| Developer(s) | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| Full name | Extensible File Allocation Table |
| Introduced | November 2006; 16 years ago with Windows Embedded CE 6.0 |
| Partition identifier |
|
| Structures | |
| Directory contents | Table |
| File allocation | bitmap, linked list |
| Bad blocks | Cluster tagging |
| Limits | |
| Max. volume size | 128 PB, 512 TB recommended[1] |
| Max. file size | 128 PB (theoretical 16 EB – 1 byte)[nb 1] |
| Max. number of files | up to 2,796,202 per directory[2] |
| Max. filename length | 255 characters |
| Allowed characters in filenames | all Unicode characters except U+0000 (NUL) through U+001F (US) / (slash) : (colon) * (asterisk) ? (question mark) " (quote) < (less than) > (greater than) and | (pipe)(encoding in UTF-16LE) |
| Features | |
| Dates recorded | Creation, last modified, last access |
| Date range | 1980-01-01 to 2107-12-31 |
| Date resolution | 10 ms |
| Forks | No |
| Attributes | Read-only, hidden, system, subdirectory, archive |
| File system permissions | ACL (Windows CE 6 only) |
| Transparent compression | No |
| Transparent encryption | Yes, EFS supported in Windows 10 v1607 and Windows Server 2016 or later. |
| Other | |
| Supported operating systems |
|
exFAT (Extensible File Allocation Table) is a file system introduced by Microsoft in 2006 and optimized for flash memory such as USB flash drives and SD cards.[5] exFAT was proprietary until 28 August 2019, when Microsoft published its specification.[6] Microsoft owns patents on several elements of its design.[2]
exFAT can be used where NTFS is not a feasible solution (due to data-structure overhead), but where a greater file-size limit than that of the standard FAT32 file system (i.e. 4 GB) is required.
exFAT has been adopted by the SD Association as the default file system for SDXC cards larger than 32 GB.
Windows 8 and later versions natively support exFAT boot, and support the installation of the system in a special way to run in the exFAT volume.[7]
History[edit]
exFAT was introduced in late 2006 as part of Windows CE 6.0, an embedded Windows operating system. Most of the vendors signing on for licenses are manufacturers of embedded systems or device manufacturers that produce media formatted with exFAT. The entire File Allocation Table (FAT) family, exFAT included, is used for embedded systems because it is lightweight and is better suited for solutions that have low memory and low power requirements, and can be easily implemented in firmware.
Features[edit]
Because file size references are stored in eight instead of four bytes, the file size limit has increased to 16 exabytes (EB) (264 − 1 bytes, or about 1019 bytes, which is otherwise limited by a maximum volume size of 128 PB,[nb 1] or 257 − 1 bytes), raised from 4 GB (232 − 1 bytes) in a standard FAT32 file system.[1] Therefore, for the typical user, this enables seamless interoperability between Windows and macOS platforms for files in excess of 4 GB.
Other specifications, features, and requirements of the exFAT file system include:
- Scalability to large disk sizes: about 128 PB (257 − 1 bytes)[8][nb 2] maximum, 512 TB (249 − 1 bytes) recommended maximum, raised from the 32-bit limit (2 TB for a sector size of 512 bytes) of standard FAT32 partitions.[9]
- Support for up to 2,796,202 files per directory.[2][nb 3] Microsoft documents a limit of 65,534 (216 − 2) files per sub-directory for their FAT32 implementation, but other operating systems have no special limit for the number of files in a FAT32 directory. FAT32 implementations in other operating systems allow an unlimited number of files up to the number of available clusters (that is, up to 268,304,373 files on volumes without long filenames).[nb 4]
- Maximum number of files on volume C[clarification needed], to 4,294,967,285 (232 − 11, up from about 228 − 11[nb 4] in standard FAT32).
- Free space allocation and delete performance improved due to introduction of a free-space bitmap.
- Timestamp granularity of 10 ms for creation and modified times (down from 2 s on FAT, but not as fine as NTFS’s 100 ns).[2]
- Timestamp granularity for last-access time to double seconds (FAT had date only).
- Timestamps come with a time zone marker in offset relative to UTC (starting with Vista SP2).[10]
- Optional support for access-control lists (not currently supported in Windows Desktop/Server versions).[11]
- Optional support for TexFAT, a transactional file system standard (optionally WinCE activated function, not supported in Windows Desktop/Server versions).
- Boundary alignment offset for the FAT table.
- Boundary alignment offset for the data region.
- Provision for OEM-definable parameters to customize the file system for specific device characteristics.[12][13]
- Valid data length (VDL): through the use of two distinct lengths fields – one for «allocated space» and the other for «valid data» – exFAT can preallocate a file without leaking data that was previously on-disk.
- Cluster size up to 32 MB.[14]
- Metadata integrity with checksums.[clarification needed]
- Template-based metadata structures.[clarification needed]
- Removal of the physical
.and..directory entries that appear in subdirectories. - exFAT no longer stores the short 8.3 filename references in directory structure and natively uses extended file names, whereas legacy FAT versions implement extended file names through the VFAT extension.
Windows XP requires update KB955704 to be installed, and Windows Vista requires its SP1 or SP2 be installed.[14][15][16] Windows Vista is unable to use exFAT drives for ReadyBoost. Windows 7 removes this limitation, enabling ReadyBoost caches larger than 4 GB.[17] Windows 10 only allows formatting exFAT on volumes sized 32 GB or larger with the default user interface, and FAT32 format is suggested for smaller volumes; command-line utilities still accept a full range of file systems and allocation unit sizes.
The standard exFAT implementation is not journaled and only uses a single file allocation table and free-space map. FAT file systems instead used alternating tables, as this allowed recovery of the file system if the media was ejected during a write (which occurs frequently in practice with removable media). The optional TexFAT component adds support for additional backup tables and maps, but may not be supported.
The exFAT format allows individual files larger than 4 GB, facilitating long continuous recording of HD video, which can exceed the 4 GB limit in less than an hour. Current digital cameras using FAT32 will break the video files into multiple segments of approximately 2 or 4 GB.
EFS supported in Windows 10 v1607 and Windows Server 2016 or later.[18]
Efficiency[edit]
SDXC cards running at UHS-I have a minimum guaranteed write speed of 10 MB/s, and exFAT plays a factor in achieving this throughput through the reduction of the file-system overhead in cluster allocation. This is achieved through the introduction of a separate cluster bitmap where the reservation state of each cluster (reserved/free) is tracked by only one bit, reducing writes to the much larger FAT that originally served this purpose.
Additionally, a single bit in the directory record indicates that the file is contiguous (unfragmented), telling the exFAT driver to ignore the FAT. This optimization is analogous to an extent in other file systems, except that it only applies to whole files, as opposed to contiguous parts of files.
Adoption[edit]
exFAT is supported in Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 with update KB955704,[1] Windows Embedded CE 6.0, Windows Vista with Service Pack 1,[19] Windows Server 2008,[20] Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows Server 2008 R2 (except Windows Server 2008 Server Core), Windows 10, macOS starting from 10.6.5, Linux via FUSE or natively starting from kernel 5.4, and iPadOS as well as iOS starting from 13.1.[21][22][23]
Companies can integrate exFAT into a specific group of consumer devices, including cameras, camcorders, and digital photo frames for a flat fee. Mobile phones, PCs, and networks have a different volume pricing model.[5]
exFAT is supported in a number of media devices such as modern flat-panel TVs,[24] media centers, and portable media players.[25]
exFAT is the official file system of SDXC cards. As mentioned in the respective article, this implies any device not supporting exFAT (such as the Nintendo 3DS) might not legally advertise itself as SDXC compatible despite supporting such cards as mass storage devices per se.
Some vendors of other flash media, including USB pen drives, compact flash (CF) and solid-state drives (SSD) ship some of their high-capacity media pre-formatted with the exFAT file system. For example, Sandisk ships their 256 GB CF cards as exFAT.
Microsoft has entered into licensing agreements with BlackBerry,[26][27] Panasonic, Sanyo, Sony, Canon, Aspen Avionics,[28] Audiovox, Continental, Harman, LG Automotive[29] and BMW.[30]
Mac OS X Snow Leopard 10.6.5 and later can create, read, write, verify, and repair exFAT file systems.[21][22]
Linux has support for exFAT via FUSE since 2009.[4] In 2013, Samsung Electronics published a Linux driver for exFAT under GPL.[31]
On 28 August 2019, Microsoft published the exFAT specification[6] and released the patent to the Open Invention Network members.[32] The Linux kernel introduced native exFAT support with the 5.4 release in November 2019.[33]
ChromeOS can read and write to exFAT partitions.[34]
Technical specialities[edit]
| Volume size |
Cluster size |
Cluster count |
|---|---|---|
| 007–256 MB | 004 KB | <64 K |
| 256 MB–32 GB | 032 KB | 0<1 M |
| 032–512 GB[A][B] | 128 KB | 0<4 M |
| 512 GB–1 TB | 256 KB | |
| 001–2 TB | 512 KB | |
| 002–4 TB | 001 MB | |
| 004–8 TB | 002 MB | |
| 008-16 TB | 004 MB | |
| 016–32 TB | 008 MB | |
| 032–64 TB | 016 MB | |
| 064–512 TB | 032 MB | <16 M |
Notes:
|
File name lookup[edit]
exFAT employs a filename hash-based lookup phase to speed certain cases, which is described in US patent Quick File Name Lookup Using Name Hash.[2] Appendix A of the document contains details helpful in understanding the file system.
File and cluster pre-allocation[edit]
Like NTFS, exFAT can pre-allocate disk space for a file by just marking arbitrary space on disk as «allocated». For each file, exFAT uses two separate 64-bit fields in the directory: the valid data length (VDL), which indicates the real size of the file, and the physical data length.
To provide improvement in the allocation of cluster storage for a new file, Microsoft incorporated a method to pre-allocate contiguous clusters and bypass the use of updating the FAT table, which was patented December 10, 2013.[35] One feature of exFAT (used in the exFAT implementation within embedded systems) provides atomic transactions for the multiple steps of updating the file-system metadata. The feature called Transaction Safe FAT, or TexFAT, was granted a patent on November 3, 2009.[36]
Directory file set[edit]
exFAT and the rest of the FAT family of file systems do not use indexes for file names, unlike NTFS, which uses B-trees for file searching. When a file is accessed, the directory must be sequentially searched until a match is found. For file names shorter than 16 characters in length, one file name record is required but the entire file is represented by three 32-byte directory records. This is called a directory file set, and a 256 MB sub-directory can hold up to 2,796,202 file sets. (If files have longer names, this number will decrease, but this is the maximum based on the minimal three-record file set.) To help improve the sequential searching of the directories (including the root) a hash value of the file name is derived for each file and stored in the directory record. When searching for a file, the file name is first converted to upper case using the upcase table (file names are case-insensitive) and then hashed using a proprietary patented algorithm into a 16-bit (2-byte) hash value. Each record in the directory is searched by comparing the hash value. When a match is found, the file names are compared to ensure that the proper file was located in case of hash collisions. This improves performance because only 2 bytes have to be compared for each file. This significantly reduces the CPU load because most file names are more than 2 characters (bytes) in size and virtually every comparison is performed on only 2 bytes at a time until the intended file is located.
Metadata and checksums[edit]
exFAT introduces metadata integrity through the use of checksums. There are three checksums currently in use.
- The volume boot record (VBR) is a 12-sector region that contains the boot records, BIOS parameter block (BPB), OEM parameters and the checksum sector. (There are two VBR type regions, the main VBR and the backup VBR.) The checksum sector is a checksum of the previous 11 sectors, with the exception of three bytes in the boot sector (flags and percent used). This provides integrity of the VBR by determining whether the VBR was modified. The most common cause could be a boot-sector virus, but this would also catch any other corruption to the VBR.
- A second checksum is used for the upcase table. This is a static table and should never change. Any corruption in the table could prevent files from being located because this table is used to convert the filenames to upper case when searching to locate a file.
- The third checksum is in the directory file sets. Multiple directory records are used to define a single file, and this is called a file set. This file set has metadata including the file name, time stamps, attributes, address of first cluster location of the data, file lengths, and the file name. A checksum is taken over the entire file set, and a mismatch would occur if the directory file set was accidentally or maliciously changed.
When the file system is mounted, and the integrity check is conducted, these hashes are verified. Mounting also includes comparison of the version of the exFAT file system by the driver to make sure the driver is compatible with the file system it is trying to mount, and to make sure that none of the required directory records are missing (for example, the directory record for the upcase table and allocation bitmap are required, and the file system can’t run if they are missing). If any of these checks fail, the file system should not be mounted, although in certain cases it may mount read-only.
The file system provides extensibility through template-based metadata definitions using generic layouts and generic patterns.[37][38]
Flash optimizations[edit]
exFAT contains a few features that, according to Microsoft, makes it flash-friendly:
- Boundary alignment for filesystem structures. The offsets for the FAT and the cluster heap is adjustable at format time, so that writes to these areas will happen in as few flash blocks as possible.
- An «OEM parameters» field can be used to record features such as block size of the underlying storage. One single type for flash storage is pre-defined.[39]
- The lack of a journal, so that less data is written. (Although FAT32 also lacks a journal.)
The first feature requires support from the formatting software. Compliant implementations will follow existing offsets. The OEM parameter may be ignored. Implementations may also use TRIM to reduce wear.
| Boundary alignment (format) | OEM parameters (use) | TRIM (use) | Note | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows CE | Yes | Yes | Unknown | |
| Windows Desktop and Server | Yes | Yes | No | |
| Linux kernel | since 5.7[40] | ignored | since 5.13[41] | exfatprogs is assumed to be used for formatting. |
Other implementations[edit]
|
|
This section needs to be updated. Please help update this article to reflect recent events or newly available information. (September 2019) |
Legal status[edit]
exFAT was a proprietary file system until 2019, when Microsoft released the specification and allowed OIN members to use their patents.[42] This lack of documentation along with the threat of a patent infringement lawsuit, as happened previously when Microsoft sued various companies over the VFAT long file name patent (before it expired), hampered the development of free and open-source drivers for exFAT, and led to a situation where Linux distributions could not even tell users how to get an exFAT driver. Accordingly, exFAT official support was effectively limited to Microsoft’s own products and those of Microsoft’s licensees. This, in turn, inhibited exFAT’s adoption as a universal exchange format, as it was safer and easier for vendors to rely on FAT32 than it was to pay Microsoft or risk being sued.
Interoperability requires that certain results be achieved in a particular, predefined way (an algorithm). For exFAT, this potentially requires every implementation to perform certain procedures in exactly the same way as Microsoft’s implementation. Some of the procedures used by Microsoft’s implementation are patented, and these patents are owned by Microsoft.[43] A license to use these algorithms can be purchased from Microsoft,[44][43] and some companies – including Apple, Google and Samsung – have done so.[45] However, in the open-source ecosystem, users have typically responded to vendors being unwilling to pay for patent licenses by procuring an implementation for themselves from unofficial sources. For example, this is what happened with LAME when MP3 patents were still valid. (Alternatively, the user may decide that the feature is unimportant to them.)
