Содержание
- Перечень основных команд
- Запуск системных утилит
- Работа с файлами и папками
- Работа с текстовыми файлами
- Работа с учетными записями
- Работа с процессами
- Работа в сети
- Другие команды
- Вопросы и ответы
В Windows 7 существуют такие операции, которые невозможно или затруднительно выполнить через обычный графический интерфейс, но их реально осуществить через интерфейс «Командной строки» при помощи интерпретатора CMD.EXE. Рассмотрим основные команды, которые могут применять пользователи при использовании указанного инструмента.
Читайте также:
Основные команды Linux в «Терминале»
Запуск «Командной строки» в Windows 7
Перечень основных команд
С помощью команд в «Командной строке» запускаются различные утилиты и выполняются определенные операции. Зачастую основное командное выражение используется вместе с рядом атрибутов, которые записываются через косую черту (/). Именно эти атрибуты инициируют выполнение конкретных операций.
Мы не ставим перед собой цель описать абсолютно все команды, применяемые при использовании инструмента CMD.EXE. Для этого пришлось бы написать не одну статью. Мы же постараемся уместить на одной странице информацию о наиболее полезных и популярных командных выражениях, разбив их на группы.
Запуск системных утилит
Прежде всего, рассмотрим выражения, которые отвечают за запуск важных системных утилит.
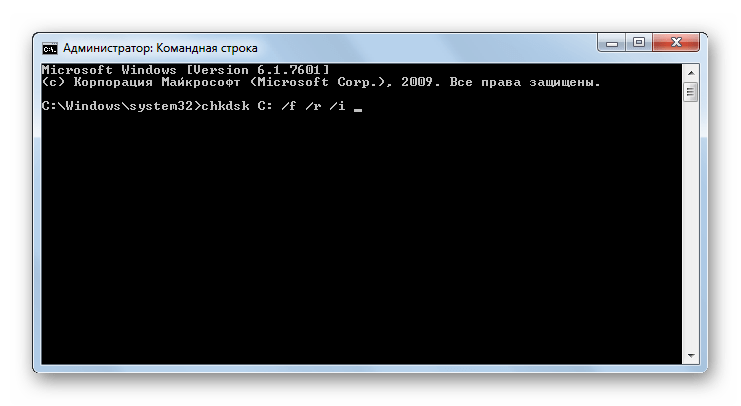
CHKDSK – запускает утилиту Check Disk, которая выполняет проверку жестких дисков компьютера на ошибки. Данное командное выражение можно вводить с дополнительными атрибутами, которые, в свою очередь, запускают выполнение определенных операций:
- /f – восстановление диска в случае обнаружения логических ошибок;
- /r – восстановление секторов накопителя в случае обнаружения физических повреждений;
- /x – отключение указанного жесткого диска;
- /scan – сканирование на упреждение;
- C:, D:, E: … — указание логических дисков для сканирования;
- /? – вызов справки о работе утилиты Check Disk.
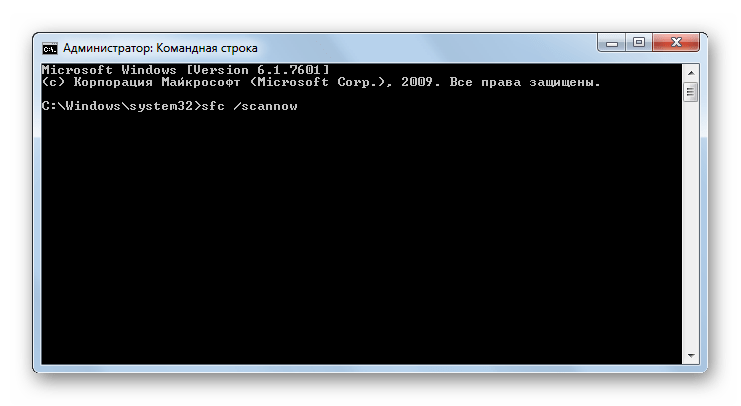
SFC – запуск утилиты проверки целостности системных файлов Windows. Данное командное выражение чаще всего используется с атрибутом /scannow. Оно запускает инструмент, который проверяет файлы ОС на соответствие стандартам. В случае повреждений, при наличии установочного диска существует возможность восстановления целостности системных объектов.
Работа с файлами и папками
Следующая группа выражений предназначена для работы с файлами и папками.
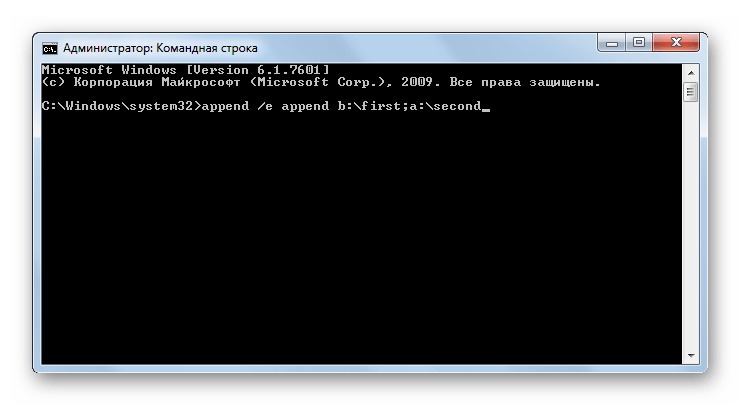
APPEND – открытие файлов в указанной пользователем папке в том виде, как если бы они находились в требуемом каталоге. Обязательным условием является указание пути к папке, к которой будет применено действие. Запись производится по следующему шаблону:
append [;] [[диск компьютера:]путь[;...]]
При использовании данной команды можно применять следующие атрибуты:
- /e – запись полного списка файлов;
- /? – запуск справки.
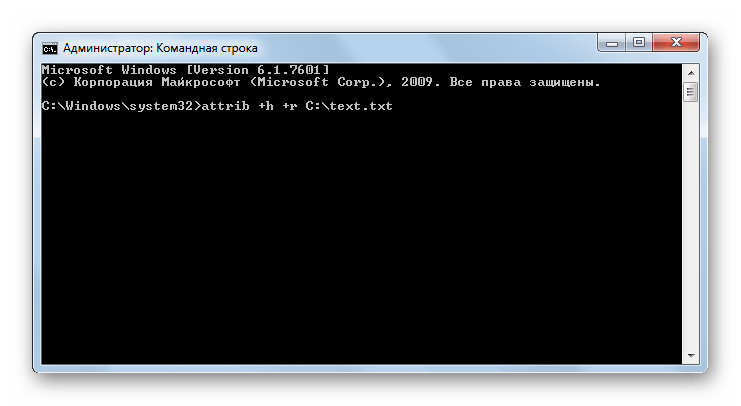
ATTRIB – команда предназначена для изменения атрибутов файлов или папок. Так же, как и в предыдущем случае, обязательным условием является ввод вместе с командным выражением полного пути к обрабатываемому объекту. Для установки атрибутов используются следующие ключи:
- h – скрытый;
- s – системный;
- r – только для чтения;
- a – архивный.
Для того чтобы применить или отключить атрибут, перед ключом соответственно ставится знак «+» или «-».
