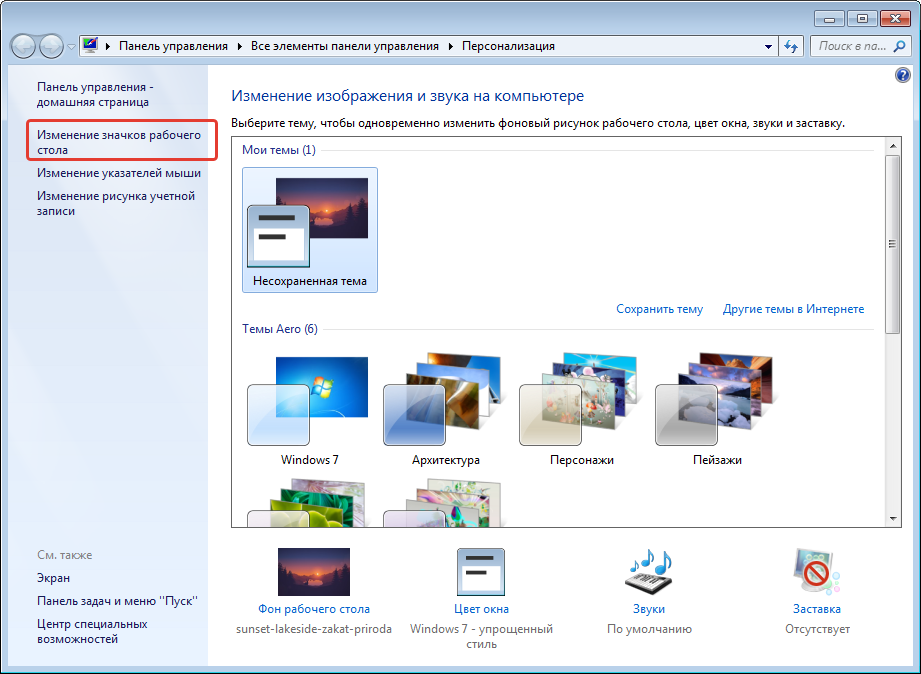
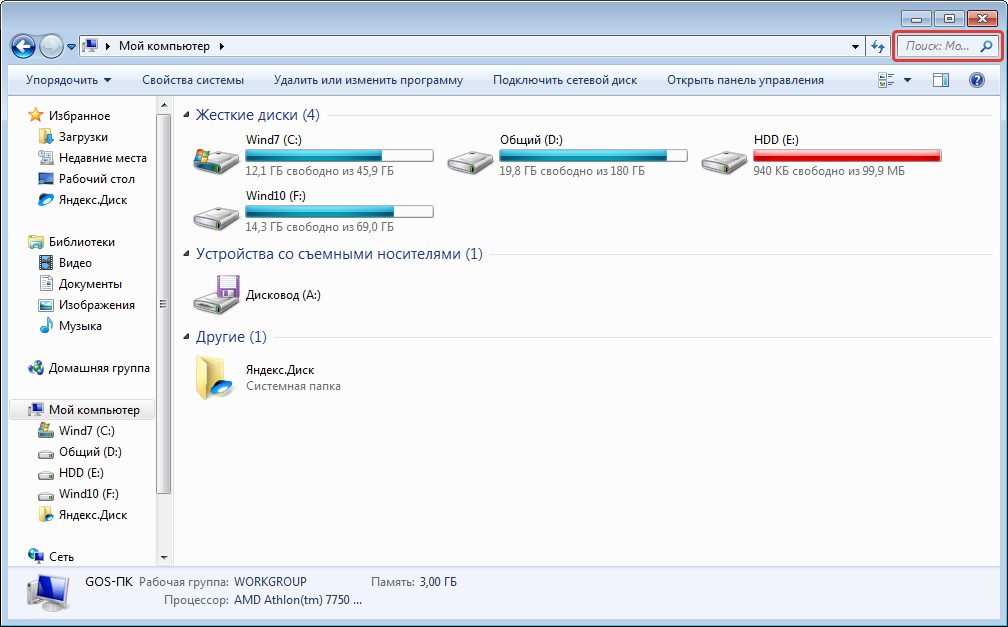
Проводник
— менеджер файлов и папок
Проводник
(Explorer
– исследователь)
— программное средство Windows, которое,
так же как и Мой
компьютер,
обеспечивает доступ к дискам, папкам и
файлам. В окне программы Проводник
имеется навигационная панель (слева),
которая представляет карту-схему
компьютера и его сетевого окружения.
Проводник
предназначен для управления файловой
системой и обеспечивает доступ к
локальным и сетевым ресурсам. Он
отображает содержимое папок, позволяет
открывать, копировать, перемещать,
удалять, переименовывать папки и файлы,
запускать программы.
В
окне программы Проводник
имеются две панели (две области): слева
– Папки
и
справа – содержимое открытой папки.
Границу между ними можно перемещать с
помощью мыши.
Левая
область Папки
облегчает
переход между папками, позволяет быстро
просматривать структуру папок, перемещать
и копировать файлы, перетаскивая их из
левой области в правую.
В
левом подокне рядом со значками некоторых
папок стоят знаки «+»
или «—«,
которыми помечены папки, содержащие
вложенные
подпапки.
Знак «+» отмечает закрытые, а знак
«-» — открытые папки. Щелчок мыши по
знакам «+» или «-» позволяет
открывать или закрывать соответствующие
папки.
Мой
компьютер
и Проводник
выполняют примерно одинаковые функции
и отличаются друг от друга форматом
представления данных о папках, файлах
и о дереве папок. Работать с окном Мой
компьютер
удобнее в том случае, если приходится
одновременно открывать два окна или
более. В окне программы Проводник
нагляднее представлена иерархия папок,
позволяющая легко переходить с уровня
на уровень одним щелчком мыши.
Проводник
– это программа для управления файлами
и папками, своего рода менеджер файлов.
Ее можно рассматривать как аналог
программы-оболочки Norton
Commander
в MS-DOS, FAR
manager и др.
Программы
Мой
компьютер,
Мои
документы
и Проводник
имеют много общего: внешний вид,
отображение содержимого папки и т.д.
Основное различие состоит в том, что
окна Моего
компьютера
не позволяют одновременно отобразить
всю иерархию и взаимосвязь различных
ресурсов компьютера. Используя Мой
компьютер
пользователь получает представление
об одной какой-либо папке.
Проводник
– программа для обслуживания файловой
системы компьютера (Windows представляет
все в виде папок), запуска программ и
открытия файлов.
Основное назначение Проводника
состоит в просмотре структуры файлов
и папок компьютера. Окно разделено на
две части (стандарт!):
слева – иерархическая структура папок
всего компьютера; справа – отображение
содержимого папки выделенной (выбранной)
в левой части.
На
вершине иерархии – Рабочий
стол
(это и есть самое начало работы с
компьютером!), далее – Мой
компьютер
(здесь можно увидеть тоже, что и в
программе Мой
компьютер),
на уровень ниже – Сетевое
окружение,
Корзина
и т.д. В папке Мой
компьютер
(как и в программе) сосредоточены все
ресурсы данного компьютера (диски,
панель управления, принтеры и т.д.), –
следовательно, Мой
компьютер
это уже как бы часть более мощной
программы Проводник.
В
левой части Проводника можно раскрывать
(-) и скрывать (+) содержимое какой-либо
папки до уровня вложенности папок, но
все содержимое папки (до уровня файлов)
можно увидеть только в правой части.
Возможности
Проводника
при работе с файлами и папками почти
такие же, как и у программы Мой
компьютер,
поэтому для большинства пользователей
они остаются как бы не востребованными.
Все, что делается с помощью Проводника,
может быть сделано и с использованием
программы Мои
компьютер.
Однако Проводник,
безусловно, выигрывает по наглядности
и удобству работы своего интерфейса.
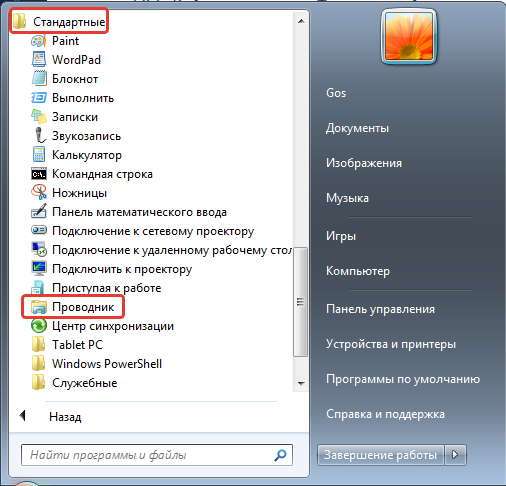
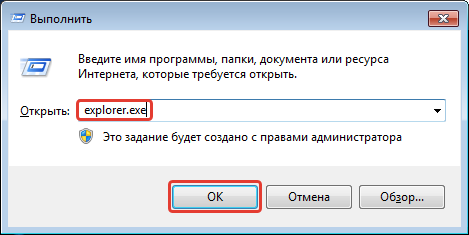
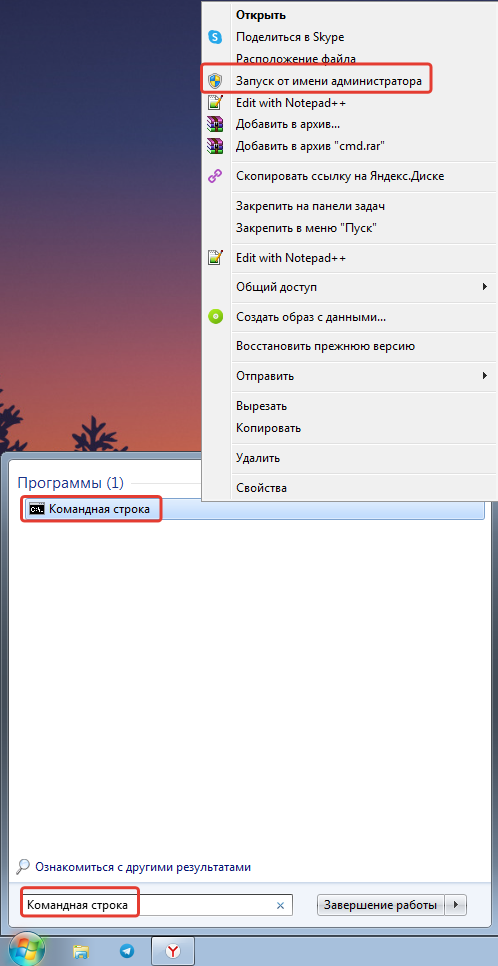
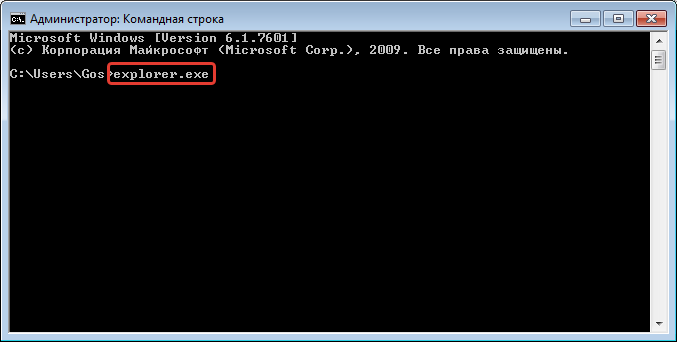
Существуют
различные виды запуска Проводника:
-
Основной
прием запуска: Контекстное
меню
кнопки Пуск
Проводник
(его используют практически всегда;
см. соответствующий рисунок) -
Пуск
Программы
Стандартные Проводник
(стандартный для всех Windows-программ)
В
виду своей важности и исключительности
при работе с файловой системой компьютера
имеется и много других способов запуска
Проводника. Например:
-
Мой
компьютер
Файл
Проводник -
Контекстное
меню
Мой
компьютер
(Корзина или другой системный объект)
Проводник
(аналогичен п.1, но если вы работаете с
какой-либо программой, то Рабочий стол
Windows закрыт её окном) -
Наконец,
Проводник
вызывается через окно Мой
компьютер,
когда вы открываете какую-либо папку
при нажатой клавише Shift.
Комбинации
клавиш в Проводнике
Если
вы приверженец использования клавиатуры,
то вам приятно будет узнать, что в
программе Проводник
предусмотрены многочисленные клавишные
комбинации (горячие клавиши), которые
повышают скорость вашей работы в этом
популярном Windows-приложении. Перечень
комбинаций клавиш и соответствующих
операций приведен в таблице.
Таблица
|
Клавиши |
Действие |
|
Alt |
Открытие |
|
Alt |
Закрытие |
|
Enter |
Открыть, |
|
Alt |
Вызов |
|
Shift |
Вызов |
|
Ctrl |
Выделение |
|
Ctrl |
Копирование |
|
Ctrl |
Вставка |
|
Ctrl |
Вырезание |
|
Ctrl |
Отмена |
|
Del |
Удаление |
|
Shift |
Удаление |
|
F2 |
Переименование |
|
F3 |
Вызов |
|
F5 |
Обновление |
|
F6 |
Переключение |
|
Alt |
Закрытие |
Кроме
клавишных комбинаций быстрый доступ к
командам Проводника
предоставляют контекстные
меню
выделенных объектов (указатель мышки
внутри выделения). Отметим, что работа
в Проводнике
с помощью правой кнопки мыши чрезвычайно
удобна.
Соседние файлы в предмете [НЕСОРТИРОВАННОЕ]
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
- #
Интерфейс программы
Проводник ОС Windows
Проводник Windows
— это специальная программа, заведующая файловой системой, предназначена для
отображения пиктограмм устройств, файлов, папок и настроек данных объектов. С
содержимым любой папки можно познакомиться в окне Проводника. Интерфейс
программы «Проводник» значительно изменился, в Windows 7 разработана новая
функция Списки переходов, позволяющая быстро переходить к часто
используемым документам, изображениям, музыкальным записям или сайтам. В
системе присутствуют 4 предустановленные библиотеки: «Видео»,
«Изображения», «Документы» и «Музыка», но можно добавлять новые
библиотеки.
