The Hosts file in Windows 11/10, is used to map hostnames to IP addresses. This Hosts file is located deep down in the Windows folder. It is a plain text file, and the size of the original default Hosts file is around 824 bytes.
The HOSTS file is used by Microsoft TCP/IP for Windows. This file contains the mappings of IP addresses to host names. Each entry should be kept on an individual line. The IP address should be placed in the first column, followed by the corresponding host name. Moreover, the IP address and the host name should be separated by at least one space.
In this post, we will see its location and also how to manage, lock, or edit the Hosts file in Windows 11/10. We will discuss the following:
- Host file location
- Lock Hosts file to prevent hijacking
- Block website using the Hosts file
- How to edit the Hosts file
- Using free Hosts File Editor software.
Let us take a look at them.
Host file location
The Hosts file in Windows is located at the following location:
C:WindowsSystem32driversetc
Lock Hosts file to prevent hijacking
Imagine clicking on www.thewindowsclub.com and seeing a completely different website load in your browser. Malware can redirect Web addresses on your computer by altering your Hosts file. This is referred to as the Host File Hijack.
To prevent Host file hijacks, you may navigate to it, right-click on it, select Properties and make it a Read-only file. This will lock down your Hosts file and prevent anyone or any malware from writing to it.
Block website using the Hosts file
To block a website using the Hosts File, simply add the following entry:
127.0.0.1 blocksite.com
Although I do not do it, many users like to manually add entries to it in order to block the opening of one or more particular websites. Others, like to download and use List from well-known sources like mvps.org, to add entries that block malware sites from opening.
How to edit Hosts file in Windows 11/10
To edit the Hosts file in Windows 11/10:
- Open Explorer
- Navigate to System32driversetc location
- Locate Hosts file
- Right-click on it and select Notepad
- Make the changes and Save.
Now let us go into a detailed explanation.
To edit the Hosts file, navigate to the following folder location:
C:WindowsSystem32driversetc
Here you will see the Hosts file. Right-click on it and select Notepad. Make the changes and Save.
But sometimes, even when you are logged on with administrative credentials, you may receive the following error message:
Access to C:WindowsSystem32driversetc hosts was denied
Or
Cannot create the C:WindowsSystem32driversetchosts file. Make sure that the path and file name are correct.
In this case, type Notepad in Start search and right-click on the Notepad result. Select Run as administrator.
Open the Hosts file, make the necessary changes, and then click Save.
Using free Hosts File Editor software
If you are looking for an easier way, you can use a free Hosts file Editor software.
1] Using HostsMan
While you can always manually manage or edit Hosts file manually, I would like to suggest that you use a third-party freeware tool like HostsMan to do it.
HostsMan is a feature-rich tool that lets you add, remove, edit entries in the Hosts file. It also lets you easily add third-party Hosts lists that help in blocking malware sites and lets you easily enable or disable the Hosts file. It includes a built-in hosts file updater & a hosts editor. It lets you scan the hosts file for errors, duplicates, and possible hijacks – and also lets you create an Exclusion list. One more useful feature it offers is the Hosts file backup manager. Backup your Hosts file to a safe place and use it to restore it, should the need arise.
Hostman also lets you Flush DNS cache, open Hosts with a text editor, count the number of hosts, find duplicates, replace IP, scan hosts for malicious entries, rearrange hosts, manage DNS Client Service and more. In short, it’s the only Hosts Manager that you will even need. You can download it from its home page.
2] Using SysMate Hosts File Manager
SysMate Hosts File Manager and is another tool that lets you do so. With Host File Walker you can add as many records to the system hosts file. It even lets you backup and restore the Hosts File.
3] Using Host File Editor tool
Host File Editor is another good tool that you can use. It has the following features:
- Enable and disable hosts file from the system tray
- Cut, copy, paste, duplicate, enable, disable and move entries
- Filter and sort host entries
- Backup and restore various hosts file configurations when switching between environments
- Ping endpoints to check availability.
You can download it from here. It offers a portable version too.
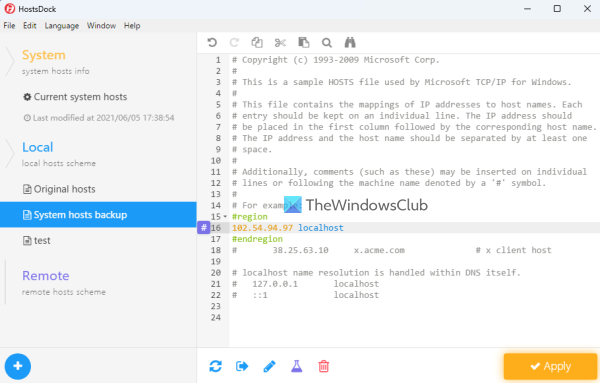
4] HostsDock
HostsDock is another useful software to edit the hosts file on Windows 11/10 computers. This is an open-source hosts file editor software that also lets you create new local hosts files and save them. You can also connect to a remote hosts file which is an important option. Some other interesting features are also available which are as follows:
- Syntax Highlighter that can automatically highlight IP addresses, comments, domains, etc., present in the hosts file. It detects all these items by itself and then highlights them
- Basic editing options like undo/redo, search and replace, cut, paste, etc.
- Create folding block
- Test IP addresses in the hosts file with the ping command
- A navigation pane to quickly switch to local and remote hosts files, check system hosts info, etc.
You can download this tool from eshengsky.github.io. Launch the tool after installation and it will show the system hosts file. After that, you can use the available options to add or create a new hosts file, use editing options, export the hosts file, and more.
5] Hosts File Editor PowerToy
The Hosts File Editor PowerToy also lets you edit the Hosts file.
How do I grant permission to edit the Hosts file in Windows 11/10?
If you want to grant permission to edit the hosts file in Windows 11/10 using Notepad, then you need to run Notepad as an administrator. You should also sign in to your Windows 11/10 system with an administrator account to edit hosts file so that you won’t get any errors while saving the hosts file.
Do not have permission to edit the Hosts file?
If you are unable to edit the hosts file on Windows 11/10 or you do not have permission to edit the hosts file, then you can use the following solutions:
- Use Notepad with administrative privileges and then open a hosts file to edit it
- Copy the hosts file from the original location to the desktop or some other location, edit that file, and then copy the edited file and paste it into the original location to overwrite the hosts file
- Use some third-party hosts file editing tools, etc.
TIP: See this post if Hosts File is not working in Windows. How to manually reset the Hosts file back to default in Windows may also interest you.
If your browser has been hijacked, you might find this post on Browser Hijacking and Free Browser Hijacker Removal Tools helpful.
Файл hosts — текстовый документ, который содержит в себе информацию о домене и IP-адресе, который ему соответствует. Файл hosts появился во времена зарождения Интернета (ARPANET) и служил неким маршрутизатором, пока на замену ему не пришла служба DNS. Но до сих пор он не утратил важности и по-прежнему используется как инструмент, который обладает приоритетом перед обращением к DNS-серверам.
Зачем нужен файл hosts
Предположим: вы зарегистрировали домен и привязали его к Hosting Linux. Но чтобы увидеть сайт, вам нужно дождаться делегирования домена на DNS-серверы. В файле hosts вы можете указать ваш домен и IP-адрес хостинга, а затем открыть браузер и зайти на ваш сайт, не дожидаясь делегирования домена. Также с его помощью вы можете заблокировать на локальном компьютере доступ к определённому сайту, указав соответствующую запись.
Где находится файл hosts
Путь к папке, где лежит файл hosts, зависит от операционной системы, которая установлена на вашем компьютере:
- Windows XP, 2003, Vista, 7, 8, 10 — c:windowssystem32driversetchosts
- Linux, Ubuntu, Unix, BSD — /etc/hosts
- macOS — /private/etc/hosts
Редактировать файл etc hosts нужно от имени администратора, иначе вы не сможете сохранить внесённые изменения.
