| description | ms.assetid | title | ms.topic | ms.date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Describes the memory limits for supported Windows and Windows Server releases and provides lists of memory limits. |
de09c8af-0ed8-4fd4-b8e8-2c921aafe6f2 |
Memory Limits for Windows and Windows Server Releases |
article |
09/10/2021 |
Memory Limits for Windows and Windows Server Releases
This topic describes the memory limits for supported Windows and Windows Server releases.
Limits on memory and address space vary by platform, operating system, and by whether the IMAGE_FILE_LARGE_ADDRESS_AWARE value of the LOADED_IMAGE structure and 4-gigabyte tuning (4GT) are in use. IMAGE_FILE_LARGE_ADDRESS_AWARE is set or cleared by using the /LARGEADDRESSAWARE linker option.
4-gigabyte tuning (4GT), also known as application memory tuning, or the /3GB switch, is a technology (only applicable to 32 bit systems) that alters the amount of virtual address space available to user mode applications. Enabling this technology reduces the overall size of the system virtual address space and therefore system resource maximums. For more information, see What is 4GT.
Limits on physical memory for 32-bit platforms also depend on the Physical Address Extension (PAE), which allows 32-bit Windows systems to use more than 4 GB of physical memory.
Memory and Address Space Limits
The following table specifies the limits on memory and address space for supported releases of Windows. Unless otherwise noted, the limits in this table apply to all supported releases.
| Memory type | Limit on X86 | Limit in 64-bit Windows |
|---|---|---|
| User-mode virtual address space for each 32-bit process | 2 GB Up to 3 GB with IMAGE_FILE_LARGE_ADDRESS_AWARE and 4GT |
2 GB with IMAGE_FILE_LARGE_ADDRESS_AWARE cleared (default) 4 GB with IMAGE_FILE_LARGE_ADDRESS_AWARE set |
| User-mode virtual address space for each 64-bit process | Not applicable | With IMAGE_FILE_LARGE_ADDRESS_AWARE set (default): x64: Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2 or later: 128 TB x64: Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012 or earlier 8 TB Intel Itanium-based systems: 7 TB 2 GB with IMAGE_FILE_LARGE_ADDRESS_AWARE cleared |
| Kernel-mode virtual address space | 2 GB From 1 GB to a maximum of 2 GB with 4GT |
Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2 or later: 128 TB Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012 or earlier 8 TB |
| Paged pool | 384 GB or system commit limit, whichever is smaller. Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2: 15.5 TB or system commit limit, whichever is smaller. Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows 7, Windows Server 2008 and Windows Vista: Limited by available kernel-mode virtual address space. Starting with Windows Vista with Service Pack 1 (SP1), the paged pool can also be limited by the PagedPoolLimit registry key value. Windows Home Server and Windows Server 2003: 530 MB Windows XP: 490 MB |
384 GB or system commit limit, whichever is smaller Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2: 15.5 TB or system commit limit, whichever is smaller. Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows 7, Windows Server 2008 and Windows Vista: 128 GB or system commit limit, whichever is smaller Windows Server 2003 and Windows XP: Up to 128 GB depending on configuration and RAM. |
| Nonpaged pool | 75% of RAM or 2 GB, whichever is smaller. Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2: RAM or 16 TB, whichever is smaller (address space is limited to 2 x RAM). Windows Vista: Limited only by kernel mode virtual address space and physical memory. Starting with Windows Vista with SP1, the nonpaged pool can also be limited by the NonPagedPoolLimit registry key value. Windows Home Server, Windows Server 2003 and Windows XP: 256 MB, or 128 MB with 4GT. |
RAM or 128 GB, whichever is smaller (address space is limited to 2 x RAM) Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2: RAM or 16 TB, whichever is smaller (address space is limited to 2 x RAM). Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008: 75% of RAM up to a maximum of 128 GB Windows Vista: 40% of RAM up to a maximum of 128 GB. Windows Server 2003 and Windows XP: Up to 128 GB depending on configuration and RAM. |
| System cache virtual address space (physical size limited only by physical memory) | Limited by available kernel-mode virtual address space or the SystemCacheLimit registry key value. Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2: 16 TB. Windows Vista: Limited only by kernel mode virtual address space. Starting with Windows Vista with SP1, system cache virtual address space can also be limited by the SystemCacheLimit registry key value. Windows Home Server, Windows Server 2003 and Windows XP: 860 MB with LargeSystemCache registry key set and without 4GT; up to 448 MB with 4GT. |
Always 1 TB regardless of physical RAM Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2: 16 TB. Windows Server 2003 and Windows XP: Up to 1 TB depending on configuration and RAM. |
Physical Memory Limits: Windows 11
The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for Windows 11.
| Version | Limit on X64 | Limit on ARM64 |
|---|---|---|
| Windows 11 Enterprise | 6 TB | 6 TB |
| Windows 11 Education | 2 TB | 2 TB |
| Windows 11 Pro for Workstations | 6 TB | 6 TB |
| Windows 11 Pro | 2 TB | 2 TB |
| Windows 11 Home | 128 GB | 128 GB |
Physical Memory Limits: Windows 10
The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for Windows 10.
| Version | Limit on X86 | Limit on X64 |
|---|---|---|
| Windows 10 Enterprise | 4 GB | 6 TB |
| Windows 10 Education | 4 GB | 2 TB |
| Windows 10 Pro for Workstations | 4 GB | 6 TB |
| Windows 10 Pro | 4 GB | 2 TB |
| Windows 10 Home | 4 GB | 128 GB |
Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2016
The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for Windows Server 2016.
| Version | Limit on X64 |
|---|---|
| Windows Server 2016 Datacenter | 24 TB |
| Windows Server 2016 Standard | 24 TB |
Physical Memory Limits: Windows 8
The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for Windows 8.
| Version | Limit on X86 | Limit on X64 |
|---|---|---|
| Windows 8 Enterprise | 4 GB | 512 GB |
| Windows 8 Professional | 4 GB | 512 GB |
| Windows 8 | 4 GB | 128 GB |
Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2012
The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for Windows Server 2012. Windows Server 2012 is available only in X64 editions.
| Version | Limit on X64 |
|---|---|
| Windows Server 2012 Datacenter | 4 TB |
| Windows Server 2012 Standard | 4 TB |
| Windows Server 2012 Essentials | 64 GB |
| Windows Server 2012 Foundation | 32 GB |
| Windows Storage Server 2012 Workgroup | 32 GB |
| Windows Storage Server 2012 Standard | 4 TB |
| Hyper-V Server 2012 | 4 TB |
Physical Memory Limits: Windows 7
The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for Windows 7.
| Version | Limit on X86 | Limit on X64 |
|---|---|---|
| Windows 7 Ultimate | 4 GB | 192 GB |
| Windows 7 Enterprise | 4 GB | 192 GB |
| Windows 7 Professional | 4 GB | 192 GB |
| Windows 7 Home Premium | 4 GB | 16 GB |
| Windows 7 Home Basic | 4 GB | 8 GB |
| Windows 7 Starter | 2 GB | N/A |
Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2008 R2
The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for Windows Server 2008 R2. Windows Server 2008 R2 is available only in 64-bit editions.
| Version | Limit on X64 | Limit on IA64 |
|---|---|---|
| Windows Server 2008 R2 Datacenter | 2 TB | |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise | 2 TB | |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 for Itanium-Based Systems | 2 TB | |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 Foundation | 8 GB | |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard | 32 GB | |
| Windows HPC Server 2008 R2 | 128 GB | |
| Windows Web Server 2008 R2 | 32 GB |
Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2008
The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for Windows Server 2008. Limits greater than 4 GB for 32-bit Windows assume that PAE is enabled.
| Version | Limit on X86 | Limit on X64 | Limit on IA64 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Windows Server 2008 Datacenter | 64 GB | 1 TB | |
| Windows Server 2008 Enterprise | 64 GB | 1 TB | |
| Windows Server 2008 HPC Edition | 128 GB | ||
| Windows Server 2008 Standard | 4 GB | 32 GB | |
| Windows Server 2008 for Itanium-Based Systems | 2 TB | ||
| Windows Small Business Server 2008 | 4 GB | 32 GB | |
| Windows Web Server 2008 | 4 GB | 32 GB |
Physical Memory Limits: Windows Vista
The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for Windows Vista.
| Version | Limit on X86 | Limit on X64 |
|---|---|---|
| Windows Vista Ultimate | 4 GB | 128 GB |
| Windows Vista Enterprise | 4 GB | 128 GB |
| Windows Vista Business | 4 GB | 128 GB |
| Windows Vista Home Premium | 4 GB | 16 GB |
| Windows Vista Home Basic | 4 GB | 8 GB |
| Windows Vista Starter | 1 GB |
Physical Memory Limits: Windows Home Server
Windows Home Server is available only in a 32-bit edition. The physical memory limit is 4 GB.
Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2003 R2
The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for Windows Server 2003 R2. Limits over 4 GB for 32-bit Windows assume that PAE is enabled.
| Version | Limit on X86 | Limit on X64 |
|---|---|---|
| Windows Server 2003 R2 Datacenter Edition | 64 GB (16 GB with 4GT) |
1 TB |
| Windows Server 2003 R2 Enterprise Edition | 64 GB (16 GB with 4GT) |
1 TB |
| Windows Server 2003 R2 Standard Edition | 4 GB | 32 GB |
Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2003 with Service Pack 2 (SP2)
The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for Windows Server 2003 with Service Pack 2 (SP2). Limits over 4 GB for 32-bit Windows assume that PAE is enabled.
| Version | Limit on X86 | Limit on X64 | Limit on IA64 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Windows Server 2003 with Service Pack 2 (SP2), Datacenter Edition | 64 GB (16 GB with 4GT) |
1 TB | 2 TB |
| Windows Server 2003 with Service Pack 2 (SP2), Enterprise Edition | 64 GB (16 GB with 4GT) |
1 TB | 2 TB |
| Windows Server 2003 with Service Pack 2 (SP2), Standard Edition | 4 GB | 32 GB |
Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2003 with Service Pack 1 (SP1)
The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for Windows Server 2003 with Service Pack 1 (SP1). Limits over 4 GB for 32-bit Windows assume that PAE is enabled.
| Version | Limit on X86 | Limit on X64 | Limit on IA64 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Windows Server 2003 with Service Pack 1 (SP1), Datacenter Edition | 64 GB (16 GB with 4GT) |
1 TB | 1 TB |
| Windows Server 2003 with Service Pack 1 (SP1), Enterprise Edition | 64 GB (16 GB with 4GT) |
1 TB | 1 TB |
| Windows Server 2003 with Service Pack 1 (SP1), Standard Edition | 4 GB | 32 GB |
Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2003
The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for Windows Server 2003. Limits over 4 GB for 32-bit Windows assume that PAE is enabled.
| Version | Limit on X86 | Limit on IA64 |
|---|---|---|
| Windows Server 2003, Datacenter Edition | 64 GB (16 GB with 4GT) |
512 GB |
| Windows Server 2003, Enterprise Edition | 64 GB (16 GB with 4GT) |
512 GB |
| Windows Server 2003, Standard Edition | 4 GB | |
| Windows Server 2003, Web Edition | 2 GB | |
| Windows Small Business Server 2003 | 4 GB | |
| Windows Compute Cluster Server 2003 | 32 GB | |
| Windows Storage Server 2003, Enterprise Edition | 8 GB | |
| Windows Storage Server 2003 | 4 GB |
Physical Memory Limits: Windows XP
The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for Windows XP.
| Version | Limit on X86 | Limit on X64 | Limit on IA64 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Windows XP | 4 GB | 128 GB | 128 GB (not supported) |
| Windows XP Starter Edition | 512 MB | N/A | N/A |
Physical Memory Limits: Windows Embedded
The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for Windows Embedded.
| Version | Limit on X86 | Limit on X64 |
|---|---|---|
| Windows XP Embedded | 4 GB | |
| Windows Embedded Standard 2009 | 4 GB | |
| Windows Embedded Standard 7 | 4 GB | 192 GB |
How graphics cards and other devices affect memory limits
Devices have to map their memory below 4 GB for compatibility with non-PAE-aware Windows releases. Therefore, if the system has 4GB of RAM, some of it is either disabled or is remapped above 4GB by the BIOS. If the memory is remapped, X64 Windows can use this memory. X86 client versions of Windows don’t support physical memory above the 4GB mark, so they can’t access these remapped regions. Any X64 Windows or X86 Server release can.
X86 client versions with PAE enabled do have a usable 37-bit (128 GB) physical address space. The limit that these versions impose is the highest permitted physical RAM address, not the size of the IO space. That means PAE-aware drivers can actually use physical space above 4 GB if they want. For example, drivers could map the «lost» memory regions located above 4 GB and expose this memory as a RAM disk.
Related topics
-
4-Gigabyte Tuning
-
IMAGE_FILE_LARGE_ADDRESS_AWARE
-
Physical Address Extension
| description | ms.assetid | title | ms.topic | ms.date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Describes the memory limits for supported Windows and Windows Server releases and provides lists of memory limits. |
de09c8af-0ed8-4fd4-b8e8-2c921aafe6f2 |
Memory Limits for Windows and Windows Server Releases |
article |
09/10/2021 |
Memory Limits for Windows and Windows Server Releases
This topic describes the memory limits for supported Windows and Windows Server releases.
Limits on memory and address space vary by platform, operating system, and by whether the IMAGE_FILE_LARGE_ADDRESS_AWARE value of the LOADED_IMAGE structure and 4-gigabyte tuning (4GT) are in use. IMAGE_FILE_LARGE_ADDRESS_AWARE is set or cleared by using the /LARGEADDRESSAWARE linker option.
4-gigabyte tuning (4GT), also known as application memory tuning, or the /3GB switch, is a technology (only applicable to 32 bit systems) that alters the amount of virtual address space available to user mode applications. Enabling this technology reduces the overall size of the system virtual address space and therefore system resource maximums. For more information, see What is 4GT.
Limits on physical memory for 32-bit platforms also depend on the Physical Address Extension (PAE), which allows 32-bit Windows systems to use more than 4 GB of physical memory.
Memory and Address Space Limits
The following table specifies the limits on memory and address space for supported releases of Windows. Unless otherwise noted, the limits in this table apply to all supported releases.
