You can avoid the commas by using /-C on the DIR command.
FOR /F "usebackq tokens=3" %%s IN (`DIR C: /-C /-O /W`) DO (
SET FREE_SPACE=%%s
)
ECHO FREE_SPACE is %FREE_SPACE%
If you want to compare the available space to the space needed, you could do something like the following. I specified the number with thousands separator, then removed them. It is difficult to grasp the number without commas. The SET /A is nice, but it stops working with large numbers.
SET EXITCODE=0
SET NEEDED=100,000,000
SET NEEDED=%NEEDED:,=%
IF %FREE_SPACE% LSS %NEEDED% (
ECHO Not enough.
SET EXITCODE=1
)
EXIT /B %EXITCODE%
UPDATE:
Much has changed since 2014. Here is a better answer. It uses PowerShell which is available on all currently supported Microsoft Windows systems.
The code below would be much clearer and easier to understand if the script were written in PowerShell without using cmd.exe as a wrapper. If you are using PowerShell Core, change powershell to pwsh.
SET "NEEDED=100,000,000"
SET "NEEDED=%NEEDED:,=%"
powershell -NoLogo -NoProfile -Command ^
$Free = (Get-PSDrive -Name 'C').Free; ^
if ($Free -lt [int64]%NEEDED%) { exit $true } else { exit $false }
IF ERRORLEVEL 1 (
ECHO "Not enough disk space available."
) else (
ECHO "Available disk space is adequate."
)
What to Know
- Checking free space on a drive is helpful if you suspect it’s filling up or you’re getting random error messages.
- Open This PC, Computer, or My Computer (depending on your OS), right-click the drive, choose Properties.
- Follow the same steps for hard drives as well as network drives and external drives like flash drives.
You can’t just add stuff to a drive forever, be it your main hard drive, the little flash drive in your pocket, or the giant external hard drive on your desk.
Even an arguably humongous 16 TB hard disk has a limit: 16 TB! As crazy as it sounds, it, too, can fill up. True, it’ll take two million high-quality photos to do it, but «only» about 150 feature-length 4K movies.
Performance Suffers on a Full Hard Drive
Regardless, you get the idea—you may need to check the free space on a drive from time to time, especially if it starts to slow down or act funny, which is very often the not-so-clear consequence of too much stuff in a single place.
Unfortunately, especially in Windows operating systems, you don’t get a friendly «Hey, your hard drive is almost full!» warning. Instead, you get strange behavior, cryptic error messages, or serious problems like a Blue Screen of Death (BSOD).
How to Check Free Hard Drive Space in Windows
Fortunately, it’s super easy to check how much free space you have on any of your drives, and it only takes a minute or two.
Maddy Price / Lifewire
These steps work for Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
-
In Windows 11 or Windows 10, select the Start button, followed by File Explorer (the small folder icon). If you don’t see it, check under the All apps or Windows System folder, or type file explorer into the search box.
In Windows 8 or Windows 10, search for this pc and then select This PC.
In Windows 7 or Windows Vista, select the Start button, followed by Computer.
In Windows XP, go to Start and then My Computer.
-
On the left-hand side of File Explorer or Windows Explorer (depending on your version of Windows), make sure This PC, Computer, or My Computer is selected (again, based on your version of Windows).
Windows 10 This PC.
If you don’t see anything on the left side of this screen, open the View menu and enable the Navigation pane. In older versions of Windows, go instead to Organize > Layout > Navigation Pane (7 and Vista), or View > Explorer Bar > Folders (XP).
-
On the right-hand side, find the drive on which you want to know how much free space is left.
In Windows 11/10/8, all storage devices are listed in the Devices and drives area. In Windows 7/Vista/XP, Hard Disk Drives and Devices with Removable Storage are listed separately.
-
In newer versions of Windows, you can see right under the drive listing how much free space is left on it, as well as the total size of the drive, in a format like this:
Local Disk (C:)[storage space indicator]535 GB free of 931 GBIf that’s all you need to know then you’re done! However, there is a bit more information about your drive’s capacity buried just a bit deeper:
-
To see more, right-click or tap-and-hold the drive you want more storage space information on, and then choose Properties.
-
In the General tab, you’ll see all the important details about the storage device you’re looking at, reported in bytes as well as rounded GB.
- Used space is the sum total of every piece of data on this device.
- Free space is the difference in the total formatted capacity of the device and the sum total of every piece of data being stored on it. This number indicates how much more storage you’re allowed to fill.
- Capacity is the total formatted capacity of the drive.
- Also there is a pie graph, showing used vs free space on the drive, helpful for visualizing how much space you’re using on this hard drive or other device.
You should now know exactly how much hard drive space is available on your computer. If you’re running low, delete files you don’t need or move them to a different hard drive that has more free space.
How to Check Free Hard Drive Space Using Command Prompt
Another way to check free space is with Command Prompt. The results aren’t as easy to read because the values are represented in bytes instead of gigabytes, but it’s still possible with this command:
wmic logicaldisk get size,freespace,caption
How Much Free Space Do You Need?
Microsoft has historically recommended that to avoid problems, you should leave at least 100 MB of free space on whatever drive you have Windows installed on. However, because we’ve seen issues at levels higher than 100 MB, we have always recommended 10 percent free space instead.
How to Disable Low Disk Space Checks in Windows
Calculate 10 Percent Free Space on Windows PC
To calculate 10 percent free space, just take the number next to Capacity from Step 6 and move the decimal to the left one space. For example, if the hard drive you’re viewing has a total capacity of 250.0 GB, moving the decimal one space to the left makes it 25.0 GB, meaning that you shouldn’t let the free space drop below that for that particular device.
