Популярность смартфонов, планшетов, ноутбуков и прочих мобильных устройств вынуждает компании принимать политику, позволяющую сотрудникам использовать персональные электронные устройства для работы и доступа к корпоративным ресурсам. Однако внедрение этой концепции порождает ряд проблем
:
- Возникает угроза безопасности корпоративных данных, поскольку устройство может быть украдено или потеряно.
- Хранение данных пользователя только на локальном жестком диске ноутбука или планшета неэффективно. В такой ситуации, например, невозможно управлять процессом создания резервных копий, а это означает, что в случае выхода жесткого диска из строя данные могут быть утрачены.
- Пользователи часто работают с несколькими устройствами (например, с ноутбуком и планшетом или планшетом и смартфоном), что затрудняет синхронизацию данных. Для обеспечения актуальности данных на всех используемых устройствах часто применяется Microsoft SkyDrive, Dropbox, Google Drive или аналогичное «облачное» хранилище. Однако эти службы изначально предназначены для хранения пользовательских, а не корпоративных данных. Хранение данных компании в таком месте ставит под угрозу их безопасность. Кроме того, администратор не может управлять работой этих служб на личных компьютерах пользователей, что затрудняет их применение в корпоративной среде.
- Пользователям, работающим на мобильных компьютерах (ноутбуках, планшетах и др.), включенных в корпоративный домен Active Directory, часто требуется доступ к данным компании, когда они находятся в автономном режиме. В Windows Server 2012 и более ранних версиях Windows для обеспечения локальной доступности данных на компьютере пользователя даже при отсутствии подключения к сети преимущественно применяется технология автономных файлов Offline Files. Однако при этом файлы синхронизируются только при подключении пользователя к локальной корпоративной сети. При продолжительном нахождении в автономном режиме существует большая вероятность, что данные, с которыми работает пользователь, окажутся устаревшими.
Для решения всех этих проблем в Windows Server 2012 R2 реализована новая технология рабочих папок Work Folders, позволяющая пользователю получать доступ к корпоративным данным независимо от его местонахождения, а администратору – управлять параметрами этой функции и данными пользователя.
Функция Work Folders открывает доступ к актуальным данным независимо от того, имеет ли пользователь подключение к локальной сети, то есть выполняет практически те же функции, что и «облачные» службы, с одним лишь отличием, которое заключается в том, что рабочие папки управляемы. Work Folders позволяет администратору управлять данными пользователей и их подключениями к рабочим папкам. Администратор может применять шифрование, управлять доступом пользователей к этой функции, а также принудительно устанавливать параметры безопасности на устройствах, использующих Work Folders, даже если они не принадлежат домену.
Применение Work Folders доступно для различных типов устройств независимо от их доменной принадлежности и наличия подключения к локальной сети (например, дома или в дороге). В отличие от других технологий аналогичного назначения в более ранних версиях Windows, рабочие папки могут быть опубликованы в интернете с помощью Web Application Proxy (возможность, также впервые реализованная в Server 2012 R2), что позволяет пользователям синхронизировать данные в любом месте, где есть подключение к интернету. Для публикации рабочих папок можно применять и другие механизмы, такие как Microsoft Forefront Unified Access Gateway (UAG). Можно также задействовать Forefront Threat Management Gateway (TMG), но это решение является устаревшим.
Реализация Work Folders
На момент написания этой статьи клиентская поддержка Work Folders доступна только для устройств под управлением Windows 8.1 и Windows RT 8.1. Однако Microsoft планирует распространить поддержку на устройства под Windows 8, Windows 7, а также на устройства на базе Apple iOS, такие как iPad. Есть сведения, что будут поддерживаться и устройства на базе Google Android. Так или иначе, очевидно, что Microsoft открывает двери AD для других платформ, от чего клиенты только выиграют.
Для включения Work Folders необходим, как минимум, один файловый сервер Server 2012 R2. Должны быть применены обновления схемы Server 2012 R2 по причинам, которые будут изложены ниже. Для полной реализации возможностей Work Folders (например, для использования групповой политики для установки параметров клиентов) рекомендуется (не обязательно) иметь, как минимум, один контроллер домена (DC) под управлением Server 2012 R2.
Применение Work Folders не требует повышения функционального уровня домена до Server 2012. Функциональность Work Folders фактически составляет подмножество роли файловых служб и служб хранилища File and Storage Services и легко устанавливается с помощью диспетчера серверов. Для более эффективного управления данными пользователя рекомендуется (не обязательно) также установить диспетчер ресурсов файлового сервера и включить дедупликацию данных. Диспетчер ресурсов файлового сервера File Server Resource Manager позволяет устанавливать квоты и политики блокировки файлов для папок пользователей. Дедупликация данных, впервые появившаяся в Server 2012, позволяет оптимизировать использование дискового пространства за счет того, что идентичные блоки данных записываются лишь однократно. Для защиты критически важных корпоративных данных, хранящихся в рабочих папках, рекомендуется также использовать службу управления правами Active Directory (AD RMS) или шифрованную файловую систему (EFS).
При установке функции Work Folders устанавливаются также ведущий базовый экземпляр IIS (Hostable Web Core) и средства управления IIS. Настройка параметров IIS не требуется, но необходимо назначить доверенный SSL-сертификат файловому серверу в консоли IIS и привязать его к порту 443 для веб-сайта по умолчанию. Сертификат должен содержать имя файлового сервера и имя, под которым будут публиковаться рабочие папки (если эти имена не совпадают). Сертификат должен быть доверенным для клиентов. Обычно доверенный статус не проблема для устройств, принадлежащих домену, но для собственных устройств, используемых в рамках концепции BYOD, могут понадобиться дополнительные действия (например, импорт сертификата Root CA в локальное хранилище сертификатов Trusted Root CA клиента), кроме тех случаев, когда используется общий сертификат от удостоверяющего центра (СА), который является доверенным в глобальном масштабе. Если предполагается задействовать функцию автообнаружения, которая будет рассматриваться ниже, то в сертификате должно быть указано SAN-имя workfolders.имя домена, где имя домена – это DNS-имя вашего домена.
После установки Work Folders подготовьте общий ресурс для хранения данных пользователя. Общий ресурс может располагаться в любом месте, доступном для файлового сервера, на котором установлены Work Folders. Для созданного корневого общего ресурса рекомендуется оставить предусмотренные по умолчанию разрешения для общего ресурса и разрешения NTFS и включить перечисление на основе доступа. Если перечисление на основе доступа включено, пользователи могут видеть только те папки, к которым им разрешен доступ.
Когда создан корневой общий ресурс, в диспетчере серверов запустите мастер создания общего ресурса синхронизации New Sync Share Wizard. В диспетчере серверов нажмите File and Storage Services, затем Work Folders, и в меню Tasks выберите New Sync Share. Мастер последовательно проходит процесс создания структуры рабочих папок. После выбора корневой папки, подготовленной в качестве общего ресурса, выберите формат образования имен вложенных папок («псевдоним пользователя» или «псевдоним@домен»). Если в лесу AD DS имеется несколько доменов, для образования имен рекомендуется использовать формат «псевдоним@домен».
Управление доступом к рабочим папкам может быть организовано по пользователям или группам. Соответствующая установка выполняется на странице Sync Access (см. экран 1). Пользователи или группа должны быть частью домена AD DS. Это означает, что, хотя принадлежность домену не является обязательной для устройств, пользователи все же должны иметь достоверные учетные данные Active Directory (AD). Для облегчения последующего управления рекомендуется задать группу. Рекомендуется также отключить наследование разрешений для Work Folders, чтобы каждый пользователь имел монопольный доступ к своим файлам.
 |
| Экран 1. Управление доступом к рабочим папкам |
На последней странице мастера можно задать дополнительные параметры безопасности для устройств, используемых для доступа к рабочим папкам. Как показано на экране 2, можно задать шифрование и автоматическую блокировку экрана, которая снимается после ввода пароля.
 |
| Экран 2. Настройка дополнительных параметров безопасности на устройствах, используемых для?доступа к рабочим папкам |
Отметим, что применение параметров безопасности, относящихся к Work Folders, осуществляется не с помощью групповой политики. Параметры вступают в силу, когда пользователь устанавливает соединение с Work Folders, и применяются на компьютерах, как принадлежащих, так и не принадлежащих домену.
Настройка Work Folders на клиентах
На клиентах Windows 8.1 и Windows RT 8.1 настройка Work Folders может выполняться вручную или автоматически с помощь групповой политики. На компьютерах, принадлежащих домену, параметры проще устанавливать с помощью групповой политики, но в этом случае необходимо иметь, как минимум, один контроллер домена Server 2012 R2. Настройка клиентов, не принадлежащих домену, выполняется вручную. Рассмотрим оба метода, а также случай, когда имеется несколько файловых серверов.
Настройка клиентов с помощью групповой политики. Автоматическая настройка Work Folders на клиентах с помощью групповой политики требует установки нескольких параметров объектов групповой политики (GPO). Рабочие папки организованы по пользователям, поэтому в редакторе групповой политики (GPE) перейдите к разделу User ConfigurationPoliciesAdministrative TemplatesWindows ComponentsWork Folders и включите политику Specify Work Folders settings. Укажите URL-адрес рабочих папок, определяя местонахождение файлового сервера, где выполнена установка Work Folders. Обычно таким адресом является https://fileserverFQDN, где fileserverFQDN – полное доменное имя файлового сервера (FQDN).
Существует возможность принудительной автоматической настройки для каждого пользователя, которую следует применять с осторожностью, так как при ее включении у всех пользователей, к которым применим данный объект GPO, на каждом устройстве, где они будут регистрироваться (если это устройство поддерживает Work Folders), будет выполняться настройка Work Folders без запроса на подтверждение данного действия. В некоторых случаях (например, если пользователи работают на многих рабочих станциях) это может оказаться нежелательным.