| Memory type | Limit on X86 | Limit in 64-bit Windows |
|---|---|---|
| User-mode virtual address space for each 32-bit process | 2 GB Up to 3 GB with IMAGE_FILE_LARGE_ADDRESS_AWARE and 4GT |
2 GB with IMAGE_FILE_LARGE_ADDRESS_AWARE cleared (default) 4 GB with IMAGE_FILE_LARGE_ADDRESS_AWARE set |
| User-mode virtual address space for each 64-bit process | Not applicable | With IMAGE_FILE_LARGE_ADDRESS_AWARE set (default): x64: Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2 or later: 128 TB x64: Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012 or earlier 8 TB Intel Itanium-based systems: 7 TB 2 GB with IMAGE_FILE_LARGE_ADDRESS_AWARE cleared |
| Kernel-mode virtual address space | 2 GB From 1 GB to a maximum of 2 GB with 4GT |
Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2 or later: 128 TB Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012 or earlier 8 TB |
| Paged pool | 384 GB or system commit limit, whichever is smaller. Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2: 15.5 TB or system commit limit, whichever is smaller. Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows 7, Windows Server 2008 and Windows Vista: Limited by available kernel-mode virtual address space. Starting with Windows Vista with Service Pack 1 (SP1), the paged pool can also be limited by the PagedPoolLimit registry key value. Windows Home Server and Windows Server 2003: 530 MB Windows XP: 490 MB |
384 GB or system commit limit, whichever is smaller Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2: 15.5 TB or system commit limit, whichever is smaller. Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows 7, Windows Server 2008 and Windows Vista: 128 GB or system commit limit, whichever is smaller Windows Server 2003 and Windows XP: Up to 128 GB depending on configuration and RAM. |
| Nonpaged pool | 75% of RAM or 2 GB, whichever is smaller. Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2: RAM or 16 TB, whichever is smaller (address space is limited to 2 x RAM). Windows Vista: Limited only by kernel mode virtual address space and physical memory. Starting with Windows Vista with SP1, the nonpaged pool can also be limited by the NonPagedPoolLimit registry key value. Windows Home Server, Windows Server 2003 and Windows XP: 256 MB, or 128 MB with 4GT. |
RAM or 128 GB, whichever is smaller (address space is limited to 2 x RAM) Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2: RAM or 16 TB, whichever is smaller (address space is limited to 2 x RAM). Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008: 75% of RAM up to a maximum of 128 GB Windows Vista: 40% of RAM up to a maximum of 128 GB. Windows Server 2003 and Windows XP: Up to 128 GB depending on configuration and RAM. |
| System cache virtual address space (physical size limited only by physical memory) | Limited by available kernel-mode virtual address space or the SystemCacheLimit registry key value. Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2: 16 TB. Windows Vista: Limited only by kernel mode virtual address space. Starting with Windows Vista with SP1, system cache virtual address space can also be limited by the SystemCacheLimit registry key value. Windows Home Server, Windows Server 2003 and Windows XP: 860 MB with LargeSystemCache registry key set and without 4GT; up to 448 MB with 4GT. |
Always 1 TB regardless of physical RAM Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2: 16 TB. Windows Server 2003 and Windows XP: Up to 1 TB depending on configuration and RAM. |
Physical Memory Limits: Windows 11
The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for Windows 11.
| Version | Limit on X64 | Limit on ARM64 |
|---|---|---|
| Windows 11 Enterprise | 6 TB | 6 TB |
| Windows 11 Education | 2 TB | 2 TB |
| Windows 11 Pro for Workstations | 6 TB | 6 TB |
| Windows 11 Pro | 2 TB | 2 TB |
| Windows 11 Home | 128 GB | 128 GB |
Physical Memory Limits: Windows 10
The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for Windows 10.
| Version | Limit on X86 | Limit on X64 |
|---|---|---|
| Windows 10 Enterprise | 4 GB | 6 TB |
| Windows 10 Education | 4 GB | 2 TB |
| Windows 10 Pro for Workstations | 4 GB | 6 TB |
| Windows 10 Pro | 4 GB | 2 TB |
| Windows 10 Home | 4 GB | 128 GB |
Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2016
The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for Windows Server 2016.
| Version | Limit on X64 |
|---|---|
| Windows Server 2016 Datacenter | 24 TB |
| Windows Server 2016 Standard | 24 TB |
Physical Memory Limits: Windows 8
The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for Windows 8.
| Version | Limit on X86 | Limit on X64 |
|---|---|---|
| Windows 8 Enterprise | 4 GB | 512 GB |
| Windows 8 Professional | 4 GB | 512 GB |
| Windows 8 | 4 GB | 128 GB |
Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2012
The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for Windows Server 2012. Windows Server 2012 is available only in X64 editions.
| Version | Limit on X64 |
|---|---|
| Windows Server 2012 Datacenter | 4 TB |
| Windows Server 2012 Standard | 4 TB |
| Windows Server 2012 Essentials | 64 GB |
| Windows Server 2012 Foundation | 32 GB |
| Windows Storage Server 2012 Workgroup | 32 GB |
| Windows Storage Server 2012 Standard | 4 TB |
| Hyper-V Server 2012 | 4 TB |
Physical Memory Limits: Windows 7
The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for Windows 7.
| Version | Limit on X86 | Limit on X64 |
|---|---|---|
| Windows 7 Ultimate | 4 GB | 192 GB |
| Windows 7 Enterprise | 4 GB | 192 GB |
| Windows 7 Professional | 4 GB | 192 GB |
| Windows 7 Home Premium | 4 GB | 16 GB |
| Windows 7 Home Basic | 4 GB | 8 GB |
| Windows 7 Starter | 2 GB | N/A |
Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2008 R2
The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for Windows Server 2008 R2. Windows Server 2008 R2 is available only in 64-bit editions.
| Version | Limit on X64 | Limit on IA64 |
|---|---|---|
| Windows Server 2008 R2 Datacenter | 2 TB | |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise | 2 TB | |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 for Itanium-Based Systems | 2 TB | |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 Foundation | 8 GB | |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard | 32 GB | |
| Windows HPC Server 2008 R2 | 128 GB | |
| Windows Web Server 2008 R2 | 32 GB |
Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2008
The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for Windows Server 2008. Limits greater than 4 GB for 32-bit Windows assume that PAE is enabled.
| Version | Limit on X86 | Limit on X64 | Limit on IA64 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Windows Server 2008 Datacenter | 64 GB | 1 TB | |
| Windows Server 2008 Enterprise | 64 GB | 1 TB | |
| Windows Server 2008 HPC Edition | 128 GB | ||
| Windows Server 2008 Standard | 4 GB | 32 GB | |
| Windows Server 2008 for Itanium-Based Systems | 2 TB | ||
| Windows Small Business Server 2008 | 4 GB | 32 GB | |
| Windows Web Server 2008 | 4 GB | 32 GB |
Physical Memory Limits: Windows Vista
The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for Windows Vista.
| Version | Limit on X86 | Limit on X64 |
|---|---|---|
| Windows Vista Ultimate | 4 GB | 128 GB |
| Windows Vista Enterprise | 4 GB | 128 GB |
| Windows Vista Business | 4 GB | 128 GB |
| Windows Vista Home Premium | 4 GB | 16 GB |
| Windows Vista Home Basic | 4 GB | 8 GB |
| Windows Vista Starter | 1 GB |
Physical Memory Limits: Windows Home Server
Windows Home Server is available only in a 32-bit edition. The physical memory limit is 4 GB.
Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2003 R2
The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for Windows Server 2003 R2. Limits over 4 GB for 32-bit Windows assume that PAE is enabled.
| Version | Limit on X86 | Limit on X64 |
|---|---|---|
| Windows Server 2003 R2 Datacenter Edition | 64 GB (16 GB with 4GT) |
1 TB |
| Windows Server 2003 R2 Enterprise Edition | 64 GB (16 GB with 4GT) |
1 TB |
| Windows Server 2003 R2 Standard Edition | 4 GB | 32 GB |
Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2003 with Service Pack 2 (SP2)
The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for Windows Server 2003 with Service Pack 2 (SP2). Limits over 4 GB for 32-bit Windows assume that PAE is enabled.
| Version | Limit on X86 | Limit on X64 | Limit on IA64 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Windows Server 2003 with Service Pack 2 (SP2), Datacenter Edition | 64 GB (16 GB with 4GT) |
1 TB | 2 TB |
| Windows Server 2003 with Service Pack 2 (SP2), Enterprise Edition | 64 GB (16 GB with 4GT) |
1 TB | 2 TB |
| Windows Server 2003 with Service Pack 2 (SP2), Standard Edition | 4 GB | 32 GB |
Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2003 with Service Pack 1 (SP1)
The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for Windows Server 2003 with Service Pack 1 (SP1). Limits over 4 GB for 32-bit Windows assume that PAE is enabled.
