some reason that fails the TCP layer will answer the SYN packet from the client with a Reset packet.
A device in the middle between the RPC Client and RPC Server will be resetting the connection attempt.
In the client side trace it will appear as if the server sent the TCP Reset while the trace from the server indicates the client is the source of the TCP Reset.
For both these scenarios, check for the presence of a Reset packet in the TCP three way handshake by using the display filter specification of “TCP.flags.reset==1”.
For troubleshooting this step see the following sections in this document:
- How to identify RPC traffic in a trace
- Connectivity
- RPC Services
- RPC Client Registry
If the 3-way handshake is successful, continue to the RPC Discovery phase.
↑
Back to top
RPC Discovery
The RPC Discovery phase will occur one of two ways. In both methods the client will know the identifier for the RPC Server it wants to contact and will supply that to the computer hosting the RPC Server and ask for information on how to contact the RPC Server.
The identifier is different depending on which method is used and the RPC client will know ahead of time which method it wishes to use.
Discovery — RPC Over TCPIP
This method is a two-step process. First the RPC client will contact the End Point Mapper (EPM) on the machine hosting the RPC Server to find out what port and IP address that Server is listening on. Upon successful completion of this the RPC client will
contact the RPC Server directly on the indicated IP address and Port. Below is a sample of what this would look like and a step by step explanation below it. This step depends on the successful TCP session establishment twice, first to the EPM and then to
the RPC Server.
- The RPC Client will open a TCP session with TCP port 135 on the computer hosting RPC Server of interest. This can be picked out using the following filter syntax in Netmon or Wireshark: “tcp.port==135”
- The RPC Client will send an RPC Bind request using the UUID of the End Point Mapper and the RPC EPM should respond with a Bind ACK packet.
- The RPC Client will make a MAP request to the EPM to locate the IP address and port of the RPC Server of interest, identifying the RPC Server based on its UUID.
- The EPM will send back a MAP Response that indicates the IP and port the RPC Server is listening on.
- The RPC Client will then open a TCP session with the IP and port it received in the EPM MAP response.
- The client will send an RPC Bind Request to the RPC Server specifying the UUID of the RPC Server application and should get back a Bind ACK from the RPC Server.
- There will be an RPC Alter Context Request/Response in which authentication will take place. If an error is noted here then see the following section for help determining why the error is occurring —
Authentication
- Perform some RPC operations…(Go to RPC Communication phase)
Discovery — RPC Over SMB
The second method an RPC Client may use to contact an RPC Server is RPC over SMB. This method depends upon first establishing an SMB session with the computer hosting the RPC Server and then using the Named Pipes protocol to communicate using RPC. So in
effect there are several levels of encapsulation – RPC over Named Pipes over SMB over TCP. We will not address the SMB session setup in this document and the TCP session establishment has already been discussed.
With a successfully opened TCP and SMB session, next:
- The RPC Client will issue a SMB TreeConnectAndX for the tree name “IPC$”. This is a special hidden share for inter-process communication. It should get a positive response from the computer hosting the RPC Server.
- The RPC Client will then issue an SMB NTCreateAndX for the name of the PIPE of the RPC Server Application and should get back a positive response. Some examples are:
EVENTLOG = The Event log service
winreg = Remote Registry
svcctl = Service Control Manager
srvsvc = Server Service
- Next there is a Bind handshake. This is to “bind” the RPC client to the RPC server. There are a total of four packets involved:
- The RPC Client bind request containing the UUID of the desired RPC Server.
- A Write AndX response from the RPC Server
- A Read AndX request from the RPC Client.
- A Bind ACK response from the RPC Server.
- At this time a RPC request to the RPC server component is expected.
RPC Communication
At this point RPC communication is occurring between the RPC Client and RPC Server. The troubleshooting steps involved at this stage are largely based on the application reporting the RPC failure.
For Active Directory processes or services please see
Active Directory Symptoms.
For Microsoft Exchange related RPC errors please see:
Analyzing Exchange RPC traffic over TCP/IP
↑
Back to top
How to identify the RPC traffic in a trace
RPC network traffic can take multiple forms. It is important to understand which form is in use in order to identify which TCP session is responsible for the RPC communication.
RPC over TCPIP
This is sometimes referred to as Traditional RPC or Sockets based RPC. An example of this is Outlook without “Outlook anywhere” or without http settings configured. A TCP session on TCP port 135 is established with the RPC server. To view this traffic in
a trace use the filter: “tcp.port==135”. This session will be used in the RPC Discovery phase to locate the endpoint of the desired application.
RPC over HTTP
RPC connectivity for Internet connected hosts will typically use RPC over HTTP in order to traverse firewalls. Some examples of this can be seen with Terminal Services Gateway, Outlook Web Access, Outlook via “Outlook Anywhere”. This communication will be
established on one or more connections to either TCP port 80 or 443(SSL). Since this typically traverses a public network, SSL or TCP port 443 is the more common method. Use the filter “tcp.port==80 or tcp.port==443” to locate either form inside network trace.
RPC over HTTP Port 80
For sessions over TCP port 80, the HTTP requests associated with RPC over HTTP will include a UserAgent header that contains the text “OutlookConnectorDS” and the version number of the connector.
RPC over HTTP Port 443
Sessions using TCP port 443 will initially establish a TLS session. After this TLS negotiation, the TCP Payload will be encrypted in TLS/SSL and the contents of the frames will not be readable in the trace. In this phase, look for failures due to improper
certificates, inaccessible Certificate Revocation Lists, or untrusted certificate chains.
For more information on troubleshooting SSL/TLS see:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc783349(WS.10).aspx
↑
Back to top
RPC over SMB aka “Named Pipes”
RPC can also take advantage of SMB sessions for the purpose of RPC communication. Some examples of this can be seen with Computer Management or the Remote Registry service. With the use of RPC over SMB:
- Establish TCP connection on TCP port 139 or 445.
