- Минимальные
- Рекомендуемые
Минимальные системные требования
- Разрядность: x86 (32-bit) или x64 (64-bit)
- ЦП [CPU]: 1 GHz x86, 1.4 GHz x64
- Видеоадаптер [GPU]: Встроенная или дискретная
- Видеопамять [VRAM]: 32 Mb
- Винчестер [HDD]: 32 Gb
- Оперативная память [RAM]: 0.5 Gb
- Аудиокарта [AUDIO]: Любая
- Контроллер: Клавиатура, Мышь
- Интернет: Необходим для обновлений
- DirectX: —
- Разрешение экрана: SVGA 800×600
- Дополнительно: DVD/CD привод
Рекомендуемые системные требования
- Разрядность: x64 (64-bit)
- ЦП [CPU]: от 2 GHz
- Видеоадаптер [GPU]: 3D адаптер
- Винчестер [HDD]: 40 Gb
- Оперативная память [RAM]: 2 Gb
- Аудиокарта [AUDIO]: Любая
- Контроллер: Клавиатура, Мышь Microsoft Mouse
- Разрешение экрана: SVGA 800×600
- Дополнительно: DVD/CD привод или USB
Чтобы нужная нам ОС Виндовс сервер 2008 Р2 запустилась персональном компьютере, его системные характеристики должны являться примерно такими: CPU обязан являться 32-бит или 64-бит, со скоростью тактовой частоты 1.4 гигагерц. «Оперативки» желаемым сочетанием будет 0.5 Гб, это даст возможность работать за персональным компьютером. Объем винчестера должно быть хотя-бы 32 гигабайта.
| Version of the Windows NT operating system | |
 |
|

Screenshot of Windows Server 2008 showing the Server Manager application which is automatically opened when an administrator logs on. |
|
| Developer | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| OS family | Microsoft Windows |
| Source model |
|
| Released to manufacturing |
February 4, 2008; 15 years ago[1] |
| General availability |
February 27, 2008; 14 years ago[1] |
| Latest release | Service Pack 2 with March 19, 2019 or later update rollup (6.0.6003)[2] / March 19, 2019; 3 years ago |
| Marketing target | Business |
| Update method | Windows Update, Windows Server Update Services, SCCM |
| Platforms | IA-32, x86-64, Itanium |
| Kernel type | Hybrid (Windows NT kernel) |
| Default user interface |
Windows shell (Graphical) |
| License | Proprietary commercial software |
| Preceded by | Windows Server 2003 (2003) |
| Succeeded by | Windows Server 2008 R2 (2009) |
| Official website | Windows Server 2008 |
| Support status | |
| Mainstream support ended on January 13, 2015[3][4] Extended support ended on January 14, 2020[3][4] Windows Server 2008 is eligible for the paid ESU (Extended Security Updates) program.[5] This program allowed volume license customers to purchase, in yearly installments, security updates for the operating system until January 10, 2023,[3] only for Standard, Enterprise and Datacenter volume licensed editions. The updates are included with a Microsoft Azure purchase and Azure customers receive ESU updates until January 9, 2024.[6][5][7] Installing Service Pack 2 is required for users to receive updates and support after July 12, 2011[3][4] |
Windows Server 2008 is the fourth release of the Windows Server operating system produced by Microsoft as part of the Windows NT family of the operating systems. It was released to manufacturing on February 4, 2008, and generally to retail on February 27, 2008. Derived from Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008 is the successor of Windows Server 2003 and the predecessor to Windows Server 2008 R2.
Windows Server 2008 is the final version of Windows Server that supports IA-32-based processors (also known as 32-bit processors). Its successor, Windows Server 2008 R2, requires a 64-bit processor in any supported architecture (x86-64 for x86 and Itanium).
History[edit]
Microsoft had released Windows Vista to mixed reception, and their last Windows Server release was based on Windows XP. The operating system’s working title was Windows Server Codename «Longhorn», but was later changed to Windows Server 2008 when Microsoft chairman Bill Gates announced it during his keynote address at WinHEC on May 16, 2007.[8]
Beta 1 was released on July 27, 2005; Beta 2 was announced and released on May 23, 2006, at WinHEC 2006 and Beta 3 was released publicly on April 25, 2007.[9] Release Candidate 0 was released to the general public on September 24, 2007[10] and Release Candidate 1 was released to the general public on December 5, 2007. Windows Server 2008 was released to manufacturing on February 4, 2008, and officially launched on the 27th of that month.[11]
Features[edit]
Windows Server 2008 is built from the same codebase as Windows Vista and thus it shares much of the same architecture and functionality. Since the codebase is common, Windows Server 2008 inherits most of the technical, security, management and administrative features new to Windows Vista such as the rewritten networking stack (native IPv6, native wireless, speed and security improvements); improved image-based installation, deployment and recovery; improved diagnostics, monitoring, event logging and reporting tools; new security features such as BitLocker and address space layout randomization (ASLR); the improved Windows Firewall with secure default configuration; .NET Framework 3.0 technologies, specifically Windows Communication Foundation, Microsoft Message Queuing and Windows Workflow Foundation; and the core kernel, memory and file system improvements. Processors and memory devices are modeled as Plug and Play devices to allow hot-plugging of these devices. This allows the system resources to be partitioned dynamically using dynamic hardware partitioning — each partition has its own memory, processor and I/O host bridge devices independent of other partitions.[12]
Server Core[edit]
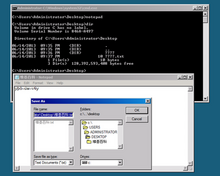
Windows Server 2008 includes a variation of installation called Server Core. Server Core is a significantly scaled-back installation where no Windows Explorer shell is installed. It also lacks Internet Explorer, and many other non-essential features. All configuration and maintenance is done entirely through command-line interface windows, or by connecting to the machine remotely using Microsoft Management Console (MMC). Notepad and some Control Panel applets, such as Regional Settings, are available.
A Server Core installation can be configured for several basic roles, including the domain controller (Active Directory Domain Services), Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services (formerly known as Active Directory Application Mode[13]), DNS Server, DHCP server, file server, print server, Windows Media Server, Internet Information Services 7 web server and Hyper-V virtual server roles. Server Core can also be used to create a cluster with high availability using failover clustering or network load balancing.
Andrew Mason, a program manager on the Windows Server team, noted that a primary motivation for producing a Server Core variant of Windows Server 2008 was to reduce the attack surface of the operating system, and that about 70% of the security vulnerabilities in Microsoft Windows from the prior five years would not have affected Server Core.[14]
Active Directory[edit]
The Active Directory domain functionality that was retained from Windows Server 2003 was renamed to Active Directory Domain Services (ADDS).[15]
- Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS) enables enterprises to share credentials with trusted partners and customers, allowing a consultant to use their company user name and password to log in on a client’s network.
- Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services (AD LDS), (formerly Active Directory Application Mode, or ADAM)
- Active Directory Certificate Services (ADCS) allow administrators to manage user accounts and the digital certificates that allow them to access certain services and systems. Identity Integration Feature Pack is included as Active Directory Metadirectory Services.
- Active Directory Rights Management Services (ADRMS)
- Read-only domain controllers (RODCs), intended for use in branch office or other scenarios where a domain controller may reside in a low physical security environment. The RODC holds a non-writeable copy of Active Directory, and redirects all write attempts to a full domain controller. It replicates all accounts except sensitive ones.[16] In RODC mode, credentials are not cached by default. Also, local administrators can be designated to log on to the machine to perform maintenance tasks without requiring administrative rights on the entire domain.[17]
- Restartable Active Directory allows ADDS to be stopped and restarted from the Management Console or the command-line without rebooting the domain controller. This reduces downtime for offline operations and reduces overall DC servicing requirements with Server Core. ADDS is implemented as a Domain Controller Service in Windows Server 2008.
- All of the Group Policy improvements from Windows Vista are included. Group Policy Management Console (GPMC) is built-in. The Group Policy objects are indexed for search and can be commented on.[18]
- Policy-based networking with Network Access Protection, improved branch management and enhanced end user collaboration. Policies can be created to ensure greater quality of service for certain applications or services that require prioritization of network bandwidth between client and server.
- Granular password settings within a single domain — ability to implement different password policies for administrative accounts on a «group» and «user» basis, instead of a single set of password settings to the whole domain.
Failover Clustering[edit]
Windows Server 2008 offers high availability to services and applications through Failover Clustering. Most server features and roles can be kept running with little to no downtime.
In Windows Server 2008, the way clusters are qualified changed significantly with the introduction of the cluster validation wizard.[19] The cluster validation wizard is a feature that is integrated into failover clustering in Windows Server 2008. With the cluster validation wizard, an administrator can run a set of focused tests on a collection of servers that are intended to use as nodes in a cluster. This cluster validation process tests the underlying hardware and software directly, and individually, to obtain an accurate assessment of how well failover clustering can be supported on a given configuration.
This feature is only available in Enterprise and Datacenter editions of Windows Server.
Disk management and file storage[edit]
- The ability to resize hard disk partitions without stopping the server, even the system partition. This applies only to simple and spanned volumes, not to striped volumes.
- Shadow Copy based block-level backup which supports optical media, network shares and Windows Recovery Environment.
- DFS enhancements — SYSVOL on DFS-R, Read-only Folder Replication Member. There is also support for domain-based DFS namespaces that exceed the previous size recommendation of 5,000 folders with targets in a namespace.[20]
- Several improvements to Failover Clustering (high-availability clusters).[21]
- Internet Storage Naming Server (iSNS) enables central registration, deregistration and queries for iSCSI hard drives.
- Self-healing NTFS: In Windows versions prior to Windows Vista, if the operating system detected corruption in the file system of an NTFS volume, it marked the volume «dirty»; to correct errors on the volume, it had to be taken offline. With self-healing NTFS, an NTFS worker thread is spawned in the background which performs a localized fix-up of damaged data structures, with only the corrupted files/folders remaining unavailable without locking out the entire volume and needing the server to be taken down. S.M.A.R.T. detection techniques were added to help determine when a hard disk may fail.[22]
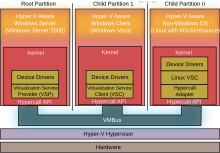
Hyper-V[edit]
Hyper-V is hypervisor-based virtualization software, forming a core part of Microsoft’s virtualization strategy. It virtualizes servers on an operating system’s kernel layer. It can be thought of as partitioning a single physical server into multiple small computational partitions. Hyper-V includes the ability to act as a Xen virtualization hypervisor host allowing Xen-enabled guest operating systems to run virtualized.[23] A beta version of Hyper-V shipped with certain x86-64 editions of Windows Server 2008, prior to Microsoft’s release of the final version of Hyper-V on 26 June 2008 as a free download. Also, a standalone variant of Hyper-V exists; this variant supports only x86-64 architecture.[24] While the IA-32 editions of Windows Server 2008 cannot run or install Hyper-V, they can run the MMC snap-in for managing Hyper-V.
Windows System Resource Manager[edit]
Windows System Resource Manager (WSRM) is integrated into Windows Server 2008. It provides resource management and can be used to control the amount of resources a process or a user can use based on business priorities. Process Matching Criteria, which is defined by the name, type or owner of the process, enforces restrictions on the resource usage by a process that matches the criteria. CPU time, bandwidth that it can use, number of processors it can be run on, and allocated to a process can be restricted. Restrictions can be set to be imposed only on certain dates as well.
Server Manager[edit]
Server Manager is a new roles-based management tool for Windows Server 2008.[25] It is a combination of Manage Your Server and Security Configuration Wizard from Windows Server 2003. Server Manager is an improvement of the Configure my server dialog that launches by default on Windows Server 2003 machines. However, rather than serve only as a starting point to configuring new roles, Server Manager gathers together all of the operations users would want to conduct on the server, such as, getting a remote deployment method set up, adding more server roles etc., and provides a consolidated, portal-like view about the status of each role.[26]
Protocol and cryptography[edit]
- Support for 128- and 256-bit AES encryption for the Kerberos authentication protocol.
- New cryptography (CNG) API which supports elliptic curve cryptography and improved certificate management.
- Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol, a new Microsoft proprietary VPN protocol.
- AuthIP, a Microsoft proprietary extension of the IKE cryptographic protocol used in IPsec VPN networks.
- Server Message Block 2.0 protocol in the new TCP/IP stack provides a number of communication enhancements, including greater performance when connecting to file shares over high-latency links and better security through the use of mutual authentication and message signing.
Miscellaneous[edit]
- Fully componentized operating system.
- Improved hot patching, a feature that allows non-kernel patches to occur without the need for a reboot.
- Support for being booted from Extensible Firmware Interface (EFI)-compliant firmware on x86-64 systems.
- Dynamic Hardware Partitioning supports hot-addition or replacement of processors and memory, on capable hardware.
- Windows Deployment Services (WDS) replacing Automated Deployment Services Windows Server 2008 home entertainment and Remote Installation Services. Windows Deployment Services supports an enhanced multicast feature when deploying operating system images.[27]
- Internet Information Services 7 — Increased security, Robocopy deployment, improved diagnostic tools, delegated administration.
- Windows Internal Database, a variant of SQL Server Express 2005, which serves as a common storage back-end for several other components such as Windows System Resource Manager, Windows SharePoint Services and Windows Server Update Services. It is not intended to be used by third-party applications.
- An optional «desktop experience» component provides the same Windows Aero user interface as Windows Vista, both for local users, as well as remote users connecting through Remote Desktop.
