Duplicating the Python 3 executable python.exe and renaming it to python3.exe suggested in another answer is a terrible idea, please don’t do it, because you would have to repeat it every time you upgrade Python to a newer version and it’s likely that you’ll forget it and you’ll be surprised that your Python is broken after the upgrade.
I suggest the following simple setup.
Solution: Symbolic Link python3.exe
Just create a symbolic link named python3.exe in a directory which is in your PATH environment variable (but which is not under the Python 3 installation directory) pointing to the Python 3 executable python3/python.exe. The symbolic link stays there and keeps pointing to the correct executable even if you upgrade the Python (since it’s outside the Python 3 installation directory, it’s not affected even when the whole directory of an outdated Python is deleted and a new Python is placed there).
It’s very easy to prepare:
- Execute an elevated Powershell Core (
pwsh.exe), Powershell (powershell.exe), or Windows command shell (cmd.exe) - Decide where you want to create the symbolic link:
- Pick a directory already in your
PATHenvironment variable (useecho $env:PATHin Powershell orecho %PATH%incmd.exeto print the variable contents) - Add any directory you like to the
PATHvariable (see below)
- Pick a directory already in your
- Navigate to the directory you chose in the previous step and create there a symbolic link named
python3.exepointing to the Python 3 executable (thetargetparameter), both paths may be absolute or relative:-
in Powershell, use the
New-Itemcommand with the-Type SymbolicLinkoption:New-Item -Type SymbolicLink -Path python3.exe -Target c:<Python3-installation-directory>python.exe -
in
cmd.exe, use themklinkcommand:mklink python3.exe c:<Python3-installation-directory>python.exe
-
Now, if you execute python3 or python3.exe from any directory, Windows searches it in the current directory and then all directories in your PATH environment variable. It finds the symbolic link you have created which «redirects» it to the Python 3 executable and Windows executes it.
Notes
Which version executes python command?
What Python version is being executed by the command python when both Python 2 and 3 are installed, depends on the order of Python directories in the PATH environment variable.
When you execute a command and it’s not being found in the current working directory, Windows iterates through all directories in the PATH variable while keeping the order as they’re listed there and executes the first executable whose name matches the command (and it stops the searching).
So, when your PATH variable contains Python installation directories in the order c:devpython2;c:devpython3;..., then the python command executes python.exe in the c:devpython2 because it was found first.
The order depends on the order in which you have installed both Python versions. Each installation adds (if you check that option) its instalation directory at the beggining of PATH, so the most recently installed version will be executed when you execute just python. But you can reorder them manually, of course.
pip
There’s no issue with pip, because there’s already an executable named pip3.exe that’s located in a directory automatically added to the PATH during the installation by Python (<installation-root>Scripts, so just use pip3 for the Python 3’s pip and pip/pip2 for the Python 2’s pip.
Editing Environment Variables
- Open the Windows’ About dialog by pressing Win + Pause/Break or right-clicking This PC and selecting Properties
- Open the System Properties dialog by clicking the link Advanced system settings on the right side of the Settings dialog
- Open the Environment Variables dialog by clicking the button Environment Variables… at the bottom of the System Properties dialog
- Here, you can manage user variables and if you have the admin rights then also system variables
Содержание
- 1. Проверьте Установленный Python
- Установите Python на Ubuntu/Debian
- Установите Python на Fedora
- Установите Python на RHEL/CentOS
- Установите Python на Arch Linux
- 2. Проверьте путь переменной окружения
- 3. Проверка Сломанной Символической Ссылки
- Заключение
Ошибка – bash: python: command not found отображается в основном по трем причинам. Прежде всего, установлен ли на компьютере исполняемый файл python? Если он установлен. Тогда проверьте правильно ли настроена переменная окружения PATH. Чтобы он мог найти установленный исполняемый файл? Третьей причиной может быть сломанная символическая ссылка .
В этом руководстве показано, как исправить ошибку — bash: python: command not found. Давайте посмотрим, как решить эту проблему.
1. Проверьте Установленный Python
В большинстве случаев эта ошибка возникает в командной строке, потому что python не установлен или поврежден. Давайте сначала проверим, установлен Python или нет.
Выполните следующие команды, чтобы найти установленное местоположение python.
$ which python3
или введите команду
$ type -a python3
Терминал ответит:
python3 is /usr/bin/python3python3 is /bin/python3
или выдаст такой ответ:
$ ls -l /usr/bin/python
$ ls -l /usr/local/bin
Следующая команда проверит версии python:
$ python3 —version
Простая команда run python3:
$ python3
Python 3.8.2 (default, Jul 16 2020, 14:00:26)
[GCC 9.3.0] on linux
Type «help», «copyright», «credits» or «license» for more information.
Если python у вас не установлен, то в следующем разделе я покажу вам, как установить python.
Установите Python на Ubuntu/Debian
Debian и Ubuntu, а так же их производные дистрибутивы поставляются с предустановленным python. В случае, если он поврежден или не установлен, используйте следующую команду.
$ sudo apt install python
Примечание: приведенная выше команда установит python версии 2.
Python 2 После 1 января 2020 года Python 2 больше не получает никаких обновлений и не рекомендует его использовать.
или
Чтобы установить python 3, Введите команду:
$ sudo apt install python3
Python установленный из исходного кода, по умолчанию устанавливается в ‘http://usr/local/bin/’. В этом случае ввод python на консоли будет выполняться не внутри файла /usr/local/bin/, а внутри файла /usr/bin/.
Если вы хотите выполнить его внутри файла /usr/local/bin/, вы можете легко настроить систему, используя псевдоним (алиас). Псевдоним должен быть помещен в файл. bashrc, как показано ниже.
alias python=/usr/local/bin/python3.9
Установите Python на Fedora
Благодаря менеджеру пакетов dnf вы можете легко установить python на Fedora с помощью:
$ sudo dnf install python38
Установите Python на RHEL/CentOS
Чтобы установить Python на RHEL, Oracle Linux и CentOS, используйте команду yum следующим образом:
$ sudo yum install python
Установите Python на Arch Linux
В Arch Linux выполните следующую команду для установки python:
$ sudo pacman -S python2
$ sudo pacman -S python3
2. Проверьте путь переменной окружения
Каждый раз, когда пользователь запускает команду на консоли, машина ищет ее местоположение или адрес в списке предопределенных каталогов. Которые хранятся в переменной окружения PATH.
Такая конструкция помогает правильно запустить программу или команду без необходимости указывать абсолютный путь на терминале.
Переменная окружения PATH может быть временно изменена для текущего сеанса терминала или навсегда.
Для отображения содержимого переменной окружения PATH на консоли требуется ввести команду:
$ echo $PATH
Ответ терминала будет следующим:
:/usr/local/opt/ruby/bin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/bin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/sbin
Убедитесь, что установленный путь python добавлен в переменную PATH. Вы можете увидеть в приведенных выше выходных данных ‘/usr/bin’ и ‘/bin’ это пути для python 3. Так что они присутствуют. Чтобы сделать его постоянным, обязательно экспортируйте переменную PATH в ~/.bash_profile или в соответствующий конфигурационный файл, который запускает оболочку.
3. Проверка Сломанной Символической Ссылки
При запуске скрипта python вы можете понять, что символическая ссылка на исполняемые файлы Python указана неправильно.
Для указания /usr/bin/python на /usr/local/bin/python3.9 введите в терминал:
$ sudo ln -s /usr/local/bin/python3.9 /usr/bin/python
Заключение
Благодаря этой статье мы узнали, как правильно исправить ошибку — bash: python: command not found в вашей ОС Linux.
