v9.1.0.0p1-Beta
This is a beta-release (non-production ready)
This release includes:
-
Upstream changes from OpenSSH 9.0 & OpenSSH 9.1.
-
Breaking changes — see upstream release notes for more information:
- Switches scp from using the legacy scp/rcp protocol to using the sftp protocol by default.
- SetEnv directives in ssh_config and sshd_config are now first-match-wins to match other directives. Previously if an environment variable was multiply specified the last set value would have been used.
- ssh-keygen -A (generate all default host key types) will no longer generate DSA keys.
-
Security Fixes:
- adds Mark of the Web (MOTW) to scp/sftp file transfers, when possible.
-
Fixes for various reliability issues listed here.
-
LibFido2 upgrade to version 1.12.0.
-
LibreSSL upgrade to version 3.6.1.
-
ZLib upgrade to version 1.2.13.
V8.9.1.0p1-Beta
This release includes
-
Security fixes
- Upgrade to LibreSSL 3.4.3. Please refer to #1917
-
Non-security fixes
- [FIDO] PIN is asked twice with keys generated with -O verify-required. #1918
- SSH-Agent installed through MSI is missing required privileges. #1914
- install-sshd.ps1 to allow silent installation #1916
V8.9.0.0p1-Beta
This release includes
-
Upstream changes from OpenSSH 8.9. Please note this release doesn’t have ssh-agent restriction feature. This is tracked as part of #1902.
-
Breaking change
- This release disables RSA signatures using the SHA-1 hash algorithm by default. For more information, refer to «Potentially-incompatible changes» here.
-
Security fixes
- Validate the ACLs of $env:programdatassh folder, it’s contents. This is not applicable for windows 10+ / windows server 2019+. For more information, refer to #1900
-
Non-security fixes
- FIDO/U2F hardware authenticators support to Win32-OpenSSH. Thanks to @martelletto, @akshayku.
- PKCS11 support to ssh-agent. Thanks to @yan4321.
- MSI installation package. Thanks to @tmeckel, @heaths.
- Fixes for various reliability issues listed here.
V8.6.0.0p1-Beta
This release includes
-
Upstream changes from OpenSSH 8.6. Please note this release doesn’t have FIDO support.
-
Breaking change
- SSH askpass requires
SSH_ASKPASS_REQUIREenvironment variable to be set as «prefer» (or) «force».
- SSH askpass requires
-
Security fixes
- For non en-us OS, enforce authorized keys for admin users are read from
$env:programdatasshadministrators_authorized_keys(#1757) - Ensure only admin users have access to modify the registry entries like DefaultShell (#1754)
- Use
$env:programdatasshssh_configonly if it has correct file permissions (non-admin users shouldn’t have write permissions)
(#1753)
- For non en-us OS, enforce authorized keys for admin users are read from
-
Non-security fixes
- Allow
authorizedKeysCommandto work with the System user. Thanks to @bkatyl, @NoMoreFood. - Add moduli support.
- Allow support to configure the custom shell arguments.
- Allow SSH connection when the machine name is the same as the user name. Thanks to @oldium.
- For downlevel OS (win10 below), fix the scrolling issue after reaching the end of the screen.
- Write non-English characters to ETW / logfile.
- X11 related bugs . Thanks to @riverar.
- Fixes for various reliability issues listed here.
- Allow
v8.1.0.0p1-Beta
This release includes
- Upstream changes from OpenSSH 8.1
- Added ZLIB compression
- Upgraded LibreSSL to version 2.9.2.1
- Added support for AuthorizedKeysCommand and AuthorizedPrincipalsCommand.
- Read the VTSequence using the console win32 APIs.
- Added support for windows long paths. Thanks to @NoMoreFood.
- Fixes for various reliability issues listed here.
v8.0.0.0p1-Beta
v7.9.0.0p1-Beta
v7.7.2.0p1-Beta
This is a pre-release (non-production ready)
UPDATE -We have updated ssh-shellhost.exe binary (fix for #1222) in V7.7.2.0 payload on 8/4/2018.
This release includes
- Support for auto updating known_hosts via ssh and ssh-keygen
- Optimized group membership resolution that results in vast performance improvement in processing simple user/group configuration rules.
- Fixed descriptor leaks in win32 fstat implementation(#1209) by @cbookg
- Support for handling user resolution in absence of explicit UPN (#1213) by @NoMoreFood
- Various other fixes listed here
Source — https://github.com/PowerShell/openssh-portable/releases/tag/v7.7.2.0
v7.7.1.0p1-Beta
This is a pre-release (non-production ready)
This release includes fixes for regressions introduced in v7.7.0.0.
Note
- If you configure a default shell, ensure that OpenSSH installation path is in system PATH. If not already present, amend system PATH and restart sshd service.
- Scp and Sftp are tested to work with Powershell and Cygwin’s bash as default shells. There are still issues with WSL bash (manifest as hung sessions), we are working on investigating these.
List of all issues fixed — here
Source — https://github.com/PowerShell/openssh-portable/releases/tag/v7.7.1.0
v7.7.0.0p1-Beta
This is a pre-release (non-production ready)
Regressions
- #1164 — scp and sftp won’t work if OpenSSH is installed in «Program Files» or any directory with a white space.
- Work around — install in a path with no white space — ex. c:openssh
- #1165 — SCP fails when using bash as alternative shell
Note
- This release introduces new rules for specifying user/group based configuration rules for domain principals — these should now adhere to NameSamCompatible format. For more info refer sshd_config manual.
