Download PC Repair Tool to quickly find & fix Windows errors automatically
In this post, we will discuss what are Windows 10 Features on Demand and why some users (specifically Windows 10 systems managed via WSUS) might be unable to download and install FOD (Features on Demand).
Windows 10 Features On Demand are additional feature options available through Windows Update. This download allows organizations to pre-configure Windows 10 installation software with these features prior to deployment. This download can also be used to install features from local media.
Features on Demand (FODs) are Windows feature packages that can be added at any time. Common features include language resources like handwriting recognition or other features like the .NET Framework (.NetFx3). When Windows 10 or Windows Server needs a new feature, it can request the feature package from Windows Update.
Unlike previous Feature Packs, Features on Demand v2 can apply to multiple Windows builds and can be added using DISM without knowing the build number. Always use Features on Demand that match the architecture of the operating system. Adding Features on Demand of the wrong architecture might not return an error immediately, but will likely cause functionality issues in the operating system.
Windows has two different types of Features on Demand:
- FODs without satellite packages: FODs with all language resources packaged into the same package. These FODs are distributed as a single .cab file and can be added using either DISM /Add-Capability or /Add-Package.
- FODs with satellite packages: When you install this type of FOD, only the packages that apply to the Windows image are installed, which reduces disk footprint. These FODs are distributed as a set of several .cab files, but are installed by specifying a single /capabilityname. They can only be added using DISM /Add-Capability (and not /Add-Package).
Windows Features on Demand not installing
Starting with Windows 10 version 1809, FOD (Features on Demand) and language packs can only be installed from Windows Update and not via WSUS.
If you cannot install Windows 10 Features on Demand, you’ll need to configure the Group Policy to go directly to Windows Update to download and install FOD.
Press Windows key + R, type gpedit.msc, hit Enter to launch the Group Policy editor.
Navigate to Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > System.
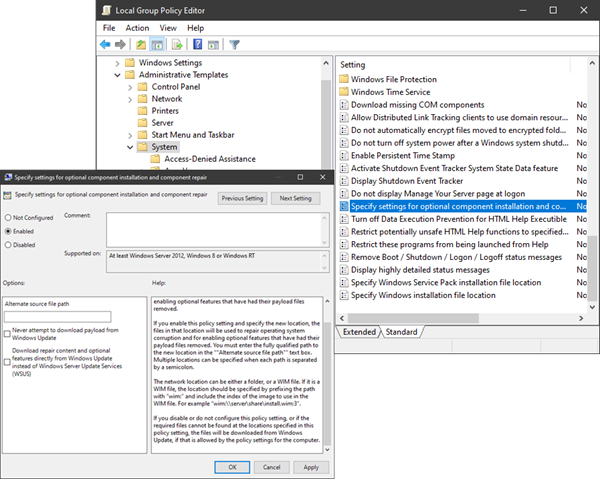
Scroll down on the right pane, locate and double-click Specify settings for optional component installation and component repair.
This policy setting specifies the network locations that will be used for the repair of operating system corruption and for enabling optional features that have had their payload files removed.
If you enable this policy setting and specify the new location, the files in that location will be used to repair operating system corruption and for enabling optional features that have had their payload files removed. You must enter the fully qualified path to the new location in the “”Alternate source file path”” text box. Multiple locations can be specified when each path is separated by a semicolon.
The network location can be either a folder, or a WIM file. If it is a WIM file, the location should be specified by prefixing the path with “wim:” and include the index of the image to use in the WIM file. For example “wim:\servershareinstall.wim:3”.
If you disable or do not configure this policy setting, or if the required files cannot be found at the locations specified in this policy setting, the files will be downloaded from Windows Update, if that is allowed by the policy settings for the computer.
Click the radio button for Enabled
Also, set the following:
- Alternate source file path: <BLANK>
- Never attempt to download payload from Windows Update: Uncheck
- Download repair content and optional features directly from Windows Update instead of Windows Server Update Services (WSUS): Check
Click Apply > OK.
Windows 10 v1809 and later users should now be able to download and install Features on Demand.
Obinna Onwusobalu has studied Information & Communication Technology and is a keen follower of the Windows ecosystem. He has been a Windows Insider MVP (2020). He runs a computer software clinic.
Содержание
- Overview
- Types of Features on Demand
- Adding or removing Features on Demand
- Using DISM /add-package to add or remove FODs
- Using DISM /add-capability to add or remove FODs
- Работаем с Windows Features
- Управление Features on Demand (FOD)
- Установка и переустановка пакетов языков (Language Interface Packs, LIP)
- Windows XP
- Свежие записи
- Топ записей
- Архивы
- Подписка на email
- Windows 10 — Features on Demand
Overview
Features on Demand (FODs) are Windows feature packages that can be added at any time. Common features include language resources like handwriting recognition or other features like the .NET Framework (.NetFx3). When Windows 10 or Windows Server needs a new feature, it can request the feature package from Windows Update.
You can also preinstall FODs so they’re ready if a user needs them. FODs are distributed as .cab files on the Feature on Demand ISO and you can use DISM to add a FOD to a Windows image. If you’re using the FOD ISO to preinstall FODs, make sure you’re using the FOD ISO that matches your Windows image version.
Add language packs, FODs, and apps, in that order, prior to installing an update. If you add an update prior to adding language packs, FODs, and apps you’ll have to reinstall the update.
Types of Features on Demand
Starting with Windows 10, version 1809 and Windows Server 2019, Windows has two different types of Features on Demand:
FODs without satellite packages: FODs with all language resources packaged into the same package. These FODs are distributed as a single .cab file.
They can be added using either DISM /Add-Capability or /Add-Package .
FODs with satellite packages: Language-neutral FODs that have language and/or architecture resources in separate packages (satellites). When you install this type of FOD, only the packages that apply to the Windows image are installed, which reduces disk footprint. These FODs are distributed as a set of several .cab files, but are installed by specifying a single /capabilityname . These are new for Windows 10, version 1809.
They can only be added using DISM /Add-Capability (and not /Add-Package ).
FODs with satellites require a well-formed FOD repository. This can either be the full FOD repository on the ISO, or a custom repository created with DISM /export-source . They cannot be added by pointing to a directory with a handful of FOD files hand-copied from the repository, because DISM requires additional metadata to make the right connections.
See Available Features on demand for more information about which FODs have satellites. Language FODs don’t have satellites.
While you can add non-satellite FODs using /add-package , we recommend adding all FODs with /add-capability because you can use it to add both satellite and non-satellite FODs.
Adding or removing Features on Demand
Using DISM /add-package to add or remove FODs
You can add non-satellite Features on demand to a Windows image with DISM /add-package . The FODs that you can add with /add-package include the language FODs, the FODs that come preinstalled with Windows, and the FODs that we recommend for preinstallation.
OEMs can generally add FODs to their Windows images using DISM /add-package , unless they need to preinstall a FOD that has satellites.
| Command | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| /add-package | Adds a package, including a FOD .cab to an image. add-package can only be used to add FODs that don’t have satellite packages. | DISM.exe /image:C:mountWindows /add-package /packagepath:E:Microsoft-Windows-Holographic-Desktop-FOD-Package |
.cab
/Get-Packages
Get a list of all packages in an image.
DISM /image:C:MountWindows /get-packages
/Get-Packageinfo
Get information of a package in an image.
DISM /image:C:mountWindows /get-packageInfo /packagename:Microsoft-Windows-Xps-Xps-Viewer-Opt-Package
10.0.17134.1000
/Remove-Package
Removes a package from an image. Note: Don’t remove a package that other packages depend on. For example, if you have the French handwriting and basic packages installed, don’t remove the basic package.
DISM.exe /image:C:mountWindows /Remove-Package /PackageName:Microsoft.Windows.Calc.Demo
Using DISM /add-capability to add or remove FODs
You can also install FODs with DISM /add-Capability . You have to use /add-capability to preinstall satellite FODs. If you’re preinstalling a FOD onto an offline image, use the /source option to tell Windows where to find the FOD installation files. The /source could be a FOD repository or a mounted FOD ISO. You can use multiple /source arguments in a command.
If you’re adding a FOD to an online image, /add-capability downloads features from Windows Update and adds them to the image. If you don’t want to install from Windows Update, you can use /LimitAccess , which tells DISM to not check Windows Update or Windows Server Update Services for the capability source files.
- Use the /online option to add the capability to your PC.
- Use /Image: with the /source option to add the capability to a mounted Windows image.
| Command | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| /add-capability |
Adds a capability to an image.
For packages with dependencies this also pulls dependent packages. For example, if you add the Speech package, you’ll also get the Text-to-speech and Basic packages in addition to Speech.
DISM looks for source files in the following locations:
- If /Source is specified, DISM looks in the specified locations first.
- If /Source is not specified, or if the source files are not found in the specified locations, DISM checks the locations specified by group policy.
- If the files still aren’t found, and if DISM is running against an online image, and if /LimitAccess is not specified, it looks for the files on Windows Update.
DISM.exe /image:C:mountWindows /add-capability /CapabilityName:Language.Basic
DISM.exe /Online /add-capability /CapabilityName:Language.Basic
0.0.1.0
/Get-Capabilities
Get capabilities in the image.
DISM /image:C:MountWindows /Get-Capabilities
/Get-CapabilityInfo
Get information of a capability in the image.
DISM /image:C:mountWindows /Get-CapabilityInfo /CapabilityName:Language.Basic
0.0.1.0
/Remove-Capability
Removes a capability from an image.
Note: You cannot remove a capability that other packages depend on. For example, if you have the French handwriting and basic capabilities installed, you can’t remove the basic capability.
DISM.exe /image:C:mountWindows /Remove-Capability /CapabilityName:Language.Basic
To see all available DISM commands for capabilities, see DISM Capabilities Package Servicing Command-Line Options.
Как известно, Windows 10 отличается набором компонентов от предыдущих версий операционных систем Windows. Зачастую требуется их включить или выключить, чтобы они не потребляли системные ресурсы, да и просто не мешали. В этой статье мы рассмотрим как это сделать быстрее и эффективнее.
Начнем с того, что существует два основных способа работы с компонентами (они еще называются features) — утилита DISM и командлеты Powershell. И то и другое встроено в Windows 10, в отличие от Windows 7, где dism можно было добавить или установив пакет Windows ADK, или руками скопировав dism.exe с другого компьютера.
Сразу отмечу, что утилиту dism и среду powershell для работы с системой необходимо запускать от имени администратора, даже если ваш аккаунт уже находится в группе локальных админов. Итак, вы или находите cmd или windows powershell в меню и, кликнув правой кнопкой мышки, выбираете «Запуск от имени администратора».
В Windows 10 есть понятие Features и Capabilities. Первое — это привычные нам компоненты, которые можно найти в Панели управления -> Программы и компоненты -> Включение и отключение компонентов Windows. То есть это встраиваемые модули, которые выполняют определенный сервисный функционал.
Capabilities — это дополнительные возможности, которые расширяют возможности интерфейса и увеличивают удобство пользователя. Среди них — Language packs, наборы шрифтов. Да, Microsoft удалил часть нестандартных шрифтов, которые теперь вынесены в опциональные компоненты. Скачать эти компоненты можно в виде ISO файла с сайта Volume Licensing Service Center или напрямую через Internet и графический интерфейс Windows. Такую концепцию Microsoft назвала Features on Demand (FOD). Их в более ранних версия Windows не было.
Работаем с Windows Features
Итак, список установленных компонентов можно посмотреть командой
Dism /online /Get-Features
Вот как в Powershell можно получить список всех компонентов командлетами Get-WindowsFeature (для Windows Server) или Get-WindowsOptionalFeature (Windows 10):
Чтобы получить список отключенных компонентов, введите:
Get-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online | ? state -eq ‘disabled’ | select featurename
Этот список также можно вывести в файл (для windows Server):
Get-WindowsFeature | Where-Object <$_.Installed -match “True”>| Select-Object -Property Name | Out-File C:TempWindowsFeatures.txt
Посмотрев список названий и их состояние, можно использовать эти названия для того, чтобы компоненты включить или выключить:
Dism /online /Enable-Feature /FeatureName:TFTP /All
ключ /All позволяет включить также все дочерние компоненты;
Установка компонентов через Powershell выполняется командой Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature.
Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName RSATClient-Roles-AD-Powershell
Параметр -All включает все дочерние компоненты.
Dism /online /Disable-Feature /FeatureName:TFTP
Аналогично, через Powershell это можно сделать командой Disable-Windowsoptionalfeature -online -featureName [feature name].
Обратите внимание, некоторые фичи имеют разные названия в Windows 7 и Windows 10. Например, RSAT в Windows 7 — это RemoteServerAdministrationTools, а в Windows 10 — RSATclient.
Управление Features on Demand (FOD)
Если вы устанавливаете их через графический интерфейс, то вам необходимо пройти “System –> App & features –> Manage optional features” и нажать знак + напротив необходимых компонентов.
