Уже в январе 2020 года заканчивается поддержка Windows 2008 R2. Сегодня я хочу поделиться подборкой субъективных причин, по которым многие (и я тоже) до сих пор проводят новые инсталляции этой старушки.
Ценителей, ностальгирующих и ненавистников — прошу под кат.
Легковесность
Если сравнивать минимальные системные требования Windows 2008R2 и Windows 2016, то они будут идентичны за исключением маленького нюанса — графическая оболочка Windows 2016 требует 2 Гб оперативной памяти. А вот по субъективным ощущениям Windows 2008R2 работает куда отзывчивее на не очень свежих серверах и слабых виртуалках, особенно по части IO нагрузки на диск.
Судя по всему, дело в меньшем количестве различных служб и в их большей простоте.
Свежеустановленная старая и новая система с идентичными ролями.
Кнопка Пуск
Даже многие системные администраторы ставят на сервера под управлением Windows 2012 и старше ПО вроде Classic Shell, чтобы вернуть старый добрый «Пуск». Что уж говорить о пользователях. Конечно, возврат к чему-то «пускоподобному» в Windows 102016 сделал жизнь чуть легче, но лишь только чуть. Искать нужное приложение приходится или мучительно вглядываясь в строки, или набирая его имя — одной мышкой не обойтись.
Да и к тому же попробуйте объяснить пользователю, как правильно выходить с терминального сервера не «крестиком», если вместо кнопки «Пуск» — плитки и недо-плитки. Сравните, насколько просто было в Windows 2008: Пуск — завершение сеанса.
Краткость — сестра таланта.
И в Windows 2016: «Нажмите туда, где раньше был пуск. Да-да, с квадратиками. Найдите там человечка. Да, такой маленький… Нет, слева! Нажмите на него и там нажмите на «выход».
Больше, больше кликов мыши!
Далее в старом меню есть прекрасный пункт — «Безопасность Windows». Пользователь может совершенно спокойно и ненапряжно сменить свой пароль. Без вот этого вот «нажмите Ctrl+Alt+End. Нет, не Delete. End. Это кнопка рядом с Delete». А если пользователь сидит на терминальном сервере с другого терминального сервера — без лайфхаков типа ярлыка на команду explorer shell:::{2559a1f2-21d7-11d4-bdaf-00c04f60b9f0} уже не обойтись.
Нет, лично я радуюсь, когда захожу на сервер с Windows 2008 и вижу кнопку «Пуск». А люди на форумах острят на тему плиточных интерфейсов, что они для того чтобы получать ачивки в аккаунте Xbox — типа «Починил Active Directory», «Не сломал DFS при обновлении домена». А что? Было бы прикольно.
Полноценный терминальный сервер без домена
Допустим, захотелось вам решить простую задачу — развернуть на далеком сервере (реальном или виртуальном) сервер терминалов для работы с 1С в небольшой компании.
В Windows 2008 все просто: все настройки проводятся через оснастку, контроллер домена не нужен. Начиная с Windows 2012, коллекцию без контроллера домена не создать. И если хочется отдельный сервер — извольте настраивать через локальные политики.
Но такая возможность, как RemoteApp без домена — увы, не работает. Нужно или использовать какие-то сторонние решения, или разворачивать домен.
Также если хочется подключаться к пользовательской сессии (т.н shadowing), то без контроллера домена штатными средствами ничего не получится. Потому что.
Старый добрый tsadmin.msc.
Даже банальная отправка сообщений пользователям (например, о скорой перезагрузке сервера) начинает превращаться в квест. Если раньше можно было выбрать нужных пользователей в оснастке tsadmin.msc, используя такие средства выделения как Ctrl и Shift, то теперь или отправляй сообщения по одному, или используй командную строку и утилиту msg.exe.
Отправка сообщений в Windows 2016.
Если вдруг вы все-таки захотите сделать полноценный сервер терминалов с коллекциями и поставите роль контроллера домена на сервер терминалов — или наоборот, — то и тут вас ждут приключения из-за работы встроенной БД Windows и правил доступа к ней. Придется ставить еще и SQl Management Studio.
Microsoft рекомендует использовать возможность установки двух виртуальных машин по одной лицензии. То есть теперь, если я хочу пользоваться всеми возможностями сервера терминалов, мне предлагается ставить Windows на железо и делать две виртуалки — для сервера терминалов и для контроллера домена. Падение производительности 1С в таком случае составляет от 10% до 20%, появляется необходимость покупать у хостера второй IP — из-за того, что на гипервизоре может быть роль только гипервизора… Спасибо, Microsoft!
Стабильность работы
Когда на одном предприятии смигрировали терминальный сервер на Windows 2016, то столкнулись с удивительными вещами при работе стареньких несетевых принтеров и 1С. Если принтеры пробрасывались в RDP или подключались к терминальной сессии как computerprinter, то они или пропадали вообще, или пропадали из 1С. И приходилось удалять настройки пользователя.
Безумие продолжалось до тех пор, пока не приняли отвратительное решение — установить принтеры на сервер как локальные с портом computerprinter и навесить на них нужный ACL.
Установленный принтер.
Подобные интересные нюансы всплывали неоднократно в разных организациях. То проблема с принтерами, то с не самым свежим ПО вплоть до BSOD-а. В одной истории пришлось воспользоваться правом лицензии VL на downgrade, так как проприетарное ПО категорически не хотело работать на Windows 2016 и на виртуальной машине.
Поэтому, если позволяет лицензия и аппаратная составляющая — Windows 2008R2 Standart поддерживает не более 32 Гб оперативной памяти, — а также нет необходимости в новых функциях свежих серверных OS, мы по-прежнему ставим Windows 2008R2 и с ужасом ждем окончания поддержки.
Надо отметить, что Windows 2008R2 уже фактически стала эталоном для «облачного» хостинга 1С — когда клиенту недостаточно тонкого клиента, а нужен полноценный доступ в 1С. Благо RemoteApp работают с 1С в 2008R2 так же плохо, как и в 2016.
Телеметрия
Кто бы что ни говорил о плюсах телеметрии, мне неприятно, когда система что-то кому-то отсылает. Особенно, если эта система в продакшене. Конечно, Microsoft заявляет, что опасаться нечего, но тем не менее. Напрашивается очевидный выход — отключить интернет на сервере. Это хорошо, если интернет не нужен для функционирования сервера. В противном случае будет разумно закрыть адреса Microsoft на фаерволе или что-то подобное.
Ведь даже в настройках телеметрии в групповых политиках в параметре Конфигурация компьютера — Административные шаблоны — Компоненты Windows — Сборки для сбора данных и предварительные сборки можно лишь поставить ограничение, но не отключить механизм полностью.
Настройка телеметрии.
Еще можно вовсе отключить телеметрию и настроить мониторинг, который уведомит о включении службы после обновления. Также сообщество создало некоторое количество скриптов и утилит, призванных отключать телеметрию совсем на Windows 10 и Windows 2016.
Например, известен батник, который правит реестр и блокирует домены MS при помощи файла host. Еще существует решение на PowerShell: оно тоже правит реестр и заодно отключает службы с назначенными заданиями, которые могут что-то передавать на сторонние сервера.
Кумулятивные обновления
Стандартная поставка обновлений безопасности на свежих версиях Windows происходит через кумулятивные обновления. Это очень удобно — не нужно выбирать 100500 обновлений для загрузки на свежеустановленную систему. Правда, удобно это разве что установщикам систем.
В реальности если какой-то патч что-то ломает — а это бывает регулярно, — то на его отлов и отключение придется потратить немало человеко-часов. Поэтому возникает необходимость держать как минимум тестовую группу серверов, где можно проверять обновления. Ну и WSUS начинает нравиться как инструмент.
Старая добрая масса обновлений.
Нет уж. Старый механизм, где можно опционально выбрать или заблокировать нужные системы безопасности, мне больше по душе.
Как продлить поддержку
Сейчас Microsoft предлагает лишь один вариант, как не остаться без поддержки с 2020 года — это перенести серверы в Azure. Тогда, по словам Microsoft, можно продлить агонию одной из самых удачных операционных систем еще на 3 года.
Стоит отметить, что это касается также Windows 2008 (единственной актуальной 32-битной серверной ОС) и SQL Server 2008.
Расскажите, планируете ли вы полностью избавиться от Windows 2008R2 за следующие пару лет?
| Version of the Windows NT operating system | |
 |
|

Screenshot of Windows Server 2008 showing the Server Manager application which is automatically opened when an administrator logs on. |
|
| Developer | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| OS family | Microsoft Windows |
| Source model |
|
| Released to manufacturing |
February 4, 2008; 15 years ago[1] |
| General availability |
February 27, 2008; 14 years ago[1] |
| Latest release | Service Pack 2 with March 19, 2019 or later update rollup (6.0.6003)[2] / March 19, 2019; 3 years ago |
| Marketing target | Business |
| Update method | Windows Update, Windows Server Update Services, SCCM |
| Platforms | IA-32, x86-64, Itanium |
| Kernel type | Hybrid (Windows NT kernel) |
| Default user interface |
Windows shell (Graphical) |
| License | Proprietary commercial software |
| Preceded by | Windows Server 2003 (2003) |
| Succeeded by | Windows Server 2008 R2 (2009) |
| Official website | Windows Server 2008 |
| Support status | |
| Mainstream support ended on January 13, 2015[3][4] Extended support ended on January 14, 2020[3][4] Windows Server 2008 is eligible for the paid ESU (Extended Security Updates) program.[5] This program allowed volume license customers to purchase, in yearly installments, security updates for the operating system until January 10, 2023,[3] only for Standard, Enterprise and Datacenter volume licensed editions. The updates are included with a Microsoft Azure purchase and Azure customers receive ESU updates until January 9, 2024.[6][5][7] Installing Service Pack 2 is required for users to receive updates and support after July 12, 2011[3][4] |
Windows Server 2008 is the fourth release of the Windows Server operating system produced by Microsoft as part of the Windows NT family of the operating systems. It was released to manufacturing on February 4, 2008, and generally to retail on February 27, 2008. Derived from Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008 is the successor of Windows Server 2003 and the predecessor to Windows Server 2008 R2.
Windows Server 2008 is the final version of Windows Server that supports IA-32-based processors (also known as 32-bit processors). Its successor, Windows Server 2008 R2, requires a 64-bit processor in any supported architecture (x86-64 for x86 and Itanium).
History[edit]
Microsoft had released Windows Vista to mixed reception, and their last Windows Server release was based on Windows XP. The operating system’s working title was Windows Server Codename «Longhorn», but was later changed to Windows Server 2008 when Microsoft chairman Bill Gates announced it during his keynote address at WinHEC on May 16, 2007.[8]
Beta 1 was released on July 27, 2005; Beta 2 was announced and released on May 23, 2006, at WinHEC 2006 and Beta 3 was released publicly on April 25, 2007.[9] Release Candidate 0 was released to the general public on September 24, 2007[10] and Release Candidate 1 was released to the general public on December 5, 2007. Windows Server 2008 was released to manufacturing on February 4, 2008, and officially launched on the 27th of that month.[11]
Features[edit]
Windows Server 2008 is built from the same codebase as Windows Vista and thus it shares much of the same architecture and functionality. Since the codebase is common, Windows Server 2008 inherits most of the technical, security, management and administrative features new to Windows Vista such as the rewritten networking stack (native IPv6, native wireless, speed and security improvements); improved image-based installation, deployment and recovery; improved diagnostics, monitoring, event logging and reporting tools; new security features such as BitLocker and address space layout randomization (ASLR); the improved Windows Firewall with secure default configuration; .NET Framework 3.0 technologies, specifically Windows Communication Foundation, Microsoft Message Queuing and Windows Workflow Foundation; and the core kernel, memory and file system improvements. Processors and memory devices are modeled as Plug and Play devices to allow hot-plugging of these devices. This allows the system resources to be partitioned dynamically using dynamic hardware partitioning — each partition has its own memory, processor and I/O host bridge devices independent of other partitions.[12]
Server Core[edit]
Windows Server 2008 includes a variation of installation called Server Core. Server Core is a significantly scaled-back installation where no Windows Explorer shell is installed. It also lacks Internet Explorer, and many other non-essential features. All configuration and maintenance is done entirely through command-line interface windows, or by connecting to the machine remotely using Microsoft Management Console (MMC). Notepad and some Control Panel applets, such as Regional Settings, are available.
A Server Core installation can be configured for several basic roles, including the domain controller (Active Directory Domain Services), Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services (formerly known as Active Directory Application Mode[13]), DNS Server, DHCP server, file server, print server, Windows Media Server, Internet Information Services 7 web server and Hyper-V virtual server roles. Server Core can also be used to create a cluster with high availability using failover clustering or network load balancing.
Andrew Mason, a program manager on the Windows Server team, noted that a primary motivation for producing a Server Core variant of Windows Server 2008 was to reduce the attack surface of the operating system, and that about 70% of the security vulnerabilities in Microsoft Windows from the prior five years would not have affected Server Core.[14]
Active Directory[edit]
The Active Directory domain functionality that was retained from Windows Server 2003 was renamed to Active Directory Domain Services (ADDS).[15]
- Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS) enables enterprises to share credentials with trusted partners and customers, allowing a consultant to use their company user name and password to log in on a client’s network.
- Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services (AD LDS), (formerly Active Directory Application Mode, or ADAM)
- Active Directory Certificate Services (ADCS) allow administrators to manage user accounts and the digital certificates that allow them to access certain services and systems. Identity Integration Feature Pack is included as Active Directory Metadirectory Services.
- Active Directory Rights Management Services (ADRMS)
- Read-only domain controllers (RODCs), intended for use in branch office or other scenarios where a domain controller may reside in a low physical security environment. The RODC holds a non-writeable copy of Active Directory, and redirects all write attempts to a full domain controller. It replicates all accounts except sensitive ones.[16] In RODC mode, credentials are not cached by default. Also, local administrators can be designated to log on to the machine to perform maintenance tasks without requiring administrative rights on the entire domain.[17]
- Restartable Active Directory allows ADDS to be stopped and restarted from the Management Console or the command-line without rebooting the domain controller. This reduces downtime for offline operations and reduces overall DC servicing requirements with Server Core. ADDS is implemented as a Domain Controller Service in Windows Server 2008.
- All of the Group Policy improvements from Windows Vista are included. Group Policy Management Console (GPMC) is built-in. The Group Policy objects are indexed for search and can be commented on.[18]
- Policy-based networking with Network Access Protection, improved branch management and enhanced end user collaboration. Policies can be created to ensure greater quality of service for certain applications or services that require prioritization of network bandwidth between client and server.
