Поддержка API удаленного разностного сжатия что это
Не так давно вышла Windows 8. Многие уже обзавелись новыми компьютерами с предустановленной версией, кто то установил её как обновление уже имеющейся более старой копии Windows по акции. Так что думаю сейчас у многих назрели вопросы по её настройке и оптимизации, чем с вами здесь и займемся.
Поскольку интерфес новой ОС сильно изменился, опишу как попасть в Панель управления, дабы не писать это каждый раз. Есть несколько способов:
— из Metro пишем «панель управления», в появившемся списке щелкаем Панель управления
— сочетание клавиш Win+Е, в открывшемся проводнике, в верхней панели нажать большую кнопу Открыть панель управления (если такой кнопки нет, щелкните мышкой по стрелке вниз в правом верхнем углу для раскрытия панели инструментов)
— на рабочем столе сочетание клавиш Win+С, в появившейся справа панели нажмите на Шестиренку, далее Панель управления
Для большего удобства также рекомендую в открывшейся Панели управления в списке Просмотр (в правом верхнем углу окна) выбрать большие или маленькие иконки. Так вы будете видеть все доступные пункты Панели управления.
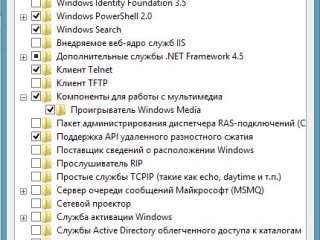
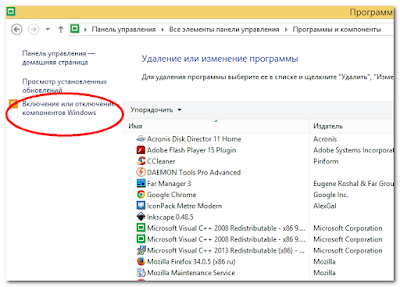
- Первым делом, после установки Windows удалить/установить все нужные/ненужные компоненты. Для это идем в Панель управления -> Программы и компоненты -> слева Включение и отключение компонентов Windows. В появившемся окне ставим галки напротив нужных компонентов и убераем галки напротив ненужных
В кратце опишу что за что отвечает:
.NET Framework 3.5 и .NET Framework 4.5 — оставляем как есть, используется многими программами
Hyper-V — используется для виртуальных машин. Знаете что такое вирутальные машины, собираетесь ими пользоваться? Нет? Тогда удаляем.
Internet Explorer — сами решайте нужен он вам или нет
SNMP-протокол — сетевой протокол для работы с сетевыми устройствами. Как правило нафиг не нужен.
Telnet-сервер — добавляет возможность управления вашим компьютером по сети. Может быть полезно на рабочих станциях корпоративной сети, дома же он не нужен.
Windows Identity Foundation 3.5 — компонент .NET Framework. Если какой то программе он понадобиться, она его сама включит.
Windows PowerShell — современная инкарнация командной строки, если не знаете что это, оно вам не нужно.
Windows Search — выполняет индексация ваших файлов для быстрого поиска. При правильной настройке довольно полезная функция. Оставляем.
Внедряемое веб-ядро IIS — собираемся у себя на компе поднимать веб-сервер IIS? Нет? Тогда удаляем.
Клиент Telnet — позволяет удаленно управлять компьютерами на которых работает Telnet-сервер. Если вам это не надо — удаляем.
Клиент TFTP — сетевой протокол передачи файлов, грубо говоря упрощенный FTP клиент в основном для работы с бездисковыми терминалами. В домашних условиях не нужен.
Компоненты для работы с мультимедиа — речь идет о Windows Media Player и Windows Media Center, тут как и с Internet Explorer сами решайте нужены они вам или нет.
Пакет администрирования диспетчера RAS-подключений (CMAK) — для создания профилей удаленных подключений типа VPN. В повседневной жизни он вам вряд ли понадобиться. Удаляем.
Поддержка API удаленного разностного сжатия — передает различие между двумя объектами, минимизируя объем передаваемых данных. Поидее вещь полезная, но как она влияет на скорость если честно не проверял. Да и работает она только при условии поддержки в ПО. Так что можно оставить.
Поставщик сведений о расположении Windows — говоря русским языком, это компонент отвечает за сообщение программам о расположении вашего компьютера на планете. В случае планшета это ещё можно понять, но во всех остальных случаях она бесполезна. Удаляем.
Прослушиватель RIP — получение измененных конфигураций от маршрутизаторов. В домашних условиях бесполезна.
Простые службы TCPIP — для знатоков, всем остальным не нужно.
Сервер очереди сообщений Microsoft (MSMQ) — в большинстве случаев не нужно, так что убираем.
Сетевой проектор — для работы с проекторами работающими по сети. Если у вас такого нет, удаляем.
Служба активации Windows — на процесс активации Windows(легальности) не влияет, так что удаляем.
Службы Active Directory — если ваш компьютер не в домене, то вам это не надо.
Службы IIS — собираемся у себя на компе поднимать веб-сервер IIS? Нет? Тогда удаляем.
Службы XPS — добавляет XPS принтер, который позволяет делать печать в файл, а не на бумагу. В большинстве случаев не нужен.
Средство просмотра XPS — а это смотрелка этих самых XPS файлов, как правило также не нужна.
Службы печати документов — если у вас есть сканер и вы используете стандартную виндовую программу сканирования оставьте Факсы и сканирование Windows, а все остальное в топку.
Фильтр Windows TIFF IFilter — добавляет индексирование TIFF файлов по содержимому на них тексту. В большинстве случаев не нужен. - Желающие вернуть старый добрый Пуск, могут установить себе Start8 . В особых настройках он не нуждается и готов к употреблению сразу после установки.
- Отключаем Защиты системы (подразумевается резервное копирование системных файлов перед их изменением) ибо сама по себе она бесполезна и довольно часто занимается сбором вирусов. Лучше использовать сторонние программы для резервного копирования (например Acronis).
Панель управления -> Система -> слева Защита системы -> в списке дисков проверяем чтобы защита была везде выключена. - Отключаем Автозапуск с портативных носителей, именно благодаря ему многие хватают вирусы с флэшек и дисков.
Панель управление -> Автозапуск -> убираем галку Использовать автозапуск для всех носителей и устройств - Оптимизация дисков — Пуск -> Дефрагментация дисков -> Изменить параметры -> ставим галку Выполнять по расписанию -> Выбираем интервал времени, у меня данные меняются не так часто, поэтому поставил Месяц -> диски Выбрать -> убираем галку Автоматически оптимизировать новые диски и убрать галки с дисков которые не хотите оптимизировать (например SSD)
- Ускорение загрузки Windows — сочетание Win+R -> msconfig -> вкладка Загрузка -> Дополнительные параметры -> выставляем число процессоров соответствующие вашему компьютеру (например для четырех ядерного процессора выставляем 4)
- Настройка новомодных фишек ОС можно найти в сплывающей справа панели -> значек Шестеренки -> Изменить параметры компьютера:
Персонализация — имеет три подпункта Экран блокировки (картинка экрана, приложения отображающиеся на экране блокировки), Начальный экран (здесь выбираем цветовую гамму и фон для Metro) и Аватар (картинка вашего пользователя).