- Negotiate dialect request/response
- SessionSetupANDX request/response. This sequence is used to establish the SMB Session. Authentication occurs during the SessionSetupANDX exchange.
If a failure in step 1 occurs, see additional troubleshooting steps see:
File and Printer Sharing.
Kerberos Authentication
If Kerberos is used, and the client doesn’t currently have a Kerberos ticket for the RPC server, just after the Negotiate Dialect response is received, the client will obtain a Kerberos ticket for the Servername/cifs SPN of the RPC server. This exchange
will occur over the Kerberos ports TCP or UDP port 88 between the client and a Domain Controller. SessionSetupANDX follows and will consist of a single SessionSetupANDX request which includes the Kerberos ticket, followed by a SessionSetupANDX Response indicating
success or failure of the authentication.
For additional troubleshooting steps during authentication, see
Authentication.
NTLM Authentication
If NTLM is used, SessionSetup will result in a SessionSetupANDX response with a status of STATUS_MORE_PROCESSING_REQUIRED. This response includes the NTLM challenge. The subsequent SessionSetupANDX Request will include the hashed credentials of the client.
At this time, the RPC server must validate the credentials supplied by the user. To do this, the RPC server will contact a domain controller, and validate the credentials with the netlogon service, via RPC, on the domain controller. If this is successful,
the RPC server will then respond to the client with a SessionSetupANDX Response indicating STATUS_SUCCESS.
For additional troubleshooting steps during authentication, see
Authentication.
Troubleshooting Authentication
Verify that authentication is working correctly by checking for Time skew, UDP Fragmentation or an Invalid Kerberos Realm.
- Time skew can be verified by running net time /querysntp and net time /setsntp:<PDCe server name>. The /querysntp switch allows you to determine if a specific DC is manually configured as the authoritative time server. The /setsntp:<PDCe server name> switch
can be used to synchronize the computer receiving the error with the PDC emulator. The PDC emulator is the authoritative time server by default. - UDP fragmentation can cause replication errors that appear to have a source of RPC server is unavailable. Symptoms of UDP fragmentation being at the root of this problem include clients being unable to log on to the domain, administrators being unable
join computers to the domain and Event ID 40960 & 40961 errors with a source of LSASRV and Kerberos errors with an Event ID of 10 in the system log.Knowledge base article 244474 — «How to force Kerberos to use TCP instead of UDP in Windows Server 2003, in Microsoft Windows and XP, and in Microsoft Windows 2000» provides the steps to resolve this
problem. - An incorrect Kerberos realm can also be at the root of RPC server is unavailable problems. The symptoms that will be experience when the Kerberos realm is incorrect include the following errors when opening AD management tools:
Naming Convention could not be located because: No authority could be contacted for authentication. Contact your system administrator to verify that your domain is properly configured and is currently online.
-or-
Naming information cannot be located because: No authority could be contacted for authentication. Contact your system administrator to verify that your domain is properly configured and is currently online.
To verify that the correct Kerberos realm is configured, follow the steps in 837513 — «Domain controller is not functioning correctly».
↑
Back to top
Active Directory Symptoms:
1. If you are experiencing replication problems and getting RPC server is unavailable errors as is reported in repadmin /showreps below, use Portqry or Network Monitor to determine if RPC traffic is being blocked is the first step when attempting
to troubleshoot RPC Server is unavailable errors.
[Replications Check,DC2] A recent replication attempt failed:
From DC1 to DC2
Naming Context: CN=Schema,CN=Configuration,DC=xl
The replication generated an error (1722):
The RPC server is unavailable.
The failure occurred at 2003-10-30 11:59.47.
The last success occurred at 2003-10-28 20:50.22.
26 failures have occurred since the last success.
[DC1] DsBind() failed with error 1722,
The RPC server is unavailable..
The source remains down. Please check the machine.
BermudaDC1 via RPC objectGuid: 28c78c72-3c95-499a-bcda137a250f069f
Last attempt @ 2003-10-30 11:58.15 failed, result 1722:
The RPC server is unavailable.
Troubleshooting: If IP Security Policies in Active Directory had the Assigned Value to Server (Request Security) set to Yes then these errors will result. Knowledge base article 313190
— «How to use IPSec IP filter lists in Windows 2000» provide details about where to check these settings and more information about their impact.
2. If you are blocking all ICMP traffic between separate AD sites, you will receive the errors below in the output of DCDIAG when trying to replicate inter-site:
Testing server: contosoDC1
Starting test: Replications
* Replications Check
[Replications Check,DC1] A recent replication attempt failed:
From DC2 to DC1
Naming Context: CN=Schema,CN=Configuration,DC=litware,DC=com
The replication generated an error (1722):
The RPC server is unavailable.
The failure occurred at 2003-08-24 23:00.51.
The last success occurred at (never).
553 failures have occurred since the last success.
[DC2] DsBind() failed with error 1722,
The RPC server is unavailable..
The source remains down. Please check the machine.
REPLICATION LATENCY WARNING
DC1: A full synchronization is in progress
from DC2 to DC1
Replication of new changes along this path will be delayed.
[DC2] LDAP connection failed with error 58,
The specified server cannot perform the requested operation.
Troubleshooting: To resolve this issue, remove the ICMP traffic restriction between domain controllers. When establishing an RPC session prior to AD replication, ICMP traffic is used. If the ICMP fails, so does the RPC session establishment,
and hence AD replication also fails. ISA 2004 can prevent ICMP traffic with the exception of computers specified in the Remote Management Computers computer set which can be configured in system policy.
3. The following error will appear when attempting to connect to the computer.
«computer <\servername.domain.local> cannot be managed. The network path was not found. RPC server is unavailable.
Or when viewing the properties of the remote computer you will receive the error:
«Win32: The RPC server is unavailable».
Troubleshooting: Computer management is one of the better tools for testing RPC connectivity. When RPC traffic is being blocked, connections to other computers using the computer management console will fail.