Как внести изменения в файл hosts
Ниже мы рассмотрим, как редактировать и как сохранить изменения в файле hosts. Важно открыть файл с правами администратора, иначе система не даст вам его сохранить. Выберите вашу операционную систему и следуйте инструкции или посмотрите видеоинструкцию:
Редактирование файла hosts в Windows 7
-
1.
Запустите Блокнот или любой другой редактор от имени администратора. Откройте Пуск, найдите нужный редактор, нажмите по нему правой кнопкой мыши и выберите Запуск от имени администратора:
Как отредактировать файл hosts
-
2.
В меню «Файл» нажмите Открыть и перейдите в каталог, в котором расположен файл hosts. Измените тип файла на «Все файлы»:
-
3.
Выберите файл hosts и откройте его.
-
4.
Добавьте в конце файла необходимую запись в формате:
123.123.123.123 faq-reg.ru www.faq-reg.ruГде:
- 123.123.123.123 — IP-адрес вашего сервера или хостинга,
- faq-reg.ru — имя вашего домена.
-
5.
Сохраните изменения в файле.
Теперь вы можете открыть ваш сайт в браузере, не дожидаясь обновления DNS-серверов.
Редактирование файла hosts в Windows 8, 10
Чтобы изменить файл hosts в виндовс 10 (8), выполните следующие действия:
-
1.
Запустите Блокнот или любой другой редактор от имени администратора. Для этого найдите его в Пуске, нажмите по нему правой кнопкой мыши и выберите Запуск от имени администратора:
-
2.
В меню «Файл» нажмите Открыть и перейдите в каталог, где находится файл hosts . Измените тип файла на «Все файлы»:
-
3.
Выберите файл hosts и откройте его.
-
4.
Добавьте в конце файла необходимую запись в формате:
123.123.123.123 faq-reg.ru www.faq-reg.ruГде:
-
123.123.123.123 — IP-адрес вашего сервера или хостинга,
-
faq-reg.ru — имя вашего домена.
-
-
5.
Сохраните изменения в файле.
Теперь вы можете открыть ваш сайт в браузере, не дожидаясь обновления DNS-серверов.
Редактирование файла hosts в Linux, Unix
В Linux файл hosts находится в папке etc. Чтобы отредактировать его:
-
1.
Введите в терминал linux команду hosts:
-
2.
Добавьте в конце файла необходимую запись в формате:
123.123.123.123 faq-reg.ru www.faq-reg.ruГде:
-
123.123.123.123 — IP-адрес вашего сервера или хостинга,
-
faq-reg.ru — имя вашего домена.
-
-
3.
Сохраните изменения в файле.
Теперь вы можете открыть ваш сайт в браузере, не дожидаясь обновления DNS-серверов.
Файл hosts в Ubuntu редактируется так же, как и во всех Unix-системах.
Редактирование файла hosts в MacOS
Файл hosts в Mac OS расположен в каталоге: /private/etc/hosts. Чтобы изменить его:
-
1.
Запустите терминал с помощью горячих клавиш: Command (⌘) + T или через Spotlight.
-
2.
Введите команду:
Нажмите Enter:
-
3.
Добавьте в конце файла необходимую запись в формате:
123.123.123.123 faq-reg.ru www.faq-reg.ruГде:
-
123.123.123.123 — IP-адрес вашего сервера или хостинга,
-
faq-reg.ru — имя вашего домена.
-
-
4.
Сохраните изменения в файле.
Теперь вы можете открыть ваш сайт в браузере, не дожидаясь обновления DNS-серверов.
Видеосправка. Как изменить файл hosts
Также вы можете заблокировать определенный сайт через файл hosts, воспользовавшись инструкцией ниже:
Блокировка доступа к сайту через файл hosts
Доступ к сайту также можно ограничить для локального компьютера. Для этого укажите адрес страницы (домен) в файле hosts. Заблокировать IP нежелательного сайта не требуется. Блокировка осуществляется по локальному хосту с фиксированным IP (127.0.0.1):
-
1.
Откройте файл hosts от имени администратора на своём ПК.
-
2.
В указанной на скриншоте строке укажите IP-адрес 127.0.0.1 и через пробел адрес нежелательного сайта. Чтобы заблокировать несколько сайтов, повторите действие в следующей строке. В примере ниже в файле hosts отказано в доступе (заблокирован доступ) к сайтам «vk.com» и «youtube.com»:
-
3.
Сохраните изменения.
Готово! Доступ к сайтам будет ограничен на определенном ПК.
Оригинальный файл hosts и как его восстановить
Скачать содержимое файла hosts можно на разных ресурсах. Но мы не рекомендуем делать это, так как файл может быть заражен.
Файл hosts по умолчанию есть в каждой операционной системе, но он может быть скрыт для просмотра. Следуя инструкциям выше, вы сможете его открыть и отредактировать. Если вы удалили его, то просто создайте текстовый файл без расширения в нужной папке.
По умолчанию файл hosts выглядит следующим образом:
Для Windows
# Copyright (c) 1993-2006 Microsoft Corp.
#
# This is a sample HOSTS file used by Microsoft TCP/IP for Windows.
#
# This file contains the mappings of IP addresses to host names. Each
# entry should be kept on an individual line. The IP address should
# be placed in the first column followed by the corresponding host name.
# The IP address and the host name should be separated by at least one
# space.
#
# Additionally, comments (such as these) may be inserted on individual
# lines or following the machine name denoted by a '#' symbol.
#
# For example:
#
# 102.54.94.97 rhino.acme.com # source server
# 38.25.63.10 x.acme.com # x client host
# localhost name resolution is handle within DNS itself.
# 127.0.0.1 localhost
# ::1 localhostДля Linux
127.0.0.1 localhost
127.0.1.1 user
# The following lines are desirable for IPv6 capable hosts
::1 ip6-localhost ip6-loopback
fe00::0 ip6-localnet
ff00::0 ip6-mcastprefix
ff02::1 ip6-allnodes
ff02::2 ip6-allroutersгде user (во второй строке) — это имя вашего компьютера.
Для MacOS
##
# Host Database
#
# localhost is used to configure the loopback interface
# when the system is booting. Do not change this entry.
##
127.0.0.1 localhost
255.255.255.255 broadcasthost
::1 localhostУдалите текущее содержимое из файла hosts, вставьте текст по умолчанию и сохраните изменения.
Теперь вы знаете, как должен выглядеть файл hosts и как с ним работать.
While the internet is only about 30 years old, in many ways the hosts file is a relic of its (not so ancient) past.
In most cases you probably won’t need to update your hosts file on Windows. But knowing where it is and how it works can be helpful if:
- you’re having trouble with local development
- you suspect malware has tampered with the hosts file
- you want a quick and simple way to block some websites
- or if you want to set up some helpful shortcuts to internal IP addresses
In this article we’ll cover what a hosts file is, how to edit it on Windows, and we’ll go over some neat tricks you can do with it.
What’s a hosts file anyway?
Back in the early days of the internet, before it was widespread, computers used a hosts file to map long, hard to remember IP addresses with much shorter, easier to remember hostnames.
For example, here’s a line you’ll find in many hosts files on Windows, Linux, and macOs:
127.0.0.1 localhostThat way, instead of having to remember a long IP address, all you had to do was visit localhost.
Why hosts files fell out of favor
The hosts files system worked well for the early internet, but there were a few major problems.
As the internet grew, so did the length and complexity of the hosts files. Also, each hosts file only worked for the computer it was on, and keeping them in sync with the changes in hostnames and IP addresses became a huge pain.
For example, imagine that you have two computers, A and B. Their hosts files contain this mapping for google.com:
172.217.26.46 google.comBut when Google updates their IP addresses, only computer A updates its hosts file to match:
172.217.175.78 google.comSo everyone on computer B is stuck without Google until someone updates the hosts file. When that person does update the hosts file, they add another entry to handle Google with the www subdomain.
172.217.175.78 google.com
172.217.175.78 www.google.comNow everyone on computer B is taken to the correct website whether they visit google.com or www.google.com.
And everyone on computer A can only visit google.com, not www.google.com, at least until its own hosts file is updated to match.
As you can imagine, hosts files would get complicated, fast.