Пользователи — переключение вашей учетной записи между локальной и интернет, изменение пароля, создание новых пользователей (хотя для меня удобнее старый метод через Панель управления).
Уведомления — настройка всплывающих уведомлений (не тех что всплывают в системном трее), есть возможность выбора каким приложениям можно слать уведомления, в списке будут только Metro приложения, если Metro использовать не будете, можно все отключить.
Поиск — тоже касается только Metro интерфейса, если не используем оный, можно все отключить. В противном случае выбираем в каких приложениях вы хотите чтобы происходил поиск.
Общий доступ — опять таки в основном для Metro приложений, это что то вроде кнопки Share, дает возможность делиться своими контактами, файлами и пересылкой и прочим.
Общие — настройки часового пояса, настройка жестов переключения между приложениями, правописание, настройка языков, а также варианты восстановления Windows.
Конфиденциальность — тут всего три пункта, использование местоположения (если удалили этот компонент он будет неактивен, нужен для использования вашего местоположения в программах и сайтах, если речь идет не о планшете, думаю смысла в этом нет), использование вашего имени и аватара (для приложений и сайтов использующих аутентификацию microsoft), использование истории ваших действий в microsoft
Устройства — кастрированная версия аналога из Панели управления (Устройства и принтеры)
Специальные возможности — для людей с ограниченными возможностями
Синхронизация параметров — настройка синхронизации настроек компьютера для вашей учетной записи. Если включено, то при входе на другой компьютер под вашей интернет учетной записью будут применяться ваши сохраненные настройки. Если у вас несколько компьютеров с Windows 8 (или если вы у кого то в гостях), очень даже удобно.
Домашняя группа — настройка расшаренных ресурсов компа, пришло к нам из Windows 7
Центр обновлений Windows — опять таки кастрированная версия варианта из Панели управления. - Настройка переключения языков ввода — по умолчанию настроено так что ваша раскладка сохраняется одна и таже для всех приложений, для большинства это может и удобно, но если вы часто пользуетесь разными раскладками или привыкли к старой схеме, когда для каждого приложения выбирается свой язык, тогда идем в Панель управления -> Язык -> Дополнительные параметры -> ставим галку «Позволить выбирать метод ввода для каждого приложения»
В Windows 8 используется ряд оптимизаций для ускорения включения, которые могут привести к потери данных на диске, в случае если вы используете свои жесткие диски как переносные (например используете один и тот же диск на работе и дома). Настройки, исправляющей эту проблему, нет, но можно её избежать выключая компьютер командой:
shutdown /s /t 00
Для большего удоство можно создать ярлык на рабочем столе: правой кнопой на рабочем столе -> Создать -> Ярлык -> в расположении объекта указать команду выше.
Какие компоненты Windows 8.1 можно отключить
Вместе с основными компонентами ядра, драйверами и жизненно необходимыми для работы операционной системы программами, в Windows 8.1 имеется набор компонентов, имеющих второстепенное значение. Однако, будучи включёнными, они расходуют ресурсы компьютера впустую, а это уже не хорошо. Отключив неиспользуемые компоненты, можно увеличить производительность операционной системы. Давайте же узнаем, какие компоненты Windows 8.1 можно деактивировать.
Примечание: некоторая часть компонентов отключена по умолчанию, следовательно их можно попросту проигнорировать. Также стоит учитывать, что в разных редакциях Windows 8.1 набор компонентов может отличаться. В нашем примере была рассмотрена Windows 8.1 Industry Pro.
Список компонентов:
• Браузер Internet Explorer. Если не пользуетесь этим обозревателем, можете отключить его.
• Утилита PowerShell. Командная оболочка PowerShell обычно используется администраторами, простым пользователям она особо не нужна. Можно смело отключить.
• Клиент рабочих папок. Обеспечивает синхронизацию данных с удалённым сервером. Используется для доступа к файлам в корпоративных сетях. Можете отключить.
• Компоненты для работы с мультимедиа. Необходимы, если только вы собираетесь использовать Windows Media или Windows Media Center. Если нет, можете отключить.
• Компоненты прежних версий. NTVDM. Обеспечивает поддержку старых 16-битных программ. Если интереса к раритетному ПО не испытываете, можете NTVDM отключить. Тоже касается компонента DirectPlay, необходимого для запуска игр, выпущенных до 2008 года.
• Поддержка API удаленного разностного сжатия. Передает различие между двумя объектами, сокращая объём передаваемых данных и обеспечивая более быстрое сравнение синхронизируемых файлов. Работает компонент в немногих приложениях, так что можете его оставить включённым, но если и отключите, ничего страшного не произойдёт.
• Поддержка общего доступа к файлам SMB 1.0/CIFS. Протокол SMB обеспечивает совместное использование в частных сетях файлов и принтеров под управлением старых версий Windows (заканчивая XP). Также может служить для связи компьютеров под Windows с устройствами под Linux и Mac OS. Можно отключить, если вы не собираетесь создавать локальную сеть и использовать в ней компьютеры под управлением Linux, Mac OS или старых версий Windows.
• Поставщик сведений о расположении Windows. Компонент, определяющий ваше географическое положение. Если вы хотите обеспечить себе более высокий уровень приватности в интернете, можете его отключить. Только учтите, что программы, функционал которых основан на определении местоположения, могут начать работать некорректно.
• Служба активации Windows. В этой службе нуждаются разве что разработчики программного обеспечения. Простые пользователи могут её безболезненно отключить.
• Службы и средства просмотра XPS. Обеспечивают печать и просмотр документов формата XPS — альтернативе формату PDF. Если вы не используете в своей работе файлы этого типа, оба эти компонента можно отключить.
• Служба печати и документов. Набор служб, обеспечивающих работу с принтерами, факсами и сканерами. Этот компонент включён частично. По умолчанию активны только две службы: «Клиент интернет-печати» и «Факсы и сканирование Windows». Если вы не используете принтеры, факсы или сканеры, эти службы можно деактивировать.
Вполне вероятно, что остальные компоненты, кроме .NET Framework у вас уже будут отключены. Если же нет, список кандидатов на отключение могут пополнить:
• Hyper-V. Технология виртуализации от Microsoft. Не нужен, если вы не собираетесь запускать виртуальные машины или используете другие инструменты виртуализации, например, VirtualBox.
• SNMP-протокол. Необходим только администраторам корпоративных сетей.
• Telnet-сервер. Устаревший протокол входящих соединений.
• Клиент Telnet. Устаревший клиент командной строки, обеспечивающий двунаправленную связь с сервером Telnet.
• Внедряемое веб-ядро служб IIS. Нужен только разработчикам.
• Клиент TFTP. Инструмент передачи данных через протокол Trivial File Transfer Protocol. Простым пользователям он не нужен.
• Пакет администрирования диспетчера RAS-подключений (CMAK). Используется обычно в корпоративных сетях системными администраторами.
• Прослушиватель RIP. Опять же используется только в корпоративных сетях. Обычным пользователям эта служба не нужна.
• Простые службы TCPIP. Инструменты командной строки, которыми вам вряд ли придётся пользоваться.
• Сервер очереди сообщений Майкрософт (MSMQ). Устаревшая служба для работы с ненадёжными сетями. Вам она не понадобится.