4. When attempting to promote an additional domain controller in an Active Directory domain while the RPC service is blocked or not running, the following error will appear:
«The domain «domain.local» is not an Active Directory domain, or an Active Directory domain controller for the domain could not be contacted.
Troubleshooting:
5. Connections to computers via Remote Desktop may fail if RPC connectivity cannot be established. When attempting to logon on to the domain via Remote Desktop the following error will be produced in the form of a popup error message if RPC connectivity
is the root of the problem:
«The system cannot log you on due to the following error: The RPC server is unavailable.”
You may also see the following errors on the Terminal server:
Error 1727: The remote procedure call failed and did not execute
Error 1722: The RPC server is unavailable.
Error 1723: The RPC server is too busy to complete this operation.
Error 1721: Not enough resources are available to complete this operation.
-or-
Event ID 5719:
Source: NetLogon
Description: No Windows NT Domain Controller is available for domain domain_name.
The following error occurred: There are currently no logon servers available to
service the logon request.
Event ID: 1219
Source: Winlogon
Details: Logon rejected for CONTOSO<computername>. Unable to obtain Terminal Server
User
Configuration. Error: The RPC server is unavailable.
Troubleshooting: These errors can be a result of the TCP/IP NetBIOS Helper service being disabled on the Terminal server or NetBIOS over TCP/IP being disabled on one of the NIC’s used to access the Terminal server. You should also verify
that the Client for Microsoft networks is bound to the adapter used to access the Terminal server. You can tell if this is happening by looking at a Netdiag /v from the box for the following output:
Testing redirector and browser… Failed
NetBT transports test. . . . . . . : Failed
List of NetBt transports currently configured:
[FATAL] No NetBt transports are configured.
Redir and Browser test . . . . . . : Failed
List of transports currently bound to the Redir
NetBIOSSmb
[FATAL] The redir isn’t bound to any NetBt transports.
List of transports currently bound to the browser
[FATAL] The browser isn’t bound to any NetBt transports.
↑
Back to top
Troubleshooting Tools and Methods
Methods to generate RPC Traffic
Computer Management MMC to a remote host
Outlook to an Exchange server
RPCPing — http://support.microsoft.com/kb/831051
Tools for Testing RPC
RPCPing — http://support.microsoft.com/kb/831051
PortQry —
http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;EN-US;832919
Pipelist —
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/sysinternals/dd581625.aspx
RPCDump —
http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;EN-US;325930
NSLookup —
http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;EN-US;200525
NBLookup —
http://support.microsoft.com/default.aspx?scid=kb;EN-US;830578
Tools for monitoring RPC
Network Monitor —
Download –
FAQ
Wireshark — Download
Using PortQry
You can use the Portqry tool to verify that the required ports are open. You should run the Portqry tool on a computer that is not receiving any RPC errors against a computer that is receiving RPC errors by using the -n switch. To this, follow these steps:
a. Click «Start», click «Run», type «cmd» in the «Open» box, and then click OK».
b. Type «portqry -n <problem_server> -e 135» (without the quotation marks).
The output will appear similar to the following examples:
Querying target system called:
<problem_server>
Attempting to resolve name to IP address…
Name resolved to 169.254.1.1
querying…
<problem_server>
TCP port 135 (epmap service): LISTENING
Using ephemeral source port
Querying Endpoint Mapper Database…
Server’s response:
UUID: f5cc59b4-4264-101a-8c59-08002b2f8426 NtFrs Service
ncacn_ip_tcp:65.53.63.16[1094]
UUID: e3514235-4b06-11d1-ab04-00c04fc2dcd2 MS NT Directory DRS Interface
ncacn_ip_tcp:65.53.63.16[1025]
UUID: e3514235-4b06-11d1-ab04-00c04fc2dcd2 MS NT Directory DRS Interface
ncacn_http:65.53.63.16[1029]
UUID: e3514235-4b06-11d1-ab04-00c04fc2dcd2 MS NT Directory DRS Interface
ncacn_http:65.53.63.16[6004]
If port 135 is blocked, the following will appear:
TCP port 135 (epmap service): NOT LISTENING However, for these RPC Endpoint Mapper errors it is likely that ports greater than 1024 are blocked, and not port 135.From the output, you know the DC is using port 1094 for FRS and 1025, 1029, and 6004 for Active
Directory replication. You can use the Portqry tool again to check those ports. For example, you can test all the ports at the same time by using the Portqry tool with the -o switch. For example, type
«portqry -n <problem_server> -o 1094,1025,1029,6004″(Without the quotation marks)
If the ports all respond as «LISTENING,» it’s likely that blocked ports are not causing this problem. If any ports respond as «NOT LISTENING,» the ports are probably blocked.
↑
Back to top
Resources
RPC Blogs
Basics of RPC are covered here:
RPC to Go v.1:
http://blogs.technet.com/b/networking/archive/2008/10/24/rpc-to-go-v-1.aspx
Architecture and a closer look at a connection to the RPC Endpoint mapper in a network capture.
RPC to Go v.2:
http://blogs.technet.com/b/networking/archive/2008/12/04/rpc-to-go-v-2.aspx
This describes how RPC commands can be sent over Named Pipes in SMB via the IPC$ Tree.
RPC to Go v.3:
http://blogs.technet.com/b/networking/archive/2009/04/28/rpc-to-go-v-3-named-pipes.aspx
Troubleshooting “RPC server is unavailable” error, reported in failing
AD replication scenario.
http://blogs.technet.com/b/abizerh/archive/2009/06/11/troubleshooting-rpc-server-is-unavailable-error-reported-in-failing-ad-replication-scenario.aspx
External TechNet Magazine article
This one is good. It lays out RPC basics really quickly and then moves on RPC errors. The information on MaxUserPort would need to be updated with the information about the dynamic port ranges that are used in Vista/W2008 are the high range of ports compared
to the 1025-5000 for W2003.
