|
1. |
I Я The Письмо |
|
2. |
Bread Хлеб Answers Ответы |
|
3. |
The Об I Мне |
Обороты, состоящие
из местоимения itс глаголом
в страдательном залоге, переводятся
неопределенно-личными оборотами:
It
is said… Говорят…
It was
said… Говорили…
Itisknown…
Известно…
It
was thought…Думали, полагали…
It
is reported… Сообщают…
It
was reported…Сообщали…и т.п.
|
|
Для |
Упр.
106. Составьте предложения, употребляя
страдательный залог.
Simple Present
1)
the documents / print; 2) the window / open; 3) the shoes / buy; 4)
the car / wash; the litter / throw away; 5) the letter / send; 6)
the book / read / not; 7)the songs / sing / not; 
not; 9) the shop / close / not.
Simple
Past
1)
the test / write; 2) the table / set; 3) the cat / feed; 4) the
lights / switch on; 5) the house / build; 6) dinner / serve ; 7) this
computer / sell / not; 
/ not; 10) the children / pick up / not.
Simple
Future
1)
the exhibition / visit; 2) the windows / clean; 3) the message /
read; 4) the thief / arrest; 5) the photo / take; 6) these songs /
sing; 7) the sign / see / not ; 
9) credit cards / accept / not; 10) the ring / find / not.
Present
Perfect
1)
the postcard / send; 2) the pencils / count; 3) the door / close; 4)
the beds / make; 5) the mail / write; 6) the trees / plant; 7) the
money / spend; 
the people / inform / not
Упр.
107. Переведите, обращая внимание на
залог:
1.
He was much spoken about. 2. New subjects will be studied next term.
3. The text has already been written by them. 4. The text is being
translated at the moment. 5. This book was written by our teacher. 6.
The work will have been done when he comes. 7. The letter had been
written before we came. 8. These toys are made in Japan. 9. They can
be seen in our library every day. 10. The delegation is headed by the
Prime Minister. 11. The child was often left home alone. 12. These
houses were built last year. 13. All letters had been written when we
came. 14. This film is much spoken about. 15. The machine is
being tested now. 16. His work has been already finished. 17. I was
told to wait for him. 18. Your letter will have been answered by
Monday. 19. The experiment was being carried out from ten till twelve
o’clock. 20. Children under sixteen will not be admitted here.
Упр.108.
Раскройте скобки,
употребляя глаголы
в нужном
времени и
залоге
Simple
Present
1. He
(sell) cars. 2. The blue car (sell) . 3. In summer, more ice-cream
(eat) than in winter. 4. She (call) her grandparents every Friday.
5. The letters (type) . 6. He (take) his medicine every day. 7.
Jane (take / not) to school by her father. 8. We (go) to school by
bus. 9. She (work / not) for a bank. 10. Milk (keep) in the
refrigerator.
Simple
Past
1. They
(visit) their granny. 2. We (visit) by our teacher. 3. My friend
Paul (bear) in Dallas. 4. She (go) to school in Boston. 5. Antony
(grow up) in the country. 6. The new shopping centre (build) last
year. 7. The film (produce / not) in Hollywood. 8. Barbara (know)
James very well. 9. The jewels (hide / not) in the cellar. 10. We
(spend / not) all day on the beach.
Future
Simple
1.
The house (build) here. 2. You (send) home. 3. I (eat) an
ice-cream. 4. We (go) home now. 5. I (help) you. 6. The match (win
/ not) by our team. 7. The weather (improve / not) tomorrow. 8. The
trees (cut) down. 9. The meeting (cancel / not) . 10. They (do /
not) that again.
Present
Perfect
1. The car
(steal) . 2. I (bake) a cake. 3. My friends (buy) a house. 4. The
cup (put) on the table. 5. Trees (plant) in the street. 6. The boy
(fall / not) off his bike. 7. I (bite / not) by a snake. 8. He
(step) on my toe. 9. We (walk) all the way home. 10.She(pickup/not)byafriend.
Упр.109. Раскройте
скобки, употребляя глаголы в нужном
времени и залоге:
1.
I’m not reading these books today. They (return) to the library. 2.
The paintings (exhibit) till the end of the month. 3. Why your home
task (not do)? 4. She was taken to the hospital today, and (operate)
tomorrow morning. 5. This room (use) only on special occasions. 6.
Bicycles must not (leave) here. 7. This newspaper (not read). 8.
Dictionaries may not (use) at the examination. 9. Usually this street
(sweep) every day, but it (not sweep) yesterday. 10. This book
(leave) in the classroom yesterday; it (find) by the teacher. 11.
Thousands of new houses (build) every year. 12. This room (not use),
for a long time. 13. The children are very excited this morning. They
(take) to the circus this afternoon.
Упр.110.
Перепишите предложения, употребляя
страдательный залог.
Simple
Present
1.
He opens the door. 2. We set the table. 3. She pays a lot of money.
4. I draw a picture. 5. They wear blue shoes. 6. They don’t help
you. 7. He doesn’t open the book. 8. You do not write the letter.
9. Does your mum pick you up? 10. Does the police officer catch the
thief?
Future
Simple
1.
Jane will buy a new computer. 2. Her boyfriend will install it. 3.
Millions of people will visit the museum. 4. Our boss will sign the
contract. 5. You will not do it. 6. They will not show the new
film. 7. He won’t see Sue. 8. They will not ask him. 9. Will the
company employ a new worker? 10. Will the plumber repair the shower?
Present Perfect
1.
Kerrie has paid the bill. 2. I have eaten a hamburger. 3. We have
cycled five miles. 4. I have opened the present. 5. They have not
read the book. 6. You have not sent the parcel. 7. We have
not agreed to this issue. 8. They have not caught the thieves. 9.
Has she phoned him? 10. Have they noticed us?
Modal
Verbs
1.
I can answer the question. 2. She may carry the box. 3. You should
open the window. 4. We might play cards. 5. You ought to wash the
car. 6. He must fill in the form. 7. They need not buy bread. 8.
He could not read the sentence. 9. Must the teacher test our
English? 10. Could Jenny lock the door?
Present
Continuous
1.
Sheila is drinking a cup of tea. 2. My father is washing the car.
3. Farmer Joe is milking the cows. 4. She is taking a picture of
him. 5. I am writing a poem. 6. We are not playing football. 7. He
is not wearing a tie. 8. Is she preparing the party? 9. Are they
talking about the meeting? 10. Is she watering the flowers?
Past
Continuous
1.