• Сетевой проектор. Компонент, обеспечивающий удаленный доступ с сетевым проекторам. Чаще всего используется на предприятиях.
• Службы Active Directory для облегченного доступа к каталогам. Этот компонент найдут для себя полезным разве что разработчики.
• Фильтр Windows TIFF IFilter. Как правило, этот компонент по умолчанию отключен. TIFF IFilter позволяет распознавать текст внутри файлов формата TIFF. Если у вас он окажется включенным, отключите его, так как в процессе распознавания он потребляет большой объём оперативной памяти.
В Windows 8.1 есть ещё один компонент, на который вам стоит обратить внимание. Это .NET Framework 3.5 (включает .NET 2.0 и 3.0). В окошке управления компонентами он отмечен как частично включенный. Его отключать не следует, так как некоторые программы, использующие для своей работы версии Framework 3.5 и ниже, могут перестать запускаться. Что касается компонента «Дополнительные службы .NET Framework 4.5», то здесь рекомендуем ничего не менять.
Что такое Поддержка API удаленного разностного сжатия и можно ли ее отключить в Windows10? Читал что это добавит производ
Это добавит производительности системе! Что эта функция делает вообще?
Вас чем-то не шарахнуло сегодня
Сжимает данные (в том числе файлы) при передаче пытаясь минимизировать объем передаваемой информации. Появилась в Windows Vista и Windows Server 2003.
Соотв. От этого компонента есть и польза, но есть и накладные расходы…
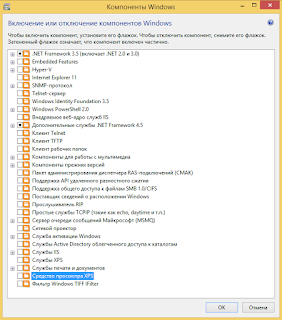
Отключить: Программы -> Включение или отключение компонентов Windows
Настройка жесткого диска Windows 10
Здравствуйте, в данной статье хотелось бы затронуть факт настройки жесткого диска Windows 10.
Если вы хотите улучшить в целом работу вашей операционной системы, то настройка жесткого диска один из главных факторов, так как этими настройками вы сможете улучшить производительность ОП в целом.
Настройка жесткого диска в Windows 10:
Кликаем ПКМ по ярлыку Мой компьютер и перейдем в пункт Свойства
Далее в Диспетчер устройств
В раскрывшимся окре кликаем Дисковые устройства, как видим у меня только 1 жесткий диск, соответственно его и будем оптимизировать.
Для этой цели нажмите ПКМ по жесткому диску и выберете раздел Свойства
После чего переходим в Политика и ставим чекбокс напротив Отключить очистку буфера кэша записей Windows для этого устройства и кликнем Ок
После выполнения данных процедур заходим в Мой компьютер и жмем ПКМ по диску который мы оптимизируем, после чего нажимаем Свойства
Убираем галку с надписи Разрешить индексировать содержимое файлов на этом диске в дополнение с свойствам файлов, после чего Ок
Что бы подтвердить изменения нажимаем Ок, применение атрибутов может занять некоторое время, многое зависит от того сколько файлов расположено у вас в разделе.
Поэтому наберитесь терпения и проделайте это для всех жестких дисков 

Что мы делаем потом? Затем мы переходим в Панель управления, находим раздел Программы и компоненты 
В левом верхнем углу жмем по разделу Включение или отключение компонентов Windows 
В появившимся окне убираем галку с Поддержка API удаленного разностного сжатия – эта функция уменьшает размер файлов и передает их по другому формату, но при этом никаких эффектов вы не заметите. Дело в проблеме которая нагружает жесткий диск поэтому ее лучше стоит убрать. 
Вот так, это были не сложные настройки жесткого диска, если у вас остались вопросы напишите мне в комментарии, и подписываемся на рассылку!
Включение и отключение компонентов Windows 10
Windows 10 содержит набор большого количества побочных функций и связанных с ними системных дополнений, которые называются компонентами. Многие из них предназначены для создания корпоративных сетей, серверов и прочих функций, которые обычному пользователю никогда не понадобятся, но будут по-прежнему занимать место на жёстком диске, даже будучи отключёнными. Однако, среди компонентов имеются и действительно важные, о необходимости которых многие не подозревают. Поэтому перед отключение и включением какого-либо компонента, необходимо узнать о его значимости.
Предостережения
Перед тем, как начать отключать всё, что не понравится вашему глазу, стоит учесть:
- Все потенциально ненужные компоненты являются по умолчанию отключёнными и наоборот. Включение и отключение процессов стоит делать только целенаправленно, если вы уверены что вам не нужен или мешает определённый компонент.
- Включённое состояние порграммы стоит понимать как «Разрешён к использованию». Без потребности в отдельном компоненте, он никогда не будет запущен.
- Исходя из предыдущего пункта, процессы просто так никогда не нагрузят вашу оперативную память, а их отключение никак не улучшит общую производительность компьютера.
- Не существует никакой оптимизации процессов для игр. Компоненты Windows 10 можно представить в виде набора инструментов доступных системе, которые никогда не будут использованы без необходимости. Единственный компонент, используемый в играх, — это .NET Framework, который будет автоматически включён при запуске игры, даже если вы запрещали его ранее. Более того, он всегда сам обновляется до необходимой версии при установке игры, независимо от подключения к интернету (во все установщики игр, которые используют .NET Framework, вшивается обновлятор этого компонента, даже в пиратские версии). Когда игра запущена, все остальные компоненты будут сидеть на месте и не работать, независимо от состояния их включенности. Включение и отключение различных компонентов никак не повлияет на работу игры, а их оптимизация является вымыслом неопытных пользователей.
- Единственной стороной компонентов, которую можно считать негативной, является занимаемое ими место на жёстком диске, но объём их очень мал, а простое отключение не поможет удалить. Полное удаление компонентов является бессмысленным, трудным и иногда опасным занятием.
- Если на компьютер будет установленно приложение, для функционирования которого потребуется один из процессов Windows, необходимый компонент будет автоматически подключён, но бывают и исключения (завит от приложения).
- Некоторые программы очень важны для повседневной функциональности вашей системы и стоит знать назначение каждой, перед тем, как приступить к отключению.
Включение и отключение программ и компонентов на Windows 10
Если вы всё же решили отключать компоненты или желаете убедиться, что у вас включено всё необходимое, сначала нужно найти их через панель управления.
- Откройте панель управления. Её можно найти через поиск в меню «Пуск» или нажав на тот же «Пуск» правой кнопкой мыши.
Панель управления можно найти через поиск в меню «Пуск»
Disclaimer: This post may contain affiliate links, meaning we get a small commission if you make a purchase through our links, at no cost to you. For more information, please visit our Disclaimer Page.
Microsoft’s Windows has a lot of useful features that you may use daily in many tasks. However, there are some unnecessary features that you never use nowadays, such as Internet Explorer 11, PowerShell 2.0, Internet Information Services or even Windows Media Player.
I marked these features as unnecessary because I have never used them, and some of these functions are outdated, such as Internet Explorer 11.
Currently, I’m using Windows 10, and I would recommend disabling most of these features in case that you don’t use them.