При желании в разделе Computer ConfigurationPoliciesAdministrative TemplatesWindows ComponentsWork Folders редактора групповой политики можно применить параметр, предусматривающий автоматическую настройку Work Folders для всех пользователей. После этого на компьютерах, где применен данный параметр объекта GPO, для каждого пользователя, выполняющего процедуру регистрации, будет выполнена соответствующая настройка Work Folders, если этому пользователю разрешено применение Work Folders.
После применения этих параметров к пользователям (и, при желании, к компьютерам), пользователи домена смогут задействовать Work Folders после обновления групповой политики или перезапуска клиентского компьютера. Если параметры Work Folders не применяются с помощью групповой политики, проверьте сертификат файлового сервера, который чаще всего является причиной проблем. Сертификат должен иметь достоверное имя, должен быть выдан доверенным корневым центром сертификации и назначен порту 443 веб-сайта по умолчанию. Также убедитесь в том, что на сервере, где выполнена настройка Work Folders, работает служба общих папок синхронизации Windows. Хотя эта служба автоматически запускается при установке Work Folders, мне доводилось наблюдать случаи, когда она прекращала работу.
Настройка клиентов вручную. Для компьютера (например, планшета), не принадлежащего домену, включение Work Folders выполняется из панели управления. В Windows 8.1 и Windows RT 8.1 на панели управления есть приложение Work Folders (см. экран 3).
 |
| Экран 3. Приложение Work Folders на панели управления |
Технология Work Folders имеет функцию автообнаружения, которая позволяет системам, не принадлежащим домену, легко находить нужный файловый сервер, где размещены Work Folders. Для использования этой функции необходимо, чтобы в общей зоне DNS был прописан узел размещения рабочих папок или псевдоним, указывающий на нужный файловый сервер. В этом случае пользователю для настройки приложения Work Folders на устройстве, не принадлежащем домену, достаточно ввести почтовый адрес. По той части почтового адреса, которая указывает на домен, устройство выполнит поиск узла размещения рабочих папок или псевдонима в DNS. Пользователь также должен указать корректные имя и пароль доменной учетной записи, для которой разрешено применение Work Folders.
Если функция автообнаружения использоваться не будет, то пользователи при настройке приложения Work Folders могут указывать URL-адрес файлового сервера (см. экран 4).
 |
| Экран 4. Ввод URL-адреса сервера, где размещаются Work?Folders |
В этом случае вручную введите URL-адрес, используемый для публикации файлового сервера, где размещаются Work Folders, в интернете. Если функция автообнаружения не включена, URL-адрес может быть любым. Как видно из примера, приведенного на экране 4, соединение устанавливается по протоколу HTTP Secure (HTTPS), что значительно упрощает публикацию Work Folders. Пользователь, регистрирующийся как локальный пользователь, после ввода URL-адреса должен указать достоверные учетные данные AD, после чего на его устройстве выполняется настройка Work Folders. Пользователь также должен принять политики безопасности, показанные на экране 5. Таким образом он выражает согласие с тем, что администратор будет управлять данными в его рабочей папке и применять меры безопасности к его устройству.
 |
| Экран 5. Принятие политик безопасности в отношении устройства, используемого для доступа к Work Folders |
Несколько файловых серверов. Если имеется несколько файловых серверов, используемых для размещения Work Folders, то для указания местоположения правильного экземпляра Work Folders для каждого пользователя можно воспользоваться новым атрибутом пользователя msDS-SyncServerUrl в AD DS (включен в схему Server 2012 R2). Этот атрибут можно найти на вкладке Attribute Editor в свойствах учетной записи пользователя. После настройки данного атрибута пользователь будет направляться к заданному файловому серверу для доступа к своему экземпляру Work Folder. Настойка этого атрибута не является обязательной в сценариях развертывания, когда для размещения Work Folders используется только один файловый сервер или если Work Folders настраивается без участия функции автообнаружения.
Использование Work Folders
После применения параметров Work Folders пользователи могут получать доступ к своим рабочим папкам. Независимо от доменной принадлежности их устройств, в проводнике появляется новый значок (см. экран 6). Используются рабочие папки так же, как и любые другие локальные папки. Единственное отличие состоит в том, что в списке возможных вариантов, открываемом щелчком правой кнопки мыши на значке Work Folders, присутствует возможность применения синхронизации с сервером. Если синхронизация не работает, убедитесь, что у вас есть локальные административные полномочия на клиентской системе, чтобы применить политики безопасности с сервера.
 |
| Экран 6. Значок Work Folders в «Проводнике» |
При желании пользователь может контролировать состояние рабочей папки независимо от доменной принадлежности своего устройства. Как показано на экране 7, можно выяснить, сколько доступного пространства имеется на сервере и когда файлы были синхронизированы в последний раз.
 |
| Экран 7. Контроль состояния рабочих папок из панели управления |
Управление Work Folders
Администраторы могут управлять рабочими папками через интерфейс Work Folders, интегрированный с консолью диспетчера серверов. В любой момент можно увидеть, какие пользователи подключены к Work Folders, как показано на экране 8.
 |
| Экран 8. Информация о пользователях, подключенных к Work Folders в данный момент |
Щелчком правой кнопки мыши на имени пользователя открываются два варианта: Properties и Suspend User (см. экран 9).
 |
| Экран 9. Переход к подробной информации |
При выборе Properties можно увидеть, сколько устройств у выбранного пользователя ассоциировано с его рабочей папкой (см. экран 10). Выбор Suspend User останавливает синхронизацию между локальной рабочей папкой пользователя и его рабочей папкой на сервере. При этом пользователь по-прежнему имеет доступ к локальной копии данных. Для возобновления синхронизации щелкните правой кнопкой на имени пользователя и выберите соответствующий вариант.
 |
| Экран 10. Отображение информации о том, сколько устройств у данного пользователя ассоциировано с его рабочей папкой |
По умолчанию администратор не имеет доступа к серверной копии рабочей папки пользователя, поскольку разрешения автоматически устанавливаются только для владельца. Однако при необходимости можно вступить во владение папкой и получить доступ к данным. Каждый пользователь имеет доступ к серверной копии своих данных. При этом другие папки для него недоступны, и в случае, если включено перечисление на основе доступа, этот пользователь даже не будет видеть других папок.
Work Folders в Server 2012 R2 – большой шаг вперед по сравнению с существующими технологиями синхронизации и обеспечения доступности данных. Функция обладает преимуществами «облачного» решения, но позволяет администраторам управлять параметрами технологии и данными пользователя. Рабочие папки могут быть очень удобны для мобильных пользователей, особенно в среде, организованной по принципу BYOD. Если Microsoft, как и было обещано, откроет эту технологию для других платформ, то пользователи смогут всегда иметь доступ к своим данным.
Содержание
- 1 Introducing Work Folders on Windows Server 2012 R2
- 1.1 Work Folders as Experienced by an Information Worker
- 1.2 Work Folders as Experienced by an IT Admin
- 1.3 Work Folders Capabilities
- 1.4 How Work Folders Compares to Other Microsoft Sync Technologies
- 1.5 More Information
- 2 Configure Work Folders in Windows Server 2012 R2
- 2.1 Work Folders: Prerequisites
- 2.2 Installing Work Folders Server Role
- 2.3 Creating Work Folders Security Groups
- 2.4 Create and Configure Work Folders Data Folders
- 2.5 Configuring SSL Certificate
- 2.6 Configuring Work Folders from a Windows 8.1 Device
- 3 Windows Server 2012 R2. Work Folders – синхронизация файлов между устройствами — Oh, MSBRO !
- 3.1 Настройка Work Folder на Windows Server 2012 R2
- 3.2 Настройка Work Folder на клиенте
- 3.3 Настройка Work Folder с помощью групповой политики
- 4 10 новых сногсшибательных возможностей в Windows Server 2012 R2
- 4.1 Work Folders («Рабочие папки»)
- 4.2 Конфигурация желаемого состояния
- 4.3 Storage Tiering (распределение данных по уровнямхранилищ)
- 4.4 Storage Pinning (прикрепление данных кхранилищу)
- 4.5 WriteBack Cache (Кэш обратной записи)
- 4.6 Дедупликация на работающих виртуальных машинах
- 4.7 Параллельное восстановление
- 4.8 Workplace Join («подключение к рабочемуместу»)
- 4.9 Многопользовательский VPN-шлюз
- 4.10 Роль Windows Server Essentials
- 5 Windows Server 2012 R2. Work Folders – синхронизация файлов между устройствами
Introducing Work Folders on Windows Server 2012 R2
This post is a part of the nine-part “What’s New in Windows Server & System Center 2012 R2” series that is featured on Brad Anderson’s In the Cloud blog. Today’s blog post covers Windows Server 2012 R2 Work Folders and how it applies to Brad’s larger topic of “People-centric IT.” To read that post and see the other technologies discussed, read today’s post: “Making Device Users Productive and Protecting Corporate Information.”
Hello, my name is Nir Ben-Zvi and I work in the Windows Server team. I’m very excited to introduce to you Windows Server Work Folders, which is a new file server based sync solution in Windows Server 2012 R2 and Windows 8.1.
During Windows Server 2012 R2 planning, we noticed two converging trends around managing and protecting corporate data:
· Users: “I need to work from anywhere on my different devices”
· IT: “I’d to empower my Information Workers (users) while reducing information leakage and keeping control of the corporate data that is sprawled across devices”
Work Folders enables IT administrators to provide Information Workers the ability to sync their work data on all their devices wherever they are while remaining in compliance with company policies. This is done by syncing user data from devices to on-premise file servers, which are now extended to include a new sync protocol.
Work Folders as Experienced by an Information Worker
To show how this works, here’s an example of how an information worker, Joe, might use Work Folders to separate his work data from his personal data while having the ability to work from any device: When Joe saves a document on his work computer in the Work Folders directory, the document is synced to an IT-controlled file server. When Joe returns home, he can pick up his Surface RT (where the document is already synced) and head to the beach. He can work on the document offline, and when he returns home the document is synced back with the file server and all of the changes are available to him the next day when he returns to the office.