Regardless of whether open-source or not, Microsoft stated that «a license is required in order to implement exFAT and use it in a product or device».[43] Unlicensed distribution of an exFAT driver would make the distributor liable for financial damages if the driver is found to have violated Microsoft’s patents.[46][47] While the patents may not be enforceable, this can only be determined through a legal process, which is expensive and time-consuming. It may also be possible to achieve the intended results without infringing Microsoft’s patents.[48] In October 2018, Microsoft released 60,000 patents to the Open Invention Network members for Linux systems, but exFAT patents were not initially included at the time. There was, however, discussion within Microsoft over whether Microsoft should allow exFAT in Linux devices,[49][50] which eventually resulted in Microsoft publishing the official specification for open usage[6] and releasing the exFAT patents to the OIN in August 2019.[32]
List of implementations[edit]
A FUSE-based implementation named fuse-exfat, or exfat-fuse,[4] with read/write support is available for FreeBSD, multiple Linux distributions, and older versions of Mac OS X. It supports TRIM.[51][52][53][54][55] An implementation called exFATFileSystem, based on fuse-exfat, is available for AmigaOS 4.1.[56]
A Linux kernel implementation by Samsung Electronics is available.[57] It was initially released on GitHub unintentionally,[58] and later released officially by Samsung in compliance with the GPLv2 in 2013.[59][60] (This release does not make exFAT royalty-free, as licensing from Samsung does not remove Microsoft’s patent rights.)[61][62] A version of this driver was first incorporated into version 5.4 of the Linux kernel.[63][64][65] A much newer version of the driver, with several bug fixes and improved reliability, was incorporated into kernel 5.7.[66][40] Prior to its being merged into the Linux kernel, this newer version had already seen adoption on Android smartphones and continued to be used on both Linux and Android thereafter.[67][68]
Proprietary read/write solutions licensed and derived from the Microsoft exFAT implementation are available for Android,[69] Linux, and other operating systems from Paragon Software Group and Tuxera.
XCFiles (from Datalight) is a proprietary, full-featured implementation, intended to be portable to 32-bit systems.[70] Rtfs (from EBS Embedded Software) is a full-featured implementation for embedded devices.[71]
Two experimental, unofficial solutions are available for DOS. The loadable USBEXFAT driver requires Panasonic’s USB stack for DOS and only works with USB storage devices; the open-source EXFAT executable is an exFAT file-system reader and requires the HX DOS extender to work.[72] There are no native exFAT real-mode DOS drivers, which would allow usage of, or booting from, exFAT volumes.
The renaming of ExFAT file system labels is natively supported by Microsoft Windows Explorer, while Linux relies on the third-party exfatlabel tool.[73]
See also[edit]
- Design of the FAT file system
- List of file systems
- Comparison of file systems
- Memory Stick XC
- Universal Disk Format
Notes[edit]
- ^ a b
Although Microsoft published a different value in KB955704, the file size is in bytes and is stored as a 64-bit number. The largest theoretical file size would be 16 EB − 1 byte, the same as in NTFS. However, since the true theoretical maximum volume size under the current specification cannot exceed 128 PB, a file can never reach that file length. Another reason for the limit is that current IDE/ATA disk addressing is LBA-48 and uses a 48-bit block address to address a sector. A 512-byte sector size would make the maximum addressable file system 512 × 248 = 257, which is 128 PB. In other words, the 128 PB limit on the architecture is a hardware restriction. This scenario does not include AF (4k sectors)[clarify], and exFAT is limited to 128 PB regardless of sector size based on the specification. - ^ The theoretical maximum volume size is defined by up to 232 − 11 possible clusters with up to 225 bytes per cluster ≈ 128 PB. The size is currently also limited by the LBA48 addressing scheme, as with a 512-byte sector size, only 248 × 512 = 257 bytes = 128 PB can be addressed.
- ^ This limit applies because the maximum directory size is 256 MB.
- ^ a b 268,304,373 files = 228 − 11 reserved clusters − 131,072, the minimum number of 64 KB clusters occupied for the 268,435,445 directory entries (32 bytes) without VFAT LFNs, which are required for 268,435,445 files with sizes between 1 and 65,535 bytes. With VFATs, the 131,072 number must be multiplied by 21 (worst case), which would result in 265,682,933 files instead.
References[edit]
- ^ a b c d e «KB955704». January 27, 2009. Archived from the original on May 24, 2011. Retrieved January 27, 2009.
Description of the exFAT file system driver update package [for Windows XP and Windows Server 2003]
- ^ a b c d e US 8321439, Pudipeddi, Ravisankar V.; Ghotge, Vishal V. & Thind, Ravinder S., «Quick filename lookup using name hash», published 2012-11-27, assigned to Microsoft Corp.; contains Microsoft exFAT specification (revision 1.00).
- ^ corbet (2019-11-25). «The 5.4 kernel has been released». LWN.net. Retrieved 2019-12-01.
- ^ a b c «exfat -Free exFAT file system implementation». GitHub. Archived from the original on December 31, 2015. Retrieved October 14, 2015.
- ^ a b Marius Oiaga (December 11, 2009). «Microsoft Licenses Windows 7’s exFAT Flash File Format». Softpedia.com. Archived from the original on December 14, 2009. Retrieved December 12, 2009.
- ^ a b c Microsoft (August 28, 2019). «exFAT Specification». Archived from the original on 2020-07-19.
- ^ Install Windows 11 on exFAT partition, retrieved 2022-07-10
- ^ «File System Functionality Comparison». Microsoft. Archived from the original on April 7, 2015. Retrieved February 26, 2015..
- ^ «Limitations of the FAT32 File System in Windows XP». Microsoft. December 1, 2007. Archived from the original on February 24, 2015. Retrieved February 11, 2011.
- ^ Nash, Mike (October 24, 2008). «Windows Vista Service Pack 2 Beta». The Windows Blog. Archived from the original on May 9, 2013.
- ^ «A Second Shot: Windows Vista SP1». Archived from the original on December 2, 2008. Retrieved November 5, 2013.
- ^ «Licensing exFAT». Microsoft. Archived from the original on March 2, 2017. Retrieved March 1, 2017.
- ^ «OEM Parameter Definition with exFAT (Windows Embedded CE 6.0)». Archived from the original on December 3, 2013. Retrieved November 25, 2013.
- ^ a b «Description of the exFAT file system driver update package». Microsoft. Archived from the original on February 26, 2015. Retrieved February 26, 2015.
- ^ «Information about support for exFAT under Windows Vista». Microsoft. Archived from the original on May 7, 2013.
- ^ «Download Windows Vista Service Pack 1 Five Language Standalone (KB936330) from Official Microsoft Download Center». Microsoft. Archived from the original on February 26, 2015. Retrieved February 26, 2015.
- ^ «exFAT Versus FAT32 Versus NTFS». February 27, 2008. Archived from the original on January 29, 2013. Retrieved October 2, 2009.
- ^ «[MS-FSCC]: Appendix B: Product Behavior». msdn.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2017-10-02.
- ^ LeBlanc, Brandon (August 28, 2007). «Vista SP1 Whitepaper». Microsoft. Archived from the original on September 2, 2007. Retrieved August 28, 2007.
- ^ «Adding Hard Disk Drives». Microsoft TechNet. Retrieved September 15, 2009.
- ^ a b «Mac OS X 10.6.5 Notes: exFAT Support, AirPrint, Flash Player Vulnerability Fixes». Archived from the original on June 18, 2013. Retrieved November 25, 2013.[unreliable source?]
- ^ a b «fsck_exfat(8) Mac OS X Manual Page». Archived from the original on June 2, 2012. Retrieved November 25, 2013.
- ^ O’Hara, Andrew (June 7, 2019). «How to use external storage on iPad and iPhone with iOS 13». AppleInsider. Archived from the original on 2019-08-02. Retrieved 2020-02-26.
- ^ «exFAT support on Sony». Archived from the original on February 19, 2012. Retrieved January 6, 2013.
- ^ Hamm, Jeff (2009). «Extended FAT File System» (PDF). Paradigm Solutions. Archived (PDF) from the original on March 14, 2016. Retrieved April 9, 2013.
- ^ «Microsoft Licenses exFAT to Research In Motion». Tom’s Hardware. September 20, 2012.
- ^ «Microsoft Signs Licensing Agreement With Research In Motion» (Press release). Microsoft. 18 September 2012. Archived from the original on 10 September 2014. Retrieved 17 March 2015.
- ^ «Microsoft Signs Patent Licensing Agreement With Aspen Avionics» (Press release). Microsoft. Archived from the original on 2013-05-15. Retrieved 2013-05-13.
- ^ «In-vehicle infotainment gets boost from new Microsoft exFAT file system deals». Stories. June 19, 2013. Archived from the original on July 28, 2019. Retrieved July 28, 2019.
- ^ «Microsoft Signs exFAT Licensing Agreement With BMW» (Press release). Microsoft. Archived from the original on 2013-01-19. Retrieved 2013-01-17.
- ^ «Conservancy Helps Samsung Resolve GPL Compliance Matter Amicably». Software Freedom Conservancy. Archived from the original on 2019-02-03. Retrieved 2019-03-15.
- ^ a b John Gossman (2019-08-28). «exFAT in the Linux kernel? Yes!». Microsoft. Archived from the original on 2019-09-01. Retrieved 2019-09-02.
- ^ Abhishek Prakash (November 25, 2019). «Linux Kernel 5.4 Release Features». itsfoss.com. Archived from the original on December 8, 2019. Retrieved April 1, 2020.
- ^ «File types and external devices that work on Chromebooks». Google Inc. Archived from the original on 2014-01-11. Retrieved 2021-06-08.
- ^ US 8606830, Pudipeddi, Ravisankar V.; Ghotge, Vishal V. & Thind, Ravinder S. et al., «Contiguous file allocation in an extensible file system», published 2013-12-10, assigned to Microsoft Corp.
- ^ US 7613738, Patel, Sachin; Gopalan, Yadhu & Rogers, Andrew, «FAT directory structure for use in transaction safe file system», published 2009-11-03, assigned to Microsoft Corp.
- ^ US 10614032, Pudipeddi, Ravisankar V.; Ghotge, Vishal V. & Thind, Ravinder S., «Quick filename lookup using name hash», published 2020-04-07, assigned to Microsoft Technology Licensing LLC; contains exFAT specification revision 1.00. See Tables 8, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17.
- ^ US 9639554, Pudipeddi, Ravisankar V.; Ghotge, Vishal V. & Havewala, Sarosh C. et al., «Extensible file system», published 2017-05-02, assigned to Microsoft Technology Licensing LLC; states in abstract and elsewhere that directory records can be custom-defined.
- ^ «OEM Parameter Definition with exFAT (Windows Embedded CE 6.0)». Microsoft documentation. Archived from the original on 2020-07-26. Retrieved 2020-04-17.
- ^ a b Larabel, Michael (April 4, 2020). «The New Microsoft exFAT File-System Driver Has Landed In Linux 5.7». Phoronix. Archived from the original on March 5, 2021. Retrieved March 11, 2021.
- ^ «Kernel/Git/Torvalds/Linux.git — Linux kernel source tree». Archived from the original on 2021-04-30. Retrieved 2021-10-14.
- ^ Larabel, Michael (28 August 2019). «Microsoft Publishes exFAT Specification, Encourages Linux Support». Phoronix. Archived from the original on 3 September 2019. Retrieved 28 August 2019.
- ^ a b c «Licensing exFAT», Microsoft IP licensing, Microsoft Legal Resources, 1 March 2017, archived from the original on 2 March 2017, retrieved 1 March 2017
- ^ Protalinski, Emil (December 10, 2009), «Microsoft licenses out exFAT file system», ArsTechnica, archived from the original on July 8, 2017, retrieved November 18, 2017.
- ^ Girard, David (21 June 2013), «Can Microsoft’s exFAT file system bridge the gap between OSes?», ArsTechnica, archived from the original on 1 December 2017, retrieved 18 November 2017.
- ^ Corbet, Jonathan (July 24, 2013), The exfiltrated exFAT driver, LWN, archived from the original on December 2, 2013, retrieved November 25, 2013.
- ^ Finley, Klint; McMillan, Robert (July 25, 2013), «Free Software Robin Hood Liberates Leaked Samsung Code», Wired Magazine, archived from the original on June 28, 2018, retrieved November 18, 2017.
- ^ Else, Sylvia (November 19, 2016), exFat patent avoidance, Linux.com kernel development forums, archived from the original on December 1, 2017, retrieved November 18, 2017.
- ^ Vaughan-Nichols, Steven J. «What does Microsoft joining the Open Invention Network mean for you?». ZDNet. Archived from the original on 2019-02-07. Retrieved 2018-12-29.
- ^ Larabel, Michael (July 10, 2019). «Merging exFAT Support For Linux Is Being Talked About — Waiting On Microsoft’s Blessing — Phoronix». www.phoronix.com. Archived from the original on 2019-08-08. Retrieved 2019-08-08.
- ^ «exFAT fs and Linux». Archived from the original on September 16, 2009. Retrieved September 28, 2009.[unreliable source?]
- ^ «exFAT fs on FUSE». GitHub. Archived from the original on December 31, 2015. Retrieved May 15, 2010.
- ^ «exFAT fs on linux UBUNTU». Archived from the original on September 28, 2012. Retrieved October 11, 2012.
- ^ «exFAT in FreeBSD». Archived from the original on June 15, 2013. Retrieved April 8, 2013.
- ^ «ExFAT support for Mac OS X 10.5 Leopard and 10.4 Tiger (via Homebrew and Fuse for macOS)». GitHub. Archived from the original on October 13, 2019. Retrieved July 6, 2018.
- ^ «Amigaworld.net». Archived from the original on February 26, 2015. Retrieved February 18, 2015.
- ^ «Open Source Release Center». Samsung. Archived from the original on December 2, 2013. Retrieved November 25, 2013.
- ^ Corbet, Jonathan (July 24, 2013). «The exfiltrated exFAT driver». LWN.net. Archived from the original on December 2, 2013. Retrieved November 25, 2013.
- ^ «Conservancy Helps Samsung Resolve GPL Compliance Matter Amicably». Software Freedom Conservancy. August 16, 2013. Archived from the original on November 20, 2013. Retrieved November 25, 2013.
- ^ «GPL’ed sources for the Samsung exfat module as released by Samsung». GitHub. Retrieved 2017-08-20.
- ^ Corbet, Jonathan (August 16, 2013), Samsung releases exFAT filesystem source, LWN, archived from the original on July 31, 2017, retrieved November 18, 2017.
- ^ McMillan, Robert (August 20, 2013), «Busted for Dodging Linux License, Samsung Makes Nice With Free Code», Wired.com, archived from the original on September 6, 2020, retrieved November 18, 2017.
- ^ Larabel, Michael (September 29, 2019). «Linux 5.4 Features Are Huge From exFAT To New GPUs To Enabling Lots Of New Hardware». Phoronix. Archived from the original on April 10, 2021. Retrieved March 11, 2021.
- ^ Larabel, Michael (November 17, 2019). «The Exciting Linux 5.4 Changes From exFAT Support To Intel Tiger Lake Graphics». Phoronix. Archived from the original on March 4, 2021. Retrieved March 11, 2021.
- ^ Larabel, Michael (November 24, 2019). «Linux 5.4 Kernel Released With exFAT Support, Faster Radeon Graphics, New Hardware». Phoronix. Archived from the original on March 9, 2021. Retrieved March 11, 2021.
- ^ Larabel, Michael (January 20, 2020). «Samsung’s Better exFAT Driver Gets Revised Ahead Of Mainline Linux Integration». Phoronix. Archived from the original on May 16, 2021. Retrieved March 11, 2021.
