Table of Contents
All Weeks Cybersecurity Roles, Processes & Operating System Security Quiz Answers
Welcome to People, Process and Operating System Fundamentals for Cybersecurity
Q1. In the video Welcome to People, Process and Operating System Fundamentals for Cybersecurity, Alex mentions especially needing which two (2) technical skills and which two (2) soft skills ?
- Effective Communications and Critical Thinking
- Firewalls and Antivirus
Q2. The statement: “The protection of computer systems from theft or damage to the hardware, software or information on them, as well as from disruption or misdirection of the services they provide.” Is a good definition for what ?
- IT Security
Quiz-02 Frameworks, Policies and Roles
Q1. When looking at security standard and compliance, which three (3) are characteristics of best practices, baselines and frameworks ?
- They seek to improve performance, controls and metrics.
- They help translate the business needs into technical or operational needs.
- They are used to improved controls, methodologies and governance for the IT department.
Q2. Which three (3) of these roles would likely exist in an Information Security organization ?
- CISO, Chief Information Security Officer
- Information Security Architect
- Vulnerability Assessor
Quiz-03 Business Process Management and IT Infrastructure Library Basics
Q1. In the video Introduction to Process, which three (3) items were called out as critical to the success of a Security Operations Center (SOC) ?
- Tools
- People
- Process
Q2. Process performance metrics typically measure items in which four (4) categories ?
- Rework
- Cost
- Quality (defect rate)
- Cycle time
Q3. Service Portfolio Management, Financial Management, Demand Management and Business Relationship Management belong to which ITIL Service Lifecycle Phase ?
- Service Strategy
Q4. Log, Assign, Track, Categorize, Prioritize, Resolve and Close are all steps in which ITIL process ?
- Incident Management
Quiz-04 People, Process and Technology
Q1. The process in ITIL where changes are released to an IT environment is called what ?
- Release Management
Q2. Which two (2) processes are operational processes? (Select 2)
- Incident Management
- Change Management
Q3. Which two (2) of these are considered best practices? (Select 2)
- ITIL
- Project Manager methodologies
Q4. Which service management process has the responsibility of understanding the root cause of a problem ?
- Problem Management
Q5. In the video What is IT Security, Elio Sanabria Echeverria put forth a definition that included which factors ?
- All of the above.
Q6. This description belongs to which information security role? “This position is in charge of testing the effectiveness of computer information systems, including the security of the systems and reports their findings.”
- Information Security Auditor
Q7. Which of these statements more accurately conveys what was stated in the video Introduction to Process ?
- As volumes of security alerts and false positives grow, more burden is placed upon Security Analysts & Incident Response teams.
Cybersecurity Roles, Processes & Operating System Security Week 02 Quiz Answers
Further discussion of confidentiality, integrity and availability
Q1. In the Alice, Bob and Trudy examples, who is always portrayed as the intruder ?
- Trudy
Q2. Which aspect of the CIA Triad would cover preserving authorized restrictions on information access and disclosure ?
- Confidentiality
Q3. A message that Bob receives from Alice is genuine and can be verified as such demonstrates which key property ?
- Authenticity
Quiz 02 Principles of the CIA Triad
Q1. The unauthorized disclosure of information would violate which aspect of the CIA Triad ?
- Confidentiality
Q2. Which aspect of the CIA Triad would cover ensuring information non-repudiation and authenticity ?
- Integrity
Q3. If Trudy intercepts and reads a message that Alice is sending to Bob, and then she deletes it without allowing it to be delivered, which 2 aspects of the CIA Triad have been violated ?
- Availability & Confidentiality
Quiz 03 What is AAA ?
Q1. Which is the correct order for gaining access to a resource ?
- Identification, Authentication, Authorization, Accountability
Q2. Which type of method would include Something you know, such as a password ?
- Authentication
Quiz 04 Access Control
Q1. Which three (3) are common methods of access control ?
- Role Based Access Control (RBAC)
- Discretionary Access Control (DAC)
- Mandatory Access Control (MAC)
Q2. Which three (3) items would be considered Physical Access Control methods ?
- Perimetral
- Building
- Work areas
Authentication and Access control
Q1. Identify the three (3) security functions associated with AAA.
- Authorization
- Accountability (Accounting)
- Authentication
Q2 . Which statement best describes DAC (Discretionary Access Control) ?