Read Article: How To Fix ‘The Requested Operation Requires Elevation’ Error In Windows 10
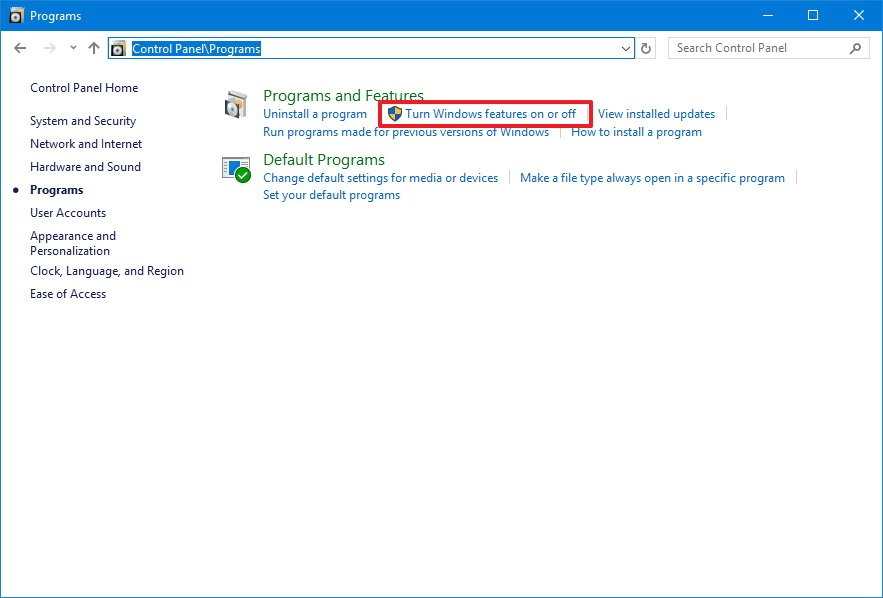
To disable Windows 10 features, go to Control Panel, click on Program and then choose Programs and Features. You can also access “Programs and Features” by right-clicking on Windows logo and choose it there.
Look at the left sidebar and choose “Turn Windows feature on or off“. The “Windows Features” window will be shown up shortly on your screen.
To disable any features, simply unselect the checkbox, choose “Yes” to confirm your selection again and then reboot your PC to take effect. You can disable multiple features and then restart the computer.
When you want to activate these features again, go here and tick the checkbox and then reboot the PC.
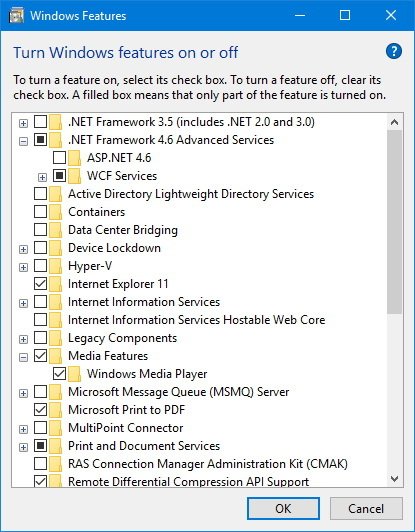
Now it’s time to show you a list of 11 Windows features that you should disable.
Read Article: What is DCB_ASSOCIATION?
1. Internet Explorer 11
As you know, Microsoft has replaced Internet Explorer with the Edge since they released Windows 10. But the Internet Explorer 11 (IE11) still kept in the operating system – there is no plan to remove it.
However, Microsoft has stopped send updates to IE11 through Windows Update. If you want to update IE11 to fix bugs or for improvements, you have to download it manually from Microsoft Update Catalog.
So if you don’t have any reasons to use IE11 when the Edge is the best choice, then just disable it.
2. Legacy Components – DirectPlay
DirectPlay is an API of Microsoft DirectX API, which was used for games in Windows Live ten years ago. Nowadays, the modern games don’t use it anymore.
3. Media Features – Windows Media Player
In fact, Windows Media Player is a popular media player that many users use it. However, the disadvantage of this media player is that doesn’t support some important audio and video types.
In Windows 10, Groove Music is the default media player, which could be replaced for Windows Media Player. Also, if you are using a third-party media player such as VLC Media Player, there is no reason to keep Windows Media Player on your computer.
4. Microsoft Print to PDF
This is an option that allows you to convert any documents into a PDF file. It acts like a virtual printer that helps to create PDF documents from your real documents in Windows. But if you are using Microsoft Office, then you don’t need this feature because you can save your document to PDF directly within the Microsoft Office.
5. Internet Printing Client
Like its name, this feature will allow you to print documents through the local network (LAN) or over the Internet with IPP protocol. But if you only use the printer that connected to your computer, this feature is useless.
6. Windows Fax and Scan
Enabling this feature on your Windows computer will allow you to use Fax or Scan devices that connected to your PC. If you don’t use any of these devices, just turn off this feature.
7. Remote Differential Compression API Support
Microsoft has introduced this feature for Windows Server 2003 R2 until now, which helps users to manage servers better. Some programs use this feature to remote access and management, such as Remote Desktop Connection. Hence if you don’t use Windows Server or any kinds of remote access, just disable it.
8. Windows PowerShell 2.0
You may be thought Windows PowerShell 2.0 is the latest version of PowerShell in Windows. However, the most recent version of PowerShell is 5.0 and therefore, it’s useless. You should disable it as soon as possible.
9. Windows Process Activation Service
If you don’t have any plans to run a home-based server, then you should turn off Windows Process Activation Service. It’s also known as Internet Information Services (IIS), which helped developers to write apps and building their projects. If you are a regular Windows user, just turn it off.
10. Work Folders Client
This feature in Windows allows you to access and work on any linked devices, such as other computers through the network. But if you are using your Windows PC alone at your home, there is no reason to keep this feature.
11. XPS Services and XPS Viewer
XPS is a type of file that was designed by Microsoft, to replace Adobe’s PDF. XPS Services and XPS Viewer are features that allow users to create, print and preview XPS documents in your computer. If you don’t have any plans to use, disable them is a good idea.
If you have any questions about these Windows features, feel free to leave your comment below. Otherwise, post your question in PCGuide forum, experts there will help you out.
Related posts:
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Remote Differential Compression (RDC) is a client–server synchronization algorithm that allows the contents of two files to be synchronized by communicating only the differences between them. It was introduced with Microsoft Windows Server 2003 R2, is included with later Windows client and server operating systems, but by 2019 is not being developed and is not used by any Microsoft product.
Unlike Binary Delta Compression (BDC), which is designed to operate only on known versions of a single file, RDC does not make assumptions about file similarity or versioning. The differences between files are computed on the fly, therefore RDC is suitable for efficient synchronization of files that have been updated independently, where network bandwidth is small, or where the files are large but the differences between them are small.
The algorithm used is based on fingerprinting blocks on each file locally at both ends of the replication partners. Since many types of file changes can cause the file contents to move without other significant change (for example, a small insertion or deletion at the beginning of a file can cause the rest of the file to become misaligned to the original content) the blocks used for comparison are not based on static arbitrary cut points but on cut points defined by the contents of each file segment. This means that if a part of a file changes in length, or blocks of the contents get moved to other parts of the file, the block boundaries for the parts that have not changed remain fixed related to the contents, and thus the series of fingerprints for those blocks do not change, they just change position. By comparing all hashes in a file to the hashes for the same file at the other end of the replication pair, RDC is able to identify which blocks of the file have changed and which have not, even if the contents of the file have been significantly reshuffled.
