В конце 2016 года компания AMD взбудоражила рынок, представив новое поколение процессоров Ryzen для настольных компьютеров. Чуть позже появились также решения для серверов и HEDT. Когда новинки появились массово у пользователей в начале-середине 2017-го года, стало понятно что серия удачна и она надолго. За сравнительно небольшие деньги AMD Ryzen предлагал до 8-ми современных быстрых ядер и до 16-ти потоков.
Чуть позже энтузиасты выяснили интересную особенность: оказалось, что производительность одного и того же процессора в Windows 7 и Windows 10 может отличаться на 10-15%. Эта информация дошла до разработчиков, и вскоре в набор драйверов для чипсетов AMD были добавлены фирменные планы питания для Windows 10. Из этой статьи вы узнаете как включить AMD Ryzen Balanced Power Plan в Windows 10.
Что такое AMD Ryzen Balanced Power Plan
Вместе с Ryzen появилась фирменная технология SenseMI (иными словами, технология умного автоматического буста), с помощью которой можно регулировать частоту процессора и его напряжение для максимального увеличения скорости работы в определённое время. Смены напряжения и, соответственно, частоты процессора происходят очень быстро, за период до 1 мс. Также переходы управляются параметром P-States — комбинацией частоты и напряжения, запрашиваемые операционной системой, следовательно, успешность работы SenseMI во многом зависит и от операционной системы Windows 10.
Проблема заниженной производительности в том, что в обычном режиме (план энергопитания Сбалансированный) пороговые значения между переключениями напряжения и, следовательно, частоты завышены. Эту проблему как раз и решает выпуск компанией AMD нового плана энергопотребления — AMD Ryzen Balanced Power Plan Windows 10.
В этом новом режиме Windows 10 лучше взаимодействует с процессорами Ryzen, при этом они остаются энергоэффективными при достижении максимально возможной производительности.
Как включить AMD Ryzen Balanced Power Plan
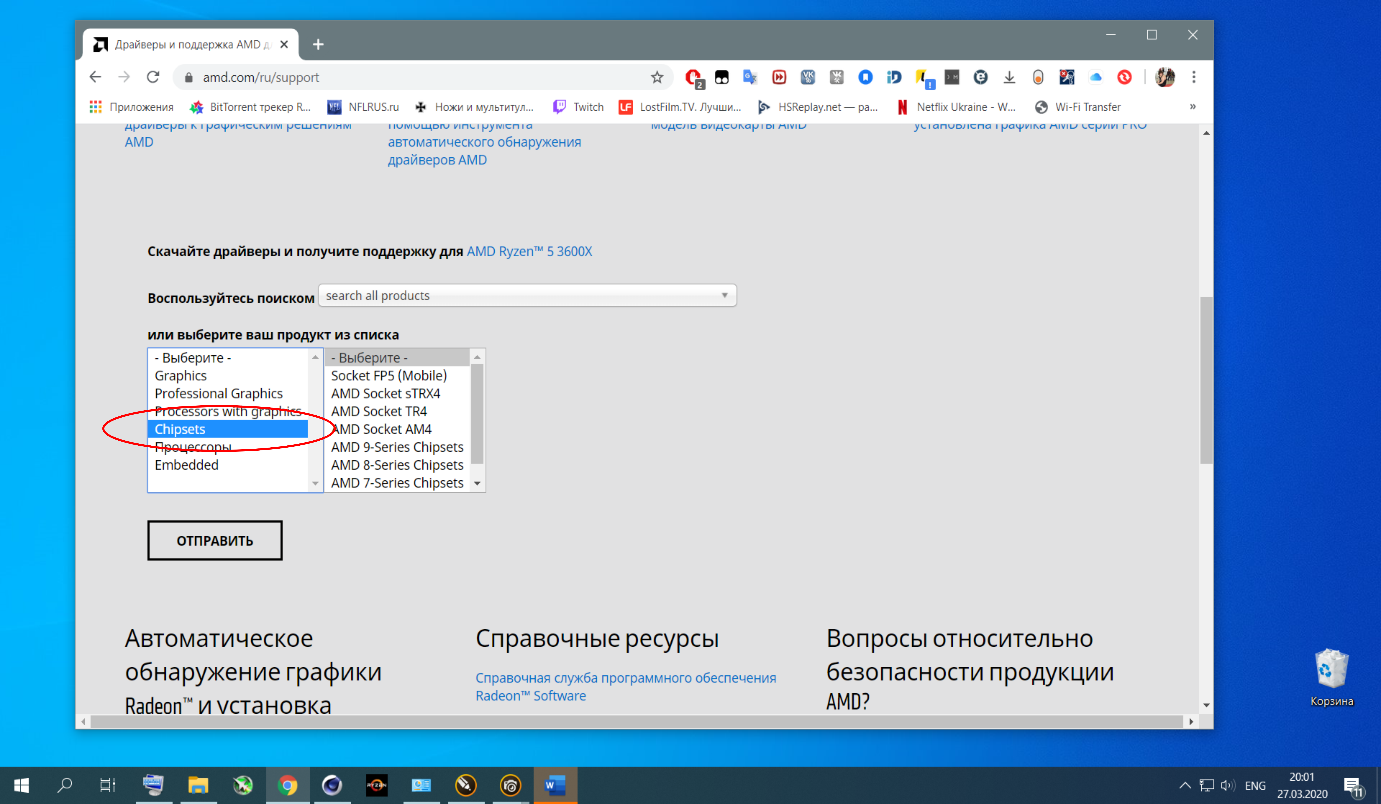
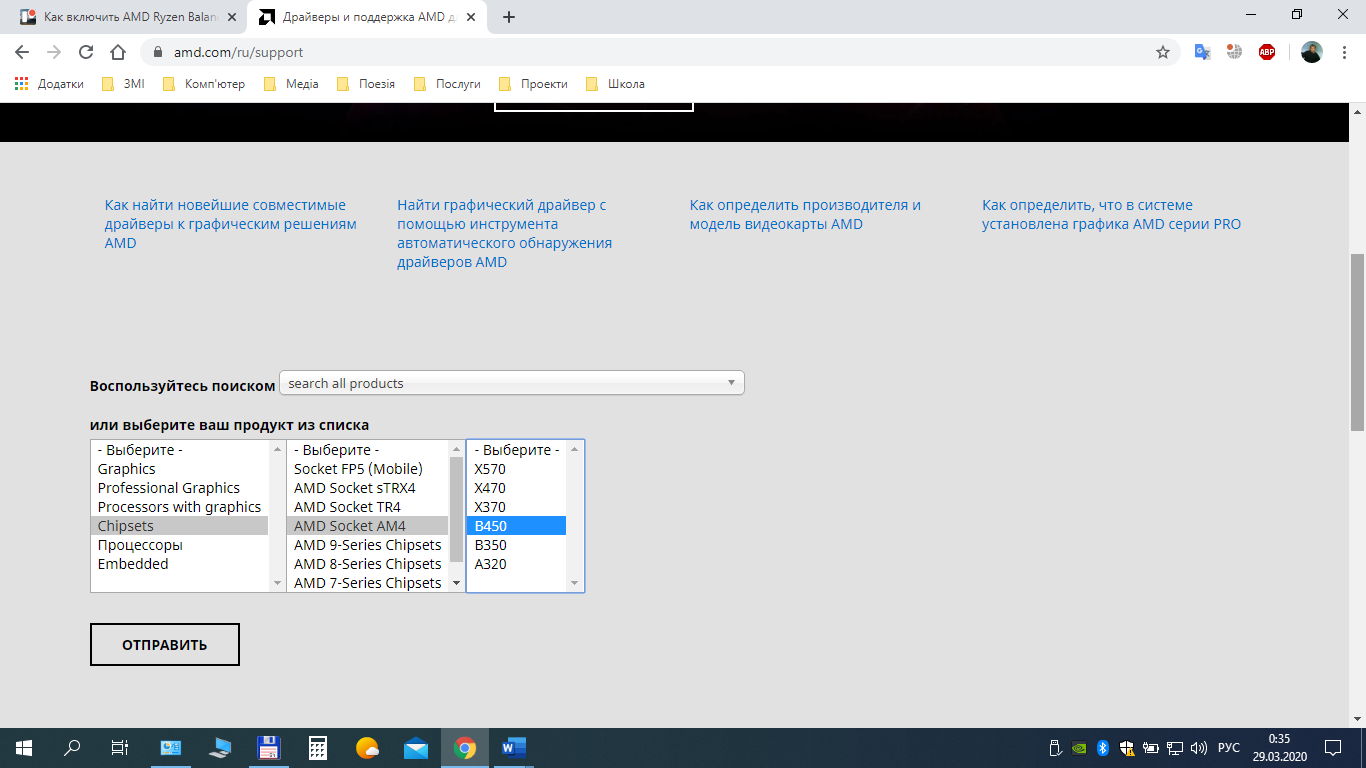
Для установки и включения AMD Ryzen Balanced Power Plan следует загрузить и установить свежий пакет драйверов для ваших комплектующих AMD на материнской плате с официального сайта поддержки продуктов компании AMD, если вы ещё этого не сделали. В меню выберите пункт Chipsets и далее — свой вариант чипсета.