- Each object (folder or file) has an owner and the owner defines the rights and privilege.
Q3. Which is an example of technical uses of physcial security controls ?
- All of the above.
Q4. Name one of the three control types.
- Technical
Q5 . Which of the following is NOT an authentication method ?
- Something you get
Q6. Hamid has access to certain resources because he is a Quality Control Inspector and he has access to other resources because he is the manager of that team. Which form of access control is his company most likely using ?
- Role Based Access Control (RBAC)
Q7. Which two (2) of these are useful tools used to monitor network access control processes ?
- Sniffers
- HoneyPots
Cybersecurity Roles, Processes & Operating System Security Week 03 Quiz Answers
User and Kernel Modes
Q1. How many unique address spaces are used by applications running in kernel mode ?
- 1
Quiz 02 File Systems and Directory Structure
Q1. Which two (2) of these file systems could you use to format a 64 GB USB drive ?
- NTFS
- FAT32
Q2. Where does Windows 10 store 64-bit applications ?
- Program Files
- Shortcuts and Commands
Q3. Which shortcut will close all applications ?
- Alt+F4
Q4. What is the shortcut for saving a screenshot ?
- Win+PrtScn
Quiz 03 Shortcuts and Commands
Q1. Which shortcut will close all applications ?
- Alt+F4
Q2. What is the shortcut for saving a screenshot ?
- Win+PrtScn
Windows Operating System Security Basics
Q1. What Windows mode do users interact with directly ?
- User mode
Q2. What does Windows create every time an applications is started in user mode ?
- A process.
Q3. If you are setting up a new Windows laptop with a 128Gb hard drive and you want only a single file partition on the drive, which file systems can choose from ?
- NTFS
Q4. A file name in Windows must be unique where ?
- Within the same directory.
Q5. Windows 10 can be purchased for which versions ?
- 32 bit or 64 bit.
Q6. If you want to roll back or undo an action, what shortcut should you use ?
- Ctrl-Z
Q7. Which shortcut will switch between running applications ?
- Alt-Tab
Q8. Where does Windows 10 store 32-bit applications ?
- Program Files (x86)
Q9. What is the shortcut to open the Task Manager
- Ctrl+Shift+Esc
Quiz 04 Key Components
Q1. Which three (3) statements about Linux are True ?
- Linux guarantees end users freedom to run, study, share, and modify the software.
- Linux is an open source operating system.
- Linux is licensed under the General Public License (GNU).
File systems
Q1. Executable files such as ping, grep and cp are stored in which directory ?
- /bin
Linux Basic Commands
Q1. The Linux “kill” command does which of the following ?
- Stop an executing process.
Q2. What permissions can be set on a file in Linux ?
- read, write, execute
Q3. Which basic Linux command deletes an empty directory ?
- rmdir
Q4. Which is not a group that can own a file ?
- anybody
Linux Operating System security basics
Q1. Which three (3) groups can “own” a file in Linux ?
- user, group, everybody
Q2. What can be known about a file with permissions set to “-rwxr-x-r–” ?
- The file is not a directory; the user can read, write and execute the file; the group cannot modify the file, and others not in the group an read it only.
Q3. A person using Linux would normally interact directly with which ?
- The shell.
Q4. In the Linux file system, what is the highest level in the directory structure ?
- root
Q5. In Linux, a directory is a special type of ____.
- file
Q6. What does the nano command do ?
- nano is a basic text file editor.
Q7. Application configuration files are usually stored in which directory ?
- /etc
macOS Resources Knowledge Check
Q1. What application can you use to see all the active running applications and processes on macOS ?
- Activity Monitor
Q2. What feature in macOS prevents unauthorized applications from being installed ?
- Gatekeeper
Q3. Which three (3) utilities are found when booting macOS to the recovery partition? (Select 3)
- Safari
- Time Machine
- Disk Utility
Cybersecurity Roles, Processes & Operating System Security Week 04 Quiz Answers
Virtualization Basics and Cloud Computing
Q1. Where does the hypervisor sit in a virtual architecture ?
- Between the hardware and the operating system(s).
Q2. Which are the first two steps to perform in a cloud deployment ?
- Consolidate and Virtualize
Q3. Which are the three (3) most common forms of Cloud computing ?
- Hybrid Cloud
- Public Cloud
- Private Cloud
Q4. Which type of cloud is the best choice for a start-up company with no existing IT infrastructure and limited funds ?