Removed features[edit]
- The Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol component in Routing and Remote Access Service was removed.[28]
- Services for Macintosh, which provided file and print sharing via the now deprecated AppleTalk protocol, has been removed. Services for Macintosh were initially removed in Windows XP but were available in Windows Server 2003.[28]
- NTBackup is replaced by Windows Server Backup, and no longer supports backing up to tape drives.[29] As a result of NTBackup removal, Exchange Server 2007 does not have volume snapshot backup functionality; however Exchange Server 2007 SP2 adds back an Exchange backup plug-in for Windows Server Backup which restores partial functionality.[30] Windows Small Business Server and Windows Essential Business Server both include this Exchange backup component.[31]
- The POP3 service has been removed from Internet Information Services 7.0.[32] The SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) service is not available as a server role in IIS 7.0, it is a server feature managed through IIS 6.0.
- NNTP (Network News Transfer Protocol) is no longer part of Internet Information Services 7.0.
- ReadyBoost, which is available in Windows Vista, is not supported in Windows Server 2008.
Editions[edit]
Installation disc of Enterprise edition (beta 3)
Most editions of Windows Server 2008 are available in x86-64 and IA-32 variants. These editions come in two DVDs: One for installing the IA-32 variant and the other for x64. Windows Server 2008 for Itanium-based Systems supports IA-64 processors. The IA-64 variant is optimized for high-workload scenarios like database servers and Line of Business (LOB) applications. As such, it is not optimized for use as a file server or media server. Windows Server 2008 is the last 32-bit Windows server operating system.[33]
Editions of Windows Server 2008 include:[34]
- Windows Server 2008 Foundation (codenamed «Lima»; x86-64) for OEMs only[35]
- Windows Server 2008 Standard (IA-32 and x86-64)
- Windows Server 2008 Enterprise (IA-32 and x86-64)
- Windows Server 2008 Datacenter (IA-32 and x86-64)
- Windows Server 2008 for Itanium-based Systems (IA-64)
- Windows Web Server 2008 (IA-32 and x86-64)
- Windows HPC Server 2008 (codenamed «Socrates»; replacing Windows Compute Cluster Server)
- Windows Storage Server 2008 (codenamed «Magni»; IA-32 and x86-64)
- Windows Small Business Server 2008 (codenamed «Cougar»; x86-64) for small businesses
- Windows Essential Business Server 2008 (codenamed «Centro»; x86-64) for medium-sized businesses[36] — this edition was discontinued in 2010.[37]
The Microsoft Imagine program, known as DreamSpark at the time, used to provide verified students with the 32-bit variant of Windows Server 2008 Standard Edition, but the version has since then been removed. However, they still provide the R2 release.
The Server Core feature is available in the Web, Standard, Enterprise and Datacenter editions.
Windows Server 2008 Foundation Released on May 21, 2009.[38]
System requirements[edit]
System requirements for Windows Server 2008 are as follows:
| Criteria | 2008 | 2008 R2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum[39] | Recommended[39] | Minimum[40] | Recommended[40] | |
| CPU |
|
2 GHz or faster | 1.4 GHz (x86-64 or Itanium) | 2 GHz or faster |
| RAM | 512 MB | 2 GB or greater | 512 MB | 2 GB or greater |
| HDD[a] |
|
40 GB or greater |
|
|
| Devices | DVD drive, 800 × 600 or higher display, keyboard and mouse |
Scalability[edit]
Windows Server 2008 supports the following maximum hardware specifications:[42][43][44]
| Specification | Windows Server 2008 SP2 | Windows Server 2008 R2 |
|---|---|---|
| Physical processors («sockets»)[43] |
|
|
| Logical processors when Hyper-V is disabled[43] |
|
256 |
| Logical processors when Hyper-V is enabled[43] |
|
64 |
| Memory on IA-32[44] |
|
— |
| Memory on x64[44] |
|
|
| Memory on Itanium[44] |
2 TB |
Updates[edit]
Windows Server 2008 shares most of its updates with Windows Vista, given that the operating systems share a codebase. A workaround using the Microsoft Update Catalog allowed the installation of updates for Windows Server 2008 on Windows Vista,[45] adding nearly 3 years of security updates to that operating system (Support for Windows Vista ended on April 11, 2017,[46] while support for Windows Server 2008 ended on January 14, 2020).
Service Pack 2[edit]
The RTM release of Windows Server 2008 already includes the updates and fixes of Windows Vista Service Pack 1.
Service Pack 2 was initially announced on October 24, 2008[47] and released on May 26, 2009. Service Pack 2 added new features, such as Windows Search 4.0, support for Bluetooth 2.1, the ability to write to Blu-ray discs, and simpler Wi-Fi configuration. Windows Server 2008 specifically received the final release of Hyper-V 1.0, improved backwards compatibility with Terminal Server license keys and an approximate 10% reduction in power usage with this service pack.[48]
Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008 share the same service pack update binary.[49]
Platform Update[edit]
On October 27, 2009, Microsoft released the Platform Update for Windows Server 2008 and Windows Vista. It backports several APIs and libraries introduced in Windows Server 2008 R2 and Windows 7 to Windows Server 2008 and Windows Vista, including the Ribbon API, DirectX 11, the XPS library, the Windows Automation API and the Portable Device Platform.[50] A supplemental update was released in 2011 to provide improvements and bug fixes.[51]
Internet Explorer 9[edit]
Windows Server 2008 shipped with Internet Explorer 7, the same version that shipped with Windows Vista. The last supported version of Internet Explorer for Windows Server 2008 is Internet Explorer 9, released in 2011. Internet Explorer 9 was continually updated with cumulative monthly update rollups until support for Internet Explorer 9 on Windows Server 2008 ended on January 14, 2020.[52] Extended Security Updates (ESU) continue until January 9, 2024 for Azure customers.
.NET Framework[edit]
The latest supported version of the .NET Framework officially is version 4.6, released on October 15, 2015.[53]
TLS 1.1 and 1.2 support[edit]
In July 2017, Microsoft released an update to add TLS 1.1 and 1.2 support to Windows Server 2008, however it is disabled by default after installing the update.[54]
SHA-2 signing support[edit]
Starting in March 2019, Microsoft began transitioning to exclusively signing Windows updates with the SHA-2 algorithm. As a result of this Microsoft released several updates throughout 2019 to add SHA-2 signing support to Windows Server 2008.[55]
Monthly update rollups[edit]
In June 2018, Microsoft announced that they would be moving Windows Server 2008 to a monthly update model beginning with updates released in September 2018[56] — two years after Microsoft switched the rest of their supported operating systems to that model.[57]
With the new update model, instead of updates being released as they became available, only two update packages were released on the second Tuesday of every month until Windows Server 2008 reached its end of life — one package containing security and quality updates, and a smaller package that contained only the security updates. Users could choose which package they wanted to install each month. Later in the month, another package would be released which was a preview of the next month’s security and quality update rollup.
Installing the preview rollup package released for Windows Server 2008 on March 19, 2019, or any later released rollup package, will update the operating system kernel’s build number from version 6.0.6002 to 6.0.6003. This change was made so Microsoft could continue to service the operating system while avoiding “version-related issues”.[58]
The last free security update rollup packages were released on January 14, 2020.[59]
Windows Server 2008 R2[edit]
A second release of Windows Server 2008 based on Windows 7, Windows Server 2008 R2, was released to manufacturing on July 22, 2009[60] and became generally available on October 22, 2009.[61] New features added in Windows Server 2008 R2 include new virtualization features, new Active Directory features, Internet Information Services 7.5 and support for up to 256 logical processors. It is the first server operating system by Microsoft to exclusively support 64-bit processors, while consumer-oriented versions of Windows maintained 32-bit support until Windows 11 in 2021.
A service pack for Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2, formally designed Service Pack 1, was released in February 2011.[62]
Support lifecycle[edit]
Support for the RTM version of Windows Server 2008 ended on July 12, 2011,[3][4] and users can no longer receive further security updates for the operating system. As a component of Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008 with Service Pack 2 continued to be supported with security updates, lasting until January 14, 2020, the same respective end-of-life dates of its successor, Windows Server 2008 R2 and Windows 7.
Microsoft planned to end support for Windows Server 2008 on January 12, 2016. However, in order to give customers more time to migrate to newer Windows versions, particularly in developing or emerging markets, Microsoft decided to extend support to January 14, 2020.[6][5][7]
Windows Server 2008 is eligible for the paid Extended Security Updates (ESU) program. The program allowed volume license customers to purchase, in yearly installments, security updates for the operating system for three additional years, until January 10, 2023. The program is also included with Microsoft Azure purchases, and Azure customers receive an extra year of support, until January 9, 2024. The licenses are paid for on a per-machine basis. If a user purchases an Extended Security Updates license in a later year of the program, they must pay for any previous years of Extended Security Updates as well. [6][63]
See also[edit]
- BlueKeep (security vulnerability)
- Comparison of Microsoft Windows versions
- Comparison of operating systems
- History of Microsoft Windows
- List of operating systems
- Microsoft Servers
Notes[edit]
- ^ Computers with more than 16 GB of RAM require more disk space for paging, hibernation, and dump files[40]
References[edit]
- ^ a b «As Windows Server 2008 RTMs, Customers and Partners Adopting with Help of New Tools, Training». News Center. Redmond, WA: Microsoft. 4 February 2008.
- ^ «Build number changing to 6003 in Windows Server 2008». support.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2021-03-26.
- ^ a b c d e «Microsoft Product Lifecycle». Support. Microsoft. Retrieved April 12, 2022.
- ^ a b c d «Install Windows Vista Service Pack 2 (SP2)». Support. Microsoft. Retrieved April 12, 2010.
- ^ a b c «Extended Security Updates for SQL Server and Windows Server 2008 and 2008 R2 | Microsoft». www.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2021-03-26.
- ^ a b c tfosmark. «Product Lifecycle FAQ — Extended Security Updates — Microsoft Lifecycle». docs.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2021-03-26.
- ^ a b «Announcing new options for SQL Server 2008 and Windows Server 2008 End of Support». azure.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2021-03-26.
- ^ Miller, Michael J. (2007-05-15). «Gates at WinHec 2007: Windows Server 2008, Rally, Home Server and More». Forward Thinking. Retrieved 2007-07-09.
- ^ Lowe, David (2007-04-25). «Beta 3 is Go!». Windows Server Division WebLog. Microsoft. Retrieved 2007-04-25.
- ^ Ralston, Ward (2007-09-24). «Windows Server 2008 Rc0 Released!». Windows Server Division WebLog. Microsoft. Retrieved 2007-09-24.
- ^ Nate Mook (10 July 2007). «New Windows Server, Visual Studio, SQL Server to Launch in February». BetaNews. Retrieved 2007-07-11.
- ^ «Dynamic Hardware Partitioning Architecture». MSDN. Retrieved 2007-07-23.
- ^ Archiveddocs. «Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services Overview». docs.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2020-01-15.
- ^ «Iain McDonald and Andrew Mason show off the new Windows Server OS». Channel 9. Microsoft. May 24, 2006. Retrieved 2008-11-01.
18:55
- ^ Hynes, Byron (November 2006). «The Future of Windows: Directory Services in Windows Server 2008». TechNet Magazine. Retrieved 2007-05-02.
- ^ «Deploying Windows Server 2008 Read Only Domain Controllers». docs.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2020-01-15.
- ^ «Q. What is a read-only domain controller (RODC)?». IT Pro. 2008-03-24. Retrieved 2020-01-15.
- ^ Ward, Keith (2007-10-08). «Top 10 Overlooked Windows Server 2008 Features, Part 2». Redmond Developer News. Archived from the original on 2009-08-04. Retrieved 2014-10-10.
- ^ «Failover Cluster Validation Error 80070005 on Windows Server 2008 R2 x64». Capitalhead. 2009-11-04. Retrieved 2013-10-28.
- ^ Zoeller, Jill (26 July 2007). «New in Windows Server 2008: Breaking the 5K Folder «Barrier» in Domain-Based Namespaces». The Storage Team at Microsoft — File Cabinet Blog. Microsoft. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- ^ «Failover Clustering with Windows Server 2008 including Cluster shared volumes». Microsoft. 2007-01-17. Retrieved 2007-07-09.
- ^ Loveall, John (2006). «Storage improvements in Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008» (PowerPoint). Microsoft Corporation. Retrieved 2007-07-09.
- ^ «Benchmarking Hyper-V on Windows Server 2008 R2 x64». 2010-01-20. Retrieved 2010-01-28.
- ^ «Microsoft Extends Virtualization Strategy, Outlines Product Road Map». Microsoft. 2006-05-22. Retrieved 2007-07-09.
- ^ «Server Manager». Windows Server 2008 Technical Library. Microsoft TechNet. 2007-06-25. Retrieved 2007-05-02.
- ^ «Unexpected error refreshing Server Manager-0x800706BE and 1601 on Window Server 2008 R2». Retrieved 2010-11-05.
- ^ «Multicasting OS deployments with Windows Server 2008». Kevinsul’s Management Blog. Microsoft. 29 August 2007. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- ^ a b «Removed technologies in Routing and Remote Access in Windows Server 2008». TechNet. Microsoft. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- ^ «Windows Server Backup Step-by-Step Guide for Windows Server 2008». TechNet. Microsoft. 17 January 2013. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- ^ «Exchange Server 2007 Service Pack 2 available in Q3 2009». The Exchange Team Blog. 11 May 2009. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- ^ Bilic, Nino (18 June 2008). «To Backup or Not to Backup? Yes! To backup!!». The Exchange Team Blog. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- ^ «IIS 7.0 Protocols». TechNet. Microsoft. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- ^ Heaton, Alex (2007-05-18). «On 64-bit and Windows Client». Windows Vista Team Blog. Retrieved 2007-07-09.
- ^
«Windows Server 2008 Product Editions». Microsoft. 2007-04-25. Retrieved 2007-07-09. - ^ «Windows Server 2008 Foundation: An Entry-Level Server Platform». Petri IT Knowledgebase. 2009-04-17. Retrieved 2014-01-08.