You are here: Home ‣ Dive Into Python 3 ‣
❝ Where’s the ANY key? ❞
— variously attributed
Diving In
FIXME
Getting to the Command Line
Throughout this book, there are examples of executing Python programs from the command line. Where is the command line?
On Linux, look in your Applications menu for a program called Terminal. (It may be in a submenu like Accessories or System.)
On Mac OS X, there is an application called Terminal in your /Applications/Utilities/ folder. To get there, click on your desktop, open the Go menu, select Go to folder..., and type /Applications/Utilities/. Then double-click the Terminal program.
On Windows, click Start, select Run..., type cmd, and press ENTER.
Running Python on the command line
Once you get to the command line, you should be able to run the Python interactive shell. On the Linux or Mac OS X command line, type python3 and press ENTER. On the Windows command line, type c:python31python and press ENTER. If all goes well, you should see something like this:
you@localhost:~$ python3 Python 3.1 (r31:73572, Jul 28 2009, 06:52:23) [GCC 4.2.4 (Ubuntu 4.2.4-1ubuntu4)] on linux2 Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information. >>>
(Type exit() and press ENTER to exit the Python interactive shell and go back to the command line. This works on all platforms.)
If you get a “command not found” error, it probably means you don’t have Python 3 installed.
you@localhost:~$ python3 bash: python3: command not found
On the other hand, if you get into a Python interactive shell but the version number is not what you expected, you may have more than one version of Python installed. This happens most often on Linux and Mac OS X systems, where an older version of Python is pre-installed. You can install the latest version without deleting the older version (they will live side-by-side in peace), but you will need to be more specific when you run Python from the command line.
For example, on my home Linux box, I have several versions of Python installed so I can test the Python software that I write. To run a specific version, I can type python3.0, python3.1, or python2.6.
mark@atlantis:~$ python3.0 Python 3.0.1+ (r301:69556, Apr 15 2009, 17:25:52) [GCC 4.3.3] on linux2 Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information. >>> exit() mark@atlantis:~$ python3.1 Python 3.1 (r31:73572, Jul 28 2009, 06:52:23) [GCC 4.2.4 (Ubuntu 4.2.4-1ubuntu4)] on linux2 Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information. >>> exit() mark@atlantis:~$ python2.6 Python 2.6.5 (r265:79063, Apr 16 2010, 13:57:41) [GCC 4.4.3] on linux2 Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information. >>> exit()
☜ ☞
© 2001–11 Mark Pilgrim
I’m very new to GitHub, I only came here for the PixelCanvas.io bots.
With that being said I have come across problems meanwhile trying to follow the instructions.
Can somebody please help?
Yes, my image is called image.png
AND I’m and the coordinates
So.. What am I doing wrong?
I do have the latest version of python
@Ungreatly Your OS = linux or winNT.
this terminal look at gitbash linux terminal emulations.
if R U use windows try it winkey+R type ‘cmd’ and following commnds
cd yoursPath
python ./setup.py
python ./main.py [yours parameters]
this is a not solved need yours
for windows echo %PATH%
for *ux printenv
wait i did it wrong lemme try again
@Ungreatly okay pls enter on cmd this command need yours result.
echo %PATH%
check yours python path.
So that seems to be the problem to this whole thing.
okey U need a adding python yours System path
referance this answer
https://stackoverflow.com/a/4855685
C:\python27 change to C:\YoursPythonPath
And try this Cmd
python —version
Thank you so much for your help!
But, I still have one issue.
It says IOError: [Errno 2] No such file or directory: ‘zoinks.jpg’
So… do I have to put the image in a certain folder?
Thanks!
You need to put the path of your image. Ex:
C:Tempzoinks.jpg
OR if you image are in the bot folder you just need to put the path relative the main folder. Ex:
imgzoinks.jpg
Generating converted image.
Alright I think I’m done with this.
I’ll just wait for the converted image.
Saved image cache file, Loading Now…
Alright, this seems good
KeyError: ‘waitSeconds’
EHHHH NEVERMIND
Fatal Python error: PyImport_GetModuleDict: no module dictionary!
this might help you solve they KeyError bug
@Ungreatly need your result, please
python --version
closed. I think it would be appropriate to move there once a similar topic has been opened.
@Ungreatly issues move at #60
Установка¶
Если у вас уже установлен Python 2.x, нет необходимости его удалять для того,
чтобы установить Python 3.0. Обе версии могут быть установлены в системе
одновременно.
Установка в GNU/Linux и BSD¶
Если вы используете один из дистрибутивов GNU/Linux, таких как Ubuntu, Fedora,
OpenSUSE, Debian, CentOS, или один из вариантов BSD, как
например, FreeBSD, то скорее всего, в вашей системе уже установлен Python.
Чтобы проверить, установлен ли Python на вашей машине с BSD или GNU/Linux,
откройте эмулятор терминала (например, konsole или gnome-terminal) и
введите команду python -V, как показано ниже.
$ — это приглашение командной строки. Оно может выглядеть по-разному
в зависимости от настроек вашей ОС, поэтому я буду обозначать приглашение
просто одним символом $.
Если вы видите информацию о версии, как показано выше, значит Python у вас уже
установлен.
Если же вы получаете такое сообщение:
$ python -V
bash: Python: command not found
значит, Python у вас не установлен. Это маловероятно, но всё же возможно.
Если у вас уже установлен Python 3.x, попробуйте python3 -V.
В этом случае у вас будут два варианта установки Python:
- Скомпилировать Python из исходных текстов
и установить его. Инструкция по компиляции есть на указанном веб-сайте. - Установить бинарные пакеты, используя пакетный менеджер, входящий в комплект
поставки вашей ОС, как например,apt-getв Ubuntu/Debian и других
дистрибутивах, основанных на Debian,yumв Fedora,pkg_addво FreeBSD,
и т. д. Обратите внимание, что для этого потребуется соединение с Интернетом.
В противном случае вы можете любым другим способом скопировать бинарники на
свой компьютер и установить оттуда.
Установка в Windows¶
Посетите страницу и загрузите последнюю версию.
Установка производится так же, как и для любых других программ для Windows.
Когда вам будет предложено отключить некоторые «опциональные» компоненты,
не отключайте ни одного! Некоторые из этих компонентов могут вам
пригодиться, особенно IDLE.
Интересно, что большую часть загрузок производят именно пользователи Windows.
Конечно, это не даёт представления о полной картине, поскольку у большинства
пользователей GNU/Linux Python установлен в системе по умолчанию.
Командная строка DOS¶
Для использования Python из командной строки Windows, т.е. приглашения DOS,
необходимо установить должным образом переменную PATH.
Для Windows 2000, XP, 2003 , перейдите в «Панель управления» —> «Система»
—> «Дополнительно» —> «Переменные среды». Нажмите на переменной с именем
PATH в отделе «Системные переменные», после этого выберите
«Редактировать» и допишите ;C:Python33 к концу того, что там уже есть
(проверьте, существует ли такой каталог, так как для более новых версий Python
он будет иметь другое имя). Конечно, укажите действительное имя каталога.
Для более старых версий Windows добавьте следующую строку в файл
C:AUTOEXEC.BAT : ‘PATH=%PATH%;C:Python33‘ (без кавычек) и
перезапустите систему. Для Windows NT используйте файл AUTOEXEC.NT.
Для Windows Vista:
- Нажмите кнопку «Пуск» и выберите «Панель управления».
- Нажмите «Система», справа вы увидите «Просмотр основных сведений о вашем
компьютере». Слева — список действий, последним из которых будет
«Дополнительные параметры системы.» Нажмите её. Отобразится вкладка
«Дополнительно» диалога параметров системы. Нажмите кнопку «Переменные
среды» справа внизу. - В нижнем поле под названием «Системные переменные» прокрутите до
Pathи
нажмите кнопку «Редактировать». - Измените путь, как нужно.