Looks familiar? Indeed, this is how consumer storage services such as SkyDrive and business collaboration services such as SkyDrive Pro work. We kept the user interaction simple and familiar so that there is little user education required. The biggest difference from SkyDrive or SkyDrive Pro is that the centralized storage for Work Folders is an on-premise file server running Windows Server 2012 R2, but we’ll get to that a little later in this post.
Work Folders as Experienced by an IT Admin
IT administrators can use Work Folders to gain more control over corporate data and user devices and centralize user work data so that they can apply the appropriate processes and tools to keep their company in compliance. This can range from simply having a copy of the data if the user leaves the company to a wide range of capabilities such as backup, retention, classification and automated encryption.
For example, when a user authors a sensitive document in Work Folders on their work PC, it gets synced to the file server. The file server then can automatically classify the document content, if configured using File Server Resource Manager, and encrypt the document using Windows Rights Management Services before syncing the document back to all the user’s devices. This allows a seamless experience for the user while keeping the organization in compliance and preventing leakage of sensitive information.
For more details about Work Folders deployment see the following blog: Deploying Work Folders in your lab and Channel 9 video
Work Folders Capabilities
Work Folders is part of the People-Centric IT pillar in Windows Server 2012 R2. This pillar includes other important capabilities such as Workplace Join, Web Application Proxy and Device management. While these capabilities are integrated, they are also independent so that you can use them as standalone solutions to get immediate value as you deploy each capability.
Our main design focus around Work Folders was to keep it simple for the Information Workers while allowing IT administrators to use the familiar low cost, high scale Windows file server with all the rich functionality available on the backend from high availability to comprehensive data management.
Here is some of the functionality that Work Folders includes:
- Provide a single point of access to work files on a user’s work and personal PCs and devices (Windows 8.1 and Windows RT 8.1, with immediate plans to follow up with Windows 7 and iPad support and other devices ly in the future)
- Access work files while offline and sync with the central file server when the PC or device next has Internet or network connectivity
- Maintain data encryption in transit as well as at rest on devices and allow corporate data wipe through device management services such as Windows Intune
- Use existing file server management technologies such as file classification and folder quotas to manage user data
- Specify security policies to instruct user PCs and devices to encrypt Work Folders and use a lock screen password, for example
- Use Failover Clustering with Work Folders to provide high-availability solution
I should mention a few scoping decisions that we made in this release so that we could complete Work Folders in the short release cycle for Windows Server 2012 R2:
- Backend storage is provided by on-premise file servers and Work Folders must be stored in local storage on the file server (e.g.: data can be on local shares on a Windows Server 2012 R2)
- Users sync to their own folder on the file server – there is no support for syncing arbitrary file shares (e.g.: sync the sales demos share to my device)
- Work Folders doesn’t provide collaboration functionality such as sharing sync files or folders with other users (we recommend using SkyDrive Pro if you need document collaboration features)
How Work Folders Compares to Other Microsoft Sync Technologies
Finally, I’d to discuss how Work Folders fits in with other sync solutions that Microsoft provides, mainly SkyDrive and SkyDrive Pro.
As described above, Work Folders provides a solution for customers that prefer to use traditional Windows file servers as the backend storage for the corporate data synced from user’s devices.
This would work well for organizations that are already using a home folders or folder redirection solution or customers that already have established practice for managing and storing user data on file servers.
For customers that use SharePoint, SkyDrive Pro is a great solution that provides additional functionality ranging from rich collaboration features to a cloud service availability using Office 365
The table below shows the different options:
| Consumer / personal data | Individual work data | Team / group work data | Personal devices | Access protocol | Data location |
| SkyDrive | X | X | HTTPS | Public cloud | |
| SkyDrive Pro | X | X | X | HTTPS | SharePoint / Office 365 |
| Work Folders | X | X | HTTPS | File server | |
| Folder Redirection / Client-Side Caching | X | SMB (only from on-prem or using VPN) | File server |
More Information
For more details about Work Folders, you can view the following presentations that are available online:
· Work Folders Overview on TechNet
· Deploying Work Folders in your lab
· Work Folders overview in TechEd 2013
· Work Folders deep dive in TechEd 2013
To see all of the posts in this series, check out the What’s New in Windows Server & System Center 2012 R2 archive.
Источник: https://blogs.technet.microsoft.com/filecab/2013/07/09/introducing-work-folders-on-windows-server-2012-r2/
Configure Work Folders in Windows Server 2012 R2
Work Folders is a new feature of Windows Server 2012 R2 that allows users to have access to individual corporate data folders, no matter where the users are and from what device they are connecting. At present, only Windows 8.1 is supported, but iOS and Android clients are reportedly in the making.
This functionality may sound a bit familiar to cloud-based file-sharing solutions Microsoft OneDrive, DropBox, and Google Drive. The Work Folders option tends to give administrators a bit more control over what data is accessible, and they can have improved control over user connections enforcing device connection policies.
Work Folders: Prerequisites
In order to install Work Folders, you need the following configured (as a minimum):
- Windows Server 2012 R2 Standard or Enterprise
- Windows 8.1 (Any versions) or Windows 8.1 RT
For external and production solutions, you also need the following:
- Public CA issued SSL certificate (internally generated SSL cert will do for domain-joined clients or in demo scenarios)
- Automatic server discovery DNS settings
- Reverse Proxy (preferred, but not required)
Installing Work Folders Server Role
No matter if the Work Folders will be used only internally or both internally and externally, the first step is installing the Work Folders Server Role.
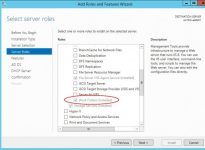
- From the Server Manager, choose Add Roles and Features.
- From the Select Server Roles, go to File and Storage Services / File and iSCSI Services, then select Work Folders.
A pop-up will inform you about the additional IIS Hostable Web Core component that will be installed as well.
Creating Work Folders Security Groups
Work Folders are working much regular NTFS folders from a security perspective. To grant/deny access, you rely on global security groups within Active Directory.
In this example, I’m going to create an Active Directory group called “Work Folders Users,” that is allowed full access rights to the Work Folders directories. Remember, these groups can be anything, or maybe you already have a full set of AD security groups in your organization than can be used for this, such as Sales, HR, Production, IT, etc.
- Logon to your Server 2012 R2 domain controller, go to the Active Directory Users and Computers console, and choose Create new group by using icon in toolbar or right-click / new / group).
- Select Global and Security as options and give it a name and description (Work Folders Users).
Create and Configure Work Folders Data Folders
In this last step, we will create and configure a sync share for work folders, granting access rights to the earlier created AD security group.
- From the Server 2012 R2 member server in the domain, go to Server Manager / File and Storage Services / Work Folders.
- Start the New Sync Share Wizard or click Task / New Sync Share.
- Select your 2012 R2 server and select Enter a local path. Browse to the directory you want to make available as sync share (c:datasample work folders directory, in my example).
- Select user [email protected] as the structure for user folders. With this option selected, if a domain user logs on, his folder structure is created as [email protected] In the other case, only the username would be visible, making it more difficult to distinguish users from different domains.
- In the Sync Access step of the configuration wizard, click Add… and select Work Folders Users from the Active Directory list of groups. Make sure the Disable inherited permissions and grant users exclusive access to their files is enabled.
- In the Device Policies window, check Encrypt Work Folders and automatically lock screen, and require a password. Encrypt work folders makes sure the synced folders to the local device will be encrypted. The latter sets certain additional security parameters for the device from which you want to use work folders sync.
- Click Next to complete the Work Folders Sync Share creation.
Configuring SSL Certificate
As the main idea of the Work Folders feature is to allow connections from outside of your network to internal file shares, security is very important. That’s why we need to present the web service with an SSL certificate. You have a few options here:
- Fulfill a certificate request from this machine to an internal Certificate Authority. Where this will work fine for internal / domain-joined clients, the internal CA won’t be trusted on non-domain joined clients.
- Import a public CA-generated certificate on the work folders server; this can be a single name, SAN (multi-name certificate) or wildcard certificate. I suggest you use “workfolders.company.com”, as this is the default naming convention.
In this example, I’ll use a wildcard certificate for my domain “*.2012R2.demo”, which is installed in my computer personal certificate store (MMC / Certificates / Computer Account / Personal / Import).
Once your SSL certificate is installed on the work folders server, you have to “bind” this certificate. As you don’t have the IIS Admin Tools installed on the server, we have to use a netsh command to do this. To make sure we enter the Thumbprint of the certificate correctly, let’s open up this certificate from the MMC again.
The netsh command looks this (Note: This isn’t a Powershell cmdlet, so run this in an elevated command prompt).
netsh http add sslcert ipport=0.0.0.0:443 certhash= c844d6ac45eadf6443c45233af8c836e29287e57 appid={CE66697B-3AA0-49D1-BDBD-A25C8359FD5D} certstorename=MY
This completes the configuration of the Work Folders sync share from the server side. Now let’s move over to the Windows 8.1 client machine.
Configuring Work Folders from a Windows 8.1 Device
In this example, the Windows 8.1 client is domain-joined. However, it’ll also work if your SSL certificate is trusted on a non-domain-joined client.
- From your Windows 8.1 client, go to Control Panel / Work Folders option / Setup Work Folders or type work folders in the Charm Bar / Search. The Manage Work Folders option comes up.
- Click Set up work folders.
- The work folders have an “autodetect” mechanism built in, which will look for an entry “workfolders.company.com” (make sure you have this entry as a host name in your internal and public DNS zone namespace). You have the option to use this autodetect or enter the connection URL yourself. In my situation, I chose autodetect by entering my email address.
- This will bring me to the configuration wizard for Work Folders on my client. I keep the default location for the synced folder on my client as c:userspeter.2012R2.demowork folders.
- Now I must accept the security policies for my client device, which were specified earlier on my server. Click I accept these policies on my PC.