- ^ Ligman, Eric (7 November 2007). «Announcing Windows Essential Business Server». Microsoft Small Business Blog. Microsoft. Retrieved 2013-08-16.
- ^ «Windows Essential Business Server 2008». Technet.microsoft.com. 2010-12-31. Retrieved 2013-01-09.
- ^ «Windows Server 2008, Microsoft Lifecycle (Look at the Note below links)». docs.microsoft.com/en-us/lifecycle/products/.
- ^ a b «Windows Server 2008 System Requirements». 31 March 2008. Retrieved 2008-03-31.
- ^ a b c «Microsoft Windows Server 2008 System Requirements». Microsoft.com. Retrieved 2013-01-09.
- ^ «Microsoft Windows Server 2008 System Requirements». Microsoft. Retrieved 2013-01-09.
- ^ Savill, John (October 28, 2011). «Q: What are Windows Server 8’s Scalability Numbers?». Windows IT Pro. Penton Media. Retrieved November 5, 2011.
- ^ a b c d Seldam, Matthijs ten (October 13, 2012). «Windows Server — Sockets, Logical Processors, Symmetric Multi Threading». Matthijs’s blog. Microsoft. Retrieved October 14, 2012.
- ^ a b c d «Memory Limits for Windows and Windows Server Releases». MSDN. Microsoft. Retrieved 13 April 2014.
- ^ «Extend Windows Vista support by installing Windows Server 2008 updates — gHacks Tech News». gHacks Technology News. 2017-06-24. Retrieved 2021-06-30.
- ^ «Windows Vista Lifecycle Policy». Microsoft. Retrieved January 2, 2017.
- ^ Justin Graham (October 24, 2008). «Windows Server 2008 Service Pack 2 beta». Microsoft. Retrieved 2008-10-29.
- ^ «Tech ARP — ED#107 : Latest Details on Windows Vista Service Pack 2 Rev. 2.2». Archived from the original on 2009-02-12.
- ^ «Windows Vista Service Pack 2 Beta». blogs.windows.com. Archived from the original on 9 May 2013. Retrieved 12 January 2022.
- ^ «Announcing Final Releases of Platform Update for Windows Vista Technologies». 27 October 2009.
- ^ «Platform Update Supplement for Windows Vista and for Windows Server 2008».
- ^ «Cumulative security update for Internet Explorer: January 14, 2020». support.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2021-03-26.
- ^ «Microsoft .NET Framework 4.6 (Web Installer)». Microsoft.
- ^ «TLS 1.2 Support added to Windows Server 2008». Microsoft Security. 2017-07-20. Retrieved 2021-03-26.
- ^ «2019 SHA-2 Code Signing Support requirement for Windows and WSUS».
- ^ Mackie, Kurt; 06/13/2018. «Microsoft Switching Windows Server 2008 SP2 to Monthly Update Rollup Model — Redmondmag.com». Redmondmag. Retrieved 2021-03-26.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ «Community». forums.ivanti.com. Retrieved 2021-03-26.
- ^ «Build number changing to 6003 in Windows Server 2008».
- ^ «January 14, 2020—KB4534303 (Monthly Rollup)». support.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2021-03-26.
- ^ «Windows Server 2008 R2 Reaches the RTM Milestone! — Windows Server Blog — Site Home — TechNet Blogs». Blogs.technet.com. 2009-07-22. Retrieved 2013-01-09.
- ^ «When to expect Windows Server 2008 R2 RTM — Windows Server Blog — Site Home — TechNet Blogs». Blogs.technet.com. 2009-07-22. Retrieved 2013-01-09.
- ^ LeBlanc, Brandon (February 9, 2011). «Announcing Availability of Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1». Windows Experience Blog. Microsoft.
- ^ «Windows Server 2008 Product Lifecycle». Microsoft. January 14, 2020. Retrieved January 9, 2022.
18:55
Further reading[edit]
- «What’s New in Networking». TechNet. Microsoft. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- «Changes in Functionality from Windows Server 2003 with SP1 to Windows Server 2008». TechNet. Microsoft. 21 January 2008. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- «Description of the Microsoft server applications that are supported on Windows Server 2008». Support. Microsoft. 23 April 2012. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- «Windows Server 2008 System Requirements». TechNet. Microsoft. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- Henderson, Tom; Dvorak, Rand (21 February 2008). «Windows Server 2008: Faster, more manageable and secure, but still missing the virtual link». Network World. IDG. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- Radzikowski, Przemek (21 February 2010). «How to Find Build and Revision Number of Windows Vista or Windows Server 2008 Installed». Capitalhead. Capitalhead Pty. Ltd. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- Stanek, William (2008). Windows Server 2008 Inside Out. Microsoft Press. ISBN 978-0-7356-2438-2.
External links[edit]
- Windows Server Performance Team Blog
| Version of the Windows NT operating system | |
 |
|

Screenshot of Windows Server 2008 showing the Server Manager application which is automatically opened when an administrator logs on. |
|
| Developer | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| OS family | Microsoft Windows |
| Source model |
|
| Released to manufacturing |
February 4, 2008; 15 years ago[1] |
| General availability |
February 27, 2008; 14 years ago[1] |
| Latest release | Service Pack 2 with March 19, 2019 or later update rollup (6.0.6003)[2] / March 19, 2019; 3 years ago |
| Marketing target | Business |
| Update method | Windows Update, Windows Server Update Services, SCCM |
| Platforms | IA-32, x86-64, Itanium |
| Kernel type | Hybrid (Windows NT kernel) |
| Default user interface |
Windows shell (Graphical) |
| License | Proprietary commercial software |
| Preceded by | Windows Server 2003 (2003) |
| Succeeded by | Windows Server 2008 R2 (2009) |
| Official website | Windows Server 2008 |
| Support status | |
| Mainstream support ended on January 13, 2015[3][4] Extended support ended on January 14, 2020[3][4] Windows Server 2008 is eligible for the paid ESU (Extended Security Updates) program.[5] This program allowed volume license customers to purchase, in yearly installments, security updates for the operating system until January 10, 2023,[3] only for Standard, Enterprise and Datacenter volume licensed editions. The updates are included with a Microsoft Azure purchase and Azure customers receive ESU updates until January 9, 2024.[6][5][7] Installing Service Pack 2 is required for users to receive updates and support after July 12, 2011[3][4] |
Windows Server 2008 is the fourth release of the Windows Server operating system produced by Microsoft as part of the Windows NT family of the operating systems. It was released to manufacturing on February 4, 2008, and generally to retail on February 27, 2008. Derived from Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008 is the successor of Windows Server 2003 and the predecessor to Windows Server 2008 R2.
Windows Server 2008 is the final version of Windows Server that supports IA-32-based processors (also known as 32-bit processors). Its successor, Windows Server 2008 R2, requires a 64-bit processor in any supported architecture (x86-64 for x86 and Itanium).
History[edit]
Microsoft had released Windows Vista to mixed reception, and their last Windows Server release was based on Windows XP. The operating system’s working title was Windows Server Codename «Longhorn», but was later changed to Windows Server 2008 when Microsoft chairman Bill Gates announced it during his keynote address at WinHEC on May 16, 2007.[8]
Beta 1 was released on July 27, 2005; Beta 2 was announced and released on May 23, 2006, at WinHEC 2006 and Beta 3 was released publicly on April 25, 2007.[9] Release Candidate 0 was released to the general public on September 24, 2007[10] and Release Candidate 1 was released to the general public on December 5, 2007. Windows Server 2008 was released to manufacturing on February 4, 2008, and officially launched on the 27th of that month.[11]
Features[edit]
Windows Server 2008 is built from the same codebase as Windows Vista and thus it shares much of the same architecture and functionality. Since the codebase is common, Windows Server 2008 inherits most of the technical, security, management and administrative features new to Windows Vista such as the rewritten networking stack (native IPv6, native wireless, speed and security improvements); improved image-based installation, deployment and recovery; improved diagnostics, monitoring, event logging and reporting tools; new security features such as BitLocker and address space layout randomization (ASLR); the improved Windows Firewall with secure default configuration; .NET Framework 3.0 technologies, specifically Windows Communication Foundation, Microsoft Message Queuing and Windows Workflow Foundation; and the core kernel, memory and file system improvements. Processors and memory devices are modeled as Plug and Play devices to allow hot-plugging of these devices. This allows the system resources to be partitioned dynamically using dynamic hardware partitioning — each partition has its own memory, processor and I/O host bridge devices independent of other partitions.[12]
Server Core[edit]
Windows Server 2008 includes a variation of installation called Server Core. Server Core is a significantly scaled-back installation where no Windows Explorer shell is installed. It also lacks Internet Explorer, and many other non-essential features. All configuration and maintenance is done entirely through command-line interface windows, or by connecting to the machine remotely using Microsoft Management Console (MMC). Notepad and some Control Panel applets, such as Regional Settings, are available.
A Server Core installation can be configured for several basic roles, including the domain controller (Active Directory Domain Services), Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services (formerly known as Active Directory Application Mode[13]), DNS Server, DHCP server, file server, print server, Windows Media Server, Internet Information Services 7 web server and Hyper-V virtual server roles. Server Core can also be used to create a cluster with high availability using failover clustering or network load balancing.
Andrew Mason, a program manager on the Windows Server team, noted that a primary motivation for producing a Server Core variant of Windows Server 2008 was to reduce the attack surface of the operating system, and that about 70% of the security vulnerabilities in Microsoft Windows from the prior five years would not have affected Server Core.[14]
Active Directory[edit]
The Active Directory domain functionality that was retained from Windows Server 2003 was renamed to Active Directory Domain Services (ADDS).[15]
- Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS) enables enterprises to share credentials with trusted partners and customers, allowing a consultant to use their company user name and password to log in on a client’s network.
- Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services (AD LDS), (formerly Active Directory Application Mode, or ADAM)
- Active Directory Certificate Services (ADCS) allow administrators to manage user accounts and the digital certificates that allow them to access certain services and systems. Identity Integration Feature Pack is included as Active Directory Metadirectory Services.
- Active Directory Rights Management Services (ADRMS)
- Read-only domain controllers (RODCs), intended for use in branch office or other scenarios where a domain controller may reside in a low physical security environment. The RODC holds a non-writeable copy of Active Directory, and redirects all write attempts to a full domain controller. It replicates all accounts except sensitive ones.[16] In RODC mode, credentials are not cached by default. Also, local administrators can be designated to log on to the machine to perform maintenance tasks without requiring administrative rights on the entire domain.[17]
- Restartable Active Directory allows ADDS to be stopped and restarted from the Management Console or the command-line without rebooting the domain controller. This reduces downtime for offline operations and reduces overall DC servicing requirements with Server Core. ADDS is implemented as a Domain Controller Service in Windows Server 2008.
- All of the Group Policy improvements from Windows Vista are included. Group Policy Management Console (GPMC) is built-in. The Group Policy objects are indexed for search and can be commented on.[18]
- Policy-based networking with Network Access Protection, improved branch management and enhanced end user collaboration. Policies can be created to ensure greater quality of service for certain applications or services that require prioritization of network bandwidth between client and server.
- Granular password settings within a single domain — ability to implement different password policies for administrative accounts on a «group» and «user» basis, instead of a single set of password settings to the whole domain.
Failover Clustering[edit]
Windows Server 2008 offers high availability to services and applications through Failover Clustering. Most server features and roles can be kept running with little to no downtime.
In Windows Server 2008, the way clusters are qualified changed significantly with the introduction of the cluster validation wizard.[19] The cluster validation wizard is a feature that is integrated into failover clustering in Windows Server 2008. With the cluster validation wizard, an administrator can run a set of focused tests on a collection of servers that are intended to use as nodes in a cluster. This cluster validation process tests the underlying hardware and software directly, and individually, to obtain an accurate assessment of how well failover clustering can be supported on a given configuration.
This feature is only available in Enterprise and Datacenter editions of Windows Server.
Disk management and file storage[edit]
- The ability to resize hard disk partitions without stopping the server, even the system partition. This applies only to simple and spanned volumes, not to striped volumes.
- Shadow Copy based block-level backup which supports optical media, network shares and Windows Recovery Environment.
- DFS enhancements — SYSVOL on DFS-R, Read-only Folder Replication Member. There is also support for domain-based DFS namespaces that exceed the previous size recommendation of 5,000 folders with targets in a namespace.[20]
- Several improvements to Failover Clustering (high-availability clusters).[21]
- Internet Storage Naming Server (iSNS) enables central registration, deregistration and queries for iSCSI hard drives.
- Self-healing NTFS: In Windows versions prior to Windows Vista, if the operating system detected corruption in the file system of an NTFS volume, it marked the volume «dirty»; to correct errors on the volume, it had to be taken offline. With self-healing NTFS, an NTFS worker thread is spawned in the background which performs a localized fix-up of damaged data structures, with only the corrupted files/folders remaining unavailable without locking out the entire volume and needing the server to be taken down. S.M.A.R.T. detection techniques were added to help determine when a hard disk may fail.[22]
Hyper-V[edit]
Hyper-V is hypervisor-based virtualization software, forming a core part of Microsoft’s virtualization strategy. It virtualizes servers on an operating system’s kernel layer. It can be thought of as partitioning a single physical server into multiple small computational partitions. Hyper-V includes the ability to act as a Xen virtualization hypervisor host allowing Xen-enabled guest operating systems to run virtualized.[23] A beta version of Hyper-V shipped with certain x86-64 editions of Windows Server 2008, prior to Microsoft’s release of the final version of Hyper-V on 26 June 2008 as a free download. Also, a standalone variant of Hyper-V exists; this variant supports only x86-64 architecture.[24] While the IA-32 editions of Windows Server 2008 cannot run or install Hyper-V, they can run the MMC snap-in for managing Hyper-V.