- Public Cloud
Q5. Which three (3) are the primary benefits of cloud computing ?
- Efficiency
- Flexibility
- Strategic Value
Q6. Which is a primary security consideration in a cloud environment ?
- All of the above.
Quiz 02 Virtualization Basics
Q1. Virtualization allows you to create multiple simulated environments or dedicated resources from how many physical hardware systems ?
- 1
Q2. What relays requests from the VM to the actual hardware ?
- hypervisor
Q3. Which two steps of a cloud deployment are performed after you move your applications to the cloud ?
- Integrate and Optimize
Q4. Which type of cloud is the best choice for a company with a robust existing IT infrastructure and very serious data privacy concerns ?
- Private Cloud
Q5. Which is a primary security consideration in a cloud environment ?
- All of the above.
All Course Quiz Answers of IBM Cybersecurity Analyst Professional Certificate
Course 01: Introduction to Cybersecurity Tools & Cyber Attacks
Course 02: Cybersecurity Roles, Processes & Operating System Security
Course 03: Cybersecurity Compliance Framework & System Administration
Course 04: Network Security & Database Vulnerabilities
Course 05: Penetration Testing, Incident Response, and Forensics
Course 06: Cyber Threat Intelligence
Course 07: Cybersecurity Capstone: Breach Response Case Studies
Course 08: IBM Cybersecurity Analyst Assessment
Improve Article
Save Article
Improve Article
Save Article
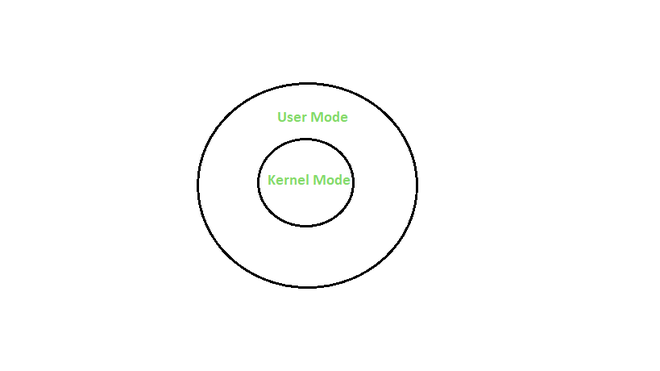
User Mode: When a Program is booted up on an Operating system let’s say windows, then it launches the program in user mode. And when a user-mode program requests to run, a process and virtual address space (address space for that process) is created for it by windows. User-mode programs are less privileged than user-mode applications and are not allowed to access the system resources directly. For instance, if an application under user-mode wants to access system resources, it will have to first go through the Operating system kernel by using syscalls.
Kernel Mode: The kernel is the core program on which all the other operating system components rely, it is used to access the hardware components and schedule which processes should run on a computer system and when, and it also manages the application software and hardware interaction. Hence it is the most privileged program, unlike other programs it can directly interact with the hardware. When programs running under user mode need hardware access for example webcam, then first it has to go through the kernel by using a syscall, and to carry out these requests the CPU switches from user mode to kernel mode at the time of execution. After finally completing the execution of the process the CPU again switches back to the user mode.
User vs Kernel Mode
Difference Between Kernel mode and User mode:
|
Criteria |
Kernel Mode |
User Mode |
|---|---|---|
| Kernel-mode vs User mode | In kernel mode, the program has direct and unrestricted access to system resources. | In user mode, the application program executes and starts. |
| Interruptions | In Kernel mode, the whole operating system might go down if an interrupt occurs | In user mode, a single process fails if an interrupt occurs. |
| Modes | Kernel mode is also known as the master mode, privileged mode, or system mode. | User mode is also known as the unprivileged mode, restricted mode, or slave mode. |
| Virtual address space | In kernel mode, all processes share a single virtual address space. | In user mode, all processes get separate virtual address space. |
| Level of privilege | In kernel mode, the applications have more privileges as compared to user mode. | While in user mode the applications have fewer privileges. |
| Restrictions | As kernel mode can access both the user programs as well as the kernel programs there are no restrictions. | While user mode needs to access kernel programs as it cannot directly access them. |
| Mode bit value | The mode bit of kernel-mode is 0. | While; the mode bit of user-mode is 1. |
| Memory References | It is capable of referencing both memory areas. | It can only make references to memory allocated for user mode. |
| System Crash | A system crash in kernel mode is severe and makes things more complicated. |
In user mode, a system crash can be recovered by simply resuming the session. |
| Access | Only essential functionality is permitted to operate in this mode. | User programs can access and execute in this mode for a given system. |
| Functionality | The kernel mode can refer to any memory block in the system and can also direct the CPU for the execution of an instruction, making it a very potent and significant mode. | The user mode is a standard and typical viewing mode, which implies that information cannot be executed on its own or reference any memory block; it needs an Application Protocol Interface (API) to achieve these things. |
Users interact indirectly through a collection of system programs that make up the operating system interface. The interface could be: A GUI, with icons and windows, etc. A command-line interface for running processes and scripts, browsing files in directories, etc.
