Table of Contents
- Applies to
- Introduction
- Download locations for RSAT
- RSAT for Windows 10 Platform and Tools Support Matrix
- RSAT for Windows 8 and Windows 8.1 Platform and Tools Support Matrix
- Related topics
- Related forum threads
Applies to
All systems
Windows 10, Windows 8.1, Windows 8, Windows 7, Windows Vista, Windows Server Technical Preview, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2012, Windows Server 2008, and Windows Server 2008 R2
Introduction
Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT) enables IT administrators to remotely manage roles and features in Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2012, Windows Server 2008 or Windows Server 2008 R2 from a computer that is running Windows 10, Windows 8.1,
Windows 8, Windows Vista, or Windows 7.
RSAT cannot be installed on computers that are running Home, Standard, or Education editions of Windows. You can only install RSAT on Professional or Enterprise editions of the Windows client operating system. Unless the download page specifically states
that RSAT applies to a Beta or Preview or other prerelease version of Windows, you must be running a full (RTM) release of the Windows operating system to install and use RSAT. Although some users have found ways of manually cracking or hacking the RSAT MSU
to install RSAT on unsupported releases or editions of Windows, this is a violation of the Windows end-user license agreement.
This is similar to installing the adminpak.msi on Windows 2000 or Windows XP client computers. There is one major difference: in Windows Vista and Windows 7, the tools are not automatically available after
RSAT is downloaded and installed . You must enable the tools that you want to use by using the Control Panel. To do so, click
Start, click Control Panel, click Programs and then click
Turn Windows features on or off (as shown in the following figure).
However, in the RSAT releases for Windows 10, Windows 8.1, and Windows 8, tools are once again all enabled by default. You can open
Turn Windows on or off to disable tools that you don’t want to use. In RSAT for Windows 10, Windows 8.1, and Windows 8, GUI-based tools are accessed from within the Server Manager console, on the
Tools menu.
For RSAT that runs on Windows Vista and Windows 7, after running the downloaded installation package, you must enable the tools for the roles and features that you want to manage (as shown in the following figure).
You don’t need to do this for RSAT for Windows 8 or later.
If you need to install management tools in Windows Server 2008, Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows Server 2012, Windows Server 2012 R2, or Windows Server 2016 Technical Preview for specific roles or features running on remote servers, there’s no need to install
additional software. Open the Add Features Wizard in Windows Server 2008 or Windows Server 2008 R2, or the
Add Roles and Features Wizard in Windows Server 2012 and later releases, and on the
Select Features page, expand Remote Server Administration Tools and select the tools that you want to install. Complete the wizard to install your management tools. See the following figure.
Download locations for RSAT
- Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows 10
- Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT) for Windows 8.1
- Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT) for Windows 8Remote
Server Administration Tools (RSAT) for Windows 7 with SP1 (both x86 and x64) - Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT) for Windows Vista 32-bit (x86)
- Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT) for Windows Vista 64-bit (x64)
RSAT for Windows 10 Platform and Tools Support Matrix
| Remote Server Administration Tools Technology | Description | Manages technology on Windows Server 2012 and Windows Server 2012 R2 | Manages technology on Windows Server 2016 Technical Preview, WS12 R2, and WS12 |
| Active Directory Certificate Services Tools | Active Directory Certificate Services Tools includes the Certification Authority, Certificate Templates, Enterprise PKI, and Online Responder Management snap-ins. | √ | √ |
| Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) Tools and Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services (AD LDS) Tools |
Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) and Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services (AD LDS) Tools includes Active Directory Administrative Center; Active Directory Domains and Trusts; Active Directory Sites and Services; Active Directory Users |
√ |
|
|
Best Practices Analyzer |
Best Practices Analyzer cmdlets for Windows PowerShell |
√ |
√ |
|
BitLocker Drive Encryption Administration Utilities |
Manage-bde; Windows PowerShell cmdlets for BitLocker; BitLocker Recovery Password Viewer for Active Directory |
√ |
√ |
|
DHCP Server Tools |
DHCP Server Tools includes the DHCP Management Console, the DHCP Server cmdlet module for Windows Powershell, and the |
√ |
√ |
|
DirectAccess, Routing and Remote Access |
Routing and Remote Access management console; Connection Manager Administration Kit console; Remote Access provider for Windows PowerShell; Web Application Proxy |
√ |
√ |
|
DNS Server Tools |
DNS Server Tools include the DNS Manager snap-in, the DNS module for Windows PowerShell, and the |
√ |
√ |
|
Failover Clustering Tools |
Failover Clustering Tools include Failover Cluster Manager, Failover Clusters (Windows PowerShell Cmdlets), MSClus, Cluster.exe, Cluster-Aware Updating management console, Cluster-Aware Updating cmdlets for Windows PowerShell |
√ |
√ GUI tools support Windows Server 2016 Technical Preview and Windows Server 2012 R2. Only PowerShell tools work on Windows Server 2012. |
|
File Services Tools |
File Services Tools include the following: Share and Storage Management Tools; Distributed File System Tools; File Server Resource Manager Tools; Services for NFS Administration Tools; iSCSI management cmdlets for Windows PowerShell; Work Folders Management |
√ |
√ The Share and Storage Management snap-in is deprecated after the release of Windows Server 2016. Storage Replica is new in Windows Server 2016 Technical Preview, and won’t work on WS12 R2 and WS12. |
|
Group Policy Management Tools |
Group Policy Management Tools include Group Policy Management Console, Group Policy Management Editor, and Group Policy Starter GPO Editor. |
√ |
√ Group Policy has some new features in Windows Server 2016 Technical Preview which are not available on older operating systems. |
|
Hyper-V Tools |
Hyper-V Tools include the Hyper-V Manager snap-in and the Virtual Machine Connection remote access tool. |
Hyper-V tools are not part of Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows 10. These tools are available as part of Windows 10; there is no need to install RSAT to use them. The Hyper-V Manager console for Windows Server 2016 Technical Preview doesn’t |
Hyper-V in Windows 10 can manage Hyper-V in Windows Server 2012 R2 and Windows Server 2012. |
|
IP Address Management (IPAM) Management Tools |
IP Address Management client console |
√ IPAM tools in Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows 10 cannot be used to manage IPAM running on Windows Server 2012 R2 and Windows Server 2012. |
√ IPAM tools in Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows 10 cannot be used to manage IPAM running on Windows Server 2012 R2 and Windows Server 2012. |
|
Network Adapter Teaming, or NIC Teaming |
NIC Teaming management console |
√ |
√ |
|
Network Controller |
Network Controller PowerShell module |
Not available |
√ |
|
Network Load Balancing Tools |
Network Load Balancing Tools include the Network Load Balancing Manager; Network Load Balancing Windows PowerShell Cmdlets; and the NLB.exe and WLBS.exe command line tools. |
√ |
√ |
|
Remote Desktop Services Tools |
Remote Desktop Services Tools include the Remote Desktop snap-ins; RD Gateway Manager, tsgateway.msc; RD Licensing Manager, licmgr.exe; RD Licensing Diagnoser, lsdiag.msc. Use Server Manager for administration of all other RDS role services except RD Gateway and RD Licensing. |
√ |
√ |
|
Server for NIS Tools |
Server for NIS Tools includes an extension to the Active Directory Users and Computers snap-in, and the Ypclear.exe command-line tool |
These tools are not available in RSAT for Windows 10 and later releases. |
|
|
Server Manager |
Server Manager includes the Server Manager console. Remote management with Server Manager is available in Windows Server 2016 Technical Preview, Windows Server 2012 R2, and Windows Server 2012. |
√ |
√ |
|
SMTP Server Tools |
SMTP Server Tools include the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) snap-in. |
These tools are not available in RSAT for Windows 8 and later releases. |
|
|
Storage Explorer Tools |
Storage Explorer Tools include the Storage Explorer snap-in. |
These tools are not available in RSAT for Windows 8 and later releases. |
|
|
Storage Manager for Storage Area Networks (SANs) Tools |
Storage Manager for SANs Tools include the Storage Manager for SANs snap-in and the |
These tools are not available in RSAT for Windows 8 and later releases. |
|
|
Volume Activation |
Manage Volume Activation, vmw.exe |
√ |
√ |
|
Windows System Resource Manager Tools |
Windows System Resource Manager Tools include the Windows System Resource Manager snap-in and the |
√ WSRM has been deprecated in Windows Server 2012 R2, and tools for managing WSRM are not available in Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows 8.1. and later releases of RSAT. |
|
|
Windows Server Update Services Tools |
Windows Server Update Services Tools include the Windows Server Update Services snap-in, WSUS.msc, and PowerShell cmdlets. |
√ |
√ |
RSAT for Windows 8 and Windows 8.1 Platform and Tools Support Matrix
| Remote Server Administration Tools technology | Description | Manages technology on Windows Server 2008 | Manages technology on Windows Server 2012 and Windows Server 2012 R2 |
| Active Directory Certificate Services Tools | Active Directory Certificate Services Tools includes the Certification Authority, Certificate Templates, Enterprise PKI, and Online Responder Management snap-ins. | √ | √ |
| Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) Tools and Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services (AD LDS) Tools |
Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) and Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services (AD LDS) Tools includes Active Directory Administrative Center; Active Directory Domains and Trusts; Active Directory Sites and Services; Active Directory Users GPFixup.exe; KSetup.exe; KtPass.exe; NlTest.exe; NSLookup.exe; W32tm.exe. — Server for NIS Tools includes an extension to the Active Directory Users and Computers snap-in, and the |
√, Windows PowerShell and ADAC remote management require the Active Directory Web Service download package. | √
Identity Management for UNIX, which includes Server for NIS, is deprecated in Windows Server 2012 R2, and tools for managing these features are no longer available in RSAT for Windows 8.1. |
| Best Practices Analyzer | Best Practices Analyzer cmdlets for Windows PowerShell | Can run on WS08 R2 when the Windows Management Framework 3.0 package is installed on WS08 R2. No BPA models are available for WS08. | √ |
| BitLocker Drive Encryption Administration Utilities | Manage-bde; Windows PowerShell cmdlets for BitLocker; BitLocker Recovery Password Viewer for Active Directory |
Not available | √ |
| Cluster-Aware Updating | Cluster-Aware Updating management console, Cluster-Aware Updating cmdlets for Windows PowerShell | Not available | √ |
| DHCP Server Tools | DHCP Server Tools includes the DHCP Management Console, the DHCP Server cmdlet module for Windows Powershell, and the Netsh command-line tool. |
√
Windows PowerShell module does not run on WS08 and WS08 R2 |
√ |
| DirectAccess, Routing and Remote Access | Routing and Remote Access management console; Connection Manager Administration Kit console; Remote Access provider for Windows PowerShell | Not available | √ |
| DNS Server Tools | DNS Server Tools include the DNS Manager snap-in, the DNS module for Windows PowerShell and the Ddnscmd.exe command-line tool. |
√ | √ |
| Failover Clustering Tools | Failover Clustering Tools include Failover Cluster Manager, Failover Clusters (Windows PowerShell Cmdlets), MSClus, Cluster.exe | √
Failover Cluster Manager runs only on Windows Server 2012. The Windows PowerShell cmdlet set supports Windows Server 2012 and WS08R2. MSClus and Cluster.EXE support Windows Server 2012, WS08R2 and WS08. |
√ |
| File and Storage Services Tools | File Services Tools include the following: Share and Storage Management Tools; Distributed File System Tools; File Server Resource Manager Tools; Services for NFS Administration Tools; iSCSI management cmdlets for Windows PowerShell
|
√
iSCSI cmdlets for Windows PowerShell can be used to manage iSCSI on Windows Server 2012 only. |
√ |
| Group Policy Management Tools | Group Policy Management Tools include Group Policy Management Console, Group Policy Management Editor, and Group Policy Starter GPO Editor. | √ | √ |
| Hyper-V Tools | Hyper-V Tools include the Hyper-V Manager snap-in and the Virtual Machine Connection remote access tool. | Hyper-V Manager console doesn’t support managing Hyper-V servers running Server 2008 or Server 2008 R2. | Hyper-V tools are not part of Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows 8 or Windows 8.1. These tools are available as part of Windows 8 and Windows 8.1; there is no need to install RSAT to use them. The Hyper-V Manager console for Windows Server 2012 doesn’t support managing Hyper-V servers running Server 2008 or Server 2008 R2. Managing Hyper-V running on Windows Server 2012 by using Windows PowerShell tools available in RSAT for Windows 8.1 works, but is not officially supported. Likewise, using RSAT for Windows 8 to manage Hyper-V on Windows Server 2012 R2 works, but is not officially supported. |
| IP Address Management (IPAM) Management Tools | IP Address Management client console | Not available | √
IPAM tools in Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows 8.1 cannot be used to manage IPAM running on Windows Server 2012. |
| Network Adapter Teaming, or NIC Teaming | Network Adapter Teaming management console | Not available | √ |
| Network Load Balancing Tools | Network Load Balancing Tools include the Network Load Balancing Manager; Network Load Balancing Windows PowerShell Cmdlets; and the NLB.exe and WLBS.exe Command Line Tools. | √ | √ |
| Remote Desktop Services Tools | Remote Desktop Services Tools include the Remote Desktop snap-ins; RD Gateway Manager, tsgateway.msc; RD Licensing Manager, licmgr.exe; RD Licensing Diagnoser, lsdiag.msc.
Server Manager should be used for administration of all other RDS role services except RD Gateway and RD Licensing. |
√ | √ |
| Server Manager | Server Manager includes the Server Manager console.