| Version | Limit on X86 | Limit on X64 | Limit on IA64 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Windows Server 2003 with Service Pack 1 (SP1), Datacenter Edition | 64 GB (16 GB with 4GT) |
1 TB | 1 TB |
| Windows Server 2003 with Service Pack 1 (SP1), Enterprise Edition | 64 GB (16 GB with 4GT) |
1 TB | 1 TB |
| Windows Server 2003 with Service Pack 1 (SP1), Standard Edition | 4 GB | 32 GB |
Physical Memory Limits: Windows Server 2003
The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for Windows Server 2003. Limits over 4 GB for 32-bit Windows assume that PAE is enabled.
| Version | Limit on X86 | Limit on IA64 |
|---|---|---|
| Windows Server 2003, Datacenter Edition | 64 GB (16 GB with 4GT) |
512 GB |
| Windows Server 2003, Enterprise Edition | 64 GB (16 GB with 4GT) |
512 GB |
| Windows Server 2003, Standard Edition | 4 GB | |
| Windows Server 2003, Web Edition | 2 GB | |
| Windows Small Business Server 2003 | 4 GB | |
| Windows Compute Cluster Server 2003 | 32 GB | |
| Windows Storage Server 2003, Enterprise Edition | 8 GB | |
| Windows Storage Server 2003 | 4 GB |
Physical Memory Limits: Windows XP
The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for Windows XP.
| Version | Limit on X86 | Limit on X64 | Limit on IA64 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Windows XP | 4 GB | 128 GB | 128 GB (not supported) |
| Windows XP Starter Edition | 512 MB | N/A | N/A |
Physical Memory Limits: Windows Embedded
The following table specifies the limits on physical memory for Windows Embedded.
| Version | Limit on X86 | Limit on X64 |
|---|---|---|
| Windows XP Embedded | 4 GB | |
| Windows Embedded Standard 2009 | 4 GB | |
| Windows Embedded Standard 7 | 4 GB | 192 GB |
How graphics cards and other devices affect memory limits
Devices have to map their memory below 4 GB for compatibility with non-PAE-aware Windows releases. Therefore, if the system has 4GB of RAM, some of it is either disabled or is remapped above 4GB by the BIOS. If the memory is remapped, X64 Windows can use this memory. X86 client versions of Windows don’t support physical memory above the 4GB mark, so they can’t access these remapped regions. Any X64 Windows or X86 Server release can.
X86 client versions with PAE enabled do have a usable 37-bit (128 GB) physical address space. The limit that these versions impose is the highest permitted physical RAM address, not the size of the IO space. That means PAE-aware drivers can actually use physical space above 4 GB if they want. For example, drivers could map the «lost» memory regions located above 4 GB and expose this memory as a RAM disk.
Related topics
-
4-Gigabyte Tuning
-
IMAGE_FILE_LARGE_ADDRESS_AWARE
-
Physical Address Extension
| Версия | Ограничение на X64 |
|---|---|
| Windows Server 2008 R2 для систем на базе процессоров Itanium | |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 Foundation | 8 GB |
| Windows Server Standard 2008 R2 | 32 GB |
| Windows HPC-сервер 2008 R2 | 128 GB |
Минимальные требования к памяти для Server 2008 R2 — 512 МБ ОЗУ. Но мы рекомендуем вам запустить его на 2 ГБ ОЗУ или больше чтобы он работал гладко. Минимальный объем доступного дискового пространства, необходимого для его запуска, составляет 10 ГБ. Для лучшей производительности мы рекомендуем вам 40 ГБ или более дискового пространства, доступного для лучшей работы системы.
Каковы минимальные спецификации Server 2008 R2?
Системные требования
| Критерии | 2008 | 2008 R2 |
|---|---|---|
| минимальный | минимальный | |
| ЦП | 1 ГГц (IA-32) 1.4 ГГц (x86-64 или Itanium) | 1.4 ГГц (x86-64 или Itanium) |
| Оперативная память | 512 MB | 512 MB |
| жесткий диск | Другие выпуски, 32-разрядные: 20 ГБ Другие выпуски, 64-разрядные: 32 ГБ Foundation: 10 ГБ | Foundation: 10 ГБ Другие версии: 32 ГБ |
Какие бывают два типа установки server 2008?
Типы установки Windows 2008
- Windows 2008 может быть установлена двух типов:
- Полная установка. …
- Установка Server Core.
ReFS лучше NTFS?
Работах имеет ошеломляюще высокие пределы, но очень немногие системы используют больше, чем часть того, что может предложить NTFS. ReFS действительно обладает впечатляющими функциями устойчивости, но NTFS также обладает способностью самовосстановления, и у вас есть доступ к технологиям RAID для защиты от повреждения данных. Microsoft продолжит разработку ReFS.
Может ли Windows 7 видеть диск емкостью 4 ТБ?
Windows 7 отлично поддерживает диски 2 + ТБ, им просто нужно использовать GPT, а не MBR из-за того, что MBR ограничен разделами 2 ТБ. То же самое, если вы хотите использовать диск в качестве загрузочного, вам абсолютно НЕОБХОДИМО использовать GPT и быть в системе UEFI (которая используется с этой платой z87).
Могу ли я изменить MBR на GPT?
С графическим интерфейсом управления дисками преобразовать MBR в GPT — это одно действие. Щелкните правой кнопкой мыши диск, который вы хотите преобразовать, и выберите «Преобразовать в GPT-диск». Вы можете только конвертировать диск из MBR в GPT на котором не хранятся данные или зашифрован BitLocker с активным Bitlocker.
В чем разница между 2008 R2 Standard и Enterprise?
Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise Edition предоставляет большая функциональность и масштабируемость, чем у Standard Edition. Как и в Standard Edition, доступны как 32-битные, так и 64-битные версии. Улучшения включают поддержку до 8 процессоров и до 2 ТБ оперативной памяти.
Поддерживается ли по-прежнему Windows 2008 R2?
Расширенная поддержка Windows Server 2008 и Windows Server 2008 R2 закончился 14 января 2020 г., а расширенная поддержка Windows Server 2012 и Windows Server 2012 R2 будет прекращена 10 октября 2023 г.… Перенести существующие рабочие нагрузки Windows Server 2008 и 2008 R2 «как есть» на виртуальные машины (ВМ) Azure.
-
Shaaarnir
- Сообщения: 365
- Зарегистрирован: Ср дек 24, 2008 2:55 pm
- Откуда: Україна 🇺🇦, Харків
-
Контактная информация:
Как бы расширить ограничение в 32ГБ ОЗУ в Serv2008R2standard
Установлен терминальный сервер:
Windows Server 2008R2 Standard
Установлено ОЗУ (физически):
36 ГБ
ОЗУ стало не хватать и расширил физически до 36 ГБ (и дальше возможно необходимо будет расширить).
Уперся в ограничение выпуска Standard Ограничение на 32 ГБ
Может кто знает, есть ли честные или не очень обходы данного ограничение без переустановки целиком сервера?
Кто-то может обновлялся до Enterprise? Какие подводные камни есть при обновлении?
-
Shaaarnir
- Сообщения: 365
- Зарегистрирован: Ср дек 24, 2008 2:55 pm
- Откуда: Україна 🇺🇦, Харків
- Контактная информация:
Re: Как бы расширить ограничение в 32ГБ ОЗУ в Serv2008R2stan
Сообщение
Shaaarnir » Вс окт 07, 2012 12:49 pm
Не получается выскакивает ошибка:
Код: Выделить всё
>Dism /online /Set-Edition:ServerEnterprise /ProductKey:XXXXX-XXXXX-XXXXX-XXXXX-XXXXX
Cистема DISM
Версия: 6.1.7600.16385
Версия образа: 6.1.7600.16385
Ошибка: 50
Установка выпуска не поддерживается для оперативных образов.