- Click Next, and the configuration is completed in a few seconds. If all goes well, data from the server location will get synchronized to the specified folder on my client. Again, this data will be stored in an encrypted way (hence the green color in file explorer when viewing the folder).
That’s all! Enjoy having your corporate users’ data folders synchronized to your end-user’s client device in a safe, secure, and simple but effective way. Happy Work Folder-ing!
Источник: https://www.petri.com/configure-work-folders-windows-server-2012-r2
Windows Server 2012 R2. Work Folders – синхронизация файлов между устройствами — Oh, MSBRO !
хорошая статья.
но внесу немного поправок (текст ПРИМЕЧАНИЯ: )
Начинаем знакомиться с новыми возможностями и ключевыми усовершенствованиями, которые нас ожидают в новом обновлении серверной линейки Microsoft — Windows Server 2012 R2, До даты официального выпуска осталось чуть больше месяца (а это, напомним, случится 18 октября 2013 года). Сегодня речь пойдет о новом функционале Windows Server 2012 R2 под названием Work Folders.
Нередка ситуация, когда работник для работы с корпоративными данными используется больше чем два устройства (например, ноутбук и планшет). В этой ситуации, чтобы пользователи всегда работали с актуальными версиями своих данных, перед ИТ-службой встает задача синхронизации файлов. Для этих целей можно воспользоваться SkyDrive, DropBox или походим сервисом.
Однако не всегда возможно хранить данные в «облаке», хотя бы из соображений конфиденциальности и безопасности. Новая функция Windows Server 2012 R2 Work Folders (или «Рабочие папки») – позволяет пользователям синхронизировать свои личные файлы в корпоративной сети с любыми своими устройствами.
По сути, Work Folders является аналогом Dropbox для корпоративных пользователей.
Благодаря «Рабочим папкам» на платформе Windows Server 2012 R2 возможно организовать функциональный и безопасный сервис репликации файлов пользователей между несколькими устройствами. Work Folders на базе файлового сервера позволяет организовать «корпоративный SkyDrive.
Помимо всего прочего, к пользовательским данным на корпоративном файловом сервере можно применять такие политики, как квотирование (Quota), блокировка запрещенных типов файлов (File Screening), а также динамический контроль доступа (Dynamic Access Control) и т.д., т.е.
полный комплекс мер по обеспечению защиты информации.
Как и Dropbox, Work Folders позволяет хранить копии файлов на стороне сервера и клиента, и при каждом подключении клиента к серверу выполняется синхронизация данных. Благодаря данной функции пользователь может синхронизировать свои рабочие папки со своим мобильным устройством (ноутбуком, планшетом и т.д.) и осуществлять редактирование документов, даже без подключения к корпоративной сети (offline). При следующем соединении с корпоративной сетью клиент Work Folders осуществит синхронизацию изменений.
На данный момент технологию Work Folders поддерживают только устройства под управлением Windows 8.1, в которую клиент Work Folders уже встроен. В ближайшем будущем будет добавлена поддержка популярных мобильных устройств: девайсов на Windows 7, Windows 8, Android, а также iOS.
Служба синхронизации Work Folder должна работать на Windows 2012 R2 с установленной ролью файлового сервера. Work Folder также возможно интегрировать со службой Active Directory Rights Management Services, позволяющей обеспечить защиту пользовательских данных.
Настройка Work Folder на Windows Server 2012 R2
Функционал Work Folders в Windows Server 2012 R2 входит в состав роли File and Storage Services и включить его можно с помощью консоли Server Manager или PowerShell.
При установке функционала Work Folders также будет установлен сервер IIS Web Core, являющийся обязательным компонентом технологии и необходимый для обслуживания клиентов.
После установки функции, нужно открыть консоль Server Manager ->File Server -> Work Folders и указать каталог, в котором будут храниться «Рабочие папки» пользователей.
ПРИМЕЧАНИЯ:
желательно папку Work Folders сразу расшарить по сети. Права по сети — полный доступ, NTFS права не назначаем.
Следующий шаг – выбор структуры папок. Имена подпапкок (каталоги конечных пользователей сервиса) могут содержать только имена пользователей (псевдонимы) или их полные email адреса.
ПРИМЕЧАНИЯ:
есть смысл в тестовом варианте выбрать User Alias.
Затем нужно указать список пользователей и групп, имеющих доступ к данной папке. Если нужно, чтобы у администратора сервера не было доступа к данным пользователей, отметьте флажок «Disable inherited permissions and grant users exclusive access to their files».
ПРИМЕЧАНИЯ:
Можно группу не создавать. В тестовом варианте работает и с обычной учетной записью.
Далее необходимо указать будут ли на клиентских устройствах применяться политики защиты данных, такие как шифрование (на клиенте Windows 8.1 используется EFS) и защита данных паролем.
ПРИМЕЧАНИЕ:
EFS можно и не отмечать.Дома стояла Windows 8.1 со бновлениями за 02-2015, синхронизация сработала.
«Рабочие папки» синхронизируется посредством веб сервера IIS по протоколу HTTPS, поэтому для работы придется настроить на IIS шифрование SSL/TLS. После окончания работы мастера, нужно создать новый сертификат типа Web Server Template, содержащий FQDN имя сервера.
Примечания:
Сертификат нужно выпустить на Enterprise CA. Важно чтобы ваш клиентский компьютер доверял сертификату.
Как выпустить сертификат:
В консоли CA назначаем на шаблон ВЕБ СЕРВЕР права учетной записи компьютера и учетной записи пользователя Enfoll и Read.
Заходим в консоль НА КОМПЬЮТЕРЕ КОТОРЫЙ БУДЕТ СЕРВЕРОМ Work Folders и делаем запрос на сертификат.
Certificates — Personal — New Reqest.
Выбираем Web Server и кнопку Properties.
Заполняем поля CN и DNS.
В поле DNS всавляем ВСЕ возможные имена сертификата.
(*.myfirma.ru, workfolders.myfirma.ru, server1.domen.local, server1):
ОБЯЗАТЕЛЬНО сделайте у вашего провайдера в редакторе ДНС запись тип «А»о внешнем имени подключения. workfolders.myfirma.ru
Если все совсем плохо, тогда попробуйте выпустить сертификат на внешний IP адрес и подключаться вроде как https://200.100.15.45 (возможно сработает).
Вставляем Frendli name:
делаем отметку что ключ можно экспортировать (может пригодится):
Если все хорошо, то будет активна кнопка Enroll
И отметив Web Server сертификат можно выпустить:
Сертификат будет помещен Certificates — Local Computer — Personal.
Обязательная отметка — Нарисованный «ключик» на самом сертификате (левый верхний уголок).
Если что то пойдет не так, то выпускаем запрос на сертификат, потом импортируем запрос Submin new Request.
Далее сертификат импортируем на наш сервер в Certificates — Local Computer — Personal
После этого на IIS сертификат можно будет использовать.
Данный сертификат необходимо выбрать в качестве SSLсертификата на сайте IIS.
ПРИМЕЧАНИЯ:
Я опубликовал сервер через TMG по 443 порту.
для этого создал свое определение протокола на 443 порту:
Внутренний IP адрес сервера в сети:
Настройка Work Folder на клиенте
Следующий этап – настройка клиента Work Folder на пользовательском девайсе. Отметим, что для работы «Рабочих папок», клиент не обязательно должен состоять в тот же домене Windows, что и сервер Work Folder.
Примечание:
Для всех учетных записей на вашем домашнем компьютере должны стоять пароли.
Откройте панель управления и запустите апплет Work Folders. Система предложит указать email адрес пользователя (требует корректной настройки DNS зоны домена), или Url сервера с ролью Work Folders.
Т.к. политка на сервере Work Folders требует защиты данных с помощью шифрования и пароля, необходимо подтвердить, что вы согласны применить эти политики на своем устройстве.
После этого в панели управления появится информация о «Рабочих папках» (объем доступного пространства на сервер, время последней синхронизации, ошибки и т.д.).
ПРИМЕЧАНИЯ:
Синхронизация немного запаздывает, примерно на 2-5 мин задержка — обычное дело.
Содержимое «Рабочих папок» доступно их проводника Windows или любого файлового менеджера (по умолчанию Work Folders хранятся в каталоге c:usersusernameWorkFolders).
Если скопировать или переместить в данную папку любой файл, то после следующей синхронизации, он будет скопирован на корпоративный файловый сервер и будет доступен пользователю на других мобильных и стационарных устройствах пользователя с настроенными Рабочими папками.
Настройка Work Folder с помощью групповой политики
Настроить Work Folder на клиентах возможно также с помощью групповой политик. Это удобно в случае необходимости массовой использования данной технологии на ПК домена. Интересующая нас политика находится в разделе Users Configurations-> Policies > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Work Folders и называется Specify Work Folders settings. Чтобы задать сервер «Рабочих папок», активируйте эту политику и укажите URL путь к серверу.
Чтобы клиенты настраивали оставшиеся параметры Work Folders автоматически, также активируйте политику Force automatic setup for all users (раздел GPO: Computer Configurations> Policies > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Work Folders.
Примечание. Информация в этой статье основана на доступных на данный момент Windows 8.1 Preview and Windows Server 2012 R2 Preview, в дальнейшем она будет обновлена на основании изменений в RTM версиях.
Функционал Work Folder разработан Microsoft в рамках общего ИТ тренда под названием BYOD (BringYourOwnDevice), в концепции которого пользователи могут использоваться свои личные мобильные устройства для прозрачного и безопасного доступа к корпоративным ресурсам.