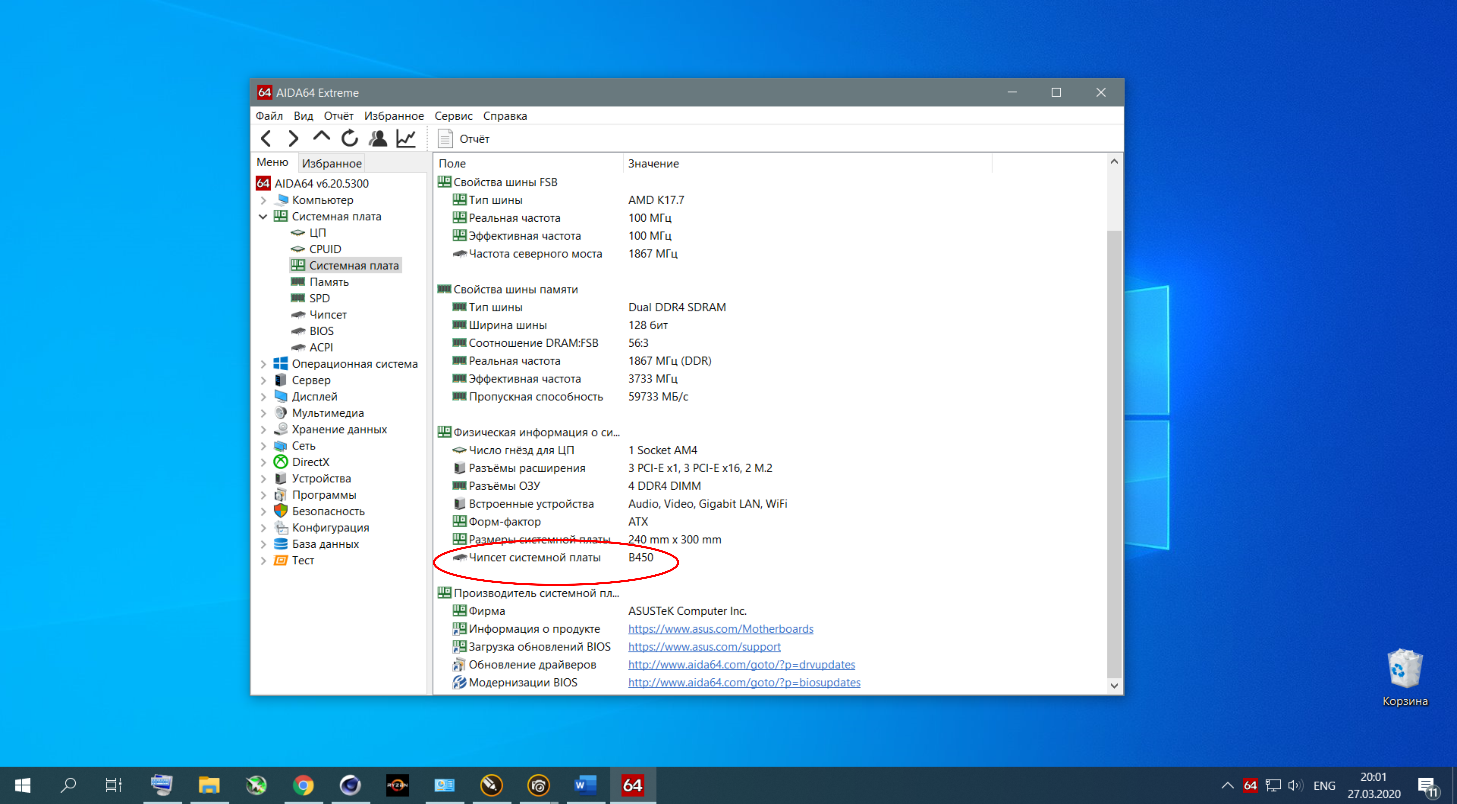
Узнать какой именно чипсет у вас можно, например, с помощью утилиты AIDA64 в разделе Системная плата:
В данном конкретном случае это чипсет B450 и он находится в группе сокетов AMD Socket AM4 промежуточного меню. Увы, поиски нужного драйвера в этом интерфейсе не очень просты и очевидны.
Нажмите кнопку Отправить (очевидно, имеется ввиду отправка информации для поиска). Появится результат:
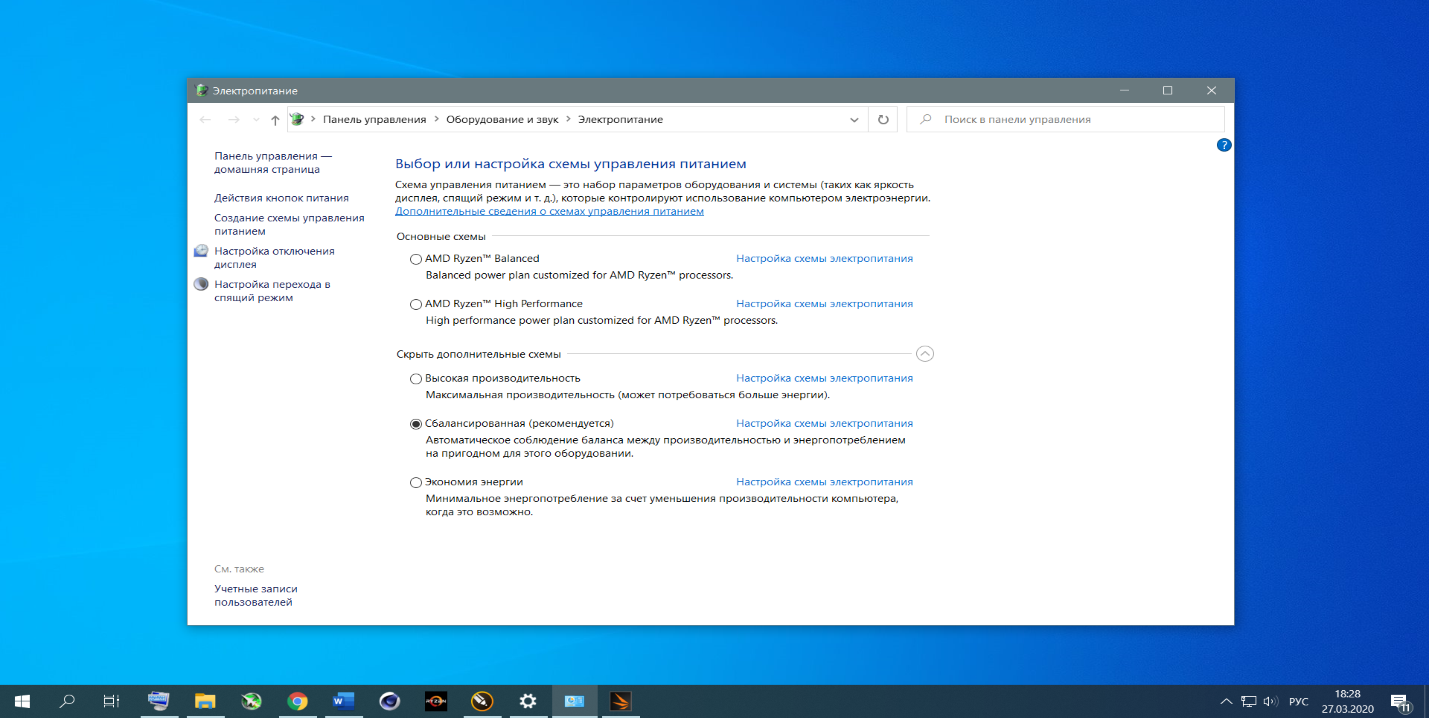
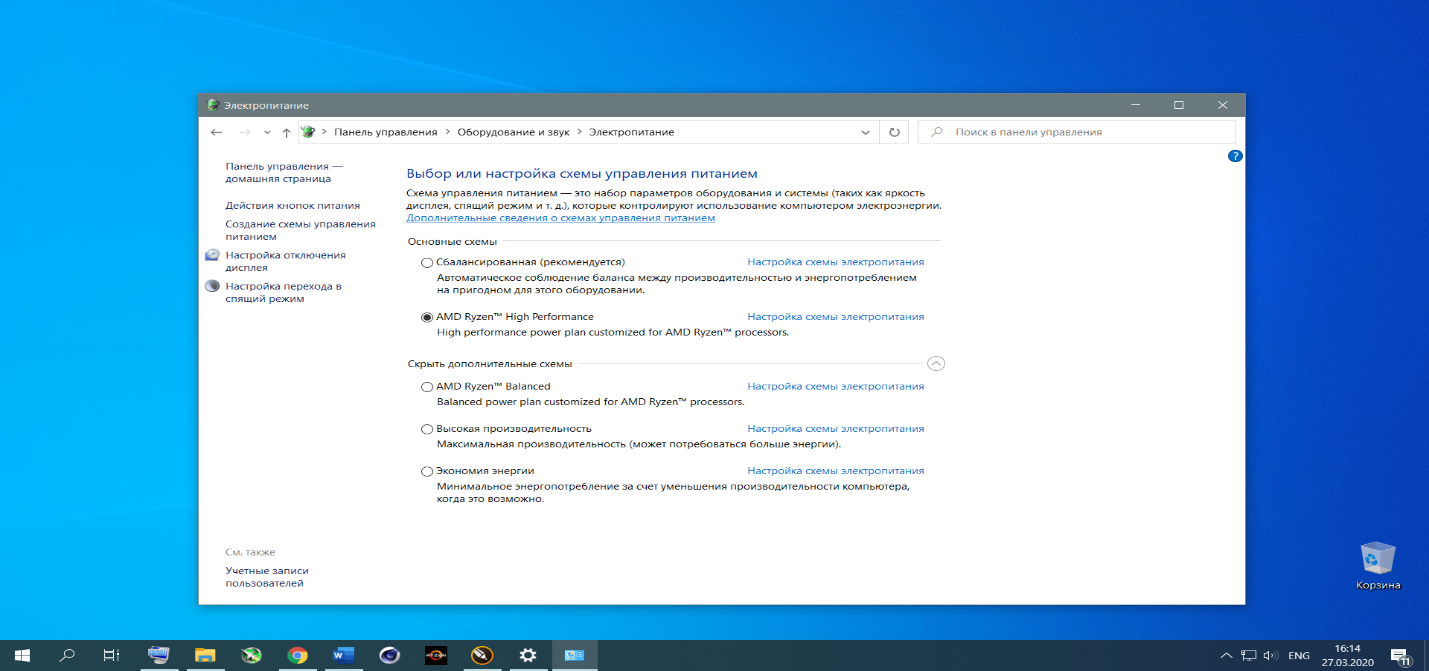
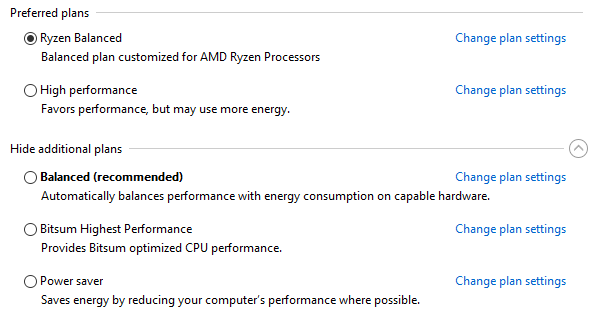
Выберите драйвер нужной разрядности (32 или 64), скачайте пакет и установите его. После окончания установки загрузите Панель управления, далее запустите апплет Электропитание.
В окне апплета можно выбрать любой из доступных планов питания для Вашей системы, в частности и планы электропитания от AMD.
Теперь вы знаете как включить ryzen balanced power plan.
Тестирование планов электропитания
Одной из самых распространённых микроархитектур от AMD является Zen 2. Её используют центральные процессоры 3000-й серии. Чтобы понять что лучше AMD Ryzen balanced или максимальная производительность проверим релевантность настройки и использования модифицированного плана электропитания от AMD на примере процессора Ryzen 3600X.
