| Particle | |
|---|---|
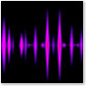
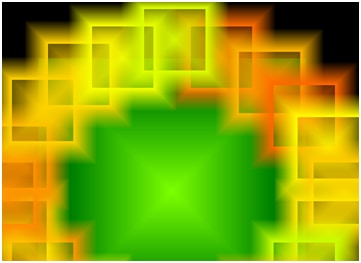
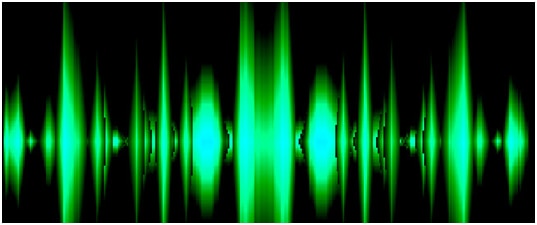
 The Particle visualization, set to the «Particle» preset. |
|
| Description | |
| Versions Available in: | 7, 7.1, 8, 9 Series, 10 |
| Current Status: | Former visualization |
| Developed by: | Averrett & Microsoft |
| Years Available: | 2000 — 2006 |
| Random Preset: | No |
| Related Visualizations: | Bars and Waves, Battery, Musical Colors, Spikes |
| Full-Screen Controls | Yes |
| Gallery |
Particle was a visualization in Windows Media Player formerly known as «Dotplane» in Windows Media Player 7, and «Particle» in 7.1 through 10. It was a flat, squared-shaped grid with red, purple, blue, and cyan dots. Unfortunately, it was removed in version 11 due to DXE problems. Other visualizations that were removed were Ambience, Musical Colors, Plenoptic, and Spikes.
Presets
- Particle
- Rotating Particle
Trivia
- Despite Particle wasn’t in alphabetical order, though Particle was originally called as «Dotplane»
- The Rotating Particle gets broken when it still for 10 minutes or more (while playing a song).
Windows 10 Windows 8.1 Windows Media Player Windows 7 Еще…Меньше
Зрительные образы — это цвета, формы и узоры, движущиеся в такт музыке, когда проигрыватель Windows Media работает в режиме «Проигрывается». У игрока есть несколько зрительных образов, и вы можете скачать дополнительные сведения на этой странице.
|
|
|
|
Загрузка & партнеров |
|
|
|
|
Загрузка & партнеров |
|
|
|
|
Загрузка & партнеров |
|
|
|
|
Нужна дополнительная помощь?
Содержание
- Plenoptic
- Smokey Circles Preset Variations
- Musical Colors
- Contents
- Musical Colors File and Installation
- For Windows XP
- For Windows Media Player 11 on XP and Windows Vista
- For Windows Media Player 12, for Windows 7, 8, 10 or 64 Bit
- Musical Colors Versions
- Windows media player visualizations
- Part 1: Top 10 Visualizations for Windows Media Player
- 1. Blazing colors
- 2. Color Cubes
- 3. Dungeon Siege
- 4. Energy Bliss
- 5. G-Force Visualization
- 6. Morphyre
- 7. Soft Skies
- 8. White Cap
- 9. Windows Media 9 series
- 10. Trilogy II
- Part 2:How to Turn On Visualizations in Windows Media Player
- Musical Colors File and Installation
- For Windows XP
- For Windows Media Player 11 on XP and Windows Vista
- For Windows Media Player 12, for Windows 7, 8, 10 or 64 Bit
- Musical Colors Versions
- More results for «Windows media player visualizations»
- Brian’s Blog
- How To Get Musical Colors Back On Windows Media Player
- Compatibility
- Musical Colors Versions
- Locating The Musical Colors File
- Installation
- Names of the Visualizations
- Lost Musical Colors Visualizations
- Windows media player 9 series musical colors
- Musical Colors
- Contents
- Musical Colors File and Installation
- For Windows XP
- For Windows Media Player 11 on XP and Windows Vista
- For Windows Media Player 12, for Windows 7, 8, 10 or 64 Bit
- Musical Colors Versions
- Brian’s Blog
- How To Get Musical Colors Back On Windows Media Player
- Compatibility
- Musical Colors Versions
- Locating The Musical Colors File
- Installation
- Names of the Visualizations
- Lost Musical Colors Visualizations
- Ambience
- Contents
- History
- Color Variations
- Thingus Preset
- About the Windows Media Codecs
- Windows Media Audio Codecs
- Windows Media Audio 9
- Windows Media Audio 10 Professional
- Windows Media Audio 9 Lossless
- Windows Media Audio 9 Voice
- Compatibility
- Windows Media Video 9 Series Codecs
- Windows Media Video 9
- Simple and Main Profiles
- Advanced Profile
- Windows Media Video 9 Screen
- Windows Media Video 9 Image Version 2
- Windows Media Video 9 VCM
- Compatibility
Plenoptic
| Plenoptic | |
|---|---|
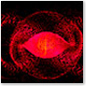
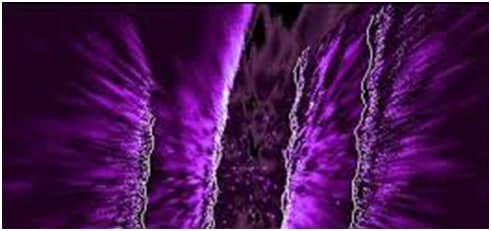
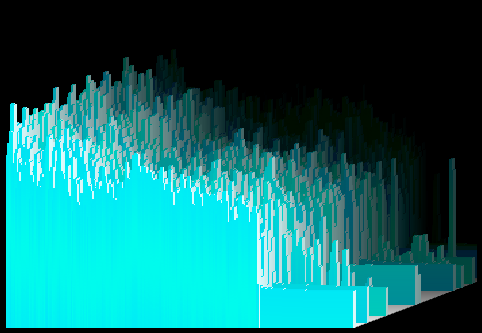
 The Plenoptic visualization, set to the «Smokey Circles» preset. |
|
| Versions Available in: | 7, 7.1, 8, 9 Series, 10 |
| Current Status: | Former visualization |
| Developed by: | Averett & Microsoft |
| Years Available: | 2000-2006 |
| Random Preset: | Yes |
| Related Visualizations: | Alchemy, Ambience, Battery, Musical Colors, Trilogy |
| Full-Screen Controls: | On Windows XP in WMP9 Series in which the graphics card driver is not installed. |
| Gallery |
Plenoptic was a visualization for Windows Media Player versions 7-10. It is in the Musical Colors Family. This kind of visualization was a paint look-a-like. Unfortunately, this visualization, like Ambience, Musical Colors, Particle, and Spikes, was removed because it had problems with full-screen controls for versions 11 and 12. Actually, Sticky Keys XP recently as of 2018 discovered Plenoptic has full screen controls if you use it on a Windows XP computer with Windows Media Player 9 Series without a graphics card driver installed (Standard VGA Driver).
Smokey Circles Preset Variations
The «Smokey Circles» preset goes from blue and green to yellow and orange first, then later to other arrangements of those colors.
Источник
Musical Colors
The Musical Colors visualization, set to the «Colors in Motion» preset.
Ice Crystals, a preset from the visualization Musical Colors.
Musical Colors is a visualization of twenty-one presets created by Averett & Microsoft. It is one of the oldest visualizations on Windows Media Player, and the visualization first appeared in Windows Media Player 7. There are two different versions to this visualization.
Musical Colors also has a large collection of «sister» visualizations in the Musical Colors Family. Shockingly, later on starting with the Windows Media Player 9 and 10 Series, Musical Colors had disappeared. This occurred because It had certain issues with certain video cards. Fortunately, it can be reinstalled by following these steps below.
Contents
Musical Colors File and Installation
Windows Media Player Visualizations are made by DLL files. The filename for Musical Colors, «wmpvis», is known as «wmpvis.dll». Find this file in [DllDump.com[1]] and copy that to «C:Program FilesWindows Media Player» Directory. If you have a 64 bit version of Windows, copy «wmpvis.dll» into «C:Program Files (x86)Windows Media Player».
For Windows XP
If you have Windows Media Player 9 Series or Windows Media Player 10 or below, Run «Windows Media Player». In your menu bar, click toolsoptions. In your options, those tabs will show up. Click Plug-InsVisualizations then you see visualizations, click add then, Navigate to your «wmpvis.dll» file. Click it and its listed!
If you have Windows Media Player 11, then you need to open «wmpvis.dll» with «Microsoft (C) Register Serverregsvr32.exe or you can just run regsvr32 «C:Program FilesWindows Media Playerwmpvis.dll».
Open «wmpvis.dll» in «Register Server» in Command Prompt Administrator mode. Once that has opened up, type in «C:Program FilesWindows Media Playerwmpvis.dll» Also, view the previous information above and use quotes.
After that, you will see this message as shown below:
«DllRegisterServer in wmpvis.dll succeeded.»
Musical Colors Versions
The difference between the two versions is that version 7.0.0.1440 has a preset known as «WinMe 3D», and additionally, that version was bundled with «Windows ME». On the other hand, version 8.0.0.4487 was bundled with «Windows XP». In version 7.0.0.1440, there was an unsupported preset named «Ice Crystals». «Ice Crystals» was one of the 3D presets for version 8.0.0.4487, and the preset «WinMe 3D» was unsupported for version 8.0.0.4487. «WinMe 3D» displays colors of blue, light blue, green, yellow, and orange, and «Ice Crystals» displays shades of only light blue.
Источник
Windows media player comes with lots of exciting features and one such feature is the visualization which makes sure that the user is prompted to choose the environment within the player window to make sure that the song is heard with full spirit and zeal. It is also to be noted that the user in this regard should make sure that the visualization is chosen as per the system and OS requirement.
Part 1: Top 10 Visualizations for Windows Media Player
Listed below are the top 10 visualizations in terms of name, size, short description, screenshot and the download URL:
1. Blazing colors
169 KB
With awesome and state of the art appearance this visualization makes sure that the user gets the best results and also gets the visualization downloaded for sure as the appearance is stunning and it makes sure that the downloading of the file is confirmed. The changing colors while the music is being played is something that each and every user wants and this visualization makes sure that the awesome is done free of charge and the overall player appearance is also made great and stellar.
2. Color Cubes
169 KB
Yet another powerful and heart touching visualizations that has been created to make sure that the user is lured into the business for sure and for the same reason it is also to be noted that the user should make sure that the visualization is downloaded from the official website of the Microsoft to make sure that the genuine and the best version is there to support the player and user also gets the best results when it comes to playing songs or other audio files as the best has already been provided in form of this visualization.
3. Dungeon Siege
837KB
It is also one of the visualizations that have been developed to make sure that the aggressive attitude of the user is pacified in this regard. It also makes sure that the user gets the results as the downloading and the installation is done from the official Microsoft website to make sure that the user gets the visualization without any issue and problem.
4. Energy Bliss
http://download.microsoft.com/download/3/b/7/3b7f92b8-d73e-4325-b402-b3e72ad6a39e/MP10_EnergyBlissViz.exe
521 KB
Full of energy and spirit this visualization makes sure that the best has been provided to the user and the state of the art effects are installed without any issue and problem. For the people who love skies this visualization is a boon and for the same reason it is also to be noted that the users in this regard should make sure that the best has been downloaded and installed as it is highly recommended.
5. G-Force Visualization
3.4 MB
Though paid this visualization is recommended to make sure that the user gets the best and the state of the art results within no time at all. The downloading is however done from an external link that has been mentioned above and the user is redirected to another website that is to be visit to make sure that the best has been done and provided to the user in this regard.