The solution
If you’re thinking that someone should have just made a central repository to map all IP addresses with all hostnames, that’s exactly what happened.
Early on, a central hosts file was manually maintained and shared by the Stanford Research Institute. This system lead to the invention of domains and top level domains like .com and .edu, Whois, and it became increasingly automated.
In the end, the humble hosts file and innovators like Elizabeth J. Feinler lead to the invention of the Domain Name System still in use today.
To edit a hosts file on Windows 10, you’ll need to open it as an administrator.
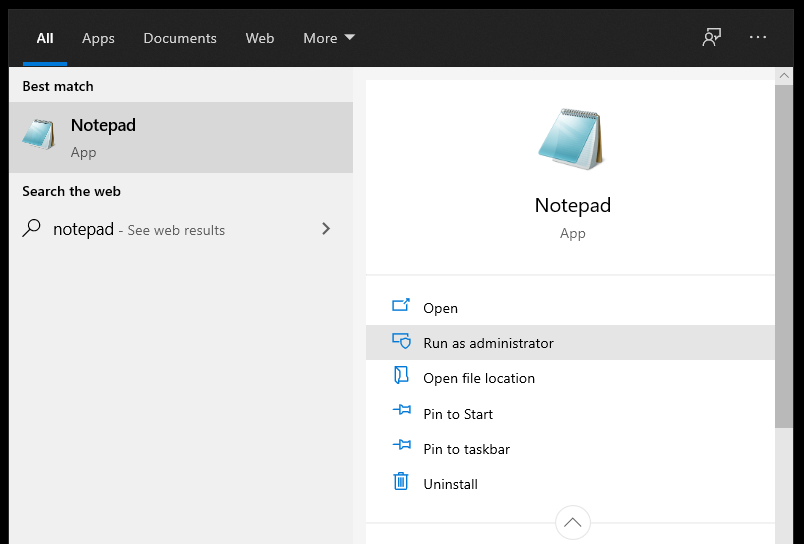
First, open Notepad as an administrator by pressing the Windows key, typing in «notepad», and clicking «Run as administrator»:
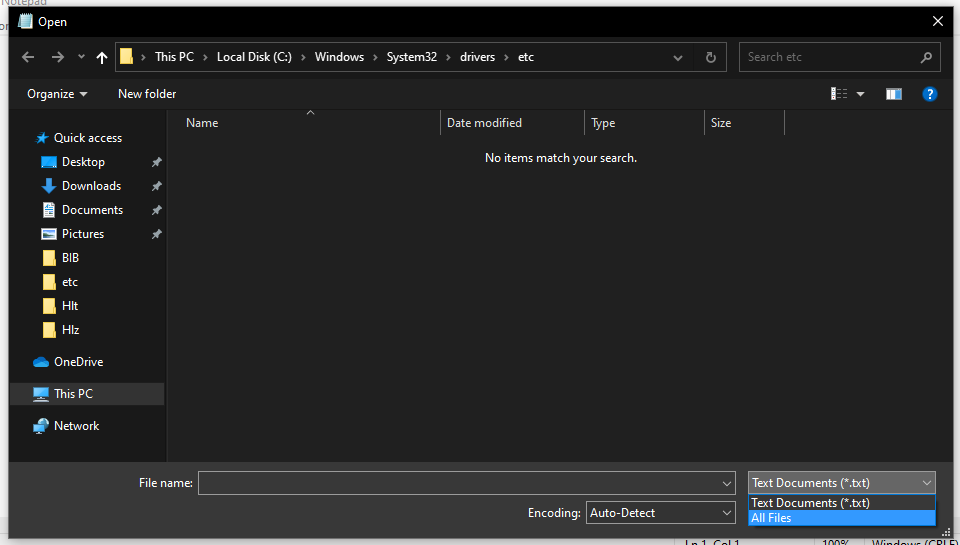
To open the hosts file in Notepad, click «File», «Open», and navigate to C:WindowsSystem32driversetc.
You won’t be able to see any files in this directory because they aren’t text documents. To change the file type, click on the dropdown in the bottom right of the Open menu and click on «All Files»:
You’ll see a file named hosts. Double click on that file to open it.
Then, you’ll see a hosts file similar to this:
# Copyright (c) 1993-2009 Microsoft Corp.
#
# This is a sample HOSTS file used by Microsoft TCP/IP for Windows.
#
# This file contains the mappings of IP addresses to host names. Each
# entry should be kept on an individual line. The IP address should
# be placed in the first column followed by the corresponding host name.
# The IP address and the host name should be separated by at least one
# space.
#
# Additionally, comments (such as these) may be inserted on individual
# lines or following the machine name denoted by a '#' symbol.
#
# For example:
#
# 102.54.94.97 rhino.acme.com # source server
# 38.25.63.10 x.acme.com # x client host
# localhost name resolution is handled within DNS itself.
# 127.0.0.1 localhost
# ::1 localhostNote that everything is commented out with # characters, meaning that nothing is actually being read from the hosts file. Modern versions of Windows include a sort of DNS system already, so if you visit localhost it’ll automatically redirect you to 127.0.0.1.
With that out of the way, here are some things you can do with the hosts file.
How to update the hosts file on Windows 10 if you have trouble with localhost
If you’re doing some local development and are having problems with localhost, you can just remove the comments from your hosts file:
...
# localhost name resolution is handled within DNS itself.
127.0.0.1 localhost
::1 localhostAfter saving the hosts file, close Notepad.
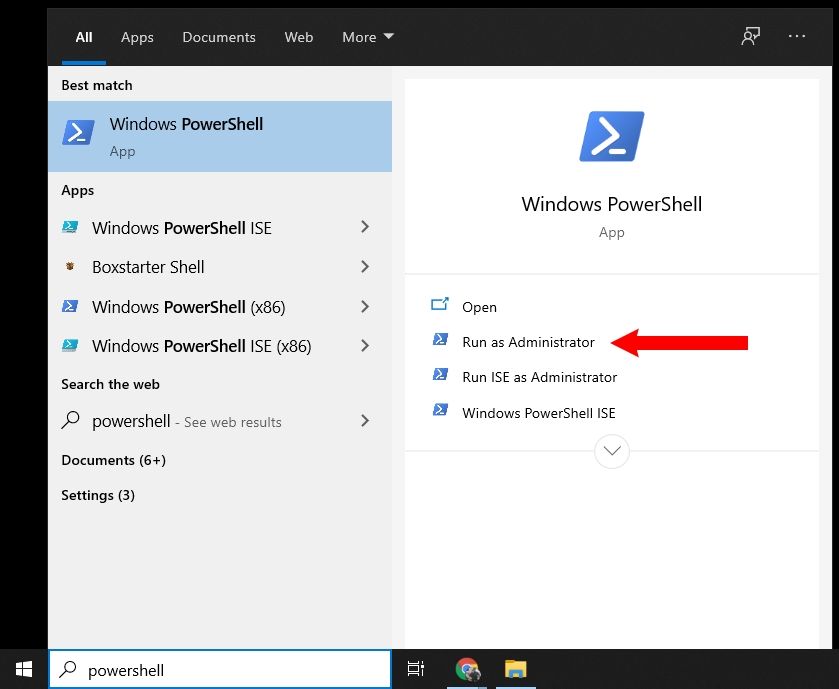
Then, open PowerShell by pressing the Windows key, searching for «powershell», and clicking «Run as Administrator»:
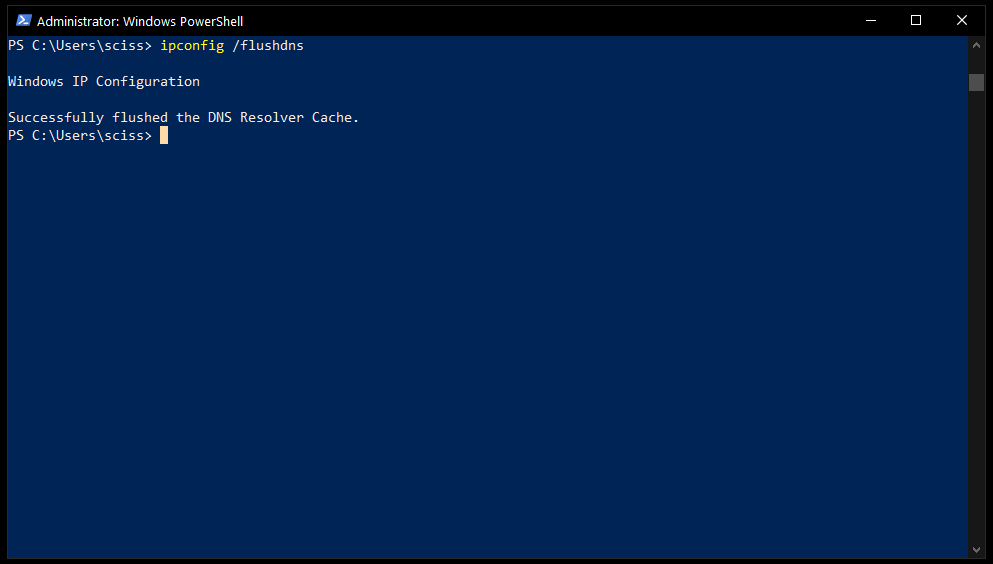
In the PowerShell window, enter ipconfig /flushdns to flush the inbuilt Windows DNS:
After that, you should be able to visit localhost in your browser and see whatever you’re hacking on. If you’re still having issues, try closing your browser completely, then open a new browser window and try again.