Чтобы сделать это автоматизированно через командную строку, наберите чтобы получить список доступных компонентов:
DISM.EXE /Online /Get-Capabilities
или на Powershell:
Как и прежде, запомните название необходимых вам компонентов, чтобы включить их командой (на примере .Net Framework 3):
DISM.EXE /Online /Add-Capability /CapabilityName:NetFx3
или на Powershell:
Add-WindowsCapability –Online -Name NetFx3
Если же у вас нет доступа в Интернет, то есть выход. Итак, вы скачиваете ISO образ диска с FOD компонентами с сайта Volume Licensing Service Center. Файлы будут разные для разных релизов Windows 10 — 1511, 1607, 1703, 1709. Важно помнить, что компоненты одного релиза не подходят к другому. Если вы сделаете in-place upgrade (установка одного релиза поверх другого через обновление), то несовместимые установленные компоненты будут удалены без вашего желания! Да, Microsoft удаляет то, что считает несовместимым при обновлении.
Так вот, ISO файл содержит набор неизвестных и сложных для понимания файлов с расширением cab. Вот чудесный файлик на сайта Microsoft, который обясняет назначение каждого файла. Итак, существуют следующие типы FOD:
- Microsoft-Windows-LanguageFeatures-Basic — проверка правописания для различных языков и раскладок клавиатуры;
- Microsoft-Windows-LanguageFeatures-Fonts — национальные шрифты, например, азиатские
- Microsoft-Windows-LanguageFeatures-OCR — средства для распознавания шрифтов
- Microsoft-Windows-LanguageFeatures-Handwriting — средства для распознавания рукописного ввода
- Microsoft-Windows-LanguageFeatures-TextToSpeech — средства преобразования текста в голос, используемые подсказчиком Cortana
- Microsoft-Windows-LanguageFeatures-Speech — распознавание голоса
- Microsoft-Windows-InternationalFeatures — пакеты национальных настроек, например, для Тайваня
Итак, для добавления таких FOD компонентов, используйте команды вида (замените имя компонента):
Dism /Online /Add-Capability /CapabilityName:Language.Basic
Для удаления FOD:
Dism /Online /Remove-Capability /CapabilityName:Language.Basic
Установка и переустановка пакетов языков (Language Interface Packs, LIP)
Язык интерфейса Windows можно поменять, установив так называемые LIP. ранее они назывались MUI (Multi user interface). Файлы LIP выглядят так: Microsoft-Windows-Client-Language-Pack_x64_es-es.cab для испанского языка. Выглядеть установка будет примерно так:
Dism /Add-Package /online /PackagePath:»C:LanguagesMicrosoft-Windows-Client-Language-Pack_x64_fr-fr.cab»
Dism /Remove-Package /online /PackageName:Microsoft-Windows-Client-LanguagePack-Package
В следующей статье мы поговорим как с помощью DISM и Powershell управлять так называемыми Modern-приложениями AppX.
Windows XP
Свежие записи
Топ записей
Архивы
- Январь 2020 (2)
- Декабрь 2019 (1)
- Ноябрь 2019 (4)
- Октябрь 2019 (2)
- Сентябрь 2019 (5)
- Июль 2019 (2)
- Май 2019 (1)
- Апрель 2019 (3)
- Март 2019 (5)
- Февраль 2019 (5)
- Январь 2019 (3)
- Декабрь 2018 (1)
- Ноябрь 2018 (3)
- Октябрь 2018 (1)
- Сентябрь 2018 (1)
- Август 2018 (1)
- Июль 2018 (3)
- Июнь 2018 (4)
- Май 2018 (3)
- Апрель 2018 (4)
- Март 2018 (1)
- Февраль 2018 (3)
- Январь 2018 (4)
- Декабрь 2017 (8)
- Ноябрь 2017 (3)
- Октябрь 2017 (2)
- Сентябрь 2017 (3)
- Август 2017 (1)
- Июль 2017 (5)
- Июнь 2017 (2)
- Май 2017 (1)
- Апрель 2017 (6)
- Март 2017 (3)
- Февраль 2017 (5)
- Январь 2017 (1)
- Декабрь 2016 (4)
- Ноябрь 2016 (3)
- Октябрь 2016 (5)
- Сентябрь 2016 (4)
- Август 2016 (6)
- Июль 2016 (5)
- Июнь 2016 (6)
- Май 2016 (8)
- Апрель 2016 (8)
- Март 2016 (7)
- Февраль 2016 (8)
- Январь 2016 (5)
- Декабрь 2015 (4)
- Ноябрь 2015 (6)
- Октябрь 2015 (14)
- Сентябрь 2015 (7)
- Август 2015 (6)
- Июль 2015 (3)
- Июнь 2015 (4)
- Май 2015 (8)
- Апрель 2015 (5)
- Март 2015 (10)
- Февраль 2015 (7)
- Январь 2015 (6)
- Декабрь 2014 (7)
- Ноябрь 2014 (14)
- Октябрь 2014 (8)
- Сентябрь 2014 (9)
- Август 2014 (8)
- Июль 2014 (6)
- Июнь 2014 (4)
- Май 2014 (8)
- Апрель 2014 (6)
- Март 2014 (7)
- Февраль 2014 (5)
- Январь 2014 (9)
- Декабрь 2013 (2)
- Ноябрь 2013 (11)
- Октябрь 2013 (10)
- Сентябрь 2013 (9)
- Август 2013 (4)
- Июль 2013 (4)
- Июнь 2013 (3)
- Апрель 2013 (6)
- Март 2013 (2)
- Февраль 2013 (1)
- Январь 2013 (4)
- Декабрь 2012 (3)
- Ноябрь 2012 (4)
- Октябрь 2012 (6)
- Сентябрь 2012 (7)
- Август 2012 (10)
- Июль 2012 (9)
- Июнь 2012 (6)
- Май 2012 (7)
- Апрель 2012 (7)
- Март 2012 (5)
- Февраль 2012 (7)
- Январь 2012 (6)
- Декабрь 2011 (4)
- Ноябрь 2011 (2)
- Сентябрь 2011 (11)
- Август 2011 (8)
- Июль 2011 (5)
- Июнь 2011 (3)
- Май 2011 (1)
- Апрель 2011 (3)
- Март 2011 (4)
- Февраль 2011 (1)
- Январь 2011 (2)
- Декабрь 2010 (4)
- Ноябрь 2010 (1)
- Сентябрь 2010 (2)
- Июль 2010 (3)
- Май 2010 (3)
- Апрель 2010 (1)
- Март 2010 (3)
- Декабрь 2009 (1)
- Ноябрь 2009 (2)
- Октябрь 2009 (11)
- Сентябрь 2009 (3)
- Август 2009 (5)
- Июль 2009 (5)
Подписка на email
Windows 10 — Features on Demand
Когда скачивал дистрибутив Windows 10 с сайта Microsoft Volume Licensing Service Center (VLSC), то обратил внимание, что есть дополнительный ISO файл en_windows_10_features_on_demand_x64_dvd_6846440_.iso.
По факту там содержались cab файлы без всяких комментариев.
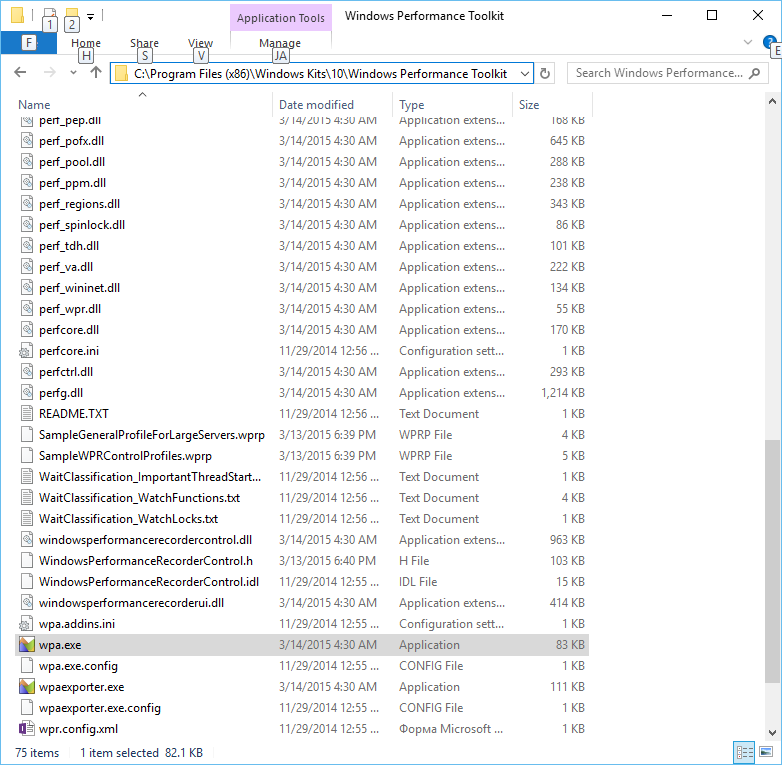
Среди них находился файл с именем Microsoft-Windows-Performance-WPT-Package.cab, которое наводило на мысль, что теперь не нужно качать и устанавливать Windows SDK, а можно сразу установить Windows Performance Toolkit.
Оказалось это действительно так:
Остальные файлы в ISO это в основном дополнения к Language Packs. Сам языковой пакет только меняет интерфейс. Если вы хотите проверку правописания, распознавание голоса, рукописного письма и другие возможности, то можете поставить дополнительные пакеты. Назначение пакетов в большинстве случаев ясно из названия.
-
Partition Wizard
-
Partition Manager
- How to Add and Remove Win 10 Features on Demand?
How to Add and Remove Win 10 Features on Demand? [Partition Manager]
By Vicky | Follow |
Last Updated December 01, 2020
Have you ever heard Windows 10 Features on Demand (FOD)? And do you know how to add and remove it? In this post, MiniTool shows you what FOD is, how to use it, and something else about it. Now, let’s check them one by one.
Features on Demand (FOD) is the Windows features package that can be added at any time. The package includes language resources like handwriting recognition or other features like the .NET Framework.
Varying from previous Features Packs, FOD V2 can be applied to multiple Windows builds and can be added using DISM without knowing the build number. But note that you should always use Features on Demand that match the architecture of the operating system because a wrong adding will likely cause functionality issues in the operating system.
There are two different types of Features on Demand when Windows 10, version 1809 and Windows Server 2019 come out.
- FODs without satellite packages: FODs with all language resources are packaged into the same package. These FODs are distributed as a single.cab file and can be added using DISM/Add-Capability or Add-package.
- FODs with satellite packages: Only the package that applies to the Windows image is installed if you install this type of FOD. This can reduce disk footprint. This type of FODs is distributed as a set of several.cab files, but are installed by specifying a single /capabilityname. Another difference from the first type is that these FODs can only be added using DISM /Add-Capability.
Add or Remove Windows 10 FOD
As the above content shows, you can use some DISM commands to add FODs without satellite packages and FODs with satellite packages. Now, let’s see more information about how to manage FOD.
Tip: You can just use the add-capability command to add both satellite and non-satellite FODs.
Use DISM /Add-Package
To just add FODs without satellite packages to a Windows image, you can use the DISM /add-package command. Now, let’s see the specific commands to add or remove Windows 10 Features on Demand.
/add-package: Adds a package that includes a FOD .cab to an image. Example: DISM.exe/image:C:MountWindows/add-package/packagepath:E:Microsoft-Holographic-Destop-FOD-package~31bf3856ad364e35~amd64~~.cab
/get-package: Get a list of all packages in image. Example: DISM /image:CMountWindows/get-package
/get-packageinfo: Get information of a package in an image. Example: DISM/image:C:MountWindows/get-packageInfo/packagename:Microsoft-Windpws-Xps -Xps-Viewer-Opt-Package~31bf3856ad364e35~amd64~~10.0.17134.1000
/remove-package: Removes a package from an image. Example: DISM.exe/image:C:Windows/remove-package/packagename:Microsoft.Windows.Calc.Demo~6595b6144ccf1df~x86~en~1.0.0.0
Use DISM/Add-Capability
The second choice to add or remove Windows 10 Features on Demand is using DISM /Add-Capability. This DISM command not only helps you add the non-satellite FODs but also satellite FODs.
But there are some things you need to note that are:
- Use the /source command to tell Windows where to find FOD installation files if you are preinstalling a FOD onto an offline image.
- Use /LimitAccess if you do not want to install FOD from Windows Update. This tells DISM to not check Windows Update or Windows Server Update Services for the capability source files.
- Use /Add-Capability to download features from Windows Update and add them to an online image if you are adding a FOD to the image.
Now, let’s see the specific commands.
