Операционная система Windows Server 2008 R2 расширяет базовые возможности операционной системы Windows Server и предоставляет новые мощные средства, помогая организациям всех размеров повышать управляемость, доступность и гибкость в соответствии с изменяющимися требованиями бизнеса. Новые веб-средства, технологии виртуализации, средства управления и расширенные возможности масштабирования экономят время, снижают затраты и предоставляют надежную платформу для создания ИТ-инфраструктуры организации.
Windows Server 2008 R2 содержит новые и усовершенствованные средства и возможности в следующих пяти категориях.
Платформа веб-приложений
В сервер Windows Server 2008 R2 включены множество усовершенствований, превращающих его в самую надежную платформу веб-приложений на основе Windows Server среди всех версий Windows. Он содержит обновленную роль веб-сервера и службы IIS 7.5 и обеспечивает расширенную поддержку .NET в режиме Server Core.
Виртуализация
Виртуализация играет важнейшую роль в работе современных центров обработки данных. Обеспечиваемое виртуализацией повышение эффективности работы позволяет организациям значительно снизить трудоемкость эксплуатации и энергопотребление. Windows Server 2008 R2 поддерживает следующие типы виртуализации: виртуализацию клиентских и серверных систем с помощью Hyper-V и виртуализацию представлений с помощью служб удаленных рабочих столов.
Масштабируемость и надежность
Windows Server 2008 R2 поддерживает недостижимые ранее объемы рабочих нагрузок, динамическую масштабируемость, доступность и надежность на всех уровнях, а также ряд других новых и обновленных возможностей, включая использование современных архитектур процессоров, повышение уровня компонентного представления операционной системы и повышение производительности и масштабируемости приложений и служб.
Управление
Постоянное управление серверами в центрах обработки данных — одна из тех задач, которые отнимают у ИТ-специалистов наибольшее время. Применяемая в организации стратегия управления должна поддерживать управление физическими и виртуальными средами. Чтобы помочь в решении этой задачи, в состав Windows Server 2008 R2 включены новые средства, уменьшающие трудоемкость управления серверами Windows Server 2008 R2 и выполнения повседневных задач по администрированию серверов.
Совместная работа с Windows 7
Операционная система Windows Server 2008 R2 поддерживает ряд функций, рассчитанных на работу с клиентскими компьютерами под управлением Windows 7.
Более подробно с основными возможностями ОС Windows Server 2008 R2 можно ознакомиться на сайте компании Microsoft.
Все редакции Windows Server 2008 R2 поддерживают основные возможности, необходимые для решения задач, которые возникают в работе ИТ-систем и организаций любого размера. Основные особенности различных редакций Windows Server 2008 R2, которые поставляются совместно с серверами DEPO Storm, описаны в данной статье.
Сравнительные характеристики различных редакций ОС Windows Server 2008 R2 приведены в таблице.
| Технические характеристики | MultiPoint Server (ОЕМ) | Windows Server 2008 R2 Foundation | Windows Small Business Server 2008 | Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard | Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise |
| Количество CPU | 1 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 8 |
| Объем ОЗУ | 8 Гб | 8 Гб | 32 Гб | 32 Гб | 2 ТБ |
| Количество подключений для удаленного управления (Remote Desktop) | Нет | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Количество клиентских лицензий в комплекте | 0 | 15 | 5 | 5 | 25 |
| Кол-во CAL (Max) | 10 | Не требуются Ограничено подключением до 15 пользователей |
75 | Без ограничений | Без ограничений |
| Кол-во терминальных лицензий (Max) | Нет | 15 | 75 | Без ограничений | Без ограничений |
| Сетевые подключения (RRAS) | Нет | 50 | 75 | 250 | Без ограничений |
| Сетевые подключения (IAS) | Нет | 10 | 50 | 50 | Без ограничений |
| Количество одновременных подключений через Шлюз Терминальных Служб | Нет | 50 | 75 | 250 | Без ограничений |
| Поддержка виртуализации | Нет | Нет | Нет | Лицензия на 1 физическую машину + лицензия на 1 виртуальную машину | Лицензия на 1 физическую машину + лицензия на 4 виртуальных машины. При использовании 4 виртуальных машин — на физической машине роль только Hyper-V. |
Для работы с Windows Server 2008 R2 компьютер должен удовлетворять следующим требованиям*
| Компонент |
Требование |
| Процессор | 1,4 ГГц (процессор с архитектурой x64) |
| Память | Минимальный объем: 512 МБ Максимальный объем: Foundation — 8 ГБ, Standard — 32 ГБ, Enterprise — 2 ТБ |
| Требования к свободному пространству на диске |
Минимальный объем: 32 ГБ |
| Монитор |
Монитор с разрешением Super VGA (800×600) или более высоким |
| Прочее |
Дисковод для DVD-дисков, клавиатура и мышь (Microsoft) или совместимое указывающее устройство, доступ в Интернет |
* Фактические требования к системе зависят от конфигурации системы и от выбранных для установки приложений и компонентов. Производительность процессора зависит не только от его тактовой частоты, но и от числа ядер и объема кэша процессора. Необходимый объем свободного дискового пространства в системном разделе указан приблизительно. При установке по сети может потребоваться дополнительное место на диске.
Windows MultiPoint Server 2010 – продукт семейства Windows, при помощи которого несколько человек могут одновременно работать на одном компьютере. MultiPoint Server является идеальным решением для образовательных учреждений, поскольку предоставляет большему числу преподавателей и учащихся доступ к компьютерным технологиям, а также:
- сокращает начальные вложения в оборудование и текущие эксплуатационные расходы;
- сокращает потребление электроэнергии;
- упрощает управление ИТ-инфраструктурой.
Более подробно с возможностями Windows MultiPoint Server 2010 можно ознакомиться на сайте компании Microsoft.
Windows Server 2008 R2 Foundation предназначена для небольших организаций, где рассматривается приобретение первого сервера или уже используется клиентская операционная система (например, Windows XP) для обеспечения базовой инфраструктуры. Это недорогая, удобная в развертывании и надежная платформа, на которой можно запускать распространенные бизнес-приложения и обеспечивать общий доступ к информации и ресурсам. Windows Server 2008 R2 Foundation основан на Windows Server 2008 R2 и сможет обеспечить все ключевые элементы ИТ в Вашем бизнесе: совместная работа с файлами и принтерами, удаленный доступ, безопасность ИТ среды.
Однако Windows Server 2008 R2 Foundation имеет ограничения по количеству клиентских подключений и не поддерживает функции виртуализации.
Windows Server 2008 R2 Foundation обладает следующими функциональными возможностями:
- поддержка 1 многоядерного процессора (количество ядер в процессоре неограниченно);
- поддержка 8 ГБ ОЗУ для 64-разрядных систем (4 ГБ для 32-разрядных систем);
- до 50 подключений службы сетевого доступа (RRAS);
- до 10 подключений сервера политики сети;
- до 50 подключений сервера терминалов;
- до 15 пользователей (учетных записей в Active Directory).
Более подробно с возможностями Windows Server 2008 R2 Foundation можно ознакомиться на сайте компании Microsoft.
Windows Small Business Server 2008 – полностью интегрированное ИТ-решение, включающее в себя все, что нужно малым и средним компаниям. Оно позволяет улучшить защиту данных и повысить эффективность работы компании, значительно снизив при этом расходы на развертывание и поддержку.
Электронная почта, подключение к Интернету, внутренние веб-узлы, удаленный доступ к файлам и почте, поддержка мобильных устройств, совместное использование файлов и принтеров, резервное копирование и восстановление – неполный список возможностей Windows Small Business Server 2008.
Windows Small Business Server 2008 поставляется в двух вариантах: Standard и Premium.
Версия Standard содержит средства для подключения локальной сети предприятия к Интернету. В состав продукта входит надежный межсетевой экран, сервер сообщений Microsoft Exchange со встроенной системой web-почты Microsoft Outlook Web Access, динамический web-сайт Remote Web Workplace, позволяющий сотрудникам получать быстрый и безопасный доступ к данным через Интернет.
Версия Premium содержит необходимые средства для подключения локальной сети предприятия к Интернету. В состав продукта входит мощный и надежный межсетевой экран, сервер сообщений Microsoft Exchange со встроенной системой web-почты Microsoft Outlook Web Access, динамический web-сайт Remote Web Workplace, позволяющий сотрудникам получать быстрый и безопасный доступ к данным через Интернет.
Более подробно с возможностями Windows Small Business Server можно ознакомиться на сайте компании Microsoft.
Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard – это самая надежная операционная система из семейства Windows Server на настоящее время. Эта система имеет встроенный веб-сервер и возможности виртуализации. Она поможет повысить надежность и гибкость серверной инфраструктуры при снижении расходов и экономии времени. Мощные инструменты обеспечивают более удобное управление серверами, упрощают настройку и управление. Надёжные средства безопасности этой операционной системы защищают сети и данные, что даёт возможность построить исключительно прочный фундамент для ИТ-среды вашего бизнеса.
Windows Server 2008 Standard обладает следующими функциональными возможностями:
- поддержка до 4-х многоядерных процессоров (количество ядер в процессоре неограниченно);
- поддержка 32 ГБ ОЗУ для 64-разрядных систем;
- до 250 подключений службы сетевого доступа (RRAS);
- до 50 подключений сервера политики сети;
- до 250 подключений сервера терминалов;
- практически неограниченное кол-во пользователей (учетных записей в Active Directory);
- поддержка виртуализации на базе технологии Hyper-V и один бесплатный виртуальный экземпляр.
Подробнее с возможностями Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard можно ознакомиться на сайте компании Microsoft.
Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise — ОС Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise обеспечивает бесперебойное функционирование, безопасность на основе новейших технологий и высокую масштабируемость, которая необходима для поддержки расширения критически важных приложений. Кроме того, она позволяет недорого и эффективно виртуализировать оборудование.
Windows Server 2008 Enterprise обладает следующими функциональными возможностями:
- поддержка до 8-ми многоядерных CPU для обработки пиковых нагрузок;
- 2 ТБ ОЗУ для эксплуатации ресурсоемких приложений;
- поддержка неограниченного количества VPN-подключений;
- проверка подлинности и авторизация для неограниченного количества подключений службы сетевого доступа и сервера политики сети;
- практически неограниченное количество подключений шлюза удаленных служб;
- поддержка виртуализации на базе технологии Hyper-V (лицензия на 1 физическую машину + лицензия на 4 виртуальных машины).
Кроме того, в Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise имеется функция горячего добавления памяти, которая позволяет без перезагрузки устанавливать на сервере дополнительные блоки памяти и сразу делать их доступными для операционной системы и приложений в рамках обычного пула памяти.
Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise — оптимальная операционная система для серверов с приложениями для управления работой сети, обмена сообщениями, инвентаризации, обслуживания заказчиков и приложениями баз данных. Она поддерживает все функциональные возможности Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard, а также имеет ряд преимуществ. Благодаря таким возможностям, как отказоустойчивые кластеры, Server Core, отказоустойчивая синхронизация памяти и распределенной файловой репликации (DFS-R), ОС Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise обеспечивает высокий уровень доступности для критически важных приложений, например баз данных, систем обмена сообщениями, файловых служб и служб печати.
Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise является идеальной платформой для виртуализации в масштабах всей компании с помощью гибкой и высокопроизводительной технологии Hyper-V™. Лицензия Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise включает право на использование до четырех дополнительных виртуальных экземпляров Windows Server на одном сервере с лицензией Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise.
Подробнее с возможностями Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise можно ознакомиться на сайте компании Microsoft.
Приложение
Редакция Datacenter предназначена только для крупного корпоративного рынка, основное отличие от Enterprise заключается в неограниченном количестве виртуальных машин, которые можно использовать с одной лицензией.
Версия Standard предназначена для малых и средних организаций, которым требуется не более двух экземпляров серверного программного обеспечения в виртуальной операционной системе. Редакция Datacenter оптимизирована для крупномасштабной виртуализации; его лицензия позволяет одному серверу запускать неограниченное количество экземпляров Windows Server.
В чем разница между Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard и Enterprise?
Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise Edition обеспечивает большую функциональность и масштабируемость, чем Standard Edition. Как и в Standard Edition, доступны как 32-битные, так и 64-битные версии. Улучшения включают поддержку до 8 процессоров и до 2 ТБ оперативной памяти.
Чем отличается версия Windows Server 2008?
Основные версии Windows 2008 включают Windows Server 2008, Standard Edition; Windows Server 2008, Enterprise Edition; Windows Server 2008, Datacenter Edition; Windows Web Server 2008; и Windows 2008 Server Core.
Какие четыре основные версии Windows 2008 Server?
Существует четыре редакции Windows Server 2008: Standard, Enterprise, Datacenter и Web.