6. Morphyre
8.71 MB
It can be rightly called as an amalgamation of several other visualizations that have been developed by different developers and the same is also depicted by the size and the appearance of the visualization. It must be downloaded by all those users who want to add something new to the media player without any hassle and issue. It is undoubtedly the best visualization that has been created ever:
7. Soft Skies
7.2 MB
Creating a cool ambiance for the user this visualization makes sure that the user gets the best and the state of the art result without any issue and it is obviously for all those users who want to make sure that soft and slow music is played in relation to their choice and overall environment. The size of the visualization is also large which means that the resolution is awesome and it fits into the media player of any genre without any issue and problem. It should be downloaded and installed instantly as it is highly recommended.
8. White Cap
753 KB
It is also one of those visualizations which make sure that the user gets the best and the state of the art results without any issue and problem when it comes to the music of choice. This is only for those users who want to listen rap and hip hop as the changes that have been embedded within the visualization makes sure that the user gets the visualization work at the right time and therefore it is also advised to download the right visualization the URL of which has been mentioned above to get the best results.
9. Windows Media 9 series
366KB
Developed by Microsoft this visualization is for those who want to make sure that the player is kept simple and unique at the same time. It is the best visualization that has been developed by the developers of windows media player and therefore it should be added to change the appearance of the player quiet often without reverting to previous versions.
10. Trilogy II
177 KB
This visualization has also been developed by the Microsoft itself and for the same reason it is to be noted that a user should make sure that the best has been downloaded that is not only trustworthy but it is also in line with the requirements of the player as well as the user.
Part 2:How to Turn On Visualizations in Windows Media Player
Following is the process that is to be followed in this regard which is simple and straightforward to follow and any user can make good use of the process to accomplish the task:
1.The Now playing window of the Media Player is to be opened:
2.The user should then right click the window and hover the cursor to Visualizations tab:
3.The user should then make sure that the desired visualization is selected as per desire:
| Musical Colors |
|---|
 |
The Musical Colors visualization, set to the «Colors in Motion» preset.
Description Versions Available in: 7, 7.1, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12 Current Status: Former/Current Visualization Developed by: Averett & Microsoft Years Available: 2000 – Present Random Preset: No Related Visualizations: Blazing Colors, Color Cubes, Eclectic Colors, Picture Viz, Plenoptic, Pulsing Colors, Royale Noir, Trilogy Full-Screen Controls: No (WMP 7 and 8)/Yes (WMP 9-12) Gallery
Ice Crystals, a preset from the visualization Musical Colors.
Musical Colors is a visualization of twenty-one presets created by Averett & Microsoft. It is one of the oldest visualizations on Windows Media Player, and the visualization first appeared in Windows Media Player 7. There are two different versions to this visualization.
Musical Colors also has a large collection of «sister» visualizations in the Musical Colors Family. Shockingly, later on starting with the Windows Media Player 9 and 10 Series, Musical Colors had disappeared. This occurred because It had certain issues with certain video cards. Fortunately, it can be reinstalled by following these steps below. Musical Colors is the only downloadable visualization left remaining.
Musical Colors File and Installation
Windows Media Player Visualizations are made by DLL files. The filename for Musical Colors, «wmpvis», is known as «wmpvis.dll». Find this file in [DllDump.com[1]] and copy that to «C:Program FilesWindows Media Player» Directory. If you have a 64 bit version of Windows, copy «wmpvis.dll» into «C:Program Files (x86)Windows Media Player».
For Windows XP
If you have Windows Media Player 9 Series or Windows Media Player 10 or below, Run «Windows Media Player». In your menu bar, click toolsoptions. In your options, those tabs will show up. Click Plug-InsVisualizations then you see visualizations, click add then, Navigate to your «wmpvis.dll» file. Click it and its listed!
If you have Windows Media Player 11, then you need to open «wmpvis.dll» with «Microsoft (C) Register Server
egsvr32.exe or you can just run regsvr32 «C:Program FilesWindows Media Playerwmpvis.dll».
Open «wmpvis.dll» in «Register Server» in Command Prompt Administrator mode. Once that has opened up, type in «C:Program FilesWindows Media Playerwmpvis.dll» Also, view the previous information above and use quotes.
After that, you will see this message as shown below:
«DllRegisterServer in wmpvis.dll succeeded.»
Musical Colors Versions
The difference between the two versions is that version 7.0.0.1440 has a preset known as «WinMe 3D», and additionally, that version was bundled with «Windows ME». On the other hand, version 8.0.0.4487 was bundled with «Windows XP». In version 7.0.0.1440, there was an unsupported preset named «Ice Crystals». «Ice Crystals» was one of the 3D presets for version 8.0.0.4487, and the preset «WinMe 3D» was unsupported for version 8.0.0.4487. «WinMe 3D» displays colors of blue, light blue, green, yellow, and orange, and «Ice Crystals» displays shades of only light blue.
Users interested in Windows media player visualizations generally download:
Plug-in for Windows Media Player creating flowing 3D images that are synchronized with the rhythm of the song you’re currently listening to.
Generate a graphical representation of the audio played in a compatible media player. Integrate the plug-in with Windows Media Player.
WhiteCap is a sleek and sophisticated music visualizer and screensaver that features futuristic.
Corona Visualization Plug-in for WMP, as the name suggests, is a nice little plugin that works very well with Microsoft Windows Media Player.
PlasmaVis is a set of three programs that will produce random graphic visuals based on your sound input.
Additional suggestions for Windows media player visualizations by our robot:
Search in solutions
Feature-rich media player with support for the most popular codecs and formats.
Essential plugin for firefox users, open Microsoft formats directly in Firefox.
the Windows Media Player in compact visualization mode
RealPlayer is one of the most popular video player.
Winamp player is designed to cover the large area of media file types.
Install audio and video codecs for playback and encoding.
Winter Wonders is a beautiful screensaver for Windows OS.
A music visualizer that produces mood-enhancing animated cloudscapes.
Fast & high quality video playback.
Free and open source media player which plays almost all multimedia formats.
Kantaris Media Player becomes unnecessary. Unlike Windows Media Player
Plane9 is a 3D visualizer that comes with over 260 predefined scenes.
Music Editing Master is an efficient and powerful audio editing and audio.
Two exciting new sets of visualizations to enhance your music with fun.
Alchemy Visualization Pack for Windows Media Player includes
A Windows Media Player visualization plug-in for your Light-O-Rama controller.
A Windows Media Player visualization plug-in
Plays Blu-ray movies, also supports 4k videos and playback capacity.
Источник
Brian’s Blog
How To Get Musical Colors Back On Windows Media Player
Musical Colors is a collection of visualizations designed for Windows Media Player. The visualizations first appeared in Windows Media Player 7 and then later disappeared starting with the release of Windows Media Player 9. Over time, people enjoyed the Musical Colors theme and upon buying a new computer, discovered that it wasn’t there anymore. The following explains some tips and info about the Musical Colors visualizations as well as instructions for installment on computers that don’t contain the Musical Colors visualizations.
Compatibility
Musical Colors works on Windows Media Player version 7 and above including version 11 & 12. Musical Colors also works with Windows Vista, 7, 8, 8.1 and 10. The only issue is that full screen viewing on a wide-screen monitor will cause the visualizations to be shifted to the left of the screen with a thick black bar to the right. This is because Musical Colors is not wide-screen capable.
Musical Colors Versions
There are two different versions of the Musical Colors visualizations. They are:
The main difference between the two versions is that 7.0.0.1440 contains a visualization called “WinMe 3D”, since that version was bundled with Windows Me. 8.0.0.4477 was bundled with Windows XP, and the WinMe 3D visualization was replaced with a similar visual named “Ice Crystals”. WinMe 3D displays colors of blue, light blue, green, yellow, and orange. Ice Crystals display shades of light blue.
Another difference between the two versions is when you pause Windows Media Player, version 7.0.0.1440 of Musical Colors continues to display the visualizations with constant movement. Version 8.0.0.4477 of Musical Colors will cut to black when paused, hiding the visualizations.
Locating The Musical Colors File
First you have to decide which version of Musical Colors you want. (See Musical Colors Versions above). Musical Colors are located inside a file called wmpvis.dll. The best way to locate the file is to copy it off of a computer that already has it installed or off of a Windows installation CD.
For Musical Colors version 7.0.0.1440
Use a computer running Windows Me with Windows Media Player 7 installed. The wmpvis.dll file can be found under the C:Program FilesWindows Media Player directory. You can also retrieve the file off of the Windows Me installation CD by going to the cabinet file win9xWIN_16.CAB and extracting the wmpvis.dll file.
For Musical Colors version 8.0.0.4477
Use a computer that was originally installed with Windows Media Player 8 and with Windows XP service pack 1 or earlier. Locate the wmpvis.dll file under the C:Program FilesWindows Media Player directory. You can also retrieve the file off of a Windows XP installation CD containing service pack 1 or earlier by going to I386 and locating WMPVIS.DL_. Copy the file to your desktop. Open your Command Prompt and type: cd desktop and press enter. Then type expand wmpvis.dl_ wmpvis.dll and press enter. This will expand and decompress the file to make it usable.
Installation
For 32-bit versions of Windows, copy wmpvis.dll to the C:Program FilesWindows Media Player folder. For 64-bit versions of Windows, copy wmpvis.dll to the C:Program Files (x86)Windows Media Player folder.
Note: If you copy/paste the command lines below, you will have to retype the quotes so they are ‘straight’. Smart quotes causes the command to fail. I keep putting straight quotes in, but WordPress reverts them back to smart quotes at some point!
For Windows XP/Vista/7/8/8.1/10 32-Bit
On the desktop, bring up the run dialog box by holding down WinKey+R. Type or copy/paste the following line including the quotes.
Regsvr32 “C:Program FilesWindows Media Playerwmpvis.dll”
For Windows Vista/7 64-Bit
For Windows 8/8.1/10 64-Bit
Click OK or press enter, A dialog box appears with the following text; “DllRegisterServer in C:Program FilesWindows Media Playerwmpvis.dll succeeded.” Click OK. Open Windows Media Player and check your visualizations. Musical Colors should now be listed.
If you are using 32-bit Windows Vista/7/8/8.1/10 and you encounter an error message after clicking OK in the Run dialog box, try using the Command Prompt, making sure it’s being run with administrator privileges.
Names of the Visualizations
In the Musical Colors menu, you will see the following names. Click on a name to see a picture of the visualization.
Lost Musical Colors Visualizations
You may have heard about a theme for Windows XP named “Royale Noir” that was cancelled or removed during development, then was leaked to the public and became popular. One day I opened the wmpvis.dll inside Notepad just to look around. After scrolling though garbled unreadable information, I found the names of each visualization near the bottom of the file. What I then found were several names that didn’t appear on the Musical Colors menu inside Windows Media Player.
Источник
Musical Colors
The Musical Colors visualization, set to the «Colors in Motion» preset.
Ice Crystals, a preset from the visualization Musical Colors.
Musical Colors is a visualization of twenty-one presets created by Averett & Microsoft. It is one of the oldest visualizations on Windows Media Player, and the visualization first appeared in Windows Media Player 7. There are two different versions to this visualization.
Musical Colors also has a large collection of «sister» visualizations in the Musical Colors Family. Shockingly, later on starting with the Windows Media Player 9 and 10 Series, Musical Colors had disappeared. This occurred because It had certain issues with certain video cards. Fortunately, it can be reinstalled by following these steps below.