Для сравнения производительности будем использовать Cinebench R20 и тесты пакета Futuremark 3DMark (ver. 5.25.802.0).
Конфигурация стендового компьютера:
- Процессор: AMD Ryzen 3600X 3.8 ГГц 6/12;
- ОЗУ: HyperX DDR4 16 Гб OC 3733 МГц;
- Материнская плата: Asus ROG Strix B-450 Gaming;
- Видеокарта: Sapphire Pulse AMD RX 5700XT;
- Блок питания: Fractal Design Edison 750W;
- Жёсткий диск: ADATA SX 8200 1 Тб;
- ОС: Windows 10 x64.
Результаты тестов Cinebench R20
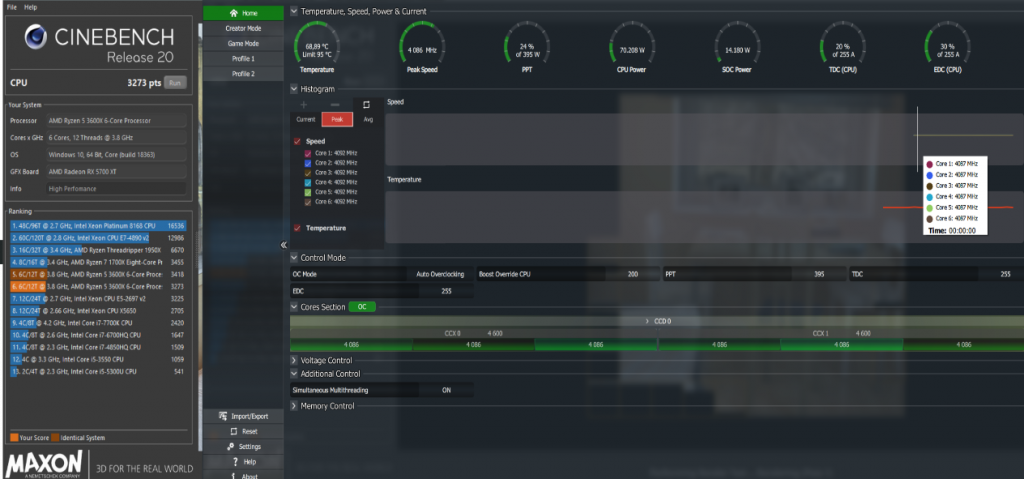
Стандартный сбалансированный режим плана электропитания от Майкрософт показывает результат 3273 балла при пиковой частоте 4093 МГц и энергопотреблении на уровне 70 Вт:
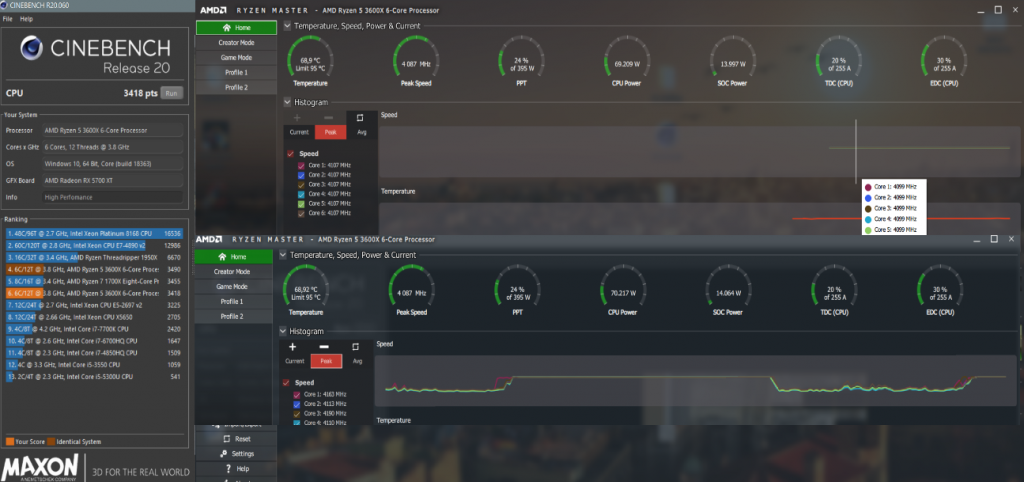
План электропитания windows 10 Ryzen Bananced и High Performance показывают результаты 3418 и 3490 балла при пиковой частоте 4107 МГц и 4190 МГц у отдельных ядер и энергопотреблении на уровне 69,2 Вт и 70,2 Вт соответственно:
Результаты тестов 3DMark
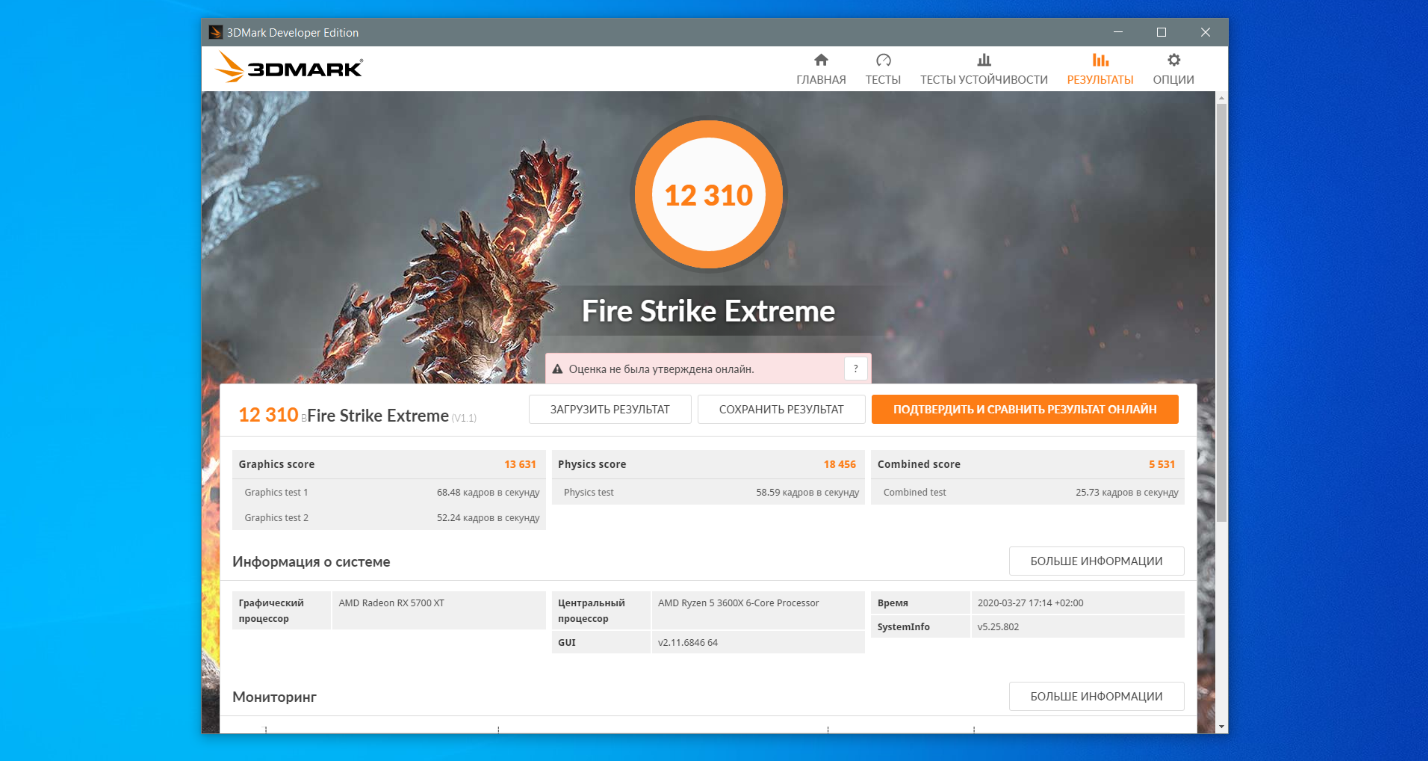
Для стандартного сбалансированного плана электропитания от Microsoft получаем такие оценки в наборе тестов Fire Strike Extreme:
- Оценка графической подсистемы — 13631.
- Оценка теста физических характеристик — 18456.
- Комбинированный тест — 5531.
- Общая оценка — 12310.
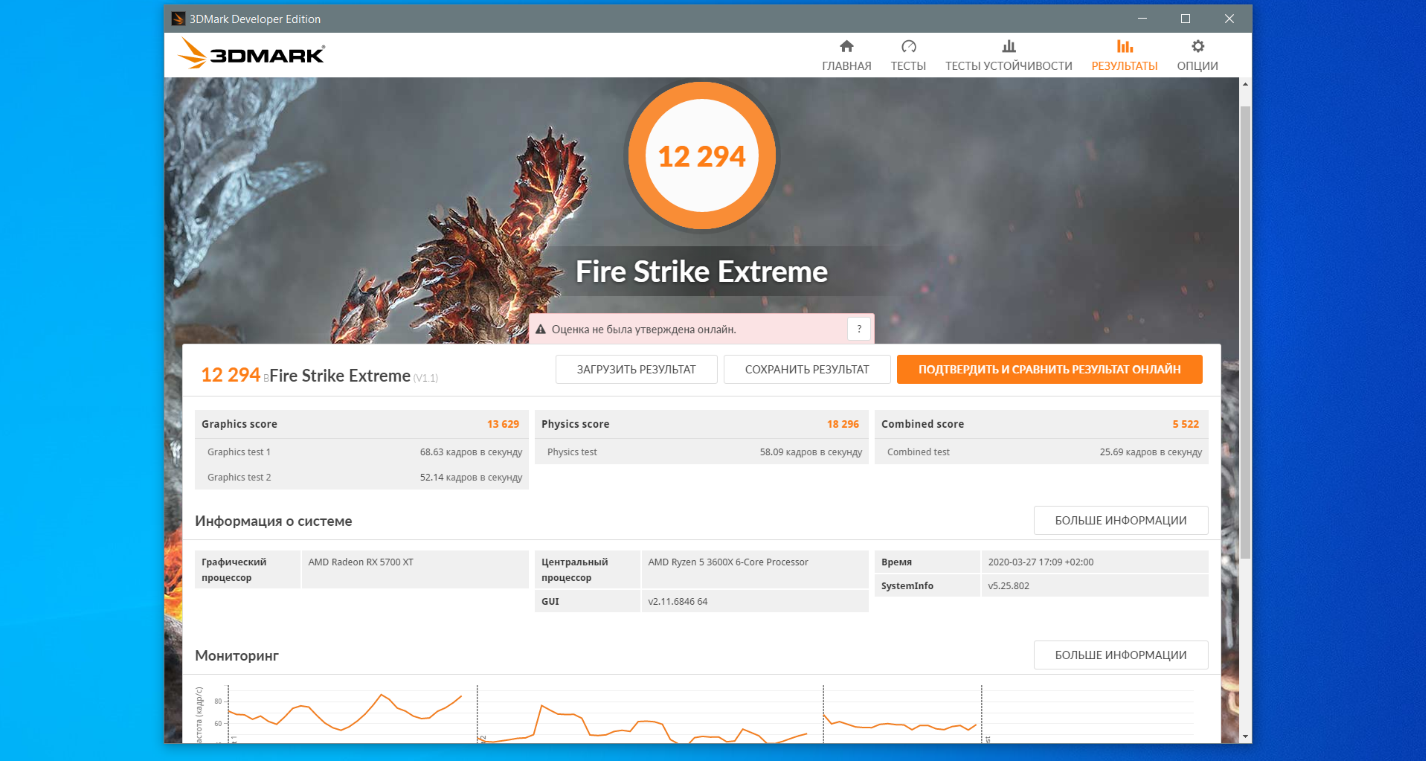
А схема питания AMD Ryzen Balanced показала такие результаты в этом тесте:
- Оценка графической подсистемы — 13659.