Есть ли в Windows Server 2019 графический интерфейс?
Windows Server 2019 доступен в двух формах: Server Core и Desktop Experience (GUI).
Windows Server 2019 бесплатна?
Нет ничего бесплатного, особенно если это от Microsoft. Microsoft признала, что запуск Windows Server 2019 будет стоить дороже, чем его предшественник, хотя не раскрывает, насколько дороже. «Весьма вероятно, что мы повысим цены на лицензирование клиентского доступа Windows Server (CAL)», — сказал Чаппл в своем сообщении во вторник.
Какой последний пакет обновления для Windows Server 2008 R2?
Версии Windows Server
| Operating System | RTM | SP1 |
|---|---|---|
| Windows 2008 R2 | 6.1.7600.16385 | 6.1.7601 |
| Windows 2008 | 6.0.6000 | 6.0.6001 32-разрядная, 64-разрядная версии |
| Windows 2003 R2 | 5.2.3790.1180 | |
| Windows 2003 | 5.2.3790 | 5.2.3790.1180 32-разрядная, 64-разрядная версии |
Какая технология виртуализации используется в Windows 2008?
Раскрытие Windows Server 2008: виртуализация Hyper-V.
Какая рекомендуемая оперативная память для ОС MS Windows Server 2008 R2?
Минимальные требования к памяти для Server 2008 R2 — 512 МБ ОЗУ. Но мы рекомендуем вам запускать его с 2 ГБ ОЗУ или больше, чтобы он работал бесперебойно. Минимальный объем доступного дискового пространства, необходимого для его запуска, составляет 10 ГБ. Для лучшей производительности мы рекомендуем вам 40 ГБ или более дискового пространства, доступного для лучшей работы системы.
Какие бывают два типа установки server 2008?
Типы установки Windows 2008
- Windows 2008 может быть установлена двух типов:
- Полная установка. …
- Установка Server Core. …
- Мы можем открыть некоторые приложения с графическим интерфейсом пользователя в установке Server Core Windows 2008, блокноте, диспетчере задач, консоли данных и времени, консоли региональных настроек и всем остальным, управляемым через удаленное управление.
21 колода 2009 г.
В чем важность Windows Server 2008?
Windows Server 2008 обеспечивает высокую доступность служб и приложений за счет отказоустойчивой кластеризации. Большинство функций и ролей сервера можно поддерживать в рабочем состоянии с минимальным временем простоя или без него.
Какая польза от Windows Server 2008?
Windows Server 2008 также функционирует как и другие типы серверов. Его можно использовать в качестве файлового сервера для хранения файлов и данных компании. Его также можно использовать в качестве веб-сервера, на котором будут размещаться веб-сайты для одного или нескольких лиц (или компаний).
Какая версия Windows Server лучшая?
Windows Server 2016 против 2019
Windows Server 2019 — это последняя версия Microsoft Windows Server. Текущая версия Windows Server 2019 улучшена по сравнению с предыдущей версией Windows 2016 в отношении лучшей производительности, улучшенной безопасности и отличной оптимизации для гибридной интеграции.
Поддерживается ли по-прежнему Windows 2008 R2?
Жизненный цикл поддержки Windows Server 2008 и Windows Server 2008 R2 подошел к концу 14 января 2020 г.… Microsoft рекомендует выполнить обновление до текущей версии Windows Server для обеспечения максимальной безопасности, производительности и инноваций.
Какая основная функция Windows Server?
Веб-серверы и серверы приложений позволяют организациям создавать и размещать веб-сайты и другие веб-приложения с использованием локальной серверной инфраструктуры. … Сервер приложений предоставляет среду разработки и инфраструктуру хостинга для приложений, которые можно использовать через Интернет.
Hardware
Software
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
© 1992-2020 Майкролэб Инвестмент |
Сравнение различных выпусков Windows Server 2008
| Возможность | Standard Edition |
Enterprise Edition |
Datacenter Edition |
Web Edition |
| Число поддерживаемых процессоров | До 4 | До 8 | До 32 на платформе x86 До 64 на платформе x64 |
До 4 |
| Количество поддерживаемой памяти | До 4 Гбайт на платформе x86 До 32 Гбайт на платформе x64 |
До 64 Гбайт на платформе x86 До 2 Тбайт на платформе x64 |
До 64 Гбайт на платформе x86 До 2 Тбайт на платформе x64 |
До 4 Гбайт на платформе x86 До 32 Гбайт на платформе x64 |
| Кластеризация | Нет | До 16 узлов | До 16 узлов | Нет |
| Права на использование виртуальных машин | 1 ВМ | До 4 ВМ | Не ограничены | Не поддерживается |
Принципы лицензирования
Windows Server 2008 лицензируется по схеме лицензия на Сервер (или на процессор) + лицензия клиентского доступа CAL + дополнительная лицензия External Connector.
- Для редакций Standard и Enterprise требуется лицензия «на сервер»
- Для редакций Datacenter и Itanium требуется лицензия «на процессор»
Редакция Windows Web Server 2008 не требует лицензий клиентского доступа.
См. также:
- Сравнение различных выпусков Windows Server 2012
Производитель: Microsoft
Назад в раздел
Сравнение редакций Windows Server 2008
| Технические характеристики | MultiPoint Server (ОЕМ) | Windows Server 2008 R2 Foundation | Windows Small Business Server 2008 | Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard | Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise |
| Количество CPU | 1 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 8 |
| Объем ОЗУ | 8 Гб | 8 Гб | 32 Гб | 32 Гб | 2 ТБ |
| Количество подключений для удаленного управления (Remote Desktop) | Нет | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Количество клиентских лицензий в комплекте | 0 | 15 | 5 | 5 | 25 |
| Кол-во CAL (Max) | 10 | Не требуются | 75 | Без ограничений | Без ограничений |
| Ограничено подключением до 15 пользователей | |||||
| Кол-во терминальных лицензий (Max) | Нет | 15 | 75 | Без ограничений | Без ограничений |
| Сетевые подключения (RRAS) | Нет | 50 | 75 | 250 | Без ограничений |
| Сетевые подключения (IAS) | Нет | 10 | 50 | 50 | Без ограничений |
| Количество одновременных подключений через Шлюз Терминальных Служб | Нет | 50 | 75 | 250 | Без ограничений |
| Поддержка виртуализации | Нет | Нет | Нет | Лицензия на 1 физическую машину + лицензия на 1 виртуальную машину | Лицензия на 1 физическую машину + лицензия на 4 виртуальных машины. |
| Version of the Windows NT operating system | |
 |
|

Screenshot of Windows Server 2008 showing the Server Manager application which is automatically opened when an administrator logs on. |
|
| Developer | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| OS family | Microsoft Windows |
| Source model |
|
| Released to manufacturing |
February 4, 2008; 15 years ago[1] |
| General availability |
February 27, 2008; 14 years ago[1] |
| Latest release | Service Pack 2 with March 19, 2019 or later update rollup (6.0.6003)[2] / March 19, 2019; 3 years ago |
| Marketing target | Business |
| Update method | Windows Update, Windows Server Update Services, SCCM |
| Platforms | IA-32, x86-64, Itanium |
| Kernel type | Hybrid (Windows NT kernel) |
| Default user interface |
Windows shell (Graphical) |
| License | Proprietary commercial software |
| Preceded by | Windows Server 2003 (2003) |
| Succeeded by | Windows Server 2008 R2 (2009) |
| Official website | Windows Server 2008 |
| Support status | |
| Mainstream support ended on January 13, 2015[3][4] Extended support ended on January 14, 2020[3][4] Windows Server 2008 is eligible for the paid ESU (Extended Security Updates) program.[5] This program allowed volume license customers to purchase, in yearly installments, security updates for the operating system until January 10, 2023,[3] only for Standard, Enterprise and Datacenter volume licensed editions. The updates are included with a Microsoft Azure purchase and Azure customers receive ESU updates until January 9, 2024.[6][5][7] Installing Service Pack 2 is required for users to receive updates and support after July 12, 2011[3][4] |
Windows Server 2008 is the fourth release of the Windows Server operating system produced by Microsoft as part of the Windows NT family of the operating systems. It was released to manufacturing on February 4, 2008, and generally to retail on February 27, 2008. Derived from Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008 is the successor of Windows Server 2003 and the predecessor to Windows Server 2008 R2.
Windows Server 2008 is the final version of Windows Server that supports IA-32-based processors (also known as 32-bit processors). Its successor, Windows Server 2008 R2, requires a 64-bit processor in any supported architecture (x86-64 for x86 and Itanium).
History[edit]
Microsoft had released Windows Vista to mixed reception, and their last Windows Server release was based on Windows XP. The operating system’s working title was Windows Server Codename «Longhorn», but was later changed to Windows Server 2008 when Microsoft chairman Bill Gates announced it during his keynote address at WinHEC on May 16, 2007.[8]
Beta 1 was released on July 27, 2005; Beta 2 was announced and released on May 23, 2006, at WinHEC 2006 and Beta 3 was released publicly on April 25, 2007.[9] Release Candidate 0 was released to the general public on September 24, 2007[10] and Release Candidate 1 was released to the general public on December 5, 2007. Windows Server 2008 was released to manufacturing on February 4, 2008, and officially launched on the 27th of that month.[11]
Features[edit]
Windows Server 2008 is built from the same codebase as Windows Vista and thus it shares much of the same architecture and functionality. Since the codebase is common, Windows Server 2008 inherits most of the technical, security, management and administrative features new to Windows Vista such as the rewritten networking stack (native IPv6, native wireless, speed and security improvements); improved image-based installation, deployment and recovery; improved diagnostics, monitoring, event logging and reporting tools; new security features such as BitLocker and address space layout randomization (ASLR); the improved Windows Firewall with secure default configuration; .NET Framework 3.0 technologies, specifically Windows Communication Foundation, Microsoft Message Queuing and Windows Workflow Foundation; and the core kernel, memory and file system improvements. Processors and memory devices are modeled as Plug and Play devices to allow hot-plugging of these devices. This allows the system resources to be partitioned dynamically using dynamic hardware partitioning — each partition has its own memory, processor and I/O host bridge devices independent of other partitions.[12]
Server Core[edit]
Windows Server 2008 includes a variation of installation called Server Core. Server Core is a significantly scaled-back installation where no Windows Explorer shell is installed. It also lacks Internet Explorer, and many other non-essential features. All configuration and maintenance is done entirely through command-line interface windows, or by connecting to the machine remotely using Microsoft Management Console (MMC). Notepad and some Control Panel applets, such as Regional Settings, are available.
A Server Core installation can be configured for several basic roles, including the domain controller (Active Directory Domain Services), Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services (formerly known as Active Directory Application Mode[13]), DNS Server, DHCP server, file server, print server, Windows Media Server, Internet Information Services 7 web server and Hyper-V virtual server roles. Server Core can also be used to create a cluster with high availability using failover clustering or network load balancing.
Andrew Mason, a program manager on the Windows Server team, noted that a primary motivation for producing a Server Core variant of Windows Server 2008 was to reduce the attack surface of the operating system, and that about 70% of the security vulnerabilities in Microsoft Windows from the prior five years would not have affected Server Core.[14]
Active Directory[edit]
The Active Directory domain functionality that was retained from Windows Server 2003 was renamed to Active Directory Domain Services (ADDS).[15]
- Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS) enables enterprises to share credentials with trusted partners and customers, allowing a consultant to use their company user name and password to log in on a client’s network.
- Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services (AD LDS), (formerly Active Directory Application Mode, or ADAM)
- Active Directory Certificate Services (ADCS) allow administrators to manage user accounts and the digital certificates that allow them to access certain services and systems. Identity Integration Feature Pack is included as Active Directory Metadirectory Services.
- Active Directory Rights Management Services (ADRMS)
- Read-only domain controllers (RODCs), intended for use in branch office or other scenarios where a domain controller may reside in a low physical security environment. The RODC holds a non-writeable copy of Active Directory, and redirects all write attempts to a full domain controller. It replicates all accounts except sensitive ones.[16] In RODC mode, credentials are not cached by default. Also, local administrators can be designated to log on to the machine to perform maintenance tasks without requiring administrative rights on the entire domain.[17]
- Restartable Active Directory allows ADDS to be stopped and restarted from the Management Console or the command-line without rebooting the domain controller. This reduces downtime for offline operations and reduces overall DC servicing requirements with Server Core. ADDS is implemented as a Domain Controller Service in Windows Server 2008.
- All of the Group Policy improvements from Windows Vista are included. Group Policy Management Console (GPMC) is built-in. The Group Policy objects are indexed for search and can be commented on.[18]
- Policy-based networking with Network Access Protection, improved branch management and enhanced end user collaboration. Policies can be created to ensure greater quality of service for certain applications or services that require prioritization of network bandwidth between client and server.