- /Add-Capability: Adds a capability to an image. Example: DISM.exe/image:C:MountWindows/add-capability/capabilityname:Language.Basic~~~en-US~0.0.1.0 /Source:E:
- /Get-Capabilities: Gets capabilities un the image. Example: DISM/image:C:MountWindwos/get-capabilities
- /Get-CapabilityInfo: Gets information of a capability in the image. Example: DISM/image:C:MountWindows/get-capabilityInfo/CapabilityName:Lamguage.Basic~~~en-US~0.0.1.0
- /Remove-Capability: Removes a capability from an image (Note that you cannot remove a capability that other packages depend). Example: DISM.exe/image:C:MountWindwos/remove-capability/CapabilityName:Language.Basic~~~en-US~0.0.1.0
About The Author
Position: Columnist
Vicky is a website editor who has been writing tech articles since she was graduated from university. Most of her articles talk about Windows PC and hard disk issues. Some of her articles also touch on YouTube usage and issues.
During her spare time, she likes to spend time reading, watching videos, and sitting on her Yoga mat to relax.
Содержание
- Download Windows 10 1809 1903 RSAT Install Using New Windows FoD
- What are Windows 10 Features on Demand?
- Download Windows 10 1809 1903 RSAT Install Using New Windows FoD
- Use PowerShell to Download Windows 10 1809 1903 RSAT FoD and Install
- Wrapping Up
- Windows 10 features on demand version 1903
- Question
- All replies
- Установка Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT) в Windows 10 v1903 в Offline-режиме
- What’s new in Windows 10, version 1903 for IT Pros
- Deployment
- Windows Autopilot
- Windows 10 Subscription Activation
- SetupDiag
- Reserved storage
- Servicing
- Security
- Windows Information Protection
- Security configuration framework
- Security baseline for Windows 10 and Windows Server
- Intune security baselines
- Microsoft Defender for Endpoint
- Microsoft Defender for Endpoint next-gen protection technologies:
- Threat Protection
- System Guard
- Identity Protection
- Security management
- Microsoft Edge
- See Also
Download Windows 10 1809 1903 RSAT Install Using New Windows FoD
For the past several versions of Windows 10, I have been used to having to pull the latest Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT) down from Microsoft from the Microsoft downloads page. Even if you have RSAT installed, when you upgrade Windows 10, the RSAT installation is wiped out. This is cumbersome, especially after finishing an upgrade and all your administration tools are gone. However, Microsoft has made a really good switch in my opinion in the way the Remote Server Administration Tools are deployed as a departure from the way we have been doing it for the past several Windows 10 versions. With Windows 10 1903, the RSAT tools are a Features on Demand (FoD) installation. In other words, RSAT is already a part of Windows 10 1903 and higher. All you have to do is turn on the feature for the Remote Server Administration Tools you want to install. Let’s take a look at download Windows 10 1809 1903 RSAT install using new Windows FoD “Features on Demand”.
What are Windows 10 Features on Demand?
You may wonder what “Features on Demand” are. Features on Demand or FoD are Windows feature packages that can be added at any time. When Windows 10 or Windows Server needs a new feature, it can request the feature package from Windows Update.
As a side note, I first got acquainted with Features on Demand with Windows Server Core. Microsoft first touted FoDs there as Server Core has the added ability to install these Features on Demand so you can extend the functionality of Windows Server Core.
There are two types of Features on Demand that can be installed:
Download Windows 10 1809 1903 RSAT Install Using New Windows FoD
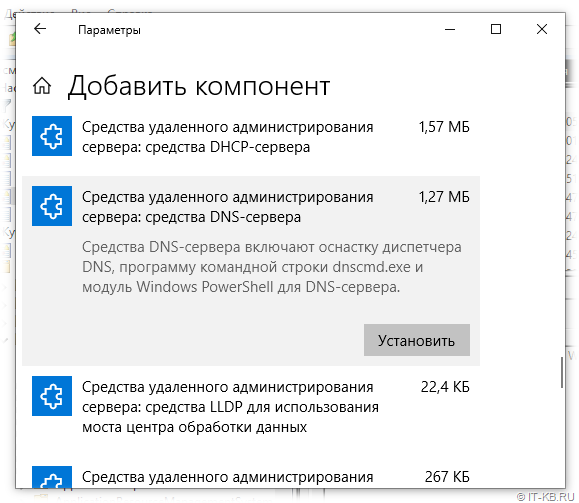
To get to the point of installing the new Remote Server Administration Tools via the Features on Demand install, navigate to the Apps & features configuration page in Windows 10 1809 and 1903 that is found under the Windows Settings page. You can get to Windows Settings quickly by pressing the “Windows key + I” buttons together.
Click the Apps menu that allows you to uninstall, configure defaults, and install optional features.
This will take you to the Apps & features page. Click the Apps & features link on the left side of the page, then click the Optional features link.
Once you click the Optional features link, click the Add a feature button.
This will launch the Add a feature page. Scroll down until you see the list of available RSAT tools available for download and install. There are several to choose from. ***Note*** the screenshot below does not include all the available RSAT tools.
Click the Features on Demand you want to install, and click the Install button for each to begin the installation.
If you go back to the Optional features page just one level back, you will see the progress of the RSAT installations.
Use PowerShell to Download Windows 10 1809 1903 RSAT FoD and Install
If you are into scripting and automation with PowerShell (which you should be :-), then you can easily install the Windows 10 1903 RSAT FoD using PowerShell. It is an easy way to especially install ALL the RSAT tools with a simple one-liner.
Launch PowerShell as an Administrator and run the following PowerShell cmdlet:
Wrapping Up
The new direction that Microsoft has taken to Download Windows 10 1809 1903 RSAT Install Using New Windows FoD is a welcomed change to the traditional RSAT download and installation that gets wiped out with every Windows Update to the next major version.
The Features on Demand RSAT installation method is super easy and is “built-in” to the Windows 10 1809 and 1903 releases and all the future releases to come. The other great thing is you can use PowerShell to install the RSAT Feature on Demand and easily install ALL the RSAT tools if desired, instead of clicking each one in the GUI to install.
Источник
Windows 10 features on demand version 1903
Question
Возникла необходимость в Win10 1909 установить оснастку AD «Пользователи и компьютеры», ПК введен в домен. Прочел, что для установки необходим диск с набором дополнительных компонент, даже нашел название iso-файла
Есть вопрос, могу ли загрузить файл законным способом? Попробовал найти файл через подписку Visual Studio (наименование подписки Visual Studio Dev Essentials), но его нет.
Доступа к другой подписке нет.
В Windows 7 свободно устанавливал компонент без необходимости загрузки дополнительного образа.
Я не волшебник, только учусь. MCTS, CCNA. Если вам помог чей-либо ответ, пожалуйста, не забывайте нажать на кнопку «отметить как ответ» или проголосовать за «полезное сообщение». Disclaimer: Мнения, высказанные здесь, являются отражением моих личных взглядов, а не позиции работодателя. Вся информация предоставляется как есть, без каких-либо на то гарантий. Блог IT Инженера, Яндекс Дзен, YouTube, GitHub, Facebook, TechNet Forum Team.
ничего вам не надо, кроме PowerShell, административных прав и подключения к интернету.
ничего вам не надо, кроме PowerShell, административных прав и подключения к интернету.
Я не волшебник, только учусь. MCTS, CCNA. Если вам помог чей-либо ответ, пожалуйста, не забывайте нажать на кнопку «отметить как ответ» или проголосовать за «полезное сообщение». Disclaimer: Мнения, высказанные здесь, являются отражением моих личных взглядов, а не позиции работодателя. Вся информация предоставляется как есть, без каких-либо на то гарантий. Блог IT Инженера, Яндекс Дзен, YouTube, GitHub, Facebook, TechNet Forum Team.
тоже самое, только с использованием PowerShell и интернет
прежде чем давать подобные советы, убедитесь в их правильности. Напомню, что автора вопроса версия ОС 1909. По ссылке, которую привели вы, RSAT для этой версии нет:
Более того, даже Microsoft не рекомендует загрузку RSAT для более современных версий. Вы хотя бы прочитайте описание скачиваемого пакета.
надо было сразу писать про ограничения с подключением к интернету.
— научить прокси пропускать этот трафик без проксирования (читайте логи, создавайте правила)
— подлючить компьютер к интернету в обход прокси.
Если изменились условия и для загрузки файла установки оснастки «Пользователи и компьютеры» нужны согласия правообладателя, то будет проще подключить ПК к интернет (чтобы был прямой выход) или загрузить файл образа features on demand по законной подписке.
Чтобы загрузить файл через прокси, нужно, чтобы клиент Windows Update работал через прокси. Пробовал, но не удалось настроить на локальном ПК. Доступа к настройке самой прокси нет.
Если изменились условия и для загрузки файла установки оснастки «Пользователи и компьютеры» нужны согласия правообладателя
Повторюсь, настройки прокси-сервер организации изменить не могу.
Прокси-сервер типа HTTP, с аутентификацией kerberos, фильтрация url не используется.
Клиент Windows Update умеет использовать HTTP-прокси (использует адрес, указанный в стандартных настройках Windows 10), но не проводит аутентификацию kerberos.
Для ее выполнения с использованием центра обновлений в Интернет (не локального WSUS-сервера) в ветке реестра
«HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREPoliciesMicrosoftWindowsWindowsUpdateAU»
задаю значение ключа «UseWUServer» равным 0 и перезапускаю службу «Центр обновления Windows».
Удалось успешно добавить оснастку с использованием стороннего ПО WinFoom (https://github.com/ecovaci/winfoom).
ПО прослушивает локальный порт и пробрасывает подключение к нему на адрес указанного прокси-сервера с использованием учетных данных текущего залогиненного пользователя.
Так можно обеспечить выход в интернет через прокси-сервер с использованием аутентификации kerberos для ПО, которое не умеет проводить аутентификацию kerberos.
В настройках WinFoom указал прослушивать локальный порт 3129, указал адрес и порт прокси-сервера организации, затем в стандартных настройках Windows 10 указал прокси-сервер localhost:3129 (вместо прокси-сервера организации).
Тогда команду powershell по добавлению оснастки выполнил успешно, оснастка добавлена.
Источник

Графический интерфейс «Параметры Windows» и UAC
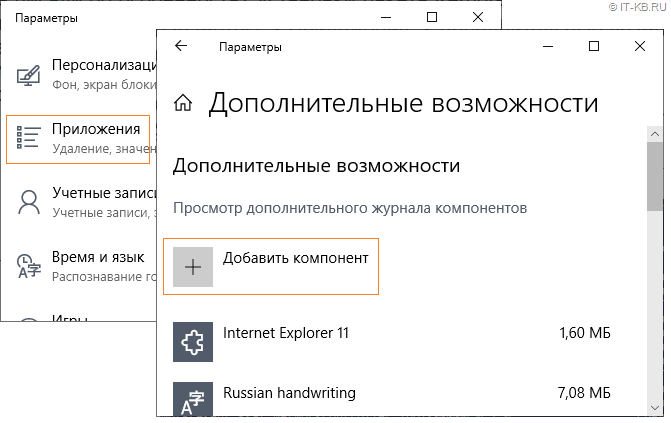
В рассматриваемой нами версии Windows 10 активацию компонент RSAT можно выполнить через графический интерфейс Windows, пройдя последовательно в Параметры Windows > Приложения > Дополнительные возможности > Добавить компонент
Однако, если с помощью этого графического интерфейса мы попытаемся выполнить добавление компонент на системе, подключенной к локальному серверу WSUS/SCCM SUP, то может получиться так, что мы даже не сможем получить перечень доступных к установке компонент.
Эта проблема будет воспроизводится в том случае, если текущий пользователь системы не имеет прав локального администратора и доступ к интерфейсу добавления компонент выполняется с запросом повышения привилегий UAC. При этом, если войти в систему интерактивно с правами администратора, то список компонент в графическом интерфейсе мы всё же сможем увидеть.
Компоненты RSAT и PowerShell
В качестве альтернативного варианта получения списка опциональных компонент Windows можно использовать оболочку PowerShell, запущенную с правами администратора. Для получения компонент, относящихся к пакету RSAT можно выполнить команду:
Установку той или иной компоненты можно выполнить командой типа:
Feature On Demand и проблема Offline-клиентов
И ошибка эта будет воспроизводиться как при использовании PowerShell, так и при использовании графического интерфейса. Правда, в графическом интерфейсе, опять же, это может быть не так очевидно.
Как я понял, связано это с тем, что для установки опциональных компонент требуется наличие доступа к комплекту пакетов установки Feature On Demand (FOD) для нашей «модной» версии Windows 1903. Именно в этот комплект включаются компоненты RSAT, начиная с обновления Windows 10 1809 от Октября 2018 года. Об этом, в частности, гласит примечание на странице загрузки Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows 10
Known issues affecting various RSAT versions:
Issue: RSAT FOD installation fails with error code 0x800f0954
Impact: RSAT FODs on Windows 10 1809 (October 2018 Update) in WSUS/SCCM environments
Resolution: To install FODs on a domain-joined PC which receives updates through WSUS or SCCM, you will need to change a Group Policy setting to enable downloading FODs directly from Windows Update or a local share.
