Веб-сервер представляет собой некоторую программу (службу), принимающую HTTP-запросы от клиентов, обычно от веб-браузеров, обрабатывающую данные запросы и выдающую им ответ, как правило, вместе с HTLM-страницей (сайтом), изображением, файлом, медиа-потоком или другими данными. Ниже подробно рассмотрим процесс установки подобной службы, а именно веб-сервера IIS 8 (Internet Information Server) входящего в поставку Microsoft Windows Server 2012 R2.
0. Оглавление
- Установка веб-сервера IIS
- Перезапуск сервера IIS
1. Установка веб-сервера IIS
Запускаем Диспетчер серверов (Server Manager). Его можно запустить с ярлыка на панели задач, или же выполнив команду servermanager.exe (Для этого необходимо нажать комбинацию клавиш Win + R, в появившемся окне в поле «Открыть» (Open) написать имя команды и нажать «ОК» ).
В диспетчере серверов, в меню, расположенном в правом верхнем углу окна, выберем «Управление» (Manage) — «Добавить роли и компоненты» (Add Roles and Features)
Запустится Мастер добавления ролей и компонентов (Add Roles and Features Wizard). Нажимаем «Далее» (Next) на стартовой странице.
Тип установки (Installation Type) отмечаем «Установка ролей или компонентов» (Role-based or feature-based installation) и нажимаем «Далее» (Next).
Выбираем текущий сервер из пула серверов (Select a server from the server pool) и снова жмем «Далее» (Next).
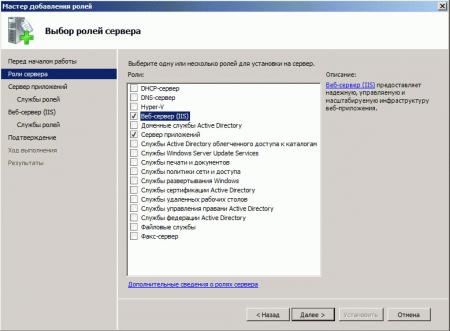
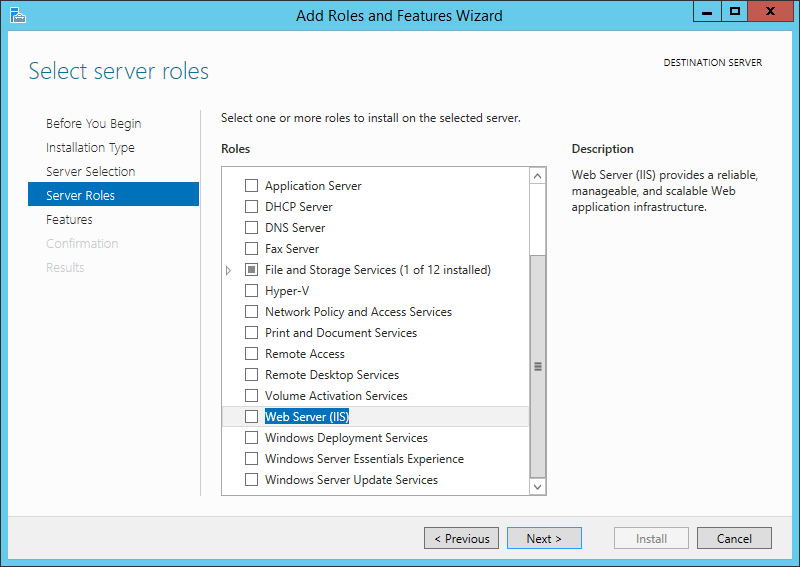
На следующем шаге выбираем роль, которую необходимо установить. В нашем случае это роль «Веб-сервер (IIS)» (Web Server). Отмечаем ее в списке.
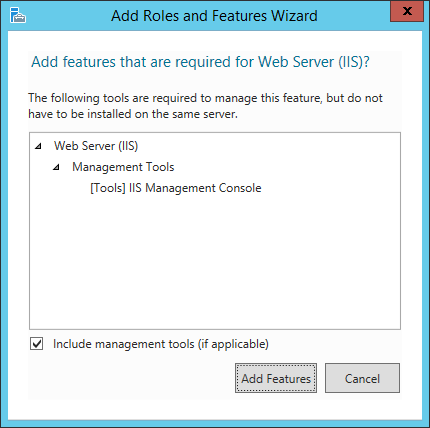
При этом мастер предложит нам добавить компоненты, необходимые для Веб-сервера, а именно «Консоль управления службами IIS» (IIS Management Console). Соглашаемся на установку дополнительных компонент нажав «Добавить компоненты» (Add Features) и жмем «Далее» (Next).
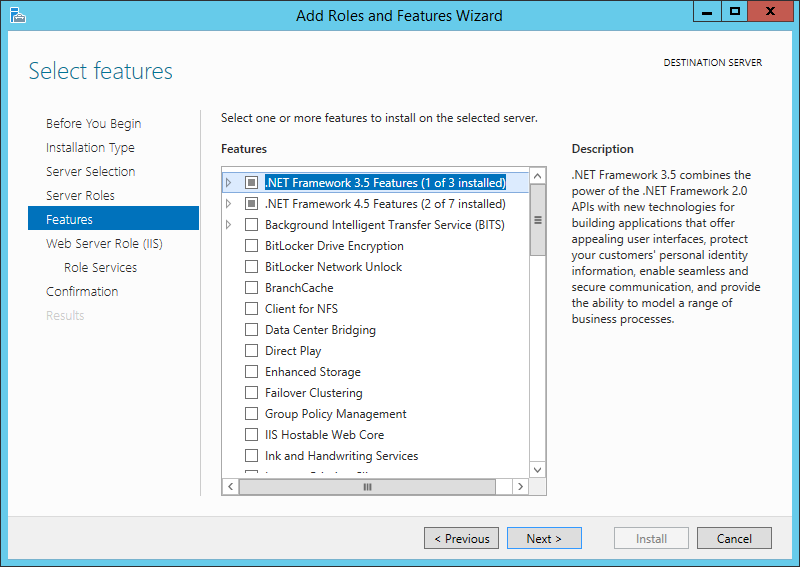
Оставляя список компонент без изменений нажимаем «Далее» (Next).
Ознакомившись с информацией о роли веб-сервера снова жмем «Далее» (Next).
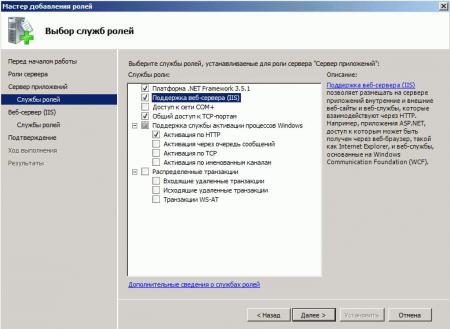
Затем необходимо выбрать службы ролей, которые будут установлены для веб-сервера. Этот набор зависит от конкретных задач, которые будет выполнять сервер IIS.
Например, для публикации баз данных «1С:Предприятие» 8 на веб-сервере или для запуска сайта на WordPress, требуется установка компонент:
- Общие функции HTTP (Common HTTP Features)
- Статическое содержимое (Static Content)
- Документ по умолчанию (Default Document)
- Обзор каталогов (Directory Browsing)
- Ошибки HTTP (HTTP Errors)
- Разработка приложений (Application Development)
- ASP
- ASP.NET 3.5
- Расширяемость .NET 3.5 (.NET Extensibility 3.5)
- Расширения ISAPI (ISAPI Extensions)
- Фильтры ISAPI (ISAPI Filters)
- Исправление и диагностика (Health and Diagnostics)
- Ведение журнала HTTP (HTTP Logging)
- Монитор запросов (Request Monitor)
- Средства управления (Management Tools)
- Консоль управления IIS (IIS Management Console)
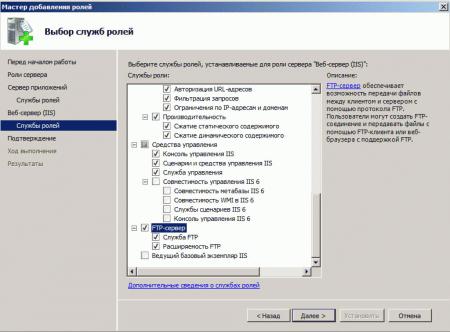
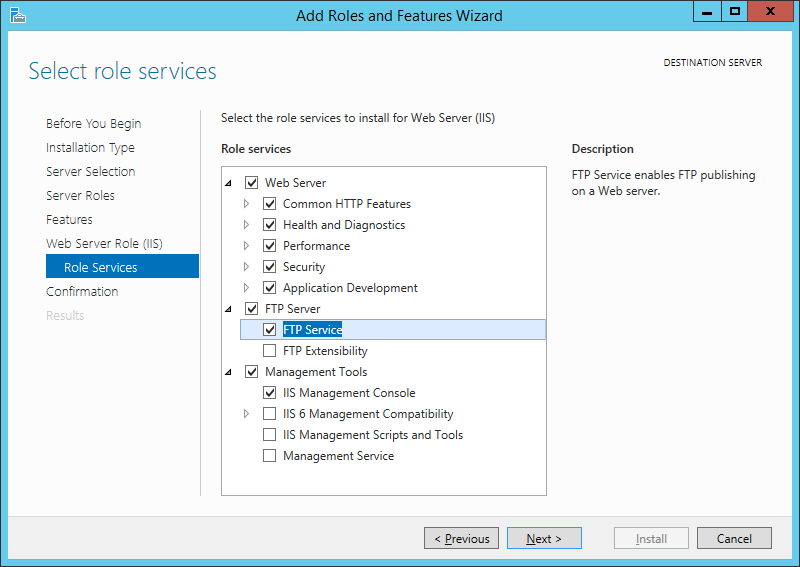
Для установки FTP-сервера требуются компоненты:
- FTP-Сервер (FTP Server)
- Служба FTP (FTP Service)
- Расширяемость FTP (FTP Extensibility)
и т. д. Если выделить службу в списке, слева доступно ее краткое описание. Выбрав необходимые службы ролей жмем «Далее» (Next).