What does an operating system do for the user?
An operating system is the most important software that runs on a computer. It manages the computer’s memory and processes, as well as all of its software and hardware. It also allows you to communicate with the computer without knowing how to speak the computer’s language.
Can a user interact with the system software?
User interface – The features of a computer system which allows the user to interact with it. A user interface, also sometimes called a human-computer interface, comprises both hardware and software components. It handles the interaction between the user and the system.
What does an operating system provides you can interact with the device?
Operating system software provides the user interface for interacting with the hardware components, whereas application software enables you to accomplish specific tasks.
What operating system am I using?
Select the Start button > Settings > System > About . Under Device specifications > System type, see if you’re running a 32-bit or 64-bit version of Windows. Under Windows specifications, check which edition and version of Windows your device is running.
What are three responsibilities of an operating system?
An operating system has three main functions: (1) manage the computer’s resources, such as the central processing unit, memory, disk drives, and printers, (2) establish a user interface, and (3) execute and provide services for applications software.
What are some examples of system software?
System software is software designed to provide a platform for other software. Examples of system software include operating systems like macOS, Linux , Android and Microsoft Windows, computational science software, game engines, industrial automation, and software as a service applications.
Which OS is freely available?
Here are five free Windows alternatives to consider.
- Ubuntu. Ubuntu is like the blue jeans of Linux distros. …
- Raspbian PIXEL. If you are planning to revive an old system with modest specs, there’s no better option than Raspbian’s PIXEL OS. …
- Linux Mint. …
- Zorin OS. …
- CloudReady.
15 апр. 2017 г.
What are the 3 types of system software?
System software is of three main types :
- Operating system.
- Language processor.
- Utility software.
What two things does an operating system do?
The operating system controls every task your computer carries out and manages system resources. At the simplest level, an operating system does two things: It manages the hardware and software resources of the system.
What devices have an operating system?
Just about every computing device has an operating system—desktops and laptops, enterprise-class server computers, your mobile phone. Even specialty devices like iPods, video game consoles, and television set top boxes run some form of OS.
What is the first operating system?
The first operating system was introduced in the early 1950’s, it was called GMOS and was created by General Motors for IBM’s machine the 701. Operating systems in the 1950’s were called single-stream batch processing systems because the data was submitted in groups.
What are the five examples of operating system?
Five of the most common operating systems are Microsoft Windows, Apple macOS, Linux, Android and Apple’s iOS.
Can Windows 7 still be used after 2020?
When Windows 7 reaches its End of Life on January 14 2020, Microsoft will no longer support the aging operating system, which means anyone using Windows 7 could be at risk as there will be no more free security patches.
What is the shortcut to check Windows version?
You can find out the version number of your Windows version as follows: Press the keyboard shortcut [Windows] key + [R]. This opens the “Run” dialog box. Enter winver and click [OK].
A processor executes programs either in User Mode or Kernel Mode. And as you use your PC, your processor regularly switches between the two depending on what it’s doing. But what is User Mode and Kernel mode, and what is the difference between the two?
Let’s see what these modes are and why does a CPU needs to switch between these modes.
What Is «User Mode» in Windows?
When you boot up a program on Windows, it launches in User Mode. Whenever a user-mode program wants to run, Windows creates a process for it. A process is just a program that a processor is executing or one that Windows has scheduled to be executed. And whenever Windows creates a process, it also creates a virtual address space for that process.
A virtual address space is the collection of logical (non-physical) addresses that Windows assigns to a process. Processes can use these addresses to store data on physical memory.
Additionally, virtual address spaces are isolated. So, one process’s virtual address space doesn’t interfere with another process’s address space. And because user-mode programs have separate address spaces, if one program crashes, it crashes alone and doesn’t take down other programs or the whole OS with it.