- Granular password settings within a single domain — ability to implement different password policies for administrative accounts on a «group» and «user» basis, instead of a single set of password settings to the whole domain.
Failover Clustering[edit]
Windows Server 2008 offers high availability to services and applications through Failover Clustering. Most server features and roles can be kept running with little to no downtime.
In Windows Server 2008, the way clusters are qualified changed significantly with the introduction of the cluster validation wizard.[19] The cluster validation wizard is a feature that is integrated into failover clustering in Windows Server 2008. With the cluster validation wizard, an administrator can run a set of focused tests on a collection of servers that are intended to use as nodes in a cluster. This cluster validation process tests the underlying hardware and software directly, and individually, to obtain an accurate assessment of how well failover clustering can be supported on a given configuration.
This feature is only available in Enterprise and Datacenter editions of Windows Server.
Disk management and file storage[edit]
- The ability to resize hard disk partitions without stopping the server, even the system partition. This applies only to simple and spanned volumes, not to striped volumes.
- Shadow Copy based block-level backup which supports optical media, network shares and Windows Recovery Environment.
- DFS enhancements — SYSVOL on DFS-R, Read-only Folder Replication Member. There is also support for domain-based DFS namespaces that exceed the previous size recommendation of 5,000 folders with targets in a namespace.[20]
- Several improvements to Failover Clustering (high-availability clusters).[21]
- Internet Storage Naming Server (iSNS) enables central registration, deregistration and queries for iSCSI hard drives.
- Self-healing NTFS: In Windows versions prior to Windows Vista, if the operating system detected corruption in the file system of an NTFS volume, it marked the volume «dirty»; to correct errors on the volume, it had to be taken offline. With self-healing NTFS, an NTFS worker thread is spawned in the background which performs a localized fix-up of damaged data structures, with only the corrupted files/folders remaining unavailable without locking out the entire volume and needing the server to be taken down. S.M.A.R.T. detection techniques were added to help determine when a hard disk may fail.[22]
Hyper-V[edit]
Hyper-V is hypervisor-based virtualization software, forming a core part of Microsoft’s virtualization strategy. It virtualizes servers on an operating system’s kernel layer. It can be thought of as partitioning a single physical server into multiple small computational partitions. Hyper-V includes the ability to act as a Xen virtualization hypervisor host allowing Xen-enabled guest operating systems to run virtualized.[23] A beta version of Hyper-V shipped with certain x86-64 editions of Windows Server 2008, prior to Microsoft’s release of the final version of Hyper-V on 26 June 2008 as a free download. Also, a standalone variant of Hyper-V exists; this variant supports only x86-64 architecture.[24] While the IA-32 editions of Windows Server 2008 cannot run or install Hyper-V, they can run the MMC snap-in for managing Hyper-V.
Windows System Resource Manager[edit]
Windows System Resource Manager (WSRM) is integrated into Windows Server 2008. It provides resource management and can be used to control the amount of resources a process or a user can use based on business priorities. Process Matching Criteria, which is defined by the name, type or owner of the process, enforces restrictions on the resource usage by a process that matches the criteria. CPU time, bandwidth that it can use, number of processors it can be run on, and allocated to a process can be restricted. Restrictions can be set to be imposed only on certain dates as well.
Server Manager[edit]
Server Manager is a new roles-based management tool for Windows Server 2008.[25] It is a combination of Manage Your Server and Security Configuration Wizard from Windows Server 2003. Server Manager is an improvement of the Configure my server dialog that launches by default on Windows Server 2003 machines. However, rather than serve only as a starting point to configuring new roles, Server Manager gathers together all of the operations users would want to conduct on the server, such as, getting a remote deployment method set up, adding more server roles etc., and provides a consolidated, portal-like view about the status of each role.[26]
Protocol and cryptography[edit]
- Support for 128- and 256-bit AES encryption for the Kerberos authentication protocol.
- New cryptography (CNG) API which supports elliptic curve cryptography and improved certificate management.
- Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol, a new Microsoft proprietary VPN protocol.
- AuthIP, a Microsoft proprietary extension of the IKE cryptographic protocol used in IPsec VPN networks.
- Server Message Block 2.0 protocol in the new TCP/IP stack provides a number of communication enhancements, including greater performance when connecting to file shares over high-latency links and better security through the use of mutual authentication and message signing.
Miscellaneous[edit]
- Fully componentized operating system.
- Improved hot patching, a feature that allows non-kernel patches to occur without the need for a reboot.
- Support for being booted from Extensible Firmware Interface (EFI)-compliant firmware on x86-64 systems.
- Dynamic Hardware Partitioning supports hot-addition or replacement of processors and memory, on capable hardware.
- Windows Deployment Services (WDS) replacing Automated Deployment Services Windows Server 2008 home entertainment and Remote Installation Services. Windows Deployment Services supports an enhanced multicast feature when deploying operating system images.[27]
- Internet Information Services 7 — Increased security, Robocopy deployment, improved diagnostic tools, delegated administration.
- Windows Internal Database, a variant of SQL Server Express 2005, which serves as a common storage back-end for several other components such as Windows System Resource Manager, Windows SharePoint Services and Windows Server Update Services. It is not intended to be used by third-party applications.
- An optional «desktop experience» component provides the same Windows Aero user interface as Windows Vista, both for local users, as well as remote users connecting through Remote Desktop.
Removed features[edit]
- The Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol component in Routing and Remote Access Service was removed.[28]
- Services for Macintosh, which provided file and print sharing via the now deprecated AppleTalk protocol, has been removed. Services for Macintosh were initially removed in Windows XP but were available in Windows Server 2003.[28]
- NTBackup is replaced by Windows Server Backup, and no longer supports backing up to tape drives.[29] As a result of NTBackup removal, Exchange Server 2007 does not have volume snapshot backup functionality; however Exchange Server 2007 SP2 adds back an Exchange backup plug-in for Windows Server Backup which restores partial functionality.[30] Windows Small Business Server and Windows Essential Business Server both include this Exchange backup component.[31]
- The POP3 service has been removed from Internet Information Services 7.0.[32] The SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) service is not available as a server role in IIS 7.0, it is a server feature managed through IIS 6.0.
- NNTP (Network News Transfer Protocol) is no longer part of Internet Information Services 7.0.
- ReadyBoost, which is available in Windows Vista, is not supported in Windows Server 2008.
Editions[edit]
Installation disc of Enterprise edition (beta 3)
Most editions of Windows Server 2008 are available in x86-64 and IA-32 variants. These editions come in two DVDs: One for installing the IA-32 variant and the other for x64. Windows Server 2008 for Itanium-based Systems supports IA-64 processors. The IA-64 variant is optimized for high-workload scenarios like database servers and Line of Business (LOB) applications. As such, it is not optimized for use as a file server or media server. Windows Server 2008 is the last 32-bit Windows server operating system.[33]
Editions of Windows Server 2008 include:[34]
- Windows Server 2008 Foundation (codenamed «Lima»; x86-64) for OEMs only[35]
- Windows Server 2008 Standard (IA-32 and x86-64)
- Windows Server 2008 Enterprise (IA-32 and x86-64)
- Windows Server 2008 Datacenter (IA-32 and x86-64)
- Windows Server 2008 for Itanium-based Systems (IA-64)
- Windows Web Server 2008 (IA-32 and x86-64)
- Windows HPC Server 2008 (codenamed «Socrates»; replacing Windows Compute Cluster Server)
- Windows Storage Server 2008 (codenamed «Magni»; IA-32 and x86-64)
- Windows Small Business Server 2008 (codenamed «Cougar»; x86-64) for small businesses
- Windows Essential Business Server 2008 (codenamed «Centro»; x86-64) for medium-sized businesses[36] — this edition was discontinued in 2010.[37]
The Microsoft Imagine program, known as DreamSpark at the time, used to provide verified students with the 32-bit variant of Windows Server 2008 Standard Edition, but the version has since then been removed. However, they still provide the R2 release.
The Server Core feature is available in the Web, Standard, Enterprise and Datacenter editions.
Windows Server 2008 Foundation Released on May 21, 2009.[38]
System requirements[edit]
System requirements for Windows Server 2008 are as follows:
| Criteria | 2008 | 2008 R2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum[39] | Recommended[39] | Minimum[40] | Recommended[40] | |
| CPU |
|
2 GHz or faster | 1.4 GHz (x86-64 or Itanium) | 2 GHz or faster |
| RAM | 512 MB | 2 GB or greater | 512 MB | 2 GB or greater |
| HDD[a] |
|
40 GB or greater |
|
|
| Devices | DVD drive, 800 × 600 or higher display, keyboard and mouse |
Scalability[edit]
Windows Server 2008 supports the following maximum hardware specifications:[42][43][44]
| Specification | Windows Server 2008 SP2 | Windows Server 2008 R2 |
|---|---|---|
| Physical processors («sockets»)[43] |
|
|
| Logical processors when Hyper-V is disabled[43] |
|
256 |
| Logical processors when Hyper-V is enabled[43] |
|
64 |
| Memory on IA-32[44] |
|
— |
| Memory on x64[44] |
|
|
| Memory on Itanium[44] |
2 TB |
Updates[edit]
Windows Server 2008 shares most of its updates with Windows Vista, given that the operating systems share a codebase. A workaround using the Microsoft Update Catalog allowed the installation of updates for Windows Server 2008 on Windows Vista,[45] adding nearly 3 years of security updates to that operating system (Support for Windows Vista ended on April 11, 2017,[46] while support for Windows Server 2008 ended on January 14, 2020).
Service Pack 2[edit]
The RTM release of Windows Server 2008 already includes the updates and fixes of Windows Vista Service Pack 1.
Service Pack 2 was initially announced on October 24, 2008[47] and released on May 26, 2009. Service Pack 2 added new features, such as Windows Search 4.0, support for Bluetooth 2.1, the ability to write to Blu-ray discs, and simpler Wi-Fi configuration. Windows Server 2008 specifically received the final release of Hyper-V 1.0, improved backwards compatibility with Terminal Server license keys and an approximate 10% reduction in power usage with this service pack.[48]
Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008 share the same service pack update binary.[49]
Platform Update[edit]
On October 27, 2009, Microsoft released the Platform Update for Windows Server 2008 and Windows Vista. It backports several APIs and libraries introduced in Windows Server 2008 R2 and Windows 7 to Windows Server 2008 and Windows Vista, including the Ribbon API, DirectX 11, the XPS library, the Windows Automation API and the Portable Device Platform.[50] A supplemental update was released in 2011 to provide improvements and bug fixes.[51]
Internet Explorer 9[edit]
Windows Server 2008 shipped with Internet Explorer 7, the same version that shipped with Windows Vista. The last supported version of Internet Explorer for Windows Server 2008 is Internet Explorer 9, released in 2011. Internet Explorer 9 was continually updated with cumulative monthly update rollups until support for Internet Explorer 9 on Windows Server 2008 ended on January 14, 2020.[52] Extended Security Updates (ESU) continue until January 9, 2024 for Azure customers.
.NET Framework[edit]
The latest supported version of the .NET Framework officially is version 4.6, released on October 15, 2015.[53]
TLS 1.1 and 1.2 support[edit]
In July 2017, Microsoft released an update to add TLS 1.1 and 1.2 support to Windows Server 2008, however it is disabled by default after installing the update.[54]
SHA-2 signing support[edit]
Starting in March 2019, Microsoft began transitioning to exclusively signing Windows updates with the SHA-2 algorithm. As a result of this Microsoft released several updates throughout 2019 to add SHA-2 signing support to Windows Server 2008.[55]
Monthly update rollups[edit]
In June 2018, Microsoft announced that they would be moving Windows Server 2008 to a monthly update model beginning with updates released in September 2018[56] — two years after Microsoft switched the rest of their supported operating systems to that model.[57]
With the new update model, instead of updates being released as they became available, only two update packages were released on the second Tuesday of every month until Windows Server 2008 reached its end of life — one package containing security and quality updates, and a smaller package that contained only the security updates. Users could choose which package they wanted to install each month. Later in the month, another package would be released which was a preview of the next month’s security and quality update rollup.
Installing the preview rollup package released for Windows Server 2008 on March 19, 2019, or any later released rollup package, will update the operating system kernel’s build number from version 6.0.6002 to 6.0.6003. This change was made so Microsoft could continue to service the operating system while avoiding “version-related issues”.[58]
The last free security update rollup packages were released on January 14, 2020.[59]
Windows Server 2008 R2[edit]
A second release of Windows Server 2008 based on Windows 7, Windows Server 2008 R2, was released to manufacturing on July 22, 2009[60] and became generally available on October 22, 2009.[61] New features added in Windows Server 2008 R2 include new virtualization features, new Active Directory features, Internet Information Services 7.5 and support for up to 256 logical processors. It is the first server operating system by Microsoft to exclusively support 64-bit processors, while consumer-oriented versions of Windows maintained 32-bit support until Windows 11 in 2021.
A service pack for Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2, formally designed Service Pack 1, was released in February 2011.[62]
Support lifecycle[edit]
Support for the RTM version of Windows Server 2008 ended on July 12, 2011,[3][4] and users can no longer receive further security updates for the operating system. As a component of Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008 with Service Pack 2 continued to be supported with security updates, lasting until January 14, 2020, the same respective end-of-life dates of its successor, Windows Server 2008 R2 and Windows 7.
Microsoft planned to end support for Windows Server 2008 on January 12, 2016. However, in order to give customers more time to migrate to newer Windows versions, particularly in developing or emerging markets, Microsoft decided to extend support to January 14, 2020.[6][5][7]
Windows Server 2008 is eligible for the paid Extended Security Updates (ESU) program. The program allowed volume license customers to purchase, in yearly installments, security updates for the operating system for three additional years, until January 10, 2023. The program is also included with Microsoft Azure purchases, and Azure customers receive an extra year of support, until January 9, 2024. The licenses are paid for on a per-machine basis. If a user purchases an Extended Security Updates license in a later year of the program, they must pay for any previous years of Extended Security Updates as well. [6][63]
See also[edit]
- BlueKeep (security vulnerability)
- Comparison of Microsoft Windows versions
- Comparison of operating systems
- History of Microsoft Windows
- List of operating systems
- Microsoft Servers
Notes[edit]
- ^ Computers with more than 16 GB of RAM require more disk space for paging, hibernation, and dump files[40]
References[edit]
- ^ a b «As Windows Server 2008 RTMs, Customers and Partners Adopting with Help of New Tools, Training». News Center. Redmond, WA: Microsoft. 4 February 2008.
