Windows 8.1 Windows Server 2012 R2 Windows Embedded 8.1 Industry Enterprise Windows Embedded 8.1 Industry Pro More…Less
Version:
Windows 8.1, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Embedded 8.1 Industry Enterprise, Windows Embedded 8.1 Industry Pro
Learn all about the security and non-security updates that are published for Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2 through Windows Update. These updates address issues and improve the overall reliability of the operating system.
Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2 rollups (monthly rollups and security-only updates) are applicable by default to the following Windows 8.1 Industry-based embedded product:
-
Windows Embedded 8.1 Industry Enterprise.
-
Windows Embedded 8.1 Industry Pro.
If a rollup is not applicable to an embedded product, we will explicitly state that it is not applicable.
On the left side of this page, there is a reference to all of the updates that have been released for this version of Windows. We recommend installing all updates for Windows that are available for your device. Installing the most recent update means you get all of the previous updates, as well, including important security fixes.
Current status of Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2
For the most up-to-date information about Known Issues for Windows and Windows Server, please go to the Windows release health dashboard.
Notes and messages
General
IMPORTANT Starting in July 2020, all Windows Updates will disable the RemoteFX vGPU feature because of a security vulnerability. For more information about the vulnerability, seeCVE-2020-1036 and KB4570006. After you install this update, attempts to start virtual machines (VM) that have RemoteFX vGPU enabled will fail, and messages such as the following will appear:
If you re-enable RemoteFX vGPU, a message similar to the following will appear:
-
“The virtual machine cannot be started because all the RemoteFX-capable GPUs are disabled in Hyper-V Manager.”
-
“The virtual machine cannot be started because the server has insufficient GPU resources.”
-
«We no longer support the RemoteFX 3D video adapter. If you are still using this adapter, you may become vulnerable to security risk. Learn more (https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=2131976)”
Related info
-
Windows Update: FAQ
-
Windows Server 2012 update history
-
Windows 7 SP1 and Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1 update history
-
Windows Server 2008 SP2 update history
-
Get Windows 10
Need more help?
Windows 8.1 Windows Server 2012 R2 Windows Embedded 8.1 Industry Enterprise Windows Embedded 8.1 Industry Pro More…Less
Version:
Windows 8.1, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Embedded 8.1 Industry Enterprise, Windows Embedded 8.1 Industry Pro
Learn all about the security and non-security updates that are published for Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2 through Windows Update. These updates address issues and improve the overall reliability of the operating system.
Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2 rollups (monthly rollups and security-only updates) are applicable by default to the following Windows 8.1 Industry-based embedded product:
-
Windows Embedded 8.1 Industry Enterprise.
-
Windows Embedded 8.1 Industry Pro.
If a rollup is not applicable to an embedded product, we will explicitly state that it is not applicable.
On the left side of this page, there is a reference to all of the updates that have been released for this version of Windows. We recommend installing all updates for Windows that are available for your device. Installing the most recent update means you get all of the previous updates, as well, including important security fixes.
Current status of Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2
For the most up-to-date information about Known Issues for Windows and Windows Server, please go to the Windows release health dashboard.
Notes and messages
General
IMPORTANT Starting in July 2020, all Windows Updates will disable the RemoteFX vGPU feature because of a security vulnerability. For more information about the vulnerability, seeCVE-2020-1036 and KB4570006. After you install this update, attempts to start virtual machines (VM) that have RemoteFX vGPU enabled will fail, and messages such as the following will appear:
If you re-enable RemoteFX vGPU, a message similar to the following will appear:
-
“The virtual machine cannot be started because all the RemoteFX-capable GPUs are disabled in Hyper-V Manager.”
-
“The virtual machine cannot be started because the server has insufficient GPU resources.”
-
«We no longer support the RemoteFX 3D video adapter. If you are still using this adapter, you may become vulnerable to security risk. Learn more (https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=2131976)”
Related info
-
Windows Update: FAQ
-
Windows Server 2012 update history
-
Windows 7 SP1 and Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1 update history
-
Windows Server 2008 SP2 update history
-
Get Windows 10
Need more help?