Windows System Resource Manager[edit]
Windows System Resource Manager (WSRM) is integrated into Windows Server 2008. It provides resource management and can be used to control the amount of resources a process or a user can use based on business priorities. Process Matching Criteria, which is defined by the name, type or owner of the process, enforces restrictions on the resource usage by a process that matches the criteria. CPU time, bandwidth that it can use, number of processors it can be run on, and allocated to a process can be restricted. Restrictions can be set to be imposed only on certain dates as well.
Server Manager[edit]
Server Manager is a new roles-based management tool for Windows Server 2008.[25] It is a combination of Manage Your Server and Security Configuration Wizard from Windows Server 2003. Server Manager is an improvement of the Configure my server dialog that launches by default on Windows Server 2003 machines. However, rather than serve only as a starting point to configuring new roles, Server Manager gathers together all of the operations users would want to conduct on the server, such as, getting a remote deployment method set up, adding more server roles etc., and provides a consolidated, portal-like view about the status of each role.[26]
Protocol and cryptography[edit]
- Support for 128- and 256-bit AES encryption for the Kerberos authentication protocol.
- New cryptography (CNG) API which supports elliptic curve cryptography and improved certificate management.
- Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol, a new Microsoft proprietary VPN protocol.
- AuthIP, a Microsoft proprietary extension of the IKE cryptographic protocol used in IPsec VPN networks.
- Server Message Block 2.0 protocol in the new TCP/IP stack provides a number of communication enhancements, including greater performance when connecting to file shares over high-latency links and better security through the use of mutual authentication and message signing.
Miscellaneous[edit]
- Fully componentized operating system.
- Improved hot patching, a feature that allows non-kernel patches to occur without the need for a reboot.
- Support for being booted from Extensible Firmware Interface (EFI)-compliant firmware on x86-64 systems.
- Dynamic Hardware Partitioning supports hot-addition or replacement of processors and memory, on capable hardware.
- Windows Deployment Services (WDS) replacing Automated Deployment Services Windows Server 2008 home entertainment and Remote Installation Services. Windows Deployment Services supports an enhanced multicast feature when deploying operating system images.[27]
- Internet Information Services 7 — Increased security, Robocopy deployment, improved diagnostic tools, delegated administration.
- Windows Internal Database, a variant of SQL Server Express 2005, which serves as a common storage back-end for several other components such as Windows System Resource Manager, Windows SharePoint Services and Windows Server Update Services. It is not intended to be used by third-party applications.
- An optional «desktop experience» component provides the same Windows Aero user interface as Windows Vista, both for local users, as well as remote users connecting through Remote Desktop.
Removed features[edit]
- The Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol component in Routing and Remote Access Service was removed.[28]
- Services for Macintosh, which provided file and print sharing via the now deprecated AppleTalk protocol, has been removed. Services for Macintosh were initially removed in Windows XP but were available in Windows Server 2003.[28]
- NTBackup is replaced by Windows Server Backup, and no longer supports backing up to tape drives.[29] As a result of NTBackup removal, Exchange Server 2007 does not have volume snapshot backup functionality; however Exchange Server 2007 SP2 adds back an Exchange backup plug-in for Windows Server Backup which restores partial functionality.[30] Windows Small Business Server and Windows Essential Business Server both include this Exchange backup component.[31]
- The POP3 service has been removed from Internet Information Services 7.0.[32] The SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) service is not available as a server role in IIS 7.0, it is a server feature managed through IIS 6.0.
- NNTP (Network News Transfer Protocol) is no longer part of Internet Information Services 7.0.
- ReadyBoost, which is available in Windows Vista, is not supported in Windows Server 2008.
Editions[edit]
Installation disc of Enterprise edition (beta 3)
Most editions of Windows Server 2008 are available in x86-64 and IA-32 variants. These editions come in two DVDs: One for installing the IA-32 variant and the other for x64. Windows Server 2008 for Itanium-based Systems supports IA-64 processors. The IA-64 variant is optimized for high-workload scenarios like database servers and Line of Business (LOB) applications. As such, it is not optimized for use as a file server or media server. Windows Server 2008 is the last 32-bit Windows server operating system.[33]
Editions of Windows Server 2008 include:[34]
- Windows Server 2008 Foundation (codenamed «Lima»; x86-64) for OEMs only[35]
- Windows Server 2008 Standard (IA-32 and x86-64)
- Windows Server 2008 Enterprise (IA-32 and x86-64)
- Windows Server 2008 Datacenter (IA-32 and x86-64)
- Windows Server 2008 for Itanium-based Systems (IA-64)
- Windows Web Server 2008 (IA-32 and x86-64)
- Windows HPC Server 2008 (codenamed «Socrates»; replacing Windows Compute Cluster Server)
- Windows Storage Server 2008 (codenamed «Magni»; IA-32 and x86-64)
- Windows Small Business Server 2008 (codenamed «Cougar»; x86-64) for small businesses
- Windows Essential Business Server 2008 (codenamed «Centro»; x86-64) for medium-sized businesses[36] — this edition was discontinued in 2010.[37]
The Microsoft Imagine program, known as DreamSpark at the time, used to provide verified students with the 32-bit variant of Windows Server 2008 Standard Edition, but the version has since then been removed. However, they still provide the R2 release.
The Server Core feature is available in the Web, Standard, Enterprise and Datacenter editions.
Windows Server 2008 Foundation Released on May 21, 2009.[38]
System requirements[edit]
System requirements for Windows Server 2008 are as follows:
| Criteria | 2008 | 2008 R2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum[39] | Recommended[39] | Minimum[40] | Recommended[40] | |
| CPU |
|
2 GHz or faster | 1.4 GHz (x86-64 or Itanium) | 2 GHz or faster |
| RAM | 512 MB | 2 GB or greater | 512 MB | 2 GB or greater |
| HDD[a] |
|
40 GB or greater |
|
|
| Devices | DVD drive, 800 × 600 or higher display, keyboard and mouse |
Scalability[edit]
Windows Server 2008 supports the following maximum hardware specifications:[42][43][44]
| Specification | Windows Server 2008 SP2 | Windows Server 2008 R2 |
|---|---|---|
| Physical processors («sockets»)[43] |
|
|
| Logical processors when Hyper-V is disabled[43] |
|
256 |
| Logical processors when Hyper-V is enabled[43] |
|
64 |
| Memory on IA-32[44] |
|
— |
| Memory on x64[44] |
|
|
| Memory on Itanium[44] |
2 TB |
Updates[edit]
Windows Server 2008 shares most of its updates with Windows Vista, given that the operating systems share a codebase. A workaround using the Microsoft Update Catalog allowed the installation of updates for Windows Server 2008 on Windows Vista,[45] adding nearly 3 years of security updates to that operating system (Support for Windows Vista ended on April 11, 2017,[46] while support for Windows Server 2008 ended on January 14, 2020).
Service Pack 2[edit]
The RTM release of Windows Server 2008 already includes the updates and fixes of Windows Vista Service Pack 1.
Service Pack 2 was initially announced on October 24, 2008[47] and released on May 26, 2009. Service Pack 2 added new features, such as Windows Search 4.0, support for Bluetooth 2.1, the ability to write to Blu-ray discs, and simpler Wi-Fi configuration. Windows Server 2008 specifically received the final release of Hyper-V 1.0, improved backwards compatibility with Terminal Server license keys and an approximate 10% reduction in power usage with this service pack.[48]
Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008 share the same service pack update binary.[49]
Platform Update[edit]
On October 27, 2009, Microsoft released the Platform Update for Windows Server 2008 and Windows Vista. It backports several APIs and libraries introduced in Windows Server 2008 R2 and Windows 7 to Windows Server 2008 and Windows Vista, including the Ribbon API, DirectX 11, the XPS library, the Windows Automation API and the Portable Device Platform.[50] A supplemental update was released in 2011 to provide improvements and bug fixes.[51]
Internet Explorer 9[edit]
Windows Server 2008 shipped with Internet Explorer 7, the same version that shipped with Windows Vista. The last supported version of Internet Explorer for Windows Server 2008 is Internet Explorer 9, released in 2011. Internet Explorer 9 was continually updated with cumulative monthly update rollups until support for Internet Explorer 9 on Windows Server 2008 ended on January 14, 2020.[52] Extended Security Updates (ESU) continue until January 9, 2024 for Azure customers.
.NET Framework[edit]
The latest supported version of the .NET Framework officially is version 4.6, released on October 15, 2015.[53]
TLS 1.1 and 1.2 support[edit]
In July 2017, Microsoft released an update to add TLS 1.1 and 1.2 support to Windows Server 2008, however it is disabled by default after installing the update.[54]
SHA-2 signing support[edit]
Starting in March 2019, Microsoft began transitioning to exclusively signing Windows updates with the SHA-2 algorithm. As a result of this Microsoft released several updates throughout 2019 to add SHA-2 signing support to Windows Server 2008.[55]
Monthly update rollups[edit]
In June 2018, Microsoft announced that they would be moving Windows Server 2008 to a monthly update model beginning with updates released in September 2018[56] — two years after Microsoft switched the rest of their supported operating systems to that model.[57]
With the new update model, instead of updates being released as they became available, only two update packages were released on the second Tuesday of every month until Windows Server 2008 reached its end of life — one package containing security and quality updates, and a smaller package that contained only the security updates. Users could choose which package they wanted to install each month. Later in the month, another package would be released which was a preview of the next month’s security and quality update rollup.
Installing the preview rollup package released for Windows Server 2008 on March 19, 2019, or any later released rollup package, will update the operating system kernel’s build number from version 6.0.6002 to 6.0.6003. This change was made so Microsoft could continue to service the operating system while avoiding “version-related issues”.[58]
The last free security update rollup packages were released on January 14, 2020.[59]
Windows Server 2008 R2[edit]
A second release of Windows Server 2008 based on Windows 7, Windows Server 2008 R2, was released to manufacturing on July 22, 2009[60] and became generally available on October 22, 2009.[61] New features added in Windows Server 2008 R2 include new virtualization features, new Active Directory features, Internet Information Services 7.5 and support for up to 256 logical processors. It is the first server operating system by Microsoft to exclusively support 64-bit processors, while consumer-oriented versions of Windows maintained 32-bit support until Windows 11 in 2021.
A service pack for Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2, formally designed Service Pack 1, was released in February 2011.[62]
Support lifecycle[edit]
Support for the RTM version of Windows Server 2008 ended on July 12, 2011,[3][4] and users can no longer receive further security updates for the operating system. As a component of Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008 with Service Pack 2 continued to be supported with security updates, lasting until January 14, 2020, the same respective end-of-life dates of its successor, Windows Server 2008 R2 and Windows 7.
Microsoft planned to end support for Windows Server 2008 on January 12, 2016. However, in order to give customers more time to migrate to newer Windows versions, particularly in developing or emerging markets, Microsoft decided to extend support to January 14, 2020.[6][5][7]
Windows Server 2008 is eligible for the paid Extended Security Updates (ESU) program. The program allowed volume license customers to purchase, in yearly installments, security updates for the operating system for three additional years, until January 10, 2023. The program is also included with Microsoft Azure purchases, and Azure customers receive an extra year of support, until January 9, 2024. The licenses are paid for on a per-machine basis. If a user purchases an Extended Security Updates license in a later year of the program, they must pay for any previous years of Extended Security Updates as well. [6][63]
See also[edit]
- BlueKeep (security vulnerability)
- Comparison of Microsoft Windows versions
- Comparison of operating systems
- History of Microsoft Windows
- List of operating systems
- Microsoft Servers
Notes[edit]
- ^ Computers with more than 16 GB of RAM require more disk space for paging, hibernation, and dump files[40]
References[edit]
- ^ a b «As Windows Server 2008 RTMs, Customers and Partners Adopting with Help of New Tools, Training». News Center. Redmond, WA: Microsoft. 4 February 2008.
- ^ «Build number changing to 6003 in Windows Server 2008». support.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2021-03-26.
- ^ a b c d e «Microsoft Product Lifecycle». Support. Microsoft. Retrieved April 12, 2022.
- ^ a b c d «Install Windows Vista Service Pack 2 (SP2)». Support. Microsoft. Retrieved April 12, 2010.
- ^ a b c «Extended Security Updates for SQL Server and Windows Server 2008 and 2008 R2 | Microsoft». www.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2021-03-26.
- ^ a b c tfosmark. «Product Lifecycle FAQ — Extended Security Updates — Microsoft Lifecycle». docs.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2021-03-26.
- ^ a b «Announcing new options for SQL Server 2008 and Windows Server 2008 End of Support». azure.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2021-03-26.
- ^ Miller, Michael J. (2007-05-15). «Gates at WinHec 2007: Windows Server 2008, Rally, Home Server and More». Forward Thinking. Retrieved 2007-07-09.
- ^ Lowe, David (2007-04-25). «Beta 3 is Go!». Windows Server Division WebLog. Microsoft. Retrieved 2007-04-25.
- ^ Ralston, Ward (2007-09-24). «Windows Server 2008 Rc0 Released!». Windows Server Division WebLog. Microsoft. Retrieved 2007-09-24.
- ^ Nate Mook (10 July 2007). «New Windows Server, Visual Studio, SQL Server to Launch in February». BetaNews. Retrieved 2007-07-11.
- ^ «Dynamic Hardware Partitioning Architecture». MSDN. Retrieved 2007-07-23.
- ^ Archiveddocs. «Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services Overview». docs.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2020-01-15.
- ^ «Iain McDonald and Andrew Mason show off the new Windows Server OS». Channel 9. Microsoft. May 24, 2006. Retrieved 2008-11-01.