This release includes
- OpenSSH 7.7 changes from upstream.
- Normalized user/group principal resolution — by @NoMoreFood
- Improvements to support nested groups while processing group based configuration rules — by @NoMoreFood
- Chroot support for sftp (and scp via custom shell). See sshd_config manual
- Support sshd in interactive mode (for testing and trouble shooting)
- various other fixes listed here
Source — https://github.com/PowerShell/openssh-portable/releases/tag/v7.7.0.0
- Downloads
- Internet Tools
- FTP Utilities
OpenSSH 9.1
OpenSSH is the premier connectivity tool for remote login with the SSH protocol. It encrypts all traffic to eliminate eavesdropping, connection hijacking, and other attacks.
In addition, OpenSSH provides a large suite of secure tunneling capabilities, several authentication methods, and sophisticated configuration options.
The OpenSSH suite consists of the following tools:
- Remote operations are done using ssh, scp, and sftp.
- Key management with ssh-add, ssh-keysign, ssh-keyscan, and ssh-keygen.
- The service side consists of sshd, sftp-server, and ssh-agent.
OpenSSH is developed by a few developers of the OpenBSD Project and made available under a BSD-style license.
Features
- Completely open source project with free licensing
- The OpenSSH source code is available free to everyone via the Internet. This encourages code reuse and code auditing. Code review ensures the bugs can be found and corrected by anyone. This results in secure code. OpenSSH is not covered by any restrictive license. It can be used for any and all purposes, and that explicitly includes commercial use. The license is included in the distribution. We feel that the world would be better if routers, network appliances, operating systems, and all other network devices had ssh integrated into them. All components of a restrictive nature (i.e. patents) have been removed from the source code. Any licensed or patented components are chosen from external libraries (e.g. LibreSSL).
- Strong cryptography (AES, ChaCha20, RSA, ECDSA, Ed25519…)
- Encryption is started before authentication, and no passwords or other information is transmitted in the clear. Encryption is also used to protect against spoofed packets. A number of different ciphers and key types are available, and legacy options are usually phased out in a reasonable amount of time.
- X11 forwarding (which also encrypts X Window System traffic)
- X11 forwarding allows the encryption of remote X windows traffic, so that nobody can snoop on your remote xterms or insert malicious commands. The program automatically sets DISPLAY on the server machine, and forwards any X11 connections over the secure channel. Fake Xauthority information is automatically generated and forwarded to the remote machine; the local client automatically examines incoming X11 connections and replaces the fake authorization data with the real data (never telling the remote machine the real information).
- Port forwarding (encrypted channels for legacy protocols)
- Port forwarding allows forwarding of TCP/IP connections to a remote machine over an encrypted channel. Insecure internet applications like POP can be secured with this.
- Strong authentication (public keys, one-time passwords)
- Strong authentication protects against several security problems: IP spoofing, fakes routes and DNS spoofing. Some authentication methods include public key authentication, one-time passwords with s/key and authentication using Kerberos (only in -portable).
- Agent forwarding
- An authentication agent, running in the user’s laptop or local workstation, can be used to hold the user’s authentication keys. OpenSSH automatically forwards the connection to the authentication agent over any connections, and there is no need to store the authentication keys on any machine in the network (except the user’s own local machine). The authentication protocols never reveal the keys; they can only be used to verify that the user’s agent has a certain key. Eventually the agent could rely on a smart card to perform all authentication computations.
- Interoperability
- Interoperability between implementations is a goal, but not a promise. As OpenSSH development progresses, older protocols, ciphers, key types and other options that have known weaknesses are routinely disabled. Some examples can be found on the legacy page.
- SFTP client and server support.
- Complete SFTP support is included, using the sftp(1) command as a client and sftp-server(8) subsystem as a server.
- Optional data compression
- Data compression before encryption improves the performance for slow network links.
What’s New
OpenSSH 9.1 was released on 2022-10-04. OpenSSH is a 100% complete SSH protocol 2.0 implementation and includes sftp client and server support.
- It is now possible[1] to perform chosen-prefix attacks against the
- SHA-1 algorithm for less than USD$50K.
- In the SSH protocol, the «ssh-rsa» signature scheme uses the SHA-1 hash algorithm in conjunction with the RSA public key algorithm. OpenSSH will disable this signature scheme by default in the near future.
- Note that the deactivation of «ssh-rsa» signatures does not necessarily require cessation of use for RSA keys. In the SSH protocol, keys may be capable of signing using multiple algorithms. In particular, «ssh-rsa» keys are capable of signing using «rsa-sha2-256» (RSA/SHA256), «rsa-sha2-512» (RSA/SHA512) and «ssh-rsa» (RSA/SHA1). Only the last of these is being turned off by default.
- This algorithm is unfortunately still used widely despite the existence of better alternatives, being the only remaining public key signature algorithm specified by the original SSH RFCs that is still enabled by default.
Security
- This release contains fixes for three minor memory safety problems. None are believed to be exploitable, but we report most memory safety problems as potential security vulnerabilities out of caution.
- ssh-keyscan(1): fix a one-byte overflow in SSH- banner processing. Reported by Qualys
Potentially-incompatible changes
This release includes a number of changes that may affect existing configurations:
- ssh(1), sshd(8): this release changes the first-preference signature algorithm from ECDSA to ED25519.