- Granular password settings within a single domain — ability to implement different password policies for administrative accounts on a «group» and «user» basis, instead of a single set of password settings to the whole domain.
Failover Clustering[edit]
Windows Server 2008 offers high availability to services and applications through Failover Clustering. Most server features and roles can be kept running with little to no downtime.
In Windows Server 2008, the way clusters are qualified changed significantly with the introduction of the cluster validation wizard.[19] The cluster validation wizard is a feature that is integrated into failover clustering in Windows Server 2008. With the cluster validation wizard, an administrator can run a set of focused tests on a collection of servers that are intended to use as nodes in a cluster. This cluster validation process tests the underlying hardware and software directly, and individually, to obtain an accurate assessment of how well failover clustering can be supported on a given configuration.
This feature is only available in Enterprise and Datacenter editions of Windows Server.
Disk management and file storage[edit]
- The ability to resize hard disk partitions without stopping the server, even the system partition. This applies only to simple and spanned volumes, not to striped volumes.
- Shadow Copy based block-level backup which supports optical media, network shares and Windows Recovery Environment.
- DFS enhancements — SYSVOL on DFS-R, Read-only Folder Replication Member. There is also support for domain-based DFS namespaces that exceed the previous size recommendation of 5,000 folders with targets in a namespace.[20]
- Several improvements to Failover Clustering (high-availability clusters).[21]
- Internet Storage Naming Server (iSNS) enables central registration, deregistration and queries for iSCSI hard drives.
- Self-healing NTFS: In Windows versions prior to Windows Vista, if the operating system detected corruption in the file system of an NTFS volume, it marked the volume «dirty»; to correct errors on the volume, it had to be taken offline. With self-healing NTFS, an NTFS worker thread is spawned in the background which performs a localized fix-up of damaged data structures, with only the corrupted files/folders remaining unavailable without locking out the entire volume and needing the server to be taken down. S.M.A.R.T. detection techniques were added to help determine when a hard disk may fail.[22]
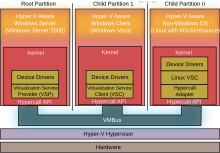
Hyper-V[edit]
Hyper-V is hypervisor-based virtualization software, forming a core part of Microsoft’s virtualization strategy. It virtualizes servers on an operating system’s kernel layer. It can be thought of as partitioning a single physical server into multiple small computational partitions. Hyper-V includes the ability to act as a Xen virtualization hypervisor host allowing Xen-enabled guest operating systems to run virtualized.[23] A beta version of Hyper-V shipped with certain x86-64 editions of Windows Server 2008, prior to Microsoft’s release of the final version of Hyper-V on 26 June 2008 as a free download. Also, a standalone variant of Hyper-V exists; this variant supports only x86-64 architecture.[24] While the IA-32 editions of Windows Server 2008 cannot run or install Hyper-V, they can run the MMC snap-in for managing Hyper-V.
Windows System Resource Manager[edit]
Windows System Resource Manager (WSRM) is integrated into Windows Server 2008. It provides resource management and can be used to control the amount of resources a process or a user can use based on business priorities. Process Matching Criteria, which is defined by the name, type or owner of the process, enforces restrictions on the resource usage by a process that matches the criteria. CPU time, bandwidth that it can use, number of processors it can be run on, and allocated to a process can be restricted. Restrictions can be set to be imposed only on certain dates as well.
Server Manager[edit]
Server Manager is a new roles-based management tool for Windows Server 2008.[25] It is a combination of Manage Your Server and Security Configuration Wizard from Windows Server 2003. Server Manager is an improvement of the Configure my server dialog that launches by default on Windows Server 2003 machines. However, rather than serve only as a starting point to configuring new roles, Server Manager gathers together all of the operations users would want to conduct on the server, such as, getting a remote deployment method set up, adding more server roles etc., and provides a consolidated, portal-like view about the status of each role.[26]
Protocol and cryptography[edit]
- Support for 128- and 256-bit AES encryption for the Kerberos authentication protocol.
- New cryptography (CNG) API which supports elliptic curve cryptography and improved certificate management.
- Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol, a new Microsoft proprietary VPN protocol.
- AuthIP, a Microsoft proprietary extension of the IKE cryptographic protocol used in IPsec VPN networks.
- Server Message Block 2.0 protocol in the new TCP/IP stack provides a number of communication enhancements, including greater performance when connecting to file shares over high-latency links and better security through the use of mutual authentication and message signing.
Miscellaneous[edit]
- Fully componentized operating system.
- Improved hot patching, a feature that allows non-kernel patches to occur without the need for a reboot.
- Support for being booted from Extensible Firmware Interface (EFI)-compliant firmware on x86-64 systems.
- Dynamic Hardware Partitioning supports hot-addition or replacement of processors and memory, on capable hardware.
- Windows Deployment Services (WDS) replacing Automated Deployment Services Windows Server 2008 home entertainment and Remote Installation Services. Windows Deployment Services supports an enhanced multicast feature when deploying operating system images.[27]
- Internet Information Services 7 — Increased security, Robocopy deployment, improved diagnostic tools, delegated administration.
- Windows Internal Database, a variant of SQL Server Express 2005, which serves as a common storage back-end for several other components such as Windows System Resource Manager, Windows SharePoint Services and Windows Server Update Services. It is not intended to be used by third-party applications.
- An optional «desktop experience» component provides the same Windows Aero user interface as Windows Vista, both for local users, as well as remote users connecting through Remote Desktop.
Removed features[edit]
- The Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol component in Routing and Remote Access Service was removed.[28]
- Services for Macintosh, which provided file and print sharing via the now deprecated AppleTalk protocol, has been removed. Services for Macintosh were initially removed in Windows XP but were available in Windows Server 2003.[28]
- NTBackup is replaced by Windows Server Backup, and no longer supports backing up to tape drives.[29] As a result of NTBackup removal, Exchange Server 2007 does not have volume snapshot backup functionality; however Exchange Server 2007 SP2 adds back an Exchange backup plug-in for Windows Server Backup which restores partial functionality.[30] Windows Small Business Server and Windows Essential Business Server both include this Exchange backup component.[31]
- The POP3 service has been removed from Internet Information Services 7.0.[32] The SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) service is not available as a server role in IIS 7.0, it is a server feature managed through IIS 6.0.
- NNTP (Network News Transfer Protocol) is no longer part of Internet Information Services 7.0.
- ReadyBoost, which is available in Windows Vista, is not supported in Windows Server 2008.
Editions[edit]
Installation disc of Enterprise edition (beta 3)
Most editions of Windows Server 2008 are available in x86-64 and IA-32 variants. These editions come in two DVDs: One for installing the IA-32 variant and the other for x64. Windows Server 2008 for Itanium-based Systems supports IA-64 processors. The IA-64 variant is optimized for high-workload scenarios like database servers and Line of Business (LOB) applications. As such, it is not optimized for use as a file server or media server. Windows Server 2008 is the last 32-bit Windows server operating system.[33]
Editions of Windows Server 2008 include:[34]
- Windows Server 2008 Foundation (codenamed «Lima»; x86-64) for OEMs only[35]
- Windows Server 2008 Standard (IA-32 and x86-64)
- Windows Server 2008 Enterprise (IA-32 and x86-64)
- Windows Server 2008 Datacenter (IA-32 and x86-64)
- Windows Server 2008 for Itanium-based Systems (IA-64)
- Windows Web Server 2008 (IA-32 and x86-64)
- Windows HPC Server 2008 (codenamed «Socrates»; replacing Windows Compute Cluster Server)
- Windows Storage Server 2008 (codenamed «Magni»; IA-32 and x86-64)
- Windows Small Business Server 2008 (codenamed «Cougar»; x86-64) for small businesses
- Windows Essential Business Server 2008 (codenamed «Centro»; x86-64) for medium-sized businesses[36] — this edition was discontinued in 2010.[37]
The Microsoft Imagine program, known as DreamSpark at the time, used to provide verified students with the 32-bit variant of Windows Server 2008 Standard Edition, but the version has since then been removed. However, they still provide the R2 release.
The Server Core feature is available in the Web, Standard, Enterprise and Datacenter editions.
Windows Server 2008 Foundation Released on May 21, 2009.[38]
System requirements[edit]
System requirements for Windows Server 2008 are as follows:
| Criteria | 2008 | 2008 R2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum[39] | Recommended[39] | Minimum[40] | Recommended[40] | |
| CPU |
|
2 GHz or faster | 1.4 GHz (x86-64 or Itanium) | 2 GHz or faster |
| RAM | 512 MB | 2 GB or greater | 512 MB | 2 GB or greater |
| HDD[a] |
|
40 GB or greater |
|
|
| Devices | DVD drive, 800 × 600 or higher display, keyboard and mouse |
Scalability[edit]
Windows Server 2008 supports the following maximum hardware specifications:[42][43][44]
| Specification | Windows Server 2008 SP2 | Windows Server 2008 R2 |
|---|---|---|
| Physical processors («sockets»)[43] |
|
|
| Logical processors when Hyper-V is disabled[43] |
|
256 |
| Logical processors when Hyper-V is enabled[43] |
|
64 |
| Memory on IA-32[44] |
|
— |
| Memory on x64[44] |
|
|
| Memory on Itanium[44] |
2 TB |
Updates[edit]
Windows Server 2008 shares most of its updates with Windows Vista, given that the operating systems share a codebase. A workaround using the Microsoft Update Catalog allowed the installation of updates for Windows Server 2008 on Windows Vista,[45] adding nearly 3 years of security updates to that operating system (Support for Windows Vista ended on April 11, 2017,[46] while support for Windows Server 2008 ended on January 14, 2020).
Service Pack 2[edit]
The RTM release of Windows Server 2008 already includes the updates and fixes of Windows Vista Service Pack 1.
Service Pack 2 was initially announced on October 24, 2008[47] and released on May 26, 2009. Service Pack 2 added new features, such as Windows Search 4.0, support for Bluetooth 2.1, the ability to write to Blu-ray discs, and simpler Wi-Fi configuration. Windows Server 2008 specifically received the final release of Hyper-V 1.0, improved backwards compatibility with Terminal Server license keys and an approximate 10% reduction in power usage with this service pack.[48]
Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008 share the same service pack update binary.[49]
Platform Update[edit]
On October 27, 2009, Microsoft released the Platform Update for Windows Server 2008 and Windows Vista. It backports several APIs and libraries introduced in Windows Server 2008 R2 and Windows 7 to Windows Server 2008 and Windows Vista, including the Ribbon API, DirectX 11, the XPS library, the Windows Automation API and the Portable Device Platform.[50] A supplemental update was released in 2011 to provide improvements and bug fixes.[51]
Internet Explorer 9[edit]
Windows Server 2008 shipped with Internet Explorer 7, the same version that shipped with Windows Vista. The last supported version of Internet Explorer for Windows Server 2008 is Internet Explorer 9, released in 2011. Internet Explorer 9 was continually updated with cumulative monthly update rollups until support for Internet Explorer 9 on Windows Server 2008 ended on January 14, 2020.[52] Extended Security Updates (ESU) continue until January 9, 2024 for Azure customers.
.NET Framework[edit]
The latest supported version of the .NET Framework officially is version 4.6, released on October 15, 2015.[53]
TLS 1.1 and 1.2 support[edit]
In July 2017, Microsoft released an update to add TLS 1.1 and 1.2 support to Windows Server 2008, however it is disabled by default after installing the update.[54]
SHA-2 signing support[edit]
Starting in March 2019, Microsoft began transitioning to exclusively signing Windows updates with the SHA-2 algorithm. As a result of this Microsoft released several updates throughout 2019 to add SHA-2 signing support to Windows Server 2008.[55]
Monthly update rollups[edit]
In June 2018, Microsoft announced that they would be moving Windows Server 2008 to a monthly update model beginning with updates released in September 2018[56] — two years after Microsoft switched the rest of their supported operating systems to that model.[57]
With the new update model, instead of updates being released as they became available, only two update packages were released on the second Tuesday of every month until Windows Server 2008 reached its end of life — one package containing security and quality updates, and a smaller package that contained only the security updates. Users could choose which package they wanted to install each month. Later in the month, another package would be released which was a preview of the next month’s security and quality update rollup.
Installing the preview rollup package released for Windows Server 2008 on March 19, 2019, or any later released rollup package, will update the operating system kernel’s build number from version 6.0.6002 to 6.0.6003. This change was made so Microsoft could continue to service the operating system while avoiding “version-related issues”.[58]
The last free security update rollup packages were released on January 14, 2020.[59]
Windows Server 2008 R2[edit]
A second release of Windows Server 2008 based on Windows 7, Windows Server 2008 R2, was released to manufacturing on July 22, 2009[60] and became generally available on October 22, 2009.[61] New features added in Windows Server 2008 R2 include new virtualization features, new Active Directory features, Internet Information Services 7.5 and support for up to 256 logical processors. It is the first server operating system by Microsoft to exclusively support 64-bit processors, while consumer-oriented versions of Windows maintained 32-bit support until Windows 11 in 2021.