Рассмотрим
элементы окна программы «Проводник»(см.рис.1).
Рис.1. Окно программы Проводник
Окно
представляет собой замкнутую область, в верхней части которой расположены
область навигации и кнопки управления окном. Ниже располагается адресная строка с
кнопками Назад, Вперед, полем Поиска.
Кнопка Назад,
используется для перехода из текущей папки в другую на шаг назад — в предыдущий
каталог.
Кнопка Вперед,
позволяет вернуться к ранее просмотренной папке.
Адресная
строка
отображает путь к активной папке. В Windows 7 навигация между папками с помощью
адресной строки упрощена, достаточно воспользоваться кнопкой списка адресной
строки, быстро перемещаясь к любой папке, находящейся выше уровня текущей.
Поле поиска осуществляет быстрый поиск
файла, находящегося в активной или в вложенной папке, а также появилась функция
сохранения результатов поиска, для дальнейшего использования.
Под адресной
строкой располагается Панель инструментов, включающая в себя команды для
выполнения стандартных действий с файлами или папками, кнопки Views и Предварительный
просмотр. Команды панели инструментов меняются, в зависимости от активной
папки.
Кнопка Views позволяет быстро
выбрать нужный тип просмотра информации. Тип просмотра информации по содержимому
позволяет увидеть некоторые метаданные файла (см.рис.2).
Рис.2. Метаданные файла
Кнопка для
отображения или скрытия области Предварительного просмотра предназначена
для быстрого и удобного просмотра графических файлов.
Рабочая область
«Проводника7» состоит из двух панелей в левой части, более узкой сосредоточена Панель
навигации, состоящая из категорий Избранное, Библиотеки, Домашняя
группа, Компьютер и Сеть. Панель навигации обеспечивает быстрый доступ к
нужной папке и ее содержимому. В правой части рабочей области расположена
область содержимого активной папки, в ней отображаются эскизы файлов и
вложенных папок.
В нижней части
окна Проводника расположена Панель подробностей или Область свойств,
на которой выводится информация о выделенном объекте (название, автор,
состояние, ключевые слова, дата создания и изменения).
В Windows 7
созданы виртуальные папки, получившие название библиотек, такие как «Документы»,
«Изображения», «Музыка», «Видео». Открыть эти папки можно выбрав панель Быстрой
Навигации «Проводника» или с помощью кнопки «Пуск» основного меню системы.
Пользователь может работать как с созданными виртуальными папками, так и
создать новые, однако в библиотеку нельзя занести папки, расположенные на
съемных носителях.
Библиотеки, как
правило, используются для организации файлов определенного типа, но можно
менять свойства файлов.
Система Windows 7
— простая, удобная и очень надежная система.
This article is about the Microsoft Windows file listing browser. For exploring file system listings, see file browser. For exploring inside files, see file viewer.

File Explorer on Windows 11 in Light App Mode showing special folders on Home, with the new command bar and tabs feature. |
|
| Developer(s) | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| Initial release | August 15, 1995; 27 years ago |
| Stable release |
22H2 (10.0.22621.1194) (January 26, 2023; 9 days ago[1]) [±] |
| Preview release |
;Release Preview Channel 22H2 (10.0.22621.1194) (January 26, 2023; 9 days ago[2][3]) [±]
22H2 (10.0.22623.1250) (February 2, 2023; 2 days ago[4]) [±]
10.0.25290.1000 (February 1, 2023; 3 days ago[5]) [±] |
| Included with | Windows 95 and later |
| Predecessor | Program Manager, File Manager |
| Type | Shell, file manager |
File Explorer, previously known as Windows Explorer, is a file manager application that is included with releases of the Microsoft Windows operating system from Windows 95 onwards. It provides a graphical user interface for accessing the file systems. It is also the component of the operating system that presents many user interface items on the screen such as the taskbar and desktop. Controlling the computer is possible without Windows Explorer running (for example, the File ▸ Run command in Task Manager on NT-derived versions of Windows will function without it, as will commands typed in a command prompt window).
Overview[edit]
Windows Explorer was first included with Windows 95 as a replacement for File Manager, which came with all versions of Windows 3.x operating systems. Explorer could be accessed by double-clicking the new My Computer desktop icon or launched from the new Start Menu that replaced the earlier Program Manager. There is also a shortcut key combination: Windows key+E. Successive versions of Windows (and in some cases, Internet Explorer) introduced new features and capabilities, removed other features, and generally progressed from being a simple file system navigation tool into a task-based file management system.
While «Windows Explorer» or «File Explorer» is a term most commonly used to describe the file management aspect of the operating system, the Explorer process also houses the operating system’s search functionality and File Type associations (based on filename extensions), and is responsible for displaying the desktop icons, the Start Menu, the Taskbar, and the Control Panel. Collectively, these features are known as the Windows shell.
After a user logs in, the explorer process is created by the userinit process. Userinit performs some initialization of the user environment (such as running the login script and applying group policies) and then looks in the registry at the Shell value and creates a process to run the system-defined shell – by default, Explorer.exe. Then Userinit exits. This is why Explorer.exe is shown by various process explorers with no parent – its parent has exited.
History[edit]
In 1995, Microsoft first released test versions of a shell refresh, named the Shell Technology Preview, and often referred to informally as «NewShell».[6] The update was designed to replace the Windows 3.x Program Manager/File Manager based shell with Windows Explorer. The release provided capabilities quite similar to that of the Windows «Chicago» (codename for Windows 95) shell during its late beta phases, however was intended to be nothing more than a test release.[7] There were two public releases of the Shell Technology Preview, made available to MSDN and CompuServe users: May 26, 1995 and August 8, 1995. Both held Windows Explorer builds of 3.51.1053.1. The Shell Technology Preview program never saw a final release under NT 3.51. The entire program was moved across to the Cairo development group who finally integrated the new shell design into the NT code with the release of NT 4.0 in July 1996.
Windows 98 and Windows Desktop Update[edit]
With the release of the Windows Desktop Update (packaged with Internet Explorer 4 as an optional component, and included in Windows 98), Windows Explorer became «integrated» with Internet Explorer, most notably with the addition of navigation arrows (back and forward) for moving between recently visited directories, as well as Internet Explorer’s Favorites menu.
An address bar was also added to Windows Explorer, which a user could type in directory paths directly, and be taken to that folder.
Another feature that was based on Internet Explorer technology was customized folders. Such folders contained a hidden web page that controlled the way the Windows Explorer displayed the contents of the folder.
Windows ME and Windows 2000[edit]
The integrated media player in Windows Explorer in Windows 2000, playing a MIDI sequence on Media folder
The «Web-style» folders view, with the left Explorer pane displaying details for the object currently selected, is turned on by default. For certain file types, such as pictures and media files, a preview is also displayed in the left pane.[8] The Windows 2000 Explorer featured an interactive media player as the previewer for sound and video files. However, such a previewer can be enabled in Windows ME through the use of folder customization templates.[9] Windows Explorer in Windows 2000 and Windows ME allows for custom thumbnail previewers and tooltip handlers. The default file tooltip displays file title, author, subject and comments;[10] this metadata may be read from a special NTFS stream, if the file is on an NTFS volume, or from a COM Structured Storage stream, if the file is a structured storage document. All Microsoft Office documents since Office 95[11] make use of structured storage, so their metadata is displayable in the Windows 2000 Explorer default tooltip. File shortcuts can also store comments which are displayed as a tooltip when the mouse hovers over the shortcut.
The right-hand pane, which usually just lists files and folders, can also be customized. For example, the contents of the system folders aren’t displayed by default, instead showing in the right pane a warning to the user that modifying the contents of the system folders could harm their computer. It’s possible to define additional Explorer panes by using DIV elements in folder template files.[12] This feature was abused by computer viruses that employed malicious scripts, Java applets, or ActiveX controls in folder template files as their infection vector. Two such viruses are VBS/Roor-C[13] and VBS.Redlof.a.[14]
Other Explorer UI elements that can be customized include columns in «Details» view, icon overlays, and search providers: the new DHTML-based search pane is integrated into Windows 2000 Explorer, unlike the separate search dialog found in all previous Explorer versions.[15]
Search capabilities were added, offering full-text searches of documents, with options to filter by date (including arbitrary ranges like «modified within the last week»), size, and file type. The Indexing Service has also been integrated into the operating system and the search pane built into Explorer allows searching files indexed by its database.[16] The ability to customize the standard buttons was also added.
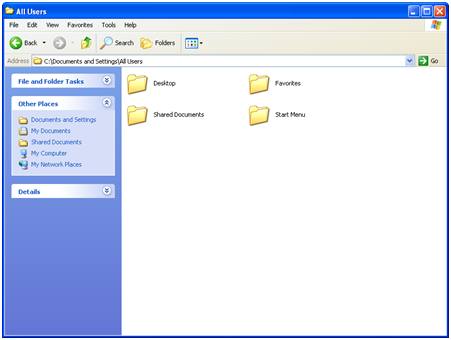
Windows XP and Windows Server 2003[edit]
Windows Explorer in Windows XP, showing All Users folder contents
There were significant changes made to Windows Explorer in Windows XP, both visually and functionally. Microsoft focused especially on making Explorer more discoverable and task-based, as well as adding several new features to reflect the growing use of a computer as a digital hub.
Windows Explorer in Windows Server 2003 contains all the same features as Windows XP, but the task panes and search companion are disabled by default.
Task pane[edit]
The task pane is displayed on the left-hand side of the window instead of the traditional folder tree view. It presents the user with a list of common actions and destinations that are relevant to the current directory or file(s) selected. For instance, when in a directory containing mostly pictures, a set of «Picture tasks» is shown, offering the options to display these pictures as a slide show, to print them out, or to go online to order prints. Conversely, a folder containing music files would offer options to play those files in a media player or to go online to purchase music. Windows XP had a Media bar but it was removed with SP1. The Media Bar was only available with Windows XP RTM.
Every folder also has «File and Folder Tasks», offering options to create new folders, share a folder on the local network, publish files or folders to a website, and other common tasks like copying, renaming, moving, and deleting files or folders. File types that have identified themselves as being printable also have an option listed to print the file.
Underneath «Other Places» is a «Details» pane which gives additional information – typically file size and date, but depending on the file type, a thumbnail preview, author, image dimensions, or other details.
The «Folders» button on the Windows Explorer toolbar toggles between the traditional tree view of folders, and the task pane. Users can get rid of the task pane or restore it using the sequence: Tools – Folder Options – General – Show Common Tasks/Use Windows Classic Folders.
Search companion[edit]
Windows Explorer’s default Search Companion, Rover, in Windows XP
Microsoft introduced animated «Search Companions» in an attempt to make searching more engaging and friendly; the default character is a puppy named Rover (previously used in Microsoft Bob), with three other characters (Merlin the magician, Earl the surfer, and Courtney) also available. These search companions use the same technology as Microsoft Office’s Office Assistants, even incorporating «tricks» and sound effects, and they can be used as Office Assistants if their files are copied into the C:Windowsmsagentchars folder.[17]
The search capability itself is fairly similar to Windows ME and Windows 2000, with one major addition: Search can also be instructed to search only files that are categorical «Documents» or «Pictures, music and video»; this feature is noteworthy largely because of how Windows determines what types of files can be classified under these categories. In order to maintain a relevant list of file types, Windows Explorer connects to Microsoft and downloads a set of XML files that define what these file types are. The Search Companion can be disabled in favor of the classic search pane used in Windows 2000 by using the Tweak UI applet from Microsoft’s PowerToys for Windows XP, or by manually editing the registry.
Image handling[edit]
Windows XP improves image preview in Explorer by offering a Filmstrip view. «Back» and «Previous» buttons facilitate navigation through the pictures, and a pair of «Rotate» buttons offer 90-degree clockwise and counter-clockwise (lossy)[18] rotation of images. Aside from the Filmstrip view mode, there is a ‘Thumbnails’ mode, which displays thumbnail-sized images in the folder. A Folder containing images will also show thumbnails of four of the images from that folder overlaid on top of a large folder icon.
Web publishing[edit]
Web sites that offer image hosting services can be plugged into Windows Explorer, which the user can use to select images on their computer, and have them uploaded correctly without dealing with comparatively complex solutions involving FTP or web interfaces.[citation needed]
Other changes[edit]
- Explorer gained the ability to understand the metadata of a number of types of files. For example, with images from a digital camera, the Exif information can be viewed, both in the Properties pages for the photo itself, as well as via optional additional Details View columns.
- A Tile view mode was added, which displays the file’s icon in a larger size (48 × 48), and places the file name, descriptive type, and additional information (typically the file size for data files, and the publisher name for applications) to the right.
- The Details view also presented an additional option called «Show in Groups» which allows the Explorer to separate its contents by headings based on the field which is used to sort the items.
- The taskbar can be locked to prevent it from accidentally being moved.
- Windows Explorer also gained the ability to burn CDs and DVD-RAM discs in Windows XP.
- Ability to create and open ZIP files called «compressed folders».[19][20]
- Ability to open Cabined (.cab) files.[21]
- If a
.HTMor.HTMLfile is copied or moved, the accompanying_filessuffix folder is copied or moved among it automatically.[22]
Removed and changed features[edit]
|
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (December 2012) |
- The sort order has changed compared to the one in Windows 2000. For file names containing numbers Windows Explorer now tries to sort based on numerical value rather than just comparing each number digit by digit.[23]
Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008[edit]
Windows Explorer in Windows Vista, showing Public folder contents
Search, organizing and metadata[edit]
Windows Explorer includes significant changes from previous versions of Windows such as improved filtering, sorting, grouping and stacking. Combined with integrated desktop search, Windows Explorer allows users to find and organize their files in new ways, such as stacks.[24][25] The new Stacks viewing mode groups files according to the criterion specified by the user.[25] Stacks can be clicked to filter the files shown in Windows Explorer. There is also the ability to save searches as virtual folders or search folders.[26] A search folder is simply an XML file, which stores the query in a form that can be used by the Windows search subsystem.[27] When accessed, the search is executed and the results are aggregated and presented as a virtual folder.[26] Windows Vista includes six search folders by default: recent documents, recent e-mail, recent music, recent pictures and videos, recent changed, and «Shared by Me».[28] Additionally, search operators for properties were introduced, such as kind:music. [29] Since at least Windows 7, comparison operators «greater than» and «less than» are supported to search for any supported attribute such as date ranges and file sizes, like size:>100MB to search for all files that are greater than 100MB.[30] Attributes sortable and searchable in Windows Explorer include pictures’ dimensions, Exif data such as aperture and exposure, video duration and framerate and width.[31]
When sorting items, the sort order no longer remains consistently Ascending or Descending. Each property has a preferred sort direction. For example, sort by date defaults to descending order, as does size. But name and type default to ascending order.
