i have windows service «monitoringservice» (account:localservice) and another service named
«uploadService» (account: local system), i installed the uploadService with setupproject and
when i start this upload service its working fine. but when i start the upload service with
the help of «monitoringservice» iam unable yo start the service iam getting the below error
«cannot open uploadService on the computer’.'»
Can any one suggest me please iam strck up with this problem
i used the following code
ServiceController sc = new ServiceController("UploadService");
if(sc!=null)
{
try
{
if (sc.Status != ServiceControllerStatus.Running && sc.Status != ServiceControllerStatus.StartPending)
{
sc.Start();
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
}
}
Thank you in advance
I need to control a Windows service (slave) from another one (master) on the same machine (Windows 7 or Server 2008). It’s unable to either start or stop the service. What do I need to do to be control the service? The master service is written in C#
UPDATE:
The master service is meant to be a sort of watchdog — it monitors an HTTP connection to the slave and restarts the slave if the slave is non-responsive (not returning any HTTP data).
asked Apr 16, 2014 at 0:37
naveednaveed
1,3552 gold badges15 silver badges29 bronze badges
3
You can have the master service create a new process that creates a hidden command window with an argument that causes it to call the windows command and start or stop the service. We use this model all the time at my job, the /C will cause the command window to exit as soon as the service finishes changing state.
System.Diagnostics.Process p = new System.Diagnostics.Process ();
System.Diagnostics.ProcessStartInfo psi = new System.Diagnostics.ProcessStartInfo ( "cmd.exe", "/C net [start or stop] [service name]");
psi.WindowStyle = System.Diagnostics.ProcessWindowStyle.Hidden;
p.StartInfo = psi;
P.Start();
You will need to replace the bracketed sections of the command, and sorry if there are any syntax errors I am typing this on my tablet.
answered Apr 16, 2014 at 0:56
BryanBryan
113 bronze badges
- Remove From My Forums
-
Question
-
i got guide line to restart the windows service using below line. now i want to plug the code into my win service and call those code when a specific condition will satisfy but i am not sure that can we restart windows service from the service itself?
if any problem would occur then please advise me in advance. thanks
private void RestartWindowsService(string serviceName) { ServiceController serviceController = new ServiceController(serviceName); try { if ((serviceController.Status.Equals(ServiceControllerStatus.Running)) || (serviceController.Status.Equals(ServiceControllerStatus.StartPending))) { serviceController.Stop(); } serviceController.WaitForStatus(ServiceControllerStatus.Stopped); serviceController.Start(); serviceController.WaitForStatus(ServiceControllerStatus.Running); } catch }
Answers
-
Your application should try to recover internally. If it encounters an exception, deal with it. If you don’t know how to handle the exception, debug your application to find out exactly what is causing the exception.
In other words, don’t paper over your bugs. Just blindly restarting your service is a poor way of dealing with errors.
Having said this, there are scenarios where there may be justification to restarting an application that has failed. There are a couple of approaches, none of them particularly appealing. Your service can simply exit, but then you need a watchdog service,
which is completely separate, who’s sole responsibility is to watch for the service, and restart it if it fails. Another approach is for your service to launch a separate application, which will perform the shutdown/restart, when it encounters an unanticipiated
exception.-
Marked as answer by
Wednesday, October 8, 2014 7:48 PM
-
Marked as answer by
Содержание
- Start or stop Windows service from command line (CMD)
- How to: Start Services
- Specify how a service should start
- Start a service from Server Explorer
- Start a service from Services
- Start a service from code
- Start & Stop a Windows Service from another Windows Service
- 2 Answers 2
- Not the answer you’re looking for? Browse other questions tagged c# windows service or ask your own question.
- Linked
- Related
- Hot Network Questions
- Subscribe to RSS
- How to open Services Manager and Manage Services using Command Line in Windows 10
- How to open Windows Services Manager
- Types of Windows Services startup
- Start, stop, disable Windows Services
- Manage Services using Command Line
- Related Posts
- System error 1058 has occurred, The service cannot be started
- Service Host Delivery Optimization High Network, Disk or CPU usage
- How do I enable Touch Keyboard and Handwriting Panel Service in Windows 11/10
- [email protected]
- Primary Sidebar
- How to start a process from windows service into currently logged in user’s session
- 8 Answers 8
Start or stop Windows service from command line (CMD)
We normally use Services.msc to start or stop or disable or enable any service. We can do the same from windows command line also using net and sc utilities. Below are commands for controlling the operation of a service.
Command to stop a service:
To start a service:
You need to have administrator privileges to run net start/stop commands. If you are just a normal user on the computer, you would get an error like below.
To disable a service:
To enable a service:
To make a service start automatically with system boot:
Note: Space is mandatory after ‘=’ in the above sc commands.
This SC command works on a Windows 7 machine and also on the down-level editions of Windows i.e Windows XP/2003 and Windows Vista. Again, if you do not have administrator previliges you would get the below error.
Note that the service name is not the display name of a service. Each service is given a unique identification name which can be used with net or sc commands. For example, Remote procedure call (RPC) is the display name of the service. But the service name we need to use in the above commands is RpcSs.
So to start Remote procedure call service the command is:
These service names are listed below for each service. The first column shows the display name of a service and the second column shows the service name that should be used in net start or net stop or sc config commands.
Источник
How to: Start Services
This documentation isn’t for the latest version of Windows Service. For the latest content on Windows Services using BackgroundService, and the Worker Service template see:
After a service is installed, it must be started. Starting calls the OnStart method on the service class. Usually, the OnStart method defines the useful work the service will perform. After a service starts, it remains active until it is manually paused or stopped.
Services can be set up to start automatically or manually. A service that starts automatically will be started when the computer on which it is installed is rebooted or first turned on. A user must start a service that starts manually.
By default, services created with Visual Studio are set to start manually.
There are several ways you can manually start a service — from Server Explorer, from the Services Control Manager, or from code using a component called the ServiceController.
You set the StartType property on the ServiceInstaller class to determine whether a service should be started manually or automatically.
Specify how a service should start
After creating your service, add the necessary installers for it. For more information, see How to: Add Installers to Your Service Application.
In the designer, click the service installer for the service you are working with.
In the Properties window, set the StartType property to one of the following:
| To have your service install | Set this value |
|---|---|
| When the computer is restarted | Automatic |
| When an explicit user action starts the service | Manual |
To prevent your service from being started at all, you can set the StartType property to Disabled. You might do this if you are going to reboot a server several times and want to save time by preventing the services that would normally start from starting up.
These and other properties can be changed after your service is installed.
There are several ways you can start a service that has its StartType process set to Manual — from Server Explorer, from the Windows Services Control Manager, or from code. It is important to note that not all of these methods actually start the service in the context of the Services Control Manager; Server Explorer and programmatic methods of starting the service actually manipulate the controller.
Start a service from Server Explorer
In Server Explorer, add the server you want if it is not already listed. For more information, see How to: Access and Initialize Server Explorer-Database Explorer.
Expand the Services node, and then locate the service you want to start.
Right-click the name of the service, and then select Start.
Start a service from Services
Open the Services app.
Select your service in the list, right-click it, and then select Start.
Start a service from code
Create an instance of the ServiceController class, and configure it to interact with the service you want to administer.
Call the Start method to start the service.
Источник
Start & Stop a Windows Service from another Windows Service
I need to control a Windows service (slave) from another one (master) on the same machine (Windows 7 or Server 2008). It’s unable to either start or stop the service. What do I need to do to be control the service? The master service is written in C#
2 Answers 2
You can have the master service create a new process that creates a hidden command window with an argument that causes it to call the windows command and start or stop the service. We use this model all the time at my job, the /C will cause the command window to exit as soon as the service finishes changing state.
You will need to replace the bracketed sections of the command, and sorry if there are any syntax errors I am typing this on my tablet.
But you will have some problems trying that because you will need administrator permissions to turn other services off, so you can handle that by following this link (for debug purposes you can open your VS as admin and everything will work):
Not the answer you’re looking for? Browse other questions tagged c# windows service or ask your own question.
Linked
Hot Network Questions
To subscribe to this RSS feed, copy and paste this URL into your RSS reader.
site design / logo © 2022 Stack Exchange Inc; user contributions licensed under cc by-sa. rev 2022.11.3.40639
By clicking “Accept all cookies”, you agree Stack Exchange can store cookies on your device and disclose information in accordance with our Cookie Policy.
Источник
How to open Services Manager and Manage Services using Command Line in Windows 10
At times you may need to open and manage your Windows Services. You may want to stop some service, start it, disable the service, delay its start-up or resume or pause the Windows Service. At such time, the Services Manager, which is a built-in tool in the Windows operating system, will help you. This post will show you how to open your Windows Services, using Services Manager as well as the Command Prompt.
Windows Services are applications that typically start when the computer is booted and run quietly in the background until it is shut down. Strictly speaking, a service is any Windows application that is implemented with the services API and handles low-level tasks that require little or no user interaction.
How to open Windows Services Manager
Here you will be able to start, stop, disable, delay Windows Services.
Let us see how to do this in a bit more detail.
Right-click on your Start button to open the WinX Menu. Select Run. This opens the Run box. Now type services.msc in it and hit Enter to open the Services Manager.
TIP: You can also write services.msc in Run box, Start search, Command Prompt, or PowerShell, and hit Enter to open Services Manager.