Since comparing large files could imply making large numbers of signature comparisons, the algorithm is recursively applied to the hash sets to detect which blocks of hashes have changed or moved around, significantly reducing the amount of data that needs to be transmitted for comparing files.
Later versions of Windows support cross-file RDC, which finds files similar to the one being replicated, and uses blocks of the similar files that are identical to the replicating file to minimize data transferred over the WAN. Cross-file RDC can use blocks of up to five similar files.[1]
RDC is similar in many ways to the older (1996) rsync protocol, but with some useful innovations, in particular the recursive algorithm and cross-file RDC.[2]
RDC is implemented in Windows operating systems by a DLL file, MSRDC.DLL, which will be present in the %SYSTEMROOT%System32 directory if and only if RDC is enabled. Very little software is available which makes use of it, particularly on non-server systems. According to Internet rumor, enabling RDC significantly slows local file transfers, and it should not be enabled; a Microsoft TechNet web page disputes this in great detail,[3] despite frequent anecdotal posts of its removal having worked to restore transfer speeds.[citation needed]
Discontinuation[edit]
With the release of Microsoft’s Windows Server 2019, RDC support was included in the section Features we’re no longer developing (which may be removed from a future update), with the comment «This support isn’t currently used by any Microsoft product».[4]
See also[edit]
- DFS replication
References[edit]
- ^ Microsoft TechNet: DFS Replication: Frequently Asked Questions, section «What is cross-file RDC?», pub. 16 October 2006, updated 30 January 2013
- ^ Remote Differential Compression (aka rsync algorithm for Windows), David Jade, Programming, 15 February 2013
- ^ Ned Pyle (26 June 2009). «Debunking the Vista Remote Differential Compression Myth». Microsoft Technet blogs. Retrieved 2 June 2019.
- ^ «Features removed or planned for removal in Windows Server 2019». Microsoft Windows IT Pro Center. 21 May 2019. Retrieved 2 June 2019.
External links[edit]
- Distributed File System
- About Remote Differential Compression
- Optimizing File Replication over Limited-Bandwidth Networks using Remote Differential Compression
Удаленное дифференциальное сжатие
Из Википедии, бесплатной энциклопедии
Перейти к навигации
Перейти к поиску
Удаленное дифференциальное сжатие ( RDC ) — это алгоритм синхронизации клиент-сервер, который позволяет синхронизировать содержимое двух файлов, сообщая только различия между ними. Он был представлен в Microsoft Windows Server 2003 R2, включен в более поздние клиентские и серверные операционные системы Windows, но к 2019 году не разрабатывается и не используется ни в одном продукте Microsoft.
В отличие от двоичного дельта-сжатия (BDC), которое предназначено для работы только с известными версиями одного файла, RDC не делает предположений о сходстве файлов или управлении версиями. Различия между файлами вычисляются на лету, поэтому RDC подходит для эффективной синхронизации файлов, которые были обновлены независимо, где пропускная способность сети мала или когда файлы большие, но различия между ними невелики.
Используемый алгоритм основан на блокировке отпечатков пальцев для каждого файла локально на обоих концах партнеров репликации. Поскольку многие типы изменений файлов могут привести к перемещению содержимого файла без других значительных изменений (например, небольшая вставка или удаление в начале файла может привести к смещению остальной части файла с исходным содержимым) используемые блоки для сравнения основаны не на статических произвольных точках разреза, а на точках разреза, определяемых содержимым каждого сегмента файла. Это означает, что если часть файла изменяется по длине или блоки содержимого перемещаются в другие части файла, границы блоков для частей, которые не изменились, остаются фиксированными по отношению к содержимому, и, таким образом, серия отпечатков пальцев поскольку эти блоки не меняются, они просто меняют положение.Сравнивая все хэши в файле с хешами того же файла на другом конце пары репликации, RDC может определить, какие блоки файла изменились, а какие нет, даже если содержимое файла было значительно изменено. перетасовали. Поскольку для сравнения больших файлов может потребоваться большое количество сравнений сигнатур, алгоритм рекурсивно применяется к хеш-наборам, чтобы определить, какие блоки хэшей были изменены или перемещены, что значительно сокращает объем данных, которые необходимо передать для сравнения файлов.алгоритм рекурсивно применяется к хеш-наборам, чтобы определить, какие блоки хэшей были изменены или перемещены, что значительно сокращает объем данных, которые необходимо передать для сравнения файлов.алгоритм рекурсивно применяется к хеш-наборам, чтобы определить, какие блоки хэшей были изменены или перемещены, что значительно сокращает объем данных, которые необходимо передать для сравнения файлов.
Более поздние версии Windows поддерживают межфайловый RDC, который находит файлы, похожие на реплицируемый, и использует блоки похожих файлов, которые идентичны реплицируемому файлу, для минимизации данных, передаваемых по глобальной сети. Межфайловый RDC может использовать блоки до пяти одинаковых файлов. [1]
RDC во многом похож на старый (1996 г.) протокол rsync , но с некоторыми полезными нововведениями, в частности, рекурсивным алгоритмом и межфайловым RDC. [2]
RDC реализуется в операционных системах Windows с помощью DLL- файла MSRDC.DLL, который будет присутствовать в каталоге% SYSTEMROOT% System32, если и только если RDC включен. Доступно очень мало программного обеспечения, которое его использует, особенно в несерверных системах. По слухам в Интернете, включение RDC значительно замедляет локальную передачу файлов, и его не следует включать; на веб-странице Microsoft TechNet это очень подробно оспаривается [3], несмотря на частые анекдотические сообщения о том, что его удаление помогло восстановить скорость передачи. [ необходима цитата ]
Прекращение
С выпуском Microsoft Windows Server 2019 поддержка RDC была включена в раздел « Функции, которые мы больше не разрабатываем» (который может быть удален из будущего обновления) с комментарием «Эта поддержка в настоящее время не используется ни одним продуктом Microsoft». . [4]
См. Также
- Репликация DFS
Ссылки
- ^ Microsoft TechNet: Репликация DFS: часто задаваемые вопросы, раздел «Что такое межфайловый RDC?», Pub. 16 октября 2006 г., обновлено 30 января 2013 г.
- ^ Удаленное дифференциальное сжатие (также известный как алгоритм rsync для Windows), Дэвид Джейд, Программирование, 15 февраля 2013 г.
- ↑ Нед Пайл (26 июня 2009 г.). «Разоблачение мифа об удаленном дифференциальном сжатии Vista» . Блоги Microsoft Technet . Дата обращения 2 июня 2019 .
- ^ «Компоненты, удаленные или запланированные для удаления в Windows Server 2019» . Центр Microsoft Windows для ИТ-специалистов . 21 мая 2019 . Дата обращения 2 июня 2019 .
Внешние ссылки
- Распределенная файловая система
- Об удаленном дифференциальном сжатии
- Оптимизация репликации файлов в сетях с ограниченной пропускной способностью с помощью удаленного разностного сжатия
Enable Remote Differential Compression API Support in Windows 10: Remote Differential Compression (RDC) allows synchronized data with a remote source by means of compression techniques to reduce the quantity of data sent across the network. If you want to use Windows Server or any sort of remote access, you can enable this useful feature in Windows 10. It helps you to manage servers and remote access better. Let’s follow the guidelines given below in order to Enable Remote Differential Compression API Support in Windows 10.