Searching for files containing a given text string became problematic with Vista unless the files had been indexed. An alternative is to use the findstr command-line function.[32] After right-clicking on a folder one can open a command-line prompt in that folder.
Windows Explorer also contains modifications in the visualization of files on a computer. A new addition to Windows Explorer in Vista and Server 2008 is the details pane, which displays metadata and information relating to the currently selected file or folder. The details pane will also display a thumbnail of the file or an icon of the filetype if the file does not contain visual information. Furthermore, different imagery is overlaid on thumbnails to give more information about the file, such as a picture frame around the thumbnail of an image file, or a filmstrip on a video file.
The details pane also allows for the change of some textual metadata such as author and title in files that support them within Windows Explorer. A new type of metadata called tags allows users to add descriptive terms to documents for easier categorization and retrieval. Some files support open metadata, allowing users to define new types of metadata for their files. Out-of-the-box, Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008 supports Microsoft Office documents and most audio and video files. Support for other file types can however be added by writing specialized software to retrieve the metadata at the shell’s request. Metadata stored in a file’s alternate data stream only on NTFS volumes cannot be viewed and edited through the summary tab of the file’s properties anymore. Instead, all metadata is stored inside the file, so that it will always travel with the file and not be dependent on the file system.[33]
Layout and icons[edit]
Windows Explorer in Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008 also introduces a new layout. The task panes from Windows XP are replaced with a toolbar on top and a navigation pane on the left. The navigation pane contains commonly accessed folders and preconfigured search folders. Eight different views are available to view files and folders, including extra large, large, medium, small, list, details, tiles, and content. In addition, column headers now appear in all icon viewing modes,[25] unlike Windows XP where they only appear in the details icon viewing mode.[24] File and folder actions such as cut, copy, paste, undo, redo, delete, rename and properties are built into a dropdown menu which appears when the Organize button is clicked. It is also possible to change the layout of the Explorer window by using the Organize button. Users can select whether to display classic menus, a search pane, a preview pane, a reading pane, and the navigation pane. The preview pane enables users to preview files (e.g., documents or media files) without opening them. If an application, such as Office 2007, installs preview handlers for file types, then these files can also be edited within the preview pane itself.[34]
Windows Vista saw the introduction of the breadcrumb bar for easier navigation. As opposed to the prior address bar which displayed the current folder in a simple editable combobox, this new style structures the path into clickable levels of folder hierarchy (though falls back to the classic edit mode when a blank area is clicked), enabling the user to skip as many levels as desired in one click rather than repeatedly clicking «Up». It is also possible to navigate to any subfolder of the current folder using the arrow to the right of the last item. The menu bar is now hidden by default but reappears temporarily when the user presses Alt.
Check boxes in Windows Explorer allow the selection of multiple files.[35] Free and used space on all drives is shown in horizontal indicator bars. Icons of various sizes are supported: 16 x 16, 24 x 24, 32 x 32, 48 x 48, 64 x 64, 96 x 96, 128 x 128 and 256 x 256. Windows Explorer can zoom the icons in and out using a slider or by holding down the Ctrl key and using the mouse scrollwheel.[36] Live icons can display the content of folders and files themselves rather than generic icons.[37]
Other changes[edit]
With the release of Windows Vista and Server 2008 and Windows Internet Explorer 7 for Windows XP, Internet Explorer is no longer integrated with Windows Explorer. In Windows Vista and Server 2008 (and in Windows XP as well if IE7 or 8 is installed), Windows Explorer no longer displays web pages, and IE7 does not support use as a file manager, although one will separately launch the other as necessary.
When moving or copying files from one folder to another, if two files have the same name, an option is now available to rename the file; in previous versions of Windows, the user was prompted to choose either a replacement or cancel moving the file. Also, when renaming a file, Explorer only highlights the filename without selecting the extension. Renaming multiple files is quicker as pressing Tab automatically renames the existing file or folder and opens the file name text field for the next file for renaming. Shift+Tab allows renaming in the same manner upwards.
Support for burning data on DVDs (DVD±R, DVD±R DL, DVD±R RW) in addition to CDs and DVD-RAM using version 2.0 of the Image Mastering API, as well as Live File System support was added.[38]
If a file is in use by another application, Windows Explorer tells users to close the application and retry the file operation. Also, a new interface IFileIsInUse is introduced into the API which developers can use to let other applications switch to the main window of the application that has the file open or simply close the file from the «File in Use» dialog. If the running application exposes these operations by means of the IFileIsInUse interface, Windows Explorer, upon encountering a locked file, allows the user to close the file or switch to the application from the dialog box itself.[39]
Windows Vista introduced precluded support for the Media Transfer Protocol.[citation needed]
Removed and changed features[edit]
The ability to customize the layout and buttons on the toolbars has been removed in Windows Vista’s Explorer, as has the ability to add a password to a zip file (compressed folder). The Toolbar button in Explorer to go up one folder from the current folder has been removed (the function still exists however, one can move up a folder by pressing Alt + ↑). Although still fully available from the menus and keyboard shortcuts, toolbar buttons for Cut, Copy, Paste, Undo, Delete, Properties and some others are no longer available. The Menu Bar is also hidden by default but is still available by pressing the Alt key or changing its visibility in the layout options. Several other features are removed such as showing the size on the status bar without selecting items, storing metadata in NTFS alternate data streams,[40] the IColumnProvider interface which allowed addition of custom columns to Explorer[41] and folder background customization using desktop.ini.
The option «Managing pairs of Web pages and folders» is also removed, and the user has no way of telling Vista that a .html file and the folder with the same name that was created when saving a complete web page from IE should be treated separately, that is, they cannot delete the folder without deleting the html file as well.[42]
The ability to right-click a folder and hit «Search» was removed in Windows Vista Service Pack 1. Users must open the folder they wish to search in and enter their keywords in the search field located on the top right corner of the window. Alternatively, users can specify other search parameters through the «Advanced Search» UI, which can be accessed by clicking on the Organize Bar and selecting Search Pane under the Layout submenu. Pressing F3 also opens the «Advanced Search» interface.
Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2[edit]
Windows Explorer in Windows 7, showing Libraries
Libraries[edit]
Windows Explorer in Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 supports libraries, virtual folders described in a .library-ms file that aggregates content from various locations – including shared folders on networked systems if the shared folder has been indexed by the host system – and present them in a unified view. Searching in a library automatically federates the query to the remote systems, in addition to searching on the local system, so that files on the remote systems are also searched. Unlike search folders, Libraries are backed by a physical location which allows files to be saved in the libraries. Such files are transparently saved in the backing physical folder. The default save location for a library may be configured by the user, as can the default view layout for each library. Libraries are generally stored in the libraries special folder, which allows them to be displayed on the navigation pane.
By default, a new user account in Windows 7 contains four libraries, for different file types: Documents, Music, Pictures, and Videos. They are configured to include the user’s profile folders for these respective file types, as well as the computer’s corresponding Public folders.
In addition to aggregating multiple storage locations, Libraries enable Arrangement Views and Search Filter Suggestions. Arrangement Views allow users to pivot their views of the library’s contents based on metadata. For example, selecting the «By Month» view in the Pictures library will display photos in stacks, where each stack represents a month of photos based on the date they were taken. In the Music library, the «By Artist» view will display stacks of albums from the artists in their collections, and browsing into an artist stack will then display the relevant albums.
Search Filter Suggestions are a new feature of the Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 Explorer’s search box. When the user clicks in the search box, a menu shows up below it showing recent searches as well as suggested Advanced Query Syntax filters that the user can type. When one is selected (or typed in manually), the menu will update to show the possible values to filter by for that property, and this list is based on the current location and other parts of the query already typed. For example, selecting the «tags» filter or typing «tags:» into the search box will display the list of possible tag values which will return search results.
The metadata written within the file, implemented in Vista, is also utilized in Windows 7. This can sometimes lead to long wait times displaying the contents of a folder. For example, if a folder contains many large video files totaling hundreds of gigabytes, and the Window Explorer pane is in Details view mode showing a property contained within the metadata (for example Date, Length, Frame Height), Windows Explorer might have to search the contents of the whole file for the meta data. Some damaged files can cause a prolonged delay as well. This is due to metadata information being able to be placed anywhere within the file, beginning, middle, or end, necessitating a search of the whole file. Lengthy delays also occur when displaying the contents of a folder with many different types of program icons. The icon is contained in the metadata. Some programs cause the activation of a virus scan when retrieving the icon information from the metadata, hence producing a lengthy delay.[33]
Arrangement Views and Search Filter Suggestions are database-backed features that require that all locations in the Library be indexed by the Windows Search service. Local disk locations must be indexed by the local indexer, and Windows Explorer will automatically add locations to the indexing scope when they are included in a library. Remote locations can be indexed by the indexer on another Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 machine, on a Windows machine running Windows Search 4 (such as Windows Vista or Windows Home Server), or on another device that implements the MS-WSP remote query protocol.[43]
Federated search[edit]
Windows Explorer also supports federating search to external data sources, such as custom databases or web services, that are exposed over the web and described via an OpenSearch definition. The federated location description (called a Search Connector) is provided as a .osdx file. Once installed, the data source becomes queryable directly from Windows Explorer. Windows Explorer features, such as previews and thumbnails, work with the results of a federated search as well.
Other changes[edit]
- Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 support showing icons in the context menu and creating cascaded context menus with static verbs in submenus using the Registry instead of a shell extension.[44]
- The search box in the Explorer window and the address bar can be resized.
- Certain folders in the navigation pane can be hidden to reduce clutter.
- Progress bars and overlay icons on an application’s button on the taskbar.
- Content view which shows thumbnails and metadata.
- Buttons to toggle the preview pane and create a new folder.
Removed or changed features[edit]
In Windows 7, several features have been removed from Windows Explorer, including the collapsible folder pane, overlay icon for shared items, remembering individual folder window sizes and positions, free disk space on the status bar, icons on the command bar, ability to disable Auto Arrange and Align to Grid, sortable column headings in other views except details view, ability to disable full row selection in details view, automatic horizontal scrolling and scrollbar in the navigation pane and maintaining selection when sorting from the Edit menu.
Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012[edit]
The new File Explorer with ribbon in Windows 8
The file manager on Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012 is renamed File Explorer and introduces new features such as a redesigned interface incorporating a ribbon toolbar, and a redesigned file operation dialog that displays more detailed progress and allows for file operations to be paused and resumed. The details pane from Windows Vista and 7 was removed and replaced with a narrower pane with no icons and fewer detail columns. But other details are displayed by hovering over the file’s name.[45][46]
Windows 10 and Windows Server 2016[edit]
The icons in File Explorer have been redesigned. They are flatter and simpler in design. The window border padding is thinner than previous versions. Windows 10 Creators Update and later versions come with a new Universal File Explorer (also known as the UWP File Explorer). Although hidden, it can be opened by creating a shortcut pointing to «explorer shell:AppsFolderc5e2524a-ea46-4f67-841f-6a9465d9d515_cw5n1h2txyewy!App» [47][48]
Windows 10, version 1809 and Windows Server 2019[edit]
A «dark mode» has been added to File Explorer in Windows 10, version 1809 and Windows Server 2019.[49] The Universal File Explorer also includes new features.[50][51]
Windows 10, version 1909[edit]
Windows Search and OneDrive have been integrated into File Explorer’s search feature in Windows 10, version 1909.[52]
Windows 11[edit]
In Windows 11, File Explorer had undergone significant UI changes with the Ribbon Interface simplified into a command bar. Translucency, shadows, and rounded geometry have also been added, following the Fluent Design System. In March 2022, Microsoft introduced adverts into the file explorer, but later stated that these were ‘not intended to be published externally’[53] after significant negative media coverage.
Windows 11 2022 Update[edit]
On April 5, 2022, Microsoft announced that it would be adding tabs, favorites, and a new homepage to File Explorer.[54] These features were eventually introduced via an update to the Windows 11 2022 Update on October 18, 2022.[55]
Extensibility[edit]
File Explorer can be extended to support non-default functionality by means of Windows shell extensions, which are COM objects that plug the extended functionality into Windows Explorer.[56] Shell extensions can be in the form of shell extension handlers, toolbars or even namespace extensions that allow certain folders (or even non-filesystem objects such as the images scanned by a scanner) to be presented as a special folder. File Explorer also allows metadata for files to be added as NTFS alternate data streams, separate from the data stream for the file.