Remote management with Server Manager is available in Windows Server 2008 R2 and Windows Server 2012. |
Available for WS08 R2 and forward, not WS08 | √ |
| SMTP Server Tools | SMTP Server Tools include the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) snap-in. | √ | The tools are not available in RSAT for Windows 8 and later |
| Storage Explorer Tools | Storage Explorer Tools include the Storage Explorer snap-in. | √ | The tools are not available in RSAT for Windows 8 and later |
| Storage Manager for Storage Area Networks (SANs) Tools | Storage Manager for SANs Tools include the Storage Manager for SANs snap-in and the Provisionstorage.exe command-line tool. |
√ | The tools are not available in RSAT for Windows 8 and later |
| Volume Activation | Manage Volume Activation, vmw.exe | The tool can be used to manage volume activation on remote servers running WS08 or WS08 R2, but cannot run on those operating systems. | √ |
| Windows System Resource Manager Tools | Windows System Resource Manager Tools include the Windows System Resource Manager snap-in and the Wsrmc.exe command-line tool. |
√ | √
WSRM has been deprecated in Windows Server 2012 R2, and thus tools for managing WSRM are not available in Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows 8.1. |
| Windows Server Update Services Tools | Windows Server Update Services Tools include the Windows Server Update Services snap-in, WSUS.msc |
√ | √ |
Reference:
KB 858830
Related topics
- Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows 10 Help
- Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows 8 and 8.1 Help
- Description of Windows Server 2008 Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows Vista Service Pack 1
- RSAT Released for Windows
7 - Remotely
Managing your Server Core Using RSAT - Screencast:
How to Install and Enable Microsoft RSAT (Remote Server Administration Tools) for Windows Vista - Using
MMC Snap-ins and RSAT
Related forum threads
- Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT)
- New
Version of RSAT for Windows 7 RTM? - RSAT
| title | description | ms.topic | ms.assetid | ms.author | author | manager | ms.date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Remote Server Administration Tools |
Top level topic for Remote Server Administration Tools |
how-to |
d54a1f5e-af68-497e-99be-97775769a7a7 |
jgerend |
JasonGerend |
mtillman |
09/09/2020 |
Remote Server Administration Tools
Applies to: Windows Server 2022, Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2012
This topic supports Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows 10.
[!IMPORTANT]
Starting with Windows 10 October 2018 Update, RSAT is included as a set of Features on Demand in Windows 10 itself. See When to use which RSAT version below for installation instructions.
RSAT lets IT admins manage Windows Server roles and features from a Windows 10 PC.
Remote Server Administration Tools includes Server Manager, Microsoft Management Console (mmc) snap-ins, consoles, Windows PowerShell cmdlets and providers, and some command-line tools for managing roles and features that run on Windows Server.
Remote Server Administration Tools includes Windows PowerShell cmdlet modules that can be used to manage roles and features that are running on Remote servers. Although Windows PowerShell remote management is enabled by default on Windows Server 2016, it is not enabled by default on Windows 10. To run cmdlets that are part of Remote Server Administration Tools against a Remote server, run Enable-PSremoting in a Windows PowerShell session that has been opened with elevated user rights (that is, Run as Administrator) on your Windows client computer after installing Remote Server Administration Tools.
Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows 10
Use Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows 10 to manage specific technologies on computers that are running Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2012 R2, and in limited cases, Windows Server 2012 , or Windows Server 2008 R2 .
Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows 10 includes support for remote management of computers that are running the Server Core installation option or the Minimal Server Interface configuration of Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2012 R2 , and in limited cases, the Server Core installation options of Windows Server 2012. However, Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows 10 cannot be installed on any versions of the Windows Server operating system.
Tools available in this release
For a list of the tools available in Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows 10, see the table in Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT) for Windows operating systems.
System requirements
Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows 10 can be installed only on computers that are running Windows 10. Remote Server Administration Tools cannot be installed on computers that are running Windows RT 8.1, or other system-on-chip devices.
Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows 10 runs on both x86-based and x64-based editions of Windows 10.
[!IMPORTANT]
Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows 10 should not be installed on a computer that is running administration tools packs for Windows 8.1, Windows 8, Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows Server 2008, Windows Server 2003 or Windows 2000 Server. Remove all older versions of Administration Tools Pack or Remote Server Administration Tools, including earlier prerelease versions, and releases of the tools for different languages or locales from the computer before you install Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows 10.
To use this release of Server Manager to access and manage Remote servers that are running Windows Server 2012 R2 , Windows Server 2012 , or Windows Server 2008 R2 , you must install several updates to make the older Windows Server operating systems manageable by using Server Manager. For detailed information about how to prepare Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2012, and Windows Server 2008 R2 for management by using Server Manager in Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows 10, see Manage Multiple, Remote Servers with Server Manager.
Windows PowerShell and Server Manager remote management must be enabled on remote servers to manage them by using tools that are part of Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows 10. Remote management is enabled by default on servers that are running Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2012 R2, and Windows Server 2012. For more information about how to enable remote management if it has been disabled, see Manage multiple, remote servers with Server Manager.
Install, uninstall and turn off/on RSAT tools
Use Features on Demand (FoD) to install specific RSAT tools on Windows 10 October 2018 Update, or later.
Starting with Windows 10 October 2018 Update, RSAT is included as a set of Features on Demand right from Windows 10. Now, instead of downloading an RSAT package you can just go to Manage optional features in Settings and click Add a feature to see the list of available RSAT tools. Select and install the specific RSAT tools you need. To see installation progress, click the Back button to view status on the Manage optional features page.
See the list of RSAT tools available via Features on Demand. In addition to installing via the graphical Settings app, you can also install specific RSAT tools via command line or automation using DISM /Add-Capability.
One benefit of Features on Demand is that installed features persist across Windows 10 version upgrades.
To uninstall specific RSAT tools on Windows 10 October 2018 Update or later (after installing with FoD)
On Windows 10, open the Settings app, go to Manage optional features, select and uninstall the specific RSAT tools you wish to remove. Note that in some cases, you will need to manually uninstall dependencies. Specifically, if RSAT tool A is needed by RSAT tool B, then choosing to uninstall RSAT tool A will fail if RSAT tool B is still installed. In this case, uninstall RSAT tool B first, and then uninstall RSAT tool A. Also note that in some cases, uninstalling an RSAT tool may appear to succeed even though the tool is still installed. In this case, restarting the PC will complete the removal of the tool.
See the list of RSAT tools including dependencies. In addition to uninstalling via the graphical Settings app, you can also uninstall specific RSAT tools via command line or automation using DISM /Remove-Capability.
When to use which RSAT version
If you have a version of Windows 10 prior to the October 2018 Update (1809), you will not be able to use Features on Demand. You will need to download and install the RSAT package.
-
Install RSAT FODs directly from Windows 10, as outlined above:
When installing on Windows 10 October 2018 Update (1809) or later, for managing Windows Server 2019 or previous versions. -
Download and install WS_1803 RSAT package, as outlined below:
When installing on Windows 10 April 2018 Update (1803) or earlier, for managing Windows Server, version 1803 or Windows Server, version 1709. -
Download and install WS2016 RSAT package, as outlined below:
When installing on Windows 10 April 2018 Update (1803) or earlier, for managing Windows Server 2016 or previous versions.
Download the RSAT package to install Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows 10
-
Download the Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows 10 package from the Microsoft Download Center. You can either run the installer from the Download Center website, or save the download package to a local computer or share.
[!IMPORTANT]
You can only install Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows 10 on computers that are running Windows 10. Remote Server Administration Tools cannot be installed on computers that are running Windows RT 8.1 or other system-on-chip devices. -
If you save the download package to a local computer or share, double-click the installer program, WindowsTH-KB2693643-x64.msu or WindowsTH-KB2693643-x86.msu, depending on the architecture of the computer on which you want to install the tools.
-
When you are prompted by the Windows Update Standalone Installer dialog box to install the update, click Yes.
-
Read and accept the license terms. Click I accept.
-
Installation requires a few minutes to finish.
To uninstall Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows 10 after RSAT package install)
-
On the desktop, click Start, click All Apps, click Windows System, and then click Control Panel.
-
Under Programs, click Uninstall a program.
-
Click View installed updates.
-
Right-click Update for Microsoft Windows (KB2693643), and then click Uninstall.
-
When you are asked if you are sure you want to uninstall the update, click Yes.
STo turn off specific tools (after RSAT package install)
-
On the desktop, click Start, click All Apps, click Windows System, and then click Control Panel.
-
Click Programs, and then in Programs and Features click Turn Windows features on or off.
-
In the Windows Features dialog box, expand Remote Server Administration Tools, and then expand either Role Administration Tools or Feature Administration Tools.
-
Clear the check boxes for any tools that you want to turn off.
[!NOTE]
If you turn off Server Manager, the computer must be restarted, and tools that were accessible from the Tools menu of Server Manager must be opened from the Administrative Tools folder. -
When you are finished turning off tools that you do not want to use, click OK.
Run Remote Server Administration Tools
[!NOTE]
After installing Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows 10, the Administrative Tools folder is displayed on the Start menu. You can access the tools from the following locations.
- The Tools menu in the Server Manager console.
- Control PanelSystem and SecurityAdministrative Tools.
- A shortcut saved to the desktop from the Administrative Tools folder (to do this, right click the Control PanelSystem and SecurityAdministrative Tools link, and then click Create Shortcut).
The tools installed as part of Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows 10 cannot be used to manage the local client computer. Regardless of the tool you run, you must specify a remote server, or multiple remote servers, on which to run the tool. Because most tools are integrated with Server Manager, you add remote servers that you want to manage to the Server Manager server pool before managing the server by using the tools in the Tools menu. For more information about how to add servers to your server pool, and create custom groups of servers, see Add servers to Server Manager and Create and manage server groups.
In Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows 10, all GUI-based server management tools, such as mmc snap-ins and dialog boxes, are accessed from the Tools menu of the Server Manager console. Although the computer that runs Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows 10 runs a client-based operating system, after installing the tools, Server Manager, included with Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows 10, opens automatically by default on the client computer. Note that there is no Local Server page in the Server Manager console that runs on a client computer.
To start Server Manager on a client computer
-
On the Start menu, click All Apps, and then click Administrative Tools.
-
In the Administrative Tools folder, click Server Manager.
Although they are not listed in the Server Manager console Tools menu, Windows PowerShell cmdlets and Command prompt management tools are also installed for roles and features as part of Remote Server Administration Tools. For example, if you open a Windows PowerShell session with elevated user rights (Run as Administrator), and run the cmdlet Get-Command -Module RDManagement, the results include a list of remote Desktop Services cmdlets that are now available to run on the local computer after installing Remote Server Administration Tools, as long as the cmdlets are targeted at a remote server that is running all or part of the remote Desktop Services role.
To start Windows PowerShell with elevated user rights (Run as administrator)
-
On the Start menu, click All Apps, click Windows System, and then click Windows PowerShell.
-
To run Windows PowerShell as an administrator from the desktop, right-click the Windows PowerShell shortcut, and then click Run as Administrator.
[!NOTE]
You can also start a Windows PowerShell session that is targeted at a specific server by right-clicking a managed server in a role or group page in Server Manager, and then clicking Windows PowerShell.
Known issues
Issue: RSAT FOD installation fails with error code 0x800f0954
Impact: RSAT FODs on Windows 10 1809 (October 2018 Update) in WSUS/Configuration Manager environments
Resolution: To install FODs on a domain-joined PC which receives updates through WSUS or Configuration Manager, you will need to change a Group Policy setting to enable downloading FODs directly from Windows Update or a local share. For more details and instructions on how to change that setting, see How to make Features on Demand and language packs available when you’re using WSUS/SCCM.
Issue: RSAT FOD installation via Settings app does not show status/progress
Impact: RSAT FODs on Windows 10 1809 (October 2018 Update)
Resolution: To see installation progress, click the Back button to view status on the Manage optional features page.
Issue: RSAT FOD uninstallation via Settings app may fail
Impact: RSAT FODs on Windows 10 1809 (October 2018 Update)
Resolution: In some cases, uninstallation failures are due to the need to manually uninstall dependencies. Specifically, if RSAT tool A is needed by RSAT tool B, then choosing to uninstall RSAT tool A will fail if RSAT tool B is still installed. In this case, uninstall RSAT tool B first, and then uninstall RSAT tool A. See the list of RSAT FODs including dependencies.
Issue: RSAT FOD uninstallation appears to succeed, but the tool is still installed
Impact: RSAT FODs on Windows 10 1809 (October 2018 Update)
Resolution: Restarting the PC will complete the removal of the tool.
Issue: RSAT missing after Windows 10 upgrade
Impact: Any RSAT .MSU package installation (prior to RSAT FODs) not automatically reinstalled
Resolution: An RSAT installation cannot be persisted across OS upgrades due to the RSAT .MSU being delivered as a Windows Update package. Please install RSAT again after upgrading Windows 10. Note that this limitation is one of the reasons why we’ve moved to FODs starting with Windows 10 1809. RSAT FODs which are installed will persist across future Windows 10 version upgrades.
See Also
- Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows 10
- Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT) for Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, Windows Server 2008, Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows Server 2012, and Windows Server 2012 R2
‘
Для управления сервером под управлением Windows Server 2012 R2 с операционной системы Windows 8.1 необходимо установить Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT).
RSAT для Windows 8.1 выпущен в двух редакциях, для x86 и x64 разрядной версии операционной системы:
- Windows8.1-KB2693643-x86 для Windows 8.1 x64
- Windows8.1-KB2693643-x64 для Windows 8.1 x32
Скачать можно на странице загрузок: http://www.microsoft.com/ru-ru/download/details.aspx?id=39296
Данный пакет подходит только для Windows 8.1 и установить его на другую операционную систему не получится. Отмечу, что некоторые консоли и оснастки подходят для управления Windows Server 2008 R2/ 2008.