- Перезапустите систему. Vista не обновляет системные пути до перезагрузки.
Для Windows 7:
- Щёлкните правой кнопкой мыши на значке «Компьютер» на рабочем столе и
выберите «Свойства»; иначе — нажмите кнопку «Пуск» и выберите «Панель
Управления» —> «Система и безопасность» —> «Система». Нажмите
«Дополнительные параметры системы» слева, а затем выберите вкладку
«Дополнительно». Внизу нажмите кнопку «Переменные среды» и в отделе
«Системные переменные» найдите переменнуюPATH, выберите её и нажмите
«Редактировать». - Перейдите к концу строки в поле «Значение переменной» и допишите
;C:Python33. - Если значение переменной было
%SystemRoot%system32;, теперь оно примет
вид%SystemRoot%system32;C:Python33 - Нажмите «Ok», и всё. Перезагрузка не требуется.
Запуск командной строки Python в Windows¶
Если вы должным образом установили значение переменной PATH,
теперь можно запускать интерпретатор из командной строки.
Чтобы открыть терминал в Windows, нажмите кнопку «Пуск» и выберите «Выполнить».
В появившемся диалоговом окне наберите cmd и нажмите Enter.
Затем наберите python и проверьте, нет ли ошибок.
Для пользователей Mac OS X¶
У пользователей Mac OS X Python уже будет установлен в системе. В противном
случае вы можете открыть терминал, нажав Command+Пробел, набрав в
открывшейся строке поиска Terminal и нажав Enter.
Затем установить Homebrew, выполнив:
ruby -e "$(curl -fsSkL raw.github.com/mxcl/homebrew/go)"
После чего установить Python 3 при помощи:
А теперь запустите python3 -V и проверьте, нет ли ошибок.
Резюме¶
У пользователей систем GNU/Linux и BSD, вероятнее всего, Python уже установлен.
В противном случае его можно установить, используя пакетный менеджер,
поставляемый с вашим дистрибутивом. Для Windows установка Python сводится к
загрузке установщика и двойному щелчку на нём. С этого момента мы будем считать,
что Python 3 в вашей системе установлен.
Далее мы приступим к написанию нашей первой программы на Python.

Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Overview
- Specify the full location to python.exe
- Add the full location of python.exe to PATH
- Manually
- Summary
- Next Steps
Introduction
One of the most frustrating aspects of learning how to code in Python doesn’t even involve any coding itself. For many beginners, simply getting Python to run on their local machine can present a significant challenge.
Windows users in particular may find themselves greeted with a strange and convoluted error message when trying to run Python from the Command Prompt: 'python' is not recognized as an internal or external command, operable program or batch file.
In this article, you’ll take a closer look at the error ‘python’ is not recognized as an internal or external command and see a few quick fixes for it.
Note that the exact spelling of this error could vary slightly, and this article may help you if you’re encountering similar errors that include messaging like Python Not Found or Python Was Not Found.
Overview
You may have seen this error if you’re running Python on a Windows machine. If you’re a Linux or Mac user, then skip to the section titled, «What if I’m on a different operating system?». But before we discuss how to fix this error, let’s get a better understanding of why it occurs.
Once Python is installed on your Windows machine, you’ll likely try to run it in one of two ways.
The first way is to locate the Python executable on your system and double-click on it. This is the actual executable file for Python itself, which you downloaded from the official Python downloads page.
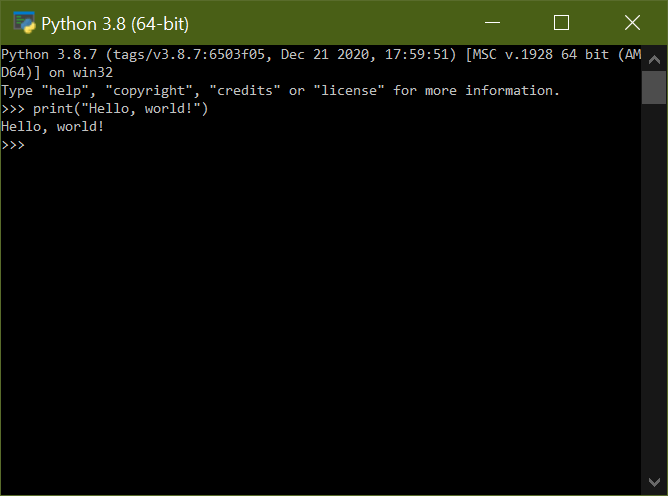
This will open up the Python IDE in a separate window, and you’ll be able to code in the interactive interpreter:
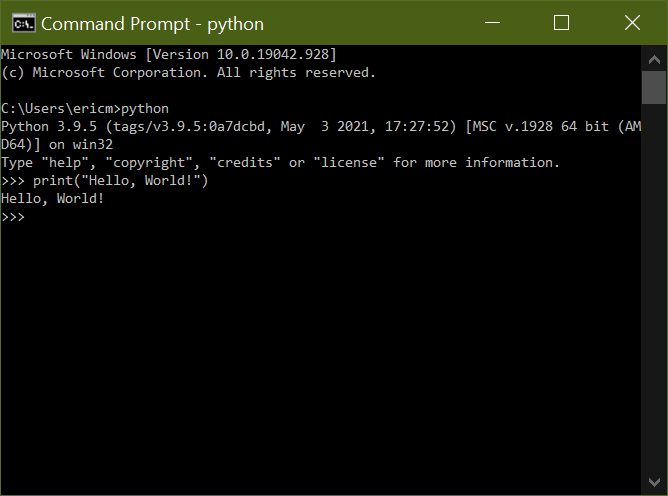
The second way is to open up a Command Prompt, type the word python, and press Enter. Ideally, this would open up an instance of Python in the same window:
Unfortunately, there’s also a chance that you could come up against this error:
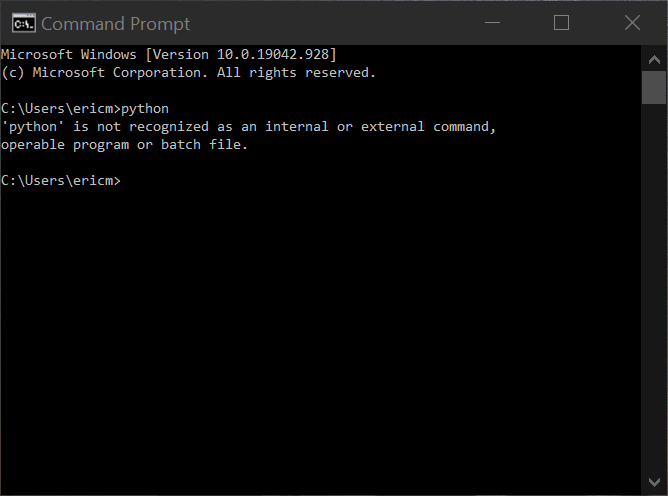
In this case, you’ll be greeted instead with an error message that reads, «‘python’ is not recognized as an internal or external command, operable program or batch file.»
So, what does this strange error mean, and why are you seeing it? Well, whenever you run a program on your machine, your computer needs to know exactly where on your machine that program file is located so it can be executed.
When you navigated to the folder that contained the executable Python file and clicked on it, Windows knew exactly what file you wanted it to run, and opened the Python interpreter with no problems.
However, when you try to run a program from the Command Prompt, Windows will only run that program if it already knows where on your machine that file is located. It does this via the PATH environment variable.
Environment variables tell the computer facts about the runtime environment of the current operating system. For example, USER will tell the computer system who the current logged-in user is, and HOME will give the location of that user’s home directory.