- ^ Larabel, Michael (December 30, 2019). «Linux’s exFAT Driver Looking To Still Be Replaced By A Newer Driver From Samsung». Phoronix. Archived from the original on March 5, 2021. Retrieved March 11, 2021.
- ^ Larabel, Michael (March 7, 2020). «The New Microsoft exFAT File-System Driver Is Set To Land With Linux 5.7». Phoronix. Archived from the original on April 23, 2021. Retrieved March 11, 2021.
- ^ Clarke, Gavin (August 8, 2012). «Sharp cuts exFAT deal with Microsoft for Android mobes». The Register. Archived from the original on August 11, 2012. Retrieved August 12, 2012.
- ^ «XCFiles». Archived from the original on July 30, 2010. Retrieved June 21, 2010.
- ^ «Rtfs». Archived from the original on June 12, 2011. Retrieved January 19, 2011.
- ^ «exFAT». February 2, 2011.
- ^ «Ubuntu Manpage: exfatlabel — get or set an exFAT file system label». manpages.ubuntu.com. Archived from the original on 2020-12-30. Retrieved 2020-12-30.
External links[edit]
- exFAT specification
- File System Functionality Comparison of exFAT, FAT32, NTFS, UDF
- exFAT overview in Windows Embedded CE
- Transaction-Safe FAT File System (TexFAT) overview in Windows Mobile 6.5
- Personal Storage : Opportunities and challenges for pocket-sized storage devices in the Windows world (PowerPoint presentation at WinHEC 2006)
- exFAT File System Licensing
- Reverse Engineering the Microsoft exFAT File System, SANS Institute.
- US application 2009164440, «Quick Filename Lookup Using Name Hash»; Microsoft Corp; contains exFAT specification revision 1.00.
- US application 2009164539, «Contiguous File Allocation In An Extensible File System»; Microsoft Corp.
- exFAT ships on all SDXC Cards, SD Card Association
- The Extended FAT file system:Differentiating with FAT32 file system, Linux Conference, October 2011.
- Benefits of exFAT over FAT32
| Developer(s) | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| Full name | Extensible File Allocation Table |
| Introduced | November 2006; 16 years ago with Windows Embedded CE 6.0 |
| Partition identifier |
|
| Structures | |
| Directory contents | Table |
| File allocation | bitmap, linked list |
| Bad blocks | Cluster tagging |
| Limits | |
| Max. volume size | 128 PB, 512 TB recommended[1] |
| Max. file size | 128 PB (theoretical 16 EB – 1 byte)[nb 1] |
| Max. number of files | up to 2,796,202 per directory[2] |
| Max. filename length | 255 characters |
| Allowed characters in filenames | all Unicode characters except U+0000 (NUL) through U+001F (US) / (slash) : (colon) * (asterisk) ? (question mark) " (quote) < (less than) > (greater than) and | (pipe)(encoding in UTF-16LE) |
| Features | |
| Dates recorded | Creation, last modified, last access |
| Date range | 1980-01-01 to 2107-12-31 |
| Date resolution | 10 ms |
| Forks | No |
| Attributes | Read-only, hidden, system, subdirectory, archive |
| File system permissions | ACL (Windows CE 6 only) |
| Transparent compression | No |
| Transparent encryption | Yes, EFS supported in Windows 10 v1607 and Windows Server 2016 or later. |
| Other | |
| Supported operating systems |
|
exFAT (Extensible File Allocation Table) is a file system introduced by Microsoft in 2006 and optimized for flash memory such as USB flash drives and SD cards.[5] exFAT was proprietary until 28 August 2019, when Microsoft published its specification.[6] Microsoft owns patents on several elements of its design.[2]
exFAT can be used where NTFS is not a feasible solution (due to data-structure overhead), but where a greater file-size limit than that of the standard FAT32 file system (i.e. 4 GB) is required.
exFAT has been adopted by the SD Association as the default file system for SDXC cards larger than 32 GB.
Windows 8 and later versions natively support exFAT boot, and support the installation of the system in a special way to run in the exFAT volume.[7]
History[edit]
exFAT was introduced in late 2006 as part of Windows CE 6.0, an embedded Windows operating system. Most of the vendors signing on for licenses are manufacturers of embedded systems or device manufacturers that produce media formatted with exFAT. The entire File Allocation Table (FAT) family, exFAT included, is used for embedded systems because it is lightweight and is better suited for solutions that have low memory and low power requirements, and can be easily implemented in firmware.
Features[edit]
Because file size references are stored in eight instead of four bytes, the file size limit has increased to 16 exabytes (EB) (264 − 1 bytes, or about 1019 bytes, which is otherwise limited by a maximum volume size of 128 PB,[nb 1] or 257 − 1 bytes), raised from 4 GB (232 − 1 bytes) in a standard FAT32 file system.[1] Therefore, for the typical user, this enables seamless interoperability between Windows and macOS platforms for files in excess of 4 GB.
Other specifications, features, and requirements of the exFAT file system include:
- Scalability to large disk sizes: about 128 PB (257 − 1 bytes)[8][nb 2] maximum, 512 TB (249 − 1 bytes) recommended maximum, raised from the 32-bit limit (2 TB for a sector size of 512 bytes) of standard FAT32 partitions.[9]
- Support for up to 2,796,202 files per directory.[2][nb 3] Microsoft documents a limit of 65,534 (216 − 2) files per sub-directory for their FAT32 implementation, but other operating systems have no special limit for the number of files in a FAT32 directory. FAT32 implementations in other operating systems allow an unlimited number of files up to the number of available clusters (that is, up to 268,304,373 files on volumes without long filenames).[nb 4]
- Maximum number of files on volume C[clarification needed], to 4,294,967,285 (232 − 11, up from about 228 − 11[nb 4] in standard FAT32).
- Free space allocation and delete performance improved due to introduction of a free-space bitmap.
- Timestamp granularity of 10 ms for creation and modified times (down from 2 s on FAT, but not as fine as NTFS’s 100 ns).[2]
- Timestamp granularity for last-access time to double seconds (FAT had date only).
- Timestamps come with a time zone marker in offset relative to UTC (starting with Vista SP2).[10]
- Optional support for access-control lists (not currently supported in Windows Desktop/Server versions).[11]
- Optional support for TexFAT, a transactional file system standard (optionally WinCE activated function, not supported in Windows Desktop/Server versions).
- Boundary alignment offset for the FAT table.
- Boundary alignment offset for the data region.
- Provision for OEM-definable parameters to customize the file system for specific device characteristics.[12][13]
- Valid data length (VDL): through the use of two distinct lengths fields – one for «allocated space» and the other for «valid data» – exFAT can preallocate a file without leaking data that was previously on-disk.
- Cluster size up to 32 MB.[14]
- Metadata integrity with checksums.[clarification needed]
- Template-based metadata structures.[clarification needed]
- Removal of the physical
.and..directory entries that appear in subdirectories. - exFAT no longer stores the short 8.3 filename references in directory structure and natively uses extended file names, whereas legacy FAT versions implement extended file names through the VFAT extension.
Windows XP requires update KB955704 to be installed, and Windows Vista requires its SP1 or SP2 be installed.[14][15][16] Windows Vista is unable to use exFAT drives for ReadyBoost. Windows 7 removes this limitation, enabling ReadyBoost caches larger than 4 GB.[17] Windows 10 only allows formatting exFAT on volumes sized 32 GB or larger with the default user interface, and FAT32 format is suggested for smaller volumes; command-line utilities still accept a full range of file systems and allocation unit sizes.
The standard exFAT implementation is not journaled and only uses a single file allocation table and free-space map. FAT file systems instead used alternating tables, as this allowed recovery of the file system if the media was ejected during a write (which occurs frequently in practice with removable media). The optional TexFAT component adds support for additional backup tables and maps, but may not be supported.
The exFAT format allows individual files larger than 4 GB, facilitating long continuous recording of HD video, which can exceed the 4 GB limit in less than an hour. Current digital cameras using FAT32 will break the video files into multiple segments of approximately 2 or 4 GB.
EFS supported in Windows 10 v1607 and Windows Server 2016 or later.[18]
Efficiency[edit]
SDXC cards running at UHS-I have a minimum guaranteed write speed of 10 MB/s, and exFAT plays a factor in achieving this throughput through the reduction of the file-system overhead in cluster allocation. This is achieved through the introduction of a separate cluster bitmap where the reservation state of each cluster (reserved/free) is tracked by only one bit, reducing writes to the much larger FAT that originally served this purpose.
Additionally, a single bit in the directory record indicates that the file is contiguous (unfragmented), telling the exFAT driver to ignore the FAT. This optimization is analogous to an extent in other file systems, except that it only applies to whole files, as opposed to contiguous parts of files.
Adoption[edit]
exFAT is supported in Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 with update KB955704,[1] Windows Embedded CE 6.0, Windows Vista with Service Pack 1,[19] Windows Server 2008,[20] Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows Server 2008 R2 (except Windows Server 2008 Server Core), Windows 10, macOS starting from 10.6.5, Linux via FUSE or natively starting from kernel 5.4, and iPadOS as well as iOS starting from 13.1.[21][22][23]
Companies can integrate exFAT into a specific group of consumer devices, including cameras, camcorders, and digital photo frames for a flat fee. Mobile phones, PCs, and networks have a different volume pricing model.[5]
exFAT is supported in a number of media devices such as modern flat-panel TVs,[24] media centers, and portable media players.[25]
exFAT is the official file system of SDXC cards. As mentioned in the respective article, this implies any device not supporting exFAT (such as the Nintendo 3DS) might not legally advertise itself as SDXC compatible despite supporting such cards as mass storage devices per se.
Some vendors of other flash media, including USB pen drives, compact flash (CF) and solid-state drives (SSD) ship some of their high-capacity media pre-formatted with the exFAT file system. For example, Sandisk ships their 256 GB CF cards as exFAT.
Microsoft has entered into licensing agreements with BlackBerry,[26][27] Panasonic, Sanyo, Sony, Canon, Aspen Avionics,[28] Audiovox, Continental, Harman, LG Automotive[29] and BMW.[30]
Mac OS X Snow Leopard 10.6.5 and later can create, read, write, verify, and repair exFAT file systems.[21][22]
Linux has support for exFAT via FUSE since 2009.[4] In 2013, Samsung Electronics published a Linux driver for exFAT under GPL.[31]
On 28 August 2019, Microsoft published the exFAT specification[6] and released the patent to the Open Invention Network members.[32] The Linux kernel introduced native exFAT support with the 5.4 release in November 2019.[33]
ChromeOS can read and write to exFAT partitions.[34]
Technical specialities[edit]
| Volume size |
Cluster size |
Cluster count |
|---|---|---|
| 007–256 MB | 004 KB | <64 K |
| 256 MB–32 GB | 032 KB | 0<1 M |
| 032–512 GB[A][B] | 128 KB | 0<4 M |
| 512 GB–1 TB | 256 KB | |
| 001–2 TB | 512 KB | |
| 002–4 TB | 001 MB | |
| 004–8 TB | 002 MB | |
| 008-16 TB | 004 MB | |
| 016–32 TB | 008 MB | |
| 032–64 TB | 016 MB | |
| 064–512 TB | 032 MB | <16 M |
Notes:
|
File name lookup[edit]
exFAT employs a filename hash-based lookup phase to speed certain cases, which is described in US patent Quick File Name Lookup Using Name Hash.[2] Appendix A of the document contains details helpful in understanding the file system.
File and cluster pre-allocation[edit]
Like NTFS, exFAT can pre-allocate disk space for a file by just marking arbitrary space on disk as «allocated». For each file, exFAT uses two separate 64-bit fields in the directory: the valid data length (VDL), which indicates the real size of the file, and the physical data length.
To provide improvement in the allocation of cluster storage for a new file, Microsoft incorporated a method to pre-allocate contiguous clusters and bypass the use of updating the FAT table, which was patented December 10, 2013.[35] One feature of exFAT (used in the exFAT implementation within embedded systems) provides atomic transactions for the multiple steps of updating the file-system metadata. The feature called Transaction Safe FAT, or TexFAT, was granted a patent on November 3, 2009.[36]
Directory file set[edit]
exFAT and the rest of the FAT family of file systems do not use indexes for file names, unlike NTFS, which uses B-trees for file searching. When a file is accessed, the directory must be sequentially searched until a match is found. For file names shorter than 16 characters in length, one file name record is required but the entire file is represented by three 32-byte directory records. This is called a directory file set, and a 256 MB sub-directory can hold up to 2,796,202 file sets. (If files have longer names, this number will decrease, but this is the maximum based on the minimal three-record file set.) To help improve the sequential searching of the directories (including the root) a hash value of the file name is derived for each file and stored in the directory record. When searching for a file, the file name is first converted to upper case using the upcase table (file names are case-insensitive) and then hashed using a proprietary patented algorithm into a 16-bit (2-byte) hash value. Each record in the directory is searched by comparing the hash value. When a match is found, the file names are compared to ensure that the proper file was located in case of hash collisions. This improves performance because only 2 bytes have to be compared for each file. This significantly reduces the CPU load because most file names are more than 2 characters (bytes) in size and virtually every comparison is performed on only 2 bytes at a time until the intended file is located.
Metadata and checksums[edit]
exFAT introduces metadata integrity through the use of checksums. There are three checksums currently in use.
- The volume boot record (VBR) is a 12-sector region that contains the boot records, BIOS parameter block (BPB), OEM parameters and the checksum sector. (There are two VBR type regions, the main VBR and the backup VBR.) The checksum sector is a checksum of the previous 11 sectors, with the exception of three bytes in the boot sector (flags and percent used). This provides integrity of the VBR by determining whether the VBR was modified. The most common cause could be a boot-sector virus, but this would also catch any other corruption to the VBR.
- A second checksum is used for the upcase table. This is a static table and should never change. Any corruption in the table could prevent files from being located because this table is used to convert the filenames to upper case when searching to locate a file.
- The third checksum is in the directory file sets. Multiple directory records are used to define a single file, and this is called a file set. This file set has metadata including the file name, time stamps, attributes, address of first cluster location of the data, file lengths, and the file name. A checksum is taken over the entire file set, and a mismatch would occur if the directory file set was accidentally or maliciously changed.
When the file system is mounted, and the integrity check is conducted, these hashes are verified. Mounting also includes comparison of the version of the exFAT file system by the driver to make sure the driver is compatible with the file system it is trying to mount, and to make sure that none of the required directory records are missing (for example, the directory record for the upcase table and allocation bitmap are required, and the file system can’t run if they are missing). If any of these checks fail, the file system should not be mounted, although in certain cases it may mount read-only.
The file system provides extensibility through template-based metadata definitions using generic layouts and generic patterns.[37][38]
Flash optimizations[edit]
exFAT contains a few features that, according to Microsoft, makes it flash-friendly:
- Boundary alignment for filesystem structures. The offsets for the FAT and the cluster heap is adjustable at format time, so that writes to these areas will happen in as few flash blocks as possible.
- An «OEM parameters» field can be used to record features such as block size of the underlying storage. One single type for flash storage is pre-defined.[39]
- The lack of a journal, so that less data is written. (Although FAT32 also lacks a journal.)