Windows Server 2012 Windows Embedded 8 Standard More…Less
Version:
Windows Server 2012
Learn all about the security and non-security updates that are published for Windows Server 2012 through Windows Update. These updates address issues and improve the overall reliability of the operating system.
On the left side of this page, there is a reference to all of the updates that have been released for this version of Windows. We recommend installing all updates for Windows that are available for your device. Installing the most recent update means you get all of the previous updates, as well, including important security fixes.
Current status of Windows Server 2012
For the most up-to-date information about Known Issues for Windows and Windows Server, please go to the Windows release health dashboard.
Notes and messages
General
IMPORTANT Starting in July 2020, all Windows Updates will disable the RemoteFX vGPU feature because of a security vulnerability. For more information about the vulnerability, seeCVE-2020-1036 and KB4570006. After you install this update, attempts to start virtual machines (VM) that have RemoteFX vGPU enabled will fail, and messages such as the following will appear:
If you re-enable RemoteFX vGPU, a message similar to the following will appear:
-
“The virtual machine cannot be started because all the RemoteFX-capable GPUs are disabled in Hyper-V Manager.”
-
“The virtual machine cannot be started because the server has insufficient GPU resources.”
-
«We no longer support the RemoteFX 3D video adapter. If you are still using this adapter, you may become vulnerable to security risk. Learn more (https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=2131976)”
As of February 11, 2020, Internet Explorer 10 is no longer in support. To get Internet Explorer 11 for Windows Server 2012 or Windows 8 Embedded Standard, see KB4492872. Install one of the following applicable updates to stay updated with the latest security fixes:
-
Cumulative Update for Internet Explorer 11 for Windows Server 2012.
-
Cumulative Update for Internet Explorer 11 for Windows 8 Embedded Standard.
-
The November 2020 Monthly Rollup.
Related info
-
Windows Update: FAQ
-
Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2 update history
-
Windows 7 SP1 and Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1 update history
-
Windows Server 2008 SP2 update history
Need more help?
Windows Server 2012/R2: List of Monthly Rollups
Table of Contents
- 2012
- 2012 R2
- Other Updates
Will be maintained monthly.
To learn more about update rollups, visit
here
2012
| KB | Download |
| GA | KB2756872 |
| 12-Nov | KB2770917 |
| 12-Dec | KB2779768 |
| 13-Jan | KB2785094 |
| 13-Feb | KB2795944 |
| 13-Mar | KB2811660 |
| 13-Apr | KB2822241 |
| 13-May | KB2836988 |
| 13-Jun | KB2845533 |
| 13-Jul | KB2855336 |
| 13-Aug | KB2862768 |
| 13-Sep | KB2876415 |
| 13-Oct | KB2883201 |
| 13-Nov | KB2889784 |
| 13-Dec | KB2903938 |
| 14-Jan | KB2911101 |
| 14-Feb | KB2919393 |
| 14-Mar | KB2928678 |
| 14-Apr | KB2934016 |
| 14-May | KB2955163 |
| 14-Jun | KB2962407 |
| 14-Jul | KB2967916 |
| 14-Aug | KB2975331 |
| 14-Sep | KB2984005 |
| 14-Oct | KB2995387 |
| 14-Nov | KB3000853 |
| 14-Dec | KB3013767 |
| 16-May | KB3156416 |
| 16-Jun | KB3161609 |