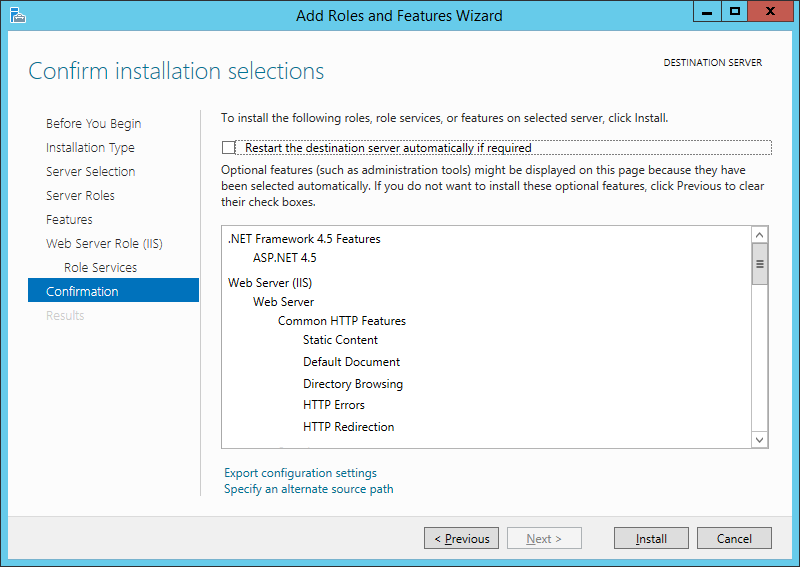
Устанавливаем флаг «Автоматический перезапуск конечного сервера, если требуется» (Restart the destination server automatically if required) если перезагрузка не помешает работе других пользователей и жмем «Установить» (Install) для начала установки указанных в списке служб.
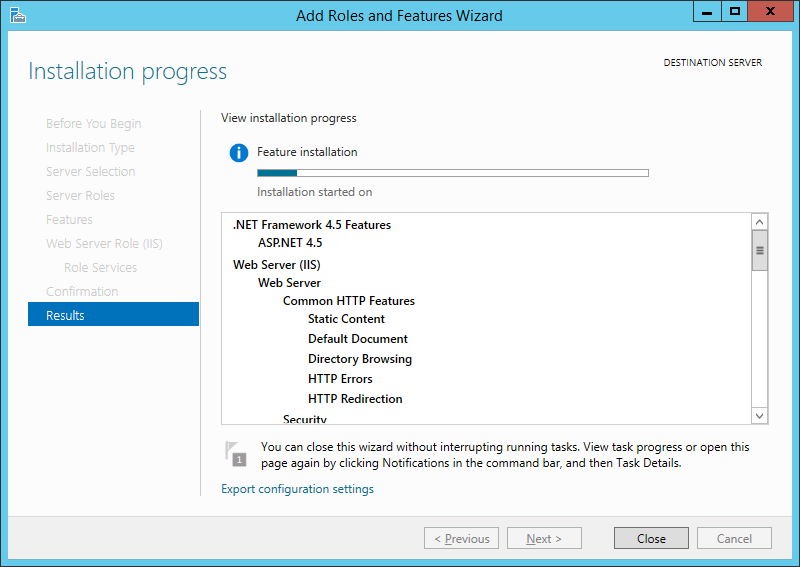
Дожидаемся завершения установки веб-сервера (может произойти перезагрузка сервера) и нажимаем «Закрыть» (Close) для завершения работы мастера.
Возвращаемся в диспетчер серверов, в меню «Средства» (Tools) выбираем появившейся там пункт «Диспетчер служб IIS» (Internet Information Services).
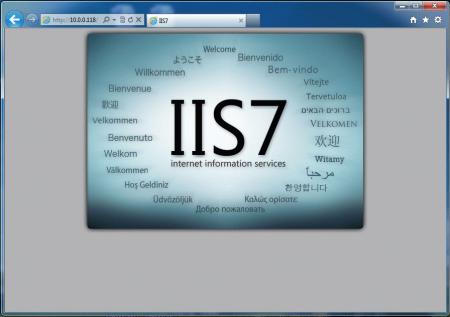
В запустившемся Диспетчере служб IIS, в окне подключений (Connections) увидим только что установленные веб-сервер (соответствует сетевому имени компьютера) а также один веб-сайт, добавленный по умолчанию, с названием Default Web Site.
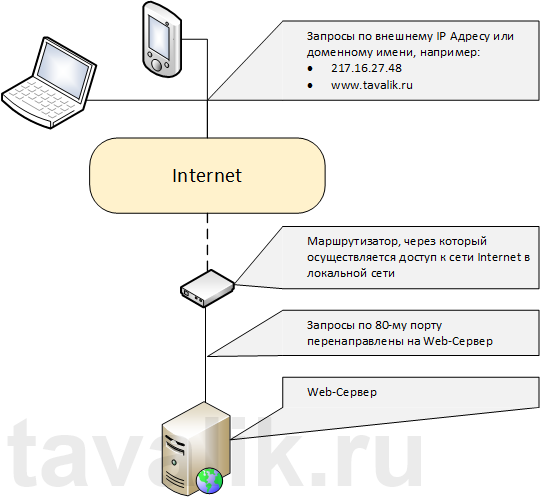
Данный сайт представляет одну веб-страницу с приветствием на различных языках и откликается на все запросы к данному веб-серверу по 80-му порту. Чтобы просмотреть его, достаточно запустить веб-браузер, например Internet Explorer, и ввести в строку адреса http://localhost.
Также этот сайт можно просмотреть с любого другого компьютера в сети, забив в строку адресе IP компьютера где установлен веб-сервер IIS.
Файлы этого сайта, как и файлы всех других добавленных позже сайтов по умолчанию располагаются в каталоге C:interpubwwwroot.
Ну и соответственно, чтобы сайты расположенные на данном веб-сервере были доступны из сети Интернет по внешнему IP-адресу или доменному имени (о том как привязать доменное имя к IP-адресу читайте здесь), необходимо на маршрутизаторе выполнить проброс 80-ого порта на компьютер с установленным веб-сервером IIS.
2. Перезапуск сервера IIS
Иногда требуется перезапустить веб сервер IIS. Сделать это можно как из Диспетчера служб IIS, кликнув правой кнопкой мыши по серверу в окне подключений или из меню «Действия» (Action)
так и из командной строки, выполнив команду
iisreset /noforce <имя_компьютера>
где:
- параметр /noforce необязателен и используется для защиты от потери данных в случае, когда службы IIS не могут быть остановлены в течение одноминутного периода ожидания.
- параметр <имя_компьютера> также необязателен при работе на локальном компьютере. В случае удаленного администрирования сервера IIS в качестве параметра <имя_компьютера> указывается имя NetBIOS компьютера, на котором выполняется перезапуск IIS.
При перезапуске веб сервера IIS происходит перезапуск следующих служб (если они устанавливались при установке компонент IIS):
| Служба | Описание |
|---|---|
| Служба IIS Admin | Эта служба управляет всеми службами IIS, кроме службы WWW (FTP, NMTP и SMTP). |
| Служба WWW | Эта служба обеспечивает подключения клиентов к веб-узлам. |
| Служба HTTP SSL | Эта служба обеспечивает безопасные подключения клиентов к веб-узлам. |
| Служба FTP | Эта служба обеспечивает FTP-подключения и администрирование в диспетчере IIS. |
| Служба SMTP | Эта служба обеспечивает передачу электронной почты по сети. |
| Служба NNTP | Эта служба обеспечивает передачу электронных новостей по сети. |
| title | author | description | ms.date | ms.assetid | msc.legacyurl | msc.type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Installing IIS 8.5 on Windows Server 2012 R2 |
rick-anderson |
This content describes how to install Internet Information Services (IIS) 8.5 on Windows Server 2012 R2 using Server Manager, DISM, or PowerShell. |
09/09/2013 |
0bdb99f5-43ee-4784-b7f4-d4f52b1949ad |
/learn/install/installing-iis-85/installing-iis-85-on-windows-server-2012-r2 |
authoredcontent |
Installing IIS 8.5 on Windows Server 2012 R2
This document describes how to install Internet Information Services (IIS) 8.5 on Windows Server® 2012 R2. IIS is the Web server role in Windows Server 2012 R2. The Windows Server 2012 R2 operating system has all the IIS features needed to support the hosting of Web content in production environments. Windows 8 also includes IIS features, but feature availability depends on the operating system version.
[!NOTE]
You can use the procedures in this document to install IIS 8.0 or IIS 8.5.
The Web server has a modular design that enables you to customize a server by adding or removing modules to meet your specific needs. The Install IIS 8.5 on Windows Server 2012 R2 section describes how to install modules, and the Modules in IIS 8.5 section below describes the functionality that each module provides and which modules are installed by default.
New in IIS 8.5
IIS 8.5 includes several new features not found in IIS 8.0 or lower:
- Enhanced logging. An administrator can enable the logging of additional custom fields from request or response headers, or from server variables.
- Logging to event tracing for Windows. An administrator can enable the sending of logging information to Event Tracing for Windows (ETW).
- Dynamic Website activation. If there are a large number of configured sites (100 or greater, by default), the service will not activate any of the sites when the service is started.
- Idle Worker Process Page-Out. An administrator can enable an idle worker process to be suspended rather than terminated.
For more information on these features, see What’s New in IIS 8.5.
For information on new features in IIS 8.0, see What’s New in IIS 8.0.