Types of Windows Services startup
Start, stop, disable Windows Services
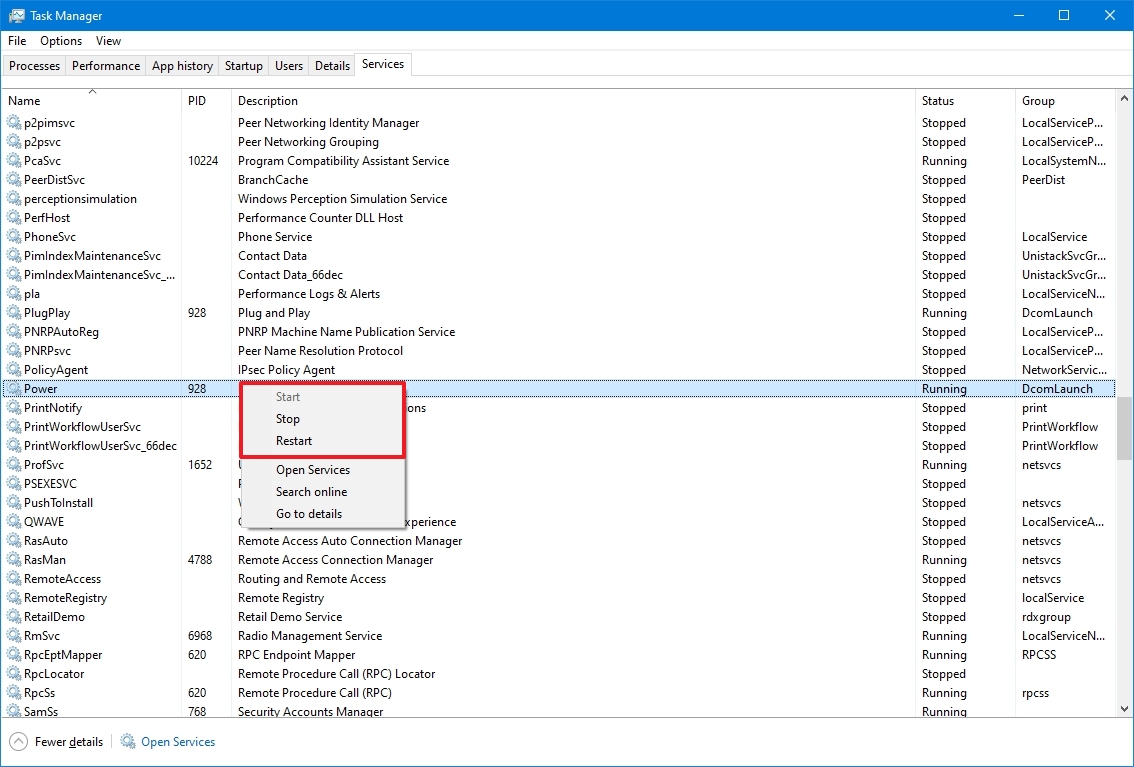
To start, stop, pause, resume or restart any Windows Service, select the Service and right-click on it. You will be offered these options.
If you wish to manage more options, double-click on the Service to open its Properties box.
Here, under the Startup type drop-down menu, you will be able to select the startup type for the Service.
Under Service status, you will see buttons to Start, Stop, Pause, Resume the Service.
In the Properties box, you will also see other tabs like Log On, Recovery & Dependencies, which offer additional options and information.
Once you have made your changes, you will have to click on Apply and restart your computer, for the changes to take effect.
Read: What does Automatic (Trigger Start) and Manual (Trigger Start) mean for Windows Services?
Manage Services using Command Line
You can also use the Command Prompt to start, stop, pause, resume service. To use it, from the WinX Menu, open Command Prompt (Admin) and execute one of the following commands:
To start a service:
To pause a service:
To resume a service:
To disable a service:
It is recommended that you not change the default settings unless you know what you are doing, as this can cause some parts of your operating system to stop working. When you stop, start, or restart a service, any dependent services are also affected, so you want to be careful here.
Date: June 28, 2020 Tags: Services
System error 1058 has occurred, The service cannot be started
Service Host Delivery Optimization High Network, Disk or CPU usage
How do I enable Touch Keyboard and Handwriting Panel Service in Windows 11/10
[email protected]
Anand Khanse is the Admin of TheWindowsClub.com, a 10-year Microsoft MVP (2006-16) & a Windows Insider MVP. Please read the entire post & the comments first, create a System Restore Point before making any changes to your system & be careful about any 3rd-party offers while installing freeware.
Источник
How to start a process from windows service into currently logged in user’s session
I need to start a program from Windows Service. That program is a user UI application. Moreover that application should be started under specific user account.
The problem is that a Window Services run in session #0, but a logged in user sessions are 1,2 etc.
So the question is: how to start a process from a window service in such a way that it run in currently logged in user’s session?
The code goes to the line «Notepad has been started by WatchdogService. Exitcode: » + exitCode. Exitcode is 3221225794. And there’s no any new notepad started. Where am I wrong?
8 Answers 8
The problem with Shrike’s answer is that it does not work with a user connected over RDP.
Here is my solution, which properly determines the current user’s session before creating the process. It has been tested to work on XP and 7.
It’s a terrific helpful post about starting a new process in interactive session from windows service on Vista/7.
For non-LocalSystem services, the basic idea is:
Enumerate the process to get the handle of the Explorer.
OpenProcessToken should give you the access token. Note : The account under which your service is running must have appropriate privileges to call this API and get process token.
Once you have the token call CreateProcessAsUser with this token. This token already have the right session Id.
It’s a bad idea to do so. Although probably not totally impossible, Microsoft did everything to make this as hard as possible, as it enables so-called Shatter Attacks. See what Larry Osterman wrote about it back in 2005:
The primary reason for this being a bad idea is that interactive services enable a class of threats known as «Shatter» attacks (because they «shatter windows», I believe).
If you do a search for «shatter attack», you can see some details of how these security threats work. Microsoft also published KB article 327618 which extends the documentation about interactive services, and Michael Howard wrote an article about interactive services for the MSDN Library. Initially the shatter attacks went after windows components that had background window message pumps (which have long been fixed), but they’ve also been used to attack 3rd party services that pop up UI.
The proposed workaround would be to use an application in the system tray of the user.
If you can safely ignore the issues and warnings above, you might follow the instructions given here:
Источник
Is there a way to restart a Windows service from the command prompt?
asked Jun 24, 2011 at 17:54
You can use net stop [service name] to stop it and net start [service name] to start it up again basically restarting the service.
To combine them just do this — net stop [service name] && net start [service name].
There is also a command built specifically for messing with services: sc
DESCRIPTION:
SC is a command line program used for communicating with the
Service Control Manager and services.
USAGE:
sc [command] [service name] ...
The option has the form "\ServerName"
Further help on commands can be obtained by typing: "sc [command]"
Commands:
query-----------Queries the status for a service, or
enumerates the status for types of services.
queryex---------Queries the extended status for a service, or
enumerates the status for types of services.
start-----------Starts a service.
pause-----------Sends a PAUSE control request to a service.
interrogate-----Sends an INTERROGATE control request to a service.
continue--------Sends a CONTINUE control request to a service.
stop------------Sends a STOP request to a service.
config----------Changes the configuration of a service (persistent).
description-----Changes the description of a service.
failure---------Changes the actions taken by a service upon failure.
failureflag-----Changes the failure actions flag of a service.
sidtype---------Changes the service SID type of a service.
privs-----------Changes the required privileges of a service.
managedaccount--Changes the service to mark the service account
password as managed by LSA.
qc--------------Queries the configuration information for a service.
qdescription----Queries the description for a service.
qfailure--------Queries the actions taken by a service upon failure.
qfailureflag----Queries the failure actions flag of a service.
qsidtype--------Queries the service SID type of a service.
qprivs----------Queries the required privileges of a service.
qtriggerinfo----Queries the trigger parameters of a service.
qpreferrednode--Queries the preferred NUMA node of a service.
qrunlevel-------Queries the run level of a service.
qmanagedaccount-Queries whether a services uses an account with a
password managed by LSA.
qprotection-----Queries the process protection level of a service.
delete----------Deletes a service (from the registry).
create----------Creates a service. (adds it to the registry).
control---------Sends a control to a service.
sdshow----------Displays a service's security descriptor.
sdset-----------Sets a service's security descriptor.
showsid---------Displays the service SID string corresponding to an arbitrary name.
triggerinfo-----Configures the trigger parameters of a service.
preferrednode---Sets the preferred NUMA node of a service.
runlevel--------Sets the run level of a service.
GetDisplayName--Gets the DisplayName for a service.
GetKeyName------Gets the ServiceKeyName for a service.
EnumDepend------Enumerates Service Dependencies.
The following commands don't require a service name:
sc
boot------------(ok | bad) Indicates whether the last boot should
be saved as the last-known-good boot configuration
Lock------------Locks the Service Database
QueryLock-------Queries the LockStatus for the SCManager Database
EXAMPLE:
sc start MyService
QUERY and QUERYEX OPTIONS:
If the query command is followed by a service name, the status
for that service is returned. Further options do not apply in
this case. If the query command is followed by nothing or one of
the options listed below, the services are enumerated.
type= Type of services to enumerate (driver, service, all)
(default = service)
state= State of services to enumerate (inactive, all)
(default = active)
bufsize= The size (in bytes) of the enumeration buffer
(default = 4096)
ri= The resume index number at which to begin the enumeration
(default = 0)
group= Service group to enumerate
(default = all groups)
SYNTAX EXAMPLES
sc query - Enumerates status for active services & drivers
sc query eventlog - Displays status for the eventlog service
sc queryex eventlog - Displays extended status for the eventlog service
sc query type= driver - Enumerates only active drivers
sc query type= service - Enumerates only Win32 services
sc query state= all - Enumerates all services & drivers
sc query bufsize= 50 - Enumerates with a 50 byte buffer
sc query ri= 14 - Enumerates with resume index = 14
sc queryex group= "" - Enumerates active services not in a group
sc query type= interact - Enumerates all interactive services
sc query type= driver group= NDIS - Enumerates all NDIS drivers
answered Jun 24, 2011 at 17:58
paradd0xparadd0x
8,9917 gold badges36 silver badges44 bronze badges
9
Please, note that if there are other services that depends on this service — usual net stop & net start will not restart them. net stop /y will stop all dependencies
Most common example — SQL Server & SQL Agent.
