Летом 2021 года Microsoft анонсировала релиз Windows Server 2022. Количество нововведений хоть и невелико, но среди них есть некоторые интересные особенности, причем две из них зарезервированы для старшего издания Azure. Ключевое внимание уделяется безопасности и модификациям для SMB и Hyper-V. Подробно обо всех возможностях новой серверной ОS от Microsoft читайте в нашей статье.
Что нового в MS Windows Server 2022
Во время анонса новой операционной системы Microsoft особо подчеркнула инновационные возможности, нацеленные на повышение безопасности. Новшества позволяют реализовать концепцию сервера с защищенным ядром, основанную на сочетании оборудования, микропрограмм и драйверов. Все заявленные функции можно будет вручную настроить в центре администрирования Windows.
Более того, впервые HTTPS и TLS 1.3 будут включены по дефолту. Также частью новой ОС стал Secure DNS (DNS поверх HTTPS), который будет включен еще и в клиентские Windows 10 21H2, а также Windows 11.
Улучшения в сетевом протоколе SMB
С появлением Server 2022 изменится и процедура шифрования для протокола Server Message Block, где с недавнего времени внедрены два надежных алгоритма AES-256. Алгоритм AES-128, как и раньше, будет работать для обеспечения совместимости.
Шифрование SMB настраивается в том числе отдельно для связи между узлами кластера, что сказывается как на CSV, так и на SSD.
Эти функции безопасности теперь также совместимы с SMB Direct, тогда как в предыдущих версиях Windows Server они вызывали снижение производительности при использовании сетевых адаптеров RDMA.
Еще одна новая функция — это возможность сжимать SMB-трафик. В Windows 10, начиная с выпуска 20H2, можно было включить сжатие SMB для xcopy и robocopy с отдельными переключателями для этих программ. В Server 2022 эту функцию теперь можно включить для обмена файлами через Центр администрирования Windows или PowerShell.
Еще одна новая функция для доступа к общим файловым ресурсам — поддержка SMB через QUIC. Протокол QUIC может использоваться как альтернатива TCP, а в сочетании с TLS 1.3 он также может использоваться для замены VPN. Однако эта функция доступна только в Windows Server 2022 Datacenter: Azure Edition.
Раздел конфигурации SMB в центре администрирования Windows однако не содержит настроек для SMB через QUIC в Server 2022 Datacenter.
В случае «горячего исправления» Microsoft резервирует для Azure еще одну интересную новую функцию. Она позволяет внедрять обновления без перезапуска сервера. Операционная система использует для этого службу автоматического управления Azure.
Помимо новых вариантов гибридных конфигураций (таких как управление локальными серверами через Azure Arc) и расширенной поддержки контейнеров, новая операционная система достигла определенных результатов, соответствующих традиционному использованию ОС.
Вложенная виртуализация для AMD
Еще одна немаловажная «фича» гарантирует поддержку вложенной виртуализации на чипах производства AMD, которая прежде была доступна лишь для процессоров Intel, начиная с версии ОС Windows Server 2016.
Касательно поддержки ЦП новых поколений, то новая версия ОС поддерживает процессоры Intel Ice Lake. На этой платформе система может оперировать объемами оперативной памяти до 48 ТБ и обеспечивать работу до 2048 ядер логического процессора.
Edge включен в Server Core
С прекращением поддержки IE 15 июня 2022 года Microsoft Edge заменит устаревший браузер на сервере. Таким образом, Edge включен в Server 2022 и также может опционально использоваться при установке Server Core. Такая конфигурация ранее уже поддерживалась, однако при ручной установке возникали некоторые препятствия.
Улучшение для Storage Spaces Direct
Для работы с гиперконвергентной инфраструктурой все будущие инновации войдут в Azure Stack HCI, однако в Windows Server по-прежнему будут улучшаться существующие функции.
Теперь это отражено в версиях Server 2022, которые по-прежнему не располагают функциями, такими как расширяемые кластеры, но при этом получили новую возможность восстановления для локальных хранилищ. Администраторы могут использовать эту функцию для контроля за ресурсами, необходимыми для восстановления копий данных или активных рабочих нагрузок.
Другие нововведения в области хранения данных
Пока Storage Spaces Direct соединяет хранилище узлов кластера в пул, Storage Spaces оперирует хранилищем лишь одного сервера. В обновленной версии операционной системы для кэширования доступно многоуровневое хранилище с поддержкой высокоскоростных накопителей по типу твердотельных SSD или NVMe.
Наконец, в Server 2022 Microsoft расширила службу миграции хранилища, представленную в выпуске 2019 года. Первоначально он был предназначен для переноса общих файловых ресурсов из устаревших систем на более новые версии Windows Server. Теперь он поддерживает отказоустойчивые кластеры, серверы Samba и NetApp FAS в качестве источников, а также переносит локальных пользователей и группы.
Формы издания
Начиная с версии 2012, Microsoft предлагает серверную ОС в двух основных редакциях, которые различаются в первую очередь правами на виртуализацию. Однако, начиная с Server 2016, Datacenter Edition получил эксклюзивные функции, которые отсутствуют в стандартной версии. К ним относятся Shielded VMs, Storage Replica и программно-определяемое хранилище с локальными дисковыми пространствами.
Это различие сохраняется в версии 2022 года, где Standard Edition ограничивается двумя виртуальными экземплярами и включает только урезанную версию Storage Replica, которая ограничена максимальным объемом томов в 2 ТБ.
К двум выпускам теперь присоединяется третий, который называется Windows Server 2022 Datacenter: Azure Edition. Как следует из названия, он предназначен только для работы в облаке Microsoft.
Microsoft Windows Server 2022 Standard
Стандартная версия предназначена для пользователей, которым требуется всего несколько виртуальных машин Windows Server. Помимо установки на физическое оборудование, с серверной лицензией также возможны две виртуальные машины под управлением Windows Server. На виртуальные машины Linux нет ограничений. Почти все функции и роли серверов из Datacentre Edition также включены в стандартную версию.
Microsoft Windows Server 2022 Essentials
Версия Essentials, рассчитанная на 25 пользователей или 50 устройств, является идеальной серверной ОС для малого бизнеса. Она включает в себя многие функции старших выпусков, таких как Windows Admin Center и System Insights, однако ограничена поддержкой одного процессора с максимум 10 ядрами.
Microsoft Windows Server 2022 Datacenter
С выпуском Datacenter пользователи получат максимально возможную гибкость в развертывании серверов и могут реализовывать крупные, быстро меняющиеся рабочие нагрузки. Количество виртуальных машин не ограничено, и программно определяемое хранилище может быть реализовано с помощью Storage Spaces Direct.
Системные требования
Процессор. На эффективность процессора влияют два ключевых фактора: число ядер и тактовая частота. Для установки Windows Server система должна быть оборудована как минимум одним 64-разрядным процессором с тактовой частотой 1,4 ГГц, совместимым с набором инструкций x64. В числе прочего должна быть обеспечена поддержка функций безопасности DEP и NX Bit.
Оперативная память. Минимальные требования к оперативной памяти на сервере — это не менее 512 МБ. Кроме того, требуется поддержка ECC.
Сетевые адаптеры. Адаптер Ethernet должен обеспечивать скорость не менее 1 гигабита в секунду. Также сетевые адаптеры также должны соответствовать спецификации архитектуры PCI Express.
Дисковое пространство. В конфигурацию сервера должен быть включен жесткий диск объемом не менее 32 ГБ данных для работы Windows Server, в то время как для установки графического интерфейса потребуются дополнительные 4 ГБ.
Резюме
Windows Server 2022 не привносит новых ролей или функций, но вместе с тем дополняет и вносит коррективы в ряд существующих функций и протоколов, некоторые из которых существенно повышают безопасность сервера.
Тем не менее, продукт от Microsoft остается одним из наиболее востребованных и надежных серверных ОС на рынке. Выбор лицензии и издания Windows Server 2022 следует делать на основе специфики бизнеса, численности штата и имеющегося оборудования — помочь в этой ситуации в любой момент готовы наши специалисты, просто обратитесь по номеру на сайте или свяжитесь с нами по электронной почте.
Пока некоторые читатели (да что уж там, и писатели — например, я) наслаждались в отпуске теплыми летними денечками, известный автор нашего англоязычного блога Адам Бертрам подготовил краткий обзор Windows Storage Spaces. В него он включил, в частности, сведения о настройке Windows Storage Spaces на популярных конфигурациях. Перевод его статьи я и предлагаю вашему вниманию.
Во многих дата-центрах и серверных фермах для хранения данных используются HDD и SSD. Статистика, однако, сообщает о том, что после трёх лет работы 10% дисков становятся негодными.
Конечно, те организации, которые заботятся о целостности и сохранности своих данных, держат руку на пульсе, а также отслеживают и другие факторы риска — будь то человеческий фактор, железо или софт. И тут тем, кто работает с Windows-инфраструктурой, могут помочь Windows Storage Spaces. Ведь их RAID-подобная функциональность (то, что мы видим в File Explorer как виртуальные диски) весьма полезна в деле обеспечения резерва мощностей хранения.
Гибкие возможности масштабирования тоже привлекательны: можно объединить 3 и более драйвов в единый сторадж-пул и затем формировать на его основе “стораджики” нужного размера. А поскольку при работе с пулом формируются и сохраняются дополнительные копии для ваших данных, то проблемы с одним из дисков не приведут к потере всего и вся. А если понадобилось больше места? Просто добавь воды еще дисков в пул.
Storage Spaces для Windows 10
— Он забирается на самую высокую сосну и оттуда планирует.
— Ага, простите, что планирует?
— Он прыгает и планирует.
(“День радио”)
Даже если сценарий развертывания, который вы хотите воплотить, входит в число самых популярных, и инструкция к нему коротка и вроде даже сходу понятна, этап подготовки и планирования все равно никто не отменял. Итак:
Если вы используете дисковые пространства Storage Spaces на машине с Windows 10, то рекомендуется обеспечить наличие минимум 2 дисков помимо системного. Эти диски могут быть как встроенными, так и внешними. Поддерживаются SSD; можно комбинировать SATA, USB и SAS.
Количество дисков рассчитывается исходя из того, какой метод обеспечения отказоустойчивости вы хотите применить. Есть вот такие варианты:
-
Simple (простой) — требует наличия минимум двух дисков. Хоть этот метод и дает хорошую производительность, но ничем вам не поможет в случае отказа. Его можно использовать, например, если вы настраиваете storage space для хранения временных данных (например, файлов видео-рендеринга, файлов-черновиков в графических редакторах, и так далее).
-
Mirror (зеркальный) — позволяет сохранять несколько копий данных на случай отказа. Так, Two-way mirror spaces хранят две копии данных, и с ними вы переживете отказ одного из дисков. Для их организации потребуется минимум два диска. Three-way mirror spaces позволят пережить отказ двух дисков, а для их организации потребуется минимум пять. Зато хранить в таких storage spaces можно самые разнообразные данные.