- ssh(1), sshd(8): set the TOS/DSCP specified in the configuration for interactive use prior to TCP connect. The connection phase of the SSH session is time-sensitive and often explicitly interactive. The ultimate interactive/bulk TOS/DSCP will be set after authentication completes.
- ssh(1), sshd(8): remove the pre-standardization cipher rijndael-cbc@lysator.liu.se. It is an alias for aes256-cbc before it was standardized in RFC4253 (2006), has been deprecated and disabled by default since OpenSSH 7.2 (2016) and was only briefly documented in ssh.1 in 2001.
- ssh(1), sshd(8): update/replace the experimental post-quantum hybrid key exchange method based on Streamlined NTRU Prime coupled with X25519.
- The previous sntrup4591761x25519-sha512@tinyssh.org method is replaced with sntrup761x25519-sha512@openssh.com. Per its designers, the sntrup4591761 algorithm was superseded almost two years ago by sntrup761. (note this both the updated method and the one that it replaced are disabled by default)
- ssh(1): disable CheckHostIP by default. It provides insignificant benefits while making key rotation significantly more difficult, especially for hosts behind IP-based load-balancers.
Changes
New features
- ssh(1): this release enables UpdateHostkeys by default subject to some conservative preconditions:
- The key was matched in the UserKnownHostsFile (and not in the GlobalKnownHostsFile).
- The same key does not exist under another name.
- A certificate host key is not in use.
- known_hosts contains no matching wildcard hostname pattern.
- VerifyHostKeyDNS is not enabled.
- The default UserKnownHostsFile is in use.
- We expect some of these conditions will be modified or relaxed in future.
- ssh(1), sshd(8): add a new LogVerbose configuration directive for that allows forcing maximum debug logging by file/function/line pattern-lists.
- ssh(1): when prompting the user to accept a new hostkey, display any other host names/addresses already associated with the key.
- ssh(1): allow UserKnownHostsFile=none to indicate that no known_hosts file should be used to identify host keys.
- ssh(1): add a ssh_config KnownHostsCommand option that allows the client to obtain known_hosts data from a command in addition to the usual files.
- ssh(1): add a ssh_config PermitRemoteOpen option that allows the client to restrict the destination when RemoteForward is used with SOCKS.
- ssh(1): for FIDO keys, if a signature operation fails with a «incorrect PIN» reason and no PIN was initially requested from the user, then request a PIN and retry the operation. This supports some biometric devices that fall back to requiring PIN when reading of the biometric failed, and devices that require PINs for all hosted credentials.
- sshd(8): implement client address-based rate-limiting via new sshd_config(5) PerSourceMaxStartups and PerSourceNetBlockSize directives that provide more fine-grained control on a per-origin address basis than the global MaxStartups limit.
Bugfixes
- ssh(1): Prefix keyboard interactive prompts with «(user@host)» to make it easier to determine which connection they are associated with in cases like scp -3, ProxyJump, etc. bz#3224
- sshd(8): fix sshd_config SetEnv directives located inside Match blocks. GHPR201
- ssh(1): when requesting a FIDO token touch on stderr, inform the user once the touch has been recorded.
- ssh(1): prevent integer overflow when ridiculously large ConnectTimeout values are specified, capping the effective value (for most platforms) at 24 days. bz#3229
- ssh(1): consider the ECDSA key subtype when ordering host key algorithms in the client.
- ssh(1), sshd(8): rename the PubkeyAcceptedKeyTypes keyword to PubkeyAcceptedAlgorithms. The previous name incorrectly suggested that it control allowed key algorithms, when this option actually specifies the signature algorithms that are accepted. The previous name remains available as an alias. bz#3253
- ssh(1), sshd(8): similarly, rename HostbasedKeyTypes (ssh) and HostbasedAcceptedKeyTypes (sshd) to HostbasedAcceptedAlgorithms.
- sftp-server(8): add missing lsetstat@openssh.com documentation and advertisement in the server’s SSH2_FXP_VERSION hello packet.
- ssh(1), sshd(8): more strictly enforce KEX state-machine by banning packet types once they are received. Fixes memleak caused by duplicate SSH2_MSG_KEX_DH_GEX_REQUEST (oss-fuzz #30078).
- sftp(1): allow the full range of UIDs/GIDs for chown/chgrp on 32bit platforms instead of being limited by LONG_MAX. bz#3206
- Minor man page fixes (capitalization, commas, etc.) bz#3223
- sftp(1): when doing an sftp recursive upload or download of a read-only directory, ensure that the directory is created with write and execute permissions in the interim so that the transfer can actually complete, then set the directory permission as the final step. bz#3222
- ssh-keygen(1): document the -Z, check the validity of its argument earlier and provide a better error message if it’s not correct. bz#2879
- ssh(1): ignore comments at the end of config lines in ssh_config, similar to what we already do for sshd_config. bz#2320
- sshd_config(5): mention that DisableForwarding is valid in a sshd_config Match block. bz3239
- sftp(1): fix incorrect sorting of «ls -ltr» under some circumstances. bz3248.
- ssh(1), sshd(8): fix potential integer truncation of (unlikely) timeout values. bz#3250
- ssh(1): make hostbased authentication send the signature algorithm in its SSH2_MSG_USERAUTH_REQUEST packets instead of the key type.
- This make HostbasedAcceptedAlgorithms do what it is supposed to — filter on signature algorithm and not key type.