Shell extension handlers are queried by the shell beforehand for modifying the action the shell takes. They can be associated on a per file type – where they will show up only when a particular action takes place on a particular file type – or on a global basis – which are always available. The shell supports the following extension handlers:
| Handler | Description | Can be implemented on | Required shell version |
|---|---|---|---|
| Context menu handler | Adds menu items to the context menu. It is called before the context menu is displayed. | Per file type | Windows 95 and later. Windows 7 introduced IExecuteCommand |
| Drag-and-drop handler | Controls the action upon right-click drag and drop and modifies the context menu that appears. | Global | Windows 95 and later |
| Drop target handler | Controls the action after a data object is dragged and dropped over a drop target such as a file. | Per file type | Windows 95 and later |
| Data object handler | Controls the action after a file is copied to the clipboard or dragged and dropped over a drop target. It can provide additional clipboard formats to the drop target. | Per file type | Windows 95 and later |
| Icon handler | Assigns a custom icon to an individual file amongst a class of file types. It is called before file icons are displayed. | Per file type | Windows 95 and later |
| Property sheet handler | Replaces or adds pages to the property sheet dialog box of an object. | Per file type | Windows 95 and later |
| Copy hook handler | Allows running, modifying or denying the action when a user or application tries to copy, move, delete, or rename an object. | Not associated with a file type | Windows 95 and later |
| Search handler | Allows shell integration of a custom search engine. | Not associated with a file type | Windows 95 through Windows XP |
| Infotip handler | Allows retrieving flags and infotip information for an item and displaying it inside a popup tooltip upon mouse hover. | Per file type | Windows Desktop Update and later |
| Thumbnail image handler | Provides for a thumbnail image to be generated and displayed along with its alpha type when a file is selected or the thumbnail view is activated. | Per file type | Windows Desktop Update and later. Windows Vista introduced a newer IThumbnailProvider interface that also shows thumbnails in the Details pane. The older IExtractImage is still supported but not in the Details pane.[57] |
| Disk Cleanup handler | Add a new entry to the Disk Cleanup application and allows specifying additional disk locations or files to clean up. | Per folder | Windows 98 and later |
| Column handler | Allows creating and displaying custom columns in Windows Explorer details view. It can be used to extend sorting and grouping. | Per folder | Windows 2000 and later |
| Icon overlay handler | Allows displaying an overlay icon over a shell object (a file or folder icon). | Per file type | Windows 2000 and later |
| Metadata handler | Allows viewing and modifying metadata stored in a file. It can be used to extend details view columns, infotips, property pages, sorting and grouping. | Per file type | Windows 2000 and later |
| Filter handler (IFilter) | Allows file properties and its contents to be indexed and searched by Indexing Service or Windows Search | Per file type | Windows 2000 and later |
| AutoPlay handler | Examines newly discovered removable media and devices and, based on content such as pictures, music or video files, launches an appropriate application to play or display the content. | Per file type category Windows XP only: per device and per file type category |
Windows XP and later |
| Property handler | Allows viewing and modifying system-defined and custom properties of a file. | Per file type | Windows Vista and later; on Windows XP if Windows Search is installed. |
| Preview handler | Renders enhanced previews of items without launching the default application when a file is selected. It can also provide file type-specific navigation such as browsing a document, or seeking inside a media file. | Per file type | Windows Vista and later |
Namespace extensions are used by Explorer and Common Dialogs to either display some data – which are not necessarily persisted as files – in a folder-like view or to present data in a way that is different from their organization on the file system. This feature can be exploited by a any hierarchical data source that can be represented as a file system like the Windows one, including Cloud-based implementation. Special folders, such as My Computer and Network Places in Windows Explorer are implemented this way, as are Explorer views that let items in a mobile phone or digital camera be explored. Source-control systems that use Explorer to browse source repositories also use Namespace extensions to allow Explorer to browse the revisions. To implement a namespace extension, the IPersistFolder, IShellView, IShellFolder, IShellBrowser and IOleWindow interfaces need to be implemented and registered. The implementation needs to provide the logic for navigating the data store as well as describing the presentation. Windows Explorer will instantiate the COM objects as required.[58]
While Windows Explorer natively exposes the extensibility points as COM interfaces, .NET Framework can also be used to write some types of extensions, using the COM Interop functionality of .NET Framework.[58] While Microsoft itself makes available extensions – such as the photo info tool[59] – which are authored using .NET Framework, they currently recommend against writing managed shell extensions, as only one instance of the CLR (prior to version 4.0) can be loaded per-process. This behavior will cause conflicts if multiple managed add-ins, targeting different versions of the CLR, are attempted to be run simultaneously.[60][61]
See also[edit]
- Comparison of file managers
- List of alternative shells for Windows
Notes and references[edit]
- ^ «January 26, 2023—KB5022360 (OS Build 22621.1194) Preview». Microsoft Support. Microsoft.
- ^ «Releasing Windows 11 Build 22621.1192 to the Release Preview Channel». Windows Insider Blog. January 17, 2023.
- ^ «January 26, 2023—KB5022360 (OS Build 22621.1194) Preview». Microsoft Support. Microsoft.
- ^ «Announcing Windows 11 Insider Preview Build 22621.1250 and 22623.1250». Windows Insider Blog. February 2, 2023.
- ^ «Announcing Windows 11 Insider Preview Build 25290». Windows Insider Blog. February 1, 2023.
- ^ Lineback, Nathan. «Misc Windows». toastytech.com. Archived from the original on July 3, 2018. Retrieved June 19, 2018.
- ^ John D. Ruley (September 1995). «NT Gets the Look But Not the Logo». How-To Columns. WinMag. Archived from the original on March 14, 2006. Retrieved September 4, 2009. Internet Archive
- ^ «Managing Files, Folders, and Search Methods: Microsoft TechNet». microsoft.com. Archived from the original on January 12, 2009. Retrieved June 19, 2018.
- ^ «Serenity Macros Home Page – Resources for MS Word». www.mvps.org. Archived from the original on June 27, 2018. Retrieved June 19, 2018.
- ^ Windows 2000 Registry: Latest Features and APIs Provide the Power to Customize and Extend Your Apps, MSDN Magazine, November 2000, archived from the original on April 15, 2003, retrieved August 26, 2007
- ^ «COM Objects and Structured Storage» Archived 2018-12-18 at the Wayback Machine, Windows Dev Center, May 31, 2018
- ^ Esposito, Dino (June 2000), More Windows 2000 UI Goodies: Extending Explorer Views by Customizing Hypertext Template Files, MSDN Magazine, archived from the original on August 24, 2007, retrieved August 26, 2007
- ^ Sophos, VBS/Roor-C threat analysis Archived 2007-11-30 at the Wayback Machine. Accessed August 26, 2007.
- ^ «Virus.VBS.Redlof.a», Virus Encyclopedia, Viruslist.com, January 15, 2004, archived from the original on October 28, 2007, retrieved August 26, 2007
- ^ Figure 1 Windows Shell Extensions, MSDN Magazine, June 2000, archived from the original on August 31, 2004, retrieved August 26, 2007
- ^ «What is Indexing Service?». msdn.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on January 1, 2011. Retrieved June 19, 2018.
- ^ «Is Microsoft Office 2003 still decent for general use on Windows 7, 8.1 and 10». answers.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on February 7, 2016. Retrieved June 19, 2018.
- ^ «What is Windows XP?». www.computerhope.com. Retrieved August 12, 2022.
- ^ «Windows XP – What’s new with files and folders». Windows. Microsoft. Archived from the original on May 23, 2007.
- ^ How to create and extract a Zip File in Windows ME/XP/2003
- ^ How To: Open a Cab file – Quote: «If you’re using Windows XP or Windows Vista, then your operating system has built-in support for opening Cab files.»
- ^ «Moving web pages saved by IE (HTM file & _FILES folder)». Directory Opus Resource Centre. May 4, 2009. Archived from the original on December 16, 2020. Retrieved December 16, 2020.
When Windows Explorer […] move a Web page both the HTML file and the directory are automatically moved together. […] Moreover, the user only has to drag EITHER part—the file or the directory and the other part will follow automatically. This way the page is kept intact irrespective of where Windows stores it.
- ^ The sort order for files and folders whose names contain numerals is different in Windows Vista, Windows XP, and Windows Server 2003 than it is in Windows 2000, support.microsoft.com, August 28, 2007, archived from the original on September 27, 2010, retrieved July 6, 2009
- ^ a b Shultz, Greg (August 10, 2006). «Examine the filtering, grouping, and stacking features in Windows Vista’s Windows Explorer». TechRepublic. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on December 22, 2015. Retrieved December 19, 2015.
- ^ a b c Reid, Rory (January 30, 2007). «Seven days of Vista — day 4: Stacking and filtering». CNET. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on December 22, 2015. Retrieved December 19, 2015.
- ^ a b Kaelin, Mark (July 17, 2007). «How do I… Save and refine desktop searches in Microsoft Windows Vista?». TechRepublic. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on November 17, 2015. Retrieved November 11, 2015.
- ^ Microsoft. «Saved Search File Format». MSDN. Archived from the original on December 10, 2015. Retrieved December 21, 2015.
- ^ Bentz, Ben (October 31, 2006). «Query Composition: Building a search upon another search». Shell: Revealed Blog. Microsoft. Archived from the original on December 15, 2006. Retrieved December 21, 2015.
- ^ Using search operators to find pictures, music and videos in Windows Vista
- ^ Windows 7: Find/Search Files By Date And Size
- ^ Windows Explorer Columns — Are you Fully Using Them?
- ^ «How to Search for Contents in Any File Type Without Indexing Service Enabled in Windows Vista and Windows 7». Wikihow.com. January 27, 2014. Archived from the original on March 19, 2017. Retrieved January 31, 2014.
- ^ a b Microsoft. «Add tags or other properties to a file». Windows How-to. Archived from the original on December 22, 2015. Retrieved December 21, 2015.
- ^ White, Nick (July 13, 2007). «10 Things – Windows Explorer Has a New Preview Pane». Windows Vista Team Blog. Microsoft. Archived from the original on July 15, 2007. Retrieved December 14, 2015.
- ^ Microsoft. «Pen and Touch Input in Windows Vista». MSDN. Archived from the original on December 22, 2015. Retrieved December 21, 2015.
- ^ Oiaga, Marius (September 27, 2006). «Quick Zoom on the Windows Vista Desktop and in Explorer». Softpedia. Archived from the original on December 22, 2015. Retrieved December 21, 2015.
- ^ McFedries, Paul (2008). Microsoft Windows Vista Unleashed. Sams Publishing. p. 87. ISBN 978-0-672-33013-1. Retrieved December 21, 2015.
- ^ Mangefeste, Tony; Walp, David (2006). «Optical Platform: Windows Vista and Beyond». Microsoft. Archived from the original (PPT) on June 4, 2011. Retrieved December 21, 2015.
- ^ Davis, Christopher (March 29, 2007). «Your File Is In Use… Demystified». Shell: Revealed Blog. Microsoft. Archived from the original on April 29, 2007. Retrieved December 21, 2015.
- ^ «Properties». msdn2.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on October 9, 2007. Retrieved June 19, 2018.
- ^ «IColumnProvider interface (Windows)». msdn2.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on April 17, 2008. Retrieved June 19, 2018.
- ^ A solution to this is provided on http://windowsxp.mvps.org/webpairs.htm Archived 2010-12-24 at the Wayback Machine. After the webpairs.reg file has been merged into the registry, the «Managing pairs of Web pages and folders» option is available in the Folder Options View tab.
- ^ «MS-WSP: Windows Search Protocol», MSDN Library, Microsoft, December 18, 2006, archived from the original on May 16, 2010, retrieved June 10, 2009
- ^ «Creating Shortcut Menu Handlers (Windows)». msdn.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on November 22, 2010. Retrieved June 19, 2018.
- ^ «Improvements in Windows Explorer». Archived from the original on November 7, 2011. Retrieved October 30, 2011.
- ^ «Microsoft switches to File Explorer name in Windows 8, bids farewell to Windows Explorer». The Verge. June 29, 2012. Archived from the original on August 17, 2012. Retrieved August 3, 2012.
- ^ «How to open UWP File Explorer on Windows 10 – Step by step». Windows Latest. May 7, 2017. Archived from the original on August 24, 2018. Retrieved August 24, 2018.
- ^ «Windows 10 Tip: Unlock the UWP File Explorer – Thurrott.com». Thurrott.com. May 6, 2017. Archived from the original on August 24, 2018. Retrieved August 24, 2018.
- ^ «Inspired by Insiders – Dark Theme in File Explorer». August 8, 2018. Archived from the original on August 12, 2018. Retrieved August 23, 2018.
- ^ «Microsoft updates universal File Explorer with new features in Windows 10 version 1809». Windows Central. Archived from the original on August 25, 2018. Retrieved August 24, 2018.
- ^ «UWP File Explorer has got new features in Windows 10 version 1809». Winaero. August 23, 2018. Archived from the original on August 25, 2018. Retrieved August 24, 2018.
- ^ «Windows 10 version 1909: new and changed features — gHacks Tech News». www.ghacks.net. October 2019. Archived from the original on October 25, 2019. Retrieved October 25, 2019.
- ^ Warren, Tom (March 15, 2022). «Microsoft says Windows 11’s File Explorer ads were ‘not intended to be published externally’«. The Verge. Retrieved July 28, 2022.
- ^ Warren, Tom (April 5, 2022). «Windows 11’s refreshed File Explorer gets tabs, favorites, and a new homepage». The Verge. Retrieved August 12, 2022.
- ^ Warren, Tom (October 18, 2022). «Windows 11’s new tabbed File Explorer and taskbar improvements are available today». The Verge. Retrieved October 18, 2022.
- ^ ShellExView v1.19 – Shell Extensions Manager for Windows, archived from the original on October 24, 2010, retrieved March 31, 2008
- ^ «Thumbnail Handlers (Windows)». msdn.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on June 19, 2018. Retrieved June 19, 2018.
- ^ a b Rensin, Dave (January 2004). «Create Namespace Extensions for Windows Explorer with the .NET Framework». msdn.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on May 8, 2008. Retrieved March 31, 2008.
- ^ «Microsoft Download Center: Windows, Office, Xbox & More». www.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on May 13, 2008. Retrieved June 19, 2018.
- ^ «MSDN Magazine Issues». msdn.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on May 21, 2008. Retrieved June 19, 2018.
- ^ Zhang, Junfeng (November 18, 2005). «Don’t do Shell Extension Handlers in .NET». msdn.com. Archived from the original on January 5, 2010. Retrieved June 19, 2018.