-
Parity (с контролем четности) — рекомендуется для хранения архивных и стриминговых данных. Хранят несколько копий на случай отказа. Если вы хотите обеспечить отказоустойчивость в случае проблемы с одним диском, то в сценарии с Parity spaces вам понадобится минимум три диска, а на случай проблемы с двумя — минимум семь дисков.
После того, как вы все рассчитали и подготовили, можно организовать собственно Storage Spaces. Для этого в Windows 10 нужно выполнить вот такие шаги:
-
Проверить, что диски, которые вы планируете задействовать, у вас подключены.
Важно! Если вы укажете, что в сторадж-пул хотите включить размеченный диск, имейте в виду, что Windows безвозвратно удалит все разделы и файлы на нём. До начала работы сделайте резервную копию всего, что вам дорого на этом диске!
-
Для простоты в поле поиска в панели задач вводим Storage Spaces и из полученного списка выбираем Storage Spaces.
-
Кликаем Create a new pool and storage space.
-
Выберем нужные нам диски и затем кликнем Сreate new storage pool.
-
Указываем имя, буквенное обозначение и файловую систему для нового сторадж пула.
-
На случай сбоя рекомендуется выбрать метод обеспечения отказоустойчивости (Resiliency) как одну из следующих опций: Two-way mirror, Three-way mirror или Parity.
Важно! Помните про количество дисков, которые потребуются в каждом из указанных вариантов, о чем мы говорили выше. Если, допустим, вы предпочтете Two-way mirror, то для нового storage space будет создаваться две копии данных. Так что для такого сценария понадобится минимум два диска (помимо системного).
-
Затем задайте максимальный размер стораджа для Storage Spaces.
Примечание: Можно указать значение, превышающее размер сторадж-пула — когда место будет заканчиваться, вы просто добавите еще один диск.
-
Когда с настройками покончено, нажимаем Create storage space.
Оптимизация работы
Рекомендуется своевременно оптимизировать работу с дисками. Вот что советует делать Microsoft:
При добавлении новых дисков в существующий пул рекомендуется оптимизировать использование диска. При этом некоторые данные будут перемещены на новый диск, чтобы оптимизировать использование емкости пула. Это стандартное действие при добавлении нового диска в обновленный пул в Windows 10: флажок Optimize to spread existing data across all drives будет установлен по умолчанию.
Однако если вы сняли этот флажок или добавили диски до обновления пула, вам нужно вручную оптимизировать использование диска. Для этого в поле поиска на панели задач введите Storage Spaces, выберите Storage Spaces из списка результатов поиска, а затем щелкните Optimize drive usage.
Автономный сервер
Если у вас один отдельно взятый сервер, то для настройки на нем дисковых пространств Storage Spaces есть подробная инструкция от Microsoft, на русском языке и даже с картинкой. Storage Spaces поддерживаются для Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2012 R2 и Windows Server 2012.
Обратите внимание: до начала настройки нужно обеспечить наличие одного или нескольких пулов, а также проверить конфигурацию на соответствие ряду требований (они перечислены в разделе «Предварительные условия»).
На базе сторадж-пула можно создать несколько виртуальных дисков. (Windows идентифицирует их как обычные диски, которые могут быть отформатированы.)
Для их создания можно использовать File and Storage Services; в настройках можно указать thin provisioning либо fixed provisioning, а также размер. Дополнительные настройки можно задать с помощью команд PowerShell.
Кластеры и Storage Spaces Direct
Если вы работаете с кластером и используете для каждой его ноды СХД с прямым подключением (DAS), то Storage Spaces Direct могут оказаться вполне разумным и эффективным вариантом по сравнению с NAS и SAN. Storage Spaces Direct отличаются хорошей масштабируемостью и возможностями управления. Технология Storage Spaces работает наряду с кэшированием, RDMA и поддержкой СХД для разных уровней (tiers). Помимо этого, поддерживаются диски NVMe.
Storage Spaces Direct поддерживаются для Windows Server 2019 Datacenter, 2016 Datacenter и Insider Preview Builds. Можно создать конвергентное или гипер-конвергентное пространство.
Вкратце, основные этапы развертывания Storage Spaces Direct — это:
-
Развертывание Windows Server — установка и настройка ОС, добавление доменных учеток, настройка ролей и необходимых фич.
-
Настройка сети (этот этап не относится к сценарию развертывания Storage Spaces Direct на виртуальных машинах).
-
Конфигурация собственно Storage Spaces Direct — очистка дисков и разделов, настройка кластеров, настройка Storage Spaces Direct, создание томов, развертывание необходимых виртуальных машин.
-
Для конвергентной инфраструктуры — развертывание масштабируемых файловых серверов, настройка ролей, создание шар, настройка ограниченного делегирования Kerberos.
Все эти этапы очень подробно описаны здесь (на русском языке).
Возможен сценарий, при котором все физические диски содержатся в enclosures с общим доступом — это т.н. JBOD enclosure. Такая инфраструктура должна соответствовать требованиям Windows Certification, а также включать в себя идентичные SAS HBA (имеющие сертификацию Storage Spaces). Такие диски в кластере не должны иметь встроенную функциональность RAID.
Storage Spaces vs. RAID
Как водится, у Windows Storage Spaces и RAID есть свои преимущества и свои недостатки. Об этом уже написана не одна сотня строк (например, здесь). Вкратце:
-
У RAID есть два аспекта: аппаратный и программный — а Windows Storage Spaces, так сказать, является software-driven, настраивается целиком через графический интерфейс или командную строку.
-
Для программных RAID, как и для Storage Spaces отсутствуют ограничения по числу сокетов (у традиционных RAID они есть).
-
ОС по-разному “видит” диски в RAID и в Storage Spaces — диски RAID предстают как цельный юнит (даже если у физических дисков разная емкость), что может приводить к неоптимальному использованию свободного пространства. Для Storage Spaces такой проблемы нет, так как есть доступ к отдельным дискам.
-
Если говорить о производительности, то RAID 0 превосходит Storage Spaces с режимом simple mode примерно вдвое. Однако на скоростях 4K они уже сравнимы. RAID 1 быстрее выполняет последовательные операции чтения, зато Storage Spaces в режиме two-way mirror mode вдвое быстрее выполняет операции записи, нежели RAID 1. Что касается hardware RAID, то операции чтения и записи для них гораздо быстрее, чем Storage Spaces в режиме parity mode.
Ссылки
Общие сведения о дисковых пространствах Storage Spaces
Развертывание Storage Space Direct
Дисковые пространства в Windows 10
Кейс о развертывании Storage Space Direct компанией-провайдером Veeam
Microsoft recently released its new flagship Windows Server operating system – Windows Server 2022. It contains the latest and most significant features available to Microsoft customers for running their business-critical workloads. Many of the new features and capabilities in Windows Server 2022 enable customers to take security and hybrid cloud capabilities to the next level. Let’s look more closely at the new features found in Windows Server 2022 and how these will benefit the enterprise.
Windows Server 2022 New Features
There are many great new features contained in Windows Server 2022 that make this the most sophisticated and powerful Windows Server operating system to date. The new Windows Server 2022 features include enhancements in the following:
- Security
- Hybrid cloud
- Windows Admin Center
- Application improvements
- Storage
- Networking
- Virtualization
Windows Server 2022 provides a robust new Windows Server platform
Security
There couldn’t be a more important topic on the minds of businesses today than security. Microsoft has introduced Secured-core server as part of the implementation of Windows Server 2022. What is a Secured-core server?
The Secured-core server is a technology that builds on the Secure-core PC, which Microsoft has already introduced as part of Windows 10. Microsoft introduces the same core features that build a secure platform based on various security pillars built into the operating system with a Secure-core server. These security features include simplified security, advanced protection, and preventative defense.
With Secured-core servers, Microsoft is working with manufacturing partners to ensure the OEM server hardware has both the hardware and firmware security features needed to enable the features of the Secured-core model. Additionally, as part of the simplification of ensuring your server is configured using the Secure-core model, Microsoft has provided this as part of the Security dashboard found in Windows Admin Center.