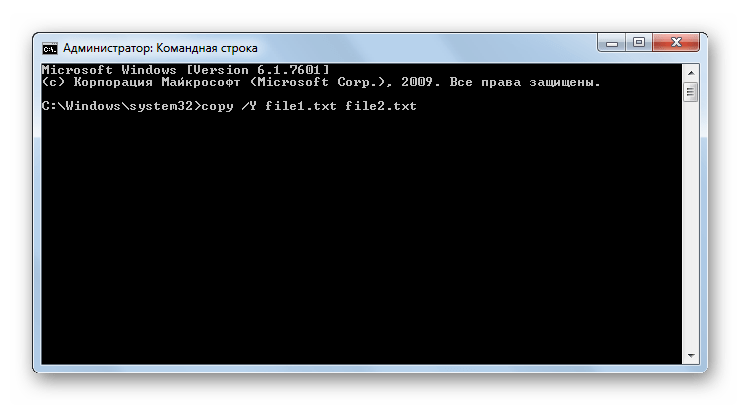
COPY – применяется для копирования файлов и каталогов из одной директории в другую. При использовании команды обязательно указание полного пути объекта копирования и папки, в которую оно будет производиться. С данным командным выражением можно использовать следующие атрибуты:
- /v – проверка корректности копирования;
- /z – копирование объектов из сети;
- /y – перезапись конечного объекта при совпадении имен без подтверждения;
- /? – активация справки.
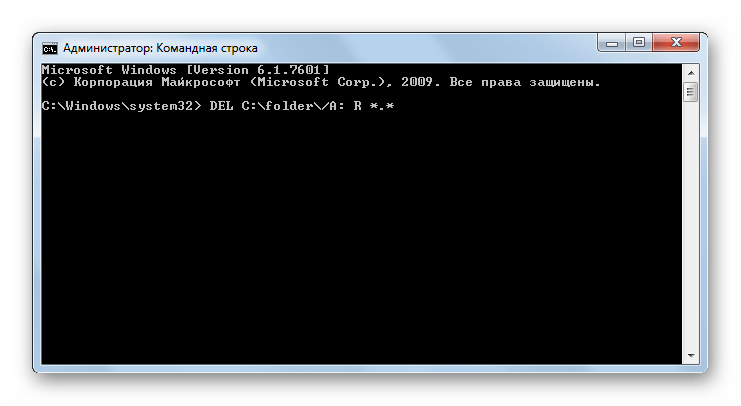
DEL – удаление файлов из указанной директории. Командное выражение предусматривает возможность использования ряда атрибутов:
- /p – включение запроса подтверждения удаления перед манипуляцией с каждым объектом;
- /q – отключение запроса при удалении;
- /s – удаление объектов в каталогах и подкаталогах;
- /a: — удаление объектов с указанными атрибутами, которые назначаются при помощи тех же ключей, что и при использовании команды ATTRIB.
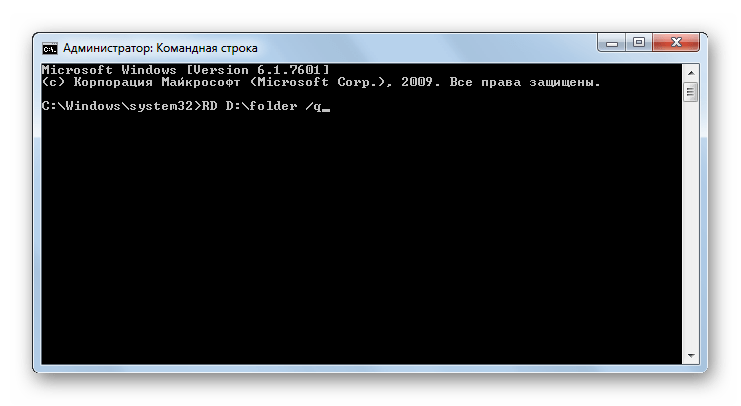
RD – является аналогом предыдущего командного выражения, но удаляет не файлы, а папки в указанной директории. При использовании можно применять те же самые атрибуты.
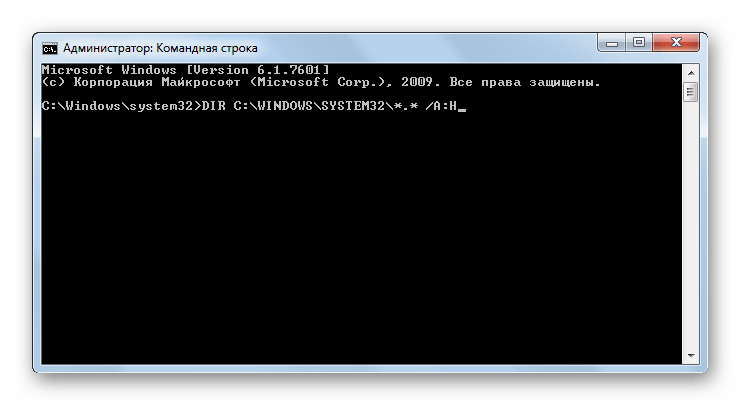
DIR – выводит список всех подкаталогов и файлов, которые расположены в указанной директории. Вместе с основным выражением применяются такие атрибуты:
- /q – получение информации о владельце файла;
- /s – отображение перечня файлов из указанного каталога;
- /w – вывод списка в несколько колонок;
- /o – сортировка перечня выводимых объектов (e – по расширению; n – по имени; d – по дате; s – по размеру);
- /d – отображение списка в несколько колонок с сортировкой по этим колонкам;
- /b – отображение исключительно имен файлов;
- /a – отображение объектов с определенными атрибутами, для указания которых используются те же ключи, что и при использовании команды ATTRIB.
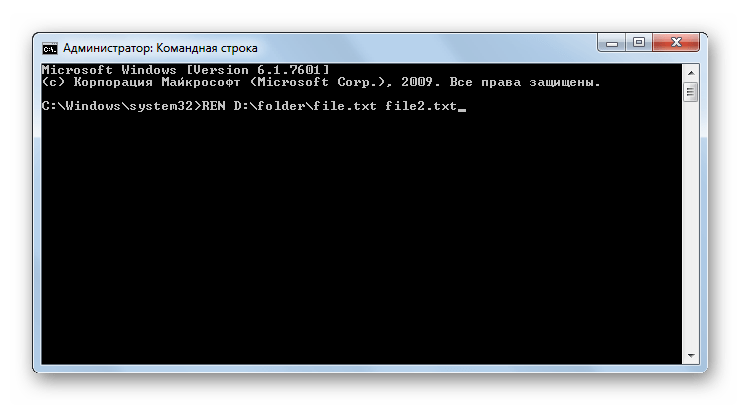
REN – используется для переименования каталогов и файлов. В качестве аргументов к данной команде указывается путь к объекту и его новое название. Например, для переименования файла file.txt, который расположен в папке «Folder», находящейся в корневой директории диска D, в файл file2.txt, нужно ввести следующее выражение:
REN D:folderfile.txt file2.txt
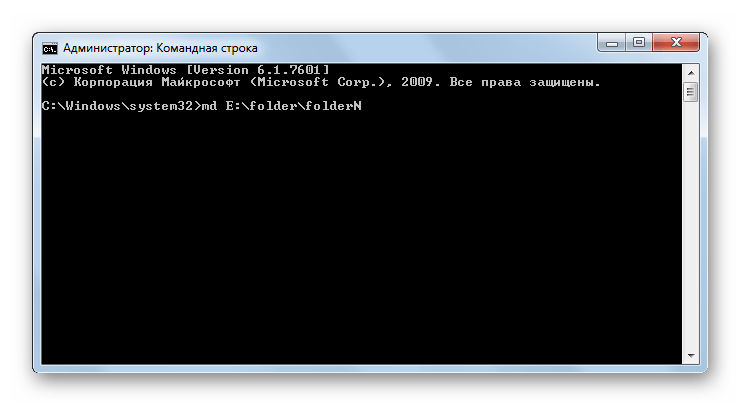
MD – предназначена для создания новой папки. В синтаксисе команды обязательно следует указать диск, на котором будет располагаться новый каталог, и директорию его размещения в том случае, если он является вложенным. Например, для создания каталога folderN, который расположен в директории folder на диске E, следует ввести такое выражение:
md E:folderfolderN
Работа с текстовыми файлами
Следующий блок команд предназначен для работы с текстом.