Одно из главных преимуществ концепции BYOD для копаний – отсутствие необходимости обеспечения сотрудников устройствами доступа (ноутбуки, телефоны, планшетные компьютеры), все, что нужно от компании – предоставить пользователям удобные службы удаленного подключений к корпоративной сети и сервисы предоставления корпоративных ресурсов
взято тут:
http://winitpro.ru/index.php/2013/09/11/windows-server-2012-r2-work-folders-sinxronizaciya-fajlov-mezhdu-ustrojstvami/
Источник: http://msbro.ru/index.php/archives/5468
Windows Server 2012 R2 предлагает кучу новых свойств,которые значительно расширяют функциональность операционной системы. Многие изэтих усовершенствований дополняют существующие возможности Windows Server 2012.
Work Folders («Рабочие папки»)
Функция «Рабочие папки» — аналог Dropbox длякорпоративных серверов. Установив ее на Windows Server 2012 R2, вы получитеполнофункциональный и безопасный сервис репликации файлов.
В первой версии доступна поддержка устройств лишь подуправлением Windows 8.1. В будущем обещают добавить поддержку для iPad,устройств на Windows 7 и Android. Подобно Dropbox, «Рабочие папки»хранят копии файлов на стороне сервера и клиента, выполняя синхронизацию прикаждом подключении клиента к серверу.
Конфигурация желаемого состояния
Поддержка конфигурации на большом количестве серверов -настоящая головная боль для системных администраторов. Для выполнения даннойзадачи разработано много точечных решений и внутрикорпоративныхспециализированных инструментов.
Теперь в Windows Server 2012 R2 появилась функция,позволяющая программным путем сформировать базу ролей и функций, а затемконтролировать и обновлять любую систему, которая не соответствует желаемомусостоянию.
Storage Tiering (распределение данных по уровнямхранилищ)
Одна эта функция уже заслуживает аплодисментов. По сути,Storage Tiering — это возможность распределять порции хранящихся данных междуразличными классами хранилища — такими, как быстрые твердотельные накопители SSDи медленные жесткие диски.
Большинство высокопроизводительных систем хранения данныхдолгое время поддерживали автоматизированное многоуровневое хранение, но толькосейчас у вас есть возможность выполнять его на уровне операционной системы.
Microsoft использует технологию тепловой карты, чтобы определить наиболеезапрашиваемые данные и автоматически размещает их на самых скоростныхносителях.
Storage Pinning (прикрепление данных кхранилищу)
Схожей со Storage Tiering является возможность прикреплятьвыбранные файлы к конкретному типу хранилища. Благодаря этому ваши файлы,которые должны находиться на самом быстром хранилище — например, загрузочныедиски для развертывания инфраструктуры виртуальных рабочих столов — никогда неперейдут на медленное.
Если файлы не запрашиваются некоторое время, вы можетепереместить их с SSD на жесткий диск.
WriteBack Cache (Кэш обратной записи)
Создавая новый том хранилища в Windows Server 2012 R2, вытакже можете включить кэш обратной записи. Эта функция отделяет частьфизической памяти — как правило, на твердотельном накопителе — дляиспользования в качестве кэша записи, чтобы «сгладить» процессввода-вывода во время интенсивной записи.
Такое часто случается в базе данных, когда дисковыйконтроллер и диски не могут справиться с огромным объемом записей на диск. Кэшустранит любые паузы, вызванные переполнением подсистемы хранения данных.
Дедупликация на работающих виртуальных машинах
Дедупликация данных — отличная функция в Windows Server2012, но дедупликация работающих виртуальных машин ей не по силам. Такой пробелзаполнят в Windows Server 2012 R2, хоть и специально для развертыванийинфраструктуры виртуальных рабочих столов (VDI) с использованием SMB 3.0.
Таким образом, это нововведение может существенно увеличитьобщую эффективность дедупликации для реализации VDI.
Параллельное восстановление
Если вы когда-нибудь сталкивались со сбоем диска в RAID-массиве,то знаете, что на его восстановление иногда уходит не один час. По мереразвертывания все большего количества физических дисков, время восстановлениябудет увеличиваться.
В Windows Server 2012 Microsoft решила проблему длительнойпроверки диска. Теперь вы можете выполнять параллельное восстановление дисковиз Storage Spaces на порядок быстрее.
Workplace Join («подключение к рабочемуместу»)
Windows Server 2012 R2 не обошла стороной и вопрос внедренияличных устройств вроде iPad в корпоративную среду.
К примеру, Web ApplicationProxy (прокси веб-приложения) организует безопасный доступ к корпоративнымресурсам, включая сайты SharePoint, всем авторизованным пользователям.
А новая функция «Workplace Join» позволитпользователям регистрировать личные устройства в Active Directory, проходитьаутентификацию с использованием сертификата и получать доступ к корпоративнымприложениям и данным с помощью технологии единого входа.
Многопользовательский VPN-шлюз
Microsoft добавила ряд новых функций, чтобы обеспечитьбезопасное взаимодействие между внутренними и внешними сетями. Новыймногопользовательский VPN-шлюз позволяет реализовать подключение site-to-site(сеть-сеть) к множеству внешних сайтов через единственный VPN-сервер.
Данная функция ориентирована на поставщиков услуг хостинга икрупные организации, которые хотят реализовать соединение к многочисленнымсайтам или внешним организациям.
Роль Windows Server Essentials
На первый взгляд ничего особенного, но Windows ServerEssentials облегчит жизнь организациям с территориально рассредоточенной сетью.В Windows Server 2012 вам придется использовать совершенно другой источникустановки Windows Server Essentials. Сервер способен повлиять на стратегиюраспространения и управление конфигурациями в крупных организациях.
источник
«,»author»:»»,»date_published»:»2013-01-05T00:00:00.000Z»,»lead_image_url»:»http://1.bp.blogspot.com/-sHOVEozLVBw/UdbiR89iGvI/AAAAAAAAFhs/kk5AMKgOF5w/w1200-h630-p-k-no-nu/excellent-windows-server-2012-r2-features-01.png»,»dek»:null,»next_page_url»:null,»url»:»http://programmers-in-ua.blogspot.com/2013/07/10-windows-server-2012-r2.html»,»domain»:»programmers-in-ua.blogspot.com»,»excerpt»:»Ð¡Ð°Ð¼Ð¾Ðµ инÑеÑеÑное в Windows Server 2012 R2 Windows Server 2012 R2 пÑÐµÐ´Ð»Ð°Ð³Ð°ÐµÑ ÐºÑÑÑ Ð½Ð¾Ð²ÑÑ ÑвойÑÑв, коÑоÑÑе знаÑиÑелÑно ÑаÑÑиÑÑÑÑ ÑÑнкх»,»word_count»:665,»direction»:»ltr»,»total_pages»:1,»rendered_pages»:1}
Источник: http://programmers-in-ua.blogspot.com/2013/07/10-windows-server-2012-r2.html
Windows Server 2012 R2. Work Folders – синхронизация файлов между устройствами
Начинаем знакомиться с новыми возможностями и ключевыми усовершенствованиями, которые нас ожидают в новом обновлении серверной линейки Microsoft — Windows Server 2012 R2, До даты официального выпуска осталось чуть больше месяца (а это, напомним, случится 18 октября 2013 года). Сегодня речь пойдет о новом функционале Windows Server 2012 R2 под названием Work Folders.
Нередка ситуация, когда работник для работы с корпоративными данными используется больше чем два устройства (например, ноутбук и планшет). В этой ситуации, чтобы пользователи всегда работали с актуальными версиями своих данных, перед ИТ-службой встает задача синхронизации файлов. Для этих целей можно воспользоваться SkyDrive, DropBox или походим сервисом.
Однако не всегда возможно хранить данные в «облаке», хотя бы из соображений конфиденциальности и безопасности. Новая функция Windows Server 2012 R2 Work Folders (или «Рабочие папки») – позволяет пользователям синхронизировать свои личные файлы в корпоративной сети с любыми своими устройствами.
По сути, Work Folders является аналогом Dropbox для корпоративных пользователей.
Благодаря «Рабочим папкам» на платформе Windows Server 2012 R2 возможно организовать функциональный и безопасный сервис репликации файлов пользователей между несколькими устройствами. Work Folders на базе файлового сервера позволяет организовать «корпоративный SkyDrive.
Помимо всего прочего, к пользовательским данным на корпоративном файловом сервере можно применять такие политики, как квотирование (Quota), блокировка запрещенных типов файлов (File Screening), а также динамический контроль доступа (Dynamic Access Control) и т.д., т.е.
полный комплекс мер по обеспечению защиты информации.
Как и Dropbox, Work Folders позволяет хранить копии файлов на стороне сервера и клиента, и при каждом подключении клиента к серверу выполняется синхронизация данных. Благодаря данной функции пользователь может синхронизировать свои рабочие папки со своим мобильным устройством (ноутбуком, планшетом и т.д.) и осуществлять редактирование документов, даже без подключения к корпоративной сети (offline). При следующем соединении с корпоративной сетью клиент Work Folders осуществит синхронизацию изменений.
На данный момент технологию Work Folders поддерживают только устройства под управлением Windows 8.1, в которую клиент Work Folders уже встроен. В ближайшем будущем будет добавлена поддержка популярных мобильных устройств: девайсов на Windows 7, Windows 8, Android, а также iOS.
Служба синхронизации Work Folder должна работать на Windows 2012 R2 с установленной ролью файлового сервера. Work Folder также возможно интегрировать со службой Active Directory Rights Management Services, позволяющей обеспечить защиту пользовательских данных.
| ms.assetid | title | ms.topic | author | manager | ms.author | ms.date | description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
a7c39656-81ee-4c2b-80ef-4d017dd11b07 |
Planning a Work Folders deployment |
article |
JasonGerend |
dongill |
jgerend |
4/5/2017 |
How to plan a Work Folders deployment including system requirements and how to prepare your network environment. |
Planning a Work Folders deployment
Applies to: Windows Server 2022, Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows 10, Windows 8.1, Windows 7
This topic explains the design process for a Work Folders implementation, and assumes that you have the following background:
-
Have a basic understanding of Work Folders (as described in Work Folders)
-
Have a basic understanding of Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) concepts
-
Have a basic understanding of Windows file sharing and related technologies
-
Have a basic understanding of SSL certificate usage
-
Have a basic understanding of enabling web access to internal resources via a web reverse proxy
The following sections will help you design your Work Folders implementation. Deploying Work Folders is discussed in the next topic, Deploying Work Folders.
