Пока некоторые читатели (да что уж там, и писатели — например, я) наслаждались в отпуске теплыми летними денечками, известный автор нашего англоязычного блога Адам Бертрам подготовил краткий обзор Windows Storage Spaces. В него он включил, в частности, сведения о настройке Windows Storage Spaces на популярных конфигурациях. Перевод его статьи я и предлагаю вашему вниманию.
Во многих дата-центрах и серверных фермах для хранения данных используются HDD и SSD. Статистика, однако, сообщает о том, что после трёх лет работы 10% дисков становятся негодными.
Конечно, те организации, которые заботятся о целостности и сохранности своих данных, держат руку на пульсе, а также отслеживают и другие факторы риска — будь то человеческий фактор, железо или софт. И тут тем, кто работает с Windows-инфраструктурой, могут помочь Windows Storage Spaces. Ведь их RAID-подобная функциональность (то, что мы видим в File Explorer как виртуальные диски) весьма полезна в деле обеспечения резерва мощностей хранения.
Гибкие возможности масштабирования тоже привлекательны: можно объединить 3 и более драйвов в единый сторадж-пул и затем формировать на его основе “стораджики” нужного размера. А поскольку при работе с пулом формируются и сохраняются дополнительные копии для ваших данных, то проблемы с одним из дисков не приведут к потере всего и вся. А если понадобилось больше места? Просто добавь воды еще дисков в пул.
Storage Spaces для Windows 10
— Он забирается на самую высокую сосну и оттуда планирует.
— Ага, простите, что планирует?
— Он прыгает и планирует.
(“День радио”)
Даже если сценарий развертывания, который вы хотите воплотить, входит в число самых популярных, и инструкция к нему коротка и вроде даже сходу понятна, этап подготовки и планирования все равно никто не отменял. Итак:
Если вы используете дисковые пространства Storage Spaces на машине с Windows 10, то рекомендуется обеспечить наличие минимум 2 дисков помимо системного. Эти диски могут быть как встроенными, так и внешними. Поддерживаются SSD; можно комбинировать SATA, USB и SAS.
Количество дисков рассчитывается исходя из того, какой метод обеспечения отказоустойчивости вы хотите применить. Есть вот такие варианты:
-
Simple (простой) — требует наличия минимум двух дисков. Хоть этот метод и дает хорошую производительность, но ничем вам не поможет в случае отказа. Его можно использовать, например, если вы настраиваете storage space для хранения временных данных (например, файлов видео-рендеринга, файлов-черновиков в графических редакторах, и так далее).
-
Mirror (зеркальный) — позволяет сохранять несколько копий данных на случай отказа. Так, Two-way mirror spaces хранят две копии данных, и с ними вы переживете отказ одного из дисков. Для их организации потребуется минимум два диска. Three-way mirror spaces позволят пережить отказ двух дисков, а для их организации потребуется минимум пять. Зато хранить в таких storage spaces можно самые разнообразные данные.
-
Parity (с контролем четности) — рекомендуется для хранения архивных и стриминговых данных. Хранят несколько копий на случай отказа. Если вы хотите обеспечить отказоустойчивость в случае проблемы с одним диском, то в сценарии с Parity spaces вам понадобится минимум три диска, а на случай проблемы с двумя — минимум семь дисков.
После того, как вы все рассчитали и подготовили, можно организовать собственно Storage Spaces. Для этого в Windows 10 нужно выполнить вот такие шаги:
-
Проверить, что диски, которые вы планируете задействовать, у вас подключены.
Важно! Если вы укажете, что в сторадж-пул хотите включить размеченный диск, имейте в виду, что Windows безвозвратно удалит все разделы и файлы на нём. До начала работы сделайте резервную копию всего, что вам дорого на этом диске!
-
Для простоты в поле поиска в панели задач вводим Storage Spaces и из полученного списка выбираем Storage Spaces.
-
Кликаем Create a new pool and storage space.
-
Выберем нужные нам диски и затем кликнем Сreate new storage pool.
-
Указываем имя, буквенное обозначение и файловую систему для нового сторадж пула.
-
На случай сбоя рекомендуется выбрать метод обеспечения отказоустойчивости (Resiliency) как одну из следующих опций: Two-way mirror, Three-way mirror или Parity.
Важно! Помните про количество дисков, которые потребуются в каждом из указанных вариантов, о чем мы говорили выше. Если, допустим, вы предпочтете Two-way mirror, то для нового storage space будет создаваться две копии данных. Так что для такого сценария понадобится минимум два диска (помимо системного).
-
Затем задайте максимальный размер стораджа для Storage Spaces.
Примечание: Можно указать значение, превышающее размер сторадж-пула — когда место будет заканчиваться, вы просто добавите еще один диск.
-
Когда с настройками покончено, нажимаем Create storage space.
Оптимизация работы
Рекомендуется своевременно оптимизировать работу с дисками. Вот что советует делать Microsoft:
При добавлении новых дисков в существующий пул рекомендуется оптимизировать использование диска. При этом некоторые данные будут перемещены на новый диск, чтобы оптимизировать использование емкости пула. Это стандартное действие при добавлении нового диска в обновленный пул в Windows 10: флажок Optimize to spread existing data across all drives будет установлен по умолчанию.
Однако если вы сняли этот флажок или добавили диски до обновления пула, вам нужно вручную оптимизировать использование диска. Для этого в поле поиска на панели задач введите Storage Spaces, выберите Storage Spaces из списка результатов поиска, а затем щелкните Optimize drive usage.
Автономный сервер
Если у вас один отдельно взятый сервер, то для настройки на нем дисковых пространств Storage Spaces есть подробная инструкция от Microsoft, на русском языке и даже с картинкой. Storage Spaces поддерживаются для Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2012 R2 и Windows Server 2012.
Обратите внимание: до начала настройки нужно обеспечить наличие одного или нескольких пулов, а также проверить конфигурацию на соответствие ряду требований (они перечислены в разделе «Предварительные условия»).
На базе сторадж-пула можно создать несколько виртуальных дисков. (Windows идентифицирует их как обычные диски, которые могут быть отформатированы.)
Для их создания можно использовать File and Storage Services; в настройках можно указать thin provisioning либо fixed provisioning, а также размер. Дополнительные настройки можно задать с помощью команд PowerShell.
Кластеры и Storage Spaces Direct
Если вы работаете с кластером и используете для каждой его ноды СХД с прямым подключением (DAS), то Storage Spaces Direct могут оказаться вполне разумным и эффективным вариантом по сравнению с NAS и SAN. Storage Spaces Direct отличаются хорошей масштабируемостью и возможностями управления. Технология Storage Spaces работает наряду с кэшированием, RDMA и поддержкой СХД для разных уровней (tiers). Помимо этого, поддерживаются диски NVMe.
Storage Spaces Direct поддерживаются для Windows Server 2019 Datacenter, 2016 Datacenter и Insider Preview Builds. Можно создать конвергентное или гипер-конвергентное пространство.
Вкратце, основные этапы развертывания Storage Spaces Direct — это:
-
Развертывание Windows Server — установка и настройка ОС, добавление доменных учеток, настройка ролей и необходимых фич.
-
Настройка сети (этот этап не относится к сценарию развертывания Storage Spaces Direct на виртуальных машинах).
-
Конфигурация собственно Storage Spaces Direct — очистка дисков и разделов, настройка кластеров, настройка Storage Spaces Direct, создание томов, развертывание необходимых виртуальных машин.
-
Для конвергентной инфраструктуры — развертывание масштабируемых файловых серверов, настройка ролей, создание шар, настройка ограниченного делегирования Kerberos.
Все эти этапы очень подробно описаны здесь (на русском языке).
Возможен сценарий, при котором все физические диски содержатся в enclosures с общим доступом — это т.н. JBOD enclosure. Такая инфраструктура должна соответствовать требованиям Windows Certification, а также включать в себя идентичные SAS HBA (имеющие сертификацию Storage Spaces). Такие диски в кластере не должны иметь встроенную функциональность RAID.
Storage Spaces vs. RAID
Как водится, у Windows Storage Spaces и RAID есть свои преимущества и свои недостатки. Об этом уже написана не одна сотня строк (например, здесь). Вкратце:
-
У RAID есть два аспекта: аппаратный и программный — а Windows Storage Spaces, так сказать, является software-driven, настраивается целиком через графический интерфейс или командную строку.
-
Для программных RAID, как и для Storage Spaces отсутствуют ограничения по числу сокетов (у традиционных RAID они есть).
-
ОС по-разному “видит” диски в RAID и в Storage Spaces — диски RAID предстают как цельный юнит (даже если у физических дисков разная емкость), что может приводить к неоптимальному использованию свободного пространства. Для Storage Spaces такой проблемы нет, так как есть доступ к отдельным дискам.
