Далее в статье подробно о том, что делает параметр «Сжать этот диск для экономии места», на что влияет и про другие возможности сжатия данных, которые присутствуют в Windows 11 и Windows 10.
Сжать этот диск для экономии места — прозрачное сжатие файлов на диске средствами NTFS
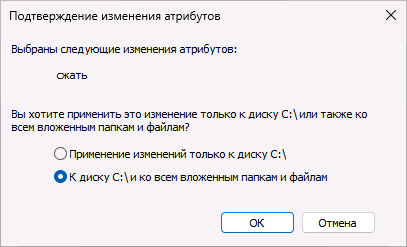
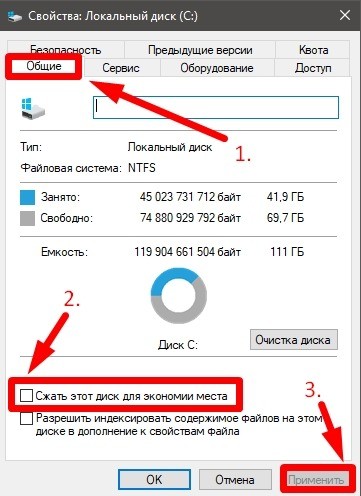
Включив отметку «Сжать этот диск для экономии места», подтвердив применение атрибутов и подождав некоторое время, вы включите встроенную функцию сжатия файлов драйвером файловой системы NTFS. Первоначальное сжатие может занять продолжительное время.
После применения атрибутов файлы на диске будут сжиматься и распаковываться «на лету» — то есть с точки зрения пользователя какого-либо изменения в поведении не произойдёт, кроме появления «стрелок» у значков папок и файлов, обозначающих сжатие.
Несмотря на то, что для компрессии и распаковки используются ресурсы процессора, используемый алгоритм LZNT1 как правило почти не сказывается на производительности современной системы.
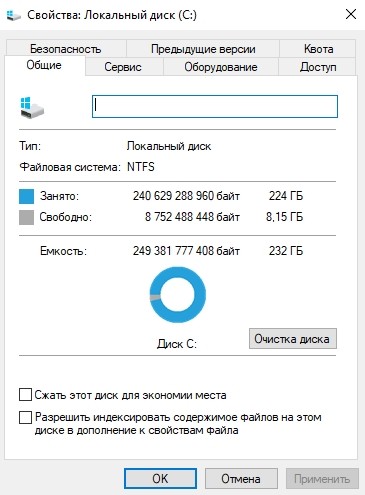
Насколько сильно влияет сжатие NTFS на размер свободного места на диске? Для большинства двоичных файлов — не слишком значительно. Выше был приведен скриншот для системного диска только что установленной Windows 11 без сжатия, а ниже вы можете увидеть результат сжатия:
Сжатие средствами NTFS можно включить не только для диска в его свойствах, но и для папки:
Достаточно зайти в свойства папки, нажать кнопку «Другие» в разделе «Атрибуты» вкладки «Общие» и включить опцию «Сжимать содержимое для экономии места на диске».
Для большинства пользователей включение опции «Сжать этот диск для экономии места» не принесёт каких-либо заметных выгод на современных компьютерах с достаточно объёмными HDD и SSD. Впрочем, вреда в большинстве случаев тоже нет, но потенциально можно допустить более проблематичное восстановление данных при необходимости.
Другие возможности сжатия данных в Windows 11 и Windows 10
В Windows последних версий присутствует ещё одна функция, предназначенная для сжатия файлов операционной системы — CompactOS. Эта функция:
- Была создана для устройств с малым объемом системного диска (планшеты, нетбуки и аналогичные).
- Обеспечивает большую степень сжатия, чем средства файловой системы. Пример
- Применяется к файлам операционной системы.
- Использует другой алгоритм сжатия (XPRESS4K) и позволяет выбрать другой алгоритм для исполняемых файлов.