External links[edit]
- Sullivan, Kent. «The Windows 95 User Interface: A Case Study in Usability Engineering» (1996) for Association for Computing Machinery. (Sullivan was a developer on the Windows 95 UI team)
- How To Customize the Windows Explorer Views in Windows XP
- MSDN: Creating Shell Extension Handlers, Windows Dev Center, May 31, 2018
- The Complete Idiot’s Guide to Writing Shell Extensions, by Michal Dunn, March 15, 2006
- Namespace extensions – the undocumented Windows Shell, by Henk Devos, November 30, 1999
This article is about the Microsoft Windows file listing browser. For exploring file system listings, see file browser. For exploring inside files, see file viewer.

File Explorer on Windows 11 in Light App Mode showing special folders on Home, with the new command bar and tabs feature. |
|
| Developer(s) | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| Initial release | August 15, 1995; 27 years ago |
| Stable release |
22H2 (10.0.22621.1194) (January 26, 2023; 9 days ago[1]) [±] |
| Preview release |
;Release Preview Channel 22H2 (10.0.22621.1194) (January 26, 2023; 9 days ago[2][3]) [±]
22H2 (10.0.22623.1250) (February 2, 2023; 2 days ago[4]) [±]
10.0.25290.1000 (February 1, 2023; 3 days ago[5]) [±] |
| Included with | Windows 95 and later |
| Predecessor | Program Manager, File Manager |
| Type | Shell, file manager |
File Explorer, previously known as Windows Explorer, is a file manager application that is included with releases of the Microsoft Windows operating system from Windows 95 onwards. It provides a graphical user interface for accessing the file systems. It is also the component of the operating system that presents many user interface items on the screen such as the taskbar and desktop. Controlling the computer is possible without Windows Explorer running (for example, the File ▸ Run command in Task Manager on NT-derived versions of Windows will function without it, as will commands typed in a command prompt window).
Overview[edit]
Windows Explorer was first included with Windows 95 as a replacement for File Manager, which came with all versions of Windows 3.x operating systems. Explorer could be accessed by double-clicking the new My Computer desktop icon or launched from the new Start Menu that replaced the earlier Program Manager. There is also a shortcut key combination: Windows key+E. Successive versions of Windows (and in some cases, Internet Explorer) introduced new features and capabilities, removed other features, and generally progressed from being a simple file system navigation tool into a task-based file management system.
While «Windows Explorer» or «File Explorer» is a term most commonly used to describe the file management aspect of the operating system, the Explorer process also houses the operating system’s search functionality and File Type associations (based on filename extensions), and is responsible for displaying the desktop icons, the Start Menu, the Taskbar, and the Control Panel. Collectively, these features are known as the Windows shell.
After a user logs in, the explorer process is created by the userinit process. Userinit performs some initialization of the user environment (such as running the login script and applying group policies) and then looks in the registry at the Shell value and creates a process to run the system-defined shell – by default, Explorer.exe. Then Userinit exits. This is why Explorer.exe is shown by various process explorers with no parent – its parent has exited.
History[edit]
In 1995, Microsoft first released test versions of a shell refresh, named the Shell Technology Preview, and often referred to informally as «NewShell».[6] The update was designed to replace the Windows 3.x Program Manager/File Manager based shell with Windows Explorer. The release provided capabilities quite similar to that of the Windows «Chicago» (codename for Windows 95) shell during its late beta phases, however was intended to be nothing more than a test release.[7] There were two public releases of the Shell Technology Preview, made available to MSDN and CompuServe users: May 26, 1995 and August 8, 1995. Both held Windows Explorer builds of 3.51.1053.1. The Shell Technology Preview program never saw a final release under NT 3.51. The entire program was moved across to the Cairo development group who finally integrated the new shell design into the NT code with the release of NT 4.0 in July 1996.
Windows 98 and Windows Desktop Update[edit]
With the release of the Windows Desktop Update (packaged with Internet Explorer 4 as an optional component, and included in Windows 98), Windows Explorer became «integrated» with Internet Explorer, most notably with the addition of navigation arrows (back and forward) for moving between recently visited directories, as well as Internet Explorer’s Favorites menu.
An address bar was also added to Windows Explorer, which a user could type in directory paths directly, and be taken to that folder.
Another feature that was based on Internet Explorer technology was customized folders. Such folders contained a hidden web page that controlled the way the Windows Explorer displayed the contents of the folder.
Windows ME and Windows 2000[edit]
The integrated media player in Windows Explorer in Windows 2000, playing a MIDI sequence on Media folder
The «Web-style» folders view, with the left Explorer pane displaying details for the object currently selected, is turned on by default. For certain file types, such as pictures and media files, a preview is also displayed in the left pane.[8] The Windows 2000 Explorer featured an interactive media player as the previewer for sound and video files. However, such a previewer can be enabled in Windows ME through the use of folder customization templates.[9] Windows Explorer in Windows 2000 and Windows ME allows for custom thumbnail previewers and tooltip handlers. The default file tooltip displays file title, author, subject and comments;[10] this metadata may be read from a special NTFS stream, if the file is on an NTFS volume, or from a COM Structured Storage stream, if the file is a structured storage document. All Microsoft Office documents since Office 95[11] make use of structured storage, so their metadata is displayable in the Windows 2000 Explorer default tooltip. File shortcuts can also store comments which are displayed as a tooltip when the mouse hovers over the shortcut.
The right-hand pane, which usually just lists files and folders, can also be customized. For example, the contents of the system folders aren’t displayed by default, instead showing in the right pane a warning to the user that modifying the contents of the system folders could harm their computer. It’s possible to define additional Explorer panes by using DIV elements in folder template files.[12] This feature was abused by computer viruses that employed malicious scripts, Java applets, or ActiveX controls in folder template files as their infection vector. Two such viruses are VBS/Roor-C[13] and VBS.Redlof.a.[14]
Other Explorer UI elements that can be customized include columns in «Details» view, icon overlays, and search providers: the new DHTML-based search pane is integrated into Windows 2000 Explorer, unlike the separate search dialog found in all previous Explorer versions.[15]
Search capabilities were added, offering full-text searches of documents, with options to filter by date (including arbitrary ranges like «modified within the last week»), size, and file type. The Indexing Service has also been integrated into the operating system and the search pane built into Explorer allows searching files indexed by its database.[16] The ability to customize the standard buttons was also added.
Windows XP and Windows Server 2003[edit]
Windows Explorer in Windows XP, showing All Users folder contents
There were significant changes made to Windows Explorer in Windows XP, both visually and functionally. Microsoft focused especially on making Explorer more discoverable and task-based, as well as adding several new features to reflect the growing use of a computer as a digital hub.
Windows Explorer in Windows Server 2003 contains all the same features as Windows XP, but the task panes and search companion are disabled by default.
Task pane[edit]
The task pane is displayed on the left-hand side of the window instead of the traditional folder tree view. It presents the user with a list of common actions and destinations that are relevant to the current directory or file(s) selected. For instance, when in a directory containing mostly pictures, a set of «Picture tasks» is shown, offering the options to display these pictures as a slide show, to print them out, or to go online to order prints. Conversely, a folder containing music files would offer options to play those files in a media player or to go online to purchase music. Windows XP had a Media bar but it was removed with SP1. The Media Bar was only available with Windows XP RTM.
Every folder also has «File and Folder Tasks», offering options to create new folders, share a folder on the local network, publish files or folders to a website, and other common tasks like copying, renaming, moving, and deleting files or folders. File types that have identified themselves as being printable also have an option listed to print the file.
Underneath «Other Places» is a «Details» pane which gives additional information – typically file size and date, but depending on the file type, a thumbnail preview, author, image dimensions, or other details.
The «Folders» button on the Windows Explorer toolbar toggles between the traditional tree view of folders, and the task pane. Users can get rid of the task pane or restore it using the sequence: Tools – Folder Options – General – Show Common Tasks/Use Windows Classic Folders.
Search companion[edit]
Windows Explorer’s default Search Companion, Rover, in Windows XP
Microsoft introduced animated «Search Companions» in an attempt to make searching more engaging and friendly; the default character is a puppy named Rover (previously used in Microsoft Bob), with three other characters (Merlin the magician, Earl the surfer, and Courtney) also available. These search companions use the same technology as Microsoft Office’s Office Assistants, even incorporating «tricks» and sound effects, and they can be used as Office Assistants if their files are copied into the C:Windowsmsagentchars folder.[17]
The search capability itself is fairly similar to Windows ME and Windows 2000, with one major addition: Search can also be instructed to search only files that are categorical «Documents» or «Pictures, music and video»; this feature is noteworthy largely because of how Windows determines what types of files can be classified under these categories. In order to maintain a relevant list of file types, Windows Explorer connects to Microsoft and downloads a set of XML files that define what these file types are. The Search Companion can be disabled in favor of the classic search pane used in Windows 2000 by using the Tweak UI applet from Microsoft’s PowerToys for Windows XP, or by manually editing the registry.
Image handling[edit]
Windows XP improves image preview in Explorer by offering a Filmstrip view. «Back» and «Previous» buttons facilitate navigation through the pictures, and a pair of «Rotate» buttons offer 90-degree clockwise and counter-clockwise (lossy)[18] rotation of images. Aside from the Filmstrip view mode, there is a ‘Thumbnails’ mode, which displays thumbnail-sized images in the folder. A Folder containing images will also show thumbnails of four of the images from that folder overlaid on top of a large folder icon.
Web publishing[edit]
Web sites that offer image hosting services can be plugged into Windows Explorer, which the user can use to select images on their computer, and have them uploaded correctly without dealing with comparatively complex solutions involving FTP or web interfaces.[citation needed]
Other changes[edit]
- Explorer gained the ability to understand the metadata of a number of types of files. For example, with images from a digital camera, the Exif information can be viewed, both in the Properties pages for the photo itself, as well as via optional additional Details View columns.
- A Tile view mode was added, which displays the file’s icon in a larger size (48 × 48), and places the file name, descriptive type, and additional information (typically the file size for data files, and the publisher name for applications) to the right.
- The Details view also presented an additional option called «Show in Groups» which allows the Explorer to separate its contents by headings based on the field which is used to sort the items.
- The taskbar can be locked to prevent it from accidentally being moved.
- Windows Explorer also gained the ability to burn CDs and DVD-RAM discs in Windows XP.
- Ability to create and open ZIP files called «compressed folders».[19][20]
- Ability to open Cabined (.cab) files.[21]
- If a
.HTMor.HTMLfile is copied or moved, the accompanying_filessuffix folder is copied or moved among it automatically.[22]
Removed and changed features[edit]
|
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (December 2012) |
- The sort order has changed compared to the one in Windows 2000. For file names containing numbers Windows Explorer now tries to sort based on numerical value rather than just comparing each number digit by digit.[23]
Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008[edit]
Windows Explorer in Windows Vista, showing Public folder contents
Search, organizing and metadata[edit]
Windows Explorer includes significant changes from previous versions of Windows such as improved filtering, sorting, grouping and stacking. Combined with integrated desktop search, Windows Explorer allows users to find and organize their files in new ways, such as stacks.[24][25] The new Stacks viewing mode groups files according to the criterion specified by the user.[25] Stacks can be clicked to filter the files shown in Windows Explorer. There is also the ability to save searches as virtual folders or search folders.[26] A search folder is simply an XML file, which stores the query in a form that can be used by the Windows search subsystem.[27] When accessed, the search is executed and the results are aggregated and presented as a virtual folder.[26] Windows Vista includes six search folders by default: recent documents, recent e-mail, recent music, recent pictures and videos, recent changed, and «Shared by Me».[28] Additionally, search operators for properties were introduced, such as kind:music. [29] Since at least Windows 7, comparison operators «greater than» and «less than» are supported to search for any supported attribute such as date ranges and file sizes, like size:>100MB to search for all files that are greater than 100MB.[30] Attributes sortable and searchable in Windows Explorer include pictures’ dimensions, Exif data such as aperture and exposure, video duration and framerate and width.[31]
When sorting items, the sort order no longer remains consistently Ascending or Descending. Each property has a preferred sort direction. For example, sort by date defaults to descending order, as does size. But name and type default to ascending order.
Searching for files containing a given text string became problematic with Vista unless the files had been indexed. An alternative is to use the findstr command-line function.[32] After right-clicking on a folder one can open a command-line prompt in that folder.
Windows Explorer also contains modifications in the visualization of files on a computer. A new addition to Windows Explorer in Vista and Server 2008 is the details pane, which displays metadata and information relating to the currently selected file or folder. The details pane will also display a thumbnail of the file or an icon of the filetype if the file does not contain visual information. Furthermore, different imagery is overlaid on thumbnails to give more information about the file, such as a picture frame around the thumbnail of an image file, or a filmstrip on a video file.
The details pane also allows for the change of some textual metadata such as author and title in files that support them within Windows Explorer. A new type of metadata called tags allows users to add descriptive terms to documents for easier categorization and retrieval. Some files support open metadata, allowing users to define new types of metadata for their files. Out-of-the-box, Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008 supports Microsoft Office documents and most audio and video files. Support for other file types can however be added by writing specialized software to retrieve the metadata at the shell’s request. Metadata stored in a file’s alternate data stream only on NTFS volumes cannot be viewed and edited through the summary tab of the file’s properties anymore. Instead, all metadata is stored inside the file, so that it will always travel with the file and not be dependent on the file system.[33]
Layout and icons[edit]
Windows Explorer in Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008 also introduces a new layout. The task panes from Windows XP are replaced with a toolbar on top and a navigation pane on the left. The navigation pane contains commonly accessed folders and preconfigured search folders. Eight different views are available to view files and folders, including extra large, large, medium, small, list, details, tiles, and content. In addition, column headers now appear in all icon viewing modes,[25] unlike Windows XP where they only appear in the details icon viewing mode.[24] File and folder actions such as cut, copy, paste, undo, redo, delete, rename and properties are built into a dropdown menu which appears when the Organize button is clicked. It is also possible to change the layout of the Explorer window by using the Organize button. Users can select whether to display classic menus, a search pane, a preview pane, a reading pane, and the navigation pane. The preview pane enables users to preview files (e.g., documents or media files) without opening them. If an application, such as Office 2007, installs preview handlers for file types, then these files can also be edited within the preview pane itself.[34]
Windows Vista saw the introduction of the breadcrumb bar for easier navigation. As opposed to the prior address bar which displayed the current folder in a simple editable combobox, this new style structures the path into clickable levels of folder hierarchy (though falls back to the classic edit mode when a blank area is clicked), enabling the user to skip as many levels as desired in one click rather than repeatedly clicking «Up». It is also possible to navigate to any subfolder of the current folder using the arrow to the right of the last item. The menu bar is now hidden by default but reappears temporarily when the user presses Alt.