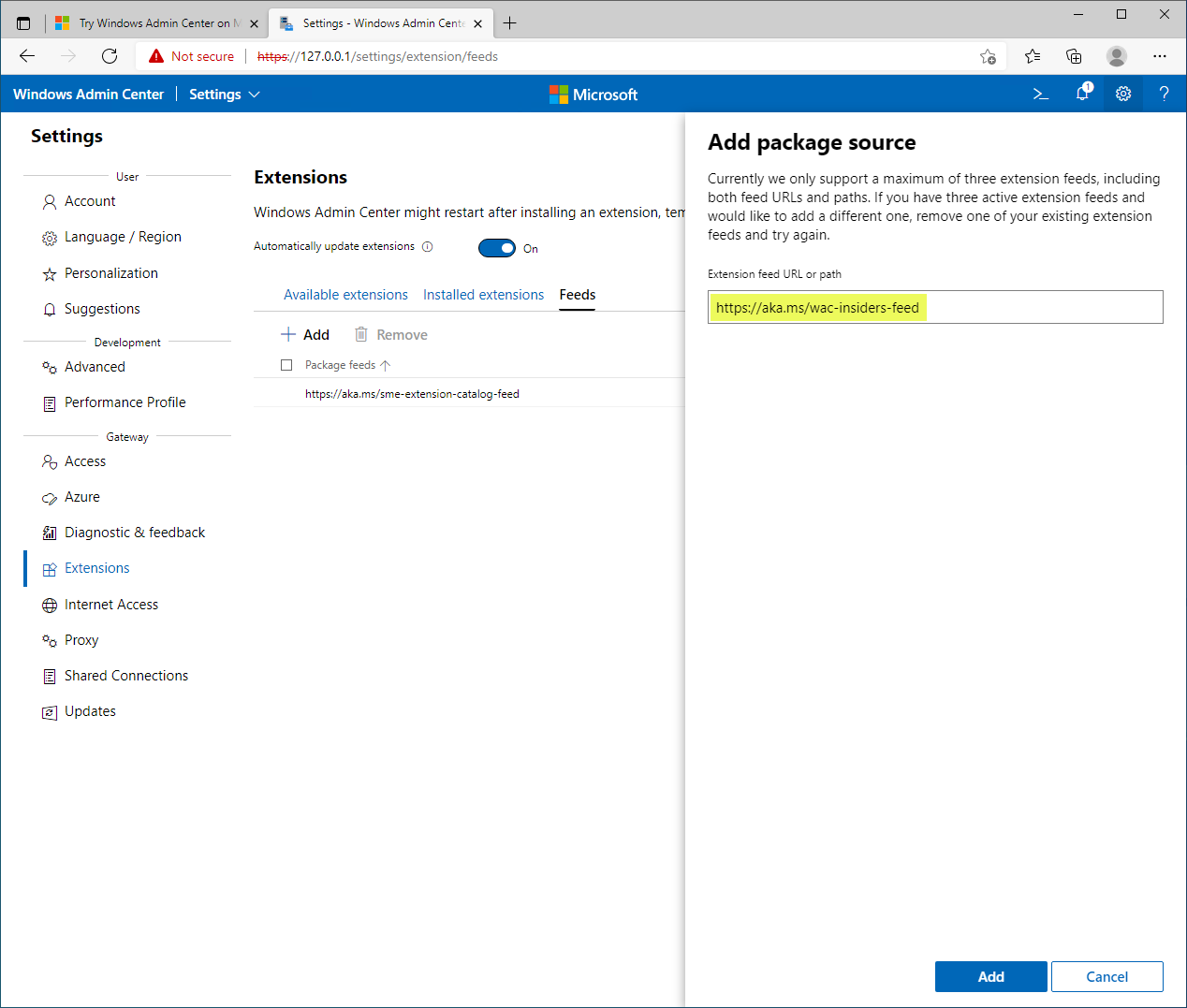
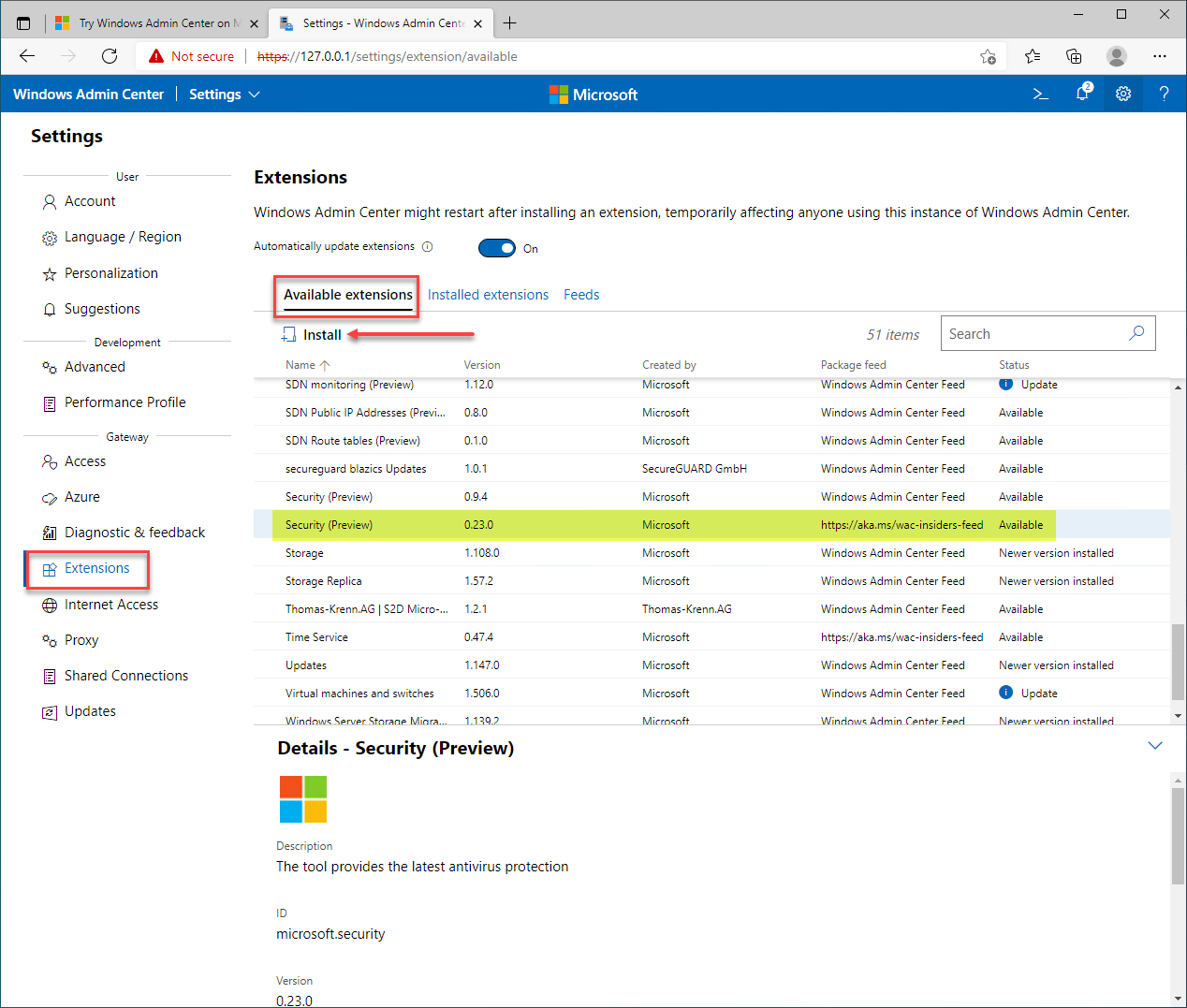
At the time of this writing, the Secured-core server Windows Admin Center extension requires you to use the “insider” Windows Admin Center extensions feed. The current version of the Security extension does not include the Secured-core functionality and configuration.
Using the Windows Admin Center Insiders feed extensions URL
After configuring the “insider’s” extension URL, you will see a new option for the Security extension (later version listed).
Installing the “insiders” version of the Security extension
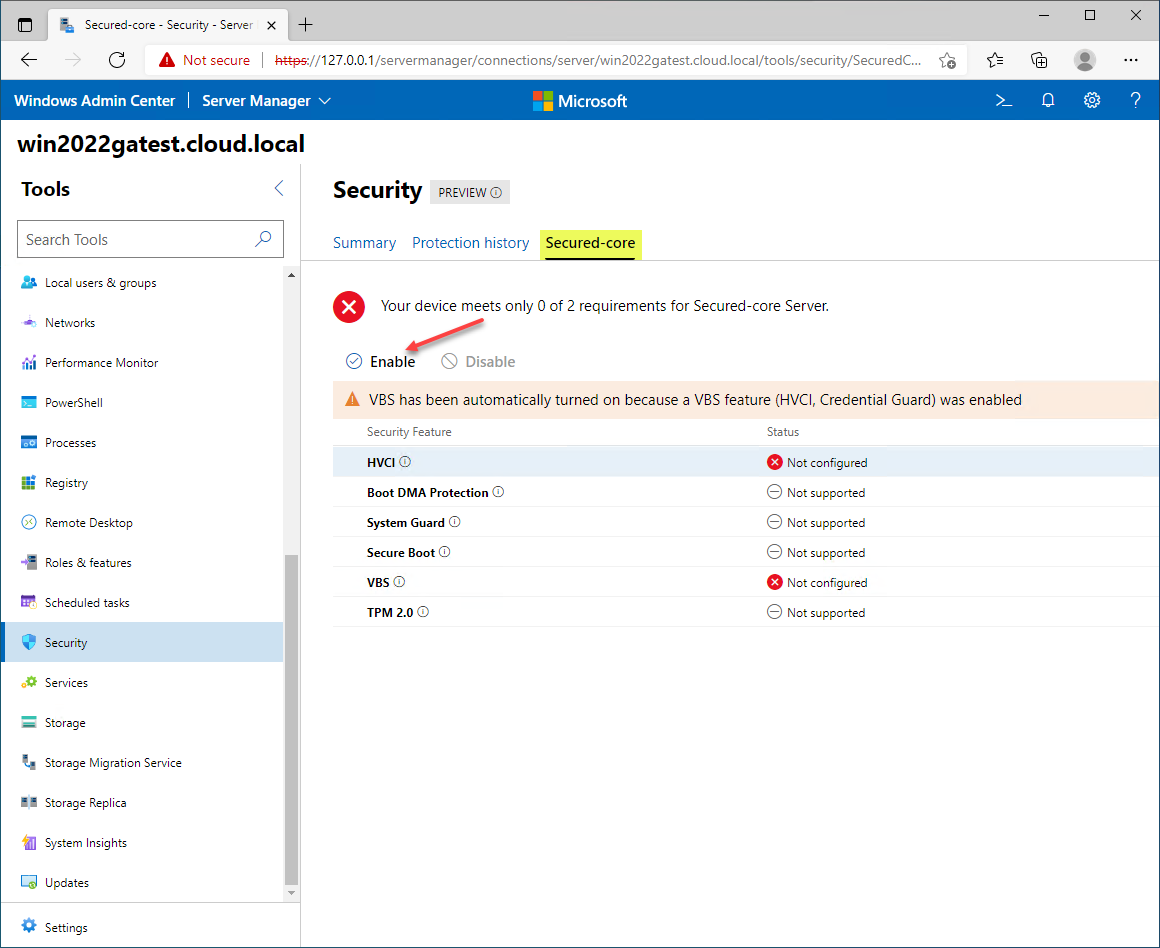
On the Secured-core server configuration, you can enable missing features that are supported on your Windows Server 2022 server. Note, the below screenshot is taken from a Windows Server 2022 VM that is missing the underlying hardware components for full Secured-core implementation. It is great to see you have quick visibility to the hardware and other components needed for Secured-core.
The Secured-core server configuration
Let’s look at the individual components of the Secured-core server. These include:
- HVI
- Boot DMA Protection
- System Guard
- Secure Boot
- VBS
- TPM 2.0
HVCI
HVCI stands for Hypervisor Enforced Code Integrity. It is used with Virtualization Based Security (VBS) and helps to protect Windows operating systems from malicious drivers and insecure or malicious system files. It also monitors for tampering with CFG, Control Flow Guard and ensures valid certificates are used with Windows security components such as Credential Guard.
Boot DMA Protection
The Secured-core Boot DMA Protection component protects against drive-by Direct Memory Access (DMA) attacks. These types of attacks can present themselves by means of hotplug PCI devices or internal/external PCIe port devices. DMA drive-by attacks are dangerous since they can lead to malware injection and bypassing security controls such as the lock screen. The DMA Protection component allows preventing any malicious drivers from starting and initiating DMA.
System Guard
Another feature of the Secured-core server implementation is the Microsoft Windows Defender System Guard protection. The primary role of the System Guard Secured-core server component is to protect the integrity of the Windows system to ensure there is no tampering. The System Guard component uses local and remote attestation to validate system integrity.
With Secured-core server implementations using modern hardware, Windows Server 2022 System Guard protects against malicious bootkits and prevents any unauthorized firmware or software from instantiating itself before the Windows bootloader.
Secure Boot
Microsoft Secured-core server uses Secure Boot, ensuring the boot firmware is validated and trusted by the OEM hardware vendor. In addition, it checks boot signatures and UEFI firmware drivers to ensure these are valid and authorized. This validation process helps to protect against boot tampering and other malicious code injection during the boot process.