- Потенциально может в большей степени влиять на производительность системы при работе, чем сжатие NTFS, но обычно это влияние не критично.
Для настройки CompactOS можно использовать командную строку, запущенную от имени Администратора и инструмент compact.exe. В отдельных случаях при недостатке места на диске сжатие может быть предложено во встроенной утилите «Очистка диска». Несколько примеров команд, а также скриншоты изменения свободного места на диске на той же системе, с которой проводились эксперименты ранее в этой статье:
В случае, если вы не испытываете недостатка в месте на системном диске, включать CompactOS не имеет смысла, а если ваше устройство оснащено миниатюрным SSD или eMMC, не исключено, что функция уже включена. Более подробно о функции я ранее писал в материале про сжатие CompactOS в Windows.
При нехватке места на диске в Windows 10 и более ранних версиях многие пользователи рассчитывают на флажок Сжать этот диск для экономии места. Разберемся, стоит ли его включать, и сколько гигабайт свободного места можно получить, в этой статье.
Как работает функция Сжать этот диск в Windows
Опция стала доступна при введении формата накопителя NTFS. На FAT она будет неактивна. При включении сжатия Windows на лету архивирует записываемые файлы. В некоторых случаях, например, для текстов, это дает заметную экономии дискового пространства. В случае видеороликов — почти никакой.
Эффективность сжатия подчиняется тому же закону, как и архивация. Используется похожий алгоритм.
Но есть у режима сжатия и оборотная сторона. Для архивации (при записи) и разархивации (при чтении) используется процессор. Если у вас слабый компьютер, то после включения этой функции он станет еще медленней, хотя свободного места на диске и прибавится.
Какой эффект дает включение Сжатия диска и когда его стоит включить
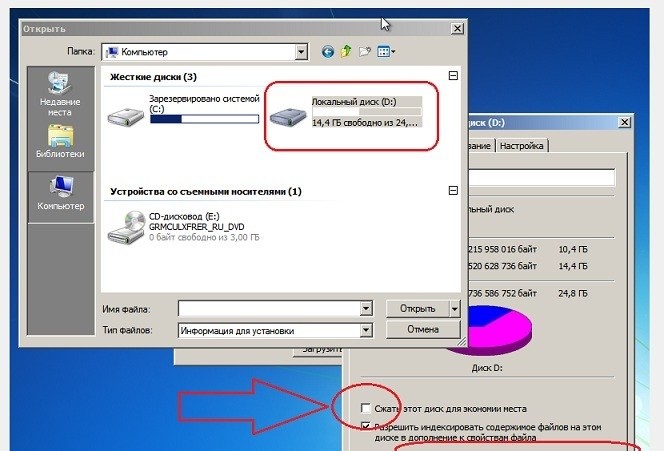
Проверить, сколько места освободит Windows, если вы включите Сжать диск для экономии места, можно самостоятельно. Войдите в свойства накопителя и установите эту галку.
Сжать можно только сам диск или все папки на нем.
В моем случае на диске D хранятся видеоролики, игры. Эффект составил чуть меньше 20 Гб. В условиях моего SSD вна 256 Гб это серьезная цифра.
Сжатие диска C принесет меньше пользы. По следующим соображениям:
- Читать и записывать файлы Windows станет медленнее.
- Большинство системных файлов уже упакованы. Поэтому выигрыша в размере не будет.
Для накопителей с данными, особенно редко используемыми, сжатие имеет смысл. Но тут стоит учитывать тип файлов. Тексты сжимаются эффективнее, фото и видео почти нет. А вот замедление чтения/записи гарантированно. Хотя оно может оказаться незаметным, если на компьютере стоит производительный процессор и достаточно оперативной памяти.
Функция автоматического сжатия файлов впервые появилась в восьмой версии Windows. В «десятке» она получила более логичный алгоритм работы, позволяющий в автоматическом режиме работать с большим количеством файлов. За счет этого пользователи получили возможность работать сразу с данными всего диска или раздела. Перед тем, как решите на Windows 10 сжать диск «С» или любой другой том, необходимо знать, как правильно это делать.