- Оценка теста физических характеристик — 18296.
- Комбинированный тест — 5522.
- Общая оценка — 12294.
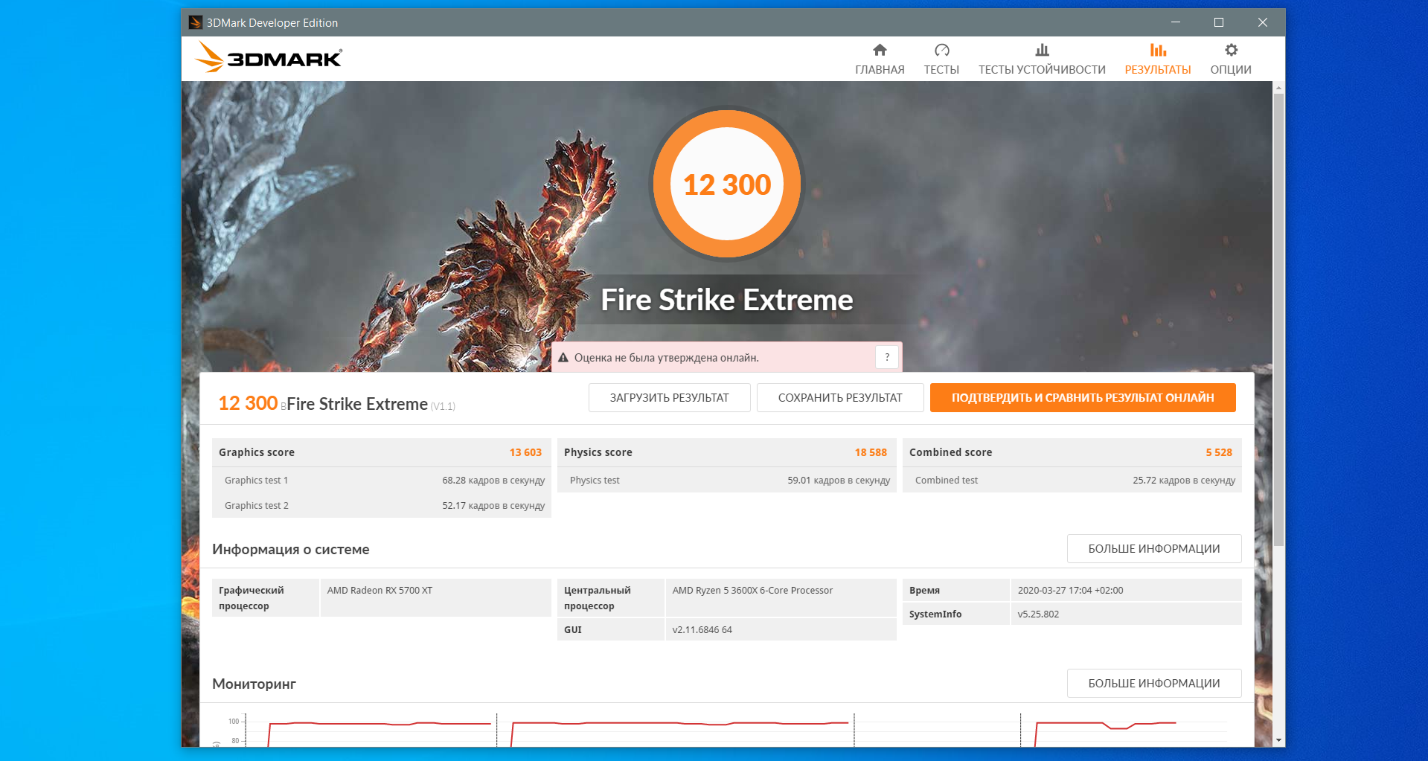
Для режима AMD Ryzen High Performance:
- Оценка графической подсистемы — 13603.
- Оценка теста физических характеристик — 18588.
- Комбинированный тест — 5528.
- Общая оценка — 12300.
Выводы
Как можно видеть по результатам тестирования выше, использование планов электропитания для Windows 10 AMD Ryzen Balanced либо AMD Ryzen High Performance даёт увеличение производительности в бенчмарке Cinebench R20 (который может служить индикатором быстродействия системы в профессиональных задачах) до 6%, при такой же энергоэффективности. Разница же оценок в 3DMark (тест производительности в играх) практически укладывается в погрешность измерений, за исключением оценки расчёта физики, но и там буст невелик.
В целом, можно рекомендовать настройку и использование планов электропитания для AMD Ryzen. Наличие такого процессора, естественно, необходимо, в противном случае, скорее всего, даже сами планы не будут установлены в систему при установке драйверов для чипсета.
Была ли эта статья полезной?
ДаНет
Оцените статью:

Загрузка…
Об авторе
Над статьей работал не только её автор, но и другие люди из команды te4h, администратор (admin), редакторы или другие авторы. Ещё к этому автору могут попадать статьи, авторы которых написали мало статей и для них не было смысла создавать отдельные аккаунты.
Шлифовка, притирка.
Неделю назад представитель AMD заявил, что готово новое обновление пакета AMD Generic Encapsulated Software Architecture (AGESA), на основании которого должен быть исправлен BIOS материнских плат для процессоров Ryzen. Точнее, с помощью BIOS будут устранены некоторые недочёты, допущенные при проектировании процессоров на архитектуре Zen. Среди прочих улучшений в первое исправление AGESA вошла коррекция состояния режима потребления платформы AMD Ryzen под управлением Windows 10. Вскоре при настройке плана потребления в Windows 10 появится выбор одного из трёх состояний: сбалансированный стандартный, сбалансированный для AMD Ryzen и план для высокой производительности (обновлённый драйвер для чипсетов AMD брать
здесь
, его надо установить самостоятельно).
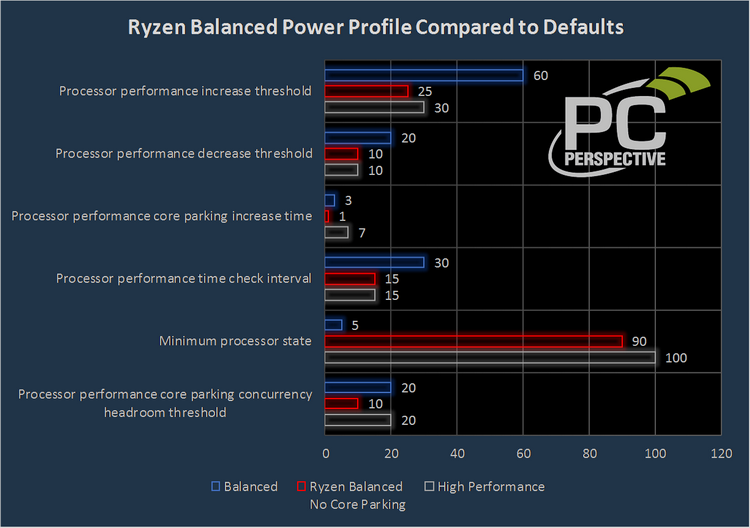
Установка драйвера и выбор плана «High Performance» делает две интересных вещи. Во-первых, снижается латентность и порог переключения процессоров Ryzen в новое состояние P-States (комбинация напряжения питания и тактовой частоты). Иначе говоря, процессоры Ryzen быстрее и агрессивнее возвращаются к производительной работе. Во-вторых, активнее включаются в работу простаивающие ядра. Например, при выборе сбалансированной работы до превышения уровня нагрузки 10% «просыпалось» только одно ядро из восьми (одно — физическое и второе — SMT). Выбор плана «High Performance» заставляет сразу включаться большему числу ядер, что может понадобиться в играх. Настолько это эффективные новшество, можно судить из графика ниже, в котором сравнивается производительности системы при выборе планов «High Performance» и «AMD Ryzen Balanced».
рекомендации
3070 Gigabyte Gaming за 50 тр с началом
MSI 3050 за 25 тр в Ситилинке
3070 Gainward Phantom дешевле 50 тр
13700K дешевле 40 тр в Регарде
10 видов <b>4070 Ti</b> в Ситилинке — все до 100 тр
3060 Gigabyte Gaming за 30 тр с началом
13600K дешевле 30 тр в Регарде
4080 почти за 100тр — дешевле чем по курсу 60
12900K за 40тр с началом в Ситилинке
RTX 4090 за 140 тр в Регарде
Компьютеры от 10 тр в Ситилинке
3060 Ti Gigabyte за 42 тр в Регарде
3070 дешевле 50 тр в Ситилинке
Пока, как мы видим, выигрыш небольшой, но он ничего не стоит для пользователей и по мере оптимизации ПО и игр будет становиться всё больше и больше.

Неделю назад представитель AMD заявил, что готово новое обновление пакета AMD Generic Encapsulated Software Architecture (AGESA), на основании которого должен быть исправлен BIOS материнских плат для процессоров Ryzen. Точнее, с помощью BIOS будут устранены некоторые недочёты, допущенные при проектировании процессоров на архитектуре Zen. Среди прочих улучшений в первое исправление AGESA вошла коррекция состояния режима потребления платформы AMD Ryzen под управлением Windows 10. Вскоре при настройке плана потребления в Windows 10 появится выбор одного из трёх состояний: сбалансированный стандартный, сбалансированный для AMD Ryzen и план для высокой производительности (обновлённый драйвер для чипсетов AMD брать здесь, его надо установить самостоятельно).