We were talking about Francis. 2. He was playing the guitar. 3. She
was watching a film. 4. I was repairing their bikes. 5. They were
not eating dinner. 6. We were not painting the gate. 7. You were not
driving him home. 8. He was not feeding the dogs. 9. Was she reading
these lines? 10. Were they carrying bags?
Past
Perfect
1.
I had worn blue shoes. 2. Joe had cleaned the tables. 3. We had
lost the key. 4. They had started a fight. 5. I had read an
article. 6. I had not closed the window. 7. They had not bought the
paper. 8. She had not noticed me. 9. Had she solved the problem? 10.
Had he recorded that song?
Future
Perfect
1.
Frank will have ordered the drinks. 2. You will have spent all the
money. 3. I will have taken the dog for a walk. 4. She will have
sold the car. 5. They will have solved the problem. 6. She will
not have read the book. 7. They will not have trusted him. 8. He
won’t have rung Barbara. 9. Will they have paid the bill? 10. Will
you have washed my socks?
|
|
Ключи к Упр.106. 1) |
Simple
Past
1)
The test was written. 2) The table was set. 3) The cat was fed. 4)
The lights were switched on. 5) The house was built. 6) The dinner
was served. 7) This computer was not sold. 
stopped. 9) The tables were not cleaned. 10) The children were not
picked up.
Simple
Future
1)
The exhibition will be visited. 2) The windows will be cleaned. 3)
The message will be read. 4) The thief will be arrested. 5) The
photo will be taken. 6) These songs will be sung. 7) The sign will
not be seen. 
not be accepted. 10) The ring will not be found.
Present
Perfect
1)
The postcard has been sent. 2) The pencils have been counted. 3) The
door has been closed. 4) The beds have been made. 5) The mail has
been written. 6) The trees have been planted. 7) The money has been
spent. 
paid. 10) The people have not been informed.
Упр.
107. 1.
О нем много говорили. 2. Новые предметы
будут изучаться в следующем семестре.
3. Текст был уже написан ими. 4. Текст
сейчас переводят. 5. Книга была написана
нашим учителем. 6. Работа будет сделана
к тому времени когда он придет. 7. Письмо
было написано до того, как мы пришли. 8.
Игрушки сделаны в Японии. 9. Их можно
увидеть в нашей библиотеке каждый день.
10. Делегацию возглавляет премьер-министр.
11. Ребенка часто оставляли дома одного.
12. Эти дома были построены в прошлом
году. 13. Все письма были написаны к тому
времени, когда мы пришли. 14. Об этом
фильме много говорят. 15. Машину испытывают
сейчас. 16. Его работа уже окончена. 17.
Мне сказали подождать его. 18. На ваше
письмо ответят к понедельнику. 19.
Эксперимент проводился с 10 до 12. 20. Детей
до 16 здесь не принимают.
Упр.108.
Simple
Present
1.
Sells. 2. Is sold . 3. Is eaten. 4. Calls. 5. Are typed . 6. Takes.
7. Is not taken. 8. Go. 9. Doesn’t work.
10.
Is kept.
Simple
Past
1.
Visited. 2. Were visited. 3. Was born. 4. Went. 5. Grew up. 6. Was
built. 7. Was not produced. 8. Knew.
9.
Were not hidden. 10. Did not spend.
Future
Simple
1.
Will be built. 2. Will be sent. 3. Shall eat. 4. Shall go. 5. Shall
help. 6. Will not be won. 7. Will not improve. 8. Will not be cut. 9.
Will not be cancelled. 10. Will not do.
Present
Perfect
1.
Has been stolen. 2. Have baked. 3. Have bought. 4. Has been put. 5.
Have been planted. 6. Hasn’t fallen. 7. Haven’t bitten. 8. Has
stepped. 9. Have walked. 10.
Hasn’t been picked up.
Упр.109.
1.
Will be returned. 2. Will have been exhibited. 3. Why wasn’t your
home task done? 4. Will be operated. 5. Is used. 6. Must not be left.
7. Is not read. 8. May not be used. 9. Is swept, was
not
swept. 10. Was left, was found. 11. Are built. 12. Has not been used.
13. Will be taken.
Упр.110.
Simple Present
1.
The door is opened by him. 2. The table is set by us. 3. A lot of
money is paid by her. 4. A picture is drawn by me. 5. Blue shoes are
worn by them. 6.You are not helped by them. 7. The book is not opened
by him. 8. The letter is not written by you. 9. Are you picked up by
your mum? 10. Is the thief caught by the police officer?
Future
Simple
1.
A new computer will be bought by Jane. 2. It will be installed by her
boyfriend. 3. The museum will be visited by millions of people. 4.
The contract will be signed by the boss. 5. It will not be done. 6.
The new film will not be shown by them. 7. Sue won’t be seen. 8. He
will not be asked. 9. Will a new worker be employed by the company?
10. Will the shower be repaired by the plumber?
Present
Perfect
1.
The bill has been paid by Kerrie. 2. A hamburger has been eaten by
me. 3. Five miles have been cycled by us. 4. The present has been
opened by me. 5. The book has not been read by them. 6. The parcel
has not been sent. 7. This issue has not been agreed. 8. The thieves
have not been caught. 9. Has he been phoned? 10. Have we been
noticed?
Modal
Verbs
1.
The question can be answered. 2. The box may be carried. 3. The
window should be opened. 4. Cards might be played. 5. The car oudght
to be washed. 6. The form must be filled in. 7. Bread need not be
bought. 8. The sentence could not be read. 9. Must our English be
tested by the teacher? 10. Could the door be locked by Jenny?
Present
Continuous
1.
A cup of tea is being drunk by Sheila. 2. The car is being washed by
my father. 3. The cows are being milked by farmer Joe. 4. A picture
of him is being taken. 5. A poem is being written. 6. Football is not
being played. 7. A tie is not being worn. 8. Is the party being
prepared? 9. Is the meeting being talked about? 10. Are the flowers
being watered?
Past
Continuous
1.
Francis was being talked about. 2. The guitar was being played. 3. A
film was being watched. 4. Their bikes were being repaired by me. 5.
Dinner was not being eaten. 6. The gate was not being painted. 7. He
was not being driven home. 8. The dogs were not being fed. 9. Were
these lines being read? 10. Were the bags being carried?
Past
Perfect
1. Blue shoes had been worn.
2. The tables had been cleaned. 3. The key had been lost. 4. A
fight had been started. 5. An article had been read. 6. The window
had not been closed. 7. The paper had not been bought. 8. I had not
been noticed. 9. Had the problem been solved? 10. Had the song been
recorded?
Future
Perfect
1.