- ^ «Build number changing to 6003 in Windows Server 2008». support.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2021-03-26.
- ^ a b c d e «Microsoft Product Lifecycle». Support. Microsoft. Retrieved April 12, 2022.
- ^ a b c d «Install Windows Vista Service Pack 2 (SP2)». Support. Microsoft. Retrieved April 12, 2010.
- ^ a b c «Extended Security Updates for SQL Server and Windows Server 2008 and 2008 R2 | Microsoft». www.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2021-03-26.
- ^ a b c tfosmark. «Product Lifecycle FAQ — Extended Security Updates — Microsoft Lifecycle». docs.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2021-03-26.
- ^ a b «Announcing new options for SQL Server 2008 and Windows Server 2008 End of Support». azure.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2021-03-26.
- ^ Miller, Michael J. (2007-05-15). «Gates at WinHec 2007: Windows Server 2008, Rally, Home Server and More». Forward Thinking. Retrieved 2007-07-09.
- ^ Lowe, David (2007-04-25). «Beta 3 is Go!». Windows Server Division WebLog. Microsoft. Retrieved 2007-04-25.
- ^ Ralston, Ward (2007-09-24). «Windows Server 2008 Rc0 Released!». Windows Server Division WebLog. Microsoft. Retrieved 2007-09-24.
- ^ Nate Mook (10 July 2007). «New Windows Server, Visual Studio, SQL Server to Launch in February». BetaNews. Retrieved 2007-07-11.
- ^ «Dynamic Hardware Partitioning Architecture». MSDN. Retrieved 2007-07-23.
- ^ Archiveddocs. «Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services Overview». docs.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2020-01-15.
- ^ «Iain McDonald and Andrew Mason show off the new Windows Server OS». Channel 9. Microsoft. May 24, 2006. Retrieved 2008-11-01.
18:55
- ^ Hynes, Byron (November 2006). «The Future of Windows: Directory Services in Windows Server 2008». TechNet Magazine. Retrieved 2007-05-02.
- ^ «Deploying Windows Server 2008 Read Only Domain Controllers». docs.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2020-01-15.
- ^ «Q. What is a read-only domain controller (RODC)?». IT Pro. 2008-03-24. Retrieved 2020-01-15.
- ^ Ward, Keith (2007-10-08). «Top 10 Overlooked Windows Server 2008 Features, Part 2». Redmond Developer News. Archived from the original on 2009-08-04. Retrieved 2014-10-10.
- ^ «Failover Cluster Validation Error 80070005 on Windows Server 2008 R2 x64». Capitalhead. 2009-11-04. Retrieved 2013-10-28.
- ^ Zoeller, Jill (26 July 2007). «New in Windows Server 2008: Breaking the 5K Folder «Barrier» in Domain-Based Namespaces». The Storage Team at Microsoft — File Cabinet Blog. Microsoft. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- ^ «Failover Clustering with Windows Server 2008 including Cluster shared volumes». Microsoft. 2007-01-17. Retrieved 2007-07-09.
- ^ Loveall, John (2006). «Storage improvements in Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008» (PowerPoint). Microsoft Corporation. Retrieved 2007-07-09.
- ^ «Benchmarking Hyper-V on Windows Server 2008 R2 x64». 2010-01-20. Retrieved 2010-01-28.
- ^ «Microsoft Extends Virtualization Strategy, Outlines Product Road Map». Microsoft. 2006-05-22. Retrieved 2007-07-09.
- ^ «Server Manager». Windows Server 2008 Technical Library. Microsoft TechNet. 2007-06-25. Retrieved 2007-05-02.
- ^ «Unexpected error refreshing Server Manager-0x800706BE and 1601 on Window Server 2008 R2». Retrieved 2010-11-05.
- ^ «Multicasting OS deployments with Windows Server 2008». Kevinsul’s Management Blog. Microsoft. 29 August 2007. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- ^ a b «Removed technologies in Routing and Remote Access in Windows Server 2008». TechNet. Microsoft. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- ^ «Windows Server Backup Step-by-Step Guide for Windows Server 2008». TechNet. Microsoft. 17 January 2013. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- ^ «Exchange Server 2007 Service Pack 2 available in Q3 2009». The Exchange Team Blog. 11 May 2009. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- ^ Bilic, Nino (18 June 2008). «To Backup or Not to Backup? Yes! To backup!!». The Exchange Team Blog. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- ^ «IIS 7.0 Protocols». TechNet. Microsoft. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- ^ Heaton, Alex (2007-05-18). «On 64-bit and Windows Client». Windows Vista Team Blog. Retrieved 2007-07-09.
- ^
«Windows Server 2008 Product Editions». Microsoft. 2007-04-25. Retrieved 2007-07-09. - ^ «Windows Server 2008 Foundation: An Entry-Level Server Platform». Petri IT Knowledgebase. 2009-04-17. Retrieved 2014-01-08.
- ^ Ligman, Eric (7 November 2007). «Announcing Windows Essential Business Server». Microsoft Small Business Blog. Microsoft. Retrieved 2013-08-16.
- ^ «Windows Essential Business Server 2008». Technet.microsoft.com. 2010-12-31. Retrieved 2013-01-09.
- ^ «Windows Server 2008, Microsoft Lifecycle (Look at the Note below links)». docs.microsoft.com/en-us/lifecycle/products/.
- ^ a b «Windows Server 2008 System Requirements». 31 March 2008. Retrieved 2008-03-31.
- ^ a b c «Microsoft Windows Server 2008 System Requirements». Microsoft.com. Retrieved 2013-01-09.
- ^ «Microsoft Windows Server 2008 System Requirements». Microsoft. Retrieved 2013-01-09.
- ^ Savill, John (October 28, 2011). «Q: What are Windows Server 8’s Scalability Numbers?». Windows IT Pro. Penton Media. Retrieved November 5, 2011.
- ^ a b c d Seldam, Matthijs ten (October 13, 2012). «Windows Server — Sockets, Logical Processors, Symmetric Multi Threading». Matthijs’s blog. Microsoft. Retrieved October 14, 2012.
- ^ a b c d «Memory Limits for Windows and Windows Server Releases». MSDN. Microsoft. Retrieved 13 April 2014.
- ^ «Extend Windows Vista support by installing Windows Server 2008 updates — gHacks Tech News». gHacks Technology News. 2017-06-24. Retrieved 2021-06-30.
- ^ «Windows Vista Lifecycle Policy». Microsoft. Retrieved January 2, 2017.
- ^ Justin Graham (October 24, 2008). «Windows Server 2008 Service Pack 2 beta». Microsoft. Retrieved 2008-10-29.
- ^ «Tech ARP — ED#107 : Latest Details on Windows Vista Service Pack 2 Rev. 2.2». Archived from the original on 2009-02-12.
- ^ «Windows Vista Service Pack 2 Beta». blogs.windows.com. Archived from the original on 9 May 2013. Retrieved 12 January 2022.
- ^ «Announcing Final Releases of Platform Update for Windows Vista Technologies». 27 October 2009.
- ^ «Platform Update Supplement for Windows Vista and for Windows Server 2008».
- ^ «Cumulative security update for Internet Explorer: January 14, 2020». support.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2021-03-26.
- ^ «Microsoft .NET Framework 4.6 (Web Installer)». Microsoft.
- ^ «TLS 1.2 Support added to Windows Server 2008». Microsoft Security. 2017-07-20. Retrieved 2021-03-26.
- ^ «2019 SHA-2 Code Signing Support requirement for Windows and WSUS».
- ^ Mackie, Kurt; 06/13/2018. «Microsoft Switching Windows Server 2008 SP2 to Monthly Update Rollup Model — Redmondmag.com». Redmondmag. Retrieved 2021-03-26.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ «Community». forums.ivanti.com. Retrieved 2021-03-26.
- ^ «Build number changing to 6003 in Windows Server 2008».
- ^ «January 14, 2020—KB4534303 (Monthly Rollup)». support.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2021-03-26.
- ^ «Windows Server 2008 R2 Reaches the RTM Milestone! — Windows Server Blog — Site Home — TechNet Blogs». Blogs.technet.com. 2009-07-22. Retrieved 2013-01-09.
- ^ «When to expect Windows Server 2008 R2 RTM — Windows Server Blog — Site Home — TechNet Blogs». Blogs.technet.com. 2009-07-22. Retrieved 2013-01-09.
- ^ LeBlanc, Brandon (February 9, 2011). «Announcing Availability of Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1». Windows Experience Blog. Microsoft.
- ^ «Windows Server 2008 Product Lifecycle». Microsoft. January 14, 2020. Retrieved January 9, 2022.
18:55
Further reading[edit]
- «What’s New in Networking». TechNet. Microsoft. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- «Changes in Functionality from Windows Server 2003 with SP1 to Windows Server 2008». TechNet. Microsoft. 21 January 2008. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- «Description of the Microsoft server applications that are supported on Windows Server 2008». Support. Microsoft. 23 April 2012. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- «Windows Server 2008 System Requirements». TechNet. Microsoft. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- Henderson, Tom; Dvorak, Rand (21 February 2008). «Windows Server 2008: Faster, more manageable and secure, but still missing the virtual link». Network World. IDG. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- Radzikowski, Przemek (21 February 2010). «How to Find Build and Revision Number of Windows Vista or Windows Server 2008 Installed». Capitalhead. Capitalhead Pty. Ltd. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- Stanek, William (2008). Windows Server 2008 Inside Out. Microsoft Press. ISBN 978-0-7356-2438-2.
External links[edit]
- Windows Server Performance Team Blog
| Version of the Windows NT operating system | |
 |
|

Screenshot of Windows Server 2008 showing the Server Manager application which is automatically opened when an administrator logs on. |
|
| Developer | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| OS family | Microsoft Windows |
| Source model |
|
| Released to manufacturing |
February 4, 2008; 15 years ago[1] |
| General availability |
February 27, 2008; 14 years ago[1] |
| Latest release | Service Pack 2 with March 19, 2019 or later update rollup (6.0.6003)[2] / March 19, 2019; 3 years ago |
| Marketing target | Business |
| Update method | Windows Update, Windows Server Update Services, SCCM |
| Platforms | IA-32, x86-64, Itanium |
| Kernel type | Hybrid (Windows NT kernel) |
| Default user interface |
Windows shell (Graphical) |
| License | Proprietary commercial software |
| Preceded by | Windows Server 2003 (2003) |
| Succeeded by | Windows Server 2008 R2 (2009) |
| Official website | Windows Server 2008 |
| Support status | |
| Mainstream support ended on January 13, 2015[3][4] Extended support ended on January 14, 2020[3][4] Windows Server 2008 is eligible for the paid ESU (Extended Security Updates) program.[5] This program allowed volume license customers to purchase, in yearly installments, security updates for the operating system until January 10, 2023,[3] only for Standard, Enterprise and Datacenter volume licensed editions. The updates are included with a Microsoft Azure purchase and Azure customers receive ESU updates until January 9, 2024.[6][5][7] Installing Service Pack 2 is required for users to receive updates and support after July 12, 2011[3][4] |
Windows Server 2008 is the fourth release of the Windows Server operating system produced by Microsoft as part of the Windows NT family of the operating systems. It was released to manufacturing on February 4, 2008, and generally to retail on February 27, 2008. Derived from Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008 is the successor of Windows Server 2003 and the predecessor to Windows Server 2008 R2.
Windows Server 2008 is the final version of Windows Server that supports IA-32-based processors (also known as 32-bit processors). Its successor, Windows Server 2008 R2, requires a 64-bit processor in any supported architecture (x86-64 for x86 and Itanium).
History[edit]
Microsoft had released Windows Vista to mixed reception, and their last Windows Server release was based on Windows XP. The operating system’s working title was Windows Server Codename «Longhorn», but was later changed to Windows Server 2008 when Microsoft chairman Bill Gates announced it during his keynote address at WinHEC on May 16, 2007.[8]
Beta 1 was released on July 27, 2005; Beta 2 was announced and released on May 23, 2006, at WinHEC 2006 and Beta 3 was released publicly on April 25, 2007.[9] Release Candidate 0 was released to the general public on September 24, 2007[10] and Release Candidate 1 was released to the general public on December 5, 2007. Windows Server 2008 was released to manufacturing on February 4, 2008, and officially launched on the 27th of that month.[11]
Features[edit]
Windows Server 2008 is built from the same codebase as Windows Vista and thus it shares much of the same architecture and functionality. Since the codebase is common, Windows Server 2008 inherits most of the technical, security, management and administrative features new to Windows Vista such as the rewritten networking stack (native IPv6, native wireless, speed and security improvements); improved image-based installation, deployment and recovery; improved diagnostics, monitoring, event logging and reporting tools; new security features such as BitLocker and address space layout randomization (ASLR); the improved Windows Firewall with secure default configuration; .NET Framework 3.0 technologies, specifically Windows Communication Foundation, Microsoft Message Queuing and Windows Workflow Foundation; and the core kernel, memory and file system improvements. Processors and memory devices are modeled as Plug and Play devices to allow hot-plugging of these devices. This allows the system resources to be partitioned dynamically using dynamic hardware partitioning — each partition has its own memory, processor and I/O host bridge devices independent of other partitions.[12]
Server Core[edit]
Windows Server 2008 includes a variation of installation called Server Core. Server Core is a significantly scaled-back installation where no Windows Explorer shell is installed. It also lacks Internet Explorer, and many other non-essential features. All configuration and maintenance is done entirely through command-line interface windows, or by connecting to the machine remotely using Microsoft Management Console (MMC). Notepad and some Control Panel applets, such as Regional Settings, are available.
A Server Core installation can be configured for several basic roles, including the domain controller (Active Directory Domain Services), Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services (formerly known as Active Directory Application Mode[13]), DNS Server, DHCP server, file server, print server, Windows Media Server, Internet Information Services 7 web server and Hyper-V virtual server roles. Server Core can also be used to create a cluster with high availability using failover clustering or network load balancing.
Andrew Mason, a program manager on the Windows Server team, noted that a primary motivation for producing a Server Core variant of Windows Server 2008 was to reduce the attack surface of the operating system, and that about 70% of the security vulnerabilities in Microsoft Windows from the prior five years would not have affected Server Core.[14]
Active Directory[edit]
The Active Directory domain functionality that was retained from Windows Server 2003 was renamed to Active Directory Domain Services (ADDS).[15]
- Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS) enables enterprises to share credentials with trusted partners and customers, allowing a consultant to use their company user name and password to log in on a client’s network.
- Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services (AD LDS), (formerly Active Directory Application Mode, or ADAM)
- Active Directory Certificate Services (ADCS) allow administrators to manage user accounts and the digital certificates that allow them to access certain services and systems. Identity Integration Feature Pack is included as Active Directory Metadirectory Services.
- Active Directory Rights Management Services (ADRMS)
- Read-only domain controllers (RODCs), intended for use in branch office or other scenarios where a domain controller may reside in a low physical security environment. The RODC holds a non-writeable copy of Active Directory, and redirects all write attempts to a full domain controller. It replicates all accounts except sensitive ones.[16] In RODC mode, credentials are not cached by default. Also, local administrators can be designated to log on to the machine to perform maintenance tasks without requiring administrative rights on the entire domain.[17]
- Restartable Active Directory allows ADDS to be stopped and restarted from the Management Console or the command-line without rebooting the domain controller. This reduces downtime for offline operations and reduces overall DC servicing requirements with Server Core. ADDS is implemented as a Domain Controller Service in Windows Server 2008.
- All of the Group Policy improvements from Windows Vista are included. Group Policy Management Console (GPMC) is built-in. The Group Policy objects are indexed for search and can be commented on.[18]
- Policy-based networking with Network Access Protection, improved branch management and enhanced end user collaboration. Policies can be created to ensure greater quality of service for certain applications or services that require prioritization of network bandwidth between client and server.
- Granular password settings within a single domain — ability to implement different password policies for administrative accounts on a «group» and «user» basis, instead of a single set of password settings to the whole domain.
Failover Clustering[edit]
Windows Server 2008 offers high availability to services and applications through Failover Clustering. Most server features and roles can be kept running with little to no downtime.
In Windows Server 2008, the way clusters are qualified changed significantly with the introduction of the cluster validation wizard.[19] The cluster validation wizard is a feature that is integrated into failover clustering in Windows Server 2008. With the cluster validation wizard, an administrator can run a set of focused tests on a collection of servers that are intended to use as nodes in a cluster. This cluster validation process tests the underlying hardware and software directly, and individually, to obtain an accurate assessment of how well failover clustering can be supported on a given configuration.
This feature is only available in Enterprise and Datacenter editions of Windows Server.
Disk management and file storage[edit]
- The ability to resize hard disk partitions without stopping the server, even the system partition. This applies only to simple and spanned volumes, not to striped volumes.
- Shadow Copy based block-level backup which supports optical media, network shares and Windows Recovery Environment.
- DFS enhancements — SYSVOL on DFS-R, Read-only Folder Replication Member. There is also support for domain-based DFS namespaces that exceed the previous size recommendation of 5,000 folders with targets in a namespace.[20]
- Several improvements to Failover Clustering (high-availability clusters).[21]
- Internet Storage Naming Server (iSNS) enables central registration, deregistration and queries for iSCSI hard drives.
- Self-healing NTFS: In Windows versions prior to Windows Vista, if the operating system detected corruption in the file system of an NTFS volume, it marked the volume «dirty»; to correct errors on the volume, it had to be taken offline. With self-healing NTFS, an NTFS worker thread is spawned in the background which performs a localized fix-up of damaged data structures, with only the corrupted files/folders remaining unavailable without locking out the entire volume and needing the server to be taken down. S.M.A.R.T. detection techniques were added to help determine when a hard disk may fail.[22]
Hyper-V[edit]
Hyper-V is hypervisor-based virtualization software, forming a core part of Microsoft’s virtualization strategy. It virtualizes servers on an operating system’s kernel layer. It can be thought of as partitioning a single physical server into multiple small computational partitions. Hyper-V includes the ability to act as a Xen virtualization hypervisor host allowing Xen-enabled guest operating systems to run virtualized.[23] A beta version of Hyper-V shipped with certain x86-64 editions of Windows Server 2008, prior to Microsoft’s release of the final version of Hyper-V on 26 June 2008 as a free download. Also, a standalone variant of Hyper-V exists; this variant supports only x86-64 architecture.[24] While the IA-32 editions of Windows Server 2008 cannot run or install Hyper-V, they can run the MMC snap-in for managing Hyper-V.
Windows System Resource Manager[edit]
Windows System Resource Manager (WSRM) is integrated into Windows Server 2008. It provides resource management and can be used to control the amount of resources a process or a user can use based on business priorities. Process Matching Criteria, which is defined by the name, type or owner of the process, enforces restrictions on the resource usage by a process that matches the criteria. CPU time, bandwidth that it can use, number of processors it can be run on, and allocated to a process can be restricted. Restrictions can be set to be imposed only on certain dates as well.
Server Manager[edit]
Server Manager is a new roles-based management tool for Windows Server 2008.[25] It is a combination of Manage Your Server and Security Configuration Wizard from Windows Server 2003. Server Manager is an improvement of the Configure my server dialog that launches by default on Windows Server 2003 machines. However, rather than serve only as a starting point to configuring new roles, Server Manager gathers together all of the operations users would want to conduct on the server, such as, getting a remote deployment method set up, adding more server roles etc., and provides a consolidated, portal-like view about the status of each role.[26]
Protocol and cryptography[edit]
- Support for 128- and 256-bit AES encryption for the Kerberos authentication protocol.
- New cryptography (CNG) API which supports elliptic curve cryptography and improved certificate management.
- Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol, a new Microsoft proprietary VPN protocol.
- AuthIP, a Microsoft proprietary extension of the IKE cryptographic protocol used in IPsec VPN networks.
- Server Message Block 2.0 protocol in the new TCP/IP stack provides a number of communication enhancements, including greater performance when connecting to file shares over high-latency links and better security through the use of mutual authentication and message signing.
Miscellaneous[edit]
- Fully componentized operating system.
- Improved hot patching, a feature that allows non-kernel patches to occur without the need for a reboot.
- Support for being booted from Extensible Firmware Interface (EFI)-compliant firmware on x86-64 systems.
- Dynamic Hardware Partitioning supports hot-addition or replacement of processors and memory, on capable hardware.
- Windows Deployment Services (WDS) replacing Automated Deployment Services Windows Server 2008 home entertainment and Remote Installation Services. Windows Deployment Services supports an enhanced multicast feature when deploying operating system images.[27]
- Internet Information Services 7 — Increased security, Robocopy deployment, improved diagnostic tools, delegated administration.
- Windows Internal Database, a variant of SQL Server Express 2005, which serves as a common storage back-end for several other components such as Windows System Resource Manager, Windows SharePoint Services and Windows Server Update Services. It is not intended to be used by third-party applications.
- An optional «desktop experience» component provides the same Windows Aero user interface as Windows Vista, both for local users, as well as remote users connecting through Remote Desktop.
Removed features[edit]
- The Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol component in Routing and Remote Access Service was removed.[28]
- Services for Macintosh, which provided file and print sharing via the now deprecated AppleTalk protocol, has been removed. Services for Macintosh were initially removed in Windows XP but were available in Windows Server 2003.[28]
- NTBackup is replaced by Windows Server Backup, and no longer supports backing up to tape drives.[29] As a result of NTBackup removal, Exchange Server 2007 does not have volume snapshot backup functionality; however Exchange Server 2007 SP2 adds back an Exchange backup plug-in for Windows Server Backup which restores partial functionality.[30] Windows Small Business Server and Windows Essential Business Server both include this Exchange backup component.[31]
- The POP3 service has been removed from Internet Information Services 7.0.[32] The SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) service is not available as a server role in IIS 7.0, it is a server feature managed through IIS 6.0.
- NNTP (Network News Transfer Protocol) is no longer part of Internet Information Services 7.0.
- ReadyBoost, which is available in Windows Vista, is not supported in Windows Server 2008.
Editions[edit]
Installation disc of Enterprise edition (beta 3)
Most editions of Windows Server 2008 are available in x86-64 and IA-32 variants. These editions come in two DVDs: One for installing the IA-32 variant and the other for x64. Windows Server 2008 for Itanium-based Systems supports IA-64 processors. The IA-64 variant is optimized for high-workload scenarios like database servers and Line of Business (LOB) applications. As such, it is not optimized for use as a file server or media server. Windows Server 2008 is the last 32-bit Windows server operating system.[33]
Editions of Windows Server 2008 include:[34]
- Windows Server 2008 Foundation (codenamed «Lima»; x86-64) for OEMs only[35]
- Windows Server 2008 Standard (IA-32 and x86-64)
- Windows Server 2008 Enterprise (IA-32 and x86-64)
- Windows Server 2008 Datacenter (IA-32 and x86-64)
- Windows Server 2008 for Itanium-based Systems (IA-64)
- Windows Web Server 2008 (IA-32 and x86-64)
- Windows HPC Server 2008 (codenamed «Socrates»; replacing Windows Compute Cluster Server)
- Windows Storage Server 2008 (codenamed «Magni»; IA-32 and x86-64)
- Windows Small Business Server 2008 (codenamed «Cougar»; x86-64) for small businesses
- Windows Essential Business Server 2008 (codenamed «Centro»; x86-64) for medium-sized businesses[36] — this edition was discontinued in 2010.[37]
The Microsoft Imagine program, known as DreamSpark at the time, used to provide verified students with the 32-bit variant of Windows Server 2008 Standard Edition, but the version has since then been removed. However, they still provide the R2 release.
The Server Core feature is available in the Web, Standard, Enterprise and Datacenter editions.
Windows Server 2008 Foundation Released on May 21, 2009.[38]
System requirements[edit]
System requirements for Windows Server 2008 are as follows:
| Criteria | 2008 | 2008 R2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum[39] | Recommended[39] | Minimum[40] | Recommended[40] | |
| CPU |
|
2 GHz or faster | 1.4 GHz (x86-64 or Itanium) | 2 GHz or faster |
| RAM | 512 MB | 2 GB or greater | 512 MB | 2 GB or greater |
| HDD[a] |
|
40 GB or greater |
|
|
| Devices | DVD drive, 800 × 600 or higher display, keyboard and mouse |
Scalability[edit]
Windows Server 2008 supports the following maximum hardware specifications:[42][43][44]
| Specification | Windows Server 2008 SP2 | Windows Server 2008 R2 |
|---|---|---|
| Physical processors («sockets»)[43] |
|
|
| Logical processors when Hyper-V is disabled[43] |
|
256 |
| Logical processors when Hyper-V is enabled[43] |
|
64 |
| Memory on IA-32[44] |
|
— |
| Memory on x64[44] |
|
|
| Memory on Itanium[44] |
2 TB |
Updates[edit]
Windows Server 2008 shares most of its updates with Windows Vista, given that the operating systems share a codebase. A workaround using the Microsoft Update Catalog allowed the installation of updates for Windows Server 2008 on Windows Vista,[45] adding nearly 3 years of security updates to that operating system (Support for Windows Vista ended on April 11, 2017,[46] while support for Windows Server 2008 ended on January 14, 2020).
Service Pack 2[edit]
The RTM release of Windows Server 2008 already includes the updates and fixes of Windows Vista Service Pack 1.
Service Pack 2 was initially announced on October 24, 2008[47] and released on May 26, 2009. Service Pack 2 added new features, such as Windows Search 4.0, support for Bluetooth 2.1, the ability to write to Blu-ray discs, and simpler Wi-Fi configuration. Windows Server 2008 specifically received the final release of Hyper-V 1.0, improved backwards compatibility with Terminal Server license keys and an approximate 10% reduction in power usage with this service pack.[48]
Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008 share the same service pack update binary.[49]
Platform Update[edit]
On October 27, 2009, Microsoft released the Platform Update for Windows Server 2008 and Windows Vista. It backports several APIs and libraries introduced in Windows Server 2008 R2 and Windows 7 to Windows Server 2008 and Windows Vista, including the Ribbon API, DirectX 11, the XPS library, the Windows Automation API and the Portable Device Platform.[50] A supplemental update was released in 2011 to provide improvements and bug fixes.[51]
Internet Explorer 9[edit]
Windows Server 2008 shipped with Internet Explorer 7, the same version that shipped with Windows Vista. The last supported version of Internet Explorer for Windows Server 2008 is Internet Explorer 9, released in 2011. Internet Explorer 9 was continually updated with cumulative monthly update rollups until support for Internet Explorer 9 on Windows Server 2008 ended on January 14, 2020.[52] Extended Security Updates (ESU) continue until January 9, 2024 for Azure customers.
.NET Framework[edit]
The latest supported version of the .NET Framework officially is version 4.6, released on October 15, 2015.[53]
TLS 1.1 and 1.2 support[edit]
In July 2017, Microsoft released an update to add TLS 1.1 and 1.2 support to Windows Server 2008, however it is disabled by default after installing the update.[54]
SHA-2 signing support[edit]
Starting in March 2019, Microsoft began transitioning to exclusively signing Windows updates with the SHA-2 algorithm. As a result of this Microsoft released several updates throughout 2019 to add SHA-2 signing support to Windows Server 2008.[55]
Monthly update rollups[edit]
In June 2018, Microsoft announced that they would be moving Windows Server 2008 to a monthly update model beginning with updates released in September 2018[56] — two years after Microsoft switched the rest of their supported operating systems to that model.[57]
With the new update model, instead of updates being released as they became available, only two update packages were released on the second Tuesday of every month until Windows Server 2008 reached its end of life — one package containing security and quality updates, and a smaller package that contained only the security updates. Users could choose which package they wanted to install each month. Later in the month, another package would be released which was a preview of the next month’s security and quality update rollup.
Installing the preview rollup package released for Windows Server 2008 on March 19, 2019, or any later released rollup package, will update the operating system kernel’s build number from version 6.0.6002 to 6.0.6003. This change was made so Microsoft could continue to service the operating system while avoiding “version-related issues”.[58]
The last free security update rollup packages were released on January 14, 2020.[59]
Windows Server 2008 R2[edit]
A second release of Windows Server 2008 based on Windows 7, Windows Server 2008 R2, was released to manufacturing on July 22, 2009[60] and became generally available on October 22, 2009.[61] New features added in Windows Server 2008 R2 include new virtualization features, new Active Directory features, Internet Information Services 7.5 and support for up to 256 logical processors. It is the first server operating system by Microsoft to exclusively support 64-bit processors, while consumer-oriented versions of Windows maintained 32-bit support until Windows 11 in 2021.
A service pack for Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2, formally designed Service Pack 1, was released in February 2011.[62]
Support lifecycle[edit]
Support for the RTM version of Windows Server 2008 ended on July 12, 2011,[3][4] and users can no longer receive further security updates for the operating system. As a component of Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008 with Service Pack 2 continued to be supported with security updates, lasting until January 14, 2020, the same respective end-of-life dates of its successor, Windows Server 2008 R2 and Windows 7.