A service pack for Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2, formally designed Service Pack 1, was released in February 2011.[62]
Support lifecycle[edit]
Support for the RTM version of Windows Server 2008 ended on July 12, 2011,[3][4] and users can no longer receive further security updates for the operating system. As a component of Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008 with Service Pack 2 continued to be supported with security updates, lasting until January 14, 2020, the same respective end-of-life dates of its successor, Windows Server 2008 R2 and Windows 7.
Microsoft planned to end support for Windows Server 2008 on January 12, 2016. However, in order to give customers more time to migrate to newer Windows versions, particularly in developing or emerging markets, Microsoft decided to extend support to January 14, 2020.[6][5][7]
Windows Server 2008 is eligible for the paid Extended Security Updates (ESU) program. The program allowed volume license customers to purchase, in yearly installments, security updates for the operating system for three additional years, until January 10, 2023. The program is also included with Microsoft Azure purchases, and Azure customers receive an extra year of support, until January 9, 2024. The licenses are paid for on a per-machine basis. If a user purchases an Extended Security Updates license in a later year of the program, they must pay for any previous years of Extended Security Updates as well. [6][63]
See also[edit]
- BlueKeep (security vulnerability)
- Comparison of Microsoft Windows versions
- Comparison of operating systems
- History of Microsoft Windows
- List of operating systems
- Microsoft Servers
Notes[edit]
- ^ Computers with more than 16 GB of RAM require more disk space for paging, hibernation, and dump files[40]
References[edit]
- ^ a b «As Windows Server 2008 RTMs, Customers and Partners Adopting with Help of New Tools, Training». News Center. Redmond, WA: Microsoft. 4 February 2008.
- ^ «Build number changing to 6003 in Windows Server 2008». support.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2021-03-26.
- ^ a b c d e «Microsoft Product Lifecycle». Support. Microsoft. Retrieved April 12, 2022.
- ^ a b c d «Install Windows Vista Service Pack 2 (SP2)». Support. Microsoft. Retrieved April 12, 2010.
- ^ a b c «Extended Security Updates for SQL Server and Windows Server 2008 and 2008 R2 | Microsoft». www.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2021-03-26.
- ^ a b c tfosmark. «Product Lifecycle FAQ — Extended Security Updates — Microsoft Lifecycle». docs.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2021-03-26.
- ^ a b «Announcing new options for SQL Server 2008 and Windows Server 2008 End of Support». azure.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2021-03-26.
- ^ Miller, Michael J. (2007-05-15). «Gates at WinHec 2007: Windows Server 2008, Rally, Home Server and More». Forward Thinking. Retrieved 2007-07-09.
- ^ Lowe, David (2007-04-25). «Beta 3 is Go!». Windows Server Division WebLog. Microsoft. Retrieved 2007-04-25.
- ^ Ralston, Ward (2007-09-24). «Windows Server 2008 Rc0 Released!». Windows Server Division WebLog. Microsoft. Retrieved 2007-09-24.
- ^ Nate Mook (10 July 2007). «New Windows Server, Visual Studio, SQL Server to Launch in February». BetaNews. Retrieved 2007-07-11.
- ^ «Dynamic Hardware Partitioning Architecture». MSDN. Retrieved 2007-07-23.
- ^ Archiveddocs. «Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services Overview». docs.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2020-01-15.
- ^ «Iain McDonald and Andrew Mason show off the new Windows Server OS». Channel 9. Microsoft. May 24, 2006. Retrieved 2008-11-01.
18:55
- ^ Hynes, Byron (November 2006). «The Future of Windows: Directory Services in Windows Server 2008». TechNet Magazine. Retrieved 2007-05-02.
- ^ «Deploying Windows Server 2008 Read Only Domain Controllers». docs.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2020-01-15.
- ^ «Q. What is a read-only domain controller (RODC)?». IT Pro. 2008-03-24. Retrieved 2020-01-15.
- ^ Ward, Keith (2007-10-08). «Top 10 Overlooked Windows Server 2008 Features, Part 2». Redmond Developer News. Archived from the original on 2009-08-04. Retrieved 2014-10-10.
- ^ «Failover Cluster Validation Error 80070005 on Windows Server 2008 R2 x64». Capitalhead. 2009-11-04. Retrieved 2013-10-28.
- ^ Zoeller, Jill (26 July 2007). «New in Windows Server 2008: Breaking the 5K Folder «Barrier» in Domain-Based Namespaces». The Storage Team at Microsoft — File Cabinet Blog. Microsoft. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- ^ «Failover Clustering with Windows Server 2008 including Cluster shared volumes». Microsoft. 2007-01-17. Retrieved 2007-07-09.
- ^ Loveall, John (2006). «Storage improvements in Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008» (PowerPoint). Microsoft Corporation. Retrieved 2007-07-09.
- ^ «Benchmarking Hyper-V on Windows Server 2008 R2 x64». 2010-01-20. Retrieved 2010-01-28.
- ^ «Microsoft Extends Virtualization Strategy, Outlines Product Road Map». Microsoft. 2006-05-22. Retrieved 2007-07-09.
- ^ «Server Manager». Windows Server 2008 Technical Library. Microsoft TechNet. 2007-06-25. Retrieved 2007-05-02.
- ^ «Unexpected error refreshing Server Manager-0x800706BE and 1601 on Window Server 2008 R2». Retrieved 2010-11-05.
- ^ «Multicasting OS deployments with Windows Server 2008». Kevinsul’s Management Blog. Microsoft. 29 August 2007. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- ^ a b «Removed technologies in Routing and Remote Access in Windows Server 2008». TechNet. Microsoft. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- ^ «Windows Server Backup Step-by-Step Guide for Windows Server 2008». TechNet. Microsoft. 17 January 2013. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- ^ «Exchange Server 2007 Service Pack 2 available in Q3 2009». The Exchange Team Blog. 11 May 2009. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- ^ Bilic, Nino (18 June 2008). «To Backup or Not to Backup? Yes! To backup!!». The Exchange Team Blog. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- ^ «IIS 7.0 Protocols». TechNet. Microsoft. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- ^ Heaton, Alex (2007-05-18). «On 64-bit and Windows Client». Windows Vista Team Blog. Retrieved 2007-07-09.
- ^
«Windows Server 2008 Product Editions». Microsoft. 2007-04-25. Retrieved 2007-07-09. - ^ «Windows Server 2008 Foundation: An Entry-Level Server Platform». Petri IT Knowledgebase. 2009-04-17. Retrieved 2014-01-08.
- ^ Ligman, Eric (7 November 2007). «Announcing Windows Essential Business Server». Microsoft Small Business Blog. Microsoft. Retrieved 2013-08-16.
- ^ «Windows Essential Business Server 2008». Technet.microsoft.com. 2010-12-31. Retrieved 2013-01-09.
- ^ «Windows Server 2008, Microsoft Lifecycle (Look at the Note below links)». docs.microsoft.com/en-us/lifecycle/products/.
- ^ a b «Windows Server 2008 System Requirements». 31 March 2008. Retrieved 2008-03-31.
- ^ a b c «Microsoft Windows Server 2008 System Requirements». Microsoft.com. Retrieved 2013-01-09.
- ^ «Microsoft Windows Server 2008 System Requirements». Microsoft. Retrieved 2013-01-09.
- ^ Savill, John (October 28, 2011). «Q: What are Windows Server 8’s Scalability Numbers?». Windows IT Pro. Penton Media. Retrieved November 5, 2011.
- ^ a b c d Seldam, Matthijs ten (October 13, 2012). «Windows Server — Sockets, Logical Processors, Symmetric Multi Threading». Matthijs’s blog. Microsoft. Retrieved October 14, 2012.
- ^ a b c d «Memory Limits for Windows and Windows Server Releases». MSDN. Microsoft. Retrieved 13 April 2014.
- ^ «Extend Windows Vista support by installing Windows Server 2008 updates — gHacks Tech News». gHacks Technology News. 2017-06-24. Retrieved 2021-06-30.
- ^ «Windows Vista Lifecycle Policy». Microsoft. Retrieved January 2, 2017.
- ^ Justin Graham (October 24, 2008). «Windows Server 2008 Service Pack 2 beta». Microsoft. Retrieved 2008-10-29.
- ^ «Tech ARP — ED#107 : Latest Details on Windows Vista Service Pack 2 Rev. 2.2». Archived from the original on 2009-02-12.
- ^ «Windows Vista Service Pack 2 Beta». blogs.windows.com. Archived from the original on 9 May 2013. Retrieved 12 January 2022.
- ^ «Announcing Final Releases of Platform Update for Windows Vista Technologies». 27 October 2009.
- ^ «Platform Update Supplement for Windows Vista and for Windows Server 2008».
- ^ «Cumulative security update for Internet Explorer: January 14, 2020». support.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2021-03-26.
- ^ «Microsoft .NET Framework 4.6 (Web Installer)». Microsoft.
- ^ «TLS 1.2 Support added to Windows Server 2008». Microsoft Security. 2017-07-20. Retrieved 2021-03-26.
- ^ «2019 SHA-2 Code Signing Support requirement for Windows and WSUS».
- ^ Mackie, Kurt; 06/13/2018. «Microsoft Switching Windows Server 2008 SP2 to Monthly Update Rollup Model — Redmondmag.com». Redmondmag. Retrieved 2021-03-26.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ «Community». forums.ivanti.com. Retrieved 2021-03-26.
- ^ «Build number changing to 6003 in Windows Server 2008».
- ^ «January 14, 2020—KB4534303 (Monthly Rollup)». support.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2021-03-26.
- ^ «Windows Server 2008 R2 Reaches the RTM Milestone! — Windows Server Blog — Site Home — TechNet Blogs». Blogs.technet.com. 2009-07-22. Retrieved 2013-01-09.
- ^ «When to expect Windows Server 2008 R2 RTM — Windows Server Blog — Site Home — TechNet Blogs». Blogs.technet.com. 2009-07-22. Retrieved 2013-01-09.
- ^ LeBlanc, Brandon (February 9, 2011). «Announcing Availability of Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1». Windows Experience Blog. Microsoft.
- ^ «Windows Server 2008 Product Lifecycle». Microsoft. January 14, 2020. Retrieved January 9, 2022.
18:55
Further reading[edit]
- «What’s New in Networking». TechNet. Microsoft. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- «Changes in Functionality from Windows Server 2003 with SP1 to Windows Server 2008». TechNet. Microsoft. 21 January 2008. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- «Description of the Microsoft server applications that are supported on Windows Server 2008». Support. Microsoft. 23 April 2012. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- «Windows Server 2008 System Requirements». TechNet. Microsoft. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- Henderson, Tom; Dvorak, Rand (21 February 2008). «Windows Server 2008: Faster, more manageable and secure, but still missing the virtual link». Network World. IDG. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- Radzikowski, Przemek (21 February 2010). «How to Find Build and Revision Number of Windows Vista or Windows Server 2008 Installed». Capitalhead. Capitalhead Pty. Ltd. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- Stanek, William (2008). Windows Server 2008 Inside Out. Microsoft Press. ISBN 978-0-7356-2438-2.
External links[edit]
- Windows Server Performance Team Blog
| Version of the Windows NT operating system | |
 |
|

Screenshot of Windows Server 2008 showing the Server Manager application which is automatically opened when an administrator logs on. |
|
| Developer | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| OS family | Microsoft Windows |
| Source model |
|
| Released to manufacturing |
February 4, 2008; 15 years ago[1] |
| General availability |
February 27, 2008; 14 years ago[1] |
| Latest release | Service Pack 2 with March 19, 2019 or later update rollup (6.0.6003)[2] / March 19, 2019; 3 years ago |
| Marketing target | Business |
| Update method | Windows Update, Windows Server Update Services, SCCM |
| Platforms | IA-32, x86-64, Itanium |
| Kernel type | Hybrid (Windows NT kernel) |
| Default user interface |
Windows shell (Graphical) |
| License | Proprietary commercial software |
| Preceded by | Windows Server 2003 (2003) |
| Succeeded by | Windows Server 2008 R2 (2009) |
| Official website | Windows Server 2008 |
| Support status | |
| Mainstream support ended on January 13, 2015[3][4] Extended support ended on January 14, 2020[3][4] Windows Server 2008 is eligible for the paid ESU (Extended Security Updates) program.[5] This program allowed volume license customers to purchase, in yearly installments, security updates for the operating system until January 10, 2023,[3] only for Standard, Enterprise and Datacenter volume licensed editions. The updates are included with a Microsoft Azure purchase and Azure customers receive ESU updates until January 9, 2024.[6][5][7] Installing Service Pack 2 is required for users to receive updates and support after July 12, 2011[3][4] |
Windows Server 2008 is the fourth release of the Windows Server operating system produced by Microsoft as part of the Windows NT family of the operating systems. It was released to manufacturing on February 4, 2008, and generally to retail on February 27, 2008. Derived from Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008 is the successor of Windows Server 2003 and the predecessor to Windows Server 2008 R2.