Как сжать том в Windows 10
Перед тем, как запустить процедуру сжатия системного тома Windows 10, нужно удостовериться в необходимости ее исполнения. В частности, есть несколько факторов, говорящих о том, что манипуляция не принесет пользы.
К таковым относятся:
- использование жесткого диска – никто не запрещает пользоваться функцией на «хардах», но в результате сжатия ОС может потерять в производительности (актуально для слабых по мощности компьютеров, работающих с жесткими дисками с малыми оборотами);
- использование процессора с малым количеством ядер, которые работают на низкой частоте – для открытия сжатых файлов необходимо больше ресурсов, соответственно, на ПК со слабым процессором выполненное сжатие системного тома может сильно сказаться на производительности системы.
Если основным хранилищем компьютера является твердотельный накопитель, а система работает на достаточно мощном процессоре, то в некоторых случаях процедура получения большего количества свободного места за счет сжатия будет актуальна. Ее можно запустить несколькими способами:
- через меню управления дисками;
- через Командную строку;
- через оболочку Windows Power Shell.
Управление дисками
Запуск сжатия через службу управления дисковым пространством в целях экономии места на системном томе выполняется следующим образом:
- Запуск службы. В меню «Выполнить» («Win+R») нужно ввести имя файла «diskmgmt.msc».
- Выбор диска для сжатия. Нужно кликнуть правой клавишей мыши по нужному разделу и выбрать вариант «Сжать том».
- Указать необходимый объем, который будет подвержен сжатию, в мегабайтах.
- Дождаться окончания выполнения процедуры.
В Командной строке
Запустить утилиту можно с помощью базовых команд консоли. Для этого нужно:
- Открыть Командную строку с правами Администратора.
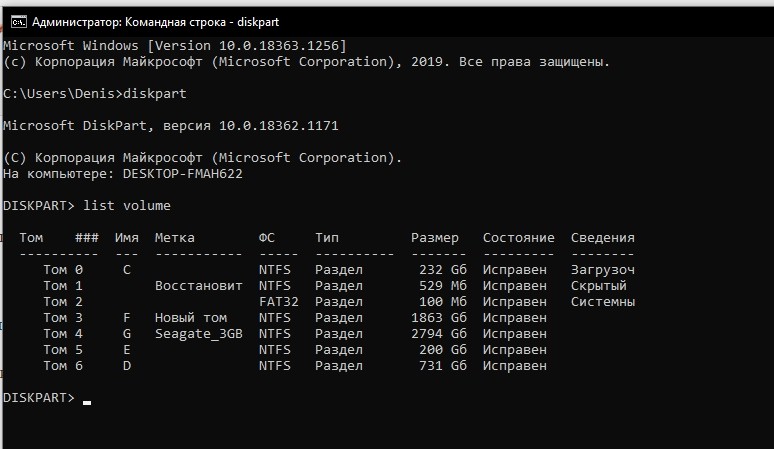
- Ввести «diskpart» для открытия утилиты.
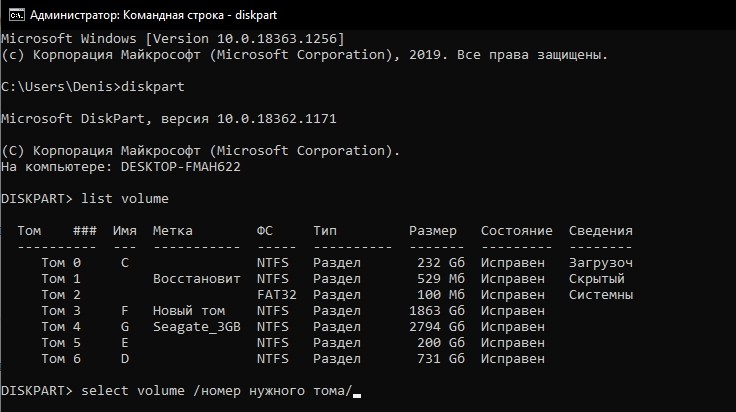
- Ввести «list volume» для отображения установленных накопителей и разделов.