Файл журнала DISM находится по адресу C:WindowsLogsDISMdism.logВ целях экономии контроллер домена поднят на этой же машине
Нашел в интернете:
«Маленький момент — машина, на которой производится смена редакции, не должна быть контроллером домена.»
Пока зашел в тупик…
Не знаю, может поднять виртуалку, контроллер перенести, а потом назад вернуть…
-
Shaaarnir
- Сообщения: 365
- Зарегистрирован: Ср дек 24, 2008 2:55 pm
- Откуда: Україна 🇺🇦, Харків
- Контактная информация:
Re: Как бы расширить ограничение в 32ГБ ОЗУ в Serv2008R2stan
Сообщение
Shaaarnir » Пн окт 08, 2012 3:13 pm
Dim-soft писал(а):Есть и не очень легальный способ — поменять внутрений токен — будет писать что стандарт а ограничения будут от enterprise.
Или на 2012 перейти — там нет ограничения в стандарте.
Спасибо за совет
надо будет на 2012 глянуть, а то не видел его еще в глаза ))))
Обновлено 14.05.2019

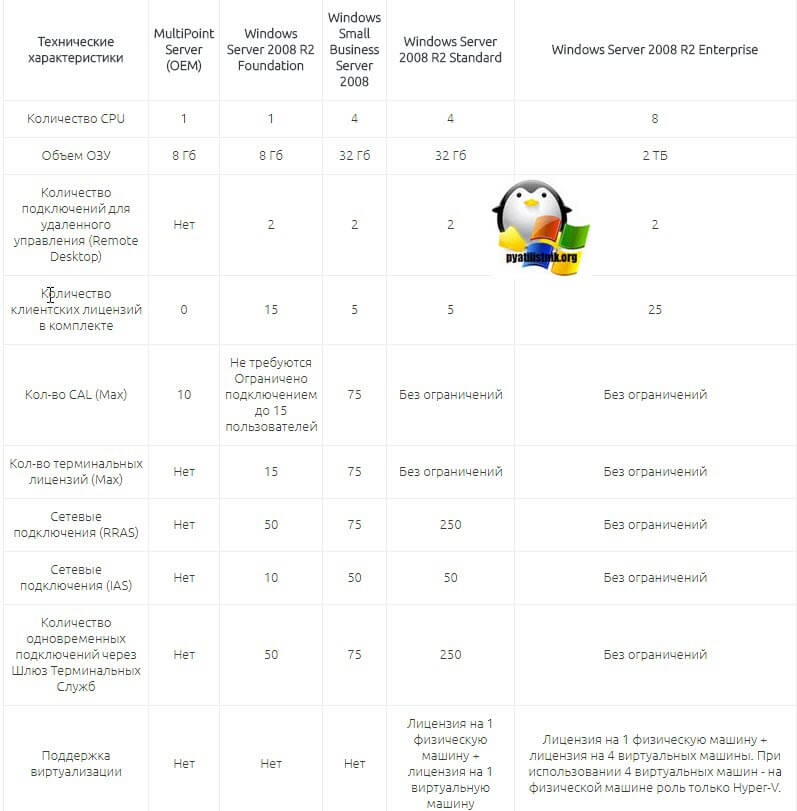
Ограничения Windows Server 2008 R2
Во времена уже Windows Server 2019, я уже совсем забыл, что ранее до Windows Server 2012 R2, редакции имели какие-то физические ограничения на работу с оборудованием, а не просто лицензирование функций или количества виртуальных машин. Вот вам сравнительная таблица в которой указаны все ограничения, которые накладываются на определенную редакцию Windows Server 2008 R2. Как видно версия Standard имеет ограничение на объем поддерживаемой оперативной памяти в 32 ГБ, а вот Enterprise уже имеет до 2 ТБ.
Чтобы решить нашу задачу и заставить виртуальную машину увидеть 64 ГБ памяти, нам необходимо провести Обновление Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard до Enterprise. Хорошо, что разработчики подумали, о такой возможности, без переустановки операционной системы и сервисов.
Хочу отметить, что есть некоторые ограничения и нюансы, которые не позволят вам провести обновление Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard до Enterprise.
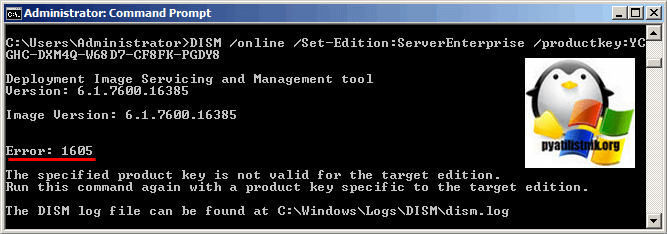
- Во первых вы не сможете таким образов обновить редакцию на сервере, который несет на себе роль контроллера домена, это такая защита от дурака. При таком раскладе, вам с начало нужно передать роли FSMO на данном сервере, если они есть, затем понизить контроллер домена до обычного сервера, при условии, что у вас в сети еще есть сервера с ролью AD DS.Затем произвести процедуру обновления Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard до Enterprise, и далее установить заново роль Active Directory Domain Services. В противном случае вы получите ошибку:
Error: 50. Setting an Edition is not supported with online images
- Вторая ошибка, это «Указанный ключ продукта недопустим для целевой версии. Повторите эту команду еще раз с ключом продукта, специфичным для целевой версии. (Error 1605. The specified product key is not valid for the target edition. Run this command again with a product key specific to the target edition)». Тут вам явно говорят, что у вас явно не валидный ключ, причины простые у вас редакция Volume, требующая GVLK ключа, а вы ему подсовываете MAC ключ. Читайте подробнее про типы ключей по ссылке слева. В обход проблемы можно использовать временный ключ:
489J6-VHDMP-X63PK-3K798-CPX3Y
Данный ключ позволит обновить редакцию, но затем попросит активацию системы.
- Если вы в момент повышения редакции используете KMS ключ, то вам нужно будет чистить старые хвосты KMS записи, как при ошибке активации Windows 0x800700B и 0x87E10BC6. Единственное перед удаление ключей продукта нужно будет выполнить очистку KMS записи через вот такую конструкцию (slmgr.vbs -ckms).
Так же нужно учитывать, что после повышения редакции вы не можете понизить ее, даунгрейда нет
Методы обновления редакции Windows Server 2008 R2
Существует два метода, позволяющие вам провести переход от версии Standard к Enterprise:
- Использование утилиты командной строки DISM, онлайн или оффлайн
- Использование дистрибутива Windows Server 2008 R2 и мастера обновления системы
Оба метода позволяют вам обновлять так Windows Server 2008 R2 в графическом режиме, так и в Core версии.
Учтите, что версию Core нельзя обновить до графической версии
Напоминаю возможные пути обновления редакций:
- С Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard до Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise или Windows Server 2008 R2 Datacenter
- С Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard Server Core до Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise Server Core или Windows Server 2008 R2 Datacenter Server Core
- С Windows Server 2008 R2 Foundation до Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard
Учитывайте это при своей стратегии перехода от редакции к редакции.