Установка драйвера и выбор плана «High Performance» делает две интересных вещи. Во-первых, снижается латентность и порог переключения процессоров Ryzen в новое состояние P-States (комбинация напряжения питания и тактовой частоты). Иначе говоря, процессоры Ryzen быстрее и агрессивнее возвращаются к производительной работе. Во-вторых, активнее включаются в работу простаивающие ядра. Например, при выборе сбалансированной работы до превышения уровня нагрузки 10% «просыпалось» только одно ядро из восьми (одно — физическое и второе — SMT). Выбор плана «High Performance» заставляет сразу включаться большему числу ядер, что может понадобиться в играх. Настолько это эффективные новшество, можно судить из графика ниже, в котором сравнивается производительности системы при выборе планов «High Performance» и «AMD Ryzen Balanced».
Пока, как мы видим, выигрыш небольшой, но он ничего не стоит для пользователей и по мере оптимизации ПО и игр будет становиться всё больше и больше.
Dako
20.09.2021
Балансед ставь и забей болт.
Ответить
Развернуть ветку
Salvador666
20.09.2021
Начиная с Windows 1909, high Performance изначально включена оптимизация для Ryzen. С Zen 3 амуде вообще их убрали. Так что, юзай тот что в виндувс или выбери balanced от амд. Разница очень минимальная
Ответить
Развернуть ветку
JoeQ
20.09.2021
High perfomance на R7 только. Ставь баланс.
Upd: и на r5 есть, мой косяк.
Ответить
Развернуть ветку
JoeQ
20.09.2021
Хм странно у знакомого почему то нету такого профиля.
Ответить
Развернуть ветку
Тогдашний украинец
20.09.2021
10, последняя. Да забей, ставь баланс, а если у тебя фризы, это не из-за power-plan-a
Ответить
Развернуть ветку
harbiter
20.09.2021
Для некоторых чипсетов/связок чипсет+cpu, в некоторых драйверах, ryzen планы выпелины за не надобностью… Если стоит актуальная версия чипсетного драйвера, то можно любой balanced/perfomance ставить.
Ответить
Развернуть ветку
Никита Лукьянов
20.09.2021
А чипсетный драйвер обязательно нужен? А то я сейчас посмотрел, автоматом у меня нифига нет, вроде и так всё норм работает
Ответить
Развернуть ветку
Salvador666
20.09.2021
В целом нет необходимости. Но и нет причин не установливать драйвера чипсета. Мало ли, что может пойти не так.
Вообще некоторые драйвера для чипсета помогают улучшить поведение процессора начиная от чрезмерного ускорения до регулировки частот.
Ответить
Развернуть ветку
Син Макс
21.09.2021
не вижу смысла на десктопе ограничивать производительность. эти настройки скорее актуальны для ноутбуков.
Ответить
Развернуть ветку
Тони Тренер
20.09.2021
ставить или макс производительность или амдэшный . лучше макс перформанс конечно
Ответить
Развернуть ветку
Читать все 25 комментариев

Новости
Самое интересное в обзорах
У процессоров AMD Ryzen очень сложная и развитая подсистема питания различных функциональных блоков; подробно об этом было рассказано в соответствующем обзоре. Возвращение AMD в качестве серьёзного игрока на рынке ЦП потребительского класса застало Microsoft врасплох — все настройки энергопотребления в Windows были созданы с учётом особенностей процессоров предыдущих поколений. Как выяснилось, особенности планировщика Windows 10 не связаны с неоптимальной производительностью Ryzen.
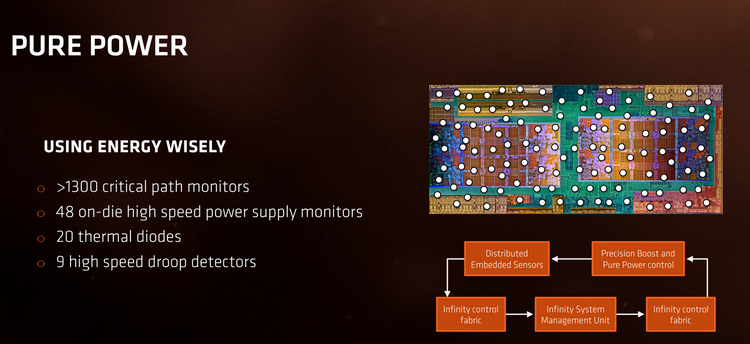
Подсистема питания Ryzen очень сложна
Сама AMD официально признала, что использование «сбалансированного» профиля может привести к падению производительности новых процессоров и рекомендовала использовать профиль с максимальными настройками в пользу скорости в ущерб экономичности. На днях компания представила то, чего ждали многие — профиль энергопотребления Windows, оптимизированный с учётом особенностей архитектуры Ryzen. Загрузить его можно использовав соответствующую ссылку. Сопутствующая информация содержится там же, в официальном блоге AMD.
Так следует настроить Windows после установки нового профиля
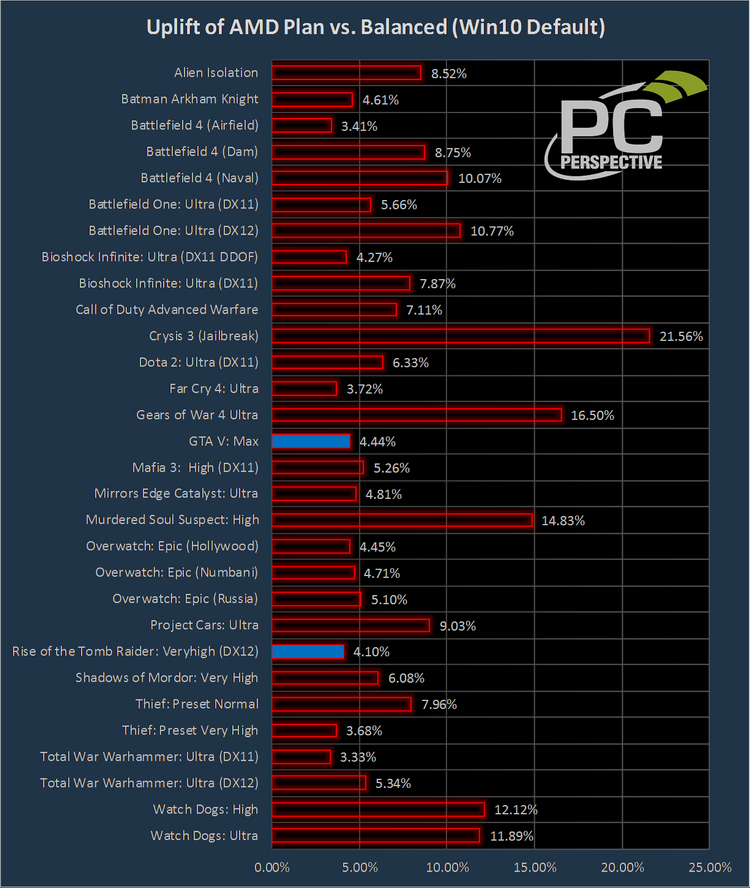
Ранее проблема заключалась в том, что система управлением питания, реализованная в Windows 10, чересчур агрессивно «парковала» ядра у Ryzen, не зная о существовании такого процессора и его особенностях. «Парковка» отключалась только для процессоров Intel, у которых есть поддержка технологии Speed Shift, минимизирующая латентность при переводе процессорных ядер из одного режима энергопотребления в другой. Теперь это исправлено, система знает об особенностях AMD Ryzen, и, как ожидалось, производительность систем на базе процессоров AMD Summit Ridge в ряде случаев заметно возросла. Серьёзное тестирование провели наши зарубежные коллеги с ресурса PC Perspective, и вот что им удалось обнаружить:
Прирост производительности в играх местами выглядит впечатляюще
Практически в каждой из протестированных игр мы видим некоторый прирост скорости, начинающийся со скромных 3,33 %, но в отдельных случаях, таких как Gears of War 4 или Crysis 3, достигающий внушительных 16,5 % и даже 21,56 %! А ведь речь всего лишь о том, чтобы поменять в настройках энергопотребления Windows 10 «сбалансированный» профиль на профиль, разработанный специально для Ryzen. На первый взгляд, разница заключается лишь в настройке «minimum processor state» (90 % против 100 %), но GUI не показывает всех особенностей нового профиля. На деле изменено большее количество параметров. За это можно покритиковать Microsoft, которая не раскрывает всех настроек ОС, которые порой могут оказывать существенное влияние на производительность; и с каждым годом ситуация отнюдь не улучшается.
Настройки AMD агрессивнее тех, которые должны обеспечивать максимальную производительность
Мы полагаем, что смысл в загрузке нового профиля энергопотребления есть для подавляющего большинства владельцев систем на базе AMD Ryzen, вне зависимости от модели и количества ядер. Разумеется, лишь в том случае, если владелец данного ПК вообще заботится о настройках энергопотребления, а не устанавливает режим высокой производительности, после чего забывает об этом разделе панели управления навсегда. Но даже тогда смысл может присутствовать, поскольку некоторые скрытые от глаз параметры у нового профиля установлены в более агрессивные значения, нежели в значении «High Performance». Мы рады видеть такое внимание AMD к нуждам игроков и владельцев ПК в целом и надеемся, что и в будущем компания продолжит придерживаться аналогичной политики.
Если вы заметили ошибку — выделите ее мышью и нажмите CTRL+ENTER.
Самые обсуждаемые публикации
Ultimate? Performance? Balance? Picking a power setting shouldn’t feel like deciding between the character stats of the latest RPG. What’s the difference between these Ryzen power plans anyway?
Ryzen offers three basic power plans: Balanced, High Performance, and Ultimate. Balanced works on saving energy and lowering heat, High Performance opens up the clock speed for faster processing, and Ultimate builds on high performance to deliver even faster speeds. The “best” power plan is the one that helps you achieve your definition of “good” performance whether that’s power savings or max speed.
Let’s get your PC working with the optimal power setting for your needs!
What Are The Different Ryzen Power Plans?
Let’s quickly run through the difference between the three Ryzen power plans that you’ll find on your Windows PC.