Another way to describe user-mode applications is to use the term “less privileged”. Windows restricts user-mode applications from accessing critical system resources directly thus making them less privileged. For instance, if an application wants access to hardware, it has to go through the OS kernel by using system calls.
Put simply, application programs like video games run in user mode. They are less privileged, so don’t have unrestricted access to system resources. Each user-mode application has its own address space. An application can’t change another application’s address space. Consequently, if one application crashes, it doesn’t affect other programs running on the computer.
What Is «Kernel Mode» in Windows?
Before we discuss Kernel mode, we have to first what a «kernel» is, and how it works with Windows.
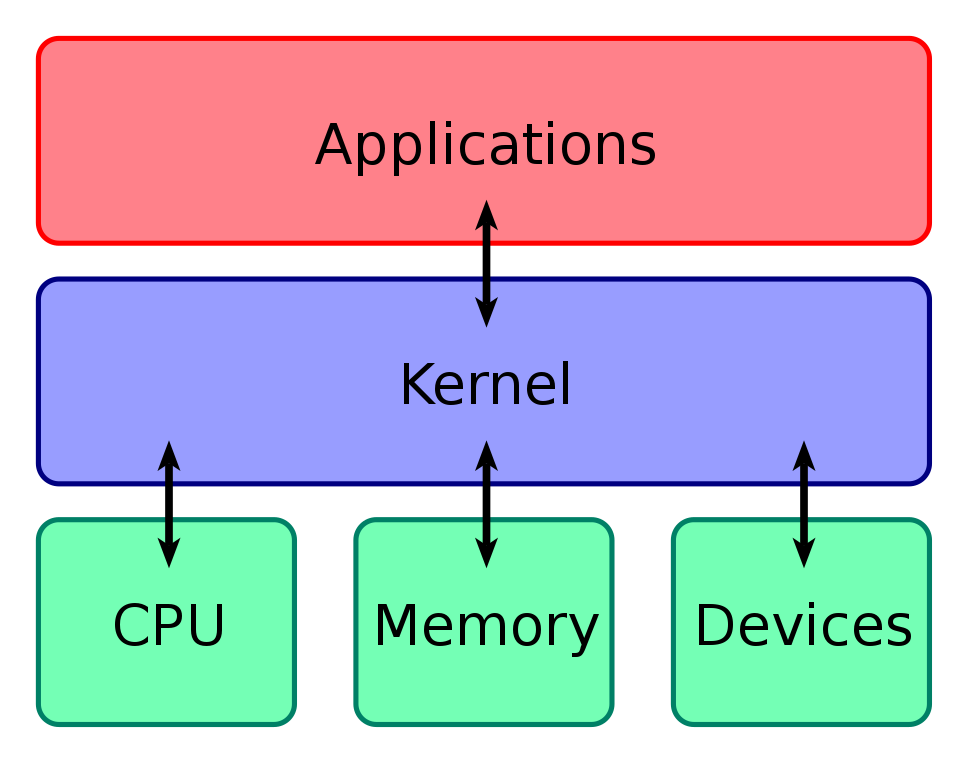
The kernel is the brain of an operating system. It is the core software component that all the other components inside the OS rely on. The kernel manages computer hardware, schedules which processes run on the computer and when, and handles interactions between the hardware and the application software.
In short, the kernel is the most privileged piece of code running on the system. That’s because it’s the code that directly interacts with the hardware. Every other program that wants to use the hardware resources has to request access through the kernel.
When an application program is running under User Mode and wants access to hardware like the webcam, it has to request the kernel by using a system call. To service these requests, the CPU, at the time of execution of the program, switches from User Mode to Kernel Mode.
After the execution of a process is complete, the CPU switches back to User Mode and starts executing the next scheduled process. This is called “Context Switching”.
What’s the Difference Between User Mode and Kernel Mode?
The key difference between User Mode and Kernel Mode is the level of privilege that each mode offers. In User Mode, applications have fewer privileges. They don’t have access direct access to hardware resources and also can’t write to the address spaces of other applications.
Code that runs in Kernel Mode has elevated privileges. It not only has direct access to computer hardware, but all the programs running in Kernel Mode, including the OS, also share one address space. So, if a program in Kernel Mode crashes, it can take the whole OS down with it. To ensure such crashes don’t occur, Windows only allows some processes to run in Kernel Mode.