The drinks will have been ordered. 2. All the money will have been
spent. 3. The dog will have been taken for a walk. 4. The car will
have been sold. 5. The problem will have been solved. 6. The book
will not have been read. 7. He will not have been trusted. 8. Barbara
won’t have been rung. 9. Will the bill have been paid? 10. Will my
socks have been washed?
|
|
Работа |
Упр.
111. Прочитайте текст и ответьте на
вопросы.
Education
Education
is a key to a good future. And schools are the first step on the
education-way.
Education
in Belarus.
The
public educational system in Belarus includes pre-schools, general
schools, specialised secondary and higher education. So-called
pre-schools are kindergartens in fact. Children there learn reading,
writing and maths. But pre-school education isn’t compulsory –
children can get it at home. Compulsory education is for children
from 6(7) to 17 years of age. The main branch in the system of
education is the general schools which prepare the younger generation
for life and work. There are various types of schools: general
secondary schools, schools specialising in a certain subject, high
schools, gymnasiums and so on. The term of study in a general
secondary school is 11 years and consists of primary, middle and
upper stages. At the middle stage of a secondary school children
learn the basic laws of nature and society at the lessons of history,
algebra, literature, physics and many others. After 9th form pupils
have to sit for examinations. Also they have a choice between
entering the 10th grade of a general secondary school or going to
professional school. Pupils who finish the general secondary school,
receive a secondary education certificate, giving them the right to
enter any higher educational establishment. One has to study in the
institute for 5 years.
Education
in Britain
In
England and Wales compulsory school begins at the age of five, but
before that age children can go to a nursery school, also called play
school. School is compulsory till the children are 16 years old.
In Primary
School and First School children learn to read and write and the
basis of arithmetic. In the higher classes of Primary School (or in
Middle School) children learn geography, history, religion and, in
some schools, a foreign language. Then children go to the Secondary
School.
When
students are 16 years old they may take exams in various subjects in
order to have a qualification. These qualifications can be either
G.C.S.E. (General Certificate of Secondary Education) or «O
level» (Ordinary level). After that students can either leave
school and start working or continue their studies in the same school
as before. If they continue, when they are 18, they have to take
further examinations which are necessary for getting into university
or college.
Some
parents choose private schools for their children. They are very
expensive but considered to provide a better education and good job
opportunities.
Higher
educational institutions train students in one or several
specialisations. In England there are 47 universities, including the
Open University which teaches via TV and radio, about 400 colleges
and institutes of higher education. The oldest universities in
England are Oxford and Cambridge. Generally, universities award two
kinds of degrees: the Bachelor’s degree and the Master’s degree.
Questions:
Education
in Belarus
1.
What types of schools does the educational system of Belarus include?
2. Is pre-school education compulsory? 3. What is the main branch in
the system of education? 4. What types of schools are there in
Belarus? 5. What right does the secondary education certificate give?
Education
in Britain
1.
When does compulsory school begin? 2. What subjects do children
learn in Primary School? 3. What exams do students have to take when
they are 16? 4. Do students have to leave school at the age of 16 or
to continue their studies? 5. How do private schools differ from the
regular ones? 6. How many universities are there in England? 7. What
is the Open University? 8. What degrees do universities award?
Упр.
112. Прочитайте
текст и ответьте на вопросы.
Belarusian
state agricultural academy
Belarusain
state Agricultural Academy was founded on April 24, 1836. Its first
name was Gory-Goretskaya agricultural school.
The
Belarusian State Agricultural Academy is one of the oldest
agricultural establishments in the Republic of Belarus.
There are
nine faculties at the Academy: agronomy department, zoo-engineering
department, land use planning deparment, farm mechanization
department, economics department, business and law, bookkeeping
deparment, hydro melioration and consctruction deparment,
agricultural ecological department.
The
Academy comprises more than 50 chairs, an experimental farm,
experimental fields, repair shops and a printing house.
The Academy
occupies sixteen study buildings. Numerous tutorial rooms, lecture
halls, an assembly hall, laboratories, a well-stocked library are at
students’ disposal.
There more
800 teachers at our Academy, among them there are professors, Doctors
of Science, assistant professors, Candidates of Science. They give
lectures and practical instructions and carry out research work in
different spheres of knowledge.
More than
ten thousand students study at the Academy. A lot of students get
shcolarships, many of them are provided with hostel accommodation.
There is an extra-murial department at the Academy too.
The Academy
has a good deal of contacts with foreign educational establishments
and it also cooperates with research institutes abroad. Many
delegations from FraGce, germany, Poland and other countries visit
the Academy.
Questions:
1. What educatioan establishment do you
study at? 2. When was the Academy founded? 3. What year student are
you? 4. What department do you study at? 5. Are you a full time
student or a student by correspondence? 6. How many faculties are
there at the Academy? What are they? 7. Does the Academy have a big
library? 8. How many students study at the Academy?
Упр.
113. Прочитайте
текст и ответьте на вопросы.
Sport
Tastes
differ. Different people like different things, different people have
different hobbies.
I go in for
sports, I like to play tennis. I go to play tennis every day. Sport
is very important part of our life. Many people go in for sports:
jogging, walking, swimming, skating, skiing.
Physical
training is an important subject at school. Pupils play volleyball,
football, basketball. I have been playing tennis for 5 years. Tennis
became very popular now. I take part in different competitions.
To
be in a good shape I jog every morning and do my morning exercises.
Everyone should do all he can to stay healthy and choose the sport he
is interested in. I do not understand people who say that they like
sport, but they only watch sport on TV.
If
one goes in for sports he feels much better, looks much better,
sleeps much better. Your physical appearance will change too. You
will be slimmer and trimmer. And what is even more important you will
not get sick often.
Why do I go
in for sports? Because I think that it is very important for a man to
be strong and well-built. Sport is not for the weak, because, you
have to learn how to lose, and it’s not easy. My favourite proverb
says: «A sound mind in sound body».
Questions:
1. What is your hobby? 2. Do you go in
for sports? 3.What sports do you go in for? 4. Do you like summer
(winter) sports? 5. What must people do to be in a good shape?
Упр.
114. Прочитайте
текст и ответьте на вопросы.
Leisure
activities
–
What do you usually do in your
leisure time?
– Unfortunately,
as I have not had much free time this year, I have done my best to
spend it wisely. It is known, that people can do all kinds of things
in their spare time. They go shopping, play football, collect records
or stamps. Of course, some of the time activities, like visiting
relatives or taking driving lessons, may not be fun. In big cities
people spend their free time by going to the theatre, cinema,
museums, art galleries, concert hall, fitness or disco clubs. When I
have some free time I can choose any of them. But when the weather is
fine, I like to go for a walk along the streets of the city with my
friends, enjoying its architecture.