Ryzen High Performance Power Plan
The Ryzen High Performance power plan is the old-school approach to delivering more power for people using demanding software. This power plan works by having all of your cores working at their maximum clock speed.
This is an ideal power solution for people who need constant, high-power for extremely demanding software.
Ryzen Balanced Power Plan
The Ryzen balanced power plan focuses on saving energy. This plan is still fully capable of playing video games and using high-end software, but it’s not going to deliver the raw power that the other options on this list are capable of achieving.
The Ryzen balanced power plan is the perfect choice for people who want to keep the noise, heat, and power consumption down.
Ryzen Ultimate Power Plan
The Ryzen ultimate power plan is the experimental, new addition to the rising power plan family. This power plan works to eliminate some of the smallest and efficiencies in your computer to deliver the fastest possible response times across the board.
You might not even notice the subtlety of the performance gains from the Ryzen ultimate power setting. That makes this setting an ideal choice for people who use software that has a very high level of demand. Even most modern gaming isn’t demanding enough to justify the Ryzen ultimate power plan on many PCs.
Which Ryzen Power Plans Are Default On Windows
Only a few of the Ryzen Power Plans will be default on your Windows PC. It all depends on your specific PC build, but Ryzen Balanced and Ryzen Performance are often available by default on Windows computers. You can use the command prompt to enable Ryzen Ultimate if it is not otherwise available.
You might also need to download the right drivers for your chipset to get these power settings working properly on your PC. We’ll cover these how-to tutorials later in the article.
Does Intel Also Offer Power Plans?
Intel offers various power plan options just like Ryzen and other CPU manufacturers. In fact, Windows computers used to favor Intel plans to the point where they would incidentally limit the overall power efficiency of AMD technology. The long rivalry between these companies is well-known, but it does appear that everyone seems to let other power plans work as intended these days.
Whether you’re using Ryzen or Intel, the best power plan for you is going to depend entirely on the type of performance you’re looking to improve on.
The balanced power setting is going to be ideal for people who value energy-savings and thermal efficiency more than anything else. You’ll still be able to do some top-tier gaming on the balanced setting as well as video and music editing.
Performance and Ultimate power settings are ideal for people who want to squeeze out every bit of performance they can while disregarding any concern for battery life, energy use, or thermal efficiency. These modes can be great especially when it comes to using demanding software such as video editing.
We do need to talk about how all of these settings impact gaming. While the Performance and Ultimate settings can definitely get a few more frames per second going, you might not even notice much of an overall difference while playing your favorite games.
Picking the best power plan all comes down to how you want to measure the efficiency of your PC.
Ryzen High Performance Power Plan
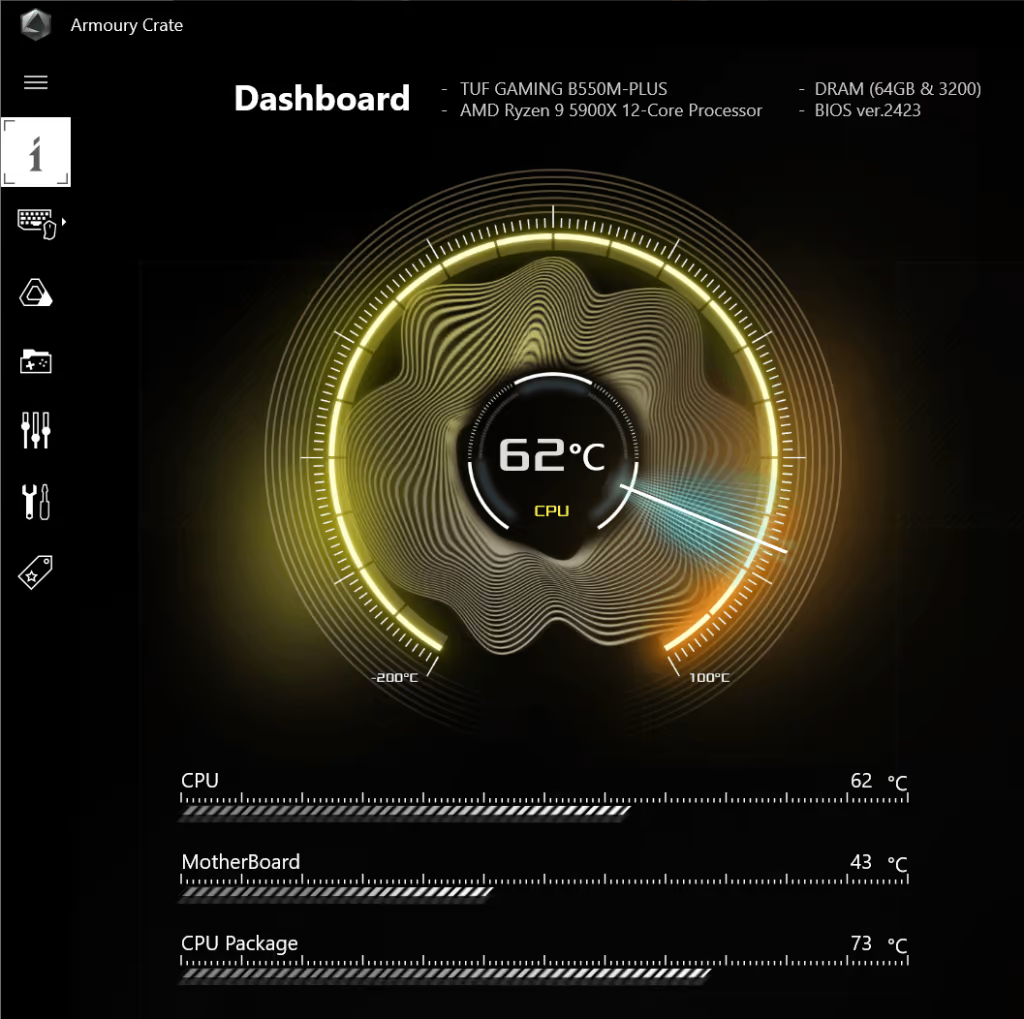
The Ryzen High Performance Power Plan is now the middle child between the balanced and ultimate options. It’s not quite the highest, but it certainly isn’t a “energy saving” choice. This is a solid option for people who always want to be on a high-power setting, but who also don’t have a need for the Ultimate Power Plan.
The Ryzen High Performance Power Plan is also a bit odd. It keeps your clock speeds high, but how that translates into better performance is very case dependent. You may or may not even notice that you have this high-powered setting on.
Pros
- Clock speeds are alway high and ready to go
- Improves latency and allows you to jump into high-demand processing faster
Cons
- Generates lots of heat
- Hard to notice the performance gains
- A bit of an awkward community reception
Ryzen Balanced Power Plan
The balanced power plan tries to level off power with energy consumption. This is ideal for people who don’t always need maximum power, but also want to be able to shift into high gear at a moment’s notice.
Ryzen’s Balanced Power Plan has a bit of a mixed reception owing to its awkward history. However, it is still a contender even though it has a dodgy past.
Pros
- When you need to save on energy, but still be ready to pick up the pace
- Often better than Windows default and balance plans
- Uses your CPU cores better than the default Windows balanced plan
Cons
- Not always better than the default Windows balanced plan
- History of bugs (even though they are typically fixed quickly)
Ryzen Ultimate Power Plan
This is the pinnacle of Ryzen’s power plans. This gives your machine as much power as it needs the exact moment that it needs it. However, all this power does come at a cost.
Pros
- Works to reduce or eliminate micro latencies caused by hardware polling
- Offers the most power to your machine
- Will show notable improvement while running high-demand software
Cons
- Your system will go through considerable power drain
- Can kill batteries faster (if it’s a laptop)
- Not enabled on every device
- Gaming gets the least from this type of power optimization
How Do You Enable The Ryzen High Or Balanced Plan?
There is a fairly straightforward way to enable any of the Ryzen power plans on your PC. It turns out that they all live in your settings and you can freely toggle between them.
Here’s how you can quickly access the different Ryzen power plans.
- Open Settings
- Select System
- Click on Power & Sleep
- Select Additional Power Settings (see below)
- Select your power plan of choice
- Click on “Show Additional Plans” to see even more options
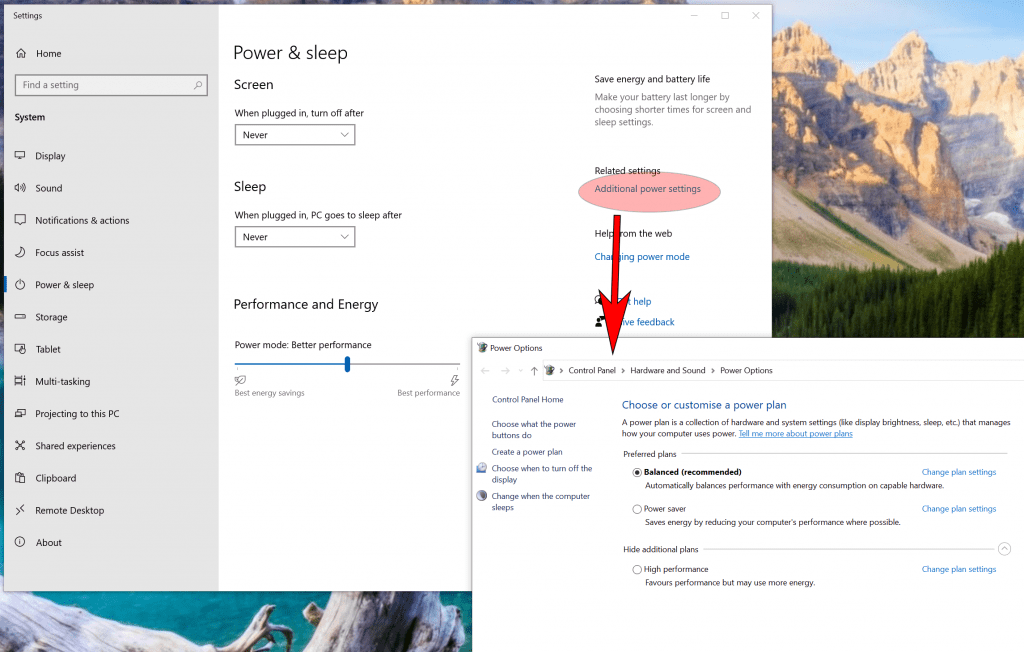
What should you do if the Ryzen power plans don’t appear in this settings menu? Well, all that means is that your hardware doesn’t have the right drivers to have these settings displayed.
Here’s how you can get Ryzen power plans to appear on your Windows PC.