Before You Begin
Ensure that you have administrative user rights on the computer on which you plan to install IIS 8.5. Note that by default, you do not have administrative user rights if you are logged on as a user other than as the built-in administrator, even if you were added to the local Administrators group on the computer.
Log on either to the built-in administrator account, or explicitly invoke applications as the built-in administrator by using the runas command-line tool.
[!NOTE]
You can run runas /user:administrator cmd.exe so that every application you run from that command line will be elevated, eliminating the need to use the runas syntax from that command line.
If you are logged on to an account other than the built-in local administrator account, you may see the following security alert dialog box.
Install IIS 8.5 on Windows Server 2012 R2
IIS is one of the server roles on Windows Server 2012 R2, named Web Server (IIS). You can use the following to install IIS:
- The Server Manager user interface in Windows Server 2012 R2
- A command-line installation using DISM (Deployment Image Servicing and Management)
- A command-line installation using PowerShell cmdlets
[!NOTE]
IIS can also be installed on Windows 8 through the Turn Windows features on or off dialog box from the Programs and Features settings of the Control Panel.
Install IIS 8.5 using the Server Manager
Server Manager provides a single dashboard to install or uninstall server roles, role services, and features. Server Manager also gives an overview of all currently installed roles and features.
When you install IIS 8.5 using the Windows Server 2012 R2 Server Manager, the steps you perform are different when you install IIS for the first time, as opposed to when you add roles, services, or features to an existing IIS installation. The two procedures are provided below. Different procedures are also used to add and remove roles, role services, and features. You cannot add and remove from the same UI
For more information on how to run the installation wizards in Server Manager, see Install or Uninstall Roles, Role Services, or Features.
Install IIS 8.5 for the first time in the Server Manager
When the Web Server (UI) role is chosen for the first time in the Add Roles and Features Wizard in Server Manager, the basic components and services needed for IIS are automatically selected. The following procedure will install Internet Information Services on a running physical server when IIS has not already been installed. To change an existing installation of IIS, perform the next procedure, Install additional role services for IIS. These two procedures involve different steps.
-
Open Server Manager by clicking the Server Manager icon on the desktop.
-
In the Server Manager window, with the Dashboard and Quick Start selected, click Add roles and features, or click the Manage menu, and then click Add Roles and Features. The Add Roles and Features Wizard will start with a Before You Begin page. The wizard asks for verification of the following:
- The administrator account has a strong password.
- The network settings, such as IP addresses, are configured.
- The most current security updates from Windows® Update are installed.
-
On the Before You Begin page, click Next.
-
On the Installation Type page, select Role-based or feature-based installation to configure a single server. Click Next.
-
On the Server Selection page, select Select a server from the server pool, and then select a server; or select Select a virtual hard disk server, select a server to mount the VHD on, and then select a VHD file. Click Next.
[!NOTE]
To connect to the virtual hard disk, the virtual machine must be turned off and disconnected. If you select a VHD file from a network share, that share must grant Read and Write permissions to the computer (local system) account of the server that you selected to mount the VHD (user-only account access is not sufficient).[!NOTE]
Servers in a server pool will be available only if they have been added by the Add other servers to manage command in Server Manager. -
On the Server Roles page, select Web Server (IIS).
-
In the Add Roles and Features wizard, click Add Features if you want to install the IIS Management Console. If you do not want to install the Management Console, uncheck Include management tools (if applicable), and then click Continue.
-
On the Server Roles page, click Next.
[!NOTE]
The features required for the default role services of Management Tools and IIS Management Console will be preselected in the Features page. -
On the Features page, select any features that you would like to install, and then click Next. Note that you do not need to select any features on this page to install IIS. IIS setup will select the features that are required.
-
On the Web Server Role (IIS) page, click Next.
-
On the Role Services page, select any additional role services that you want to install.
[!NOTE]
When you install IIS for the first time by selecting Web Server (IIS), you will get at least the default installation that includes a minimum set of role services. You can see at this point that those default services are preselected on the Server Roles page. For a list of the server roles available, and which roles are installed by default, see Modules in IIS 8.5. You will have the chance to select more role services later in this procedure.[!NOTE]
You can also deselect role services that were selected by default when you selected Web Server. However, at least one role service must be selected for Web Server to be selected and installed. -
If you selected a role service that requires other role services or features to be installed, a page will be opened indicating the role services or features to be installed. Leave Include management tools (if applicable) selected to select the install management tools associated with the server role. You may not need the management tools on the destination server if you plan to manage the role remotely. Click Add Features to add the required role services or features.
-
After you have added the role services that you need on the Role Services page, click Next.
-
On the Confirmation page, verify the role services and features that are selected. Select Restart the destination server automatically if required to restart the destination server if the settings need to take immediate effect. To save the configuration information to an XML-based file that you can use for unattended installations with Windows PowerShell, select Export configuration settings, move to the appropriate path in the Save As dialog box, enter a file name, and then click Save.
When you are ready to start the installation process on the Confirmation page, click Install.
-
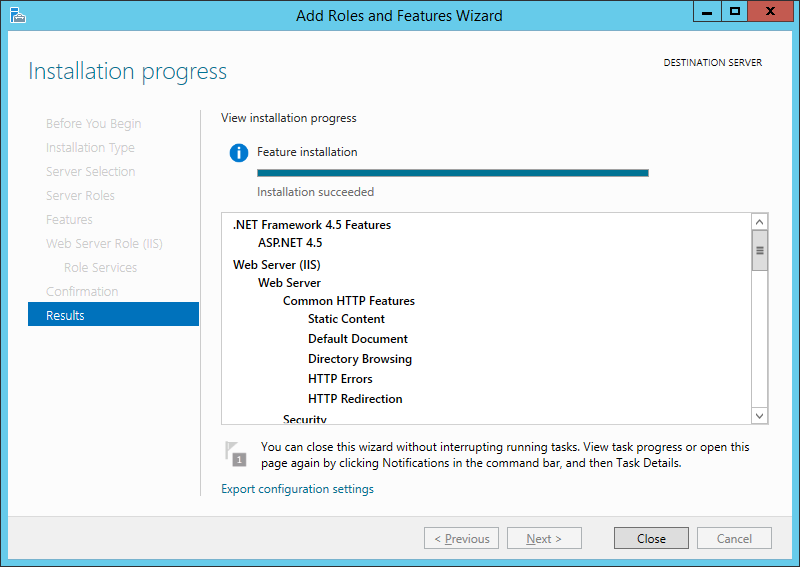
The Installation Progress page is displayed. You can close the wizard without interrupting running tasks. You can view task progress or open the page again by clicking Notifications in the notification area, and then clicking Task Details.
-
On the Results page, verify that the installation succeeds, and then click Close.
-
Confirm that the Web server works by opening a Web browser, and verifying that the following default Web page is displayed when you use the
http://localhostaddress.
Install additional IIS 8.5 role services in the Server Manager
After you have installed the Web Server role on a running physical server for the first time, you can run through the installation process again to install additional roles, role services, and features.
-
Open Server Manager by clicking the Server Manager icon on the desktop.
-
In the Server Manager window, with the Dashboard and Quick Start selected, click Add roles and features, or click the Manage menu, and then click Add Roles and Features. The Add Roles and Features wizard will start with a Before You Begin page. The wizard asks for verification of the following:
- The administrator account has a strong password.
- The network settings, such as IP addresses, are configured.
- The most current security updates from Windows® Update are installed.
-
On the Before You Begin page, click Next.
-
On the Installation Type page, select Role-based or feature-based installation to configure a single server. Click Next.
-
On the Server Selection page, select Select a server from the server pool, and then select a server; or select Select a virtual hard disk server, select the server to mount the VHD on, and then select the VHD file. Click Next.
[!NOTE]
To connect to the virtual hard disk, the virtual machine must be turned off and disconnected. If you select a VHD file from a network share, that share must grant Read and Write permissions to the computer (local system) account of the server that you selected to mount the VHD (user-only account access is not sufficient).[!NOTE]
Servers in a server pool will be available only if they have been added by the Add other servers to manage command in the Server Manager.[!NOTE]
On the Server Roles page, Web Server (IIS) will be selected when IIS 8.0 has already been installed. If Web server (IIS) is not selected, perform the procedure in Install IIS 8.5 for the first time in the Server Manager. -
On the Server Roles page, open the Web Server (IIS) tree until you see a role service that you want to install. Select the role service.
[!NOTE]
Those roles, services, and features that have already been installed will be identified by «Installed» in parentheses after the name, and the name will be grayed out. To remove a role, service, or feature, see Uninstall IIS 8.5 Using the Server Manager. Note, however, that you can expand the lower-level entries under a node even when the node is grayed out.[!NOTE]
For a list of the server roles that are available, and which roles are installed by default, see Modules in IIS 8.5 below. -
If the role service that you selected requires other role services or features to be installed, an Add Features page will be opened listing those required role services or features. Leave Include management tools (if applicable) selected to select the install management tools associated with the server role. You may not need the management tools on the destination server if you plan to manage the role remotely. Click Add Features to add the required role services or features to the installation.
-
If you need any additional role services, repeat steps 6 and 7.
[!NOTE]
Add only the modules that are necessary to minimize the IIS installation footprint and the attack surface.When you have selected all required role services, and their dependencies, on the Server Roles page, click Next.
-
On the Features page, select any features that you need to be installed. Any features required to be installed for role services that you selected in step 6 will already be selected. Click Next.
-
On the Confirmation page, verify the role services and features that are selected. Select Restart the destination server automatically if required to restart the destination server if the settings need to take immediate effect. To save the configuration information to an XML-based file that you can use for unattended installations with Windows PowerShell, select Export configuration settings, move to the appropriate path in the Save As dialog box, enter a file name, and then click Save.
When you are ready to start the installation process on the Confirmation page, click Install.
-
The Installation Progress page is displayed. You can close the wizard without interrupting running tasks. You can view task progress or open the page again by clicking Notifications in the notification area, and then clicking Task Details.