–
Are you fond of collecting
anything?
– No, I
am not. I have not enough time to collect anything. My friend
collects coins. His collection is rather rich. Coins of different
countries are gathered there. Moreover, he has a lot of books devoted
to numismatics and albums picturing the coin collections of different
museums.
– Do
you like to read books?
–
Yes, I do. I am fond of
reading books.
–
What books do you like to
read?
– I
am fond of science fiction.
–
Whose works do you like most?
– The
works of such science-fiction writers as Ray Bradbury, Frank Herbert,
Harlan Ellison, Poul Anderson, Ursula K. LeGuin, Frederik Pohl became
best-sellers. These writers’ approaches included predictions of
future societies on the Earth, analyses of the consequences of
interstellar travel, and imaginative explorations of forms of
intelligent life and their societies in other worlds.
– Is
it difficult for a person to have a hobby?
–
No, I don’t think so. I can
say that there are a lot of ways of spending one’s free time. I
always have a lot to do in my leisure time. It is great to have some
free time and do what is really pleasant.
Questions:
1. What do you usually do in your
leisure time? 2. Are you fond of collecting anything? 3. Do you like
to read books? 4. What books do you like to read? 5. Do you like to
go to the cinema? 6. Is it difficult for a person to have a hobby?
Учебник Spotlight 9. Student Book. Страница 95
6с. Grammar in Use — Применяем грамматику на практике
3. Put the verbs in brackets into the correct passive form. Complete the quiz, then listen and check. — Поставьте глаголы в скобках в правильную форму страдательного залога. Пройдите викторину, затем послушайте и проверьте.
- Host: Hello and welcome to this week’s edition of «The Winner Takes it All». I’m your host, Monty Wise, and here in the studio with me are two new contestants, Monica Goodall and Tony Roundwell. Welcome to you both. This week our subject is world monuments. You get five points for each correct answer. You’re not nervous, are you? (laughs) Good! Now Monica, it’s your turn. For five points, when was the Eiffel Tower built? — Всем привет и добро пожаловать на еженедельный выпуск передачи «Победитель забирает все». Я — ваш ведущий, Монти Уайз, и здесь в студии со мной два новых участника, Моника Гудолл и Тони Раундвелл. Приветствуем вас обоих. На этой неделе наша тема — всемирные монументы. Вы получаете пять баллов за каждый правильный ответ. Вы же не нервничаете, не так ли? (смеется) Хорошо! Теперь Моника, ваша очередь. Когда была построена Эйфелева башня?
- Monica: In 1898. — В 1898 году (На самом деле это неверный ответ. Она была построена в 1889 году)
- Host: Correct. Tony, for five points, what is the Taj Mahal in India made of? — Правильно. Тони, вопрос на пять очков, из чего сделан Тадж-Махал?
- Tony: Uumm … red sandstone? — Эээ… красный песчанник?
- Host: Sorry, no. Monica? — Извини, но нет. Моника?
- Monica: Er, white marble, I think. — Ээ, белый мрамор, я думаю.
- Host: Yes. Monica. Why were the Egyptian Pyramids built? — Да, Моника. Для чего были построены Египетские пирамиды?
- Monica: Oh, that’s easy. As a monument to the gods. — О, ну это просто. В качестве памятника богам.
- Host: No, I’m afraid not. I’ll have to ask Tony. — Нет, боюсь, что нет. Я передаю вопрос Тони.
- Tony: They were built as tombs for the pharaohs. — Они были построены как гробницы фараонов.
- Host: That is correct. Tony, for five points, which famous monument can be seen from almost every part of the city? The Acropolis in Athens or the Colosseum in Rome? — Это верный ответ. Тони, за пять очков, какой знаменитый монумент можно увидеть почти из каждой части города? Акрополь в Афинах или Колизей в Риме?
- Tony: The Acropolis in Athens. — Акрополь в Афинах.
- Host: Yes. Let’s move on. Monica, it is estimated that 2 to 3 million people died while building a famous monument. Was it Stonehenge or the Great Wall of China? — Да. Идем дальше. Моника, по оценке от 2 до 3 миллионов человек умерли при сооружении этого известного монумента. Что это было, Стоунхендж или Великая Китайская Стена?
- Monica: Pass. — Я пас.
- Host: Tony? — Тони.
- Tony: Sorry, I don’t know. — Мне так жаль, я не знаю.
- Host: The answer is the Great Wall. Now, hands on your buzzers. Machu Picchu in Peru and Uluru in Australia are both famous sites. Which one is endangered by tourism? Monica, you rang your buzzer first. — Ответ — Великая Китайская Стена. А теперь, руки на кнопках. Мачу Пикчу в Перу и Улуру в Австралии — известные достопримечательности. Какая из них находится на грани разрушения из-за туризма? Моника, твой звонок прозвенел первым.
- Monica: I think it’s Machu Picchu. — Думаю, это Мачу Пикчу.
- Host: Correct, and the last question in this round goes to you, Monica. According to legend, which famous building will be destroyed if the ravens ever leave it? — Правильно, и последний вопрос в этом раунде я задаю вам, Моника. В соответствии с легендой, какое знаменитое здание будет разрушено, если вороны покинут его?
- Monica: Is it Dracula’s home in Romania … what’s the name of it? Bran Castle? — Это дом графа Дракулы в Румынии… Как он называется? Замок Бран?
- Host: Not Bran Castle. Do you know the answer, Tony? — Это не Замок Бран. Вы знаете ответ, Тони?
- Tony: Yes, it’s the Tower of London. — Да, это Лондонский Тауэр.
- Host: Correct answer, Tony. That means this round ends in a tie. Let’s see who’s going to win the next round! We’ll be right back after a short commercial break — Правильный ответ, Тони. Это значит, что раунд заканчивается ничьей. Давайте посмотрим, кто победит в следующем раунде. Мы вернемся после короткой коммерческой паузы.
Комментарий: Обратите внимание, что в аудиозаписи указан неверный год создания Эйфелевой башни. Она была построена ко Всемирной выставке в Париже в 1889 году, а не в 1898 году, как дано в аудиозаписи.
- When was the Eiffel Tower built (the Eiffel Tower/build)? — Когда была сооружена Эйфелева башня?
A) 1889
B) 1898 - What is the Taj Mahal made (the Taj Mahal/make) of? — Из чего сделан Тадж-Махал?
A) red sandstone — красный песчанник
B) white marble — белый мрамор - Why were the Egyptian Pyramids built (the Egyptian Pyramids/build)? — Для чего были построены Египетские пирамиды?