- Head over to the AMD Drivers and Support web page
- Use the drop down menus to find your chipset
- Select your chipset
- Download the drivers for your chipset
- Run the ADM drive installer
- Make sure to check the box next to “AMD Ryzen Power Plan”
- Click Install
- Restart your computer
- Follow the regular steps for adjusting your Power Plan listed above
Why Isn’t The Ultimate Power Plan Appearing?
Not every device has Ultimate Power enabled by default. In fact, this setting was really only ever meant for high-end PCs. This means that you might not even see the Ultimate Power option when you try to change your power settings.
It’s mostly laptops and other battery-powered devices that don’t have access to the Ultimate Power Plan, but even some PC builds lack this option. However, there’s good news if you wanted to get the Ultimate Power Plan even though the option doesn’t appear.
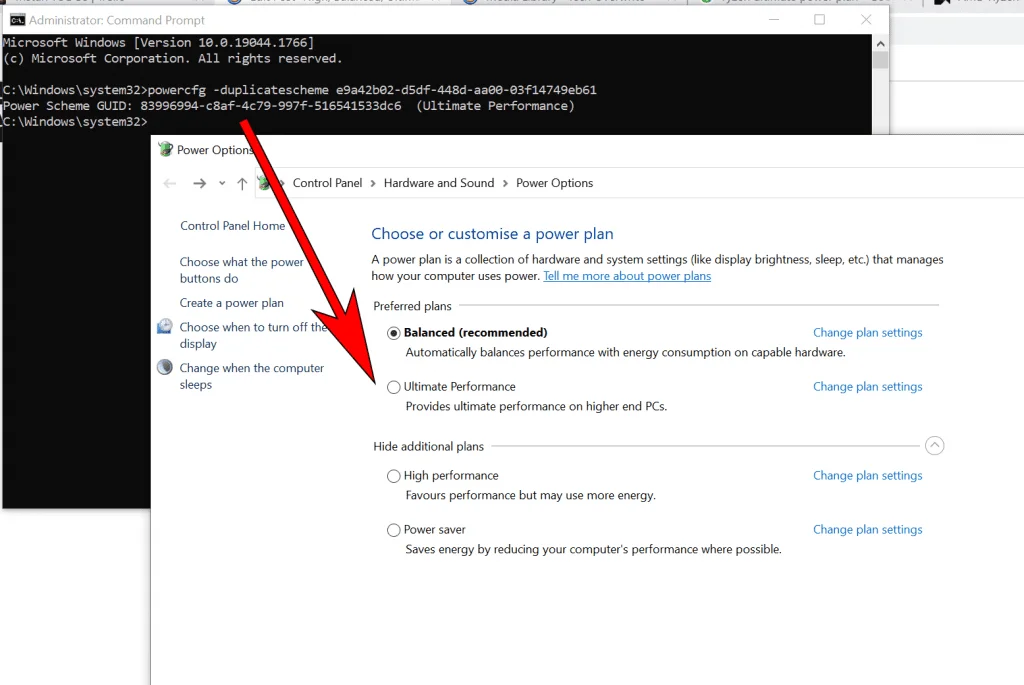
All you need to do is to open the command prompt and run it with administrator privileges. Then, you enter a quick command and your setting should appear the next time you open the menu.
Here’s how it’s done.
- Click Start
- Type “cmd” into the search bar
- Right click on Command Prompt
- Select “Run as Administrator” (see below)
- Copy, Paste, and Enter: powercfg -duplicatescheme e9a42b02-d5df-448d-aa00-03f14749eb61 (see below)
- Ultimate Power should now appear as an option
To run command prompt as administrator:
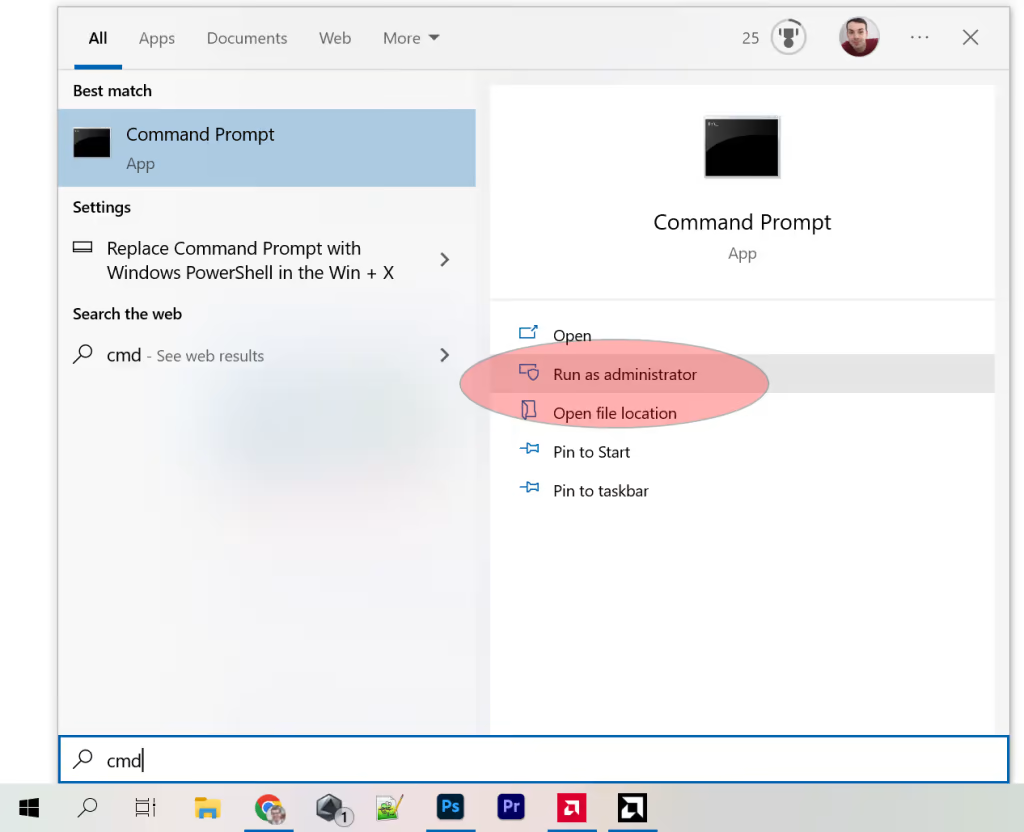
The exact command is below, which then adds the “Ultimate” power plan once you close and re-open the Windows “power plan” window:
AMD offers Ryzen Balanced power plan for Windows users to get the most performance from their Ryzen CPU. This power plan is easily won against Windows’ default Balanced plan.
Some say to get Ryzen Balanced plan, you need to install the latest CPU driver and Ryzen Master software. But I found this guide to be not quite right.
Turns out, there is one more thing to do and in this guide, I will show you the ‘last step’ to get Ryzen Balanced plan. This guide applies to Windows 10 but should be fine on Windows 7 and Windows 8 as well.
1. Go to AMD Drivers & Support page and select the chipset according to your motherboard, then click Submit. If you don’t know the motherboard version do you are using, you can find that on System Information.

2. Click Download on the AMD Chipset Drivers section.

3. Run the installer and wait for the hardware verification process.

4. Make sure “AMD Ryzen Power Plan” is checked, then click Install. It’s good to install all the features, but feel free to choose which one you need.

5. Wait for the installation process to finish.

6. Restart your computer. Make sure you have saved the ongoing tasks first.

7. Now, go to Settings.

8. Select System.
Radeon RX 5700 XT 8G Key Features
Please enable JavaScript

9. On Power & Sleep, click Additional power settings.

10. Select the AMD Ryzen Balanced option.

You can also select the AMD Ryzen High Performance plan which would improve the performance, especially for gaming. But know that power consumption will be higher too.
CPUDoc now features a custom dynamic power plan with ultra low power in standby:
These are the custom power plans I’ve made for my 5950x.
I have tested them as well on a 3800X and 5600G (not very thoroughly).
They should not interfere with PBO boost and provide same or very slightly lower performances but better thermals.
Please check before and after with AIDA64 memory benchmark; if there’s something wrong the latency could increase by 1 nanosecond.
Updated 2nd of December for Windows 11.CRITICAL FIX FOR Windows 10 & 11: no more USB voltage drop-outs
You need to have already the correct SOC and VDDG voltages to fix the USB drop-outs.
Also, if present (but I have never seen it as an option), you have to enable USB Selective Suspend in BIOS.
Renamed the custom «Ultimate Performance» to «Ultimate HighPower».
New naming scheme and introduction of Ultimate LowPower for Win10.
Installer Download
- Updated Intel Custom Plans
- Balanced LowPower, Snappy, High Performance are same, just changed naming schema
- Added Ultimate LowPower and Ultimate HighPower
Version V2:
ManniX_Custom_Power_Plans_V2.zip
Window 10:
The recommended for Performances is the Ultimate HighPower, followed by the Ultimate LowPower and Balanced Snappy (which is an in-between the Balanced and Ultimate).
The Balanced Snappy can be very satisfying for benchmarks, especially in ST performances.
All the profiles are maintaining the peak performances in GeekBench 5 for my 5950X.
The Balanced LowPower can reduce the idle power usage by 5-10W and the temperatures by 4-5° C.
Plus overall reduced temperatures and much lower spikes.
Real world usage is something different and of course Snappy and Ultimate will deliver better responsiveness and performances.
But Balanced LowPower is just a notch behind.
Too much effort to maintain the PP versions; use QuickCPU to change the setting by yourself if you need it
Which are the specific conditions or use cases when it could be better to use the PP versions?
- Terrible binning of the non best cores
- Terrible binning of the 2nd CCD
- Static OC with 2nd CCD at a much lower frequency than the 1st
- Very specific competitive benchmarking
This is the effect of using the PP version with background threads:
While with the non PP version:
In practice nothing will scheduled on the 2nd CCD unless needed.
With 1 CCD processors everything will be scheduled on the best processors and nothing on the lower CPPC Perf cores.
This is because Windows Scheduler is considering a Ryzen Processor as an heterogenous architecture, despite not being one.
All the lower perf cores will be considered as Efficient and all higher perf as Performant.
The previous custom power plans where fixing the Scheduler issues forcing the policy for heterogeneous to prefer Performant Processors and prefer Efficient Processors for background threads.
With the latest Scheduler this is not needed anymore; now it’s finally doing it with the Automatic settings.
This means not anymore hacksaw temperature graphs and spikes.
There are some cases as mentioned above where it could be more convenient to force the background task policy to PP.