Check boxes in Windows Explorer allow the selection of multiple files.[35] Free and used space on all drives is shown in horizontal indicator bars. Icons of various sizes are supported: 16 x 16, 24 x 24, 32 x 32, 48 x 48, 64 x 64, 96 x 96, 128 x 128 and 256 x 256. Windows Explorer can zoom the icons in and out using a slider or by holding down the Ctrl key and using the mouse scrollwheel.[36] Live icons can display the content of folders and files themselves rather than generic icons.[37]
Other changes[edit]
With the release of Windows Vista and Server 2008 and Windows Internet Explorer 7 for Windows XP, Internet Explorer is no longer integrated with Windows Explorer. In Windows Vista and Server 2008 (and in Windows XP as well if IE7 or 8 is installed), Windows Explorer no longer displays web pages, and IE7 does not support use as a file manager, although one will separately launch the other as necessary.
When moving or copying files from one folder to another, if two files have the same name, an option is now available to rename the file; in previous versions of Windows, the user was prompted to choose either a replacement or cancel moving the file. Also, when renaming a file, Explorer only highlights the filename without selecting the extension. Renaming multiple files is quicker as pressing Tab automatically renames the existing file or folder and opens the file name text field for the next file for renaming. Shift+Tab allows renaming in the same manner upwards.
Support for burning data on DVDs (DVD±R, DVD±R DL, DVD±R RW) in addition to CDs and DVD-RAM using version 2.0 of the Image Mastering API, as well as Live File System support was added.[38]
If a file is in use by another application, Windows Explorer tells users to close the application and retry the file operation. Also, a new interface IFileIsInUse is introduced into the API which developers can use to let other applications switch to the main window of the application that has the file open or simply close the file from the «File in Use» dialog. If the running application exposes these operations by means of the IFileIsInUse interface, Windows Explorer, upon encountering a locked file, allows the user to close the file or switch to the application from the dialog box itself.[39]
Windows Vista introduced precluded support for the Media Transfer Protocol.[citation needed]
Removed and changed features[edit]
The ability to customize the layout and buttons on the toolbars has been removed in Windows Vista’s Explorer, as has the ability to add a password to a zip file (compressed folder). The Toolbar button in Explorer to go up one folder from the current folder has been removed (the function still exists however, one can move up a folder by pressing Alt + ↑). Although still fully available from the menus and keyboard shortcuts, toolbar buttons for Cut, Copy, Paste, Undo, Delete, Properties and some others are no longer available. The Menu Bar is also hidden by default but is still available by pressing the Alt key or changing its visibility in the layout options. Several other features are removed such as showing the size on the status bar without selecting items, storing metadata in NTFS alternate data streams,[40] the IColumnProvider interface which allowed addition of custom columns to Explorer[41] and folder background customization using desktop.ini.
The option «Managing pairs of Web pages and folders» is also removed, and the user has no way of telling Vista that a .html file and the folder with the same name that was created when saving a complete web page from IE should be treated separately, that is, they cannot delete the folder without deleting the html file as well.[42]
The ability to right-click a folder and hit «Search» was removed in Windows Vista Service Pack 1. Users must open the folder they wish to search in and enter their keywords in the search field located on the top right corner of the window. Alternatively, users can specify other search parameters through the «Advanced Search» UI, which can be accessed by clicking on the Organize Bar and selecting Search Pane under the Layout submenu. Pressing F3 also opens the «Advanced Search» interface.
Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2[edit]
Windows Explorer in Windows 7, showing Libraries
Libraries[edit]
Windows Explorer in Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 supports libraries, virtual folders described in a .library-ms file that aggregates content from various locations – including shared folders on networked systems if the shared folder has been indexed by the host system – and present them in a unified view. Searching in a library automatically federates the query to the remote systems, in addition to searching on the local system, so that files on the remote systems are also searched. Unlike search folders, Libraries are backed by a physical location which allows files to be saved in the libraries. Such files are transparently saved in the backing physical folder. The default save location for a library may be configured by the user, as can the default view layout for each library. Libraries are generally stored in the libraries special folder, which allows them to be displayed on the navigation pane.
By default, a new user account in Windows 7 contains four libraries, for different file types: Documents, Music, Pictures, and Videos. They are configured to include the user’s profile folders for these respective file types, as well as the computer’s corresponding Public folders.
In addition to aggregating multiple storage locations, Libraries enable Arrangement Views and Search Filter Suggestions. Arrangement Views allow users to pivot their views of the library’s contents based on metadata. For example, selecting the «By Month» view in the Pictures library will display photos in stacks, where each stack represents a month of photos based on the date they were taken. In the Music library, the «By Artist» view will display stacks of albums from the artists in their collections, and browsing into an artist stack will then display the relevant albums.
Search Filter Suggestions are a new feature of the Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 Explorer’s search box. When the user clicks in the search box, a menu shows up below it showing recent searches as well as suggested Advanced Query Syntax filters that the user can type. When one is selected (or typed in manually), the menu will update to show the possible values to filter by for that property, and this list is based on the current location and other parts of the query already typed. For example, selecting the «tags» filter or typing «tags:» into the search box will display the list of possible tag values which will return search results.
The metadata written within the file, implemented in Vista, is also utilized in Windows 7. This can sometimes lead to long wait times displaying the contents of a folder. For example, if a folder contains many large video files totaling hundreds of gigabytes, and the Window Explorer pane is in Details view mode showing a property contained within the metadata (for example Date, Length, Frame Height), Windows Explorer might have to search the contents of the whole file for the meta data. Some damaged files can cause a prolonged delay as well. This is due to metadata information being able to be placed anywhere within the file, beginning, middle, or end, necessitating a search of the whole file. Lengthy delays also occur when displaying the contents of a folder with many different types of program icons. The icon is contained in the metadata. Some programs cause the activation of a virus scan when retrieving the icon information from the metadata, hence producing a lengthy delay.[33]
Arrangement Views and Search Filter Suggestions are database-backed features that require that all locations in the Library be indexed by the Windows Search service. Local disk locations must be indexed by the local indexer, and Windows Explorer will automatically add locations to the indexing scope when they are included in a library. Remote locations can be indexed by the indexer on another Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 machine, on a Windows machine running Windows Search 4 (such as Windows Vista or Windows Home Server), or on another device that implements the MS-WSP remote query protocol.[43]
Federated search[edit]
Windows Explorer also supports federating search to external data sources, such as custom databases or web services, that are exposed over the web and described via an OpenSearch definition. The federated location description (called a Search Connector) is provided as a .osdx file. Once installed, the data source becomes queryable directly from Windows Explorer. Windows Explorer features, such as previews and thumbnails, work with the results of a federated search as well.
Other changes[edit]
- Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 support showing icons in the context menu and creating cascaded context menus with static verbs in submenus using the Registry instead of a shell extension.[44]
- The search box in the Explorer window and the address bar can be resized.
- Certain folders in the navigation pane can be hidden to reduce clutter.
- Progress bars and overlay icons on an application’s button on the taskbar.
- Content view which shows thumbnails and metadata.
- Buttons to toggle the preview pane and create a new folder.
Removed or changed features[edit]
In Windows 7, several features have been removed from Windows Explorer, including the collapsible folder pane, overlay icon for shared items, remembering individual folder window sizes and positions, free disk space on the status bar, icons on the command bar, ability to disable Auto Arrange and Align to Grid, sortable column headings in other views except details view, ability to disable full row selection in details view, automatic horizontal scrolling and scrollbar in the navigation pane and maintaining selection when sorting from the Edit menu.
Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012[edit]
The new File Explorer with ribbon in Windows 8
The file manager on Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012 is renamed File Explorer and introduces new features such as a redesigned interface incorporating a ribbon toolbar, and a redesigned file operation dialog that displays more detailed progress and allows for file operations to be paused and resumed. The details pane from Windows Vista and 7 was removed and replaced with a narrower pane with no icons and fewer detail columns. But other details are displayed by hovering over the file’s name.[45][46]
Windows 10 and Windows Server 2016[edit]
The icons in File Explorer have been redesigned. They are flatter and simpler in design. The window border padding is thinner than previous versions. Windows 10 Creators Update and later versions come with a new Universal File Explorer (also known as the UWP File Explorer). Although hidden, it can be opened by creating a shortcut pointing to «explorer shell:AppsFolderc5e2524a-ea46-4f67-841f-6a9465d9d515_cw5n1h2txyewy!App» [47][48]
Windows 10, version 1809 and Windows Server 2019[edit]
A «dark mode» has been added to File Explorer in Windows 10, version 1809 and Windows Server 2019.[49] The Universal File Explorer also includes new features.[50][51]
Windows 10, version 1909[edit]
Windows Search and OneDrive have been integrated into File Explorer’s search feature in Windows 10, version 1909.[52]
Windows 11[edit]
In Windows 11, File Explorer had undergone significant UI changes with the Ribbon Interface simplified into a command bar. Translucency, shadows, and rounded geometry have also been added, following the Fluent Design System. In March 2022, Microsoft introduced adverts into the file explorer, but later stated that these were ‘not intended to be published externally’[53] after significant negative media coverage.
Windows 11 2022 Update[edit]
On April 5, 2022, Microsoft announced that it would be adding tabs, favorites, and a new homepage to File Explorer.[54] These features were eventually introduced via an update to the Windows 11 2022 Update on October 18, 2022.[55]
Extensibility[edit]
File Explorer can be extended to support non-default functionality by means of Windows shell extensions, which are COM objects that plug the extended functionality into Windows Explorer.[56] Shell extensions can be in the form of shell extension handlers, toolbars or even namespace extensions that allow certain folders (or even non-filesystem objects such as the images scanned by a scanner) to be presented as a special folder. File Explorer also allows metadata for files to be added as NTFS alternate data streams, separate from the data stream for the file.
Shell extension handlers are queried by the shell beforehand for modifying the action the shell takes. They can be associated on a per file type – where they will show up only when a particular action takes place on a particular file type – or on a global basis – which are always available. The shell supports the following extension handlers:
| Handler | Description | Can be implemented on | Required shell version |
|---|---|---|---|
| Context menu handler | Adds menu items to the context menu. It is called before the context menu is displayed. | Per file type | Windows 95 and later. Windows 7 introduced IExecuteCommand |
| Drag-and-drop handler | Controls the action upon right-click drag and drop and modifies the context menu that appears. | Global | Windows 95 and later |
| Drop target handler | Controls the action after a data object is dragged and dropped over a drop target such as a file. | Per file type | Windows 95 and later |
| Data object handler | Controls the action after a file is copied to the clipboard or dragged and dropped over a drop target. It can provide additional clipboard formats to the drop target. | Per file type | Windows 95 and later |
| Icon handler | Assigns a custom icon to an individual file amongst a class of file types. It is called before file icons are displayed. | Per file type | Windows 95 and later |
| Property sheet handler | Replaces or adds pages to the property sheet dialog box of an object. | Per file type | Windows 95 and later |
| Copy hook handler | Allows running, modifying or denying the action when a user or application tries to copy, move, delete, or rename an object. | Not associated with a file type | Windows 95 and later |
| Search handler | Allows shell integration of a custom search engine. | Not associated with a file type | Windows 95 through Windows XP |
| Infotip handler | Allows retrieving flags and infotip information for an item and displaying it inside a popup tooltip upon mouse hover. | Per file type | Windows Desktop Update and later |
| Thumbnail image handler | Provides for a thumbnail image to be generated and displayed along with its alpha type when a file is selected or the thumbnail view is activated. | Per file type | Windows Desktop Update and later. Windows Vista introduced a newer IThumbnailProvider interface that also shows thumbnails in the Details pane. The older IExtractImage is still supported but not in the Details pane.[57] |
| Disk Cleanup handler | Add a new entry to the Disk Cleanup application and allows specifying additional disk locations or files to clean up. | Per folder | Windows 98 and later |
| Column handler | Allows creating and displaying custom columns in Windows Explorer details view. It can be used to extend sorting and grouping. | Per folder | Windows 2000 and later |
| Icon overlay handler | Allows displaying an overlay icon over a shell object (a file or folder icon). | Per file type | Windows 2000 and later |
| Metadata handler | Allows viewing and modifying metadata stored in a file. It can be used to extend details view columns, infotips, property pages, sorting and grouping. | Per file type | Windows 2000 and later |
| Filter handler (IFilter) | Allows file properties and its contents to be indexed and searched by Indexing Service or Windows Search | Per file type | Windows 2000 and later |
| AutoPlay handler | Examines newly discovered removable media and devices and, based on content such as pictures, music or video files, launches an appropriate application to play or display the content. | Per file type category Windows XP only: per device and per file type category |
Windows XP and later |
| Property handler | Allows viewing and modifying system-defined and custom properties of a file. | Per file type | Windows Vista and later; on Windows XP if Windows Search is installed. |
| Preview handler | Renders enhanced previews of items without launching the default application when a file is selected. It can also provide file type-specific navigation such as browsing a document, or seeking inside a media file. | Per file type | Windows Vista and later |
Namespace extensions are used by Explorer and Common Dialogs to either display some data – which are not necessarily persisted as files – in a folder-like view or to present data in a way that is different from their organization on the file system. This feature can be exploited by a any hierarchical data source that can be represented as a file system like the Windows one, including Cloud-based implementation. Special folders, such as My Computer and Network Places in Windows Explorer are implemented this way, as are Explorer views that let items in a mobile phone or digital camera be explored. Source-control systems that use Explorer to browse source repositories also use Namespace extensions to allow Explorer to browse the revisions. To implement a namespace extension, the IPersistFolder, IShellView, IShellFolder, IShellBrowser and IOleWindow interfaces need to be implemented and registered. The implementation needs to provide the logic for navigating the data store as well as describing the presentation. Windows Explorer will instantiate the COM objects as required.[58]
While Windows Explorer natively exposes the extensibility points as COM interfaces, .NET Framework can also be used to write some types of extensions, using the COM Interop functionality of .NET Framework.[58] While Microsoft itself makes available extensions – such as the photo info tool[59] – which are authored using .NET Framework, they currently recommend against writing managed shell extensions, as only one instance of the CLR (prior to version 4.0) can be loaded per-process. This behavior will cause conflicts if multiple managed add-ins, targeting different versions of the CLR, are attempted to be run simultaneously.[60][61]
See also[edit]
- Comparison of file managers
- List of alternative shells for Windows
Notes and references[edit]
- ^ «January 26, 2023—KB5022360 (OS Build 22621.1194) Preview». Microsoft Support. Microsoft.