A) as tombs for the pharaohs — как гробницы фараонов
B) as monuments to the gods — как памятники богам - Which famous monument can be seen (can/see) from almost every part of the city? — Какой известный монумент можно увидеть почти из каждой части города?
A) the Colosseum, Rome — Колизей, Рим
B) the Acropolis, Athens — Акрополь, Афины - It is estimated (estimate) that 2 to 3 million people died while building a monument. Which one? — По оценке от 2 до 3 миллионов человек умерли при строительстве этого монумента. Что это за монумент?
A) the Great Wall of China — Великая Китайская Стена
B) Stonehenge — Стоунхендж - Which of these famous sites is endangered (endanger) by tourism? — Какой из этих памятников находится под угрозой уничтожения из-за туризма?
A) Machu Picchu, Peru — Мачу-Пикчу, Перу
B) Uluru, Australia — Улуру, Австралия - According to the legend, which famous building will be destroyed (destroy) if the ravens ever leave it? — По легенде какое знаменитое здание будет уничтожено, если вороны покинут его?
A) Bran Castle, Romania — Замок Бран, Румыния
B) The Tower of London — Лондонский Тауэр
4. Read the notices. Where could you see each one? Expand them into full sentences using the passive. — Прочитайте заметки. Где вы могли бы их увидеть? Расширьте их в полные предложения, используя страдательный залог.
- Dogs must be kept on a lead. (park) — Собак нужно держать на поводке (парк)
- The pool is closed. (at the entrance of the swimming pool) — Бассейн закрыт (на входе в плавательный бассейн)
- Exhibits must not be touched. (museum, art exhibition) — Экспонаты не трогать. (музей, художественная выставка).
- The museum is being renovated. (at the entrance of the museum) — Музей находится на реконструкции (на входе в музей).
- The lab has been moved to the 4th floor. (university or hospital) — Лаборатория переехала на 4 этаж (университет или больница).
5. Read the two examples. Which sentence is illustrated in the picture? Which means that someone else did something for Tom? How is the sentence formed? — Прочитайте два примера. Какое предложение иллюстрировано картинкой? Что значит, что кто-то еще сделал что-то для Тома? Как построено предложение?
- Tom is repairing his car. — Том ремонтирует свою машину.
- Tom is having his car repaired. — Машину Тома ремонтируют (кто-то другой делает это).
The first sentence is illustrated in the picture. The second sentence means that someone else is repairing the car for Tom. The sentence is formed by subject + have + object + past participle. — Первое предложение проиллюстрировано картинкой. Второе предложение означает, что кто-то другой делает ремонт машины для Тома. Предложение строится по формуле подлежащее – глагол have – дополнение – 3 форма смыслового глагола.
Комментарий: Во втором предложении мы встретились с так называемой каузативной конструкцией — одной из самых загадочных конструкций в английском языке. Давайте рассмотрим два предложения:
- I wash my car every month – Я мою мою машину каждый день.
- I have my car washed every month– Мою машину моют каждый месяц.
И в том, и в другом предложении речь идет о мойке машины. Но в первом предложении я сам выполняю это действие, а во втором подразумевается, что кто-то делает это вместо меня. В этом и заключается суть каузатива — кто-то делает что-то для кого-то. В нашем примере «Я» не являюсь непосредственным исполнителем, но выступаю в качестве инициатора действия. Если учесть, что cause по-английски означает «причина», «побуждать», «добиваться», то становится понятным, откуда пошло название конструкции.
Итак, в отличие от информации в данном учебнике, существует две каузативные конструкции, активная и пассивная. В учебнике рассматривается только пассивная конструкция. Чем они отличаются?
Пассивная конструкция: Subject – have/get – object – V3 (Подлежащее – каузативный глагол – дополнение – 3 форма глагола).
В общем виде она выглядит как have/get something done.
- I have my car washed every month — Мою машину моют каждый месяц.
- You should get your watch repaired. — Тебе нужно починить часы.
Активная конструкция:Subject + have/get/make/let/help + Person + Infinitive (Подлежащее – каузативный глагол – исполнитель – инфинитив).
- Have используется, когда мы перекладываем (или просим) выполнение действия на кого-то другого, зачастую, речь идет о выполнении услуг. She had me clean the house – Она попросила меня убрать дом.
- Get используется, когда мы побуждаем кого-то к определенному действию. We can’t get all students to attend English lessons. — Мы не можем побудить студентов посещать уроки английского языка.
- Make используется в значении «заставить». I am making him do his homework – Я заставляю его выполнить домашнее задание
- Let обычно выражает разрешение на выполнение действия. I let my brother play my computer games — Я разрешаю брату играть в мои компьютерные игры.
- Help обозначает помощь кого-либо в чем-либо. Mike helped me to clean my room. — Майк помог мне прибраться в моей комнате.
Обратите внимание, что после каузативных глаголов have, make и let не используется to перед следующим глаголом в начальной форме.
6. Make sentences using The Causative. — Составьте предложения, используя каузативную конструкцию.
Ответ: Обращайте внимание на то, в каком времени дано первоначальное предложение. Каузативное предложение должно стоять в том же самом времени.
- Andy’s gardener is tidying up his garden. — Садовник Энди убрался в его саду.
Andy is having his garden tidied up. — У Энди убрались в саду. - Meg’s friend has painted her nails. — Подруга Мэг покрасила ее ногти.
Meg has had her nails painted. — Мэг покрасили ее ногти. - The mechanic is going to fix John’s car tomorrow. — Механик собирается починить машину Джона завтра.
John is going to have his car fixed tomorrow. — Джону завтра отремонтируют машину. - The painter painted Mike’s bedroom last week. — Маляр покрасил спальну Мака на прошлой неделе.
Mike had his bedroom painted last week. — Майку на прошлой неделе покрасили спальню. - The dressmaker will shorten Sue’s dress. — Портной укоротит платье Сью.
Sue will have her dress shortened. — Сью укоротят ее платье. - Brian’s dad has built a garden shed for him. — Отец Брайана построил для него в саду сарай.
Brian has had a garden shed built. — Брайану построили сарай в саду.
7. The Smiths’ house is being renovated. Use the ideas to make sentences. — Дом Смитов реконструируется. Используйте представленные идеи, чтобы составить предложения.
- walls/paint (yesterday)
- flowers/plant (tomorrow)
- missing tiles/replace (now)
- windows/clean (2 days ago)
- fence/mend (now)
- grass/mow (next week)
Ответ: Обращайте внимание на временной указатель, чтобы подобрать правильное время для глагола в предложении.