Examine Types of Files Taking Up Storage Space
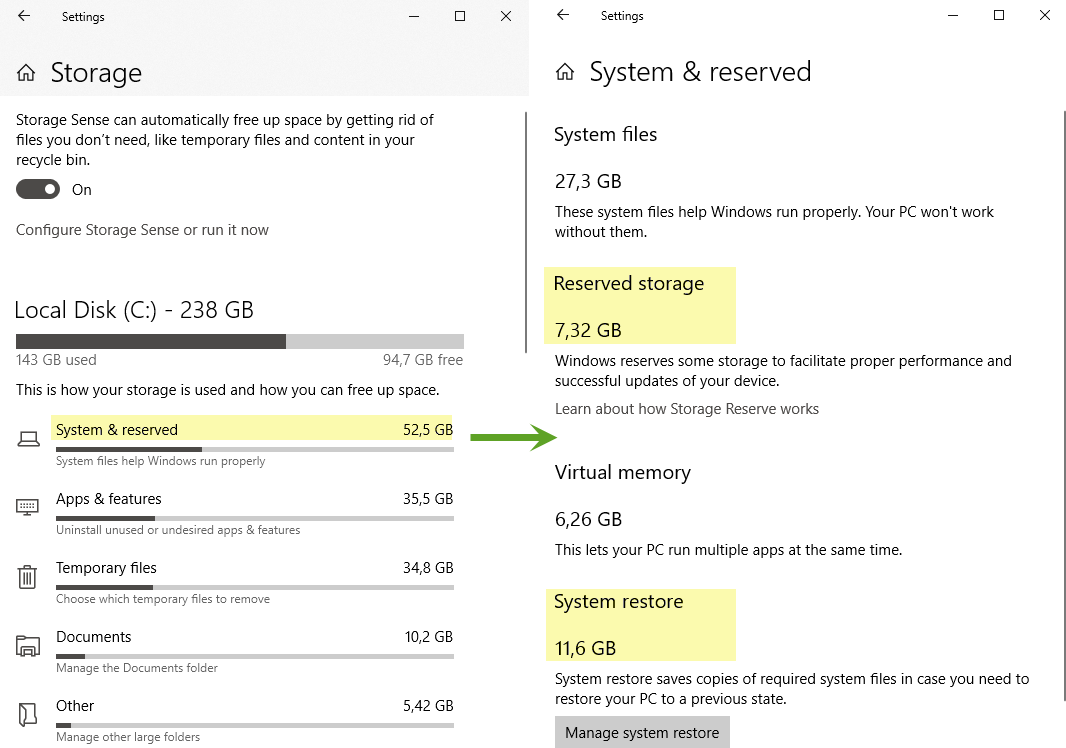
In Windows 11 & 10, much more detail about what sorts of files are using up your drive’s capacity can be found in Settings > System > Storage. Just choose a drive you’re interested in and Windows will analyze it, breaking it down into categories like System & reserved, Temporary files, Apps & features, Pictures, and more.
There are also several free disk space analyzer tools that’ll show you which files and folders are occupying the most space.
In any version of Windows, choosing Disk Cleanup from the drive’s properties (Step 6 above) will start the Disk Cleanup utility, a one-stop-shop for removing files that are no longer needed by Windows.
FAQ
-
How do I free up space on my hard drive?
Clear out extraneous files and apps by deleting downloads you no longer need in the Downloads folder. Another option is to search for %temp% and delete the temporary files that appear. Or, if you need to clear out a lot of space, wiping the hard drive will work but is a more extreme approach.
-
How much hard drive space is needed for the 64-bit version of Windows 8.1?
If you’re installing the 64-bit version of Windows 8.1, you’ll need a minimum of 3,850 MB (about 4 GB) of free hard drive space.
-
How do I check hard drive space on my Mac?
Open the Apple menu and select About This Mac > Storage. In macOS 13 Ventura, open the Apple menu and select System Settings > General > About and scroll down to Storage.
Thanks for letting us know!
Get the Latest Tech News Delivered Every Day
Subscribe
What to Know
- Checking free space on a drive is helpful if you suspect it’s filling up or you’re getting random error messages.
- Open This PC, Computer, or My Computer (depending on your OS), right-click the drive, choose Properties.
- Follow the same steps for hard drives as well as network drives and external drives like flash drives.
You can’t just add stuff to a drive forever, be it your main hard drive, the little flash drive in your pocket, or the giant external hard drive on your desk.
Even an arguably humongous 16 TB hard disk has a limit: 16 TB! As crazy as it sounds, it, too, can fill up. True, it’ll take two million high-quality photos to do it, but «only» about 150 feature-length 4K movies.
Performance Suffers on a Full Hard Drive
Regardless, you get the idea—you may need to check the free space on a drive from time to time, especially if it starts to slow down or act funny, which is very often the not-so-clear consequence of too much stuff in a single place.
Unfortunately, especially in Windows operating systems, you don’t get a friendly «Hey, your hard drive is almost full!» warning. Instead, you get strange behavior, cryptic error messages, or serious problems like a Blue Screen of Death (BSOD).
How to Check Free Hard Drive Space in Windows
Fortunately, it’s super easy to check how much free space you have on any of your drives, and it only takes a minute or two.
Maddy Price / Lifewire
These steps work for Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, and Windows XP.
-
In Windows 11 or Windows 10, select the Start button, followed by File Explorer (the small folder icon). If you don’t see it, check under the All apps or Windows System folder, or type file explorer into the search box.
In Windows 8 or Windows 10, search for this pc and then select This PC.
In Windows 7 or Windows Vista, select the Start button, followed by Computer.
In Windows XP, go to Start and then My Computer.
-
On the left-hand side of File Explorer or Windows Explorer (depending on your version of Windows), make sure This PC, Computer, or My Computer is selected (again, based on your version of Windows).
Windows 10 This PC.