I do recommend PowerShell cmdlet to solve this:
powershell -command "Restart-Service MSSQLSERVER -Force"
After MSSQLSERVER starts — cmdlet starts all previously stopped dependancies.
PS: Make sure you are running command as admin
answered Mar 15, 2017 at 13:57
2
To restart a Windows service from the command prompt or scheduled tasks, use this:
cmd /c "net stop "Service Name" & sc start "Service Name""
answered Feb 12, 2013 at 7:27
KikiKiki
1211 silver badge2 bronze badges
1
You could also use PowerShell:
stop-Service
Gaff
18.3k15 gold badges56 silver badges68 bronze badges
answered Jun 24, 2011 at 18:12
devlifedevlife
2411 gold badge2 silver badges7 bronze badges
1
To solve the annoying Wacom Intuous Driver not running Error I get on every reboot.
Windows key + R, paste, Bam!
sc stop WTabletServicePro && sc start WTabletServicePro
Simon E.
3,6875 gold badges29 silver badges30 bronze badges
answered Oct 20, 2014 at 3:45
GeorgeGeorge
511 silver badge1 bronze badge
The PsService utility from PsTools provides a restart command for services, with additional parameters to run it on another machine.
psservice [-accepteula] [\Computer [-u Username [-p Password]]] restart <service-name>
The -accepteula flag saves you the EULA window just in case it’s the first time you use this utility with the current user.
answered May 22, 2018 at 16:00
cdlvcdlvcdlvcdlv
1,34117 silver badges27 bronze badges
In case you know the service’s executable location path you could use
"[service name.exe] console"
On the command line.
That will actually help you debug the issue if the service should fail to start.
answered Aug 22, 2016 at 5:08
1
If you manage Windows Services and are comfortable working from the command line, then the Windows NET.EXE command should be in your toolkit. Use it to easily start, stop, pause or restart any service from an elevated command prompt, or in a convenient script/batch file.
Using NET to stop a Windows Service
To stop a service, run:
net stop <Service-Name>
where <Service-Name> is the name of the service. Be sure to enclose it in quotes if it contains a space!
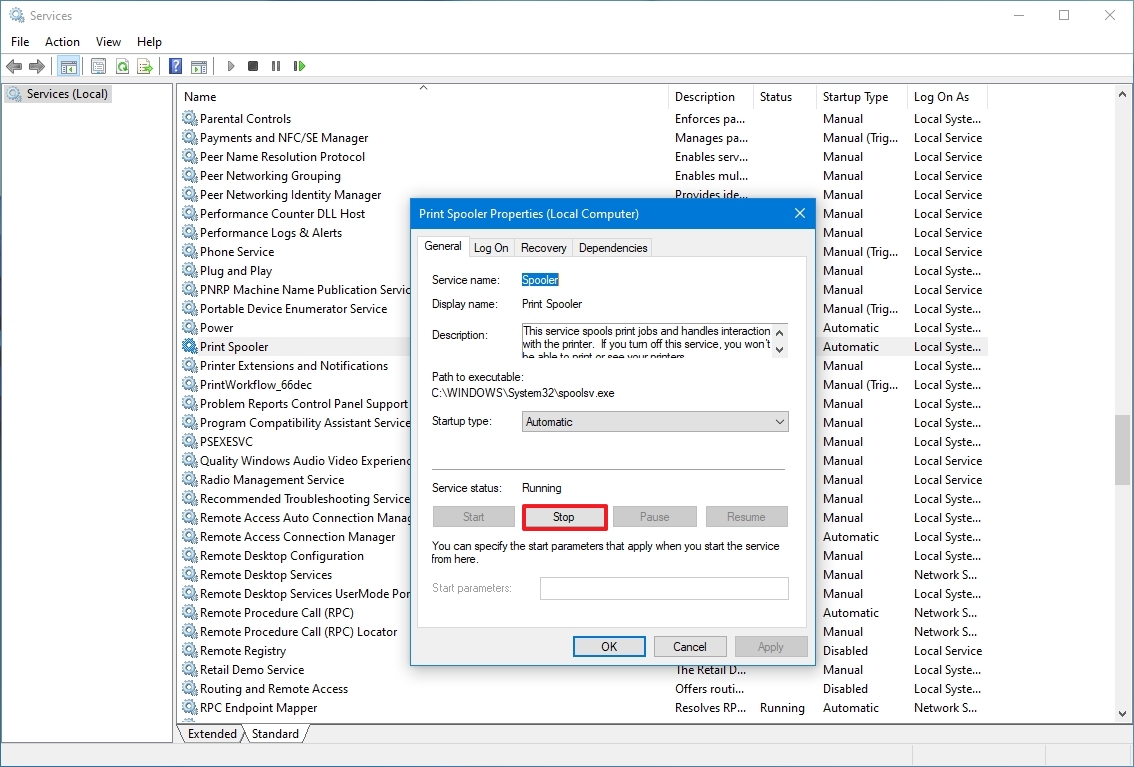
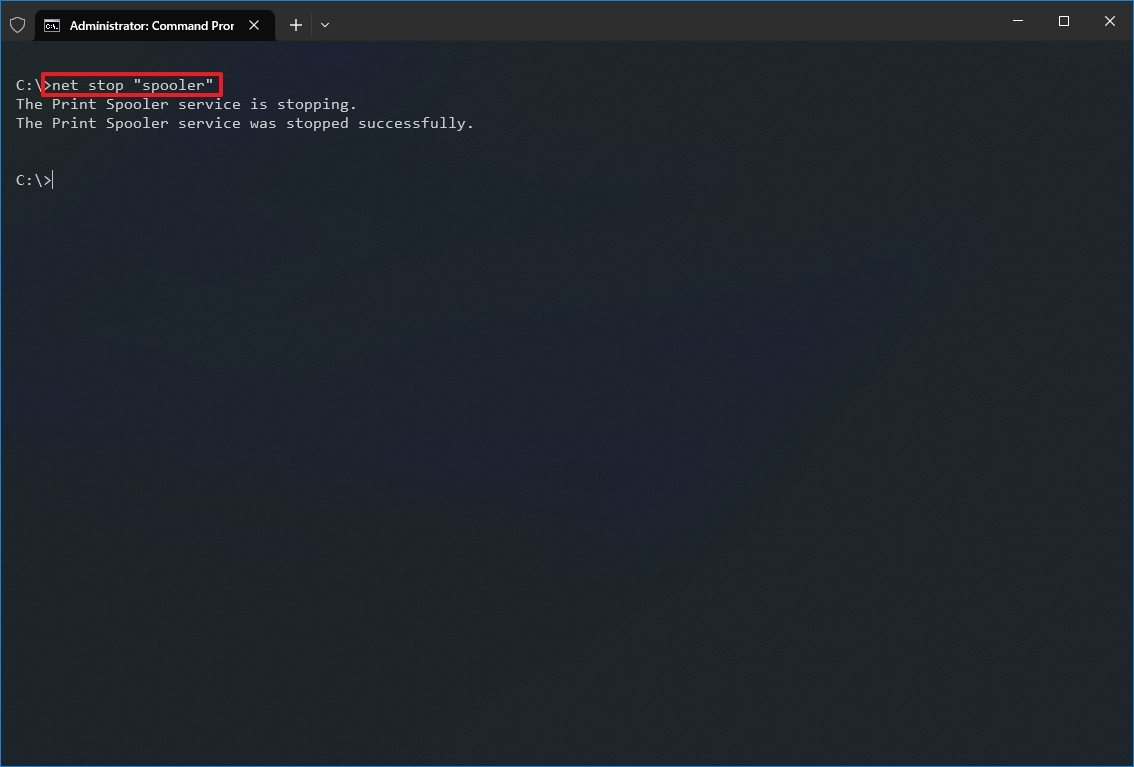
For example, to stop the Print Spooler service (named “Spooler”), run:
net stop Spooler
Here is what it looks like on our Windows Server 2016 computer:
Notice that the NET command will wait for the service to stop before continuing. The only exception is when the service is unresponsive or takes more than 30 seconds to comply.