Microsoft planned to end support for Windows Server 2008 on January 12, 2016. However, in order to give customers more time to migrate to newer Windows versions, particularly in developing or emerging markets, Microsoft decided to extend support to January 14, 2020.[6][5][7]
Windows Server 2008 is eligible for the paid Extended Security Updates (ESU) program. The program allowed volume license customers to purchase, in yearly installments, security updates for the operating system for three additional years, until January 10, 2023. The program is also included with Microsoft Azure purchases, and Azure customers receive an extra year of support, until January 9, 2024. The licenses are paid for on a per-machine basis. If a user purchases an Extended Security Updates license in a later year of the program, they must pay for any previous years of Extended Security Updates as well. [6][63]
See also[edit]
- BlueKeep (security vulnerability)
- Comparison of Microsoft Windows versions
- Comparison of operating systems
- History of Microsoft Windows
- List of operating systems
- Microsoft Servers
Notes[edit]
- ^ Computers with more than 16 GB of RAM require more disk space for paging, hibernation, and dump files[40]
References[edit]
- ^ a b «As Windows Server 2008 RTMs, Customers and Partners Adopting with Help of New Tools, Training». News Center. Redmond, WA: Microsoft. 4 February 2008.
- ^ «Build number changing to 6003 in Windows Server 2008». support.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2021-03-26.
- ^ a b c d e «Microsoft Product Lifecycle». Support. Microsoft. Retrieved April 12, 2022.
- ^ a b c d «Install Windows Vista Service Pack 2 (SP2)». Support. Microsoft. Retrieved April 12, 2010.
- ^ a b c «Extended Security Updates for SQL Server and Windows Server 2008 and 2008 R2 | Microsoft». www.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2021-03-26.
- ^ a b c tfosmark. «Product Lifecycle FAQ — Extended Security Updates — Microsoft Lifecycle». docs.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2021-03-26.
- ^ a b «Announcing new options for SQL Server 2008 and Windows Server 2008 End of Support». azure.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2021-03-26.
- ^ Miller, Michael J. (2007-05-15). «Gates at WinHec 2007: Windows Server 2008, Rally, Home Server and More». Forward Thinking. Retrieved 2007-07-09.
- ^ Lowe, David (2007-04-25). «Beta 3 is Go!». Windows Server Division WebLog. Microsoft. Retrieved 2007-04-25.
- ^ Ralston, Ward (2007-09-24). «Windows Server 2008 Rc0 Released!». Windows Server Division WebLog. Microsoft. Retrieved 2007-09-24.
- ^ Nate Mook (10 July 2007). «New Windows Server, Visual Studio, SQL Server to Launch in February». BetaNews. Retrieved 2007-07-11.
- ^ «Dynamic Hardware Partitioning Architecture». MSDN. Retrieved 2007-07-23.
- ^ Archiveddocs. «Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services Overview». docs.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2020-01-15.
- ^ «Iain McDonald and Andrew Mason show off the new Windows Server OS». Channel 9. Microsoft. May 24, 2006. Retrieved 2008-11-01.
18:55
- ^ Hynes, Byron (November 2006). «The Future of Windows: Directory Services in Windows Server 2008». TechNet Magazine. Retrieved 2007-05-02.
- ^ «Deploying Windows Server 2008 Read Only Domain Controllers». docs.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2020-01-15.
- ^ «Q. What is a read-only domain controller (RODC)?». IT Pro. 2008-03-24. Retrieved 2020-01-15.
- ^ Ward, Keith (2007-10-08). «Top 10 Overlooked Windows Server 2008 Features, Part 2». Redmond Developer News. Archived from the original on 2009-08-04. Retrieved 2014-10-10.
- ^ «Failover Cluster Validation Error 80070005 on Windows Server 2008 R2 x64». Capitalhead. 2009-11-04. Retrieved 2013-10-28.
- ^ Zoeller, Jill (26 July 2007). «New in Windows Server 2008: Breaking the 5K Folder «Barrier» in Domain-Based Namespaces». The Storage Team at Microsoft — File Cabinet Blog. Microsoft. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- ^ «Failover Clustering with Windows Server 2008 including Cluster shared volumes». Microsoft. 2007-01-17. Retrieved 2007-07-09.
- ^ Loveall, John (2006). «Storage improvements in Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008» (PowerPoint). Microsoft Corporation. Retrieved 2007-07-09.
- ^ «Benchmarking Hyper-V on Windows Server 2008 R2 x64». 2010-01-20. Retrieved 2010-01-28.
- ^ «Microsoft Extends Virtualization Strategy, Outlines Product Road Map». Microsoft. 2006-05-22. Retrieved 2007-07-09.
- ^ «Server Manager». Windows Server 2008 Technical Library. Microsoft TechNet. 2007-06-25. Retrieved 2007-05-02.
- ^ «Unexpected error refreshing Server Manager-0x800706BE and 1601 on Window Server 2008 R2». Retrieved 2010-11-05.
- ^ «Multicasting OS deployments with Windows Server 2008». Kevinsul’s Management Blog. Microsoft. 29 August 2007. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- ^ a b «Removed technologies in Routing and Remote Access in Windows Server 2008». TechNet. Microsoft. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- ^ «Windows Server Backup Step-by-Step Guide for Windows Server 2008». TechNet. Microsoft. 17 January 2013. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- ^ «Exchange Server 2007 Service Pack 2 available in Q3 2009». The Exchange Team Blog. 11 May 2009. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- ^ Bilic, Nino (18 June 2008). «To Backup or Not to Backup? Yes! To backup!!». The Exchange Team Blog. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- ^ «IIS 7.0 Protocols». TechNet. Microsoft. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- ^ Heaton, Alex (2007-05-18). «On 64-bit and Windows Client». Windows Vista Team Blog. Retrieved 2007-07-09.
- ^
«Windows Server 2008 Product Editions». Microsoft. 2007-04-25. Retrieved 2007-07-09. - ^ «Windows Server 2008 Foundation: An Entry-Level Server Platform». Petri IT Knowledgebase. 2009-04-17. Retrieved 2014-01-08.
- ^ Ligman, Eric (7 November 2007). «Announcing Windows Essential Business Server». Microsoft Small Business Blog. Microsoft. Retrieved 2013-08-16.
- ^ «Windows Essential Business Server 2008». Technet.microsoft.com. 2010-12-31. Retrieved 2013-01-09.
- ^ «Windows Server 2008, Microsoft Lifecycle (Look at the Note below links)». docs.microsoft.com/en-us/lifecycle/products/.
- ^ a b «Windows Server 2008 System Requirements». 31 March 2008. Retrieved 2008-03-31.
- ^ a b c «Microsoft Windows Server 2008 System Requirements». Microsoft.com. Retrieved 2013-01-09.
- ^ «Microsoft Windows Server 2008 System Requirements». Microsoft. Retrieved 2013-01-09.
- ^ Savill, John (October 28, 2011). «Q: What are Windows Server 8’s Scalability Numbers?». Windows IT Pro. Penton Media. Retrieved November 5, 2011.
- ^ a b c d Seldam, Matthijs ten (October 13, 2012). «Windows Server — Sockets, Logical Processors, Symmetric Multi Threading». Matthijs’s blog. Microsoft. Retrieved October 14, 2012.
- ^ a b c d «Memory Limits for Windows and Windows Server Releases». MSDN. Microsoft. Retrieved 13 April 2014.
- ^ «Extend Windows Vista support by installing Windows Server 2008 updates — gHacks Tech News». gHacks Technology News. 2017-06-24. Retrieved 2021-06-30.
- ^ «Windows Vista Lifecycle Policy». Microsoft. Retrieved January 2, 2017.
- ^ Justin Graham (October 24, 2008). «Windows Server 2008 Service Pack 2 beta». Microsoft. Retrieved 2008-10-29.
- ^ «Tech ARP — ED#107 : Latest Details on Windows Vista Service Pack 2 Rev. 2.2». Archived from the original on 2009-02-12.
- ^ «Windows Vista Service Pack 2 Beta». blogs.windows.com. Archived from the original on 9 May 2013. Retrieved 12 January 2022.
- ^ «Announcing Final Releases of Platform Update for Windows Vista Technologies». 27 October 2009.
- ^ «Platform Update Supplement for Windows Vista and for Windows Server 2008».
- ^ «Cumulative security update for Internet Explorer: January 14, 2020». support.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2021-03-26.
- ^ «Microsoft .NET Framework 4.6 (Web Installer)». Microsoft.
- ^ «TLS 1.2 Support added to Windows Server 2008». Microsoft Security. 2017-07-20. Retrieved 2021-03-26.
- ^ «2019 SHA-2 Code Signing Support requirement for Windows and WSUS».
- ^ Mackie, Kurt; 06/13/2018. «Microsoft Switching Windows Server 2008 SP2 to Monthly Update Rollup Model — Redmondmag.com». Redmondmag. Retrieved 2021-03-26.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ «Community». forums.ivanti.com. Retrieved 2021-03-26.
- ^ «Build number changing to 6003 in Windows Server 2008».
- ^ «January 14, 2020—KB4534303 (Monthly Rollup)». support.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2021-03-26.
- ^ «Windows Server 2008 R2 Reaches the RTM Milestone! — Windows Server Blog — Site Home — TechNet Blogs». Blogs.technet.com. 2009-07-22. Retrieved 2013-01-09.
- ^ «When to expect Windows Server 2008 R2 RTM — Windows Server Blog — Site Home — TechNet Blogs». Blogs.technet.com. 2009-07-22. Retrieved 2013-01-09.
- ^ LeBlanc, Brandon (February 9, 2011). «Announcing Availability of Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1». Windows Experience Blog. Microsoft.
- ^ «Windows Server 2008 Product Lifecycle». Microsoft. January 14, 2020. Retrieved January 9, 2022.
18:55
Further reading[edit]
- «What’s New in Networking». TechNet. Microsoft. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- «Changes in Functionality from Windows Server 2003 with SP1 to Windows Server 2008». TechNet. Microsoft. 21 January 2008. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- «Description of the Microsoft server applications that are supported on Windows Server 2008». Support. Microsoft. 23 April 2012. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- «Windows Server 2008 System Requirements». TechNet. Microsoft. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- Henderson, Tom; Dvorak, Rand (21 February 2008). «Windows Server 2008: Faster, more manageable and secure, but still missing the virtual link». Network World. IDG. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- Radzikowski, Przemek (21 February 2010). «How to Find Build and Revision Number of Windows Vista or Windows Server 2008 Installed». Capitalhead. Capitalhead Pty. Ltd. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- Stanek, William (2008). Windows Server 2008 Inside Out. Microsoft Press. ISBN 978-0-7356-2438-2.
External links[edit]
- Windows Server Performance Team Blog
Операционная система Windows Server 2008 R2 расширяет базовые возможности операционной системы Windows Server и предоставляет новые мощные средства, помогая организациям всех размеров повышать управляемость, доступность и гибкость в соответствии с изменяющимися требованиями бизнеса. Новые веб-средства, технологии виртуализации, средства управления и расширенные возможности масштабирования экономят время, снижают затраты и предоставляют надежную платформу для создания ИТ-инфраструктуры организации.
Windows Server 2008 R2 содержит новые и усовершенствованные средства и возможности в следующих пяти категориях.
Платформа веб-приложений
В сервер Windows Server 2008 R2 включены множество усовершенствований, превращающих его в самую надежную платформу веб-приложений на основе Windows Server среди всех версий Windows. Он содержит обновленную роль веб-сервера и службы IIS 7.5 и обеспечивает расширенную поддержку .NET в режиме Server Core.
Виртуализация
Виртуализация играет важнейшую роль в работе современных центров обработки данных. Обеспечиваемое виртуализацией повышение эффективности работы позволяет организациям значительно снизить трудоемкость эксплуатации и энергопотребление. Windows Server 2008 R2 поддерживает следующие типы виртуализации: виртуализацию клиентских и серверных систем с помощью Hyper-V и виртуализацию представлений с помощью служб удаленных рабочих столов.
Масштабируемость и надежность
Windows Server 2008 R2 поддерживает недостижимые ранее объемы рабочих нагрузок, динамическую масштабируемость, доступность и надежность на всех уровнях, а также ряд других новых и обновленных возможностей, включая использование современных архитектур процессоров, повышение уровня компонентного представления операционной системы и повышение производительности и масштабируемости приложений и служб.
Управление
Постоянное управление серверами в центрах обработки данных — одна из тех задач, которые отнимают у ИТ-специалистов наибольшее время. Применяемая в организации стратегия управления должна поддерживать управление физическими и виртуальными средами. Чтобы помочь в решении этой задачи, в состав Windows Server 2008 R2 включены новые средства, уменьшающие трудоемкость управления серверами Windows Server 2008 R2 и выполнения повседневных задач по администрированию серверов.
Совместная работа с Windows 7
Операционная система Windows Server 2008 R2 поддерживает ряд функций, рассчитанных на работу с клиентскими компьютерами под управлением Windows 7.
Более подробно с основными возможностями ОС Windows Server 2008 R2 можно ознакомиться на сайте компании Microsoft.
Все редакции Windows Server 2008 R2 поддерживают основные возможности, необходимые для решения задач, которые возникают в работе ИТ-систем и организаций любого размера. Основные особенности различных редакций Windows Server 2008 R2, которые поставляются совместно с серверами DEPO Storm, описаны в данной статье.