The first feature requires support from the formatting software. Compliant implementations will follow existing offsets. The OEM parameter may be ignored. Implementations may also use TRIM to reduce wear.
| Boundary alignment (format) | OEM parameters (use) | TRIM (use) | Note | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows CE | Yes | Yes | Unknown | |
| Windows Desktop and Server | Yes | Yes | No | |
| Linux kernel | since 5.7[40] | ignored | since 5.13[41] | exfatprogs is assumed to be used for formatting. |
Other implementations[edit]
|
|
This section needs to be updated. Please help update this article to reflect recent events or newly available information. (September 2019) |
Legal status[edit]
exFAT was a proprietary file system until 2019, when Microsoft released the specification and allowed OIN members to use their patents.[42] This lack of documentation along with the threat of a patent infringement lawsuit, as happened previously when Microsoft sued various companies over the VFAT long file name patent (before it expired), hampered the development of free and open-source drivers for exFAT, and led to a situation where Linux distributions could not even tell users how to get an exFAT driver. Accordingly, exFAT official support was effectively limited to Microsoft’s own products and those of Microsoft’s licensees. This, in turn, inhibited exFAT’s adoption as a universal exchange format, as it was safer and easier for vendors to rely on FAT32 than it was to pay Microsoft or risk being sued.
Interoperability requires that certain results be achieved in a particular, predefined way (an algorithm). For exFAT, this potentially requires every implementation to perform certain procedures in exactly the same way as Microsoft’s implementation. Some of the procedures used by Microsoft’s implementation are patented, and these patents are owned by Microsoft.[43] A license to use these algorithms can be purchased from Microsoft,[44][43] and some companies – including Apple, Google and Samsung – have done so.[45] However, in the open-source ecosystem, users have typically responded to vendors being unwilling to pay for patent licenses by procuring an implementation for themselves from unofficial sources. For example, this is what happened with LAME when MP3 patents were still valid. (Alternatively, the user may decide that the feature is unimportant to them.)
Regardless of whether open-source or not, Microsoft stated that «a license is required in order to implement exFAT and use it in a product or device».[43] Unlicensed distribution of an exFAT driver would make the distributor liable for financial damages if the driver is found to have violated Microsoft’s patents.[46][47] While the patents may not be enforceable, this can only be determined through a legal process, which is expensive and time-consuming. It may also be possible to achieve the intended results without infringing Microsoft’s patents.[48] In October 2018, Microsoft released 60,000 patents to the Open Invention Network members for Linux systems, but exFAT patents were not initially included at the time. There was, however, discussion within Microsoft over whether Microsoft should allow exFAT in Linux devices,[49][50] which eventually resulted in Microsoft publishing the official specification for open usage[6] and releasing the exFAT patents to the OIN in August 2019.[32]
List of implementations[edit]
A FUSE-based implementation named fuse-exfat, or exfat-fuse,[4] with read/write support is available for FreeBSD, multiple Linux distributions, and older versions of Mac OS X. It supports TRIM.[51][52][53][54][55] An implementation called exFATFileSystem, based on fuse-exfat, is available for AmigaOS 4.1.[56]
A Linux kernel implementation by Samsung Electronics is available.[57] It was initially released on GitHub unintentionally,[58] and later released officially by Samsung in compliance with the GPLv2 in 2013.[59][60] (This release does not make exFAT royalty-free, as licensing from Samsung does not remove Microsoft’s patent rights.)[61][62] A version of this driver was first incorporated into version 5.4 of the Linux kernel.[63][64][65] A much newer version of the driver, with several bug fixes and improved reliability, was incorporated into kernel 5.7.[66][40] Prior to its being merged into the Linux kernel, this newer version had already seen adoption on Android smartphones and continued to be used on both Linux and Android thereafter.[67][68]
Proprietary read/write solutions licensed and derived from the Microsoft exFAT implementation are available for Android,[69] Linux, and other operating systems from Paragon Software Group and Tuxera.
XCFiles (from Datalight) is a proprietary, full-featured implementation, intended to be portable to 32-bit systems.[70] Rtfs (from EBS Embedded Software) is a full-featured implementation for embedded devices.[71]
Two experimental, unofficial solutions are available for DOS. The loadable USBEXFAT driver requires Panasonic’s USB stack for DOS and only works with USB storage devices; the open-source EXFAT executable is an exFAT file-system reader and requires the HX DOS extender to work.[72] There are no native exFAT real-mode DOS drivers, which would allow usage of, or booting from, exFAT volumes.
The renaming of ExFAT file system labels is natively supported by Microsoft Windows Explorer, while Linux relies on the third-party exfatlabel tool.[73]
See also[edit]
- Design of the FAT file system
- List of file systems
- Comparison of file systems
- Memory Stick XC
- Universal Disk Format
Notes[edit]
- ^ a b
Although Microsoft published a different value in KB955704, the file size is in bytes and is stored as a 64-bit number. The largest theoretical file size would be 16 EB − 1 byte, the same as in NTFS. However, since the true theoretical maximum volume size under the current specification cannot exceed 128 PB, a file can never reach that file length. Another reason for the limit is that current IDE/ATA disk addressing is LBA-48 and uses a 48-bit block address to address a sector. A 512-byte sector size would make the maximum addressable file system 512 × 248 = 257, which is 128 PB. In other words, the 128 PB limit on the architecture is a hardware restriction. This scenario does not include AF (4k sectors)[clarify], and exFAT is limited to 128 PB regardless of sector size based on the specification. - ^ The theoretical maximum volume size is defined by up to 232 − 11 possible clusters with up to 225 bytes per cluster ≈ 128 PB. The size is currently also limited by the LBA48 addressing scheme, as with a 512-byte sector size, only 248 × 512 = 257 bytes = 128 PB can be addressed.
- ^ This limit applies because the maximum directory size is 256 MB.
- ^ a b 268,304,373 files = 228 − 11 reserved clusters − 131,072, the minimum number of 64 KB clusters occupied for the 268,435,445 directory entries (32 bytes) without VFAT LFNs, which are required for 268,435,445 files with sizes between 1 and 65,535 bytes. With VFATs, the 131,072 number must be multiplied by 21 (worst case), which would result in 265,682,933 files instead.
References[edit]
- ^ a b c d e «KB955704». January 27, 2009. Archived from the original on May 24, 2011. Retrieved January 27, 2009.
Description of the exFAT file system driver update package [for Windows XP and Windows Server 2003]
- ^ a b c d e US 8321439, Pudipeddi, Ravisankar V.; Ghotge, Vishal V. & Thind, Ravinder S., «Quick filename lookup using name hash», published 2012-11-27, assigned to Microsoft Corp.; contains Microsoft exFAT specification (revision 1.00).
- ^ corbet (2019-11-25). «The 5.4 kernel has been released». LWN.net. Retrieved 2019-12-01.
- ^ a b c «exfat -Free exFAT file system implementation». GitHub. Archived from the original on December 31, 2015. Retrieved October 14, 2015.
- ^ a b Marius Oiaga (December 11, 2009). «Microsoft Licenses Windows 7’s exFAT Flash File Format». Softpedia.com. Archived from the original on December 14, 2009. Retrieved December 12, 2009.
- ^ a b c Microsoft (August 28, 2019). «exFAT Specification». Archived from the original on 2020-07-19.
- ^ Install Windows 11 on exFAT partition, retrieved 2022-07-10
- ^ «File System Functionality Comparison». Microsoft. Archived from the original on April 7, 2015. Retrieved February 26, 2015..
- ^ «Limitations of the FAT32 File System in Windows XP». Microsoft. December 1, 2007. Archived from the original on February 24, 2015. Retrieved February 11, 2011.
- ^ Nash, Mike (October 24, 2008). «Windows Vista Service Pack 2 Beta». The Windows Blog. Archived from the original on May 9, 2013.
- ^ «A Second Shot: Windows Vista SP1». Archived from the original on December 2, 2008. Retrieved November 5, 2013.
- ^ «Licensing exFAT». Microsoft. Archived from the original on March 2, 2017. Retrieved March 1, 2017.
- ^ «OEM Parameter Definition with exFAT (Windows Embedded CE 6.0)». Archived from the original on December 3, 2013. Retrieved November 25, 2013.
- ^ a b «Description of the exFAT file system driver update package». Microsoft. Archived from the original on February 26, 2015. Retrieved February 26, 2015.
- ^ «Information about support for exFAT under Windows Vista». Microsoft. Archived from the original on May 7, 2013.
- ^ «Download Windows Vista Service Pack 1 Five Language Standalone (KB936330) from Official Microsoft Download Center». Microsoft. Archived from the original on February 26, 2015. Retrieved February 26, 2015.
- ^ «exFAT Versus FAT32 Versus NTFS». February 27, 2008. Archived from the original on January 29, 2013. Retrieved October 2, 2009.
- ^ «[MS-FSCC]: Appendix B: Product Behavior». msdn.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2017-10-02.
- ^ LeBlanc, Brandon (August 28, 2007). «Vista SP1 Whitepaper». Microsoft. Archived from the original on September 2, 2007. Retrieved August 28, 2007.
- ^ «Adding Hard Disk Drives». Microsoft TechNet. Retrieved September 15, 2009.
- ^ a b «Mac OS X 10.6.5 Notes: exFAT Support, AirPrint, Flash Player Vulnerability Fixes». Archived from the original on June 18, 2013. Retrieved November 25, 2013.[unreliable source?]
- ^ a b «fsck_exfat(8) Mac OS X Manual Page». Archived from the original on June 2, 2012. Retrieved November 25, 2013.
- ^ O’Hara, Andrew (June 7, 2019). «How to use external storage on iPad and iPhone with iOS 13». AppleInsider. Archived from the original on 2019-08-02. Retrieved 2020-02-26.
- ^ «exFAT support on Sony». Archived from the original on February 19, 2012. Retrieved January 6, 2013.
- ^ Hamm, Jeff (2009). «Extended FAT File System» (PDF). Paradigm Solutions. Archived (PDF) from the original on March 14, 2016. Retrieved April 9, 2013.
- ^ «Microsoft Licenses exFAT to Research In Motion». Tom’s Hardware. September 20, 2012.
- ^ «Microsoft Signs Licensing Agreement With Research In Motion» (Press release). Microsoft. 18 September 2012. Archived from the original on 10 September 2014. Retrieved 17 March 2015.
- ^ «Microsoft Signs Patent Licensing Agreement With Aspen Avionics» (Press release). Microsoft. Archived from the original on 2013-05-15. Retrieved 2013-05-13.
- ^ «In-vehicle infotainment gets boost from new Microsoft exFAT file system deals». Stories. June 19, 2013. Archived from the original on July 28, 2019. Retrieved July 28, 2019.
- ^ «Microsoft Signs exFAT Licensing Agreement With BMW» (Press release). Microsoft. Archived from the original on 2013-01-19. Retrieved 2013-01-17.
- ^ «Conservancy Helps Samsung Resolve GPL Compliance Matter Amicably». Software Freedom Conservancy. Archived from the original on 2019-02-03. Retrieved 2019-03-15.
- ^ a b John Gossman (2019-08-28). «exFAT in the Linux kernel? Yes!». Microsoft. Archived from the original on 2019-09-01. Retrieved 2019-09-02.
- ^ Abhishek Prakash (November 25, 2019). «Linux Kernel 5.4 Release Features». itsfoss.com. Archived from the original on December 8, 2019. Retrieved April 1, 2020.
- ^ «File types and external devices that work on Chromebooks». Google Inc. Archived from the original on 2014-01-11. Retrieved 2021-06-08.
- ^ US 8606830, Pudipeddi, Ravisankar V.; Ghotge, Vishal V. & Thind, Ravinder S. et al., «Contiguous file allocation in an extensible file system», published 2013-12-10, assigned to Microsoft Corp.
- ^ US 7613738, Patel, Sachin; Gopalan, Yadhu & Rogers, Andrew, «FAT directory structure for use in transaction safe file system», published 2009-11-03, assigned to Microsoft Corp.
- ^ US 10614032, Pudipeddi, Ravisankar V.; Ghotge, Vishal V. & Thind, Ravinder S., «Quick filename lookup using name hash», published 2020-04-07, assigned to Microsoft Technology Licensing LLC; contains exFAT specification revision 1.00. See Tables 8, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17.
- ^ US 9639554, Pudipeddi, Ravisankar V.; Ghotge, Vishal V. & Havewala, Sarosh C. et al., «Extensible file system», published 2017-05-02, assigned to Microsoft Technology Licensing LLC; states in abstract and elsewhere that directory records can be custom-defined.
- ^ «OEM Parameter Definition with exFAT (Windows Embedded CE 6.0)». Microsoft documentation. Archived from the original on 2020-07-26. Retrieved 2020-04-17.
- ^ a b Larabel, Michael (April 4, 2020). «The New Microsoft exFAT File-System Driver Has Landed In Linux 5.7». Phoronix. Archived from the original on March 5, 2021. Retrieved March 11, 2021.
- ^ «Kernel/Git/Torvalds/Linux.git — Linux kernel source tree». Archived from the original on 2021-04-30. Retrieved 2021-10-14.
- ^ Larabel, Michael (28 August 2019). «Microsoft Publishes exFAT Specification, Encourages Linux Support». Phoronix. Archived from the original on 3 September 2019. Retrieved 28 August 2019.
- ^ a b c «Licensing exFAT», Microsoft IP licensing, Microsoft Legal Resources, 1 March 2017, archived from the original on 2 March 2017, retrieved 1 March 2017
- ^ Protalinski, Emil (December 10, 2009), «Microsoft licenses out exFAT file system», ArsTechnica, archived from the original on July 8, 2017, retrieved November 18, 2017.
- ^ Girard, David (21 June 2013), «Can Microsoft’s exFAT file system bridge the gap between OSes?», ArsTechnica, archived from the original on 1 December 2017, retrieved 18 November 2017.
- ^ Corbet, Jonathan (July 24, 2013), The exfiltrated exFAT driver, LWN, archived from the original on December 2, 2013, retrieved November 25, 2013.
- ^ Finley, Klint; McMillan, Robert (July 25, 2013), «Free Software Robin Hood Liberates Leaked Samsung Code», Wired Magazine, archived from the original on June 28, 2018, retrieved November 18, 2017.
- ^ Else, Sylvia (November 19, 2016), exFat patent avoidance, Linux.com kernel development forums, archived from the original on December 1, 2017, retrieved November 18, 2017.
- ^ Vaughan-Nichols, Steven J. «What does Microsoft joining the Open Invention Network mean for you?». ZDNet. Archived from the original on 2019-02-07. Retrieved 2018-12-29.
- ^ Larabel, Michael (July 10, 2019). «Merging exFAT Support For Linux Is Being Talked About — Waiting On Microsoft’s Blessing — Phoronix». www.phoronix.com. Archived from the original on 2019-08-08. Retrieved 2019-08-08.
- ^ «exFAT fs and Linux». Archived from the original on September 16, 2009. Retrieved September 28, 2009.[unreliable source?]
- ^ «exFAT fs on FUSE». GitHub. Archived from the original on December 31, 2015. Retrieved May 15, 2010.
- ^ «exFAT fs on linux UBUNTU». Archived from the original on September 28, 2012. Retrieved October 11, 2012.
- ^ «exFAT in FreeBSD». Archived from the original on June 15, 2013. Retrieved April 8, 2013.
- ^ «ExFAT support for Mac OS X 10.5 Leopard and 10.4 Tiger (via Homebrew and Fuse for macOS)». GitHub. Archived from the original on October 13, 2019. Retrieved July 6, 2018.