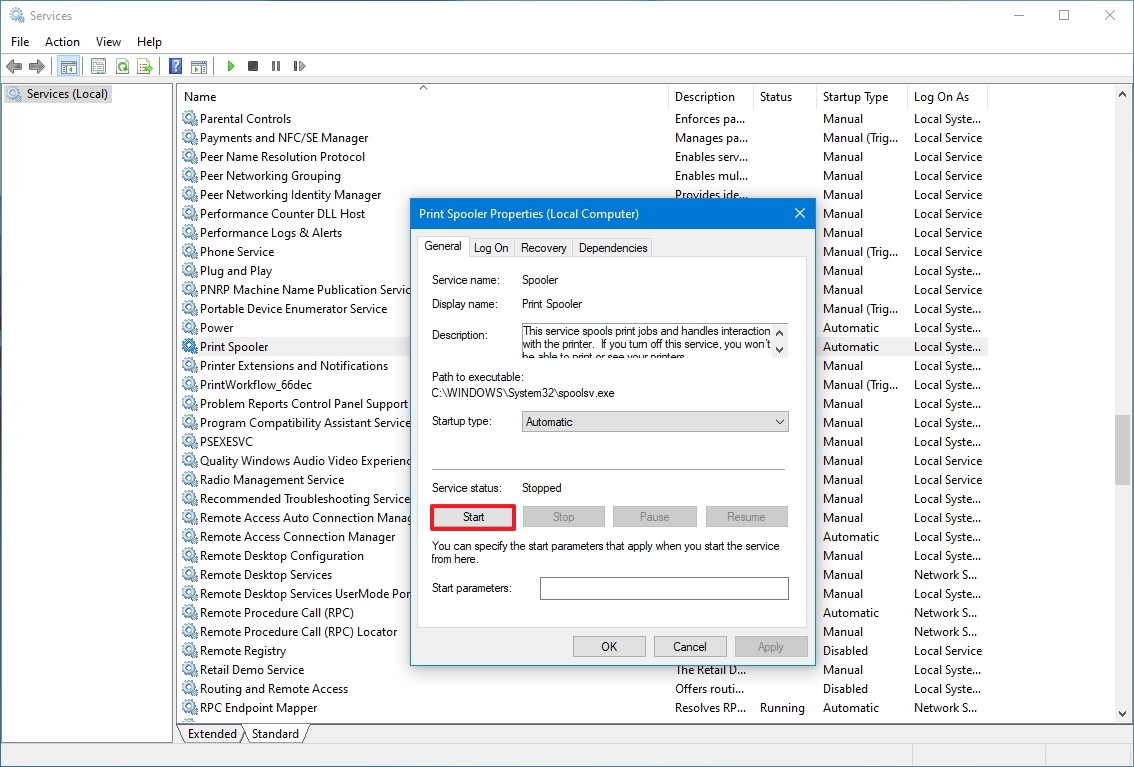
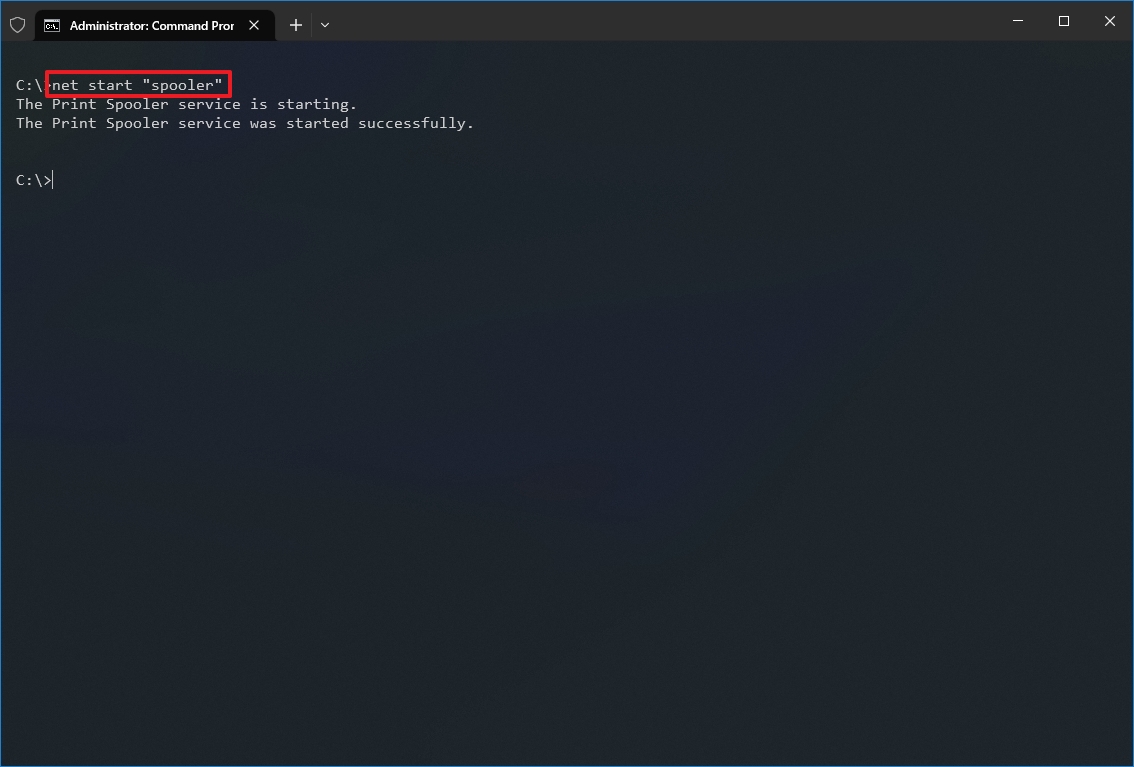
Starting a Windows Service with NET
To start an idle Windows Service, run:
net start <Service-Name>
If all goes well, your service (and any other service it depends on to operate) will be started after a few seconds:
How to Restart a Windows Service with NET.EXE
To restart a service, say from a batch file, chain the “net stop” and “net start” commands together like this:
net stop <Service-Name>
net start <Service-Name>
NET will also Pause and Resume Windows Services
Not all services support pause and resume, but if you have one that does, NET can come in handy there as well.
To pause a service, type:
net pause <Service-Name>
To resume a paused service, run:
net continue <Service-Name>
You may also like…
(Image credit: Future)
On Windows 10, services are programs that run in the background without a user interface and enable system features (such as printing, networking, remote access, File Explorer, Windows Search, updates, etc.) and apps to operate as intended.
Although the system does a pretty good job managing background services, you may sometimes need to control them manually when a feature or app isn’t working correctly or requires you to manage its services manually.
Whatever the case might be, Windows 10 includes at least four methods to stop, start, disable, or enable services using the Services console, Task Manager, Command Prompt, and PowerShell.
This guide will walk you through the steps to manage system and app services on Windows 10.
How to manage services from Services console
Using the Services consoles is perhaps the simplest method to stop, start, disable, or enable one or multiple services on Windows 10.
Stop service
To stop a running service using Services, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Services and click the top result to open the console.
- Double-click the service that you intend to stop.
- Click the Stop button.
- Quick tip: You can also manage the state by right-clicking the service and selecting the option. Or you can select the service and then use the controls at the top to start, stop, pause, or restart.
- Click the Apply button.
- Click the OK button.
Once you complete the steps, the service will stop running on the device.
If you’re unable to stop a system service, consider that some services are required for the operation of Windows 10, and they can’t be stopped.
Start service
To start a service on Windows 10, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Services and click the top result to open the console.
- Double-click the service that you intend to stop.
- Click the Start button.
- Click the Apply button.
- Click the OK button.
After you complete the steps, the service you specified will start for the current session.
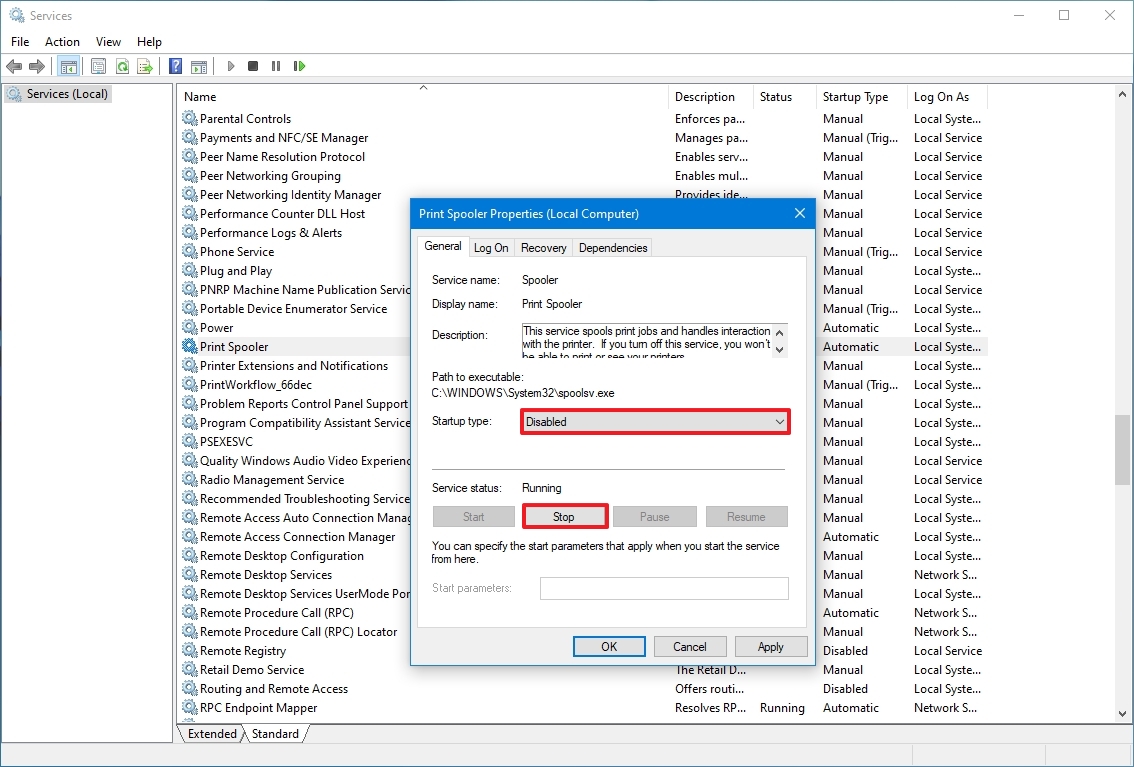
Disable service
To set a service a disabled, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Services and click the top result to open the console.