The PATH environment variable tells the system which directories it should look in for executable programs. When a user types a program name in the Command Prompt and doesn’t specify the exact file location of that program, then the computer system will search all of the directories listed in the PATH to find the location of the file and execute it.
This means that if the directory that holds the program you want to execute is not listed in the PATH environment variable, then Windows won’t search that folder for any executable files. In other words, it will never find Python and won’t be able to execute it from the Command Prompt.
In the next couple of sections we will discuss how to fix: ‘python’ is not recognized as an internal or external command, operable program or batch file
There are several ways to fix this error, but let’s take a look at some of the most common.
Specify the full location to python.exe
You learned previously that this error occurs when Windows can’t find the location of the Python executable file.
One way to fix the error would be to launch Python from the Command Prompt by passing in the full path to the executable file each time you wanted to run Python. In other words, instead of typing Python you would type something like C:Usersmepathtopython.exe.
To find the full path, open up the Start menu and search for «Python»:
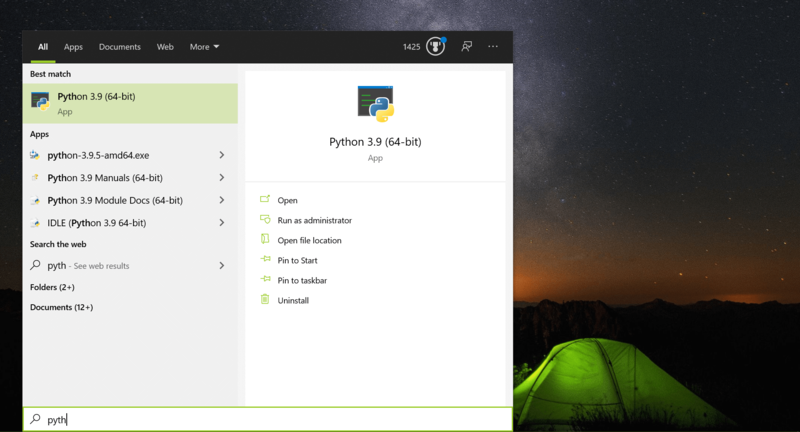
Select Open file location, which should bring up an Explorer window with the folder containing the Python executable. (Note that this may be a shortcut, in which case you’d need to right-click on the Python executable and select Open file location a second time.) In the end, you should see a file called python.exe.
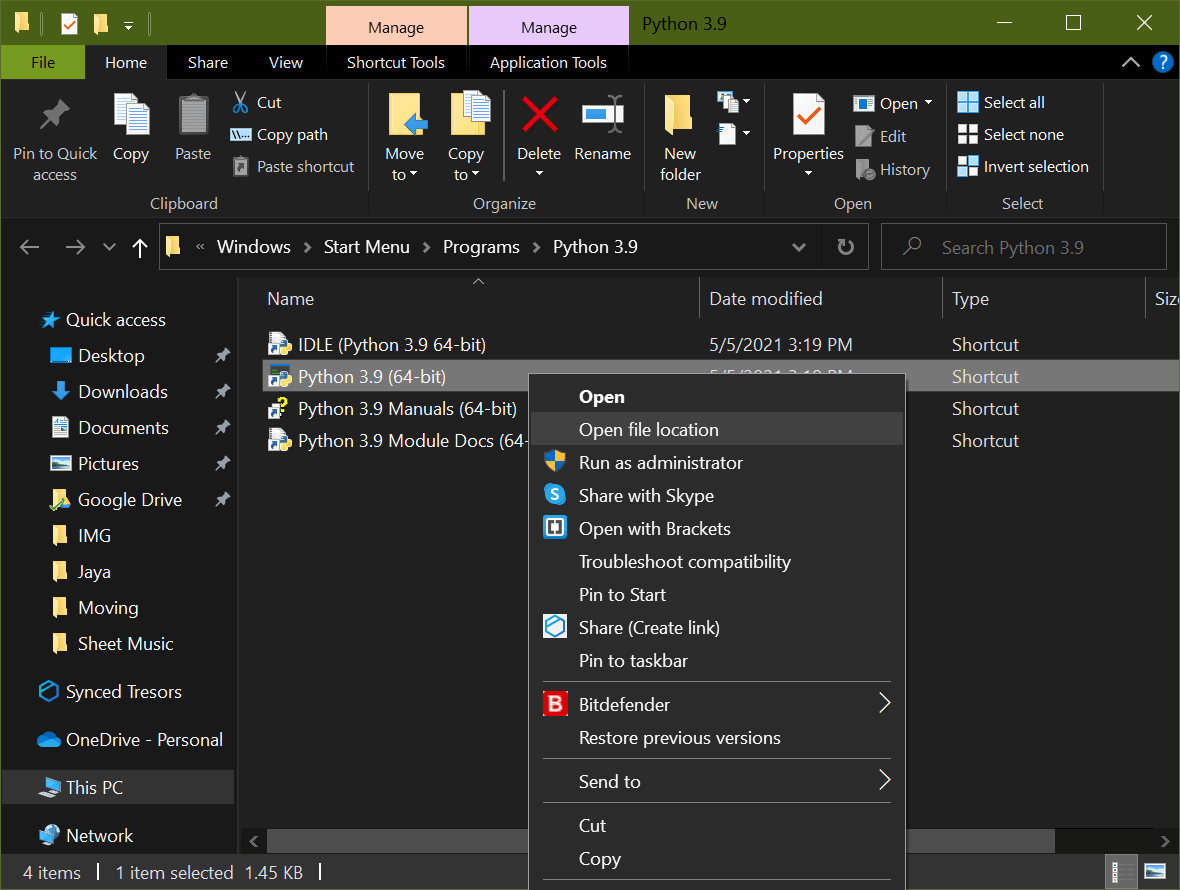
You want to right-click on this file and select Properties:
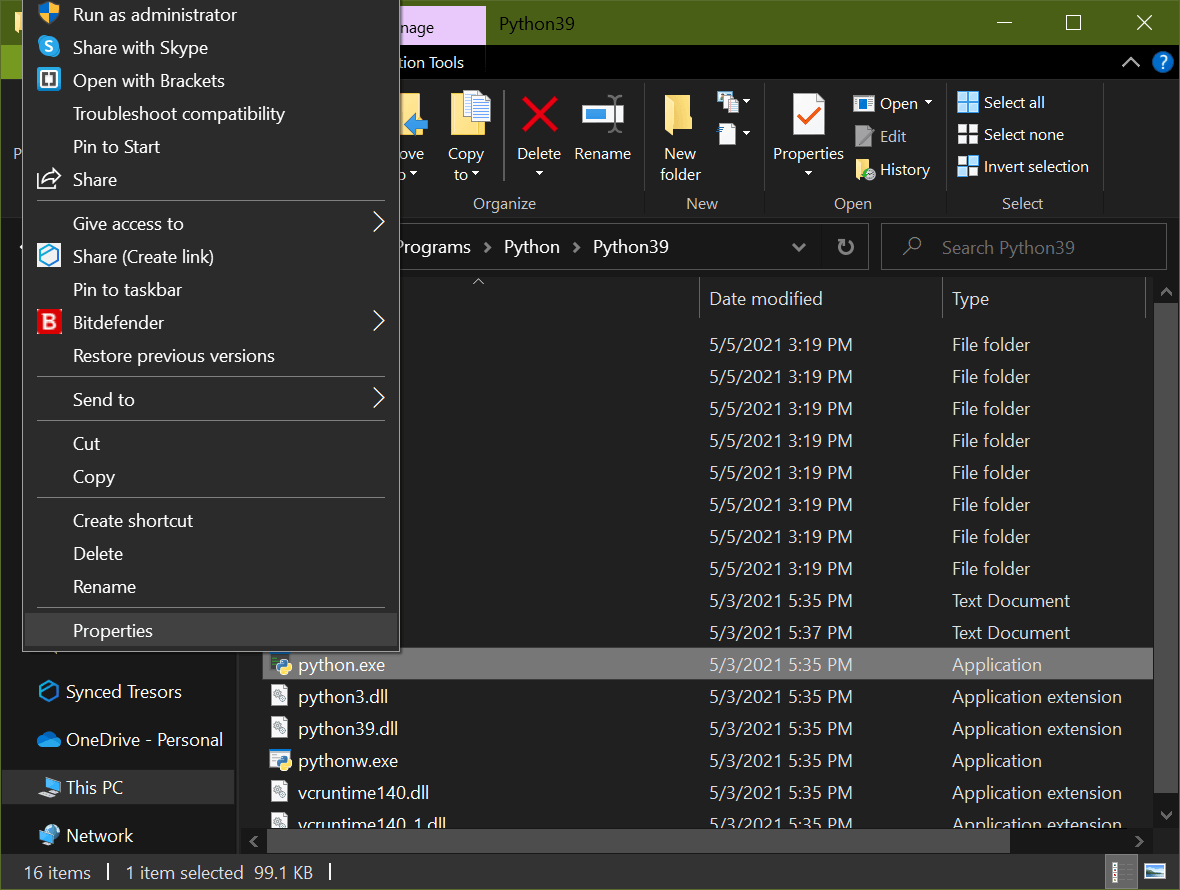
Under the General tab, you’ll see an entry titled Location which contains the full system path to this executable file:
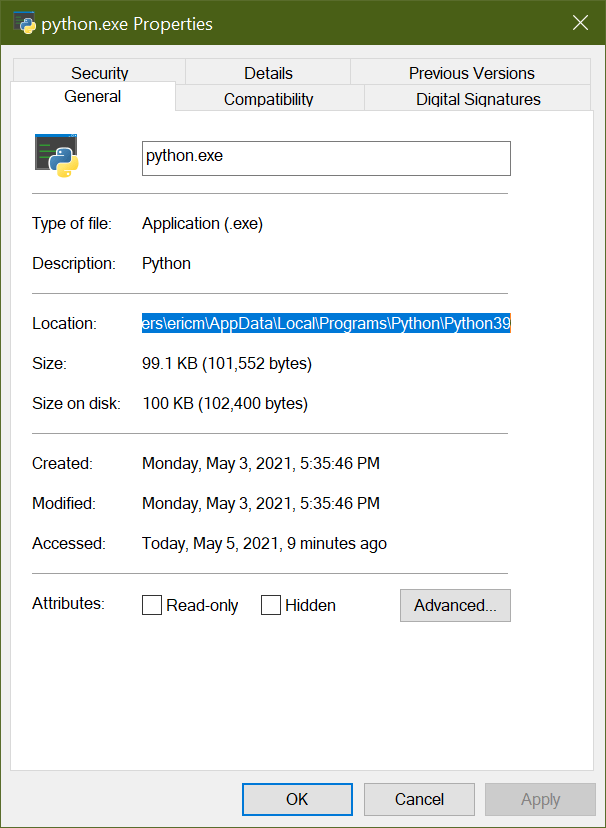
Copy this path and return to the Command Prompt. Paste it in, add a trailing slash and python.exe to denote the program file, and press Enter. Python should launch without issue:
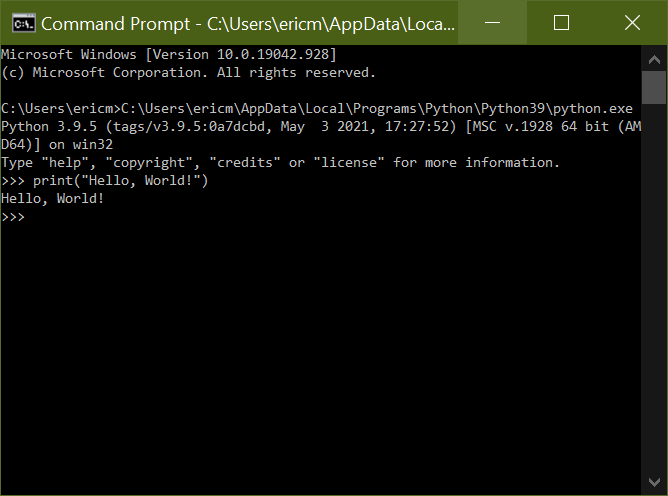
This will successfully allow you to run Python from the Command Prompt. However, the process of locating the exact file path can be tedious, and with this fix, you’d need to provide this every single time you wanted to run Python.
Thankfully, instead of specifying the full path each time, you can simply add this file location to your system PATH.
Add the full location of python.exe to PATH
Recall that the PATH environment variable tells your system which directories it should look in to locate executable programs. In order to be able to run Python from the Command Prompt, you need to make sure that the directory the Python executable file is contained in is listed in the system PATH.
When you first install Python, there is an option you can select to have the installer do this for you:
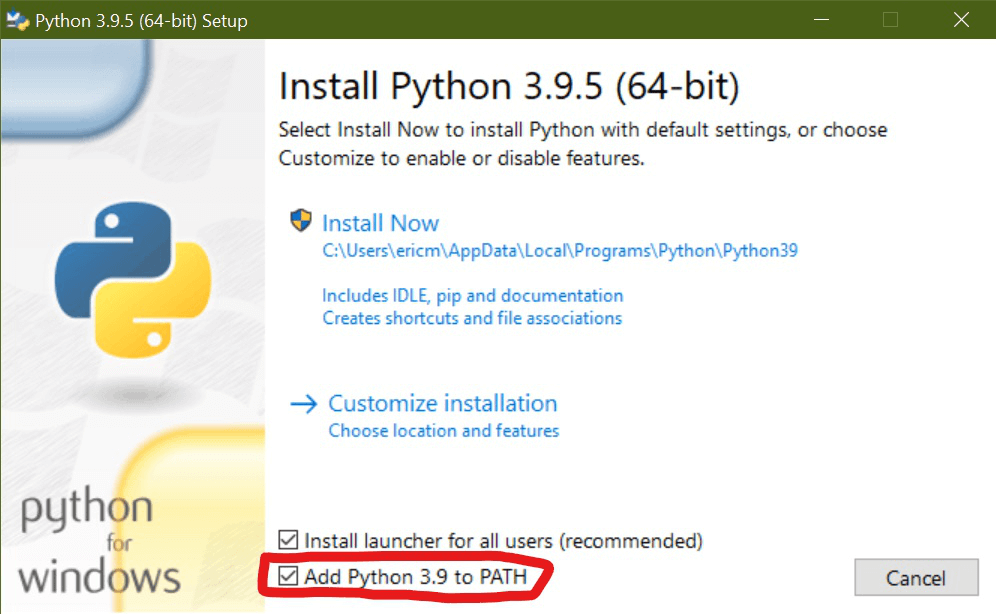
However, if you did not select this option during installation, you can still go back and add it later.
There are two main ways to accomplish this: through the installer and manually.
Installer
When you first download Python from the official Python downloads page, your computer will save an installation file titled python-3.9.5-amd64.exe or something similar to a specified directory, usually your Downloads folder. You can use this same installer to update your Python installation and add its location to your system PATH.