Virtualization-based Security (VBS)
Virtualization-based Security (VBS) is a component of a Secured-core server that uses hardware virtualization to create a protected area, a secure region of memory, that is isolated from the operating system. This isolated area memory is carved out and for security-specific tasks. The operating system can access the specialized area of memory. However, it is only allowed limited access to the VBS-protected memory. This protection makes it much more difficult for an attacker to compromise protected information such as credential hashes and other sensitive information.
The HVCI Secured-core server feature uses VBS to provide code integrity enforcement. What type of virtualization is used? In the background, Windows Server 2022 uses Hyper-V to provide the virtual secure mode used for protecting the system and critical operating system components.
TPM 2.0
A Trusted Platform Module or TPM is a hardware device used for security-related tasks. The TPM device is a crypto-processor that generates, stores, and protects cryptographic keys. The protected keys are used for attestation, which identifies any tampering by attackers or malicious code. Windows Server 2022 can take advantage of the TPM 2.0 features and capabilities to provide robust security protections as part of the Secure-core server model.
Secured connectivity features
Microsoft has also tightened security with connectivity services aside from the Secured-core server features in Windows Server 2022. What do these enhancements include?
- HTTPS and TLS 1.3 are enabled by default
- DNS-over-HTTPS
- SMB AES-256 encryption
- Internal cluster communication SMB encryption
- SMB Direct and RDMA encryption
HTTPS and TLS 1.3 are enabled by default
Enforcing the latest security protocols and standards is a great way to help ensure your business-critical data is protected by vulnerabilities in lower-level protocols and standards. With Windows Server 2022, HTTPS and TLS 1.3 are enabled by default.
DNS-over-HTTPS
DNS is getting more secure in Windows Server 2022 with DNS-over-HTTPS (DoH). With the new DNS-over-HTTPS, DNS queries are encrypted using the HTTPS protocol. This helps to keep private DNS queries secure by preventing eavesdropping by an attacker or anyone snooping around the network.
SMB AES-256 encryption
When it comes to Server Message Block (SMB), businesses want to ensure file tranfers are as secure as possible. With Windows Server 2022, it now allows AES-256-GCM and AES-256-CCM encryption for SMB and signing. Microsoft has still built-in compabitility with older cipher suites to communicate with older versions of Windows. However, in ultra-secure environments, you can mandate the use of the more robust encryption ciphers using Group Policy.
Internal cluster communication SMB encryption
There are also security improvements in Windows Failover Server Cluster (WFSC) as you can now encrypt and sign intra-node storage communications for Cluster Shared Volumes used in WFSC. Additionally, when using Storage Spaces Direct (S2D), you can turn on encryption for east-west communications intra-server clusters to have the ultimate security for data communications.
SMB Direct and RDMA encryption
Microsoft has solved some performance issues in previous versions of Windows-related to encrypting SMB data traffic using SMB Direct and RDMA encryption. Microsoft mentions the performance impact was due to encryption disabling direct data placement. Now, with Windows Server 2022, data is encrypted before placement which drastically improves performance with these technologies.
SMB over QUIC
New in Windows Server 2022, you can use the QUIC protocol with SMB 3.1.1. It allows accessing data from edge file servers running in Azure, and users no longer need to establish a VPN connection to access data.
Hybrid cloud
With each successive Windows Server operating system, it has been easy to see the progression of hybrid cloud features and integration with Microsoft Azure. Windows Server 2019 brought about significant advancements in the area of hybrid cloud integration.
The writing has been on the wall, especially since Windows Server 2019, that Azure integration would be baked into every Windows version moving forward. Microsoft provides easy integration between the Windows Server operating system and Azure.
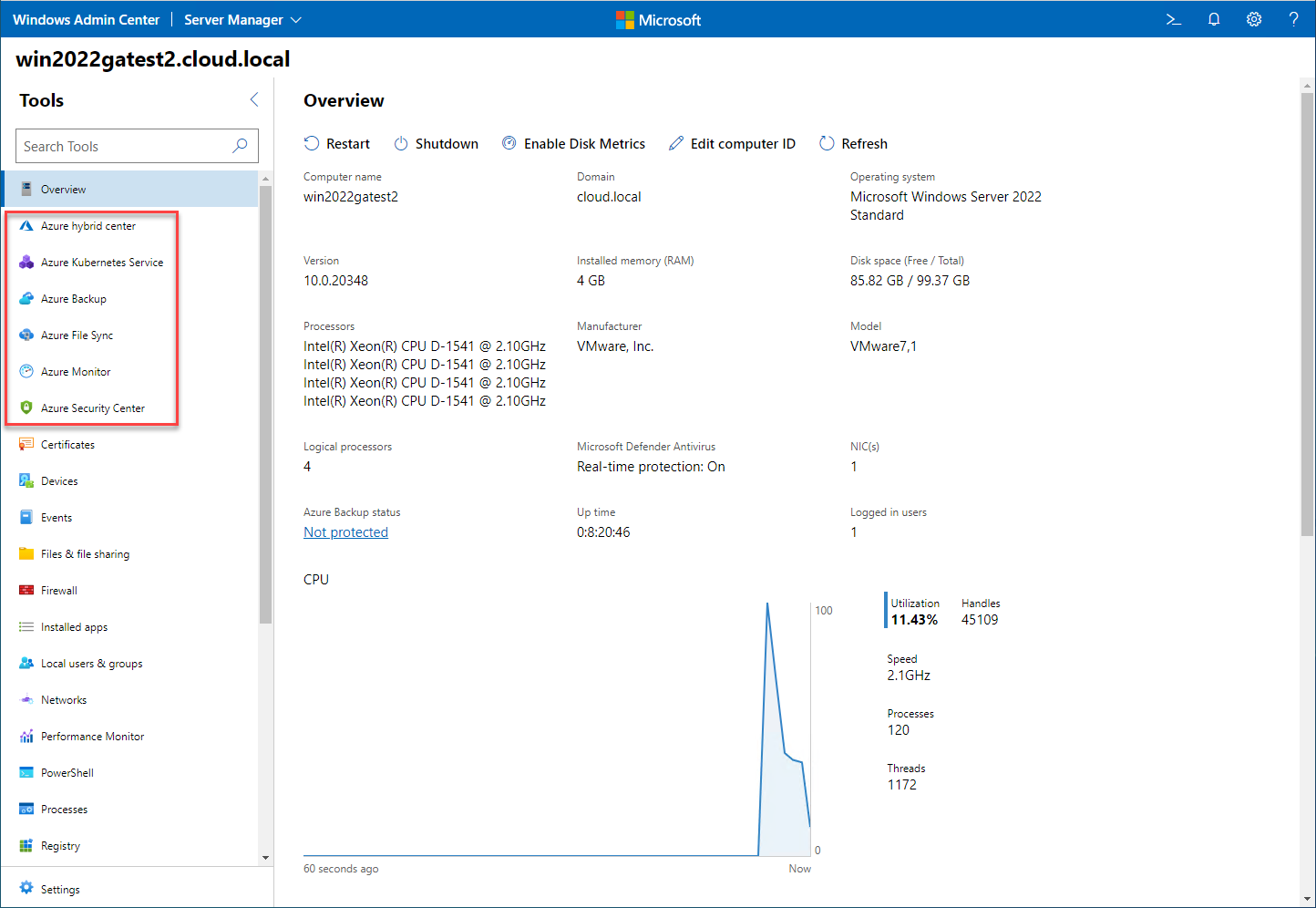
There is a wide variety of Azure services that integrate directly with Windows Server 2022. In addition, Microsoft is making it easier than ever to integrate with Azure using the Windows Admin Center management tool. Windows Admin Center, as shown above, provides an easy way to manage on-premises servers and integrate with Azure services right from the Windows Admin Center dashboard and extensions.
Below is a look at the Windows Admin Center connected to a Windows Server 2022 server and the default Azure extensions that are preinstalled. Note how you have access to:
- Azure hybrid center
- Azure Kubernetes Service
- Azure Backup
- Azure File Sync
- Azure Monitor
- Azure Security Center
Viewing default Azure services extensions preinstalled with Windows Admin Center
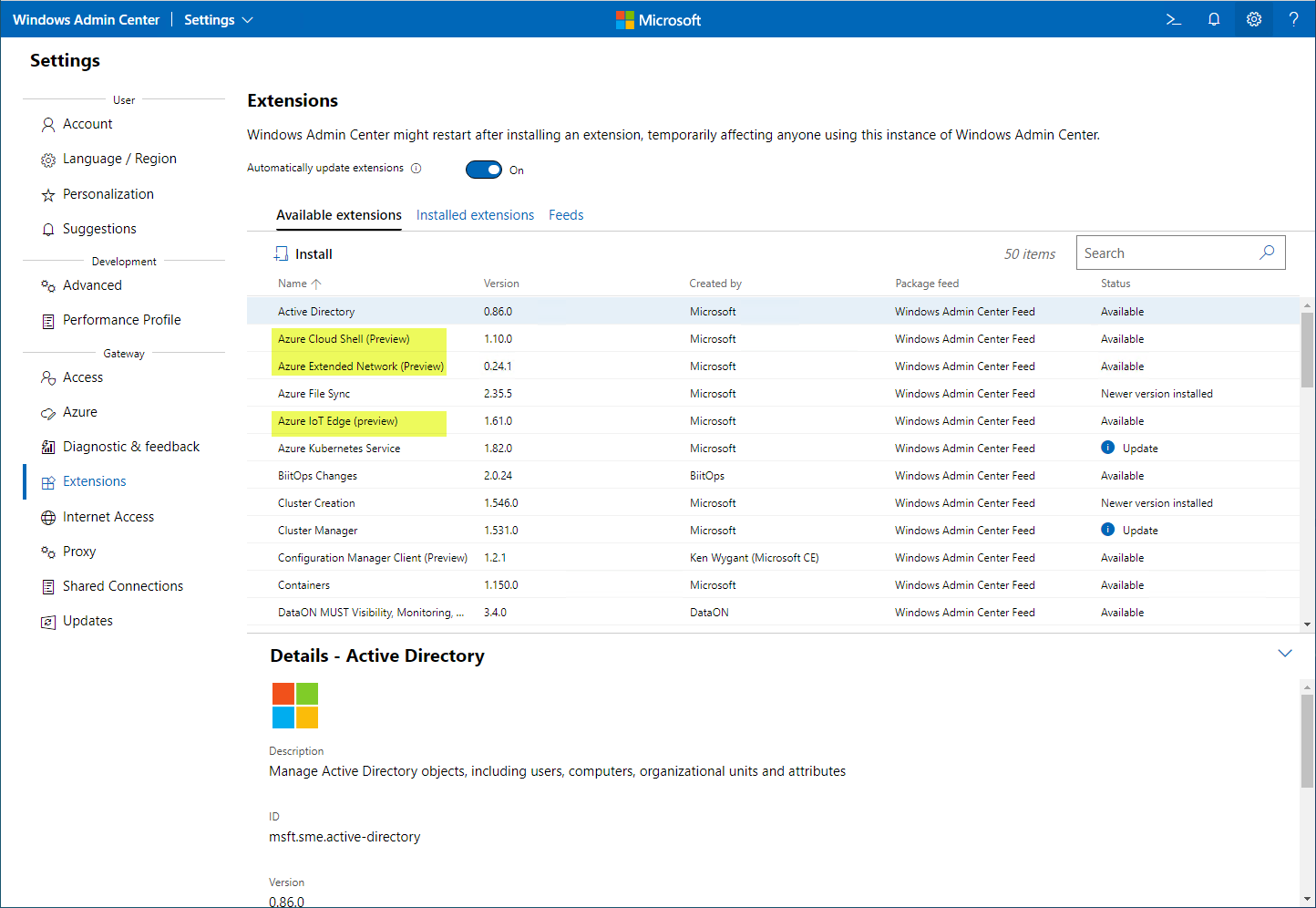
From another view, there are still more services that are available for installation.