If you don’t see anything on the left side of this screen, open the View menu and enable the Navigation pane. In older versions of Windows, go instead to Organize > Layout > Navigation Pane (7 and Vista), or View > Explorer Bar > Folders (XP).
-
On the right-hand side, find the drive on which you want to know how much free space is left.
In Windows 11/10/8, all storage devices are listed in the Devices and drives area. In Windows 7/Vista/XP, Hard Disk Drives and Devices with Removable Storage are listed separately.
-
In newer versions of Windows, you can see right under the drive listing how much free space is left on it, as well as the total size of the drive, in a format like this:
Local Disk (C:)[storage space indicator]535 GB free of 931 GBIf that’s all you need to know then you’re done! However, there is a bit more information about your drive’s capacity buried just a bit deeper:
-
To see more, right-click or tap-and-hold the drive you want more storage space information on, and then choose Properties.
-
In the General tab, you’ll see all the important details about the storage device you’re looking at, reported in bytes as well as rounded GB.
- Used space is the sum total of every piece of data on this device.
- Free space is the difference in the total formatted capacity of the device and the sum total of every piece of data being stored on it. This number indicates how much more storage you’re allowed to fill.
- Capacity is the total formatted capacity of the drive.
- Also there is a pie graph, showing used vs free space on the drive, helpful for visualizing how much space you’re using on this hard drive or other device.
You should now know exactly how much hard drive space is available on your computer. If you’re running low, delete files you don’t need or move them to a different hard drive that has more free space.
How to Check Free Hard Drive Space Using Command Prompt
Another way to check free space is with Command Prompt. The results aren’t as easy to read because the values are represented in bytes instead of gigabytes, but it’s still possible with this command:
wmic logicaldisk get size,freespace,caption
How Much Free Space Do You Need?
Microsoft has historically recommended that to avoid problems, you should leave at least 100 MB of free space on whatever drive you have Windows installed on. However, because we’ve seen issues at levels higher than 100 MB, we have always recommended 10 percent free space instead.
How to Disable Low Disk Space Checks in Windows
Calculate 10 Percent Free Space on Windows PC
To calculate 10 percent free space, just take the number next to Capacity from Step 6 and move the decimal to the left one space. For example, if the hard drive you’re viewing has a total capacity of 250.0 GB, moving the decimal one space to the left makes it 25.0 GB, meaning that you shouldn’t let the free space drop below that for that particular device.
Examine Types of Files Taking Up Storage Space
In Windows 11 & 10, much more detail about what sorts of files are using up your drive’s capacity can be found in Settings > System > Storage. Just choose a drive you’re interested in and Windows will analyze it, breaking it down into categories like System & reserved, Temporary files, Apps & features, Pictures, and more.
There are also several free disk space analyzer tools that’ll show you which files and folders are occupying the most space.
In any version of Windows, choosing Disk Cleanup from the drive’s properties (Step 6 above) will start the Disk Cleanup utility, a one-stop-shop for removing files that are no longer needed by Windows.
FAQ
-
How do I free up space on my hard drive?
Clear out extraneous files and apps by deleting downloads you no longer need in the Downloads folder. Another option is to search for %temp% and delete the temporary files that appear. Or, if you need to clear out a lot of space, wiping the hard drive will work but is a more extreme approach.
-
How much hard drive space is needed for the 64-bit version of Windows 8.1?
If you’re installing the 64-bit version of Windows 8.1, you’ll need a minimum of 3,850 MB (about 4 GB) of free hard drive space.
-
How do I check hard drive space on my Mac?
Open the Apple menu and select About This Mac > Storage. In macOS 13 Ventura, open the Apple menu and select System Settings > General > About and scroll down to Storage.
Thanks for letting us know!
Get the Latest Tech News Delivered Every Day
Subscribe
You can avoid the commas by using /-C on the DIR command.
FOR /F "usebackq tokens=3" %%s IN (`DIR C: /-C /-O /W`) DO (
SET FREE_SPACE=%%s
)
ECHO FREE_SPACE is %FREE_SPACE%
If you want to compare the available space to the space needed, you could do something like the following. I specified the number with thousands separator, then removed them. It is difficult to grasp the number without commas. The SET /A is nice, but it stops working with large numbers.
SET EXITCODE=0
SET NEEDED=100,000,000
SET NEEDED=%NEEDED:,=%
IF %FREE_SPACE% LSS %NEEDED% (
ECHO Not enough.
SET EXITCODE=1
)
EXIT /B %EXITCODE%
UPDATE:
Much has changed since 2014. Here is a better answer. It uses PowerShell which is available on all currently supported Microsoft Windows systems.
The code below would be much clearer and easier to understand if the script were written in PowerShell without using cmd.exe as a wrapper. If you are using PowerShell Core, change powershell to pwsh.
SET "NEEDED=100,000,000"
SET "NEEDED=%NEEDED:,=%"
powershell -NoLogo -NoProfile -Command ^
$Free = (Get-PSDrive -Name 'C').Free; ^
if ($Free -lt [int64]%NEEDED%) { exit $true } else { exit $false }
IF ERRORLEVEL 1 (
ECHO "Not enough disk space available."
) else (
ECHO "Available disk space is adequate."
)
You can avoid the commas by using /-C on the DIR command.
FOR /F "usebackq tokens=3" %%s IN (`DIR C: /-C /-O /W`) DO (
SET FREE_SPACE=%%s
)
ECHO FREE_SPACE is %FREE_SPACE%
If you want to compare the available space to the space needed, you could do something like the following. I specified the number with thousands separator, then removed them. It is difficult to grasp the number without commas. The SET /A is nice, but it stops working with large numbers.
SET EXITCODE=0
SET NEEDED=100,000,000
SET NEEDED=%NEEDED:,=%
IF %FREE_SPACE% LSS %NEEDED% (
ECHO Not enough.