-
On the Results page, verify that the installation succeeds, and then click Close.
-
Confirm that the Web server works by opening a Web browser, and verifying that the following default Web page when you use the
http://localhostaddress.
Uninstall IIS 8.5 using the Server Manager
In the Add Roles and Features wizard of Server Manager, you cannot delete existing features that have already been installed. To delete roles and features, use the Remove Roles and Features wizard of Server Manager. You can remove an individual role, role service, or feature by unchecking it in the wizard, or you can uninstall all of IIS by unchecking the IIS Web Server Role.
-
Open Server Manager by clicking the Server Manager icon on the desktop.
-
Click Manage at the top of the Server Manager, and then click Remove Roles and Features.
-
On the Before you begin page, click Next.
-
On the Server Selection page, select the server from the server pool, and then click Next.
-
On the Remove Server Roles page, clear the check box of any server role or role service that you would like to remove.
-
If you uncheck a role service that has feature dependencies, the Remove Features dialog box will be displayed showing the dependencies. Click Remove Features to remove them. You can remove all of IIS by unchecking Web Server (IIS).
-
On the Remove Server Roles page, select any other role or role service that you want to remove, and then click Next.
-
On the Features page, uncheck any feature that you would like to remove. If you uncheck a feature that has feature dependencies, a dialog box will be displayed showing the dependencies. Click Remove Features to remove them. On the Features page, click Next.
-
On the Confirmation page, verify that the roles, role services, and features to be removed are correct, and then click Remove.
[!NOTE]
It is recommended that you do a restart if you are prompted to do so, unless you have other activities that you want to do before the restart takes place. A restart is especially important when you remove roles, role services, or features. -
The Removal Progress page is displayed. You can close the wizard without interrupting running tasks. You can view task progress or open the page again by clicking Notifications in the notification area, and then clicking Task Details.
-
On the Results page, click Close.
-
Restart the destination server to finish removing features.
Install IIS 8.5 from the Command Line
You can install IIS 8.5 from the command line using DISM or PowerShell. Note that DISM and PowerShell have different namespaces for installation parameters, so the parameter names used in their commands will be different. For more information, see Modules in IIS 8.5.
[!NOTE]
Pkgmgr.exe has been deprecated. Use DISM instead for scripts installing IIS 8.5.
Install IIS 8.5 using DISM
Automating the installation of IIS by using unattended scripts is very useful if you need to deploy multiple Web servers and want to ensure that each of the Web servers is set up with identical components and services. In Windows Server 2012 R2, DISM is used for unattended scripts, letting you install or uninstall optional features from a command prompt or scripts. To use DISM, you must make sure you have administrative user rights on the computer. For more information about DISM, see DISM Overview
If you do not explicitly include in the DISM code a feature that the IIS installation has a dependency on, the installation will fail, and will not generate an error message. For a list of dependencies required, see Feature Dependencies.
For a full list of the DISM parameters corresponding to IIS roles, services, and features, see Modules in IIS 8.5.
The following script will install all roles, role services, and features of IIS 8.5, getting the full IIS installation that includes all available feature packages. If there are roles, role services, or features that you do not need, you should edit the script to include only those that you require. The order of the commands in the DISM script does not matter. The entire script will be handed off to the engine and treated as one transaction. To install IIS 8.5 with a script, type the following on one line in an elevated command prompt.
[!code-consoleMain]
Install IIS 8.5 using PowerShell
You can use the following PowerShell cmdlets to install all of IIS 8.5:
[!code-powershellMain]
To install only specific features, list them in the PowerShell cmdlet, as in the following example:
[!code-powershellMain]
The following points apply to running the PowerShell cmdlets:
- The cmdlet requires elevation. You must be running a Windows PowerShell session as an administrator to run the cmdlet.
- The cmdlet does not install management tools for roles, role services, and features by default. You must add the IncludeManagementTools parameter to the cmdlet to do so.
For a full list of the PowerShell parameters corresponding to IIS 8.5 roles, services, and features, with more information, see Modules in IIS 8.5. The following lists all these parameters.
- Web-Server
- Web-WebServer
- Web-Security
- Web-Filtering
- Web-Cert-Auth
- Web-IP-Security
- Web-Url-Auth
- Web-Windows-Auth
- Web-Basic-Auth
- Web-Client-Auth
- Web-Digest-Auth
- Web-CertProvider
- Web-Common-Http
- Web-Http-Errors
- Web-Dir-Browsing
- Web-Static-Content
- Web-Default-Doc
- Web-Http-Redirect
- Web-DAV-Publishing
- Web-Performance
- Web-Stat-Compression
- Web-Dyn-Compression
- Web-Health
- Web-Http-Logging
- Web-ODBC-Logging
- Web-Log-Libraries
- Web-Custom-Logging
- Web-Request-Monitor
- Web-Http-Tracing
- Web-App-Dev
- Web-Net-Ext
- Web-Net-Ext45
- Web-ASP
- Web-Asp-Net
- Web-Asp-Net45
- Web-CGI
- Web-ISAPI-Ext
- Web-ISAPI-Filter
- Web-WebSockets
- Web-AppInit
- Web-Includes
- Web-Ftp-Server
- Web-Ftp-Service
- Web-Ftp-Ext
- Web-Mgmt-Tools
- Web-Mgmt-Console
- Web-Mgmt-Compat
- Web-Metabase
- Web-WMI
- Web-Lgcy-Mgmt-Console
- Web-Lgcy-Scripting
- Web-Scripting-Tools
- Web-Mgmt-Service
Uninstall IIS 8.5 using PowerShell
You can use the PowerShell cmdlet UnInstall-WindowsFeature to uninstall IIS 8.5. Run get-help Install-WindowsFeature at a PowerShell command line to see the syntax of the cmdlet. The following points apply to running the cmdlet:
- The cmdlet requires elevation. You must be running a Windows PowerShell session as an administrator to run the cmdlet.
- The cmdlet does not uninstall management tools for roles, role services, and features by default. You must add the IncludeManagementTools parameter to the cmdlet to do so.
Modules in IIS 8.5
IIS modules are individual role services that the server uses to process requests. The following table shows which modules are available to be installed in the Web server, which are installed by default, which role the role service is included in, the parameter used in DISM or PowerShell to install them, and a brief description of the functionality that they provide.
[!NOTE]
An asterisk (*) in the table below denotes a role or role service that is installed by default when the Web Server (IIS) role is installed.
| Role | Role Service | DISM Parameter | PowerShell Parameter | Functionality |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Web Server Role | IIS-WebServerRole | Web-Server | Provides support for HTML Web sites and optional support for ASP.NET, ASP, and Web server extensions, enabling you to host an internal or external Web site or create Web-based applications. | |
| Web Server* | IIS-WebServer | Web-WebServer | Provides support for HTML Web sites and optional support for ASP.NET, ASP, and Web server extensions, enabling you to host an internal or external Web site or create Web-based applications. | |
| Common HTTP Features* | IIS-CommonHttpFeatures | Web-Common-Http | Supports basic HTTP functionality, such as delivering standard file formats and configuring custom server properties. | |
| Default Document* | IIS-DefaultDocument | Web-Default-Doc | Enables you to configure a default file for the Web server to return when users do not specify a file in a request URL. | |
| Directory Browsing* | IIS-DirectoryBrowsing | Web-Dir-Browsing | Enables users to see the contents of a directory on a Web server when they do not specify a file in a request URL and default documents are either disabled or not configured. | |
| HTTP Errors* | IIS-HttpErrors | Web-Http-Errors | Enables you to customize the error messages that are returned to the users’ browsers when the Web server detects a fault condition, improving the user experience. | |
| Static Content* | IIS-StaticContent | Web-Static-Content | Enables the Web server to publish static Web file formats, such as HTML pages and image files that can be viewed using a Web browser. | |
| HTTP Redirection | IIS-HttpRedirect | Web-Http-Redirect | Enables the Web server to redirect user requests that are sent to a specific destination. | |
| WebDAV Publishing | IIS-WebDAV | Web-DAV-Publishing | Web Distributed Authoring and Versioning. Enables you to publish files to and from a Web server by using the HTTP protocol, working through most firewalls without modification. | |
| Health and Diagnostics* | IIS-HealthAndDiagnostics | Web-Health | Provides an infrastructure to monitor, manage, and troubleshoot the health of Web servers, sites, and applications. | |
| HTTP Logging* | IIS-HttpLogging | Web-Http-Logging | Provides logging of Web site activity for the server, in addition to the logging provided by the operating system. | |