Many Azure services are available for installation in Windows Admin Center
With the tight integration between Windows Server 2022, Windows Admin Center, and Microsoft Azure, it is easier than ever for IT admins to take advantage of the hybrid services in Azure.
Azure Arc
One of the headaches for IT admins is having multiple management interfaces, processes, solutions, and other tools needed to manage the entire estate of enterprise resources. In addition, these processes and tools can become even more disparate between on-premises and cloud environments.
Microsoft Arc helps to alleviate this challenge by allowing organizations to extend the boundaries of the Azure Resource Manager (ARM) to on-premises environments. Azure Resource Manager (ARM) controls and automates resources across the Azure environment. With Azure Arc, organizations can manage and control their on-premises resources (Windows, Linux, VMware vSphere VMs, and even other public cloud resources) from the Azure management plane.
On-premises resources managed with Azure Arc are managed as native resources in Azure. These objects receive an Azure resource identifier and are organized using the Resource Groups in the Azure subscription. As a result, organizations will be able to manage their on-premises and cloud-hosted Windows Server 2022 instances in the same way and using the same processes and tooling.
Windows Admin Center
We have already discussed a great deal of the functionality of the Windows Admin Center, covering the other new Windows Server 2022 features as many of these are exposed using Windows Admin Center. The Windows Admin Center tool is the modern way to manage Windows Servers. It was released in tandem with Windows Server 2019, and Microsoft has been making steady improvements to the tool ever since.
Windows Admin Center provides a single-pane-of-glass interface to manage Windows Server 2022
There are no cumbersome MSC dashboard console tools to remember or install. Once you have Windows Admin Center installed in Gateway mode, it allows a management workstation/server to manage multiple remote Windows Servers, all in a modern and straightforward web interface.
Windows Admin Center for Windows Server 2022 is not built into Server 2022 by default. However, it is available for download for free from the Microsoft Evaluation site. While Windows Admin Center is not new with Windows Server 2022, its maturity since Windows Server 2019 increases the robust feel with Windows Server 2022.
Application improvements
Windows Server 2022 containers represent a major step forward for running modern applications on containerized infrastructure. With Windows Server 2022, the container image size has been reduced by 40%. Having lean, efficient containers backing the applications is key to performance and other crucial benefits with containers and containerized applications.
Using group Managed Services Accounts (gMSA) allows running applications that depend on Azure Active Directory without domain joining a Windows Server 2022 container host. In addition, containers in Windows Server 2022 now support Microsoft Distributed Transaction Control (MSDTC) and Microsoft Message Queuing (MSMQ).
Note the following enhancements with Kubernetes as well:
- Host-process containers for node configuration
- IPv6
- Consistent network policy implementation with Calico
- Windows Admin Center can containerize .NET applications
- Host it on Azure Container Registry
Storage
There have been many new improvements with Windows Server 2022 and storage capabilities. One of the key enhancements of Windows Server 2022 storage is an enhanced version of the Storage Migration Service. With the new Storage Migration Service, you have the following capabilities with Windows Server 2022:
- Migrate local users and groups to the new server
- Migrate storage from:
– failover clusters
– migrate to failover clusters
– migrate between standalone servers and failover clusters
- Migrate Linux Samba shares
- Synchronize migrated shares into Azure by using Azure File Sync
- Migrate to new networks such as Azure
- Migrate NetApp CIFS servers from NetApp FAS arrays
Another new Storage Spaces Direct (S2D) feature is providing user-adjustable storage repair speed. This new capability allows having more control over the data resync process to repair data copies while not sacrificing performance. In addition, new SMB compression enhancements in Windows Server 2022 allow compression during a network copy. This feature means you no longer must first zip a file before copying it across the network. Lastly, storage bus cache is now available for standalone servers.
Networking
Microsoft has made various networking performance improvements across the board. These new improvements include:
- UDP performance improvements – includes UDP Segmentation Offload (USO), UDP Receive Side Scaling, and improved UDP data path
- TCP performance improvements – Windows Server 2022 uses TCP HyStart++, RACK, and smoother network data flow
- Hyper-V virtual switch improvements – Enhanced Receive Segment Coalescing (RSC), improved performance in both network traffic from an external host and received by a virtual NIC, and virtual NIC to another virtual NIC
Virtualization
One of the great new virtualization features in Windows Server 2022 is the new ability to use AMD processors in nested virtualization. Nested virtualization provides the ability to run Hyper-V inside of a Hyper-V virtual machine. It is an excellent tool for labs, POCs, and other test environments.
StarWind Backup Appliance (BA) is an industry-first all-NVMe backup appliance that provides unprecedented levels of backup and recovery speed. It comes as a tiny, pre-configured, ready-to-backup solution that eliminates the backup server storage bottleneck and fits even the strictest RTPO. Consisting of the best commodity hardware, your chosen hypervisor, and a StarWind SDS engine backed by 24/7/365 ProActive Support, StarWind BA ushers in a new age of a future-proof, eco-friendly, transparent, and reasonably priced backup infrastructure.
Explore Backup Appliance from StarWind
StarWind Backup Appliance Datasheet
Wrapping Up
The new Windows Server 2022 release provides many new features across the board with the Windows Server operating system. It effectively brings together hybrid cloud features for businesses to take advantage of the power of Microsoft Azure. Windows Admin Center is designed to help IT admins realize the best management experience as well as easily unlock the hybrid cloud features contained in Windows Server 2022. In addition, Windows Server 2022 provides enhancements in security, applications, networking, storage, and virtualization.
You can download an evaluation copy of Windows Server 2022 here.
- Installing Oracle Database 19c on Windows Server 2019
- Upgrade AD FS 3.0 to Windows Server 2016/2019
In the first part of this article, we looked at the benefits of S2D, its building blocks and how the technology behind the scenes achieves the necessary fault tolerance. In this post, we look at networking, monitoring, managing and setting up S2D clusters.
Contents
- Networking
- Setting up an S2D cluster
- Monitoring and managing S2D
- Conclusion
- Author
- Recent Posts
Paul Schnackenburg works part time as an IT teacher as well as running his own business in Australia. He has MCSE, MCT, MCTS and MCITP certifications. Follow his blog TellITasITis.
Networking
One of the big benefits S2D has over «traditional» Storage Spaces is the simpler networking. In 2012/2012 R2, you had two NICs dedicated to storage traffic between the SOFS and Hyper-V nodes as well as another network between the cluster nodes and another set of NICs for client and VM-to-VM traffic.
In a hyper-converged S2D solution, you can have only two NICs over which storage, cluster heartbeat and VM-to-VM/client data flows. Switch Embedded Teaming (SET) allows you to mix these networking loads together and use QoS or DCB to control bandwidth allocation. RDMA network interfaces are among the best, on average seeing a 30% increase in throughput over standard Ethernet while at the same time seeing an approximate 30% reduction in CPU usage. This last point is important because in a hyper-converged cluster, you want as many CPU cycles as possible to be available to run your VM workloads.
Setting up an S2D cluster
In my test lab, I have four physical computers running Windows Server 2016 Hyper-V, each with 32 GB of RAM. Two nodes have Chelsio 40 Gb RDMA NICs (2 x 40 Gb ports), and two nodes have Chelsio 10 Gb RDMA NICs (2 x 10 Gb ports). A 10 Gb spider cable connects the 40 Gb NICs to a Dell 12-port 10 Gb switch, providing a total bandwidth of 40 Gbps per host. The 10 Gb hosts have both ports connected, providing a total of 20 Gbps bandwidth per node.
I prefer to use iWarp RDMA networking over ROCE/Infiniband. It’s easier because it avoids the complex DCB configuration of the switch. In addition, because it’s just TCP/IP, you can use ordinary switches. This means you don’t need all new infrastructure to implement iWarp, unlike ROCE. RDMA isn’t limited to servers either. Microsoft now supports it in Windows 10, enabling scenarios where a high-speed trading application or video-editing station can connect to backend S2D storage over RDMA. As a side note, Chelsio is releasing a solution where their NICs can act as switches, thus eliminating the need for an expensive 10 or 40 Gbps switch altogether.
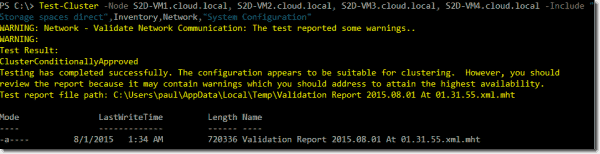
Each host has two SATA SSDs and two SATA 2 TB HDDs installed. I started by installing the OS on each node, followed by the latest driver for the Chelsio NIC. I ran the Test-Cluster cmdlet to see if the nodes met the requirements for a Failover Cluster.
Testing S2D cluster nodes before creating the cluster
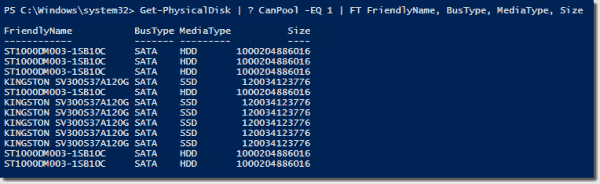
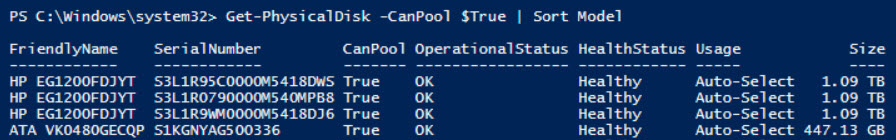
I then used PowerShell to create a new cluster (starting with three nodes; I wanted to see how easy it was to add a fourth node later). To check availability of all drives for use, I ran Get-PhysicalDisk.