- ^ «Releasing Windows 11 Build 22621.1192 to the Release Preview Channel». Windows Insider Blog. January 17, 2023.
- ^ «January 26, 2023—KB5022360 (OS Build 22621.1194) Preview». Microsoft Support. Microsoft.
- ^ «Announcing Windows 11 Insider Preview Build 22621.1250 and 22623.1250». Windows Insider Blog. February 2, 2023.
- ^ «Announcing Windows 11 Insider Preview Build 25290». Windows Insider Blog. February 1, 2023.
- ^ Lineback, Nathan. «Misc Windows». toastytech.com. Archived from the original on July 3, 2018. Retrieved June 19, 2018.
- ^ John D. Ruley (September 1995). «NT Gets the Look But Not the Logo». How-To Columns. WinMag. Archived from the original on March 14, 2006. Retrieved September 4, 2009. Internet Archive
- ^ «Managing Files, Folders, and Search Methods: Microsoft TechNet». microsoft.com. Archived from the original on January 12, 2009. Retrieved June 19, 2018.
- ^ «Serenity Macros Home Page – Resources for MS Word». www.mvps.org. Archived from the original on June 27, 2018. Retrieved June 19, 2018.
- ^ Windows 2000 Registry: Latest Features and APIs Provide the Power to Customize and Extend Your Apps, MSDN Magazine, November 2000, archived from the original on April 15, 2003, retrieved August 26, 2007
- ^ «COM Objects and Structured Storage» Archived 2018-12-18 at the Wayback Machine, Windows Dev Center, May 31, 2018
- ^ Esposito, Dino (June 2000), More Windows 2000 UI Goodies: Extending Explorer Views by Customizing Hypertext Template Files, MSDN Magazine, archived from the original on August 24, 2007, retrieved August 26, 2007
- ^ Sophos, VBS/Roor-C threat analysis Archived 2007-11-30 at the Wayback Machine. Accessed August 26, 2007.
- ^ «Virus.VBS.Redlof.a», Virus Encyclopedia, Viruslist.com, January 15, 2004, archived from the original on October 28, 2007, retrieved August 26, 2007
- ^ Figure 1 Windows Shell Extensions, MSDN Magazine, June 2000, archived from the original on August 31, 2004, retrieved August 26, 2007
- ^ «What is Indexing Service?». msdn.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on January 1, 2011. Retrieved June 19, 2018.
- ^ «Is Microsoft Office 2003 still decent for general use on Windows 7, 8.1 and 10». answers.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on February 7, 2016. Retrieved June 19, 2018.
- ^ «What is Windows XP?». www.computerhope.com. Retrieved August 12, 2022.
- ^ «Windows XP – What’s new with files and folders». Windows. Microsoft. Archived from the original on May 23, 2007.
- ^ How to create and extract a Zip File in Windows ME/XP/2003
- ^ How To: Open a Cab file – Quote: «If you’re using Windows XP or Windows Vista, then your operating system has built-in support for opening Cab files.»
- ^ «Moving web pages saved by IE (HTM file & _FILES folder)». Directory Opus Resource Centre. May 4, 2009. Archived from the original on December 16, 2020. Retrieved December 16, 2020.
When Windows Explorer […] move a Web page both the HTML file and the directory are automatically moved together. […] Moreover, the user only has to drag EITHER part—the file or the directory and the other part will follow automatically. This way the page is kept intact irrespective of where Windows stores it.
- ^ The sort order for files and folders whose names contain numerals is different in Windows Vista, Windows XP, and Windows Server 2003 than it is in Windows 2000, support.microsoft.com, August 28, 2007, archived from the original on September 27, 2010, retrieved July 6, 2009
- ^ a b Shultz, Greg (August 10, 2006). «Examine the filtering, grouping, and stacking features in Windows Vista’s Windows Explorer». TechRepublic. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on December 22, 2015. Retrieved December 19, 2015.
- ^ a b c Reid, Rory (January 30, 2007). «Seven days of Vista — day 4: Stacking and filtering». CNET. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on December 22, 2015. Retrieved December 19, 2015.
- ^ a b Kaelin, Mark (July 17, 2007). «How do I… Save and refine desktop searches in Microsoft Windows Vista?». TechRepublic. CBS Interactive. Archived from the original on November 17, 2015. Retrieved November 11, 2015.
- ^ Microsoft. «Saved Search File Format». MSDN. Archived from the original on December 10, 2015. Retrieved December 21, 2015.
- ^ Bentz, Ben (October 31, 2006). «Query Composition: Building a search upon another search». Shell: Revealed Blog. Microsoft. Archived from the original on December 15, 2006. Retrieved December 21, 2015.
- ^ Using search operators to find pictures, music and videos in Windows Vista
- ^ Windows 7: Find/Search Files By Date And Size
- ^ Windows Explorer Columns — Are you Fully Using Them?
- ^ «How to Search for Contents in Any File Type Without Indexing Service Enabled in Windows Vista and Windows 7». Wikihow.com. January 27, 2014. Archived from the original on March 19, 2017. Retrieved January 31, 2014.
- ^ a b Microsoft. «Add tags or other properties to a file». Windows How-to. Archived from the original on December 22, 2015. Retrieved December 21, 2015.
- ^ White, Nick (July 13, 2007). «10 Things – Windows Explorer Has a New Preview Pane». Windows Vista Team Blog. Microsoft. Archived from the original on July 15, 2007. Retrieved December 14, 2015.
- ^ Microsoft. «Pen and Touch Input in Windows Vista». MSDN. Archived from the original on December 22, 2015. Retrieved December 21, 2015.
- ^ Oiaga, Marius (September 27, 2006). «Quick Zoom on the Windows Vista Desktop and in Explorer». Softpedia. Archived from the original on December 22, 2015. Retrieved December 21, 2015.
- ^ McFedries, Paul (2008). Microsoft Windows Vista Unleashed. Sams Publishing. p. 87. ISBN 978-0-672-33013-1. Retrieved December 21, 2015.
- ^ Mangefeste, Tony; Walp, David (2006). «Optical Platform: Windows Vista and Beyond». Microsoft. Archived from the original (PPT) on June 4, 2011. Retrieved December 21, 2015.
- ^ Davis, Christopher (March 29, 2007). «Your File Is In Use… Demystified». Shell: Revealed Blog. Microsoft. Archived from the original on April 29, 2007. Retrieved December 21, 2015.
- ^ «Properties». msdn2.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on October 9, 2007. Retrieved June 19, 2018.
- ^ «IColumnProvider interface (Windows)». msdn2.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on April 17, 2008. Retrieved June 19, 2018.
- ^ A solution to this is provided on http://windowsxp.mvps.org/webpairs.htm Archived 2010-12-24 at the Wayback Machine. After the webpairs.reg file has been merged into the registry, the «Managing pairs of Web pages and folders» option is available in the Folder Options View tab.
- ^ «MS-WSP: Windows Search Protocol», MSDN Library, Microsoft, December 18, 2006, archived from the original on May 16, 2010, retrieved June 10, 2009
- ^ «Creating Shortcut Menu Handlers (Windows)». msdn.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on November 22, 2010. Retrieved June 19, 2018.
- ^ «Improvements in Windows Explorer». Archived from the original on November 7, 2011. Retrieved October 30, 2011.
- ^ «Microsoft switches to File Explorer name in Windows 8, bids farewell to Windows Explorer». The Verge. June 29, 2012. Archived from the original on August 17, 2012. Retrieved August 3, 2012.
- ^ «How to open UWP File Explorer on Windows 10 – Step by step». Windows Latest. May 7, 2017. Archived from the original on August 24, 2018. Retrieved August 24, 2018.
- ^ «Windows 10 Tip: Unlock the UWP File Explorer – Thurrott.com». Thurrott.com. May 6, 2017. Archived from the original on August 24, 2018. Retrieved August 24, 2018.
- ^ «Inspired by Insiders – Dark Theme in File Explorer». August 8, 2018. Archived from the original on August 12, 2018. Retrieved August 23, 2018.
- ^ «Microsoft updates universal File Explorer with new features in Windows 10 version 1809». Windows Central. Archived from the original on August 25, 2018. Retrieved August 24, 2018.
- ^ «UWP File Explorer has got new features in Windows 10 version 1809». Winaero. August 23, 2018. Archived from the original on August 25, 2018. Retrieved August 24, 2018.
- ^ «Windows 10 version 1909: new and changed features — gHacks Tech News». www.ghacks.net. October 2019. Archived from the original on October 25, 2019. Retrieved October 25, 2019.
- ^ Warren, Tom (March 15, 2022). «Microsoft says Windows 11’s File Explorer ads were ‘not intended to be published externally’«. The Verge. Retrieved July 28, 2022.
- ^ Warren, Tom (April 5, 2022). «Windows 11’s refreshed File Explorer gets tabs, favorites, and a new homepage». The Verge. Retrieved August 12, 2022.
- ^ Warren, Tom (October 18, 2022). «Windows 11’s new tabbed File Explorer and taskbar improvements are available today». The Verge. Retrieved October 18, 2022.
- ^ ShellExView v1.19 – Shell Extensions Manager for Windows, archived from the original on October 24, 2010, retrieved March 31, 2008
- ^ «Thumbnail Handlers (Windows)». msdn.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on June 19, 2018. Retrieved June 19, 2018.
- ^ a b Rensin, Dave (January 2004). «Create Namespace Extensions for Windows Explorer with the .NET Framework». msdn.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on May 8, 2008. Retrieved March 31, 2008.
- ^ «Microsoft Download Center: Windows, Office, Xbox & More». www.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on May 13, 2008. Retrieved June 19, 2018.
- ^ «MSDN Magazine Issues». msdn.microsoft.com. Archived from the original on May 21, 2008. Retrieved June 19, 2018.
- ^ Zhang, Junfeng (November 18, 2005). «Don’t do Shell Extension Handlers in .NET». msdn.com. Archived from the original on January 5, 2010. Retrieved June 19, 2018.
External links[edit]
- Sullivan, Kent. «The Windows 95 User Interface: A Case Study in Usability Engineering» (1996) for Association for Computing Machinery. (Sullivan was a developer on the Windows 95 UI team)
- How To Customize the Windows Explorer Views in Windows XP
- MSDN: Creating Shell Extension Handlers, Windows Dev Center, May 31, 2018
- The Complete Idiot’s Guide to Writing Shell Extensions, by Michal Dunn, March 15, 2006
- Namespace extensions – the undocumented Windows Shell, by Henk Devos, November 30, 1999
Сегодня отвечу на вопрос, что такое проводник Виндовс. Постараюсь рассказать о нем новичкам простыми словами. Покажу все действия на практике.
Что такое проводник Виндовс
Здравствуйте, читатели! Многие новички задают вопрос, что такое проводник Виндовс?
Это нормально, ведь не все пользователи компьютеров об этом знают. Особенно,
когда впервые включаешь компьютер, впервые за ним работаешь.
Итак, отвечаю. Проводник Виндовс (Windows) – это программа, приложение. С помощью проводника у человека появляется доступ к различным файлам на компьютере. Появляется возможность управлять операционной системой Windows.
Проводником Windows можно считать то, что видим сейчас на рабочем столе компьютера. То есть, меню «Пуск», панель задач компьютера, пиктограммы Виндовс и другое. Все это помещается в одну программу, под названием «Проводник» (Скрин 1).
Как правило, проводник Виндовс встроен в компьютер, его
не нужно искать в Интернете и устанавливать. Он достаточно удобный в
использовании, с простыми функциями и настройками.
Далее, рассмотрим функции проводника и поработаем с ним.
Функции проводника Windows
Поговорим об основных функциях программы «Проводник». Тем
самым определим, что он умеет:
- Перемещает
файлы и папки на компьютере. - Выделяет
и удаляет папки с файлами. - Сортирует
файлы и папки. - Изменяет
вид папок, например, на крупные значки. - Может
давать общий доступ к папкам на компьютере. - Добавляет
папки и файлы в «Избранное». - Умеет
записывать файлы на компакт-диск, посредством специальной программы. - В
проводнике работает функция «Печать». - Есть
функция сжатие файлов. - Через проводник можно запустить
командную строку.
Всей статьи не хватит, чтобы описать все функции
программы проводник Виндовс. Этих вполне достаточно, чтобы понять, что
проводником можно пользоваться, как полноценной программой.
Как включить проводник в Windows
Включается проводник в Windows одним кликом. Для этого
нажмите «Пуск», перейдите в раздел «Служебные программы» и кликните на
Проводник.
Вместе с тем, вы можете обратиться к поиску на компьютере и ввести название программы. После чего, Виндовс найдет это приложение (Скрин 2).
Далее, нажимаем по нему левой кнопкой мыши и открываем на
компьютере.
Как использовать проводник
Выше мы говорили о том, что такое проводник Виндовс. Теперь, рассмотрим
его использование.