Contents
Musical Colors File and Installation
Windows Media Player Visualizations are made by DLL files. The filename for Musical Colors, «wmpvis», is known as «wmpvis.dll». Find this file in [DllDump.com[1]] and copy that to «C:Program FilesWindows Media Player» Directory. If you have a 64 bit version of Windows, copy «wmpvis.dll» into «C:Program Files (x86)Windows Media Player».
For Windows XP
If you have Windows Media Player 9 Series or Windows Media Player 10 or below, Run «Windows Media Player». In your menu bar, click toolsoptions. In your options, those tabs will show up. Click Plug-InsVisualizations then you see visualizations, click add then, Navigate to your «wmpvis.dll» file. Click it and its listed!
If you have Windows Media Player 11, then you need to open «wmpvis.dll» with «Microsoft (C) Register Serverregsvr32.exe or you can just run regsvr32 «C:Program FilesWindows Media Playerwmpvis.dll».
Open «wmpvis.dll» in «Register Server» in Command Prompt Administrator mode. Once that has opened up, type in «C:Program FilesWindows Media Playerwmpvis.dll» Also, view the previous information above and use quotes.
After that, you will see this message as shown below:
«DllRegisterServer in wmpvis.dll succeeded.»
Musical Colors Versions
The difference between the two versions is that version 7.0.0.1440 has a preset known as «WinMe 3D», and additionally, that version was bundled with «Windows ME». On the other hand, version 8.0.0.4487 was bundled with «Windows XP». In version 7.0.0.1440, there was an unsupported preset named «Ice Crystals». «Ice Crystals» was one of the 3D presets for version 8.0.0.4487, and the preset «WinMe 3D» was unsupported for version 8.0.0.4487. «WinMe 3D» displays colors of blue, light blue, green, yellow, and orange, and «Ice Crystals» displays shades of only light blue.
Brian’s Blog
How To Get Musical Colors Back On Windows Media Player
Musical Colors is a collection of visualizations designed for Windows Media Player. The visualizations first appeared in Windows Media Player 7 and then later disappeared starting with the release of Windows Media Player 9. Over time, people enjoyed the Musical Colors theme and upon buying a new computer, discovered that it wasn’t there anymore. The following explains some tips and info about the Musical Colors visualizations as well as instructions for installment on computers that don’t contain the Musical Colors visualizations.
Compatibility
Musical Colors works on Windows Media Player version 7 and above including version 11 & 12. Musical Colors also works with Windows Vista, 7, 8, 8.1 and 10. The only issue is that full screen viewing on a wide-screen monitor will cause the visualizations to be shifted to the left of the screen with a thick black bar to the right. This is because Musical Colors is not wide-screen capable.
Musical Colors Versions
There are two different versions of the Musical Colors visualizations. They are:
The main difference between the two versions is that 7.0.0.1440 contains a visualization called “WinMe 3D”, since that version was bundled with Windows Me. 8.0.0.4477 was bundled with Windows XP, and the WinMe 3D visualization was replaced with a similar visual named “Ice Crystals”. WinMe 3D displays colors of blue, light blue, green, yellow, and orange. Ice Crystals display shades of light blue.
Another difference between the two versions is when you pause Windows Media Player, version 7.0.0.1440 of Musical Colors continues to display the visualizations with constant movement. Version 8.0.0.4477 of Musical Colors will cut to black when paused, hiding the visualizations.
Locating The Musical Colors File
First you have to decide which version of Musical Colors you want. (See Musical Colors Versions above). Musical Colors are located inside a file called wmpvis.dll. The best way to locate the file is to copy it off of a computer that already has it installed or off of a Windows installation CD.
For Musical Colors version 7.0.0.1440
Use a computer running Windows Me with Windows Media Player 7 installed. The wmpvis.dll file can be found under the C:Program FilesWindows Media Player directory. You can also retrieve the file off of the Windows Me installation CD by going to the cabinet file win9xWIN_16.CAB and extracting the wmpvis.dll file.
For Musical Colors version 8.0.0.4477
Use a computer that was originally installed with Windows Media Player 8 and with Windows XP service pack 1 or earlier. Locate the wmpvis.dll file under the C:Program FilesWindows Media Player directory. You can also retrieve the file off of a Windows XP installation CD containing service pack 1 or earlier by going to I386 and locating WMPVIS.DL_. Copy the file to your desktop. Open your Command Prompt and type: cd desktop and press enter. Then type expand wmpvis.dl_ wmpvis.dll and press enter. This will expand and decompress the file to make it usable.
Installation
For 32-bit versions of Windows, copy wmpvis.dll to the C:Program FilesWindows Media Player folder. For 64-bit versions of Windows, copy wmpvis.dll to the C:Program Files (x86)Windows Media Player folder.
Note: If you copy/paste the command lines below, you will have to retype the quotes so they are ‘straight’. Smart quotes causes the command to fail. I keep putting straight quotes in, but WordPress reverts them back to smart quotes at some point!
For Windows XP/Vista/7/8/8.1/10 32-Bit
On the desktop, bring up the run dialog box by holding down WinKey+R. Type or copy/paste the following line including the quotes.
Regsvr32 “C:Program FilesWindows Media Playerwmpvis.dll”
For Windows Vista/7 64-Bit
For Windows 8/8.1/10 64-Bit
Click OK or press enter, A dialog box appears with the following text; “DllRegisterServer in C:Program FilesWindows Media Playerwmpvis.dll succeeded.” Click OK. Open Windows Media Player and check your visualizations. Musical Colors should now be listed.
If you are using 32-bit Windows Vista/7/8/8.1/10 and you encounter an error message after clicking OK in the Run dialog box, try using the Command Prompt, making sure it’s being run with administrator privileges.
Names of the Visualizations
In the Musical Colors menu, you will see the following names. Click on a name to see a picture of the visualization.
Lost Musical Colors Visualizations
You may have heard about a theme for Windows XP named “Royale Noir” that was cancelled or removed during development, then was leaked to the public and became popular. One day I opened the wmpvis.dll inside Notepad just to look around. After scrolling though garbled unreadable information, I found the names of each visualization near the bottom of the file. What I then found were several names that didn’t appear on the Musical Colors menu inside Windows Media Player.
Ambience
| Ambience | |
|---|---|
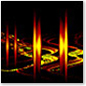
 The «Swirl» preset from Ambience, running in Windows Media Player 10. |
|
| Description | |
| Versions Available in: 7, 7.1, 8, 9 Series and 10 | |
| Current Status: | Former visualization |
| Developed by: | Averett and Associates & Microsoft |
| Years Available: | 1999-2006 |
| Random Preset: | Yes |
| Related Visualizations: | Alchemy, Bars and Waves, Battery, Musical Colors, Particle, Plenoptic Spikes |
| Full Screen | No |
| Gallery |
Ambience is a former visualization for Windows Media Players 7-10, also known as one of the «sisters» in the Ambience Family and in the Musical Colors Family. Similar visualizations include Battery, Alchemy, and 3D Alchemy. Ambience has a total of fourteen presets, including a random preset, that appear to look soft and calm. However, one of the visualization’s sisters, Battery, has twice the amount of presets that Ambience has. This means that Battery has twenty-six presets. Ambience was also one of the most popular selectable visualizations, back when it was still listed as a current visualization.
Contents
History
Ambience is one of the oldest visualizations, first appearing in 1999 on Windows Media Player 7. People really enjoyed the presets, especially the «Water» preset. This visualization lasted until 2005. But unfortunately, this visualization was removed in 2006, starting with Windows Media Player 11, due to incompatability issues with the full screen controls alongside the Particle, Plenoptic, and Spikes visualizations.
Color Variations
The Ambience visualization also fades in and out into several colors. When first selected, it is blue. Later on, the visualization will fade in and out into the following colors, including red, orange, yellow, green, cyan, light blue, blue, magenta, pink, purple, peach and gray.
Thingus Preset
Unlike all the other thirteen presets (from Random to Down the Drain), which originally came for version 7, the fourteenth preset, Thingus, did not appear until version 8 arrived on the Windows XP operating system.
Windows Media Audio 9
This codec samples audio at 44.1 or 48 kilohertz (kHz) using 16 bits, similar to the current CD standard, offering CD quality at data rates from 64 to 192 kilobits per second (Kbps). The resulting sound quality is 20 percent better than audio sampled with Windows Media Audio 8 at equivalent data rates.
The Windows Media Audio 9 codec (WMA 9) supports variable bit rate encoding (VBR), which enables even higher quality audio at smaller file sizes by automatically varying the encoding bit rate according to the complexity of the audio data. With VBR, the encoding bit rate increases to capture complex sections of data and then decreases to maximize the compression of the less complex sections, producing compact, high-quality compression.
WMA 9 is backward-compatible with previous Windows Media Audio-compatible decoders, which means that WMA 9 content can be played with previous versions of Windows Media Player or older consumer electronic devices that support Windows Media. As with all Windows Media 9 Series codecs, it supports the Windows Media digital rights management platform, which is used to securely package and distribute copy-protected digital media.
Windows Media Audio 10 Professional
Windows Media Audio 10 Professional (WMA 10 Pro) is the most flexible Windows Media audio codec available – supporting profiles that include everything from full-resolution 24-bit/96 kHz audio in stereo, 5.1 channel, or even 7.1 channel surround sound, to highly efficient mobile capabilities at 24 Kbps to 96 Kbps for stereo, and 128 Kbps to 256 Kbps for 5.1-channel sound. WMA 10 Pro offers incredible quality for consumers using high-fidelity hardware and 5.1 channel surround sound-equipped computers — and for consumers playing audio content on their mobile devices. WMA 10 Pro supports streaming, progressive download, or download-and-play delivery at 128 to 768 Kbps.
When using 5.1 surround sound audio compressed at 384 Kbps with WMA 10 Pro, most listeners cannot discern any differences between the compressed music and the original pulse code modulation (PCM) files. WMA Pro also offers dynamic range control using the maximum and average audio amplitudes that are calculated during the encoding process. Using the Quiet Mode feature in Windows Media Player 9 and later, users can hear either the full dynamic range, a medium difference range up to 12 decibels (dB) above the average, or a little difference range up to 6 dB above the average.
If a user tries to play back a file that was encoded using the 5.1 channel, 24-bit, 96 kHz sampling capabilities, but does not have a system or sound card that supports multi-channel or high-resolution sound, multiple channels are combined into stereo audio (for example, 16-bit, two channel audio), ensuring that users get the best playback experience their systems can provide.
The following table compares WMA Pro to competing compression technology.
| Audio Data | Industry Compression* | Windows Media* | Compression Savings |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 ch x 48 kHz x 16 bits | Dolby Digital 2.0 at 220 Kbps | WMA 10 Pro at 128 Kbps | 1.7:1 |
| 6 ch x 48 kHz x 20 bits | Dolby Digital 5.1 at 384 Kbps | WMA 10 Pro at 192–256 Kbps | 1.5–2:1 |
| 6 ch x 48 kHz x 24 bits | DTS 5.1 at 1,536 Kbps | WMA 10 Pro at 768 Kbps | 2:1 |
Windows Media Audio 9 Lossless
The audio quality of content that is compressed using this codec is the best of all Windows Media Audio codecs. It creates a bit-for-bit duplicate of the original audio file so that no data is lost, which makes it ideal for archiving content masters.