Сравнительные характеристики различных редакций ОС Windows Server 2008 R2 приведены в таблице.
| Технические характеристики | MultiPoint Server (ОЕМ) | Windows Server 2008 R2 Foundation | Windows Small Business Server 2008 | Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard | Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise |
| Количество CPU | 1 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 8 |
| Объем ОЗУ | 8 Гб | 8 Гб | 32 Гб | 32 Гб | 2 ТБ |
| Количество подключений для удаленного управления (Remote Desktop) | Нет | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Количество клиентских лицензий в комплекте | 0 | 15 | 5 | 5 | 25 |
| Кол-во CAL (Max) | 10 | Не требуются Ограничено подключением до 15 пользователей |
75 | Без ограничений | Без ограничений |
| Кол-во терминальных лицензий (Max) | Нет | 15 | 75 | Без ограничений | Без ограничений |
| Сетевые подключения (RRAS) | Нет | 50 | 75 | 250 | Без ограничений |
| Сетевые подключения (IAS) | Нет | 10 | 50 | 50 | Без ограничений |
| Количество одновременных подключений через Шлюз Терминальных Служб | Нет | 50 | 75 | 250 | Без ограничений |
| Поддержка виртуализации | Нет | Нет | Нет | Лицензия на 1 физическую машину + лицензия на 1 виртуальную машину | Лицензия на 1 физическую машину + лицензия на 4 виртуальных машины. При использовании 4 виртуальных машин — на физической машине роль только Hyper-V. |
Для работы с Windows Server 2008 R2 компьютер должен удовлетворять следующим требованиям*
| Компонент |
Требование |
| Процессор | 1,4 ГГц (процессор с архитектурой x64) |
| Память | Минимальный объем: 512 МБ Максимальный объем: Foundation — 8 ГБ, Standard — 32 ГБ, Enterprise — 2 ТБ |
| Требования к свободному пространству на диске |
Минимальный объем: 32 ГБ |
| Монитор |
Монитор с разрешением Super VGA (800×600) или более высоким |
| Прочее |
Дисковод для DVD-дисков, клавиатура и мышь (Microsoft) или совместимое указывающее устройство, доступ в Интернет |
* Фактические требования к системе зависят от конфигурации системы и от выбранных для установки приложений и компонентов. Производительность процессора зависит не только от его тактовой частоты, но и от числа ядер и объема кэша процессора. Необходимый объем свободного дискового пространства в системном разделе указан приблизительно. При установке по сети может потребоваться дополнительное место на диске.
Windows MultiPoint Server 2010 – продукт семейства Windows, при помощи которого несколько человек могут одновременно работать на одном компьютере. MultiPoint Server является идеальным решением для образовательных учреждений, поскольку предоставляет большему числу преподавателей и учащихся доступ к компьютерным технологиям, а также:
- сокращает начальные вложения в оборудование и текущие эксплуатационные расходы;
- сокращает потребление электроэнергии;
- упрощает управление ИТ-инфраструктурой.
Более подробно с возможностями Windows MultiPoint Server 2010 можно ознакомиться на сайте компании Microsoft.
Windows Server 2008 R2 Foundation предназначена для небольших организаций, где рассматривается приобретение первого сервера или уже используется клиентская операционная система (например, Windows XP) для обеспечения базовой инфраструктуры. Это недорогая, удобная в развертывании и надежная платформа, на которой можно запускать распространенные бизнес-приложения и обеспечивать общий доступ к информации и ресурсам. Windows Server 2008 R2 Foundation основан на Windows Server 2008 R2 и сможет обеспечить все ключевые элементы ИТ в Вашем бизнесе: совместная работа с файлами и принтерами, удаленный доступ, безопасность ИТ среды.
Однако Windows Server 2008 R2 Foundation имеет ограничения по количеству клиентских подключений и не поддерживает функции виртуализации.
Windows Server 2008 R2 Foundation обладает следующими функциональными возможностями:
- поддержка 1 многоядерного процессора (количество ядер в процессоре неограниченно);
- поддержка 8 ГБ ОЗУ для 64-разрядных систем (4 ГБ для 32-разрядных систем);
- до 50 подключений службы сетевого доступа (RRAS);
- до 10 подключений сервера политики сети;
- до 50 подключений сервера терминалов;
- до 15 пользователей (учетных записей в Active Directory).
Более подробно с возможностями Windows Server 2008 R2 Foundation можно ознакомиться на сайте компании Microsoft.
Windows Small Business Server 2008 – полностью интегрированное ИТ-решение, включающее в себя все, что нужно малым и средним компаниям. Оно позволяет улучшить защиту данных и повысить эффективность работы компании, значительно снизив при этом расходы на развертывание и поддержку.
Электронная почта, подключение к Интернету, внутренние веб-узлы, удаленный доступ к файлам и почте, поддержка мобильных устройств, совместное использование файлов и принтеров, резервное копирование и восстановление – неполный список возможностей Windows Small Business Server 2008.
Windows Small Business Server 2008 поставляется в двух вариантах: Standard и Premium.
Версия Standard содержит средства для подключения локальной сети предприятия к Интернету. В состав продукта входит надежный межсетевой экран, сервер сообщений Microsoft Exchange со встроенной системой web-почты Microsoft Outlook Web Access, динамический web-сайт Remote Web Workplace, позволяющий сотрудникам получать быстрый и безопасный доступ к данным через Интернет.
Версия Premium содержит необходимые средства для подключения локальной сети предприятия к Интернету. В состав продукта входит мощный и надежный межсетевой экран, сервер сообщений Microsoft Exchange со встроенной системой web-почты Microsoft Outlook Web Access, динамический web-сайт Remote Web Workplace, позволяющий сотрудникам получать быстрый и безопасный доступ к данным через Интернет.
Более подробно с возможностями Windows Small Business Server можно ознакомиться на сайте компании Microsoft.
Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard – это самая надежная операционная система из семейства Windows Server на настоящее время. Эта система имеет встроенный веб-сервер и возможности виртуализации. Она поможет повысить надежность и гибкость серверной инфраструктуры при снижении расходов и экономии времени. Мощные инструменты обеспечивают более удобное управление серверами, упрощают настройку и управление. Надёжные средства безопасности этой операционной системы защищают сети и данные, что даёт возможность построить исключительно прочный фундамент для ИТ-среды вашего бизнеса.
Windows Server 2008 Standard обладает следующими функциональными возможностями:
- поддержка до 4-х многоядерных процессоров (количество ядер в процессоре неограниченно);
- поддержка 32 ГБ ОЗУ для 64-разрядных систем;
- до 250 подключений службы сетевого доступа (RRAS);
- до 50 подключений сервера политики сети;
- до 250 подключений сервера терминалов;
- практически неограниченное кол-во пользователей (учетных записей в Active Directory);
- поддержка виртуализации на базе технологии Hyper-V и один бесплатный виртуальный экземпляр.
Подробнее с возможностями Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard можно ознакомиться на сайте компании Microsoft.
Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise — ОС Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise обеспечивает бесперебойное функционирование, безопасность на основе новейших технологий и высокую масштабируемость, которая необходима для поддержки расширения критически важных приложений. Кроме того, она позволяет недорого и эффективно виртуализировать оборудование.
Windows Server 2008 Enterprise обладает следующими функциональными возможностями:
- поддержка до 8-ми многоядерных CPU для обработки пиковых нагрузок;
- 2 ТБ ОЗУ для эксплуатации ресурсоемких приложений;
- поддержка неограниченного количества VPN-подключений;
- проверка подлинности и авторизация для неограниченного количества подключений службы сетевого доступа и сервера политики сети;
- практически неограниченное количество подключений шлюза удаленных служб;
- поддержка виртуализации на базе технологии Hyper-V (лицензия на 1 физическую машину + лицензия на 4 виртуальных машины).
Кроме того, в Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise имеется функция горячего добавления памяти, которая позволяет без перезагрузки устанавливать на сервере дополнительные блоки памяти и сразу делать их доступными для операционной системы и приложений в рамках обычного пула памяти.
Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise — оптимальная операционная система для серверов с приложениями для управления работой сети, обмена сообщениями, инвентаризации, обслуживания заказчиков и приложениями баз данных. Она поддерживает все функциональные возможности Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard, а также имеет ряд преимуществ. Благодаря таким возможностям, как отказоустойчивые кластеры, Server Core, отказоустойчивая синхронизация памяти и распределенной файловой репликации (DFS-R), ОС Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise обеспечивает высокий уровень доступности для критически важных приложений, например баз данных, систем обмена сообщениями, файловых служб и служб печати.
Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise является идеальной платформой для виртуализации в масштабах всей компании с помощью гибкой и высокопроизводительной технологии Hyper-V™. Лицензия Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise включает право на использование до четырех дополнительных виртуальных экземпляров Windows Server на одном сервере с лицензией Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise.
Подробнее с возможностями Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise можно ознакомиться на сайте компании Microsoft.
Приложение
Наряду с выходом новых операционных систем для пользователей выходят и новые серверные операционные системы от Windows. Самой последней версией серверной операционной системой является Windows Server 2008 R2.
Многие системные администраторы и it-специалисты используют до сих пор операционную систему Windows Server 2003, потому что она является очень удобной, надежной и просто всех устраивает и переходить на новую систему никто не хочет. Тем более с появлением Windows Vista, которая мягко сказать провалилась, вышла и новая версия серверной операционной системы Windows Server 2008, она в свою очередь также не принесла большую пользу и не обрела такого успеха как Server 2003 и все администраторы сетей остались на своей старой, но надежной операционной системе Windows Server 2003.
После того как Windows Server 2008 также как и Vista не приобрела широкую популярность, компания Microsoft практически сразу выпускает новые операционные системы, такие как: Windows 7 и Windows Server 2008 R2. Server 2008 r2 поступает в продажу 22 октября 2009 года. И уже эти операционные системы понравились пользователям и постепенно приобретают популярность, как у пользователей, так и у системных администраторов.
Сегодня мы с Вами поговорим о преимуществах и новых возможностях операционной системы Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2.
Содержание
- Обзор Windows Server 2008 R2
- Редакции Windows Server 2008 R2
- Новые возможности Windows Server 2008 R2
Операционная система Windows Server 2008 R2, созданная на основе Windows Server 2008, и она расширяет базовые возможности операционной системы Windows Server и предоставляет новые мощные средства, помогая организациям и компаниям всех размеров повышать управляемость, доступность и гибкость в соответствии с изменяющимися требованиями бизнеса.
Как и все операционные системы Windows Server 2008 R2 имеет свои редакции, для более гибкого предоставления этой системы пользователям: (описание взято с официального сайта Microsoft).
Редакции Windows Server 2008 R2
Windows Server 2008 R2 Foundation — это недорогое и экономичное техническое решение для бизнеса. Данная редакция предназначена для владельцев небольших компаний и ИТ-специалистов, занимающихся их поддержкой. Это недорогая, удобная в развертывании и надежная платформа, на которой можно запускать распространенные бизнес-приложения и обеспечивать общий доступ к информации и ресурсам.

Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard — это самая надежная операционная система из семейства Windows Server на настоящее время. Эта система имеет встроенный веб-сервер и возможности виртуализации. Она поможет повысить надежность и гибкость серверной инфраструктуры при снижении расходов и экономии времени. Мощные инструменты обеспечивают более удобное управление серверами, упрощают настройку и управление. Надёжные средства безопасности этой операционной системы защищают сети и данные, что даёт возможность построить исключительно прочный фундамент для ИТ-среды Вашего бизнеса.
Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise — это мощная серверная платформа, обеспечивающая надежную поддержку для самых важных процессов и нагрузок. В этой редакции предусмотрены расширенные возможности виртуализации, экономии электроэнергии; улучшена управляемость; мобильные сотрудники могут проще получать доступ к ресурсам компании.
Windows Server 2008 R2 Datacenter является платформой корпоративного уровня для важнейших бизнес-приложений и крупномасштабной виртуализации на небольших или мощных серверах. Эта редакция отличается повышенной доступностью, улучшенным управлением электропитанием и встроенными решениями для мобильных сотрудников и работников филиалов. Эта редакция также включает неограниченные лицензионные права на виртуальные системы, что позволяет значительно сократить затраты на инфраструктуру путем консолидации приложений. Данная редакция поддерживает от 2 до 64 процессоров. Windows Server R2 2008 Datacenter — это надежная основа для решений виртуализации корпоративного уровня и крупномасштабных систем.
Windows Web Server 2008 R2 представляет собой мощную платформу для веб-приложений и веб-служб. Эта редакция содержит службы Internet Information Services (IIS) 7.5 и предназначена исключительно для интернет-серверов; в ней предусмотрены улучшенные средства администрирования и диагностики, позволяющие снизить затраты при использовании с несколькими популярными платформами разработки. Эта платформа поддерживает роли веб-сервера и DNS-сервера, обладает повышенной надежностью и масштабируемостью и обеспечивает управление в самых разных средах, от отдельного веб-сервера до фирмы веб-серверов.
Новые возможности Windows Server 2008 R2
- Платформа веб-приложений. В Windows Server 2008 R2 включены множество усовершенствований, превращающих его в самую надежную платформу веб-приложений на основе Windows Server среди всех версий Windows. Он содержит обновленную роль веб-сервера и службы IIS 7.5 и обеспечивает расширенную поддержку .NET в режиме Server Core;
- Виртуализация. Виртуализация играет важнейшую роль в работе современных центров обработки данных. Обеспечиваемое виртуализацией повышение эффективности работы позволяет организациям значительно снизить трудоемкость эксплуатации и энергопотребление. Windows Server 2008 R2 поддерживает следующие типы виртуализации: виртуализацию клиентских и серверных систем с помощью Hyper-V и виртуализацию представлений с помощью служб удаленных рабочих столов;
- Масштабируемость и надежность. Windows Server 2008 R2 поддерживает недостижимые ранее объемы рабочих нагрузок, динамическую масштабируемость, доступность и надежность на всех уровнях, а также ряд других новых и обновленных возможностей, включая использование современных архитектур процессоров, повышение уровня компонентного представления операционной системы и повышение производительности и масштабируемости приложений и служб;
- Управление. Постоянное управление серверами в центрах обработки данных — одна из тех задач, которые отнимают у ИТ-специалистов наибольшее время. Применяемая в организации стратегия управления должна поддерживать управление физическими и виртуальными средами. Чтобы помочь в решении этой задачи, в состав Windows Server 2008 R2 включены новые средства, уменьшающие трудоемкость управления серверами Windows Server 2008 R2 и выполнения повседневных задач по администрированию серверов.
И одной из самых главных (на мой взгляд) возможностей и усовершенствований Windows Server 2008 R2 является то, что она отлично совместно используется с операционной системой Windows 7. Компания Microsoft представляет нам следующие преимущества совместной работы Windows Server 2008 R2 и Windows 7.
- Упрощение удаленного подключения к корпоративным компьютерам благодаря применению функции DirectAccess;
- Безопасное удаленное подключение частных и общедоступных компьютеров;
- Повышение производительности филиалов;
- Повышение безопасности филиалов;
- Повышение эффективности управления питанием;
- Повышение эффективности интеграции с виртуальными рабочими столами;
- Повышение устойчивости соединений между сайтами;
- Повышение защищенности съемных носителей;
- Более эффективная защита от потери данных мобильных пользователей.
Более подробное описание всех новых функций, возможностей, и преимуществ описаны на официальном сайте компании Microsoft.
На сегодняшний день операционная система Windows Server 2008 R2 получила популярность и охотно используется многими системными администраторами и it-специалистами.

Операционная система Windows Server 2008 даёт возможность пользователям, где бы они ни находились иметь доступ к сетевым услугам. Также здесь реализованы функции для анализа и диагностики состояния операционной системы. Windows Server 2008 основано на версии 2003. Она была усовершенствована и реализована с обновлением.