Windows Server 2008 is the final version of Windows Server that supports IA-32-based processors (also known as 32-bit processors). Its successor, Windows Server 2008 R2, requires a 64-bit processor in any supported architecture (x86-64 for x86 and Itanium).
History[edit]
Microsoft had released Windows Vista to mixed reception, and their last Windows Server release was based on Windows XP. The operating system’s working title was Windows Server Codename «Longhorn», but was later changed to Windows Server 2008 when Microsoft chairman Bill Gates announced it during his keynote address at WinHEC on May 16, 2007.[8]
Beta 1 was released on July 27, 2005; Beta 2 was announced and released on May 23, 2006, at WinHEC 2006 and Beta 3 was released publicly on April 25, 2007.[9] Release Candidate 0 was released to the general public on September 24, 2007[10] and Release Candidate 1 was released to the general public on December 5, 2007. Windows Server 2008 was released to manufacturing on February 4, 2008, and officially launched on the 27th of that month.[11]
Features[edit]
Windows Server 2008 is built from the same codebase as Windows Vista and thus it shares much of the same architecture and functionality. Since the codebase is common, Windows Server 2008 inherits most of the technical, security, management and administrative features new to Windows Vista such as the rewritten networking stack (native IPv6, native wireless, speed and security improvements); improved image-based installation, deployment and recovery; improved diagnostics, monitoring, event logging and reporting tools; new security features such as BitLocker and address space layout randomization (ASLR); the improved Windows Firewall with secure default configuration; .NET Framework 3.0 technologies, specifically Windows Communication Foundation, Microsoft Message Queuing and Windows Workflow Foundation; and the core kernel, memory and file system improvements. Processors and memory devices are modeled as Plug and Play devices to allow hot-plugging of these devices. This allows the system resources to be partitioned dynamically using dynamic hardware partitioning — each partition has its own memory, processor and I/O host bridge devices independent of other partitions.[12]
Server Core[edit]
Windows Server 2008 includes a variation of installation called Server Core. Server Core is a significantly scaled-back installation where no Windows Explorer shell is installed. It also lacks Internet Explorer, and many other non-essential features. All configuration and maintenance is done entirely through command-line interface windows, or by connecting to the machine remotely using Microsoft Management Console (MMC). Notepad and some Control Panel applets, such as Regional Settings, are available.
A Server Core installation can be configured for several basic roles, including the domain controller (Active Directory Domain Services), Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services (formerly known as Active Directory Application Mode[13]), DNS Server, DHCP server, file server, print server, Windows Media Server, Internet Information Services 7 web server and Hyper-V virtual server roles. Server Core can also be used to create a cluster with high availability using failover clustering or network load balancing.
Andrew Mason, a program manager on the Windows Server team, noted that a primary motivation for producing a Server Core variant of Windows Server 2008 was to reduce the attack surface of the operating system, and that about 70% of the security vulnerabilities in Microsoft Windows from the prior five years would not have affected Server Core.[14]
Active Directory[edit]
The Active Directory domain functionality that was retained from Windows Server 2003 was renamed to Active Directory Domain Services (ADDS).[15]
- Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS) enables enterprises to share credentials with trusted partners and customers, allowing a consultant to use their company user name and password to log in on a client’s network.
- Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services (AD LDS), (formerly Active Directory Application Mode, or ADAM)
- Active Directory Certificate Services (ADCS) allow administrators to manage user accounts and the digital certificates that allow them to access certain services and systems. Identity Integration Feature Pack is included as Active Directory Metadirectory Services.
- Active Directory Rights Management Services (ADRMS)
- Read-only domain controllers (RODCs), intended for use in branch office or other scenarios where a domain controller may reside in a low physical security environment. The RODC holds a non-writeable copy of Active Directory, and redirects all write attempts to a full domain controller. It replicates all accounts except sensitive ones.[16] In RODC mode, credentials are not cached by default. Also, local administrators can be designated to log on to the machine to perform maintenance tasks without requiring administrative rights on the entire domain.[17]
- Restartable Active Directory allows ADDS to be stopped and restarted from the Management Console or the command-line without rebooting the domain controller. This reduces downtime for offline operations and reduces overall DC servicing requirements with Server Core. ADDS is implemented as a Domain Controller Service in Windows Server 2008.
- All of the Group Policy improvements from Windows Vista are included. Group Policy Management Console (GPMC) is built-in. The Group Policy objects are indexed for search and can be commented on.[18]
- Policy-based networking with Network Access Protection, improved branch management and enhanced end user collaboration. Policies can be created to ensure greater quality of service for certain applications or services that require prioritization of network bandwidth between client and server.
- Granular password settings within a single domain — ability to implement different password policies for administrative accounts on a «group» and «user» basis, instead of a single set of password settings to the whole domain.
Failover Clustering[edit]
Windows Server 2008 offers high availability to services and applications through Failover Clustering. Most server features and roles can be kept running with little to no downtime.
In Windows Server 2008, the way clusters are qualified changed significantly with the introduction of the cluster validation wizard.[19] The cluster validation wizard is a feature that is integrated into failover clustering in Windows Server 2008. With the cluster validation wizard, an administrator can run a set of focused tests on a collection of servers that are intended to use as nodes in a cluster. This cluster validation process tests the underlying hardware and software directly, and individually, to obtain an accurate assessment of how well failover clustering can be supported on a given configuration.
This feature is only available in Enterprise and Datacenter editions of Windows Server.
Disk management and file storage[edit]
- The ability to resize hard disk partitions without stopping the server, even the system partition. This applies only to simple and spanned volumes, not to striped volumes.
- Shadow Copy based block-level backup which supports optical media, network shares and Windows Recovery Environment.
- DFS enhancements — SYSVOL on DFS-R, Read-only Folder Replication Member. There is also support for domain-based DFS namespaces that exceed the previous size recommendation of 5,000 folders with targets in a namespace.[20]
- Several improvements to Failover Clustering (high-availability clusters).[21]
- Internet Storage Naming Server (iSNS) enables central registration, deregistration and queries for iSCSI hard drives.
- Self-healing NTFS: In Windows versions prior to Windows Vista, if the operating system detected corruption in the file system of an NTFS volume, it marked the volume «dirty»; to correct errors on the volume, it had to be taken offline. With self-healing NTFS, an NTFS worker thread is spawned in the background which performs a localized fix-up of damaged data structures, with only the corrupted files/folders remaining unavailable without locking out the entire volume and needing the server to be taken down. S.M.A.R.T. detection techniques were added to help determine when a hard disk may fail.[22]
Hyper-V[edit]
Hyper-V is hypervisor-based virtualization software, forming a core part of Microsoft’s virtualization strategy. It virtualizes servers on an operating system’s kernel layer. It can be thought of as partitioning a single physical server into multiple small computational partitions. Hyper-V includes the ability to act as a Xen virtualization hypervisor host allowing Xen-enabled guest operating systems to run virtualized.[23] A beta version of Hyper-V shipped with certain x86-64 editions of Windows Server 2008, prior to Microsoft’s release of the final version of Hyper-V on 26 June 2008 as a free download. Also, a standalone variant of Hyper-V exists; this variant supports only x86-64 architecture.[24] While the IA-32 editions of Windows Server 2008 cannot run or install Hyper-V, they can run the MMC snap-in for managing Hyper-V.
Windows System Resource Manager[edit]
Windows System Resource Manager (WSRM) is integrated into Windows Server 2008. It provides resource management and can be used to control the amount of resources a process or a user can use based on business priorities. Process Matching Criteria, which is defined by the name, type or owner of the process, enforces restrictions on the resource usage by a process that matches the criteria. CPU time, bandwidth that it can use, number of processors it can be run on, and allocated to a process can be restricted. Restrictions can be set to be imposed only on certain dates as well.
Server Manager[edit]
Server Manager is a new roles-based management tool for Windows Server 2008.[25] It is a combination of Manage Your Server and Security Configuration Wizard from Windows Server 2003. Server Manager is an improvement of the Configure my server dialog that launches by default on Windows Server 2003 machines. However, rather than serve only as a starting point to configuring new roles, Server Manager gathers together all of the operations users would want to conduct on the server, such as, getting a remote deployment method set up, adding more server roles etc., and provides a consolidated, portal-like view about the status of each role.[26]
Protocol and cryptography[edit]
- Support for 128- and 256-bit AES encryption for the Kerberos authentication protocol.
- New cryptography (CNG) API which supports elliptic curve cryptography and improved certificate management.
- Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol, a new Microsoft proprietary VPN protocol.
- AuthIP, a Microsoft proprietary extension of the IKE cryptographic protocol used in IPsec VPN networks.
- Server Message Block 2.0 protocol in the new TCP/IP stack provides a number of communication enhancements, including greater performance when connecting to file shares over high-latency links and better security through the use of mutual authentication and message signing.
Miscellaneous[edit]
- Fully componentized operating system.
- Improved hot patching, a feature that allows non-kernel patches to occur without the need for a reboot.
- Support for being booted from Extensible Firmware Interface (EFI)-compliant firmware on x86-64 systems.
- Dynamic Hardware Partitioning supports hot-addition or replacement of processors and memory, on capable hardware.
- Windows Deployment Services (WDS) replacing Automated Deployment Services Windows Server 2008 home entertainment and Remote Installation Services. Windows Deployment Services supports an enhanced multicast feature when deploying operating system images.[27]
- Internet Information Services 7 — Increased security, Robocopy deployment, improved diagnostic tools, delegated administration.
- Windows Internal Database, a variant of SQL Server Express 2005, which serves as a common storage back-end for several other components such as Windows System Resource Manager, Windows SharePoint Services and Windows Server Update Services. It is not intended to be used by third-party applications.
- An optional «desktop experience» component provides the same Windows Aero user interface as Windows Vista, both for local users, as well as remote users connecting through Remote Desktop.
Removed features[edit]
- The Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol component in Routing and Remote Access Service was removed.[28]
- Services for Macintosh, which provided file and print sharing via the now deprecated AppleTalk protocol, has been removed. Services for Macintosh were initially removed in Windows XP but were available in Windows Server 2003.[28]
- NTBackup is replaced by Windows Server Backup, and no longer supports backing up to tape drives.[29] As a result of NTBackup removal, Exchange Server 2007 does not have volume snapshot backup functionality; however Exchange Server 2007 SP2 adds back an Exchange backup plug-in for Windows Server Backup which restores partial functionality.[30] Windows Small Business Server and Windows Essential Business Server both include this Exchange backup component.[31]
- The POP3 service has been removed from Internet Information Services 7.0.[32] The SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) service is not available as a server role in IIS 7.0, it is a server feature managed through IIS 6.0.
- NNTP (Network News Transfer Protocol) is no longer part of Internet Information Services 7.0.
- ReadyBoost, which is available in Windows Vista, is not supported in Windows Server 2008.
Editions[edit]
Installation disc of Enterprise edition (beta 3)
Most editions of Windows Server 2008 are available in x86-64 and IA-32 variants. These editions come in two DVDs: One for installing the IA-32 variant and the other for x64. Windows Server 2008 for Itanium-based Systems supports IA-64 processors. The IA-64 variant is optimized for high-workload scenarios like database servers and Line of Business (LOB) applications. As such, it is not optimized for use as a file server or media server. Windows Server 2008 is the last 32-bit Windows server operating system.[33]
Editions of Windows Server 2008 include:[34]
- Windows Server 2008 Foundation (codenamed «Lima»; x86-64) for OEMs only[35]
- Windows Server 2008 Standard (IA-32 and x86-64)
- Windows Server 2008 Enterprise (IA-32 and x86-64)
- Windows Server 2008 Datacenter (IA-32 and x86-64)
- Windows Server 2008 for Itanium-based Systems (IA-64)
- Windows Web Server 2008 (IA-32 and x86-64)
- Windows HPC Server 2008 (codenamed «Socrates»; replacing Windows Compute Cluster Server)
- Windows Storage Server 2008 (codenamed «Magni»; IA-32 and x86-64)
- Windows Small Business Server 2008 (codenamed «Cougar»; x86-64) for small businesses
- Windows Essential Business Server 2008 (codenamed «Centro»; x86-64) for medium-sized businesses[36] — this edition was discontinued in 2010.[37]
The Microsoft Imagine program, known as DreamSpark at the time, used to provide verified students with the 32-bit variant of Windows Server 2008 Standard Edition, but the version has since then been removed. However, they still provide the R2 release.