How to update your hosts file on Windows 10 if you think it’s been tampered with
Even though hosts files have fallen out of favor with newer systems like DNS, they still work for legacy reasons. And hackers have definitely taken advantage of this in the past.
What they would do is point a common website like google.com towards an unsafe IP address. This IP address could serve a site that looks just like Google’s, but is actually trying to steal your sensitive information.
While this was a problem in the past, most security software like the Windows Security Suite can recognize and fix problems with the hosts file automatically.
That said, if you open up your hosts file and see a lot of strange entries, then you may want to revert to the default Windows hosts file.
Just copy and paste the default hosts file from earlier in the article into your hosts file and save. Then, open PowerShell and use the ipconfig /flushdns command to flush the Windows DNS.
Note that some third-party security software uses the hosts file to block dangerous websites. If that’s the case, no worries – your security software should add all those entries back to your hosts file. We’ll go over how this works in the next section.
How to use the hosts file on Windows 10 to block websites
Don’t want friends or family to visit certain websites on your computer? Or are you like me and get distracted by all the cat photos on the internet?
If so, then you can use the hosts file to block websites entirely.
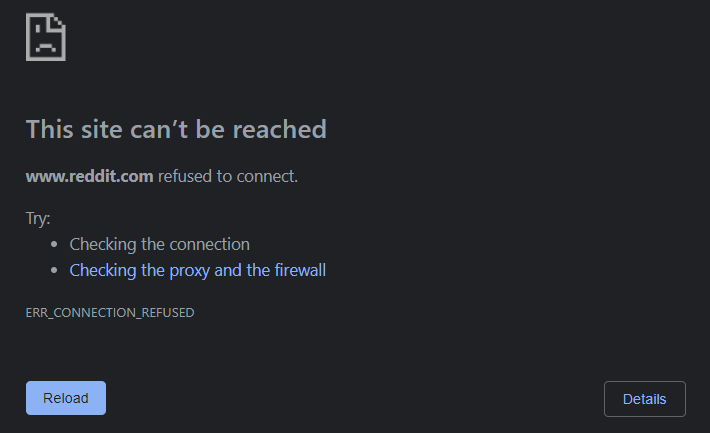
For example, if you want to block Reddit, just add this to the bottom of your hosts file:
127.0.0.1 reddit.com
127.0.0.1 www.reddit.comThen, open PowerShell and run ipconfig /flushdns to flush the Windows 10 DNS. Also, close the browser windows that are open and reopen them.
After that, every time you try to visit Reddit, or click on a Reddit URL like https://www.reddit.com/r/FreeCodeCamp/, your browser will be redirected to 127.0.0.1, or localhost.
Since there’s no website there, your browser will show an error message:
The one downside is that this only works on one device – you could just reach for your phone and browse Reddit on that instead. Still, it’s a neat way to create some friction on your work computer.
This leads nicely into the last trick, which is to use the hosts file to make your life a little bit easier.
How to use the hosts file on Windows 10 to set up helpful shortcuts
If you spend a lot of time adjusting your router’s settings, or you have a cool project running on a Raspberry Pi, you’ll know that typing in a long IP address is a drag.
Instead, you can use the hosts file to make connecting to other devices on your local network much faster.
For example, if your router is at 192.168. 0.1, you can add the following to your hosts file:
192.168.0.1 my.routerThen, flush your Windows 10 DNS with ipconfig /flushdns and restart your browser.
And then any time you visit my.router, you should be redirected to 192.168.0.1.
Just note that you may need to visit http://my.router, at least the first time. Otherwise your browser might not recognize .router as a valid top-level domain (TLD), and will try to search for the term my.router instead.
To get around this, you could use a hostname like this instead:
192.168.0.1 router.myThis should work right away because .my is the TLD for people and companies in Malaysia.
Fortunately there are a whole lot of valid TLDs nowadays. Here’s a list of some of the most common TLDs out there: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_Internet_top-level_domains
Again, the one downside to this method is that it only works on once device. You’d have to update the hosts files on your other devices to enable the same shortcuts.
And that should be just about everything you need to know about the hosts file on Windows 10. And a lot of this knowledge should carry over to Linux and macOS.
So get out there and customize your hosts file like the pioneers of the internet once did.
Did you find this helpful? Are there any other hosts file tricks you know? Let me know over on Twitter.
Stay safe and happy hosts file editing!
Learn to code for free. freeCodeCamp’s open source curriculum has helped more than 40,000 people get jobs as developers. Get started
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The computer file hosts is an operating system file that maps hostnames to IP addresses. It is a plain text file. Originally a file named HOSTS.TXT was manually maintained and made available via file sharing by Stanford Research Institute for the ARPANET membership, containing the hostnames and address of hosts as contributed for inclusion by member organizations. The Domain Name System, first described in 1983 and implemented in 1984,[1] automated the publication process and provided instantaneous and dynamic hostname resolution in the rapidly growing network. In modern operating systems, the hosts file remains an alternative name resolution mechanism, configurable often as part of facilities such as the Name Service Switch as either the primary method or as a fallback method.
Purpose[edit]
The hosts file is one of several system facilities that assists in addressing network nodes in a computer network. It is a common part of an operating system’s Internet Protocol (IP) implementation, and serves the function of translating human-friendly hostnames into numeric protocol addresses, called IP addresses, that identify and locate a host in an IP network.
In some operating systems, the contents of the hosts file is used preferentially to other name resolution methods, such as the Domain Name System (DNS), but many systems implement name service switches, e.g., nsswitch.conf for Linux and Unix, to provide customization. Unlike remote DNS resolvers, the hosts file is under the direct control of the local computer’s administrator.[2]
File content[edit]
The hosts file contains lines of text consisting of an IP address in the first text field followed by one or more host names. The host names map to the IPs, not vice versa. Each field is separated by white space – tabs are often preferred for historical reasons, but spaces are also used. Comment lines may be included; they are indicated by an octothorpe (#) in the first position of such lines. Entirely blank lines in the file are ignored.[3] For example, a typical hosts file may contain the following:
127.0.0.1 localhost loopback ::1 localhost
This example only contains entries for the loopback addresses of the system and their host names, a typical default content of the hosts file. The example illustrates that an IP address may have multiple host names (localhost and loopback), and that a host name may be mapped to both IPv4 and IPv6 IP addresses, as shown on the first and second lines respectively.