- Ввести «select volume /номер нужного тома/».
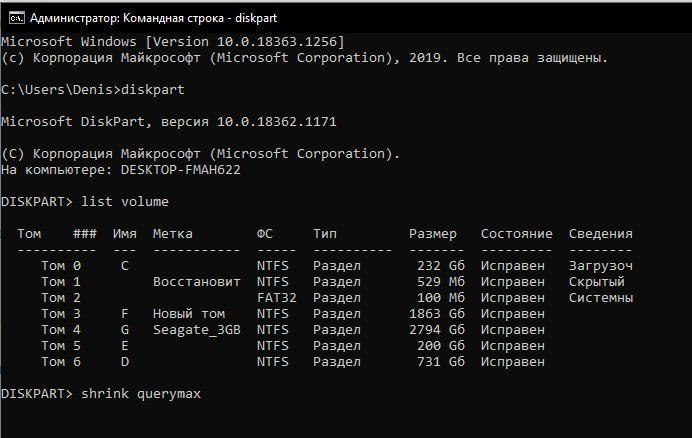
- Ввести «shrink querymax» для определения максимально допустимого объема памяти, который можно подвергнуть сжатию.
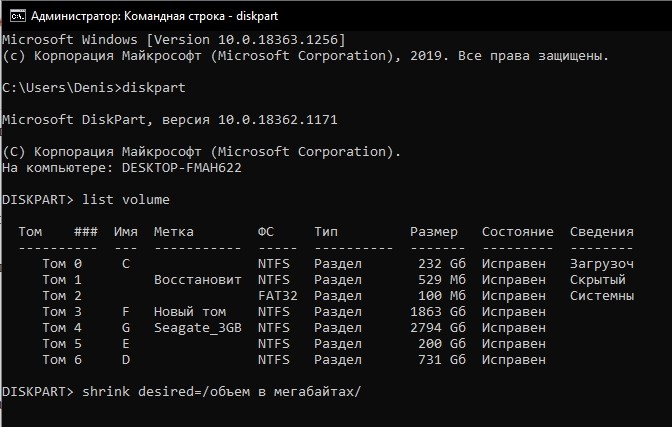
- Ввести «shrink desired=/объем в мегабайтах/».
- Дождаться завершения операции.
Через Power Shell
Альтернативный вариант сжатия с помощью команд – это использование оболочки Windows Power Shell. Для выполнения задачи нужно следовать пошаговому алгоритму:
- Запуск консоли Power Shell с правами учетной записи Администратора.
- Ввод «get-partition» для отображения томов.
- Ввод «get-partitionsupportedsize-driveletter “буква раздела, который нужно подвергнуть сжатию”».
- Ввод «resize-partition-driveletter “буква раздела, который нужно сжать” -size “объем, который нужно обработать, указанный в гигабайтах”».
Отмена сжатия диска
Часто дополнительное пространство на накопителе необходимо для установки обновления. Это связано с тем, что ОС сначала скачивает необходимые файлы, для чего, естественно, необходимо место, и только после этого производит установку, что, опять же, требует отдельного объема памяти.
В такой ситуации после инсталляции обновлений продолжать работать с уменьшенным системным томом бессмысленно, так как сжатие, в любом случае, сказывается на производительности. Поэтому будет целесообразно отменить процедуру.
Сделать это можно следующим образом:
- Открыть «Компьютер».
- Нажать правой клавишей мыши по диску, для которого будет выполняться отмена, и выбрать вариант «Свойства».
- В разделе «Общие» убрать галку с пункта «Сжать для экономии места».
- Подтвердить изменения.
- Проигнорировать окно отказа в доступе, нажав кнопку «Продолжить».
- Дождаться окончания выполнения операции.