How IT Works, Troubleshooting RPC Errors by Zubair Alexander:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/magazine/2007.07.howitworks.aspx
KB Article
Troubleshooting RPC Endpoint Mapper errors using the Windows Server 2003 Support Tools from the product CD
https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/help/839880/troubleshooting-rpc-endpoint-mapper-errors-using-the-windows-server-20
↑
Back to top
Shortcuts
Port 135 Details
known port assignments and vulnerabilities
threat/application/port search:
| Port(s) | Protocol | Service | Details | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 135 | tcp,udp | loc-srv | Remote Procedure Call (RPC) port 135 is used in client/server applications (might be on a single machine) such as Exchange clients, the recently exploited messenger service, as well as other Windows NT/2K/XP software. If you have remote users who VPN into your network, you might need to open this port on the firewall to allow access to the Exchange server.
There is a RPC (a RPC’s Endpoint Mapper component) vulnerability in Windows NT where a malformed request to port 135 could cause denial of service (DoS). RPC contains a flaw that causes it to fail upon receipt of a request that contains a particular type of malformed data. To restore normal functionality victim has to reboot the system. Alternatively, you can upgrade/patch your OS (there is patch downloadable from Microsoft), or you can close port 135. Port 135 is used by Messenger Service (not MSN Messenger) and exploited in popup net send messenger spam [MSKB 330904]. To stop the popups you’d need to filter port 135 at the firewall level or stop the messenger service. The service uses all the following ports: 135/tcp, 135/udp, 137/udp 138/udp, 139/tcp, 445/tcp. MS Security Bulletin [MS03-026] outlines another critical Buffer Overrun RPC vulnerability that can be exploited via ports 135, 139, 445, 593 (or any other specifically configured RPC port). You should filter the above mentioned ports at the firewall level and not allow RPC over an unsecure network, such as the Internet. W32.Blaster.Worm [Symantec-2003-081113-0229-99] — a widely spread worm that exploits the DCOM RPC vulnerability described above (MS Security Bulletin [MS03-026]). The worm allows remote access to an infected computer via ports 4444/tcp and 69/UDP, and spreads through port 135/tcp. To avoid being infected consider closing those ports. Port is also used by Messenger Service (not MSN Messenger) and exploited in popup net send messenger spam [MSKB 330904]. To stop the popups you’d need to filter port 135 at the firewall level or stop the messenger service. The service uses all the following ports: 135/tcp, 135/udp, 137/udp 138/udp, 139/tcp, 445/tcp. W32.Reatle.E@mm [Symantec-2005-080215-5809-99] — a mass-mailing worm that opens a backdoor and also spreads by exploiting the MS DCOM RPC Vulnerability [MS03-026] on port 135/tcp. It uses its own SMTP engine to email itself to gathered email addresses. Opens an FTP server on port 1155/tcp. Opens a proxy server on port 2005/tcp. It also attempts to perform denial of service (DDoS) attack agains known security websites on port 1052/tcp. Note: port 1052 corresponds to the dynamic DNS service. A vulnerability has been identified in LOGO!8 BM (incl. SIPLUS variants) (All versions). The vulnerability could lead to an attacker reading and modifying the device configuration and obtain project files from affected devices. The security vulnerability could be exploited by an unauthenticated attacker with network access to port 135/tcp. No user interaction is required to exploit this security vulnerability. The vulnerability impacts confidentiality, integrity, and availability of the device. At the time of advisory publication no public exploitation of this security vulnerability was known. |
SG |
| 135 | tcp,udp | DCE endpoint resolution (official) | Wikipedia | |
| 135 | tcp,udp | Microsoft EPMAP (End Point Mapper), also known as DCE/RPC Locator service, used to remotely manage services including DHCP server, DNS server and WINS (unofficial) | Wikipedia | |
| 135 | tcp | loc-srv | NCS local location broker | SANS |
| 135 | udp | loc-srv | Location Service | SANS |
| 135 | tcp,udp | msrpc | Microsoft RPC services | Nmap |
| 135 | tcp,udp | loc-srv | NCS Location Service | Neophasis |
| 135 | tcp | threat | Secefa | Bekkoame |
| 135 | tcp | threat | W32.Kiman | Bekkoame |
| 135 | tcp,udp | threat | Femot | Bekkoame |
| 135 | tcp,udp | threat | W32.Blaster.Worm | Bekkoame |
| 135 | tcp,udp | threat | W32.Cissi | Bekkoame |
| 135 | tcp,udp | threat | W32.Explet | Bekkoame |
| 135 | tcp,udp | threat | W32.Francette.Worm | Bekkoame |
| 135 | tcp,udp | threat | W32.HLLW.Gaobot | Bekkoame |
| 135 | tcp,udp | threat | W32.HLLW.Polybot | Bekkoame |
| 135 | tcp,udp | threat | W32.Kassbot | Bekkoame |
| 135 | tcp,udp | threat | W32.Kibuv.Worm | Bekkoame |
| 135 | tcp,udp | threat | W32.Lovgate | Bekkoame |
| 135 | tcp,udp | threat | W32.Maslan | Bekkoame |
| 135 | tcp,udp | threat | W32.Mytob | Bekkoame |
| 135 | tcp,udp | threat | W32.Reatle | Bekkoame |
| 135 | tcp,udp | threat | W32.Spybot | Bekkoame |
| 135 | tcp,udp | threat | W32.Welchia | Bekkoame |
| 135 | tcp,udp | threat | W32.Yaha | Bekkoame |
| 135 | tcp,udp | epmap | DCE endpoint resolution | IANA |
26 records found
Related ports: 111 137 138 139 445
« back to SG Ports
External Resources
SANS Internet Storm Center: port 135
Notes:
Port numbers in computer networking represent communication endpoints. Ports are unsigned 16-bit integers (0-65535) that identify
a specific process, or network service. IANA is responsible for internet protocol resources, including the registration of commonly
used port numbers for well-known internet services.