- Click the Start button, type Control Panel and click Enter.
Control Panel
- In the Control Panel window, you have to click on Programs.
Programs
- Now, you have to select Turn Windows features on or off.
Turn Windows features on or off
- A pop-up window will appear. Scroll down and select the check-box of the Remote Differential Compression API Support and click OK.
Remote Differential Compression API Support
- Now, Windows will look for the required files.
Search files
- It will apply the changes it made.
Related Guides: How to Fix Windows Error Code 0x80070422? (*Quick Steps*)
Apply changes
- Once the Windows completed the necessary changes, you have to click Close.
Close
- Remote Differential Compression API Support should now be enabled in your device.
Conclusion:
We hope that this tutorial assisted you to Enable Remote Differential Compression API Support quickly and easily in Windows 10. This feature is utilized by a small number of Windows apps and programs, so it is best to keep it enabled. Please leave a reply in the below comment box. Thanks for visiting Windows Jet.
Related Articles:
Windows 10 is a sophisticated OS that includes an extensive array of features, some of which you have to turn on or off as needed. These are known as «optional features,» and they’re available through the «Windows Features» page in Control Panel. While most of them are meant to add server functionality to your computer, there are some features that are useful for all users.
These optional features can’t be entirely removed from your device, and they’ll continue to use space on your hard drive, but depending on the functionalities required, you can enable or disable them as needed. Many of these Windows 10 features are advanced, and turning them on could potentially make your computer vulnerable or slow if you don’t know how to configure them correctly.
In this Windows 10 guide, we’ll walk you through the steps to optional features turn on and off, and we’ll provide details on what they are.
- How to manage optional features using Control Panel
- The optional features available in Windows 10
- How to manage optional features using Settings
How to manage optional features using Control Panel
Although Windows 10 includes the Settings app, you still need to use Control Panel to manage optional features on your computer, if you want to create virtual machines using Hyper-V, use Internet Information Services (IIS) to set up an FTP server, or add the Linux Bash command-line tool.
Here’s how to turn on or off optional features on Windows 10 using Control Panel:
- Open Control Panel.
- Click on Programs.
- Click the Turn Windows features on or off link.
- On Windows Features, check or clear the feature you want.
- Click OK to enable and disable the feature.
- Restart your computer as indicated by the wizard to complete the task.
While you’re in Windows Features, you’ll see a long list with all the optional features you can manage. If they have a check mark, then it means that the feature is currently enabled on your computer.
You’ll also notice that some features have multiple features under them. If you see a feature with a black square, instead of a check mark, then it means that only part of the feature is enabled. You can always enable sub-features by expanding and checking the ones you want to enable. Of course, those that don’t have any check marks indicate that they’re not currently enabled on your computer.
Optional features available in Windows 10
The optional features available will depend on the edition of Windows 10 installed on your computer. For example, even though, you can manage features on Windows 10 Home and Pro, some advanced features won’t be available in the Home version of the OS.
Here’s a list with a description of the features you can enable or disable in Windows 10 Pro:
- .NET Framework 3.5 (includes .NET 2.0 and 3.0): This feature is essential to run applications built using Microsoft .NET software framework version 3.5 or older. You can safely enable earlier support, but usually it’ll turn on automatically when needed.
- .NET Framework 4.6 Advanced Services: You’ll need to enable this feature for apps built with version 4.6 of the framework.
- Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services: Adds Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) support for directory-enabled applications. This is an alternative to Windows Active Directory, which is a more complex directory solution. Usually, you’ll need this feature in certain corporate network scenarios.
- Containers: Provides services and tools to create and manage Windows Server Containers and Hyper-V containers on your desktop.
- Data Center Bridging: This feature is an IEEE standard that enables converged fabrics in a data center, where network, storage, clustering and traffic managements share the same Ethernet network infrastructure. Data center bridging is only useful in corporate networks.
- Device Lockdown: You can enable this feature to add services and tools to provide a more controlled experience. Typically, you’ll enable this feature when setting up a kiosk or a temporary device.
- Hyper-V: Microsoft offers its own virtualization technology that allows you to create and manage virtual machines on your computer.
- Internet Explorer 11: Although Windows 10 includes Edge, Microsoft continues to ship Internet Explorer 11 for compatibility purposes, but it’s possible to disable it if you don’t need it.
- Internet Information Services: Commonly known as IIS, it allows you to set up an FTP server or a server to host websites with management services.
- Internet Information Services Hostable Web Core: Allows you to set an environment to host applications on the web. Typically, developers will find this feature beneficial to test applications on Windows 10 Pro.
- Legacy Components: Allows you to add support for old components on Windows. This includes DirectPlay, a feature that was used to be part of DirectX.
- Media Features: Provides a way to remove Windows Media Player from Windows 10.
- Microsoft Message Queue (MSMO) Server: Enables applications to run correctly on unreliable networks by queuing messages instead of sending them as they’re generated. Usually, you’ll only find this feature useful on particular corporate network environments.
- Microsoft Print to PDF: Instead of printing a document directly to paper, you can print to PDF and save the content as a file. However, it’s possible to disable the feature if you don’t use it.
- MultiPoint Connector: If you enable this feature, you can monitor and manage your computer using a MultiPoint Manager and MultiPoint Manager Dashboard applications.
- Print and Document Services: This feature deals with printing services on Windows 10. Here’s where you can enable or disable services for scan, fax and network printing.
- RAS Connection Manager Administration Kit (CMAK): You can use CHMAK to create custom profiles to connect to remote access servers. This is a feature that you’ll only use if you’re an IT administrator.
- Remote Differential Compression API Support: Provides synchronization algorithm that intelligently compares two files that are about to be synchronized and only updating the differences between them. Only certain applications can use this feature.
- RIP Listener: If you’re in a network using the old RIP protocol version 1, you can use RIP Listener to listen to RIP updates in the network. If you’re on a home network, chances are you’ll never use this.
- Services for NFS: Allows you to access files using the Network File System (NFS) protocol. Typically, you’ll use this feature to access files on Network Attached Storage (NAS).
- Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP): Enables SNMP agents on your computer that monitors switches, routers, and other devices in the network, and reports to the network console. This feature isn’t useful unless you’re connected to a network using the protocol.
- Simple TCPIP Services (echo, daytime etc): Provides support for additional TCP/IP protocol services, including «Echo», «Character Generator (CHARGEN)», «Daytime», «Discard», and «Quote of the Day (QUOTE)».
- SMB 1.0/CIFS File Sharing Support: Adds support to configure file and printer sharing for previous versions of the OS, including Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 R2.
- SMB Direct: Allows the use of network adapters with Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA) capability to improve file sharing support using SMB 3.x.
- Telnet Client: This is a command-line utility that allows you to connect to other computers or devices, such as routers and switches, running a telnet server. This network protocol isn’t secure, and you shouldn’t use it outside of your network.
- TFTP Client: This is a command-line utility that you can use to upload and download files using Trivial File Transfer Protocol. This protocol isn’t secure, and you shouldn’t use it unless is a requirement.