-
Если говорить о производительности, то RAID 0 превосходит Storage Spaces с режимом simple mode примерно вдвое. Однако на скоростях 4K они уже сравнимы. RAID 1 быстрее выполняет последовательные операции чтения, зато Storage Spaces в режиме two-way mirror mode вдвое быстрее выполняет операции записи, нежели RAID 1. Что касается hardware RAID, то операции чтения и записи для них гораздо быстрее, чем Storage Spaces в режиме parity mode.
Ссылки
Общие сведения о дисковых пространствах Storage Spaces
Развертывание Storage Space Direct
Дисковые пространства в Windows 10
Кейс о развертывании Storage Space Direct компанией-провайдером Veeam
Storage Spaces Direct (S2D) is the award-winning software-defined storage (SDS) tecnhology that was first introduced in Windows Server 2016. Since that moment, S2D has become my one of the favourite and frequently used role in Windows Server (on-premises and even in Azure).
Windows Server 2019 that is going to be generally available in the second half of this year (September or October – in accordance with WS 2012-2016 release dates) continues to develop S2D by adding new features. Why don’t we discuss them right now?
TIP: Windows Server 2019 preview build is available here
Scalability
More volumes, bigger capacity per server and cluster
USB Witness
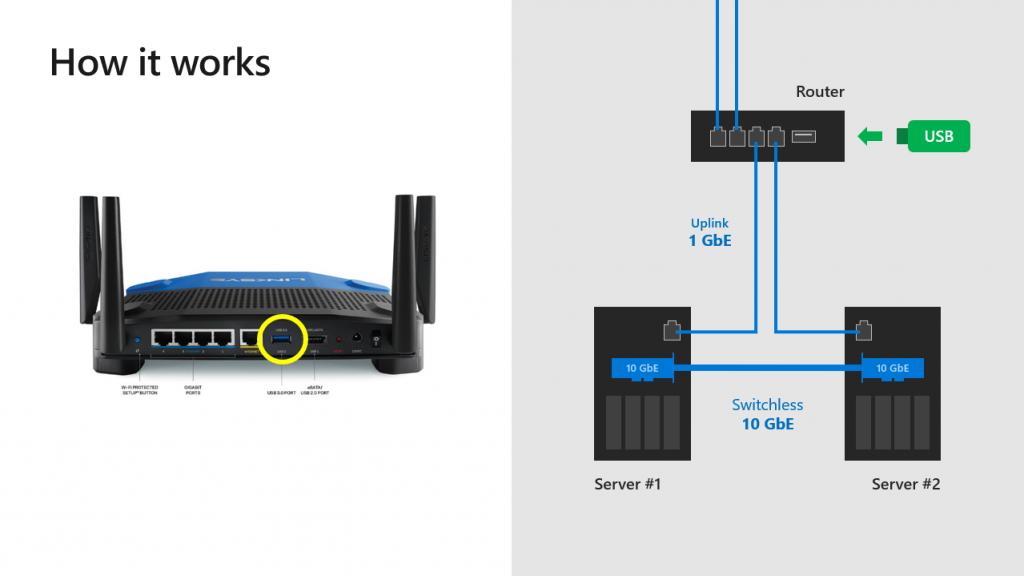
Storage Spaces Direct can be configured with just two nodes. However, we will need to design witness placement to protect our cluster from unexpected failure (in other words, we should achieve quorum). In Windows Server 2016, you can place witness on a file share, cloud (details here) or disk witness (it’d be very strange if it was actually used in S2D clusters). What about customers who don’t have any AD infrastructure or Azure/Internet access? Here is a breakthrough – USB Witness.
In short, you will be able to configure a true two-node S2D by using USB thumb drive connected to the router that is already used for VM/management traffic between nodes, for instance. Other two network interfaces (shown on the picture above), could be RDMA-adapters (recommended and supported) or Thunderbolt (POC, Project Kepler-47).
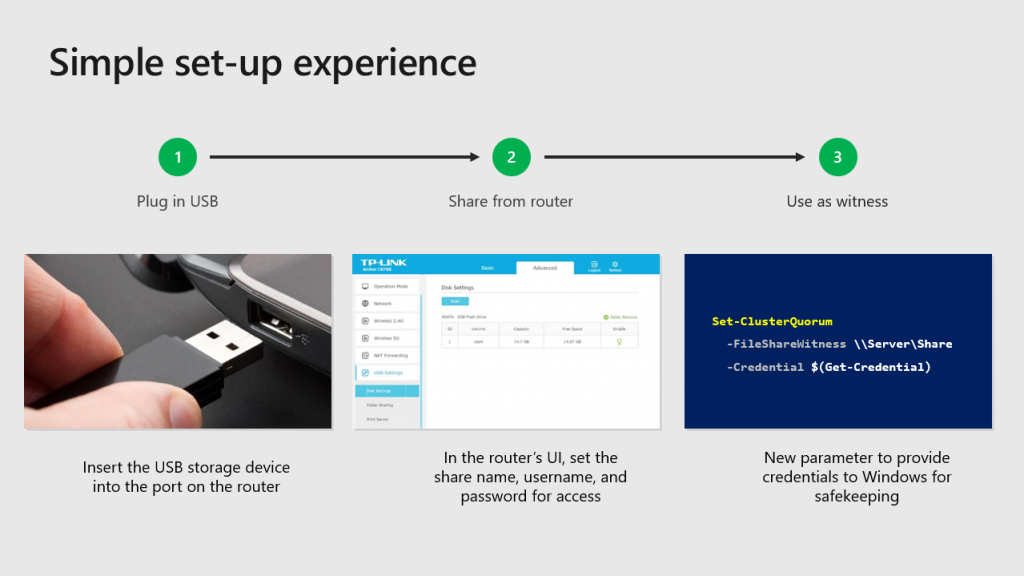
Simply insert the USB drive into the port on the router, set the share name and access information, configure witness in PowerShell: Set-ClusterQuorum -FileShareWitness path -Credential and you are ready to go.
TIP: the router should support SMB2+ and USB. And, given that a witness.log is a quite small file (just kilobytes), you can use any-sized USB drives. The list of the supported routers will be available later.
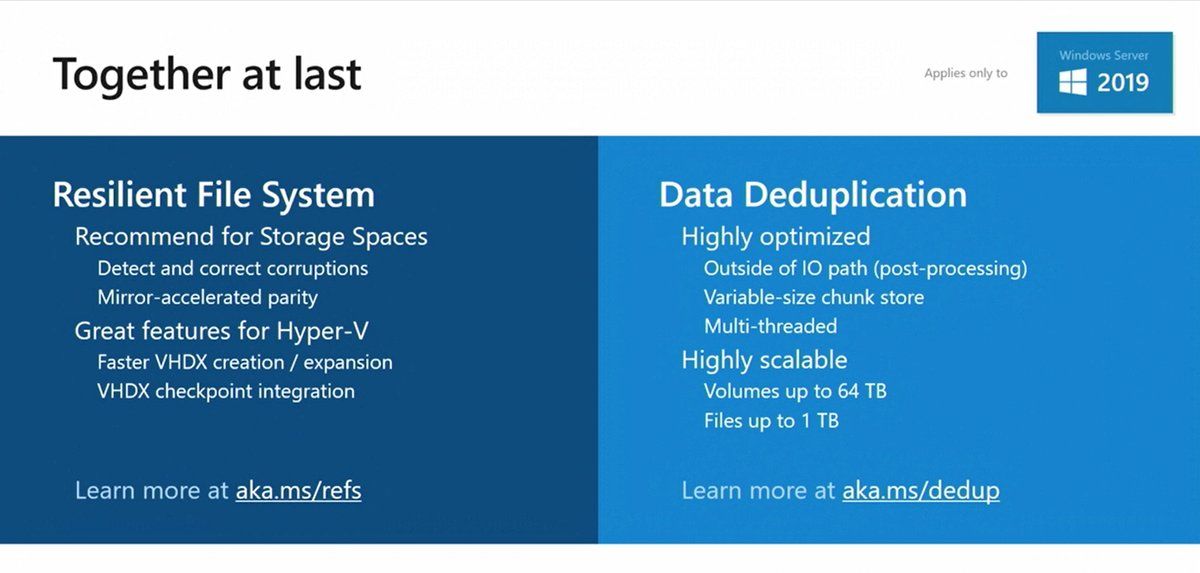
Data Deduplication
ReFS is the recommended file system for S2D, improves VHDX creation/expansion speed (enables Accelerated VHDX operations), provides higher stability by detecting corruptions and allowing you to repair them with no volume downtime. However, some features such as ODX, Data Deduplication are not supported by ReFS in Windows Server 2016.
Starting with the Windows Server 2019 (1709 and later), Data Deduplication has been fully supported for ReFS. It means that you no longer need to choose between NTFS and ReFS file systems while planning S2D volumes. Create ReFS volume, enable Data Deduplication (PowerShell/Windows Admin Center), and then check the savings of storage space (use PowerShell and Get-DedupVolume cmdlet).