Location in the file system[edit]
The location of the hosts file in the file system hierarchy varies by operating system. It is usually named hosts, without an extension.
| Operating System | Version(s) | Location |
|---|---|---|
| Unix, Unix-like, POSIX | /etc/hosts[4] | |
| Microsoft Windows | 3.1 | %WinDir%HOSTS |
| 95, 98, ME | %WinDir%hosts[5] | |
| NT, 2000, XP,[6] 2003, Vista, 2008, 7, 2012, 8, 10, 11 |
%SystemRoot%System32driversetchosts[7] | |
| Windows Mobile, Windows Phone | Registry key under HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINECommTcpipHosts | |
| Apple Macintosh | 9 and earlier | Preferences or System folder |
| Mac OS X 10.0–10.1.5[8] | (Added through NetInfo or niload) | |
| Mac OS X 10.2 and newer | /etc/hosts (a symbolic link to /private/etc/hosts)[8] | |
| Novell NetWare | SYS:etchosts | |
| OS/2, eComStation, ArcaOS | «bootdrive»:mptnetc | |
| Symbian | Symbian OS 6.1–9.0 | C:systemdatahosts |
| Symbian OS 9.1+ | C:private10000882hosts | |
| MorphOS | NetStack | ENVARC:sys/net/hosts |
| AmigaOS | < 4 | AmiTCP:db/hosts |
| 4 | DEVS:Internet/hosts | |
| AROS | ENVARC:AROSTCP/db/hosts | |
| Android | /etc/hosts (a symbolic link to /system/etc/hosts) | |
| iOS | iOS 2.0 and newer | /etc/hosts (a symbolic link to /private/etc/hosts) |
| TOPS-20 | <SYSTEM>HOSTS.TXT | |
| Plan 9 | /lib/ndb/hosts | |
| BeOS | /boot/beos/etc/hosts[9] | |
| Haiku | /system/settings/network/hosts[10] | |
| OpenVMS | UCX | UCX$HOST |
| TCPware | TCPIP$HOST | |
| RISC OS | 3.7, 5 | !Boot.Resources.!Internet.files.Hosts |
| later boot sequence | !Boot.Choices.Hardware.Disabled.Internet.Files.Hosts[11] |
History[edit]
The ARPANET, the predecessor of the Internet, had no distributed host name database. Each network node maintained its own map of the network nodes as needed and assigned them names that were memorable to the users of the system. There was no method for ensuring that all references to a given node in a network were using the same name, nor was there a way to read the hosts file of another computer to automatically obtain a copy.
The small size of the ARPANET kept the administrative overhead small to maintain an accurate hosts file. Network nodes typically had one address and could have many names. As local area TCP/IP computer networks gained popularity, however, the maintenance of hosts files became a larger burden on system administrators as networks and network nodes were being added to the system with increasing frequency.
Standardization efforts, such as the format specification of the file HOSTS.TXT in RFC 952, and distribution protocols, e.g., the hostname server described in RFC 953, helped with these problems, but the centralized and monolithic nature of hosts files eventually necessitated the creation of the distributed Domain Name System (DNS).
On some old systems a file named networks is present that is similar to a hosts file, containing names of networks.[12]
Extended applications[edit]
In its function of resolving host names, the hosts file may be used to define any hostname or domain name for use in the local system.
- Redirecting local domains
- Some web service and intranet developers and administrators define locally defined domains in a LAN for various purposes, such as accessing the company’s internal resources or to test local websites in development.[13]
- Internet resource blocking
- Entries in the hosts file may be used to block online advertising, or the domains of known malicious resources and servers that contain spyware, adware, and other malware. This may be achieved by adding entries for those sites to redirect requests to another address that does not exist or to a harmless destination such as the local machine.[14] Commercial software applications may be used to populate the hosts file with entries of known undesirable Internet resources automatically. In addition, user-created hosts files which block nuisance servers are publicly available.[15][16]
- Fravia described these files variously as «scrolls», «precious», and «powerful» in his anti-advertisement pages, where this usage of hosts was first published.[16]
- Software piracy
- Some pirated versions of software rely on a modified hosts file to prevent software from contacting the activation servers of the publisher, although activation servers sometimes appear in general purpose hosts files.[17]
Security issues[edit]
The hosts file may present an attack vector for malicious software. The file may be modified, for example, by adware, computer viruses, or trojan horse software to redirect traffic from the intended destination to sites hosting malicious or unwanted content.[18] The widespread computer worm Mydoom.B blocked users from visiting sites about computer security and antivirus software and also affected access from the compromised computer to the Microsoft Windows Update website.
In some cases, malware has modified the library responsible for loading the hosts file in order to redirect it to a file it is able to control freely.[19]
See also[edit]
- DNSBL, a DNS-based blackhole list
- Content-control software
- Ad filtering
References[edit]
- ^ Internet Systems Consortium. «The Most Widely Used Name Server Software: BIND». History of BIND. Retrieved 2017-07-01.
- ^ Cisco Networking Academy Program: First-Year Companion Guide (2nd ed.). Cisco Systems. 2002. p. 676. ISBN 1-58713-025-4.
- ^ https://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man5/hosts.5.html
- ^ «Linux Network Administrators Guide: Writing hosts and networks files». Retrieved May 16, 2010.
- ^ «Hosts File». Retrieved August 10, 2011.
- ^ «Microsoft KB Q314053: TCP/IP and NBT configuration parameters for Windows XP». Retrieved August 28, 2010.
- ^ «Microsoft KB 972034 Revision 2.0: default hosts files». Retrieved August 28, 2010.
- ^ a b «Mac OS X: How to Add Hosts to Local Hosts File». Retrieved August 28, 2010.
- ^ «The Haiku/BeOS Tip Server». Archived from the original on January 28, 2013. Retrieved November 30, 2012.
- ^ «Haiku UserGuide:Network». Retrieved January 17, 2019.
- ^ RISC OS 6.14
- ^ «Writing hosts and networks Files». tldp.org. Retrieved 2021-03-02.
- ^ «Building / Testing via the Hosts File». Ohio State University Web Hosting. OCIO. 9 October 2015. Retrieved 5 August 2018.
- ^ Gordon; -Tx. «Gordon and -Tx explanations about the use of Gordon’s hosts file». Web Searchlores. +Fravia. Retrieved 5 August 2018.
- ^ Hofstetter, Constantin. «/etc/hosts to block shock sites etc». GitHub. Retrieved 5 August 2018.
- ^ a b Vianello, Francesco «Fravia». «Antiadvertisement Lab». Web Searchlores. +Fravia. Retrieved 5 August 2018.
- ^ «yhosts». GitHub. Retrieved 21 June 2021.
- ^ «Remove Trojan.Qhosts». Symantec. Retrieved May 16, 2010.
- ^ Arntz, Pieter. «Hosts file hijacks». Malwarebytes Labs. Retrieved 5 August 2018.
External links[edit]
- Windows
- Beginners Guide on Editing Hosts File
- Microsoft TCP/IP Host Name Resolution Order
- List of Microsoft domains that Windows won’t redirect with a host file
- Mac
- How to block unwanted domains with a HOSTS file on Mac OS X 10.2 or later
- Linux
- How to block unwanted advertisements with /etc/hosts file on Linux
Содержание
- Windows Hosts File
- Windows Hosts File Location and Basic Usage
- Windows Hosts File Location
- How to Edit Your Hosts File in Windows 10
- What is a Hosts File?
- Why is a Hosts File Useful?
- Where is the Hosts File Located?
- What Does a Hosts File Contain?
- How Do I Edit my Hosts File?
- Conclusion
- How to Edit the HOSTS File in Windows
- Customize your network settings in Windows 10, 8, or 7
- How to Edit the Windows HOSTS File
- What If I Can’t Save the HOSTS File?
- What Is the HOSTS File Used For?
- 7 Ways to Use Hosts File on Your Computer
- What is Hosts File?
- Where to Find Hosts File in Windows 10?
- Where to Find Hosts File in Mac?
- How to Modify Hosts File in Windows 10?
- How to Use Modify File in Mac?