Software requirements
Work Folders has the following software requirements for file servers and your network infrastructure:
-
A server running Windows Server 2012 R2 or Windows Server 2016 for hosting sync shares with user files
-
A volume formatted with the NTFS file system for storing user files
-
To enforce password policies on Windows 7 PCs, you must use Group Policy password policies. You also have to exclude the Windows 7 PCs from Work Folders password policies (if you use them).
-
A server certificate for each file server that will host Work Folders. These certificates should be from a certification authority (CA) that is trusted by your users—ideally a public CA.
-
(Optional) An Active Directory Domain Services forest with schema extensions in Windows Server 2012 R2 to support automatically referring PCs and devices to the correct file server when using multiple file servers.
To enable users to sync across the Internet, there are additional requirements:
-
The ability to make a server accessible from the Internet by creating publishing rules in your organization’s reverse proxy or network gateway
-
(Optional) A publicly registered domain name and the ability to create additional public DNS records for the domain
-
(Optional) Active Directory Federation Services (AD FS) infrastructure when using AD FS authentication
Work Folders has the following software requirements for client computers:
-
Computers must be running one of the following operating systems:
-
Windows 10
-
Windows 8.1
-
Windows RT 8.1
-
Windows 7
-
Android 4.4 KitKat and later
-
iOS 10.2 and later
-
-
Windows 7 PCs must be running one of the following editions of Windows:
-
Windows 7 Professional
-
Windows 7 Ultimate
-
Windows 7 Enterprise
-
-
Windows 7 PCs must be joined to your organization’s domain (they can’t be joined to a workgroup).
-
Enough free space on a local, NTFS-formatted drive to store all the user’s files in Work Folders, plus an additional 6 GB of free space if Work Folders is located on the system drive, as it is by default. Work Folders uses the following location by default: %USERPROFILE%Work Folders
However, users can change the location during setup (microSD cards and USB drives formatted with the NTFS file system are supported locations, though sync will stop if the drives are removed).
The maximum size for individual files is 10 GB by default. There is no per-user storage limit, although administrators can use the quotas functionality of File Server Resource Manager to implement quotas.
-
Work Folders doesn’t support rolling back the virtual machine state of client virtual machines. Instead perform backup and restore operations from inside the client virtual machine by using System Image Backup or another backup app.
[!NOTE]
Make sure to install the Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2 General Availability update rollup on all Work Folders servers and any client computers running Windows 8.1 or Windows Server 2012 R2. For more information, see article 2883200 in the Microsoft Knowledge Base.
Deployment scenarios
Work Folders can be implemented on any number of file servers within a customer environment. This allows Work Folders implementations to scale based on customer needs and can result in highly individualized deployments. However, most deployments will fall into one of the following three basic scenarios.
Single-Site Deployment
In a single-site deployment, file servers are hosted within a central site in the customer infrastructure. This deployment type is seen most often in customers with a highly centralized infrastructure or with smaller branch offices that do not maintain local file servers. This deployment model can be easier for IT staff to administer, since all server assets are local, and internet ingress/egress is likely centralized at this location as well. However, this deployment model also relies on good WAN connectivity between the central site and any branch offices, and users in branch offices are vulnerable to an interruption of service due to network conditions.
Multiple-Site Deployment
In a multiple-site deployment, file servers are hosted in multiple locations within the customer’s infrastructure. This could mean multiple datacenters or it could mean that branch offices maintain individual file servers. This deployment type is seen most often in larger customer environments or in customers that have several larger branch offices that maintain local server assets. This deployment model is more complex for IT personnel to administer, and relies on careful coordination of data storage and maintenance of Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) to ensure that users are using the correct sync server for Work Folders.
Hosted Deployment
In a hosted deployment, sync servers are deployed in an IAAS (Infrastructure-as-a-Service) solution such as Windows Azure VM. This deployment method has the advantage of making the availability of file servers less dependent on WAN connectivity within a customer’s business. If a device is able to connect to the Internet, it can get to its sync server. However, the servers deployed in the hosted environment still need to be able to reach the organization’s Active Directory domain to authenticate users, and the customer trades infrastructure requirements on-premises for additional complexity in maintaining that connection.
Deployment technologies
Work Folders deployments consist of a number of technologies that work together to provide service to devices on both the internal and external networks. Before designing a Work Folders deployment, customers should be familiar with the requirements of each of the following technologies.
Active Directory Domain Services
AD DS provides two important services in a Work Folders deployment. First, as the back-end for Windows authentication, AD DS provides the security and authentication services that are used to grant access to user data. If a domain controller cannot be reached, a file server will be unable to authenticate an incoming request and the device will not be able to access any data stored in that file server’s sync share.
Second, AD DS (with the Windows Server 2012 R2 schema update) maintains the msDS-SyncServerURL attribute on each user, which is used to automatically direct users to the appropriate sync server.
File Servers
File servers running Windows Server 2012 R2 or Windows Server 2016 host the Work Folders role service, and host the sync shares that store users’ Work Folders data. File servers can also host data stored by other technologies operating on the internal network (such as file shares), and can be clustered to provide fault tolerance for user data.
Group Policy
If you have Windows 7 PCs in your environment, we recommend the following:
-
Use Group Policy to control password policies for all domain-joined PCs that use Work Folders.
-
Use the Work Folders Automatically lock screen, and require a password policy on PCs that aren’t joined to your domain.
You can also use Group Policy to specify a Work Folders server to domain-joined PCs. This simplifies Work Folders setup a little bit– users would otherwise need to enter their work email address to lookup the settings (assuming that Work Folders is set up properly), or enter the Work Folders URL that you explicitly provided them via email or another means of communication.
You can also use Group Policy to forcibly set up Work Folders on a per-user or per-computer basis, though doing so causes Work Folders to sync on every PC a user signs in to (when using the per-user policy setting), and prevents users from specifying an alternate location for Work Folders on their PC (such as on a microSD card to conserve space on the primary drive). We suggest carefully evaluating your user’s needs before forcing automatic setup.
Windows Intune
Windows Intune also provides a layer of security and manageability for non-domain-joined devices that would not otherwise be present. You can use Windows Intune to configure and manage users’ personal devices such as tablets that connect to Work Folders from across the Internet. Windows Intune can provide devices with the sync server URL to use – otherwise users must enter their work email address to lookup the settings (if you publish a public Work Folders URL in the form of https://workfolders.contoso.com), or enter the sync server URL directly.
Without a Windows Intune deployment, users must configure external devices manually, which can result in increased demands on a customer’s help desk staff.
You can also use Windows Intune to selectively wipe the data from Work Folders on a user’s device without affecting the rest of their data – handy for if a user leaves your organization or has their device stolen.
Web Application Proxy/Azure AD Application Proxy
Work Folders is built around the concept of allowing Internet-connected devices to retrieve business data securely from the internal network, which allows users to «take their data with them» on their tablets and devices that would not normally be able to access work files. To do this, a reverse proxy must be used to publish sync server URLs and make them available to Internet clients.
Work Folders supports using Web Application Proxy, Azure AD Application Proxy or 3rd party reverse proxy solutions:
-
Web Application Proxy is an on-premises reverse proxy solution. To learn more, see Web Application Proxy in Windows Server 2016.
-
Azure AD Application Proxy is a cloud reverse proxy solution. To learn more, see How to provide secure remote access to on-premises applications
Additional design considerations
In addition to understanding each of the components noted above, customers need to spend time in their design thinking about the number of sync servers and shares to operate, and whether or not to leverage failover clustering to provide fault tolerance on those sync servers
Number of Sync Servers
It is possible for a customer to operate multiple sync servers in an environment. This can be a desirable configuration for several reasons:
-
Geographic distribution of users – for example, branch office files servers or regional datacenters
-
Data storage requirements – certain business departments might have specific data storage or handling requirements that are easier with a dedicated server
-
Load balancing – in large environments, storing user data on multiple servers can increase server performance and uptime.
For information on Work Folders server scaling and performance, see Performance Considerations for Work Folders Deployments.
[!NOTE]
When using multiple sync servers, we recommend setting up automatic server discovery for users. This process relies upon the configuration of an attribute on each user account in AD DS. The attribute is named msDS-SyncServerURL and becomes available on user accounts after a Windows Server 2012 R2 domain controller is added to the domain or the Active Directory schema updates are applied. This attribute should be set for each user to ensure that users connect to the appropriate sync server. By using automatic server discovery, organizations can publish Work Folders behind a «friendly» URL such as https://workfolders.contoso.com, regardless of the number of sync servers in operation.
Number of Sync Shares
Individual sync servers can maintain multiple sync shares. This can be useful for the following reasons:
-
Auditing and security requirements – If data used by a certain department must be more heavily audited or retained for a longer period of time, separate sync shares can help administrators keep user folders with differing audit levels separated.
-
Differing quotas or file screens – If you want to set different storage quotas or limits on which file types are allowed in Work Folders (file screens) for different groups of users, separate sync shares can help.
-
Departmental control – If administrative duties are distributed by department, utilizing separate shares for different departments can aid administrators in enforcing quotas or other policies.
-
Differing device policies –If an organization needs to maintain multiple device policies (such as encrypting Work Folders) for different groups of users, using multiple shares enables this.
-
Storage capacity –If a file server has multiple volumes, additional shares can be used to take advantage of these additional volumes. An individual share has access to only the volume that it is hosted on, and is unable to take advantage of additional volumes on a file server.
Access to Sync Shares
While the sync server that a user accesses is determined by the URL entered at their client (or the URL published for that user in AD DS when using server automatic discovery), access to individual sync shares is determined by the permissions present on the share.