Depending on the complexity of the original, content will be compressed at a 2:1 or 3:1 ratio. Although this is lower than the ratio achieved with other Windows Media Audio 9 Series codecs, it provides the same benefits of compression while leaving the data intact.
Like Windows Media Audio 9 Professional, the Windows Media Audio 9 Lossless codec also offers dynamic range control using the maximum and average audio amplitudes that are calculated during the encoding process. Using the Quiet Mode feature in Windows Media Player 9 and later, users can hear the full dynamic range, a medium difference range up to 12 dB above the average, or a little difference range up to 6 dB above the average.
Windows Media Audio 9 Voice
This low-bit-rate codec is primarily targeted for speech content, but performs very well with mixed-mode content that includes both voice and music. In voice mode, the codec takes advantage of the relatively less complicated and narrower frequency range of the human voice to maximize compression. In music mode, the codec operates like the standard Windows Media Audio 9 codec. Encoded content can be configured to switch between voice and music modes automatically.
The Windows Media Audio 9 Voice codec offers superior quality for low-bit-rate streaming scenarios (less than 20 Kbps), such as radio broadcasts, advertising, e-books, podcasts, and voiceovers. The voice codec can also compress content to as low as 4 Kbps at 8 kHz.
Compatibility
The following table outlines what your audience will experience when playing Windows Media Audio 9 Series content on earlier Microsoft Windows operating systems than Windows XP or with earlier versions of Windows Media Player. This table also lists the compatibility for Apple Mac OS X and Windows CE–based platforms.
| Codec | Feature | Player backward compatibility |
|---|---|---|
| Windows Media Audio 9 | Constant-bit rate (CBR) encoding | Windows Media Player 6.4 or later on non-portable devices (using transcoding as needed) Windows Media Player 9 for Mac OS X Windows Media Player 9 Series and Windows Media Player 9.1 for Pocket PC* Windows Media Player 9 Series and Windows Media Player 9.1 for Smartphone* |
| Variable-bit-rate (VBR) encoding | Windows Media Player 7 or later on all devices that support the Player (using transcoding as needed) | |
| Windows Media Audio 9 Professional | General | Windows Media Player 7 or later Windows Media Player 9 for Mac OS X |
| Discrete channel playback (for instance, 5.1) | Requires Windows Media Player 9 Series (or SDK) or later, Windows XP, and a multichannel audio card. | |
| High-resolution audio (24-bit, 96 kHz) | Requires Windows Media Player 9 Series (or SDK) or later, Windows XP, and a high-resolution audio card. | |
| Dynamic range control | Requires Windows Media Player 9 Series (or SDK) or later and Windows XP. | |
| Windows Media Audio 9 Lossless | General | Windows Media Player 7 or later Windows Media Player 9 for Mac OS X |
| Discrete channel playback (for instance, 5.1) | Requires Windows Media Player 9 Series (or SDK) or later, Windows XP, and a multichannel audio card. | |
| Windows Media Audio 9 Voice | General | Windows Media Player 6.4 or later Windows Media Player 9 for Mac OS X Windows Media Player 9 Series and Windows Media Player 9.1 for Pocket PC* Windows Media Player 9 Series and Windows Media Player 9.1 for Smartphone* |
* All versions of Windows Media Player for Pocket PC and Smartphone are shipped as part of the Microsoft Windows Mobile operating system. Windows Media Player for Pocket PC and Windows Media Player for Smartphone are not available for download from Microsoft.
In 2006, the Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers (SMPTE) formally published the Final Specification for SMPTE 421M, also known as VC-1. Formal standardization of VC-1 represents the culmination of years of technical scrutiny by over 75 companies, leading to a codec that is well-documented, extremely stable, easily licensable, and accepted by the industry. VC-1 supports three profiles: Simple, Main, and Advanced. The Simple and Main profiles have been complete for several years, and existing implementations such as WMV 9 have long supported the creation and playback of content using these profiles, as well as an early implementation of the Advanced profile. The completion of the Advanced profile and consequent standardization of all profiles in VC-1 represents the final step in a comprehensive specification that delivers high definition content—either interlaced or progressive—across any medium and to any capable device.
Windows Media Video 9
Windows Media Video 9 is the Microsoft implementation of the VC-1 SMPTE standard. It supports Simple, Main, and Advanced profiles.
Simple and Main Profiles
The Windows Media Video 9 Simple and Main profiles fully conform to the SMPTE VC-1 standard and provide high-quality video for streaming and downloading. These profiles support a wide range of bit rates, from high-definition content at one-half to one-third the bit rate of MPEG-2, to low-bit-rate Internet video delivered over a dial-up modem. This codec also supports professional-quality downloadable video with two-pass and variable bit rate (VBR) encoding. Windows Media Video 9 is already supported by a wide variety of players and devices.
Advanced Profile
The Windows Media Video 9 Advanced profile fully conforms to the SMPTE VC-1 standard, supports interlaced content, and is transport-independent. Content creators can use this profile to deliver either progressive or interlaced content at data rates as low as one-third that of the MPEG-2 codec—with the same quality as MPEG-2.
In the past, interlaced video content was always de-interlaced before encoding with the Windows Media Video codec. Now, encoding applications such as Windows Media 9 Series, and third-party encoding solutions can support compression of interlaced content without first converting it to progressive content. Maintaining interlacing in an encoded file is important if the content is ever rendered on an interlaced display, such as a television.
Transport independence also enables the delivery of Windows Media Video 9 Advanced Profile over systems that are not Windows Media-based, such as standards-based broadcast infrastructures (through native MPEG-2 transport streams), wireless infrastructures (using real-time transfer protocol [RTP]), or even DVDs.
The following table compares Windows Media Video 9 Advanced Profile to competing compression technology.
| Video Data | Industry Compression* | Windows Media* | Compression Savings |
|---|---|---|---|
| 480/24p 720×480 pixels/frame x 8 bits per channel x 24 fps | MPEG-2 at 4–6 Mbps | Windows Media Video 9 Advanced Profile at 1.3–2 Mbps | 3:1 |
| 480/30i 720×480 pixels/frame x 8 bits per channel x 30 fps | MPEG-2 at 6–8 Mbps | Windows Media Video 9 Advanced Profile at 2–4 Mbps | 2–3:1 |
| 720/24p 1280×720 pixels/frame x 8 bits per channel x 24 fps | MPEG-2 at 19 Mbps | Windows Media Video 9 Advanced Profile at 5–8 Mbps | 2.4–3.8:1 |
Windows Media Video 9 Screen
The Windows Media Video 9 Screen codec is optimized for compressing sequential screen shots and highly static video that is captured from the computer display, which makes it ideal for delivering demos or demonstrating computer use for training. The codec takes advantage of the typical image simplicity and relative lack of motion to achieve a very high compression ratio.
During the encoding process, the codec automatically switches between lossy and lossless encoding modes, depending on the complexity of the video data. For complex data, the lossless mode preserves an exact copy of the data. For less complex data, the lossy mode discards some data to achieve a higher compression ratio. By automatically switching between these two modes, the codec maintains video quality while maximizing compression.
Overall, the Windows Media Video 9 Screen codec delivers better handling of bitmap images and screen motion, even on relatively modest CPUs. It is also up to 100 times more efficient than the commonly-used run length encoding.
Windows Media Video 9 Image Version 2
The Windows Media Video 9 Image Version 2 codec is different from the other video codecs. Instead of processing uncompressed video, it transforms still images into video by using pan, zoom, and cross-fade transitions between clips to create an unlimited number of effects.
The results can then be delivered at data rates as low as 20 kilobits per second (Kbps). These files are compressed using either constant bit rate (CBR) or one-pass variable bit rate (VBR) modes.
The Windows Media Video 9 Image Version 2 codec is not compatible with the Windows Media Video 9 Image codec.
Windows Media Video 9 VCM
The Video Compression Manager (VCM) version of the Windows Media Video 9 Series codec enables earlier versions of encoding and editing applications to support the Windows Media Video 9 Series codec in file containers such as Audio Video Interleaved (AVI). This codec package also allows Windows Media Video (WMV) files based on Windows Media Format 9 Series to be played in Windows Media Player 6.4, in both ASF and AVI file containers.
Compatibility
The following table outlines what your audience will experience when playing Windows Media Video 9 Series content on earlier Microsoft Windows operating systems or with earlier versions of Windows Media Player. This table also lists the compatibility for Apple Mac OS X and Windows CE–based platforms.
| Codec | Feature | Player backward compatibility |
|---|---|---|
| Windows Media Video 9 | General | Windows Media Player 6.4 or later Windows Media Player 9 for Mac OS X Windows Media Player 9 Series and Windows Media Player 9.1 for Pocket PC* Windows Media Player 9 Series and Windows Media Player 9.1 for Smartphone* |
| Frame Interpolation | Requires Windows Media Player 9 Series (or Software Development Kit) or later and Windows XP. | |
| Windows Media Video 9 Advanced Profile | General | Windows Media Player 7 or later |
| Windows Media Video 9 Screen | General | Windows Media Player 7 or later |
| Windows Media Video 9 Image Version 2 | General | Windows Media Player 7 or later |
*All versions of Windows Media Player for Pocket PC and Smartphone are shipped as part of the Microsoft Windows Mobile operating system. Windows Media Player for Pocket PC and Windows Media Player for Smartphone are not available for download from Microsoft.
Источник
Due to a planned power outage on Friday, 1/14, between 8am-1pm PST, some services may be impacted.
- About
- Blog
- Projects
- Help
-
Donate
Donate icon
An illustration of a heart shape - Contact
- Jobs
- Volunteer
- People
Item Preview
There Is No Preview Available For This Item
This item does not appear to have any files that can be experienced on Archive.org.
Please download files in this item to interact with them on your computer.
Show all files
Windows Media Player 9
English — Spanish
Windows XP, 1995, 1998
Netscape Plugin
- Addeddate
- 2017-03-23 15:43:55
- Identifier
- WindowsMediaPlayer9
- Identifier-ark
- ark:/13960/t9b61t92r
- Scanner
- Internet Archive HTML5 Uploader 1.6.3
comment
Reviews
There are no reviews yet. Be the first one to
write a review.
1,018
Views
2
Favorites
DOWNLOAD OPTIONS
Uploaded by
OldChicho3
on March 23, 2017
SIMILAR ITEMS (based on metadata)
Хотя в наши дни большинство людей транслируют музыку, некоторые предпочитают иметь собственную аудиотеку. Если вы придерживаетесь такого же мышления, вероятно, вам также интересно по-прежнему использовать Windows Media Player.
Несмотря на многочисленные современные альтернативы, есть что-то ностальгическое по поводу загрузки вашего любимого альбома в WMP и просмотра этих классических визуализаторов. Однако, если вам надоел предустановленный визуализатор, мы шокируем вас некоторыми из самых крутых альтернативных визуализаторов.
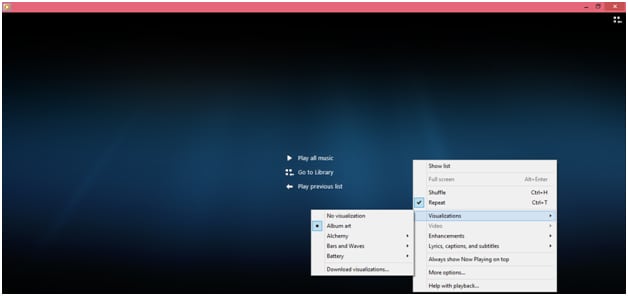
Для большинства этих различных визуализаторов вы сможете получить их в одном месте: на веб-сайте Microsoft. Откройте Windows Media Player и начните воспроизведение аудиофайла. Нажмите кнопку «Сейчас исполняется», чтобы просмотреть окно «Сейчас исполняется».