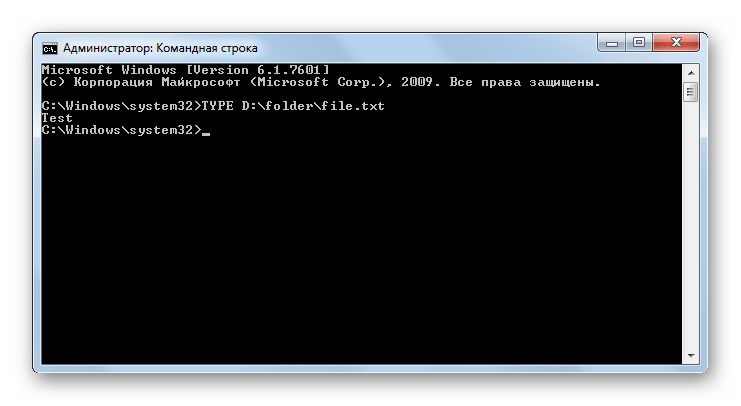
TYPE – отображает на экране содержимое текстовых файлов. Обязательными аргументом данной команды является полный путь к объекту, текст в котором следует просмотреть. Например, для просмотра содержимого файла file.txt, находящегося в папке «Folder» на диске D, требуется ввести следующее командное выражение:
TYPE D:folderfile.txt
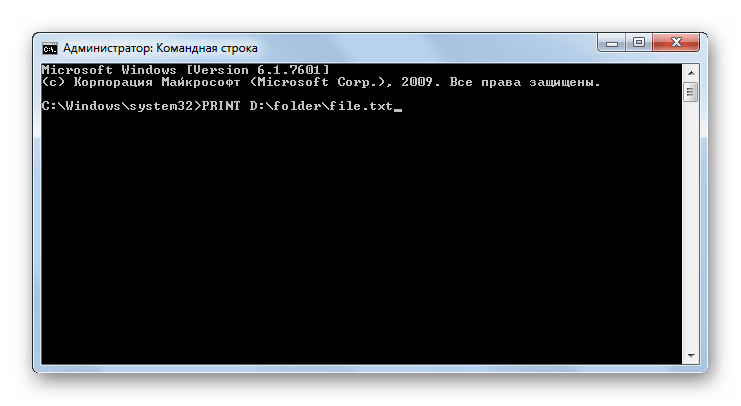
PRINT – распечатка содержимого текстового файла. Синтаксис данной команды аналогичен предыдущему, но вместо вывода текста на экран производится его распечатка.
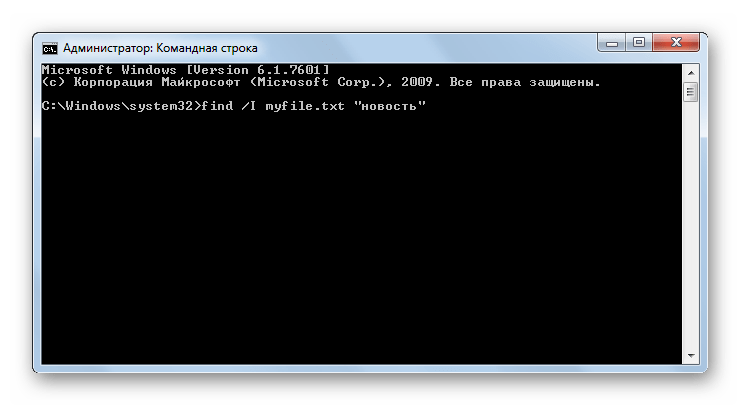
FIND – производит поиск текстовой строки в файлах. Вместе с этой командой обязательно указывается путь к объекту, в котором выполняется поиск, а также название искомой строки, заключенное в кавычки. Кроме того, вместе с данным выражением применяются следующие атрибуты:
- /c – выводится общее количество строк, содержащих искомое выражение;
- /v – вывод строк, которые не содержат искомое выражение;
- /I – поиск без учета регистра.
Работа с учетными записями
С помощью командной строки можно просматривать информацию о пользователях системы и управлять ими.
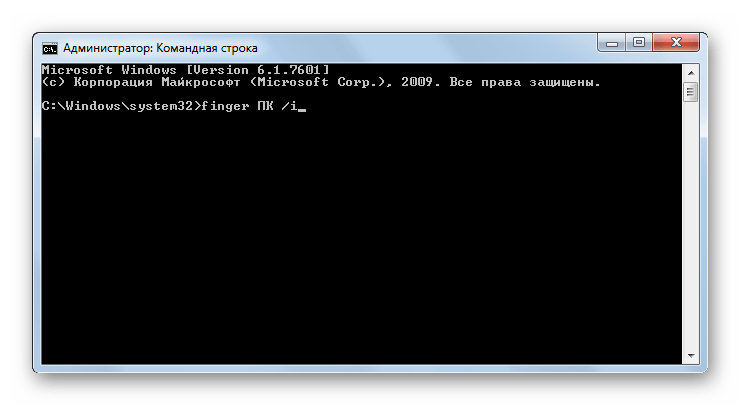
FINGER – отображение информации о зарегистрированных в операционной системе пользователях. Обязательным аргументом данной команды является имя юзера, о котором требуется получить данные. Кроме того, можно использовать атрибут /i. В этом случае вывод информации будет производиться в списочном варианте.
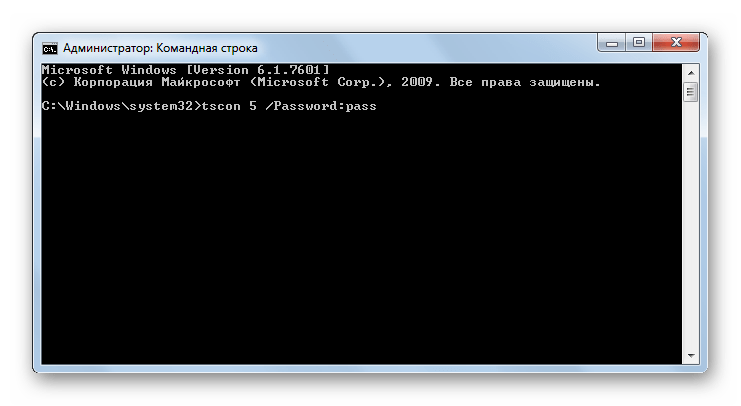
TSCON – выполняет присоединение сеанса пользователя к сеансу терминала. При использовании данной команды обязательно требуется указать ID сеанса или его имя, а также пароль того юзера, которому он принадлежит. Пароль следует указывать после атрибута /PASSWORD.