Для установки, переходим на указанную выше ссылку и скачиваем пакет подходящей вашей системе
Запускаем скачанный пакет
Принимаем лицензионное соглашение
В отличии от предыдущих систем, в windows 8.1 не надо дополнительно заходить в «программы и компоненты» и устанавливать необходимое. Если раньше надо было выбрать что установить, то теперь выбираем что отключить )))
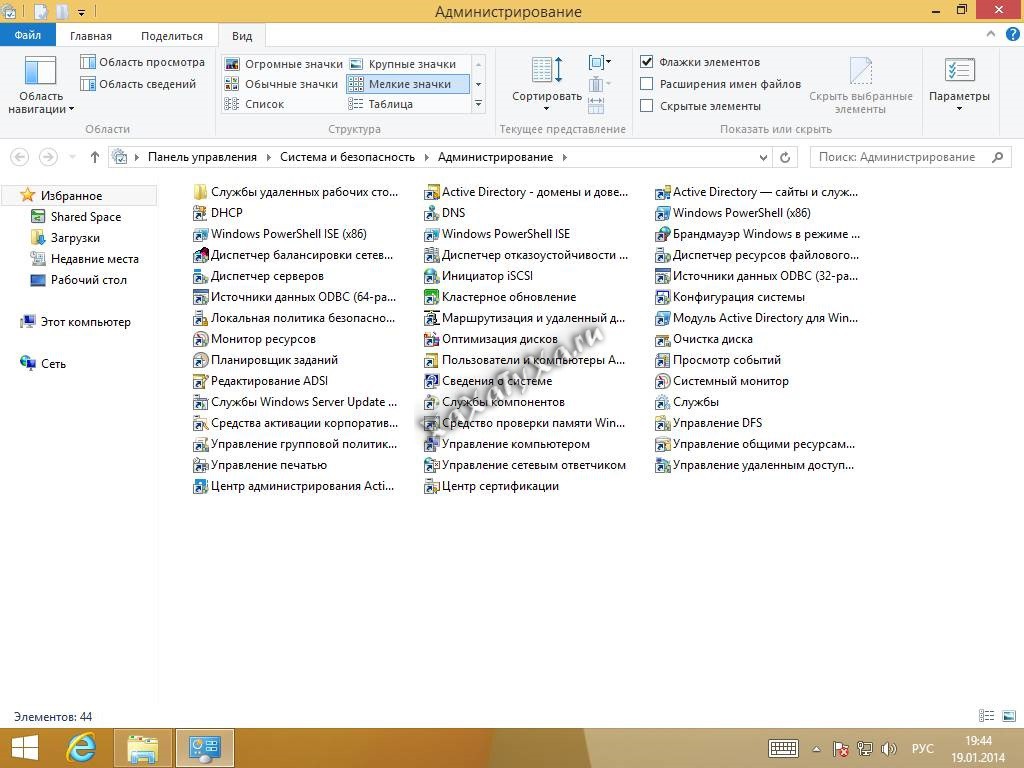
Нажимаем «ПУСК» и набираем в поиске «Администрирование»
Откроется окно со всеми утилитами.
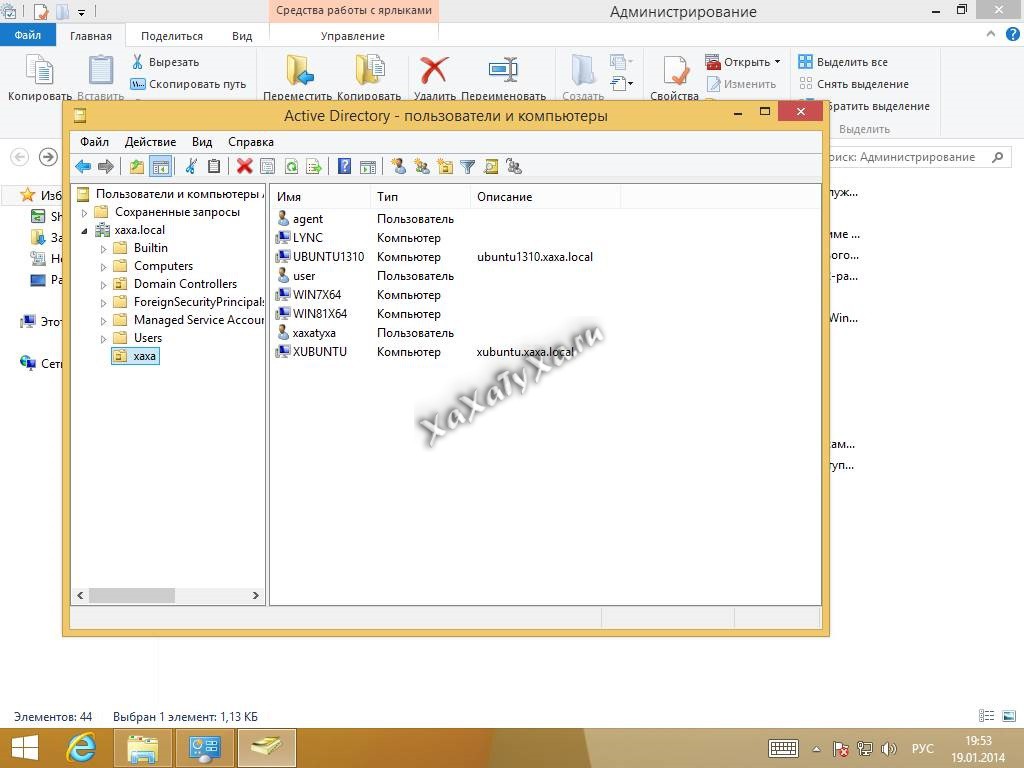
Для примера запустим консоль управления «Пользователи и компьютеры Active Directory»
Ссылки и документация по RSAT для вкуривания:
- http://www.microsoft.com/ru-ru/download/details.aspx?id=39296
- http://www.microsoft.com/ru-ru/download/details.aspx?id=28972
- http://www.microsoft.com/ru-ru/download/details.aspx?id=7887
- http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mTm-VMPNF3A
Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT) Background
The Remote Server Management Tools have been with Windows Server since Windows Server 2000. These tools enable the remote management of Server Roles and Features and were later released as part of a separate installation package called Remote Server Administration Tools that could be installed on the server and client/professional versions of the Windows operation system.
The following tools are included as part of the installation:
- SMTP Server Tools
- Hyper-V Management Tools
- Hyper-V Module for Windows PowerShell
- Hyper-V GUI Management Tools
- Windows Server Update Services Tools
- API and PowerShell cmdlets
- User Interface Management Console
- Active Directory Users and Computers Snap-in
- Active Directory Sites and Services Snap-in
- Active Directory Domains and Trusts Snap-in
- Active Directory Administrative Center Snap-in
- ADSI Edit Snap-in
- Active Directory Schema Snap-in (Not Registered)
- Active Directory Command Line Tools
- Active Directory Module for Windows PowerShell
- IIS Management Tools
- IIS Management Console
- IIS Management Compatibility
Prerequisites for installing Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT)
You will require a Windows Server 2012 computer with the “Graphical Management Tools and Infrastructure” installed to install the Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT) using the Server Manager graphical user interface.
Instructions for installing Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT)
To install the Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT) on Windows Server 2012 please follow these instructions.
- On the Windows Server 2012 open Server Manager. If Server Manager does not start by default press the “Windows + R” keys, Type “ServerManager” in the “Open” field and press “Enter” or click the OK button.
- On the Server Manager main windows Click “Add roles and features”.
- In the “Add Roles and Features Wizard” under “Installation Type” check the “Role-based or feature-based installation” radio button and click “Next”
- In the “Add Roles and Features Wizard” under “Server Selection” check the “Select a server from the server pool” radio button, select the server you want to install the Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT) on and click “Next”
- In the “Add Roles and Features Wizard” under “Server Roles” click “Next”
- In the “Add Roles and Features Wizard” under “Features” scroll down and check the “Remote Server Administration Tools” check box. Click “Next”.
- In the “Add Roles and Features Wizard” at the “Confirmation” page click “Install” to begin the installation of the Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT)
- The installation of the Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT) will begin and the progress will be displayed. You may be required to restart the server after the Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT) installation is complete.
I am setting up a couple of 2012 R2 RDS servers in a small RDS farm (of 2..) and thought it a good opportunity to see what I could do with powershell.
These RDS servers are for system administrators to manager the environment from. This saves them installing all this stuff on their PC
I tried an add-feature RSAT first, but all it did was install the RSAT tools for roles that were already installed on the server, what I actually wanted was ALL the RSAT tools, so that clusters DCs , ADCS, Bitlocker etc , could all be managed from the one location.
This script installs all the RSAT Features apart from RSAT-NIS, which is deprecated
#HTTP://Britv8.com
# Install all the RSAT Features apart from RSAT-NIS, which is deprecated
#Get a list of features and order them by name
$ListofFeatures = Get-WindowsFeature |Sort-Object -Property name
#Foreach feature , check if it starts with RSAT- and install it
#IF it is RSAT-NIS , don't install it , as it is a deprecated feature
foreach ($RSATFeature in $ListofFeatures)
{
if ($RSATFeature.name -eq "RSAT-NIS")
{
write-host "Don't install " $RSATFeature.name
}
else
{
if ($RSATFeature.name -like "RSAT-*")
{
write-host "Installing " $RSATFeature.name
Add-WindowsFeature $RSATFeature.name
}
else
{
write-host "Don't install " $RSATFeature.name
}
}
}
#These ones are not prfixed with RSAT, but are part of the tools, so install them anyhow <img draggable="false" class="emoji" alt="🙂" src="https://s.w.org/images/core/emoji/2.3/svg/1f642.svg">
Add-WindowsFeature RDS-Licensing-UI
Add-WindowsFeature WDS-AdminPack
Add-WindowsFeature IPAM-Client-Feature
#
Prologue
Ace here again. This discusses remote administration. Simple, right? Maybe not!
Server Manager in Windows Server® 2012 R2 can be used to perform various management tasks on remote servers. By default, remote management is enabled on Windows Server 2012 R2.You can add remote servers to the Server Manager Server pool in Windows Server 2012 R2 Server Manager.
Objectives
Discuss the following remote admin methods
- What is Remote Management?
- How to Enable and Disable Remote Management
- Remote Management and Tools Commands
- Server Manager
- WinRM
- PowerShell Remoting
- Remote Desktop
- Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT)
- SCONFIG
What is Remote Management?
Windows Server 2012 R2 provides the ability to remotely manage multiple servers with a number of methods. One of the newest features in Windows Server 2012 is the ability to use Server Manager for this task.
In addition to Windows Remote Management, you can also use Remote Shell and Remote Windows PowerShell to manage remote computers. This provides you the ability to locally load Windows PowerShell modules, such as Server Manager, and execute PowerShell cmdlets available in the loaded module on remote servers. This allows you the ability to run PowerShell commands and scripts. This works including when the script is only on the local server
Windows Remote Management (WinRM) is the Windows implementation of WS-Management, which is an industry standard, Web-based services based protocol. Windows runs the WinRM as a service under the same name, WinRM. WinRM provides secure local and remote communications for management applications and scripts.
In addition, Windows Remote Management is one of the components of the Windows Hardware Management features to allow secure local and remote Windows Server management across a firewall using standard Web service-based protocols.
If the server hardware has an optional, built-in Baseboard Management Controller (BMC) provided by the hardware vendor, you can also remotely manage a system even if the Windows operating system has not yet booted or has failed. This also allows access to the server’s BIOS.
A BMC is an option m provided by hardware vendors, that consists of a microcontroller and an independent network connection that you can communicate to if the server ever becomes offline.
When a server is not connected to a BMC, WinRM can still be used to connect to WMI remotely in situations where firewalls may block DCOM communications, because WinRM uses the secure web-based port, TCP 443.
Additional Reading on WinRM:
About Windows Remote Management
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/windows/desktop/aa384291(v=vs.85).aspx
Hardware Management Introduction (includes BMC information)
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/f550cac0-5344-41cb-8e89-6e5c93236886
.
How to Enable and Disable Remote Management
There are a number of methods to administer WinRM.
· Winrm.cmd – Command line tool that allows administrators to configure WinRM, get data, or manage resources. For syntax, you can run winrm /? for online help.
· Win-RM Scripting API – Allows you to create remote administration scripts that expose the WS-Management APIs and protocols.
· Winrs.exe –A command line tool to execute CMD commands on remote servers using WS-Management APIs. For example, to remotely get an ipconfig /all from a remote machine, you can run:
winrs –r:DC12.trimagna.com “ipconfig /all”;tasklist
You can also use the help command to see all possible options and syntax:
winrs –?
· IPMI and WMI Providers – The IPMI provider and drivers allow remote hardware management using BMC. These can be used programmatically.
· WMI Service – Using the WMI plug-in, WMI runs together with WinRM to provide data or control functions for remote management.
· WS-Management protocol – SOAP based protocol using XML messages. It is a web-based, firewall friendly protocol running across secure TCP 443 providing industry-standard interoperability to transfer and exchange management information.
Remote Management Tools and Commands
There are a number of ways to enable, disable and configure Remote Management.
Server Manager
To enable or disable Remote Management, in Server Manager Local Server node, click the text next to Remote Management icon.
WinRM Command
You can use the WinRM command to enable, disable, and configure Remote Management.
The syntax is:
WinRM OPERATION RESOURCE_URI [-SWITCH:VALUR [-SWITCH:VAKLUE] …] [@{KEY=VALUR [;KEP=VALUE]…}]
You can use the following to check the current Remote Management configuration and status:
winrm get winrm/config
Or you can run it remotely on another server using the WinRS command:
winrs –r:DC12-1.trimagna.com “winrm /config”;tasklist
To enable or disable Remote Management:
WinMR qc
When the WinRM qc command is run, it performs a number of steps to enable and configure the Remote Management service:
- Configures and changes the WinRM service from Manual to Automatic startup.