SET EXITCODE=1
)
EXIT /B %EXITCODE%
UPDATE:
Much has changed since 2014. Here is a better answer. It uses PowerShell which is available on all currently supported Microsoft Windows systems.
The code below would be much clearer and easier to understand if the script were written in PowerShell without using cmd.exe as a wrapper. If you are using PowerShell Core, change powershell to pwsh.
SET "NEEDED=100,000,000"
SET "NEEDED=%NEEDED:,=%"
powershell -NoLogo -NoProfile -Command ^
$Free = (Get-PSDrive -Name 'C').Free; ^
if ($Free -lt [int64]%NEEDED%) { exit $true } else { exit $false }
IF ERRORLEVEL 1 (
ECHO "Not enough disk space available."
) else (
ECHO "Available disk space is adequate."
)
Вы тут: Главная → Windows → diskusage vs. dfp: анализ занятого места на диске из командной строки
В предновогодних инсайдерских сборках Windows 10 20277 и 21277 появилась консольная утилита diskusage для анализа дискового пространства. Сегодня я разберу некоторые нюансы работы новой утилиты и поделюсь с вами результатами ее испытаний в сравнении с утилитой dfp.
Предвосхищая вопрос, diskusage работает и в предыдущих версиях Windows 10, если перекинуть в них исполняемый файл и MUI-ресурсы (проверялось на 20H2).
[+] Сегодня в программе
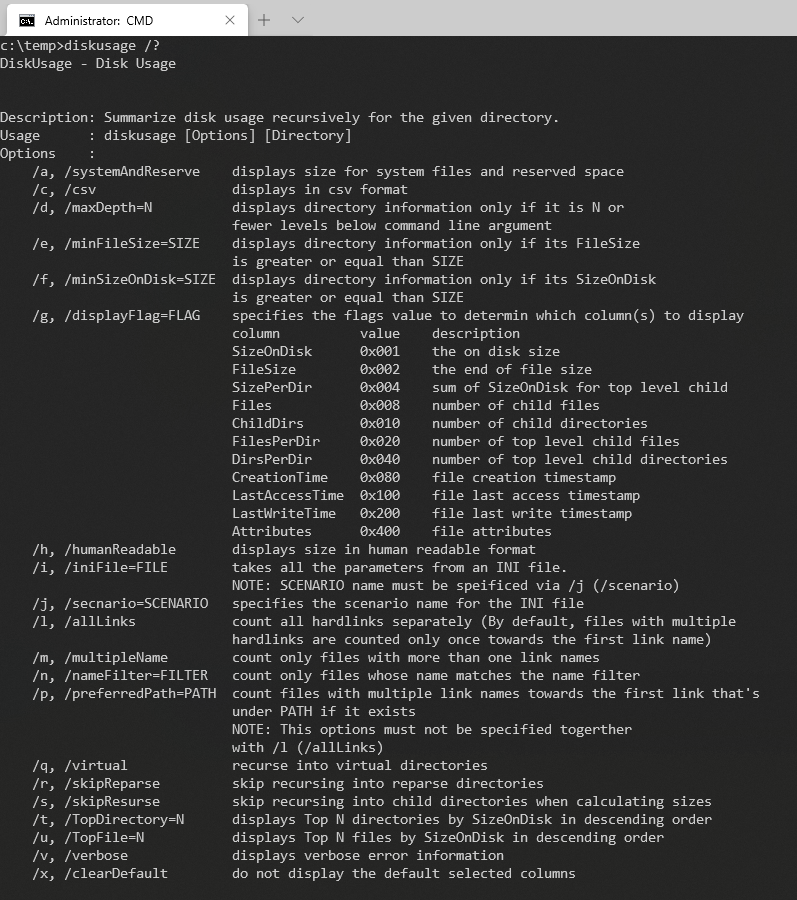
Параметры командной строки и примеры команд
Утилита обладает развесистым списком ключей, причем в двух вариантах (для публикации я выбрал длинные, но понятные). Поскольку речь о предварительной версии, все может поменяться в будущем.
Если путь не указан, по умолчанию утилита рекурсивно сканирует начиная с текущей папки. Отмечу, что я практически всегда использовал ключи /humanReadable /skipReparse помимо прочих. Первый отображает размеры в GB/MB нежели только в байтах, а второй я разберу ниже.
В справке не хватает примеров, но я восполню пробел этой статьей. Парочка для затравки:
- Показать 25 самых больших папок на диске C.
diskusage C: /TopDirectory=25 /humanReadable /skipReparse
- Показать 30 самых больших файлов в папке Загрузки наряду с датой их создания.
diskusage "%userprofile%Downloads" /TopFile=30 /displayFlag=0x080 /humanReadable /skipReparse
Отмечу несколько нюансов diskusage в сравнении с dfp, которая давно исключена из поставки Windows, хотя до сих пор прекрасно работает и входит в мой арсенал.
Определение размера системных файлов и зарезервированного пространства
Ключ /systemAndReserve. Логично было бы добавлять этот параметр к первоначальному сканированию системного диска, но пока ключ не срабатывает в сочетании с некоторыми другими. Если смотреть отдельно, то быстрее всего результат получается, если натравить утилиту на пустую папку.
diskusage C:new /systemAndReserve /humanReadable
SizeOnDisk Files Directory path
0 ( 0.0 KB) 0 C:new
20 293 710 083 ( 18.9 GB) 47 [System Files and Reserved Space]
168 317 841 408(156.8 GB)/254 588 350 464(156.8 GB) 66.1% of disk in use
Сведения отображаются в конце вывода. Утилита показывает 18.9GB. Это сильно расходится со сводкой в Параметрах, но картина проясняется при изучении подробностей.