| Custom Logging | IIS-CustomLogging | Web-Custom-Logging | Enables you to create a custom logging module that performs logging of Web server activity in a format that differs from the logging normally performed by IIS. | |
| Logging Tools | IIS-LoggingLibraries | Web-Log-Libraries | Provides an infrastructure to manage Web server logs and automate common logging tasks. | |
| ODBC Logging | IIS-ODBCLogging | Web-ODBC-Logging | Provides an infrastructure that supports logging Web server activity to an ODBC-compliant database, enabling you to programmatically display and manipulate logging data on an HTML page. | |
| Request Monitor | IIS-RequestMonitor | Web-Request-Monitor | Provides an infrastructure to monitor Web application health by capturing information about HTTP requests. | |
| Tracing | IIS-HttpTracing | Web-Http-Tracing | Provides an infrastructure to diagnose and troubleshoot Web applications, including poor performance and authentication-related failures. | |
| Performance* | IIS-Performance | Web-Performance | Provides an infrastructure to enable more efficient use of bandwidth by performing compression of static and/or dynamic content. | |
| Static Content Compression* | IIS-HttpCompressionStatic | Web-Stat-Compression | Provides an infrastructure to configure HTTP compression of static content. | |
| Dynamic Content Compression | IIS-HttpCompressionDynamic | Web-Dyn-Compression | Provides an infrastructure to configure HTTP compression of dynamic content. | |
| Security* | IIS-Security | Web-Security | Provides an infrastructure for securing the Web server from users and requests, using one of multiple authentication methods. | |
| Request filtering* | IIS-RequestFiltering | Web-Filtering | Enables screening of all incoming requests to the server, and filters the requests based upon rules set by the administrator. | |
| Basic Authentication | IIS-BasicAuthentication | Web-Basic-Auth | An authentication method in which users are prompted to supply credentials that are transmitted unencrypted across the network. | |
| Centralized SSL Certificate | IIS-CertProvider | Web-CertProvider | An authentication method that uses SSL server certificates that are managed centrally using a file share. | |
| Client Certificate Mapping Authentication | IIS-ClientCertificateMappingAuthentication | Web-Client-Auth | An authentication method that uses client certificates to authenticate users, using Active Directory to offer one-to-one certificate mappings across multiple Web servers. | |
| Digest Authentication | IIS-DigestAuthentication | Web-Digest-Auth | An authentication method that sends a password hash to a Windows domain controller to authenticate users, especially useful if users who must be authenticated will access the Web site from behind firewalls and proxy servers. | |
| IIS Client Certificate Mapping Authentication | IIS-IISCertificateMappingAuthentication | Web-Cert-Auth | An authentication method that uses client certificates to authenticate users, using IIS to offer one-to-one or many-to-one certificate mapping. | |
| IP and Domain Restrictions | IIS-IPSecurity | Web-IP-Security | An authentication method that enables you to enable or deny content based upon the originating IP address or the domain name of the request. | |
| URL Authorization | IIS-URLAuthorization | Web-Url-Auth | An authentication method that enables you to create URL authorization rules that restrict access to Web content. | |
| Windows Authentication | IIS-WindowsAuthentication | Web-Windows-Auth | An authentication method that enables administrators in a Windows domain to take advantage of the domain infrastructure for authenticating users, a low-cost authentication solution for internal Web sites. | |
| Application Development | IIS-ApplicationDevelopment | Web-App-Dev | Provides an infrastructure for developing and hosting Web applications, useful for creating Web content and extending the functionality of IIS. | |
| .NET Extensibility 3.5 | IIS-NetFxExtensibility | Web-Net-Ext | Enables managed code developers to change, add, and extend Web server functionality in the entire request pipeline, the configuration, and the UI. | |
| .NET Extensibility 4.5 | IIS-NetFxExtensibility45 | Web-Net-Ext45 | Enables managed code developers to change, add, and extend Web server functionality in the entire request pipeline, the configuration, and the UI. | |
| Application Initialization | IIS-ApplicationInit | Web-AppInit | Enables you to perform expensive Web application initialization tasks before serving Web pages. | |
| ASP | IIS-ASP | Web-ASP | Provides a server-side scripting environment for building Web sites and Web applications, especially for existing applications. | |
| ASP.NET 3.5 | IIS-ASPNET | Web-Asp-Net | Provides a server-side object-oriented programming environment for building Web sites and Web applications using managed code. | |
| ASP.NET 4.5 | IIS-ASPNET45 | Web-Asp-Net45 | Provides a server-side object-oriented programming environment for building Web sites and Web applications using managed code. | |
| CGI | IIS-CGI | Web-CGI | Defines how a Web server passes information to an external program. | |
| ISAPI Extensions | IIS-ISAPIExtensions | Web-ISAPI-Ext | Internet Server Programming Interface Extensions. Provides support for dynamic Web content development. | |
| ISAPI Filters | IIS-ISAPIFilter | Web-ISAPI-Filter | Internet Server Programming Interface Filters. Enables you to extend or change the functionality provided by IIS, reviewing every request made to the Web server and processing the appropriate requests. | |
| Server Side Includes | IIS-ServerSideIncludes | Web-Includes | A scripting language used to dynamically generate HTML pages, using script that is run on the server before the page is delivered to the client. | |
| WebSocket Protocol | IIS-WebSockets | Web-WebSockets | Provides communication channels for server applications created with IIS 8.x and ASP.NET 4.5. | |
| FTP Server | IIS-FTPServer | Web-Ftp-Server | Enables the transfer of files between a client and a server, using either an FTP client or an FTP-enabled Web browser. | |
| FTP Service | IIS-FTPSvc | Web-Ftp-Service | Enables FTP publishing on a Web server. | |
| FTP Extensibility | IIS-FTPExtensibility | Web-Ftp-Ext | Enables support for FTP extensibility features such as customer providers, ASP.NET users, or IIS Manager users. | |
| IIS Hostable Web Core (IIS 8.0, not IIS 8.5) | IIS-HostableWebCore | Web-WHC | Enables you to write custom code that will host core IIS functionality in your own application that serves HTTP requests and uses its own applicationHost.config and root Web.config configuration files. | |
| Management Tools* | IIS-WebServerManagementTools | Web-Mgmt-Tools | Provides an infrastructure for managing a Web server that runs IIS 7.0 or later. | |
| IIS Management Console* | IIS-ManagementConsole | Web-Mgmt-Console | Provides an infrastructure for managing an IIS 7.0 or later Web server, local or remote, using a user interface. | |
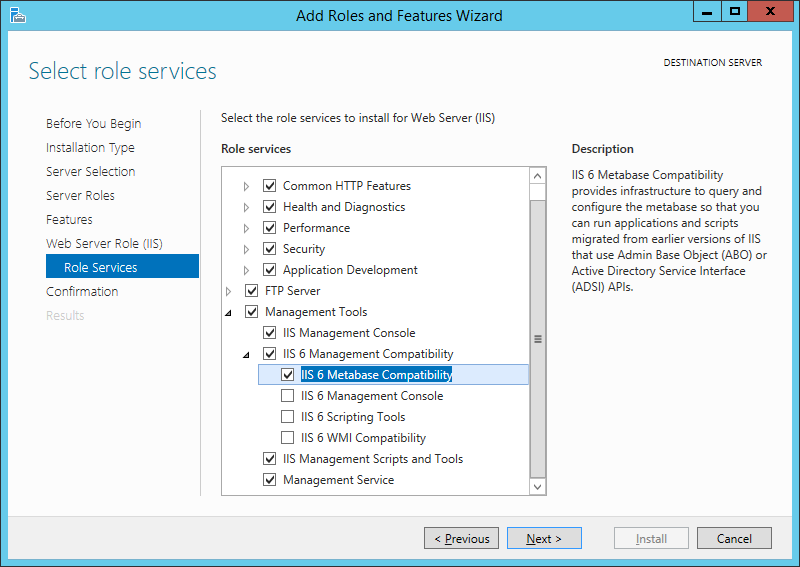
| IIS 6 Management Compatibility | IIS-IIS6ManagementCompatibility | Web-Mgmt-Compat | Provides forward compatibility for applications and scripts that use the IIS 6 APIs, Admin Base Object (ABO) and Active Directory Service Interface (ADSI). | |
| IIS 6 Metabase Compatibility | IIS-Metabase | Web-Metabase | Provides an infrastructure for querying and configuring the Metabase, so that you can run applications and scripts migrated from earlier versions of IIS that use Admin Base Object (ABO), and Active Directory Service Interface (ADSI). | |
| IIS 6 Management Console | IIS-LegacySnapIn | Web-Lgcy-Mgmt-Console | Provides an infrastructure for administration of remote IIS 6.0 servers. | |
| IIS 6 Scripting Tools | IIS-LegacyScripts | Web-Lgcy-Scripting | Enable you to continue to use scripts built to manage IIS 6 in IIS 7.0 or later, especially if your applications and scripts use ActiveX Data Objects (ADO) or Active Directory Service Interface (ADSI). | |
| IIS 6 WMI Compatibility | IIS-WMICompatibility | Web-WMI | Provides Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) scripting interfaces to programmatically manage and automate tasks for an IIS 8.0 or later Web server. | |
| IIS Management Scripts and Tools | IIS-ManagementScriptingTools | Web-Scripting-Tools | Provides an infrastructure to programmatically manage an IIS 7.0 or later Web server by using commands in a command window or by running scripts. | |
| Management Service | IIS-ManagementService | Web-Mgmt-Service | Enables the Web server to be managed remotely from another computer using IIS Manager. |
Feature Dependencies
The following table shows which role services and features must be installed for the role service or features in the table row to be installed.
The Add Roles and Features Wizard and Remove Roles and Features Wizard of Server Manager take care of dependencies by prompting you to add dependencies when adding a role service or feature, or to remove dependencies when removing a role service or feature. However, when you install IIS using DISM, you need to include in the DISM code any dependency that a role service or feature being installed has, or the installation will fail, and you may not receive an indication why it failed.