Well Known Ports: 0 through 1023.
Registered Ports: 1024 through 49151.
Dynamic/Private : 49152 through 65535.
TCP ports use the Transmission Control Protocol, the most commonly used protocol
on the Internet and any TCP/IP network. TCP enables two hosts
to establish a connection and exchange streams of data. TCP guarantees delivery of data
and that packets will be delivered in the same order in which they were sent.
Guaranteed communication/delivery is the key difference between TCP and UDP.
UDP ports use the Datagram Protocol. Like TCP, UDP is used in combination with IP (the Internet Protocol)
and facilitates the transmission of datagrams from one computer to applications on another computer,
but unlike TCP, UDP is connectionless and does not guarantee reliable communication; it’s up to the application that received
the message to process any errors and verify correct delivery. UDP is often used with time-sensitive
applications, such as audio/video streaming and realtime gaming, where dropping some packets is preferable to waiting for delayed data.
When troubleshooting unknown open ports, it is useful to find exactly what services/processes are listening to them.
This can be accomplished in both Windows command prompt and Linux variants using the «netstat -aon» command.
We also recommend runnig multiple anti-virus/anti-malware scans to rule out the possibility of active malicious software.
For more detailed and personalized help please use our forums.
| Please use the «Add Comment» button below to provide additional information or comments about port 135. |
This TechNet article is fantastic, I recommend you bookmark it. It lists the ports used by various Windows services and is quite thorough.
In versions of Windows earlier than Vista/2008, NetBIOS was used for the «RPC Locator» service, which managed the RPC name service database. But in Vista/2008 and beyond, the RPC Locator service is no longer necessary or useful. It’s vestigial. From this point on I am only going to talk about MSRPC on Vista/2008+.
Ports 137, 138 and 139 are for NetBIOS, and are not required for the functionality of MSRPC.
All the ports used by RPC are as follows:
RPC EPM TCP 135
RPC over HTTPS TCP 593
SMB (for named pipes) TCP 445
Ephemeral Range, Dynamic *
Other applications, such as Remote Desktop Gateway, will use RPC over HTTP proxy and use port 443, etc.
Although the article I linked to above lists the NetBIOS ports, those are legacy and are not required for RPC, assuming you can acquire name resolution through other means (DNS,) and assuming the remote service itself is not dependent on NetBIOS.
Port 145 is bogus. It’s not used for anything. Wherever you heard that it «makes things better,» is wrong.
Basic MSRPC uses ports 135, and the high-numbered dynamic range. That high-numbered dynamic range is ports 1024-5000 on XP/2003 and below, and 49152-65535 on Vista/2008 and above. You can also call that port range ephemeral ports.
You can define a custom port range if you wish, like so:
reg add HKLMSOFTWAREMicrosoftRpcInternet /v Ports /t REG_MULTI_SZ /f /d 8000-9000
reg add HKLMSOFTWAREMicrosoftRpcInternet /v PortsInternetAvailable /t REG_SZ /f /d Y
reg add HKLMSOFTWAREMicrosoftRpcInternet /v UseInternetPorts /t REG_SZ /f /d Y
And/Or
netsh int ipv4 set dynamicport tcp start=8000 num=1001
netsh int ipv4 set dynamicport udp start=8000 num=1001
netsh int ipv6 set dynamicport tcp start=8000 num=1001
netsh int ipv6 set dynamicport udp start=8000 num=1001
TCP port 135 is the MSRPC endpoint mapper. You can bind to that port on a remote computer, anonymously, and either enumerate all the services (endpoints) available on that computer, or you can request what port a specific service is running on if you know what you’re looking for.
Let me show you an example of querying the RPC Enpoint Mapper:
C:>PortQry.exe -n 192.168.1.1 -e 135
Querying target system called:
192.168.1.1
Attempting to resolve IP address to a name...
IP address resolved to host01.labs.myotherpcisacloud.com
querying...
TCP port 135 (epmap service): LISTENING
Using ephemeral source port
Querying Endpoint Mapper Database...
Server's response:
UUID: d95afe70-a6d5-4259-822e-2c84da1ddb0d
ncacn_ip_tcp:192.168.1.1[49152]
UUID: 12345778-1234-abcd-ef00-0123456789ac
ncacn_np:192.168.1.1[\pipe\lsass]
UUID: 12345778-1234-abcd-ef00-0123456789ac
ncacn_ip_tcp:192.168.1.1[49159]
UUID: 6b5bdd1e-528c-422c-af8c-a4079be4fe48 Remote Fw APIs
ncacn_ip_tcp:192.168.1.1[49158]
UUID: 367abb81-9844-35f1-ad32-98f038001003
ncacn_ip_tcp:192.168.1.1[49157]
UUID: 12345678-1234-abcd-ef00-0123456789ab
ncacn_ip_tcp:192.168.1.1[49155]
UUID: 0b6edbfa-4a24-4fc6-8a23-942b1eca65d1
ncacn_ip_tcp:192.168.1.1[49155]
UUID: ae33069b-a2a8-46ee-a235-ddfd339be281
ncacn_ip_tcp:192.168.1.1[49155]
UUID: 4a452661-8290-4b36-8fbe-7f4093a94978
ncacn_ip_tcp:192.168.1.1[49155]
UUID: 76f03f96-cdfd-44fc-a22c-64950a001209
ncacn_ip_tcp:192.168.1.1[49155]
UUID: 7f1343fe-50a9-4927-a778-0c5859517bac DfsDs service
ncacn_np:192.168.1.1[\PIPE\wkssvc]
UUID: 3473dd4d-2e88-4006-9cba-22570909dd10 WinHttp Auto-Proxy Service
ncacn_np:192.168.1.1[\PIPE\W32TIME_ALT]
UUID: 1ff70682-0a51-30e8-076d-740be8cee98b
ncacn_np:192.168.1.1[\PIPE\atsvc]
...