Работа с процессами
Следующий блок команд предназначен для управления процессами на компьютере.
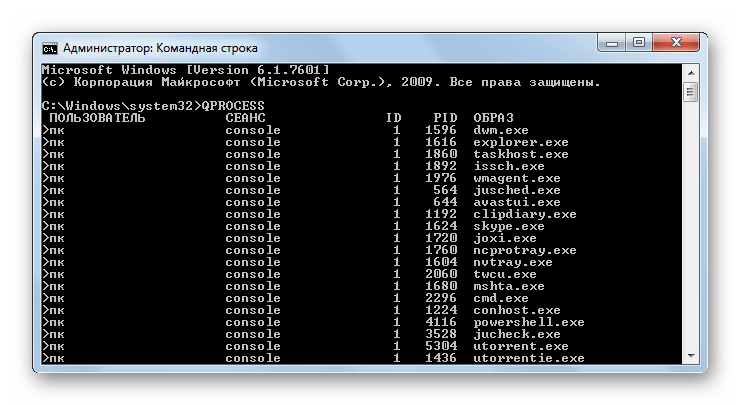
QPROCESS – предоставление данных о запущенных процессах на ПК. Среди выводимой информации будет представлено наименование процесса, имя пользователя, его запустившего, название сеанса, ID и PID.
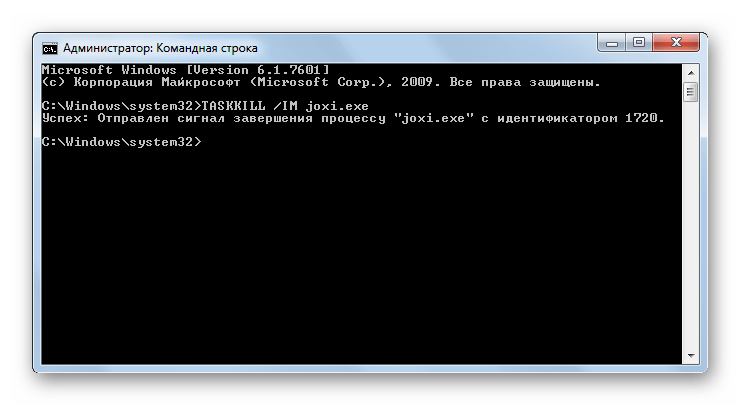
TASKKILL – используется для завершения процессов. Обязательным аргументом является наименование элемента, который нужно остановить. Он указывается после атрибута /IM. Также можно произвести завершение не по имени, а по идентификатору процесса. В этом случае используется атрибут /PID.
Работа в сети
С помощью командной строки существует возможность управлять различными действиями в сети.
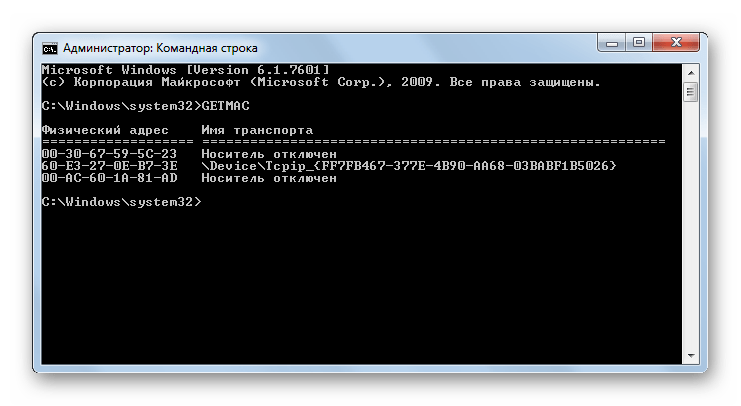
GETMAC – запускает отображение MAC-адреса подключенной к компьютеру сетевой карты. В случае наличия нескольких адаптеров отображаются все их адреса.
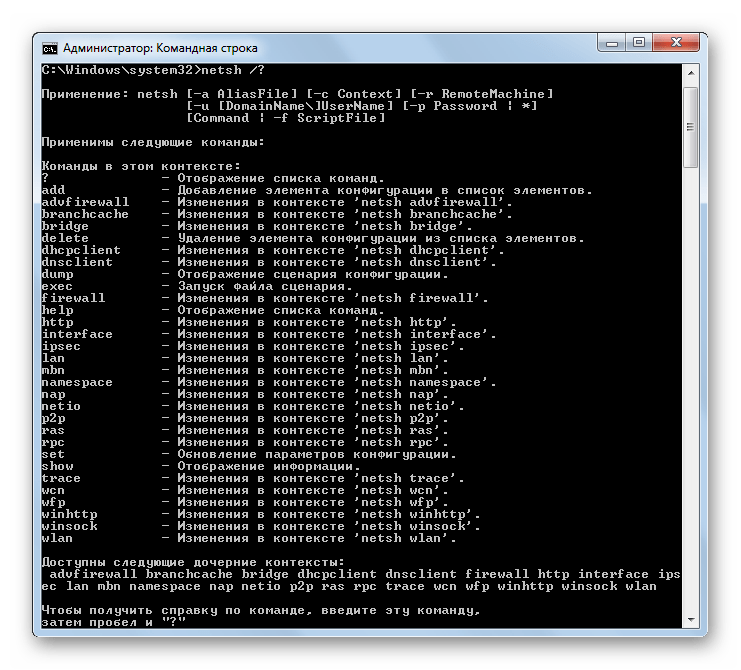
NETSH – инициирует запуск одноименной утилиты, с помощью которой производится демонстрация информации о параметрах сети и их изменение. Данная команда, ввиду своей очень широкой функциональности, имеет огромное количество атрибутов, каждый из которых отвечает за выполнение определенной задачи. Для получения подробной информации о них можно воспользоваться справкой, применив следующее командное выражение:
netsh /?
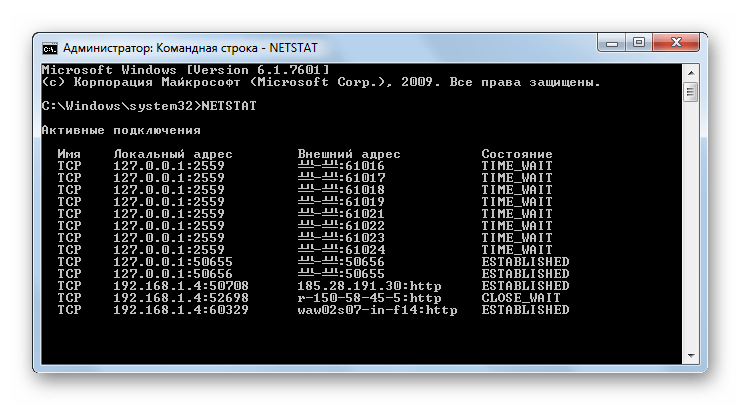
NETSTAT – отображение статистической информации о сетевых подключениях.
Другие команды
Также существует ряд других командных выражений, применяемых при использовании CMD.EXE, которые нельзя выделить в отдельные группы.