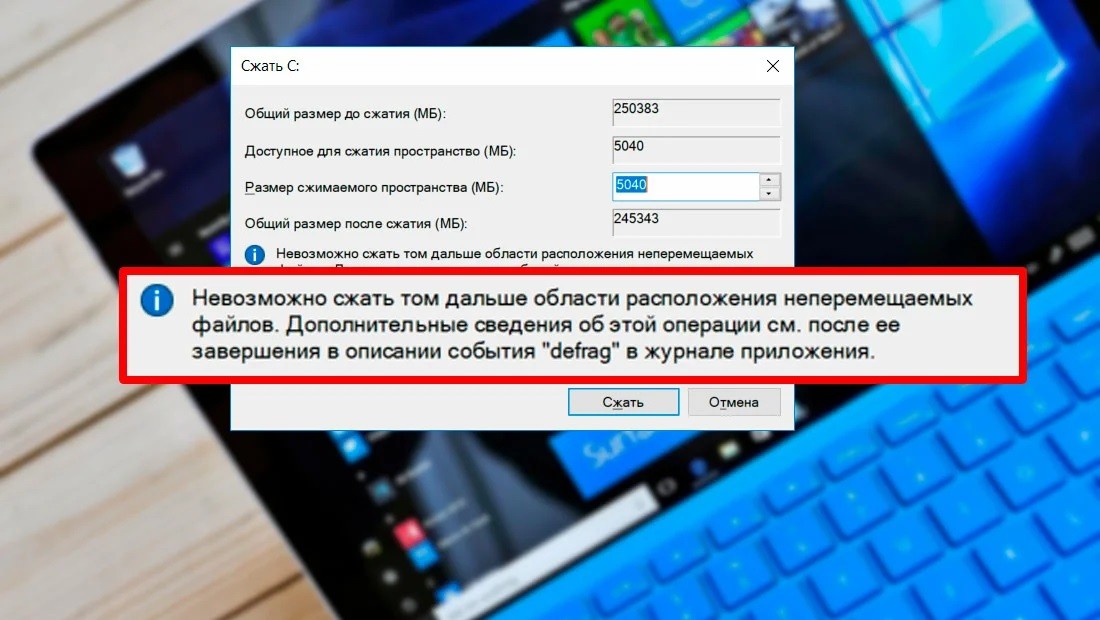
Не сжимается том
При запуске утилиты сжатия дисков возможны ошибки. Причины этого могут заключаться в следующем:
- активирована политика запрета на выполнение сжатия раздела или разделов;
- часть объема накопителя, отправленного в обработку, используется в качестве ресурсов для файла подкачки ОС;
- на томе расположены файлы, в отношении которых установлен запрет на перемещение.
Вам помогло? Поделитесь с друзьями — помогите и нам!