- Double-click the service that you intend to stop.
- Click the Stop button.
- Use the «Start type» drop-down menu and select the Disabled option.
- Click the Apply button.
- Click the OK button.
Once you complete the steps, the service will no longer start automatically after restarting your device.
Enable service
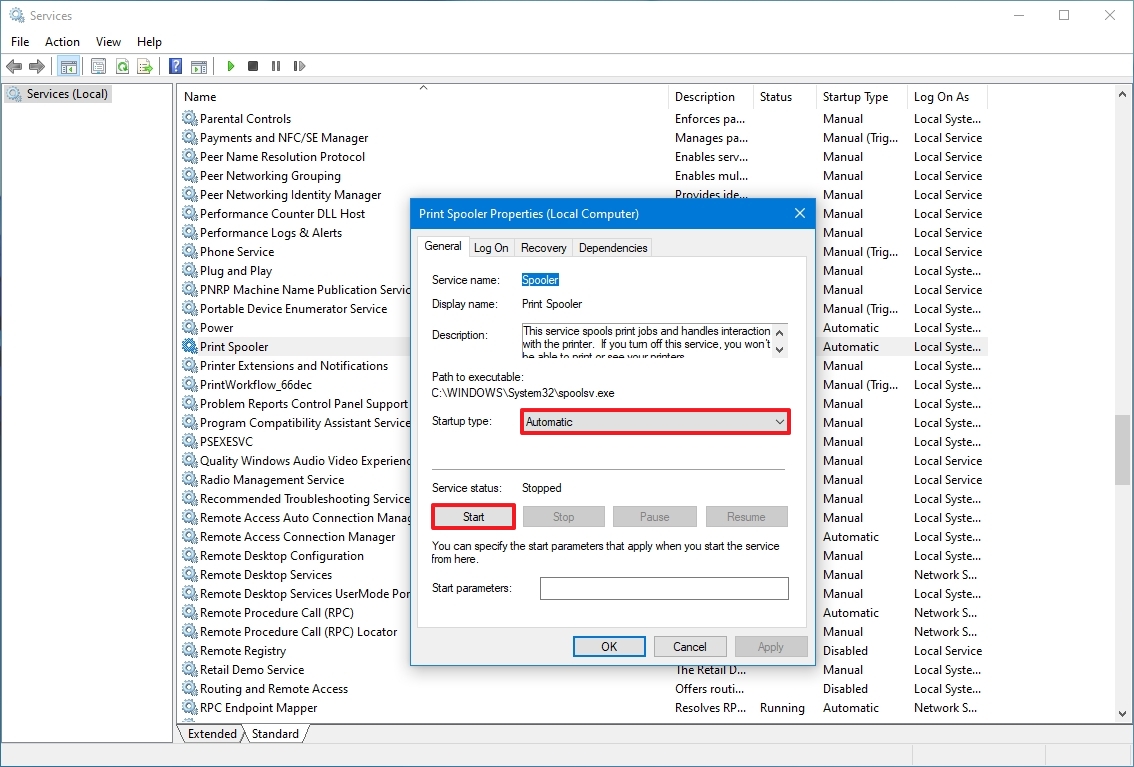
To enable a specific service, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Services and click the top result to open the console.
- Double-click the service that you intend to stop.
- Click the Start button.
- Use the «Start type» drop-down menu and select the Automatic option. These are the Startup types on Windows 10:
- Automatic – service starts at boot.
- Automatic (Delayed Start) – service start after boot.
- Manual – starts service manually as needed.
- Disabled – stops service from running.
- Click the Apply button.
- Click the OK button.
After you complete the steps, the Windows 10 or app service will enable, but if it was in a stopped state, you’d need to start it manually or restart the device for the service to run.
How to manage services from Task Manager
Task Manager also includes a section to manage services for Windows 10 and apps quickly.
To stop, start, or restart a service using Task Manager, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Task Manager and click the top result to open the app.
- Quick tip: Windows 10 includes many other ways to open the experience, including right-clicking the taskbar and selecting the Task Manager option, and using the «Ctrl + Shift + ESC» keyboard shortcut.
- Click the Services tab.
- Right-click the service name and select one of the options:
- Stop.
- Start.
- Restart.
- Quick note: Task Manager only displays the service name, not the display name. For example, if you’re using this method, you’ll the «Print Spooler» defined as «Spooler.»
Once you complete the steps, the service will respond to the option you selected.
How to manage services from PowerShell
You can also use PowerShell commands to manage background services for Windows 10 and apps.
Stop service
To stop a specific service with PowerShell, use these steps:
- Open Start.
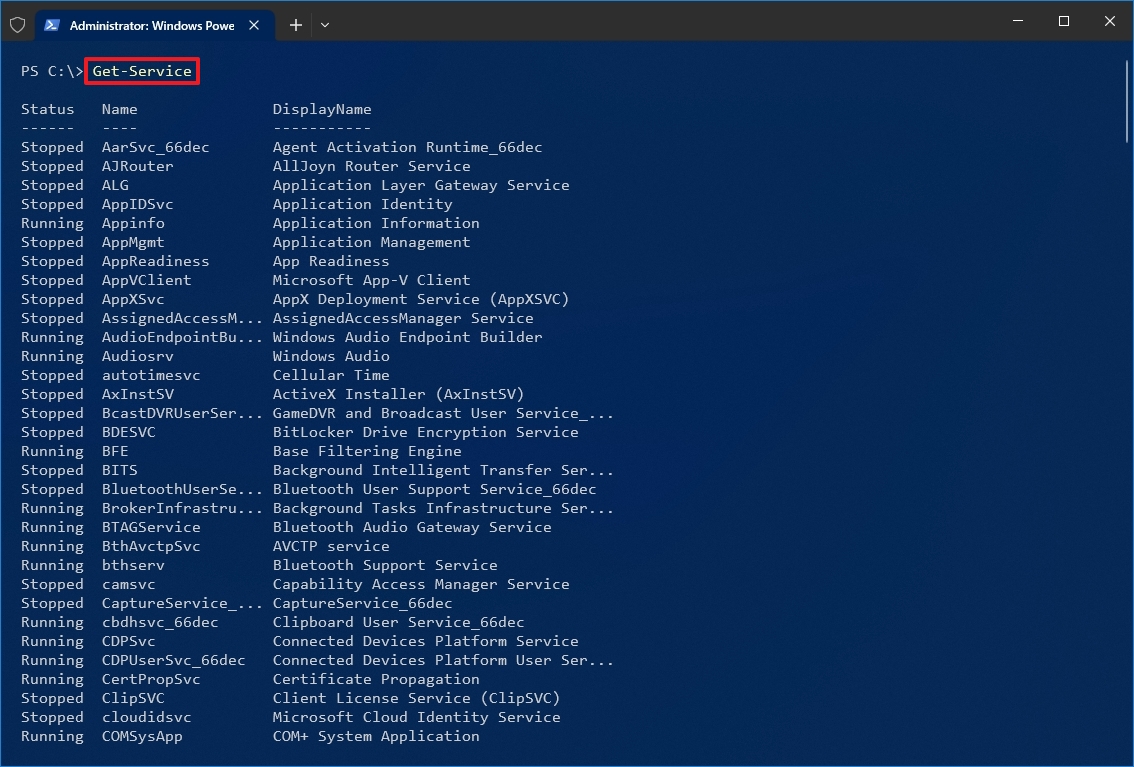
- Search for PowerShell, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
- (Optional) Type the following command to view a list of all the services and press Enter: Get-Service
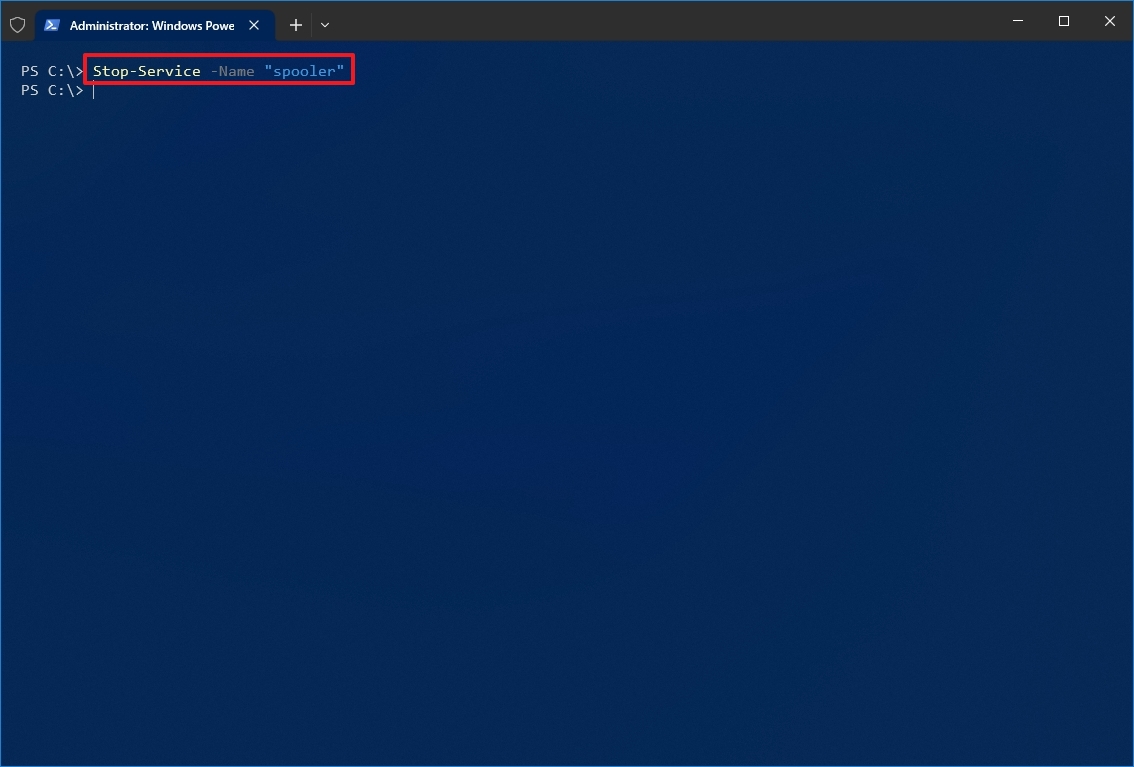
- Type the following command to stop a service and press Enter: Stop-Service -Name «SERVICE-NAME»
For example, this command stops the printer spooler service on Windows 10: Stop-Service -Name «spooler»
In the command, replace «SERVICE-NAME» with the name of the service you intend to stop. If you want to use the display name, replace -Name with -DisplayName and then specify the service’s display name.