И в этой ситуации администраторы используют разные пути. Некоторые идут по пути наименьшего сопротивления, не заморачиваясь при этом вопросами удобства и безопасности, и отключают на время установки RSAT нацеливание клиента на WSUS с последующей организацией прямого доступа к Windows Update.
На мой взгляд, этот метод «так себе», так как далеко не всегда и не во всех ситуациях возможно, или даже временно допустимо, обеспечивать прямой доступ на внешние интернет-узлы. К тому же решение с временной правкой реестра и последующим перезапуском службы клиента Windows Update назвать удобным язык не повернётся. При этом ведь ещё нужно помнить про том, что нигде в групповых политиках не должно быть настроено явных запретов на до-загрузку контента Windows c Windows Update.
Feature On Demand и WSUS
Не найдя нигде в открытых источниках вменяемого развёрнутого описания этой позиции (…впрочем, как и многих других…) мы решили включить её и проверить, что она нам даст. По итогу могу сказать, что среди метаданных о более, чем тысячи обновлений, прилетевших после синхронизации WSUS с Windows Update, я увидел только некоторые компоненты FOD, большинство из которых применимы только для старых версий Windows 10. Ну и в придачу мы получили целый ворох языковых пакетов на всех мыслимых и немыслимых языках, невзирая на то, что в настройках сервера WSUS у нас включены только английский и русский языки. В общем и целом эта позиция на WSUS для нас оказалась бесполезной и даже вредительской.
Раздача Feature On Demand для Offline-клиентов
В результате проведённых экспериментов стало очевидно, что единственным приемлемым в нашей ситуации вариантом, позволяющим выполнять Offline-установку RSAT, является вариант с развёртыванием специального сетевого каталога с компонентами Feature On Demand с нацеливанием клиентов на этот каталог через групповые политики.
Для начала нам потребуется получить образы дисков с компонентами FOD для нашей версии Windows 10. Загрузить эти образы можно вручную с сайта Volume Licensing Service Center (VLSC)
Распакованный контент будет представлять из себя множество *.cab файлов, среди которых есть и интересующие нас опциональные компоненты RSAT.
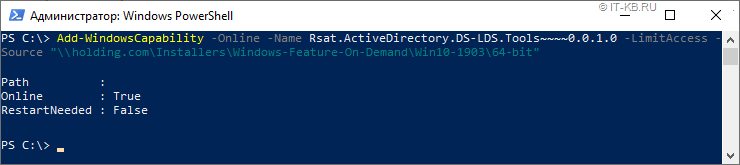
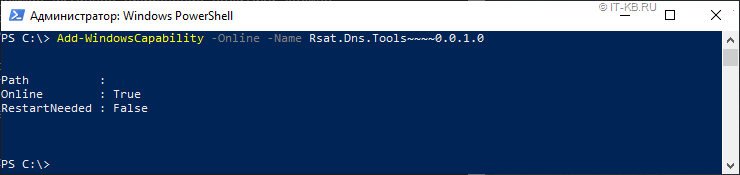
Теперь на любом Offline-клиенте c Windows 10 1903 мы можем попытаться выполнить установку компонент RSAT c помощью PowerShell, указывая в качестве источника получения подготовленный сетевой каталог:
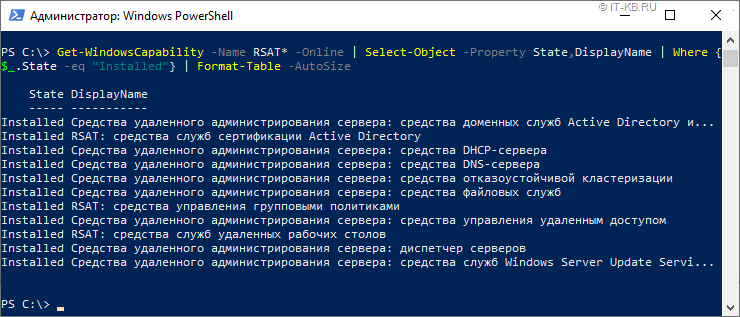
Имейте в виду, что командлет Add-WindowsCapability работает довольно специфично. То есть он может отработать без ошибки, но если в указанном источнике не будут найдены файлы, подходящие для данной системы, никакой установки на самом деле не произойдёт… Разумеется, «это не баг, а фича»… Поэтому после выполнения командлета установки всех нужных компонент, лучше повторно проверять установленные компоненты:
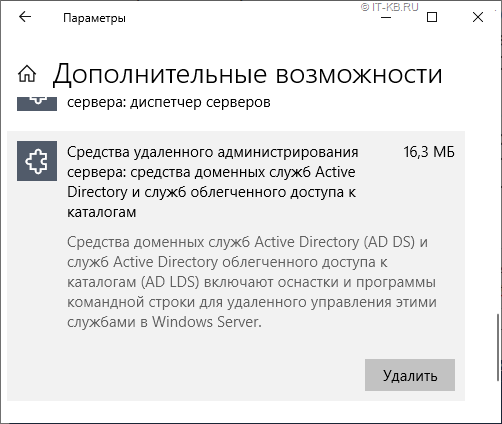
После этого установленные компоненты RSAT можно будет видеть в уже «горячо полюбившейся» нам графической оболочке Windows 10 1903 в ранее упомянутом перечне дополнительных компонент Windows
И отсюда же их можно будет удалить при необходимости.
Таким образом все администраторы в организации смогут с помощью PowerShell вручную установить нужные им компоненты RSAT на свои системы Windows 10 1903, не имея прямого доступа в интернет. Однако Offline-установку можно сделать ещё удобней, если дополнительно настроить специальный параметр групповой политики, указывающий клиентам расположение сетевого каталога с компонентами FOD. Описан этот параметр GPO, например, в документе: How to make Features on Demand and language packs available when you’re using WSUS/SCCM.
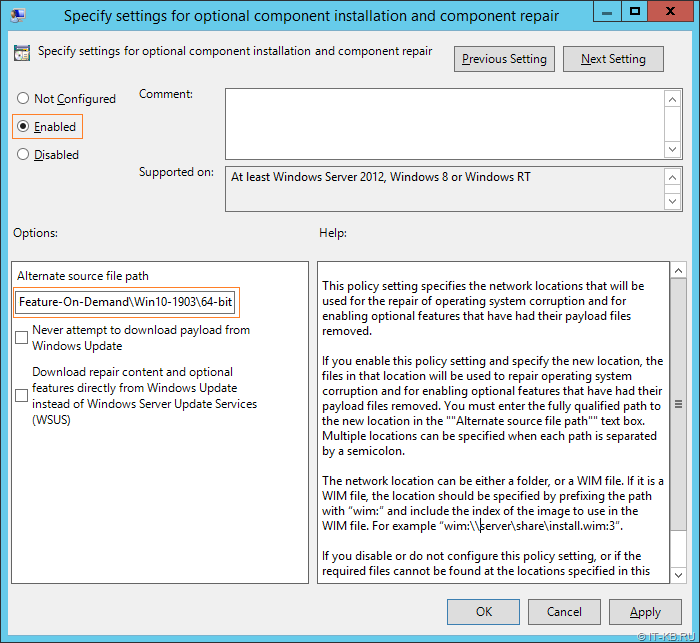
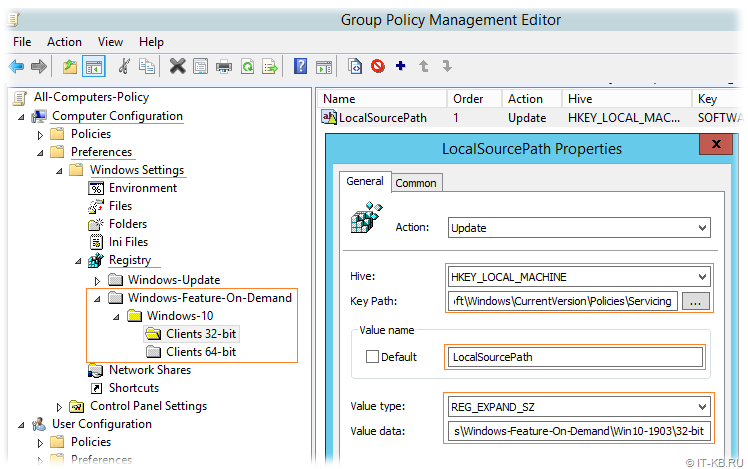
Переходим в консоль управления групповыми политиками и в разделе политик Administrative Templates > System находим параметр «Specify settings for optional component installation and component repair«
Включаем этот параметр и указываем путь к сетевому каталогу с компонентами FOD в поле «Alternate source file path«.
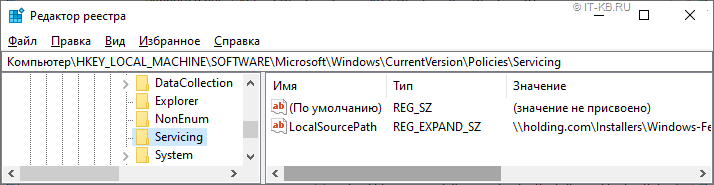
Этот параметр групповой политики фактически принесёт на клиентские системы параметр реестра » LocalSourcePath » в ключе HKLMSOFTWAREMicrosoftWindowsCurrentVersionPoliciesServicing
После этого Offline-установка компонент FOD станет доступна и через графический интерфейс Windows без использования танцев с PowerShell
Однако при этом стоит помнить про ранее обозначенный нюанс с пустым списком компонент в случае использования графического интерфейса в связке с UAC. То есть выполнять установку компонент FOD через графический интерфейс окна «Параметры Windows» нужно только при интерактивном входе в систему из под административной учётной записи. Если по какой-то причине заходить в систему администратором интерактивно нет желания/возможности, то можно использовать выше описанный метод с установкой через PowerShell.
При этом опять же стоит отметить то, что приятным плюсом использования настройки пути к компонентам FOD через групповую политику станет и то, что теперь при использовании PowerShell не потребуется явно указывать путь для установки нужных компонент:
И вроде бы теперь всё здорово, результат достигнут, то есть Offline-установка работает и через графический интерфейс и через PowerShell. Но дивные «фичи» на этом не кончаются.
Обработка «LocalSourcePath» с несколькими путями
Ещё одной странной штукой, которая была обнаружена при работе с выше обозначенным параметром групповой политики, это то, что, судя по описанию в GPO, значение опции «Alternate source file path» может принимать несколько путей с разделителем в виде точки с запятой. Однако практические эксперименты с Windows 10 1903 показали, что при считывании значения » LocalSourcePath » из реестра система заглядывает только в первый по счёту каталог (указанный до точки с запятой), а остальные игнорирует. Такое поведение вполне вписывается в рамки обработки значения ключа -Source командлета Add-WindowsCapability, в описании которого есть соответствующее примечание
If you specify multiple Source arguments, the files are gathered from the first location where they are found and the rest of the locations are ignored.
Вариантом выхода из этой ситуации может быть отказ от использования классического параметра из административных шаблонов GPO и настройка пути в реестре средствами Group Policy Preferences (GPP) с использованием таргетинга по версии и разрядности клиентской операционной системы.
По крайней мере именно на таком варианте мы и остановились, как на наиболее гибком и работоспособном.
Финиш
В итоге квест под названием «Выполнить Offline-установку RSAT в Windows 10 и не слететь с катушек» пройден, и теперь все административные пользователи, работающие на новой Windows 10 1903, могут устанавливать компоненты RSAT, как через графический интерфейс Windows, так и через PowerShell фактически в Offline-режиме и без дополнительных сложностей и манипуляций по аналогии с Online-клиентами.
Источник
What’s new in Windows 10, version 1903 for IT Pros
Applies to
This article lists new and updated features and content that are of interest to IT Pros for Windows 10 version 1903, also known as the Windows 10 May 2019 Update. This update also contains all features and fixes included in previous cumulative updates to Windows 10, version 1809.
New disk space requirement for Windows 10, version 1903 applies only to OEMs for the manufacture of new PCs. This new requirement does not apply to existing devices. PCs that don’t meet new device disk space requirements will continue to receive updates and the 1903 update will require about the same amount of free disk space as previous updates. For more information, see Reserved storage.
Deployment
Windows Autopilot
Windows Autopilot is a collection of technologies used to set up and pre-configure new devices, getting them ready for productive use. The following Windows Autopilot features are available in Windows 10, version 1903 and later:
Windows 10 Subscription Activation
Windows 10 Education support has been added to Windows 10 Subscription Activation.
With Windows 10, version 1903, you can step-up from Windows 10 Pro Education to the enterprise-grade edition for educational institutions – Windows 10 Education. For more information, see Windows 10 Subscription Activation.
SetupDiag
SetupDiag version 1.4.1 is available.