Обновление редакции через утилиту DISM
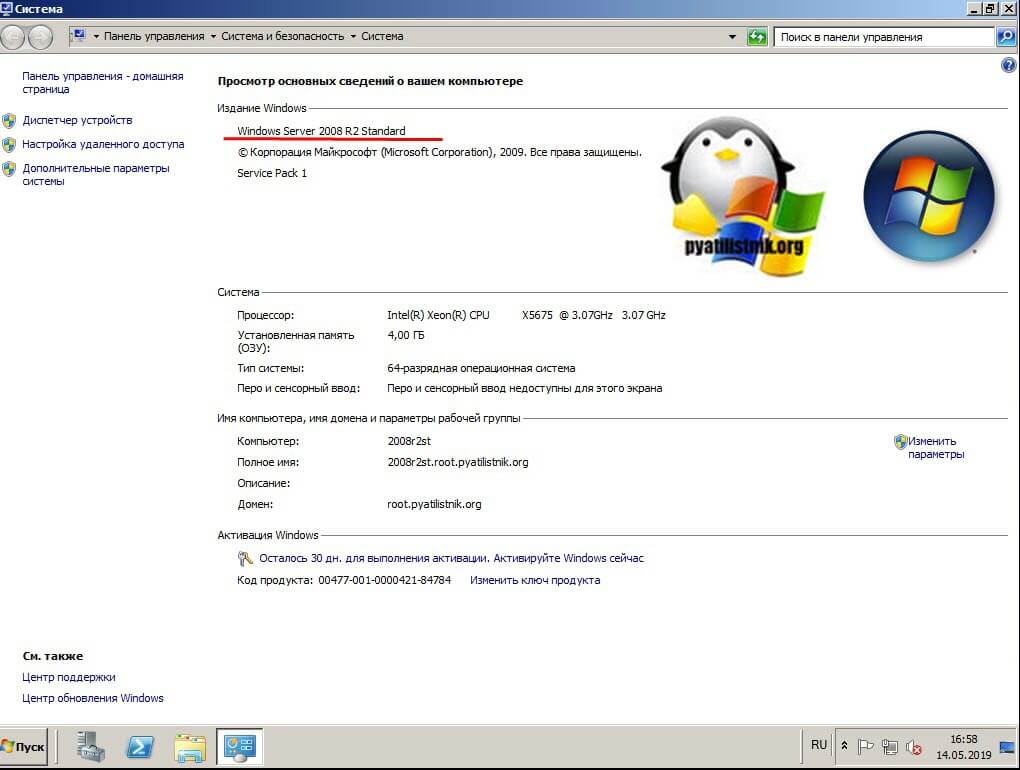
Чем хорош данный метод, так это тем, что все необходимые файлы он скачает из интернета и вам потребуется всего одна перезагрузка. Что делаем, первым делом нам нужно идентифицировать вашу текущую редакцию Windows, для этого вы можете открыть окно свойств системы, через оснастку control /name Microsoft.System или сочетания клавиш WIN+Pause Break.
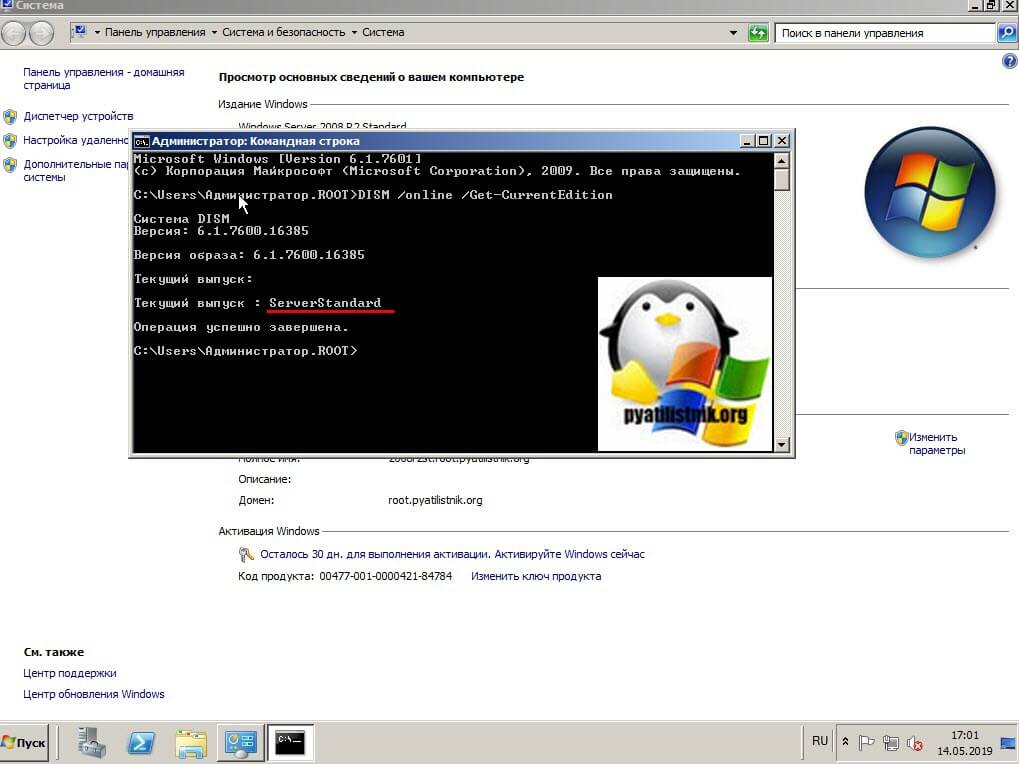
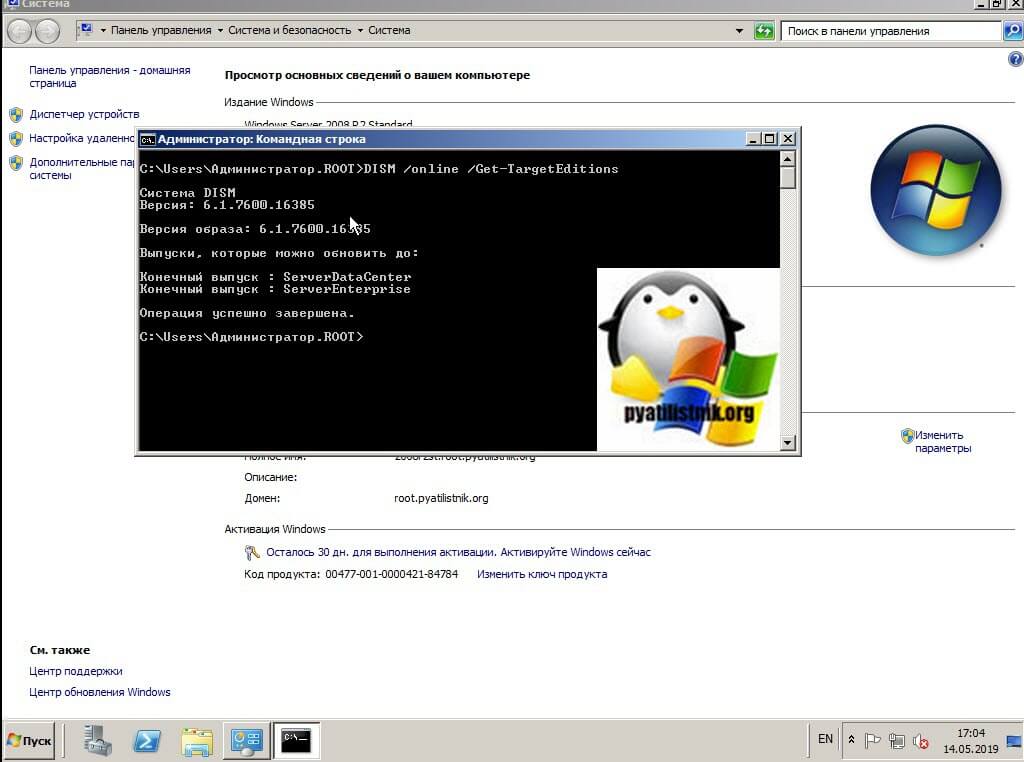
Но можно и самой утилитой DISM, если речь идет про Server Core версию. Для этого откройте командную строку или запустите оболочку PowerShell, после чего введите:
DISM /online /Get-CurrentEdition
Видно, что текущий выпуск ServerStandard.