В окне «Сейчас исполняется» щелкните правой кнопкой мыши и наведите указатель мыши на «Визуализации». Внизу списка выберите Загрузить визуализацию, чтобы перейти на веб-сайт поддержки Microsoft.
Обратите внимание, что Microsoft официально больше не поддерживает Windows Media Player. Загрузки, доступные на этом сайте, не могут быть загружены безопасным образом, поэтому читатели делают это на свой страх и риск.
На сайте поддержки щелкните правой кнопкой мыши кнопку «Загрузить» для нужного визуализатора и выберите «Сохранить ссылку как». После загрузки исполняемого файла запустите его, чтобы установить новый визуализатор.
Если все сработало, вы должны найти новую опцию в контекстном меню Windows Media Player.
Связанный: VLC Media Player: все сочетания клавиш Windows
Итак, теперь вы знаете, где их взять и как использовать, но какой из этих визуализаторов Windows Media Player самый крутой? Мы составили для вас список самых интересных.
1. Пакет Psychedelia Viz
В этот пакет входит семь новых визуализаторов, которые вы можете попробовать, и, как следует из названия, все может стать немного странным. Помимо 3D-версии визуализатора обложек альбомов, вы также получаете доступ к большему количеству психоделических визуальных эффектов, чем музыкальное видео Tool.
Особым моментом, вероятно, является режим искажения с гигантским изображением обложки вашего альбома, подергивающейся под музыку под голубым небом, в то время как текст лениво вращается.
Скачать: Пакет Psychedelia Viz (Бесплатно)
2. Windows Media серии 9
Несмотря на то, что у него может быть самое грубое имя во вселенной, визуализатор Windows Media 9 Series отлично подходит для немного более расслабленного и тонкого эффекта. Он имеет реактивный бассейн с водой на дне и некоторые уровни звука, проецируемые на фон.
Одна из лучших частей этой визуализации — насколько она настраиваема. Вы можете изменить размер отображения уровня звука и удалить с экрана отражения и логотипы.
Скачать: Windows Media 9 серии (Бесплатно)
3. WhiteCap
WhiteCap — довольно известный визуализатор для проигрывателя Windows Media, и легко понять, почему. WhiteCap предлагает вам больше, чем любой другой визуализатор в этом списке. Вы можете настраивать формы, цвета, фон. Вы называете это.
Причина, по которой WhiteCap не занимает более высокое место в этом списке, заключается в том, что этот визуализатор не является бесплатным. Вы можете получить бесплатную пробную версию с урезанными функциями, но для полной версии программного обеспечения вам нужно будет потратить 20 или 30 долларов за золотую / платиновую версии.
Скачать: WhiteCap (Бесплатная пробная версия)
4. Трилогия III
Было много вариантов Trilogy на выбор в списке доступных визуализаторов, но Trilogy III почти одерживает победу. Все три пакета Trilogy довольно хороши, в каждом есть три совершенно новых визуализатора, которые вам понравятся.
Trilogy III — лучшая благодаря включенному визуализатору Mystic Cloud. У него не только невероятно подходящее название для названия, но и тонкий и жуткий тон, когда вы наблюдаете, как визуализатор вспыхивает цветом, только чтобы исчезнуть с экрана через несколько секунд.
Скачать: Трилогия III (Бесплатно)
5. Святочный журнал
Последний новый визуализатор, который вам нужно заполучить, очень ситуативный. Если это летние месяцы, вам, вероятно, будет меньше интересно, но визуализатор Святочного журнала — отличное украшение зимой.
Этот визуализатор имитирует горящее полено, потрескивающее в огне, и пламя танцует в точности под звук, который вы слушаете. Если вы пытаетесь создать настроение в зимние месяцы, этот визуализатор заставит вас почувствовать себя теплым, безопасным и поджаренным. Очень жаль, что вам нужно установить Winter Fun Pack 2004, чтобы получить его.
Скачать: Святочный журнал (Бесплатно)
Вот и все. Мы представили наш окончательный список лучших визуализаторов для Windows Media Player в 2021 году. Однако, если вы все еще используете WMP, вы можете изучить некоторые альтернативы, благодаря тому, что Microsoft отказалась от поддержки продукта.
Обновлено
2019-05-13 13:56:42
Совместимость
Windows 98, Windows ME, Windows 2000, Windows XP
Язык
Другое,
Русский,
Английский
Описание
Windows Media Player 9 — программа, хорошо знакомая всем тем, кто когда-либо использовал Windows XP. С её помощью, вы сможете воспроизводить аудио и видео файлы в большинстве существующих форматов.
Описание
Используя эту программу, вы сможете в любой момент насладиться прослушиванием любимой музыки или просмотром видео в форматах MP3, MPG, MP2, AVI, WAV, WMA или многих других. При этом, Windows Media Player 9 обеспечивает высокое качество изображения и звука. В сравнении с предшественницей, программа получила более 120 функций, которые откроют перед вами новые возможности по взаимодействию с мультимедийным контентом на компьютере.
Программа может похвастаться встроенным инструментом для потоковой передачи мультимедиа, возможностью записи компакт-дисков, удобной мультимедийной библиотекой, радио-тюнером и рядом других приятных особенностей. Также, Windows Media Player 9 обладает набором функций, необходимых для современного проигрывателя, включая создание списков воспроизведения, настройка звука при помощи эквалайзера, отображение формы волны, а также изменение темы оформления. А обновленный интерфейс проигрывателя не оставит равнодушным никого.
Обратите внимание, что программа разработана специально для Windows XP и может не поддерживать более новые версии операционной системы.
Версии
This article is about the original version used prior to Windows 8. For the successor version, see Media Player (Windows 11).
Windows Media Player (WMP) is the first media player and media library application that was developed by Microsoft for playing audio, video and viewing images on personal computers running the Microsoft Windows operating system, as well as on Pocket PC and Windows Mobile-based devices. Editions of Windows Media Player were also released for classic Mac OS, Mac OS X, and Solaris but development of these has since been discontinued.
Windows Media Player was eventually replaced in Windows 8 with Groove Music. Groove Music persisted in Windows 8.1 and Windows 10, before being replaced in turn with the Media Player in Windows 11.

Windows Media Player 12 Legacy running on Windows 11 2022 Update |
|
| Developer(s) | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| Stable release | 12.0.22621.457 (September 20, 2022; 4 months ago) [±] |
| Preview release | 12.0.25120.1000 (May 18, 2022; 8 months ago) [±] |
| Operating system |
|
| Included with |
|
| Predecessor | ActiveMovie Control, CD Player, DVD Player (Win32 version) |
| Successor | Microsoft Movies & TV, Groove Music, Media Player (Windows 11) |
| Type | Media player |
| Website | support.microsoft.com/en-gb/windows/windows-media-player-d10303a5-896c-2ce2-53d4-5bd5b9fd888b |
In addition to being a media player, the application has the ability to rip audio file from and copy to compact discs, burn recordable discs in Audio CD format or as data discs with playlists such as an MP3 CD, synchronize content with a digital audio player (MP3 player) or other mobile devices, and enable users to purchase or rent music from a number of online music stores.
Windows Media Player 11 was made available for Windows XP and included in Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008. The default file formats are Windows Media Video (WMV), Windows Media Audio (WMA), and Advanced Systems Format (ASF), and its own XML based playlist format called Windows Playlist (WPL). The player is also able to utilize a digital rights management service in the form of Windows Media DRM.
Windows Media Player 12 is the most recent version of Windows Media Player prior to Windows 11. It was released on October 22, 2009, along with Windows 7[b] and has not been made available for previous versions of Windows nor has it been updated since for Windows 8, Windows 8.1, Windows 10, and Windows 11.[2][3] Windows 8 and later instead use Groove Music (for audio) and Microsoft Movies & TV (for video) as the default playback applications for most media; As of October 2021, Windows Media Player is still included as a Windows component. Windows RT does not run Windows Media Player.
On November 16, 2021, Microsoft announced that it would replace Groove Music with the new Media Player application, though the legacy Windows Media Player will continue to be optionally available with Windows 11.[4]
HistoryEdit
Media Player 5 running in Windows 2000.
The first version of Windows Media Player appeared in 1991, when Windows 3.0 with Multimedia Extensions was released.[5] Originally called Media Player, this component was included with «Multimedia PC»-compatible machines but not available for retail sale. It was capable of playing .mmm animation files, and could be extended to support other formats.[6] It used MCI to handle media files. Being a component of Windows, Media Player shows the same version number as that of the version Windows with which it was included.
WMP running in Windows 8.
Microsoft continually produced new programs to play media files. In November of the following year, Video for Windows was introduced with the ability to play digital video files in an AVI container format,[7] with codec support for RLE and Video1, and support for playing uncompressed files. Indeo 3.2 was added in a later release. Video for Windows was first available as a free add-on to Windows 3.1, and later integrated into Windows 95 and Windows NT 4.0. In 1995, Microsoft released ActiveMovie with DirectX Media SDK. ActiveMovie incorporates a new way of dealing with media files, and adds support for streaming media (which the original Media Player could not handle). In 1996, ActiveMovie was renamed DirectShow.[8] However, Media Player continued to come with Windows until Windows XP, in which it was officially renamed Windows Media Player v5.1.[9] («v5.1» is the version number of Windows XP).
In 1999, Windows Media Player’s versioning broke away from that of Windows itself. Windows Media Player 6.4 came as an out-of-band update for Windows 95-98 and Windows NT 4.0 that co-existed with Media Player and became a built-in component of Windows 2000, Windows ME, and Windows XP with an mplayer2.exe stub allowing to use this built-in instead of newer versions.[10] Windows Media Player 7.0 and its successors also came in the same fashion, replacing each other but leaving Media Player and Windows Media Player 6.4 intact. Windows XP is the only operating system to have three different versions of Windows Media Player (v5.1, v6.4, and v8) side by side. All versions branded Windows Media Player (instead of simply Media Player) support DirectShow codecs. Windows Media Player version 7 was a large revamp, with a new user interface, visualizations and increased functionality. Windows Vista, however, dropped older versions of Windows Media Player in favor of v11, which included the removal of the Windows Media Source Filter (DirectShow codec).
In 2004, Microsoft launched digital music store MSN Music for new Windows Media Player 10 to compete with Apple iTunes.[11][12]
However, MSN Music was discontinued already in 2006 with the launch of Zune music players.[13]
Beginning with Windows Vista, Windows Media Player supports the Media Foundation framework besides DirectShow; as such it plays certain types of media using Media Foundation as well as some types of media using DirectShow.[14] Windows Media Player 12 was released with Windows 7. It included support for more media formats and added new features. With Windows 8, however, the player did not receive an upgrade.