Alternatively, you can also use this variant of the command to stop the service: Set-Service -Name «SERVICE-NAME» -Status stopped
In the command, replace «SERVICE-NAME» with the name of the service you intend to stop. If you want to use the display name, replace -Name with -DisplayName and then specify the service’s display name. You only need quotation marks if there’s a space within the name.
- Quick tip: If you’re getting a dependency error, you can append the -force option in either of the commands to stop the service. For example, Stop-Service -Name «SERVICE-NAME» -Force.
After you complete the steps, the PowerShell command will stop the service on your device.
Start service
To start a Windows 10 or app service with PowerShell, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for PowerShell, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
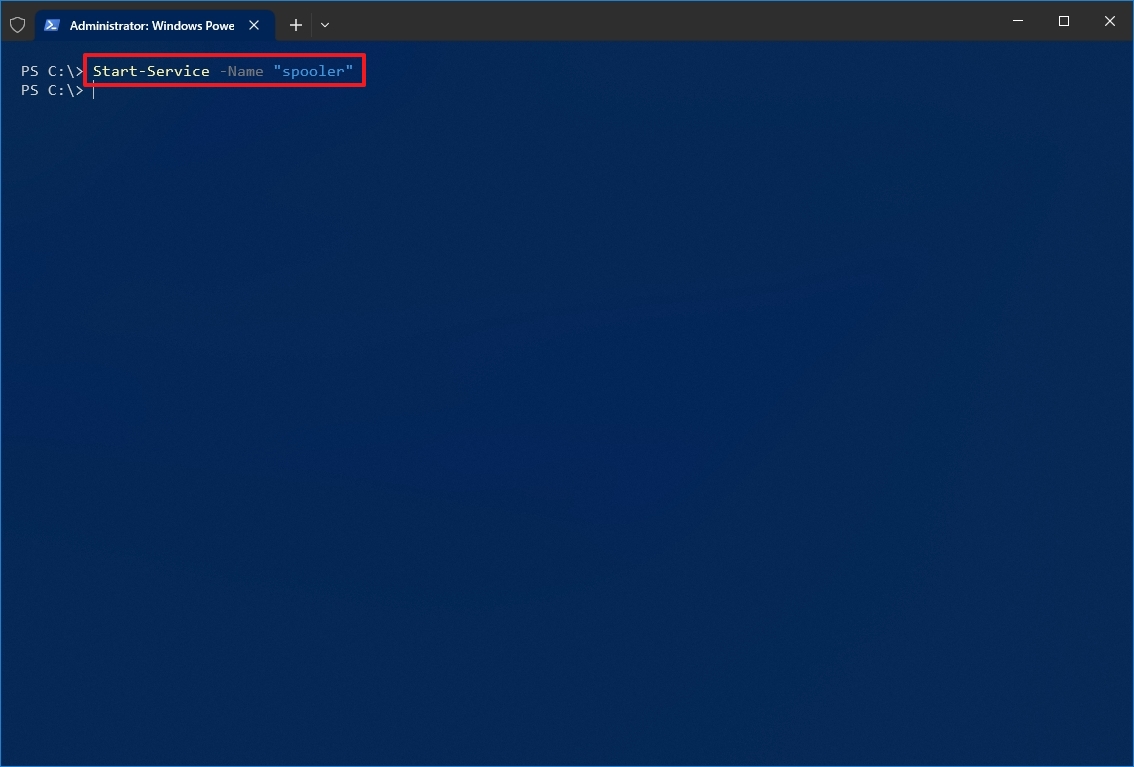
- Type the following command to start a service and press Enter: Start-Service -Name «SERVICE-NAME»
For example, this command starts the printer spooler service on Windows 10: Start-Service -Name «spooler»
In the command, replace «SERVICE-NAME» with the name of the service. Using the display name is supported, replacing -Name with -DisplayName and specifying the service’s display name.
Alternatively, you can also use this variant of the command to start a service: Set-Service -Name «SERVICE-NAME» -Status running
In the command, replace «SERVICE-NAME» with the name of the service. If you want to use the display name, replace -Name with -DisplayName and then specify the service’s display name.
Once you complete the steps, the service will start on your computer.
Disable service
To disable a service using a PowerShell command, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for PowerShell, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
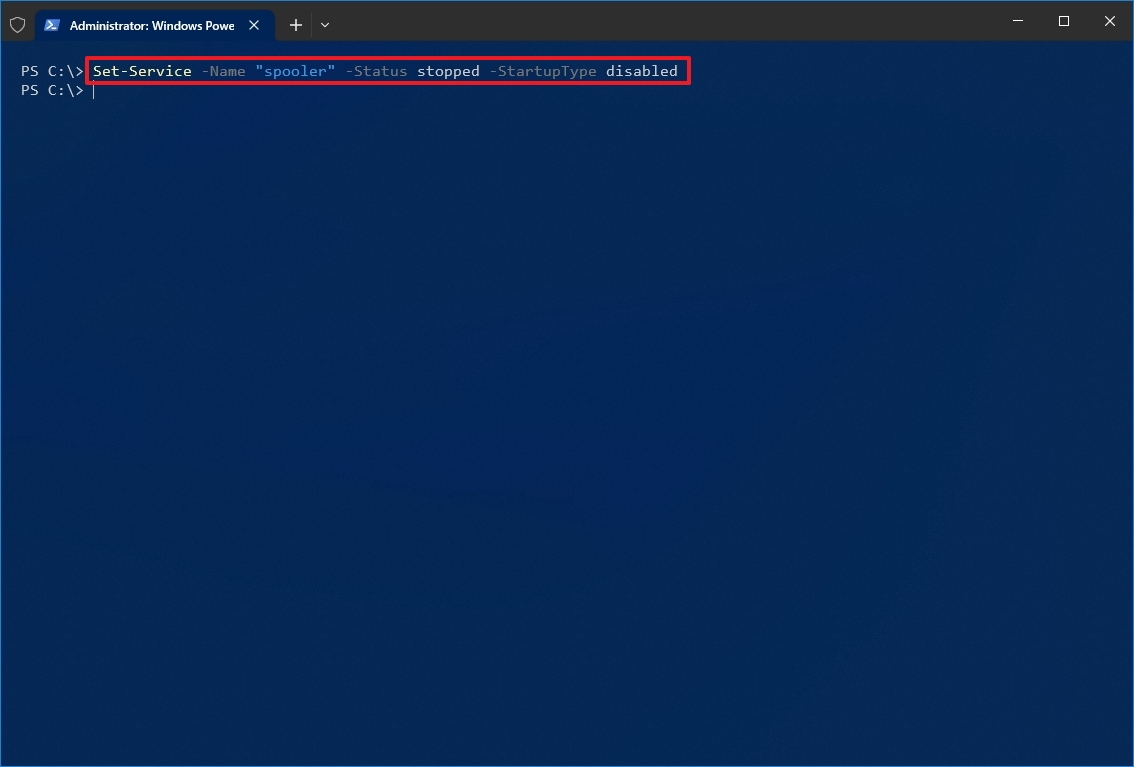
- Type the following command to disable a service and press Enter: Set-Service -Name «SERVICE-NAME» -Status stopped -StartupType disabled
In the command, update «SERVICE-NAME» for the name of the service. If you want to use the service’s display name, replace -Name with -DisplayName and specify the service name. If you want to disable the service without stopping it immediately, you can remove the -Status stopped portion of the command.
For example, this command disables the printer spooler service on Windows 10: Set-Service -Name «spooler» -Status stopped -StartupType disabled
After you complete the steps, the PowerShell command will disable the specified service.