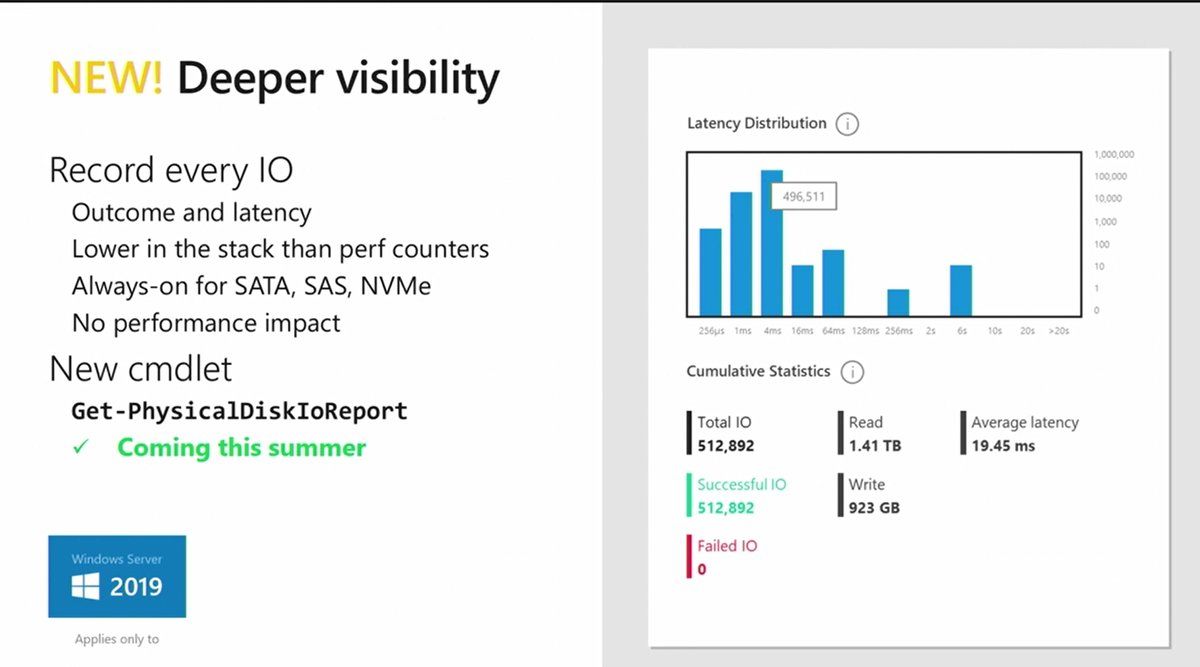
Proactive outlier detection
It was quite challenging to investigate performance issues in S2D in Windows Server 2016. We had to use PowerShell or performance counters (+VMFleet) to get a full picture of our setup’s behavior. Windows Server 2019 significantly simplifies that. S2D now records the outcome (success/failure) and latency (elapsed time) for every read/write IO to every drive without any performance impact. Therefore, drives with latency/outcome issues will be marked in PowerShell and Windows Admin Center as “Abnormal Latency” status. In addition, you can organize pooled drives into peer groups, and then compare latency against peers to quickly find any bottlenecks (new cmdlet: Get-PhysicalDiskIoReport).
This azure-inspired mechanism works on the lower level than performance counters and enabled by default for every SATA,SAS,NVMe drives.
Others
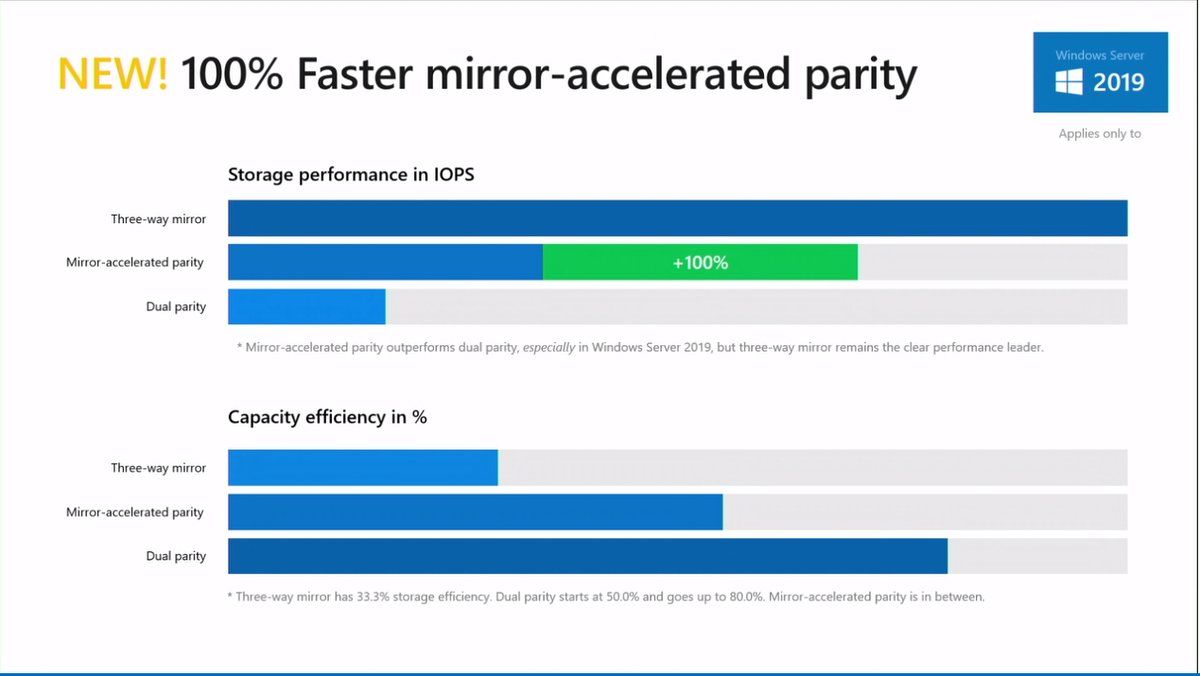
-Faster mirror-accelerated parity volumes (~x2)
-PMEM (Persistent Memory) drives support (Intel Optane/NVDIMM-N) for use as cache and capacity
-Deep integration with Windows Admin Center (a free HTML5-based management interface for entire Windows Server infrastructure. We’ll look at this a bit later)
-New networking recommendations for high performance, at scale, or deployments of 4+ nodes: 25 Gbps (or higher) NICs (two or more) that are remote-direct memory access (RDMA) capable, iWARP (recommended) or RoCE
В этой статье я рассмотрю установку и использование фичи Storage Space Direct на WinServer 2019.
Чуть подробней опишу некоторые нюансы установки связанные с требованием к типу дисков(Media type) и типу шины (BusType).
Задача: Организовать кластер hyper-V без внешнего хранилища, но с отказоустойчивостью и возможностью миграции ВМ на лету
Среда развертывания
Нам дано 3 сервера IBM x3650 M4 со следующей конфигурацией:
— встроенный Raid контроллер LSI ServeRaid M5110e;
— 2 SSD диска по 256ГБ в рейде 1 под ОС;
— 4 SSD диска по 512ГБ под данные;
— 4 Ethernet-порта 1Гбит/с
проц и память по вкусу.
Начнем, пожалуй.
1. Начать стоит с настройки биоса, уефи-хуефи, настройки IMM, выбора режима включения по отказу питания и т.п. вещей. После того как сервак заработает в биос попасть будет проблематично, ведь для этого его потребуется выключить, а выключенный сервер это не нормально 
2. После этого заходим в настройки Рейд-контроллера, создаем зеркало из дисков под ОС. Диски под данные пока не трогаем, оставляем в режиме JBOD (если в JBOD выставить нельзя — следует обновить контроллер последней прошивкой, в моем случае версия — 23.22.0-0024 )
3. Ставим ОС, там всё стандартно.
4. После загрузки ОС и настройки под ваши условия (типа имени, IP, участии в домене), если зайдете в управление дисками не активируйте оставшиеся диски, они должны остаться без партиций.
5. Ставим роли Hyper-V и отказоустойчивого кластера, не должно возникнуть проблем.
6 .Создаём кластер из всех узлов, с проверкой.
7. А дальше начинаются мероприятия связанные непосредственно с Storage Space Direct.
7.1 Включается фича из повершелла, командлетом
Enabe-ClusterS2D
но! из-за требований фичи диски с типом шины отличным от SAS, SATA, NVMe — не поддерживаются!
посмотреть тип шины дисков можно другим командлетом:
Get-PhysicalDisk | ft UniqueId, FriendlyName, BusType, MediaType
Как выясняется, у нас неподдерживаемый тип шины — RAID, и несмотря на выставленный на контроллере и поддерживаемы фичей режим JBOD, ОС видит диски как RAID. Отступая в сторону, скажу что все мои поиски и варианты решения проблемы с видимостью типы шины не принесли плодов, и если найдутся люди которые знают как это сделать, я буду сильно благодарен если опишите это в комментариях.