SetupDiag is a command-line tool that can help diagnose why a Windows 10 update failed. SetupDiag works by searching Windows Setup log files. When searching log files, SetupDiag uses a set of rules to match known issues. In the current version of SetupDiag there are 53 rules contained in the rules.xml file, which is extracted when SetupDiag is run. The rules.xml file will be updated as new versions of SetupDiag are made available.
Reserved storage
Reserved storage: Reserved storage sets aside disk space to be used by updates, apps, temporary files, and system caches. It improves the day-to-day function of your PC by ensuring critical OS functions always have access to disk space. Reserved storage will be enabled automatically on new PCs with Windows 10, version 1903 pre-installed, and for clean installs. It will not be enabled when updating from a previous version of Windows 10.
Servicing
Security
Windows Information Protection
With this release, Microsoft Defender for Endpoint extends discovery and protection of sensitive information with Auto Labeling.
Security configuration framework
With this release of Windows 10, Microsoft is introducing a new taxonomy for security configurations, called the SECCON framework, comprised of 5 device security configurations.
Security baseline for Windows 10 and Windows Server
The draft release of the security configuration baseline settings for Windows 10, version 1903 and for Windows Server version 1903 is available.
Intune security baselines
Intune Security Baselines (Preview): Now includes many settings supported by Intune that you can use to help secure and protect your users and devices. You can automatically set these settings to values recommended by security teams.
Microsoft Defender for Endpoint
Microsoft Defender for Endpoint next-gen protection technologies:
Threat Protection
Windows Sandbox: Isolated desktop environment where you can run untrusted software without the fear of lasting impact to your device.
Microphone privacy settings: A microphone icon appears in the notification area letting you see which apps are using your microphone.
Standalone users can install and configure their Windows Defender Application Guard settings without needing to change Registry key settings. Enterprise users can check their settings to see what their administrators have configured for their machines to better understand the behavior.
WDAG is now an extension in Google Chrome and Mozilla Firefox. Many users are in a hybrid browser environment, and would like to extend WDAG’s browser isolation technology beyond Microsoft Edge. In the latest release, users can install the WDAG extension in their Chrome or Firefox browsers. This extension will redirect untrusted navigations to the WDAG Edge browser. There is also a companion app to enable this feature in the Microsoft Store. Users can quickly launch WDAG from their desktop using this app. This feature is also available in Windows 10, version 1803 or later with the latest updates.
To try this extension:
WDAG allows dynamic navigation: Application Guard now allows users to navigate back to their default host browser from the WDAG Microsoft Edge. Previously, users browsing in WDAG Edge would see an error page when they try to go to a trusted site within the container browser. With this new feature, users will automatically be redirected to their host default browser when they enter or click on a trusted site in WDAG Edge. This feature is also available in Windows 10, version 1803 or later with the latest updates.
Windows Defender Application Control (WDAC): In Windows 10, version 1903 WDAC has a number of new features that light up key scenarios and provide feature parity with AppLocker.
System Guard
This new feature is displayed under the Device Security page with the string “Your device exceeds the requirements for enhanced hardware security” if configured properly:
Identity Protection
Security management
Microsoft Edge
Several new features are coming in the next version of Edge. See the news from Build 2019 for more information.
See Also
What’s New in Windows Server, version 1903: New and updated features in Windows Server.
Windows 10 Features: Review general information about Windows 10 features.
What’s New in Windows 10: See what’s new in other versions of Windows 10.
What’s new in Windows 10: See what’s new in Windows 10 hardware.
What’s new in Windows 10 for developers: New and updated features in Windows 10 that are of interest to developers.
Источник

For the past several versions of Windows 10, I have been used to having to pull the latest Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT) down from Microsoft from the Microsoft downloads page. Even if you have RSAT installed, when you upgrade Windows 10, the RSAT installation is wiped out. This is cumbersome, especially after finishing an upgrade and all your administration tools are gone. However, Microsoft has made a really good switch in my opinion in the way the Remote Server Administration Tools are deployed as a departure from the way we have been doing it for the past several Windows 10 versions. With Windows 10 1903, the RSAT tools are a Features on Demand (FoD) installation. In other words, RSAT is already a part of Windows 10 1903 and higher. All you have to do is turn on the feature for the Remote Server Administration Tools you want to install. Let’s take a look at download Windows 10 1809 1903 RSAT install using new Windows FoD “Features on Demand”.
What are Windows 10 Features on Demand?
You may wonder what “Features on Demand” are. Features on Demand or FoD are Windows feature packages that can be added at any time. When Windows 10 or Windows Server needs a new feature, it can request the feature package from Windows Update.
As a side note, I first got acquainted with Features on Demand with Windows Server Core. Microsoft first touted FoDs there as Server Core has the added ability to install these Features on Demand so you can extend the functionality of Windows Server Core.
The Features on Demand are available as .CAB files that can be preinstalled if a user needs them, if you are building images as an example. You can use DISM to add a FoD to a Windows image and if you are using the FoD ISO to preinstall FoDs, you want to make sure you are using the FoD ISO that matches your Windows version you are working with.

There are two types of Features on Demand that can be installed:
- FoDs without satellite packages – These have all the resources needed such as language files in teh same package. They are also distributed as a single CAB file. These are added using the DISM /Add-Capability or /Add-Package commands.
- FoDs with satellite packages – These types of FoDs are Features on Demand that have no language or other resources that may be needed included in the particular FoD being installed. They are somtimes referred to as “language-neutral” FoDs. These are distributed as a set of several .CAB files and installed using the DISM /Add-Capability command but NOT the /Add-Package DISM command.
To get to the point of installing the new Remote Server Administration Tools via the Features on Demand install, navigate to the Apps & features configuration page in Windows 10 1809 and 1903 that is found under the Windows Settings page. You can get to Windows Settings quickly by pressing the “Windows key + I” buttons together.
Click the Apps menu that allows you to uninstall, configure defaults, and install optional features.

This will take you to the Apps & features page. Click the Apps & features link on the left side of the page, then click the Optional features link.

Once you click the Optional features link, click the Add a feature button.

This will launch the Add a feature page. Scroll down until you see the list of available RSAT tools available for download and install. There are several to choose from. ***Note*** the screenshot below does not include all the available RSAT tools.

Click the Features on Demand you want to install, and click the Install button for each to begin the installation.

If you go back to the Optional features page just one level back, you will see the progress of the RSAT installations.

Use PowerShell to Download Windows 10 1809 1903 RSAT FoD and Install
If you are into scripting and automation with PowerShell (which you should be :-), then you can easily install the Windows 10 1903 RSAT FoD using PowerShell. It is an easy way to especially install ALL the RSAT tools with a simple one-liner.
Launch PowerShell as an Administrator and run the following PowerShell cmdlet:
Get-WindowsCapability -Name RSAT* -Online | Add-WindowsCapability -Online

Wrapping Up
The new direction that Microsoft has taken to Download Windows 10 1809 1903 RSAT Install Using New Windows FoD is a welcomed change to the traditional RSAT download and installation that gets wiped out with every Windows Update to the next major version.
The Features on Demand RSAT installation method is super easy and is “built-in” to the Windows 10 1809 and 1903 releases and all the future releases to come. The other great thing is you can use PowerShell to install the RSAT Feature on Demand and easily install ALL the RSAT tools if desired, instead of clicking each one in the GUI to install.
To see all available DISM commands for capabilities, see DISM Capabilities Package Servicing Command-Line Options.
Источник
Включение и отключение компонентов Windows 10
Как известно, Windows 10 отличается набором компонентов от предыдущих версий операционных систем Windows. Зачастую требуется их включить или выключить, чтобы они не потребляли системные ресурсы, да и просто не мешали. В этой статье мы рассмотрим как это сделать быстрее и эффективнее.
Начнем с того, что существует два основных способа работы с компонентами (они еще называются features) — утилита DISM и командлеты Powershell. И то и другое встроено в Windows 10, в отличие от Windows 7, где dism можно было добавить или установив пакет Windows ADK, или руками скопировав dism.exe с другого компьютера.
Сразу отмечу, что утилиту dism и среду powershell для работы с системой необходимо запускать от имени администратора, даже если ваш аккаунт уже находится в группе локальных админов. Итак, вы или находите cmd или windows powershell в меню и, кликнув правой кнопкой мышки, выбираете «Запуск от имени администратора».
В Windows 10 есть понятие Features и Capabilities. Первое — это привычные нам компоненты, которые можно найти в Панели управления -> Программы и компоненты -> Включение и отключение компонентов Windows. То есть это встраиваемые модули, которые выполняют определенный сервисный функционал.
Capabilities — это дополнительные возможности, которые расширяют возможности интерфейса и увеличивают удобство пользователя. Среди них — Language packs, наборы шрифтов. Да, Microsoft удалил часть нестандартных шрифтов, которые теперь вынесены в опциональные компоненты. Скачать эти компоненты можно в виде ISO файла с сайта Volume Licensing Service Center или напрямую через Internet и графический интерфейс Windows. Такую концепцию Microsoft назвала Features on Demand (FOD). Их в более ранних версия Windows не было.
Работаем с Windows Features
Итак, список установленных компонентов можно посмотреть командой
Dism /online /Get-Features
Вот как в Powershell можно получить список всех компонентов командлетами Get-WindowsFeature (для Windows Server) или Get-WindowsOptionalFeature (Windows 10):
Чтобы получить список отключенных компонентов, введите:
Get-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online | ? state -eq ‘disabled’ | select featurename
Этот список также можно вывести в файл (для windows Server):
Get-WindowsFeature | Where-Object <$_.Installed -match “True”>| Select-Object -Property Name | Out-File C:TempWindowsFeatures.txt
Посмотрев список названий и их состояние, можно использовать эти названия для того, чтобы компоненты включить или выключить:
Dism /online /Enable-Feature /FeatureName:TFTP /All
ключ /All позволяет включить также все дочерние компоненты;
Установка компонентов через Powershell выполняется командой Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature.
Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -Online -FeatureName RSATClient-Roles-AD-Powershell
Параметр -All включает все дочерние компоненты.
Dism /online /Disable-Feature /FeatureName:TFTP
Аналогично, через Powershell это можно сделать командой Disable-Windowsoptionalfeature -online -featureName [feature name].
Обратите внимание, некоторые фичи имеют разные названия в Windows 7 и Windows 10. Например, RSAT в Windows 7 — это RemoteServerAdministrationTools, а в Windows 10 — RSATclient.
Управление Features on Demand (FOD)
Если вы устанавливаете их через графический интерфейс, то вам необходимо пройти “System –> App & features –> Manage optional features” и нажать знак + напротив необходимых компонентов.
Чтобы сделать это автоматизированно через командную строку, наберите чтобы получить список доступных компонентов:
DISM.EXE /Online /Get-Capabilities
Как и прежде, запомните название необходимых вам компонентов, чтобы включить их командой (на примере .Net Framework 3):
DISM.EXE /Online /Add-Capability /CapabilityName:NetFx3
Add-WindowsCapability –Online -Name NetFx3
Если же у вас нет доступа в Интернет, то есть выход. Итак, вы скачиваете ISO образ диска с FOD компонентами с сайта Volume Licensing Service Center. Файлы будут разные для разных релизов Windows 10 — 1511, 1607, 1703, 1709. Важно помнить, что компоненты одного релиза не подходят к другому. Если вы сделаете in-place upgrade (установка одного релиза поверх другого через обновление), то несовместимые установленные компоненты будут удалены без вашего желания! Да, Microsoft удаляет то, что считает несовместимым при обновлении.
Так вот, ISO файл содержит набор неизвестных и сложных для понимания файлов с расширением cab. Вот чудесный файлик на сайта Microsoft, который обясняет назначение каждого файла. Итак, существуют следующие типы FOD:
- Microsoft-Windows-LanguageFeatures-Basic — проверка правописания для различных языков и раскладок клавиатуры;
- Microsoft-Windows-LanguageFeatures-Fonts — национальные шрифты, например, азиатские
- Microsoft-Windows-LanguageFeatures-OCR — средства для распознавания шрифтов
- Microsoft-Windows-LanguageFeatures-Handwriting — средства для распознавания рукописного ввода
- Microsoft-Windows-LanguageFeatures-TextToSpeech — средства преобразования текста в голос, используемые подсказчиком Cortana
- Microsoft-Windows-LanguageFeatures-Speech — распознавание голоса
- Microsoft-Windows-InternationalFeatures — пакеты национальных настроек, например, для Тайваня
Итак, для добавления таких FOD компонентов, используйте команды вида (замените имя компонента):
Dism /Online /Add-Capability /CapabilityName:Language.Basic
Dism /Online /Remove-Capability /CapabilityName:Language.Basic
Установка и переустановка пакетов языков (Language Interface Packs, LIP)
Язык интерфейса Windows можно поменять, установив так называемые LIP. ранее они назывались MUI (Multi user interface). Файлы LIP выглядят так: Microsoft-Windows-Client-Language-Pack_x64_es-es.cab для испанского языка. Выглядеть установка будет примерно так:
Dism /Add-Package /online /PackagePath:»C:LanguagesMicrosoft-Windows-Client-Language-Pack_x64_fr-fr.cab»
Dism /Remove-Package /online /PackageName:Microsoft-Windows-Client-LanguagePack-Package
В следующей статье мы поговорим как с помощью DISM и Powershell управлять так называемыми Modern-приложениями AppX.