| 16-Jul | KB3172615 |
| 16-Aug | KB3179575 |
| 16-Sep | KB3185280 |
2012 R2
| KB | Download |
| GA | KB2883200 |
| 13-Oct | KB2884846 |
| 13-Nov | KB2887595 |
| 13-Dec | KB2903939 |
| 14-Jan | KB2911106 |
| 14-Feb | KB2919394 |
| 14-Mar | KB2928680 |
| 14-Apr | KB2919355 |
| 14-May | KB2955164 |
| 14-Jun | KB2962409 |
| 14-Jul | KB2967917 |
| 14-Aug | KB2975719 |
| 14-Sep | KB2984006 |
| 14-Oct | KB2995388 |
| 14-Nov | KB3000850 |
| 14-Dec | KB3013769 |
| 16-May | |
| 16-Jun | |
| 16-Jul | KB3172614 |
| 16-Aug | KB3179574 |
| 16-Sep | KB3185279 |
Other Updates
- Windows Server 2012 update history
- Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2 update history
- KB2821526 Available updates for Remote Desktop Services in Windows Server 2012
- KB2933664 Available updates for Remote Desktop Services in Windows
Server 2012 R2 - KB2899011 List of currently available hotfixes for the File Services
technologies in Windows Server 2012 and in Windows Server 2012 R2 - KB2951262 List of currently available hotfixes for Distributed
File System (DFS) technologies in Windows Server 2012 and Windows Server 2012 R2 - KB2883952 Recommended hotfixes and updates for Windows Server 2012
DirectAccess and Windows Server 2012 R2 DirectAccess - KB2784261 Recommended hotfixes and updates for Windows Server 2012-based
failover clusters - KB2920151 Recommended hotfixes and updates for Windows Server 2012
R2-based failover clusters - KB3135020 Recommended hotfixes, updates, and known solutions for
Windows Server 2012 R2 Hyper-V environments - KB2974503 Recommended hotfixes, updates, and known solutions for
Windows Server 2012 R2 Hyper-V Network Virtualization (HNV) environments - KB894199 Description of Software Update Services and Windows Server
Update Services changes in content for 2017
Comments
-
19 Nov 2014 2:29 AM
Please check latest 2012 R2 article you listed above.
The Nov Rollup update is not KB3008188 as added here but KB3000850.
-
20 Nov 2014 6:38 AM
thank you, it’s been corrected.
Though the purpose of Windows updates is to enhance the system performance, speed and security, sometimes that can create an issue too. It is very important to identify which updates were installed recently if you face issues with Windows OS or applications on your computer.
When you manage the server administration, you must take extra care while installing Windows updates. Some updates may cause problems with the installed applications or client-server setup. This guide explains where and how to view the installed updates/patches on your Windows 10/11 PC and Windows 2012 R2 (and the latest servers).
Checking the installed Windows update is not a tough task, but you may miss or confuse the place you must check since each interface on every Windows Operating System is different.
It can be checked in the control panel. That will show the details of updates with its KB number and date of installation.
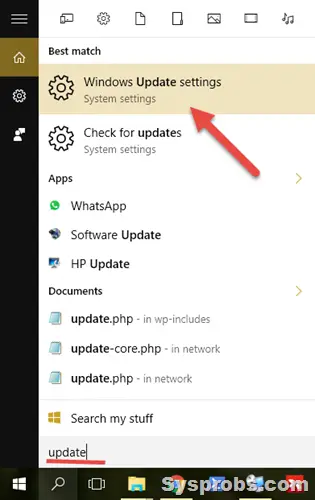
1. To go to the ‘Windows Update’ settings, type ‘Update’ in the search. This will take you to the settings app on Windows 10 or 11. Click on ‘Windows Update settings’ as below.
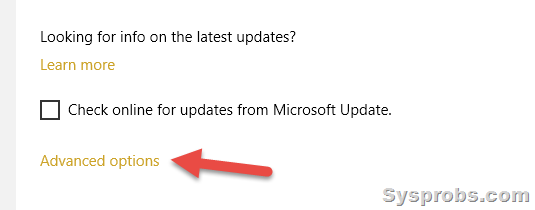
2) On the next screen, click Advanced options to see the history of installed updates.