Другими словами, поддерживаемое Микрософтом решение собрать нам уже точно не удастся.
НО! Есть решение рабочее, но неподдерживаемое.
Мы просто снимаем требование к типу шины кластером для активации этой фичи.
(Get-Cluster).S2DBusTypes=4294967295
либо инвертируем требование, т.е. приниматься будет только RAID:
(Get-Cluster).S2DBusTypes=0x100
Всё 
В результате у нас появится пул из всех дисков для данных:
Продолжение следует…
В следующих сериях:
Изменяем свойства пула, для получения отказоустойчивости.
Создаём общий кластерный диск для размещений дисков виртуальных машин.
Проверяем отказоустойчивость выключением узла кластера, имитируя неплановый отказ оборудования.
For the first time, Microsoft made an online Windows Server Summit at June 26th 2019. Microsoft talked about hybrid cloud, security, cloud native application and hyperconverged solution. Some of the new features which are coming with Windows Server 2019 were unleashed. In this topic, I’d like to summary what are the new features and why you should consider Storage Spaces Direct for a new installation or to update your existing cluster.
Deduplication and ReFS
With Storage Spaces Direct, Microsoft recommends the use of ReFS as the file system. ReFS brings accelerated VHDX operations and some features against corruption. However, data deduplication and ReFS are not supported together in Windows Server 2016. Some customers didn’t want to adopt S2D because the capacity required by the resiliency was to important (especially with 3-way Mirroring, where 66% of the raw capacity is used by the resiliency).
Tomorrow, with Windows Server 2019 we will be able to enable data deduplication on ReFS file system to save some storage space at the cost of some CPU workloads. Cosmos Darwin introduced this slide during Windows Server Summit.
Performance improved in Mirror-accelerated parity
One way to reduce the capacity used by the resiliency is the usage of Mirror-accelerated parity. Shortly, a Mirror-Accelerated Parity volume is a volume splited in two tiers:
- A fast tier, usually hosted on SSD and configured in 3-Way Mirroring
- A capacity tier usually hosted on HDD and configured in dual parity
All writes go to the fast tier and when it is almost full (80%), data which are less frequently used are moved to capacity tier. Mirror-Accelerated Parity is the best of mirroring and parity world on the paper. But with Windows Server 2016, Mirror-Accelerated Parity suffers of poor performance in some scenarios and is not fast as expected.
With Windows Server 2019, Microsoft announces that Mirror-Accelerated Parity has been improved and is 100% faster compared to Windows Server 2016. The following screenshot comes from Cosmos Darwin slide desk during Windows Server Summit:
So, data deduplication and Mirror-Accelerated Parity can help you to reduce the capacity used previously by the resiliency. It is an excellent news for customers.
A better monitoring of drive latencies
In Microsoft solution (and in all hyperconverged solution), it is complicated to monitor the latency per drive. Often this is an average latency and we can’t sort IO by latency. So, we can’t get information about IOs which took the longest time (or the highest latency). With Windows Server 2019, IO will be sorted in latency timeframes to get statistics for each IO. I’m sure this feature will help to troubleshoot performance issues especially if we are able to get information about tail IOs.
Moreover, drives will be sorted in group regarding their performances. For example, NVMe will be in one group and HDD will be added to another group. This is automatic and handled by the system. Then the system will monitor each drive latency against its peer. If a drive has abnormal latency, an alert will be raised. Sure it will help to find a defective drive!
Support of persistent memory
For those require high performance with the lowest latency, persistent memory is your salvation. Below you can find the latency comparisons per kind of drives:
As you can see, the Persistent Memory (PMEM) can drastically reduce your latency for applications that require low latency. PMEM will be supported by Windows Server 2019 for cache or capacity.
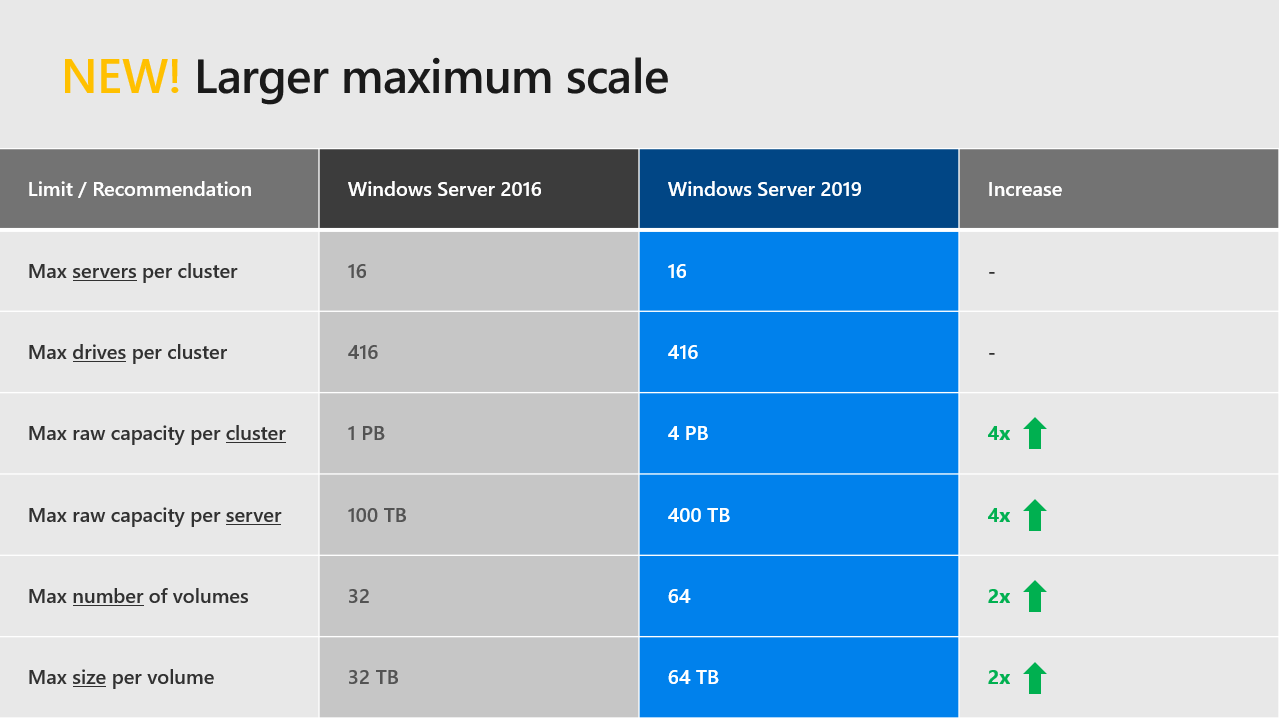
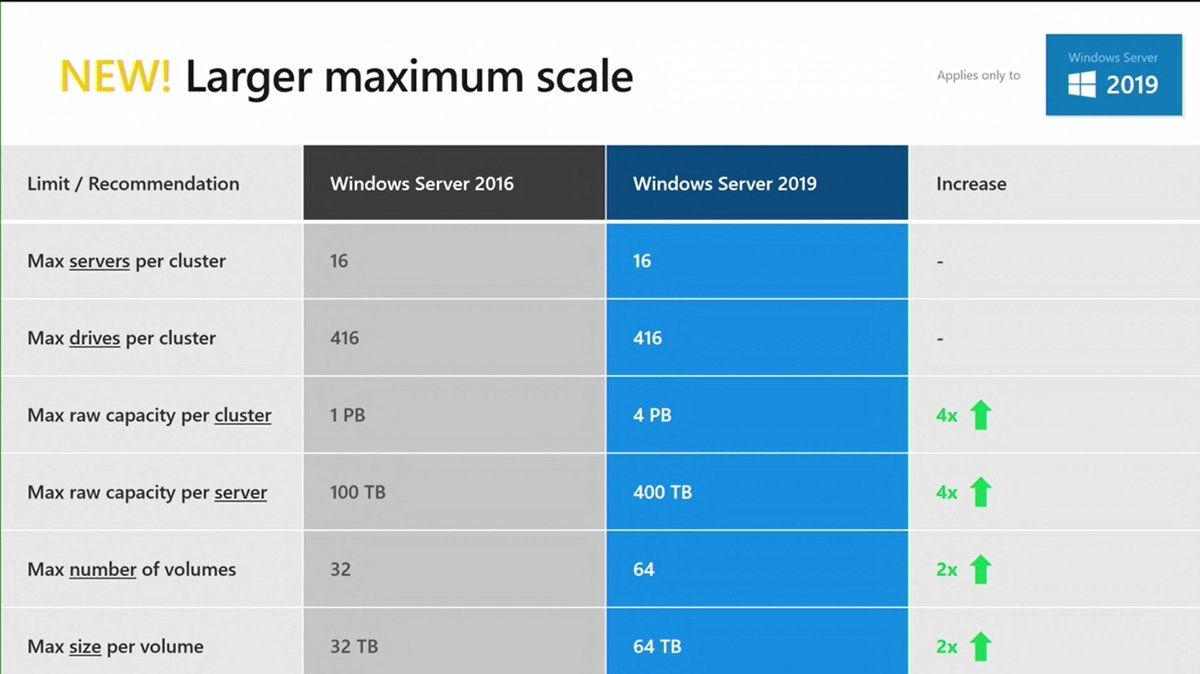
A larger maximum scale
With Windows Server 2019, Microsoft has increased the maximum capacity and volume per server and cluster. Now a cluster can support a maximum of 4PB and you can deploy nodes with 400TB of raw capacity. In Windows Server 2019 you will be able to host 64 volumes per cluster with a maximum size of 64TB.