In general it’s not recommended; for a very small single thread performance increase in normal usage the temperature goes up a lot and the spikes are huge.
With some workloads, mainly benchmarks, could be useful because often the Scheduler is just mistaken an spawns an heavy thread on an Efficient Processor.
The EP is not only slower but once the Scheduler realizes the mistake it has to move it to a PP causing delay and additional loss of performances.
Tip: best would be to use Process Lasso to switch specific applications to use the Ultimate HighPower or Snappy profile only when needed. Or just use CPUDoc.
Windows 11:
If you are using Windows 11 and care about performance and latency use the Ultimate HighPower or Ultimate LowPower plans.
There’s a bug in W11 power management which is causing all plans except Ultimate to have increased and spotty latency and low boost peak clocks.
I have received some reports about W11 plans being not much responsive also on Intel, therefore I guess it’s not only related to AMD.
You can verify testing with AIDA64 memory latency test.
AIDA does not work really well with W11, it will give you very often spotty and inconsistent results.
Test only at fresh boot, close all the open tabs in Edge before rebooting or else they’ll be loaded in background.
Don’t run the whole benchmark with Cache & Memory, double click only on the Latency box in Memory row.
The first run should give you the peak boost clock, not always though. Mine went to up to 5125 MHz for the first time while it was stuck to 5075 MHz before.
The latency on the first run is usually bogus; wait 10 seconds, repeat, wait, repeat, etc.
You should get a much better latency on average, more consistent between runs, and some much lower scores than with any other plan.
I managed to get a 54.7ns, which is only slightly above the 54.4ns result from Win10, while with any other plan I couldn’t go below 55.2ns (with very often 57-58-61-66ns).
Performance delta between Ultimate and High Performance plan can be seen also in Sandra Inter-Thread Efficiency test.
It’s quite hard to compare as the results are very very inconsistent over runs thanks to Windows 11.
Anyway you should see an average improvement of 0.5-1.0ns on Inter-Thread latency and quite some substantial bandwidth improvements with specific data set sizes.
The most relevant metric seems to be the «Aggregate Inter-Thread Bandwidth» under «Performance vs. Speed» which improved for me from around 35 to 45 MB/s/MHz
The Ultimate LowPower is excellent; better average power consumption with a small edge in idle but still same great latency and boost and same benchmark scores as the full Ultimate.
The Ultimate HighPower is as expected with minimal power savings, very consistent results.
The Balanced LowPower is really only recommended if you want maximum power savings and lower temperatures.
The latency and boost clock drop is quite substantial and the performances lower.
It does have the power slider but I couldn’t see a very big difference in power consumption between the settings.
The difference with Ultimate LowPower seems so small that I would recommend to use it instead of the Balanced LowPower.
Here’s a performance comparison between the standard Windows High Performance & Ultimate Performance plans vs my custom Ultimate Performance V2 and Ultimate LowPower V2:
As you can see the Ultimate Performance plan is trashing High Performance and all the other standard plans by a big margin.
Ultimate Performance V2 has a small edge vs the standard Ultimate plan and LowPower is just below it.
The standard Power Plans in Windows 11 are pretty good. With some exceptions of course.
Microsoft as usual made one step forward and two backwards.
The Scheduler now works pretty well in terms of performances and core idling, impressive improvements versus the previous releases and Win10.
This is mainly because all the profiles are using Autonomous mode and it can finally properly drive a Ryzen CPU.
For instance the vCore is finally going up only when needed and the performances really great.
What is very disappointing is that basically many of the plan settings are completely disregarded.
Plus while running in Autonomous mode is worse, the Scheduler is disregarding even more.
The Autonomous mode in Windows 11 is a big improvement but it’s not perfect.
Temperatures and spikes are quite horrible.
That’s why I’ve created only one LowPower custom plan.
Unless you have a problem with the temperatures, just use the Balanced with slider in the middle or max.
Or the High Performance or the Ultimate.
They all are configured mostly the same and deliver mostly the same experience…
Maybe the High Performance has a drop of performances more but it’s really one drop in the ocean.
The LowPower will deliver 2-3° C less on idle, same power consumption as Balanced (Why? How? What…) and at least 4-6 °C less during load.
Temperatures spikes are quite decent with LowPower, absolutely awful for all the standard plans.
Microsoft has definitely something to fix there…
Just moving the mouse from one screen to another causes the CPU temperature to jump to 45-48 °C with the Balanced plan.
With the LowPower it’s slowly going up to 40-41 °C.
This is achieved mainly disabling the Autonomous mode, plus scheduling tweaking that actually works once not in Autonomous.
Of course the price to pay it’s measurable lower performances, about 10-20p ST and 50-60p MT in GeekBench 5.
All Windows 11 Power Plans have prefer PP for background threads.
Forcing otherwise is hardly taken into consideration by the Scheduler.
Let me know if you experience issues.
Custom plans for Windows 11
AMD Ryzen™ Ultimate LowPower
For Windows 11
Modified out of the Ultimate Performance plan so it doesn’t the Power Slider.
It’s a performance oriented plan with excellent latency but still has a lot of performance saving features enabled with great savings and lower temperatures.
Highly recommend as daily driver.
NEW 02/12/2022 v4:
- Fixed USB voltage drop-outs
- New naming-scheme to differentiate between Win10 & Win11
Version v4:
AMD Ryzen™ Ultimate LowPower 11-v4-Backup-2022.02.12-17.49.08.pow
NEW 02/12/2022 v3:
- New heterogeneous policy; boost FPS in gaming
Version v3:
Version v2:
Version v1:
AMD Ryzen™ Ultimate HighPower
For Windows 11
Modified out of the Ultimate Performance plan so it doesn’t the Power Slider.
It’s a performance oriented plan with excellent latency, almost no compromise but still delivers good idle power consumption and low temperatures.
Recommend as daily driver if you want always the max and don’t care about power savings.
NEW 02/12/2022 v4:
- Fixed USB voltage drop-outs
- New naming-scheme to differentiate between Win10 & Win11
- Fixed gaming performances, now comparable to LowPower
- Renamed to HighPower to differentiate from the standard plan
Version v4:
AMD Ryzen™ Ultimate HighPower 11-v4-Backup-2022.02.12-17.49.15.pow
NEW 02/12/2022 v3:
- New heterogeneous policy; boost FPS in gaming
Version v3:
Version v2:
Version v1:
AMD Ryzen™ Balanced LowPower
For Windows 11
Modified out of the Balanced plan so it has the Power Slider.
It’s a nice compromise between performance and power consumption in the middle setting for the slider.
It does have increased latency, lower boost clock and performances vs the Ultimate plans.
Not recommended unless you want to squeeze every possible watt in energy saving.
NEW 02/12/2022 v2:
- Fixed USB voltage drop-outs
- New naming-scheme to differentiate between Win10 & Win11
- Fixed gaming performances, now comparable to LowPower
- Updated with Heterogeneous policies same as the other plans
Version v2:
AMD Ryzen™ Balanced LowPower 11-v2-Backup-2022.02.12-17.48.54.pow
Custom plans for Windows 10
AMD Ryzen™ Ultimate LowPower
For Windows 10
Modified out of the Ultimate Performance plan so it doesn’t the Power Slider.
It’s a performance oriented plan with excellent latency but still has a lot of performance saving features enabled with great savings and lower temperatures.
Highly recommend as daily driver.
NEW 02/12/2022 v1:
- Fixed USB voltage drop-outs
- New naming-scheme to differentiate between Win10 & Win11
Version v1:
AMD Ryzen™ Ultimate LowPower 10-v1-Backup-2022.02.12-17.03.34.pow
AMD Ryzen™ Balanced LowPower
For Windows 10
Modified out of the Balanced plan so it has the Power Slider.
It’s a nice compromise between performance and power consumption in the middle setting for the slider.
Quite reactive to user input; should behave same as Balanced or better.
Slider to the max will keep the vCore high and will be a bit more reactive, in the middle vCore will drop down in idle.
NEW 02/12/2022 v11:
- Fixed USB voltage drop-outs
- New naming-scheme to differentiate between Win10 & Win11
Version v11:
NEW 25/10/2022 v10:
- Adapted for the latest Windows 10 release
Version v10:
Version v10 (PP):
Version v8:
Version v7:
Version v6:
Version v5:
Version v4:
Version v3:
AMD Ryzen™ Ultimate HighPower
For Windows 10
Modified out of the Ultimate Performance plan so it doesn’t have the Power Slider.
It’s an almost no-compromise for performances, slight increased power consumption but yet nice temperatures in idle.
NEW 02/12/2022 v7:
- Fixed USB voltage drop-outs
- New naming-scheme to differentiate between Win10 & Win11
- Fixed gaming performances, now comparable to LowPower
- Renamed to HighPower to differentiate from the standard plan
Version v7:
AMD Ryzen™ Ultimate HighPower 10-v7-Backup-2022.02.12-17.09.05.pow
NEW 25/10/2022 v6:
- Adapted for the latest Windows 10 release
Version v6:
Version v6 (PP):
Version v5:
Version v4:
Version v3:
Version v2:
AMD Ryzen™ Balanced Snappy
For Windows 10
Modified out of the Balanced plan so it has the Power Slider.
It’s a more power hungry profile focused on responsiveness with autonomous mode enabled.
Less spikey than the Ultimate, sometimes with better ST performances.
Best suited for Audio/Video and Professional, lower IPC/DPC latency.
NEW 02/12/2022 v3:
- Fixed USB voltage drop-outs
- New naming-scheme to differentiate between Win10 & Win11
- Fixed gaming performances, now comparable to LowPower
Version v3:
AMD Ryzen™ Balanced Snappy 10-v3-Backup-2022.02.12-17.04.03.pow
NEW 25/10/2022 v2:
- Adapted for the latest Windows 10 release
Version v2:
Version v2 (PP):
Version v1:
How to install
Download the POW file.
Start a Command prompt with Administrative privilege (search for command prompt in start menu).
Import the plan with «powercfg -import filename.pow»:
Replace the directory name as needed.
Tools
QuickCPU
Highly recommended if you want to make your own customizations or compare with other profiles
First versions (outdated):
The first one is modified out of the Balanced profile so it has the Power Slider.
It’s a nice compromise between performance and power consumption in the middle setting for the slider.
Min state on my 5950x: 2200 MHz and 0.9V
The second one is modified out of the Ultimate Power profile so it doesn’t have the Power Slider.
It’s a no-compromise for performances, slight increased power consumption but yet nice temperatures in idle.
Min state on my 5950x: 2880 MHz and 0.95V