As a result, if a customer is hosting multiple sync shares on the same server, care must be taken to ensure that individual users have permissions to access only one of those shares. Otherwise, when users connect to the server, their client may connect to the wrong share. This can be accomplished by creating a separate security group for each sync share.
Further, access to an individual user’s folder inside a sync share is determined by ownership rights on the folder. When creating a sync share, Work Folders by default grants users exclusive access to their files (disabling inheritance and making them the owner of their individual folders).
Design checklist
The following set of design questions is intended to aid customers in designing a Work Folders implementation that best serves their environment. Customers should work through this checklist prior to attempting to deploy servers.
-
Intended Users
-
Which users will use Work Folders?
-
How are users organized? (Geographically, by office, by department, etc)
-
Do any users have special requirements for data storage, security, or retention?
-
Do any users have specific device policy requirements, such as encryption?
-
Which client computers and devices do you need to support? (Windows 8.1, Windows RT 8.1, Windows 7)
If you’re supporting Windows 7 PCs and want to use password policies, exclude the domain storing their computer accounts from the Work Folders password policy, and instead use Group Policy password policies for domain-joined PCs in that domain.
-
Do you need to interoperate with or migrate from other user data management solutions such as Folder Redirection?
-
Do users from multiple domains need to sync across the Internet with a single server?
-
Do you need to support users who aren’t members of the Local Administrators group on their domain-joined PCs? (If so, you’ll need to exclude the relevant domains from Work Folders device policies such as encryption and password policies)
-
-
Infrastructure and Capacity Planning
-
In what sites should sync servers be located on the network?
-
Will any sync servers be hosted by an Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) provider such as in an Azure VM?
-
Will dedicated servers be needed for any specific user groups, and if so, how many users for each dedicated server?
-
Where are the Internet ingress/egress points on the network?
-
Will sync servers be clustered for fault-tolerance?
-
Will sync servers need to maintain multiple data volumes to host user data?
-
-
Data Security
-
Will multiple sync shares need to be created on any sync servers?
-
What groups will be used to provide access to sync shares?
-
If you’re using multiple sync servers, what security group will you create for the delegated ability to modify the msDS-SyncServerURL property of user objects?
-
Are there any special security or auditing requirements for individual sync shares?
-
Is multi-factor authentication (MFA) required?
-
Do you need the ability to remotely wipe Work Folders data from PCs and devices?
-
-
Device Access
-
What URL will be used to provide access for Internet-based devices (the default URL that is required for email-based automatic server discovery is workfolders.domainname)?
-
How will the URL be published to the Internet?
-
Will automatic server discovery be used?
-
Will Group Policy be used to configure domain-joined PCs?
-
Will Windows Intune be used to configure external devices?
-
Will Device Registration be required for devices to connect?
-
Next steps
After designing your Work Folders implementation, it’s time to deploy Work Folders. For more information, see Deploying Work Folders.
Additional References
For additional related information, see the following resources.
| Content type | References |
|---|---|
| Product evaluation | — Work Folders — Work Folders for Windows 7 (blog post) |
| Deployment | — Designing a Work Folders Implementation — Deploying Work Folders — Deploying Work Folders with AD FS and Web Application Proxy (WAP) — Deploying Work Folders with Azure AD Application Proxy — Performance Considerations for Work Folders Deployments — Work Folders for Windows 7 (64 bit download) — Work Folders for Windows 7 (32 bit download) — Work Folders Test Lab Deployment (blog post) |
| ms.assetid | title | ms.topic | author | manager | ms.author | ms.date | description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
a7c39656-81ee-4c2b-80ef-4d017dd11b07 |
Planning a Work Folders deployment |
article |
JasonGerend |
dongill |
jgerend |
4/5/2017 |
How to plan a Work Folders deployment including system requirements and how to prepare your network environment. |
Planning a Work Folders deployment
Applies to: Windows Server 2022, Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows 10, Windows 8.1, Windows 7
This topic explains the design process for a Work Folders implementation, and assumes that you have the following background:
-
Have a basic understanding of Work Folders (as described in Work Folders)
-
Have a basic understanding of Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) concepts
-
Have a basic understanding of Windows file sharing and related technologies
-
Have a basic understanding of SSL certificate usage
-
Have a basic understanding of enabling web access to internal resources via a web reverse proxy
The following sections will help you design your Work Folders implementation. Deploying Work Folders is discussed in the next topic, Deploying Work Folders.
Software requirements
Work Folders has the following software requirements for file servers and your network infrastructure:
-
A server running Windows Server 2012 R2 or Windows Server 2016 for hosting sync shares with user files
-
A volume formatted with the NTFS file system for storing user files
-
To enforce password policies on Windows 7 PCs, you must use Group Policy password policies. You also have to exclude the Windows 7 PCs from Work Folders password policies (if you use them).
-
A server certificate for each file server that will host Work Folders. These certificates should be from a certification authority (CA) that is trusted by your users—ideally a public CA.
-
(Optional) An Active Directory Domain Services forest with schema extensions in Windows Server 2012 R2 to support automatically referring PCs and devices to the correct file server when using multiple file servers.
To enable users to sync across the Internet, there are additional requirements:
-
The ability to make a server accessible from the Internet by creating publishing rules in your organization’s reverse proxy or network gateway
-
(Optional) A publicly registered domain name and the ability to create additional public DNS records for the domain
-
(Optional) Active Directory Federation Services (AD FS) infrastructure when using AD FS authentication
Work Folders has the following software requirements for client computers:
-
Computers must be running one of the following operating systems:
-
Windows 10
-
Windows 8.1
-
Windows RT 8.1
-
Windows 7
-
Android 4.4 KitKat and later
-
iOS 10.2 and later
-
-
Windows 7 PCs must be running one of the following editions of Windows:
-
Windows 7 Professional
-
Windows 7 Ultimate
-
Windows 7 Enterprise
-
-
Windows 7 PCs must be joined to your organization’s domain (they can’t be joined to a workgroup).
-
Enough free space on a local, NTFS-formatted drive to store all the user’s files in Work Folders, plus an additional 6 GB of free space if Work Folders is located on the system drive, as it is by default. Work Folders uses the following location by default: %USERPROFILE%Work Folders
However, users can change the location during setup (microSD cards and USB drives formatted with the NTFS file system are supported locations, though sync will stop if the drives are removed).
The maximum size for individual files is 10 GB by default. There is no per-user storage limit, although administrators can use the quotas functionality of File Server Resource Manager to implement quotas.
-
Work Folders doesn’t support rolling back the virtual machine state of client virtual machines. Instead perform backup and restore operations from inside the client virtual machine by using System Image Backup or another backup app.
[!NOTE]
Make sure to install the Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2 General Availability update rollup on all Work Folders servers and any client computers running Windows 8.1 or Windows Server 2012 R2. For more information, see article 2883200 in the Microsoft Knowledge Base.
Deployment scenarios
Work Folders can be implemented on any number of file servers within a customer environment. This allows Work Folders implementations to scale based on customer needs and can result in highly individualized deployments. However, most deployments will fall into one of the following three basic scenarios.
Single-Site Deployment
In a single-site deployment, file servers are hosted within a central site in the customer infrastructure. This deployment type is seen most often in customers with a highly centralized infrastructure or with smaller branch offices that do not maintain local file servers. This deployment model can be easier for IT staff to administer, since all server assets are local, and internet ingress/egress is likely centralized at this location as well. However, this deployment model also relies on good WAN connectivity between the central site and any branch offices, and users in branch offices are vulnerable to an interruption of service due to network conditions.
Multiple-Site Deployment
In a multiple-site deployment, file servers are hosted in multiple locations within the customer’s infrastructure. This could mean multiple datacenters or it could mean that branch offices maintain individual file servers. This deployment type is seen most often in larger customer environments or in customers that have several larger branch offices that maintain local server assets. This deployment model is more complex for IT personnel to administer, and relies on careful coordination of data storage and maintenance of Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) to ensure that users are using the correct sync server for Work Folders.
Hosted Deployment
In a hosted deployment, sync servers are deployed in an IAAS (Infrastructure-as-a-Service) solution such as Windows Azure VM. This deployment method has the advantage of making the availability of file servers less dependent on WAN connectivity within a customer’s business. If a device is able to connect to the Internet, it can get to its sync server. However, the servers deployed in the hosted environment still need to be able to reach the organization’s Active Directory domain to authenticate users, and the customer trades infrastructure requirements on-premises for additional complexity in maintaining that connection.
Deployment technologies
Work Folders deployments consist of a number of technologies that work together to provide service to devices on both the internal and external networks. Before designing a Work Folders deployment, customers should be familiar with the requirements of each of the following technologies.
Active Directory Domain Services
AD DS provides two important services in a Work Folders deployment. First, as the back-end for Windows authentication, AD DS provides the security and authentication services that are used to grant access to user data. If a domain controller cannot be reached, a file server will be unable to authenticate an incoming request and the device will not be able to access any data stored in that file server’s sync share.
Second, AD DS (with the Windows Server 2012 R2 schema update) maintains the msDS-SyncServerURL attribute on each user, which is used to automatically direct users to the appropriate sync server.
File Servers
File servers running Windows Server 2012 R2 or Windows Server 2016 host the Work Folders role service, and host the sync shares that store users’ Work Folders data. File servers can also host data stored by other technologies operating on the internal network (such as file shares), and can be clustered to provide fault tolerance for user data.
Group Policy
If you have Windows 7 PCs in your environment, we recommend the following:
-
Use Group Policy to control password policies for all domain-joined PCs that use Work Folders.
-
Use the Work Folders Automatically lock screen, and require a password policy on PCs that aren’t joined to your domain.
You can also use Group Policy to specify a Work Folders server to domain-joined PCs. This simplifies Work Folders setup a little bit– users would otherwise need to enter their work email address to lookup the settings (assuming that Work Folders is set up properly), or enter the Work Folders URL that you explicitly provided them via email or another means of communication.