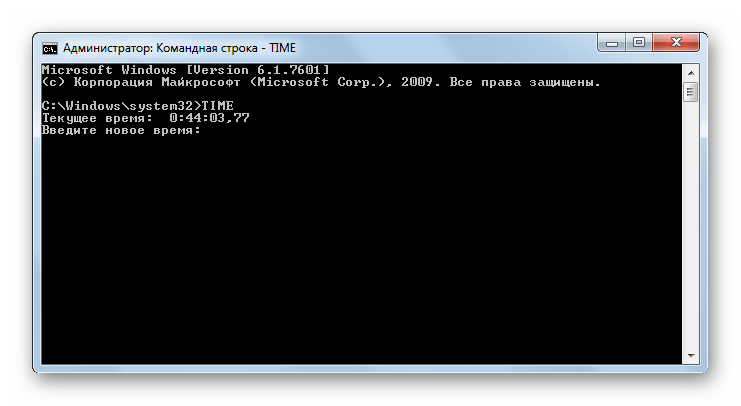
TIME – просмотр и установка системного времени ПК. При вводе данного командного выражения происходит вывод на экран текущего времени, которое в самой нижней строке можно изменить на любое другое.
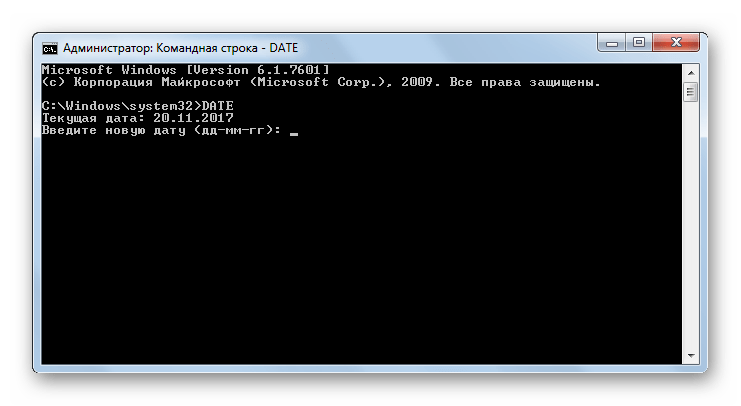
DATE – команда по синтаксису полностью аналогична предыдущей, но применяется не для вывода и изменения времени, а для запуска данных процедур в отношении даты.
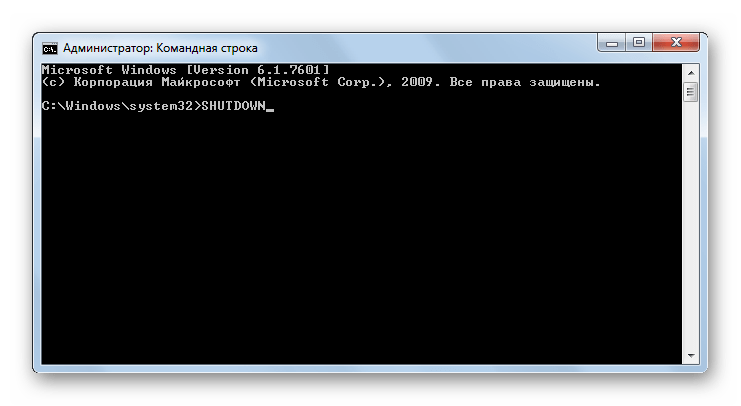
SHUTDOWN – выключает компьютер. Данное выражение можно использовать, как локально, так и удаленно.
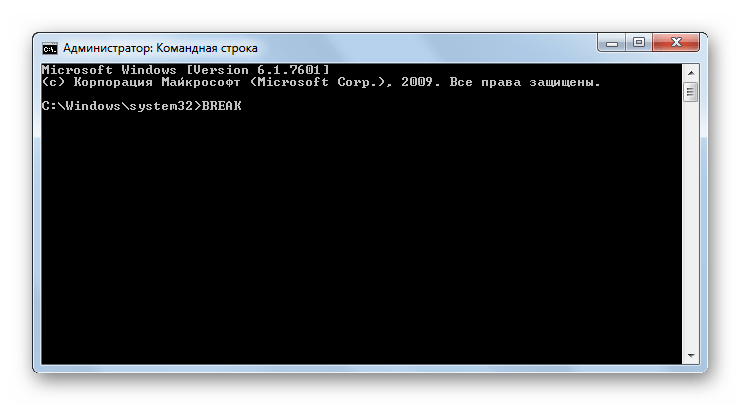
BREAK – отключение или запуск режима обработки сочетания кнопок Ctrl+C.
ECHO – выводит текстовые сообщения и применяется для переключения режимов их отображения.
Это далеко не полный список всех команд, которые применяются при использовании интерфейса CMD.EXE. Тем не менее мы попытались раскрыть наименования, а также вкратце описать синтаксис и основные функции самых востребованных из них, для удобства разбив на группы по назначению.
This section provides an overview of what cmd is, and why a developer might want to use it.
It should also mention any large subjects within cmd, and link out to the related topics. Since the Documentation for cmd is new, you may need to create initial versions of those related topics.
Opening a Command Prompt
The command prompt comes pre-installed on all Windows NT, Windows CE, OS/2 and eComStation operating systems, and exists as cmd.exe, typically located in C:Windowssystem32cmd.exe
On Windows 7 the fastest ways to open the command prompt are:
-
Press
, type «cmd» and then press Enter.
-
Press
+R, type «cmd» then then press Enter.
It can also be opened by navigating to the executable and double-clicking on it.
In some cases you might need to run cmd with elevated permissions, in this case right click and select «Run as administrator». This can also be achieved by pressing Control+ Shift+Enter instead of Enter.
Navigating in cmd
One of the most common things you’ll need to do in the command prompt is navigate your file system. To do this, we’ll utilize the cd and dir keywords. Start by opening up a command prompt using one of the methods mentioned here. You most likely see something similar to what’s below, where UserName is your user.
C:UsersUserName>
Regardless of where in your file structure you are, if your system is like most, we can start with this command:
cd C:
This will change your current directory to the C: drive. Notice how the screen now looks like this
C:>
Next, run a dir so we can see anything in the C: drive
dir
This will show you a list of files and folders with some information about them, similar to this:
There’s lots of good info here, but for basic navigation, we just care about the right-most column. Notice how we have a Users folder. That means we can run this
cd Users
Now if you run dir again, you’ll see all the files and folders in your C:Users directory. Now, we didn’t find what we wanted here, so let’s go back to the parent folder. Rather than type the path to it, we can use .. to go up one folder like so
cd ..
Now we are back in C:. If you want to go up multiple folders at once, you can put a backslash and another set of periods like so: cd ...., but we only needed one folder.
Now we want to look in that Program Files folder. To avoid confusing the system, it’s a good idea to put quotes around the directories, especially when there are spaces in the name. So this time, we’ll use this command
C:>cd "Program Files"
Now you are in C:Program Files> and a dir command now will tell you anything that’s in here.
So, say we get tired of wandering around to find the folder and looked up exactly where we were needing to go. Turns out it’s C:WindowsLogs Rather than do a .. to Windows to Logs, we can just put the full path like so:
cd "C:WindowsLogs"
And that’s the basics of navigating the command prompt. You can now move through all your folders so you can run your other commands in the proper places.
Commands in CMD
The available commands will be displayed, including a brief description, in tabular format.