On April 16, 2012, Microsoft announced that Windows Media Player would not be included in Windows RT, the line of Windows designed to run on ARM-based devices.[15]
Windows 11Edit
A different app called Media Player is the successor to Groove Music for Windows 10 (previously Xbox Music) and Windows Media Player. Media Player started to be offered to all Windows 11 users on February 15, 2022.[16]
The new Media Player can also play video, as part of Groove’s rebranding from a music streaming service to a media player.[17] Other changes include the album cover view being in fullscreen, and a refresh to the mini player.[18] Accessibility has also been optimized, with some improved keyboard shortcuts and hotkey support for keyboard users and with other assistive technologies.[19]
FeaturesEdit
Core playback and library functionsEdit
Windows Media Player supports playback of audio, video and pictures, along with fast forward, reverse, file markers (if present) and variable playback speed (seek & time compression/dilation introduced in WMP 9 Series). It supports local playback, streaming playback with multicast streams and progressive downloads. Items in a playlist can be skipped over temporarily at playback time without removing them from the playlist. Full keyboard-based operation is possible in the player.
Windows Media Player supports full media management, via the integrated media library introduced first in version 7, which offers cataloguing and searching of media and viewing media metadata. Media can be arranged according to album, artist, genre, date et al. Windows Media Player 9 Series introduced Quick Access Panel to browse and navigate the entire library through a menu. The Quick Access Panel was also added to the mini mode in version 10 but was entirely removed in version 11. WMP 9 Series also introduced ratings and Auto Ratings. Windows Media Player 10 introduced support for aggregating pictures, Recorded TV shows, and other media into the library. A fully featured tag editor was featured in versions 9-11 of WMP, called the Advanced Tag Editor. However, the feature was removed in Windows Media Player 12. Since WMP 9 Series, the player features dynamically updated Auto Playlists based on criteria. Auto Playlists are updated every time users open them. WMP 9 Series and later also supports Auto Ratings which automatically assigns ratings based on the number of times a song is played. Pre-populated auto playlists are included in Windows Media Player 9 Series. Custom Auto Playlists can be created only on Windows XP and later.
In Windows Media Player 11, the Quick Access Panel was removed and replaced with an Explorer-style navigation pane on the left which can be customized for each library to show the user selected media or metadata categories, with contents appearing on the right, in a graphical manner with thumbnails featuring album art or other art depicting the item. Missing album art can be added directly to the placeholders in the Library itself (though the program re-renders all album art imported this way into 1×1 pixel ratio, 200×200 resolution JPEGs). There are separate Tiles, Icons, Details or Extended Tiles views for Music, Pictures, Video and Recorded TV which can be set individually from the navigation bar. Entries for Pictures and Video show their thumbnails. Version 11 also introduced the ability to search and display results on-the-fly as characters are being entered, without waiting for Enter key to be hit. Incremental search results are refined based on further characters that are typed. Stacking allows graphical representations of how many albums there are in a specific category or folder. The pile appears larger as the category contains more albums. The List pane includes an option to prompt the user to remove items skipped in a playlist upon save or skip them only during playback.
VisualizationsEdit
Windows Media Player 11 running in mini mode (in Windows XP MCE) showing the «Bars and Waves» visualization
While playing music, Windows Media Player can show visualizations. The current three visualizations are Alchemy, which was first introduced in version 9, Bars and Waves, which has been used since version 7, and Battery, introduced version 8. «Musical Colors» was removed starting with version 9, but is retained if Windows Media Player was upgraded from version 7 or 8. Version 11 and above refrains from having the former «Ambience,” «Particle,” «Plenoptic,” and «Spikes» visualizations. The «Battery» visualization was similarly removed in later editions of version 12. The reason for their removal was that the visualizations do not support full screen controls (either the visualization gets shifted to the left while there is a thick black bar to the right side of the screen, that there are no full screen controls, or that the visualization have DXE Problems). More visualizations such as «BlazingColors,” «ColorCubes,” «Softie the Snowman,» and «Yule Log» used to be downloadable however, the downloads from Microsoft’s website have mostly been taken down and it’s available on the WMP Goodies site.
Format supportEdit
The player includes intrinsic support for Windows Media codecs and also WAV and MP3 media formats. On Windows XP and above with WMP 9 Series and later, the Windows Media Audio Professional codec is included which supports multichannel audio at up to 24-bit 192 kHz resolution. Windows Media Player 11 includes the Windows Media Format 11 runtime which adds low bitrate support (below 128 kbit/s for WMA Pro), support for ripping music to WMA Pro 10 and updates the original WMA to version 9.2.[citation needed]
Support for any media codec and container format can be added using specific DirectShow filters or Media Foundation codecs (Media Foundation codecs only in Windows Vista and later). The player will not play MP3 files that contain compressed ID3 headers («tags»), trying to do so results in a «The input media file is invalid» error message. MP3 playback support was built-in beginning with version 6.1 and audio CD playback was natively supported with version 7.[citation needed]
DVD playback features minus the necessary decoders were integrated into Windows Media Player 8 for Windows XP. The player activates DVD and Blu-ray playback functionality with support for menus, titles and chapters, parental controls and audio track language selection if compatible decoders are installed. MPEG-2 and Dolby Digital (AC-3) decoders were included beginning with Windows Media Player 11 on Windows Vista (Home Premium and Ultimate editions only) and Windows 7 (Home Premium, Ultimate, or Enterprise editions) to allow DVD playback without additional software. However, the decoders were subsequently removed in Windows 8 and Windows 10 due to licensing costs.[20]
Windows Media Player 12 adds native support for H.264 and MPEG-4 Part 2 video formats, ALAC, AAC audio[21] and 3GP[clarification needed got no codec available for 3GP], MP4 and MOV container formats.[22] Windows Media Player 12 is also able to play AVCHD formats (.M2TS and .mts).[23]
As of Windows 10 version 1507, Windows Media Player 12 can play FLAC, HEVC, and SubRip subtitle, and Matroska container formats.[24] Although the WebM file type is not officially associated with Windows Media Player 12 (the default player is Microsoft Movies & TV), playback of VP9 video in WebM container is possible on Windows 10 version 1809 and later.[25]
Windows Media Player MobileEdit
Windows Media Player Mobile 10 on Windows Mobile 6.5 supports MP3, ASF, WMA, and WMV using WMV or MPEG-4 codecs.[26]
Disc burning, ripping, and playbackEdit
Windows Media Player features integrated Audio CD-burning support since version 7 as well as data CD burning support since Windows Media Player 9 Series on Windows XP and later. Data CDs can have any of the media formats supported by the player. While burning Data CDs, the media can, optionally, be transcoded into WMA format and playlists can be added to the CD as well. Starting with WMP 9 Series, audio CDs can be burnt with volume leveling.
Audio CDs can be ripped as WMA or WMA 10 Pro (WMA 10 Pro in WMP 11 and later) at 48, 64, 96, 128, 160, and 192 kbit/s, WMA lossless (470 to 940 kbit/s) (9 Series on XP and later), WMA variable bitrate (from 40 to 75 kbit/s up to 240-355 kbit/s), MP3 at 128, 192, 256, and 320 kbit/s, or uncompressed WAV (WAV ripping in WMP 11 and later). Since WMP 9 Series, 20 bit high-resolution CDs (HDCDs) are also supported, if capable audio hardware is present. Audio can be ripped using error correction and ripped audio can be protected with Windows Media DRM. Ripping to MP3 is supported only in Windows Media Player 8 for Windows XP and later if a compatible MP3 encoder is installed. Windows Media Player 10 included the Fraunhofer MP3 Professional encoder. Information on CDs such as album name, artist and track listings can optionally be automatically downloaded from the online Windows Media database when the CD is inserted. Version 11 added support for ripping audio CDs to WAV and WMA 10 Pro formats. With their 2015 implementation in Windows 10, Version 12 also added lossless FLAC and ALAC formats for ripping and playback. For burning, version 11 shows a graphical bar indicating how much space will be used on the disc and introduced Disc spanning which splits a burn list onto multiple discs in case the content does not fit on one disc.
Portable device syncEdit
Windows Media Player allows the user to connect, share and sync data with portable handheld devices and game consoles since version 7. Media can be optionally transcoded to a format better suited for the target device, automatically, when synchronizing. When deleting playlists from devices, Windows Media Player can automatically remove their contents. Devices can be formatted using Windows Media Player 9 Series and later. Version 10 and later support the Media Transfer Protocol and Auto Sync. Auto Sync allows users to specify criteria such as recently added music or highest rated songs, by which media will be automatically synchronized with the portable device and other advanced features like setting the clock on the portable device automatically, communicating with the device to retrieve the user’s preferences. Windows Media Player 10 also introduced the UMDF-based Windows Portable Devices API.
Version 11 has improved synchronization features for loading content onto PlaysForSure-compatible portable players. WMP 11 supports reverse-synchronization, by which media present on the portable device can be replicated back to the PC. Shuffle Sync can be used to randomize content synced with the portable device, Multi PC Sync to synchronize portable device content across multiple PCs and Guest Sync to synchronize different content from multiple PCs with the portable device. Portable devices appear in the navigation pane of the library where their content can be browsed and searched.
Windows Media Player’s ‘Sync’ function has options that allow it to be set to automatically down-convert (transcode) high bit-rate song files to a lower bit-rate. This down-conversion function is switched on by default. This is useful for providing low bit-rate files to those portable devices that need them, and to save space on portable devices with smaller storage capacities. For high bit-rate capable devices with sufficient storage capabilities, the down conversion process can be omitted.
In versions 11 (2006) and 12 (2009), the Quality settings that the user has selected in the Windows Media Player settings for Sync, for that specific portable device, are used to control the quality (bit-rate) of files that are copied to the portable device. Leaving the Quality settings to Automatic will often result in 192kbs files being copied to the portable device. Manual settings can also be made. 192kbs is the highest quality down-conversion bit-rate that can be manually selected when the Sync function’s down-conversion function is turned on. Lower bit-rates can also be selected.
For portable devices that can handle high bit-rate files, the best quality files are obtained by leaving the down-conversion process switched off (unchecked) for that specific device. In Windows Media Player Version 11, switching off the down-conversion function is done in the Quality tab of the Advanced Options of the Sync settings for the device. In Windows Media Player Version 12, switching off the down-conversion function is done in the Quality tab of the Properties for the device in the Select Settings for the device in the Sync Options menu.
When set up in such a way, Windows Media Player’s ‘Sync’ function can be used to sync unchanged high bit-rate song files to suitable portable devices (i.e. those capable of using file formats such as WMA Lossless, mp3-360kbs, etc.). For example, some users have created large song libraries on their PCs containing .wma formatted song files using the high bit-rate WMA Lossless (WMA-LL) protocol, or using other high bit-rate song file formats. The WMA-LL protocol is selectable in Windows Media Player as an option when ripping songs from CDs. The resulting bit-rates seen on ripped WMA-LL files are often 3 to 6 times higher than 192kbs, and can typically fall anywhere in the range of 600kbs to 1200kbs, depending on the quality of the source file that was present on the CD in the first place. The sound quality is much improved over the default rate, although the file size is larger.
At the time that Versions 11 and 12 were released, the capabilities and capacities of portable devices typically required down-conversion of the bit-rates of the files placed on the portable devices. Thus, Sync down-conversion was turned on by default. This was to ensure playability of the files and to ensure that the file sizes were small enough to efficiently fit a reasonably large selection of songs on the portable device.
In recent years (circa 2012), portable devices became available that could natively play these Windows Media Player produced high bit-rate WMA-LL files (and others), and that have storage capacities suitable for large collections of high bit-rate song files. This made it much more practicable and desirable to use software programs such as Windows Media Player to synchronize previously PC-bound libraries of high bit-rate songs to these new portable devices.