True two-nodes solution
Microsoft has added also some goodies for Storage Spaces Direct. Instead of using Microsoft Azure (which I do not recommend in two nodes solution) or traditional file share, you can use a USB key connected to a router. The file share witness should be hosted outside the cluster (not in a VM hosted by S2D) so usually it’s require a physical server or another infrastructure. With this solution, you can plug the USB key to the the router and set a share inside the router on the USB key.
Higher number of hardware partners
Thanks to the high value of Storage Spaces Direct and its performance, more vendors and partners are interested by this solution. In the WSSD catalog (certified hardware for S2D), you can find a higher number of offers and components compared to last year.
VSAN from StarWind is software-defined storage (SDS) solution created with restricted budgets and maximum output in mind. It pulls close to 100% of IOPS from existing hardware, ensures high uptime and fault tolerance starting with just two nodes. StarWind VSAN is hypervisor and hardware agnostic, allowing you to forget about hardware restrictions and crazy expensive physical shared storage.
Build your infrastructure with off-the-shelf hardware, scale however you like, increase return on investment (ROI) and enjoy Enterprise-grade virtualization features and benefits at SMB price today!
Conclusion
Microsoft is working hard on Storage Spaces Direct because hyperconverged solution is the future of datacenter. The future is not in legacy SAN or NAS but in software-defined solution. With Windows Server 2019, Microsoft adds expected features such as deduplication or better monitoring. I think these new features followed by those included in other parts of Windows Server 2019 such as Windows System Inisght, Windows Admin Center or Cluster Sets will help the adoption of Storage Spaces Direct. If you are already running Storage Spaces Direct in production, I suggest you to make the migration when Windows Server 2019 will be released 😊.
- Unveiling Microsoft Windows Server 2019 – Here’s Everything You Should Know About It
- Crashed Microsoft Exchange 2013 Database? No sweat. Learn how to recover it with ease
| ms.assetid | title | description | ms.author | manager | ms.topic | author | ms.date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
0f2a7f7b-aca8-4e5d-ad67-4258e88bc52f |
What’s new in storage in Windows Server |
Learn more about: What’s new in Storage in Windows Server |
jgerend |
dongill |
article |
jasongerend |
05/29/2019 |
What’s new in Storage in Windows Server
Applies to: Windows Server 2022, Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2016
This topic explains the new and changed functionality in storage in Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2016, and Windows Server Semi-Annual Channel releases.
What’s new in storage in Windows Server, version 1903
This release of Windows Server adds the following changes and technologies.
Storage Migration Service now migrates local accounts, clusters, and Linux servers
Storage Migration Service makes it easier to migrate servers to a newer version of Windows Server. It provides a graphical tool that inventories data on servers and then transfers the data and configuration to newer servers—all without apps or users having to change anything.
When using this version of Windows Server to orchestrate migrations, we’ve added the following abilities:
- Migrate local users and groups to the new server
- Migrate storage from failover clusters
- Migrate storage from a Linux server that uses Samba
- More easily sync migrated shares into Azure by using Azure File Sync
- Migrate to new networks such as Azure
For more info about Storage Migration Service, see Storage Migration Service overview.
System Insights disk anomaly detection
System Insights is a predictive analytics feature that locally analyzes Windows Server system data and provides insight into the functioning of the server. It comes with a number of built-in capabilities, but we’ve added the ability to install additional capabilities via Windows Admin Center, starting with disk anomaly detection.
Disk anomaly detection is a new capability that highlights when disks are behaving differently than usual. While different isn’t necessarily a bad thing, seeing these anomalous moments can be helpful when troubleshooting issues on your systems.
This capability is also available for servers running Windows Server 2019.
Windows Admin Center enhancements
A new release of Windows Admin Center is out, adding new functionality to Windows Server. For info on the latest features, see Windows Admin Center.
What’s new in storage in Windows Server 2019 and Windows Server, version 1809
This release of Windows Server adds the following changes and technologies.
Manage storage with Windows Admin Center
Windows Admin Center is a new locally deployed, browser-based app for managing servers, clusters, hyper-converged infrastructure with Storage Spaces Direct, and Windows 10 PCs. It comes at no additional cost beyond Windows and is ready for production use.
To be fair, Windows Admin Center is a separate download that runs on Windows Server 2019 and other versions of Windows, but it’s new and we didn’t want you to miss it…
Storage Migration Service
Storage Migration Service is a new technology that makes it easier to migrate servers to a newer version of Windows Server. It provides a graphical tool that inventories data on servers, transfers the data and configuration to newer servers, and then optionally moves the identities of the old servers to the new servers so that apps and users don’t have to change anything. For more info, see Storage Migration Service.
Storage Spaces Direct (Windows Server 2019 only)
There are a number of improvements to Storage Spaces Direct in Windows Server 2019 (Storage Spaces Direct isn’t included in Windows Server, Semi-Annual Channel):
-
Deduplication and compression for ReFS volumes
Store up to ten times more data on the same volume with deduplication and compression for the ReFS filesystem. (It’s just one click to turn on with Windows Admin Center.) The variable-size chunk store with optional compression maximizes savings rates, while the multi-threaded post-processing architecture keeps performance impact minimal. Supports volumes up to 64 TB and will deduplicate the first 4 TB of each file.
-
Native support for persistent memory
Unlock unprecedented performance with native Storage Spaces Direct support for persistent memory modules, including Intel® Optane™ DC PM and NVDIMM-N. Use persistent memory as cache to accelerate the active working set, or as capacity to guarantee consistent low latency on the order of microseconds. Manage persistent memory just as you would any other drive in PowerShell or Windows Admin Center.
-
Nested resiliency for two-node hyper-converged infrastructure at the edge
Survive two hardware failures at once with an all-new software resiliency option inspired by RAID 5+1. With nested resiliency, a two-node Storage Spaces Direct cluster can provide continuously accessible storage for apps and virtual machines even if one server node goes down and a drive fails in the other server node.
-
Two-server clusters using a USB flash drive as a witness
Use a low-cost USB flash drive plugged into your router to act as a witness in two-server clusters. If a server goes down and then back up, the USB drive cluster knows which server has the most up-to-date data. For more info, see the Storage at Microsoft blog and documentation on how to deploy a file share witness.
-
Windows Admin Center
Manage and monitor Storage Spaces Direct with the new purpose-built Dashboard and experience in Windows Admin Center. Create, open, expand, or delete volumes with just a few clicks. Monitor performance like IOPS and IO latency from the overall cluster down to the individual SSD or HDD. Available at no additional cost for Windows Server 2016 and Windows Server 2019.
-
Performance history
Get effortless visibility into resource utilization and performance with built-in history. Over 50 essential counters spanning compute, memory, network, and storage are automatically collected and stored on the cluster for up to one year. Best of all, there’s nothing to install, configure, or start – it just works. Visualize in Windows Admin Center or query and process in PowerShell.
-
Scale up to 4 PB per cluster
Achieve multi-petabyte scale – great for media, backup, and archival use cases. In Windows Server 2019, Storage Spaces Direct supports up to 4 petabytes (PB) = 4,000 terabytes of raw capacity per storage pool. Related capacity guidelines are increased as well: for example, you can create twice as many volumes (64 instead of 32), each twice as large as before (64 TB instead of 32 TB). Stitch multiple clusters together into a cluster set for even greater scale within one storage namespace. For more info, see the Storage at Microsoft blog.
-
Mirror-accelerated parity is 2X faster
With mirror-accelerated parity you can create Storage Spaces Direct volumes that are part mirror and part parity, like mixing RAID-1 and RAID-5/6 to get the best of both. (It’s easier than you think in Windows Admin Center.) In Windows Server 2019, the performance of mirror-accelerated parity is more than doubled relative to Windows Server 2016 thanks to optimizations.
-
Drive latency outlier detection
Easily identify drives with abnormal latency with proactive monitoring and built-in outlier detection, inspired by Microsoft Azure’s long-standing and successful approach. Whether it’s average latency or something more subtle like 99th percentile latency that stands out, slow drives are automatically labeled in PowerShell and Windows Admin Center with ‘Abnormal Latency’ status.