You can also use Group Policy to forcibly set up Work Folders on a per-user or per-computer basis, though doing so causes Work Folders to sync on every PC a user signs in to (when using the per-user policy setting), and prevents users from specifying an alternate location for Work Folders on their PC (such as on a microSD card to conserve space on the primary drive). We suggest carefully evaluating your user’s needs before forcing automatic setup.
Windows Intune
Windows Intune also provides a layer of security and manageability for non-domain-joined devices that would not otherwise be present. You can use Windows Intune to configure and manage users’ personal devices such as tablets that connect to Work Folders from across the Internet. Windows Intune can provide devices with the sync server URL to use – otherwise users must enter their work email address to lookup the settings (if you publish a public Work Folders URL in the form of https://workfolders.contoso.com), or enter the sync server URL directly.
Without a Windows Intune deployment, users must configure external devices manually, which can result in increased demands on a customer’s help desk staff.
You can also use Windows Intune to selectively wipe the data from Work Folders on a user’s device without affecting the rest of their data – handy for if a user leaves your organization or has their device stolen.
Web Application Proxy/Azure AD Application Proxy
Work Folders is built around the concept of allowing Internet-connected devices to retrieve business data securely from the internal network, which allows users to «take their data with them» on their tablets and devices that would not normally be able to access work files. To do this, a reverse proxy must be used to publish sync server URLs and make them available to Internet clients.
Work Folders supports using Web Application Proxy, Azure AD Application Proxy or 3rd party reverse proxy solutions:
-
Web Application Proxy is an on-premises reverse proxy solution. To learn more, see Web Application Proxy in Windows Server 2016.
-
Azure AD Application Proxy is a cloud reverse proxy solution. To learn more, see How to provide secure remote access to on-premises applications
Additional design considerations
In addition to understanding each of the components noted above, customers need to spend time in their design thinking about the number of sync servers and shares to operate, and whether or not to leverage failover clustering to provide fault tolerance on those sync servers
Number of Sync Servers
It is possible for a customer to operate multiple sync servers in an environment. This can be a desirable configuration for several reasons:
-
Geographic distribution of users – for example, branch office files servers or regional datacenters
-
Data storage requirements – certain business departments might have specific data storage or handling requirements that are easier with a dedicated server
-
Load balancing – in large environments, storing user data on multiple servers can increase server performance and uptime.
For information on Work Folders server scaling and performance, see Performance Considerations for Work Folders Deployments.
[!NOTE]
When using multiple sync servers, we recommend setting up automatic server discovery for users. This process relies upon the configuration of an attribute on each user account in AD DS. The attribute is named msDS-SyncServerURL and becomes available on user accounts after a Windows Server 2012 R2 domain controller is added to the domain or the Active Directory schema updates are applied. This attribute should be set for each user to ensure that users connect to the appropriate sync server. By using automatic server discovery, organizations can publish Work Folders behind a «friendly» URL such as https://workfolders.contoso.com, regardless of the number of sync servers in operation.
Number of Sync Shares
Individual sync servers can maintain multiple sync shares. This can be useful for the following reasons:
-
Auditing and security requirements – If data used by a certain department must be more heavily audited or retained for a longer period of time, separate sync shares can help administrators keep user folders with differing audit levels separated.
-
Differing quotas or file screens – If you want to set different storage quotas or limits on which file types are allowed in Work Folders (file screens) for different groups of users, separate sync shares can help.
-
Departmental control – If administrative duties are distributed by department, utilizing separate shares for different departments can aid administrators in enforcing quotas or other policies.
-
Differing device policies –If an organization needs to maintain multiple device policies (such as encrypting Work Folders) for different groups of users, using multiple shares enables this.
-
Storage capacity –If a file server has multiple volumes, additional shares can be used to take advantage of these additional volumes. An individual share has access to only the volume that it is hosted on, and is unable to take advantage of additional volumes on a file server.
Access to Sync Shares
While the sync server that a user accesses is determined by the URL entered at their client (or the URL published for that user in AD DS when using server automatic discovery), access to individual sync shares is determined by the permissions present on the share.
As a result, if a customer is hosting multiple sync shares on the same server, care must be taken to ensure that individual users have permissions to access only one of those shares. Otherwise, when users connect to the server, their client may connect to the wrong share. This can be accomplished by creating a separate security group for each sync share.
Further, access to an individual user’s folder inside a sync share is determined by ownership rights on the folder. When creating a sync share, Work Folders by default grants users exclusive access to their files (disabling inheritance and making them the owner of their individual folders).
Design checklist
The following set of design questions is intended to aid customers in designing a Work Folders implementation that best serves their environment. Customers should work through this checklist prior to attempting to deploy servers.
-
Intended Users
-
Which users will use Work Folders?
-
How are users organized? (Geographically, by office, by department, etc)
-
Do any users have special requirements for data storage, security, or retention?
-
Do any users have specific device policy requirements, such as encryption?
-
Which client computers and devices do you need to support? (Windows 8.1, Windows RT 8.1, Windows 7)
If you’re supporting Windows 7 PCs and want to use password policies, exclude the domain storing their computer accounts from the Work Folders password policy, and instead use Group Policy password policies for domain-joined PCs in that domain.
-
Do you need to interoperate with or migrate from other user data management solutions such as Folder Redirection?
-
Do users from multiple domains need to sync across the Internet with a single server?
-
Do you need to support users who aren’t members of the Local Administrators group on their domain-joined PCs? (If so, you’ll need to exclude the relevant domains from Work Folders device policies such as encryption and password policies)
-
-
Infrastructure and Capacity Planning
-
In what sites should sync servers be located on the network?
-
Will any sync servers be hosted by an Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) provider such as in an Azure VM?
-
Will dedicated servers be needed for any specific user groups, and if so, how many users for each dedicated server?
-
Where are the Internet ingress/egress points on the network?
-
Will sync servers be clustered for fault-tolerance?
-
Will sync servers need to maintain multiple data volumes to host user data?
-
-
Data Security
-
Will multiple sync shares need to be created on any sync servers?
-
What groups will be used to provide access to sync shares?
-
If you’re using multiple sync servers, what security group will you create for the delegated ability to modify the msDS-SyncServerURL property of user objects?
-
Are there any special security or auditing requirements for individual sync shares?
-
Is multi-factor authentication (MFA) required?
-
Do you need the ability to remotely wipe Work Folders data from PCs and devices?
-
-
Device Access
-
What URL will be used to provide access for Internet-based devices (the default URL that is required for email-based automatic server discovery is workfolders.domainname)?
-
How will the URL be published to the Internet?
-
Will automatic server discovery be used?
-
Will Group Policy be used to configure domain-joined PCs?
-
Will Windows Intune be used to configure external devices?
-
Will Device Registration be required for devices to connect?
-
Next steps
After designing your Work Folders implementation, it’s time to deploy Work Folders. For more information, see Deploying Work Folders.
Additional References
For additional related information, see the following resources.
| Content type | References |
|---|---|
| Product evaluation | — Work Folders — Work Folders for Windows 7 (blog post) |
| Deployment | — Designing a Work Folders Implementation — Deploying Work Folders — Deploying Work Folders with AD FS and Web Application Proxy (WAP) — Deploying Work Folders with Azure AD Application Proxy — Performance Considerations for Work Folders Deployments — Work Folders for Windows 7 (64 bit download) — Work Folders for Windows 7 (32 bit download) — Work Folders Test Lab Deployment (blog post) |
Windows 8.1 представляет новую функцию Рабочие папки . Если вам нужно работать из любого места с разных устройств, то рабочие папки – это то, что вам нужно.
Рабочие папки в Windows 8.1/10

Рабочие папки в Windows 8.1 и Windows Server 2012 R2 – это расширение Принеси свое собственное устройство , которое позволит ИТ-администраторам предоставлять информационным работникам возможность синхронизировать свои рабочие данные на всех своих устройствах. Это делается путем синхронизации пользовательских данных с устройств на локальных файловых серверах. Короче говоря, вы можете рассматривать как альтернативу SkyDrive бесплатное синхронизированное хранилище, которое любой бизнес может самостоятельно размещать для своих сотрудников. Думайте об этом как о SkyDrive, размещенном на вашем собственном сервере.
Для настройки Рабочих папок откройте Панель управления Все элементы панели управления Рабочие папки. Нажмите на Настроить рабочие папки. Вам будет предложено ввести адрес электронной почты вашего домена или URL-адрес рабочих папок. После того, как вы ввели эти данные, нажмите Далее. Вы увидите сообщение «Поиск ваших данных» на сервере рабочих папок.
Вы также найдете параметры для рабочих папок в групповой политике в разделе:
Пользователи> Политики> Административные шаблоны> Компоненты Windows> Рабочие папки
Здесь вы должны включить параметры «Задать рабочие папки» и настроить их.
Особенности рабочих папок:
- Обеспечение единой точки доступа к рабочим файлам на рабочем месте пользователя и персональных компьютерах и устройствах.
- Доступ к рабочим файлам в автономном режиме и синхронизация с центральным файловым сервером, когда ПК или устройство затем подключены к Интернету или сети
- Поддерживайте шифрование данных при передаче и в состоянии покоя на устройствах и позволяйте корпоративным данным стереть с помощью служб управления устройствами, таких как Windows Intune.
- Использование существующих технологий управления файловым сервером, таких как классификация файлов и квоты папок, для управления пользовательскими данными
- Укажите политики безопасности, чтобы, например, указать, что пользовательские ПК и устройства должны шифровать рабочие папки и использовать пароль экрана блокировки.
- Используйте отказоустойчивую кластеризацию с рабочими папками, чтобы обеспечить решение высокой доступности
В настоящее время рабочие папки доступны только для Windows 10/8.1, но вскоре Microsoft выпустит дополнительный клиент для Windows 7 и приложение для iPad. ОБНОВЛЕНИЕ . Пользователи Windows 7 могут увидеть этот пост о том, как настроить рабочие папки в Windows 7.
Вы можете прочитать больше о рабочих папках на TechNet.