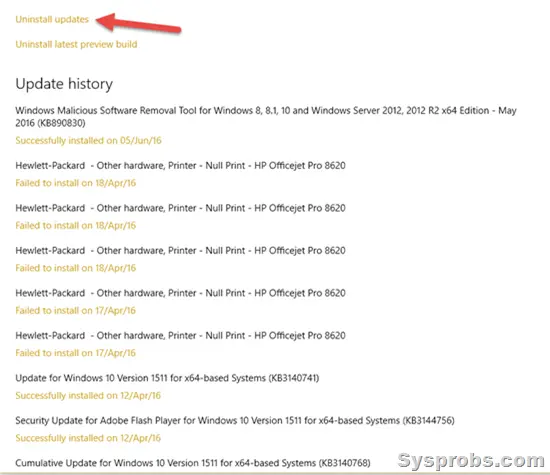
3) Click on ‘View your update history.’

Few Drawbacks in this Method
- Unfortunately, this will not show all the updates on your computer. It shows the recent success or failure updates only.
- You can’t directly uninstall a specific update from this settings app; you have to click on ‘Uninstall updates, ’ which will take you to classic control panel settings.
Best Way to Check Installed Updates/Patches on Windows 10/11/2012 R2/2016/2019
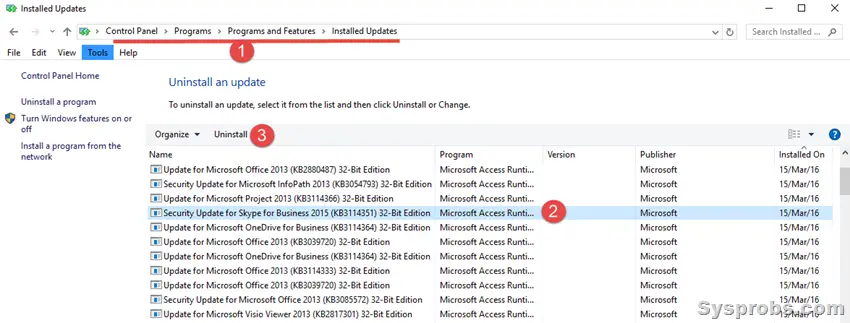
Go to the classic (we call it ‘normal’) control panel and click on ‘Programs and Features’.
Here you can view the installed updates on the server or client Operating System with the installation date. It is easy to select individual installed updates and uninstall them (if you think that particular update is causing the issue on your computer or server).
View Windows Update Patches History in Command Prompt and PowerShell
We can use a few commands to check the Windows patch history in Windows client and Server Operating Systems. It is an ideal way to use when you connect a remote computer/server or in a Windows server core installation.
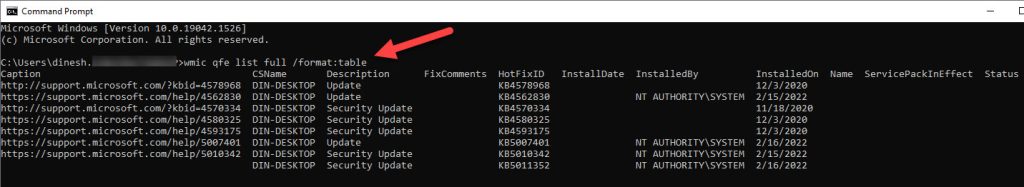
Open command prompt or Powershell and enter the below command to see the installed patches and hotfixes with the installation date in table format.
wmic qfe list full /format:table
If your computer has plenty of updates and you need to find the specific update, use the KB number in the below command.
wmic qfe | find “5007401”
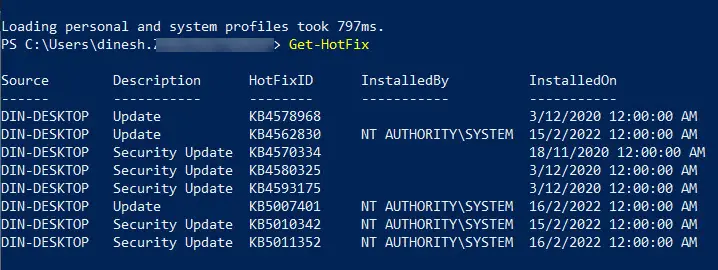
Here is a similar PowerShell command:
Get-Hotfix
You can find more about each update and its implication by searching on Google or Microsoft websites for the particular KB number.