-
Manually delimit the allocation of volumes to increase fault tolerance
This enables admins to manually delimit the allocation of volumes in Storage Spaces Direct. Doing so can significantly increase fault tolerance under certain conditions, but imposes some added management considerations and complexity. For more info, see Delimit the allocation of volumes.
Storage Replica
There are a number of improvements to Storage Replica in this release:
Storage Replica in Windows Server, Standard Edition
You can now use Storage Replica with Windows Server, Standard Edition in addition to Datacenter Edition. Storage Replica running on Windows Server, Standard Edition, has the following limitations:
- Storage Replica replicates a single volume instead of an unlimited number of volumes.
- Volumes can have a size of up to 2 TB instead of an unlimited size.
Storage Replica log performance improvements
We also made improvements to how the Storage Replica log tracks replication, improving replication throughput and latency, especially on all-flash storage as well as Storage Spaces Direct clusters that replicate between each other.
To gain the increased performance, all members of the replication group must run Windows Server 2019.
Test failover
You can now temporarily mount a snapshot of the replicated storage on a destination server for testing or backup purposes. For more information, see Frequently Asked Questions about Storage Replica.
Windows Admin Center support
Support for graphical management of replication is now available in Windows Admin Center via the Server Manager tool. This includes server-to-server replication, cluster-to-cluster, as well as stretch cluster replication.
Miscellaneous improvements
Storage Replica also contains the following improvements:
- Alters asynchronous stretch cluster behaviors so that automatic failovers now occur
- Multiple bug fixes
SMB
-
SMB1 and guest authentication removal: Windows Server no longer installs the SMB1 client and server by default. Additionally, the ability to authenticate as a guest in SMB2 and later is off by default. For more information, review SMBv1 is not installed by default in Windows 10, version 1709 and Windows Server, version 1709.
-
SMB2/SMB3 security and compatibility: Additional options for security and application compatibility were added, including the ability to disable oplocks in SMB2+ for legacy applications, as well as require signing or encryption on per-connection basis from a client. For more information, review the SMBShare PowerShell module help.
Data Deduplication
- Data Deduplication now supports ReFS: You no longer must choose between the advantages of a modern file system with ReFS and the Data Deduplication: now, you can enable Data Deduplication wherever you can enable ReFS. Increase storage efficiency by upwards of 95% with ReFS.
- DataPort API for optimized ingress/egress to deduplicated volumes: Developers can now take advantage of the knowledge Data Deduplication has about how to store data efficiently to move data between volumes, servers, and clusters efficiently.
File Server Resource Manager
Windows Server 2019 includes the ability to prevent the File Server Resource Manager service from creating a change journal (also known as a USN journal) on all volumes when the service starts. This can conserve space on each volume, but will disable real-time file classification. For more information, see File Server Resource Manager overview.
What’s new in storage in Windows Server, version 1803
File Server Resource Manager
Windows Server, version 1803 includes the ability to prevent the File Server Resource Manager service from creating a change journal (also known as a USN journal) on all volumes when the service starts. This can conserve space on each volume, but will disable real-time file classification. For more information, see File Server Resource Manager overview.
What’s new in storage in Windows Server, version 1709
Windows Server, version 1709 is the first Windows Server release in the Semi-Annual Channel. The Semi-Annual Channel is a Software Assurance benefit and is fully supported in production for 18 months, with a new version every six months.
For more information, see Windows Server Semi-annual Channel Overview.
Storage Replica
The disaster recovery protection added by Storage Replica is now expanded to include:
- Test failover: the option to mount the destination storage is now possible through the test failover feature. You can mount a snapshot of the replicated storage on destination nodes temporarily for testing or backup purposes. For more information, see Frequently Asked Questions about Storage Replica.
- Windows Admin Center support: Support for graphical management of replication is now available in Windows Admin Center via the Server Manager tool. This includes server-to-server replication, cluster-to-cluster, as well as stretch cluster replication.
Storage Replica also contains the following improvements:
- Alters asynchronous stretch cluster behaviors so that automatic failovers now occur
- Multiple bug fixes
SMB
-
SMB1 and guest authentication removal: Windows Server, version 1709 no longer installs the SMB1 client and server by default. Additionally, the ability to authenticate as a guest in SMB2 and later is off by default. For more information, review SMBv1 is not installed by default in Windows 10, version 1709 and Windows Server, version 1709.
-
SMB2/SMB3 security and compatibility: Additional options for security and application compatibility were added, including the ability to disable oplocks in SMB2+ for legacy applications, as well as require signing or encryption on per-connection basis from a client. For more information, review the SMBShare PowerShell module help.
Data Deduplication
- Data Deduplication now supports ReFS: You no longer must choose between the advantages of a modern file system with ReFS and the Data Deduplication: now, you can enable Data Deduplication wherever you can enable ReFS. Increase storage efficiency by upwards of 95% with ReFS.
- DataPort API for optimized ingress/egress to deduplicated volumes: Developers can now take advantage of the knowledge Data Deduplication has about how to store data efficiently to move data between volumes, servers, and clusters efficiently.
What’s new in storage in Windows Server 2016
Storage Spaces Direct
Storage Spaces Direct enables building highly available and scalable storage using servers with local storage. It simplifies the deployment and management of software-defined storage systems and unlocks use of new classes of disk devices, such as SATA SSD and NVMe disk devices, that were previously not possible with clustered Storage Spaces with shared disks.
What value does this change add?
Storage Spaces Direct enables service providers and enterprises to use industry standard servers with local storage to build highly available and scalable software defined storage. Using servers with local storage decreases complexity, increases scalability, and enables use of storage devices that were not previously possible, such as SATA solid state disks to lower cost of flash storage, or NVMe solid state disks for better performance.
Storage Spaces Direct removes the need for a shared SAS fabric, simplifying deployment and configuration. Instead it uses the network as a storage fabric, leveraging SMB3 and SMB Direct (RDMA) for high-speed, low-latency CPU efficient storage. To scale out, simply add more servers to increase storage capacity and I/O performance
For more information, see the Storage Spaces Direct.
What works differently?
This capability is new in Windows Server 2016.
Storage Replica
Storage Replica enables storage-agnostic, block-level, synchronous replication between servers or clusters for disaster recovery, as well as stretching of a failover cluster between sites. Synchronous replication enables mirroring of data in physical sites with crash-consistent volumes to ensure zero data loss at the file-system level. Asynchronous replication allows site extension beyond metropolitan ranges with the possibility of data loss.
What value does this change add?
Storage Replication enables you to do the following:
- Provide a single vendor disaster recovery solution for planned and unplanned outages of mission critical workloads.
- Use SMB3 transport with proven reliability, scalability, and performance.
- Stretch Windows failover clusters to metropolitan distances.
- Use Microsoft software end to end for storage and clustering, such as Hyper-V, Storage Replica, Storage Spaces, Cluster, Scale-Out File Server, SMB3, Deduplication, and ReFS/NTFS.
- Help reduce cost and complexity as follows:
- Is hardware agnostic, with no requirement for a specific storage configuration like DAS or SAN.
- Allows commodity storage and networking technologies.
- Features ease of graphical management for individual nodes and clusters through Failover Cluster Manager.
- Includes comprehensive, large-scale scripting options through Windows PowerShell.
- Help reduce downtime, and increase reliability and productivity intrinsic to Windows.
- Provide supportability, performance metrics, and diagnostic capabilities.
For more information, see the Storage Replica in Windows Server 2016.
What works differently?
This capability is new in Windows Server 2016.
Storage Quality of Service
You can now use storage quality of service (QoS) to centrally monitor end-to-end storage performance and create management policies using Hyper-V and CSV clusters in Windows Server 2016.
What value does this change add?
You can now create storage QoS policies on a CSV cluster and assign them to one or more virtual disks on Hyper-V virtual machines. Storage performance is automatically readjusted to meet policies as the workloads and storage loads fluctuate.
- Each policy can specify a reserve (minimum) and/or a limit (maximum) to be applied to a collection of data flows, such as a virtual hard disk, a single virtual machine or a group of virtual machines, a service, or a tenant.
- Using Windows PowerShell or WMI, you can perform the following tasks:
- Create policies on a CSV cluster.
- Enumerate policies available on a CSV cluster.
- Assign a policy to a virtual hard disk of a Hyper-V virtual machine.
- Monitor the performance of each flow and status within the policy.
- If multiple virtual hard disks share the same policy, performance is fairly distributed to meet demand within the policy’s minimum and maximum settings. Therefore, a policy can be used to manage a virtual hard disk, a virtual machine, multiple virtual machines comprising a service, or all virtual machines owned by a tenant.
What works differently?
This capability is new in Windows Server 2016. Managing minimum reserves, monitoring flows of all virtual disks across the cluster via a single command, and centralized policy based management were not possible in previous releases of Windows Server.