In Windows 10 the following commands are listed:
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| ASSOC | Displays or modifies file extension associations. |
| ATTRIB | Displays or changes file attributes. |
| BREAK | Sets or clears extended CTRL+C checking. |
| BCDEDIT | Sets properties in boot database to control boot loading. |
| CACLS | Displays or modifies access control lists (ACLs) of files. |
| CALL | Calls one batch program from another. |
| CD | Displays the name of or changes the current directory. |
| CHCP | Displays or sets the active code page number. |
| CHDIR | Displays the name of or changes the current directory. |
| CHKDSK | Checks a disk and displays a status report. |
| CHKNTFS | Displays or modifies the checking of disk at boot time. |
| CLS | Clears the screen. |
| CMD | Starts a new instance of the Windows command interpreter. |
| COLOR | Sets the default console foreground and background colors. |
| COMP | Compares the contents of two files or sets of files. |
| COMPACT | Displays or alters the compression of files on NTFS partitions. |
| CONVERT | Converts FAT volumes to NTFS. You cannot convert the |
| current drive. | |
| COPY | Copies one or more files to another location. |
| DATE | Displays or sets the date. |
| DEL | Deletes one or more files. |
| DIR | Displays a list of files and subdirectories in a directory. |
| DISKPART | Displays or configures Disk Partition properties. |
| DOSKEY | Edits command lines, recalls Windows commands, and |
| creates macros. | |
| DRIVERQUERY | Displays current device driver status and properties. |
| ECHO | Displays messages, or turns command echoing on or off. |
| ENDLOCAL | Ends localization of environment changes in a batch file. |
| ERASE | Deletes one or more files. |
| EXIT | Quits the CMD.EXE program (command interpreter). |
| FC | Compares two files or sets of files, and displays the |
| differences between them. | |
| FIND | Searches for a text string in a file or files. |
| FINDSTR | Searches for strings in files. |
| FOR | Runs a specified command for each file in a set of files. |
| FORMAT | Formats a disk for use with Windows. |
| FSUTIL | Displays or configures the file system properties. |
| FTYPE | Displays or modifies file types used in file extension |
| associations. | |
| GOTO | Directs the Windows command interpreter to a labeled line in |
| a batch program. | |
| GPRESULT | Displays Group Policy information for machine or user. |
| GRAFTABL | Enables Windows to display an extended character set in |
| graphics mode. | |
| HELP | Provides Help information for Windows commands. |
| ICACLS | Display, modify, backup, or restore ACLs for files and |
| directories. | |
| IF | Performs conditional processing in batch programs. |
| LABEL | Creates, changes, or deletes the volume label of a disk. |
| MD | Creates a directory. |
| MKDIR | Creates a directory. |
| MKLINK | Creates Symbolic Links and Hard Links |
| MODE | Configures a system device. |
| MORE | Displays output one screen at a time. |
| MOVE | Moves one or more files from one directory to another |
| directory. | |
| OPENFILES | Displays files opened by remote users for a file share. |
| PATH | Displays or sets a search path for executable files. |
| PAUSE | Suspends processing of a batch file and displays a message. |
| POPD | Restores the previous value of the current directory saved by |
| PUSHD. | |
| Prints a text file. | |
| PROMPT | Changes the Windows command prompt. |
| PUSHD | Saves the current directory then changes it. |
| RD | Removes a directory. |
| RECOVER | Recovers readable information from a bad or defective disk. |
| REM | Records comments (remarks) in batch files or CONFIG.SYS. |
| REN | Renames a file or files. |
| RENAME | Renames a file or files. |
| REPLACE | Replaces files. |
| RMDIR | Removes a directory. |
| ROBOCOPY | Advanced utility to copy files and directory trees |
| SET | Displays, sets, or removes Windows environment variables. |
| SETLOCAL | Begins localization of environment changes in a batch file. |
| SC | Displays or configures services (background processes). |
| SCHTASKS | Schedules commands and programs to run on a computer. |
| SHIFT | Shifts the position of replaceable parameters in batch files. |
| SHUTDOWN | Allows proper local or remote shutdown of machine. |
| SORT | Sorts input. |
| START | Starts a separate window to run a specified program or command. |
| SUBST | Associates a path with a drive letter. |
| SYSTEMINFO | Displays machine specific properties and configuration. |
| TASKLIST | Displays all currently running tasks including services. |
| TASKKILL | Kill or stop a running process or application. |
| TIME | Displays or sets the system time. |
| TITLE | Sets the window title for a CMD.EXE session. |
| TREE | Graphically displays the directory structure of a drive or |
| path. | |
| TYPE | Displays the contents of a text file. |
| VER | Displays the Windows version. |
| VERIFY | Tells Windows whether to verify that your files are written |
| correctly to a disk. | |
| VOL | Displays a disk volume label and serial number. |
| XCOPY | Copies files and directory trees. |
| WMIC | Displays WMI information inside interactive command shell. |
To get more insight about a specific command use the /? option, e.g. the tree command gives:
tree /?
Graphically displays the folder structure of a drive or path.
TREE [drive:][path] [/F] [/A]
/F Display the names of the files in each folder.
/A Use ASCII instead of extended characters.
Features
Microsoft Command Prompt is a command-line interpreter (CLI) for the Windows operating systems.
A CLI is program intended primarily to read operating system instructions typed on a keyboard by the user.
It is therefore addressed also as a command-line interface, to contrast it with graphical interfaces.
As these interfaces (whether textual or graphical) shield the user from directly accessing to the operating system kernel, they are also said shells.
Given the name of the Command Prompt executable file, cmd.exe, the Command Prompt is friendly named cmd.
Given its OS piloting role, it is also said the console.
Like other shells, cmd can read batch of instructions from a file. In this case the cmd shell acts as a language interpreter and the file content can be regarded as an actual program. When executing these batch programs, there is no intermediate compilation phase. They are typically read, interpreted and executed line by line. Since there is no compilation, there is no production of a separated executable file. For this reason the programs are denoted batch scripts or shell scripts.
Note that the instructions entered interactively might have a slightly different syntax from those submitted as a script, but the general principle is that what can be entered from the command line can be also put in a file for later reuse.
Hello World
Command Prompt batch scripts have extension .cmd or .bat, the latter for compatibility reasons.
To create a hello-word-script, you first need a place where to type it.
For simple scripts, also the Windows Notepad will do. If you are serious about shell scripting, you need more effective tools. There are anyway several free alternatives, such as Notepad++.
In your designated editor type:
echo Hello World
pause
Save it as hello.cmd
If you are using «Notepad» as an editor, you should pay much attention to the saved name, as Notepad tends to add always a .txt extension to your files, which means that the actual name of your file might be hello.cmd.txt. To avoid this, in the save dialog box:
- In the
File namefield enter the name in double quotes, e.g."hello.cmd" - In the
Save as typefield select All Files, instead of the default Text Document option.
If the file has been saved properly, its icon should be similar to (Windows Vista):
You may also consider to disable the option «Hide extension for known file types» in File Explorer folder view options. In this case, file names are always displayed with their extensions.
To execute hello.cmd there are two possibilities. If you are using the Windows graphical shell, just double click on its icon.
If you want to use the Command Prompt itself, you must first identify the directory where you saved hello.cmd.
In this regard, if you open File Explorer with 
hello.cmd. Windows directory names tend to be quite long and typing them is error prone. It is better if you select and copy the directory path in the clipboard for later pasting.
Start the Command Prompt. You read a line similar to this.
Microsoft Windows [Version ...]
(c) ... Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
C:Users...>
The version/year of Windows of course depends on yours.