Search for the installer from the Start menu or locate it in your Downloads folder (or whichever folder you downloaded it to). When you click on it this time, instead of asking you to install Python, it should present you with several options for modifying your setup:
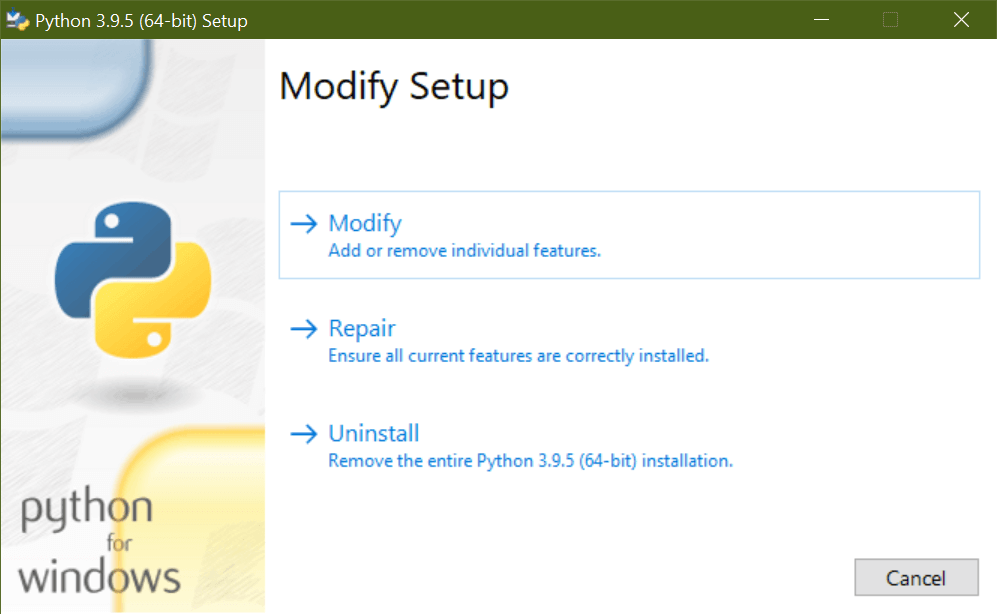
Clicking Modify will take you to the Optional Features page:
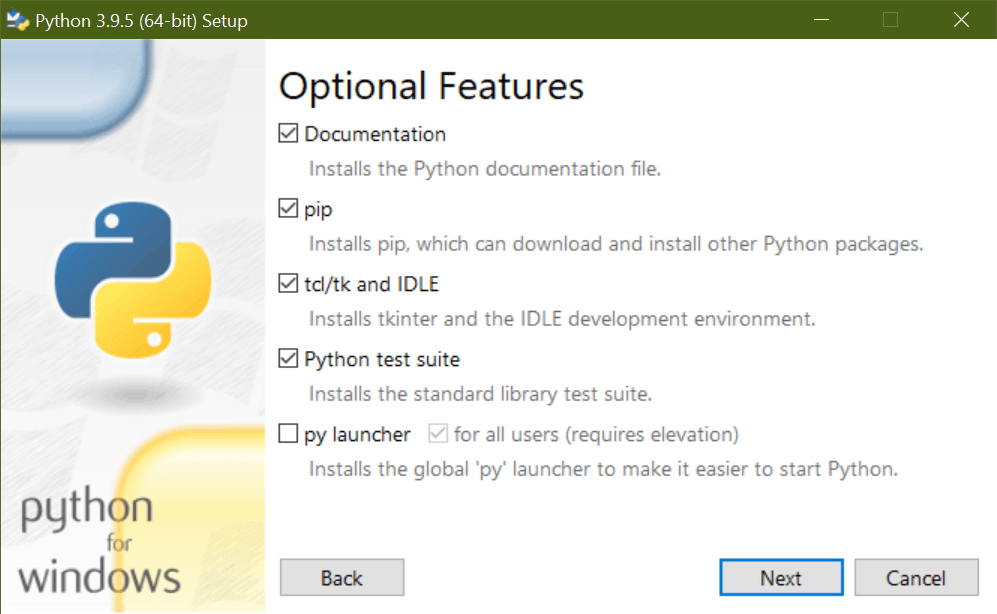
From here, you should click Next until you see the Advanced Options page. On this page, select the checkbox that says Add Python to environment variables:
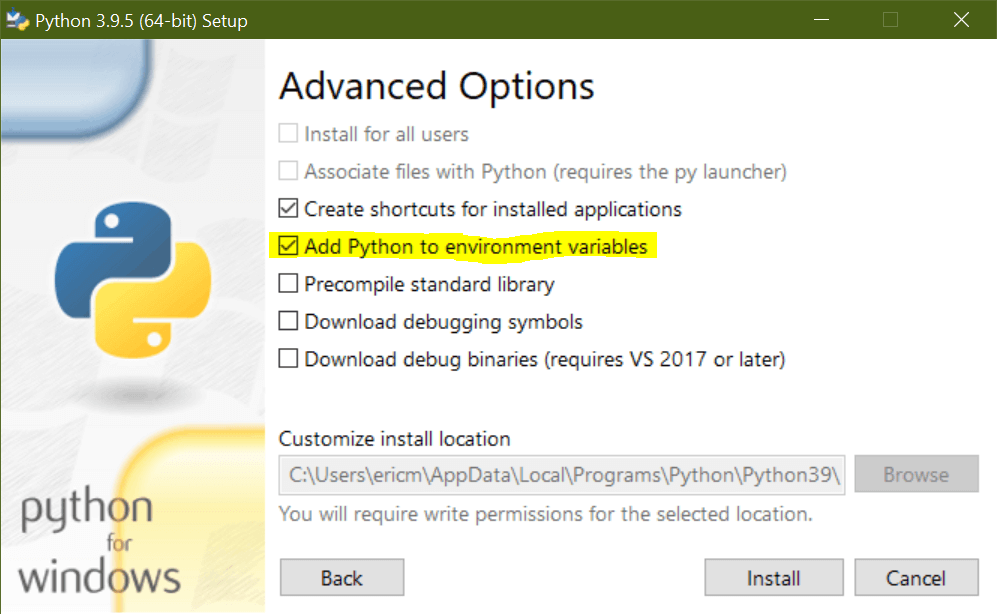
The installer will modify your Python installation and add the executable program location to your system PATH variable. Once the modification is complete, you can open up the Command Prompt and type python to enter the interpreter:

You should see no errors at this point.
Manually
If you can’t find where you downloaded the Python installer, or you removed it from your computer already, you can always modify the PATH environment variable yourself. This section walks you through how to accomplish this.
First, you need to have the full path to the directory containing the python.exe program file. (Refer to the section «Specify the full location to python.exe» for how to do this.)