Содержание
- Роли Windows Server 2008
- Улучшения системы Windows Server 2008
- Гибкость системы
- Технология Windows Server 2008
- Защита системы
Роли Windows Server 2008
Для организаций обновлённая система даёт возможность увеличить производительность платформы, улучшить функциональность работы приложений, сетей рабочих групп, то есть в целом улучшить работу операционной системы.
Улучшения системы Windows Server 2008
У новой системы есть три основных преимущества.
Во-первых, это улучшенный контроль. Пользователь имеет возможность контролировать всю инфраструктуру серверов и сети. Таким образом, пользователь может свое внимание сконцентрировать на решении нужных ему задач.
В Windows Server 2008 упростили управление ит-инфраструктурой, для этого используются средства, которые дают единый удобный интерфейс для того, чтобы пользователь выполнил все настройки по своему желанию. Также у пользователей есть возможность отслеживать сервера и автоматизировать некоторые ежедневные операции.
Была оптимизирована система установки Server 2008, пользователь имеет возможность выбрать только нужные роли и функции. Теперь меньше уязвимых мест за счёт улучшенной конфигурации, реже нужно обновлять систему, в целом проще ей управлять.
При обнаружении неполадок, пользователь может быстро их устранить. Для этого предусмотрены средства диагностики, чтобы можно было видеть актуальное состояние рабочий среды. Пользователю стало проще вести контроль над удаленными серверами, например своих филиалов. Можно обслуживать пользователей, не тратя лишнее время на управленческие проблемы, это возможно благодаря оптимизации работы администрирования серверов.
В системе есть платформа сервис 7.0 для приложений. Благодаря этому пользователь имеет возможность управлять Web сервисами. Это модульная платформа с простым интерфейсом, тем не менее, там строгий контроль по взаимодействию элементов, и высоким уровнем безопасности.
Гибкость системы
Пользователь имеет возможность создавать гибкие и динамичные центры данных, которые можно изменять под потребности компании.
В Windows Server 2008 есть технология для того, чтобы виртуализировать на сервере две или три операционные системы, это может быть Windows и Linux, например. Упрощена политика лицензирования, и преимущества использования разных операционных систем дает возможность получить экономические выгоды.
В новой системе есть централизованный доступ к приложениям. Также можно подключиться к удаленным приложениям через межсетевой экран, и для этого не нужен vpn. Это важно для быстрого реагирования при выявлении проблем пользователей, и неважно, где эти пользователи сейчас находятся.
Появились разные варианты развертывания. Гибкая работа приложений позволяют связывать сотрудников друг с другом и необходимыми данными, то есть можно совместно использовать и обрабатывать какую-либо информацию.
На протяжении работы операционной системы пользователя будут поддерживать, и помогать при возникновении вопросов.
Улучшенная система защиты операционной системы Windows Server 2008 даёт возможность обезопасить систему, благодаря надежному фундаменту для развития бизнеса. Безопасность на высоком уровне благодаря тому, что сервер практически не уязвим, и рабочая среда защищена. Это возможно благодаря изоляции компьютеров, у которых требования по безопасности не отвечают политике. В системе предусмотрено принудительное обеспечение соблюдения правил безопасности.
Защита данных обеспечена благодаря тому, что доступ к информации имеют только те пользователи, у кого высокий уровень безопасности.
Защита от вирусов работает благодаря функции контроля учетных записей. В целом система более устойчива, уменьшен риск потери доступа к управлению и результатам работы, и контроля.
Технология Windows Server 2008
Диспетчер серверов. Это новая функция в операционной системе. Это единый интерфейс, благодаря которому администратор настраивает серверные роли и компоненты операционной системы пользователем для управления ими. Диспетчер серверов объединил в себе различные функции предыдущей версии операционной системы.
Windows powershell. Это обновленная оболочка для командной строки, со встроенным языком программирования. Благодаря этой оболочке администратор имеет возможность контролировать и автоматизировать ежедневные задачи для управления системой, особенно это важно, когда работа касается нескольких серверов. Новая оболочка для Windows powershell не требует миграции уже действующих сценариев, её можно использовать для автоматизации новых функций.
Internet Information Services 7.0. В новой операционной системе есть унифицированная платформа для публикации, она объединяет предыдущее платформы. Данная служба это главное усовершенствование веб-сервисов Windows, и она очень важна для интеграции технологий в платформе. Данная технология дает возможность администраторам осуществлять контроль над интерфейсом в сети интернет, используя основные функции, куда входит делегирование управления, повышение безопасности, и контроль над приложениями для снижения уязвимости.
Гибкость системы. К серверным технологиям всегда растут требования, также увеличиваются их возможности, технологии. Всё это влияет на то, как пользователи используют данную технологию. Система Windows Server 2008 устроена так, что администратор имеет возможность изменять инфраструктуру сети и подстраивать её потребности под пользователя, при этом сохраняя гибкость. Есть компании, для которых важно разместить контроллер домена в небезопасном месте, здесь Windows Server 2008 предлагает новый вариант конфигурации, то есть контроллер домена только для чтения RODC.
Служба терминалов. Данная служба нужна для того, чтобы пользователи могли подключаться к удаленным компьютерам и приложениям. В новом варианте удалённые программы интегрируют приложения с удаленного терминала так, как-будто пользователь работает в локальной системе. Так же есть возможность использовать программы на удаленных терминалах и одновременно на своём компьютере. У пользователей есть гибкий доступ к удаленным приложениям, как будто используют веб-обозреватель, есть разные способы подключения для работы на удалённых терминалах. Также шлюз службы терминалов даёт возможность получить доступ к терминалам через межсетевой экран.
Служба развертывания wds. Это новая версия службы удаленной установки для Windows Server 2008. Благодаря ей пользователь может быстро развернуть операционную систему на основе имеющихся образов. То есть можно установить Windows Vista и Windows Server 2008 по сети на другие компьютеры, где нет операционной системы. Эта служба даёт возможность комплексно развернуть операционную систему у клиента на компьютере и сервере.
Защита системы
Благодаря этой технологии администратор может устанавливать нужные ему требования для того, чтобы сеть была работоспособна, и не компьютер неудовлетворяющий этим требованиям, не будет иметь доступ к сети.
Хотя многим в это трудно поверить, но следующая версия серверной операционной системы от Microsoft — Windows Server 2008 R2 — уже готова. Рассмотрим ее основные новые функции.
Клуб 64-х разрядов
Windows Server 2008 R2 — это первая операционная система Microsoft Windows Server с исключительно 64-разрядной архитектурой. Это не должно стать проблемой при установке, поскольку большинство современных серверов x64-совместимы. Но Server 2008 R2 не будет работать на 32-разрядных серверах устаревших моделей. Установленные 32-разрядные приложения смогут работать на Server 2008 R2 при использовании подсистемы Windows-On-Windows (WoW) этой операционной системы, поддерживающей 32-разрядность.
Помимо перехода только на 64 разряда, Windows Server 2008 R2 также использует преимущества большей масштабируемости и может обращаться к 256 логическим процессорам на одном сервере — выше максимального числа 64 в исходном варианте редакции Windows Server 2008.
Новый Hyper-V
В Server 2008 R2 добавлена новая версия Hyper-V. Предварительная версия Hyper-V была включена в поставку исходной редакции Server 2008, потом финальный выпуск Hyper-V был добавлен в виде обновления. Версия Hyper-V для Server 2008 R2 может использовать более 32 логических процессоров хостируемой виртуальной машины. Этот новый выпуск Hyper-V может использовать преимущества самой новой аппаратной поддержки виртуализации SLAT (Second Level Address Translation — адресная трансляция на втором уровне) от Intel и AMD. SLAT позволяет гипервизору обходиться без таблиц теневых страниц и хорошо управляется с трансляцией памяти виртуальной машины в физическую память, что повышает эффективность виртуальной машины. Новый выпуск Hyper-V в Server 2008 R2 также увеличивает поддержку памяти для виртуальной машины до 64 Гбайт. Разгрузочные и крупные фреймы протокола TCP обеспечивают повышение сетевой эффективности. Дополнительное улучшение Hyper-V в Server 2008 R2 дает поддержка управления через PowerShell с помощью набора специальных команд. Однако самая существенная функция Server 2008 R2, связанная с виртуализацией, — это поддержка Live Migration.
Live Migration
Функция Live Migration — это ответ Microsoft на технологию VMotion от VMware. Данная функция позволяет переносить виртуальные машины Hyper-V с хоста Server 2008 R2 на хост Server 2008 R2 без выключения виртуальных машин. Как и VMotion, Live Migration позволяет администратору реализовывать сценарии планового выключения виртуальных машин, сохраняя их доступность на прежнем уровне. Live Migration использует технологию обработки сбоев Windows Failover Clustering, службы кластеризации Windows Clustering Services и новую технологию общих кластерных томов Cluster Shared Volumes, чтобы произвести перенос виртуальной машины между хостами за миллисекунды. Новая технология Cluster Shared Volumes в Server 2008 R2 позволяет обеспечивать доступ нескольких кластерных узлов по одному и тому же логическому номеру (LUN), что в свою очередь дает им доступ к тем же самым виртуальным жестким дискам Virtual Hard Disk (VHD). Таким образом, осуществлять физическую миграцию VHD для выполнения функции Live Migration не обязательно. На рисунке показана схема работы Live Migration.
Для выполнения Live Migration администратор инициирует перенос виртуальной машины с узла-источника на целевой кластерный узел. Live Migration создает контейнер виртуальной машины на целевом узле. Перенос VHD не нужен, поскольку Cluster Shared Volumes имеет полный доступ к файлу VHD, который хранится на сети SAN. Потом текущее состояние памяти исходной виртуальной машины копируется на целевой узел. Клиенты, подключенные к исходной виртуальной машине, не прекращают работы, а все измененные страницы памяти на исходной виртуальной машине копируются зеркально. Эти зеркальные страницы затем копируются на целевую виртуальную машину, пока не будут отображены полностью или до достижения определенного числа повторов. По выполнении этого условия Live Migration останавливает исходную виртуальную машину на сервере-источнике, копирует оставшиеся не перенесенные страницы и состояние раздела, запускает виртуальную машину на целевом узле и направляет все подключения клиентов с виртуальной машины-источника на целевую виртуальную машину. Таким образом, миграция заканчивается и исходная виртуальная машина удаляется.
Улучшения Active Directory
Для администраторов Windows новый административный центр ADAC — Active Directory Administrative Center — будет, несомненно, самым существенным изменением в Server 2008 R2. Менеджер управления ADAC представляет современный интерфейс управления заданиями для Active Directory (AD). Прежние оснастки Users and Computers, Site and Services, а также Domains and Trusts еще существуют, однако интерфейс управления заданиями нового центра позволяет лучше справляться с такими каждодневными задачами, как работа с пользователями, компьютерами, группами и организационными подразделениями. Менеджер ADAC устанавливается при запуске Dcpromo для того, чтобы сделать систему Server 2008 R2 контроллером домена (DC). На экране 1 показан интерфейс нового менеджера ADAC.
Центр ADAC использует навигацию, во многом похожую на навигацию Windows Explorer. По умолчанию навигационная панель ADAC в левой части экрана выводит дерево или простой список объектов. Однако можно настроить этот вид, добавляя обычно используемые контейнеры в эту навигационную панель. Новый центр ADAC может работать с AD, используя учетные данные, отличные от учетных данных при регистрации. Данная версия ADAC работает только на Server 2008 R2. В выходящих одновременно с ним версиях Windows 7 центр управления ADAC также будет работать. Подробнее о центре ADAC рассказано в статье Microsoft TechNet «What’s New in AD DS: Active Directory Administrative Center» (http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd378856.aspx).
Дополнительные улучшения работы с AD в Server 2008 R2 дает добавление 75 новых команд управления AD. Новый центр ADAC построен с помощью этих команд. При использовании ADAC для выполнения действий в фоновом режиме фактически создается и выполняется сценарий PowerShell.
Новые доменные службы Active Directory Domain Services в Server 2008 R2 тоже усовершенствованы. Новая функция автономного присоединения к домену позволяет присоединить компьютер к домену, не подключая его к этому домену. Данная функция может помочь автоматизировать развертывание клиентских рабочих мест. Еще одну полезную функцию в новых доменных службах демонстрирует корзина AD Recycle Bin, которая позволяет восстанавливать стертые объекты AD без выполнения принудительного восстановления.
Управление удаленными системами с помощью Server Manager
В Windows Server 2008 администраторам должен понравиться Server Manager, который предоставляет централизованную консоль управления. Можно использовать Server Manager для управления ролями и функциями, для проверки статуса и просмотра событий в журналах регистрации. Однако в первоначальном выпуске Server 2008 Server Manager работал только с локальной системой. Выпуск Server 2008 R2 позволяет задействовать Server Manager для управления как локальными, так и удаленными системами Server 2008. В то же время Server Manager может устанавливаться на сетевых клиентах Windows Vista или Windows 7, что позволяет выполнять задания по сетевому управлению с клиентских рабочих станций.
Remote Desktop Services — ребрендинг Terminal Services
Еще одно изменение в Server 2008 R2 — это замена терминальных служб Terminal Services новыми службами удаленного рабочего стола — Remote Desktop Services. В таблице приведены имена компонентов Terminal Services и их аналоги в Remote Desktop Services.
Remote Desktop Services в Server 2008 R2 — это не только другие имена. Новый компонент RemoteApp & Desktop Connection (RAD) включает поддержку интерфейса Aero Glass, истинную поддержку нескольких мониторов, переадресацию мультимедиа, звукозаписи и поддержку переадресации DirectX 9, 10 и 11.
Изменения в процессе создания сценариев с помощью PowerShell 2.0
Server 2008 R2 включает новую версию PowerShell 2.0, которая совместима с PowerShell 1.0, имеет усовершенствованные команды управления Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI), поддерживает работу сценариев на удаленных системах, создание Script Cmdlets и запуск фоновых заданий. Вместе с Server 2008 R2 изначально поставляется более 240 новых команд.
Server 2008 R2 имеет новый графический пользовательский интерфейс PowerShell для разработки и отладки сценариев PowerShell. Новая интегрированная среда PowerShell Integrated Scripting Environment (ISE) является графической платформой разработки PowerShell с поддержкой вкладок. В PowerShell ISE происходит выделение цветом элементов синтаксиса и предусмотрены средства отладки для установки контрольных точек и пошагового выполнения сценариев PowerShell. На экране 2 показано окно PowerShell ISE.