- The Smiths had the walls painted yesterday. — Смитам вчера покрасили стены.
- The Smiths will have the flowers planted tomorrow. — Смитам завтра посадят цветы.
- The Smiths are having the missing tiles replaced now. — Смитам сейчас меняют недостающие плитки.
- The Smiths had the windows cleaned two days ago. — Смитам помыли окна два дня назад.
- The Smiths are having the fence mended now. — Смитам сейчас чинят забор.
- The Smiths will have the grass mowed next week. — Смитам подстригут траву на следующей неделе.
8. Read the theory, then compare with: whatever, whichever, whenever, wherever, whoever or however. — Прочитайте теорию, затем сравните слова: что-нибудь, какой угодно, когда-нибудь, где-нибудь, кто-нибудь или сколь угодно (однако).
«Ever» can be added to question words to mean «any» (however = in any way that; whatever = anything that; whenever = any time that; wherever = any place that; whichever = any of; whoever = anyone who). Come to my house whenever you like!
Слово «Ever» может быть добавлено к вопросительным словам, чтобы получить значение «любой» (сколько угодно = любым способом; что-угодно = что-либо, когда-либо = в любое время; где угодно = любое место; какой бы то ни было = любой из; кто-угодно = любой). Приходи ко мне домой, когда хочешь!
- Wherever Ann goes, her sister goes too. — Куда бы Анна ни пошла, ее сестра идет туда же.
- Whatever you do, don’t drop the camera! — Делай что угодно, только не бросай камеру!
- Whenever I try to visit that museum, it’s closed. — Когда бы я ни пытался пойти в музей, он закрыт.
- Whoever wants to come, join me. — Если кто-то хочет пойти, присоединяйтесь.
- However hard I try, I can never please Mike. — Как бы я ни старался, мне никогда не угодить Майку.
- «Where shall I sit?» — «Wherever you like.» — Где мне сесть? — Где угодно.
- Whatever Brian cooks, it’s always delicious. — Что бы Брайан не приготовил, это всегда вкусно.
- TV is so boring lately, whichever channel I watch. — По телевизору в последнее время скукотища, на какой бы канал ни переключил.
9. Portfolio: Write your own quiz like the one in Ex. 3 about endangered world monuments using the passive. Give your quiz to your partner to complete. You can visit this website: http://www.wmf.org — Составьте свою собственную викторину по образцу упражнения 3 о находящихся под угрозой разрушения памятниках. Используйте страдательный залог. Дайте пройти свою викторину партнеру. Вы можете посетить сайт http://www.wmf.org.
- Which of these places is located on one of the many hundreds of islands on tranquil Lake Onega in the northern region of Karelia? — Какое из этих мест находится на одном из многих сотен островов на спокойном Онежском озере в северном регионе Карелии?
A) Kizhi Pogost — Погост Кижи
B) Kondopoga Assumption Church — Церковь вознесения в Кондопоге - The Statue of Liberty was built in …? — Статуя Свободы была изготовлена в …
A) The United States — США
B) France — Франции - The Leshan Giant Buddha monument is carved from… — Гигантский Будда в Лэшане вырезан из…
A) stone — камень
B) wood — дерево - Which material was used in construction of 11-floor 30 meters high houses in the ancient desert town Shibam? — Из какого материала построены 11-этажные дома высотой 30 метров в древнем пустынном городке Шибам?
A) stone — камень
B) clay — глина
Слайд 1
Презентация к урокам английского языка по теме «Пассивный залог» (для 8 класса) Подготовила учитель английского языка Карцева Татьяна Юрьевна
Слайд 2
Образование пассивного залога в английском языке PRESENT SIMPLE PAST SIMPLE FUTURE SIMPLE PRESENT CONTINUOUS
Слайд 3
THE PASSIVE VOICE TO BE + III ФОРМА ГЛАГОЛА
Слайд 4
PRESENT SIMPLE BE AM IS ARE RITA WRITES A LETTER. A LETTER IS WRITTEN BY RITA. + III
Слайд 5
Make Passive sentences in Simple Present. 1. the window / open 2. the shoes / buy 3. the car / wash 4. the letter / send 5. the book / read / not 6. the songs / sing / not 7.the shop / close / not
Слайд 6
PAST SIMPLE BE WAS WERE + III RITA WROTE A LETTER. A LETTER WAS WRITTEN BY RITA.
Слайд 7
1. the cat / feed 2. the test / write 3. the table / set 4. the house / build 5. dinner / serve 6. this computer / sell / not 7. the tables / clean / not Make Passive sentences in Simple Past.
Слайд 8
FUTURE SIMPLE BE WILL BE + III RITA WILL BE WRITE A LETTER . A LETTER WILL BE WRITTEN BY RITA.
Слайд 9
Make Passive sentences in Future . 1. the exhibition / visit 2. the windows / clean 3. the message / read 4. the photo / take 5. these songs / sing 6. a dictionary / use / not 7. credit cards / accept / not
Слайд 10
Раскройте скобки, употребляя глаголы в Present, Past или Future Simple: Many houses (to build) in our town every year. We (to invite) to a performance last weekend. Lost time never (to find) again. Rome (not to build) in a day. This magazine (to receive) last week. Bread (to eat) every day. In a couple of days they (to meet) by the guide at the station. Your luggage (to bring) to your room in ten minutes. The mail (to load) into the train yesterday. The letters (to sort) into the different towns every day.
Слайд 11
AM IS ARE PRESENT CONTINUOUS PASSIVE BE + ING + III HE IS READ ING A BOOK. A BOOK IS BE ING READ .
Слайд 12
Christmas tree (decorate) now. 2. Grandfather (meet) at the station. Grandfather is being met at the station. 1.The book (translate) now. The book is being translated now . Christmas tree is being decorated now . My brother (congratulate) me. The campfire (make). The cars (wash) now. The campfire is being made . The cars are being washed now. I am being congratulated by my brother.
Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Содержание
-
1.
Passive voice -
2.
В английском языке существуют два способа описывать -
3.
Страдательный залог образуется с помощьюглагола to be -
4.
Make Passive sentences in Simple Present. 1. -
5.
Make Passive sentences in Simple Past.1. the -
6.
Make Passive sentences in Future .1. the -
7.
Make Active sentences to Passive :Simple Present1. -
8.
Make Active sentences to Passive :Simple Past1. -
9.
Make Active sentences to Passive :Simple Future1. -
10.
Слайд 10 -
11.
Complete the sentences (Active or Passive Voice). -
12.
Complete the sentences (Active or Passive Voice). -
13.