Portability
- sshd(8): add a number of platform-specific syscalls to the Linux seccomp-bpf sandbox. bz#3232 bz#3260
- sshd(8): remove debug message from sigchld handler that could cause deadlock on some platforms. bz#3259
- Sync contrib/ssh-copy-id with upstream.
- unittests: add a hostname function for systems that don’t have it. Some systems don’t have a hostname command (it’s not required by POSIX). The do have uname -n (which is), but not all of those have it report the FQDN.
Fast servers and clean downloads. Tested on TechSpot Labs. Here’s why you can trust us.

Last updated:
December 6, 2022
User rating:
7 votes
Software similar to OpenSSH 4
-
62 votes
PuTTY is a free implementation of Telnet and SSH.
- Freeware
- Windows/Linux
-
21 votes
KiTTY is a fork from version of PuTTY, the best telnet / SSH client in the world. KiTTY is only designed for the Microsoft Windows platform.
- Freeware
- Windows
-
183 votes
SecureCRT is a Windows terminal emulator that supports Secure Shell (SSH), Telnet, rlogin, serial, and TAPI protocols.
- Free to Try
- Windows/macOS/Linux
-
More similar downloads
Popular apps
in FTP Utilities
В современных версиях Windows уже есть встроенный SSH сервер на базе пакета OpenSSH. В этой статье мы покажем, как установить и настроить OpenSSH сервер в Windows 10/11 и Windows Server 2022/2019 и подключиться к нему удаленно по защищенному SSH протоколу (как к Linux).
Содержание:
- Установка сервера OpenSSH в Windows
- Настройка SSH сервера в Windows
- Sshd_config: Конфигурационный файл сервера OpenSSH
- Подключение по SSH к Windows компьютеру
- Логи SSH подключений в Windows
Установка сервера OpenSSH в Windows
Пакет OpenSSH Server включен в современные версии Windows 10 (начиная с 1803), Windows 11 и Windows Server 2022/2019 в виде Feature on Demand (FoD). Для установки сервера OpenSSH достаточно выполнить PowerShell команду:
Get-WindowsCapability -Online | Where-Object Name -like ‘OpenSSH.Server*’ | Add-WindowsCapability –Online
Или при помощи команды DISM:
dism /Online /Add-Capability /CapabilityName:OpenSSH.Server~~~~0.0.1.0
Если ваш компьютер подключен к интернету, пакет OpenSSH.Server будет скачан и установлен в Windows.
Также вы можете установить сервер OpenSSH в Windows через современную панель Параметры (Settings -> Apps and features -> Optional features -> Add a feature, Приложения -> Управление дополнительными компонентами -> Добавить компонент. Найдите в списке OpenSSH Server и нажмите кнопку Install).
На изолированных от интернета компьютерах вы можете установить компонент с ISO образа Features On Demand (доступен в личном кабинете на сайте Microsoft: MSDN или my.visualstudio.com). Скачайте диск, извлеките его содержимое в папку c:FOD (достаточно распаковать извлечь файл
OpenSSH-Server-Package~31bf3856ad364e35~amd64~~.cab
), выполните установку из локального репозитория:
Add-WindowsCapability -Name OpenSSH.Server~~~~0.0.1.0 -Online -Source c:FOD
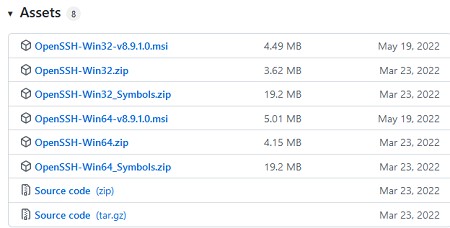
Также доступен MSI установщик OpenSSH для Windows в официальном репозитории Microsoft на GitHub (https://github.com/PowerShell/Win32-OpenSSH/releases/). Например, для Windows 10 x64 нужно скачать и установить пакет OpenSSH-Win64-v8.9.1.0.msi. Следующая PowerShell команда скачает MSI файл и установит клиент и сервер OpenSSH:
Invoke-WebRequest https://github.com/PowerShell/Win32-OpenSSH/releases/download/v8.9.1.0p1-Beta/OpenSSH-Win64-v8.9.1.0.msi -OutFile $HOMEDownloadsOpenSSH-Win64-v8.9.1.0.msi -UseBasicParsing
msiexec /i c:usersrootdownloadsOpenSSH-Win64-v8.9.1.0.msi
Также вы можете вручную установить OpenSSH сервер в предыдущих версиях Windows (Windows 8.1, Windows Server 2016/2012R2). Пример установки Win32-OpenSSH есть в статье “Настройка SFTP сервера (SSH FTP) в Windows”.
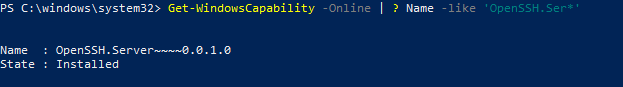
Чтобы проверить, что OpenSSH сервер установлен, выполните:
Get-WindowsCapability -Online | ? Name -like 'OpenSSH.Ser*'
State : Installed
Настройка SSH сервера в Windows
После установки сервера OpenSSH в Windows добавляются две службы:
- ssh-agent (OpenSSH Authentication Agent) – можно использовать для управления закрытыми ключами если вы настроили SSH аутентификацию по ключам;
- sshd (OpenSSH SSH Server) – собственно сам SSH сервер.