Интегрированная среда PowerShell ISE содержит три панели: панель сценария, панель результатов и панель команд. Панель сценария находится в верхней части экрана 1; она предназначена для редактирования и отладки сценариев PowerShell. Панель результатов (в середине экрана 1) показывает результаты работы сценария, который выполняется в ISE. И панель команд, находящаяся в нижней части экрана 1, предназначена для выполнения сценария и других команд PowerShell.
Поддержка .NET Framework в Server Core
В исходном выпуске Server 2008 отсутствие поддержки .NET Framework в варианте установки Server Core было самым существенным недостатком. Отдельные технологии, которые казались предназначенными для использования в Server Core, например приложения PowerShell и ASP.NET, не могли работать в режиме Server Core. Выпуск Server 2008 R2 исправляет это положение, добавляя поддержку версий .NET Framework 2.0, 3.0, 3.5 и 4.0. Поддержка .NET Framework позволяет в варианте установки Server Core запускать как приложения ASP.NET, так и сценарии PowerShell. Но Server Core в версии 2008 R2 еще не поддерживает SQL Server или Exchange.
IIS 7.5
Еще одна новая функция Server 2008 R2 — IIS 7.5. Существенные улучшения в IIS 7.5 коснулись управления и развертывания Web-приложений. IIS 7.5 имеет новый PowerShell Provider для IIS, а также несколько новых команд управления PowerShell для заданий IIS. Эти новые команды дают возможность добавлять и изменять свойства Web-сайтов, настройки Web-приложений, виртуальных каталогов и пулов приложений.
Новый редактор Configuration Editor расширяет возможности IIS Manager. Он позволяет менять все параметры настройки IIS 7.5, в том числе такие, как FastCGI, которые в прежней версии IIS были скрыты.
Что касается безопасности Web-приложений, то новый модуль фильтрации запросов Request Filtering обеспечивает возможность усиления защиты протокола HTTP, которую ранее обеспечивал отдельный продукт URLScan. Дополнительно сервер IIS 7.5 обеспечивает повышение безопасности приложений запуском каждого пула приложений с уникальными для него пониженными привилегиями. Добавлены также новые версии Best Practices Analyzer (BPA) и обновленные версии Secure FTP и WebDAV.
Core Parking и P-состояния
Функция Core Parking в Server 2008 R2 позволяет операционной системе динамически изменять число используемых ядер многоядерного сервера и постоянно отслеживать загрузку центрального процессора многоядерных серверных систем. В случае недостаточного объема работ для процессорных ядер Core Parking отправляет эти ядра в спящий режим, уменьшая энергопотребление системы. Когда объем работы на активных ядрах увеличивается, спящие ядра переходят в активное состояние, восстанавливая вычислительную мощность. Например, Core Parking может заставить сервер, в котором 64 логических ядра, превратиться в двухъядерную систему при низкой загрузке и восстановить сервер до полной 64-ядерной системы при больших объемах рабочей нагрузки. Примечательно, что с Core Parking одно ядро всегда остается активным для управления состоянием других ядер.
Другой функцией управления энергопотреблением, встроенной в Server 2008 R2, является возможность настраивания P-состояний интерфейса Advanced Configuration and Power Interface (ACPI). Этот интерфейс существенно улучшает контроль потребляемой энергии. Изменение P-состояния процессора влияет на его частоту. Работа процессорных ядер на более низких частотах также уменьшает потребляемую мощность. Как Core Parking, так и статус состояний ACPI P можно настраивать через параметры новой групповой политики Group Policy.
Лучшая из Windows Server
Версия Server 2008 R2 значительно увеличивает ценность операционной системы Server 2008 благодаря таким функциям как Live Migration, новому менеджеру ADAC и интегрированной среде разработок PowerShell ISE. Другие важные функции — усовершенствованная защита DNS и DHCP, репликация файловой системы только в режиме чтения — read-only DFS Replication (DFSR) — и возможность загрузки с VHD. Подключение Windows 7 к Server 2008 R2 дает еще больше преимуществ; подробнее об этом рассказано во врезке «Windows Server 2008 R2 и Windows 7: вместе им лучше». Server 2008 R2 также содержит большое количество мелких изменений, которые рассмотрены во врезке «Небольшие изменения в Windows Server 2008 R2».
Я пользовался бета-версией Server 2008 R2; в финальном выпуске, возможно, будут дополнительные изменения. Вывод пока один: Server 2008 R2, безусловно, является на сегодня лучшей из операционных систем Windows Server.
Майкл Оти (mikeo@windowsitpro.com) — редактор Windows IT Pro и президент компании TECA (Портленд, шт. Орегон), занимающейся разработкой программного обеспечения и консалтингом
Таблица. Имена компонентов Terminal Services и их аналогов в Remote Desktop Services
Windows Server 2008 R2 и Windows 7: вместе им лучше
Выпуск Windows Server 2008 R2 включает возможности, предназначенные специально для улучшения работы клиентских систем Windows 7.
- DirectAccess. Новая функция прямого доступа DirectAccess предлагает альтернативу виртуальным частным сетям (VPN) для удаленного доступа, что особенно ценно для безопасного подключения мобильных сотрудников организации. DirectAccess использует протокол IPsec для шифрования подключения клиентской системы Windows 7 к Server 2008 R2. Подробно о новой технологии DirectAccess рассказано в статье Microsoft’s Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 DirectAccess Executive Overview page по адресу http://www.microsoft.com/downloads/details.aspx?familyid=d8eb248b-8bf7-4798-a1d1-04d37f2e013c.
- BranchCache. Функция BranchCache позволяет филиалам организаций иметь доступ к хранимым локально копиям кэшируемых файлов. С помощью BranchCache можно восстанавливать файлы с других клиентских систем филиалов или со специального сервера BranchCache на сайте филиала, а не получать контент с удаленного сервера. Специальный сервер BranchCache отслеживает изменения файлов и обеспечивает доступ всех клиентов к обновленным версиям файлов.
- Новая групповая политика управления питанием — Group Policy Power Management — в Server 2008 R2 использует преимущества усовершенствованных настроек управления питанием систем Windows 7.
Небольшие изменения в Windows Server 2008 R2
В основной статье рассматриваются крупные изменения в новой серверной операционной системе. Но есть в этой версии и несколько небольших, но важных изменений, по большей части заимствованных из интерфейса Windows 7.
- Новая панель задач (Taskbar). Первое, что сразу бросается в глаза, — это новая панель задач Windows Taskbar, в которой объединены окно быстрого запуска Quick Launch и старая панель задач. Есть мнение, что новая панель стирает различия между работающими и неработающими приложениями. Согласен. Раньше можно было легко определить по панели задач, что работает, а что нет. Теперь надо очень внимательно следить за подсветкой вокруг значка, которая показывает активность приложения. Мне кажется, что нет особого преимущества в запуске приложений с панели задач по сравнению с меню или рабочим столом.
- Кнопка перезапуска, завершения, отключения Restart/Log Off/Shut Down. Новая функция — очевидное преимущество этой кнопки. Найти ее легко — рядом с меню Start. Кнопка настраивается, можно менять ее действие по умолчанию. Если нужно выполнить новое действие, а не действие по умолчанию — просто щелкните стрелку.
- Отсутствует Classic View. Если вы никогда не отказывались от классического представления панели управления Control Panel в Windows XP, то Server 2008 R2 легко заставит это сделать. Возможности выбора Classic View теперь нет. Однако новое представление All Control Panel Items выглядит почти так же.
- Библиотеки Libraries. Другая функция Windows 7, которая вошла в Server 2008 R2, — новые библиотеки Libraries. Они представляют собой особые каталоги по типам данных и файлов — музыкальные, видео, текстовые документы. Libraries лучше открывать в Windows Explorer, но используются они во всех компонентах Windows 7 и Server 2008 R2.
- Контроль учетных записей User Account Control (UAC) также присутствует в Server 2008 R2. Хотя в Windows Vista контроль учетных записей, на мой взгляд, порой назойлив, все же в целом это хорошая идея для обеспечения безопасности, и UAC реализована в Server 2008 R2 лучше, чем в Vista.
- Internet Explorer 8. Server 2008 R2 включает Internet Explorer 8 (IE
с просмотром в закладках, ускорителями Accelerators, InPrivate Browsing для анонимного Web-просмотра, панелями Web Slices для отслеживания избранного Web-контента и повышения безопасности просмотра с помощью SmartScreen Filters. Как и прежние версии Windows Server, Server 2008 R2 выходит с Internet Explorer Enhanced Security Configuration (IE ESC), причем этот браузер с усовершенствованной защитой доступен по умолчанию. Администраторы и пользователи имеют возможность детальной настройки параметров IE ESC.


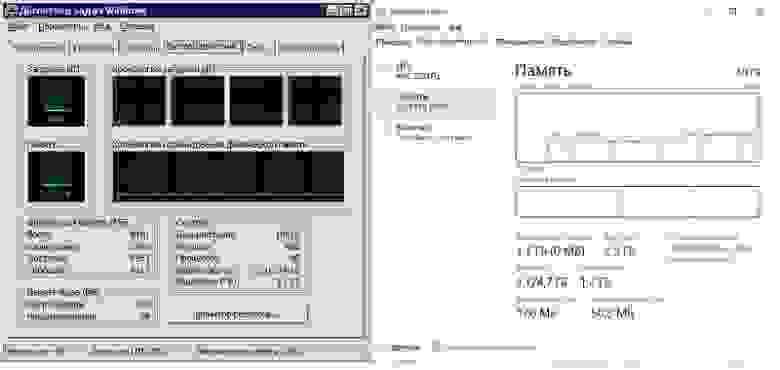
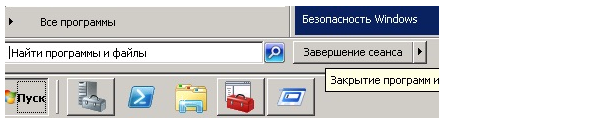
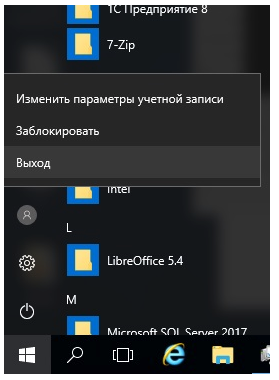
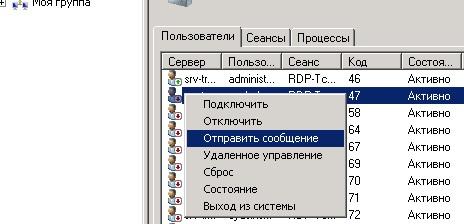
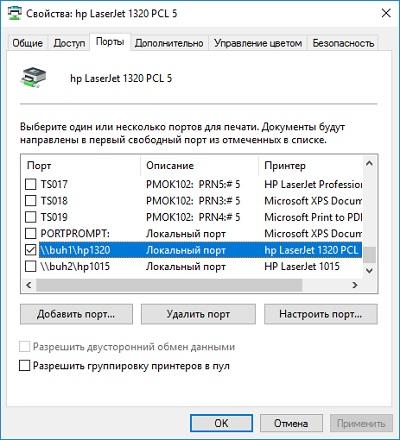
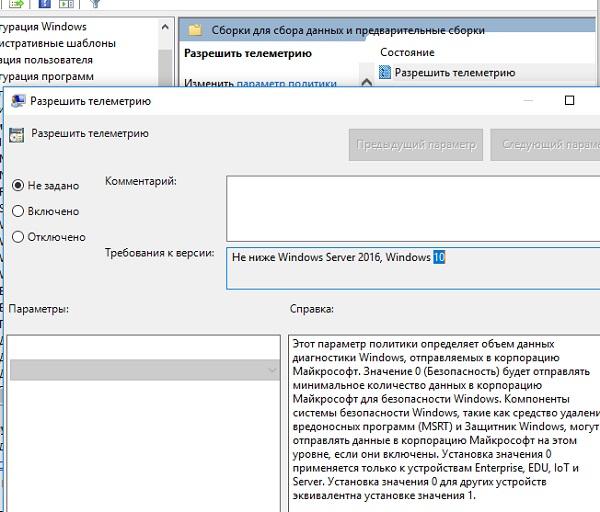
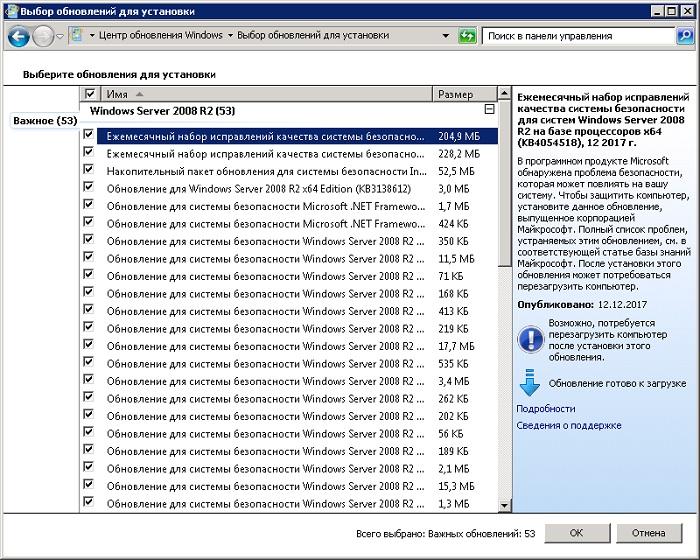
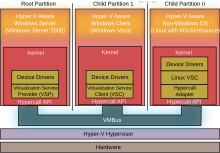










 с просмотром в закладках, ускорителями Accelerators, InPrivate Browsing для анонимного Web-просмотра, панелями Web Slices для отслеживания избранного Web-контента и повышения безопасности просмотра с помощью SmartScreen Filters. Как и прежние версии Windows Server, Server 2008 R2 выходит с Internet Explorer Enhanced Security Configuration (IE ESC), причем этот браузер с усовершенствованной защитой доступен по умолчанию. Администраторы и пользователи имеют возможность детальной настройки параметров IE ESC.
с просмотром в закладках, ускорителями Accelerators, InPrivate Browsing для анонимного Web-просмотра, панелями Web Slices для отслеживания избранного Web-контента и повышения безопасности просмотра с помощью SmartScreen Filters. Как и прежние версии Windows Server, Server 2008 R2 выходит с Internet Explorer Enhanced Security Configuration (IE ESC), причем этот браузер с усовершенствованной защитой доступен по умолчанию. Администраторы и пользователи имеют возможность детальной настройки параметров IE ESC.