- Starts the WinRM service.
- Creates and configures a listener that will accept WinRM requests on any IP address.
- Creates a Windows Firewall exception for WS-Management traffic for the HTTP protocol.
If the Windows Firewall is disabled, you will see one of the following error messages:
- WSManFault
- Message
- ProviderFault
- WSManFault
- Message = Unable to check the status of the firewall.
- Error number: -2147023143 0x800706D9
- There are no more endpoints available from the endpoint mapper.
To view the command syntax and options, you can run winrm -?
WinRM supports the following commands:
- PUT
- GET
- ENUMERATION
- INVOKE
WinRM Examples:
Start a service on a remote machine:
winrm invoke startservice wmicimv2/Win32_Service?name=w32time -r:DC12
Reboot a remote machine:
winrm invoke reboot wmicimv2/Win32_OperatingSystem -r:FS1
Additional Reading on the WinRM commands:
An Introduction to WinRM Basics – From the EPS Windows Server Performance Team
http://blogs.technet.com/b/askperf/archive/2010/09/24/an-introduction-to-winrm-basics.aspx
.
PowerShell Remoting
There a number of cmdlets that use WMI for remote administration. The cmdlets invoke a temporary connection the remote computer using WMI, runs the command, then closes the session.
These cmdlets do not use WS-Management based remoting, therefore the computer does not require to be configured for WS-Management nor does it have to meet the system requirement for WS-Management. Because they are not WS-Management service related, you can use the ComputerName parameter in any of these cmdlets
You can run the Invoke-Command cmdlets to run commands on other computers.
For example, to get a list of all services on a remote computer that are either running or stopped, you can run the following command
Invoke-Command –computername DC12 –scriptblock {get-service)
Or to see the status of a single service:
Invoke-Command –computername DC12 –scriptblock {get-service WinRm)
Additional Reading on Remote PowerShell:
Windows PowerShell Remoting – Complete list of commands
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/windows/desktop/ee706585(v=vs.85).aspx
.
Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT) for Windows
Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows® includes Server Manager, Microsoft Management Console (MMC) snap-ins, consoles, Windows PowerShell® cmdlets and providers, and some command-line tools for managing roles and features that run on Windows Server 2012 R2.
.
SCONFIG
For Server Core, you can use the SCONFIG command and choosing Option #4, then choosing Option #1 to Enable Remote Management, or Option #2 to Disable Remote Management.

Additional Reading on WinRM tools
About Windows Remote Management
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/windows/desktop/aa384291(v=vs.85).aspx
.
Remote Desktop
Remote Desktop has been used for a number of years, and it is the most common method to remotely administer a remote machine. To use Remote Desktop, it must be enabled first on the remote computer. To enable Remote Desktop on the full version of Windows Server 2012, perform the following steps”
- Open Server Manager
- Click the Local Server Node
- Click the “Disabled” status next to Remote Desktop.
- The System Properties page appears and is focused on the Remote tab.
- Under the Remote tab, select one of the following:
- Don’t allow connections to this computer – Default disabled.
- Allow connections only from Computers running:
- Checkbox: Allow Remote Desktop with Network Level Authentication – If you check this box, this setting enables and only allows secure connections from Remote Desktop clients that support network-level authentication.

You can also enable Remote Desktop on Sever Core using the SCONFIG command.
==================================================================
Ace Fekay
MVP, MCT, MCSE 2012, MCITP EA & MCTS Windows 2008/R2, Exchange 2013, 2010 EA & 2007, MCSE & MCSA 2003/2000, MCSA Messaging 2003
Microsoft Certified Trainer
Microsoft MVP – Directory Services
Complete List of Technical Blogs: http://www.delawarecountycomputerconsulting.com/technicalblogs.php
This posting is provided AS-IS with no warranties or guarantees and confers no rights.
Обновлено 19.08.2022
Добрый день уважаемые читатели и гости блога, продолжаем наши уроки по системному администрированию. Задачей любого администратора, помимо организации безотказной работы сервисов, является организация удобной среды администрирования. Если мы говорим про Windows платформы, то там сервера запускают сервисы, посредством серверных ролей, для администрирования которых используются mmc оснастки, расположенные на сервере, но согласитесь, что не совсем удобно для, того чтобы, что-то подправить или проверить на сервере, нужно на него заходить и открывать оснастку там, удобнее было бы открывать ее на привычном, своем компьютере, на котором может стоять Windows 7 или Windows 8.1. Проблема в том, что данные серверные оснастки там в комплекте не идут и их нужно до устанавливать, сегодня я расскажу как их установить с помощью пакета RSAT, для клиентских версий Windows.
И так задача перед нами стоит такая, нужно на клиентской, рабочей станции администратора, сделать возможным запускать серверные оснастки, для примера:
- Active Directory — Пользователи и компьютеры
- DNS
- WSUS
Что хорошо, их потом можно будет включать в единую консоль управления Windows серверами, о которой я рассказывал. Для установки оснасток ролей Windows, нам потребуется дополнительный пакет обновлений под названием RSAT (Remote Server Administration Tools) или как в России средства удаленного администрирования сервера. Он скачивается и устанавливается отдельно на клиентскую версию операционной системы, для расширения ее возможностей, а точнее компонентов системы.
Какие оснастки добавляет RSAT
Давайте я приведу список оснасток, которые добавляются при установке RSAT:
- Диспетчер сервера > RemoteServerAdministrationTools-ServerManager
- Клиент управления IP адресами (IPAM) > RemoteServerAdministrationTools-Features-IPAM
- Средство балансировки сетевой нагрузки > RemoteServerAdministrationTools-Features-LoadBalancing
- Средства объединения сетевых карт > RemoteServerAdministrationTools-Features-NICTeaming
- Средства отказоустойчивой кластеризации > RemoteServerAdministrationTools-Features-Clustering
- Средства управления групповыми политиками > RemoteServerAdministrationTools-Features-GP
- Средство просмотра пароля восстановления Bitlocker > RemoteServerAdministrationTools-Features-BitLocker
- Модуль Active Directory для power shell > RemoteServerAdministrationTools-Roles-AD-Powershell
- Оснастки и программы командной строки AD DS > RemoteServerAdministrationTools-Roles-AD-DS
- Средства сервера для NIS > RemoteServerAdministrationTools-Roles-AD-DS-NIS
- Центр администрирования Active Directory > RemoteServerAdministrationTools-Roles-AD-DS-AdministrativeCenter
- Средства активации корпоративных лицензий > RemoteServerAdministrationTools-Roles-VA
- Средства серверов DHCP > RemoteServerAdministrationTools-Roles-DHCP
- Средства серверов DNS > RemoteServerAdministrationTools-Roles-DNS
- Средства серверов WSUS > RemoteServerAdministrationTools-Roles-WSUS
- Средства служб сертификации Active Directory > RemoteServerAdministrationTools-Roles-CertificateServices
- Средства сетевого ответчика > RemoteServerAdministrationTools-Roles-CertificateServices-OnlineResponder
- Средства центра сертификации > RemoteServerAdministrationTools-Roles-CertificateServices-CA
- Средства служб удаленных рабочих столов > RemoteServerAdministrationTools-Roles-RDS
- Средства диагностики лицензирования удаленных рабочих столов > RemoteServerAdministrationTools-Roles-RDS-LicensingDiagUI
- Средства лицензирования удаленных рабочих столов > RemoteServerAdministrationTools-Roles-RDS-LicensingUI
- Средства шлюзов удаленных рабочих столов > RemoteServerAdministrationTools-Roles-RDS-Gateway
- Средства управления удаленным доступом > RemoteServerAdministrationTools-Roles-RemoteAccess
- Средства файловых служб > RemoteServerAdministrationTools-Roles-FileServices
- Средства администрирования NFS > RemoteServerAdministrationTools-Roles-FileServices-Nfs
- Средства диспетчера ресурсов файлового сервера > RemoteServerAdministrationTools-Roles-FileServices-Fsrm
- Средства распределенной файловой системы > RemoteServerAdministrationTools-Roles-FileServices-Dfs
- Средства управления общими ресурсами и хранилищем > RemoteServerAdministrationTools-Roles-FileServices-StorageMgmt
Установка пакета RSAT в Windows 11
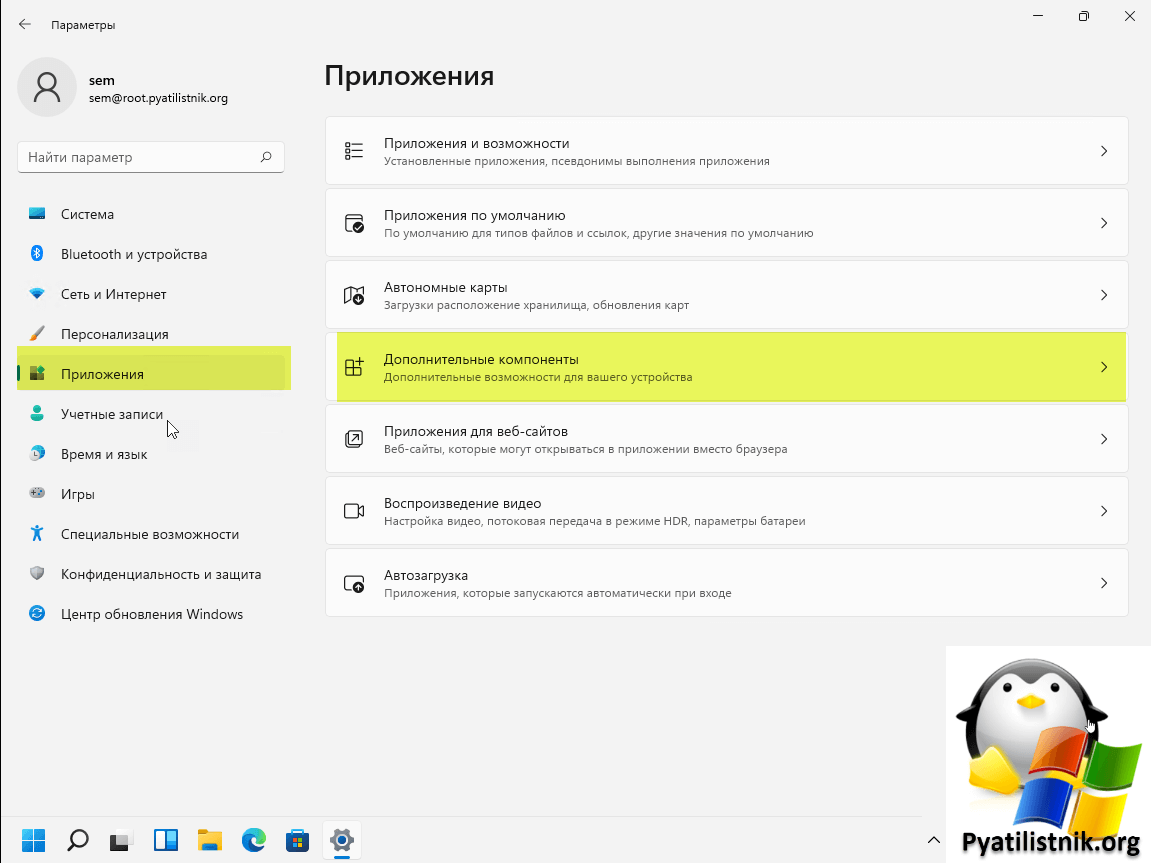
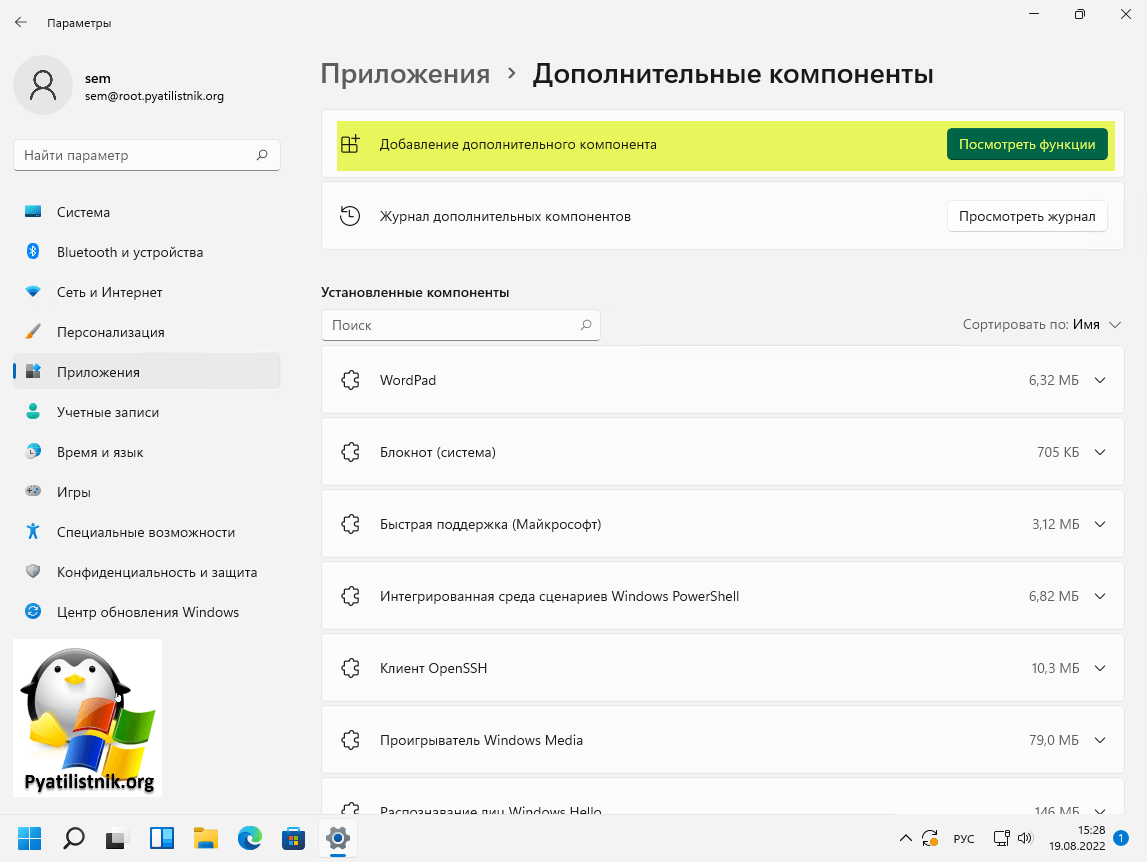
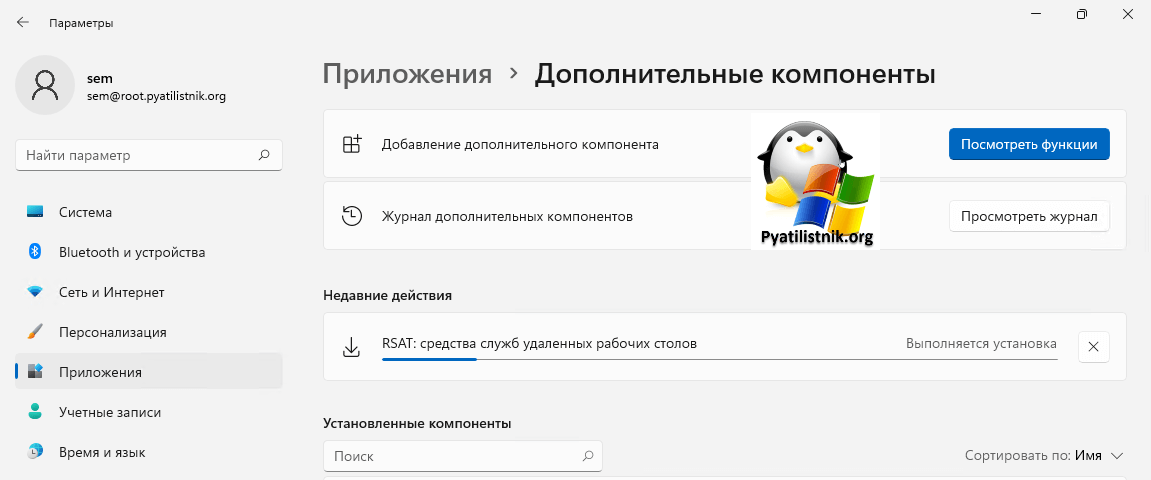
Установить RSAT в Windows 11 проще простого, по сути он уже у вас присутствует в системе, и тут необходимо выбрать нужные компоненты и нажать добавить. Открываем параметры Windows (Нажмите сочетание клавиш Win и I). Перейдите в раздел «Приложения — Дополнительные компоненты«.