18:55
- ^ Hynes, Byron (November 2006). «The Future of Windows: Directory Services in Windows Server 2008». TechNet Magazine. Retrieved 2007-05-02.
- ^ «Deploying Windows Server 2008 Read Only Domain Controllers». docs.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2020-01-15.
- ^ «Q. What is a read-only domain controller (RODC)?». IT Pro. 2008-03-24. Retrieved 2020-01-15.
- ^ Ward, Keith (2007-10-08). «Top 10 Overlooked Windows Server 2008 Features, Part 2». Redmond Developer News. Archived from the original on 2009-08-04. Retrieved 2014-10-10.
- ^ «Failover Cluster Validation Error 80070005 on Windows Server 2008 R2 x64». Capitalhead. 2009-11-04. Retrieved 2013-10-28.
- ^ Zoeller, Jill (26 July 2007). «New in Windows Server 2008: Breaking the 5K Folder «Barrier» in Domain-Based Namespaces». The Storage Team at Microsoft — File Cabinet Blog. Microsoft. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- ^ «Failover Clustering with Windows Server 2008 including Cluster shared volumes». Microsoft. 2007-01-17. Retrieved 2007-07-09.
- ^ Loveall, John (2006). «Storage improvements in Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008» (PowerPoint). Microsoft Corporation. Retrieved 2007-07-09.
- ^ «Benchmarking Hyper-V on Windows Server 2008 R2 x64». 2010-01-20. Retrieved 2010-01-28.
- ^ «Microsoft Extends Virtualization Strategy, Outlines Product Road Map». Microsoft. 2006-05-22. Retrieved 2007-07-09.
- ^ «Server Manager». Windows Server 2008 Technical Library. Microsoft TechNet. 2007-06-25. Retrieved 2007-05-02.
- ^ «Unexpected error refreshing Server Manager-0x800706BE and 1601 on Window Server 2008 R2». Retrieved 2010-11-05.
- ^ «Multicasting OS deployments with Windows Server 2008». Kevinsul’s Management Blog. Microsoft. 29 August 2007. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- ^ a b «Removed technologies in Routing and Remote Access in Windows Server 2008». TechNet. Microsoft. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- ^ «Windows Server Backup Step-by-Step Guide for Windows Server 2008». TechNet. Microsoft. 17 January 2013. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- ^ «Exchange Server 2007 Service Pack 2 available in Q3 2009». The Exchange Team Blog. 11 May 2009. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- ^ Bilic, Nino (18 June 2008). «To Backup or Not to Backup? Yes! To backup!!». The Exchange Team Blog. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- ^ «IIS 7.0 Protocols». TechNet. Microsoft. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- ^ Heaton, Alex (2007-05-18). «On 64-bit and Windows Client». Windows Vista Team Blog. Retrieved 2007-07-09.
- ^
«Windows Server 2008 Product Editions». Microsoft. 2007-04-25. Retrieved 2007-07-09. - ^ «Windows Server 2008 Foundation: An Entry-Level Server Platform». Petri IT Knowledgebase. 2009-04-17. Retrieved 2014-01-08.
- ^ Ligman, Eric (7 November 2007). «Announcing Windows Essential Business Server». Microsoft Small Business Blog. Microsoft. Retrieved 2013-08-16.
- ^ «Windows Essential Business Server 2008». Technet.microsoft.com. 2010-12-31. Retrieved 2013-01-09.
- ^ «Windows Server 2008, Microsoft Lifecycle (Look at the Note below links)». docs.microsoft.com/en-us/lifecycle/products/.
- ^ a b «Windows Server 2008 System Requirements». 31 March 2008. Retrieved 2008-03-31.
- ^ a b c «Microsoft Windows Server 2008 System Requirements». Microsoft.com. Retrieved 2013-01-09.
- ^ «Microsoft Windows Server 2008 System Requirements». Microsoft. Retrieved 2013-01-09.
- ^ Savill, John (October 28, 2011). «Q: What are Windows Server 8’s Scalability Numbers?». Windows IT Pro. Penton Media. Retrieved November 5, 2011.
- ^ a b c d Seldam, Matthijs ten (October 13, 2012). «Windows Server — Sockets, Logical Processors, Symmetric Multi Threading». Matthijs’s blog. Microsoft. Retrieved October 14, 2012.
- ^ a b c d «Memory Limits for Windows and Windows Server Releases». MSDN. Microsoft. Retrieved 13 April 2014.
- ^ «Extend Windows Vista support by installing Windows Server 2008 updates — gHacks Tech News». gHacks Technology News. 2017-06-24. Retrieved 2021-06-30.
- ^ «Windows Vista Lifecycle Policy». Microsoft. Retrieved January 2, 2017.
- ^ Justin Graham (October 24, 2008). «Windows Server 2008 Service Pack 2 beta». Microsoft. Retrieved 2008-10-29.
- ^ «Tech ARP — ED#107 : Latest Details on Windows Vista Service Pack 2 Rev. 2.2». Archived from the original on 2009-02-12.
- ^ «Windows Vista Service Pack 2 Beta». blogs.windows.com. Archived from the original on 9 May 2013. Retrieved 12 January 2022.
- ^ «Announcing Final Releases of Platform Update for Windows Vista Technologies». 27 October 2009.
- ^ «Platform Update Supplement for Windows Vista and for Windows Server 2008».
- ^ «Cumulative security update for Internet Explorer: January 14, 2020». support.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2021-03-26.
- ^ «Microsoft .NET Framework 4.6 (Web Installer)». Microsoft.
- ^ «TLS 1.2 Support added to Windows Server 2008». Microsoft Security. 2017-07-20. Retrieved 2021-03-26.
- ^ «2019 SHA-2 Code Signing Support requirement for Windows and WSUS».
- ^ Mackie, Kurt; 06/13/2018. «Microsoft Switching Windows Server 2008 SP2 to Monthly Update Rollup Model — Redmondmag.com». Redmondmag. Retrieved 2021-03-26.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ «Community». forums.ivanti.com. Retrieved 2021-03-26.
- ^ «Build number changing to 6003 in Windows Server 2008».
- ^ «January 14, 2020—KB4534303 (Monthly Rollup)». support.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2021-03-26.
- ^ «Windows Server 2008 R2 Reaches the RTM Milestone! — Windows Server Blog — Site Home — TechNet Blogs». Blogs.technet.com. 2009-07-22. Retrieved 2013-01-09.
- ^ «When to expect Windows Server 2008 R2 RTM — Windows Server Blog — Site Home — TechNet Blogs». Blogs.technet.com. 2009-07-22. Retrieved 2013-01-09.
- ^ LeBlanc, Brandon (February 9, 2011). «Announcing Availability of Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1». Windows Experience Blog. Microsoft.
- ^ «Windows Server 2008 Product Lifecycle». Microsoft. January 14, 2020. Retrieved January 9, 2022.
18:55
Further reading[edit]
- «What’s New in Networking». TechNet. Microsoft. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- «Changes in Functionality from Windows Server 2003 with SP1 to Windows Server 2008». TechNet. Microsoft. 21 January 2008. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- «Description of the Microsoft server applications that are supported on Windows Server 2008». Support. Microsoft. 23 April 2012. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- «Windows Server 2008 System Requirements». TechNet. Microsoft. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- Henderson, Tom; Dvorak, Rand (21 February 2008). «Windows Server 2008: Faster, more manageable and secure, but still missing the virtual link». Network World. IDG. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- Radzikowski, Przemek (21 February 2010). «How to Find Build and Revision Number of Windows Vista or Windows Server 2008 Installed». Capitalhead. Capitalhead Pty. Ltd. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- Stanek, William (2008). Windows Server 2008 Inside Out. Microsoft Press. ISBN 978-0-7356-2438-2.
External links[edit]
- Windows Server Performance Team Blog
- 14.06.2021
В данной статье рассмотрим системные требования для различных версий Windows Server.
Приобрести лицензионные ключи активации Windows Server различных версий можете в нашем каталоге по самым низким ценам 999 ₽, а так же скачать оригинальные MSDN дистрибутивы можете с нашего сервера.
Системные требования Windows Server 2022
Процессор: x64, 1.4 ГГц или больше
Оперативная память (ОЗУ): 2 ГБ
Жесткий диск: 32 ГБ
Системные требования Windows Server 2019
Процессор: x64, 1.4 ГГц или больше
Оперативная память (ОЗУ): 512 Мб (4 ГБ для установки с рабочим столом)
Жесткий диск: 64 ГБ
Системные требования Windows Server 2016
Процессор: x64, 1.4 ГГц или больше
Оперативная память (ОЗУ): 512 Мб (2 ГБ для установки с рабочим столом)
Жесткий диск: 32 ГБ
Системные требования Windows Server 2012 r2
Процессор: x64, 1.4 ГГц или больше
Оперативная память (ОЗУ): 2 ГБ
Жесткий диск: 32 ГБ
Системные требования Windows Server 2008 r2
Процессор: x32 / x64, 1 ГГц или больше
Оперативная память (ОЗУ): 512 Мб / 1 ГБ
Жесткий диск: 32 ГБ / 4 ГБ
Hardware
Software
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
© 1992-2020 Майкролэб Инвестмент |
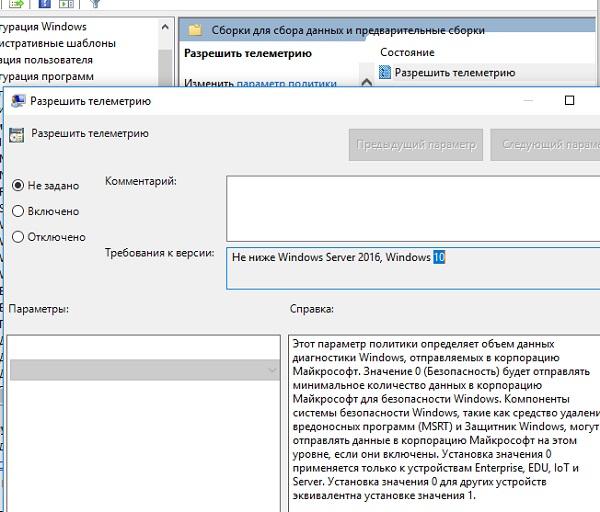
Минимальные требования Windows Server 2008
Перед установкой Windows Server 2008 R2 как в лабораторной, так и в производственной среде необходимо удостовериться, что выбранное оборудование отвечает минимальным требованиям к системе. В большинстве ситуаций соответствия оборудования официальным минимальным требованиям далеко не достаточно.
|
Компонент |
Минимальные требования |
Рекомендуемые требования |
Максимальные требования |
|
Процессор |
1,4 ГГц, 64-разрядная архитектура |
2 ГГц или больше |
Отсутствуют |
|
ОЗУ |
512 Мбайт |
2 Гбайт или больше |
322 Гбайт для установки версии Standard Edition и 2 Тбайт для установки версии Enterprise Edition или Datacenter Edition. |
|
Пространство на диске |
32 Гбайт |
40 Гбайт для установки в полном режиме или 10 Гбайт для установки в режиме Server Core |
Отсутствуют |
Обратите внимание, что при проектировании и выборе технических характеристик системы для нового серверного решения даже предлагаемых Microsoft оптимальных требований к системе может оказаться не достаточно. Поэтому рекомендуется оценивать характеристики сервера для выбранной серверной роли с учетом нагрузки во время развертывания и возможности ее увеличения в будущем.
В Windows Server 2008 R2 поддерживается использование процессоров только с 64-разрядной архитектурой. Серверы, работающие под управлением процессоров с 32-разрядной архитектурой, больше не поддерживаются.
| Версия Windows NT Операционная система | |
 |
|

Снимок экрана Windows Server 2008, показывающий приложение Server Manager, которое автоматически открывается при входе администратора в систему. |
|
| Разработчик | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| Семейство ОС | Майкрософт Виндоус |
| Рабочее состояние | ток |
| Исходная модель |
|
| Выпущено в производство |
4 февраля 2008 г.; 12 лет назад[1] |
| Общее доступность |
27 февраля 2008 г.; 12 лет назад[1] |
| Последний релиз | Пакет обновления 2 с накопительным пакетом обновления от 19 марта 2019 г. или более поздней версии (сборка 6.0.6003)[2] / 19 марта 2019 г.; 20 месяцев назад |
| Маркетинговая цель | Бизнес |
| Метод обновления | Центр обновления Windows, Службы обновления Windows Server, SCCM |
| Платформы | IA-32, x86-64, Itanium |
| Ядро тип | Гибридный (Ядро Windows NT ) |
| По умолчанию пользовательский интерфейс | Оболочка Windows (Графический ) |
| Лицензия | Проприетарный коммерческое программное обеспечение |
| Предшествует | Windows Server 2003 (2003) |
| Преемник | Windows Server 2008 R2 (2009) |
| Официальный веб-сайт | Майкрософт.com/ windowsserver2008 |
| Статус поддержки | |
| Основная поддержка закончилась 13 января 2015 г.[3] Расширенная поддержка закончилась 14 января 2020 г.[4] Расширенные обновления безопасности оплачиваются в виде ежегодной установки на 1, 2 или 3 года (или бесплатно для пользователей виртуальных рабочих столов Windows) до 10 января 2023 г. только для выпусков с корпоративной лицензией Standard, Enterprise и Datacenter.[5][6][7] |
|
| Статьи в серии | |
|
Windows Server 2008 это третья версия Windows Server Операционная система произведено Microsoft, на основе Windows NT 6.0. Это было выпущен в производство 4 февраля 2008 г. и достиг общедоступность 27 февраля 2008 г., примерно через 13 месяцев после запуска Виндоус виста Операционная система. Windows Server 2008 является преемником Windows Server 2003, который получается из Windows XP codebase, выпущенная почти пятью годами ранее.