In the the final line, before >, you read the path of the directory which is current. You should make current the directory where your script is. For this reason enter the change directory command cd, using a line similar to the following:
cd <dirpath>
Instead of <dirpath>, paste the name of the directory you previously copied.
To paste the directory path, in Windows 10, you just need to type Ctrl—C, as you would in an editor.
For older systems you should be able to do this by right clicking in the cmd window.
After entering the command, note that current path, before >, changes accordingly.
You can now run your hello script by simply entering:
hello
Comments
The script prints an output similar to:
C:Users...>echo Hello World
Hello World
C:Users...>pause
Press any key to continue . . .
The lines hosting the symbol > restate the script instructions as if you had entered interactively.
This can be disabled writing:
@echo off
as the first line of your script.
This might reduce the clutter, but you have less hints on what is going on, with respect to those script commands that do not give visible outputs.
The last command, pause, prompts you to hit any key. When you do, you exit hello.
If you run hello from the console, you don’t really need it, because, when hello terminates its execution, cmd.exe remains open and you can to read hello output.
When double-clicking in Explorer, you start cmd.exe for the time necessary to execute hello. When hello terminates, cmd.exe does the same and you have no possibility to read hello output.
pause command prevents hellofrom exiting until you hit a key, which gives also the possibility to read the output.
Finally, despite the name of the script is hello.cmd, it is not necessary to type the whole name, its hello stem is sufficient. This mechanism works for executables too, with extension .exe. What if there is a script hello.cmd and an executable hello.exe in the same directory? The former has priority in the Command Prompt, so hello.cmd will be executed.
Download Article
A painless guide to accessing the Windows command prompt
Download Article
This wikiHow teaches you how to open the Command Prompt program in Windows. There are several ways to do this, from simply searching in the Start menu to using a Run command. Keep in mind that some computers, such as school computers, will not be able to run Command Prompt due to restrictions.
-
1
Open Start
. Click the Windows logo in the bottom-left corner of the screen, or press the ⊞ Win key. You can search for Command Prompt on all supported versions of Windows.
- If you’re using Windows 8, instead place your mouse cursor in the top-right corner of the screen, then click the magnifying glass icon when it appears.
-
2
Type command prompt into Start. The Start search bar is at the bottom of the Start window. Searching for Command Prompt here will look for Command Prompt.
Advertisement
-
3
Click
Command Prompt. You should see the Command Prompt icon appear near the top of the Start window. Clicking its icon will open Command Prompt.
Advertisement
-
1
Open the Run program. Hold the ⊞ Win key and press the R key to open the Run window.
- You can also right-click the Start icon (or press ⊞ Win+X) and then click Run to do this.
-
2
Type cmd into Run. This is the command to open Command Prompt.
-
3
Click OK. Doing so runs the «cmd.exe» command, which opens Command Prompt.
Advertisement
-
1
Open Start
. Click the Windows logo in the bottom-left corner of the screen. You can also press the ⊞ Win key.
-
2
Scroll down to Windows System and click it. This folder will be near the bottom of the Start window.
-
3
Click
Command Prompt. It should be near the top of the Windows System folder. Doing so will open Command Prompt.
Advertisement
Add New Question
-
Question
How do I close out Command Prompt?
ClixTech Australia
Community Answer
Type «exit» in the Command Prompt, or press the red «X» in the top right corner, or press Alt+F4 on the keyboard. Check out the Close Command Prompt article for more detailed instructions!
-
Question
What do I do if I can’t use Microsoft Edge and the Start button?
Press the Windows Key + R, then type in cmd.exe and hit enter.
-
Question
How do I stop Windows command prompt from starting up automatically?
If it starts up every time, then something is causing it. It may be a program or a shortcut to command prompt that is saved in your Windows start folder. If you want to stop it from appearing altogether by uninstalling it, you won’t be able to.
See more answers
Ask a Question
200 characters left
Include your email address to get a message when this question is answered.
Submit
Advertisement
Video
-
Command Prompt is a good place to run legacy or specialty software. You might also use it if you’re trying to manipulate specific files.[1]
-
To run Command Prompt in administrator mode, right-click the Command Prompt icon and click Run as administrator.
Advertisement
-
If you’re using a computer with restricted access to settings and programs, you may not be able to open Command Prompt.
Advertisement
About This Article
Article SummaryX
1. Open Start.
2. Type in command prompt.
3. Click Command Prompt at the top.
Did this summary help you?
Thanks to all authors for creating a page that has been read 581,301 times.
Is this article up to date?
Содержание
- 1 Немного теории и фактов
- 2 Зачем обычному пользователю командная строка
- 3 Как открыть командную строку в Windows 7
- 4 Как пользоваться командной строкой
- 5 Видео по теме
Самые ранние операционные системы не имели привычного для современного пользователя графического интерфейса. Ранее для управления компьютером использовались исключительно текстовые команды.
Однако и сегодня, несмотря на разнообразие возможностей, обеспечивающих лёгкое и удобное общение пользователя с ПК, они всё ещё используются. Существуют и такие ОС, которые работают только при помощи ввода в них текстовых команд. Их обычно используют администраторы баз данных, программисты и другие IT-специалисты.
Отличный пример управления операционной системой при помощи текстовых команд — командная строка Windows 7. Она присутствует в любом дистрибутиве этой ОС и её можно запустить на любом ПК под управлением этой операционной системы. Вам не нужно быть администратором или каким-либо IT-специалистом, чтобы научиться ею пользоваться. Давайте, рассмотрим этот вопрос подробней.
Немного теории и фактов
Командная строка Windows представляет собой инструментарий, позволяющий пользователю осуществлять различные действия над операционной системой либо над отдельными программами путём ввода текстовых команд. Командная строка состоит, как правило, из интерпретатора команд (оболочки) и текстового интерфейса. Первый отвечает за передачу и выполнение команд операционной системой, второй — обеспечивает пользователя возможностью ввода этих самых команд и просмотра результата их выполнения.
Командная строка предлагает большие возможности для управления операционной системой. Практически всё, что можно настроить в Windows при помощи мышки, можно сделать и через неё. Отсюда следует вывод — командная строка способна выполнить достаточно большой список задач, каждая из которых выполняется посредством поочерёдного ввода уникальной команды. Именно из-за необходимости запоминания синтаксиса этих команд и умения ими пользоваться большинство рядовых пользователей имеют затруднения в работе с командной строкой.
Даже несмотря на это, использование командной строки не такая уж и сложная задача. Здесь главное научиться понимать сам принцип её работы, о чём и будет подробнее сказано далее.
Зачем обычному пользователю командная строка
Наверняка, каждый из вас сталкивался с различными статьями в Интернете, в которых авторы призывают воспользоваться той или иной командой для решения определённой задачи. К примеру, через командную строку можно осуществлять управление файлами, хранящимися на любом носителей, изменять параметры работы системы или даже создавать подключение к Интернету. Однако перечисленное выше можно с легкостью выполнить и с помощью привычной мыши и клавиатуры.
Важность командной строки заключается в том, что любые операции с системой можно произвести в случае, когда пропал доступ к графическому интерфейсу либо отсутствует иное решение.
Вот несколько примеров:
- Регистрация в системе динамических DLL-библиотек (зачастую необходимо проделывать при копировании в системную папку Windows нового DLL-файла — регистрация «даст понять» системе, что появилась новая библиотека);
- Настройка сетевого адаптера компьютера в качестве беспроводной точки доступа Wi-Fi;
- Можно даже выйти в Интернет, произведя соединение с сетью через одно из существующих подключений.