- Windows Identity Foundation 3.5: Newer applications use .NET 4 that adds a new identity framework, but applications created with older .NET technologies may still require this feature.
- Windows PowerShell 2.0: This is an advanced command-line scripting tool, similar to Command Prompt. PowerShell comes enabled by default, but it’s possible to disable the feature on Windows 10.
- Windows Process Activation Service: Installs services that may be required if you’re using IIS web services.
- Windows Subsystem for Linux (Beta): Installs the Ubuntu Bash shell command-line utility on Windows 10. However, there are additional steps that you must follow to complete the installation.
- Windows TIFF iFilter: When this feature is enabled, Windows 10 can index and search Tagged Image File Format (TIFF) using optical character recognition (OCR), but it typically uses more system resources than traditional file indexing and searching. However, if you work with these type of documents, it can help you to find those scanned documents quicker.
- Work Folders Client: Allows file synchronization with network file servers.
- XPS Services: This is an old Microsoft feature similar to PDF. You can still print documents to XPS, but PDF is a format that’s more widely supported. If you don’t use it, you can clear the check mark to remove it.
- XPS Viewer: This is an application that Microsoft includes with the OS to open XPS files. If you don’t work with any XPS files, you can safely disable this feature.
As you can see, there are a lot of optional features that you can turn on or off in Windows 10, but many of them won’t be useful unless you’re in a corporate environment.
How to manage optional features using Settings
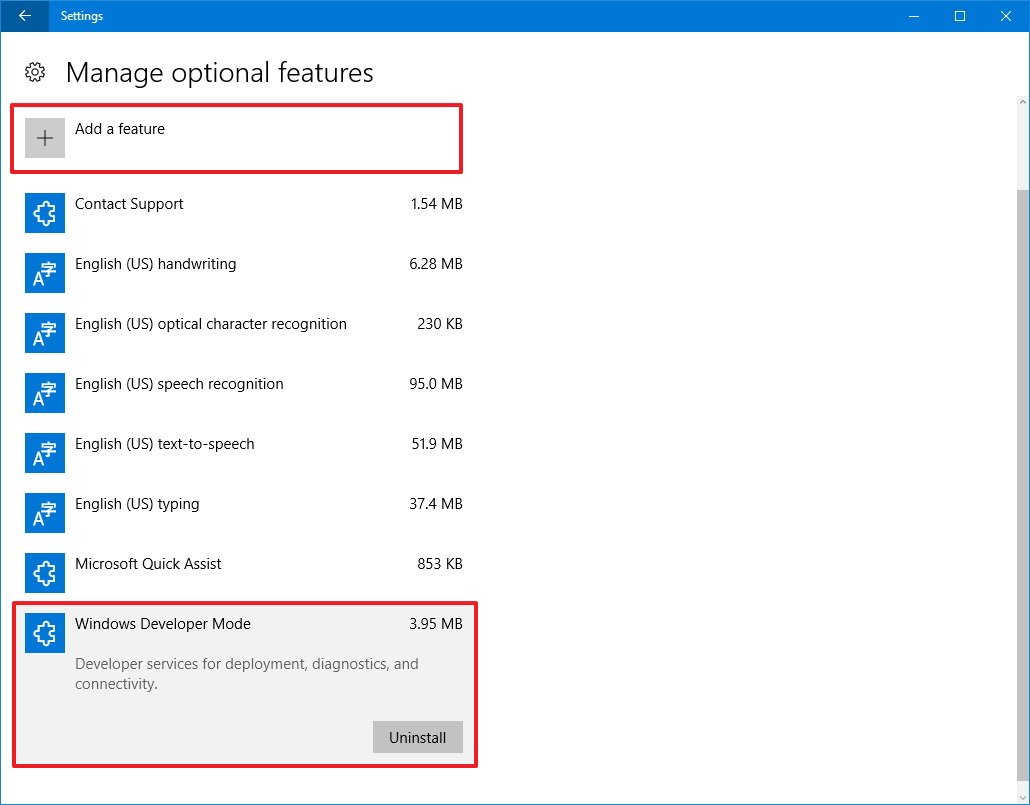
The Settings app also includes a section to manage optional features, but it’s not the same as the one in Control Panel. It’s only a place to manage particular modern Windows 10 features, such as Windows Developer Mode, Contact Support, and Microsoft Quick Assist.
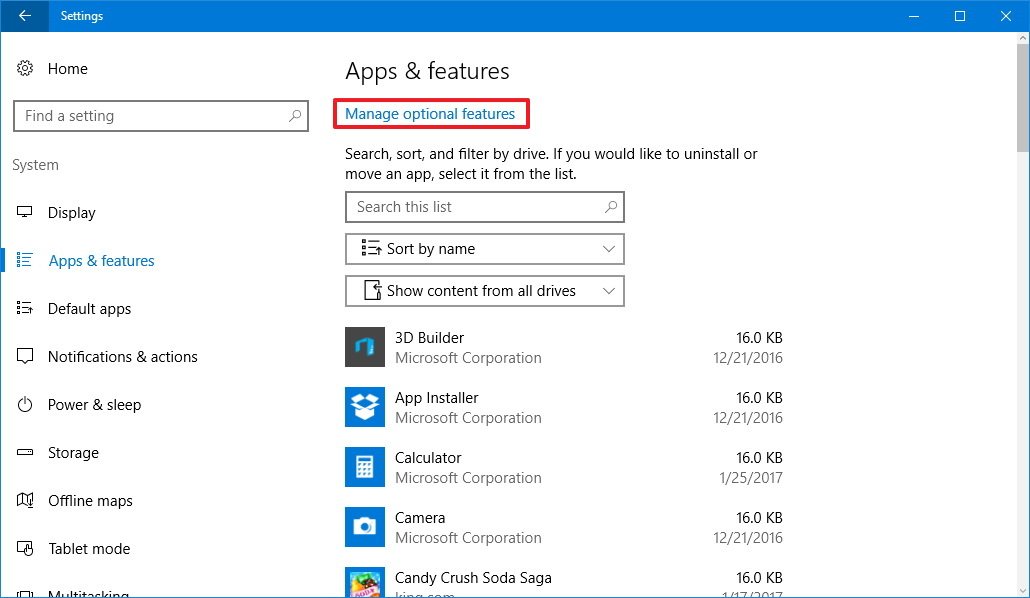
To manage optional features using the Settings app on Windows 10, do the following:
- Open Settings.
- Click on System.
- Click on Apps & features.
- Click the Manage optional features link.
- Select the feature you want, and you’ll notice a button to Uninstall or Manage, which will redirect you to the settings page where the feature is located.