- ^ «Amigaworld.net». Archived from the original on February 26, 2015. Retrieved February 18, 2015.
- ^ «Open Source Release Center». Samsung. Archived from the original on December 2, 2013. Retrieved November 25, 2013.
- ^ Corbet, Jonathan (July 24, 2013). «The exfiltrated exFAT driver». LWN.net. Archived from the original on December 2, 2013. Retrieved November 25, 2013.
- ^ «Conservancy Helps Samsung Resolve GPL Compliance Matter Amicably». Software Freedom Conservancy. August 16, 2013. Archived from the original on November 20, 2013. Retrieved November 25, 2013.
- ^ «GPL’ed sources for the Samsung exfat module as released by Samsung». GitHub. Retrieved 2017-08-20.
- ^ Corbet, Jonathan (August 16, 2013), Samsung releases exFAT filesystem source, LWN, archived from the original on July 31, 2017, retrieved November 18, 2017.
- ^ McMillan, Robert (August 20, 2013), «Busted for Dodging Linux License, Samsung Makes Nice With Free Code», Wired.com, archived from the original on September 6, 2020, retrieved November 18, 2017.
- ^ Larabel, Michael (September 29, 2019). «Linux 5.4 Features Are Huge From exFAT To New GPUs To Enabling Lots Of New Hardware». Phoronix. Archived from the original on April 10, 2021. Retrieved March 11, 2021.
- ^ Larabel, Michael (November 17, 2019). «The Exciting Linux 5.4 Changes From exFAT Support To Intel Tiger Lake Graphics». Phoronix. Archived from the original on March 4, 2021. Retrieved March 11, 2021.
- ^ Larabel, Michael (November 24, 2019). «Linux 5.4 Kernel Released With exFAT Support, Faster Radeon Graphics, New Hardware». Phoronix. Archived from the original on March 9, 2021. Retrieved March 11, 2021.
- ^ Larabel, Michael (January 20, 2020). «Samsung’s Better exFAT Driver Gets Revised Ahead Of Mainline Linux Integration». Phoronix. Archived from the original on May 16, 2021. Retrieved March 11, 2021.
- ^ Larabel, Michael (December 30, 2019). «Linux’s exFAT Driver Looking To Still Be Replaced By A Newer Driver From Samsung». Phoronix. Archived from the original on March 5, 2021. Retrieved March 11, 2021.
- ^ Larabel, Michael (March 7, 2020). «The New Microsoft exFAT File-System Driver Is Set To Land With Linux 5.7». Phoronix. Archived from the original on April 23, 2021. Retrieved March 11, 2021.
- ^ Clarke, Gavin (August 8, 2012). «Sharp cuts exFAT deal with Microsoft for Android mobes». The Register. Archived from the original on August 11, 2012. Retrieved August 12, 2012.
- ^ «XCFiles». Archived from the original on July 30, 2010. Retrieved June 21, 2010.
- ^ «Rtfs». Archived from the original on June 12, 2011. Retrieved January 19, 2011.
- ^ «exFAT». February 2, 2011.
- ^ «Ubuntu Manpage: exfatlabel — get or set an exFAT file system label». manpages.ubuntu.com. Archived from the original on 2020-12-30. Retrieved 2020-12-30.
External links[edit]
- exFAT specification
- File System Functionality Comparison of exFAT, FAT32, NTFS, UDF
- exFAT overview in Windows Embedded CE
- Transaction-Safe FAT File System (TexFAT) overview in Windows Mobile 6.5
- Personal Storage : Opportunities and challenges for pocket-sized storage devices in the Windows world (PowerPoint presentation at WinHEC 2006)
- exFAT File System Licensing
- Reverse Engineering the Microsoft exFAT File System, SANS Institute.
- US application 2009164440, «Quick Filename Lookup Using Name Hash»; Microsoft Corp; contains exFAT specification revision 1.00.
- US application 2009164539, «Contiguous File Allocation In An Extensible File System»; Microsoft Corp.
- exFAT ships on all SDXC Cards, SD Card Association
- The Extended FAT file system:Differentiating with FAT32 file system, Linux Conference, October 2011.
- Benefits of exFAT over FAT32
Содержание
- Описание драйвера файловой системы exFAT пакета обновления
- Введение
- Информация о скачивании
- Обновление для Windows XP, версия x64
- Обновление для Windows Server 2003 Пакет обновления 2 версии x86
- Обновление для Windows Server 2003 Пакет обновления 2 версии x64
- Обновление для Windows Server 2003 Пакет обновления 1 и Windows Server 2003 Пакет обновления 2 версии ia64 bsed
- Дополнительные сведения
- Сведения об обновлении для систем Windows XP с пакетом обновления 3
- Файловая система exFAT
- exFAT в современных операционных системах
- ExFAT и FAT32
- exFat или NTFS
- В чём разница между FAT32, NTFS и exFAT
- Содержание:
- Файловые системы Windows
- FAT32: Очевидный выбор
- NTFS: системный диск
- exFAT: лучшее, если поддерживается…
- Восстановление файловых систем Windows
- Часто задаваемые вопросы
- Часто задаваемые вопросы по использованию различных файловых систем на внешних накопителях
- Я хочу, чтобы мой внешний винчестер (флэш-накопитель) работал с максимальным количеством компьютеров. Какую файловую систему мне нужно выбрать?
- Дал знакомому попользоваться флэш-картой Secure Digital на 2 ГБ, а теперь мой фотоаппарат ее не видит. Почему?
- Недавно купил б/у внешний винчестер. Он прекрасно работает на всех компьютерах с Windows Seven, но виден лишь на части машин с Windows Vista и Windows XP. Почему?
- Внешний винчестер прекрасно работает (по крайней мере, читается) на всех компьютерах с Windows 2000/XP/Vista, Linux, MacOS, но у моих родственников есть старый компьютер с Windows ME — он этот накопитель вообще не видит. Почему?
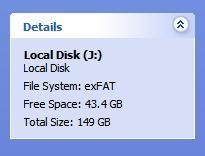
- Попробовал записать файл размером 4,7 ГБ (ISO-образ DVD-диска) на свежекупленный USB-винчестер. Информации на нем нет, емкость 500 ГБ, однако система сообщает, что места недостаточно для завершения операции. Почему?
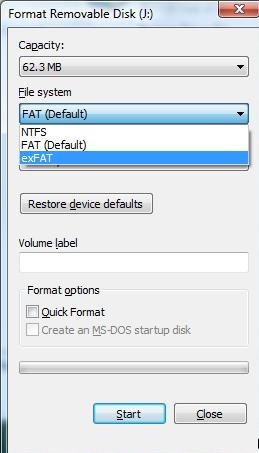
- Хочу отформатировать внешний винчестер под FAT32, дабы его увидел DVD-плеер, однако система предлагает только NTFS (или NTFS и exFAT). Почему?
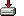
- Купил флэш-накопитель на 64 ГБ, подключил к компьютеру с Windows XP. Хочу его отформатировать, однако при выборе из контекстного меню опции «Форматировать» мне не предлагают никакой файловой системы, так что выполнить операцию невозможно. Почему?
- Как отформатировать флэшку под NTFS на компьютере под управлением Windows XP?
- Как отформатировать устройство под exFAT на компьютере с Windows XP? Обновление стоит, однако найти такую возможность не могу.
- Как отформатировать под exFAT внешний винчестер или флэшку с интерфейсом eSATA на компьютере под управлением Windows Vista/Seven?
- Недавно купил себе MacBook. Подключил к нему внешний винчестер. Все файлы видны, скопировать их на Mac могу, но ничего записать не получается. Почему?
- Почему-то не работает Time Machine с USB-винчестером. Мне нужно поменять его на специальную версию «for Mac» или есть другие варианты?
Описание драйвера файловой системы exFAT пакета обновления
Введение
В данной статье рассматриваются основные возможности и преимущества драйверы расширенная таблица размещения файлов (exFAT) файловой системы для Windows XP и Windows Server 2003.
В файловых системах FAT семейства файловую систему exFAT является преемником FAT32. Файловую систему exFAT является новый формат файловой системы, устраняющего растущих потребностей мобильных личного хранилища в разных операционных системах. Файловую систему exFAT обрабатывает большие файлы, такие как те, которые используются для хранения носителей, и он делает возможным эффективное взаимодействие между настольных компьютеров и устройств, таких как переносные устройства мультимедиа. При наличии этой функции Вы можете легко копировать файлы между настольным компьютером и внешними устройствами или между настольным компьютером и другими операционными системами.
После загрузки файла, описанного в разделе «Дополнительная информация» можно форматировать внешний носитель в формате exFAT. Дополнительно, Вы можете форматировать внешний носитель, размер которого превышает 32 ГБ, и носитель, отформатированный в exFAT, будет распознан на компьютере. Дополнительные усовершенствования файловой системы exFAT, описаны в разделе «Дополнительные сведения».
Информация о скачивании
Следующие файлы доступны для скачивания из Центра загрузки Майкрософт:
Обновление для Windows XP, версия x64
Обновление для Windows Server 2003 Пакет обновления 2 версии x86
Обновление для Windows Server 2003 Пакет обновления 2 версии x64
Обновление для Windows Server 2003 Пакет обновления 1 и Windows Server 2003 Пакет обновления 2 версии ia64 bsed
Для получения дополнительных сведений о том, как скачать файлы поддержки Майкрософт, щелкните следующий номер статьи базы знаний Майкрософт.
Как загрузить файлы поддержки Microsoft через оперативные службы
Корпорация Майкрософт проверила этот файл на наличие вирусов. Корпорация Майкрософт использует последнее антивирусное программное обеспечение, доступное на период публикации файла. Файл хранится на защищенных серверах, что предотвращает его несанкционированное изменение.
Дополнительные сведения
Файловая система exFAT включает ряд улучшений по сравнению с FAT32. Тем не менее она сохраняет простоту файловых систем, основанных на FAT. Эти улучшения включают следующие основные достижения:
Поддержка очень больших файлов и устройств хранения данных
Поддержка для улучшения производительности
Поддержка функции расширяемости для будущего развития коммуникационных технологий
Добавлена совместимость с флэш-носителями
Драйвер файловой системы exFAT привносит равносильность поддержки файловой системы для следующих операционных систем:
Драйвер файловой системы exFAT включает в себя дополнительные структуры для масштабируемости в будущем. Файловую систему exFAT использует 64 бита для описания размера файла. Это делает возможным использование приложений, которые зависят от очень больших файлов. Файловая система exFAT также поддерживает кластеры размером до 32 МБ, позволяя эффективно работать с очень большими запоминающими устройствами. В частности exFAT добавляет следующие возможности:
Поддержка тома, размер которых превышает 32 ГБ, абстрактной максимальный размер для файловой системы FAT32 в Windows XP
Теоретически максимальный размер — 64 ZB.
Рекомендуемый максимальный размер — 512 Тбайт.
Поддержка файлов, размер которых превышает 4 ГБ, абстрактной максимальный размер файла для файловой системы FAT32 в Windows XP
Теоретически максимальный размер файла — 64 ZB.
Рекомендуемый максимальный размер файла — 512 Тбайт.
Драйвер файловой системы exFAT включает в себя следующие дополнительные структуры для повышения производительности:
Для быстрого выделения растрового изображения кластера
Немного непрерывной-файл для быстрого доступа
Лучшее непрерывное размещение на диске (полезно для записи фильмов)
Поддержка всемирного согласованного времени (UTC) в полях даты-времени файла
Драйвер файловой системы exFAT предназначен для расширяемости для включения в файловой системе, чтобы не отстать от нововведений в хранилище и изменения в использовании и позволяет поставщикам вычислительной техники и независимым поставщикам программного обеспечения легко добавлять расширения. В частности exFAT добавляет следующие возможности:
Добавление структуры метаданных на основе шаблона для включения пользовательских расширений
Разрешает реализации для сохранения этих расширений не зная их формата
Драйвер файловой системы exFAT добавляет повышенную совместимость с флэш-носитель. Это включает следующие возможности:
Метаданные файловой системы на оптимальное Выравнивание границ устройства записи
Выравнивание кучи кластера на границах оптимальной записи устройства
Сведения об обновлении для систем Windows XP с пакетом обновления 3
Важно. При установке данного обновления на компьютере, на котором выполняется пакет многоязыкового интерфейса пользователя (MUI) пользовательского интерфейса переключается на английский язык.
Чтобы устранить эту проблему, выполните следующие действия:
Загрузите обновление для языка, который вы хотите использовать по ссылке выше в этой статье.
Распакуйте исправление в папку, используя параметр командной строки /x. Для этого введите следующую команду в командной строке: WindowsXP-KB955704-v3-x86-LanguageCode.exe/x
Примечание. LanguageCode представляет букв в имени файла, которые указывают язык.
При появлении целевой папки, выберите папку и нажмите кнопку ОК.
В папке SP3QFE в целевую папку скопируйте следующие файлы в папку %systemroot%System32Mui nnnn:
Папка SP3QFE содержит правильные двоичные файлы для системы Пакет обновления 3. Пакет обновления 2 для системы используют папку SP2QFE в качестве источника, вместо SP3QFE.
nnnn представляет собой код, который указывает, какой язык. Данный пример кода является так же, как папки nnnn %systemroot%System32Mui.
Повторите эти шаги для любого языка, используемого на компьютере.
Источник
Файловая система exFAT
Вместе с выходом Vista SP1 Microsoft представила новую файловую систему. ExFAT (Extended File Allocation Table) – это преемник старой файловой системы FAT32. Так в чем же основные преимущества и недостатки файловой системы exFAT. В чем отличия между exFAT и FAT32? И когда лучше использовать систему exFAT а не NTFS?
Файловая система FAT32 это достаточно старая и привычная всем файловая систем, однако она имеет ряд существенных недостатков:она не поддерживает разделы больше, чем 2 Тб, и файлы, размер которых более 4 Гб. Для решения описанных проблем в FAT32 и была создана файловая система exFAT. ExFAT – это разработка Microsoft, предназначенная в основном для мобильных носителей (флешки, SSD-диски, смарткарты). Сразу стоит отметить, что ExFAT не используется для форматирования жестких дисков. Все последние версии Windows, а также Mac OS X поддерживают эту файловую систему. ExFAT также часто называют FAT64, что подразумевает возможность работы с накопителями и файлами большего размера.
Основные преимущества файловой системы exFAT:
Стоит отметить, что при форматировании в exFAT количество доступного места на устройства хранения больше, чем при использовании FAT32. Например, если USB флешку размеров 4 Гб (номинальная емкость 4023 Мб) отформатировать в различных файловых системах, то получится следующее:
ExFAT оптимизирована для работы с флеш накопителями, такими USB флешки, карты памяти и SSD диски, размер кластера в 32 Кб хорошо подходит для карт большого объёма и устройств с повышенным износом при выполнении операций чтения-записи. В системе exFAT также появилась возможность управления правами доступа на файлы/каталоги, а время доступа к данным уменьшилось. Одним из главных недостатком системы exFAT является то, что эта на эту технологию распространяется лицензионная политика Microsoft, и ни в каких open source решениях она применяться не может. Для ее использования в любой операционной системе необходимо будет осуществить лицензионные отчисления в Microsoft (данное правило не относится к простым мобильным устройствам, таким как фотоаппараты, плееры и т.д.).
exFAT в современных операционных системах
Windows 7
Новая версия ОС Microsoft Windows 7 полностью поддерживает файловую систему exFAT и все ее функции как в 32- так и в 64-битной версии. Кроме того, внешние флешки, отформатированные в exFAT можно использовать для работы с технологией ReadyBoost (причем лимита на 4 Гб больше не будет).