Источник
ILYA Sazonov: ITPro
Windows XP
Свежие записи
Топ записей
Архивы
- Октябрь 2020 (1)
- Сентябрь 2020 (1)
- Август 2020 (1)
- Май 2020 (1)
- Апрель 2020 (2)
- Март 2020 (2)
- Февраль 2020 (1)
- Январь 2020 (4)
- Декабрь 2019 (1)
- Ноябрь 2019 (4)
- Октябрь 2019 (2)
- Сентябрь 2019 (5)
- Июль 2019 (2)
- Май 2019 (1)
- Апрель 2019 (3)
- Март 2019 (5)
- Февраль 2019 (5)
- Январь 2019 (3)
- Декабрь 2018 (1)
- Ноябрь 2018 (3)
- Октябрь 2018 (1)
- Сентябрь 2018 (1)
- Август 2018 (1)
- Июль 2018 (3)
- Июнь 2018 (4)
- Май 2018 (3)
- Апрель 2018 (4)
- Март 2018 (1)
- Февраль 2018 (3)
- Январь 2018 (4)
- Декабрь 2017 (8)
- Ноябрь 2017 (3)
- Октябрь 2017 (2)
- Сентябрь 2017 (3)
- Август 2017 (1)
- Июль 2017 (5)
- Июнь 2017 (2)
- Май 2017 (1)
- Апрель 2017 (6)
- Март 2017 (3)
- Февраль 2017 (5)
- Январь 2017 (1)
- Декабрь 2016 (4)
- Ноябрь 2016 (3)
- Октябрь 2016 (5)
- Сентябрь 2016 (4)
- Август 2016 (6)
- Июль 2016 (5)
- Июнь 2016 (6)
- Май 2016 (8)
- Апрель 2016 (8)
- Март 2016 (7)
- Февраль 2016 (8)
- Январь 2016 (5)
- Декабрь 2015 (4)
- Ноябрь 2015 (6)
- Октябрь 2015 (14)
- Сентябрь 2015 (7)
- Август 2015 (6)
- Июль 2015 (3)
- Июнь 2015 (4)
- Май 2015 (8)
- Апрель 2015 (5)
- Март 2015 (10)
- Февраль 2015 (7)
- Январь 2015 (6)
- Декабрь 2014 (7)
- Ноябрь 2014 (14)
- Октябрь 2014 (8)
- Сентябрь 2014 (9)
- Август 2014 (8)
- Июль 2014 (6)
- Июнь 2014 (4)
- Май 2014 (8)
- Апрель 2014 (6)
- Март 2014 (7)
- Февраль 2014 (5)
- Январь 2014 (9)
- Декабрь 2013 (2)
- Ноябрь 2013 (11)
- Октябрь 2013 (10)
- Сентябрь 2013 (9)
- Август 2013 (4)
- Июль 2013 (4)
- Июнь 2013 (3)
- Апрель 2013 (6)
- Март 2013 (2)
- Февраль 2013 (1)
- Январь 2013 (4)
- Декабрь 2012 (3)
- Ноябрь 2012 (4)
- Октябрь 2012 (6)
- Сентябрь 2012 (7)
- Август 2012 (10)
- Июль 2012 (9)
- Июнь 2012 (6)
- Май 2012 (7)
- Апрель 2012 (7)
- Март 2012 (5)
- Февраль 2012 (7)
- Январь 2012 (6)
- Декабрь 2011 (4)
- Ноябрь 2011 (2)
- Сентябрь 2011 (11)
- Август 2011 (8)
- Июль 2011 (5)
- Июнь 2011 (3)
- Май 2011 (1)
- Апрель 2011 (3)
- Март 2011 (4)
- Февраль 2011 (1)
- Январь 2011 (2)
- Декабрь 2010 (4)
- Ноябрь 2010 (1)
- Сентябрь 2010 (2)
- Июль 2010 (3)
- Май 2010 (3)
- Апрель 2010 (1)
- Март 2010 (3)
- Декабрь 2009 (1)
- Ноябрь 2009 (2)
- Октябрь 2009 (11)
- Сентябрь 2009 (3)
- Август 2009 (5)
- Июль 2009 (5)
Подписка на email
Windows 10 — Features on Demand
Когда скачивал дистрибутив Windows 10 с сайта Microsoft Volume Licensing Service Center (VLSC), то обратил внимание, что есть дополнительный ISO файл en_windows_10_features_on_demand_x64_dvd_6846440_.iso.
По факту там содержались cab файлы без всяких комментариев.
Среди них находился файл с именем Microsoft-Windows-Performance-WPT-Package.cab, которое наводило на мысль, что теперь не нужно качать и устанавливать Windows SDK, а можно сразу установить Windows Performance Toolkit.
Оказалось это действительно так:
Остальные файлы в ISO это в основном дополнения к Language Packs. Сам языковой пакет только меняет интерфейс. Если вы хотите проверку правописания, распознавание голоса, рукописного письма и другие возможности, то можете поставить дополнительные пакеты. Назначение пакетов в большинстве случаев ясно из названия.
Источник
Adblock
detector
As it involves quick reflexes and hand-eye coordination, this post may qualify as Jacques Bensimon’s weirdest ever. You be the judge:
I recently started creating a new Microsoft Windows 10 Build 1809 image at a client (happens to be the LTSC flavor, but that’s not relevant here). For reasons we need not go into, the machine on which the build is being done has no Internet access, nor is the option to even temporarily give it access available. No problem (I thought), done it before: install Windows from ISO, use WSUS and/or downloads from the Windows Update Catalog site for updates, and add any required additional features (“Features On Demand”, aka FODs) from downloadable CAB files. I soon discovered, however, that unlike for previous Windows 10 builds through 1803, FOD CABs are no longer available for download as of build 1809, and that (per this article, for example) they are only found on a separate “FOD ISO” officially available only to “Windows OEMs” (presumably the Dells , HPs, and Lenovos of this world) and Microsoft “Device Partners” (the hardware folks) – no idea why that is! I did come across a rumor that it may be available to MSDN subscribers, but I have not been able to confirm it or locate it via that avenue (anybody?). According to the mentioned article, lowly IT Professionals can get their hands on Language Packs, via their Volume Licensing site, but no mention of other FOD types.
So, what to do? My first thought was to try to locate the CABs on an Internet-connected machine (of the same build & bitness) on which the FODs I wanted had already been installed (via the “normal” Settings GUI route), but they were nowhere to be found after installation. My next thought however did bear fruit: what if the CAB corresponding to a given FOD is downloaded and available during the FOD installation, only to later be automatically deleted?
Armed with the (amazing) “Everything” utility that displays an (optionally wildcard-filtered) dynamic listing of every local NTFS file system item (using the NTFS Master File Table & Change Journal rather than tediously “walking” the drives’ directory trees), I was able to confirm that yes, CABs are downloaded and briefly available during FOD installations.
So, here using the example of capturing the “Japanese Supplemental Fonts” FOD CAB and later installing it on a different machine, are the steps I followed:
- On an Internet-connected machine (again, of the same build and bitness as your target machine) that does not yet have the desired FOD installed (more on that later), download and run the Everything utility (of the correct bitness for the OS, elevated), type *.cab in the search/filter bar, and sort on the “Date Modified” column, most recent first (I initially added and used the “Date Created” column, but that turned out to be unnecessary since the CABs are downloaded without their original timestamps) – see the second screenshot below for an idea of what this looks like. Leave the Everything window open in a visible area of the desktop.
- Open the Windows Settings app (making sure you don’t obscure the top few items in the Everything window) and navigate to Apps | Apps & Features | Manage Optional Features | Add a feature, select the desired feature, and (deep breath, get ready to act quickly :-)), click Install. [Note: some language-related FODs, such as language-specific keyboard layouts & input methods, OCR, handwriting, text-to-speech, etc. are installed instead via Time & Language | Language | Add a language – use the Options button to install each component of a new input language separately, so you don’t have to simultaneously capture multiple CABs.]
- Back in the Everything window, you’ll soon see a procession of new small CAB files with uninspiring names appear and disappear at the top of the list – you can ignore those, they’re not what you’re after: you’re waiting for a CAB with a long name descriptive of the FOD being installed to appear at the top of the list, and for its size to stabilize (to ensure it’s been fully downloaded). Once that’s happened, you’ll have several more seconds (but far from an eternity) to copy (Ctrl + drag) the CAB to your Desktop – don’t move the CAB (if it’s even feasible), might freak out Windows! [Note: the longer it takes your machine to install the FOD the better for your purposes, so use the slowest appropriate machine available, i.e. a VM! ;-)]
- Once you’ve captured an FOD CAB file in this fashion and made it available to your offline target machine, you can now install it from an elevated console window using the command
DISM /online /add-package /packagepath:pathcab_name.cab
In this particular example, it was
DISM /online /add-package /packagepath:Microsoft-Windows-LanguageFeatures-Fonts-Jpan-Package~31bf3856ad364e35~amd64~~.cab
As one of my buddies always says (I hope deliberately), Viola!
Notes:
- If the FOD you’re after is already installed on your Internet-connected machine, or if you’ve followed the above steps but failed to grab a copy of the CAB file in time (or grabbed it prematurely), you can always start over after first uninstalling the FOD in question. In the case of FODs installed from the “Add a feature” panel, it’s generally sufficient to select it in the “Manage Optional Features” panel and click Uninstall. For language-related FODs installed from “Add a language”, using the Remove button for that language in the Language panel may only remove its association with your profile and leave the underlying package installed. Regardless of the FOD, you can always confirm whether its package is installed or not by reviewing the output of DISM /online /get-packages, possibly filtered with Find as in this screenshot:
If an FOD package you wish to re-install from scratch is still present, remove it first using DISM /online /remove-package /packagename:package_identity (where package_identity is whatever was displayed by the previous DISM /get-packages command).
- If you’d like a better idea in advance of the names of the FOD CABs you want to capture (and of their corresponding package identities), you can get them from this page for non-language-related FODs, and from this page for language-related ones.
- This page describes FODs with “satellite packages” that must be installed using DISM’s “/add-capability” rather than “/add-package”. They involve multiple CABs rather than a single one, and would require an adjustment to the above method to capture them all. I had no need for any such FOD on this occasion, so didn’t get around to testing the process.
- Finally, I’ll repeat here again that none of this tomfoolery would be necessary if the “Feature on Demand ISO” were readily available to IT pros, so if any of you reading this know of a legit way to get ahold of it, I for one would sure appreciate you sharing the info in the comments below.
Have a great 2019, everybody!
JB
Be sure to follow @JacqBens on Twitter.
Содержание
- 1 RSAT в Windows 10 как Features on Demand (FoD)
- 2 Установка RSAT в Windows 10 с помощью PowerShell
- 3 Ошибка 0x800f0954 при установке RSAT в Windows 10
- 4 Установка RSAT в Windows 10 в офлайн режиме
- 5 Table of Contents
- 6 Running the Server Manager
- 7 Pro-Tip
- 8 Known Issue
- 9 Summary
Ранее мы уже писали об особенностях установки пакета Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT) в Windows 10. Но время идёт и новые релизы Windows 10 вносят новые правила работы с этим пакетом. В этой заметке мы поговорим об особенностях автономной установки RSAT в актуальной версии Windows 10 1903.
Графический интерфейс «Параметры Windows» и UAC
В рассматриваемой нами версии Windows 10 активацию компонент RSAT можно выполнить через графический интерфейс Windows, пройдя последовательно в Параметры Windows > Приложения > Дополнительные возможности > Добавить компонент
Однако, если с помощью этого графического интерфейса мы попытаемся выполнить добавление компонент на системе, подключенной к локальному серверу WSUS/SCCM SUP, то может получиться так, что мы даже не сможем получить перечень доступных к установке компонент.
Эта проблема будет воспроизводится в том случае, если текущий пользователь системы не имеет прав локального администратора и доступ к интерфейсу добавления компонент выполняется с запросом повышения привилегий UAC. При этом, если войти в систему интерактивно с правами администратора, то список компонент в графическом интерфейсе мы всё же сможем увидеть.