The Server Core feature is available in the Web, Standard, Enterprise and Datacenter editions.
Windows Server 2008 Foundation Released on May 21, 2009.[38]
System requirements[edit]
System requirements for Windows Server 2008 are as follows:
| Criteria | 2008 | 2008 R2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum[39] | Recommended[39] | Minimum[40] | Recommended[40] | |
| CPU |
|
2 GHz or faster | 1.4 GHz (x86-64 or Itanium) | 2 GHz or faster |
| RAM | 512 MB | 2 GB or greater | 512 MB | 2 GB or greater |
| HDD[a] |
|
40 GB or greater |
|
|
| Devices | DVD drive, 800 × 600 or higher display, keyboard and mouse |
Scalability[edit]
Windows Server 2008 supports the following maximum hardware specifications:[42][43][44]
| Specification | Windows Server 2008 SP2 | Windows Server 2008 R2 |
|---|---|---|
| Physical processors («sockets»)[43] |
|
|
| Logical processors when Hyper-V is disabled[43] |
|
256 |
| Logical processors when Hyper-V is enabled[43] |
|
64 |
| Memory on IA-32[44] |
|
— |
| Memory on x64[44] |
|
|
| Memory on Itanium[44] |
2 TB |
Updates[edit]
Windows Server 2008 shares most of its updates with Windows Vista, given that the operating systems share a codebase. A workaround using the Microsoft Update Catalog allowed the installation of updates for Windows Server 2008 on Windows Vista,[45] adding nearly 3 years of security updates to that operating system (Support for Windows Vista ended on April 11, 2017,[46] while support for Windows Server 2008 ended on January 14, 2020).
Service Pack 2[edit]
The RTM release of Windows Server 2008 already includes the updates and fixes of Windows Vista Service Pack 1.
Service Pack 2 was initially announced on October 24, 2008[47] and released on May 26, 2009. Service Pack 2 added new features, such as Windows Search 4.0, support for Bluetooth 2.1, the ability to write to Blu-ray discs, and simpler Wi-Fi configuration. Windows Server 2008 specifically received the final release of Hyper-V 1.0, improved backwards compatibility with Terminal Server license keys and an approximate 10% reduction in power usage with this service pack.[48]
Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008 share the same service pack update binary.[49]
Platform Update[edit]
On October 27, 2009, Microsoft released the Platform Update for Windows Server 2008 and Windows Vista. It backports several APIs and libraries introduced in Windows Server 2008 R2 and Windows 7 to Windows Server 2008 and Windows Vista, including the Ribbon API, DirectX 11, the XPS library, the Windows Automation API and the Portable Device Platform.[50] A supplemental update was released in 2011 to provide improvements and bug fixes.[51]
Internet Explorer 9[edit]
Windows Server 2008 shipped with Internet Explorer 7, the same version that shipped with Windows Vista. The last supported version of Internet Explorer for Windows Server 2008 is Internet Explorer 9, released in 2011. Internet Explorer 9 was continually updated with cumulative monthly update rollups until support for Internet Explorer 9 on Windows Server 2008 ended on January 14, 2020.[52] Extended Security Updates (ESU) continue until January 9, 2024 for Azure customers.
.NET Framework[edit]
The latest supported version of the .NET Framework officially is version 4.6, released on October 15, 2015.[53]
TLS 1.1 and 1.2 support[edit]
In July 2017, Microsoft released an update to add TLS 1.1 and 1.2 support to Windows Server 2008, however it is disabled by default after installing the update.[54]
SHA-2 signing support[edit]
Starting in March 2019, Microsoft began transitioning to exclusively signing Windows updates with the SHA-2 algorithm. As a result of this Microsoft released several updates throughout 2019 to add SHA-2 signing support to Windows Server 2008.[55]
Monthly update rollups[edit]
In June 2018, Microsoft announced that they would be moving Windows Server 2008 to a monthly update model beginning with updates released in September 2018[56] — two years after Microsoft switched the rest of their supported operating systems to that model.[57]
With the new update model, instead of updates being released as they became available, only two update packages were released on the second Tuesday of every month until Windows Server 2008 reached its end of life — one package containing security and quality updates, and a smaller package that contained only the security updates. Users could choose which package they wanted to install each month. Later in the month, another package would be released which was a preview of the next month’s security and quality update rollup.
Installing the preview rollup package released for Windows Server 2008 on March 19, 2019, or any later released rollup package, will update the operating system kernel’s build number from version 6.0.6002 to 6.0.6003. This change was made so Microsoft could continue to service the operating system while avoiding “version-related issues”.[58]
The last free security update rollup packages were released on January 14, 2020.[59]
Windows Server 2008 R2[edit]
A second release of Windows Server 2008 based on Windows 7, Windows Server 2008 R2, was released to manufacturing on July 22, 2009[60] and became generally available on October 22, 2009.[61] New features added in Windows Server 2008 R2 include new virtualization features, new Active Directory features, Internet Information Services 7.5 and support for up to 256 logical processors. It is the first server operating system by Microsoft to exclusively support 64-bit processors, while consumer-oriented versions of Windows maintained 32-bit support until Windows 11 in 2021.
A service pack for Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2, formally designed Service Pack 1, was released in February 2011.[62]
Support lifecycle[edit]
Support for the RTM version of Windows Server 2008 ended on July 12, 2011,[3][4] and users can no longer receive further security updates for the operating system. As a component of Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008 with Service Pack 2 continued to be supported with security updates, lasting until January 14, 2020, the same respective end-of-life dates of its successor, Windows Server 2008 R2 and Windows 7.
Microsoft planned to end support for Windows Server 2008 on January 12, 2016. However, in order to give customers more time to migrate to newer Windows versions, particularly in developing or emerging markets, Microsoft decided to extend support to January 14, 2020.[6][5][7]
Windows Server 2008 is eligible for the paid Extended Security Updates (ESU) program. The program allowed volume license customers to purchase, in yearly installments, security updates for the operating system for three additional years, until January 10, 2023. The program is also included with Microsoft Azure purchases, and Azure customers receive an extra year of support, until January 9, 2024. The licenses are paid for on a per-machine basis. If a user purchases an Extended Security Updates license in a later year of the program, they must pay for any previous years of Extended Security Updates as well. [6][63]
See also[edit]
- BlueKeep (security vulnerability)
- Comparison of Microsoft Windows versions
- Comparison of operating systems
- History of Microsoft Windows
- List of operating systems
- Microsoft Servers
Notes[edit]
- ^ Computers with more than 16 GB of RAM require more disk space for paging, hibernation, and dump files[40]
References[edit]
- ^ a b «As Windows Server 2008 RTMs, Customers and Partners Adopting with Help of New Tools, Training». News Center. Redmond, WA: Microsoft. 4 February 2008.
- ^ «Build number changing to 6003 in Windows Server 2008». support.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2021-03-26.
- ^ a b c d e «Microsoft Product Lifecycle». Support. Microsoft. Retrieved April 12, 2022.
- ^ a b c d «Install Windows Vista Service Pack 2 (SP2)». Support. Microsoft. Retrieved April 12, 2010.
- ^ a b c «Extended Security Updates for SQL Server and Windows Server 2008 and 2008 R2 | Microsoft». www.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2021-03-26.
- ^ a b c tfosmark. «Product Lifecycle FAQ — Extended Security Updates — Microsoft Lifecycle». docs.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2021-03-26.
- ^ a b «Announcing new options for SQL Server 2008 and Windows Server 2008 End of Support». azure.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2021-03-26.
- ^ Miller, Michael J. (2007-05-15). «Gates at WinHec 2007: Windows Server 2008, Rally, Home Server and More». Forward Thinking. Retrieved 2007-07-09.
- ^ Lowe, David (2007-04-25). «Beta 3 is Go!». Windows Server Division WebLog. Microsoft. Retrieved 2007-04-25.
- ^ Ralston, Ward (2007-09-24). «Windows Server 2008 Rc0 Released!». Windows Server Division WebLog. Microsoft. Retrieved 2007-09-24.
- ^ Nate Mook (10 July 2007). «New Windows Server, Visual Studio, SQL Server to Launch in February». BetaNews. Retrieved 2007-07-11.
- ^ «Dynamic Hardware Partitioning Architecture». MSDN. Retrieved 2007-07-23.
- ^ Archiveddocs. «Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services Overview». docs.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2020-01-15.
- ^ «Iain McDonald and Andrew Mason show off the new Windows Server OS». Channel 9. Microsoft. May 24, 2006. Retrieved 2008-11-01.
18:55
- ^ Hynes, Byron (November 2006). «The Future of Windows: Directory Services in Windows Server 2008». TechNet Magazine. Retrieved 2007-05-02.
- ^ «Deploying Windows Server 2008 Read Only Domain Controllers». docs.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2020-01-15.
- ^ «Q. What is a read-only domain controller (RODC)?». IT Pro. 2008-03-24. Retrieved 2020-01-15.
- ^ Ward, Keith (2007-10-08). «Top 10 Overlooked Windows Server 2008 Features, Part 2». Redmond Developer News. Archived from the original on 2009-08-04. Retrieved 2014-10-10.
- ^ «Failover Cluster Validation Error 80070005 on Windows Server 2008 R2 x64». Capitalhead. 2009-11-04. Retrieved 2013-10-28.
- ^ Zoeller, Jill (26 July 2007). «New in Windows Server 2008: Breaking the 5K Folder «Barrier» in Domain-Based Namespaces». The Storage Team at Microsoft — File Cabinet Blog. Microsoft. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- ^ «Failover Clustering with Windows Server 2008 including Cluster shared volumes». Microsoft. 2007-01-17. Retrieved 2007-07-09.
- ^ Loveall, John (2006). «Storage improvements in Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008» (PowerPoint). Microsoft Corporation. Retrieved 2007-07-09.
- ^ «Benchmarking Hyper-V on Windows Server 2008 R2 x64». 2010-01-20. Retrieved 2010-01-28.
- ^ «Microsoft Extends Virtualization Strategy, Outlines Product Road Map». Microsoft. 2006-05-22. Retrieved 2007-07-09.
- ^ «Server Manager». Windows Server 2008 Technical Library. Microsoft TechNet. 2007-06-25. Retrieved 2007-05-02.
- ^ «Unexpected error refreshing Server Manager-0x800706BE and 1601 on Window Server 2008 R2». Retrieved 2010-11-05.
- ^ «Multicasting OS deployments with Windows Server 2008». Kevinsul’s Management Blog. Microsoft. 29 August 2007. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- ^ a b «Removed technologies in Routing and Remote Access in Windows Server 2008». TechNet. Microsoft. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- ^ «Windows Server Backup Step-by-Step Guide for Windows Server 2008». TechNet. Microsoft. 17 January 2013. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- ^ «Exchange Server 2007 Service Pack 2 available in Q3 2009». The Exchange Team Blog. 11 May 2009. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- ^ Bilic, Nino (18 June 2008). «To Backup or Not to Backup? Yes! To backup!!». The Exchange Team Blog. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- ^ «IIS 7.0 Protocols». TechNet. Microsoft. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- ^ Heaton, Alex (2007-05-18). «On 64-bit and Windows Client». Windows Vista Team Blog. Retrieved 2007-07-09.
- ^
«Windows Server 2008 Product Editions». Microsoft. 2007-04-25. Retrieved 2007-07-09. - ^ «Windows Server 2008 Foundation: An Entry-Level Server Platform». Petri IT Knowledgebase. 2009-04-17. Retrieved 2014-01-08.
- ^ Ligman, Eric (7 November 2007). «Announcing Windows Essential Business Server». Microsoft Small Business Blog. Microsoft. Retrieved 2013-08-16.
- ^ «Windows Essential Business Server 2008». Technet.microsoft.com. 2010-12-31. Retrieved 2013-01-09.
- ^ «Windows Server 2008, Microsoft Lifecycle (Look at the Note below links)». docs.microsoft.com/en-us/lifecycle/products/.
- ^ a b «Windows Server 2008 System Requirements». 31 March 2008. Retrieved 2008-03-31.
- ^ a b c «Microsoft Windows Server 2008 System Requirements». Microsoft.com. Retrieved 2013-01-09.
- ^ «Microsoft Windows Server 2008 System Requirements». Microsoft. Retrieved 2013-01-09.
- ^ Savill, John (October 28, 2011). «Q: What are Windows Server 8’s Scalability Numbers?». Windows IT Pro. Penton Media. Retrieved November 5, 2011.