Без использования командной строки также не обойтись в случае невозможности управления компьютером при помощи графического интерфейса. К примеру, существует не одна разновидность вирусных программ, которые отключают проводник Windows, не давая пользователю доступа к папкам или запуску программ.
При помощи командной строки не только можно выполнить запуск приложения, но и зайти в любую папку с целью работы над какими-либо файлами (копирование, перемещение, задание нового имени и так далее). И это лишь часть возможностей командной строки. Давайте теперь перейдём к практике.
Как открыть командную строку в Windows 7
Первое, что необходимо сделать — выполнить запуск командной строки и лучше от имени администратора.
Запускается она одним из следующих способов:
Выполнив одно из вышеприведённых действий, вы осуществите вызов командной строки — обычно это небольшое окно чёрного цвета.
Для чего нужны права администратора? Дело в том, что существует ряд команд, которые способны изменять системные настройки. Вызвать выполнение таких команд можно только с правами администратора. Сделано это для безопасности. Поэтому, если вы находитесь в учётной записи гостя, у вас не получится осуществить вызов командной строки от имени администратора, а значит и выполнять команды, связанные с системными настройками.
Как пользоваться командной строкой
По причине того, что команд достаточно большое количество, весь их список невозможно отобразить в рамках одной статьи. По этой причине мы рассмотрим наиболее простые команды, которые можно выполнять и без прав администратора. Начнём.
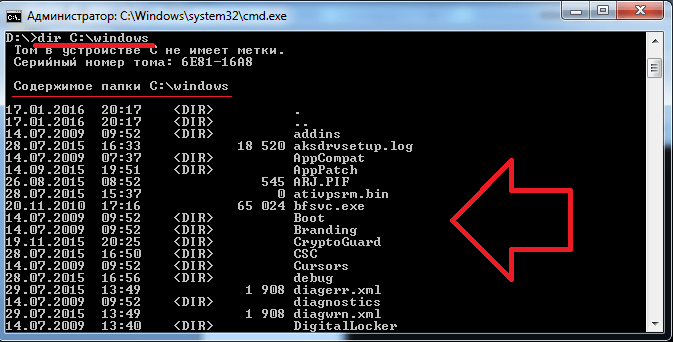
После запуска командной строки вы увидите примерно такое окно:
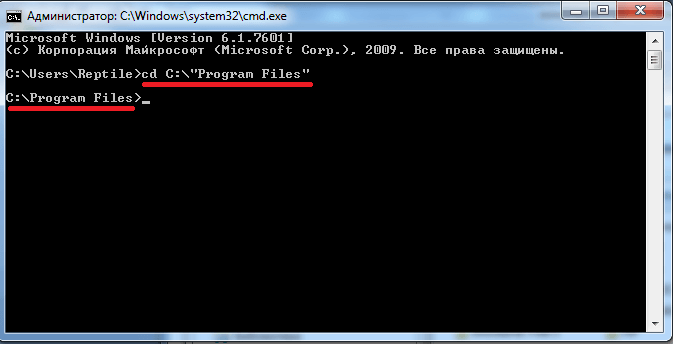
Адресная строка, предшествующая мигающему курсору — это адрес текущей папки на жёстком диске (или на любом другом подключенном устройстве). Переход по папкам (смена текущей папки) — одно из самых простых действий. Давайте, выполним эту команду. Для этого в окно необходимо вписать команду cd и указать полный путь до имени нужной нам папки, а затем нажать Enter для запуска выполнения. Например, если требуется попасть по адресу «C:Program Files», для этого достаточно ввести cd C:”Program Files”
Важно! При переходе к папке с пробелом в имени, её необходимо указывать в кавычках.
Таким образом, можно попасть в любую директорию жёсткого диска. Также необходимо знать, что если папка расположена в текущей папке командной строки, то при помощи «cd» она открывается без необходимости указания полного пути (достаточно после команды указать имя папки).
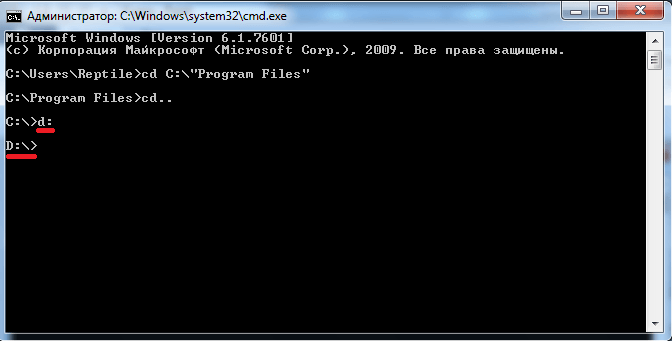
Чтобы выйти из текущей папки в папку более высокого уровня, то есть родительскую, используйте команду cd .. (две точки означают родительский каталог).
Теперь выполним переход на другой локальный диск. Для этого достаточно указать буквы диска с двоеточием. Например, мы хотим попасть на диск «D:» — пишем команду d: а затем нажимаем Enter.
Просмотр содержимого папки осуществляется при помощи команды «dir». Введите её и командная строка покажет список содержимого диска «D:». Команду «dir» можно вызывать из любой папки — даже для просмотра содержимого каталога на другом диске (для этого необходимо ввести полный путь до имени нужной папки). Например, выполните: dir c:windows
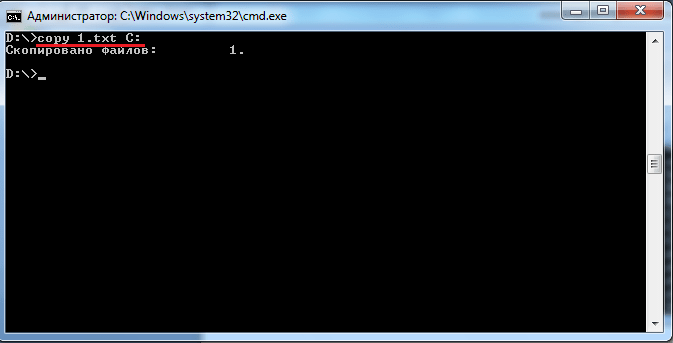
Рассмотрим ещё одну команду — «copy». Как ясно из названия, она служит для копирования данных. Например, вы находитесь на диске «D:» и вам нужно скопировать файл «1.txt» на флешку. Для этого вводим copy 1.txt F: Вместо «F:» можно указать любую другую букву диска (в нашем случае копируем на диск «C:») или полный путь до того каталога, куда необходимо скопировать файлы или папки.
Более продвинутая версия команды копирования — команда «robocopy», в отличие от своей предшественницы, она умеет копировать не только файлы, но и папки, включая их содержимое.
Вам не обязательно запоминать названия всех команд. Для вывода полного перечня с кратким описанием наберите: help
Для получения подробнейшей информации, к примеру, для robocopy, наберите: help robocopy
Обратите внимание, что help отображает все описания на русском языке, конечно же, если версия Windows у вас русифицированная.
Всё, что рассмотрено здесь — лишь малая часть возможностей командной строки. Если у вас есть интерес к её использованию, рекомендуем посетить официальный сайт Microsoft, где имеется полная информация по работе с ней.