Enhanced playback featuresEdit
Windows Media Player features universal brightness, contrast, saturation and hue adjustments and pixel aspect ratio for supported video formats. It also includes a 10-band graphic equalizer with presets and SRS WOW audio post-processing system. Windows Media Player can also have attached audio and video DSP plug-ins which process the output audio or video data. Video Smoothing was introduced in WMP 9 Series (Windows XP and later only) which upscales frame-rate by interpolating added frames, in effect giving a smoother playback on low-framerate videos. The player supports subtitles and closed-captioning for local media, video on demand streaming or live streaming scenarios. Typically Windows Media captions support the SAMI file format but can also carry embedded closed caption data.
The player can use video overlays or VMR (Video Mixing Renderer) surfaces, if the video card supports them. In Windows XP, it uses VMR7 by default, but can also be made to use the more advanced YUV mixing mode by enabling the «Use high quality mode» option in Advanced Performance settings. This turns on deinterlacing, scaling and improved color accuracy.[27] WMP 9 Series introduced native playback for deinterlacing for TV output. Version 9 introduced DXVA accelerated playback. Version 11 introduced improved support for DirectX accelerated decoding of WMV video (DXVA decoding). Up to version 11, it supported static lyrics and «Synchronized Lyrics,” by which different lines of lyrics can be time-stamped, so that they display only at those times. Synchronized Lyrics also were accessible through the Advanced Tag Editor which was removed in version 12.
Since Windows Media Player 9 Series, the player supports crossfading, audio dynamic range (Quiet Mode) for WMA Pro and WMA Lossless, and auto volume leveling for certain media which includes volume level/gain information such as MP3 or Windows Media. The player also supports extensive configurable privacy and security settings.
Shell integrationEdit
The player has Windows Explorer shell integration to add files and playlist to the Now Playing pane and other playlists can be controlled from the Windows Explorer shell itself, via right-click menu. The My Music folder also includes a separate My Playlists folder where playlists are maintained. When the player is closed and reopened, simply clicking the play button restores the last playlist even if it was not saved. Starting with Windows Media Player 10, the playlist pane is also visible from the Library view. AutoPlay handlers in Windows expose various Windows Media Player tasks.
Windows Media Player 11 running in mini mode in Windows Vista and Windows XP respectively. Notice the difference in the logo.
Up to version 11, it featured a taskbar-mounted Mini mode in which the most common media control buttons are presented as a toolbar on the Windows taskbar. Flyout windows can display media information, the active visualization or the video being played back. Mini-mode was introduced as a shell player powertoy for Windows Media Player 8 in Windows XP and integrated later into WMP 9 Series. Mini-mode has been removed in Windows Media Player 12 in favor of controls in the taskbar’s interactive thumbnail preview which lacks volume control, a progress bar and information displayed whenever a new song is played.
The user interface has been redesigned in Windows Media Player 12 such that the Now Playing view plays media in a separate minimalist window with floating playback controls, and also gives access to the current playlist, visualizations, and enhancements.[21] Enhancements are housed in individual undocked windows. The library view includes the rest of the media management functions. It also can preview songs from the library when users hover over the media file and click the Preview button.[21] Windows Media Player 12 can play unprotected songs from the iTunes library. The taskbar-integrated Mini-player has been replaced with controls in the taskbar’s interactive thumbnail preview (called the Thumbnail Toolbar),[28] albeit minus the volume control function, track and album information shown whenever a new song is played and the progress bar. The taskbar icon also supports jump lists introduced in Windows 7.
The thumbnail viewer of Windows Media Player 12 in Windows 7 Home Premium
ExtensibilityEdit
The player has had skinning support since Windows Media Player (WMP) 7 and includes a color chooser since the WMP 9 Series. Not all functions are usually exposed in skin mode. Windows Media Player 10 allows setting the video border color. Color chooser has been removed in WMP 12. It supports visualizations and Info Center View (Info Center View in WMP 9 Series and later) which displays media metadata fetched from the internet. Full screen visualizations are supported in WMP 9 Series and later. It supports Background plug-ins, window plug-ins and Now Playing plug-ins to control media playback besides DSP and renderer plug-ins. Plug-in support was introduced in WMP 9 Series.
Online featuresEdit
The player integrates web-browsing support to browse online music stores, shop for music and tune to internet radio stations since version 7. It provides an embeddable ActiveX control for Internet Explorer so that developers can play Windows Media on web pages. Windows Media Player 10 and later feature integration with a large number of online music stores and selecting a music store switches the Info Center view, radio and other online features to use services from that store. Purchased music from a particular store appears in a separate library node under the respective category.
Media streamingEdit
Previously, Microsoft had released Windows Media Connect for Windows XP to stream media content with its built-in UPnP media server. With version 11 of Windows Media Player, Media Sharing was integrated and allows content (Music, Pictures, Video) to be streamed to and from Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) AV enabled devices such as the PS3, Xbox 360, and Roku SoundBridge. This includes DRM protected PlaysForSure content. WMP 11 on Windows Vista can also act as a client to connect to remote media libraries using this feature; this is not available on the Windows XP version.
With version 12, media streaming was further improved. While previous versions streamed media to UPnP compliant devices (Digital Media Server role) and could play media by fetching it from a network share (Digital Media Player role),[29] Windows Media Player 12 can access media from the shared media libraries on the network or HomeGroup, stream media to DLNA 1.5 compliant devices and allows itself (once the remote control option is turned on) to be remotely controlled by Digital Media Controller devices which stream media (Digital Media Renderer role).[29] Similarly, the Play To feature once enabled for remote PCs, by turning on remote control of the player, allows compliant devices and computers to be discovered and controlled remotely from a computer running Windows Media Player 12 (Digital Media Controller role).[29] If the devices do not support the streamed format, Windows Media Player 12 transcodes the format on-the-fly. Media from a home network can also be streamed over the internet using an Online ID Provider service, which handles discovery of the computer’s IP address, authorization, security, connectivity and Quality of Service issues.[29]
Skin ModeEdit
Windows Media Player also features skins. Currently, Windows Media Player has two default skins: «Corporate,” which was first introduced in version 8, and «Revert,” which first shipped with version 9. In versions 7 and 8, there were many unusual skins such as «Heart,” «Headspace,” «Canvas,” «Goo,” and «Atomic,” which were removed starting with version 9, but are retained if the player is upgraded, although some can still be downloaded from an archive of the Microsoft website.[30] In versions 7, 8, 9, and 10 there were many usual skins such as «9SeriesDefault,” «Atomic,” «Bluesky,” «Canvas,” «Classic,” «Compact,” «goo,” «Headspace,” «heart,” «iconic,” «Miniplayer,” «Optic,” «Pyrite,” «QuickSilver,” «Radio,” «Roundlet,” «Rusty,” «splat,” «Toothy,” «Windows Classic,” and «Windows XP,” which were removed starting with version 11. This Corporate skin is not deletable.
Security issuesEdit
Microsoft Windows Media Runtime in Windows 2000, Windows XP, Windows Vista and Windows Server contained a bug that permitted «remote code execution if a user opened a specially crafted media file». Such a file would allow the attacker to «then install programs; view, change, or delete data; or create new accounts with full user rights», if the account on which the file was played had administrator privileges.[31] The problem was addressed in a critical update issued on September 8, 2009.[32]
Other versionsEdit
Microsoft has also released versions of Windows Media Player for other platforms including Windows Mobile, classic Mac OS, Mac OS X, Palm-size PC, Handheld PC, and Solaris. Of these, only the Windows Mobile edition continues to be actively developed and supported by Microsoft. Version 1 of the Zune software was also based on Windows Media Player; later versions are not.
Windows MobileEdit
Windows Media Player 10.3 Mobile on a Windows Mobile Professional device
Windows Media Player for Pocket PC was first announced on January 6, 2000, and has been revised on a schedule roughly similar to that of the Windows version.[33] Currently known as «Media Player 10 Mobile,” this edition (released in October 2004) closely resembles the capabilities of the Windows version of WMP 10, including playlist capabilities, a media library, album art, WMA Lossless playback, support for DRM-protected media, video playback at 640×480 with stereo sound, and the same Energy Blue interface aesthetics also seen in Windows XP Media Center Edition 2005. It also supports synchronization with the desktop version of WMP 10, and additionally supports synchronizing and transcoding of recorded television shows from Media Center. Media Player 10 Mobile is not available as a download from Microsoft, distribution is done solely through OEM partners, and is typically included on devices based on Windows Mobile.
Windows Mobile 6 includes a copy of Windows Media Player 10 Mobile, but with a similar (but not quite identical) theme as Windows Media Player 11.
Mac OS XEdit
Version 9 was the final version of Windows Media Player to be released for Mac OS X before development was canceled by Microsoft. It was developed by the Windows Media team at Microsoft instead of the Macintosh Business Unit and released in 2003. On release the application lacked many basic features that were found in other media players such as Apple’s iTunes and QuickTime.[citation needed] It also lacked support for many media formats that version 9 of the Windows counterpart supported on release 10 months earlier.
The Mac version supported only Windows Media encoded media (up to version 9) enclosed in the ASF format, lacking support for all other formats such as MP4, MPEG, and Microsoft’s own AVI format. On the user interface front, it did not prevent screensavers from running during playback, it did not support file drag-and-drop, nor did it support playlists. While Windows Media Player 9 had added support for some files that use the WMV9 codec (also known as the WMV3 codec by the FourCC), in other aspects it was seen as having degraded in features from previous versions.
On January 12, 2006, Microsoft announced it had ceased development of Windows Media Player for Mac. Microsoft now distributes a third-party plugin called WMV Player (produced and maintained by Flip4Mac) which allows some forms of Windows Media to be played within Apple’s QuickTime Player and other QuickTime-aware applications.[34]
European Commission caseEdit
In March 2004, the European Commission in the European Union Microsoft antitrust case fined Microsoft €497 million and ordered the company to provide a version of Windows without Windows Media Player, claiming Microsoft «broke European Union competition law by leveraging its near monopoly in the market for PC operating systems onto the markets for work group server operating systems and for media players.” The company has made available a compliant version of its flagship operating system under the negotiated name «Windows XP N,” though the product has not been very successful. Windows Vista, Windows 7 and Windows 8 are also available in «N» editions. However, it is possible to either install Windows Media Player (XP/Vista)[35] or the Media Restore Pack through Windows Update (Vista) to add the media player.