Total endpoints found: 50
==== End of RPC Endpoint Mapper query response ====
You will notice that if you perform that query on the local computer, you will find many more endpoints than if you perform the query from a remote computer. That’s because many RPC endpoints are not exposed remotely and are only used for local interprocess communication.
Further reading: http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc738291(v=WS.10).aspx
And also: https://www.myotherpcisacloud.com/post/2014/02/16/verifying-rpc-network-connectivity-like-a-boss.aspx
Ошибка “
Сервер RPC недоступен
” (
The RPC server is unavailable
) появляется в Windows при ошибке коммуникации между двумя компьютерами по сети, когда компьютер (клиент RPC) не может подключиться к удаленному компьютеру (сервер RPC). В результате программа, которую вы запустили, не работает и возвращает ошибку, т.к. не можете получить данные с удаленного сервера. В этой статье мы разберем наиболее частые проблемы, которые могут препятствовать нормальному взаимодействию компьютеров через сеть по протоколу RPC.
Протокол RPC (Remote Process Call, удаленный вызов процедур) – это распространённый протокол взаимодействия приложений в локальной сети. В основном он используется для обмена данными с удалённым компьютерам, но есть некоторые программы, которые используют RPC для локальных взаимодействий между приложением и запущенной локально службой.
В типовом сеансе клиент RPC подключается к службе RPC Endpoint Mapper (сопоставления конечных точек) на RPC сервере по TCP порту 135 и запрашивает номер порта, на котором запущено нужное ему RPC приложение (служба). Служба RPC Endpoint Mapper возвращает клиенту номер динамического RPC порта, назначенного указанной службе при запуске. Затем RPC клиент взаимодействует с RPC службой по указанному TCP порту.
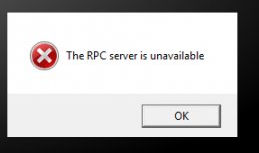
Если RPC клиент не смог подключиться к RPC серверу, в приложении появится ошибка:
The RPC server is unavailable
В современных версиях Windows (начиная с Windows Vista/2008) используется следующий диапазон динамических RPC портов (Dynamic RPC Port range): 49152 — 65535 (в Windows Server 2003 / XP и ниже использовался другой диапазон 1024 – 65535.
Наиболее распространённые проблемы, из-за которых не работает RPC взаимодействие между компьютерами:
- Удаленный компьютер выключен;
- Не запущены службы RPC на сервере;
- Вы пытаетесь подключиться к RPC серверу по неправильному имени (или как вариант, DNS имени сервера соответствует неверный IP адрес);
- Используются некорректные настройки сетевого подключение на клиенте или сервере;
- RPC трафик между клиентом и сервером блокируется файерволом;
Проверка доступности удаленного компьютера
Убедитесь, что удаленный компьютер включен, отвечает на ping по имени и IP адресу. Если RPC сервер не доступен по имени, проверьте корректность DNS записей и попробуйте сбросить DNS кэш на клиенте:
ipconfig /flushdns
.
Если имя компьютера, на котором запущен RPC-сервер недавно изменилось, попробуйте перерегистрировать его в DNS Active Directory:
ipconfig /registerdns
Проверка служб RPC
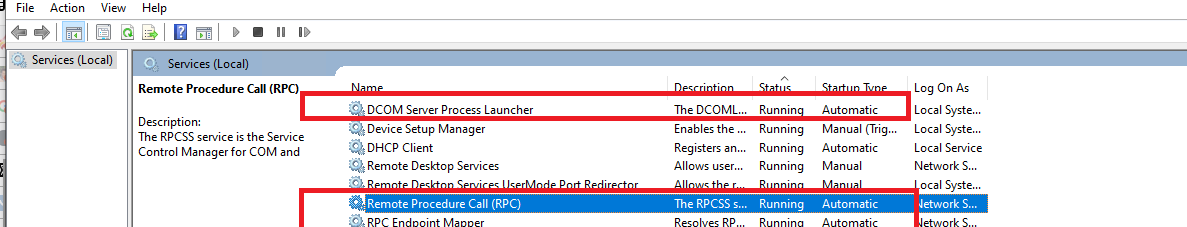
Проверьте, что на сервере запущены службы, которые необходимы для обработки входящих RPC подключений:
- Откройте консоль управления службами (services.msc);
- Убедитесь, что следующие службы запущены (статус Running), а тип их запуска – автоматический: Remote Procedure Call (RPC), RPC Endpoint Mapper и DCOM Server Process Launcher;
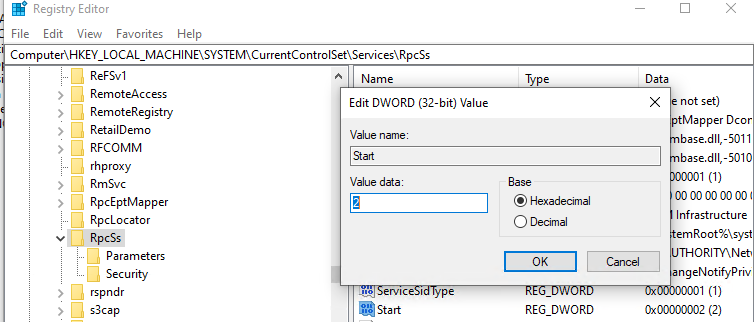
Если RPC службы отключены и не запускаются, попробуйте активировать их через реестр. Найдите ветки этих служб в реестре и измените значение параметра Start на 2 (автоматический запуск службы):
- Удаленный вызов процедур (RPC) — ветка реестра HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetservicesRpcSs
- Сопоставитель конечных точек RPC — HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetservicesRpcEptMapper
- Модуль запуска процессов DCOM-сервера — HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetservicesDcomLaunch
RPC блокируется файерволом (брандмауэром)
Убедитесь, что RPC трафик между компьютерами не блокируется файеволом. Если у вас используется Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security, нужно проверить или создать правила, разрешающие RPC трафик. Одно правило, разрешающее доступ к службе RPC Endpoint Mapper по порту TCP/135; второе должно разрешать доступ к RPC службе, которая вам нужна по динамическим RPC портам (RPC Dynamic Ports). Правила нужно создать для всех трех сетевых профилей: Domain, Private и Public.