- 7 Ways to Use Hosts File on Your Computer
- 1. Editing Hosts File to Block a website
- 2. Re-directing a Website Using Hosts File
- 3. Create Shortcuts for Websites or Intranet Services
- 4. Testing Network / Web Servers
- 5. Content Filtering and Ads Blocking
- 6. Adding Websites to Hosts File to Improve Browsing Speed
- 7. Preventing Malicious Attacks
- Conclusion
- How to Lock, Manage, Edit Hosts File in Windows 11/10
- Hosts File in Windows 11/10
- Host file location
- Lock Hosts file to prevent hijacking
- Block website using the Hosts file
- How to edit Hosts file in Windows 11/10
- Using free Hosts File Editor software
- 1] Using HostsMan
- 2] Using SysMate Hosts File Manager
- 3] Using Host File Editor tool
Windows Hosts File
Windows Hosts File Location and Basic Usage
Has this page answered your question?
Thank you for your feedback!
Please use the below form to report a problem. Email is not required, but it is useful if we need to ask you any questions about the problem (it will never be used for marketing). Please be as descriptive as possible.
When you visit a website, for example Save Location, the domain (in this case, savelocation.net) is just an alias for an IP address. If we think about the IP address as the host, and the domain as the name, it’s quite clear to see where the name «hostname» comes from: it’s the name for a host.
It would also be possible to use the hosts file to declare these. A hosts file defines any and all hostnames that aren’t in the domain name system, in fact, one can even override the DNS by changing the hosts file (as it has priority). If you want to learn how to open up the hosts file, read on.
Windows Hosts File Location
The hosts file location on Windows 10, Windows 8, and Windows 7 is the same. You can find it at the following path:
On Windows 8 and 10, you’ll need to run the application you wish to open the hosts file with as administrator in order to access it. We’ll use Notepad as an example. First, open Notepad as an administrator by right clicking it and selecting Run as Administrator :
Then, go to File > Open (or hit CTRL + O ):
Finally, paste the hosts file location from above into the File name: field and hit Open :
And that’s you, inside the hosts file and ready to edit it! If you want to learn how to use the hosts file, read on.
Источник
How to Edit Your Hosts File in Windows 10
What is a Hosts File?
The hosts file is a local plain text file that maps servers or hostnames to IP addresses. This file has been in use since the time of ARPANET. It was the original method to resolve hostnames to a specific IP address. The hosts file is usually the first process in the domain name resolution procedure. Here is an example of a hosts file entry.
We use the above code as an example since it almost always included in every hosts file. Another example would be similar to the following entry.
We would add the above entry to our hosts file to associate the hostname (or domain name)В liquidweb.comВ with the IP addressВ 67.225.187.61. To provide a working example, let’s move on to the next section.
Why is a Hosts File Useful?
Let’s say we have just completed a migration to a new server. In order to see how our domains will look and operate on our new server before we move our DNS settings, we cannot just type in one of our current domain names as it will resolve to the old server we are moving away from (since we never move our DNS A records from the old server until we are sure the new site is working as expected).
So, to see how our domain will look on the new server, (without having to change our DNS records) we can simply modify our local hosts file to point the domain to the new servers IP. If our domain is liquidweb.com and the old IP is 67.225.187.61 and our new IP will be 72.30.35.10, we can temporarily comment out the current liquidweb.com entry (using a ‘#‘ symbol) and add an alternate entry which points to the new servers IP.
If we added the above entry to our hosts file, every time we open liquidweb.com in our browser, we will now be redirected to the 72.30.35.10 IP.
Where is the Hosts File Located?
The location of the hosts file will differ by operating system. The typical locations are noted below.
What Does a Hosts File Contain?
A hosts file contains entries similar to the following information. Your entries may differ significantly.
How Do I Edit my Hosts File?
Our etchosts file is only editable as a Windows administrator. В Here is a short video on how to edit a hosts file.
Here are the directions on how to modify your hosts file.
Step 1.
Click the Windows button and type Notepad in the search bar.
Step 2.
Right click on Notepad and then Run as Administrator.
Step 3.
You’ll be asked, “Do you want to allow this app to make changes to your device?”. Choose Yes.
Step 4.
In Notepad, choose File then Open.
Step 5.
Navigate to C:WindowsSystem32driversetchosts or click the address bar at the top and paste in the path and choose Enter.  If you don’t readily see the host file in the /etc directory then select All files from the File name: drop-down list, then click on the hosts file.
Step 6.
Add the appropriate IP and hostname at the end of your hosts’ file, select Save, and then close the file.
Step 7.
Finally, you will want to flush your DNS cache for your computer to recognize changes to the file. Click the Windows button and search command prompt.
Step 8.
Type the following command in the terminal and press Enter
Conclusion
Modifying a hosts file has many benefits which can significantly impact how you view your new domain or website. Using this method to view a site allows us to see how any new changes affect the layout and functionality of a domain.
Should you have any issues when modifying this file, our Support Teams are filled with experienced Linux technicians and talented system administrators who have an intimate knowledge of how to facilitate this modification. We are always available to answer any inquiries with issues related to this article, 24 hours a day, 7 days a week 365 days a year.
If you are a Fully Managed VPS server, Cloud Dedicated, VMWare Private Cloud, Private Parent server, Managed Cloud Servers, or a Dedicated server owner and you are uncomfortable with performing any of the steps outlined above, we can be reached via phone at 800.580.4985, or via a chat or support ticket to assist you with this process.
Источник
How to Edit the HOSTS File in Windows
Customize your network settings in Windows 10, 8, or 7
The Windows HOSTS file functions like a local copy of a DNS server, so knowing how to edit it might come in handy if you want to make custom domain redirects, block websites, or remove malicious entries set by malware. That said, you might run into permission errors and other problems when you make changes to this file in some versions of Windows.
The instructions in this article apply to Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8, and Windows 10.
How to Edit the Windows HOSTS File
In Windows 7, 8, and 10, you can’t save edits to the HOSTS file unless you open it directly from Notepad or another text editor. To do so:
Open Notepad or another text editor like Notepad++.
In the text editor, select File > Open and open the HOST file location at C:WindowsSystem32driversetc.
Select Text Documents (*txt) in the bottom-right of the Open window and change it to All Files.
When files appear in the folder, double click hosts to open it.
Edit the HOSTS file and save your changes.
What If I Can’t Save the HOSTS File?
In some versions of Windows, you don’t have permission to save directly to the etc folder. If this is the case, you might see an error like this one when you try to save:
Instead, you must save the file elsewhere like the Documents or Desktop folder. After saving, go to that folder, copy the HOSTS file, and paste it directly into the location where the HOSTS file should be (C:WindowsSystem32driversetc). You’ll be prompted with permission validation and will have to confirm overwriting the file.
If you still have trouble saving the modified HOSTS file, check the file’s attributes to see if it’s been marked read-only. Right-click the file and select Properties to see the attributes.
Another option is to open your text editor program as an administrator so that the permissions are already applied to the editor. Then, saving the HOSTS file over the original can be performed without having to verify your admin credentials.
If you still can’t save to the HOSTS file location, you probably don’t have the correct permissions to be editing files in that folder. You should be logged in under an account that has administrative rights over the HOSTS file, which you can check by right-clicking the file and going to the Security tab.
What Is the HOSTS File Used For?
The HOSTS file is the virtual equivalent of a phone company’s directory assistance. Where directory assistance matches a person’s name to a phone number, the HOSTS file maps domain names to IP addresses.
Entries in the HOSTS file override DNS entries maintained by the ISP. While this hierarchy might come in handy for regular use, like to block ads or certain malicious IP addresses, its functions also make this file a common target of malware.
By modifying it, malware can block access to antivirus updates or force you to a malicious website. Thus, it’s a good idea to check the HOSTS file periodically or at least know how to remove false entries.
A much easier way to block certain domains from your computer is to use a custom DNS service that supports content filtering or blocklists.
Источник
7 Ways to Use Hosts File on Your Computer
The web is a giant network. There are many things happen in the backend when you type a domain name (website address) on the browser’s address bar and hit enter. One of the first things is that your browser will check the mapping on your computer’s hosts file. In this article, let us explore more on hosts file, where you can find, how to edit and how to use it properly for different reasons.