When you remove a role service or feature, make sure that you do not remove a service or feature that another service or feature has a dependency on. There can be an intersection of dependencies, for example between ASP and ASP.NET. So if you were to remove ASP, and remove its feature dependencies, you could remove dependencies for ASP.NET, as well.
| Role | Role Service | Dependency |
|---|---|---|
| Web Server Role | None | |
| Web Server* | None | |
| Common HTTP Features* | None | |
| Default Document* | None | |
| Directory Browsing* | None | |
| HTTP Errors* | None | |
| Static Content* | None | |
| HTTP Redirection | None | |
| WebDAV Publishing | Static Content | |
| Health and Diagnostics* | None | |
| HTTP Logging* | None | |
| Custom Logging | None | |
| Logging Tools | None | |
| ODBC Logging | None | |
| Request Monitor | None | |
| Tracing | None | |
| Performance* | None | |
| Static Content Compression* | None | |
| Dynamic Content Compression | None | |
| Security* | None | |
| Request filtering* | None | |
| Basic Authentication | None | |
| Centralized SSL Certificate | None | |
| Client Certificate Mapping Authentication | None | |
| Digest Authentication | None | |
| IIS Client Certificate Mapping Authentication | None | |
| IP and Domain Restrictions | None | |
| URL Authorization | None | |
| Windows Authentication | None | |
| Application Development | None | |
| .NET Extensibility 3.5 | — .NET Framework 3.5 (includes .NET 2.0 and 3.0) — ASP.NET 4.5 — .NET Framework 4.5 — Application Development — Request Filtering | |
| .NET Extensibility 4.5 | — ASP.NET 4.5 — .NET Framework 4.5 — Application Development — Request Filtering | |
| Application Initialization | None | |
| ASP | — Web Server (IIS)-Web Server- Application Development- ISAPI Extensions — Request Filtering | |
| ASP.NET 3.5 | — .NET Framework 3.5 (includes .NET 2.0 and 3.0) — ASP.NET 4.5 — .NET Framework 4.5 — ISAPI Extensions — ISAPI Filters — .NET Extensibility 3.5 — Request Filtering | |
| ASP.NET 4.5 | — ASP.NET 4.5 — .NET Framework 4.5 — ISAPI Extensions — ISAPI Filters — .NET Extensibility 3.5 — Request Filtering | |
| CGI | None | |
| ISAPI Extensions | None | |
| ISAPI Filters | None | |
| Server Side Includes | None | |
| WebSocket Protocol | None | |
| FTP Server | None | |
| FTP Service | None | |
| FTP Extensibility | FP Service | |
| IIS Hostable Web Core (IIS 8.0, not IIS 8.5) | None | |
| Management Tools* | — .NET Framework 4.5 — Graphic Management Tools and Infrastructure — Windows PowerShell 3.0 | |
| IIS Management Console* | — .NET Framework 4.5 — Graphic Management Tools and Infrastructure — Management Tools — Windows PowerShell 3.0 | |
| IIS 6 Management Compatibility | None | |
| IIS 6 Metabase Compatibility | None | |
| IIS 6 Management Console | — .NET Framework 4.5 — Graphic Management Tools and Infrastructure — IIS 6 Metabase Compability — Windows PowerShell 3.0 | |
| IIS 6 Scripting Tools | — IIS 6 Metabase Compatibility — IIS 6 WM Compatibility | |
| IIS 6 WMI Compatibility | IIS 6 Metabase Compatibility | |
| IIS Management Scripts and Tools | None | |
| Management Service | — ASP.NET 4.5 — .NET Framework 4.5 — Management Tools |
See also
- Install or Uninstall Roles, Role Services, or Features
- IIS.NET Install
- What’s New in IIS 8.5
- DISM Overview
- Editing Configuration Files
- Extending IIS Configuration
Обычно, когда говорят о web-сервере, подразумевают решения на базе платформы Linux. Но если ваша инфраструктура развернута на основе Windows Server то логично будет использовать веб-сервер IIS. Вопреки распространенному мнению, это весьма популярная платформа, которая позволяет работать как с большинством популярных CMS, так и имеет широкий спектр систем, предназначенных для работы именно на Windows и IIS.
Научиться настраивать MikroTik с нуля или систематизировать уже имеющиеся знания можно на углубленном курсе по администрированию MikroTik. Автор курса, сертифицированный тренер MikroTik Дмитрий Скоромнов, лично проверяет лабораторные работы и контролирует прогресс каждого своего студента. В три раза больше информации, чем в вендорской программе MTCNA, более 20 часов практики и доступ навсегда.
Несомненным достоинством IIS является его тесная интеграция с другими технологиями и средствами разработки Microsoft. В частности веб-решения для IIS могут использовать богатые возможности .NET и легко взаимодействовать с настольными приложениями на этой платформе. Если же вас это пока не интересует, то к вашим услугам богатый выбор готовых CMS, в том числе написанных специально для IIS. Сегодня мы рассмотрим как установить и настроить IIS для работы с веб-решениями на базе ASP.NET и установим одну из популярных CMS для этой платформы.
Для установки веб-сервера на платформе Windows перейдем в оснастку Роли в Диспетчере сервера и выберем установку ролей Веб-сервер (IIS) и Сервер приложений.
Но не спешите нажимать Далее, слева, под названием каждой роли, доступна опция Службы ролей, перейдем на нее и установим для Сервера приложений следующие опции: Поддержка веб-сервера (IIS), Общий доступ к TCP-портам и Активация через HTTP.
А для веб-сервера установите службу FTP-сервер.
После чего установите выбранные роли. Для проверки работоспособности IIS наберите в браузере IP-адрес вашего сервера, вы должны будете увидеть стандартную страницу-заглушку веб-сервера.
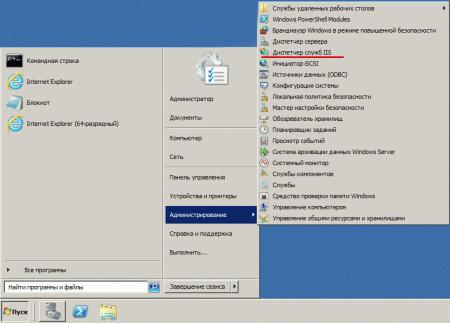
Теперь перейдем в к настройке сервера, для этого откроем Диспетчер служб IIS (находится в Пуск — Администрирование).
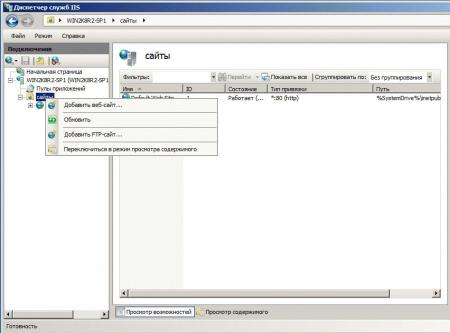
Первым делом создадим новый сайт, для этого щелкните правой кнопке на пункте Сайты в боковом меню Диспетчера IIS и выберите Создать новый сайт.
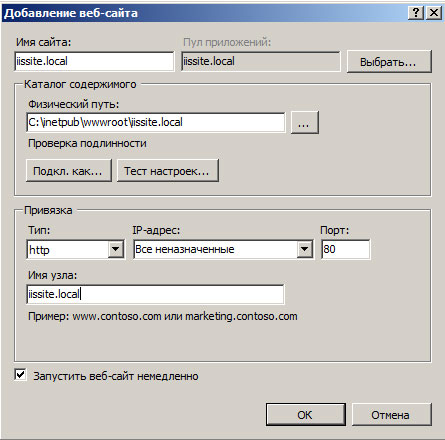
В открывшемся окне укажите имя сайта, путь к корневой папке (по умолчанию сайты пользователей располагаются в C:inetpubwwwroot), которую следует предварительно создать и укажите имя узла (доменное имя сайта), в нашем случае iissite.local
Не забудьте добавить A-запись с именем вашего сайта на DNS-сервер или пропишите необходимые строки в файлы hosts тех рабочих станций, откуда будете обращаться к сайту
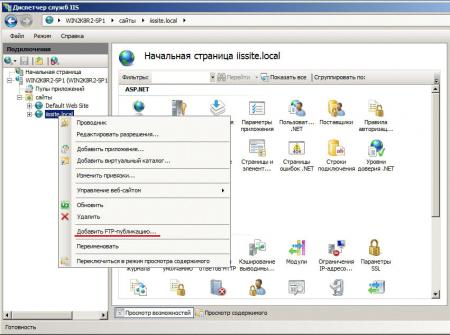
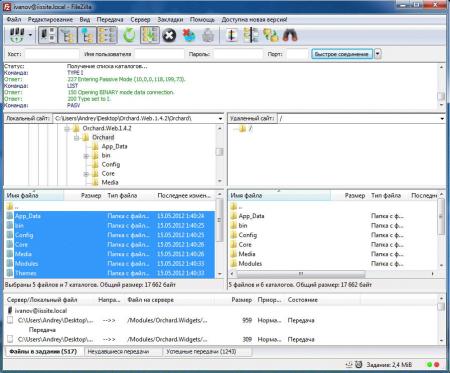
В принципе вы уже можете размещать в папке сайта web-страницы и получать к ним доступ через браузер, но для полноценной работы с сайтом не помешает FTP-доступ к нему. Для этого щелкните правой кнопкой по названию вашего сайте в боковом меню и выберите Добавить FTP-публикацию
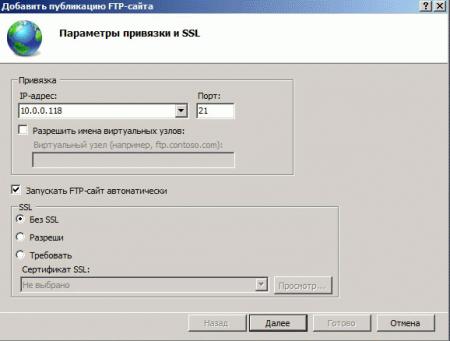
Далее укажите привязку FTP-cлужбы к сетевым интерфейсам и портам, а также настройте параметры безопасности. Если вы собираетесь использовать SSL, то учтите что вам потребуется сертификат, хотя если вы будете использовать FTP-доступ только для собственных нужд, то можно обойтись самоподписанным сертификатом. Не забудьте поставить галочку для автоматического запуска FTP-сайта.
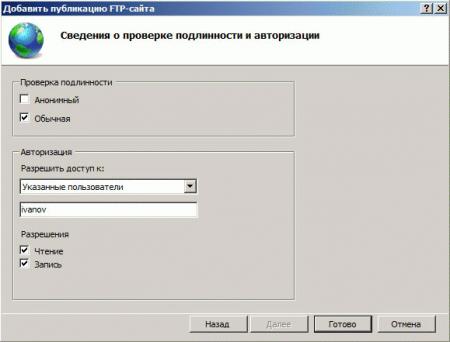
На следующей странице укажите параметры доступа к серверу, мы советуем указывать конкретных пользователей, которые будут работать с данным сайтом.