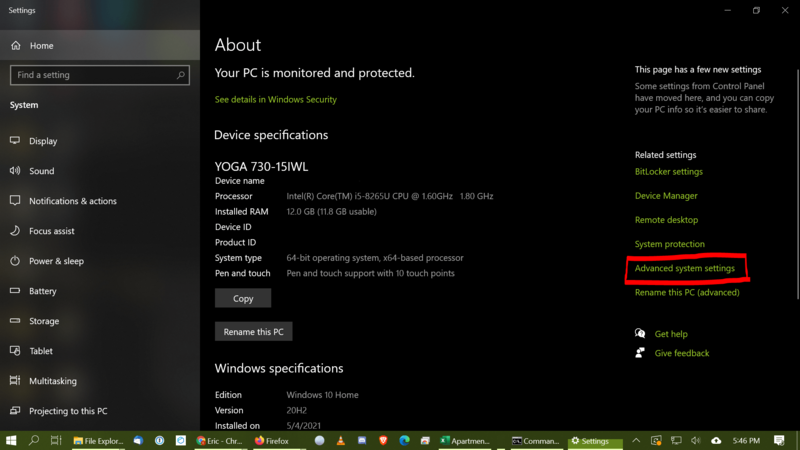
Once you have the file location, you’ll need to append it to the end of your system PATH. To modify the path, first open your system settings. You can usually get to the system settings by opening the Start menu and searching for About your PC. Click on Advanced system settings (located in the menu on the right-hand side):
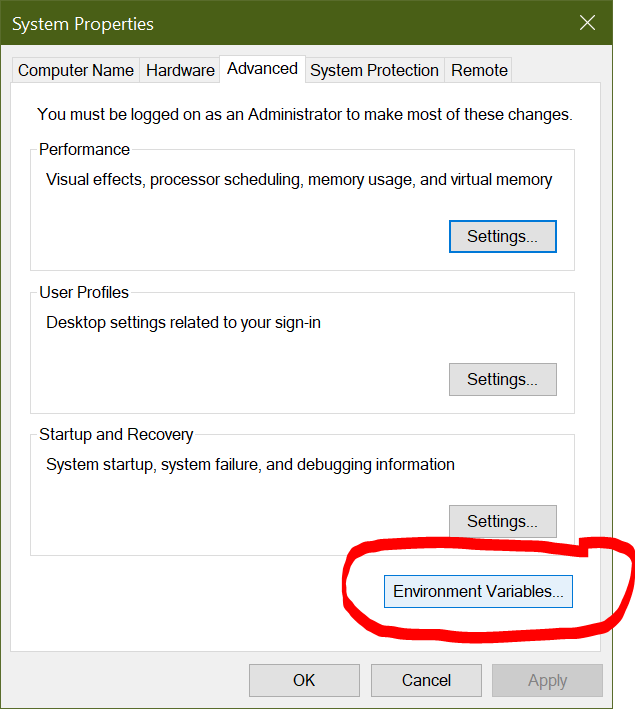
You’ll be redirected to a System Properties dialog box. Under the Advanced tab, click Environment Variables:
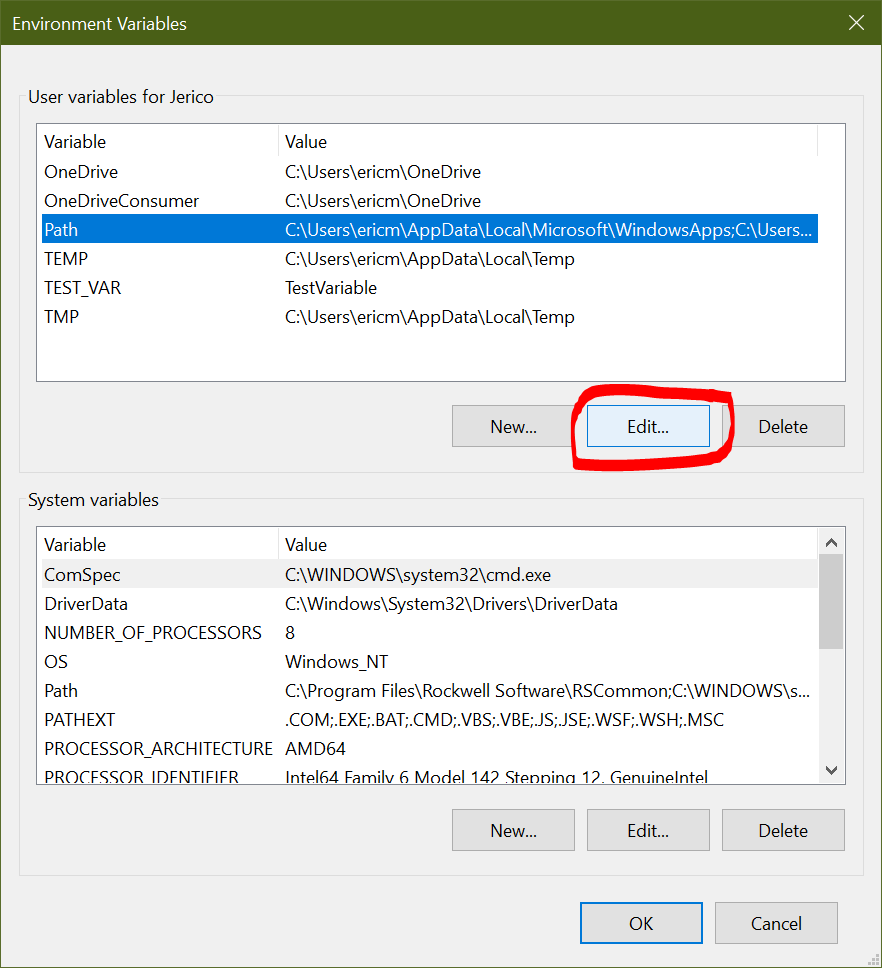
This will open up the Environment Variables dialog box. Here is where your system PATH is defined. This is the variable you’ll want to change to tell your Windows machine where to find the Python executable program. Make sure you’ve selected the path environment variable, then click Edit:
Now, you’ll have the option to edit the PATH environment variable. Click New, which should append a new element to the list:
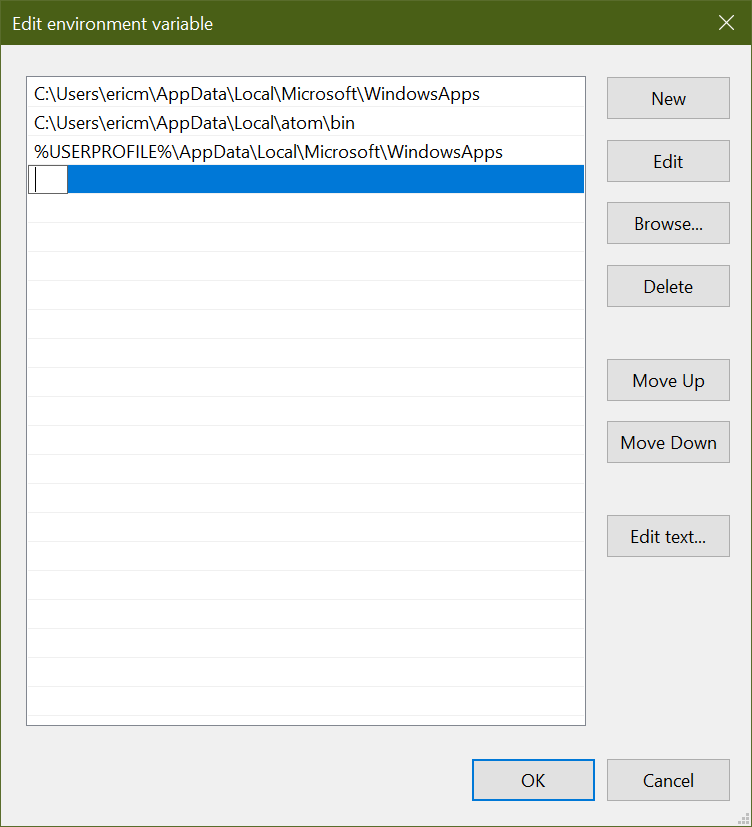
This is where you’ll want to enter the full path to the directory containing the python.exe file you located earlier:
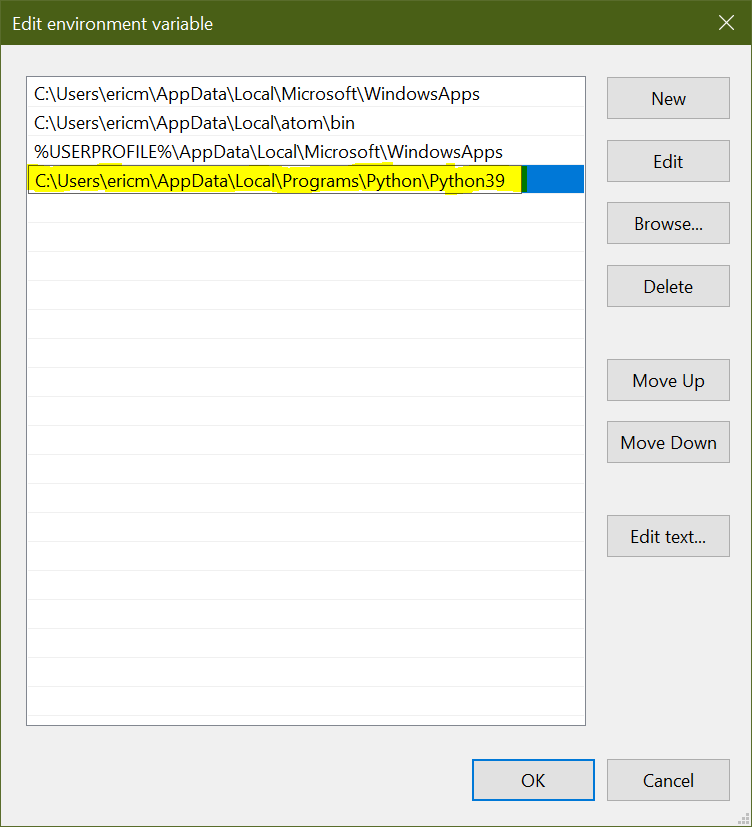
Click OK on each dialog box until you’ve exited out of all of them completely.