Убедитесь, что у вас редакция Professional и Enterprise, в Home так не получиться
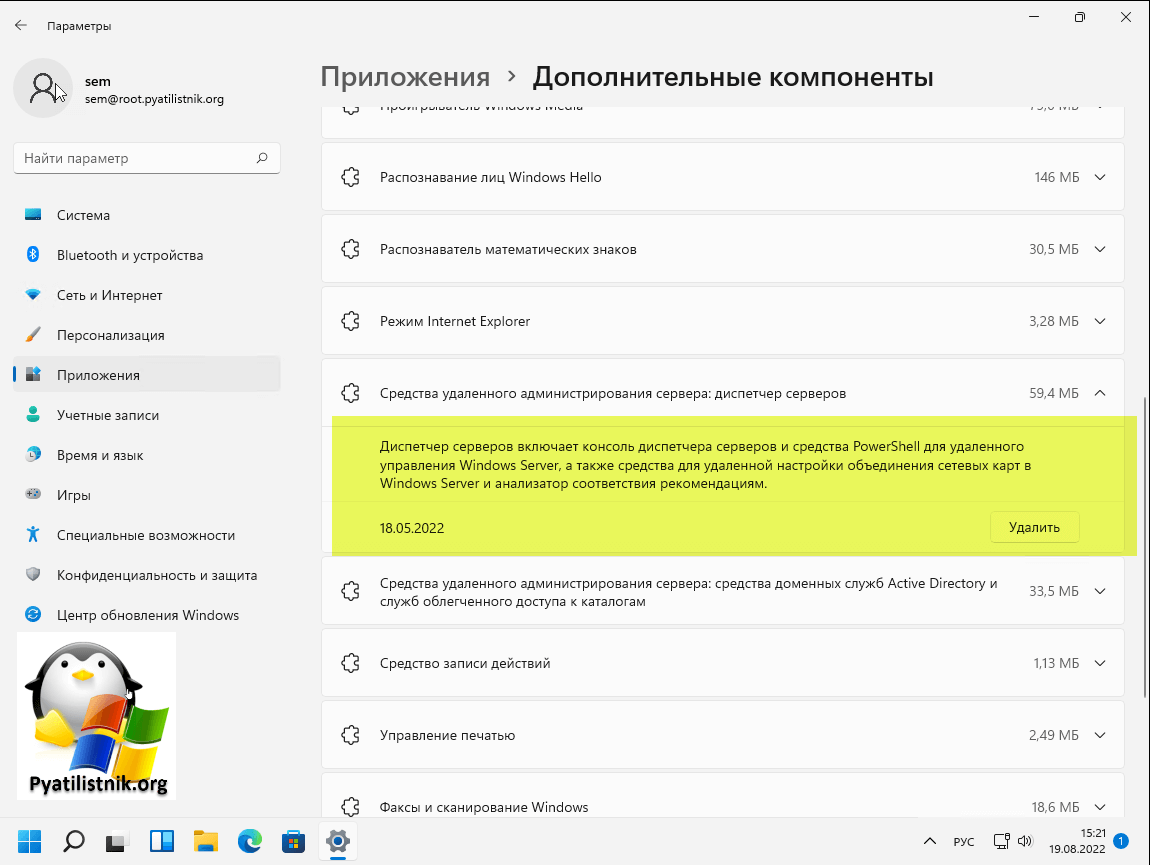
Найдите пункт «Средства удаленного администрирования сервера: диспетчер серверов (RSAT)«, он должен быть добавлен, если нет. то нажмите соответствующую кнопку.
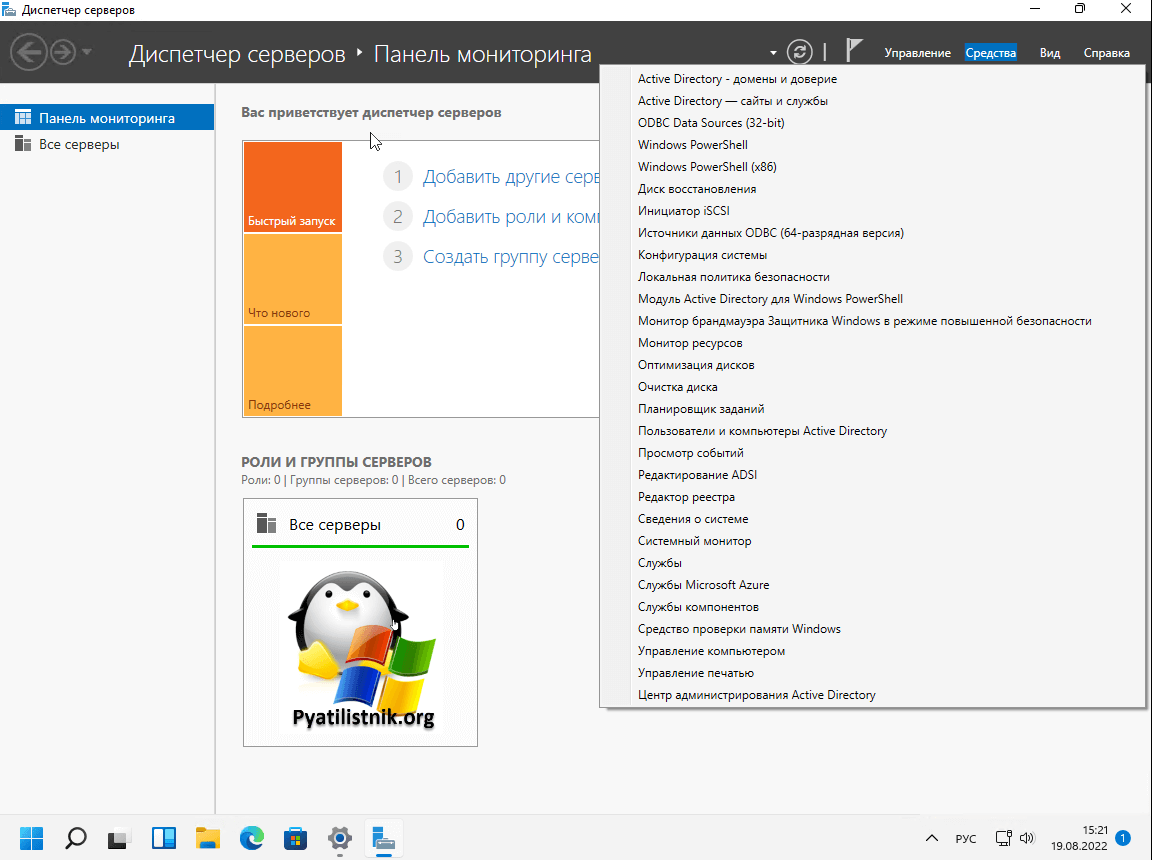
Когда он присутствует в Windows 11, то вы можете его легко найти в меню пуск. Когда вы запустите «Диспетчер серверов», то сможете там обнаружить большую часть административных оснасток RSAT.
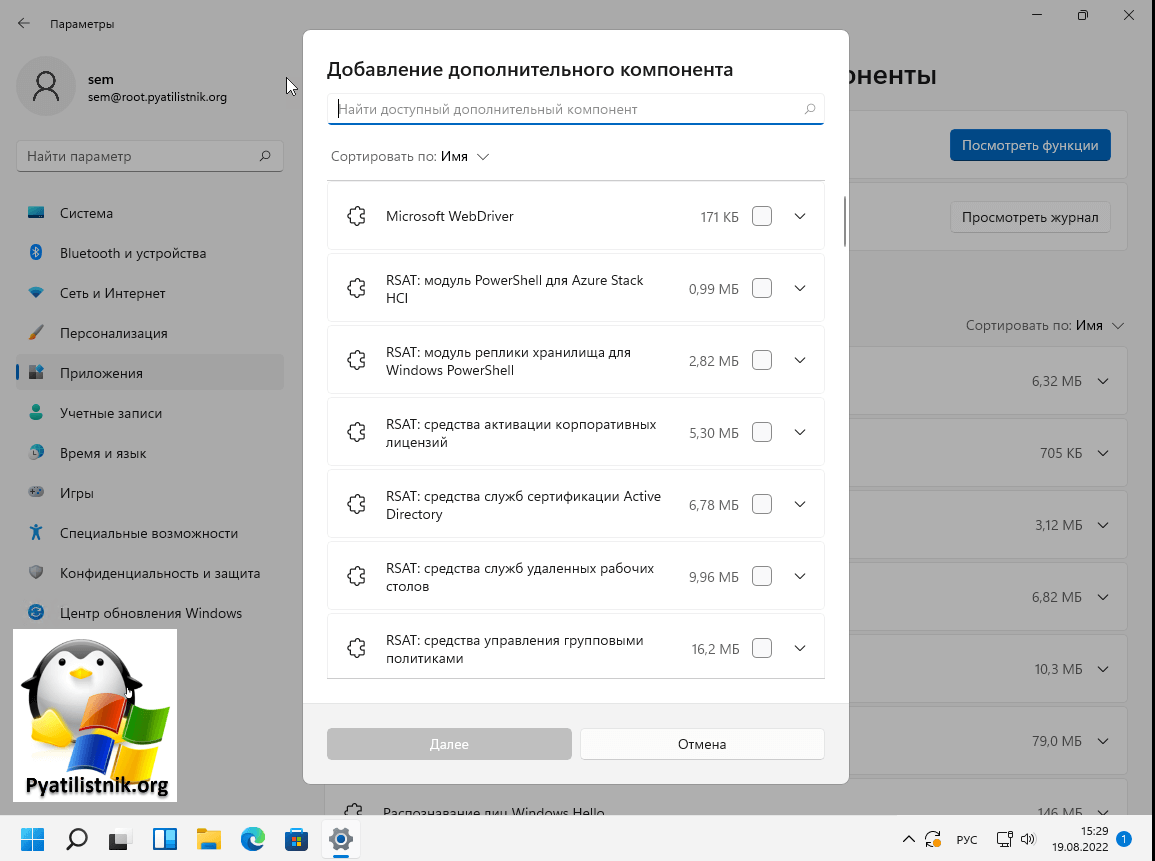
Так же у вас есть возможность добавлять компоненты отдельно, для этого нажмите кнопку «Добавление дополнительного компонента — Посмотреть функции«.