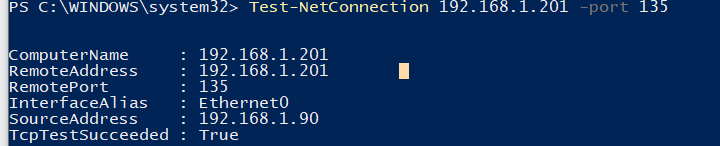
Проверьте с клиента, что на RPC сервере доступен 135 порт TCP (должен слушаться службой RPC Endpoint Mapper). Можно проверить доступность порта из PowerShell:
Test-NetConnection 192.168.1.201 -port 135
Если RPC порт доступен, должен появится ответ
TcpTestSucceeded:True
.
Вы можете получить список конечных точек RPC (сервисов и приложений), которые зарегистрированы на удаленном компьютере и анонсируются службой RPC Endpoint Mapper с помощью утилиту PortQry
portqry -n 192.168.1.201 -p tcp -e 135
В выводе PortQry можно найти номер порта, назначенный нужной вам службе RPC (она запущена?) и проверить, что этот порт не блокируется с клиента.
Если у вас используется сторонний файервол/антивирус, убедитесь, что он не блокирует RPC трафик и умеет корректно обрабатывать трафик динамических RPC портов.
Проверка сетевых протоколов и настроек
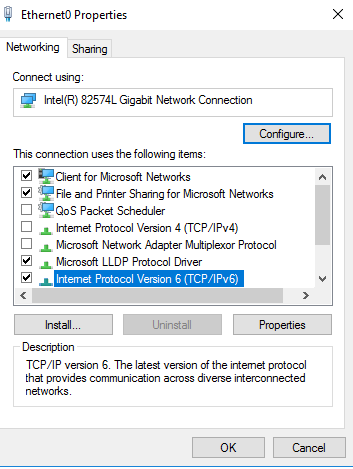
Убедитесь, что на вашем компьютере заданы корректные сетевые настройки: IP адрес, шлюз, маска сети, настройки DNS серверов (можно проверить настройки сети из PowerShell). Проверьте, что в настройках сетевого адаптера, используемого для подключения включены протоколы Internet Protocol Version 6 (TCP/IPv6) и File and Printer Sharing for Microsoft Networks
Некоторые сетевые приложения некорректно работают при отключенном протоколе TCP/IPv6, возвращая ошибку:
1722 The RPC server is unavailable
. Если после включения ipv6 ошибка RPC сохраняется, попробуйте отключить протокол Teredo через реестр:
Создайте в ветке реестра HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesTcpip6Parameters параметр типа DWORD с именем DisabledComponents и значением 8:
reg add hklmsystemcurrentcontrolsetservicestcpip6parameters /v DisabledComponents /t REG_DWORD /d 8
В некоторых случаях приходится получаить дамп трафика на RPC сервера и анализирвать его с помощью Microsoft Network Monitor 3.4 или Message Analyzer.
|
IFID value |
Named pipe |
Description |
|
12345778-1234-abcd-ef00-0123456789ab |
pipelsarpc |
LSA interface, used to enumerate users |
|
3919286a-b10c-11d0-9ba8-00c04fd92ef5 |
pipelsarpc |
LSA Directory Services (DS) interface, used to enumerate domains and trust relationships |
|
12345778-1234-abcd-ef00-0123456789ac |
pipesamr |
LSA SAMR interface, used to access public SAM database elements (e.g., usernames) and brute-force user passwords regardless of account lockout policy Oreilly library |
|
1ff70682-0a51-30e8-076d-740be8cee98b |
pipeatsvc |
Task scheduler, used to remotely execute commands |
|
338cd001-2244-31f1-aaaa-900038001003 |
pipewinreg |
Remote registry service, used to access the system registry |
|
367abb81-9844-35f1-ad32-98f038001003 |
pipesvcctl |
Service control manager and server services, used to remotely start and stop services and execute commands |
|
4b324fc8-1670-01d3-1278-5a47bf6ee188 |
pipesrvsvc |
Service control manager and server services, used to remotely start and stop services and execute commands |
|
4d9f4ab8-7d1c-11cf-861e-0020af6e7c57 |
pipeepmapper |
DCOM interface, supporting WMI |
Ports are channels through which information can be transferred. Contrary to the common perception of hardware ports such as a USB port, the article is in fact about software port 135. But they do share some sort of similarity in their function.
The article is about one port, in particular, port 135. You probably have a lot of questions about this port in your mind since there is not much-organized info about the port on the internet. So in this article, we will go over the basic meanings of software ports, port 135 and a bunch of related terms. We will also show you why and how you can close the port.
Contents
- 1 What exactly is a port?
- 1.1 TCP and UDP
- 2 What is Port 135?
- 2.1 Port 135 exploit
- 3 How to check live status of port 135?
- 4 How to close port 135 Windows?
- 4.1 Method 1: Using Windows Firewall
- 4.2 Method 2: Using Registry Editor
What exactly is a port?
There is no way that you are not familiar with the term ‘ports’ when it comes to hardware. Indeed you must have used a USB port at some point in your life. A port is an interface between your computer and external devices such as printers, mobiles, portable storage devices or other computers. They make use of data cables or chords to establish a link through which the flow of information takes place. But the topic at hand is not about these ports.
The ports that we mean have a software origin. Nonetheless, they serve the same purpose. These ports are locations to which data can be sent. They also do the job of recognizing this data and then handling them as required. But to put it more technically, ports are logical constructs in an operating system to identify a specific process or network. The port in the discussion, i.e port 135, is one of the many used in Windows OS.