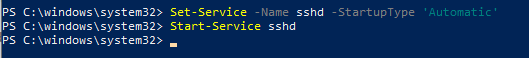
Вам нужно изменить тип запуска службы sshd на автоматический и запустить службу с помощью PowerShell:
Set-Service -Name sshd -StartupType 'Automatic'
Start-Service sshd
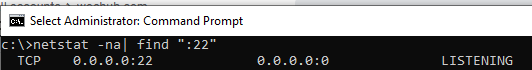
С помощью nestat убедитесь, что теперь в системе запущен SSH сервер и ждет подключений на порту TCP:22 :
netstat -na| find ":22"
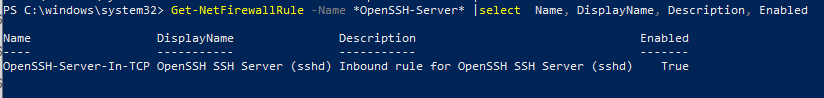
Проверьте, что включено правило брандмауэра (Windows Defender Firewall), разрешающее входящие подключения к Windows по порту TCP/22.
Get-NetFirewallRule -Name *OpenSSH-Server* |select Name, DisplayName, Description, Enabled
Name DisplayName Description Enabled ---- ----------- ----------- ------- OpenSSH-Server-In-TCP OpenSSH SSH Server (sshd) Inbound rule for OpenSSH SSH Server (sshd) True
Если правило отключено (состоянии Enabled=False) или отсутствует, вы можете создать новое входящее правило командой New-NetFirewallRule:
New-NetFirewallRule -Name sshd -DisplayName 'OpenSSH Server (sshd)' -Enabled True -Direction Inbound -Protocol TCP -Action Allow -LocalPort 22
Рассмотрим, где храниться основные компоненты OpenSSH:
- Исполняемые файлы OpenSSH Server находятся в каталоге
C:WindowsSystem32OpenSSH
(sshd.exe, ssh.exe, ssh-keygen.exe, sftp.exe и т.д.) - Конфигурационный файл sshd_config (создается после первого запуска службы):
C:ProgramDatassh - Файлы authorized_keys и ssh ключи можно хранить в профиле пользователей:
%USERPROFILE%.ssh
Sshd_config: Конфигурационный файл сервера OpenSSH
Настройки сервере OpenSSH хранятся в конфигурационном файле %programdata%sshsshd_config. Это обычный текстовый файл с набором директив. Для редактирования можно использовать любой текстовый редактор (я предпочитаю notepad++). Можно открыть с помощью обычного блокнота:
start-process notepad C:Programdatasshsshd_config
Например, чтобы запретить SSH подключение для определенного доменного пользователя (и всех пользователей указанного домена), добавьте в конце файле директивы:
DenyUsers winitpro[email protected] DenyUsers corp*
Чтобы разрешить подключение только для определенной доменной группы:
AllowGroups winitprosshadmins
Либо можете разрешить доступ для локальной группы:
AllowGroups sshadmins
По умолчанию могут к openssh могут подключаться все пользователи Windows. Директивы обрабатываются в следующем порядке: DenyUsers, AllowUsers, DenyGroups,AllowGroups.
Можно запретить вход под учетными записями с правами администратора, в этом случае для выполнения привилегированных действий в SSH сессии нужно делать runas.
DenyGroups Administrators
Следующие директивы разрешают SSH доступ по ключам (SSH аутентификации в Windows с помощью ключей описана в отдельной статье) и по паролю:
PubkeyAuthentication yes PasswordAuthentication yes
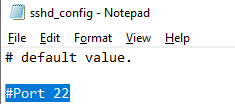
Вы можете изменить стандартный SSH порт TCP/22, на котором принимает подключения OpenSSH в конфигурационном файле sshd_config в директиве Port.
После любых изменений в конфигурационном файле sshd_config нужно перезапускать службу sshd:
restart-service sshd
Подключение по SSH к Windows компьютеру
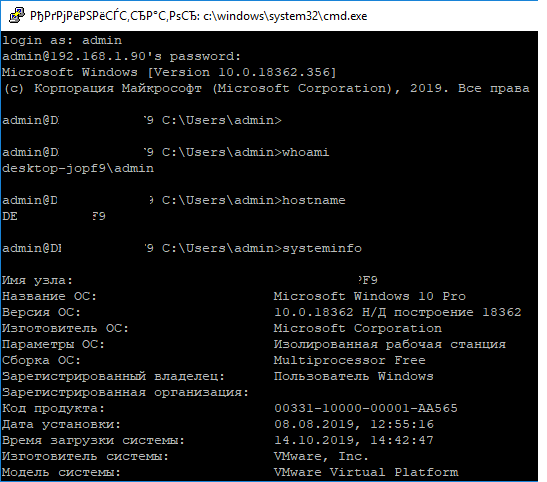
Теперь вы можете попробовать подключиться к своей Windows 10 через SSH клиент (в этом примере я использую putty).
Вы можете использовать встроенный SSH клиентом Windows для подключения к удаленному хосту. Для этого нужно в командной строке выполнить команду:
ssh [email protected]
В этом примере
alexbel
– имя пользователя на удаленном Windows компьютере, и 192.168.31.102 – IP адрес или DNS имя компьютера.