Компоненты RSAT и PowerShell
В качестве альтернативного варианта получения списка опциональных компонент Windows можно использовать оболочку PowerShell, запущенную с правами администратора. Для получения компонент, относящихся к пакету RSAT можно выполнить команду:
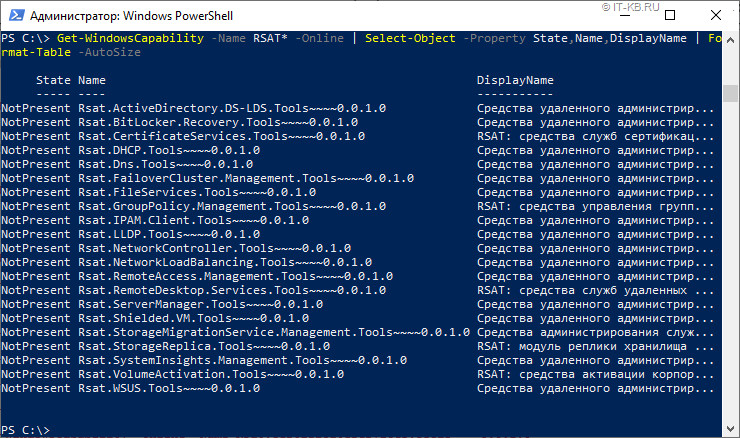
Get-WindowsCapability-NameRSAT*-Online | Select-Object-Property State,Name,DisplayName | Format-Table-AutoSize
Установку той или иной компоненты можно выполнить командой типа:
Add-WindowsCapability-Online-NameRsat.ActiveDirectory.DS-LDS.Tools~~~~0.0.1.0
Feature On Demand и проблема Offline-клиентов
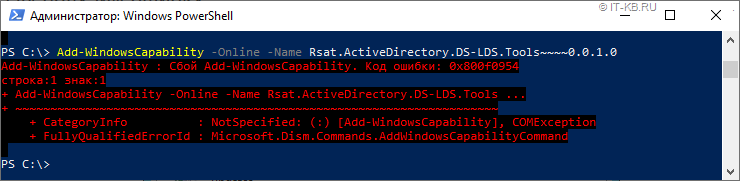
Теперь нам понятно, что графический интерфейс Windows 10 1903 работает с UAC криво, а в PowerShell всё в этом плане хорошо. Однако, безотносительно способа установки, в том случае, если компьютер настроен на использование WSUS/SUP и не имеет прямого доступа в интернет, при попытке установки выбранной компоненты мы можем получить ошибку 0x800f0954.
И ошибка эта будет воспроизводиться как при использовании PowerShell, так и при использовании графического интерфейса. Правда, в графическом интерфейсе, опять же, это может быть не так очевидно.
Как я понял, связано это с тем, что для установки опциональных компонент требуется наличие доступа к комплекту пакетов установки Feature On Demand (FOD) для нашей «модной» версии Windows 1903. Именно в этот комплект включаются компоненты RSAT, начиная с обновления Windows 10 1809 от Октября 2018 года. Об этом, в частности, гласит примечание на странице загрузки Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows 10
Интересно то, что на этой же веб-странице имеется сноска о том, что пользователям, использующим WSUS/SUP, и получающим выше обозначенную ошибку 0x800f0954, для возможности установки компонент RSAT придётся настраивать прямой доступ на Windows Update, либо использовать метод с сетевым каталогом.
Known issues affecting various RSAT versions:
И в этой ситуации администраторы используют разные пути. Некоторые идут по пути наименьшего сопротивления, не заморачиваясь при этом вопросами удобства и безопасности, и отключают на время установки RSAT нацеливание клиента на WSUS с последующей организацией прямого доступа к Windows Update.
На мой взгляд, этот метод «так себе», так как далеко не всегда и не во всех ситуациях возможно, или даже временно допустимо, обеспечивать прямой доступ на внешние интернет-узлы. К тому же решение с временной правкой реестра и последующим перезапуском службы клиента Windows Update назвать удобным язык не повернётся. При этом ведь ещё нужно помнить про том, что нигде в групповых политиках не должно быть настроено явных запретов на до-загрузку контента Windows c Windows Update.
Feature On Demand и WSUS
А что же нам в этой ситуации может предложить наш локальный источник обновлений — WSUS? Если заглянуть в свойствах сервера WSUS в перечень продуктов, относящихся к Windows 10 (…интересно, в Microsoft сами ориентируются в этом списке?…), то мы увидим такую интересную позицию, как Windows 10 Feature On Demand.
Не найдя нигде в открытых источниках вменяемого развёрнутого описания этой позиции (…впрочем, как и многих других…) мы решили включить её и проверить, что она нам даст. По итогу могу сказать, что среди метаданных о более, чем тысячи обновлений, прилетевших после синхронизации WSUS с Windows Update, я увидел только некоторые компоненты FOD, большинство из которых применимы только для старых версий Windows 10. Ну и в придачу мы получили целый ворох языковых пакетов на всех мыслимых и немыслимых языках, невзирая на то, что в настройках сервера WSUS у нас включены только английский и русский языки. В общем и целом эта позиция на WSUS для нас оказалась бесполезной и даже вредительской.
Раздача Feature On Demand для Offline-клиентов
В результате проведённых экспериментов стало очевидно, что единственным приемлемым в нашей ситуации вариантом, позволяющим выполнять Offline-установку RSAT, является вариант с развёртыванием специального сетевого каталога с компонентами Feature On Demand с нацеливанием клиентов на этот каталог через групповые политики.
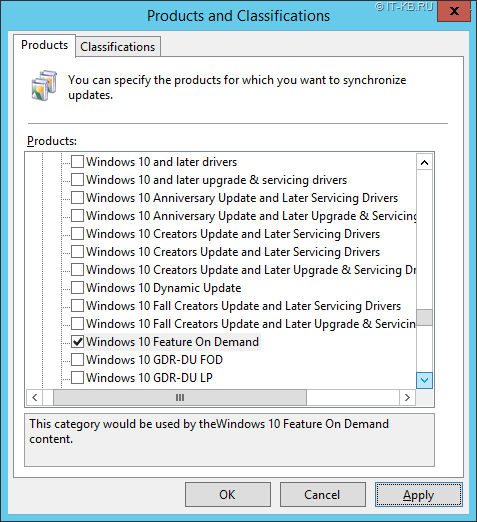
Для начала нам потребуется получить образы дисков с компонентами FOD для нашей версии Windows 10. Загрузить эти образы можно вручную с сайта Volume Licensing Service Center (VLSC)
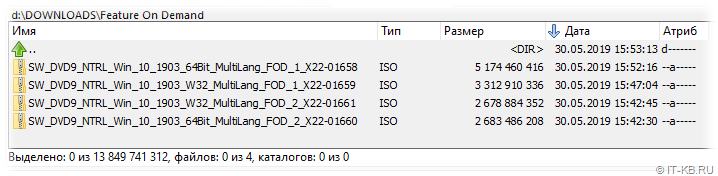
Создаём на файловом сервере общедоступный сетевой ресурс для клиентских систем 64-bit и распаковываем в него всё содержимое образов SW_DVD9_NTRL_Win_10_1903_64Bit_MultiLang_FOD_.ISO. Рядом создаём аналогичный ресурс для систем 32-bit и распаковываем туда образы SW_DVD9_NTRL_Win_10_1903_W32_MultiLang_FOD_.ISO.
Распакованный контент будет представлять из себя множество *.cab файлов, среди которых есть и интересующие нас опциональные компоненты RSAT.
Теперь на любом Offline-клиенте c Windows 10 1903 мы можем попытаться выполнить установку компонент RSAT c помощью PowerShell, указывая в качестве источника получения подготовленный сетевой каталог:
Add-WindowsCapability-Online-NameRsat.ActiveDirectory.DS-LDS.Tools~~~~0.0.1.0-LimitAccess-Sourceholding.comInstallersWindows-Feature-On-DemandWin10-190364-bit
Имейте в виду, что командлет Add-WindowsCapability работает довольно специфично. То есть он может отработать без ошибки, но если в указанном источнике не будут найдены файлы, подходящие для данной системы, никакой установки на самом деле не произойдёт… Разумеется, «это не баг, а фича»… Поэтому после выполнения командлета установки всех нужных компонент, лучше повторно проверять установленные компоненты:
Get-WindowsCapability-Name RSAT*-Online | Select-Object-Property State,DisplayName | Where {$_.State -eq"Installed"} | Format-Table-AutoSize
После этого установленные компоненты RSAT можно будет видеть в уже «горячо полюбившейся» нам графической оболочке Windows 10 1903 в ранее упомянутом перечне дополнительных компонент Windows
И отсюда же их можно будет удалить при необходимости.
Таким образом все администраторы в организации смогут с помощью PowerShell вручную установить нужные им компоненты RSAT на свои системы Windows 10 1903, не имея прямого доступа в интернет. Однако Offline-установку можно сделать ещё удобней, если дополнительно настроить специальный параметр групповой политики, указывающий клиентам расположение сетевого каталога с компонентами FOD. Описан этот параметр GPO, например, в документе: How to make Features on Demand and language packs available when you’re using WSUS/SCCM.
Переходим в консоль управления групповыми политиками и в разделе политик Administrative Templates > System находим параметр «Specify settings for optional component installation and component repair«
Включаем этот параметр и указываем путь к сетевому каталогу с компонентами FOD в поле «Alternate source file path«.
Этот параметр групповой политики фактически принесёт на клиентские системы параметр реестра «LocalSourcePath» в ключе HKLMSOFTWAREMicrosoftWindowsCurrentVersionPoliciesServicing
После этого Offline-установка компонент FOD станет доступна и через графический интерфейс Windows без использования танцев с PowerShell
Однако при этом стоит помнить про ранее обозначенный нюанс с пустым списком компонент в случае использования графического интерфейса в связке с UAC. То есть выполнять установку компонент FOD через графический интерфейс окна «Параметры Windows» нужно только при интерактивном входе в систему из под административной учётной записи. Если по какой-то причине заходить в систему администратором интерактивно нет желания/возможности, то можно использовать выше описанный метод с установкой через PowerShell.
При этом опять же стоит отметить то, что приятным плюсом использования настройки пути к компонентам FOD через групповую политику станет и то, что теперь при использовании PowerShell не потребуется явно указывать путь для установки нужных компонент:
И вроде бы теперь всё здорово, результат достигнут, то есть Offline-установка работает и через графический интерфейс и через PowerShell. Но дивные «фичи» на этом не кончаются.
Обработка «LocalSourcePath» с несколькими путями
Ещё одной странной штукой, которая была обнаружена при работе с выше обозначенным параметром групповой политики, это то, что, судя по описанию в GPO, значение опции «Alternate source file path» может принимать несколько путей с разделителем в виде точки с запятой. Однако практические эксперименты с Windows 10 1903 показали, что при считывании значения «LocalSourcePath» из реестра система заглядывает только в первый по счёту каталог (указанный до точки с запятой), а остальные игнорирует. Такое поведение вполне вписывается в рамки обработки значения ключа -Source командлета Add-WindowsCapability, в описании которого есть соответствующее примечание
If you specify multiple Source arguments, the files are gathered from the first location where they are found and the rest of the locations are ignored.
Вариантом выхода из этой ситуации может быть отказ от использования классического параметра из административных шаблонов GPO и настройка пути в реестре средствами Group Policy Preferences (GPP) с использованием таргетинга по версии и разрядности клиентской операционной системы.
По крайней мере именно на таком варианте мы и остановились, как на наиболее гибком и работоспособном.
Финиш
В итоге квест под названием «Выполнить Offline-установку RSAT в Windows 10 и не слететь с катушек» пройден, и теперь все административные пользователи, работающие на новой Windows 10 1903, могут устанавливать компоненты RSAT, как через графический интерфейс Windows, так и через PowerShell фактически в Offline-режиме и без дополнительных сложностей и манипуляций по аналогии с Online-клиентами.
PS: Никогда ещё установка RSAT в Windows у меня не была такой увлекательной и долгой. Чем больше смотрю на новые релизы Windows 10, тем становится интересней, во что же вся эта тенденция в итоге выльется. Коллега предположил, что в итоге получится, что-то вроде ранних выпусков Mandriva Linux – жутко красиво, но пользоваться этим без слёз невозможно
Начиная с Windows 10 1809 Microsoft изменила способ установки пакета удаленного администрирования серверов RSAT (Remote Server Administration Tools). Ранее после каждого апгрейда билда Windows 10 (например, с 1809 до 1903), вы должны были вручную скачать msu пакет с последней версией дистрибутива c RSAT и установить его на компьютере, то теперь на странице загрузки RSAT на сайте Microsoft висит следующая надпись:
IMPORTANT: Starting with Windows 10 October 2018 Update, RSAT is included as a set of «Features on Demand» in Windows 10 itself.
Содержание:
RSAT в Windows 10 как Features on Demand (FoD)
Дело в том, что, начиная с Windows 10 1809 (17763) вы более не должны вручную скачивать последнюю версию RSAT с сайта Майкрософт. Теперь пакет Remote Server Administration Tools встроен в образ Windows 10 и устанавливается в виде отдельной опции (Функции по требованию / Features on Demand). Установка RSAT возможно из приложения Параметры.
Дистрибутив Windows 10 не включает в себя установочные файлы RSAT, для их установки вашему компьютеру нужен прямой доступ в интернет. Кроме того, вы не может установить RSAT в Windows 10 Home редакции, подойдут только Professional и Enterprise версии.