Windows Vista
Windows Vista поддерживает exFAT только начиная с Service Pack 1. Кроме того некоторые фичи, такие как управление доступом также не поддерживаются. В отличии от Windows 7, устройства с exFAT в Vista не поддерживаются для ReadyBoost.
Windows XP
ExFAT в Windows XP не поддерживается, однако на сайте Microsoft можно скачать драйвер (описание в KB 9555704 — http://support.microsoft.com/kb/955704), однако он требует установленного Service Pack 2.
Для более старых версий Windows официальная поддержка exFAT отсутствует.
Windows Server
ExFAT целиком поддерживается в Windows Server 2008, а при установке вышеуказанного драйвера и в Windows Server 2003.
Snow Leopard
Mac OS X поддерживает exFAT начиная с версии 10.6.4 (15 июня 2010), однако только на Mac-ах с кард-ридером SDXC. Mac mini и iMac совместимы с exFAT.
Linux
На системах семейства Linux поддержка exFAT отсутствует, хотя и есть несколько решений, но большинство из них платно или неудобно, кроме того еще и Microsoft со своей пропри тарной лицензией вставляет палки в колеса независимым разработчикам.
ExFAT и FAT32
При тестировании на Windows 7 показала такую же производительность, как и FAT32, однако NTFS все таки немного быстрее. Заменит ли exFAT FAT32? Вероятно, это произойдёт только после массового переходу на Windows 7 или более новые версии Windows. Для потребителей же основное преимущество exFAT будет заключаться в преодолении файловых ограничений FAT32 (увеличение размера файла в exFat).
Нужно не забывать так же, что файловая система exFAT требует более новой версии ОС (может потребоваться апгрейд железа), а также тот факт, что на старых устройствах (фотоаппараты, mp3-плееры) exFAT может просто не поддерживаться.
exFat или NTFS
ExFAT можно считать конкурентом NTFS на системах с ограниченной вычислительной мощности и памяти. Кроме того файловую систему NTFS на флэш-картах использовать очень неудобно и неэффективно (падает скорость работы и уменьшается срок службы флеш памяти), и именно ExFAT будет идеальной файловой системой для таких устройств.
Источник
В чём разница между FAT32, NTFS и exFAT
Вы знаете, что Windows Phone использует NTFS? Почему большинство карт памяти и почти все USB-накопители по-прежнему используют старый-добрый FAT? Почему вы можете хранить полноразмерные HD-фильмы на некоторых флеш-накопителях и не можете на других? Почему некоторые устройства поддерживают только карты памяти SDHC до 32 ГБ, и что можно сделать, чтобы заставить их использовать 64 ГБ SDXC? Эти и многие другие вопросы связаны с типом файловой системы, используемой конкретным устройством хранения. Но как это связано с Windows?
Содержание:
Файловые системы Windows
В начале истории персональных компьютеров (думаю, в эпоху текстовых DOS-боксов и дискет) единственной используемой файловой системой была FAT12. С появлением жестких дисков, способных хранить несколько мегабайт данных (да, именно мегабайт, а не гигабайт!) была разработана новая версия FAT под названием FAT16. Под эту файловую систему и разрабатывался Windows 95, получив лишь «апгрейд» в виде поддержки более длинных имен файлов. В Windows 98 Microsoft добавили поддержку еще одной новой версии FAT под названием FAT32 для поддержки больших жестких дисков (да, к тому времени мы уже начали измерять дисковое пространство в гигабайтах).
В параллельной вселенной Windows NT Microsoft все время использовала файловую систему новых технологий, или NTFS. Windows NT 4, Windows 2000, а затем Windows XP, Vista, Windows 7, 8, 8.1 и новые Windows 10 используют NTFS.
В еще одной параллельной вселенной – вселенной съемного хранилища вы можете выбирать между универсальным FAT32 (при этом столкнувшись с его ограничением в размерах файлов в 4 ГБ) и более новым, но не так широко поддерживаемым (из-за ограничений по лицензированию) exFAT. Кстати, exFAT используется в качестве файловой системы по выбору на всех картах SDXC емкостью 64 ГБ и более.
Итак, в настоящее время у нас есть три различных семейства файловых систем: древняя, но все же широко применяемая FAT32, новая NTFS и свежеразработанная, оптимизированная на основе Solid ExFAT. Какую из этих файловых систем использовать, и когда? И каковы различия между ними?
FAT32: Очевидный выбор
FAT32 по-прежнему остается единственной файловой системой, используемой в Windows 98 или Windows ME. FAT32 фактически является файловой системой выбора для карт памяти SD до 32ГБ включительно. Наконец, FAT32 часто используется для форматирования USB-накопителей, в том числе емкостью 64ГБ и выше.
Старичок FAT32… Его основные ограничения хорошо известны. FAT32 поддерживает работу с файлами размером не более 4 ГБ. Если кажется, что для одного файла это много, вспомните о том, что один видеоролик в формате HD занимает от 4,5 до 10 ГБ, и сразу станет понятно, насколько данное ограничение существенно в современных реалиях. Его другие ограничения включают в себя отсутствие надежной поддержки, абсолютное отсутствие контроля доступа, отсутствия шифрования, сжатия или отказоустойчивости.
Иначе говоря, это совершенно простая и легкая файловая система, которая подходит практически для любой портативной электроники с низкой производительностью, такой как цифровые камеры и видеокамеры, простые смартфоны, MP3-плееры и аналогичные устройства. Из-за его почтенного возраста и широкой популярности в Windows с 1997 года FAT32 поддерживается практически всей техникой, включая холодильник и кофеварку. Другими словами, если вы хотите носить с собой одно съемное запоминающее устройство и быть уверенным, что его можно использовать с любым подключаемым модулем, FAT32 – то, что вам нужно.
NTFS: системный диск
Однако ограничения FAT32 не позволят эффективно использовать ее в современных вычислительных средах. Отсутствие контроля доступа – это одно, абсолютное отсутствие ведения журнала и каких-либо намеков на отказоустойчивость – это другое. Ограниченный размер файла также является огромным минусом. В результате Microsoft представила новую файловую систему, которую они назвали файловой системой новых технологий, или NTFS.
В NTFS есть все, чего не хватает FAT. Мощные параметры контроля доступа? Пожалуйста. Отказоустойчивость и ведение журнала? Получите. Мгновенное сжатие и шифрование отдельных файлов, папок и целых томов диска? Конечно. Альтернативные потоки данных, повышенные меры безопасности, резервное копирование самой файловой системы и важных системных файлов и многие другие функции… Начиная с его первоначального выпуска в 1994 году, NTFS получала все новые обновления, в том числе, повышающие ее совместимость. Ее великолепный дизайн и простая реализация по-прежнему не имеют аналогов среди других файловых систем даже сегодня. Она достаточно универсальна для использования даже на смартфонах начального уровня под управлением Windows Phone 8 и 8.1. Но, если это такая отличная файловая система, почему ее не используют все и везде?
Как вы могли ожидать, NTFS не лишена недостатков. Разработанная еще в 1994 году для серверных операций, эта файловая система всегда требовала большой вычислительной мощности для поддержания своих многочисленных структур. Ее системные записи быстро растут, занимают драгоценное пространство и добавляют дополнительную нагрузку на эти устройства хранения, использующие флэш-память NAND. Наконец, если использовать что-либо, кроме больших жестких дисков, ее накладные расходы окажутся слишком велики, поэтому всеобщее признание система пока так и не завоевала. И последнее, но не менее важное: NTFS запатентована Microsoft, которые не желают открывать лицензии на эту файловую систему конкурентам.
exFAT: лучшее, если поддерживается…
Чтобы преодолеть ограничения FAT32 и уменьшить дополнительную нагрузку, оказываемую NTFS на носители на основе NAND, Microsoft разработала еще одну файловую систему под названием Extended FAT или exFAT. Эта файловая система в значительной степени основана на той же концепции, что и оригинальный FAT, только теперь она является настоящей 64-битной файловой системой без ограничения размера файла, существующего в FAT32. Именно поэтому exFAT используется как стандарт для больших SD-карт (стандарт SDXC требует, чтобы все SD-карты размером 64 ГБ и более были отформатированы с помощью exFAT). Поэтому, если вы покупаете 64-гигабайтную карту microSDXC, она будет работать на основе exFAT … и по этой причине она может не распознаваться вашим смартфоном или планшетом.
Причина, по которой exFAT не заменила древний FAT32 повсюду – платное лицензирование. В отличие от FAT32, которая бесплатна для всех без роялти, с производителей, которые хотят использовать exFAT на своих устройствах Microsoft взимает плату за лицензирование. В результате создатели телефонов Android, низкоуровневых Android-планшетов и дешевых камеры предпочитают сэкономить несколько центов стоимости устройств (в пересчете на единицу выпущенной техники) на лицензировании, предпочитая исключить exFAT из списка поддерживаемых файловых систем. В результате, если вы вставляете новую 64-гигабайтную микро SD-карту в такое устройство, карта, скорее всего, не будет распознана.
Можете ли вы самолично преодолеть это ограничение? В большинстве случаев да, и довольно легко. Просто подключите свою SD-карту к ПК через устройство чтения карт и отформатируйте ее с помощью … вы догадались… FAT32! Таким образом, вы потеряете возможность хранить на ней файлы размером более 4 ГБ, но ваша карта памяти, скорее всего, будет распознана и будет бесперебойно работать на устройстве Android, которое по техническим характеристикам вроде как и не должно поддерживать SD-карты емкостью более 32 ГБ.
(Обратите внимание, что некоторые устройства могут быть слишком старыми, чтобы распознавать карты памяти SDXC чисто физически. Да, таковые не производятся вот уже несколько лет, но выпущенные ранее устройства могут по-прежнему не поддерживать карту SDXC независимо от того, с какой файловой системой она поставляются)
Однако минуточку… Windows Phone – это ОС Microsoft, так не будут ли устройства Windows Phone поддерживать exFAT по умолчанию? Так и есть! Windows Phone 8 и 8.1 действительно поставляются со встроенной поддержкой exFAT, бесплатной для производителей, которые хотят выпускать устройства для платформы Windows Phone. Microsoft предлагает бесплатную лицензию exFAT в рамках своего «пакета стимулирования», призванного побудить большее число производителей присоединиться к платформе Windows Phone.
Наконец, все или почти все планшеты с операционной системой Windows RT и полной версией Windows 8 или 8.1 поддерживают exFAT и распознают 64-ГБ и более крупные SD-карты без труда.
Восстановление файловых систем Windows
Практически каждый инструмент восстановления данных на базе Windows предлагает поддержку FAT32 и NTFS. Инструменты, поддерживающие exFAT, гораздо менее доступны из-за ограничений лицензирования Microsoft. Одним из инструментов поддержки всех трех файловых систем Windows является RS Partition Recovery.
Наконец, если вам нужна только поддержка одной из файловых систем, вы можете сэкономить, выбрав RS NTFS Recovery или RS FAT Recovery.
Часто задаваемые вопросы
Это сильно зависит от емкости вашего жесткого диска и производительности вашего компьютера. В основном, большинство операций восстановления жесткого диска можно выполнить примерно за 3-12 часов для жесткого диска объемом 1 ТБ в обычных условиях.
Если файл не открывается, это означает, что файл был поврежден или испорчен до восстановления.
Используйте функцию «Предварительного просмотра» для оценки качества восстанавливаемого файла.
Когда вы пытаетесь получить доступ к диску, то получаете сообщение диск «X: не доступен». или «Вам нужно отформатировать раздел на диске X:», структура каталога вашего диска может быть повреждена. В большинстве случаев данные, вероятно, все еще остаются доступными. Просто запустите программу для восстановления данных и отсканируйте нужный раздел, чтобы вернуть их.
Пожалуйста, используйте бесплатные версии программ, с которыми вы можете проанализировать носитель и просмотреть файлы, доступные для восстановления.
Сохранить их можно после регистрации программы – повторное сканирование для этого не потребуется.
Источник
Часто задаваемые вопросы по использованию различных файловых систем на внешних накопителях
Я хочу, чтобы мой внешний винчестер (флэш-накопитель) работал с максимальным количеством компьютеров. Какую файловую систему мне нужно выбрать?
На данный момент наилучшую совместимость обеспечивает FAT32, а для накопителей менее 2 ГБ идеальным вариантом является FAT16. Такие устройства поддерживаются повсеместно.
Дал знакомому попользоваться флэш-картой Secure Digital на 2 ГБ, а теперь мой фотоаппарат ее не видит. Почему?
Если карта вообще хоть где-то работает (т. е. исправна физически), проблема может быть в файловой системе. Дело в том, что стандартной для SD-карт (не SDHC) является FAT16, и большинство устройств, рассчитанных на эти карты, никаких других «не понимают». Впрочем, обычно они при этом хотя бы сообщают, что карта не отформатирована, и предлагают выполнить означенную операцию, но если это не получается, придется воспользоваться картоводом и отформатировать карту при помощи компьютера.
Недавно купил б/у внешний винчестер. Он прекрасно работает на всех компьютерах с Windows Seven, но виден лишь на части машин с Windows Vista и Windows XP. Почему?
Судя по всему, предыдущий владелец отформатировал накопитель под exFAT. Поддержка этой системы является штатной для Seven, а вот для Vista требует наличия как минимум первого сервис-пака. На XP же нужно ставить опциональный апдейт KB955704 (приведена ссылка на английскую версию — для систем с русским или иным базовым языком его можно выбрать самостоятельно). Учтите, что способов «увидеть» накопитель с exFAT под более старыми версиями Windows нет (по крайней мере, нам они не известны), да и с другими операционными системами или бытовой техникой дело обстоит немногим лучше, так что если вопрос совместимости для вас важен, лучше выбрать другую файловую систему.
Внешний винчестер прекрасно работает (по крайней мере, читается) на всех компьютерах с Windows 2000/XP/Vista, Linux, MacOS, но у моих родственников есть старый компьютер с Windows ME — он этот накопитель вообще не видит. Почему?
Судя по симптомам, ВЖД отформатирован под NTFS, а все системы линейки Windows 9x понимают только FAT32 (оригинальная Windows 95 — так и вовсе только FAT16). В данном случае у вас два пути. Первый: если компьютеры со старыми версиями Windows на вашем пути встречаются лишь эпизодически, и все места, где они встречаются, вам известны, на них можно установить специальный драйвер для работы с NTFS (особенно это удобно, если данные нужно переносить только на эти компьютеры, но не обратно — драйверы с поддержкой только чтения бесплатны, да и по вполне понятным причинам ничего на внешнем диске не испортят). Второй: если просто нужна совместимость с Windows 9x везде и всюду, накопитель стоит отформатировать под FAT32. Учтите только, что если его емкость более 120 ГБ, делать это нужно исключительно на компьютере с новой версией Windows, причем на этом пути есть некоторое количество подводных камней, рассмотренных в следующих вопросах. Да, и еще — если речь идет не о МЕ, а о Windows 98/98SE, то для начала вам придется установить на компьютер отдельный драйвер для поддержки USB-накопителей, поскольку эти системы изначально протокол UMS не поддерживают. Если это 98SE, а накопитель снабжен не только USB, но и FireWire, имеет смысл использовать именно этот интерфейс — дополнительные драйверы не потребуются.