Complete the sentences (Active or Passive Voice). -
14.
The Statue of Liberty Complete the sentences -
15.
The Statue of Liberty (be) -
16.
В презентации использовались материалыс сайта http//www.ego4u.com/enGoog luck! -
17.
Скачать презентанцию
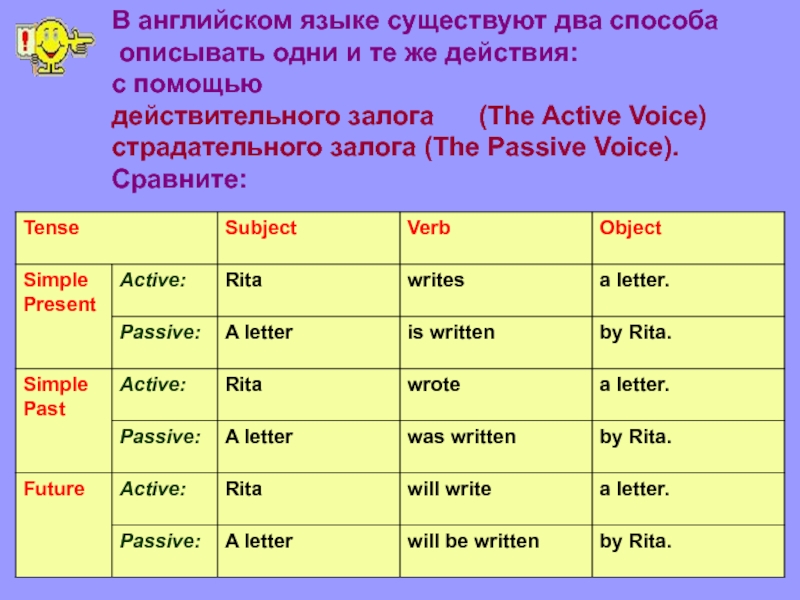
В английском языке существуют два способа описывать одни и те же действия: с помощьюдействительного залога (The Active Voice)страдательного залога (The Passive Voice).Сравните:
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 1Passive voice
Грамматический материал
для использования в 7 классе

Слайд 2В английском языке существуют два способа
описывать одни и те же
действия:
с помощью
действительного залога (The Active Voice)
страдательного залога (The Passive Voice).
Сравните:
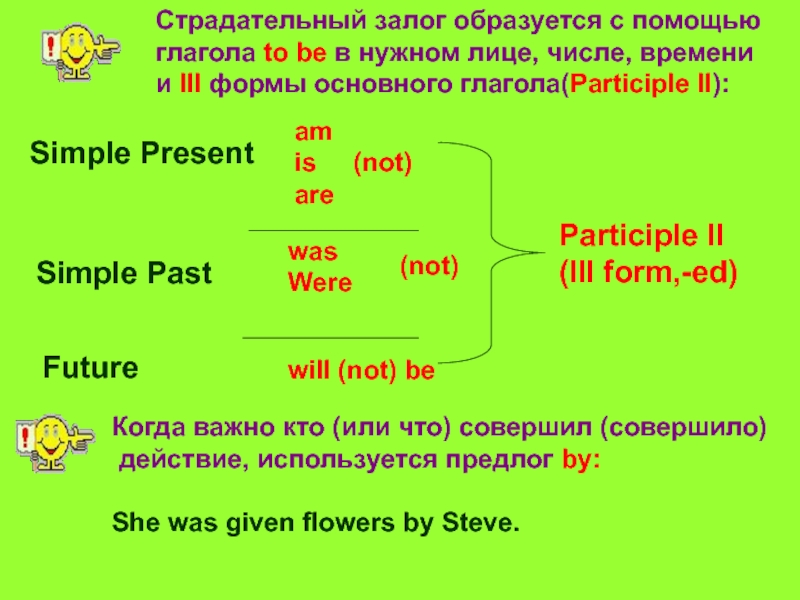
Слайд 3Страдательный залог образуется с помощью
глагола to be в нужном лице, числе,
времени
и III формы основного глагола(Participle II):
Simple Present
Simple Past
Future
am
is (not)
are
was
Were
will (not) be
Participle II
(III form,-ed)
Когда важно кто (или что) совершил (совершило)
действие, используется предлог by:
She was given flowers by Steve.
(not)
Слайд 4Make Passive sentences in Simple Present.
1. the window / open
2. the shoes / buy
3. the car / wash
4. the letter / send
5. the book / read / not
6. the songs / sing / not
7.the shop / close / not

Слайд 5Make Passive sentences in Simple Past.
1. the cat / feed
2. the
test / write
3. the table / set
4. the house / build
5. dinner / serve
6. this computer / sell / not
7. the tables / clean / not

Слайд 6Make Passive sentences in Future .
1. the exhibition / visit
2.
the windows / clean
3. the message / read
4. the photo / take
5. these songs / sing
6. a dictionary / use / not
7. credit cards / accept / not

Слайд 7Make Active sentences to Passive :
Simple Present
1. He opens the door.
—
2. We set the table. —
3. She pays a lot of money. —
4. I draw a picture. —
5. He doesn’t open the book. –
6. You do not write the letter. —
7. Does the police officer catch the thief? —

Слайд 8Make Active sentences to Passive :
Simple Past
1. She sang a song.
—
2. We stopped the bus. —
3. A thief stole my car. —
4. They didn’t let him go. —
5. She didn’t win the prize. —
6. I did not tell them. —
7. Did he send the letter? —

Слайд 9Make Active sentences to Passive :
Simple Future
1. Jane will buy a
new computer. —
2. Millions of people will visit the museum. —
3. You will not do it. —
4. They will not show the new
film. —
5. They will not ask him. —
6. Will the company employ a new worker? —

Слайд 11Complete the sentences (Active or Passive Voice).
Use Simple Present.
1. He
(sell) cars.
2. The blue car (sell) .
3. In summer, more ice-cream (eat) than in winter.
4. She (call) her grandparents every Friday.
5. The letters (type) .
6. We (go) to school by bus.
7. She (work / not) for a bank.

Слайд 12Complete the sentences (Active or Passive Voice).
Use Simple Past.
1. They
(visit) their granny.
2. We (visit) by our teacher.
3. She (go) to school in Boston.
4. The new shopping centre (build) last year.
5. The film (produce / not) in Hollywood.
6. Barbara (know) James very well.
7. We (spend / not) all day on the beach.

Слайд 13Complete the sentences (Active or Passive Voice).
Use Future.
1. The house
(build) here.