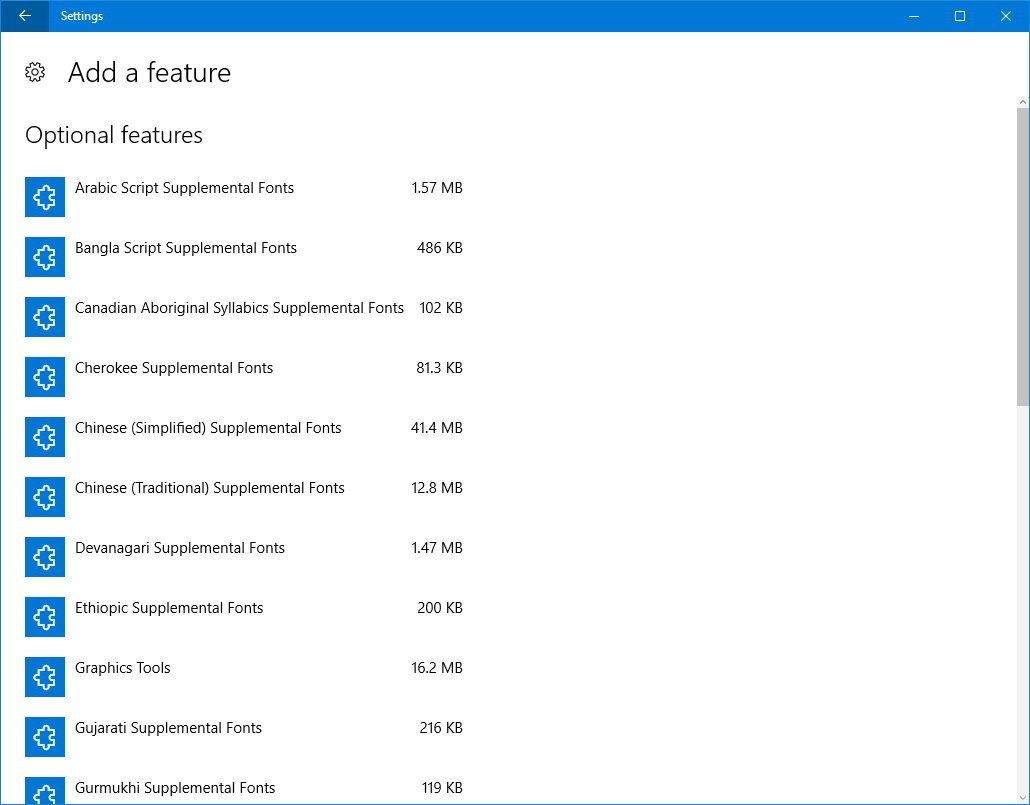
You can also click the Add a feature button to add a number of fonts for different languages.
Wrapping things up
While it can be good to have a basic understanding of these optional features and how to manage them, for the most part, regular users don’t have to worry about them. Windows 10 and applications are typically smart enough to detect and automatically turn on features as needed.
However, sometimes there are particular scenarios where you may need to turn on or off an optional feature manually. For example, when you want to test upcoming features of Windows 10 using a virtual machine using Microsoft’s Hyper-V virtualization tool. Of if you’re a developer working on Windows and Linux, and you need a command-line tool like the Bash shell on Ubuntu. Or when you want to set up an FTP server to create your private cloud and share files without restrictions.
The list of features we mentioned in this guide covers all the ones included with the Windows 10 Anniversary Update, but remember that they can change in future releases.
What optional features do you have enabled on Windows 10? Let us know in the comments.
More Windows 10 resources
For more help articles, coverage, and answers to common questions about Windows 10, visit the following resources:
- Windows 10 on Windows Central – All you need to know
- Windows 10 help, tips, and tricks
- Windows 10 forums on Windows Central
Get the best of Windows Central in in your inbox, every day!
Mauro Huculak is technical writer for WindowsCentral.com. His primary focus is to write comprehensive how-tos to help users get the most out of Windows 10 and its many related technologies. He has an IT background with professional certifications from Microsoft, Cisco, and CompTIA, and he’s a recognized member of the Microsoft MVP community.
Windows 10 has proved to be one of the most popular and stable operating systems to have seen the light of the day.
Despite its extreme popularity, it also gets bogged down by its fair share of errors. One of the most persistent errors is the file transfer to a drive, a USB, or over the network either totally stops or suffers from extreme lags while being processed.
Many users have reported this problem on Windows’ official website but to no avail. However, some tech geeks have been able to find workable methods to solve the problem. Let’s check them out right away.
Note: The following solutions will only help if the HDD and RAM aren’t faulty.
Before we dive into the solutions that can help you with the file transfer coming to an abrupt end in Windows 10, here is a neat computer program that can help you copy/ move vast troves of data from one location to another (local hard disk or USB) by simplifying it even further than the File Explorer method. Rather than going deep into the file directory by making your way to the target folder, you simply get to select the target destination by browsing to the file from the file system hierarchy. The whole process is absolutely safe, and you can try it out without hesitating.
Easily Copy/ Move Files in Windows 10
Easy File Renamer adheres to Clean Software Association Guidelines
Solutions
Solution 1: Disable Remote Differential Compression
The Remote Differential Compression task compresses data before it is sent over the network. This takes a considerable amount of time and can lead to congestion. Speed up the file copying, moving or deleting process by disabling this process.
- Open Control Panel and select Programs and Features.
- Now select Turn Windows features on or off from the pane on the left-hand side.
- Search for Remote Differential Compression API Support and uncheck the box next to it.
- Click OK to save the changes.
Solution 2: Disable Indexing of your Drives
Indexing of files on a drive can also result in a slowdown in the copying of data. Indexing basically allows the computer to work more efficiently by creating a table of all drives in the cache. However, this has an adverse effect on the file transfer speed. So here is how you can disable the indexing of drives.
- Search for Type in services.msc in the Run command box and press Enter to open up Services.
- Disable Windows Search by right-clicking it and selecting Stop.
Solution 3: Update all Drivers
Windows prefers to install its own drivers for computer peripherals, whereas using other drivers can result in decreased performance sometimes. Therefore, it is possible that updating the driver can fix the problem under discussion.
- Download latest drivers for BIOS, Chipset, HDD and IDE Controllers.
- Open Device Manager.
- Right-click on the device you want to update the driver for and click Update driver.
A complete process to do the same is provided here.
Solution 4: Run Disk Defragmenter on both drives
This process is not always helpful but there is a probability nevertheless that the congestion in between file transfers is caused due to fragmentation. Reduce it by defragmenting the disk concerned or both the disks that you are trying to use during the copy-paste process.
- Click the Windows button and search for Disk Defragmenter.
- Select the concerned drive and then click Optimize.
Solution 5: Format the drive (to which you are copying data) in NTFS
Sometimes the only reason a drive isn’t copying data is that it isn’t formatted properly. This happens when the drive is new and comes factory formatted. There is a rare chance that the drive wasn’t formatted properly at the factory and must be formatted afresh before it can perform properly.
- Right-click on the drive you are trying to copy data to and select Format.
- Choose NTFS in the File System drop-down menu.
- Uncheck the Quick format checkbox.
- Finally, click Start.
Solution 6: Disabling Antivirus and Windows Defender
Many users have reported that their slow speed file transfer problem was solved when they disabled real-time protection of their antivirus software and then turned off the Windows Defender.
The name of the exact option to disable the antivirus software’s real-time protection varies, however they are disabled by right-clicking the antivirus icon in the taskbar and selecting the appropriate option. Windows Defender can be disabled in the following manner:
- Press Windows key and type in Windows Defender.
- Open it from the Search Results and click the shield icon on the left to open up Virus & threat protection.
- Now click Virus & threat protection settings.
- Move the slider for Real-time protection to the left to turn it off.
- Click Yes in the prompt to confirm your selection.