История
Первоначально известный как Кодовое имя Windows Server «Longhorn», Microsoft председатель Билл Гейтс объявил свое официальное название (Windows Server 2008) во время своего основного выступления на WinHEC 16 мая 2007 г.[8]
Бета 1 была выпущена 27 июля 2005 г .; Бета 2 была анонсирована и выпущена 23 мая 2006 г. на WinHEC 2006 и Beta 3 была выпущена публично 25 апреля 2007 года.[9] Release Candidate 0 был выпущен для широкой публики 24 сентября 2007 г.[10] и Release Candidate 1 был выпущен для широкой публики 5 декабря 2007 г. Windows Server 2008 был выпущен в производство 4 февраля 2008 г. и официально запущен 27 числа того же месяца.[11]
Функции
Windows Server 2008 построен на той же кодовой базе, что и Виндоус виста и, следовательно, он имеет большую часть той же архитектуры и функциональности. Поскольку кодовая база является общей, Windows Server 2008 наследует большую часть технический, безопасность, управленческий и административный новые возможности Windows Vista например, переписанный сетевой стек (родные IPv6, улучшенная беспроводная связь, скорость и безопасность); улучшен на основе изображений установка, развертывание и восстановление; улучшенные инструменты диагностики, мониторинга, регистрации событий и отчетности; новые функции безопасности такие как BitLocker и рандомизация разметки адресного пространства (ASLR); улучшенный Брандмауэр Windows с безопасной конфигурацией по умолчанию; .NET Framework 3.0 технологии, в частности Фонд связи Windows, Очередь сообщений Microsoft и Windows Workflow Foundation; и улучшения ядра, памяти и файловой системы. Процессоры и устройства памяти моделируются как Подключи и играй устройства, позволяющие горячее подключение этих устройств. Это позволяет динамически разделять системные ресурсы с помощью динамического аппаратного разделения — каждый раздел имеет свою собственную память, процессор и устройства моста ввода-вывода, независимо от других разделов.[12]
Ядро сервера
Windows Server 2008 включает вариант установки, называемый Ядро сервера. Server Core — это значительно уменьшенная установка, где нет проводник Виндоус оболочка установлена. Вся настройка и обслуживание полностью осуществляется через Интерфейс командной строки windows, или подключившись к машине удаленно с помощью Консоль управления Microsoft (MMC). Однако, Блокнот и некоторые апплеты панели управления, такие как региональные настройки, доступны.
Server Core не включает .NET Framework, Internet Explorer, Windows PowerShell или многие другие функции, не связанные с функциями главного сервера. Установку Server Core можно настроить для нескольких основных ролей, включая контроллер домена (Доменные службы Active Directory ), Службы Active Directory облегченного доступа к каталогам (ранее известный как режим приложения Active Directory[13]), DNS сервер, DHCP-сервер, файловый сервер, сервер печати, Сервер Windows Media, Информационные службы Интернета 7 веб-сервер и Hyper-V роли виртуального сервера. Ядро сервера также можно использовать для создания кластер с высокая доступность с помощью отказоустойчивая кластеризация или балансировка сетевой нагрузки.
Эндрю Мейсон, менеджер программы в группе Windows Server, отметил, что основной мотивацией для создания варианта Server Core Windows Server 2008 было сокращение поверхность атаки операционной системы, и что около 70% уязвимостей безопасности в Microsoft Windows за предыдущие пять лет не затронули Server Core.[14]
Active Directory
Функциональные возможности домена Active Directory, сохраненные в Windows Server 2003, были переименованы в доменные службы Active Directory (ADDS).[15]
- Службы федерации Active Directory (ADFS) позволяет предприятиям обмениваться учетными данными с доверенными партнерами и клиентами, позволяя консультанту использовать имя пользователя и пароль своей компании для входа в сеть клиента.
- Службы Active Directory облегченного доступа к каталогам (AD LDS) (ранее — режим приложений Active Directory или ADAM)
- Службы сертификатов Active Directory (ADCS) позволяют администраторам управлять учетными записями пользователей и цифровые сертификаты которые позволяют им получить доступ к определенным услугам и системам. Пакет функций интеграции идентификационной информации включен как Службы метакаталогов Active Directory.
- Службы управления правами Active Directory (ADRMS)
- Только чтение контроллеры домена (RODC), предназначенные для использования в филиалах или других сценариях, где контроллер домена может находиться в среде с низким уровнем физической безопасности. Контроллер домена только для чтения содержит копию Active Directory, не допускающую запись, и перенаправляет все попытки записи на полный контроллер домена. Он реплицирует все учетные записи, кроме конфиденциальных.[16] В режиме RODC учетные данные по умолчанию не кэшируются. Кроме того, можно назначить локальных администраторов для входа в систему для выполнения задач обслуживания, не требуя прав администратора во всем домене.[17]
- Перезапускаемый Active Directory позволяет останавливать и перезапускать ADDS из консоли управления или из командной строки без перезагрузки контроллера домена. Это сокращает время простоя для автономных операций и снижает общие требования к обслуживанию ЦОД с помощью Ядро сервера. ADDS реализован как Служба контроллера домена в Windows Server 2008.
- Все из Групповая политика улучшения из Windows Vista включены. Консоль управления групповой политикой (GPMC) встроена. Объекты групповой политики индексируются для поиска, и их можно комментировать.[18]
- Сеть на основе политик с Защита доступа к сети, улучшенное управление филиалами и улучшенное взаимодействие с конечными пользователями. Могут быть созданы политики для обеспечения большего Качество обслуживания для определенных приложений или служб, требующих приоритезации пропускной способности сети между клиентом и сервером.
- Детализированная настройка паролей в пределах одного домена — возможность реализации различных политик паролей для административных учетных записей для «группы» и «пользователя» вместо единого набора настроек паролей для всего домена.
Отказоустойчивая кластеризация
Windows Server 2008 обеспечивает высокую доступность служб и приложений за счет Отказоустойчивая кластеризация. Большинство функций и ролей сервера можно поддерживать в рабочем состоянии практически без простоев.
В Windows Server 2008 способ квалификации кластеров значительно изменился с появлением мастера проверки кластеров.[19] Мастер проверки кластера — это функция, которая интегрирована в отказоустойчивый кластер в Windows Server 2008. С помощью мастера проверки кластера администратор может запустить набор специализированных тестов для набора серверов, которые предназначены для использования в качестве узлов в кластере. Этот процесс проверки кластера проверяет базовое оборудование и программное обеспечение напрямую и индивидуально, чтобы получить точную оценку того, насколько хорошо отказоустойчивый кластер может поддерживаться в данной конфигурации.
Эта функция доступна только в выпусках Windows Server Enterprise и Datacenter.
Управление дисками и файловое хранилище
- Возможность изменять размер разделов жесткого диска без остановки сервера, даже системного раздела. Это применимо только к простым и составным томам, но не к чередующимся томам.
- Теневая копия резервное копирование на уровне блоков, поддерживающее оптические носители, общие сетевые ресурсы и Среда восстановления Windows.
- DFS улучшения — SYSVOL на DFS-R, член репликации папок только для чтения. Также имеется поддержка доменных пространств имен DFS, которые превышают предыдущий рекомендуемый размер 5000 папок с целевыми объектами в пространстве имен.[20]
- Несколько улучшений в Отказоустойчивая кластеризация (кластеры высокой доступности ).[21]
- Сервер имен хранилищ в Интернете (iSNS ) обеспечивает централизованную регистрацию, отмену регистрации и запросы для iSCSI жесткие диски.
- Самовосстановление NTFS: в версиях Windows до Windows Vista, если операционная система обнаружила повреждение в файловая система из NTFS объем, он пометил объем «грязный»; чтобы исправить ошибки на томе, его нужно было отключить. С самовосстановлением NTFS рабочий поток NTFS создается в фоновом режиме, который выполняет локализованное исправление поврежденных структур данных, при этом только поврежденные файлы / папки остаются недоступными без блокировки всего тома и необходимости отключения сервера . УМНАЯ. Были добавлены методы обнаружения, помогающие определить, когда жесткий диск может выйти из строя.[22]
Hyper-V
Архитектура Hyper-V
Hyper-V — это гипервизор -на основании виртуализация программное обеспечение, составляющее основную часть стратегии виртуализации Microsoft. Он виртуализирует серверы в операционной системе. ядро слой. Это можно представить как разделение одного физического сервера на несколько небольших вычислительных разделов. Hyper-V включает возможность действовать как Xen хост гипервизора виртуализации, позволяющий гостевым операционным системам с поддержкой Xen работать в виртуальном режиме.[23] Бета-версия Hyper-V поставляется с определенными x86-64 выпуски Windows Server 2008, до того, как Microsoft выпустила финальную версию Hyper-V 26 июня 2008 года в качестве бесплатной загрузки. Также существует автономный вариант Hyper-V; этот вариант поддерживает только архитектуру x86-64.[24] Хотя выпуски Windows Server 2008 IA-32 не могут запускать или устанавливать Hyper-V, они могут запускать MMC оснастка для управления Hyper-V.
Диспетчер системных ресурсов Windows
Диспетчер системных ресурсов Windows (WSRM) интегрирован в Windows Server 2008. Он обеспечивает управление ресурсами и может использоваться для управления количеством ресурсов обработать или пользователь может использовать в зависимости от бизнес-приоритетов. Критерии соответствия процессов, который определяется именем, типом или владельцем процесса, накладывает ограничения на использование ресурсов процессом, который соответствует критериям. Время ЦП, пропускная способность, которую он может использовать, количество процессоров, на которых он может быть запущен, и выделяемые процессу могут быть ограничены. Также можно установить ограничения на определенные даты.
Диспетчер сервера
Server Manager — это новый инструмент управления на основе ролей для Windows Server 2008.[25] Это комбинация Manage Your Server и мастера настройки безопасности из Windows Server 2003. Server Manager является улучшенной версией Настроить мой сервер диалоговое окно, которое запускается по умолчанию на компьютерах с Windows Server 2003. Однако вместо того, чтобы служить только отправной точкой для настройки новых ролей, Диспетчер сервера собирает вместе все операции, которые пользователи хотели бы выполнять на сервере, такие как настройка метода удаленного развертывания, добавление дополнительных ролей сервера и т. д., и обеспечивает консолидированное, похожее на портал представление о состоянии каждой роли.[26]
Протокол и криптография
- Поддержка 128- и 256-битных AES шифрование для Kerberos аутентификация протокол.
- Новый криптография (CNG) API, поддерживающий криптография на основе эллиптических кривых и улучшенное управление сертификатами.
- Протокол безопасного туннелирования сокетов, новый Microsoft проприетарный VPN протокол.
- AuthIP, проприетарное расширение Microsoft АЙК криптографический протокол используется в IPsec VPN сети.
- Блок сообщений сервера 2.0 протокол в новом стеке TCP / IP обеспечивает ряд улучшений связи, в том числе более высокую производительность при подключении к файловые ресурсы по каналам с высокой задержкой и лучшей безопасности за счет использования взаимная аутентификация и подписание сообщения.
Разное
- Полностью компонентная операционная система.
- Улучшен горячее исправление, функция, которая позволяет устанавливать исправления, не относящиеся к ядру, без необходимости перезагрузки.
- Поддержка загрузки с Расширяемый интерфейс прошивки (EFI)-совместимая прошивка на x86-64 системы.
- Dynamic Hardware Partitioning поддерживает горячее добавление или замену процессоров и памяти на соответствующем оборудовании.
- Службы развертывания Windows (WDS) заменяет службы автоматического развертывания Windows Server 2008 для домашних развлечений и Услуги удаленной установки. Службы развертывания Windows поддерживают расширенную функцию многоадресной рассылки при развертывании образов операционных систем.[27]
- Информационные службы Интернета 7 — Повышенная безопасность, Робокопия развертывание, улучшенные средства диагностики, делегированное управление.
- Внутренняя база данных Windows, вариант SQL Server Express 2005, который служит общей серверной частью хранилища для нескольких других компонентов, таких как Диспетчер системных ресурсов Windows, Службы Windows SharePoint Services и Службы обновления Windows Server. Он не предназначен для использования сторонними приложениями.
- Дополнительный компонент «взаимодействия с компьютером» обеспечивает то же Windows Aero пользовательский интерфейс как Windows Vista, как для локальных пользователей, так и для удаленных пользователей, подключающихся через удаленный рабочий стол.
Удаленные функции
- В Сначала откройте кратчайший путь (OSPF) протокол маршрутизации компонент в Служба маршрутизации и удаленного доступа был удален.[28]
- Услуги для Macintosh, который обеспечивал общий доступ к файлам и принтерам через устаревший AppleTalk протокол, был удален. Службы для Macintosh изначально были удалены в Windows XP, но были доступны в Windows Server 2003.[28]
- NTBackup заменен на Windows Server Backup и больше не поддерживает резервное копирование на ленточные накопители.[29] В результате удаления NTBackup Exchange Server 2007 не имеет функции резервного копирования моментальных снимков тома; однако Exchange Server 2007 с пакетом обновления 2 (SP2) добавляет обратно подключаемый модуль резервного копирования Exchange для Windows Server Backup, который частично восстанавливает функциональность.[30] Windows Small Business Server и Windows Essential Business Server оба включают этот компонент резервного копирования Exchange.[31]
- В POP3 служба была удалена из Internet Information Services 7.0.[32] В SMTP Служба (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) недоступна в качестве роли сервера в IIS 7.0, это функция сервера, управляемая через IIS 6.0.
- NNTP (Протокол передачи сетевых новостей ) больше не является частью Internet Information Services 7.0.
- ReadyBoost, который доступен в Windows Vista, не поддерживается в Windows Server 2008.