The two compress options aren’t the same, but more on that later. The first thing to note is that compressing data is not the best solution when the drive is full. NTFS will suffer badly from lack of space, because there are no more good places to allocate new files or move old files around and fragmentation will increase. Especially when it begins to use the reserved space for the MFT then the MFT might become fragmented and worse things may happen
So at first some other things need to be done:
-
Reduce pagefile size. Your system will crawl to death if just 1-3GB of pagefile is used. But you can’t disable it entirely (at least not a good idea), so a lower limit of 1GB and upper limit of 4GB might be a fine choice. That will save you a few GBs compared to the default setting. You can add more page files on other drives if available
-
Reduce hiberfil.sys size. Open cmd as admin and run
powercfg /h /size 40to set the size to 40% of your RAM. From Windows 7 onward it defaults to 75% the amount of RAM, so setting it to 50% will save you 3GB of disk space. You can also turn it off completely withpowercfg /h offif you don’t need hibernation, or if you want to turn off hibernation while still enabling fast boot then usepowercfg /h /type reducedwhich shrinks the file to only 20% -
Clean up the WinSxS folder with the
DISMcommand. For more information read How to Reduce the Size of Your WinSXS Folder -
Check your data usage and move/remove some unnecessary files
You can use some tools like WizTree, TreeSize or WinDirStat. You’ll be surprised to see how big some files/folders are, esp. some temp and cache folders. WizTree is likely the fastest and more correct one because it reads information directly from the MFT. Remember to run them as admin
For more suggestions see How can I visualize the file system usage on Windows? or The Four Best Free Tools to Analyze Hard Drive Space on Your Windows PC
-
If you have another HDD then don’t store too many unnecessary things on the system drive. Leave it for apps and files that need fast access
- Move the documents folders to another drive
- Move the store app install folder and save folder
- Some other folders can also be moved by changing some configurations, or by creating a symlink. For example many folders in WindowsSystem32 or Program Files can be moved to HDD. Some tutorials on that
- Moving Windows folders around with Junction links (mklink)
- Using mklink on Windows to move data off of SSDs
- How to Reclaim Space Used by Games with Symbolic Links
- How to Maximize Space on your SSD using Symbolic Links
-
Delete Windows.old if you don’t need to roll back to the previous version, or back it up and remove it
- How to copy windows.old folder to another drive?
- Copy/Move Windows.old Folder to External Hard Drive
Just doing the first 2 steps above saves you tons of space immediately. Then after doing everything if more space is still needed then just compact the OS. By deleting files first you also make it faster to compress the OS. The performance difference is often negligible
The CompactOS feature does indeed worth it on small SSDs compared to HDDs. My old laptop has a 1TB HDD with a 32GB SSD cache. I’ve tried installing Windows onto the 32GB SSD and it ran noticeably smoother than on the HDD+cache
Regarding your questions:
I’m not sure whether there are any performance penalty associating with compressing the OS drive.
Compressing files always have a CPU time penalty. That doesn’t mean that it’ll be slow though, since on slow storage devices like HDDs that penalty might be far less than the wasted time on accessing/reading the data from HDD. That’s why sometimes compressing easily-compressed data will make it faster to access. One example is that hibernation in newer Windows compresses data before writing to disk, which makes shutdown much faster because the CPU can compress faster than the drive can write
The difference may be less obvious on SSDs, but there’s no way to know that for sure except benchmarking for your specific situation. Each use case is different, and not all disks are created equal. For example old SSDs may run at only ~200MB/s which is just about as fast as an HDD nowadays (but their obvious advantage is the very fast access time and high IOPs), whereas newer algorithms like LZ4 (which is used in Linux’s zram) or Zstd can sustain ~2-5GB/s which is even faster than modern SSDs. See
- With SSDs and Compact, Windows can speed up even more for an example where CompactOS boosts system performance
- I tested 25 games against the Windows Compact function: 51GB more free space, and all the games run with no performance issues
- Gaming & NTFS Compression?
There’s often no need to worry, because Windows will do a benchmark while installing to assess whether CompactOS should be enabled or not. Although after installing apps and things that benchmark result may not be correct anymore and you may want to do a reassessment yourself
And I’m not even sure whether this option is the same with «Compress this drive to save disk space» at the C drive property as per below
Basically both use the compression feature of NTFS and can be configured by compact.exe, but there are many major differences
-
The «Compress your OS drive» (i.e. CompactOS) feature uses the newly introduced compression algorithms XPRESS* and LZX in Windows 10’s NTFS. They’re designed for efficient storage for «static» files that don’t change much (like executables)
OTOH the «Compress this drive to save disk space» feature uses LZNT1 algorithm and is designed for compressing frequently changed data files for optimum performance. That means it’ll be faster but the compression ratio will not be as high. It’s like checking the «Compress contents to save disk space» option for all files and folders on the drive
-
Files compacted by CompactOS will not be marked as compressed (either shown in blue or with double arrows) if that feature is enabled
-
CompactOS compresses selected system files, while NTFS whole-disk-compression compresses every file on the disk
In fact you can use the new algorithms for CompactOS for any user files, but you can’t do on-the-fly editing on them, as they’re designed for static read-only files like mentioned above. Writing to those files will uncompress them. For more information about that as you can read NTFS compressed folders: is it possible to tweak compression ratio?