Обратите внимание что можно использовать следующие форматы имен пользователей Windows при подключении через SSH:
-
[email protected]
– локальный пользователь Windows -
[email protected]@server1
–пользователь Active Directory (в виде UPN) или аккаунт Microsoft/ Azure(Microsoft 365) -
winitpro[email protected]
– NetBIOS формат имени
В домене Active Directory можно использовать Kerberos аутентификацию в SSH. Для этого в sshd_config нужно включить параметр:
GSSAPIAuthentication yes
После этого можно прозрачно подключать к SSH сервер с Windows компьютера в домене из сессии доменного подключается. В этом случае пароль пользователя не указывается и выполняется SSO аутентификация через Kerberos:
ssh -K server1
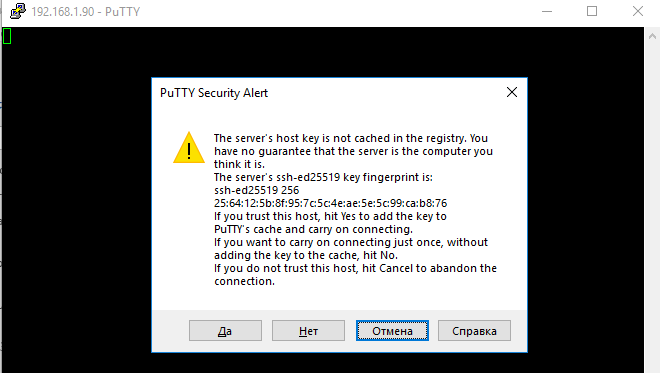
При первом подключении появится стандартный запрос на добавление узла в список известных SSH хостов.
Нажимаем Да, и в открывшееся окне авторизуемся под пользователем Windows.
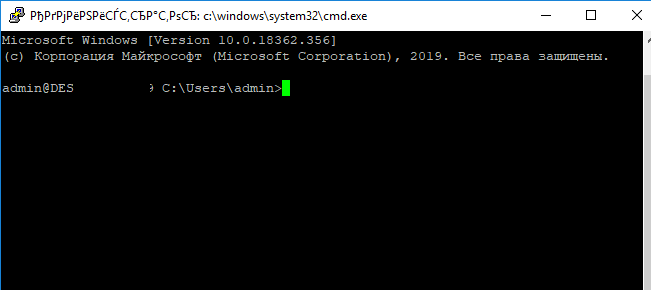
При успешном подключении запускается командная оболочка cmd.exe со строкой-приглашением.
[email protected] C:Usersadmin>
В командной строке вы можете выполнять различные команды, запускать скрипты и программы.
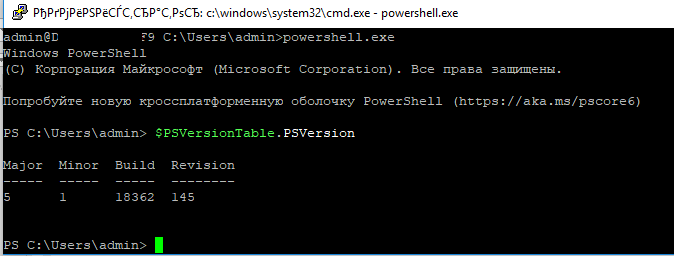
Я предпочитаю работать в командной строке PowerShell. Чтобы запустить интерпретатор PowerShell, выполните:
powershell.exe
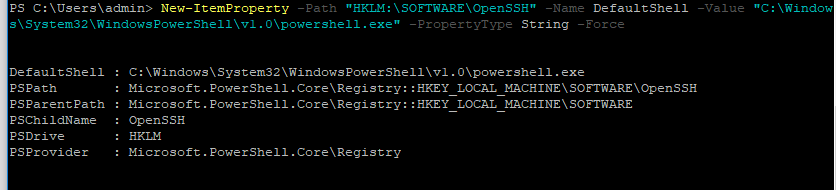
Чтобы изменить командную оболочку (Shell) по умолчанию в OpenSSH с cmd.exe на PowerShell, внесите изменение в реестр такой командой:
New-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:SOFTWAREOpenSSH" -Name DefaultShell -Value "C:WindowsSystem32WindowsPowerShellv1.0powershell.exe" -PropertyType String –Force
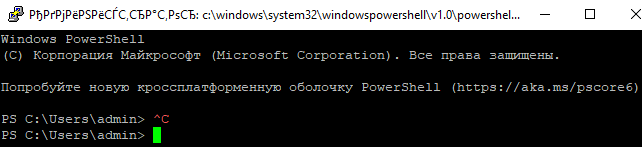
Осталось перезапустить SSH подключение и убедиться, что при подключении используется командный интерпретатор PowerShell (об этом свидетельствует приглашение
PS C:Usersadmin>
).
В SSH сессии запустилась командная строка PowerShell, в которой работают привычные функции: авто дополнение, раскраска модулем PSReadLine, история команд и т.д. Если текущий пользователь входит в группу локальных администраторов, то все команды в его сессии выполняются с повышенными правами даже при включенном UAC.
Логи SSH подключений в Windows
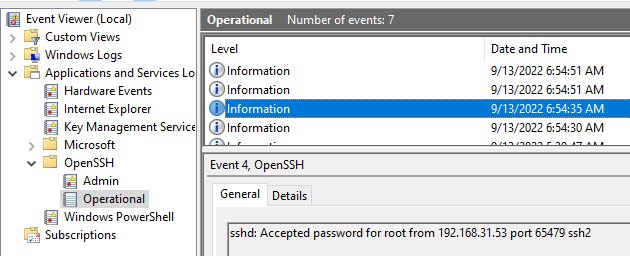
В Windows логи подключений к SSH серверу по-умолчанию пишутся не в текстовые файлы, а в отдельный журнал событий через Event Tracing for Windows (ETW). Откройте консоль Event Viewer (
eventvwr.msc
>) и перейдите в раздел Application and services logs -> OpenSSH -> Operational.