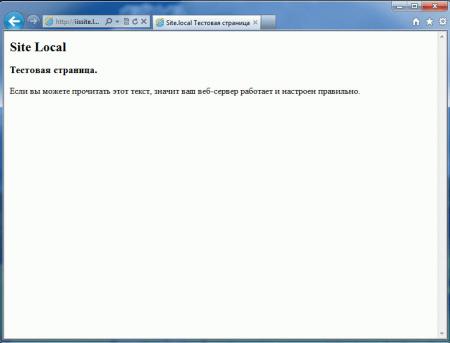
Попробуйте подключиться через FTP используя любой клиент и загрузите проверочную html страницу с именем index.html, пример такой страницы мы приводили здесь. Если все сделано правильно, то, набрав в браузере имя нашего сайта, вы увидите такую страницу:
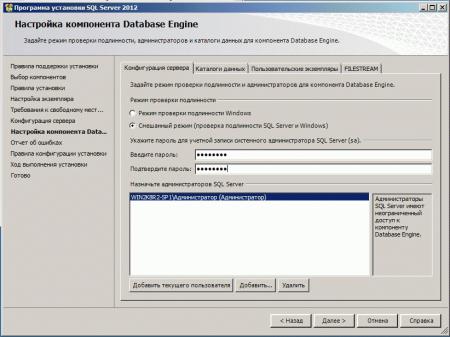
Веб-сервер настроен и вы можете использовать его для размещения HTML-страниц, однако современные сайты используют для хранения своих данных СУБД, поэтому следующим шагом установим MS SQL Express 2012, возможностей которого с лихвой хватит для наших задач. Установка производится со значениями по умолчанию, кроме Режима проверки подлинности, который следует переключить в Смешанный режим и задать пароль суперпользователю SQL-сервера sa.
Теперь попробуем установить какую либо популярную CMS созданную на базе технологии ASP.NET, обширный выбор таких решений представлен в галерее web-приложений Microsoft. Обратите внимание, что по кнопке скачать вы получите пакет для установки через Web PI, для установки на IIS вам потребуется перейти на сайт разработчика и скачать полный пакет с CMS
Мы будем устанавливать Orchard CMS, для получения пакета пройдите по ссылке и выберите Загрузить как zip, распакуйте полученный архив и закачайте в корень сайта содержимое папки Orchard.
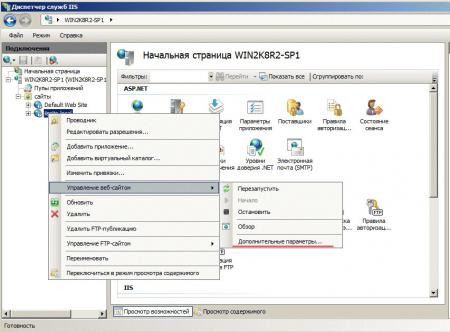
Данная CMS создана на базе ASP.NET 4, поэтому настроим наш сайт на использование необходимых технологий. Для этого щелкните правой кнопкой на имени сайта в боковом меню и выберите Управление веб-сайтом — Дополнительные параметры
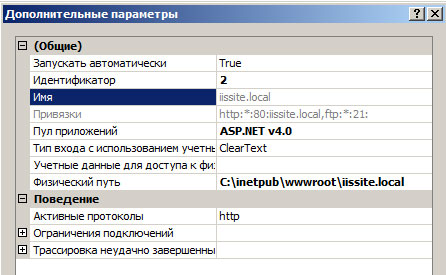
В открывшемся окне измените параметр Пул приложений, указав там ASP.NET v.4
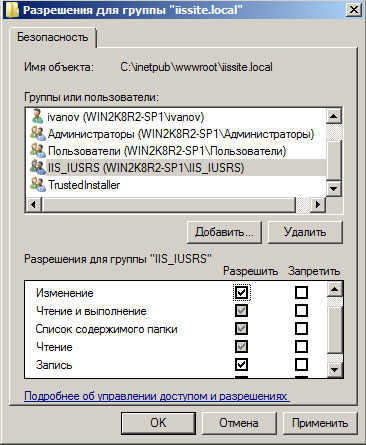
Затем установите необходимые права на папку с сайтом, вам нужно добавить пользователю IIS_IUSRS возможность записи и изменения содержимого данной папки.
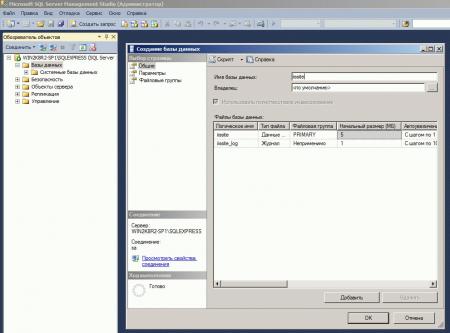
Также не забудьте создать базу данных для сайта, для этого зайдите в SQL Server Management Studio и, щелкнув правой кнопкой на пункте Базы данных в боковом меню, создайте новую базу.
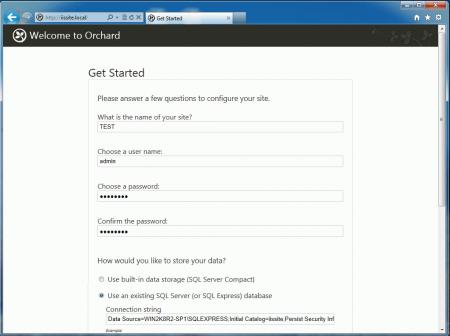
Для установки CMS наберите в браузере адрес сайта и следуйте указаниям скрипта установки. Никаких сложностей там нет, единственное затруднение может вызвать правильное указание параметров подключения к SQL-серверу. Укажите что вы используете SQL Server (или SQL Express)
В строке подключения ниже укажите следующее:
server=SERVERNAMESQLEXPRESS;database=iissite;user=sa;password=sapasswd;где:
- server=SERVERNAMESQLEXPRESS — имя сервера, на котором установлен SQL-сервер, и экземпляра SQL-сервера.
- database=iissite — имя базы данных (в нашем случае iissite)
- user=sa — пользователь СУБД (в нашем случае sa)
- password=sapasswd — пароль пользователя sa.
Так как наш сайт предназначен для внутреннего использования и использует изолированный экземпляр SQL, то мы использовали для доступа к серверу параметры пользователя sa, если же вы собираетесь размещать на веб-сервере несколько сайтов и администрировать их будут разные пользователи, то заведите на SQL сервере дополнительных пользователей и для подключения используйте их учетные данные, не забыв ограничить им доступ только к «своим» базам.
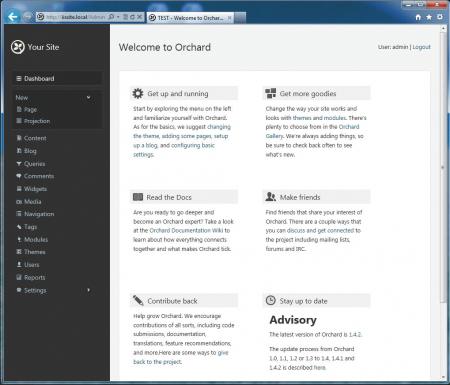
Спустя некоторое время, необходимое для установки CMS, в вашем браузере отобразиться страница сайта с тестовым содержимым. Можете переходить в админ-панель и настраивать сайт согласно ваших потребностей.
Несмотря на то, что мы рассмотрели установку только одного «движка», установка других CMS производится аналогичным образом и сложностей вызвать не должна
В следующей части нашей статьи мы расскажем как добавить нашему серверу поддержку PHP для запуска на нем популярных CMS написанных на этом языке.
Научиться настраивать MikroTik с нуля или систематизировать уже имеющиеся знания можно на углубленном курсе по администрированию MikroTik. Автор курса, сертифицированный тренер MikroTik Дмитрий Скоромнов, лично проверяет лабораторные работы и контролирует прогресс каждого своего студента. В три раза больше информации, чем в вендорской программе MTCNA, более 20 часов практики и доступ навсегда.
Пришла задача поднять IIS на Windows Server 2012 R2 для CRM BPM Online от Terrasoft. Указанные ниже настройки достаточны для работы данной приблуды. Однако, пришлось также забраться в конфиги данной сторонней системы и кое что править руками. Но это уже не относится к установке IIS и описываться здесь не будет.
Для ваших задач, скорее всего, потребуется ставить уже другие галки. Приступим.
Ссылки
Установка IIS в Windows 10
Установка
Запускаем Server Manager. Manage > Add Roles and Features.
Запускается мастер добавления ролей и фич.
Кликаем Next. Попадаем в выбор типа установки.
Оставляем Role-based or feature-based installation. Next. Попадаем на страницу выбора сервера.
У меня один сервер. Next. Наконец попадаем в выбор ролей.
Ставим галку на Web Server (IIS). Сразу же всплывает окно.
Нам предлагают с выбором роли Web Server (IIS) также поставить необходимые обязательные для этой роли фичи. Кликаем Add Features. Переходим к окну выбора фич.
Кликаем Next. Переходим на вкладку Web Server Role (IIS).
Кликаем Next. Переходим на вкладку Role Services.
Теперь настраиваем фичи для выбранной роли. Нас интересует раздел Web Server. Ставим галки на фичах.
Теперь нас интересует раздел FTP Server. Ставим галки на фиче FTP Service.
В разделе Management Tools ставим галки на фичах.
- IIS Management Console
- IIS 6 Management Compatibility
- IIS 6 Metabase Compatibility
- IIS Management Scripts and Tools
- Management Service
Кликаем Next. Попадаем на страницу подтверждения.
Кликаем Install. Начинается установка.
Installation succeeded.
Даже не пришлось ребутать сервер.