Судя по всему, значение складывается из размера зарезервированного пространства и теневых копий (точек восстановления). Объем зарезервированного пространства и так можно посмотреть из консоли с fsutil, см. статью по ссылке↑ А к теневым копиям я еще вернусь.
Переход по символическим ссылкам и соединениям
Утилита подсчитывает размер папок, в которые ведут символические ссылки и соединения. Это – поведение по умолчанию, а выключается оно ключом /skipReparse. На мой взгляд, стоило сделать наоборот. У меня при первом тестовом запуске diskusage полезла в теневые копии по ссылке, что сделало анализ бесполезным 
Не самая ценная фича для анализа отдельно взятого диска, но сценарии под нее найдутся, наверное.
Подсчет размера только одной жесткой ссылки
Утилита dfp ведет себя так же. Однако diskusage умеет считать и размер всех жестких ссылок с ключом /allLinks. Большой практической ценности это не несет, но для исследований бывает полезно. Ниже я разверну этот тезис на примере.
Анализ файлов
Ключ /TopFile. Он позволяет выявить самые большие файлы. В утилите dfp для анализа на уровне файлов служит ключ /all.
Фильтры по именам и размерам
Ключи /nameFilter для имен и /minSizeOnDisk, /minFileSize для размеров папок. Другими словами, можно выводить папки и/или файлы, размер которых превышает заданный порог.
Топ-5 файлов размером более 10GB:
diskusage E:Movies /minSizeOnDisk=10000000000 /TopFile=5 /humanReadable /skipReparse
Топ-5 файлов mp4:
diskusage E:Movies /nameFilter=*.mp4 /TopFile=5 /humanReadable /skipReparse
Вывод столбцов с датами создания, изменения и доступа
Ключ /displayFlag. Пример в начале статьи.
Пожалуй, последние три пункта в списке наиболее полезны на практике. Из остального отмечу вывод в формате CSV и параметры запуска в… INI-файле, в 2021 году:)
Замечу, что в отличие от dfp, в новой утилите нет снимков, позволяющих быстро выявлять повторно засоряющиеся папки.
Скорость работы и результаты анализа
Практическое сравнение показало высокую скорость работы diskusage и более осмысленные результаты.
У меня подход к анализу с dfp простой — сначала я рекурсивно анализирую топ-25 из корня диска, потом выбираю папки из топа для более пристального изучения. Это обусловлено тем, что при первом запуске много капитанства – корень диска, папки Windows, Users и т.д.
На моем системном диске занято 150GB. Первичный анализ dfp занял 111 секунд.
dfp /b /top 25 /elapsed /study {largest} C:
Size On Disk Files Folders Path
137.5G 658033 158499 C:
64.1G 226614 43550 C:Users
63.0G 217951 37544 C:UsersVadim
34.1G 7360 426 C:UsersVadimDownloads
24.1G 301184 96431 C:Windows
15.9G 198613 34846 C:UsersVadimAppData
12.8G 174917 31220 C:UsersVadimAppDataLocal
11.6G 31 17 C:System Volume Information
10.7G 97674 12828 C:Program Files
10.3G 695 328 C:UsersVadimDocuments
9.8G 13018 3422 C:ProgramData
9.1G 76806 37420 C:WindowsWinSxS
8.1G 8510 2342 C:ProgramDataMicrosoft
7.2G 82213 7694 C:Program FilesWindowsApps
6.9G 22553 3265 C:WindowsSystem32
6.8G 18443 2092 C:Program Files (x86)
5.7G 90 154 C:UsersVadimDocumentsWPR Files
4.8G 29596 3568 C:UsersVadimAppDataLocalMicrosoft
4.2G 945 85 C:iso
4.2G 861 71 C:isosources
4.1G 6 3 C:WindowsLiveKernelReports
4.1G 3572 1386 C:ProgramDataMicrosoftWindows
4.0G 3 4 C:UsersVadimDocumentsVirtual Machines
4.0G 3 3 C:UsersVadimDocumentsVirtual MachinesWin10
4.0G 3 1 C:UsersVadimDocumentsVirtual MachinesWin10Virtual Machines
Схожий анализ diskusage занял 39 секунд.