Listing disks eligible for S2D
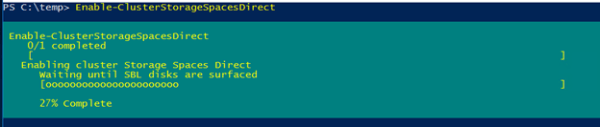
Finally, I ran Enable-ClusterStorageSpacesDirect, which automatically grabbed all SSDs and HDDs and added them to a single pool. The last step is creating a virtual disk on top of the pool. Here’s where things are a bit different from Storage Spaces. In the old world, you had to choose your tiering and whether to use mirroring or parity manually. S2D automatically picks this for you based on number of nodes and number of disks.
Creating a virtual disk
Overall, setting up S2D is a lot more straightforward in the RTM release than the fiddling around required in the Technical Previews.
If you have System Center Virtual Machine Manager 2016 (VMM) you can attach an existing S2D cluster to it. On the other hand, if you have new physical servers, you can use VMM’s deployment technology to install Windows Server 2016, turn the nodes into Hyper-V hosts and deploy S2D to them, all with a single checkbox in the VMM create cluster wizard.
Monitoring and managing S2D
As the name implies, System Center Operations Manager provides a management pack for S2D with a dashboard to visualize performance metrics and warn about issues. But unlike in earlier releases, the logic to gather the necessary data is not in the management pack. Instead, Microsoft has built a health service for storage (also covering Storage Replica and Storage QoS) directly into the OS. This provides information about health state as well as performance metrics. You can run Get-StorageSubSystem Name | Get-StorageHealthReport to access cluster-wide health data.
Datacom is an early adopter of S2D here in Australia. They built their own dashboard in Grafana using a PowerShell script to gather the data from the health service. DataON Storage is a popular vendor in Storage Spaces/S2D; they have built a beautiful HTML5-based dashboard for their products. You can opt in to report disk failures directly to them so they can ship a replacement drive, possibly before you’re even aware of the failure.
Cluster-Aware Updating (CAU) is the inbox and cluster-aware engine for patching each cluster node in an orchestrated fashion. As of 2016, it’s aware of S2D. It will only patch a node in which all virtual disks are healthy.
Conclusion
Storage Spaces Direct is a game changer. I suspect it’ll be the default deployment for Hyper-V clusters going forward. This comes from the general hype about hyper-convergence in the IT industry and the benefits S2D brings. Such benefits include ease of setup, cost-effective components and fantastic performance. For the latter, Microsoft has demonstrated six million IOPS for reading in an S2D cluster. With SQL Server 2016 supported to store databases directly on S2D, that’ll also be an interesting option, since many database deployments are very storage intensive. S2D is also another reminder to look seriously at RDMA networking. The enhancements in throughput and minimal CPU overhead are very attractive.
There are some words of caution, however. S2D is not a small business/branch office solution in most cases, since it requires a Windows Server Datacenter license at approximately five times the cost of the Standard license. For these smaller deployments, virtual SAN solutions such as those from StarWind still have their place.
Subscribe to 4sysops newsletter!
Since you can use S2D with almost any type of local storage, you can easily set up a lab with a few VMs and learn the technology in preparation for production deployments.
It’s that time again! A new version of Windows Server is upon us and as usual, we produced a comprehensive webinar for system admins that covers all of the “What’s New?” questions that go along with a new release of Windows Server.
In Windows Server 2022, we’ve seen a number of enhancements in security, SMB, and hybrid cloud capabilities along with a new edition referred to as “Azure Edition”. On top of that, we have an entirely new deployment methodology in Azure Stack HCI, which while not Windows Server 2022 directly, shares the underlying features and capabilities and is now a huge source of focus for Microsoft moving forward.
To help you get up to speed on this release, we recommend you watch the webinar on-demand, along with a follow-up video with discussions on some of the more in-depth questions asked during the webinar. Finally, at the bottom of this article, you’ll find a list of questions asked during the webinar with their associated answers!
Watch the webinar What’s New in Windows Server 2022
Note: we’ve had several questions for more information on how the KDC proxy service works along with SMB over QUIC. This particular topic warrants its own article, which we’ll be working on in the near future so stay tuned for that!
Windows Server 2022 Frequently Asked Questions
What is “Azure Edition” exactly and how do I purchase it? I’m seeing datacenter and standard edition only
Azure Edition is a version of Windows Server 2022 that is designed to run as a VM within Microsoft Azure or on top of Azure Stack HCI on-prem. You can obtain it from the Azure Marketplace. For on-prem deployment, see the below question.
How do I obtain Windows Server 2022 Azure Edition to run on-prem?
This is still unclear, and we’re still waiting for guidance from Microsoft on how this will work exactly. In the meantime, it’s best to run the Azure Edition of Windows Server 2022 in Azure.
For Windows Server 2022 Essentials, does 1 CPU with 10 cores mean 20 “threads” per license?
Up to 10 cores and 1 VM on single-socket servers. Windows Server Essentials is available through our OEM Server Hardware partners. Microsoft counts physical cores for licensing on SQL / Win Standard/DC so I’m going to say this is physical cores NOT A REAL ESSENTIALS
Could XCP-ng be used as an alternative to the Free Hyper-V Server SKU?
While I don’t have any direct experience with the tool mentioned, at first glance it looks like a viable alternative, especially if you have experience with Xen hypervisors.
Is TPM 2.0 required to run Windows Server 2022?
TPM 2 required for Secure Core Server, not listed as a req for the general server (good idea to have though)
Is it required to keep Azure Stack HCI clusters “online” at all times?
Yes, Azure Stack HCI needs to contact Azure every 30 days for licensing purposes. If the check doesn’t happen the cluster goes into a reduced functionality mode
Is RDS a supporting role with Windows Server 2022 Essentials?
Yes, RDSH is one of the available roles just like previous versions of Windows
Can you license Windows Server 2022 with 2012 R2 User CALs?
No, you must purchase CALs that match the version of Windows Server you’re running. In this case, Windows Server 2022.
Do you get any virtualization rights with Windows Server 2022 Essentials?
Yes, you have the rights to run a single VM with Windows Server 2022 Essentials Edition.
Is there an upgrade path from Windows Server 2012 R2 to Windows Server 2022?
Normally only two version differences of Windows Server are supported for an in-place upgrade, so you’d be looking at a fresh install and a migration in this case.
You talked about some CLI tools in the webinar for migration purposes. Those are PowerShell tools, correct?
Yes
The maximum memory supported by Windows Server 2022 is 48TB? Why so much?
The increases in memory capacity are often driven by large memory-intensive workloads such as SQL or SAP. Plus, when you look at the length of support for Windows Server 2022, who knows how much memory we’ll need in 10 years.
Any chance that TLS 1.3 will be backported to Windows Server 2012 R2?
This is unlikely, but we suspect there is a high chance for Windows Server 2016/2019
Will SMB over QUIC support Azure AD joined devices in the future?
Maybe, but nothing definitive has been mentioned thus far to our knowledge
Now, in order to get SMB over QUIC on-prem, I have to buy new hardware that is Azure HCI compliant, pay per month for the license to only run a single Server 2022 file server in order to get that feature?
As it stands right now, yes. Additionally, you’ll have to migrate your files to that server as well. Now that said you’d be able to run additional workloads on that Azure Stack HCI cluster. Your other alternative is to run that VM out of Azure.
Where else can I run the Azure Edition of Windows Server 2022 besides Azure Stack HCI?
You can also run this edition from a VM in Azure.
What are the minimum system requirements for Windows Server 2022?
64-bit CPU, 2 GB RAM for Server with Desktop (512 MB for Core), 32 GB disk space MINIMUM
You talked about Windows Server 2022 Essentials in the webinar, is TRUE Windows Server Essentials back?
As mentioned, not really an Essentials, just a cheaper Standard with some limitations on size/no. of users/clients
How does Azure Stack HCI stack up against vSphere with VSAN?
It’s generally cheaper and offers more cloud-based integrations. From a performance perspective, it’s all dependent on the chosen hardware.
Does “Azure Edition” Mean it will only run in Azure?
No, you still have the usual Standard and Datacenter Editions, plus you’ll have the option of running “Azure Edition” in an on-prem Azure Stack HCI cluster if desired.
When do you think Windows Server 2022 will be ready for a production 2-node cluster?
Looks pretty ready right now! The version is GA, so ready to go! =)
In the Essentials edition of Windows Server 2022, “10 cores” means physical cores of logical cores?
From what we know so far, this is in reference to physical cores
Are there any changes to shielded VMs in Windows Server 2022 Hyper-V?
There are no changes here. In fact, Microsoft will not be developing this feature further at this point and will be leveraging Azure Stack HCI and azure service to fill this need moving forward. Check out this post from Microsoft for more info.
Any changes to the max number of vCPU per VM in Hyper-V in Windows Server 2022?
The defined vCPU max for VMs on Windows Server 2022 is 240 vCPUs for Gen2 VMs.
Is there any new information you can share regarding Storage Spaces Direct in Windows Server 2022?
One big enhancement is the adjustable storage repair speed. This is not to mention the enhancements specifically for SMB, which is leveraged heavily by S2D.
I would love to hear more about SMB over QUIC, where can I see it in action?
We did a webinar on Enhancements in Windows Server Storage earlier this year. In that webinar, Didier Van Hoye does an excellent demo of SMB over QUIC in action. That webinar can be watched here.
From a resource perspective, is consumption about the same as previous versions of Windows Server?
From the testing we’ve done, it looks to be about the same as Windows Server 2019
Do I need to re-deploy Windows Admin Center in order to manage Windows Server 2022?
Not at all. You should be able to connect to Windows Server 2022 just like any other server!
Was there any mention of What’s new in Group Policy in this webinar or any talk about GPO support for Azure Objects?
No. We didn’t cover GPO as not much has changed. Also no mention of Azure objects coming to GPO preferences from what we know today.
With Windows Server 2022 Essentials Edition, is it like Small Business Server is Back?
Nope, there are no SMB features in Essentials. The only difference is in sizing and pricing.
When will the desktop experience be removed from Windows Server?
We don’t see this happening anytime soon. Many admins still love the GUI
Are there any improvements in Windows Server 2022 in terms of Migration? FSMO roles for example?
No improvements here from what we’ve seen thus far.
Storage Spaces Direct has been available in Windows Server 2019 standard edition. So, for Windows Server 2022, did S2D really move to Datacenter Only?
A Clarification here, “Storage Spaces” is in Standard, “Storage Spaces Direct” is only in Datacenter Edition in Window Server 2016/19/22 – https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server/storage/storage-spaces/storage-spaces-direct-overview
Will there be a Free Hyper-V Server 2022?