Большинство пользователей при работе в тонком или веб-клиенте используют в основном публикацию информационных баз на основании протокола HTTP. С одной стороны — это простой и быстрый способ дать доступ к информационной базе пользователю, у которого нет дистрибутива тонкого клиента, и он может работать только в веб-клиенте или у пользователя нет прямого доступа к серверу «1С:Предприятие». С другой стороны – информационные базы, опубликованным таким образом, категорически не рекомендуются публиковать в глобальной сети Интернет, так как в таком случае используется незащищенный канал, данные по которому могут быть перехвачены злоумышленниками. Например, распространенные виды атак это:
- анализаторы траффика
- man in middle
Решением этих проблем является использование расширения протокола HTTP и в данной статье рассмотрены публикации информационных баз с использование протокола с шифрованием (HTTPS) для веб-сервера IIS.
Внимание! В статье не рассматривается выпуск и получение сертификата проверенных поставщиков. Этот пункт должен быть выполнен самостоятельно на основании предпочтений выбора провайдера услуг. В статье предполагается что, пропуская шаг выпуска самоподписанных сертификатов, у пользователя или администратора он имеется в наличие и будет подставлен в настроечные файлы, вместо указанных в статье самоподписанных сертификатов.
План работ:
- Включение компонент веб-сервера.
- Windows 10.
- Windows Server 2012 R2, 2016 и 2019.
- Выпуск самоподписанного сертификата (Необязательно).
- Привязка сертификата.
- Проверка публикации.
По умолчанию в операционной среде Windows компоненты веб-сервера не установлены. В зависимости от версии установка может несущественно различаться. Мы будем рассматривать два варианта – это распространенный дистрибутив Windows 10, если планируются использовать для пробного включения шифрования протокола и Windows Server 2016/2018, если уже планируется непосредственное разворачивание публикации в продуктивной зоне.
1.1. Windows 10
Включение компонентов веб-сервера IIS в операционной системе Windows 10 выполняется достаточно просто. Для начала нужно открыть раздел «Программы и компоненты» («Programs and Features») в панели управления (Control panel). Сделать можно это несколькими способами:
- Нажать сочетание клавиш Win + R и в открывшемся окне ввести «appwiz.cpl» и нажать ОК.
- Открыть панель управления (Control panel) и выбрать пункт меню Программы – Программы и компоненты (Programs – Programs and features).
В окне «Программы и компоненты» («Programs and Features») нажмите на кнопку «Включение и отключение компонентов Windows» («Turn Windows features on or off»).
Когда откроется окно «Компоненты Windows» («Windows features») в нем необходимо будет проставить флажки для следующих элементов:
- Службы IIS
- Службы интернета
- Компоненты разработки приложений
- Расширение ISAPI
- Фильтры ISAPI
- Компоненты разработки приложений
- Средства управления веб-сайтом
- Консоль управления IIS
- Службы интернета
После этого нажимайте на кнопку «OK» и дождитесь завершения выполнения операции. После того как включение компонент будет выполнено, можно переходить к пункту «2. Публикация информационной базы».
1.2 Windows Server 2012 R2, 2016 и 2019
Настройка компонент для Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2016 и Windows Server 2019 одинаковая и все настройки производятся в диспетчере серверов (Server Manager).
Откройте диспетчер серверов (Server Manager) и нажмите Управление – Добавить роли и компоненты (Manage – Add Roles and Features).
В ответ на нажатие откроется окно мастера добавления ролей и компонентов (Add Roles and Features).
В этом окне нажмите два раза «Далее» («Next») пока мастер не переключится на страницу ролей сервера (Server Roles).
Во вкладке роли сервера (Server Roles) установите флажок «Web Server IIS». Так как эта роль зависит от другой роли ([Tools] IIS Management Console), то будет предложено установить ее дополнительно. Это можно сделать с помощью нажатия кнопки «Добавить компоненты» (Add Features) в открывшемся окне. После чего нажимаем кнопку «Далее» («Next») пока мастер не дойдет до вкладки «Роль веб-сервера IIS» («Web Server Role IIS»). На этой вкладке нажимайте кнопку «Далее» («Next») и попадете на вкладку «Службу ролей» («Role Services»). Во вкладке нужно найти пункт «Application Development» и выбрать в нем с помощью флажков пункты «ISAPI Extensions» и «ISAPI Filters». Как только закончите с установкой флажков нажимайте «Далее» («Next») и «Установить» («Install»).
На этом установка веб-сервера завершена. Можно переходить к настройкам сертификатов.
2. Выпуск самоподписанного сертификата
Выпуск самоподписанного сертификата для веб-сервера IIS максимально простой.
Для реальных систем не рекомендуем использовать самоподписанный сертификат.
Для начала процедуры выпуска откройте окно Диспетчера служб IIS (Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager) и выделите сервер в списке Подключений (Connections). После этого нажмите на ссылку «Сертификаты сервера» («Server Certificates»).
Откроется окно доступных сертификатов сервера (Server Certificates) в котором нужно нажать «Создать самозаверенный сертификат…» («Create Self-Signed Certificate…»).
В окне мастера создания самоподписанного сертификата остается указать только произвольное название сертификата. В большинстве случаев, во избежание путаницы лучше явно указывать в качестве значения «Полное имя сертификата» («Specify a friendly name for the certificate») адрес сервера, на котором расположен сервер IIS. Как только имя сертификата будет задано нажимайте на кнопку OK и переходите к пункту привязки сертификата.
3. Привязка сертификата
Предполагается, что сертификат получен и добавлен в список сертификатов сервера. Если сертификат получен с помощью распространенного сертифицирующего центра, то его нужно предварительно импортировать в окне «Сертификаты сервера» («Server Certificates»).
Как только сертификат появится в списке, переходим непосредственно к его привязки к публикации сайта. Для этого выделяем «Default Web Site» и в окне «Действия» («Actions») нажимаем на пункт «Привязки…» («Binding…»).
В этом окне можно увидеть, что публикация работает только на порту 80, который относится к незащищенному протоколу HTTP. Чтобы его расширить, нажмите кнопку Добавить… (Add…) слева от списка привязок сайта и в открывшемся окне выберите Тип (Type) в качестве значения «https». Завершением настройки будет выбор ранее импортированного сертификата в списке «SSL-сертификат» («SSL certificate»). Нажимаем кнопку OK и закрываем мастер привязок сайта.
Можно переходить к публикации информационной и проверки его работоспособности.
4. Проверка публикации
Для публикации информационной базы нужно открыть конфигуратор конкретной базы от имени администратора и перейти в пункт меню «Администрирование». После этого выбрать «Публикация информационной базы».
В окне публикации указать имя публикации и по желанию определить каталог, где будут находиться настройки публикации. Его также можно оставить по умолчанию.
После этого требуется нажать кнопку «Опубликовать» и дождаться окончания операции.
Для проверки корректной работы нужно открыть страницу в браузере и перейти по ссылке, которая состоит из двух частей:
- Имя вашего сервера (например, server1)
- Имя публикации базы (которое было указано в окне настройки публикации)
Для таких параметров ссылка будет иметь вид:
https://server1/test_1c_iis
Если все хорошо, то откроется страница с вашей информационной базой.
Опубликовано
⏰ 27.06.2019
Привет всем, уважаемые читатели. Сегодня у нас тема: «WEB-сервер в Windows Server 2012-2016». И снова две версии ОС в одной статье. На очереди Веб-сервер, роль позволяющая создавать на сервере веб-сайты, веб-приложения, и прочие веб-ресурсы.
Установка WEB-сервера в Windows Server 2012-2016
- В диспетчере сервера, переходим в раздел «Добавить роли и компоненты».

- Появляется памятка мастера добавления ролей.
- Жмём «Далее».

Следующий шаг, это «выбор типа установки».
- Нас интересует «Установка ролей и компонентов».
- Жмём «Далее».

На следующем шаге, нам нужно выбрать целевой сервер.
- Выбираем нужный сервер, или виртуальный диск.

Открывается окно выбора ролей сервера.
- Находим «Веб-сервер», и выбираем его.

- Появляется окно, с предложением установить необходимые Веб-серверу компоненты.
- Жмём «Добавить компоненты».

- В окне выбора ролей, жмём «Далее».

- На следующем шаге можно добавить нужные компоненты, помимо тех, которые уже выбраны.
- Если нужно, добавляем.
- Жмём «Далее».

Появляется информативное окно о роли веб-сервера.
- Жмём «Далее».

Следующим шагом идёт «Выбор служб ролей».
- Если что-то нужно, выбираем и двигаемся дальше.

Появляется сводка выбранных нами параметров.
- Можно вернутся и что-то изменить.
- Если всё устраивает, то жмём «Установить».

- Ждём завершения процесса добавления роли.
- По окончании, сводка произведённых действий. Жмём «Закрыть».

- Веб сервер появился на панели мониторинга.
- Удаляем задачу в области уведомлений, чтобы не висела.

Теперь делаем проверку.
- Открываем браузер и вводим ip адрес Вашего сервера. (Если в Вашей сети есть DNS-сервер, и Ваш сервер имеет доменное имя, то можно ввести доменное имя.)
- Открывается индекс страница WEB-сервера.

Сегодня мы рассмотрели тему: «WEB-сервер в Windows Server 2012-2016». Добавили роль Веб-сервера с основными компонентами, и проверили его работу.
Надеюсь статья была вам полезна. До встречи в новых статьях.
✍
С уважением, Андрей Бондаренко.
Видео на тему «WEB-сервер в Windows Server 2012»:
Видео на тему «WEB-сервер в Windows Server 2016»:
✧✧✧
Поблагодарить автора за полезную статью:
WMZ-кошелёк = Z667041230317
✧ Рубрика «Windows server»
✧ Комментарии: нет
Похожие записи