Теперь давайте мы удостоверимся, до каких выпусков мы можем обновиться, для этого введите:
DISM /online /Get-TargetEditions
Видно, что я могу провести обновление до двух выпусков, это
- Конечный выпуск : ServerDataCenter
- Конечный выпуск : ServerEnterprise
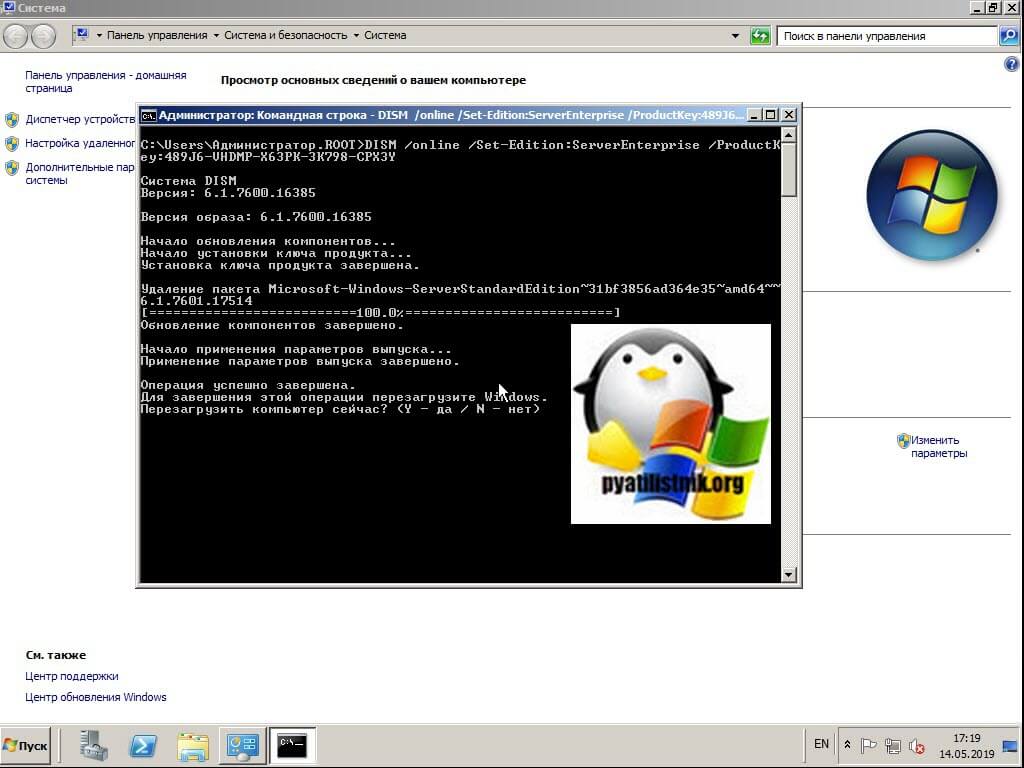
Я буду обновляться до ServerEnterprise, выше я приводил временный ключ или GVLK ключ, они потребуются для команды:
DISM /online /Set-Edition:ServerEnterprise /ProductKey: 489J6-VHDMP-X63PK-3K798-CPX3Y (ваш ключ приобретенный Вами для соответствующей редакции Windows 2008 R2).
KMS — Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise — 489J6-VHDMP-X63PK-3K798-CPX3Y
KMS — Windows Server 2008 R2 Datacenter — 74YFP-3QFB3-KQT8W-PMXWJ-7M648
Соглашаемся с с выполнением обновления выпуска и пишем «Y», учтите, что нужен будет доступ к интернету и потребуется потом перезагрузка
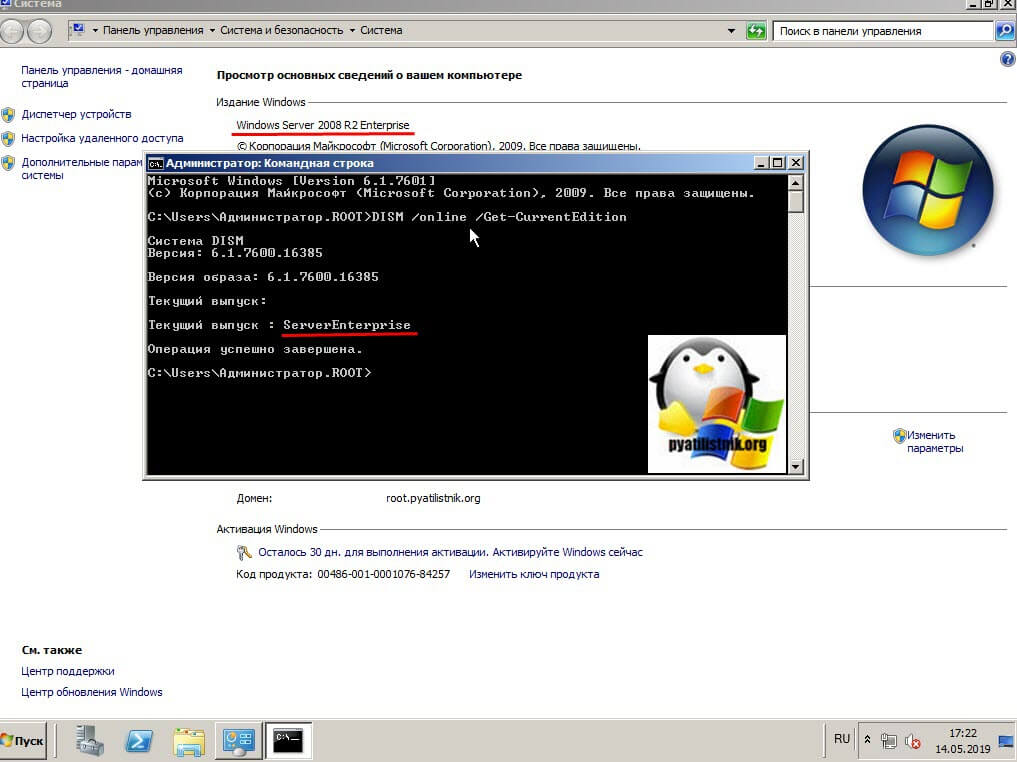
Проверяем после перезагрузки редакцию системы.