При успешном подключении с помощью к SSH серверу с помощью пароля в журнале появится событие:
EventID: 4 sshd: Accepted password for root from 192.168.31.53 port 65479 ssh2
Если была выполнена аутентификация с помощью SSH ключа, событие будет выглядеть так:
sshd: Accepted publickey for locadm from 192.168.31.53 port 55772 ssh2: ED25519 SHA256:FEHDEC/J72Fb2zC2oJNb45678967kghH43h3bBl31ldPs
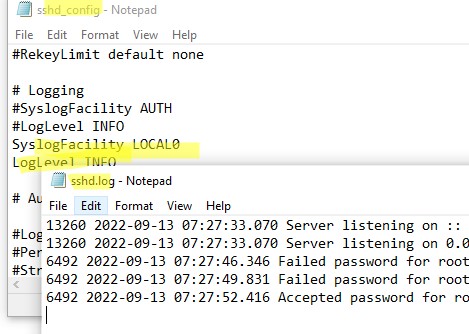
Если вы хотите, чтобы логи писались в локальный текстовый файл, нужно в файле sshd_config включить параметры:
SyslogFacility LOCAL0 LogLevel INFO
Перезапустите службу sshd и провеьте, что теперь логи SSH сервера пишутся в файл C:ProgramDatasshlogssshd.log

Join the Chocolatey Team on our regular monthly stream where we discuss all things Community, what we do, how you can get involved and answer your Chocolatey questions.

Join the Chocolatey Team on our regular monthly stream where we put a spotlight on the most recent Chocolatey product releases. You’ll have a chance to have your questions answered in a live Ask Me Anything format.

Livestream from
Thursday, 06 October 2022
We recently released our largest update to Chocolatey Central Management so far. Join Gary and Steph to find out more about Chocolatey Central Management and the new features and fixes we’ve added to this release.
Watch On-Demand

Webinar Replay from
Wednesday, 30 March 2022
At Chocolatey Software we strive for simple, and teaching others. Let us teach you just how simple it could be to keep your 3rd party applications updated across your devices, all with Intune!
Watch On-Demand

Livestream from
Thursday, 9 June 2022
Join James and Josh to show you how you can get the Chocolatey For Business recommended infrastructure and workflow, created, in Azure, in around 20 minutes.
Watch On-Demand

Livestream from
Thursday, 04 August 2022
Join Paul and Gary to hear more about the plans for the Chocolatey CLI in the not so distant future. We’ll talk about some cool new features, long term asks from Customers and Community and how you can get involved!
Watch On-Demand

Livestreams from
October 2022
For Hacktoberfest, Chocolatey ran a livestream every Tuesday! Re-watch Cory, James, Gary, and Rain as they share knowledge on how to contribute to open-source projects such as Chocolatey CLI.
Watch On-Demand

Livestream from
Thursday, 03 November 2022
Join Paul and Gary for this months Chocolatey product livestream where we look at the latest release of Chocolatey 1.2.0, Chocolatey Licensed Extension 5.0.0 and shine a spotlight on the new hook scripts functionality. This opens up so many possibilities for Chocolatey CLI users!
Watch On-Demand

Livestream from
Tuesday, 29 November 2022
Join Josh as he adds the ability to manage Chocolatey GUI config and features with the Chocolatey Ansible Collection.
Watch On-Demand

Webinar from
Tuesday, 13 December 2022
Join Gary, Paul, and Maurice as they introduce and demonstrate how to use Chocolatey! Questions will be answered live in an Ask Me Anything format.
Watch On-Demand
Documentation » Using WinSCP » Guides » Other »
Recently, Microsoft has released a port of OpenSSH for Windows. You can use the package to set up an SFTP/SSH server on Windows.
- Installing SFTP/SSH Server
- On Windows 11 and Windows 10
- On earlier versions of Windows
- Configuring SSH server
- Setting up SSH public key authentication
- Connecting to the server
- Finding Host Key
- Connecting
- Further reading
Advertisement
Installing SFTP/SSH Server
On Windows 11 and Windows 10
- On Windows 11:
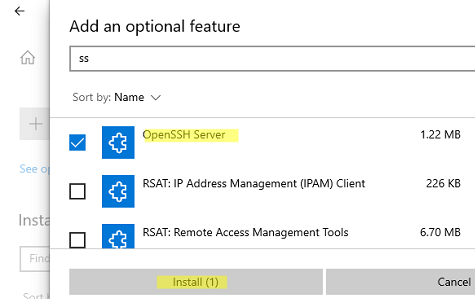
- Go to Settings > Apps > Optional features and click on View features.
- Locate “OpenSSH server” feature, select it, click Next, and then click Install.
- On Windows 10 (version 1803 and newer):
- Go to Settings > Apps > Apps & features > Optional features and click on Add a feature.
- Locate “OpenSSH server” feature, expand it, and select Install.
Binaries are installed to %WINDIR%System32OpenSSH. Configuration file (sshd_config) and host keys are installed to %ProgramData%ssh (only after the server is started for the first time).
You may still want to use the following manual installation if you want to install a newer version of OpenSSH than the one built into Windows.