diskusage C: /humanReadable /skipReparse /TopDirectory=25
SizeOnDisk Files SizePerDir Directory path
36 656 173 056 ( 34.1 GB) 7 360 28 660 928 512 ( 26.7 GB) C:UsersVadimDownloads
136 884 260 864 (127.5 GB) 618 167 6 728 695 808 ( 6.3 GB) C:
6 164 135 936 ( 5.7 GB) 90 5 904 556 032 ( 5.5 GB) C:UsersVadimDocumentsWPR Files
4 390 891 520 ( 4.1 GB) 6 4 389 044 224 ( 4.1 GB) C:WindowsLiveKernelReports
4 468 154 368 ( 4.2 GB) 861 4 373 553 152 ( 4.1 GB) C:isosources
4 299 321 344 ( 4.0 GB) 3 4 299 321 344 ( 4.0 GB) C:UsersVadimDocumentsVirtual MachinesWin10Virtual Machines
4 160 749 568 ( 3.9 GB) 1 4 160 749 568 ( 3.9 GB) C:ProgramDataMicrosoftWindowsHyper-VVirtual Machines57269E6F-58C0-4826-AD96-76BAFDE889CD
2 791 686 144 ( 2.6 GB) 8 2 791 686 144 ( 2.6 GB) C:UsersVadimDownloadsODTOfficeData16.0.13231.20262
2 416 443 392 ( 2.3 GB) 35 2 416 443 392 ( 2.3 GB) C:ProgramDataMicrosoftDiagnosisETLLogs
2 470 723 584 ( 2.3 GB) 1 135 2 361 192 448 ( 2.2 GB) C:UsersVadimDownloadsTelegram Desktop
1 773 436 928 ( 1.7 GB) 2 1 773 436 928 ( 1.7 GB) C:UsersVadimMusicplaylists
1 496 182 784 ( 1.4 GB) 323 1 325 723 648 ( 1.2 GB) C:WindowsInstaller
1 172 525 056 ( 1.1 GB) 3 1 172 525 056 ( 1.1 GB) C:UsersVadimAppDataLocalTechSmithSnagItCrashDumps
1 166 528 512 ( 1.1 GB) 95 1 165 533 184 ( 1.1 GB) C:ProgramDataMicrosoftSearchDataApplicationsWindows
5 471 752 192 ( 5.1 GB) 12 553 973 971 456 (928.9 MB) C:WindowsSystem32
886 448 128 (845.4 MB) 894 886 448 128 (845.4 MB) C:UsersVadimAppDataLocalMicrosoftOffice16.0OfficeFileCache
1 780 797 440 ( 1.7 GB) 3 020 863 371 264 (823.4 MB) C:Program Files (x86)Microsoft OfficerootOffice16
773 963 776 (738.1 MB) 84 773 963 776 (738.1 MB) C:WindowsSystem32DriverStoreFileRepositorynvlt.inf_amd64_5e2cc60b5ece0c53
656 900 096 (626.5 MB) 34 656 896 000 (626.5 MB) C:UsersVadimAppDataLocalMicrosoftWindowsExplorer
907 816 960 (865.8 MB) 60 964 608 763 904 (580.6 MB) C:WindowsservicingLCUPackage_for_RollupFix~31bf3856ad364e35~amd64~~19041.685.1.6
840 912 896 (802.0 MB) 59 081 593 412 096 (565.9 MB) C:WindowsservicingLCUPackage_for_RollupFix~31bf3856ad364e35~amd64~~19041.662.1.10
849 870 848 (810.5 MB) 55 488 573 169 664 (546.6 MB) C:WindowsservicingLCUPackage_for_RollupFix~31bf3856ad364e35~amd64~~19041.630.1.6
536 915 968 (512.0 MB) 568 521 830 400 (497.7 MB) C:UsersVadimAppDataLocalPackagesCanonicalGroupLimited.UbuntuonWindows_79rhkp1fndgscLocalStaterootfsvarcacheaptarchives
511 778 816 (488.1 MB) 88 511 778 816 (488.1 MB) C:UsersVadimOneDriveMusic
524 681 216 (500.4 MB) 527 500 322 304 (477.1 MB) C:WindowsSoftwareDistributionDownloadbaa66f28726f701d6508d16b26235240
Сопоставляя результаты, можно увидеть ряд совпадений. Но очевидно, что у diskusage вывод топ-25 лучше конкретизирован. Однако в нем есть и странности.
Например, dfp четко показывает размер папки System Volume Information с теневыми копиями. А diskusage в ней ничего не видит, поэтому в топе ее нет. Точнее, не видит от имени администратора, но прозревает при запуске от имени системы.
Дальнейшие эксперименты подтвердили, что diskusage не способна оценивать дисковое пространство в папках, в которые у администратора нет доступа.
Это существенно снижает ценность анализа, но пока спишем на предварительную версию.
Подсчет размера папок с учетом и без учета жестких ссылок
Размер папки WinSxS долго волновал умы пользователей Windows 
Dism.exe /Online /Cleanup-Image /AnalyzeComponentStore
Component Store (WinSxS) information:
Windows Explorer Reported Size of Component Store : 9.94 GB
Actual Size of Component Store : 9.65 GB
Shared with Windows : 5.64 GB
Backups and Disabled Features : 4.01 GB
Cache and Temporary Data : 0 bytes
Date of Last Cleanup : 2020-12-21 15:53:59
Number of Reclaimable Packages : 9
Component Store Cleanup Recommended : Yes
Утилита diskusage предлагает свой взгляд на этот вопрос. По умолчанию она считает размер только одного экземпляра жесткой ссылки, но с ключом /allLinks учитывает все экземпляры.
Ниже фрагмент вывода двух команд, анализирующих системный диск. В обоих случаях ключ /maxDepth=1 ограничивает глубину вывода одной папкой, т.е. показывает только папки в корне диска. Из результатов я убрал все кроме папки Windows.
diskusage C: /maxDepth=1 /humanReadable /skipReparse /TopDirectory=25
SizeOnDisk Files Directory path
21 543 395 328 ( 20.1 GB) 263 633 C:Windows
diskusage C: /maxDepth=1 /humanReadable /skipReparse /TopDirectory=25 /allLinks
SizeOnDisk Files Directory path
28 009 570 304 ( 26.1 GB) 300 827 C:Windows
Утилита оценивает объем жестких ссылок в папке Windows в 26.1-20.1=6GB, что близко к оценке DISM в 5.64GB. Заодно мы видим количество жестких ссылок — утилита насчитала 37 194, что тоже полезно для исследований. В принципе, можно скриптовать перебор файлов с fsutil, и я когда-то такое делал, но с diskusage явно проще.
Заключение
Я в курсе, что многие читатели предпочитают для анализа дискового пространства приложения с графическим интерфейсом — WinDirStat, Scanner и прочие. Но консольные утилиты очень удобны для удаленной диагностики, а встроенные — незаменимы в ограниченной корпоративной среде. В моей практике dfp вытеснила Scanner даже в домашних условиях.
Причина выпиливания dfp из Windows 10 так и осталась загадкой. Теперь Microsoft возвращает в состав ОС полезный диагностический инструмент. Правда, в стабильную версию он, видимо, попадет только осенью 2021 года, но лучше поздно, чем никогда.
А чем пользуетесь вы?
Неплохой скрипт. Только будет требовать повышенных прав запуска в ОС >= Vista с UAC.