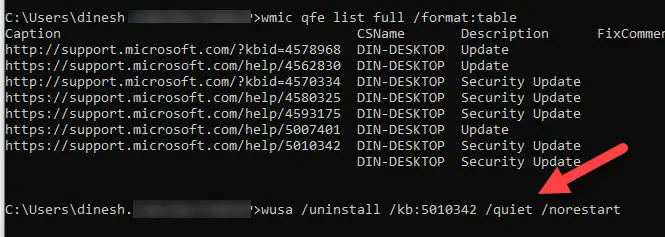
How to Remove a Windows Update from CLI?
It is possible to uninstall a particular Windows update/patch from the command prompt or PowerShell if you have administrative access.
Use one of the commands to find the installed updates and correct KB numbers, then execute the below command.
wusa /uninstall /kb:5010342
/quiet
/norestart
Those are additional keys you can use to uninstall without notifying the user and not restarting the computer or server.
We hope this guide will be useful for finding out the installed Windows updates on Windows 10/11, 2012 R2 and any server Operating Systems.

Огромное количество обновлений — источник головной боли. Наиболее актуальный дистрибутив сервера, так называемый «Update2», в который интегрированы обновления по ноябрь 2014 года, безнадежно устарел. Установив с него операционную систему, вы получите вдогонку еще 200+ обновлений, которые будут устанавливаться 2-4 часа.
В этой короткой инструкции мы освежим ноябрьский дистрибутив, интегрировав в него все кумулятивные пакеты обновлений и обновления безопасности.
Помимо дистрибутива мы освежим и память администратора, вспомнив как обновляется носитель для установки, зачем выполняется каждый шаг, и какие нас может ожидать подвохи на разных этапах.
Делать будем по максимуму просто, используя штатные инструменты.
Все работы лучше проводить на сервере с уже развернутом Windows Server 2012 R2, чтобы не было накладок с версией утилиты DISM. Так же на нем удобно подключать ISO файлы, не распаковывая их.
Готовим рабочие директории
Для работы потребуются следующие каталоги:
ISO — в этот каталог копируются файлы дистрибутива. В скопируйте в него содержимое дистрибутива SW_DVD9_Windows_Svr_Std_and_DataCtr_2012_R2_64Bit_English_-4_MLF_X19-82891.ISO, предварительно смонтировав образ, а затем размонтировав.
MOUNT — пустой каталог, в него будут монтироваться образы из wim-файла.
CU — в этот каталог поместим кумулятивные обновления
SU — в этом каталоге будут находиться обновления безопасности и другие обновления
mkdir D:WS2012R2ISO
mkdir D:WS2012R2MOUNT
mkdir D:WS2012R2CU
mkdir D:WS2012R2SUСкачиваем кумулятивные обновления
Tip & Trick #1. Microsoft выпускает для Windows Server 2012 R2 кумулятивные пакеты обновлений, но в них входят только обновления, исправляющие ошибки и улучшающие функционал. Обновления безопасности не включены. При этом обновления и не особо кумулятивны. Некоторые не включают в себя предыдущие обновления, и надо ставить «кумулятивное» за каждый месяц. Бардак. В октябре эта ситуация изменится к лучшему.
Со списком кумулятивных обновлений вы можете ознакомиться на этой wiki странице.
С ноября 2014 года нам потребуется интегрировать следующие обновления:
1. December 2014 Windows RT 8.1, Windows 8.1, and Windows Server 2012 R2. KB3013769, cкачать.
2. July 2016 Windows RT 8.1, Windows 8.1, and Windows Server 2012 R2. KB3172614, скачать.
Пакеты за май и июнь поглощены этим июльским пакетом. Но перед установкой обязательно обновление April 2015 servicing stack update for Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2. KB3021910, скачать.
3. August 2016 Windows RT 8.1, Windows 8.1, and Windows Server 2012 R2. KB3179574, скачать.
Обновленный клиент центра обновления можно не интегрировать
Свежий Windows Update Client for Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2: June 2016 вошел в KB3161606
KB3161606 поглощен KB3172614.