The random on-the-fly write ability also makes the «Compress this drive to save disk space» even worse for your use case, because it increases fragmentation significantly. CompactOS compresses the whole file (AFAIK) like a *.cab or *.wim file so you’ll get a contiguous file. OTOH NTFS transparent compression works by splitting the file to 16-cluster chunks and compress them separately. Each chunk will be a fragment after that, which makes your contiguous file now has tons of holes between the chunks.
You may think «why worry about that» but SSD’s complete immunity to fragmentation is a myth! For fast operations and small metadata size modern file systems store files as extents which is a file’s contiguous section on disk, so each fragment will be stored as a separate extent. Hence a file with 1000 fragments will consume more space in the MFT for the metadata compared to a 2-fragment one, and the CPU also needs more time to parse them to get the next block of data. As a result Windows defragmenter still does some mild defragmentation for SSD drives to optimize metadata usage
Further reading:
- File Compression versus Compact OS in Win 10?
- How can Windows 10 function on as little as 32 GB of disk space?
The link given by Xen2050 is also good. It shows that even with the drive compression feature the difference is not that much, and in some cases it’ll be faster, as I mentioned above
The two compress options aren’t the same, but more on that later. The first thing to note is that compressing data is not the best solution when the drive is full. NTFS will suffer badly from lack of space, because there are no more good places to allocate new files or move old files around and fragmentation will increase. Especially when it begins to use the reserved space for the MFT then the MFT might become fragmented and worse things may happen
So at first some other things need to be done:
-
Reduce pagefile size. Your system will crawl to death if just 1-3GB of pagefile is used. But you can’t disable it entirely (at least not a good idea), so a lower limit of 1GB and upper limit of 4GB might be a fine choice. That will save you a few GBs compared to the default setting. You can add more page files on other drives if available
-
Reduce hiberfil.sys size. Open cmd as admin and run
powercfg /h /size 40to set the size to 40% of your RAM. From Windows 7 onward it defaults to 75% the amount of RAM, so setting it to 50% will save you 3GB of disk space. You can also turn it off completely withpowercfg /h offif you don’t need hibernation, or if you want to turn off hibernation while still enabling fast boot then usepowercfg /h /type reducedwhich shrinks the file to only 20% -
Clean up the WinSxS folder with the
DISMcommand. For more information read How to Reduce the Size of Your WinSXS Folder -
Check your data usage and move/remove some unnecessary files
You can use some tools like WizTree, TreeSize or WinDirStat. You’ll be surprised to see how big some files/folders are, esp. some temp and cache folders. WizTree is likely the fastest and more correct one because it reads information directly from the MFT. Remember to run them as admin
For more suggestions see How can I visualize the file system usage on Windows? or The Four Best Free Tools to Analyze Hard Drive Space on Your Windows PC
-
If you have another HDD then don’t store too many unnecessary things on the system drive. Leave it for apps and files that need fast access
- Move the documents folders to another drive
- Move the store app install folder and save folder
- Some other folders can also be moved by changing some configurations, or by creating a symlink. For example many folders in WindowsSystem32 or Program Files can be moved to HDD. Some tutorials on that
- Moving Windows folders around with Junction links (mklink)
- Using mklink on Windows to move data off of SSDs
- How to Reclaim Space Used by Games with Symbolic Links
- How to Maximize Space on your SSD using Symbolic Links
-
Delete Windows.old if you don’t need to roll back to the previous version, or back it up and remove it
- How to copy windows.old folder to another drive?