For more information, see Storage Quality of Service
Data Deduplication
| Functionality | New or Updated | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Support for Large Volumes | Updated | Prior to Windows Server 2016, volumes had to specifically sized for the expected churn, with volume sizes above 10 TB not being good candidates for deduplication. In Windows Server 2016, Data Deduplication supports volume sizes up to 64 TB. |
| Support for Large Files | Updated | Prior to Windows Server 2016, files approaching 1 TB in size were not good candidates for deduplication. In Windows Server 2016, files up to 1 TB are fully supported. |
| Support for Nano Server | New | Data Deduplication is available and fully supported in the new Nano Server deployment option for Windows Server 2016. |
| Simplified Backup Support | New | In Windows Server 2012 R2, Virtualized Backup Applications, such as Microsoft’s Data Protection Manager, were supported through a series of manual configuration steps. In Windows Server 2016, a new default Usage Type «Backup», has been added for seamless deployment of Data Deduplication for Virtualized Backup Applications. |
| Support for Cluster OS Rolling Upgrades | New | Data Deduplication fully supports the new Cluster OS Rolling Upgrade feature of Windows Server 2016. |
SMB hardening improvements for SYSVOL and NETLOGON connections
In Windows 10 and Windows Server 2016 client connections to the Active Directory Domain Services default SYSVOL and NETLOGON shares on domain controllers now require SMB signing and mutual authentication (such as Kerberos).
What value does this change add?
This change reduces the likelihood of man-in-the-middle attacks.
What works differently?
If SMB signing and mutual authentication are unavailable, a Windows 10 or Windows Server 2016 computer won’t process domain-based Group Policy and scripts.
[!NOTE]
The registry values for these settings aren’t present by default, but the hardening rules still apply until overridden by Group Policy or other registry values.
For more information on these security improvements — also referred to as UNC hardening, see Microsoft Knowledge Base article 3000483 and MS15-011 & MS15-014: Hardening Group Policy.
Work Folders
Improved change notification when the Work Folders server is running Windows Server 2016 and the Work Folders client is Windows 10.
What value does this change add?
For Windows Server 2012 R2, when file changes are synced to the Work Folders server, clients are not notified of the change and wait up to 10 minutes to get the update. When using Windows Server 2016, the Work Folders server immediately notifies Windows 10 clients and the file changes are synced immediately.
What works differently?
This capability is new in Windows Server 2016. This requires a Windows Server 2016 Work Folders server and the client must be Windows 10.
If you’re using an older client or the Work Folders server is Windows Server 2012 R2, the client will continue to poll every 10 minutes for changes.
ReFS
The next iteration of ReFS provides support for large-scale storage deployments with diverse workloads, delivering reliability, resiliency, and scalability for your data.
What value does this change add?
ReFS introduces the following improvements:
- ReFS implements new storage tiers functionality, helping deliver faster performance and increased storage capacity. This new functionality enables:
- Multiple resiliency types on the same virtual disk (using mirroring in the performance tier and parity in the capacity tier, for example).
- Increased responsiveness to drifting working sets.
- The introduction of block cloning substantially improves the performance of VM operations, such as .vhdx checkpoint merge operations.
- The new ReFS scan tool enables the recovery of leaked storage and helps salvage data from critical corruptions.
What works differently?
These capabilities are new in Windows Server 2016.
Additional References
- What’s New in Windows Server 2016

The world of software defined storage is certainly the way of the future with enterprise storage. The wild success of VMware’s vSAN product is proof that customers are excited about and confident in software defined storage as such. Microsoft has certainly had catching up to do in this space. The recent progression howevever with the introduction of Storage Spaces Direct in Windows Server 2016 has shown that Microsoft is serious about software defined storage and hyperconverged solutions. With the soon to be released Windows Server 2019, the progress of functionality and features with Storage Spaces Direct is set to be enhanced even further. Let’s take a look a Windows Server 2019 Storage Spaces Direct Features and Improvements and look into the details of what is to come with Microsoft’s next generation software defined storage solution in the Windows Server product line.
Microsoft has certainly done their homework on the new release of Windows Server 2019 and the features and functionality contained to enhance software defined storage. Since the inception of Storage Spaces Direct, Microsoft claims that the worldwide adoption of Storage Spaces Direct is 10,000 clusters in 18 months since its general availability. Microsoft has set about three objectives with Storage Spaces Direct in Windows Server 2019 – to lower costs, simplify infrastructure, and increase performance. Let’s take a look at the new features that speak to each of those areas with Storage Spaces Direct.
Windows Server 2019 Storage Spaces Direct Lower Costs
One of the great things about software defined storage in general is that it typically can lower costs as it allows customers to use more commodity hardware to achieve their enterprise storage objectives. There are many more servers that are sold each year compared to SAN devices. The shift towards utilizing locally attached server storage for enterprise software defined storage makes total sense from a business perspective. In Microsoft’s aim to lower costs for customers when it comes to storage spaces direct includes the following:
-
- New configuration maximums
- Data Deduplication can now be used with ReFS
- “True Two-Node” S2D clusters
As for configuration maximums, the new configuration maximums in Windows Server 2019 in some cases have increased by a factor of X4. One specific example of that is the maximum storage pool size has gone from 1 Petabyte or PB in Windows Server 2016 to 4 PB in Windows Server 2019.

A long awaited new feature for Storage Spaces Direct and utilizing ReFS is the ability to use Deduplication. A major downside with ReFS and Storage Spaces Direct in previous versions was you could not enable deduplication with the ReFS files system. The wait is over now with Windows Server 2019. Now with Windows Server 2019 ReFS on Storage Spaces Direct, customers can enable deduplication and reclaim up to 10X the amount of space in the storage pool!
Taking the lowering of costs objective even further, with Windows Server 2019, Microsoft has introduced something they call “True Two-node”. What is “True Two-Node”? Microsoft cites the competitors here (VMware) with how two node HCI clusters are formed. VMware’s vSAN requires a Witness appliance. Even with Microsoft Windows Server 2016 and past, you had to either have a third “node” for the “two” node cluster, a file share, or a cloud witness file share.
New with Windows Server 2019 is the ability to use a USB key hosting a file share that simply plugs into a commodity router with a USB port. The USB drive can host a file share that acts as the Quorum tie breaker. This is especially a well-suited use case with edge environments or specialized environments such as a cruise ship or an other environment where you may not have a lot of extra infrastructure or additional server to host even a file share.
The configuration of the “True Two-Node” cluster is simple. Just plugin in the drive to the commodity router, setup a share name, user name and password, and then use the new Set-ClusterQuorum cmdlet to provide credentials for the router hosted file share.
Windows Server 2019 Storage Spaces Direct Simplified Architecture
Another major object with Windows Server 2019 Storage Spaces Direct is to enable a simplified approach to the infrastructure. This is accomplished with three new mechanisms that allow for better visibility and automated health metrics and recommendations.
Windows Admin Center is certainly been shown to be Microsoft’s way forward from a server management perspective. The Windows Admin Center dashboards provide a wide range of metrics and capabilities that are certainly a step forward for Windows administrators from the legacy tools being used. Microsoft has introduced a new Windows Admin Center for HyperConverged Infrastructure. By default it keeps performance metrics and history for the Storage Spaces Direct cluster for past day, week, month, and year. This way it allows S2D administrators to have an accurate historical view of the environment and see how things are performing and trend any issues that may be arising.
Another new feature is individual physical drive health and performance metrics. Windows Server 2019 provides deeper visibility for recording the individual performance of every drive in each of the cluster hosts. Windows Server 2019 records every IO and the outcome of the the IO operation along with the latency measured. Administrators can use PowerShell and the Get-PhysicalDiskIOReport commandlet to display historical performance information for an individual hard drive by the serial number.
Microsoft has taken this a step further however in implementing an automated mechanism in Windows Server 2019 that groups the drives by media and usage. Windows Server 2019 runs a variety of analyses, including rolling average and tail latency which can see a drive standing out as an outlier. Using an Azure-inspired outlier detection algorithm, the administrator can be alerted if a single drive is displaying issues.
Windows Server 2019 Storage Spaces Direct Performance Improvements
New performance enhancing features of Windows Server 2019 Storage Spaces Direct include:
Persistent memory – full support with storage spaces direct. It can be used as cache, capacity and is available to interact with via the Admin Center and PowerShell. The order of magnitude in performance increase is as major as the leap from HDD to SSD.
Mirror Accelerated Parity – Allows to create one volume that’s part mirror, part parity. Data can be written to mirror, and rotated to partity later. The compute-intensive calculation of parity can be deferred to nearline. You can choose the ratio of mirror-to-parity. You trade off performance for storage efficiency. When you create a volume you can choose mirror-accelerated parity in a simple dropdown box. Mirror accelerated partity is more than double the performance of Windows Server 2016, so a 100% improvement.