Особенно понравился момент сравнения меня с яндексом 
Сообщение от denisk37
перевод в Gb ведется тупо обрезанием последних 9-ти цифорок.
Дам Вам еще пищу для размышлений.
Только что написал от себя (хоть и деревянный), но рабочий скрипт поразрядного деления (с разг. «деление в столбик»). Т.е. еще другими словами: обход ограничения CMD на предельное значение числового типа данных.
Можете воспользоваться наработкой:
StrDiv.CMD
| Bash | ||
|
И для Вас еще пару идей, которые думаю будет интересно реализовать:
1) такой скрипт не требует повышения прав:
| Bash | ||
|
Где что, разберетесь. Здесь требуется красивый перевод в гигабайты.
Лучше конечно постепенно делить на 1024 и смотреть сколько цифр остается (соответственно такой префикс и подставлять).
2) такой скрипт тоже требует повышенных прав, но он показывает в единицах, уже сконвертированных к приемлемым величинам:
Алгоритм:
1. Берете предыдущую WMIC, прогоняете каждый том под циклом, подставляя в такой текст
select volume c:
detail volume
select volume d:
detail volume
и т.д. постепенно формируете внешний текстовой файл.
2. Выполняете команду
| Bash | ||
|
3. Результат парсите по две строки.
Уфф. Вообщем, по-разному можно.
На чтение 5 мин. Просмотров 5.7k. Опубликовано 23.08.2019
Содержание
- Вот как найти емкость вашего диска, использованное пространство или свободное место
- Как проверить свободное место на жестком диске в Windows
- Подробнее о свободном пространстве диска в Windows
Вот как найти емкость вашего диска, использованное пространство или свободное место
Вы не можете просто добавлять вещи на диск навсегда, будь то основной жесткий диск, маленькая флешка в вашем кармане или гигантский внешний жесткий диск на вашем столе.
Даже жесткий диск емкостью 16 ТБ имеет ограничение: 16 ТБ! Как бы безумно это ни звучало, оно тоже может наполниться. Правда, потребуется два миллиона фотографий высокого качества, но «всего» около 150 полнометражных 4K-фильмов.
Независимо от того, вы поняли – вам может понадобиться время от времени проверять свободное место на диске, особенно если он начинает замедляться или вести себя забавно, что очень часто является непонятным следствием слишком большого количества материала в единственное место.
К сожалению, особенно в операционных системах Windows, вы не получите дружеское предупреждение «Эй, ваш жесткий диск почти заполнен!» . Вместо этого вы получаете странное поведение, загадочные сообщения об ошибках или серьезные проблемы, такие как BSOD.
К счастью, очень легко проверить, сколько свободного места у вас есть на любом из ваших дисков, и это займет всего минуту или две.
Эти шаги работают для Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista и Windows XP.
Как проверить свободное место на жестком диске в Windows
-
В Windows 10 нажмите кнопку «Пуск», а затем Проводник (значок небольшой папки). Если вы этого не видите, проверьте папку Система Windows или введите Проводник файлов в поле поиска.
В Windows 8 или Windows 10 найдите этот компьютер и выберите Этот компьютер .
В Windows 7 или Windows Vista нажмите кнопку «Пуск», а затем – Компьютер .
В Windows XP перейдите в раздел Пуск , а затем Мой компьютер .
Посмотреть, какая версия Windows у меня установлена? если вы не уверены, какой вы используете.
-
В левой части Проводника или Проводника Windows (в зависимости от вашей версии Windows) убедитесь, что Этот компьютер , Компьютер или Мой компьютер выбран (опять же, в зависимости от вашей версии Windows).
Если вы ничего не видите в левой части этого экрана, откройте меню Вид и включите Панель навигации . В старых версиях Windows вместо этого выберите Организовать > Макет > Панель навигации (7 и Vista) или Просмотреть > Панель обозревателя > Папки (XP).
-
Справа найдите диск, на котором вы хотите узнать, сколько свободного места осталось.
В Windows 10 и 8 все устройства хранения перечислены в области Устройства и диски . В Windows 7, Vista и XP Жесткие диски и Устройства со съемным хранилищем перечислены отдельно.
-
В новых версиях Windows прямо под диском вы можете увидеть, сколько на нем осталось свободного места, а также общий размер диска в следующем формате:
Локальный диск (C :) [индикатор места для хранения] 49,0 ГБ без 118 ГБ
Если это все, что вам нужно знать, то все готово! Тем не менее, есть немного больше информации о емкости вашего диска, скрытой чуть глубже:
-
Чтобы узнать больше, щелкните правой кнопкой мыши или удерживайте нажатой клавишу на диске, на котором вы хотите получить больше информации о пространстве хранения, а затем выберите Свойства .
-
На вкладке Общие вы увидите все важные сведения об устройстве хранения, на которое вы смотрите, в байтах, а также в округленном ГБ … свободное место включает:
- Использованное пространство . Это общая сумма каждого фрагмента данных на этом устройстве.
- Свободное пространство . Это разница в общей отформатированной емкости устройства и общей сумме каждого фрагмента данных, хранящихся на нем. Это число указывает, сколько памяти вы можете заполнить.
- Емкость . Это общая емкость диска.
- Также есть круговая диаграмма, показывающая используемое и свободное место на диске, которая помогает визуализировать, сколько места вы используете на этом жестком диске или другом устройстве.
Теперь вы должны точно знать, сколько места на жестком диске доступно на вашем компьютере. Если у вас заканчивается, удалите ненужные файлы или переместите их на другой жесткий диск, на котором больше свободного места.