Попробовал записать файл размером 4,7 ГБ (ISO-образ DVD-диска) на свежекупленный USB-винчестер. Информации на нем нет, емкость 500 ГБ, однако система сообщает, что места недостаточно для завершения операции. Почему?
По-видимому, вы столкнулись с ограничением FAT32 на размер файлов. Проверьте — какая файловая система на винчестере (под Windows для этого выберите его в папке «Мой компьютер», нажмите правую кнопку мыши и выберите «Свойства»). Если это FAT32, то записать такой большой файл не получится — нужно либо разбивать файл на части (например, при помощи архиватора), либо переформатировать накопитель под другую файловую систему.
Хочу отформатировать внешний винчестер под FAT32, дабы его увидел DVD-плеер, однако система предлагает только NTFS (или NTFS и exFAT). Почему?
Политика компании Microsoft такова — FAT32 только для дисков, меньших чем 32 ГБ. Поэтому штатными средствами Windows 2000 и более новых отформатировать больший накопитель под FAT32 не получится, хотя сама система спокойно работает с томами FAT32 емкостью до 2 ТБ. Очень часто производители винчестеров и флэш-накопителей предлагают для скачивания утилиты форматирования, лишенные этого ограничения. Если для вашего устройства таковой нет, поможет бесплатная консольная программа fat32format, которую несложно найти в интернете.
Купил флэш-накопитель на 64 ГБ, подключил к компьютеру с Windows XP. Хочу его отформатировать, однако при выборе из контекстного меню опции «Форматировать» мне не предлагают никакой файловой системы, так что выполнить операцию невозможно. Почему?
Немного смешная, но вполне реальная ситуация 🙂 Дело в том, что, с точки зрения Microsoft, форматировать устройство емкостью более 32 ГБ под FAT32 нельзя, а под NTFS по умолчанию нельзя форматировать сменное устройство — других же файловых систем Windows XP по умолчанию «не знает». Соответственно, у вас три варианта действий: воспользоваться советом по форматированию большого накопителя под FAT32, воспользоваться расположенным ниже советом по форматированию флэшки под NTFS или установить на компьютер обновление с поддержкой exFAT и отформатировать устройство под эту файловую систему.
Как отформатировать флэшку под NTFS на компьютере под управлением Windows XP?
По умолчанию штатные утилиты не поддерживают форматирование сменных накопителей под NTFS, если для них включена оптимизация для быстрого удаления (извлечения устройства). Для изменения политики откройте свойства накопителя в диспетчере устройств, выберите там закладку «Политика» и установите переключатель в положение «Оптимизировать для выполнения» — после этого NTFS появится в списке доступных файловых систем в диалоге форматирования. Альтернативный вариант — воспользоваться сторонней утилитой, однако переключить политику рекомендуется все равно: без этого кэширование записи полноценно работать не будет, что уменьшит производительность. Заметим, что Windows Vista или Seven такого ограничения не накладывают, всегда предлагая NTFS в качестве возможного способа форматирования (причем любые другие варианты при определенных типе и емкости накопителя могут и отсутствовать).
Как отформатировать устройство под exFAT на компьютере с Windows XP? Обновление стоит, однако найти такую возможность не могу.
К сожалению, выпущенное компанией Microsoft обновление для Windows XP нельзя назвать совсем полноценным — оно не заменяет консольную программу format и не модифицирует стандартное средство «Управление дисками». Поэтому форматировать накопитель под exFAT можно только при помощи контекстного меню диска, причем даже в этом случае нет возможности вручную выбрать размер кластера.
Как отформатировать под exFAT внешний винчестер или флэшку с интерфейсом eSATA на компьютере под управлением Windows Vista/Seven?
По неизвестной прогрессивной науке причине, компания Microsoft оставила в GUI-утилитах этих систем возможность форматирования под exFAT только для сменных устройств, но не для внутренних винчестеров, а eSATA-устройства рассматриваются системой как внутренние. Варианта два: либо подключите накопитель к USB, если есть такая возможность, либо воспользуйтесь утилитой format с ключом /FS:exFAT из командной строки (выполняться сеанс должен обязательно с правами администратора — UAC не поможет).
Недавно купил себе MacBook. Подключил к нему внешний винчестер. Все файлы видны, скопировать их на Mac могу, но ничего записать не получается. Почему?
Судя по всему, винчестер отформатирован под NTFS — MacOS работает с такими накопителями только на чтение. Вы можете либо установить специальный драйвер с поддержкой записи (например, выпущенный компанией Paragon), либо переформатировать винчестер под другую файловую систему.
Почему-то не работает Time Machine с USB-винчестером. Мне нужно поменять его на специальную версию «for Mac» или есть другие варианты?
Time Machine совместима только с дисками, отформатированными под HFS+. Менять винчестер не обязательно — достаточно его просто переформатировать подобающим образом (что по умолчанию выполнено для «маковских» версий). Если необходимо будет получить доступ к винчестеру и на компьютере с Windows, следует установить туда один из имеющихся драйверов для поддержки HFS+.
Источник
Шаблон:Карточка файловой системы
exFAT (от Шаблон:Lang-en — «расширенная FAT»), иногда называется FAT64 — проприетарная файловая система, предназначенная главным образом для флэш-накопителей. Впервые представлена фирмой Microsoft для встроенных устройств в Windows Embedded CE 6.0. Размер кластера по умолчанию для файловой системы exFAT составляет от 4 КБ до 128 КБ в зависимости от размера тома[1].
Преимущества[]
Основными преимуществами exFAT перед предыдущими версиями FAT являются:
- Уменьшение количества перезаписей одного и того же сектора, что важно для флеш-накопителей, у которых ячейки памяти необратимо изнашиваются после определённого количества операций записи (это сильно смягчается выравниванием износа (Шаблон:En), встроенным в современные USB-накопители и SD-карты). Это было основной причиной разработки exFAT.
- Теоретический лимит на размер файла 264 байт (16 эксабайт).
- Максимальный размер кластера увеличен до 225 байт (32 мегабайта).
- Улучшение распределения свободного места за счёт введения бит-карты свободного места, что может уменьшать фрагментацию диска.
- Введена поддержка списка прав доступа[2].
- Поддержка транзакций (опциональная возможность, должна поддерживаться устройством).
Ограничения[]
- Более старые версии Windows NT, вплоть до Windows Vista без Service Pack 1 не поддерживают exFAT. Однако существуют официальные обновления от Microsoft, которые позволяют запускать exFAT на Windows XP SP2 и более поздних версиях.
- Windows Vista не способна использовать exFAT-размеченные устройства под ReadyBoost. В Windows 7 это ограничение устранено.[3]
- Более сложная структура, в сравнении с FAT, вызывает большее потребление вычислительных ресурсов.
- Количество файлов в подкаталогах ограничено числом 2,796,202 (223/3). Для корневого каталога ограничения нет.[4]
Поддержка[]
Поддержка exFAT имеется в Windows XP с Service Pack 2 и 3 с обновлением KB955704, Windows Vista с Service Pack 1[5], Windows Server 2008, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows 10, в Mac OS X начиная с версии 10.6.5[6], а также Linux (требуется компиляция исходного кода Samsung).
Технология ReadyBoost в Windows Vista не совместима с устройствами с файловой системой exFAT.[7] Однако в Windows 7 это ограничение снято.
Существует свободный драйвер exFAT в виде патча для ядра Linux, поддерживающий только чтение этой файловой системы[8]. Также существует драйвер, работающий через FUSE, в том числе для ОС FreeBSD и OpenBSD (sysutils/fuse-exfat). Данный драйвер поддерживает как чтение, так и запись[9]. Кроме того, в августе 2013 года Samsung опубликовала драйвер для ядра Linux под лицензией GPL[10]. Легальность использования всех этих реализаций стоит под вопросом.Шаблон:Где
Лицензирование[]
Лицензионный статус сначала был не определён. Однако Microsoft успешно запатентовала файловую систему FAT[11], и в феврале 2009 года подала в суд на компанию TomTom, обвиняя её в нарушении патента.[12]
Существует также сторонняя реализация exFAT для Windows XP[13] / Windows Server 2003, однако она предназначена для непосредственной интеграции в дистрибутив продукта без возможности ручной установки драйвера. Данный порт выполнен на базе драйвера Windows Vista.[14]
В декабре 2009 года Microsoft начала лицензировать файловую систему exFAT для сторонних производителей.[15]
См. также[]
- FAT32
- NTFS
Примечания[]
- ↑ Размер кластера по умолчанию для FAT, NTFS и exFAT
- ↑ Windows File Systems
- ↑ exFAT Versus FAT32 Versus NTFS (2008-02-27). Проверено 2 октября 2009. Архивировано из первоисточника 2 февраля 2013.
- ↑ Ошибка скрипта: Модуля «String» не существует. Reverse Engineering the Microsoft exFAT File (en). The SANS Institute.
- ↑ Ошибка скрипта: Модуля «String» не существует. Vista SP1 Whitepaper (en). Microsoft (28 августа 2007). Проверено 15 октября 2007. Архивировано из первоисточника 5 июня 2012.
- ↑ Файловая система ExFAT — универсальное решение для Mac OS X и Windows.
- ↑ Перечень допустимых файловых систем, отображаемых в Windows Vista при попытке использования ReadyBoost с флеш-накопителем, использующим файловую систему exFAT
- ↑ Fat64 / exFat fs and Linux — fa.linux.kernel | Google Groups
- ↑ exfat — Project Hosting on Google Code
- ↑ Conservancy Helps Samsung Resolve GPL Compliance Matter Amicably — Software Freedom Conservancy
- ↑ Ошибка скрипта: Модуля «String» не существует. Microsoft FAT patents upheld (en). Computerworld (11 января 2006). Проверено 2 ноября 2008. Архивировано из первоисточника 5 июня 2012.
- ↑ Ошибка скрипта: Модуля «String» не существует. Microsoft suit over FAT patents could open OSS Pandora’s Box (en). Ars Technica. Condé Nast Publications (25 февраля 2009). Проверено 9 марта 2009. Архивировано из первоисточника 22 августа 2011.
- ↑ После 26 января 2009 года она утратила смысл с вводом в обновлении KB955704 официальной поддержки данной файловой системы
- ↑ Ошибка скрипта: Модуля «String» не существует. exFAT File System Driver for XP/2k3, Ported from Vista. WinCert.net (28 августа 2007). Проверено 1 июля 2008. Архивировано из первоисточника 1 марта 2012.
- ↑ Microsoft лицензирует файловую систему exFAT для сторонних производителей. Ferra.ru (11 декабря 2009). Проверено 13 декабря 2009. Архивировано из первоисточника 1 марта 2012.
Ссылки[]
- TFAT OverviewШаблон:Ref-en
- Extended FAT File SystemШаблон:Ref-en
- Обновление Windows XP и 2003 (KB955704) для поддержки файловой системы exFAT
- Компания-разработчик NTFS-3G подписала соглашение с Microsoft, касающиеся exFAT
- Файловая система ExFAT — универсальное решение для Mac OS X и Windows
- Сравнение Fat32, NTFS, exFAT на флэш-носителях и внешних жестких дисках
| |
|
|---|---|
| Основные |
Aero • |
| Службы управления |
Архивация и восстановление • |
| Приложения |
Контакты • |
| Игры |
Chess Titans • |
| Ядро ОС |
Ntoskrnl.exe • |
| Службы |
Autorun.inf • |
| Файловые системы |
ReFS • |
| Сервер |
Active Directory • |
| Архитектура |
NT • |
| Безопасность |
BitLocker • |
| Совместимость |
Подсистема UNIX (Interix) • |
Шаблон:Файловые системы
Вместе с выходом Vista SP1 Microsoft представила новую файловую систему. ExFAT (Extended File Allocation Table) – это преемник старой файловой системы FAT32. Так в чем же основные преимущества и недостатки файловой системы exFAT. В чем отличия между exFAT и FAT32? И когда лучше использовать систему exFAT а не NTFS?
Файловая система FAT32 это достаточно старая и привычная всем файловая систем, однако она имеет ряд существенных недостатков:она не поддерживает разделы больше, чем 2 Тб, и файлы, размер которых более 4 Гб. Для решения описанных проблем в FAT32 и была создана файловая система exFAT. ExFAT – это разработка Microsoft, предназначенная в основном для мобильных носителей (флешки, SSD-диски, смарткарты). Сразу стоит отметить, что ExFAT не используется для форматирования жестких дисков. Все последние версии Windows, а также Mac OS X поддерживают эту файловую систему. ExFAT также часто называют FAT64, что подразумевает возможность работы с накопителями и файлами большего размера.
Основные преимущества файловой системы exFAT:
- Максимальный размер кластера увеличен до 32 Мб
- Увеличен максимальный размер файла в exFAT с 4Гб до 264 байт (16 EB).
- Нет ограничения на количество файлов в каталоге
- Поддержка прав доступа на файлы/каталоги
- Поддержка транзакций при записи (если поддерживается физическим устройством)
- Эффективное использование свободного места, что помогает существенно снизить фрагментацию диска.
Стоит отметить, что при форматировании в exFAT количество доступного места на устройства хранения больше, чем при использовании FAT32. Например, если USB флешку размеров 4 Гб (номинальная емкость 4023 Мб) отформатировать в различных файловых системах, то получится следующее:
- FAT32 – 4014 Мб
- HFS+ – 3997 Мб
- NTFS – 3974 Мб
- exFAT – 4022 Мб
ExFAT оптимизирована для работы с флеш накопителями, такими USB флешки, карты памяти и SSD диски, размер кластера в 32 Кб хорошо подходит для карт большого объёма и устройств с повышенным износом при выполнении операций чтения-записи. В системе exFAT также появилась возможность управления правами доступа на файлы/каталоги, а время доступа к данным уменьшилось. Одним из главных недостатком системы exFAT является то, что эта на эту технологию распространяется лицензионная политика Microsoft, и ни в каких open source решениях она применяться не может. Для ее использования в любой операционной системе необходимо будет осуществить лицензионные отчисления в Microsoft (данное правило не относится к простым мобильным устройствам, таким как фотоаппараты, плееры и т.д.).
exFAT в современных операционных системах
Windows 7
Новая версия ОС Microsoft Windows 7 полностью поддерживает файловую систему exFAT и все ее функции как в 32- так и в 64-битной версии. Кроме того, внешние флешки, отформатированные в exFAT можно использовать для работы с технологией ReadyBoost (причем лимита на 4 Гб больше не будет).
Windows Vista
Windows Vista поддерживает exFAT только начиная с Service Pack 1. Кроме того некоторые фичи, такие как управление доступом также не поддерживаются. В отличии от Windows 7, устройства с exFAT в Vista не поддерживаются для ReadyBoost.
Windows XP
ExFAT в Windows XP не поддерживается, однако на сайте Microsoft можно скачать драйвер (описание в KB 9555704 — http://support.microsoft.com/kb/955704), однако он требует установленного Service Pack 2.
Для более старых версий Windows официальная поддержка exFAT отсутствует.
Windows Server
ExFAT целиком поддерживается в Windows Server 2008, а при установке вышеуказанного драйвера и в Windows Server 2003.