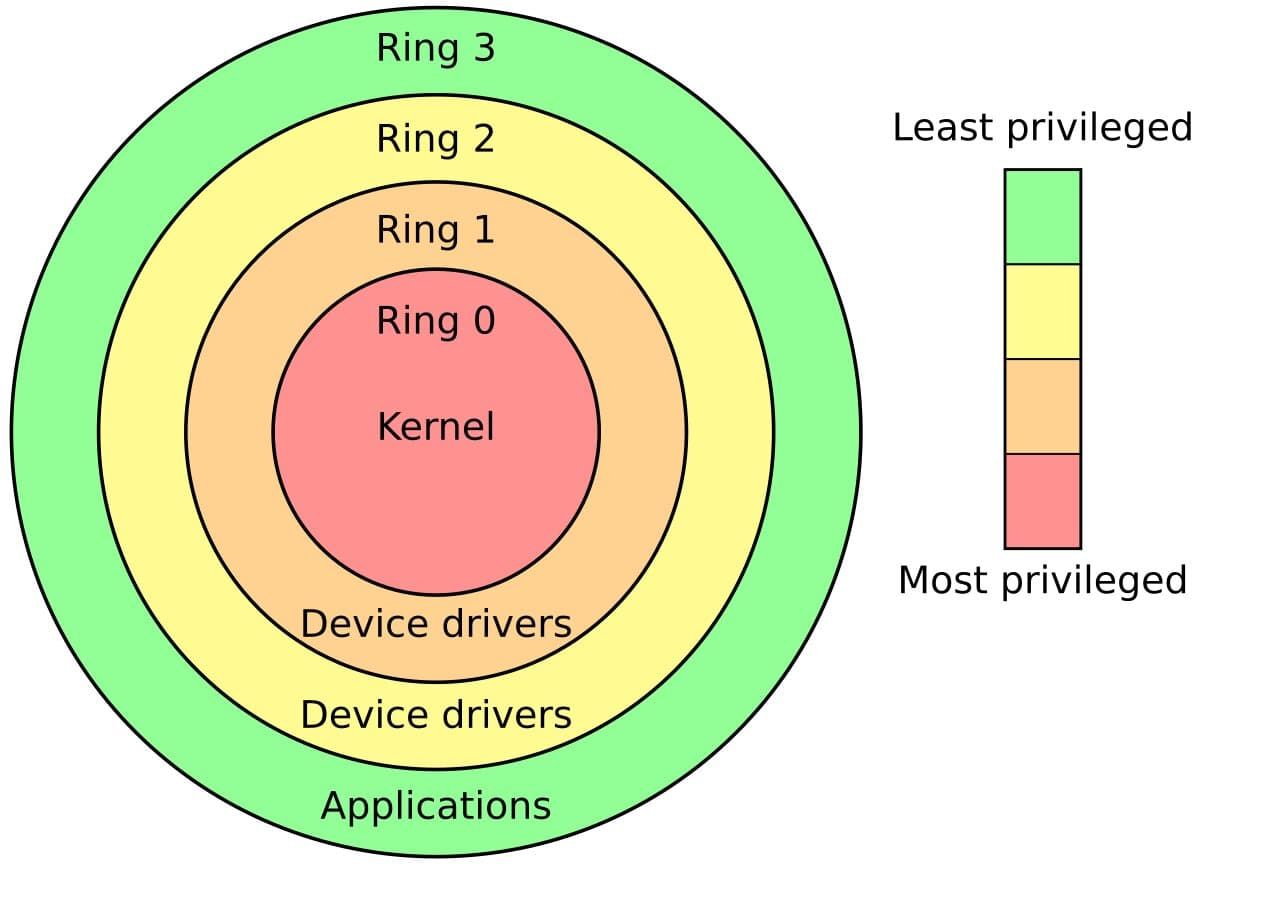
Windows Adopts a Layered Approach to Separate User Programs From System Resources
Windows uses a layered model to determine the level of privilege of processes. Applications that reside on the outermost layer are the ones with the lease privilege. At the core of these layers is the kernel. As a consequence, the kernel has unlimited access to OS resources.
The layered approach also protects vital OS functionality. When programs in the upper layer crash randomly, it doesn’t affect the OS. On the other hand, when the kernel crashes, the whole OS goes down.