Enable service
To enable a specific background service with PowerShell, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for PowerShell, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
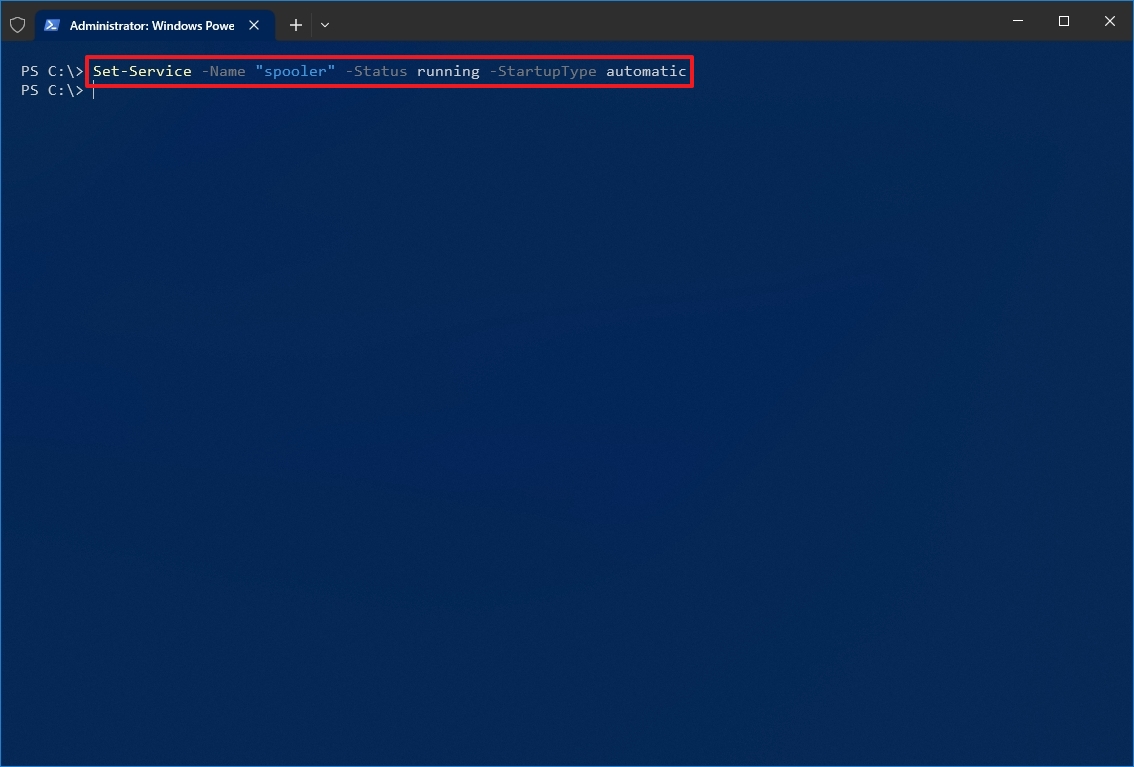
- Type the following command to enable a service and press Enter: Set-Service -Name «SERVICE-NAME» -Status running -StartupType automatic
For example, this command enables the printer spooler service using PowerShell: Set-Service -Name «spooler» -Status running -StartupType automatic
- Quick note: You may able to use the display -DisplayName option, but the command may also prompt you to supply the name of the service, adding an extra step to the process. If you want to enable the service without starting it immediately, you can remove the -Status running portion of the command.
Once you complete the steps, PowerShell will enable the service specified with the command.
How to manage services from Command Prompt
If you’re comfortable using the command line, Command Prompt offers the «net» command (older) to stop or start or the «sc» command (newer) to stop, start, disable, or enable services on Windows 10.
Stop service
To stop a Windows 10 or app service with Command Prompt, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Command Prompt, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
- (Optional) Type the following command to view a list of all the services and press Enter: sc queryex state=all type=service
- Type the following command to stop a service and press Enter: net stop «SERVICE-NAME»
In the command, replace «SERVICE-NAME» with the name or display the name of the service. You only need quotation marks if there’s a space within the name. For example, this command stops the printer spooler using the service name: net stop «spooler»
Alternatively, you can also use the more advanced «sc» command: sc stop «SERVICE-NAME»
For example, this command stops the printer spooler using the service name: sc stop «spooler»
After you complete the steps, the command will stop the specified service on Windows 10.
Start service
To start a service with the command line, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Command Prompt, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
- Type the following command to start a service and press Enter:
net start «SERVICE-NAME»
In the command, replace «SERVICE-NAME» with the name or display the name of the service. You only need quotation marks if there’s a space within the name. For example, this command starts the printer spooler using the service name: net start «spooler»
Alternatively, you can also use the «sc» command: sc start «SERVICE-NAME»
For example, this command starts the printer spooler using the service name: sc start «spooler»
Once you complete the steps, the command will execute and start the service you specified.
Disable service
To disable a service with Command Prompt, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Command Prompt, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
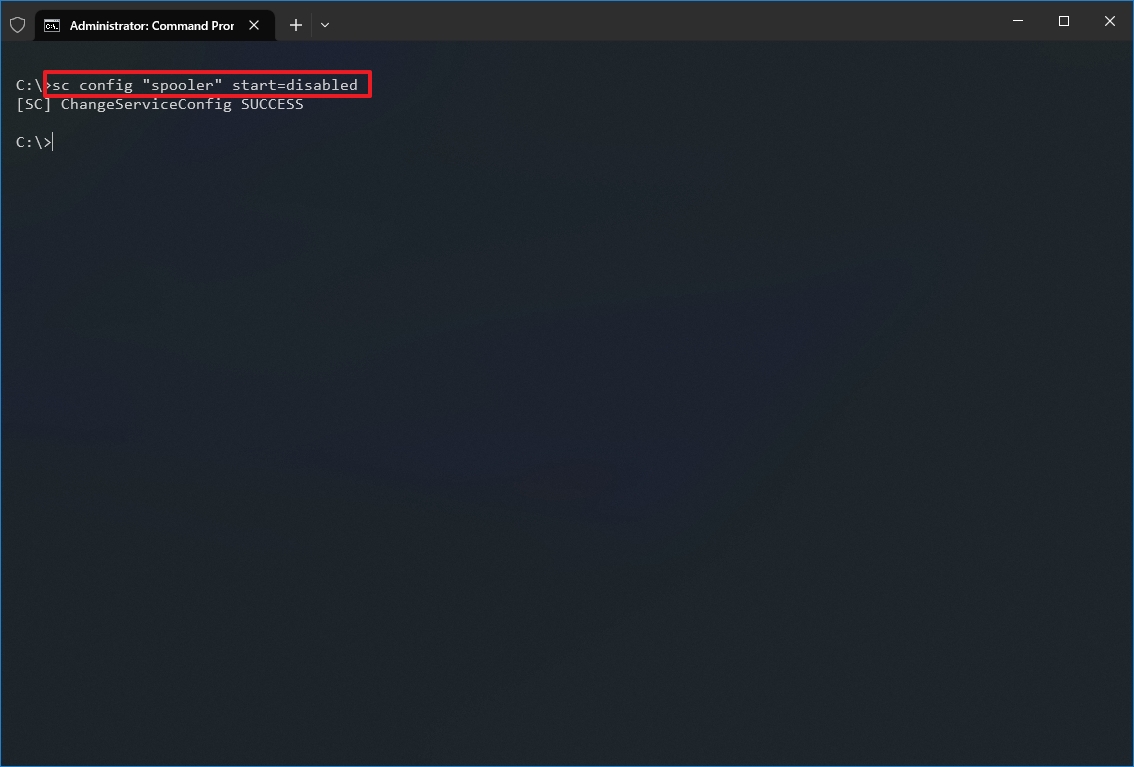
- Type the following command to disable a service and press Enter: sc config «SERVICE-NAME» start=disabled
In the command, replace «SERVICE-NAME» with the name of the service that you want to disable.
For example, this command disables the printer spooler using the service name: sc config «spooler» start=disabled
- (Optional) Type the following command to stop the service and press Enter: sc stop «SERVICE-NAME»
- Quick note: When you disable a service, it doesn’t stop the current state of the service. You can either restart your computer or stop the service using the above command.
After you complete the steps, the sc command will run disabling the Windows 10 or app service you specified.
Enable service
To enable a service with a command, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Command Prompt, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
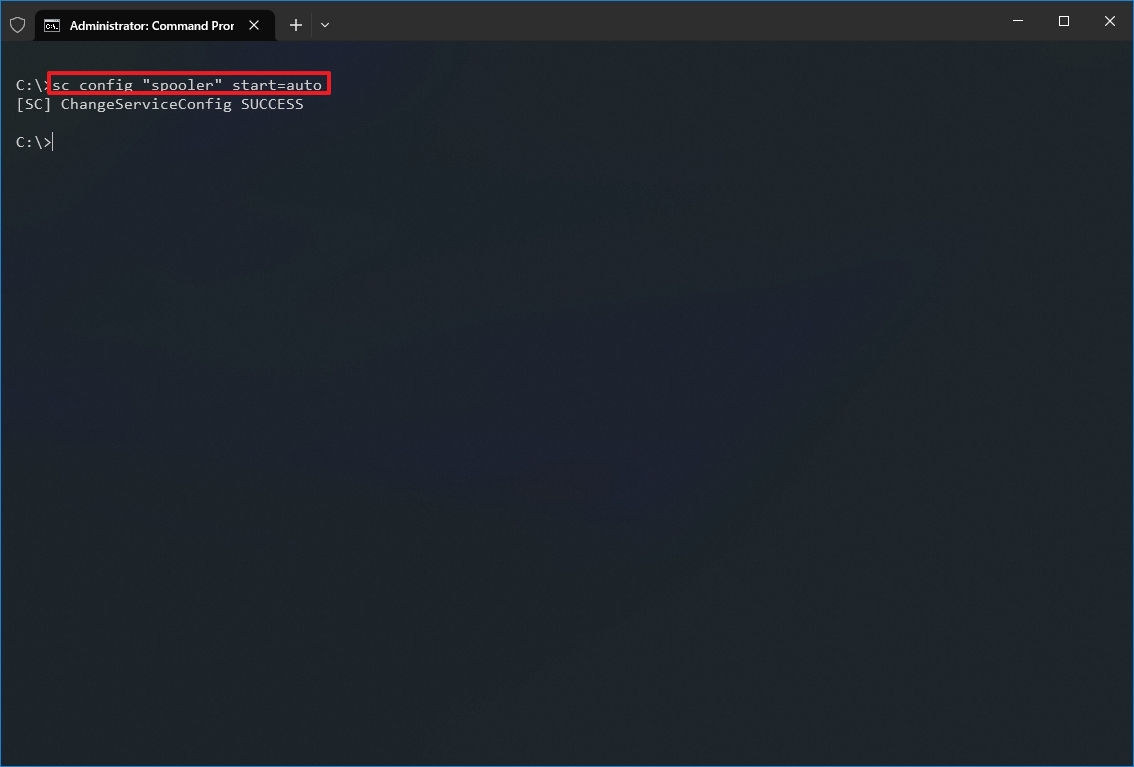
- Type the following command to enable a particular service and press Enter:
sc config «SERVICE-NAME» start=auto
In the command, replace «SERVICE-NAME» with the name of the service that you want to enable. For example, this command enables the printer spooler automatically using the service name: sc config «spooler» start=auto
These are alternative commands to enable a particular service:
- Manual: sc config «SERVICE-NAME» start=demand
- Automatic Delayed: sc config «SERVICE-NAME» start=delayed-auto
- (Optional) Type the following command to start the service and press Enter: sc start «SERVICE-NAME»
Once you complete the steps, the service will enable and start automatically on reboot according to the command you used.