Snow Leopard
Mac OS X поддерживает exFAT начиная с версии 10.6.4 (15 июня 2010), однако только на Mac-ах с кард-ридером SDXC. Mac mini и iMac совместимы с exFAT.
Linux
На системах семейства Linux поддержка exFAT отсутствует, хотя и есть несколько решений, но большинство из них платно или неудобно, кроме того еще и Microsoft со своей пропри тарной лицензией вставляет палки в колеса независимым разработчикам.
ExFAT и FAT32
При тестировании на Windows 7 показала такую же производительность, как и FAT32, однако NTFS все таки немного быстрее. Заменит ли exFAT FAT32? Вероятно, это произойдёт только после массового переходу на Windows 7 или более новые версии Windows. Для потребителей же основное преимущество exFAT будет заключаться в преодолении файловых ограничений FAT32 (увеличение размера файла в exFat).
Нужно не забывать так же, что файловая система exFAT требует более новой версии ОС (может потребоваться апгрейд железа), а также тот факт, что на старых устройствах (фотоаппараты, mp3-плееры) exFAT может просто не поддерживаться.
exFat или NTFS
ExFAT можно считать конкурентом NTFS на системах с ограниченной вычислительной мощности и памяти. Кроме того файловую систему NTFS на флэш-картах использовать очень неудобно и неэффективно (падает скорость работы и уменьшается срок службы флеш памяти), и именно ExFAT будет идеальной файловой системой для таких устройств.
exFAT поддерживается в Windows XP и Windows Server 2003 с обновлением KB955704, Windows Embedded CE 6.0, Windows Vista с пакетом обновления 1, Windows Server 2008, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows Server 2008 R2 (кроме Windows Server 2008 Server Core), Windows 10, macOS начиная с 10.6.
exFAT полезен при работе с разными операционными системами, так как формат работает с Mac, Windows и Linux и поддерживаются все носители информации — от жестких дисков до USB-накопителей и SD-карт. exFAT решает описанные ранее проблемы с хранением огромных файлов на разных платформах.
Поддерживается ли exFAT в Windows?
Ваш диск или раздел в формате exFAT может теперь можно использовать как для Windows, так и для Mac.
Может ли Windows 10 работать на exFAT?
ExFAT, также совместим с Windows и Mac. По сравнению с FAT32 exFAT не имеет ограничений FAT32. Таким образом, многие пользователи предпочли бы, чтобы файловая система exFAT была совместима как с Windows, так и с Mac. Однако, как сказано в сценарии, Windows обычно не может читать диски, отформатированные для Mac.
Когда использовать жир или exFAT?
Если вам нужно передать файлы размером более 4 ГБ между Mac и ПК: Используйте exFAT. Во всех остальных случаях: используйте MS-DOS (FAT), также известную как FAT32.
Может ли Android читать exFAT?
Android поддерживает файловую систему FAT32 / Ext3 / Ext4. Большинство новейших смартфонов и планшетов поддерживают файловую систему exFAT. Обычно, поддерживается ли файловая система устройством или нет, зависит от программного / аппаратного обеспечения устройства. Пожалуйста, проверьте файловую систему, которую поддерживает ваше устройство.
Что лучше FAT32 exFAT или NTFS?
Что лучше fat32 или NTFS? NTFS идеально подходит для внутренних дисков, в то время как exFAT вообще идеален для флешек и внешних накопителей. FAT32 имеет гораздо лучшую совместимость по сравнению с NTFS, но поддерживает только отдельные файлы размером до 4 ГБ и разделы до 2 ТБ.
В чем преимущества файловой системы exFAT?
Преимущества файловой системы exFAT
- Нет коротких имен файлов. Файлы exFAT имеют только одно имя, которое на диске закодировано как Unicode и может содержать до 255 символов.
- 64-битный размер файла. …
- Размер кластера до 32M. …
- Только один FAT. …
- Бесплатное растровое изображение кластера. …
- Оптимизация непрерывных файлов. …
- Хэши имен файлов.
Каков наилучший размер единицы распределения для exFAT?
Простое решение — переформатировать exFAT с размером единицы размещения 128 КБ или меньше. Тогда все подходит, так как не так уж много места для каждого файла.
Следует ли использовать exFAT для внешнего жесткого диска?
exFAT — хороший вариант, если вы часто работать с компьютерами Windows и Mac. Передача файлов между двумя операционными системами менее хлопотна, поскольку вам не нужно постоянно выполнять резервное копирование и переформатирование каждый раз. Linux также поддерживается, но вам нужно будет установить соответствующее программное обеспечение, чтобы в полной мере использовать его.
Может ли Windows 7 видеть exFAT?
Флэш-накопители также могут быть отформатированы в exFAT.
…
Операционные системы, поддерживающие файловую систему exFAT.
| Operating System | поддержка exFAT | Патч скачать |
|---|---|---|
| Windows 7 | Поддерживается изначально | |
| Windows Vista | Требуется обновление до Service Pack 1 или 2 (оба поддерживают exFAT) | Загрузить Service Pack 1 (с поддержкой exFAT) Загрузить Service Pack 2 (с поддержкой exFAT) |
| exFAT | |
| Разработчик |
Microsoft |
|---|---|
| Файловая система |
Расширенная таблица размещения файлов (англ. Extended File Allocation Table) |
| Дата представления |
Ноябрь 2006 (Windows Embedded CE 6.0) |
| Метка тома |
0x07 (MBR) |
| Структура | |
| Содержимое папок |
Таблица |
| Размещение файлов |
Битовые поля, Связный список |
| Сбойные сектора |
Пометка кластеров |
| Ограничения | |
| Максимальный размер файла |
16 эксбибайт |
| Возможности | |
| Диапазон дат |
1 января 1980 — 31 декабря 2107 |
| Атрибуты |
Только для чтения, скрытый, системный, метка тома, подкаталог, архивный |
| Права доступа |
Не поддерживаются |
| Поддерживается ОС |
Windows Embedded CE 6.0 (для встроенных систем) |
exFAT (от англ. Extended FAT — «расширенная FAT») — проприетарная файловая система, предназначенная главным образом для флэш-накопителей. Впервые представлена фирмой Microsoft для встроенных устройств в Windows Embedded CE 6.0.
Преимущества
Основными преимуществами exFAT перед предыдущими версиями FAT являются:
- Уменьшение количества перезаписей одного и того же сектора, что важно для флеш-накопителей, у которых ячейки памяти необратимо изнашиваются после определённого количества операций записи (это сильно смягчается выравниванием износа — wear leveling, — встроенным в современные USB-накопители и SD-карточки). Это была основная причина разработки ExFAT.
- Теоретический лимит на размер файла 264 байт (16 эксабайт).
- Максимальный размер кластера увеличен до 225 байт (32 мегабайта).
- Улучшение распределения свободного места за счёт введения бит-карты свободного места, что может уменьшать фрагментацию диска.
- Введена поддержка списка прав доступа.
- Поддержка транзакций (опциональная возможность, должна поддерживаться устройством).
Ограничения
Количество файлов в подкаталогах ограничено числом 2,796,202 (223/3). Для корневого каталога ограничения нет.[1]
Поддержка
Поддержка exFAT имеется в Windows XP с Service Pack 2 и 3 с обновлением KB955704, Windows Vista с Service Pack 1[2], Windows Server 2008, Windows 7, Windows 8, а также в Mac OS X Snow Leopard начиная с версии 10.6.5[3].
Технология ReadyBoost в Windows Vista не совместима с устройствами с файловой системой exFAT.[4]
Существует свободный драйвер exFAT в виде патча для ядра Linux, поддерживающий только чтение этой файловой системы[5]. Также существует драйвер, работающий через FUSE. Данный драйвер поддерживает как чтение, так и запись[6].
Лицензирование
Лицензионный статус неясен. Однако известно, что Microsoft успешно запатентовала файловую систему FAT[7], и в феврале 2009 года подала в суд на компанию TomTom, обвиняя её в нарушении патента.[8]
Существует также сторонняя реализация exFAT для Windows XP[9] / Windows Server 2003, однако она предназначена для непосредственной интеграции в дистрибутив продукта без возможности ручной установки драйвера. Данный порт выполнен на базе драйвера Windows Vista.[10]
В декабре 2009 года Microsoft начала лицензировать файловую систему exFAT для сторонних производителей.[11]
Примечания
- ↑ Robert Shullich. Reverse Engineering the Microsoft exFAT File (англ.). The SANS Institute.
- ↑ Brandon LeBlanc. Vista SP1 Whitepaper (англ.). Microsoft (28 августа 2007). Архивировано из первоисточника 5 июня 2012. Проверено 15 октября 2007.
- ↑ Файловая система ExFAT — универсальное решение для Mac OS X и Windows.
- ↑ Перечень допустимых файловых систем, отображаемых в Windows Vista при попытке использования ReadyBoost с флеш-накопителем, использующим файловую систему exFAT
- ↑ Fat64 / exFat fs and Linux — fa.linux.kernel | Google Groups
- ↑ exfat — Project Hosting on Google Code
- ↑ Elizabeth Montalbano. Microsoft FAT patents upheld (англ.). Computerworld (11 января 2006). Архивировано из первоисточника 5 июня 2012. Проверено 2 ноября 2008.
- ↑ Ryan Paul. Microsoft suit over FAT patents could open OSS Pandora’s Box (англ.). Ars Technica. Condé Nast Publications (25 февраля 2009). Архивировано из первоисточника 22 августа 2011. Проверено 9 марта 2009.
- ↑ После 26 января 2009 года она утратила смысл с вводом в обновлении KB955704 официальной поддержки данной файловой системы
- ↑ ricktendo64. exFAT File System Driver for XP/2k3, Ported from Vista. WinCert.net (28 августа 2007). Архивировано из первоисточника 1 марта 2012. Проверено 1 июля 2008.
- ↑ Microsoft лицензирует файловую систему exFAT для сторонних производителей. Ferra.ru (11 декабря 2009). Архивировано из первоисточника 1 марта 2012. Проверено 13 декабря 2009.
Ссылки
- TFAT Overview (англ.)
- Extended FAT File System (англ.)
- Обновление Windows XP (KB955704) для поддержки файловой системы exFAT
- Компания-разработчик NTFS-3G подписала соглашение с Microsoft, касающиеся exFAT
- Файловая система ExFAT — универсальное решение для Mac OS X и Windows
- Сравнение Fat32, NTFS, exFAT на флэш-носителях и внешних жестких дисках
| |
|
|---|---|
| Основные |
Aero • ClearType • Диспетчер рабочего стола • DirectX • Панель задач (Пуск • Область уведомлений) • Проводник (Пространство имён • Специальные папки • Ассоциации файлов) • Windows Search (Smart folders • iFilters) • GDI • WIM • SMB • .NET Framework • XPS • Active Scripting (WSH • VBScript • JScript) • COM (OLE • DCOM • ActiveX • Структурированное хранилище • Сервер транзакций) • Теневая копия • WDDM • UAA • Консоль Win32 |
| Службы управления |
Архивация и восстановление • COMMAND.COM • cmd.exe • Средство переноса данных • Просмотр событий • Установщик • netsh.exe • PowerShell • Отчёты о проблемах • rundll32.exe • Программа подготовки системы (Sysprep) • Настройка системы (MSConfig) • Проверка системных файлов • Индекс производительности • Центр обновления • Восстановление системы • Дефрагментация диска • Диспетчер задач • Диспетчер устройств • Консоль управления • Очистка диска • Панель управления (элементы) |
| Приложения |
Контакты • DVD Maker • Факсы и сканирование • Internet Explorer • Журнал • Экранная лупа • Media Center • Проигрыватель Windows Media • Программа совместной работы • Центр устройств Windows Mobile • Центр мобильности • Экранный диктор • Paint • Редактор личных символов • Удалённый помощник • Распознавание речи • WordPad • Блокнот • Боковая панель • Звукозапись • Календарь • Калькулятор • Ножницы • Почта • Таблица символов • Исторические: Movie Maker • NetMeeting • Outlook Express • Диспетчер программ • Диспетчер файлов • Фотоальбом |
| Игры |
Chess Titans • Mahjong Titans • Purble Place • Пасьянсы (Косынка • Паук • Солитер) • Сапёр • Пинбол • Червы |
| Ядро ОС |
Ntoskrnl.exe • Слой аппаратных абстракций (hal.dll) • Бездействие системы • svchost.exe • Реестр • Службы • Диспетчер управления сервисами • DLL (формат модулей) • PE • NTLDR • Диспетчер загрузки • Программа входа в систему (winlogon.exe) • Консоль восстановления • Windows RE • Windows PE • Защита ядра от изменений |
| Службы |
Autorun.inf • Фоновая интеллектуальная служба передачи • Файловая система стандартного журналирования • Отчёты об ошибках • Планировщик классов мультимедиа • Теневая копия • Планировщик задач • Беспроводная настройка |
| Файловые системы |
Protogon • NTFS (Жёсткая ссылка • Точка соединения • Точка монтирования • Точка повторной обработки • Символьная ссылка • TxF • EFS) • WinFS • FAT • exFAT • CDFS • UDF • DFS • IFS |
| Сервер |
Active Directory • Службы развёртывания • Служба репликации файлов • DNS • Домены • Перенаправление папок • Hyper-V • IIS • Media Services • MSMQ • Защита доступа к сети (NAP) • Службы печати для UNIX • Удалённое разностное сжатие • Службы удаленной установки • Служба управления правами • Перемещаемые профили пользователей • SharePoint • Диспетчер системных ресурсов • Удаленный рабочий стол • WSUS • Групповая политика • Координатор распределённых транзакций |
| Архитектура |
NT • Диспетчер объектов • Пакеты запроса ввода/вывода • Диспетчер транзакций ядра • Диспетчер логических дисков • Диспетчер учетных записей безопасности • Защита ресурсов • lsass.exe • csrss.exe • smss.exe • spoolsv.exe • Запуск |
| Безопасность |
BitLocker • Защитник • Предотвращение выполнения данных • Обязательный контроль целостности • Защищенный канал данных • UAC • UIPI • Брандмауэр • Центр обеспечения безопасности • Защита файлов |
| Совместимость |
Подсистема UNIX (Interix) • Виртуальная машина DOS • Windows on Windows • WOW64 |
| |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Дисковые |
ADFS • AdvFS • BeFS • Btrfs • EFS • ext • ext2 • ext3 • ext3cow • Next3 • ext4 • FAT • FATX • VFAT • FFS • Files-11 • GFS • HFS • HFS Plus • XFSX • HPFS • ISO 9660 • JFS • LFS • MFS (Macintosh) • MFS (Tivo) • Minix • MUFS • NWFS • NILFS • NSS • NTFS • Protogon (В разработке) • PFS • Qnx4fs • Qnx6fs • ReiserFS • Reiser4 • SFS • SpadFS • UFS • UFS2 • UDF • VxFS • WinFS • WAFL • XFS • ZFS • Больше…
|
||||||
| Распределённые (сетевые) |
AFS • OpenAFS • AFP • Ceph • DFS • GlusterFS • GPFS • Google File System • Lustre • NCP • NFS • POHMELFS • Hadoop • Kosmos • HAMMER • SMB (CIFS) • Больше… | ||||||
| Специальные |
cramfs • FUSE • Squashfs • UMSDOS • UnionFS • Больше…
|