What is Hosts File?
A hosts file is a computer system file that maps human-friendly hostnames (domain names) to their IP address. It uses IP address in IPv4 or IPv6 format to resolve the hostname and the browser can quickly connect to the hosting server.
Where to Find Hosts File in Windows 10?
By default, you can find Windows 10 hosts file using the path C:WindowsSystem32driversetchosts.
To open the file, right-click “hosts” and open with a text editor like Notepad or Notepad++.
Where to Find Hosts File in Mac?
Follow the below instructions on macOS to find hosts file.
How to Modify Hosts File in Windows 10?
To modify the hosts file;
How to Use Modify File in Mac?
In order to edit hosts file on Mac, you need to open Terminal app.
7 Ways to Use Hosts File on Your Computer
While the DNS remains the standard domain name resolution service over the internet, the hosts file overrides the DNS servers. Therefore, you can use the hosts file for various reasons including redirecting or blocking websites, creating local domains and sites shortcuts among other purposes.
1. Editing Hosts File to Block a website
127.0.0.1 twitter.com www.twitter.com
0.0.0.0 twitter.com www.twitter.com
Note: ensure there is a space between the IP address and the hostname and no ‘#’ before the IP as this would deactivate the entry.
2. Re-directing a Website Using Hosts File
You can also redirect the website to a particular domain. For example, you may edit the hosts file such that whenever a user tries to access Twitter, they are redirected to the company’s site or any other website.
3. Create Shortcuts for Websites or Intranet Services
You can also modify Windows hosts file to create shortcuts for public or internal sites or web services.
4. Testing Network / Web Servers
When you are running a web development server on your local network, it will be safe to test its functionality before publishing it live.
192.168.0.11 mysite1.com
192.168.0.11 mysite2.com
5. Content Filtering and Ads Blocking
6. Adding Websites to Hosts File to Improve Browsing Speed
Add a site to the hosts file can increase the browsing speed. This is simply because the computer doesn’t need to query DNS server for IP and waste time waiting for a response.
7. Preventing Malicious Attacks
The hosts file can be a target for malicious attack. Attackers can use viruses, PUPs and malware to modify the hosts file, redirecting you to malicious sites or hijack your sites.
Conclusion
A hosts file is one of the powerful and useful tools for Windows users, allowing you to improve your online experience through the above uses. When editing the hosts file ensure that you have administrative rights.
Источник
How to Lock, Manage, Edit Hosts File in Windows 11/10
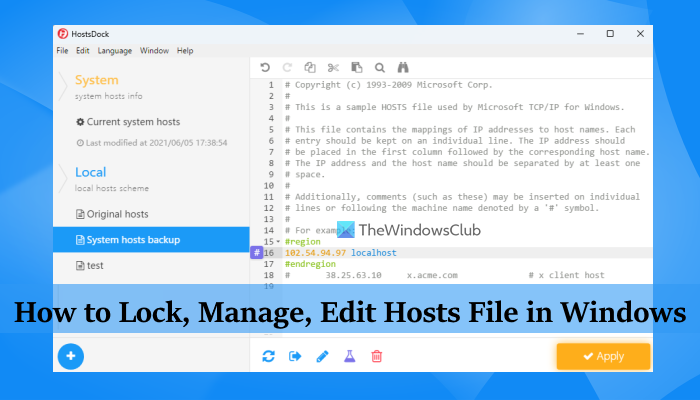
The Hosts file in Windows 11/10, is used to map hostnames to IP addresses. This Hosts file is located deep down in the Windows folder. It is a plain text file, and the size of the original default Hosts file is around 824 bytes.
Hosts File in Windows 11/10
Let us take a look at them.
Host file location
The Hosts file in Windows is located at the following location:
Lock Hosts file to prevent hijacking
Imagine clicking on www.thewindowsclub.com and seeing a completely different website load in your browser. Malware can redirect Web addresses on your computer by altering your Hosts file. This is referred to as the Host File Hijack.
To prevent Host file hijacks, you may navigate to it, right-click on it, select Properties and make it a Read-only file. This will lock down your Hosts file and prevent anyone or any malware from writing to it.
Block website using the Hosts file
To block a website using the Hosts File, simply add the following entry:
Although I do not do it, many users like to manually add entries to it in order to block the opening of one or more particular websites. Others, like to download and use List from well-known sources like mvps.org, to add entries that block malware sites from opening.
How to edit Hosts file in Windows 11/10
Now let us go into a detailed explanation.
To edit the Hosts file, navigate to the following folder location:
Here you will see the Hosts file. Right-click on it and select Notepad. Make the changes and Save.
But sometimes, even when you are logged on with administrative credentials, you may receive the following error message:
Access to C:WindowsSystem32driversetc hosts was denied
Cannot create the C:WindowsSystem32driversetchosts file. Make sure that the path and file name are correct.
In this case, type Notepad in Start search and right-click on the Notepad result. Select Run as administrator.
Open the Hosts file, make the necessary changes, and then click Save.
Using free Hosts File Editor software
If you are looking for an easier way, you can use a free Hosts file Editor software.
1] Using HostsMan
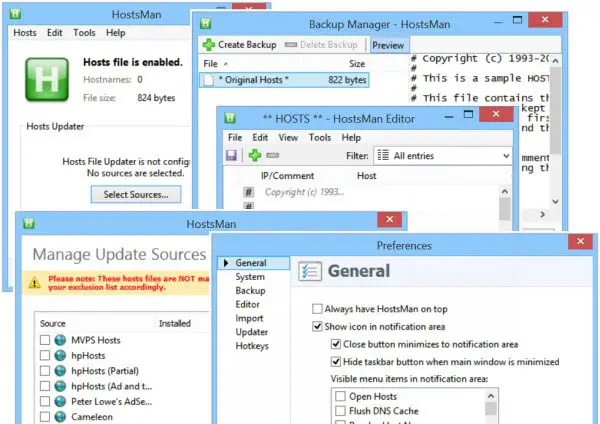
While you can always manually manage or edit Hosts file manually, I would like to suggest that you use a third-party freeware tool like HostsMan to do it.
HostsMan is a feature-rich tool that lets you add, remove, edit entries in the Hosts file. It also lets you easily add third-party Hosts lists that help in blocking malware sites and lets you easily enable or disable the Hosts file. It includes a built-in hosts file updater & a hosts editor. It lets you scan the hosts file for errors, duplicates, and possible hijacks – and also lets you create an Exclusion list. One more useful feature it offers is the Hosts file backup manager. Backup your Hosts file to a safe place and use it to restore it, should the need arise.
Hostman also lets you Flush DNS cache, open Hosts with a text editor, count the number of hosts, find duplicates, replace IP, scan hosts for malicious entries, rearrange hosts, manage DNS Client Service and more. In short, it’s the only Hosts Manager that you will even need. You can download it from its home page.
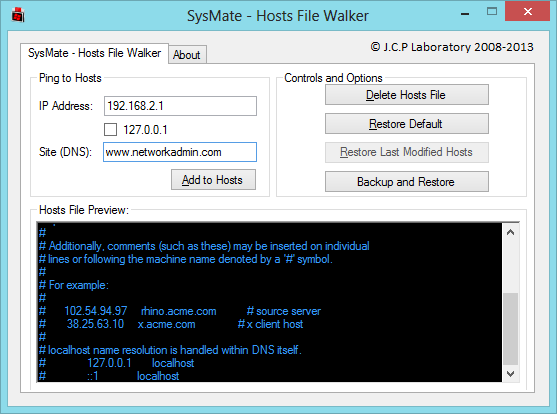
2] Using SysMate Hosts File Manager
SysMate Hosts File Manager and is another tool that lets you do so. With Host File Walker you can add as many records to the system hosts file. It even lets you backup and restore the Hosts File.