That’s it! You should be able to open up a Command Prompt and type python, and the command should execute with no errors:

What if I’m on a different operating system?
The error «‘python’ is not recognized as an internal or external command, operable program or batch file» is specific to the Windows operating system. If you’re on a different operating system, you likely won’t see these exact words. In particular, Unix-based systems like Linux or macOS will say something a little bit different:
user@host:~$ python
bash: python: command not found
In this case, the problem is often the same — the operating system cannot find the python command, because the location of the binary file is not defined in the system PATH.
Luckily, for Unix-based systems, the fix is often much simpler — just check to make sure that you actually have Python installed! These operating systems will typically install Python under /usr/bin or /usr/local/bin, directories which are included in the system path by default.
You can confirm this by echoing the PATH environment variable to stdout:
user@host:~$ echo $PATH
/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin:
If you’re seeing a python: command not found error on a Unix-like operating system, simply use your package manager to install the latest version of Python and then try running the command again.
Summary
In this tutorial, you saw how to solve an error that many Windows users encounter when they first try to run Python on their machines: 'python' is not recognized as an internal or external command, operable program or batch file. This error appears on Windows operating systems when the location of the Python executable file has not been properly specified in the system PATH environment variable.
You saw how to circumvent this error by simply specifying the full location to the python.exe file each time you wanted to run Python from the Command Prompt. You also learned how to add this file location to your system PATH so Windows will be able to find it automatically. You did this using the Python installer as well as manually by editing the PATH environment variable.
Finally, you saw a similar error that users of Unix-based systems might come up against, as well as a quick way to solve it.
Next Steps
Congrats! Now that you’ve got Python up and running on your machine, it’s time to dive deep into coding. Looking for the basics to get started? Check out our tutorial on comparing Python strings or using the sum function in Python.
Do be aware that the error you solved in this tutorial won’t be the only one you encounter on your Python journey. For example, the return outside function error in Python is another one that’s likely to come up early on.
If you’re interested in learning more about the basics of Python, coding, and software development, check out our Coding Essentials Guidebook for Developers, where we cover the essential languages, concepts, and tools that you’ll need to become a professional developer.
Thanks and happy coding! We hope you enjoyed this article. If you have any questions or comments, feel free to reach out to jacob@initialcommit.io.
Final Notes
Ошибка – bash: python: command not found Error отображается в основном по трем причинам. Прежде всего, установлен ли на машине исполняемый файл python? Если он установлен, правильно ли настроена переменная среды PATH, чтобы она могла найти установленный исполняемый файл? Третьей причиной может быть неработающая символическая ссылка.
В этой статье показано, как исправить ошибку – bash: python: command not found. Давайте посмотрим, как решить эту проблему.
1. Проверьте, установлен ли Python.
В большинстве случаев эта ошибка возникает в приглашении оболочки или командной строке, потому что python не установлен или поврежден. Давайте сначала проверим, установлен ли Python.
Выполните следующие команды, чтобы найти установленное местоположение Python.
$ which python3
или же
$ type -a python3
Вывод:
python3 is/usr/bin/python3 python3 is/bin/python3
или же
$ ls -l/usr/bin/python $ ls -l/usr/local/bin
Запустите команду, чтобы проверить версию Python:
$ python3 --version
Простая команда запуска python3:
$ python3 Python 3.8.2 (default, Jul 16 2020, 14:00:26) [GCC 9.3.0] on linux Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
Если вы не нашли установленный python, в следующем разделе я покажу вам, как установить python.
Установите Python в Ubuntu/Debian
Debian, Ubuntu и производные от них дистрибутивы поставляются с предустановленным python. Если он поврежден или не установлен, используйте следующую команду.
Чтобы установить python 2, введите:
$ sudo apt install python
After January 1, 2020 Python 2 no longer receives any updates, and recommend not using it.
или же
Чтобы установить python 3, введите:
$ sudo apt install python3
Python установлен из исходников, по умолчанию установлен в http://usr/local/bin/. В этом случае при вводе python в консоли будет выполняться не тот, который находится внутри /usr/local/bin/, а тот, который находится внутри/usr/bin/.
Если вы хотите выполнить тот, который находится внутри /usr/local/bin/, вы можете легко настроить систему, используя псевдоним. Псевдоним следует поместить в файл.bashrc, как показано ниже.
alias python=/usr/local/bin/python3.9
Установите Python в Fedora
Благодаря диспетчеру пакетов dnf вы можете легко установить python в Fedora:
$ sudo dnf установить python38
Установите Python на RHEL/CentOS
Чтобы установить Python на RHEL, Oracle Linux и CentOS, используйте команду yum следующим образом:
$ sudo yum установить python
Установите Python в Arch Linux
В Arch Linux выполните следующую команду для установки python:
$ sudo pacman -S python2
$ sudo pacman -S python3
2. Проверьте переменную среды PATH.
Каждый раз, когда вы, как пользователь, запускаете команду на своей консоли, машина ищет ее местоположение или адрес в списке предопределенных каталогов, которые хранятся в переменной среды PATH.
Такой дизайн помогает правильно запускать программу или команду без необходимости указывать абсолютный путь в терминале.
Переменная окружения PATH может быть изменен временно для текущего сеанса терминала, или на постоянной основе .
Чтобы отобразить содержимое переменной среды PATH на консоли:
$ echo $ PATH
Вывод:
:/usr/local/opt/ruby/bin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/bin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/sbin
Убедитесь, что установленный путь Python добавлен в переменную PATH. Вы можете видеть в приведенном выше выводе пути ‘/usr/bin’ и ‘/bin’ для python 3. Чтобы сделать его постоянным, обязательно экспортируйте переменную PATH в ~/.bash_profile или в соответствующий файл конфигурации, запускающий оболочку.
3. Отметьте битую символическую ссылку.
При запуске скрипта python вы можете понять, что символическая ссылка на исполняемые файлы Pythons указана неправильно.
Чтобы изменить каталог /usr/bin/python на/usr/local/bin/python3.9, введите:
$ sudo ln -s/usr/local/bin/python3.9/usr/bin/python
Вывод
В этой статье мы узнали, как правильно исправить ошибку -bash: python: command not found на вашем компьютере с Linux.
Если вы нашли ошибку, пожалуйста, выделите фрагмент текста и нажмите Ctrl+Enter.