Другой способ проверить свободное место – с помощью командной строки.Результаты не так легко прочитать, потому что значения представлены в байтах, а не в гигабайтах, но это все еще возможно с этой командой:
wmic логический диск, получить размер, свободное пространство, заголовок
Подробнее о свободном пространстве диска в Windows
Microsoft исторически рекомендовала, чтобы во избежание проблем вы оставляли как минимум 100 МБ свободного места на любом диске, на котором установлена Windows. Однако, поскольку мы видели проблемы на уровнях выше 100 МБ, мы всегда рекомендовали вместо этого 10% свободного места.
Чтобы рассчитать это, просто возьмите число рядом с Capacity из шага 6 и переместите десятичную дробь влево на один пробел. Например, если общий объем просматриваемого жесткого диска составляет 80,0 ГБ, перемещение десятичного разделителя влево делает его равным 8,0 ГБ, а это означает, что вы не должны оставлять свободное место ниже этого конкретного устройства.
В Windows 10 гораздо больше подробностей о том, какие файлы используют емкость вашего диска, можно найти в Настройки > Система > Хранилище . Просто выберите интересующий вас диск, и Windows проанализирует его, разбив его на категории, такие как Система и резервирование , Временные файлы , Приложения и игры , Картинки и другие.
Есть также несколько бесплатных инструментов анализатора дискового пространства, которые вы можете загрузить для Windows 10 и более ранних версий Windows, которые покажут вам, какие файлы и папки занимают больше всего места.
В любой версии Windows, выбрав Очистка диска в свойствах диска (шаг 6 выше), запустите утилиту очистки диска, универсальное средство для удаления файлов, которые больше не нужны Windows.
█ 03.12.2009 14:45
Есть идеи, как штатными средствами в винде получить список жестких дисков и свободное место на них?
█ 03.12.2009 14:46
Без привилегий администратора
█ 03.12.2009 16:08
DISKPART
DISKPART> list disk
Disk ### Состояние Размер Свободно Дин Gpt
——— ———- ——- ——- — —
Диск 0 Подключен 37 GB 0 B
DISKPART> list volume
Том ### Имя Метка ФС Тип Размер Состояние Сведения
———- — ———— —— ———- ——- ——— ———
Том 0 C NTFS Раздел 10 GB Исправен Системны
Том 1 D NTFS Раздел 28 GB Исправен
Том 2 E KINGSTON FAT32 Съемное ус 3826 MB
========
правда, запускал под админом..
надо проверять
█ 03.12.2009 17:57
если в винде есть vbs (а он практически везде есть), то можно так:
сохранить код ниже в файл с расширением vbs и выполнить
должно работать под любой учеткой и из cmd тоже
результаты гонит на экран, но можно перенаправить куда надо
=============================
strComputer = «.»
Set objWMIService = GetObject(«winmgmts:\» & strComputer & «rootcimv2»)
Set colDiskDrives = objWMIService.ExecQuery(«SELECT * FROM Win32_DiskDrive»)
For Each objDrive In colDiskDrives
strDeviceID = Replace(objDrive.DeviceID, «», «\»)
Set colPartitions = objWMIService.ExecQuery («ASSOCIATORS OF {Win32_DiskDrive.DeviceID=»»» & strDeviceID & «»»} WHERE AssocClass = » & «Win32_DiskDriveToDiskPartition»)
For Each objPartition In colPartitions
Set colLogicalDisks = objWMIService.ExecQuery («ASSOCIATORS OF {Win32_DiskPartition.DeviceID=»»» & objPartition.DeviceID & «»»} WHERE AssocClass = » & «Win32_LogicalDiskToPartition»)
For Each objLogicalDisk In colLogicalDisks
Set colDisks = objWMIService.ExecQuery («Select * from Win32_LogicalDisk Where DeviceID = ‘» & objLogicalDisk.DeviceID & «‘»)
For Each objDisk in colDisks
Wscript.Echo objLogicalDisk.DeviceID & » — » & objDisk.FreeSpace & » byte»
Next
Next
Next
Next
=============================
█ 03.12.2009 21:28
Увы, речь о сохранении файлов тоже не идет 
А diskpart у меня вообще что-то не завелся…
█ 04.12.2009 07:09
Олег, сейчас проверил — в Windows XP /2003 есть Diskpart
в Windows 2000 — отсутствует..
█ 04.12.2009 07:12
Да нет, я на терминалке работал, 2003… Такое впечатление, что утилитка просто падала. Но у меня не было админских прав.
█ 04.12.2009 07:28
возможно, из-за прав..
ей много чего можно сделать
C админскими правами в терминальном режиме запускается
==
Цитата:
Для выполнения этой процедуры необходимо входить в группу «Операторы архива» или «Администраторы» на локальном компьютере или получить соответствующие полномочия путем делегирования. Если компьютер присоединен к домену, эту процедуру могут выполнять члены группы «Администраторы домена». При этом по соображениям безопасности рекомендуется использовать команду Запуск от имени.
█ 04.12.2009 09:15
Увы… Имеются только юзерские.
Цитата:
C:>diskpart
Microsoft DiskPart, (
Службам управления дисками не удается завершить эту операцию.
█ 04.12.2009 13:52
Цитата:
OlegON ➤ Увы, речь о сохранении файлов тоже не идет 
А diskpart у меня вообще что-то не завелся…
ну чем вам всем так vbs не нравится? :unsure_mini:
команда дир — устроит? состряпай обычный батник — работает для текущего диска
===================
@echo off
chcp 1251 > nul
for /f «tokens=3 delims= » %%A in (‘dir /s/-c ^|find «байт свободно»‘) do (
echo free: %%A
)
chcp 866 > nul
pause
===================
а вот с количеством и буковками дисков надо еще подумать…
Часовой пояс GMT +3, время: 09:50.
Форум на базе vBulletin®
Copyright © Jelsoft Enterprises Ltd.
В случае заимствования информации гипертекстовая индексируемая ссылка на Форум обязательна.