Если вы включили компьютер, открываете в нем папки,
перемещаете файлы – вы уже используете проводник. Эта программа работает в
фоновом режиме, даже без открытия на компьютере.
Когда проводник запущен, можно сделать ряд действий,
чтобы проверить его работу.
Допустим, нужно переместить папку с диска/D на/C (Скрин 3).
Открываем проводник и щелкаем левой кнопкой мыши по
папке, далее правой клавишей. Из меню выбираем «Копировать». После чего открываете
другой локальный диск и просто вставляете эту папку клавишами CTRL+V.
Заключение
Надеюсь вы нашли ответ на вопрос, что такое проводник Виндовс. В статье было
дано четкое определение проводника, рассмотрены его функции и им
воспользовались на практике. Вы можете сами потренироваться и поработать с
проводником.
Удачи Вам!
С уважением, Сергей Ёлчев.
Одной из наиболее полезных приложений на компьютере является проводник. С его помощью можно открывать файлы и папки, а также запускать другие программы. Этот объект также имеет большое количество дополнительных возможностей.
Проводник является частью ОС Windows. Он загружается вместе с операционной системой и позволяет открывать файлы и переходить между папками. Его использование обеспечивает более комфортную работу с компьютером. В диспетчере задач, в более старых версиях Windows он отображался, как explorer.exe. В современных версиях, несмотря на то, что сам процесс так и называется explorer, в диспетчере он называется Проводник.
После запуска компьютера, пользователь может устанавливать различные программы и игры. Все они размещены на одном из дисков. Обычно, создаются два и более разделов. Первый, системный или диск С, предназначен для хранения файлов, которые обеспечивают работу операционной системы.
На остальные устанавливаются приложения пользователей и хранятся файлы. Такая структура позволяет разделить информацию, которая важна системе или человеку. Распределение обезопасит пользователя от удаления важных файлов.
Чтобы найти нужную программу, следует воспользоваться проводником. Именно он обеспечивает понятный интерфейс хранения всех файлов на компьютере. Достаточно найти нужный документ, открывая соответствующую папку.
Окно поделено на две части. В левой можно заметить древовидную структуру, которая позволяет быстро переходить из одного каталога в другой. В правой части находится обычный интерфейс. Папки можно открывать по определенной иерархии.
Если простыми словами, то все, что отображается на экране Windows, касательно папок и файлов – это работа проводника. Т.е. проводник предназначен для отображения окон на экране. Если его отключить, то пользователь увидит только обои рабочего стола и запущенные приложения. Меню пуск, панель задач, текущие процессы копирования и все открытые папки исчезнут.
Функции и возможности
Проводник предоставляет пользователю определенные функции и возможности. Некоторые из ни используются каждый день. В то время как о существовании других пользователь может и не догадываться.
Данный объект служит не только для просмотра установленных программ. Он позволяет быстро перемещать файлы межу каталогами. Некоторые пользователи предпочитают открывать два окна или копировать содержимое. Но можно переместить нужные файлы с правого окна, в нужную папку левого.
Также, можно воспользоваться дополнительными параметрами, которые предоставляет окно. В верхней части экрана находится набор функций, которые облегчат работу с системой. Здесь можно сразу посмотреть свойства, добавить ярлык, переименовать, удалить объекты и многое другое.
Пользователь может самостоятельно ознакомиться со всеми возможностями. Доступно переключение между вкладками, для просмотра всех функций, которые предоставляет проводник.
История появления
Впервые проводник был внедрен в Windows 95. Он представлял собой окно с набором папок и файлов. От количества содержимого изменялся и размер окна. Так, если в директории находилось более 100 документов, то они представлялись списком.
В Windows 98 была добавлена навигация. Теперь можно было переходить между недавно посещенными каталогами. Также, появилась адресная строка, в которую можно ввести полный путь и панель инструментов.
Проводник стал существенной частью системы в XP версии. Разработчики добавили большой набор функций. Изменился и внешний вид. Появился помощник в поиске. С его помощью можно найти необходимый файл, введя его имя в соответствующее поле.
К проводнику относятся не только каталоги. В Windows 7 существенным изменениям подверглась Панель задач. Теперь на нее можно закреплять программы, и запускать их без открытия сторонних окон. Кроме того, добавились каталоги «Избранное», «Сеть» и другие.
В восьмой версии операционной системы появился интерфейс Metro. Приложения можно закреплять в меню «Пуск», которое открывается на полный экран. Разработчики также вернули в область навигации кнопку «Вверх». Это считается одной из самых неудачных реализаций.
В «Десятке» расширились возможности, но внешний вид стал снова более напоминать «Семерку».
Как запустить проводник?
Проводник запускается автоматически при старте Windows, если этого не произошло, то пользователь увидит пустой рабочий стол. В этом случае можно выполнить принудительный запуск.
Для этого можно нажать сочетание клавиш «Win+R». После чего следует ввести explorer.exe.
Если ничего не произошло, можно нажать сочетание Ctrl+Shift+Esc. Появится Диспетчер задач, где нужно выбрать Файл – Новая Задача.
И в окне ввести explorer.exe.
Если оба действия не привели к нужному результату, сначала в диспетчере задач нужно найти сам процесс explorer.exe или проводник, завершить его, а уже после этого заново проводить запуск.
Также, можно провести запуск Проводника прямо из системы. Для этого есть несколько способов.
Пользователь может выбрать наиболее удобный для себя. Начиная с Windows 7, он закреплен на панели задач. Достаточно кликнуть по нужному значку.
В меню «Пуск» находится нужная команда. Необходимо найти надпись «Компьютер» или соответствующий ярлык, в зависимости от версии операционной системы.
В том же меню «Пуск» можно перейти в раздел «Стандартные». Для этого нужно нажать «Все программы», или отобразить все приложения. После этого следует нажать по соответствующей надписи.
Пользователь может кликнуть правой клавишей мыши по знаку меню «Пуск». На экране отобразится список команд. Следует выбрать команду, которая отвечает за открытие проводника.
Объект получится открыть через поиск. Достаточно ввести слово и выбрать из списка.
Часто используются горячие клавиши. Чтобы открыть проводник, нужно нажать на комбинацию «Win+E». При этом открывается «Мой компьютер».
Также, можно прописать команду в командной строке. Запустить ее можно через опцию выполнить (Win+R) и «cmd». В открытом окне следует ввести explorer.exe.
Как закрыть?
Закрывается проводник как обычное окно. Достаточно кликнуть на крестик, который находится в правом верхнем углу окна.
Но этот способ закроет только текущее окно проводника. Полное закрытие происходит через Диспетчер задач:
- Нажимаем Ctrl+Shift+Esc.
- Выбираем процесс explorer.exe.
- Нажимаем «Снять задачу» и подтверждаем действие.
Проводник — базовый компонент операционной системы Windows, выполняющий функции графической оболочки. В широком понимании для рядового пользователя эта программа является файловым менеджером. Запустить утилиту на компьютере возможно несколькими способами, которые отличаются в зависимости от версии системы и используемых инструментов.
Содержание
- Что такое Проводник
- Как открыть Проводник в Windows
- Панель задач
- Ярлык на рабочем столе
- Меню «Пуск»
- Окно «Выполнить»
- Через системный поиск
- Горячие клавиши
- Командная строка
- Интерфейс приложения
- Заключение
Что такое Проводник
Проводник — часть графического интерфейса операционных систем (ОС) семейства Windows. Главная функция заключается в визуализации выполнения пользовательских команд и предоставлении наглядной информации касательно отдельных компонентов.
Проводник у большинства ассоциируется с файловым менеджером — утилитой, предоставляющей доступ к инструментам взаимодействия с дисковым пространством компьютера. Эту роль программа тоже выполняет, но имеет еще задачу отображения отдельных модулей системы:
- пиктограммы рабочего стола;
- меню «Пуск» со всеми элементами;
- панель задач.
Если программа Проводник прекращает свою работу, в системе перестанут отображаться вышеперечисленные элементы. Поэтому следует знать методы повторного запуска процесса.
Способов запуска Проводника Windows существует множество, но есть различия в исполнении. Чтобы включить графическую оболочку (процесс explorer.exe), необходимо воспользоваться окном «Выполнить» или Командной строкой. А для запуска файлового менеджера подойдут следующие методы:
- Панель задач.
- Ярлык на рабочем столе.
- Меню «Пуск».
- Системный поиск.
- Горячие клавиши.
Обратите внимание! Одни и те же способы отличаются в зависимости от используемой версии ОС. Ниже будут представлены инструкции для основных редакций: Windows 7 и 10.
Панель задач
По умолчанию после установки системы на панели задач закреплен ярлык приложения Проводник. Значок расположен ближе к меню «Пуск» и имеет вид папки желтого цвета. Чтобы запустить файловый менеджер, потребуется кликнуть левой кнопкой мыши (ЛКМ) по иконке.
Ярлык на рабочем столе
Открыть проводник в Windows можно через ярлык на рабочем столе, который в десятой версии ОС называется «Этот компьютер», в седьмой — «Мой компьютер». Для запуска файлового менеджера потребуется дважды кликнуть ЛКМ по значку.
Важно! Ярлык может отсутствовать вследствие изменения параметров ОС.
Включить отображение этого элемента можно в меню «Параметры значков рабочего стола». В Windows 7 для отображения потребуется:
- Нажать на пустом месте рабочего стола правой кнопкой мыши (ПКМ), выбрать пункт «Персонализация».
- В появившемся окне кликнуть по гиперссылке «Изменение значков рабочего стола», расположенной на боковой панели слева.
- В новом меню установить отметку «Компьютер», кликнуть по кнопке Применить.
Для добавления на главный экран ярлыка запуска файлового менеджера в Windows 10 потребуется:
- В поисковой строке ввести запрос «Параметры меню «Пуск», кликнуть по одноименному элементу.
- Войти во вкладку «Темы», перейти по гиперссылке «Параметры значков рабочего стола».
- В открывшемся меню поставить галочку напротив пункта «Компьютер», нажать Применить.
Меню «Пуск»
Ярлык приложения Проводник, который служит для запуска файлового менеджера, находится в меню «Пуск». В Windows 7 потребуется:
- Развернуть меню, нажав по соответствующей иконке на панели задач, перейти в раздел «Все программы».
- Открыть каталог «Стандартные», кликнуть по пункту «Проводник».
В Windows 10 алгоритм действий следующий:
- Развернуть меню «Пуск», кликнув по иконке или нажав клавишу Win.
- Пролистать список установленных приложений вниз и открыть каталог «Служебные — Windows».
- Запустить файловый менеджер, нажав по соответствующей иконке.
Обратите внимание! Для быстрого доступа к элементу в десятой версии ОС есть возможность через контекстное меню добавить ярлык на главный экран.
В качестве альтернативы для запуска файлового менеджера можно воспользоваться меню, которое вызывается нажатием ПКМ по иконке «Пуск». В списке требуется выбрать пункт «Проводник».
Окно «Выполнить»
Через окно «Выполнить» можно запустить процесс explorer.exe, который отобразит графическую оболочку системы, или файловый менеджер. Алгоритм во всех версиях ОС одинаковый:
- Нажать сочетание горячих клавиш Win + R.
- В соответствующее поле ввести команду explorer.exe.
- Нажать Enter или ОК.
Через системный поиск
Запустить Проводник Windows можно через системный поиск, который в седьмой версии ОС находится в меню «Пуск», а в десятой — на панели задач.
Пошаговое руководство:
- Установить курсор в поисковое поле.
- Ввести запрос «Проводник».
- В выдаче нажать по одноименному значку.
Обратите внимание! В качестве альтернативы можно использовать англоязычное название элемента — explorer.exe.
Горячие клавиши
В рамках операционной системы предусмотрен набор горячих клавиш для управления отдельными компонентами. Для запуска файлового менеджера применяется комбинация Win + E. Этот метод является универсальным во всех версиях Windows.
Важно! Способ применим только при запущенном процессе explorer.exe. В противном случае необходимо воспользоваться окном «Выполнить» или Командной строкой для инициализации графической оболочки.
Командная строка
Командная строка позволяет запускать графическую оболочку и файловый менеджер. Для этого потребуется:
- Используя системный поиск, найти утилиту «Командная строка».
- В выдаче нажать ПКМ по иконке приложения и выбрать опцию «Запуск от имени администратора».
- В окне консоли ввести команду explorer.exe, нажать Enter.
Обратите внимание! Утилита запустится и без прав суперпользователя, но список доступных функций будет ограничен.
Интерфейс приложения
Файловый менеджер имеет собственный интерфейс, который позволяет взаимодействовать с данными на диске. Ниже будет рассмотрен стандартный вид программы без внесенных пользователем изменений.
- Кнопки навигации. В верхней левой части расположены три кнопки, которые позволяют вернуться в предыдущую директорию (←), повторить предыдущий переход (→) и открыть каталог, находящийся выше по иерархии (↑).
- Адресная строка. Позволяет вручную прописать путь к папке, в которую необходимо перейти. Например: C:WindowsSystem32.
- Рабочая область. Отображает разметку диска со всеми вложенными папками и файлами. Позволяет производить манипуляции над данными: копировать, удалять, переименовывать, перемещать и так далее.
- Поисковая строка. Служит для осуществления быстрого поиска по названию файла или директории. Имеет дополнительные инструменты для гибкой настройки.
- Панель навигации. Отображает ссылки для быстрого перехода в нужные директории. По умолчанию установлены стандартные папки: «Видео», «Загрузки», «Документы», «Изображения», «Музыка», «Рабочий стол», но пользователь может самостоятельно добавить новые.
Основные возможности программы реализуются в рабочей области через контекстное меню, которое вызывается нажатием ПКМ.
Заключение
Для запуска файлового менеджера рекомендуется пользоваться стандартными способами: через ярлык на панели задач или рабочем столе, меню «Пуск» или посредством горячих клавиш. Остальные методы служат альтернативой, необходимой лишь в крайнем случае.
( 2 оценки, среднее 3 из 5 )