- Copy/Move Windows.old Folder to External Hard Drive
Just doing the first 2 steps above saves you tons of space immediately. Then after doing everything if more space is still needed then just compact the OS. By deleting files first you also make it faster to compress the OS. The performance difference is often negligible
The CompactOS feature does indeed worth it on small SSDs compared to HDDs. My old laptop has a 1TB HDD with a 32GB SSD cache. I’ve tried installing Windows onto the 32GB SSD and it ran noticeably smoother than on the HDD+cache
Regarding your questions:
I’m not sure whether there are any performance penalty associating with compressing the OS drive.
Compressing files always have a CPU time penalty. That doesn’t mean that it’ll be slow though, since on slow storage devices like HDDs that penalty might be far less than the wasted time on accessing/reading the data from HDD. That’s why sometimes compressing easily-compressed data will make it faster to access. One example is that hibernation in newer Windows compresses data before writing to disk, which makes shutdown much faster because the CPU can compress faster than the drive can write
The difference may be less obvious on SSDs, but there’s no way to know that for sure except benchmarking for your specific situation. Each use case is different, and not all disks are created equal. For example old SSDs may run at only ~200MB/s which is just about as fast as an HDD nowadays (but their obvious advantage is the very fast access time and high IOPs), whereas newer algorithms like LZ4 (which is used in Linux’s zram) or Zstd can sustain ~2-5GB/s which is even faster than modern SSDs. See
- With SSDs and Compact, Windows can speed up even more for an example where CompactOS boosts system performance
- I tested 25 games against the Windows Compact function: 51GB more free space, and all the games run with no performance issues
- Gaming & NTFS Compression?
There’s often no need to worry, because Windows will do a benchmark while installing to assess whether CompactOS should be enabled or not. Although after installing apps and things that benchmark result may not be correct anymore and you may want to do a reassessment yourself
And I’m not even sure whether this option is the same with «Compress this drive to save disk space» at the C drive property as per below
Basically both use the compression feature of NTFS and can be configured by compact.exe, but there are many major differences
-
The «Compress your OS drive» (i.e. CompactOS) feature uses the newly introduced compression algorithms XPRESS* and LZX in Windows 10’s NTFS. They’re designed for efficient storage for «static» files that don’t change much (like executables)
OTOH the «Compress this drive to save disk space» feature uses LZNT1 algorithm and is designed for compressing frequently changed data files for optimum performance. That means it’ll be faster but the compression ratio will not be as high. It’s like checking the «Compress contents to save disk space» option for all files and folders on the drive
-
Files compacted by CompactOS will not be marked as compressed (either shown in blue or with double arrows) if that feature is enabled
-
CompactOS compresses selected system files, while NTFS whole-disk-compression compresses every file on the disk
In fact you can use the new algorithms for CompactOS for any user files, but you can’t do on-the-fly editing on them, as they’re designed for static read-only files like mentioned above. Writing to those files will uncompress them. For more information about that as you can read NTFS compressed folders: is it possible to tweak compression ratio?
The random on-the-fly write ability also makes the «Compress this drive to save disk space» even worse for your use case, because it increases fragmentation significantly. CompactOS compresses the whole file (AFAIK) like a *.cab or *.wim file so you’ll get a contiguous file. OTOH NTFS transparent compression works by splitting the file to 16-cluster chunks and compress them separately. Each chunk will be a fragment after that, which makes your contiguous file now has tons of holes between the chunks.
You may think «why worry about that» but SSD’s complete immunity to fragmentation is a myth! For fast operations and small metadata size modern file systems store files as extents which is a file’s contiguous section on disk, so each fragment will be stored as a separate extent. Hence a file with 1000 fragments will consume more space in the MFT for the metadata compared to a 2-fragment one, and the CPU also needs more time to parse them to get the next block of data. As a result Windows defragmenter still does some mild defragmentation for SSD drives to optimize metadata usage
Further reading:
- File Compression versus Compact OS in Win 10?
- How can Windows 10 function on as little as 32 GB of disk space?
The link given by Xen2050 is also good. It shows that even with the drive compression feature the difference is not that much, and in some cases it’ll be faster, as I mentioned above