2. You (send) home.
3. I (eat) an ice-cream.
4. I (help) you.
5. The match (win / not) by our team.
6. The weather (improve / not) tomorrow.
7. They (do / not) that again.

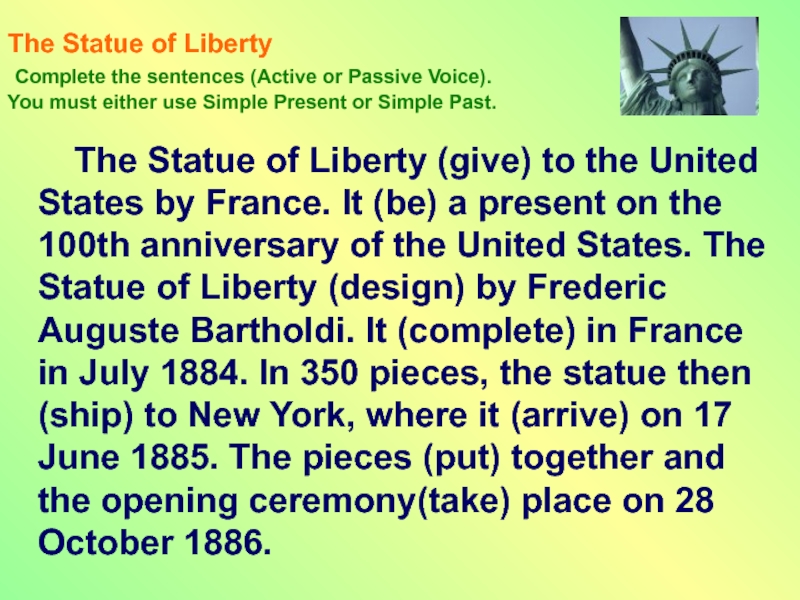
Слайд 14The Statue of Liberty
Complete the sentences (Active or Passive Voice).
You must either use Simple Present or Simple Past.
The Statue of Liberty (give) to the United States by France. It (be) a present on the 100th anniversary of the United States. The Statue of Liberty (design) by Frederic Auguste Bartholdi. It (complete) in France in July 1884. In 350 pieces, the statue then (ship) to New York, where it (arrive) on 17 June 1885. The pieces (put) together and the opening ceremony(take) place on 28 October 1886.
Слайд 15 The Statue of Liberty (be) 46 m high (93
m including the base). The statue (represent) the goddess of liberty. She (hold) a torch in her right hand and a tablet in her left hand. On the tablet you (see / can) the date of the Declarationof Independence (July 4, 1776). Every year,the Statue of Liberty (visit) by many people from all over the world.

Слайд 16В презентации использовались материалы
с сайта http//www.ego4u.com/en
Goog luck!

1
Passive voice Грамматический материал для использования в 7 классе Васильева Р.Д., учитель английского языка МБОУ ООШ 6 г.Старый Оскол, Белгородской области.
2
В английском языке существуют два способа описывать одни и те же действия: с помощью действительного залога (The Active Voice) страдательного залога (The Passive Voice). Сравните: TenseSubjectVerbObject Simple Present Active:Ritawritesa letter. Passive:A letteris writtenby Rita. Simple Past Active:Ritawrotea letter. Passive:A letterwas writtenby Rita. FutureActive:Ritawill writea letter. Passive:A letterwill be writtenby Rita.
3
Страдательный залог образуется с помощью глагола to be в нужном лице, числе, времени и III формы основного глагола(Participle II): Simple Present Simple Past Future am is (not) are was Were will (not) be Participle II (III form,-ed) Когда важно кто (или что) совершил (совершило) действие, используется предлог by: She was given flowers by Steve. (not)
4
Make Passive sentences in Simple Present. 1. the window / open 2. the shoes / buy 3. the car / wash 4. the letter / send 5. the book / read / not 6. the songs / sing / not 7.the shop / close / not
5
Make Passive sentences in Simple Past. 1. the cat / feed 2. the test / write 3. the table / set 4. the house / build 5. dinner / serve 6. this computer / sell / not 7. the tables / clean / not
6
Make Passive sentences in Future. 1. the exhibition / visit 2. the windows / clean 3. the message / read 4. the photo / take 5. these songs / sing 6. a dictionary / use / not 7. credit cards / accept / not
7
Make Active sentences to Passive : Simple Present 1. He opens the door We set the table She pays a lot of money I draw a picture He doesn’t open the book. – 6. You do not write the letter Does the police officer catch the thief? —
8
Make Active sentences to Passive : Simple Past 1. She sang a song We stopped the bus A thief stole my car They didn’t let him go She didn’t win the prize I did not tell them Did he send the letter? —
9
Make Active sentences to Passive : Simple Future 1. Jane will buy a new computer Millions of people will visit the museum You will not do it They will not show the new film They will not ask him Will the company employ a new worker? —
10
11
Complete the sentences (Active or Passive Voice). Use Simple Present. 1. He (sell) cars. 2. The blue car (sell). 3. In summer, more ice-cream (eat) than in winter. 4. She (call) her grandparents every Friday. 5. The letters (type). 6. We (go) to school by bus. 7. She (work / not) for a bank.
12
Complete the sentences (Active or Passive Voice). Use Simple Past. 1. They (visit) their granny. 2. We (visit) by our teacher. 3. She (go) to school in Boston. 4. The new shopping centre (build) last year. 5. The film (produce / not) in Hollywood. 6. Barbara (know) James very well. 7. We (spend / not) all day on the beach.
13
Complete the sentences (Active or Passive Voice). Use Future. 1. The house (build) here. 2. You (send) home. 3. I (eat) an ice-cream. 4. I (help) you. 5. The match (win / not) by our team. 6. The weather (improve / not) tomorrow. 7. They (do / not) that again.
14
The Statue of Liberty Complete the sentences (Active or Passive Voice). You must either use Simple Present or Simple Past. The Statue of Liberty (give) to the United States by France. It (be) a present on the 100th anniversary of the United States. The Statue of Liberty (design) by Frederic Auguste Bartholdi. It (complete) in France in July In 350 pieces, the statue then (ship) to New York, where it (arrive) on 17 June The pieces (put) together and the opening ceremony(take) place on 28 October 1886.
15
The Statue of Liberty (be) 46 m high (93 m including the base). The statue (represent) the goddess of liberty. She (hold) a torch in her right hand and a tablet in her left hand. On the tablet you (see / can) the date of the Declarationof Independence (July 4, 1776). Every year,the Statue of Liberty (visit) by many people from all over the world.
16
В презентации использовались материалы с сайта http//