- ^ a b c d Seldam, Matthijs ten (October 13, 2012). «Windows Server — Sockets, Logical Processors, Symmetric Multi Threading». Matthijs’s blog. Microsoft. Retrieved October 14, 2012.
- ^ a b c d «Memory Limits for Windows and Windows Server Releases». MSDN. Microsoft. Retrieved 13 April 2014.
- ^ «Extend Windows Vista support by installing Windows Server 2008 updates — gHacks Tech News». gHacks Technology News. 2017-06-24. Retrieved 2021-06-30.
- ^ «Windows Vista Lifecycle Policy». Microsoft. Retrieved January 2, 2017.
- ^ Justin Graham (October 24, 2008). «Windows Server 2008 Service Pack 2 beta». Microsoft. Retrieved 2008-10-29.
- ^ «Tech ARP — ED#107 : Latest Details on Windows Vista Service Pack 2 Rev. 2.2». Archived from the original on 2009-02-12.
- ^ «Windows Vista Service Pack 2 Beta». blogs.windows.com. Archived from the original on 9 May 2013. Retrieved 12 January 2022.
- ^ «Announcing Final Releases of Platform Update for Windows Vista Technologies». 27 October 2009.
- ^ «Platform Update Supplement for Windows Vista and for Windows Server 2008».
- ^ «Cumulative security update for Internet Explorer: January 14, 2020». support.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2021-03-26.
- ^ «Microsoft .NET Framework 4.6 (Web Installer)». Microsoft.
- ^ «TLS 1.2 Support added to Windows Server 2008». Microsoft Security. 2017-07-20. Retrieved 2021-03-26.
- ^ «2019 SHA-2 Code Signing Support requirement for Windows and WSUS».
- ^ Mackie, Kurt; 06/13/2018. «Microsoft Switching Windows Server 2008 SP2 to Monthly Update Rollup Model — Redmondmag.com». Redmondmag. Retrieved 2021-03-26.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ «Community». forums.ivanti.com. Retrieved 2021-03-26.
- ^ «Build number changing to 6003 in Windows Server 2008».
- ^ «January 14, 2020—KB4534303 (Monthly Rollup)». support.microsoft.com. Retrieved 2021-03-26.
- ^ «Windows Server 2008 R2 Reaches the RTM Milestone! — Windows Server Blog — Site Home — TechNet Blogs». Blogs.technet.com. 2009-07-22. Retrieved 2013-01-09.
- ^ «When to expect Windows Server 2008 R2 RTM — Windows Server Blog — Site Home — TechNet Blogs». Blogs.technet.com. 2009-07-22. Retrieved 2013-01-09.
- ^ LeBlanc, Brandon (February 9, 2011). «Announcing Availability of Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1». Windows Experience Blog. Microsoft.
- ^ «Windows Server 2008 Product Lifecycle». Microsoft. January 14, 2020. Retrieved January 9, 2022.
18:55
Further reading[edit]
- «What’s New in Networking». TechNet. Microsoft. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- «Changes in Functionality from Windows Server 2003 with SP1 to Windows Server 2008». TechNet. Microsoft. 21 January 2008. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- «Description of the Microsoft server applications that are supported on Windows Server 2008». Support. Microsoft. 23 April 2012. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- «Windows Server 2008 System Requirements». TechNet. Microsoft. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- Henderson, Tom; Dvorak, Rand (21 February 2008). «Windows Server 2008: Faster, more manageable and secure, but still missing the virtual link». Network World. IDG. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- Radzikowski, Przemek (21 February 2010). «How to Find Build and Revision Number of Windows Vista or Windows Server 2008 Installed». Capitalhead. Capitalhead Pty. Ltd. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- Stanek, William (2008). Windows Server 2008 Inside Out. Microsoft Press. ISBN 978-0-7356-2438-2.
External links[edit]
- Windows Server Performance Team Blog
Задаваясь вопросом, какую версию Windows Server выбрать для своего бизнеса, пользователи, как правило, сталкиваются с большим разнообразием, и далеко не всегда понятно как выбрать наиболее подходящий вариант. У операционной системы Windows Server существуют не только разные версии, но и разные редакции. Давайте разберемcя в чем же отличия между ними.
Что такое версия Windows Server?
В 90-е годы, во времена Windows NT, каждая версия Windows Server имела уникальный номер. Например, у Windows NT были номера 3.1, 3.51 и 4.0. Но начиная с 2000 года Microsoft вместо номера начала добавлять после названия год запуска операционной системы: Microsoft Windows 2000, Windows Server 2003, 2008 (которая также имела версию R2), 2012 (также с R2), 2016 и 2019, и т.д.
Каждая новая версия Microsoft Windows Server представляет новые функциональные возможности. Например, виртуализация Hyper-V, Server Core и BitLocker были представлены в Windows Server 2008, контейнеры Windows и Nano Server были представлены в Windows Server 2016, а Windows Server 2019 принес с собой Windows Admin Center — новый способ удаленного администрирования серверной инфраструктуры, улучшения гиперконвергентной инфраструктуры и глубокую поддержку подсистемы Linux.
Что такое завершение поддержки?
Как говорится, ничто не вечно. И в определенный момент Microsoft прекращает выпуск патчей для устаревшего программного обеспечения. Дата, до которой Microsoft выпускает обновления для продукта, называется датой окончания поддержки. И после того, как эта дата пройдет, устаревшая версия ОС станет легкой мишенью для вредоносных программ, поскольку она больше не будет получать обновления безопасности и, следовательно, будет уязвима для новых эксплоитов.
Операционные системы Microsoft обычно поддерживаются не менее 10 лет. Например, популярный Windows Server 2003, выпущенный в апреле 2003 года, имел расширенную поддержку, которая закончились в 2015 году. Расширенная поддержка Windows Server 2008 R2 должна закончиться в январе 2020 года, а Windows Server 2012 R2 продолжит получать обновления по крайней мере до октября 2023 года. Версии Server 2016 и 2019 будут получать обновления по 2027 и 2029 год соответственно. Поэтому в целях безопасности организациям на самом деле следует использовать только свежие версии Windows Server.
Что такое редакция Windows Server?
Когда вы покупаете автомобиль, вам доступно, как минимум, несколько комплектаций одной и той же модели. Например, базовый экономичный вариант, роскошный вариант с кожаными сиденьями и люком на крыше, а также спортивный вариант с большими колесами и более мощным двигателем. Другими словами, каждая версия автомобиля имеет свою цену и набор функций для групп клиентов с разными бюджетами и потребностями.
То же самое касается выпусков Windows Server. Каждый вариант включает в себя функциональность, которая подходит для разных компаний, в зависимости от их размера и бюджета. Например, разные редакции могут поддерживать разное количество пользователей.
Различия между редакциями Windows Server 2012 R2
Чтобы помочь понять некоторые различия между редакциями ОС, давайте разберем их на примере Windows Server 2012 R2:
- Foundation — серверная ОС общего назначения, лучше всего подходящая для серверов нижнего уровня. ОС поддерживает только один процессор и 32 ГБ RAM. Редакция Foundation (недоступная в Windows Server 2016) ограничена 15 пользователями, что делает ее пригодной только для небольших офисов. Foundation доступен только через OEM-производителей, что обычно означает, что он предустановлен на компьютерах, которые вы покупаете у таких компаний, как Dell и HPE.
- Essentials (ранее SBS или Small Business Server) — это простое в настройке серверное решение, которое поддерживает до 25 пользователей и 50 устройств, что делает его подходящим для небольших офисов. Essentials поддерживает более мощное оборудование с объемом оперативной памяти до 64 ГБ и двумя процессорами. В отличие от других выпусков Windows Server, в Essentials предварительно настроены роли, такие как Active Directory, DNS, файловые службы, IIS и удаленный рабочий стол, что делает его идеальным для организаций с менее развитым ИТ-направлением или менее опытным ИТ-персоналом.
- Standard не ограничивает пользователей, но в отличие от Foundation и Essentials вам придется отдельно приобретать клиентские лицензии (CAL) в зависимости от того, сколько людей вам нужно поддерживать. Standard поддерживает максимум 4 ТБ RAM, а каждая приобретаемая лицензия распространяется на два процессора. Если вы заинтересованы в виртуализации, этот выпуск позволит вам использовать гипервизор Hyper-V для запуска до двух виртуальных экземпляров операционной системы (дополнительные виртуальные экземпляры Windows Server потребуют дополнительных затрат) на одном физическом оборудовании, что делает редакцию Standard подходящей для легкой виртуализированной среды.
- Datacenter — это самая лучшая и самая дорогая редакция Windows Server. Windows Server 2012 R2 Datacenter практически идентичен стандартной версии с одним большим исключением. С лицензией Datacenter вы можете запускать неограниченное количество виртуальных экземпляров с Windows Server в качестве гостевой ОС на одном двухпроцессорном компьютере. Эта небольшая разница имеет большое влияние, так как компании могут сэкономить, запустив десятки экземпляров ОС на одном сервере.
Различия между редакциями Windows Server 2016 и 2019
- Hyper-V — это бесплатная редакция Windows Server, предназначенная только для запуска роли гипервизора Hyper-V. Его цель — быть гипервизором для вашей виртуальной среды. У него нет графического интерфейса. По сути, это урезанная версия Server Core. Вы будете использовать sconfig.cmd, чтобы включить гипервизор, а затем управлять средой с помощью диспетчера Hyper-V (как часть RSAT) с рабочей станции Windows 10 в вашей сети. Рекомендуется использовать именно эту редакцию для вашего гипервизора, чтобы сохранить чистоту и простоту лицензирования.
- Essentials — идеально подходит как для малого и среднего бизнеса, так и для людей с потребностями в базовых функциях сервера. Графический интерфейс в значительной степени такой же, как и в Standard, за исключением мастера настройки Essentials.
Права на виртуализацию
Вам разрешено запускать один физический экземпляр Essentials в качестве хоста Hyper-V, на котором размещен один виртуальный экземпляр Essentials. Вам нужно удалить все роли, кроме роли Hyper-V, из физического экземпляра Essentials для обеспечения соответствия. Essentials также подходит для одного виртуального экземпляра на любом другом гипервизоре.
Модель лицензирования
На базе процессора. Клиентские лицензии не требуются, но вы ограничены 25 пользователями и 50 устройствами, подключающимися к серверу.
Аппаратные ограничения
Essentials ограничен до 64 ГБ RAM и 2 CPU на компьютере, на котором он установлен.
- Standard — идеально подходит для любой компании или для лиц, которым требуются расширенные функции, но при этом они не будут интенсивно виртуализироваться.
Права на виртуализацию
Разрешено запускать до двух виртуальных машин или контейнеров Hyper-V или один физический экземпляр со стандартной лицензией. Если вы используете роль Hyper-V только на физическом экземпляре, то можете использовать ее в качестве хоста Hyper-V, а затем разместить на этом хосте две виртуальные машины Hyper-V. Если вы хотите использовать несколько ролей на физическом экземпляре, вы не можете запускать виртуальную машину поверх с одной и той же лицензией.
Модель лицензирования
Основанная на ядре. Клиентские лицензии необходимы для каждого пользователя или устройства, которые подключаются косвенно или напрямую к серверу. Например, если вы используете сервер в качестве файлового сервера, вам потребуется лицензия CAL для каждой учетной записи пользователя или компьютера, которые обращаются к этому файловому серверу в сети.
Аппаратные ограничения
Стандарт ограничен максимум 24 ТБ оперативной памяти и 512 ядрами.
- Datacenter — идеально подходит для любой компании с высокой степенью виртуализации. Вы приобретаете лицензию в зависимости от того, сколько ядер есть у ваших хостов, на которых может жить любая виртуальная машина с версией Datacenter (запускаться или потенциально запускаться после Vmotion). Это лицензирование, на первый взгляд, кажется дорогим, но оно позволяет создавать неограниченное количество виртуальных машин, работающих под управлением Datacenter на хостах, которые вы учитывали. Если у вас небольшое количество хостов (а впоследствии и ядер) и большое количество потенциальных виртуальных машин, тогда эта лицензия не представляет никакой сложности.
Права на виртуализацию
Неограниченное количество виртуальных машин или контейнеров Hyper-V. Как было озвучено выше, вы будете покупать лицензии в зависимости от того, сколько ядер у вас на хостах. На этом этапе вы можете запустить на хостах столько угодно виртуальных машин, используя любые роли.
Модель лицензирования
Основанная на ядрах. Убедитесь, что вы случайно не выбрали этот выпуск при установке на физический сервер, на котором не размещаются виртуальные машины. Клиентские лицензии необходимы для каждого пользователя или устройства, которые подключаются косвенно или напрямую к серверам в вашей среде.