У вас появится доступный список компонентов, чтобы выбрать нужный, просто установите на нем галочку. Например, отдельно можно установить:
- RSAT: модули для Azure
- RSAT: средство активации корпоративных лицензий (RSAT: Volume Activation Tools (KMS server console)
- RSAT: средства служб сертификации Active Directory (RSAT: Active Directory Certificate Services Tools)
- RSAT: средства служб удаленных рабочих столов (RSAT: Remote Desktop Services Tools)
- RSAT: средства управления групповыми политиками (RSAT: Group Policy Management Tools)
- RSAT: доменные службы Active Directory и инструменты облегченных служб каталогов
- RSAT: утилиты администрирования шифрования диска BitLocker
- RSAT: инструменты DHCP-сервера (используются для настройки и управления DHCP-сервером в Windows Server)
- RSAT: инструменты DNS-сервера (RSAT: DNS Server Tools)
- RSAT: инструменты отказоустойчивой кластеризации (RSAT: Failover Clustering Tools)
- RSAT: инструменты файловых служб (RSAT: File Services Tools)
- RSAT: клиент управления IP-адресами (IPAM) (RSAT: IP Address Management (IPAM) Client)
- RSAT: инструменты LLDP для объединения центров обработки данных (RSAT: Data Center Bridging LLDP Tools)
- RSAT: средства управления сетевым контроллером (RSAT: Network Controller Management Tools)
- RSAT: средства балансировки сетевой нагрузки (RSAT: Network Load Balancing Tools)
- RSAT: средства управления удаленным доступом (RSAT: Remote Access Management Tools)
- RSAT: диспетчер серверов (RSAT: Server Manager)
- RSAT: инструменты для экранированных виртуальных машин (RSAT: Shielded VM Tools)
- RSAT: средства управления службой миграции хранилища (RSAT: Storage Migration Service Management Tools)
- RSAT: модуль реплики хранилища для Windows PowerShell (RSAT: Storage Replica Module for Windows PowerShel)
- RSAT: модуль анализа системы для Windows PowerShell (RSAT: System Insights Module for Windows PowerShell)
- RSAT: инструменты служб обновления Windows Server (RSAT: Windows Server Update Services Tools)
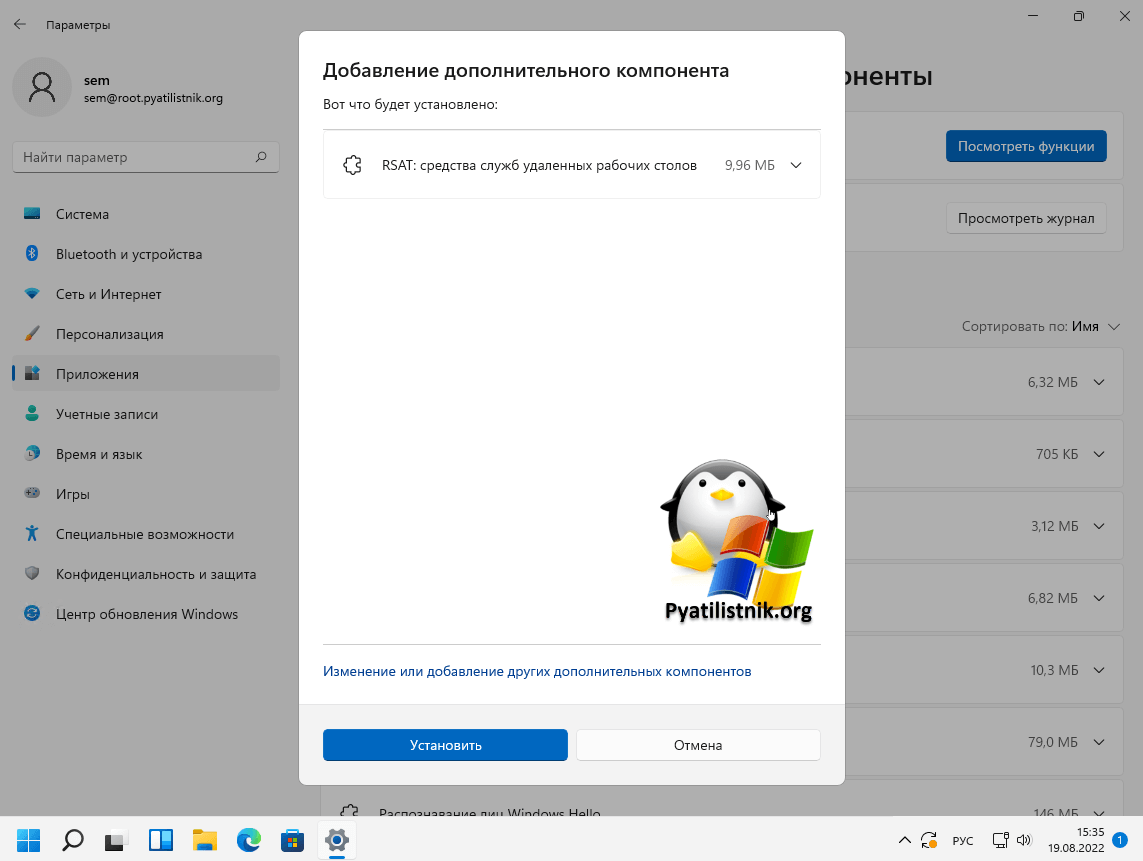
После выбора нужных компонентов нажмите далее, у вас появится новое окно, где от вас потребуется нажать кнопку «Установить.«
В результате вам остается только дождаться окончания процесса.
Как установить RSAT через PowerShell
Сразу отмечу, что ваша версия PowerShell должна быть не ниже 5-ой, поэтому узнайте свою версию и обновите ее. В Windows 10 и Windows 11, это не требуется, там уже идет нужная версия.
- 1️⃣Метод для Windows 10
Откройте PowerShell в режиме администратора, первое что нужно сделать, это проверить, что из компонентов RSAT уже установлено:
Get-WindowsCapability -Name RSAT* -Online | Select-Object -Property DisplayName, State
Установка RSAT Windows 8.1
Так как я везде у себя имею установленную Windows 8.1, то в первую очередь, хочу иметь консоли администрирования, на ней. Для установки средства удаленного администрирования сервера в Windows 8.1, вам потребуется понять какая у вас разрядность системы, и скачать соответствующий пакет.
Скачать RSAT для Windows 8.1, можно с официального сайта Microsoft.
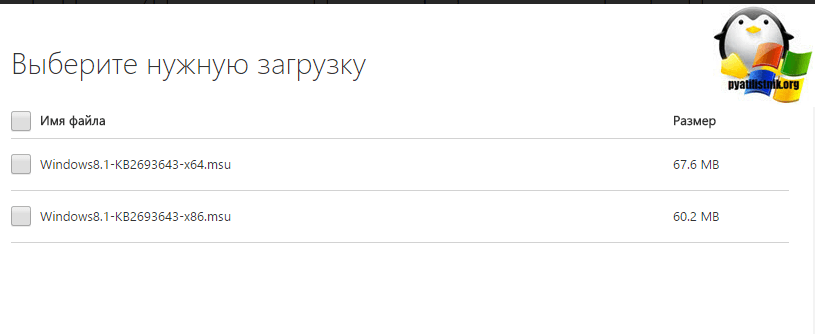
Как видите, тут средство удаленного администрирования сервера, представлено в виде двух обновлений:
- Windows8.1-KB2693643-x64
- Windows8.1-KB2693643-x86
Скачиваете исходя из своей архитектуры Windows 8.1
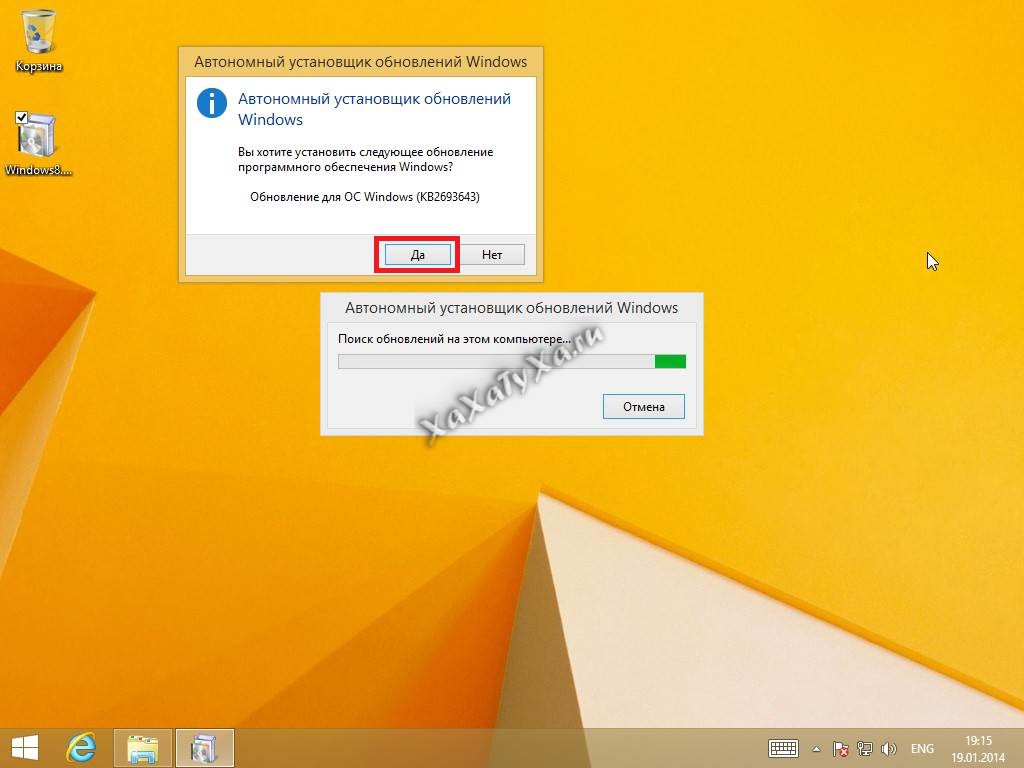
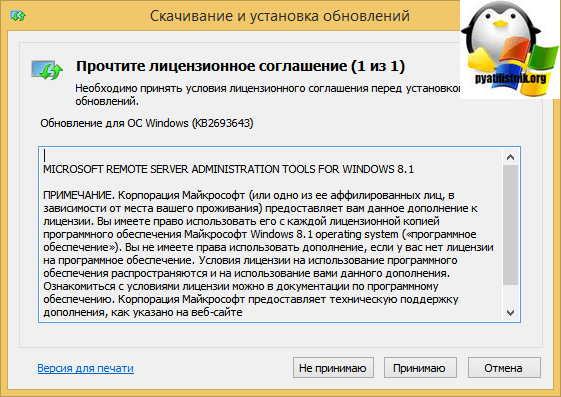
Начинаем установку обновления KB2693643-x64.
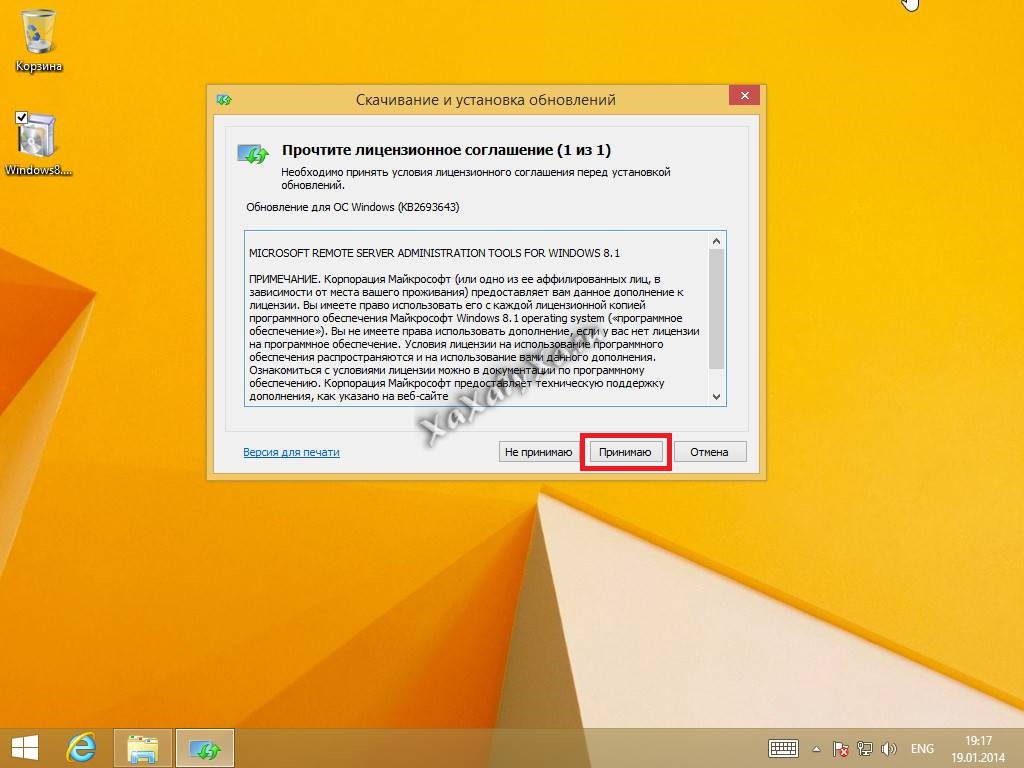
Соглашаемся с лицензионным соглашением.
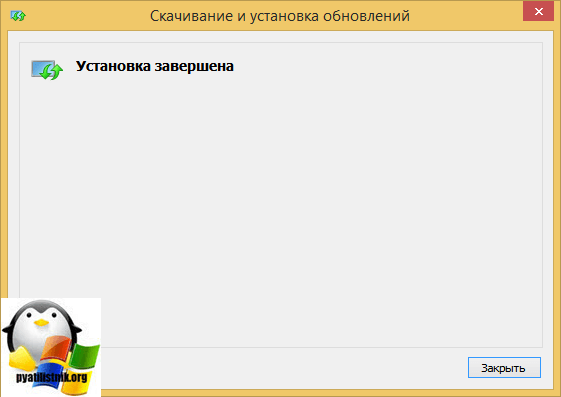
Через пару минут, обновление KB2693643-x64 будет установлено.