No. While the free SKU called “Hyper-V Server 2019” will no longer be getting feature updates, it will be officially supported for a number of years yet. You’ll want to move to an alternative solution at that time. The new strategic direction for Microsoft on-prem is Azure Stack HCI and they’re suggested replacement for Hyper-V Server. That said the Azure Stack HCI solution (as many have noted) is not free sadly.
What are the major difference and changes in Windows Server 2022 in how we pitch it to a customer?
Good question here! The big selling points for customers would be focused on the security enhancements and the ease of management from the cloud with hybrid cloud deployments. Additionally features like hot-patch, and SMB over QUIC could be strong features to mention as well.
Does Azure Stack differ a lot from the old Azure Pack in terms of roles you need to deploy for it to work? Azure Pack required many – many resources just to get it up and running alone. Is this feasible on a 2 – 3 node cluster for small/medium-sized businesses?
Yes, Azure Stack HCI installation is greatly improved over Azure Pack. It’s very wizard-driven, and assuming you’ve done your homework on deployment best practices and you’re using supported hardware, the deployment should be fairly straightforward. Very feasible for a small organization with properly vetted hardware.
So no changes if you are already buying server licenses correct?
As far as we know today, correct.
Does Azure Edition run on Premises?
Yes, it can be run on Azure Stack HCI on-prem
Does Windows Admin Center basically replace Failover Cluster Manager?
Yes, it’s the best place to manage most Windows server features, including failover clusters. That said, Failover Cluster Manager and the other MMC snap-ins will continue to be around for some time.
That wraps us up! If you asked a question that you don’t see here, or if you have any new questions that you’d like to get an answer on, use the questions form below this article and we’ll be sure to get an answer to you.
That all said, what are your thoughts on Windows Server 2022 so far? Let us know in the comments section below! We’d love to hear your input!
Storage Spaces Direct (S2D) – новая технология распределенного хранения данных, представленная в Windows Server 2016. Благодаря использованию Storage Spaces Direct локальные диски нескольких серверов можно организовать в отказоустойчивое, масштабируемое хранилище, защищенное от выхода из строя как отдельных дисков, так и целых серверов. Цена такого «программного» хранилища получается значительно меньше, чем стоимость организации полноценного SAN или NAS, а за счет простого масштабирования (до 16 серверов и 400 дисков) и возможности использовать различных накопителей (в том числе SSD и NVMe) можно обеспечить значительную производительность.
Содержание:
- Что такое Storage Spaces Direct (S2D)
- Требования к Storage Spaces Direct
- Включаем Storage Spaces Direct
Что такое Storage Spaces Direct (S2D)
S2D является дальнейшим развитием технологии Storage Spaces и позволяет объединить локальные диски узлов (серверов) кластер Hyper-V в пулы хранения (Storage Pool). На данных пулах можно создать виртуальные тома (диски) и использовать их в качестве общего тома кластера Cluster Shared Volume (CSV) для хранения файлов виртуальных машин Hyper-V и файловых шар SOFS-серверов. При необходимости расширить размер хранилища достаточно добавить в S2D новый сервер или накопитель. По сути, технология Storage Spaces Direct является ответом Microsoft на VMware vSAN.
Требования к Storage Spaces Direct
В S2D поддерживаются следующие типы устройств хранения:
- Обычные HDD диски (SAS)
- SATA / SAS SSD диски
- NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) — SSD диски, подключенные не через классический интерфейс SATA/SAS, а через более скоростную шину PCI Express
В дальнейшем разные типы дисков можно комбинировать в различные массивы (по скорости и емкости), например, логично расположить кэш и транзакционные логи приложений на скоростных NVMe SSD, медленные и недорогие диски лучше использовать для хранения больших файлов, доступ к которым не требует повышенной производительности и т.д.
Для работы S2D нужно организовать отказоустойчивый кластер, к узлам которого выдвигаются следующие требования:
Требования к узлам кластера S2D
- Редакция Windows Server 2016 — DataCenter
- На серверах нужно установить следующие компоненты: роли Hyper-V, File Services и фичу Failover Clustering
Примечание. Не забудьте отключить SMB 1:
Remove-WindowsFeature –Name FS-SMB1 -Verbose -Restart - Как минимум два сервера в кластере (в идеале не менее 4 для обеспечения высокой отказоустойчивости)
- Наличие дисков. Помимо системного должен иметь как минимум один физический диск на каждом узле. Все диски, которые планируется добавить в хранилище Storage Spaces Direct должны быть не размечены (не должны быть разбиты и не содержать таблицы разделов)
Итак, предполагаем, что у нас уже собран отказоустойчивый кластер из двух серверов с Windows Server 2016 (можно собрать такой кластер даже в рабочей группе).
Примечание. Если в кластере четное число серверов, придется настроить ресурс-свидетель. Если количество узлов нечетное – свидетель не нужен.
Перед тем, как включить Storage Spaces Direct, проверьте, что ваши диски можно объединить в такой пул.
Get-PhysicalDisk –CanPool $True | Sort Model
Включаем Storage Spaces Direct
Активируем S2D с помощью командлета:
Enable-ClusterStorageSpacesDirect
Командлет отрабатывает довольно долго (около 10 минут), в течении которых будет проанализированы все доступные диски и их производительность, и автоматически создан кластерный пул. Также автоматически создаются два тира: Performance и Capacity с разным типом отказоустойчивости хранения: mirror и parity соответственно.
Всего поддерживаются 3 типа организации отказоустойчивого хранения данных:
- Mirrored (3) – данные синхронно реплицируются между 3 (или 2 в минимальной конфигурации) узлами. Высокая скорость чтения обеспечивается распределением операции между всеми серверами.
- Parity (2) – данные с хранением четности распределены между разными дисками. Данные хранятся более эффективно, т.к. не надо как в первом случае хранить несколько копий одних и тех же данных.
- Tiered (1) – используется комбинация обоих техник.
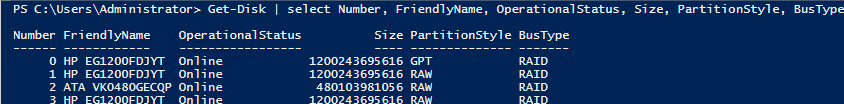
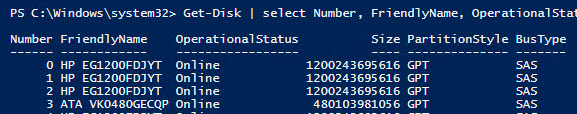
Примечание 1. В том случае, если при выполнении команды Enable-ClusterS2D появится ошибка «no disks with supported bus types found to be used for S2D», скорее всего тип шины (BusType) ваших дисков – RAID (что с точки зрения S2D – неподдерживаемая конфигурация). Проверим тип шины
Get-Disk | select Number, FriendlyName, OperationalStatus, Size, PartitionStyle, BusType | sort Number | ft -AutoSize
«BusType»=dword:0000000b (вместо 00000008)Другие примеры использования командлетов PowerShell для управления локальными дисками приведены в статье Управление дисками и разделами из PowerShell.
Примечание 2. Если в массиве обнаружен диск типа дисков SSD, NVMe, он автоматически используется в качестве диска для хранения кэша. Если таких дисков нет, в процессе создания S2D будут появляться предупреждения. Можно отключить кэш с помощью параметра
-CacheState Disabled
.
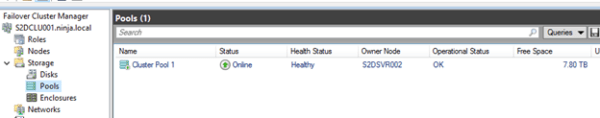
Откроем консоль управления кластером и убедимся, что в разделе Storage новый появился Cluster Pool 1.
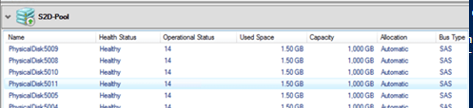
Выбрав пул, можно увидеть из каких дисков он состоит.
В случае необходимости, имя пула можно изменить:
Set-StoragePool –FriendlyName “Cluster Pool 1” –NewFriendlyName “S2D”
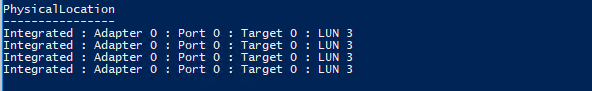
Если нужно создать том из определенных дисков, можно воспользоваться к примеру, такой командой. Сначала выбираем все диски с LUN 3, а затем собираем из них пул.
$HDDs = Get-PhysicalDisk | ? PhysicalLocation -like "*LUN 3"
New-StoragePool -StorageSubSystemFriendlyName *Cluster* -FriendlyName S2DPool -ProvisioningTypeDefault Fixed -PhysicalDisk $HDDs
Вывести список дисков в пуле:
Get-StoragePool -FriendlyName S2D | Get-PhysicalDisk | ft PhysicalLocation
Добавить в пул новый диск:
$HDDs = Get-PhysicalDisk | ? PhysicalLocation -like "*LUN 4"
Add-PhysicalDisk -PhysicalDisks $HDDs -StoragePoolFriendlyName S2D
Диски, помеченные как S2D, в консоли управления дисками более не отображаются, это нормально.
При наличии разнородных накопителей можно использовать тиринг (не обязательно). Тир типа зеркало из SSD дисков создается так:
New-StorageTier -StoragePoolFriendlyName S2D -FriendlyName "Mirror_Tier" -MediaType SSD -ResiliencySettingName Mirror
Тир из обычных HDD с хранением четности:
New-StorageTier -StoragePoolFriendlyName S2D -FriendlyName "Parity_Tier" -MediaType HDD -ResiliencySettingName Parity
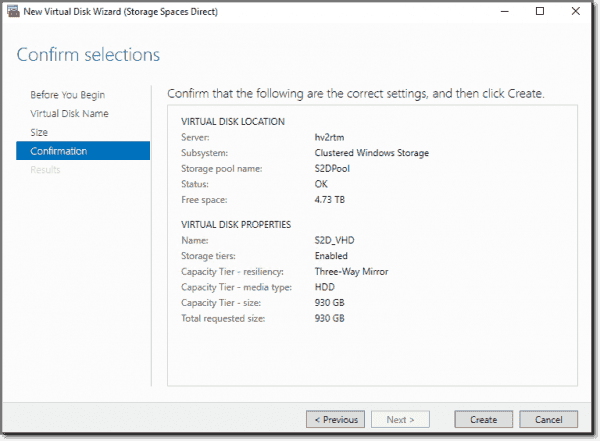
Теперь можно создать том CSV (Cluster Shared Volume):
New-Volume –StoragePoolFriendlyName S2D –FriendlyName CSV001 –PhysicalDiskRedudancy 2 -FileSystem CSVFS_ReFS -Size 200GB
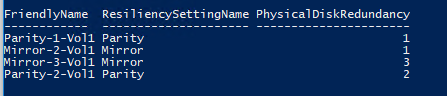
Список томов и типом избыточности можно вывести так
Get-VirtualDisk | ft FriendlyName, ResiliencySettingName, PhysicalDiskRedundancy
Новый CSV том появится в консоли управления дисками.