Чтобы установить RSAT в Windows 10 1809, нужно перейти в раздел Settings -> Apps -> Manage Optional Features -> Add a feature (Параметры Windows -> Приложения -> Дополнительные возможности -> Добавить компонент). Здесь вы можете выбрать и установить нужные вам инструменты из пакета RSAT.
Доступны следующие инструменты администрирования:
- RSAT: Active Directory Domain Services and Lightweight Directory Services Tools
- RSAT: BitLocker Drive Encryption Administration Utilities
- RSAT: Active Directory Certificate Services Tools
- RSAT: DHCP Server Tools
- RSAT: DNS Server Tools
- RSAT: Failover Clustering Tools
- RSAT: File Services Tools
- RSAT: Group Policy Management Tools
- RSAT: IP Address Management (IPAM) Client
- RSAT: Data Center Bridging LLDP Tools
- RSAT: Network Controller Management Tools
- RSAT: Network Load Balancing Tools
- RSAT: Remote Access Management Tools
- RSAT: Remote Desktop Services Tools
- RSAT: Server Manager
- RSAT: Shielded VM Tools
- RSAT: Storage Migration Service Management Tools
- RSAT: Storage Replica Module for Windows PowerShell
- RSAT: System Insights Module for Windows PowerShell
- RSAT: Volume Activation Tools
- RSAT: Windows Server Update Services Tools
Установка RSAT в Windows 10 с помощью PowerShell
Вы можете установить компоненты администрирования RSAT с помощью PowerShell. В этом примере мы покажем, как управлять компонентами RSAT в Windows 10 1903.
С помощью следующей команды можно проверить, установлены ли компоненты RSAT в вашем компьютере:
Get-WindowsCapability -Name RSAT* -Online
Можно представить статус установленных компонентов RSAT в более удобной таблице:
Get-WindowsCapability -Name RSAT* -Online | Select-Object -Property DisplayName, State
Как вы видите, компоненты RSAT не установлены (NotPresent).
Для установки данных опций Windows можно использовать командлет Add-WindowsCapacity.
Чтобы установить конкретный инструмент RSAT, например инструменты управления AD (в том числе консоль ADUC и модуль Active Directory для Windows Powershell), выполните команду:
Add-WindowsCapability –online –Name “Rsat.ActiveDirectory.DS-LDS.Tools~~~~0.0.1.0”
Для установки консоли управления DNS и модуля PowerShell DNSServer, выполните:
Add-WindowsCapability –online –Name “Rsat.Dns.Tools~~~~0.0.1.0”
И т.д.
Add-WindowsCapability -Online -Name Rsat.BitLocker.Recovery.Tools~~~~0.0.1.0Add-WindowsCapability -Online -Name Rsat.CertificateServices.Tools~~~~0.0.1.0Add-WindowsCapability -Online -Name Rsat.DHCP.Tools~~~~0.0.1.0Add-WindowsCapability -Online -Name Rsat.FailoverCluster.Management.Tools~~~~0.0.1.0Add-WindowsCapability -Online -Name Rsat.FileServices.Tools~~~~0.0.1.0Add-WindowsCapability -Online -Name Rsat.GroupPolicy.Management.Tools~~~~0.0.1.0Add-WindowsCapability -Online -Name Rsat.IPAM.Client.Tools~~~~0.0.1.0Add-WindowsCapability -Online -Name Rsat.LLDP.Tools~~~~0.0.1.0Add-WindowsCapability -Online -Name Rsat.NetworkController.Tools~~~~0.0.1.0Add-WindowsCapability -Online -Name Rsat.NetworkLoadBalancing.Tools~~~~0.0.1.0Add-WindowsCapability -Online -Name Rsat.RemoteAccess.Management.Tools~~~~0.0.1.0Add-WindowsCapability -Online -Name Rsat.RemoteDesktop.Services.Tools~~~~0.0.1.0Add-WindowsCapability -Online -Name Rsat.ServerManager.Tools~~~~0.0.1.0Add-WindowsCapability -Online -Name Rsat.Shielded.VM.Tools~~~~0.0.1.0Add-WindowsCapability -Online -Name Rsat.StorageMigrationService.Management.Tools~~~~0.0.1.0Add-WindowsCapability -Online -Name Rsat.StorageReplica.Tools~~~~0.0.1.0Add-WindowsCapability -Online -Name Rsat.SystemInsights.Management.Tools~~~~0.0.1.0Add-WindowsCapability -Online -Name Rsat.VolumeActivation.Tools~~~~0.0.1.0Add-WindowsCapability -Online -Name Rsat.WSUS.Tools~~~~0.0.1.0
Чтобы установить сразу все доступные инструменты RSAT, выполните:
Get-WindowsCapability -Name RSAT* -Online | Add-WindowsCapability –Online
Чтобы установить только отсутствующие компоненты RSAT, выполните:
Get-WindowsCapability -Online |? {$_.Name -like "*RSAT*" -and $_.State -eq "NotPresent"} | Add-WindowsCapability -Online
Теперь убедитесь, что инструменты RSAT установлены (статус Installed);
После этого установленные инструменты RSAT отобразятся в панели Manage Optional Features.
Ошибка 0x800f0954 при установке RSAT в Windows 10
Если у вас на десктопах с Windows 10 есть доступ в Интернет, но при установке RSAT через Add-WindowsCapability или DISM (DISM.exe /Online /add-capability /CapabilityName:Rsat.ActiveDirectory.DS-LDS.Tools~~~~0.0.1.0), вы видите ошибку 0x800f0954, значит ваш компьютер настроен на обновление с локального сервера обновлений WSUS при помощи групповой политики.
Для корректно установки компонентов RSAT в Windows 10 1809+ вы можете временно отключить обновление со WSUS сервера в реестре (HKLMSOFTWAREPoliciesMicrosoftWindowsWindowsUpdateAU параметр UseWUServer = 0) и перезапустить службу обновления.
Можно воспользоваться таким PowerShell скриптом:
$val = Get-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:SOFTWAREPoliciesMicrosoftWindowsWindowsUpdateAU" -Name "UseWUServer" | select -ExpandProperty UseWUServerSet-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:SOFTWAREPoliciesMicrosoftWindowsWindowsUpdateAU" -Name "UseWUServer" -Value 0Restart-Service wuauservGet-WindowsCapability -Name RSAT* -Online | Add-WindowsCapability –OnlineSet-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:SOFTWAREPoliciesMicrosoftWindowsWindowsUpdateAU" -Name "UseWUServer" -Value $valRestart-Service wuauserv
Либо вы можете настроить новый параметр GPO, который позволяет настраивать параметры установки дополнительных компонентов Windows и Feature On Demand (в том числе RSAT).
- Откройте редактор локальной GPO –
gpedit.msc; - Перейдите в раздел Computer Configuration -> Administrative Templates -> System;
- Включите политику Specify settings for optional component installation and component repair, и включите опцию Download repair content and optional features directly from Windows Updates instead of Windows Server Updates Services (WSUS) (Скачайте содержимое для восстановления и дополнительные компненты непосредственно из Центра обновления Windows вместо использования службы WSUS);
- Сохраните изменения и обновите настройки политик (
gpupdate /force).
Теперь установка RSAT через PowerShell или Dism должна выполняться без ошибок.
Установка RSAT в Windows 10 в офлайн режиме
Если при установке RSAT вы столкнетесь с ошибкой Add-WindowsCapability failed. Error code = 0x800f0954, или в списке дополнительных компонентов вы не видите RSAT (Компоненты для установки отсутствуют), скорее всего ваш компьютер настроен на получение обновлений со внутреннего WSUS/SCCM SUP сервера.
Рассмотрим, как установить RSAT в Windows 10 1903 в офлайн режиме (корпоративная сеть без прямого доступа в Интеренет).
Для офлайн установки RSAT нужно скачать ISO образ диска с FoD для вашей версии Windows 10 из вашего личного кабинета на сайте лицензирования Microsoft — Volume Licensing Service Center (VLSC). Образ называется примерно так: Windows 10 Features on Demand, version 1903.
Например, для Windows 10 1903 x64 нужно скачать образ SW_DVD9_NTRL_Win_10_1903_64Bit_MultiLang_FOD_.ISO (около 5 Гб). Распакуйте образ в сетевую папку. У вас получится набор из множества *.cab файлов.
Теперь для установки компонентов RSAT на десктопе Windows 10 нужно указывать путь к данному сетевому каталогу с FoD. Например:
Add-WindowsCapability -Online -Name Rsat.ActiveDirectory.DS-LDS.Tools~~~~0.0.1.0 -LimitAccess -Source msk-fs01DistrWindows-FODWin101903x64
Также вы можете указать путь к каталогу с компонентами FoD с помощью рассмотренной выше групповой политики. Для этого в паромере Alternative source file path нужно указать UNC путь к каталогу.
Или можете задать этот параметр через реестр отдельной политикой, указав путь к каталогу в параметр LocalSourcePath (тип REG_Expand_SZ) в ветке реестра HKLMSOFTWAREMicrosoftWindowsCurrentVersionPoliciesServicing.
После этого, пользователи смогут самостоятельно устанавливать компоненты RSAT через графический интерфейс добавления компонент Windows 10.
Table of Contents
-
You have to choose the installer appropriate for your architecture. This is a 64-bit machine so in this case, we will go ahead and download the the WindowsTH-KB2693643-x64.msu file.
-
Double-click the installer file to start the installation. Accept the license terms and let it complete.
-
In earlier versions of Windows, one had to manually enable these tools after installing the RSAT package. But in Windows 10, once installed, these tools are readily available. You will notice that the tick box near the RSAT tools is checked which means we are good to go.
- Now go to Control PanelSystem and SecurityAdministrative Tools to find all the tools installed by RSAT.
To uninstall the RSAT package —
-
Go to Control Panel —> Programs —> Uninstall a Program.
-
Click View Installed Updates.
-
Right-click Update for Microsoft Windows (KB2693643), and then click Uninstall.
-
When asked for confirmation, click Yes.
To remove specific tools in the package —
-
Go to Control Panel —> Programs —> Programs and Features and click on Turn Windows Feature on and off.
-
Clear the check marks against the tools that you want to remove.
Running the Server Manager
The tools included in the RSAT package cannot be used to manage the local computer. A remote server or multiple remote servers must be specified in the Server Manager. Most of the tools in the RSAT package are integrated in the Server Manager so it’s a good idea to first add the server pools to the Server Manager before deploying these tools. To start the Server Manager,
- Click the Start button to bring up the Start Menu and click on the Server Manager tile. (or) Click on the Cortana search box in the taskbar and start typing ‘Server Manager’. You should be able to see the entry in Cortana. Click on the entry to start Server Manager.
- This opens the Server Manager dashboard.
-
From here, you can add remote servers and assign roles as needed.
-
If your part of a domain, you can search for servers in your organization’s Active Directory or you can input an IP address of your choice. You can also import server addresses from a file.
-
The Tools menu lists all the RSAT tools that are available for deployment on the remote server.
Pro-Tip
Sometimes you might be moving between clients and would want to still be able to control the remote server. But reconfiguring all settings again can be a hassle. If the Server Manager versions are similar, you can copy the files from the locations below on the initial client to the same locations on the new client. So the next time you start Server Manager on the new client, you’re previous configuration will be visible.
Copy the files from the following locations —
%appdata%MicrosoftWindowsServerManagerServerList.xml %appdata%LocalMicrosoft_CorporationServerManager.exe_StrongName_GUID6.2.0.0user.config Do remember that the Server Manager versions on the former and latter clients should be identical.
Known Issue
RSAT currently supports only the EN-US locale. If you install RSAT on a region other than EN-US, the installation will happen fine but you will not see any of the tools listed in the Turn Windows Features on and off dialog. As a workaround, install the EN-US language pack before installing RSAT. Once you are able to configure the tools in the Turn Windows Features on and off dialog, you can go back to your region and language of choice.
Summary
So that was a brief introduction to the RSAT package and the Server Manager program. As we have seen above, it is very easy to install and configure RSAT which enables efficient remote server administration from supported clients. There’s a lot to explore in Server Manager which begets a tutorial on its own. Absence of the GUI in servers is highly preferred as it minimizes the risk layer and frees up the CPU cycles and RAM to the designated server task, thereby enhancing overall efficiency. Although you can still RDP into the server, using RSAT greatly minimizes the need as the server is always available and multiple servers can be configured in one instance.
Используемые источники:
- https://blog.it-kb.ru/2019/05/31/offline-install-rsat-remote-server-administration-tools-from-feature-on-demand-sources-in-fod-share-for-windows-10-1903/
- https://winitpro.ru/index.php/2018/10/04/ustanovka-rsat-v-windows-10-iz-powershell/
- https://devops.ionos.com/tutorials/install-and-configure-remote-server-administration-tools-on-windows-10/