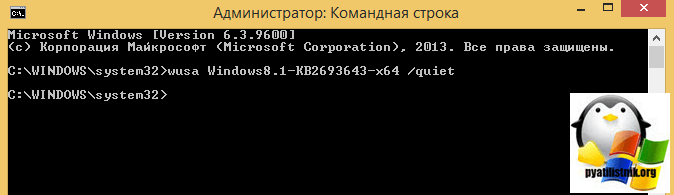
Еще есть альтернативный метод, через командную строку, для этого воспользуйтесь командой:
- wusa Windows8.1-KB2693643-x64 /quiet
- wusa Windows8.1-KB2693643-x86 /quiet
В итоге Центр обновления Windows дотащит, данные обновления.
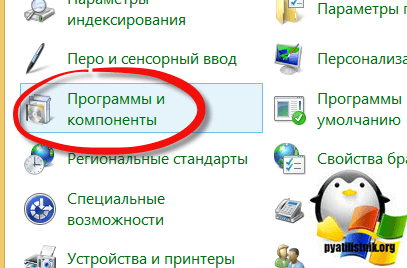
Все теперь можно запускать консоли удаленного администрирования на Windows 8.1, для этого нажмите Win+R и введите control panel.
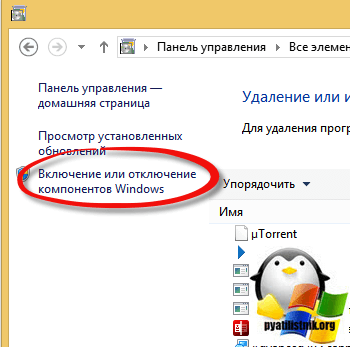
В открывшемся окне панели управления, найдите пункт Программы и компоненты.
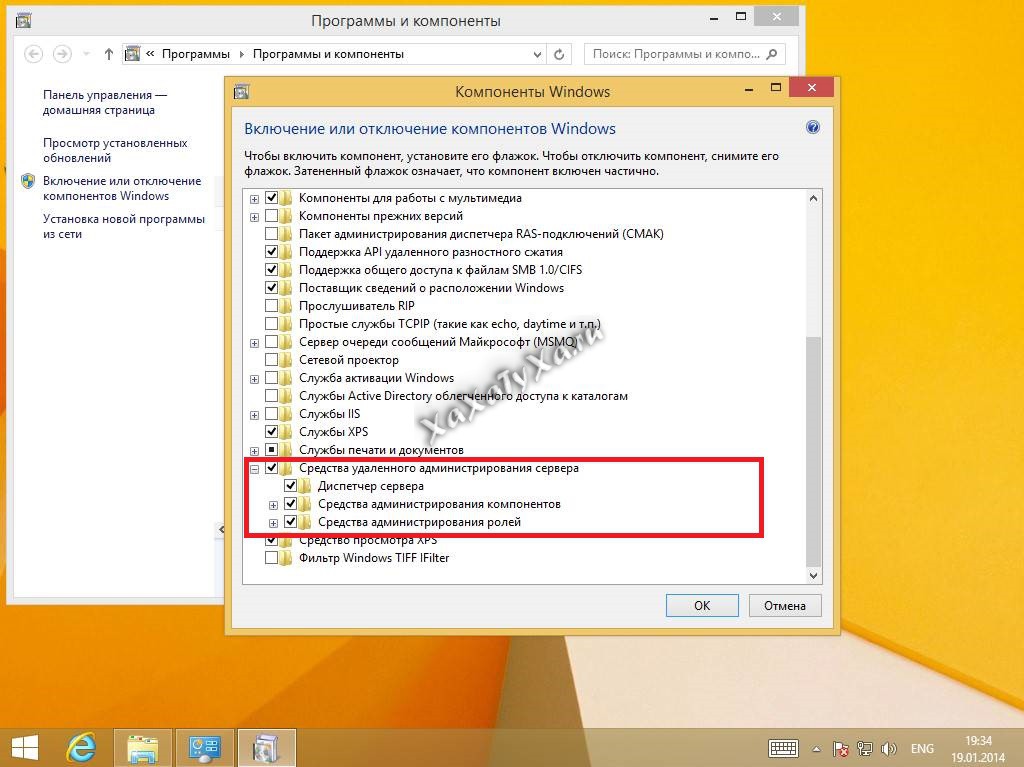
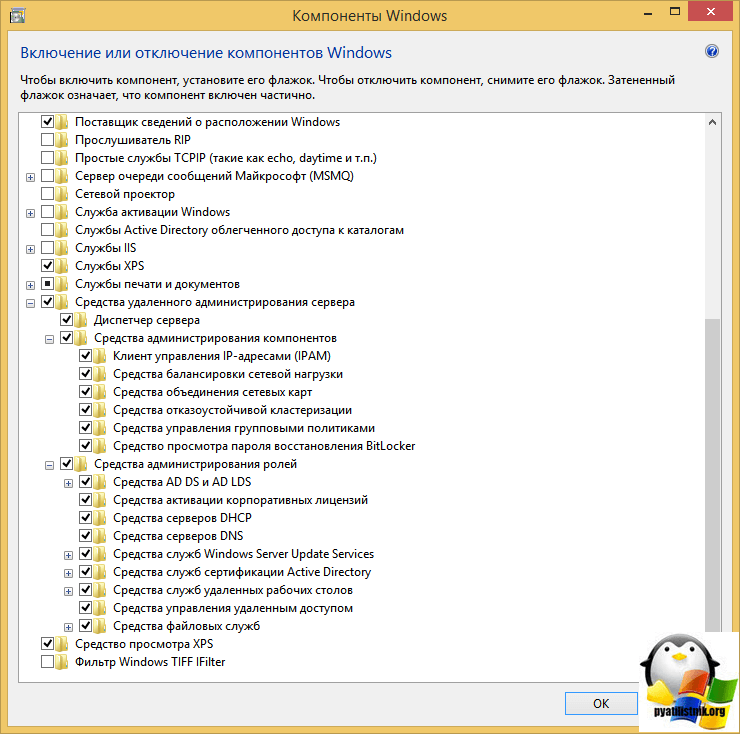
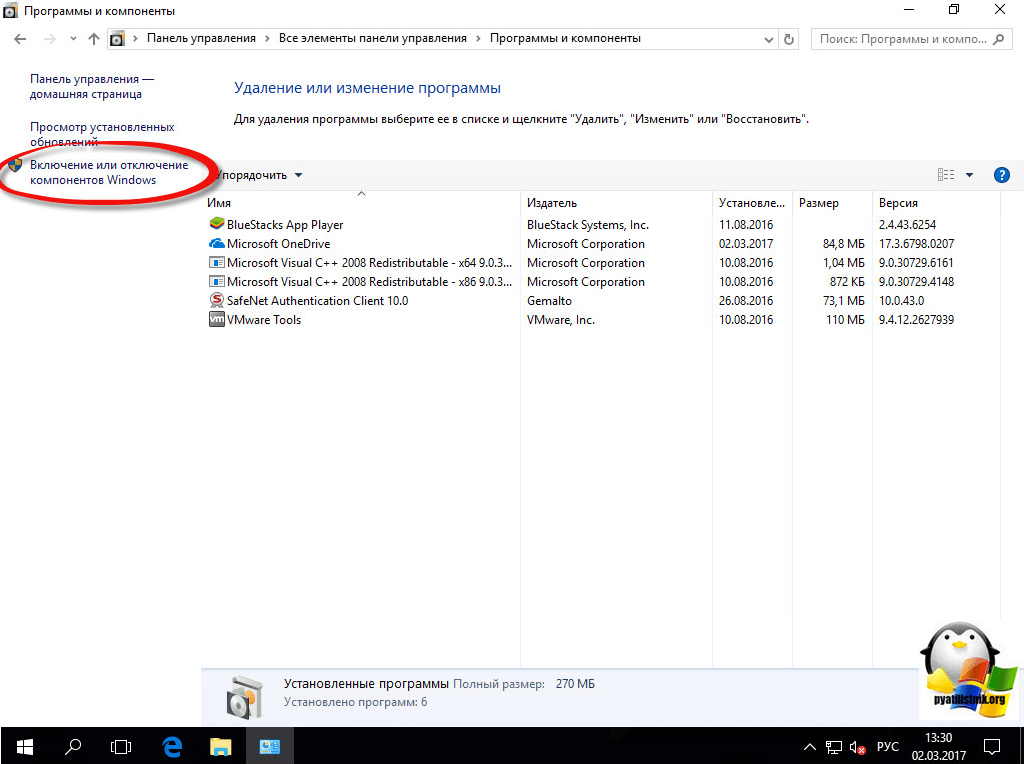
Далее выбираете Включение или отключение компонентов Windows.
Ну вот собственно и средства удаленного администрирования сервера. Вы должны отметить нужные вам компоненты, и они будут добавлены.
Далее установленные компоненты, в виде оснасток серверных ролей, вы сможете найти в панели управления, в пункте Администрирование.
Вот я спокойно открыл диспетчер серверов в операционной системе Windows 8.1 и теперь спокойно могу подключаться к нужному мне серверу.
Установка RSAT в Windows 10
Давайте теперь разберем установку RSAT (Remote Server Administration Tools) в Windows 10 Redstone. По сути вам нужно проделать похожие действия. RSAT windows 10, это точно такие же обновления, под определенную архитектуру системы.
Скачать rsat windows 10 с сайта Microsoft. За него отвечают такие KB:
- WindowsTH-RSAT_WS2016-x64.msu
- WindowsTH-RSAT_WS2016-x86.msu
Так как у меня 64-х битная система, то я запускаю WindowsTH-RSAT_WS2016-x64.msu. Соглашаемся с установкой.
Принимаем лицензионное соглашение.
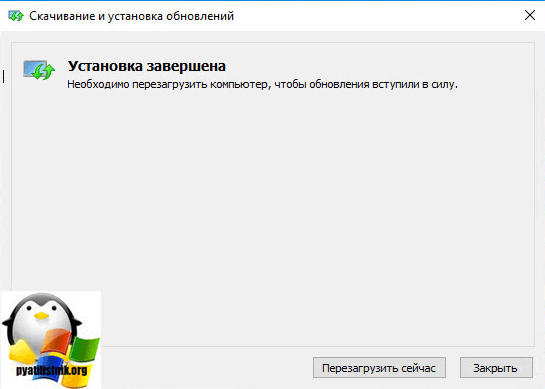
После установки обновления WindowsTH-RSAT_WS2016-x64.msu, нужно перезагрузиться.
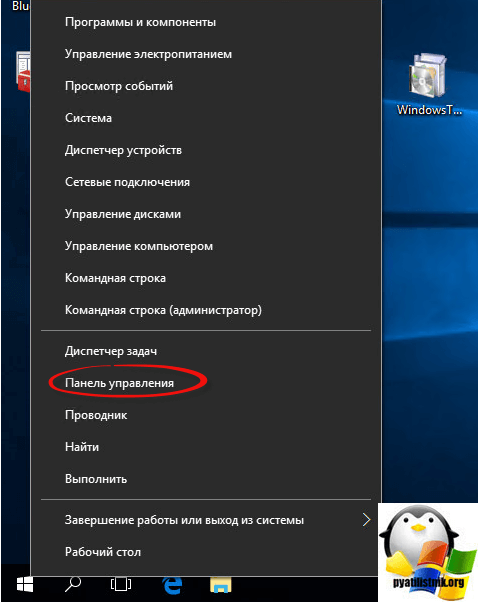
Теперь нажимаем правым кликом по кнопке пуск и выбираем панель управления.
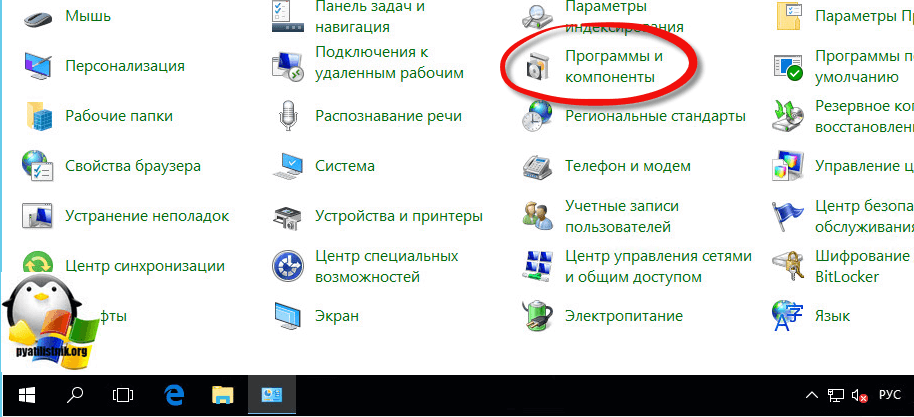
Заходим в программы и компоненты.
Далее нажимаем включение или отключение компонентов Winwods.
И тут вы удивитесь, так как средств удаленного администрирования сервера, вы тут не найдете, так как они по умолчанию все уже включены.
В итоге в администрировании вы увидите все доступные оснастки по администрированию серверов.
Установка RSAT в Windows 7
Установить RSAT в семерке, производится точно так же, заходим на сайт скачивания RSAT Windows 7.
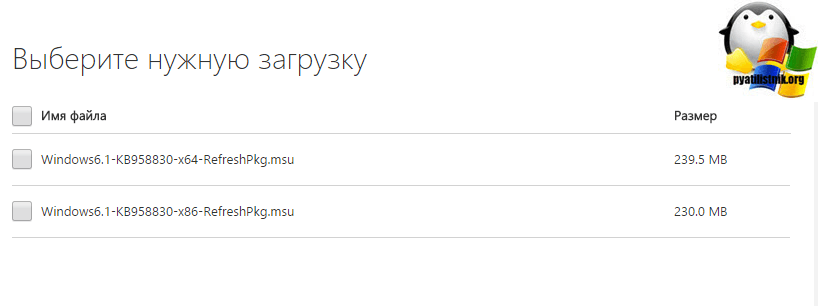
Тут будет два обновления:
- Windows6.1-KB958830-x64-RefreshPkg.msu
- Windows6.1-KB958830-x86-RefreshPkg.msu
Я для себя начинаю установку Windows6.1-KB958830-x64-RefreshPkg.msu, жмем да.