You can only use the «net» command to start or stop services. The «sc» command allows you to perform more tasks, including start, stop, enable, or disable services, among other options. If you’re choosing to manage services with command lines, then, in either case, it’s best to use the service name instead of the display name.
Also, when using any of the methods outlined above, consider that making modifications to the default settings can alter the operation of one or more features that depend on that service, negatively affecting the experience. Furthermore, if you restart a service, you might be required to start its dependencies manually as well to make the app or feature operational again.
We’re focusing this guide on Windows 10, but the ability to manage services has been available for several years, which means that you can refer to this guide if you’re still running Windows 8.1, Windows 7, and older versions.
More resources
For more helpful articles, coverage, and answers to common questions about Windows 10 and Windows 11, visit the following resources:
- Windows 11 on Windows Central — All you need to know
- Windows 10 on Windows Central — All you need to know
(opens in new tab)
Cutting-edge operating system
A refreshed design in Windows 11 enables you to do what you want effortlessly and safely, with biometric logins for encrypted authentication and advanced antivirus defenses.
Get the best of Windows Central in in your inbox, every day!
Mauro Huculak is technical writer for WindowsCentral.com. His primary focus is to write comprehensive how-tos to help users get the most out of Windows 10 and its many related technologies. He has an IT background with professional certifications from Microsoft, Cisco, and CompTIA, and he’s a recognized member of the Microsoft MVP community.
- Download source — 93.1 KB
Introduction
In Windows XP, Windows Server 2003 and earlier Windows versions, a Windows service could start an application with a user interface, and this application would be visible in the session of the currently logged-in user. In Windows Vista and later, Windows services run in Session 0 which does not allow any interaction with the user. A Windows Service may launch a UI application but this application will never be displayed on the currently logged-in user’s desktop. This tip shows how to launch a UI application from a Windows Service by using the Windows API.
Background
This problem emerged when migrating a Cluster Resource from Windows Server 2003 to Windows Server 2012. In Windows Server 2003, a Cluster Resource could be a UI application. In Windows Server 2012, when bringing online the same Cluster Resource, the UI application does not become visible. This happens, because the Cluster Service is also a Windows Service, and the Cluster Resources launched by the Cluster Service are run in Session 0, which does not have user interaction. The workaround is to create a Windows Service that launches the UI application, and make this Windows Service a Cluster Resource. Only the Windows Service will be explained here.
Through the Windows API, it is possible to launch a new process in the currently interactive session. Only Windows Services that run under the local system account have the right to do that. However, the new process also runs under the local system account, whereas the requirement is for the new process to run under a specific user. The solution is for the new process to launch a second new process under a specific user. Once the second new process is started, the first new process terminates. At the end, the Windows Service and the second new process are running, the first in session 0 which is non interactive, and the latter in the currently interactive session. The Windows Service finds the process id of the second new process by the process name. When the service is stopped, it kills that process id. The Windows Service monitors if the process id exists, and stops if it no longer exists. The Windows Service can be made a Cluster Resource. When the second new process fails, the Windows Service will also stop and a Fail Over is initiated.
Using the Code
Two Visual Studio projects are provided:
WindowsService1: Runs under the local system account, and startsWindowsApplication1in the currently interactive session. InstructsWindowsApplication1through the command line parameters to start Notepad.WindowsApplication1: Starts a new process given by the command line arguments. In this case, the new process is Notepad. The new process runs under a specific user, defined in the configuration file. WhenWindowsApplication1is started without command line arguments, a form is shown to enter the user credentials and save them to the configuration file.
WindowsService1
Contains the following items:
WindowsApi: Contains the Windows API signatures ofWTSGetActiveConsoleSessionId,WTSQueryUserToken,CreateProcessAsUser. You can get these at www.pinvoke.net.Service1: Implements the Windows Service.OnStart: CallsWTSGetActiveConsoleSessionIdto get the current interactive session and puts it into the variableuserTokenHandlewithWTSQueryUserToken. LaunchesWindowsApplication1withCreateProcessAsUserW. Passes as command line parameter «C:WindowsSystem32notepad.exe a b c«. CallsGetProcIdto get the process id that was created byWindowsApplication1. Starts the methodMonitorProcessin a new thread.GetProcId: Gets the process id withProcess.GetProcessesByName, in this case it will be Notepad. If no such process is found, or more than one processes are found, an exception is thrown.MonitorProcess: Checks withProcess.GetProcessByIdif the process id still exists. If it does not exist, calls theStopmethod of the service.OnStop: UsesProcess.Killto kill the process id, in this case the Notepad process.
ProjectInstaller: This class is needed for installing the service.
WindowsApplication1
Contains the following items:
- App.config: contains the credentials of the user under which the created process should run.
ModMainMain: is the main entrypoint. If command line arguments exist, thenProcessStartis called, otherwiseForm1is shown.ProcessStart: A new process is created. The user credentials are read from the configuration file withConfiguration.ConfigurationManager.AppSettings. The password is set by callingSetPassword. The first of the command line arguments defines the executable to be started, and the rest of the command line arguments, define the command line arguments for the newly created process. The process is started withProcess.Start.SetPassword: CallsDecryptto decrypt the password and fills aSecureString.
Form1: Provides textboxes to fill the domain, username and password. Upon pressing the button ok, the password is encrypted by callingEncryptand the values are saved to the configuration file. The configuration file is opened withConfigurationManager.OpenExeConfigurationand it is saved withConfiguration.Save.ModCrypto: provides methods for encryption and decryption.Encrypt: UsesSystem.Security.Cryptography.ProtectedData.Protectto encrypt astring. The entropy makes guessing the password more difficult.Decrypt: UsesSystem.Security.Cryptography.ProtectedData.UnProtectto decrypt astring.
Test
This program has been tested on Windows 7 and Windows Server 2012. It should run on Windows versions of Vista and later. To run the program, follow these steps:
- With Visual Studio 2010, open solution CreateAppFromService.sln.
- Build the solution.
- In Windows Explorer, double click on Source/bin/WindowsApplication1.exe. A form to enter the credentials is shown.
- Enter the credentials under which the Notepad launched by
WindowsApplication1should run. - Press Ok. The credentials are saved to bin/WindowsApplication1.exe.config. You may see that the Password is encrypted.
- In Windows Explorer, double click on Source/InstallService.bat. If the message «The transacted install has completed.» is shown in the console, then
Service1has been installed successfully. Otherwise, try right-click and choose Run as administrator. - Start/Run/services.msc. This starts the Services Management Console. Check that
Service1is installed. - Right-click on
Service1and choose Start. The service’sStatusshould change toStarted. - A Notepad should open asking: Cannot find the a b c.txt file. Do you want to create a new file?
You may click Yes or No. This is to demonstrate that parameters may be passed to the UI application.
- Start/Run/taskmgr to start the Windows Task Manager. Check that Notepad runs under the User Name entered in step 4. If this is the case, it seems that all worked well, that means, Windows Service «
Service1» successfully startedWindowsApplication1, which in turn started Notepad under the specified user. - Right-click on
Service1and choose Stop. The Notepad should close and the service’s Status should change to Stopped. - Start again the
Service1to test the monitoring thread. - Notepad should start again. Close the Notepad window.
- Right-click on
Service1and choose Refresh. The service’s status should change to Stopped, because the monitoring thread found out that Notepad is no more running, and therefore the monitoring thread instructed the service to stop. - If the service did not start, check the Application Log in the Event Viewer. You may start the event viewer with Start/Run/eventvwr.msc.
- You may find for example the following error:
- Source:
WindowsApplication1 - Message: Main Logon failure: unknown user name or bad password.
- Source:
- In Windows Explorer, double click on Source/UnInstallService.bat. If the message «The uninstall has completed.» is shown in the console, then
Service1has been uninstalled successfully. Otherwise, try right-click and choose Run as administrator. If this does not work either, in a command prompt type:sc delete Service1.
History
WindowsService1launchingWindowsApplication1launching Notepad with credentials in the configuration file encrypted byProtectedData.Protect.
This member has not yet provided a Biography. Assume it’s interesting and varied, and probably something to do with programming.