Редакции
Установочный диск Enterprise edition (beta 3)
Большинство выпусков Windows Server 2008 доступны в x86-64 и IA-32 варианты. Эти выпуски поставляются на двух DVD-дисках: один для установки варианта IA-32, а другой — для x64. Windows Server 2008 для систем на базе процессоров Itanium поддерживает IA-64 процессоры. Вариант IA-64 оптимизирован для сценариев с высокой нагрузкой, таких как серверы баз данных и Отрасль производства (LOB) приложения. Таким образом, он не оптимизирован для использования в качестве файловый сервер или медиа-сервер. Windows Server 2008 — последняя 32-разрядная серверная операционная система Windows.[33]Редакции Windows Server 2008 включают:[34]
- Windows Server 2008 Foundation (кодовое название «Lima»; x86-64) только для OEM-производителей.[35]
- Windows Server 2008 Standard (IA-32 и x86-64)
- Windows Server 2008 Enterprise (IA-32 и x86-64)
- Windows Server 2008 Datacenter (IA-32 и x86-64)
- Windows Server 2008 для Itanium -системы (IA-64)
- Windows Web Server 2008 (IA-32 и x86-64)
- Windows HPC Server 2008 (кодовое название «Сократ»; заменяет Сервер вычислительного кластера Windows )
- Windows Storage Server 2008 (кодовое название «Magni»; IA-32 и x86-64)
- Windows Small Business Server 2008 (кодовое название «Cougar»; x86-64) для малый бизнес
- Windows Essential Business Server 2008 (кодовое название Centro; x86-64) для среднего бизнеса[36] — выпуск этого издания был прекращен в 2010 году.[37]
В Microsoft Imagine Программа, известная в то время как DreamSpark, использовалась для предоставления проверенных студентов 32-разрядной версии Windows Server 2008 Standard Edition, но с тех пор эта версия была удалена. Однако они по-прежнему предоставляют выпуск R2.
Функция Server Core доступна в редакциях Web, Standard, Enterprise и Datacenter.
Обновления
Windows Server 2008 разделяет большинство своих обновлений с Windows Vista из-за своей кодовой базы.
Пакет обновления 2
Поскольку операционная система основана на той же кодовой базе, что и Windows Vista, и выпущена в тот же день, что и первоначальный выпуск Виндоус виста Пакет обновления 1 RTM-версия Windows Server 2008 уже включает Service Pack 1.
Пакет обновления 2 был первоначально анонсирован 24 октября 2008 г.[38] и выпущен 26 мая 2009 г. В Service Pack 2 добавлены новые функции, такие как Windows Search 4.0, поддержка Bluetooth 2.1, возможность записи в Блю рей диски и более простая конфигурация Wi-Fi. Windows Server 2008 специально получила финальную версию Hyper-V 1.0, улучшена обратная совместимость с лицензионными ключами сервера терминалов и примерно на 10% снижено потребление энергии с помощью этого пакета обновления.[39]
Виндоус виста и Windows Server 2008 используют один и тот же двоичный файл обновления пакета обновления, поскольку кодовые базы двух операционных систем едины — Виндоус виста и Windows Server 2008 — первые клиентские и серверные операционные системы Microsoft, использующие одну и ту же кодовую базу с момента выпуска Windows 2000.[40] Предшественники Виндоус виста и Windows Server 2008, Windows XP и Windows Server 2003, имели уникальные кодовые базы, в которых использовались собственные обновления и пакеты обновлений.
Обновление платформы
27 октября 2009 г. Microsoft выпустила обновление платформы для Windows Server 2008 и Виндоус виста. Это резервные копии несколько API и библиотек, представленных в Windows Server 2008 R2 и Windows 7 к Windows Server 2008 и Виндоус виста, в том числе Лента API, DirectX 11, библиотека XPS, API автоматизации Windows и платформа портативных устройств.[41] В 2011 году было выпущено дополнительное обновление для улучшения и исправления ошибок.[42]
Internet Explorer 9
Windows Server 2008 поставляется с Internet Explorer 7, той же версии, что поставлялась с Windows Vista. Последней версией браузера, совместимой с Windows Server 2008, является Internet Explorer 9, выпущенный в 2011 году. Internet Explorer 9 постоянно обновлялся ежемесячными накопительными пакетами обновлений, пока поддержка Windows Server 2008 не прекратилась 14 января 2020 года.[43]
.NET Framework
Последняя поддерживаемая версия .NET Framework официально — версия 4.6, выпущенная 15 октября 2015 года.[44]
Поддержка TLS 1.1 и 1.2
В июле 2017 года Microsoft выпустила обновление, чтобы добавить TLS 1.1 и 1.2 поддерживают Windows Server 2008, однако по умолчанию после установки обновления она отключена.[45]
Поддержка подписи SHA-2
Начиная с марта 2019 г., Microsoft начала переходить исключительно на подписание Обновления Windows с SHA-3 алгоритм. В результате этого Microsoft выпустила несколько обновлений в течение 2019 года, чтобы добавить поддержку подписи SHA-2 в Windows Server 2008.[46]
Ежемесячные накопительные пакеты обновлений
В июне 2018 года Microsoft объявила о переводе Windows Server 2008 на модель ежемесячного обновления, начиная с обновлений, выпущенных в сентябре 2018 года.[47] — через два года после того, как Microsoft перевела остальные поддерживаемые операционные системы на эту модель.[48]
С новой моделью обновления, вместо того, чтобы выпускать обновления по мере их появления, только два пакета обновлений были выпущены на второй вторник каждого месяца пока Windows Server 2008 не подошел к концу — один пакет содержал обновления безопасности и качества, а меньший пакет содержал только обновления безопасности. Пользователи могли выбирать, какой пакет устанавливать каждый месяц. Позже в этом месяце будет выпущен еще один пакет, представляющий собой предварительную версию накопительного пакета обновлений безопасности и качества, который состоится в следующем месяце.
При установке накопительного пакета предварительной версии, выпущенного для Windows Server 2008 19 марта 2019 г., или любого более позднего накопительного пакета, номер сборки ядра операционной системы будет обновлен с версии 6.0.6002 до 6.0.6003. Это изменение было внесено для того, чтобы Microsoft могла продолжать обслуживать операционную систему, избегая «проблем, связанных с версией».[49]
Последние накопительные пакеты обновлений без расширенных обновлений были выпущены 14 января 2020 г., в последний день расширенной поддержки Windows Server 2008.[50]
Расширенные обновления безопасности
Windows Server 2008 имеет право на участие в программе расширенных обновлений безопасности. Эта программа позволяет клиентам с корпоративной лицензией ежегодно приобретать обновления безопасности для операционной системы максимум до 10 января 2023 г. Лицензии оплачиваются отдельно для каждой машины. Если пользователь приобретает лицензию на расширенные обновления безопасности в более поздний год действия программы, он также должен оплатить все предыдущие годы расширенных обновлений безопасности. Расширенные обновления безопасности выпускаются только по мере их появления.[51]
Windows Server 2008 R2
Второй выпуск Windows Server 2008, названный Windows 7 -на основании Windows Server 2008 R2 был выпущен в производство 22 июля 2009 г.[52] и стал общедоступный 22 октября 2009 г.[53] Новые функции добавлены в Windows Server 2008 R2 включают новые функции виртуализации, новые функции Active Directory, Internet Information Services 7.5 и поддержку до 256 логических процессоров. Это первая серверная операционная система от Microsoft, которая поддерживает исключительно 64-разрядные процессоры.
Системные Требования
Системные требования для Windows Server 2008 следующие:
| Критерии | 2008 | 2008 R2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Минимум[54] | рекомендуемые[54] | Минимум[55] | рекомендуемые[55] | |
| ЦПУ |
|
2 ГГц или быстрее | 1,4 ГГц (x86-64 или Itanium) | 2 ГГц или быстрее |
| баран | 512 МБ | 2 ГБ или больше | 512 МБ | 2 ГБ или больше |
| HDD[а] |
|
40 ГБ или больше |
|
|
| Устройства | DVD-привод, 800 × 600 или выше дисплей, клавиатура и мышь |
Масштабируемость
Windows Server 2008 поддерживает следующие максимальные характеристики оборудования:[57][58][59]
| Технические характеристики | Windows Server 2008 с пакетом обновления 2 (SP2) | Windows Server 2008 R2 |
|---|---|---|
| Физические процессоры («Розетки»)[58] |
|
|
| Логические процессоры когда Hyper-V выключен[58] |
|
256 |
| Логические процессоры когда Hyper-V включен[58] |
|
64 |
| объем памяти на IA-32[59] |
|
Нет данных |
| объем памяти на x64[59] |
|
|
| объем памяти на Itanium[59] |
2 ТБ |
Смотрите также
- BlueKeep (уязвимость безопасности)
- Сравнение версий Microsoft Windows
- Сравнение операционных систем
- История Microsoft Windows
- Список операционных систем
- Серверы Microsoft
Примечания
- ^ Компьютерам с более чем 16 ГБ ОЗУ требуется больше дискового пространства для файлов подкачки, гибернации и дампа.[55]
использованная литература
- ^ а б «Как Windows Server 2008 RTM, клиенты и партнеры осваивают новые инструменты, обучение». Центр новостей. Редмонд, Вашингтон: Microsoft. 4 февраля 2008 г.
- ^ https://support.microsoft.com/en-au/help/4495374/build-number-changing-to-6003-in-windows-server-2008
- ^ Microsoft. «Политика жизненного цикла Windows Server 2008». Microsoft. Получено 2012-09-25.
- ^ Microsoft. «Жизненный цикл поддержки Microsoft». Microsoft. Получено 2018-04-01.
- ^ https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/help/4497181/lifecycle-faq-extended-security-updates
- ^ https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/cloud-platform/extended-security-updates
- ^ https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/blog/announcing-new-options-for-sql-server-2008-and-windows-server-2008-end-of-support/
- ^ Миллер, Майкл Дж. (15 мая 2007 г.). «Гейтс на WinHec 2007: Windows Server 2008, Rally, Home Server и многое другое». Дальновидное мышление. Получено 2007-07-09.
- ^ Лоу, Дэвид (2007-04-25). «Beta 3 — это вперед!». Windows Server Division WebLog. Microsoft. Получено 2007-04-25.
- ^ Ралстон, Уорд (24 сентября 2007 г.). «Выпущен Windows Server 2008 Rc0!». Windows Server Division WebLog. Microsoft. Получено 2007-09-24.
- ^ Нейт Мук. «Новые Windows Server, Visual Studio, SQL Server будут запущены в феврале». BetaNews. Получено 2007-07-11. Его также обычно называют Vista Server.
- ^ «Архитектура динамического разделения оборудования». MSDN. Получено 2007-07-23.
- ^ Архивные документы. «Обзор служб Active Directory облегченного доступа к каталогам». docs.microsoft.com. Получено 2020-01-15.
- ^ «Иэн Макдональд и Эндрю Мейсон демонстрируют новую ОС Windows Server». Канал 9. Microsoft. 24 мая 2006 г.. Получено 2008-11-01.
18:55
- ^ Хайнс, Байрон (ноябрь 2006 г.). «Будущее Windows: службы каталогов в Windows Server 2008». TechNet Журнал. Получено 2007-05-02.
- ^ «Развертывание контроллеров домена только для чтения Windows Server 2008». docs.microsoft.com. Получено 2020-01-15.
- ^ «В. Что такое контроллер домена только для чтения (RODC)?». IT Pro. 2008-03-24. Получено 2020-01-15.
- ^ Уорд, Кит (2007-10-08). «10 самых недооцененных функций Windows Server 2008, часть 2». Новости разработчиков Redmond. Архивировано из оригинал на 2014-10-10. Получено 2014-10-10.
- ^ «Ошибка проверки отказоустойчивого кластера 80070005 в Windows Server 2008 R2 x64». Capitalhead. 2009-11-04. Получено 2013-10-28.
- ^ Зеллер, Джилл (26 июля 2007 г.). «Новое в Windows Server 2008: преодоление« барьера »папок 5K в доменных пространствах имен». Команда хранилищ в Microsoft — блог о картотеке. Microsoft. Получено 16 августа 2013.
- ^ «Отказоустойчивая кластеризация с Windows Server 2008, включая общие тома кластера». Microsoft. 2007-01-17. Получено 2007-07-09.
- ^ Ловол, Джон (2006). «Улучшения хранилища в Windows Vista и Windows Server 2008» (Силовая установка). Корпорация Майкрософт. Получено 2007-07-09.
- ^ «Тестирование Hyper-V на Windows Server 2008 R2 x64». Тестирование Hyper-V на Windows Server 2008 R2 x64. 2010-01-20. Получено 2010-01-28.
- ^ «Microsoft расширяет стратегию виртуализации, излагает дорожную карту продукта». Microsoft. 2006-05-22. Получено 2007-07-09.
- ^ «Диспетчер сервера». Техническая библиотека Windows Server 2008. Microsoft TechNet. 2007-06-25. Получено 2007-05-02.
- ^ «Неожиданная ошибка при обновлении Server Manager-0x800706BE и 1601 в Window Server 2008 R2». Неожиданная ошибка обновления Server Manager-0x800706BE и 1601 в Window Server 2008 R2. Получено 2010-11-05.
- ^ «Многоадресные развертывания ОС с Windows Server 2008». Блог руководства Кевинсула. Microsoft. 29 августа 2007 г.. Получено 16 августа 2013.
- ^ а б «Удаленные технологии в маршрутизации и удаленном доступе в Windows Server 2008». TechNet. Microsoft. Получено 16 августа 2013.
- ^ «Пошаговое руководство по резервному копированию Windows Server для Windows Server 2008». TechNet. Microsoft. 17 января 2013 г.. Получено 16 августа 2013.