Takeaways
Windows Server 2019 Storage Spaces Direct Features and Improvements are shaping up to be well worth the wait! There are a ton of new features contained in Windows Server 2019 Storage Spaces Direct that many environments have been desperately wanting to see. It is looking like Windows Server 2019 hyperconverged infrastructure features are chalked full of new enhancements across the board that help to lower costs, simplify administration and improve performance. Be sure to sign up for the Windows Insiders program if you haven’t already to get a preview copy of Windows Server 2019. The general release date of Windows Server 2019 looks to be coming up soon with a Q3 or Q4 release in 2018.
В Windows Server 2016 была впервые добавлена новая возможность организации дискового пространства для много-узловых отказоустойчивых систем: Storage Spaces Direct. Пришло время познакомиться с технологией поближе.
Storage Spaces Direct использует стандартные серверы с локально подключенными накопителями для создания высоко доступного, легко масштабируемого программно-определенного хранилища вместо традиционных массивов SAN и NAS. Такая конвергентная (Converged) или гипер-конвергентная (Hyper-converged) архитектура радикальным образом упрощает приобретение и развертывание решений; в то же время такие возможности как кэширование, многоуровневое хранилище и очищающее кодирование, вместе с новейшим оборудованием, таким как сеть RDMA и накопители NVMe обеспечивают непревзойденные эффективность и производительность.
Storage Spaces Direct входит в состав Windows Server 2016 и Windows Server 2019 в редакции Datacenter.
Опции развертывания.
Storage Spaces Direct разработан для двух независимых опций развертывания:
Конвергентное (Converged) решение.
Конвергентное (Converged) решение – хранилище и вычислительные мощности разнесены в отдельные кластеры. Опция конвергентного развертывания, также известного как «разделенное», предоставляет уровень Scale-out File Server (SoFS) поверх уровня Storage Spaces Direct, для предоставления подключенного к сети хранилища (NAS) через общие ресурсы SMB3. Это позволяет масштабировать вычислительные/рабочие нагрузки независимо от кластера хранилища. В основном подобные решения предназначены для высоко масштабируемых развертываний таких как инфраструктура Hyper-V в качестве сервиса (IaaS) для провайдеров услуг и корпоративных окружений.
Гипер-конвергентное (Hyper-Converged) решение.
Гипер-конвергентное (Hyper-Converged) решение – один кластер для вычисления и хранилища. Опция гипер-конвергентного развертывания запускает виртуальные машины Hyper-V или базы данных SQL напрямую на узлах, которые предоставляют хранилище, сохраняя файлы на локальных томах. Это устраняет необходимость настраивать доступы и права файлового сервера, а также сокращает стоимость для клиентов от малого до среднего бизнеса или для развертываний в удаленных офисах и филиалах.
Принцип работы Storage Spaces Direct.
Storage Spaces Direct – это развитие Storage Spaces, впервые появившегося в Windows Server 2012. Он усиливает множество компонентов Windows Server, таких как отказоустойчивую кластеризацию (Failover Clustering), файловую систему Cluster Shared Volume (CSV), Server Message Block 3 (SMB3) и конечно же Storage Spaces. Также Storage Spaces Direct представляет новую технологию, известную как программная шина хранилища (Software Storage Bus).
Сетевое оборудование (Networking Hardware). Storage Spaces Direct использует SMB3, в том числе SMB Direct и SMB Multichannel over Ethernet для коммуникаций между серверами. Рекомендуется использовать 10+ GbE с удаленным доступом к памяти (RDMA), iWARP или RoCE.
Оборудование хранилища (Storage Hardware). От 2 до 16 серверов с локально подключенными накопителями SATA, SAS или NVMe. Каждый сервер должен иметь как минимум 2 твердотельных накопителя (SSD) и как минимум 4 дополнительных накопителя. Настоятельно рекомендуется использовать оборудование от партнеров поддерживающих данную технологию.
Отказоустойчивая кластеризация (Failover Clustering). Встроенный компонент кластеризации Windows Server используется для объединения серверов.
Программная шина хранилища (Software Storage Bus). Программная шина хранилища — это новинка в Storage Spaces Direct. Она объединяет кластер и связывает программно-определенное хранилище таким образом, чтобы все серверы могли видеть все локальные накопители каждого из серверов. Данная технология позиционируется в качестве замены для более дорогих и строгих решений общего хранилища на базе Faber Channel или SAS.
Кэш уровня шины хранилища (Storage Bus Layer Cache). Программная шина хранилища связывает наиболее быстрые, из представленных накопителей (такие как SSD) c более медленными (такими как HDD), для предоставления на стороне сервера кэширования чтения/записи которое увеличивает ввод/вывод и ускоряет пропускную способность.
Пул хранилища (Storage Pool). Коллекция накопителей, которые формируют базу Storage Spaces называется пулом хранилища. Пул хранилища (Storage Pool) автоматически создается и все подходящие накопители автоматически обнаруживаются и добавляются в него. Настоятельно рекомендуется использовать один пул на кластер с параметрами по умолчанию.
Storage Spaces. Storage Spaces предоставляет механизм обработки отказов виртуальных дисков при помощи зеркалирования, очищающего кодирования (Erase Coding) или обоих сразу. Storage Spaces можно представить как распределенный программно-определенный RAID использующий накопители в пуле. В Storage Spaces Direct виртуальные диски обычно используют устойчивость к одновременному выходу из строя 2 накопителей или серверов (то есть тройное зеркалирование, в котором каждая копия данных находится на разных серверах). Также доступны отказоустойчивость на уровне шасси (Chassis) и стоек (Rack).
Resilient File System (ReFS). ReFS – это основная файловая система предназначенная и разработанная специально для виртуализации. Она включает в себя существенное ускорение операций VHDX, таких как создание, расширение и объединение контрольных точек, встроенную проверку контрольных сумм для обнаружения и исправления ошибок на битовом уровне. Также ReFS представляет разбиение на уровни в реальном времени, которое перемешивает данные между так называемыми «горячим» и «холодным» уровнями хранилища в зависимости от использования.
Cluster Shared Volumes (CSV). Файловая система CSV объединяет все тома в единое пространство имен доступное всем серверам таким образом, что каждый сервер видит каждый том, как будто он смонтирован локально.
Scale-Out File Server (SOFS). Это финальный уровень, он является обязательным при развертывании конвергентного решения. Он предоставляет удаленный доступ к файлам при помощи протокола доступа SMB3 для клиентов, таких как другие кластеры с Hyper-V. Эффективно переключая Storage Spaces Direct в Network Attached Storage (NAS).
PS> Я начал готовить веб-касты по технологии Storage Spaces Direct больше года назад еще на базе Windows Server 2016, несколько раз рассказывал о технологии на вебинарах и вот теперь, уже на базе Windows Server 2019 процесс записи сдвинулся с мертвой точки – самое ближайшее время опубликую первый веб-каст: «Развертывание Storage Spaces Direct в Windows Server 2019».

in Storage
June 5, 2018
15,294 Views
When Windows Server 2016 has been released, the data deduplication was not available for ReFS file system. With Storage Spaces Direct, the volume should be formatted in ReFS to get latest features (Accelerated VHDX operations) and to get the best performance. So, for Storage Spaces Direct data deduplication was not available. Data Deduplication can reduce the storage usage by removing duplicated blocks by replacing by metadata.
Since Windows Server 1709, Data deduplication is supported for ReFS volume. That means that it will be also available in Windows Server 2019. I have updated my S2D lab to Windows Server 2019 to show you how it will be easy to enable deduplication on your S2D volume.
Requirements
To implement data deduplication on S2D volume in Windows Server 2019 you need the following:
- An up and running S2D cluster executed by Windows Server 2019
- (Optional) Windows Admin Center: it will help to implement deduplication
- Install the deduplication feature on each node: Install-WindowsFeature FS-Data-Deduplication
Enable deduplication
Storage Spaces Direct in Windows Server 2019 will be fully manageable from Windows Admin Center (WAC). That means that you can also enable deduplication and compression from WAC. Connect to your hyperconverged cluster from WAC and navigate to Volumes. Select the volume you want and enable Deduplication and compression.
WAC raises an information pop-up to explain you what deduplication and compression is. Click on Start.
Select Hyper-V as deduplication mode and click on Enable deduplication.
Once it is activated, WAC should tell you the percent of saved state. Currently it is not working in WAC 1804.
Get information by using PowerShell
To get deduplication information on S2D node, open a PowerShell prompt. You can get the list of data deduplication command by running Get-Command *Dedup*.
If you run Get-DedupStatus, you should get the following data deduplication summary. As you can see in the following screenshot, I have saved some spaces in my CSV volume.
By running Get-DedupVolume, you can get the saving rate of the data deduplication. In my lab, data deduplication helps me to save almost 50% of storage space. Not bad.
Conclusion
Data deduplication on S2D was expected by many of customers. With Windows Server 2019, the feature will be available. Currently when you deploy 3-way Mirroring for VM, only 33% of raw storage is available. With Data Deduplication we can expect 50%. Thanks to this feature, the average cost of a S2D solution will be reduced.