Данный том можно использовать для размещения виртуальных машин Hyper-V или сетевого хранилища Scale-out File Server.
Итак, при использовании Storage Spaces Direct из нескольких серверов с локальными дисками можно с легкостью создать программное сетевое хранилище данных. За счет технологии S2D обеспечивается как защита от одновременного выхода из строя любых двух дисков или двух серверов (4+ нодовый кластер). Кластер S2D автоматически запускает процесс перераспределения данных между оставшимися устройствами в случае обнаружения неполадок с дисками или серверами. В тестовой среде можно убедится, что при отключении двух любых дисков хранилище продолжает быть доступным, а ВМ, запущенные на нем штатно работают. Процедура замены неисправного диска в хранилище S2D описана в следующей статье.
Windows Storage Server — специальная редакция ОС Windows Server, которую используют в файловых хранилищах. Эту редакцию распространяют только Embedded/IoT дистрибьюторы Microsoft, а приобрести могут производители и сборщики систем хранения и других специализированных систем.
В отличие от «классических» редакций Standard и Datacenter, этому продукту не нужны лицензии клиентского доступа CAL, поэтому это более экономный вариант для использования на файловых серверах хранения.
Компания Кварта Технологии продолжает оказывать услуги по настройке операционных систем, созданием образов ОС на заказ и помогать с настройкой промышленного тиражирования образов. Более подробнаяя информация доступна на соответствующей странице.
Редакции и сроки доступности и поддержки
|
Выпуск |
Поддержка до |
Купить можно до |
|
Windows Storage Server 2008 and 2008 R2 |
закончилась | 2023 |
|
Windows Storage Server 2012 R2 |
2023 |
недоступна |
|
Windows Storage Server 2016 |
2027 |
31.12.2023 |
|
Windows Server IoT 2019 for Storage |
09.06.2029 |
09.06.2029 |
|
Windows Server IoT 2022 for Storage |
2031 |
2031 |
Значимые нововведения в Storage Server 2022
Служба миграции хранилища
Усовершенствования службы миграции хранилища в Windows Server 2022 упрощают перенос хранилища на Windows Server или в Azure из большего количества источников. Вот функции, которые доступны при запуске оркестратора Storage Migration Server на Windows Server 2022:
- Перенесите локальных пользователей и группы на новый сервер.
- Миграция хранилища из отказоустойчивых кластеров, миграция в отказоустойчивые кластеры и миграция между автономными серверами и отказоустойчивыми кластерами.
- Перенести хранилище с сервера Linux, использующего Samba.
- Упростите синхронизацию перенесенных общих ресурсов в Azure с помощью службы «Синхронизация файлов».
- Переходите на новые сети, такие как Azure.
- Миграция серверов NetApp CIFS с массивов NetApp FAS на серверы и кластеры Windows.
Регулируемая скорость восстановления хранилища
Регулируемая пользователем скорость восстановления хранилища — это новая функция в Storage Spaces Direct, которая предлагает больший контроль над процессом повторной синхронизации данных, выделяя ресурсы либо для восстановления копий данных (отказоустойчивость), либо для запуска активных рабочих нагрузок (производительность). Это помогает повысить доступность и позволяет более гибко и эффективно обслуживать кластеры.
Кэш шины хранения с дисковыми пространствами на автономных серверах
Кэш шины хранения теперь доступен для автономных серверов. Это может значительно улучшить производительность чтения и записи, сохраняя при этом эффективность хранения и низкие эксплуатационные расходы. Подобно его реализации для Storage Spaces Direct, эта функция связывает вместе более быстрые носители (например, NVMe или SSD) с более медленными носителями (например, HDD) для создания уровней. Часть более быстрого уровня мультимедиа зарезервирована для кеша.
Сравнение Windows Storage Server 2016-2022
| Возможности | Windows Storage Server 2016 | Windows Server IoT 2019 | Windows Server IoT 2022 | |||
| Workgroup | Standard | Storage Workgroup | Storage Standard | Storage Workgroup | Storage Standard | |
| Core based licensing | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Client Access License (CAL) | ||||||
| Maximum #CPU | 1 | 2 | 1 | n/a | 1 | n/a |
| Virtual Machine Rights | 2 | 2 | 2 | |||
| # Users | 50 | Unlimited | 50 | Unlimited | 50 | Unlimited |
| NVMe-enabled hardware | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| # Disks | 6 | Unlimited | 6 | Unlimited | 6 | Unlimited |
| External Serial Attached SCSI (SAS) interconnect | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| Maximum Memory | 32 GB | 24 TB | 24 TB | 24 TB | 48 TB | 48 TB |
| Hardware RAID | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Concurrent SMB Connections | 250 | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited |
| File Sharing (SMB&NFS) | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Online Backup | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| DFS Replication | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Storage Replica | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| File Classification Infrastructure | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| File Server Resource Manager | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Domain Join | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Shared Block Storage (iSCSI Target + Boot) | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| OEM Customizable Out of Box Experience | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Storage Spaces | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Storage Spaces Direct/Volume Replication | ||||||
| Deduplication | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| BranchCache — Hosted Cache | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| Clustering (Including AD/DNS) | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| Simplified Cluster Setup | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| Networking Infra (DHCP, DNS & WINS) | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
Доступные редакции Windows Storage Server
Для приобретения доступны две редакции. Сравнение ниже.
| Windows Storage Server | Workgroup | Standard |
| Maximum # CPU and VM rights | 1 + 0 | 2 + 2 |
| Maximum Memory | 32 GB | Unlimited |
| # Disks | 6 | Unlimited |
| hardware RAID | Yes | Yes |
| Concurrent SMB Connections | 250 | Unlimited |
| # Users | 50 | Unlimited |
| File sharing (SMB & NFS) | Yes | Yes |
| Online Backup | Yes | Yes |
| DFS-Replication | Yes | Yes |
| File Classification Infrastructure (FCI) | Yes | Yes |
| File Server Resourse Manager (FSRM) | Yes | Yes |
| Domain Join | Yes | Yes |
| Shared block storage (iSCSI Target + Boot) | Yes | Yes |
| OEM Customizable Out of Box Experience | Yes | Yes |
| Storage Spaces | Yes | Yes |
| Deduplication | No | Yes |
| BranchCache — Hosted Cache | No | Yes |
| Virtualization | No | Host + 2 VM |
| Clustering (including AD/DNS) | No | Yes |
| Simplified Cluster Setup | No | Yes |
| Networking infra (DHCP, DNS & WINS) | No | Yes |
| Storage Spaces Direct and Volume Replication | No | No |
| AD Roles Including Domain Controller (RODS) | No | No |
| Active Directory (Domain Controller, Certificate Services, Federation Services, Rights Managment) |
No | No |
| Application Server, Network Policy, Remote Desktop Broker, WDS and Fax Server |
No | No |
Системные требования Windows Storage Server
| Процессор | 2 ГГц |
| Оперативная память | 2 ГБ |
| Свободное метсо на диске | 8 ГБ |
В декабре вышло масштабное обновление очередного релиза серверной операционной системы Microsoft, который изначально был выпущен в августе, придя на смену Windows Server 2019.
В очередном обновлении Windows Server выросло количество поддерживаемых сетевых протоколов, появились новые инструменты администрирования, повышена производительность, усилена безопасность работы с хранилищем.
В декабре вышло масштабное обновление Windows Server 2022, нового релиза серверной операционной системы Microsoft, который изначально был выпущен в августе, придя на смену Windows Server 2019.
Основной акцент в обновлении сделан на повышении производительности. Это касается, в частности, поддержки новых сетевых протоколов, в том числе QUIC — интернет-протокола, разработанного в Google, который функционирует поверх UDP и характеризуется сниженной задержкой. Реализация QUIC позволила добавить протокол SMB over QUIC, одна из главных возможностей которого — защищенный доступ к файлам: весь трафик SMB передается через TLS-туннель, предотвращающий перехват данных внутри сети.
Улучшения функций работы с хранилищем в основном касаются укрепления безопасности без влияния на производительность: реализованы криптографические наборы AES-256 для SMB и шифрование для высокоскоростных сетевых хранилищ, использующих SMB Direct и RDMA. Тем самым обеспечена возможность шифрования трафика нагрузок, требующих очень высокой производительности, таких как Storage Spaces Direct, Hyper-V, Scale-out File Server и др. Еще одна доработка — автоматическая компрессия файлов, передаваемых по SMB.
Реализован ряд улучшений, направленных на повышение скорости работы с хранилищами, в частности, построенными по технологии Storage Spaces Direct. Одна из ее главных функций — синхронизация, лежащая в основе механизмов избыточности и оптимизации производительности. Если раньше она работала в автоматическом режиме, то теперь можно вручную назначить синхронизации более низкий приоритет, а активным рабочим задачам — повышенный.
Расширены возможности сервиса Storage Migration Service, облегчающего перенос данных и приложений из различных источников на Windows Server и в Azure — теперь миграцию можно осуществлять между отказоустойчивыми кластерами, а также из папок общего доступа Samba.
В ознакомительной версии доступен инструментарий Azure Automanage, обеспечивающий автоматизацию многих задач, связанных с настройкой, администрированием и обновлением ПО виртуальных машин на базе Windows Server 2022 и других операционных систем.
Реализован ряд доработок, связанных с виртуализацией и контейнеризованными приложениями и облегчающих создание гибридных облаков с участием Azure и локальных систем. В частности, введена поддержка контейнеров HostProcess для Kubernetes. Такие контейнеры работают непосредственно на хост-системах Windows, имея такой же уровень доступа к ОС, как нативные процессы. Контейнеры HostProcess удобно использовать для задач администрирования и DevOps-процессов.
Новшеством Windows Server 2022 стала поддержка вложенных виртуальных машин (возможности выполнения Hyper-V внутри гостевой системы Hyper-V) на процессорах AMD — прежде это было доступно только на системах с процессорами Intel.
Расширены возможности использования функции Group Managed Service Accounts (gMSA), которая позволяет приложениям, в том числе распределенным между несколькими узлами, осуществлять доступ к сетевым ресурсам без ручного управления соответствующими учетными записями — необоходимые операции выполняются сервисом Active Directory в автоматическом режиме. В Windows Server 2022 этой функцией могут пользоваться хосты, не присоединенные к домену Active Directory, — учетные записи создаются в сервисе Azure AD. Благодаря этому контейнерные приложения на таких хостах могут осуществлять доступ к нужным им ресурсам, пользуясь возможностями gMSA.