- ^ «Пакет обновления 2 для Exchange Server 2007 доступен в третьем квартале 2009 года». Блог команды разработчиков Exchange. 11 мая 2009 года. Получено 16 августа 2013.
- ^ Билич, Нино (18 июня 2008 г.). «Резервное копирование или не резервное копирование? Да! Резервное копирование !!». Блог команды разработчиков Exchange. Получено 16 августа 2013.
- ^ «Протоколы IIS 7.0». TechNet. Microsoft. Получено 16 августа 2013.
- ^ Хитон, Алекс (18 мая 2007 г.). «На 64-битной и Windows-клиенте». Блог группы разработчиков Windows Vista. Получено 2007-07-09.
- ^ «Версии продукта Windows Server 2008». Microsoft. 2007-04-25. Получено 2007-07-09.
- ^ «Windows Server 2008 Foundation: серверная платформа начального уровня». База знаний Petri IT. 2009-04-17. Получено 2014-01-08.
- ^ Лигман, Эрик (7 ноября 2007 г.). «Представляем Windows Essential Business Server». Блог Microsoft Small Business. Microsoft. Получено 2013-08-16.
- ^ «Windows Essential Business Server 2008». Technet.microsoft.com. 2010-12-31. Получено 2013-01-09.
- ^ Джастин Грэм (24 октября 2008 г.). «Бета-версия пакета обновления 2 для Windows Server 2008». Microsoft. Получено 2008-10-29.
- ^ https://web.archive.org/web/20090212213723/http://techarp.com/showarticle.aspx?artno=605&pgno=0#vista_new
- ^ https://web.archive.org/web/20130509023652/http://blogs.windows.com/windows/archive/b/windowsvista/archive/2008/10/24/windows-vista-service-pack-2- beta.aspx
- ^ https://blogs.windows.com/windowsexperience/2009/10/27/announcing-final-releases-of-platform-update-for-windows-vista-technologies/
- ^ https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/help/2117917/platform-update-supplement-for-windows-vista-and-for-windows-server-20
- ^ https://support.microsoft.com/en-au/help/4534251/cumulative-security-update-for-internet-explorer
- ^ https://www.microsoft.com/en-au/download/details.aspx?id=48130
- ^ https://www.microsoft.com/security/blog/2017/07/20/tls-1-2-support-added-to-windows-server-2008/
- ^ https://support.microsoft.com/en-hk/help/4472027/2019-sha-2-code-signing-support-requirement-for-windows-and-wsus
- ^ https://redmondmag.com/articles/2018/06/13/windows-server-2008-sp2-update-model-change.aspx?m=1
- ^ https://forums.ivanti.com/s/article/Microsoft-Patching-Changes-Starting-In-October-2016
- ^ https://support.microsoft.com/en-au/help/4495374/build-number-changing-to-6003-in-windows-server-2008
- ^ https://support.microsoft.com/en-au/help/4534303
- ^ https://support.microsoft.com/en-au/help/4497181/lifecycle-faq-extended-security-updates
- ^ «Windows Server 2008 R2 достигает вехи RTM! — Блог Windows Server — Домашняя страница сайта — Блоги TechNet». Blogs.technet.com. 2009-07-22. Получено 2013-01-09.
- ^ «Когда ожидать Windows Server 2008 R2 RTM — Блог Windows Server — Домашняя страница — Блоги TechNet». Blogs.technet.com. 2009-07-22. Получено 2013-01-09.
- ^ а б «Системные требования Windows Server 2008». 31 марта 2008 г.. Получено 2008-03-31.
- ^ а б c «Системные требования Microsoft Windows Server 2008». Microsoft.com. Получено 2013-01-09.
- ^ «Системные требования Microsoft Windows Server 2008». Microsoft. Получено 2013-01-09.
- ^ Сэвилл, Джон (28 октября 2011 г.). «В: Каковы показатели масштабируемости Windows Server 8?». Windows для ИТ-специалистов. Пентон Медиа. Получено 5 ноября, 2011.
- ^ а б c d Seldam, Matthijs ten (13 октября 2012 г.). «Windows Server — сокеты, логические процессоры, симметричная многопоточность». Блог Маттейса. Microsoft. Получено 14 октября, 2012.
- ^ а б c d «Ограничения памяти для выпусков Windows и Windows Server». MSDN. Microsoft. Получено 13 апреля 2014.
дальнейшее чтение
- «Что нового в сети». TechNet. Microsoft. Получено 16 августа 2013.
- «Изменения функциональности с Windows Server 2003 с пакетом обновления 1 до Windows Server 2008». TechNet. Microsoft. 21 января 2008 г.. Получено 16 августа 2013.
- «Описание серверных приложений Microsoft, которые поддерживаются в Windows Server 2008». Поддержка. Microsoft. 23 апреля 2012 г.. Получено 16 августа 2013.
- «Системные требования Windows Server 2008». TechNet. Microsoft. Получено 16 августа 2013.
- Хендерсон, Том; Дворжак, Рэнд (21 февраля 2008 г.). «Windows Server 2008: быстрее, управляемее и безопаснее, но по-прежнему отсутствует виртуальная связь». Сетевой мир. IDG. Получено 16 августа 2013.
- Радзиковски, Пшемек (21 февраля 2010 г.). «Как узнать номер сборки и версии установленной Windows Vista или Windows Server 2008». Capitalhead. Capitalhead Pty. Ltd. Получено 16 августа 2013.
- Станек, Уильям (2008). Windows Server 2008 наизнанку. Microsoft Press. ISBN 978-0-7356-2438-2.
внешняя ссылка
- Блог группы разработчиков по производительности Windows Server
Уже в январе 2020 года заканчивается поддержка Windows 2008 R2. Сегодня я хочу поделиться подборкой субъективных причин, по которым многие (и я тоже) до сих пор проводят новые инсталляции этой старушки.
Ценителей, ностальгирующих и ненавистников — прошу под кат.
Легковесность
Если сравнивать минимальные системные требования Windows 2008R2 и Windows 2016, то они будут идентичны за исключением маленького нюанса — графическая оболочка Windows 2016 требует 2 Гб оперативной памяти. А вот по субъективным ощущениям Windows 2008R2 работает куда отзывчивее на не очень свежих серверах и слабых виртуалках, особенно по части IO нагрузки на диск.
Судя по всему, дело в меньшем количестве различных служб и в их большей простоте.
Свежеустановленная старая и новая система с идентичными ролями.
Кнопка Пуск
Даже многие системные администраторы ставят на сервера под управлением Windows 2012 и старше ПО вроде Classic Shell, чтобы вернуть старый добрый «Пуск». Что уж говорить о пользователях. Конечно, возврат к чему-то «пускоподобному» в Windows 102016 сделал жизнь чуть легче, но лишь только чуть. Искать нужное приложение приходится или мучительно вглядываясь в строки, или набирая его имя — одной мышкой не обойтись.
Да и к тому же попробуйте объяснить пользователю, как правильно выходить с терминального сервера не «крестиком», если вместо кнопки «Пуск» — плитки и недо-плитки. Сравните, насколько просто было в Windows 2008: Пуск — завершение сеанса.
Краткость — сестра таланта.
И в Windows 2016: «Нажмите туда, где раньше был пуск. Да-да, с квадратиками. Найдите там человечка. Да, такой маленький… Нет, слева! Нажмите на него и там нажмите на «выход».
Больше, больше кликов мыши!
Далее в старом меню есть прекрасный пункт — «Безопасность Windows». Пользователь может совершенно спокойно и ненапряжно сменить свой пароль. Без вот этого вот «нажмите Ctrl+Alt+End. Нет, не Delete. End. Это кнопка рядом с Delete». А если пользователь сидит на терминальном сервере с другого терминального сервера — без лайфхаков типа ярлыка на команду explorer shell:::{2559a1f2-21d7-11d4-bdaf-00c04f60b9f0} уже не обойтись.
Нет, лично я радуюсь, когда захожу на сервер с Windows 2008 и вижу кнопку «Пуск». А люди на форумах острят на тему плиточных интерфейсов, что они для того чтобы получать ачивки в аккаунте Xbox — типа «Починил Active Directory», «Не сломал DFS при обновлении домена». А что? Было бы прикольно.
Полноценный терминальный сервер без домена
Допустим, захотелось вам решить простую задачу — развернуть на далеком сервере (реальном или виртуальном) сервер терминалов для работы с 1С в небольшой компании.
В Windows 2008 все просто: все настройки проводятся через оснастку, контроллер домена не нужен. Начиная с Windows 2012, коллекцию без контроллера домена не создать. И если хочется отдельный сервер — извольте настраивать через локальные политики.
Но такая возможность, как RemoteApp без домена — увы, не работает. Нужно или использовать какие-то сторонние решения, или разворачивать домен.
Также если хочется подключаться к пользовательской сессии (т.н shadowing), то без контроллера домена штатными средствами ничего не получится. Потому что.
Старый добрый tsadmin.msc.
Даже банальная отправка сообщений пользователям (например, о скорой перезагрузке сервера) начинает превращаться в квест. Если раньше можно было выбрать нужных пользователей в оснастке tsadmin.msc, используя такие средства выделения как Ctrl и Shift, то теперь или отправляй сообщения по одному, или используй командную строку и утилиту msg.exe.
Отправка сообщений в Windows 2016.
Если вдруг вы все-таки захотите сделать полноценный сервер терминалов с коллекциями и поставите роль контроллера домена на сервер терминалов — или наоборот, — то и тут вас ждут приключения из-за работы встроенной БД Windows и правил доступа к ней. Придется ставить еще и SQl Management Studio.
Microsoft рекомендует использовать возможность установки двух виртуальных машин по одной лицензии. То есть теперь, если я хочу пользоваться всеми возможностями сервера терминалов, мне предлагается ставить Windows на железо и делать две виртуалки — для сервера терминалов и для контроллера домена. Падение производительности 1С в таком случае составляет от 10% до 20%, появляется необходимость покупать у хостера второй IP — из-за того, что на гипервизоре может быть роль только гипервизора… Спасибо, Microsoft!
Стабильность работы
Когда на одном предприятии смигрировали терминальный сервер на Windows 2016, то столкнулись с удивительными вещами при работе стареньких несетевых принтеров и 1С. Если принтеры пробрасывались в RDP или подключались к терминальной сессии как computerprinter, то они или пропадали вообще, или пропадали из 1С. И приходилось удалять настройки пользователя.
Безумие продолжалось до тех пор, пока не приняли отвратительное решение — установить принтеры на сервер как локальные с портом computerprinter и навесить на них нужный ACL.
Установленный принтер.
Подобные интересные нюансы всплывали неоднократно в разных организациях. То проблема с принтерами, то с не самым свежим ПО вплоть до BSOD-а. В одной истории пришлось воспользоваться правом лицензии VL на downgrade, так как проприетарное ПО категорически не хотело работать на Windows 2016 и на виртуальной машине.
Поэтому, если позволяет лицензия и аппаратная составляющая — Windows 2008R2 Standart поддерживает не более 32 Гб оперативной памяти, — а также нет необходимости в новых функциях свежих серверных OS, мы по-прежнему ставим Windows 2008R2 и с ужасом ждем окончания поддержки.
Надо отметить, что Windows 2008R2 уже фактически стала эталоном для «облачного» хостинга 1С — когда клиенту недостаточно тонкого клиента, а нужен полноценный доступ в 1С. Благо RemoteApp работают с 1С в 2008R2 так же плохо, как и в 2016.
Телеметрия
Кто бы что ни говорил о плюсах телеметрии, мне неприятно, когда система что-то кому-то отсылает. Особенно, если эта система в продакшене. Конечно, Microsoft заявляет, что опасаться нечего, но тем не менее. Напрашивается очевидный выход — отключить интернет на сервере. Это хорошо, если интернет не нужен для функционирования сервера. В противном случае будет разумно закрыть адреса Microsoft на фаерволе или что-то подобное.
Ведь даже в настройках телеметрии в групповых политиках в параметре Конфигурация компьютера — Административные шаблоны — Компоненты Windows — Сборки для сбора данных и предварительные сборки можно лишь поставить ограничение, но не отключить механизм полностью.
Настройка телеметрии.
Еще можно вовсе отключить телеметрию и настроить мониторинг, который уведомит о включении службы после обновления. Также сообщество создало некоторое количество скриптов и утилит, призванных отключать телеметрию совсем на Windows 10 и Windows 2016.
Например, известен батник, который правит реестр и блокирует домены MS при помощи файла host. Еще существует решение на PowerShell: оно тоже правит реестр и заодно отключает службы с назначенными заданиями, которые могут что-то передавать на сторонние сервера.
Кумулятивные обновления
Стандартная поставка обновлений безопасности на свежих версиях Windows происходит через кумулятивные обновления. Это очень удобно — не нужно выбирать 100500 обновлений для загрузки на свежеустановленную систему. Правда, удобно это разве что установщикам систем.
В реальности если какой-то патч что-то ломает — а это бывает регулярно, — то на его отлов и отключение придется потратить немало человеко-часов. Поэтому возникает необходимость держать как минимум тестовую группу серверов, где можно проверять обновления. Ну и WSUS начинает нравиться как инструмент.
Старая добрая масса обновлений.
Нет уж. Старый механизм, где можно опционально выбрать или заблокировать нужные системы безопасности, мне больше по душе.
Как продлить поддержку
Сейчас Microsoft предлагает лишь один вариант, как не остаться без поддержки с 2020 года — это перенести серверы в Azure. Тогда, по словам Microsoft, можно продлить агонию одной из самых удачных операционных систем еще на 3 года.
Стоит отметить, что это касается также Windows 2008 (единственной актуальной 32-битной серверной ОС) и SQL Server 2008.
Расскажите, планируете ли вы полностью избавиться от Windows 2008R2 за следующие пару лет?