TCP and UDP
Regardless of what kind of port you are going to read about, you will surely come across these two words a lot. So, it is obvious that you need to get a good grasp of what they actually mean. These terms are associated with the dispatch of bits of data otherwise called packets.
First, they travel from your computer to your router. Thereafter, these packets make way to a particular IP address. The first one, TCP, stands for Transmission Control Protocol. It is the protocol that makes it possible for you to mess around with the internet as you do.
When you search for something using a browser, you are actually trying to get into a new webpage. So, TCP sends a particular set of packets to the server’s address. Consequently, the server transmits a response likewise. The data received is then rearranged, like solving a puzzle, and you finally get into the web page.
The word, UDP, stands for User Datagram Protocol. It uses datagram for the dispatch of data and it is rather similar to packets. The key difference between UDP and TCP is that UDP will keep on sending one set of data after the other without caring about receiving responses.
On the other hand, TCP will resend a packet if it does not receive a response. Hence TCP is more responsible. Furthermore, checks the data it transmits for errors or corruption. But by eliminating the checking and receiving response processes, UDP is certainly a lot faster of the two.
What is Port 135?
It is the port that is mainly used in client-server relations, one among several ports that are used in the Windows Operating System. Client-server relation is one where a party called client, you in the majority of the time, requests for the particular information or access to a particular area and the server provides it. It is also closely involved with RPC and DCOM.
RPC stands for Remote Procedure Call. When you perform an action on your computer, your CPU runs the required procedures for it. Whereas in remote procedure call when you perform an action, its procedure can be run by some other computer or device in the network.
DCOM stands or Distributed Component Object Model and it consists of several programs and concepts that help the client program to send requests to the server in a Windows Operating System environment. Port 135 is one of the main interfaces that help out DCOM.
Port 135 exploit
While being very useful and essential to the working of your computer, ports, in general, are gateways to your system. Hence an open port may just what an outside may be looking for in order to extract your private information or to infect your system.
All the services and applications in your PC can, therefore, become an easy target. You certainly can’t risk opening Port 135 to the internet unnecessarily. There are hacking tools out there than can easily recognize the DCOM related activities in your system and easily exploit vulnerabilities.
How to check live status of port 135?
Before going through the whole procedure of closing a port you might want to first check if the port is actually open or not. You can use the Command prompt to achieve this without much hassle. In fact, the following procedure will give you the details of several ports or not. It is the fastest way to find out if ports are listening or not.
- Use your keyboard to press the Windows key and R key simultaneously.
- The Run dialogue box will appear. In the space against open, type in cmd and then press Enter or choose OK. Alternatively, you can use the Windows Search bar to look for cmd or Command prompt.
- Once the command prompt opens, type the following command and press Enter: netstat -na
The process of scanning all the ports of your port occurs next and it completes in the blink of an eye. You will be quickly shown the results on the screen. Find tcp port 135 under the local address column and if its state says “LISTENING” then it will be open.
How to close port 135 Windows?
At first, there is no absolute need for disabling port 135 for normal PC users. But if you are working around pirated, cracked versions of software regularly, you may want to disable TCP port 135 to avoid intrusion of harmful ransomware like WannaCry.
Method 1: Using Windows Firewall
This is the easiest method out there to close this port. It may seem a little wordy and long but don’t worry. Because most steps just include clicking options kind of how you install a game on your computer.
- Place the cursor on the Windows Search bar.
- Now, type in Control Panel and then press the Enter button.
- You will quickly get the search results. Open the app form them.
- Here you can see several tiles. Proceed to choose the System and Security option.
- Next, select Windows Defender Firewall.
- On the left pane, you will see an option called Advanced settings with a small shield icon. Choose it.
- Look at the left side yet again, there will be a lot of tiles. From them, choose the Inbound Rules option.
- This time around, look at the right side. And then select the New Rule option once you find it.
- A new window will open. Here you have to select the Port option and then hit Next.
- You will be faced with two questions. For the first one, you would want to choose TCP.
- For the second one choose Specific local ports and type in 135 in the accompanying space. Hit Next once you are done.
- On the next page go right ahead and choose the Block the connection option and then proceed with Next.
- Be sure to tick in the three checkboxes provided and then go on to the next page.
- Give it a name and description as you wish and then bring it home by hitting Finish.
- If you want to check the rules that you just set up open its properties.
- Click on the Protocols and Ports tab.
- Now you can check under Local Port.
In some cases, the Port will only close after a reboot.
Method 2: Using Registry Editor
The Registry editor is a pretty neat tool that you can use to modify a lot of programs on your PC. But do keep in mind that it is a database for all the system files and installed applications on your computer. Therefore be very careful while operating it.
- Open the Run dialogue box by pressing the Windows key and R key on your keyboard simultaneously.
- In the space beside open, type in Regedit and then press OK or hit Enter. (You can always use the windows search bar instead. Just type in Registry editor or Regedit and hit enter. Then you can find it in the search results.)
- On the navigation pane on your left side, expand the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE by using a double-click.
- Now look for the SOFTWARE file under it and expand it as well.
- Similarly, expand the Microsoft file and then proceed to open the Ole key under Microsoft.
- Look to the right side of the screen. Double click on the EnableDCOM option.
- Once it opens, change its data value from Y to N.
- Once this is done, navigate to this registry key: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE SOFTWARE Microsoft RPC
- On the right side, double-click on the DCOM Protocols option. You will see some data under the value data tab. Select it all and then delete it. This will leave it blank and that’s the way you need it to be.
- Port 135 has now been closed.
To disable other programs or services related to DCM, follow Control Panel >> Administrative Tools >> Services. Then disable these services: COM+ Event System, COM + System Application and, System Event Notification.
Wrapping up,
You have now learned a decent bit about port 135. We have also discussed checking port listening and closing the port. Do try out some tinkering with it if you need to. But careful though and you should know what you are doing.