Различия в лицензировании Windows Server 2016 и новее
Хотя цены на Windows Server 2012 R2, 2016, 2019 одинаковы, если вы используете стандартную лицензию или лицензию Datacenter на Windows Server 2016 или новее, есть некоторые ключевые изменения, о которых вам необходимо знать. Прежде всего, в то время как лицензии Windows Server исторически продавались для каждого процессора / сокета, в Windows Server 2016 модель лицензирования переключалась на каждое ядро.
Таким образом, если у вас есть сервер, содержащий 2 процессора с 24 ядрами , в Windows Server 2012 вам нужно будет купить только одну лицензию Standard или Datacenter. В Windows Server 2016 вам придется покупать лицензии на все 24 ядра. Это становится довольно сложно, так как есть много правил, но главное — если у вас есть 16-ядерный сервер, затраты будут примерно такими же. Однако лицензирование ОС может быть более дорогим на серверах с более высокой плотностью ядра.
Несмотря на изменение лицензии на ядро, правила виртуализации остаются такими же в Windows Server 2016 и новее. После того, как вы лицензировали все свои ядра на сервере, со стандартной версией вы получаете 2 лицензии гостевой ОС Windows Server по сравнению с неограниченным количеством в версии Datacenter.
Кроме того, набор функций в Windows Server 2012 Standard и Datacenter был одинаковым. Но некоторые функции Windows Server 2016, например, такие, как Storage Spaces Direct или экранированные виртуальные машины, доступны только в выпуске Datacenter.
Сравнение параметров установки Windows Server 2016 и 2019
В редакциях Standard и Datacenter можно выбрать различные варианты установки. Эти варианты влияют на то, какие функции будут доступны после установки, такие как наличие графического интерфейса пользователя и набор сервисов. Присутствуют следующие варианты установки:
- Desktop Experience (с графическим интерфейсом);
- Core;
- Nano.
Desktop Experience — это вариант установки, с которым знакомо большинство людей. Этот параметр устанавливает большинство функций и ролей из коробки, включая интерфейс графического интерфейса рабочего стола. Вы получите Диспетчер серверов, который позволяет добавлять и удалять роли и компоненты. Преимущество в том, что система может быть проще в управлении для людей, привыкших использовать графический интерфейс. Недостаток в том, что у вас появляется больше обновлений, перезагрузок и открытых портов с которыми предстоит иметь дело.
Узнайте больше от Microsoft здесь.
В Server Core отсутствует графический интерфейс и несколько ролей, которые устанавливаются по умолчанию под опцией Desktop Experience. Серверное ядро имеет меньший объем занимаемого дискового пространства и, следовательно, меньшую область атаки из-за меньшей кодовой базы. Здесь также меньше обновлений, перезагрузок и открытых портов для работы. Это отличный вариант для серверов инфраструктуры, таких как контроллеры домена Active Directory и DNS-серверы.
В этой редакции отсутствуют инструменты специальных возможностей, встроенные инструменты настройки сервера и поддержка звука. Эта версия без излишеств. Не лишним будет убедиться, что вы знакомы с администрированием на основе командной строки.
Подробнее об этом можно прочитать на сайте Microsoft.
Nano
Начиная с Windows Server 2019, Nano доступен только как контейнеризированный образ операционной системы. Он предназначен для запуска в качестве контейнера внутри хоста контейнеров, такого как Server Core, упомянутого выше. Если вы опираетесь на контейнерные приложения, предназначенные для серверных ОС, то эту версию вы будете использовать для компиляции этих приложений.
Nano можно развернуть с помощью версий Standard или Datacenter, но у вас должна быть прикреплена Software Assurance к лицензированию хост-сервера. Узнать об этом подробнее можно на сайте Microsoft.
Различия между клиентскими и серверными версиями
Windows поставляется как в клиентских, так и в серверных версиях. Наданныймоментсуществуетшестьклиентскихверсий Windows 7: Windows 7 Home Basic, Windows 7 Home Premium, Windows 7 Professional, Windows 7 Ultimate, Windows 7 Enterprise и Windows 7 Starter.
Существуетсемьразличныхсерверныхверсий Windows Server 2008 R2: Windows Server 2008 R2 Foundation, Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard, Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise, Windows Server 2008 R2 Datacenter, Windows Web Server 2008 R2, Windows HPC Server 2008 R2 и Windows Server 2008 R2 for Itanium-Based Systems (выпуском Windows дляпроцессора Intel Itanium).
Кроме этого существуют клиентские «N»-версии, не включающие в себя WindowsMediaPlayer. И наконец, версии WindowsServer 2008 R2 Standard, Enterprise и Datacenter также включают выпуски «с Hyper-V», в которых присутствует Hyper-V.
Все эти версии отличаются друг от друга следующими показателями:
- числом поддерживаемых процессоров (в понятиях сокетов, а не ядер или потоков);
- объемом поддерживаемой физической памяти (фактически, самый большой физический адрес, доступный для оперативной памяти);
- количеством поддерживаемых параллельных сетевых подключений (Например, в клиентской версии к файловым и принтерным службам допускается максимально 10 параллельных подключений.);
- поддержкой Media Center;
- поддержкой Multi-Touch, Aero и Диспетчера рабочего стола (Desktop Compositing);
- поддержкой таких свойств, как BitLocker, VHD Booting, AppLocker, Windows XP Compatibility Mode и более ста других значений настраиваемой политики лицензирования;
- многоуровневыми службами, поставляемыми с версиями Windows Server и не поставляемыми с клиентскими версиями (например, службами каталогов и кластеризации).
Различия в поддержке памяти и процессоров для Windows 7 и Windows Server 2008 R2 показаны в табл. 2.2. Подробная сравнительная таблица различных версий Windows Server 2008 R2 представлена на веб-сайте www.microsoft.com/windowsserver2008/en/us/r2-compare-specs.aspx.
Содержание:
- 1 Различиямежду Windows 7 и Windows Server 2008 R2.
- 2 Значения параметра ProductType, имеющегося в реестре.
- 3 Эксперимент: Определение возможностей, разрешенных политикой лицензирования.
Различиямежду Windows 7 и Windows Server 2008 R2.
| Количество поддерживаемых Сокетов (32-разр. версия) |
Объем поддерживаемой физической памяти (32-разр. версия), Гбайт |
Количество поддерживаемых сокетов (64-разр. версия) |
Объем поддерживаемой физической памяти (Itanium- версии), Гбайт |
Объем поддерживаемой физической памяти (x64- версии), Гбайт |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Windows 7 Starter 1 | 1 | 2 | Нет | Нет | 2 |
| Windows 7 Home Basic |
1 | 4 | 1 | Нет | 8 |
| Windows 7 Home Premium |
1 | 4 | 1 | Нет | 16 |
| Windows 7 Professional |
2 | 4 | 2 | Нет | 192 |
| Windows 7 Enterprise | 2 | 4 | 2 | Нет | 192 |
| Windows 7 Ultimate | 2 | 4 | 2 | Нет | 192 |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 Foundation |
Нет | Нет | 1 | Нет | 8 |
| Windows Web Server 2008 R2 |
Нет | Нет | 4 | Нет | 32 |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard |
Нет | Нет | 4 | Нет | 32 |
| Windows HPC Server 2008 R2 |
Нет | Нет | 4 | Нет | 128 |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise |
Нет | Нет | 8 | Нет | 2048 |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 Datacenter |
Нет | Нет | 64 | Нет | 2048 |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 for Itanium-Based Systems |
Нет | Нет | 64 | 2048 | Нет |
Несмотря на то что операционная система Windows распространяется в виде нескольких клиентских и серверных пакетов поставки, все они используют один и тот же набор основных системных файлов, включая образ ядра, Ntoskrnl.exe (а в PAE-версии Ntkrnlpa.exe), HAL-библиотеки, драйверы устройств и базовые системные утилиты и DLL-библиотеки. Эти файлы идентичны для всех версий Windows 7 и WindowsServer 2008 R2.
Откуда, при наличии такого разнообразия версий Windows с одинаковым образом ядра, система знает, какую именно версию загружать? Для этого делается запрос значений реестра ProductType и ProductSuite, находящихся в разделе HKLMSYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlProductOptions. Значение ProductType используется для того, чтобы отличить клиентскую систему от серверной (любой разновидности).
Эти значения загружаются в реестр на основе рассмотренного ранее файла политики лицензирования. Допустимые значения перечислены в таблице. Это значение может быть запрошено из функции пользовательского режима GetVersionEx или из драйвера устройства с помощью вспомогательной функции режима ядра RtlGetVersion.
Значения параметра ProductType, имеющегося в реестре.
| Версия Windows | Значение ProductType |
|---|---|
| Windows client | WinNT |
| Windows server (контроллер домена) | LanmanNT |
| Windows server (только сервер) | ServerNT |
Другое значение реестра, ProductPolicy, содержит кэшированную копию данных, находящихся в файле tokens.dat, который устанавливает различия между версиями Windows и допускаемыми в них функциями.
Если пользовательским программам нужно определить, под какой версией Windows они работают, они могут вызвать Windows-функцию VerifyVersionInfo (см. документацию по SDK). Драйверы устройств могут вызвать функцию режима ядра RtlVerifyVersionInfo (см. документацию по WDK).
Но если основные файлы, по сути, одинаковы для клиентской и серверной версий, чем системы отличаются в работе? Вкратце, серверные системы по умолчанию оптимизированы под системную пропускную способность, позволяющую им выступать в роли высокопроизводительных серверов приложений, а клиентская версия (при наличии серверных возможностей) оптимизирована по времени отклика для интерактивного использования в качестве рабочего стола.
Например, на основе типа продукта по-другому принимается ряд решений по распределению ресурсов в процессе загрузки системы. В частности, это касается размеров и количества областей памяти, выделяемых программе для динамически размещаемых структур данных (или пулов), количества внутренних рабочих потоков системы и размера кэш-памяти системных данных. Также серверная и клиентская версии отличаются друг от друга решениями политики времени выполнения, способом учета диспетчером памяти потребностей в системной памяти и в памяти процессов.
Отличия между двумя семействами прослеживаются даже в некоторых деталях диспетчеризации потоков, составляющих их поведение по умолчанию. Все существенные функциональные различия между двумя продуктами выделены в соответствующих главах данной книги. Если не сделано специальных оговорок, то все, описанное в данной книге, относится как к клиентским, так и к серверным версиям.
Эксперимент: Определение возможностей, разрешенных политикой лицензирования.
Как уже ранее упоминалось, Windows поддерживает более ста различных функций, которые могут быть разрешены посредством механизма лицензирования программного обеспечения. Соответствующие настройки политики определяют различия не только между клиентской и серверной установками, но также и отличие каждой версии (или идентификатора товарной позиции — stock-keeping unit, SKU) операционной системы, в частности это касается поддержки такого средства, как BitLocker (доступного на серверных версиях Windows, а также на клиентских версиях Windows Ultimate и Enterprise). Для отображения значений политики, определенной для вашей машины, можно воспользоваться средством SlPolicy, доступным на веб-сайте Winsider Seminars & Solutions (www.winsiderss.com/tools/slpolicy.htm).
Настройки политики организованы по объектам, представляющим владельца модуля, к которому применяется политика. Запустив программу Slpolicy.exe с ключом –f, можно вывести список всех объектов, имеющихся в вашей системе:
C:>SlPolicy.exe -f
SlPolicy v1.05 — Show Software Licensing Policies
Copyright (C) 2008-2011 Winsider Seminars & Solutions Inc.
www.winsiderss.com
Software Licensing Facilities:
Kernel
Licensing and Activation
Core
DWM
SMB
IIS
.
.
.
Чтобы вывести значение политики в отношении любого объекта, можно после ключа добавить его имя. Например, чтобы просмотреть ограничения, касающиеся центральных процессоров, доступной памяти нужно указать объект ядра — Kernel. Для машины с запущенной системой Windows 7 Ultimate можно ожидать следующий вывод:
C:>SlPolicy.exe -f Kernel
SlPolicy v1.05 — Show Software Licensing Policies
Copyright (C) 2008-2011 Winsider Seminars & Solutions Inc.
www.winsiderss.com
Kernel
——
Processor Limit: 2
Maximum Memory Allowed (x86): 4096
Maximum Memory Allowed (x64): 196608
Maximum Memory Allowed (IA64): 196608
Maximum Physical Page: 4096
Addition of Physical Memory Allowed: No
Addition of Physical Memory Allowed, if virtualized: Yes
Product Information: 1
Dynamic Partitioning Supported: No
Virtual Dynamic Partitioning Supported: No
Memory Mirroring Supported: No
Native VHD Boot Supported: Yes
Bad Memory List Persistance Supported: No
Number of MUI Languages Allowed: 1000
List of Allowed Languages: EMPTY
List of Disallowed Languages: EMPTY
MUI Language SKU:
Expiration Date: 0