On earlier versions of Windows
- Download the latest OpenSSH for Windows binaries (package
OpenSSH-Win64.ziporOpenSSH-Win32.zip) - As the Administrator, extract the package to
C:Program FilesOpenSSH - As the Administrator, install sshd and ssh-agent services:
powershell.exe -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -File install-sshd.ps1
Configuring SSH server
- Allow incoming connections to SSH server in Windows Firewall:
- When installed as an optional feature, the firewall rule “OpenSSH SSH Server (sshd)” should have been created automatically. If not, proceed to create and enable the rule as follows.
- Either run the following PowerShell command as the Administrator:
New-NetFirewallRule -Name sshd -DisplayName 'OpenSSH SSH Server' -Enabled True -Direction Inbound -Protocol TCP -Action Allow -LocalPort 22 -Program "C:WindowsSystem32OpenSSHsshd.exe"
Replace
C:WindowsSystem32OpenSSHsshd.exewith the actual path to thesshd.exe(C:Program FilesOpenSSHssh.exe, had you followed the manual installation instructions above). - or go to Windows Security > Firewall & network protection1 > Advanced Settings > Inbound Rules and add a new rule for port 22.
- Start the service and/or configure automatic start:
- Go to Control Panel > System and Security > Administrative Tools and open Services. Locate OpenSSH SSH Server service.
- If you want the server to start automatically when your machine is started: Go to Action > Properties (or just double-click the service). In the Properties dialog, change Startup type to Automatic and confirm.
- Start the OpenSSH SSH Server service by clicking the Start the service link or Action > Start in the menu.
Advertisement
These instructions are partially based on the official deployment instructions.
Setting up SSH public key authentication
Follow a generic guide for Setting up SSH public key authentication in *nix OpenSSH server, with the following difference:
- Create the
.sshfolder (for theauthorized_keysfile) in your Windows account profile folder (typically inC:Usersusername.ssh).2 - For permissions to the
.sshfolder and theauthorized_keysfile, what matters are Windows ACL permissions, not simple *nix permissions. Set the ACL so that the respective Windows account is the owner of the folder and the file and is the only account that has a write access to them. The account that runs OpenSSH SSH Server service (typicallySYSTEMorsshd) needs to have read access to the file. - Though, with the default Win32-OpenSSH configuration there is an exception set in
sshd_configfor accounts inAdministratorsgroup. For these, the server uses a different location for the authorized keys file:%ALLUSERSPROFILE%sshadministrators_authorized_keys(i.e. typicallyC:ProgramDatasshadministrators_authorized_keys).
Connecting to the server
Finding Host Key
Before the first connection, find out the fingerprint of the server’s host key by using ssh-keygen.exe for each file.
In Windows command-prompt, use:
for %f in (%ProgramData%sshssh_host_*_key) do @%WINDIR%System32OpenSSHssh-keygen.exe -l -f "%f"
Replace %WINDIR%System32 with %ProgramFiles%, if appropriate.
In PowerShell, use:
Get-ChildItem $env:ProgramDatasshssh_host_*_key | ForEach-Object { . $env:WINDIRSystem32OpenSSHssh-keygen.exe -l -f $_ }
Replace $env:WINDIRSystem32 with $env:ProgramFiles, if appropriate.
You will get an output like this:
C:WindowsSystem32OpenSSH>for %f in (%ProgramData%sshssh_host_*_key) do @%WINDIR%System32OpenSSHssh-keygen.exe -l -f "%f" 1024 SHA256:K1kYcE7GHAqHLNPBaGVLOYBQif04VLOQN9kDbiLW/eE martin@example (DSA) 256 SHA256:7pFXY/Ad3itb6+fLlNwU3zc6X6o/ZmV3/mfyRnE46xg martin@example (ECDSA) 256 SHA256:KFi18tCRGsQmxMPioKvg0flaFI9aI/ebXfIDIOgIVGU martin@example (ED25519) 2048 SHA256:z6YYzqGiAb1FN55jOf/f4fqR1IJvpXlKxaZXRtP2mX8 martin@example (RSA)
Connecting
Start WinSCP. Login dialog will appear. On the dialog:
- Make sure New site node is selected.
- On New site node, make sure the SFTP protocol is selected.
- Enter your machine/server IP address (or a hostname) into the Host name box.
- Enter your Windows account name to the User name box. It might have to be entered in the format
user@domainif running on a domain. - For a public key authentication:
- Press the Advanced button to open Advanced site settings dialog and go to SSH > Authentication page.
- In Private key file box select your private key file.
- Submit Advanced site settings dialog with the OK button.
- For a password authentication:
- Enter your Windows account password to the Password box.
- If your Windows account does not have a password, you cannot authenticate with the password authentication (i.e. with an empty password), you need to use the public key authentication.
- Save your site settings using the Save button.
- Login using Login button.
- Verify the host key by comparing fingerprints with those collected before (see above).
Advertisement
If you cannot authenticate to the server and use Windows 10 Developer mode, make sure that your OpenSSH server does not conflict with an internal SSH server used by the Developer mode. You may need to turn off the SSH Server Broker and SSH Server Proxy Windows services. Or run your OpenSSH server on a different port than 22.
Further reading
- Guide to Installing Secure FTP Server on Windows using IIS;
- Guide to uploading files to SFTP server;
- Guide to automating operations (including upload).
Last modified: 2022-10-24 by martin