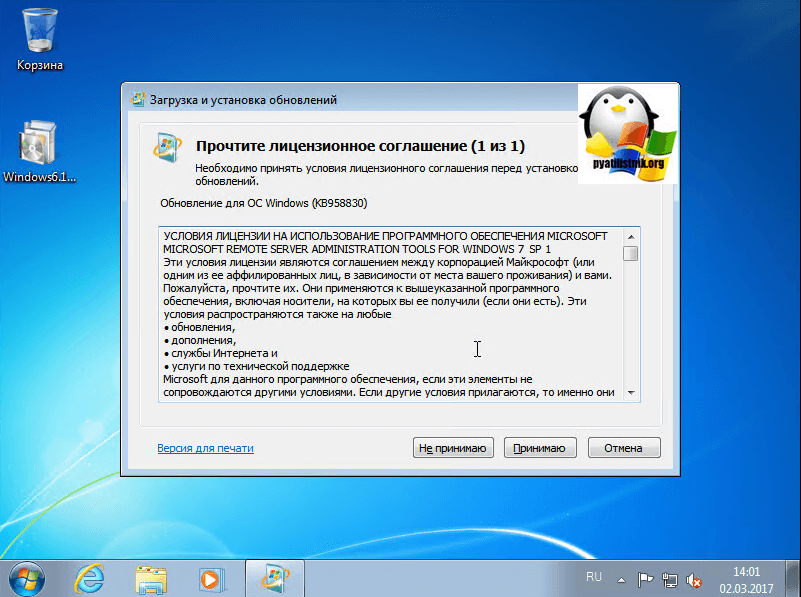
Принимаем лицензионное соглашение.
Дожидаемся установки средства удаленного администрирования сервера.
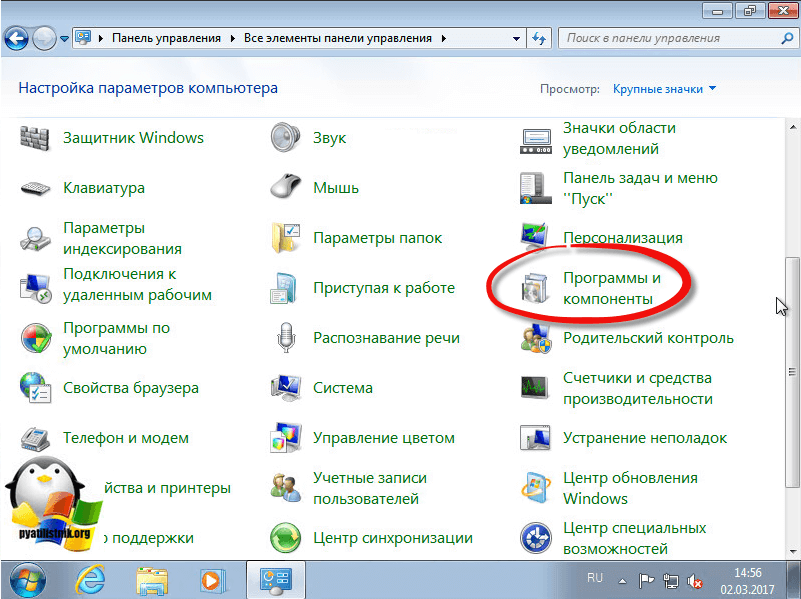
Далее идем в программы и компоненты.
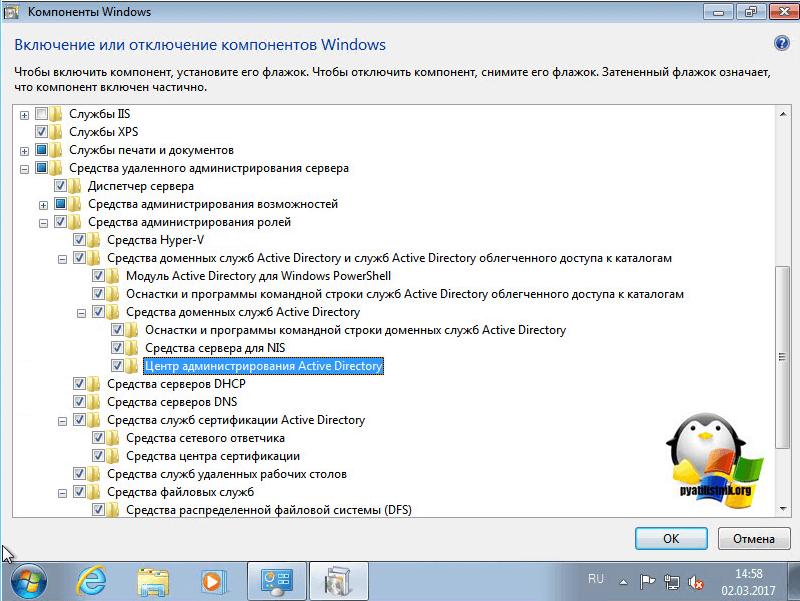
Далее идем в пункт включение или отключение компонентов Windows,
Находим пункт средства удаленного администрирования сервера и выбираем нужные компоненты.
Все начинается установка.
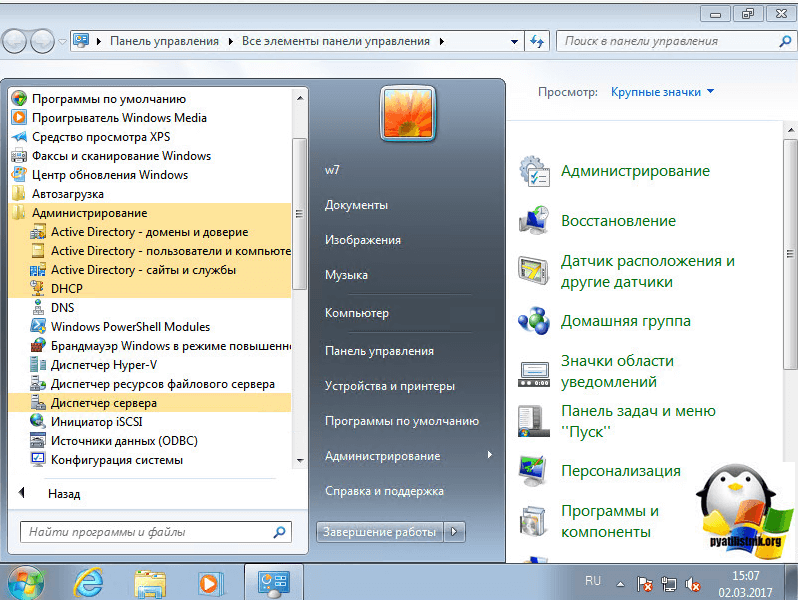
Все теперь открываем пункт администрирование, можно через пуск и видим новые консоли администрирования.
Добавление компонентов Windows RSAT через командную строку (Актуально для Windows 7/8.1/10 до 20H2)
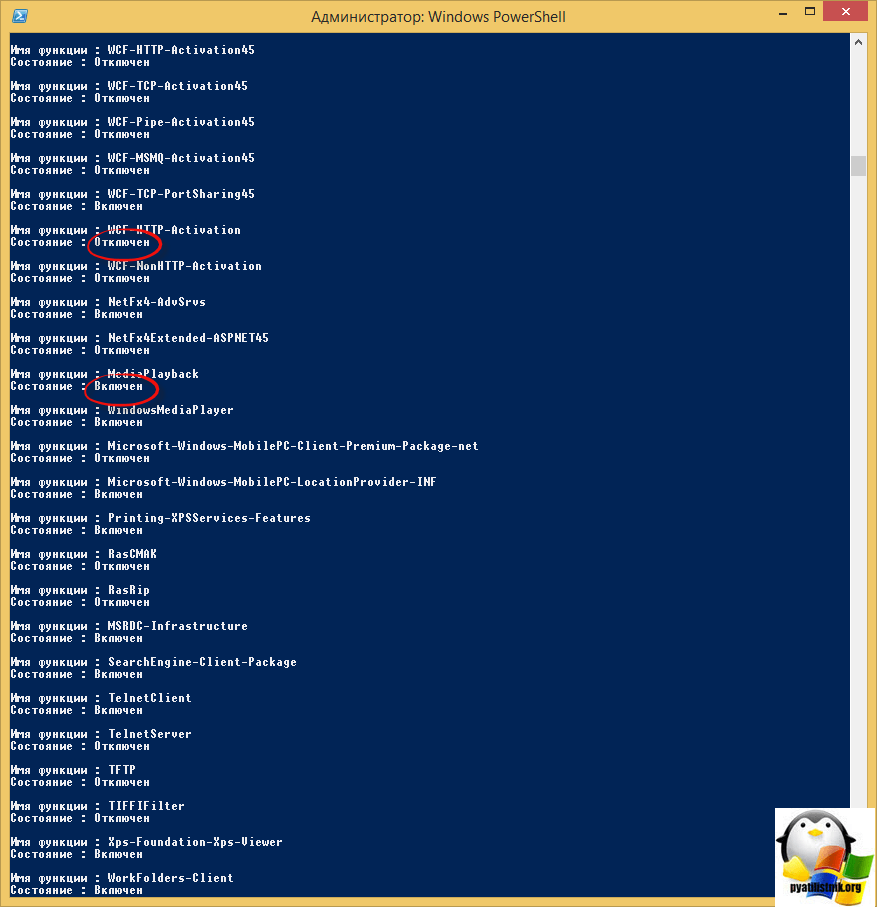
Так же после того, как вы установили пакет администрирования RSAT, вы легко можете добавить любую консоль администрирования, через командную строку, работающую от имени администратора. Тут нам поможет утилита DISM. Давайте для начала получим список всех компонентов в системе.
dism /Online /Get-Features
Обратите внимание, что у компонентов будут статусы Включен или Отключен.
Далее, что установить нужную консоль администрирования введите команду:
dism /Online /Enable-Feature /FeatureName:<FeatureName>
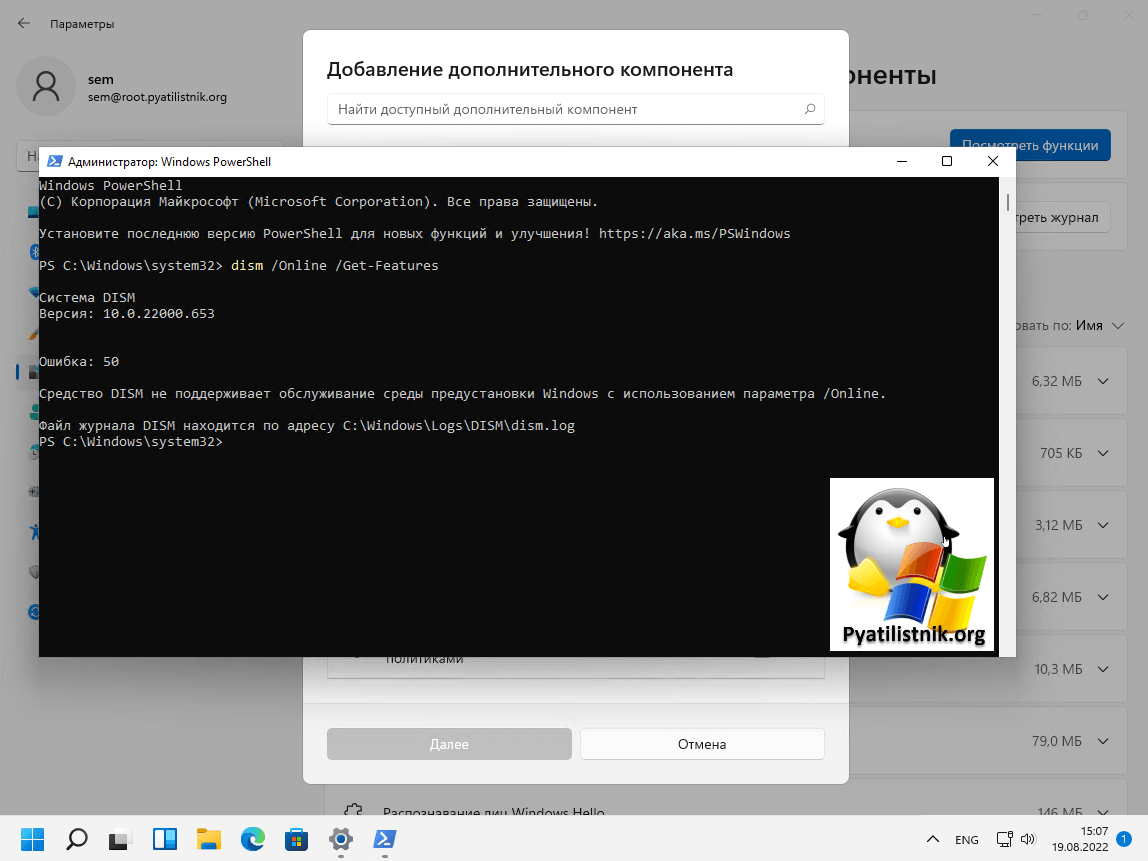
Список название, вверху статьи.
Напоминаю, что в Windows 11 данная команда с ключом /Online уже не поддерживается, вы будите получать ошибку:
Ошибка: 50
Средство DISM не поддерживает обслуживание среды предустановки Windows с использованием параметра /Online.
Файл журнала DISM находится по адресу C:WindowsLogsDISMdism.log