Обновление редакции через диск с дистрибутивом
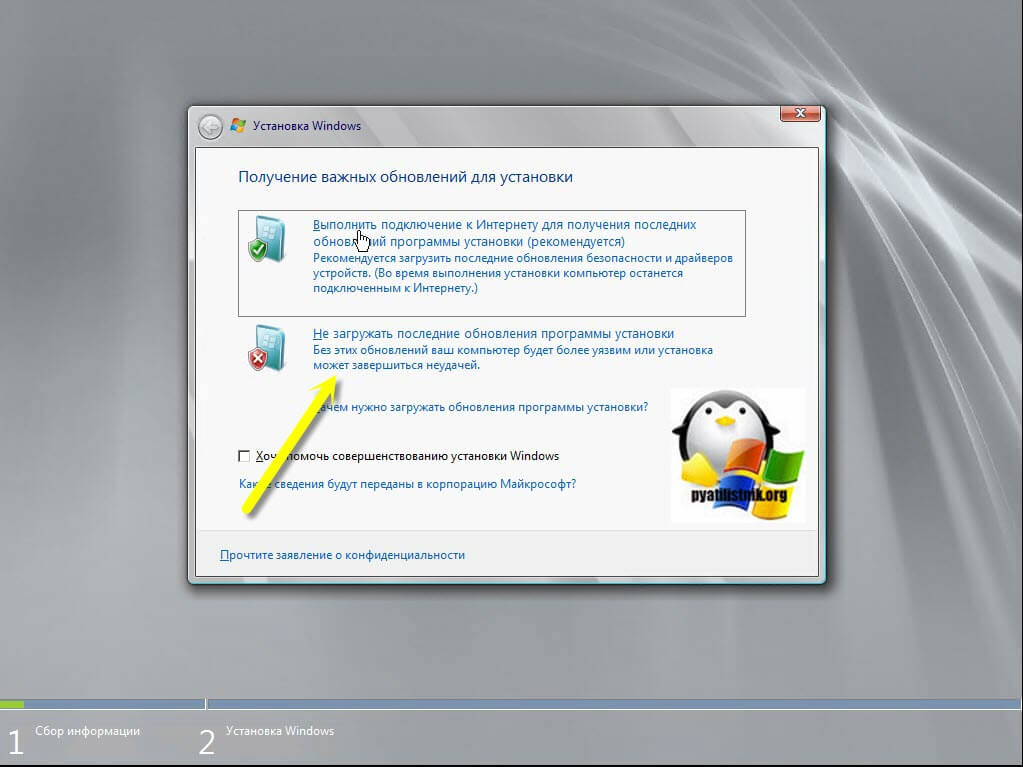
Данный метод хорош тем, что не требует интернет соединения, подойдет для автономных сетей, но за то более длительный и требует иметь скачанный Windows Server 2008 R2. Выясняем, как я показывал выше текущий выпуск и до каких редакций вы можете обновиться. Далее монтируете ваш дистрибутив с нужным выпуском. Запускаем setup.exe и новую установку, пропускаем поиск обновлений Windows.
Принимаем лицензию и до ходим до момента выбора типа установки, выбираем верхний пункт «Обновление».
Начнется проверка совместимости.
Если в отчете нет критических ошибок, то нажимаем далее.
Начнется процесс распаковки и установки файлов обновления, после двух перезагрузок вы получите результат. В среднем такое обновление занимает минут 15-20.
Надеюсь данная, небольшая инструкция оказалась для вас полезной. С вами был Иван Семин, автор и создатель IT блога Pyatilistnik.org.
Относительно недавно один из наших серверов стал требовать значительно больше оперативной памяти. Так как на сервере была установлена операционная система Windows Server Standart 2008 R2, которая имеет ограничение 32Гб на оперативную память, помимо добавления оперативки пришлось купить и обновить версию операционки. Мануальчик по апдейту ниже.
Вариант первый. Онлайн-обновление.
Если сервер подключен к интернету проще всего обновиться консольной утилитой DISM.
Команды:
DISM /online /Get-CurrentEdition
— просмотреть текущую версию ОС.
DISM /online /Get-TargetEditions
— просмотреть версии на которые можно обновиться.
DISM /online /Set-Edition:<edition ID> /ProductKey:XXXXX-XXXXX-XXXXX-XXXXX-XXXXX
— команда для обновления, <edition ID> — версия ОС на которую обновляемся, XXXXX-XXXXX-XXXXX-XXXXX-XXXXX — лицензионный ключ версии на которую обновляемся.
Возможные проблемы:
1. DISM не принимает лицензионный ключ, пишет:
Error: 1605
The specified product key is not valid for the target edition.
Run this command again with a product key specific to the target edition.
The DISM log file can be found at C:WindowsLogsDISMdism.log
Я так понимаю, dism не нравятся MAK-ключи. Вводим для обновления KMS-ключ. Взять можно отсюда. На всякий случай зеркало:
KMS-ключи Windows Vista/7/Server2008/Server2008R2
|
Platform |
Operating system edition |
Product key |
|
Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 |
||
|
Client |
Windows 7 Professional |
FJ82H-XT6CR-J8D7P-XQJJ2-GPDD4 |
|
Client |
Windows 7 Professional N |
MRPKT-YTG23-K7D7T-X2JMM-QY7MG |
|
Client |
Windows 7 Professional E |
W82YF-2Q76Y-63HXB-FGJG9-GF7QX |
|
Client |
Windows 7 Enterprise |
33PXH-7Y6KF-2VJC9-XBBR8-HVTHH |
|
Client |
Windows 7 Enterprise N |
YDRBP-3D83W-TY26F-D46B2-XCKRJ |
|
Client |
Windows 7 Enterprise E |
C29WB-22CC8-VJ326-GHFJW-H9DH4 |
|
Server |
Windows Server 2008 R2 Web |
6TPJF-RBVHG-WBW2R-86QPH-6RTM4 |
|
Server |
Windows Server 2008 R2 HPC edition |
TT8MH-CG224-D3D7Q-498W2-9QCTX |
|
Server |
Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard |
YC6KT-GKW9T-YTKYR-T4X34-R7VHC |
|
Server |
Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise |
489J6-VHDMP-X63PK-3K798-CPX3Y |
|
Server |
Windows Server 2008 R2 Datacenter |
74YFP-3QFB3-KQT8W-PMXWJ-7M648 |
|
Server |
Windows Server 2008 R2 for Itanium-based Systems |
GT63C-RJFQ3-4GMB6-BRFB9-CB83V |
|
Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008 |
||
|
Client |
Windows Vista Business |
YFKBB-PQJJV-G996G-VWGXY-2V3X8 |
|
Client |
Windows Vista Business N |
HMBQG-8H2RH-C77VX-27R82-VMQBT |
|
Client |
Windows Vista Enterprise |
VKK3X-68KWM-X2YGT-QR4M6-4BWMV |
|
Client |
Windows Vista Enterprise N |
VTC42-BM838-43QHV-84HX6-XJXKV |
|
Server |
Windows Web Server 2008 |
WYR28-R7TFJ-3X2YQ-YCY4H-M249D |
|
Server |
Windows Server 2008 Standard |
TM24T-X9RMF-VWXK6-X8JC9-BFGM2 |
|
Server |
Windows Server 2008 Standard without Hyper-V |
W7VD6-7JFBR-RX26B-YKQ3Y-6FFFJ |
|
Server |
Windows Server 2008 Enterprise |
YQGMW-MPWTJ-34KDK-48M3W-X4Q6V |
|
Server |
Windows Server 2008 Enterprise without Hyper-V |
39BXF-X8Q23-P2WWT-38T2F-G3FPG |
|
Server |
Windows Server 2008 HPC |
RCTX3-KWVHP-BR6TB-RB6DM-6X7HP |
|
Server |
Windows Server 2008 Datacenter |
7M67G-PC374-GR742-YH8V4-TCBY3 |
|
Server |
Windows Server 2008 Datacenter without Hyper-V |
22XQ2-VRXRG-P8D42-K34TD-G3QQC |
|
Server |
Windows Server 2008 for Itanium-Based Systems |
4DWFP-JF3DJ-B7DTH-78FJB-PDRHK |
После обновления заходим в свойства системы, внизу нажимаем ввести ключ продукта и вводим свой ключ. Также сменить ключ можно командой:
slmgr /ipk XXXXX-XXXXX-XXXXX-XXXXX-XXXXX
2. Если на сервере включена роль сервера терминалов, слетает активация сервера лицензирования удаленных рабочих столов. У меня спокойно заново активировался по тем же данным. Также слетают лицензии стороннего ПО, которые привязаны к версии операционной системы, что логично. Тут уже всё зависит от софта.
Вариант второй. Оффлайн-обновление.
На сайте мелкомягких пишут, что достаточно вставить диск с дистрибутивом ОС на которую обновляемся, запустить setup.exe и выбрать вариант «Обновление». После чего программа установки попросит ввести ключ и обновит ОС.
Сам данный способ не пробовал, так что не знаю какие проблемы могут возникнуть.