Release historyEdit
Prior to the release of Windows Media Player in Windows 98 Second Edition, separate programs, CD Player, Deluxe CD Player, DVD Player and Media Player, were included in old versions of Microsoft Windows for playback of media files.
| Version | Original release | Included with | Available for | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microsoft Windows | ||||
| Media Player | February 15, 2022 | Windows 11 | — | |
| Windows Media Player 12 | July 22, 2009 | Windows 7 Windows 8 Windows 8.1 Windows 10 Windows 11 Windows Server 2008 R2 Windows Server 2012 Windows Server 2012 R2 Windows Server 2016 Windows Server 2019 Windows Server 2022 |
— | |
| Windows Media Player 11 | October 18, 2006 | Windows Vista Windows Server 2008 |
Windows XP (SP2+) Windows XP x64 Edition |
|
| Windows Media Player 10 | August 25, 2004 | Windows XP x64 Edition Windows XP Media Center Edition 2005 Windows Server 2003 (SP1+) |
Windows Server 2003 Windows XP[37] |
|
| Windows Media Player 9 Series | January 7, 2003[38] | Windows XP (SP2+) Windows Server 2003 (RTM) |
Windows XP Windows ME Windows 2000 Windows 98 SE[39] |
|
Windows Media Player for Windows XP (version  |
August 24, 2001 | Windows XP (RTM & SP1) | — | |
| Windows Media Player 7.1 | May 16, 2001 | Windows 2000 (SP2+) | Windows ME Windows 2000 Windows 98[39][40] |
|
| Windows Media Player 7.0 | June 19, 2000[41] | Windows ME | Windows 2000 Windows 98 Windows 95 |
|
| Windows Media Player 6.4[c] | September 15, 1999 | Windows 2000 Windows ME (hidden) Windows XP (hidden) Windows Server 2003 (hidden) Internet Explorer 5.01 Internet Explorer 5.5 Internet Explorer 6.0 |
Windows 98 Windows NT 4.0 Windows 95 |
|
| Windows Media Player 6.1 | March 1999 | Windows 98 SE Internet Explorer 5.0 |
Windows 98 Windows NT 4.0 Windows 95 |
|
| Microsoft Media Player 5.1 | 2001 | Windows XP (hidden) | — | |
| Media Player 5.0 | 1999 | Windows 2000 (hidden) | — | |
| Media Player 4.9 | 2000 | Windows ME (hidden) | — | |
| Media Player 4.1 | 1998 | Windows 98 Windows 98 SE (hidden) |
— | |
| Media Player 4.0 | 1995 | Windows 95 Windows NT 4.0 |
— | |
| Media Player 3.51 | 1995 | Windows NT 3.51 | — | |
| Media Player 3.5 | 1994 | Windows NT 3.5 | — | |
| Media Player 3.15 | 1992 | — | Windows 3.1 with Video for Windows | |
| Media Player 3.1 | 1992 | Windows 3.1 Windows NT 3.1 |
— | |
| Media Player 3.0 | 1991 | — | Windows 3.0 with Multimedia Extension | |
| Windows Mobile | ||||
| Windows Media Player 10.3 Mobile | February 12, 2007 (Windows Mobile 6) | Windows Mobile 6.1 Windows Mobile 6 |
Windows Mobile 5.0 | |
| Windows Media Player 10.2 Mobile | ? | Windows Mobile 5.0 | — | |
| Windows Media Player 10.1 Mobile | May 10, 2005 | Windows Mobile 5.0 | — | |
| Windows Media Player 10 Mobile | October 12, 2004 | Windows Mobile 2003 SE | — | |
| Windows Media Player 9.0.1 | March 24, 2004 | Windows Mobile 2003 SE | — | |
| Windows Media Player 9 Series | June 23, 2003 | Windows Mobile 2003 | — | |
| Windows Media Player 8.5 | October 11, 2002 | Pocket PC 2002 | — | |
| Windows Media Player 8.01 | July 2002 | Pocket PC 2002 | — | |
| Windows Media Player 8 | October 4, 2001 (Pocket PC) | Pocket PC 2002 Smartphone 2002 |
— | |
| Windows Media Player 7.1 | May 21, 2001 | Pocket PC 2000 | — | |
| Windows Media Player 7 | December 12, 2000 | Pocket PC 2000 | — | |
| Windows Media Player 1.2 | September 7, 2000 | Handheld PC 2000 | — | |
| Windows Media Player 1.1 | ? | Palm-size PC CE 2.11 | — | |
| Windows Media Player | April 19, 2000 | Pocket PC 2000 | — | |
| Mac | ||||
| Windows Media Player 9 Series | November 7, 2003 | — | Mac OS X | |
| Windows Media Player 7 | July 24, 2001 | Mac OS 9 | Mac OS 8.x | |
| Windows Media Player 6.3 | July 17, 2000 | Mac OS 8 | Mac OS 7.x | |
| Solaris | ||||
| Windows Media Player 6.3 | July 17, 2000 | — | Solaris |
See alsoEdit
- Comparison of media players
- Comparison of video player software
- Groove Music
- Media Player Classic, a media player that mimics the appearance of Windows Media Player 6.4
- Media Transfer Protocol
- Windows Media Encoder
- Windows Media Services
FootnotesEdit
- ^ Except for «N» and «KN» editions of Windows, as well as Windows RT
- ^ N and KN versions of Windows 7 do not include Windows Media Player by default.[1]
- ^ Windows Media Player 6.4 was shipped side-by-side with later versions of WMP in Windows ME and Windows XP
ReferencesEdit
- ^ «Microsoft Documentation Page». Microsoft Docs. October 22, 2020. Archived from the original on February 9, 2021.
- ^ LeBlanc, Brandon (July 22, 2009). «Windows 7 Has Been Released to Manufacturing». Blogging Windows. Microsoft. Archived from the original on September 26, 2015. Retrieved December 21, 2020.
- ^ «Windows Media Player 12 — Windows 7 features». Windows. Microsoft. Archived from the original on September 22, 2009. Retrieved June 15, 2011.
- ^ Hachman, Mark (2021-11-16). «Windows Media Player is getting a long-overdue upgrade». PCWorld.
- ^ «Windows Version History». Support (4.0 ed.). Microsoft. September 23, 2011. Archived from the original on February 26, 2015. Retrieved May 2, 2009.
- ^ Lineback, Nathan. «Windows 3.0 with Multimedia Extensions». Toasty Tech. Archived from the original on April 15, 2009. Retrieved May 2, 2009.
- ^ «Video for Windows». PC Tech Guide. Archived from the original on April 10, 2009. Retrieved May 2, 2009.
- ^ Blome, Michael; Wasson, Mike (July 2002). «DirectShow: Core Media Technology in Windows XP Empowers You to Create Custom Audio/Video Processing Components». MSDN Magazine. Microsoft. Archived from the original on September 14, 2008. Retrieved May 1, 2009.
- ^
C:Windowssystem32myplay32.exe. Windows XP. Microsoft Corporation. - ^ «MPLAYER2.EXE Is Linked to Missing Export MSDXM.OCX». Support. Microsoft. April 25, 2006. Archived from the original on March 14, 2007. Retrieved February 13, 2015.
- ^ «MSN Music to offer free songs». Archived from the original on 2020-09-21. Retrieved 2020-05-21.
- ^ «MSN Launches Preview Release of Music Download Service». September 2004. Archived from the original on 2020-08-06. Retrieved 2020-05-21.
- ^ «MSN Music Shutting Down for Zune». Archived from the original on 2020-08-13. Retrieved 2020-05-21.
- ^ «DSP Plug-in Packaging». MSDN. Microsoft. Archived from the original on 2010-11-05. Retrieved 2010-04-08.
- ^ LeBlanc, Brandon (April 16, 2012). «Windows Announcing the Windows 8 Editions». The Windows Blog. Archived from the original on April 18, 2012.
- ^ «Media Player is available for Windows 11». 16 November 2021.
- ^ «Microsoft is replacing Windows Media Player with Media Player for Windows 11». Engadget. Retrieved 2021-11-18.
- ^ «Full screen album art». 16 November 2021.
- ^ «Optimized accessibility». 16 November 2021.
- ^ «DVD playback options for Windows». Windows help & learning.
- ^ a b c Peter Bright (October 30, 2008). «Hands on: Windows Media Player 12’s surprising new features». ArsTechnica. Condé Nast Digital. Archived from the original on March 27, 2009. Retrieved March 25, 2009.
- ^ «Windows 7 RC to natively support .mov files». Chakkaradeep Chandran. Neowin.net. February 26, 2009. Archived from the original on July 3, 2012. Retrieved March 25, 2009.
- ^ «Windows 7 next generation camera support». Download Center. Microsoft. Archived from the original (PPTX) on December 27, 2008.
- ^ «Native MKV, FLAC And HEVC Support In Windows 10». Lifehacker Australia. 29 November 2014.
- ^ «Windows 10 1809 Built-In Apps: What to Keep». Vacuum Breather.
- ^ «Formats supported by Windows Media Player Mobile». MSDN. Microsoft. April 8, 2010. Archived from the original on November 18, 2012. Retrieved November 7, 2012.
- ^ «Windows Media Player manual». Download Center. Microsoft. September 1, 2004. Archived from the original (DOC) on June 7, 2005.
- ^ Kiriaty, Yochay; Goldshtein, Sasha (July 2009). «Introducing The Taskbar APIs». MSDN Magazine. Microsoft. Thumbnail Toolbars. Archived from the original on 2015-03-25. Retrieved 2015-04-23.
- ^ a b c d Sinofsky, Steven (May 12, 2009). «Media Streaming with Windows 7». Engineering Windows 7. Microsoft. Archived from the original on July 12, 2011. Retrieved April 23, 2015.
- ^ «Skins for Windows Media Player». Windows. Microsoft. Archived from the original on June 9, 2016.
- ^ «Microsoft Security Bulletin MS09-047: Critical Vulnerabilities in Windows Media Format Could Allow Remote Code Execution». Microsoft TechNet. Microsoft. September 8, 2009. Archived from the original on July 31, 2010. Retrieved June 5, 2010.
- ^ «MS09-047: Description of the security update for Windows Media Format Runtime, Windows Media Services, and Media Foundation: September 8, 2009». Support. Microsoft. September 10, 2009. Archived from the original on May 19, 2010. Retrieved June 5, 2010.
- ^ «Microsoft Unveils Windows Media Player for Palm-Size and Pocket PCs». News Center. Microsoft. January 6, 2000. Archived from the original on August 6, 2020. Retrieved January 31, 2017.
- ^ «Windows Media Components for QuickTime». Microsoft. Archived from the original on January 12, 2006. Retrieved March 30, 2007.
- ^ Microsoft. Download Center Archived 2017-07-25 at the Wayback Machine. «be used to restore Windows Media Player and related technologies to N and KN editions of Windows Vista.» Retrieved July 26, 2008
- ^ «Get Windows Media Player». Windows. Microsoft. Archived from the original on August 25, 2010. Retrieved November 5, 2011.
- ^ «MS09-037: Description of the security update for Windows Media Player: August 11, 2009». Support. Microsoft. May 8, 2012. Archived from the original on September 21, 2013. Retrieved August 12, 2013.
- ^ «Final Release of Windows Media 9 Series Starts Next Wave of Digital Media». News Center. Microsoft. January 7, 2003. Archived from the original on February 3, 2016. Retrieved September 29, 2015.
- ^ a b Petri, Daniel (2009-01-08). «Download Windows Media Player 9». Petri. Archived from the original on 2019-02-13. Retrieved 2019-02-12.
- ^ «Windows Media Player 7.1 for Windows 98, 2000, and Me 7.1 — BumperSoft». www.bumpersoft.com. Archived from the original on 2019-02-13. Retrieved 2019-02-12.
- ^ «Microsoft Windows Media Player 7 Brings Click and Play Digital Media To Millions Around the Globe». News Center. Microsoft. July 17, 2000. Archived from the original on May 27, 2015. Retrieved June 15, 2011.
Further readingEdit
- Liron, Marc (2004). «A Little Windows Media Player History…» Windows XP Media Player — The Best There Is?. Archived from the original on January 18, 2008. Retrieved October 7, 2011.
- «The default codecs that are included with Windows Media Player 9 and with Windows Media Player 10 (Revision 1.1)». Microsoft Support Center. Microsoft Corporation. August 4, 2005. Archived from the original on November 20, 2011. Retrieved October 7, 2011.
External linksEdit
- Official website
- The Vintage Windows Media Player
- wmplugins.com — The place to find and share plug-ins, skins and visualizations.


 а
а