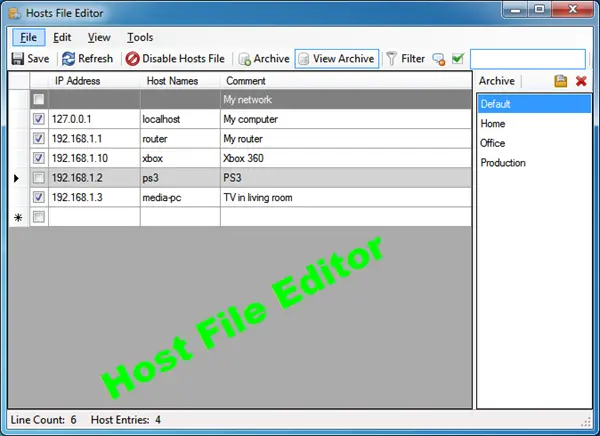
3] Using Host File Editor tool
You can download it from here. It offers a portable version too.
TIP: How to manually reset Hosts file back to default in Windows may also interest you.
If your browser has been hijacked, you might find this post on Browser Hijacking and Free Browser Hijacker Removal Tools helpful.
Date: January 23, 2022 Tags: Hosts, Security
Источник
- What’s My DNS?
- Hosts File — How and why to edit your DNS Hosts File
The hosts file is a file on your computer or other device that is used as the first step in the DNS lookup process for DNS hostname resolution.
This is the process of converting a domain name like www.example.com into an IP address like 192.168.2.1 which computers and network devices use to communicate with each other.
Making changes to your systems hosts file lets you intercept the normal DNS lookup process and set any IP address for any domain name you like which can be useful for many reasons, but also potentially harmful in some circumstances.
The hosts file can be found in the following locations depending on your operating system:
- Windows:
C:WindowsSystem32Driversetchosts - Linux:
/etc/hosts - MacOS:
/etc/hosts
There are several reasons why you may be interested in viewing or editing your hosts file which include:
Testing DNS changes — A common use for making changes to the hosts file is to test changes to DNS records before making them live on the internet. This allows you to make sure a new server setup is behaving as expected before making the changes to your DNS setup and having them live for everyone.
Forcing DNS changes — Often when having made changes to your domain names DNS settings, you will need to wait for DNS propagation as you may have locally cached DNS records and are not seeing the expected updated results. You can flush your DNS cache, or modify your hosts file to temporarily force changes which are not updating fast enough.
Local development — Often setting up custom hostnames for local testing and development can be quite useful. This allows you to configure your system to respond to your local web server on https://www.mysite.test and have your real site live on https://www.mysite.com.
Ad & content blocking — As the hosts file lets you override DNS entries for any domain name, people often create hosts file entries for common tracking, spyware, malware domains as well as product activation servers to assist with software piracy. There are lists of common ad networks and tracking servers available online which you can use to keep an up-to-date list of sites to block. Blocking is achieved by setting the IP address of the ad networks to a loopback address like 127.0.0.1 which will not return anything.
Checking for compromise — Often if your device is infected with malware, then your hosts file may be compromised to included entries which could cause you harm. For example, if your hosts file had been unknowingly changed to point your banks domain name to the IP address of a hacker. This type of DNS attack is known as DNS pharming, and checking your hosts file can uncover potential infection.
Where is the hosts file located?
The most common question that many people have around the host file is how do you find it? What is the path and location of the hosts file?
Depending on your operating system, the hosts file is located in different locations and requires different methods for editing as it is a protected system file.
Windows host file location
The hosts file for all recent versions of Windows including Windows 7, 8, 10, 11 & Windows Server is located in C:WindowsSystem32Driversetchosts.
There are a few important notes to remember when opening the hosts file on Windows:
- You will need to use a plain text editor like Notepad, not a word processor like Microsoft Word.
- You will need to open the file as the local system administrator. This can be done by right clicking on for example Notepad and choosing «Run as administrator».
- When navigating to the directory containing the hosts file, they may be hidden depending on your setup. Additionally you may need to select to show «All Files (*.*)» instead of the default «Text Documents (*.txt)».
Linux host file location
The hosts file for Unix, Linux and other Unix like operating systems is located in /etc/hosts
As this is a protected system file, you will need to make sure that you edit it as the root user. This can be done using sudo for example sudo vim /etc/hosts from the terminal.
Apple MacOS host file location
The hosts file for MacOS is located in /etc/hosts as MacOS is a Unix based system and follows many of the common file location conventions.
As this is a protected system file, you will need to make sure that you edit it as the root user. This can be done using sudo for example sudo vim /etc/hosts from the terminal.
How do you edit your hosts file?
Once you’ve found the location of your hosts file for your specific operating system, all you need to edit it is a simple plaintext text editor. You can use Windows Notepad, TextEdit on the Mac, as well as command line text editors like vim or nano on Unix based systems.
You will need to make sure that when you’re editing this file that you do so with an account which has administrator privileges as this is a protected system file.
Hosts file format
Once you have located the hosts file, the format is very simple. On a new blank line you need to enter the desired IP address followed by one or more spaces (or tabs) and then the hostname you would like to assign to this. You can add additional hostnames separated by one or more spaces (or tabs) as well.
IP address considerations:
You can use either IPv4 A Records or IPv6 AAAA Records for the IP address which you would like to assign.
If using an IPv6 address, you may want to consider using either the IPv6 expanded format or IPv6 compressed format for all IPv6 entries to ensure consistency and making searching for entries easier if you have large number of them.
Hostname considerations:
When specifying the host name for a hosts file entry, make sure to only include the domain name itself. Do not enter the protocol (http://), or document path (/some-page.html). For example for the webpage http://www.example.com/some-page.html the hostname would be simply www.example.com. If you would also like to include both example.com and www.example.com then you will need to specify both individually.
If using an International Domain Name (IDN), then it will first need to be converted to Punycode format as the host file is plain text and does not accept UTF-8 characters.
Wildcard domains (*.example.com) are not supported in the hosts file.
It is important to make sure that you use a plain text editor like Notepad rather than a word processor like Microsoft Word to edit the hosts file as advanced word processors can introduce unrecognized data like font information.
Example hosts file:
An example hosts file entry may look like the following:
127.0.0.1 example.comor with multiple entries:
127.0.0.1 example.com
127.0.0.1 www.example.comor multiple entries on a single line
127.0.0.1 example.com www.example.comHosts file comments:
It can sometimes be useful to add comments to your hosts file, especially if you have many entries or entries that you switch between from time to time.
To add a comment, you simply need to use the # character, and anything after this will be ignored.
# this entire line is a comment
127.0.0.1 example.com # this text at the end of a host file entry is a comment
# 127.0.0.2 example.com this entire line a comment and not a valid hosts file entryThe above only includes a single valid hosts file entry for example.com pointing to 127.0.0.1.
How to test changes made to the hosts file?
When you have made changes to your hosts file, you will not be able to use any of the Online DNS Tools to check your changes, instead you will need to rely on your local device for testing.
Using built in DNS tools like nslookup on Windows or dig on Linux and MacOS will query your devices locally configured nameservers directly, skipping reading the hosts file so is not an ideal way of testing changes.
One of the best methods is to use the ping command-line tool, simply run ping example.com and observe which IP address is resolved for the given hostname.
Which hosts file to edit when using Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL)?
You may wonder which hosts file you need to edit when running multiple operating systems on Windows by taking advantage of WSL.
Making changes to the Linux guest operating systems hosts file at /etc/hosts file will only have changes reflected within the Linux instance.
Editing the Windows hosts file at C:WindowsSystem32Driversetchosts will have the changes reflected on both Windows and within the Linux instance.







:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ryanperiansquare-de5f69cde760457facb17deac949263e-180a645bf10845498a859fbbcda36d46.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/005_how-to-edit-the-hosts-file-153661-5bb512474cedfd0026cf0260.png)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/001_how-to-edit-the-hosts-file-153661-5bb5126446e0fb0026320d9b.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/002_how-to-edit-the-hosts-file-153661-5bb51296c9e77c0051385665.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/003_how-to-edit-the-hosts-file-153661-5bb512bdc9e77c0026e3bdf1.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/004_how-to-edit-the-hosts-file-153661-5bb512ff46e0fb00263227bc.jpg)