UPD: Я несколько преувеличил то, насколько Microsoft качественно подготовила дистрибутив. Обновления April 2014 и November 2014 действительно интегрированы. А все промежуточные — нет. Поэтому добавляем
May 2014 update rollup for Windows RT 8.1, Windows 8.1, and Windows Server 2012 R2. KB2955164, скачать
June 2014 update rollup for Windows RT 8.1, Windows 8.1, and Windows Server 2012 R2. KB2962409, скачать.
July 2014 update rollup for Windows RT 8.1, Windows 8.1, and Windows Server 2012 R2. KB2967917, скачать.
August 2014 update rollup for Windows RT 8.1, Windows 8.1, and Windows Server 2012 R2. KB2975719, скачать.
September 2014 update rollup for Windows RT 8.1, Windows 8.1, and Windows Server 2012 R2. KB2984006, скачать.
October 2014 update rollup for Windows RT 8.1, Windows 8.1, and Windows Server 2012 R2. KB2995388, скачать.
Tip & Trick #2. В разных статьях для интеграции обновлений предлагается извлечь из msu cab-файл. Делать это для offline-образа необязательно — интегрируйте msu без распаковки.
В папку CU разместите упомянутые выше msu файлы — Windows8.1-KB3013769-x64.msu, Windows8.1-KB3021910-x64.msu, Windows8.1-KB3138615-x64.msu, Windows8.1-KB3172614-x64.msu, Windows8.1-KB3179574-x64.msu.
Скачиваем обновления безопасности
Помимо кумулятивных обновлений интегрируем обновления, которые способна скачать утилита WSUS Offline Update.
Для этого:
- Скачиваем программу download.wsusoffline.net
- Выбираем обновления для Windows Server 2012 R2
- После скачивания открываем каталог wsusofflineclientw63-x64glb и *.cab файлы копируем в каталог C:WS2012R2SU
ОСТОРОЖНО: Если в список попали KB2966828 или KB2966827, удалите их, иначе после установки не получится добавить компонент Net Framework 3.5 (подробности).
Обновления готовы, приступим к интеграции.
Интеграция обновлений
Для интеграции обновлений нам потребуется:
- Смонтировать содержимое одного из образов в install.wim
dism /mount-wim /wimfile:{путь к wim файлу} /Index:{N} /mountdir:{путь к директории монтирования} - Интегрировать в offline установку каждое обновление
dism /image:{путь к директории монтирования} /add-package /packagepath:{путь к *.msu или *.cab файлу} - Сохранить изменения
dism /Unmount-WIM /MountDir:{путь к директории монтирования} /Commit
Этот процесс легко следующим автоматизировать командным файлом:
for /l %%N in (1,1,4) do (
dism /mount-wim /wimfile:"D:WS2012R2ISOsourcesinstall.wim" /Index:%%N /mountdir:D:WS2012R2MOUNT
for %%f in (D:WS2012R2CU*.*) DO (dism /image:D:WS2012R2MOUNT /add-package /packagepath:%%f)
for %%f in (D:WS2012R2SU*.*) DO (dism /image:D:WS2012R2MOUNT /add-package /packagepath:%%f)
dism /unmount-WIM /MountDir:D:WS2012R2MOUNT /Commit
)
Tip: Запуская командный файл, перенаправьте вывод в журнал
UpdateWIM.cmd >>log.txt 2>>&1
В результате мы получим файл D:WS2012R2ISOsourcesinstall.wim размером в 6.15Gb. Можем ли мы его уменьшить? Да, с помощью экспорта можно получить оптимизированный файл размером в 5.85Gb.
Экономия небольшая, кроме того после этого не очень красиво выглядит диалог выбора операционной системы при установке, поэтому следующий шаг опционален.
Что надо сделать?
Для получения сжатого образа необходимо:
- Экспортировать первый образ из оригинального wim-файла в новый файл
dism /export-image /sourceimagefile:{путь к исходному файлу wim} /sourceindex:1 /destinationimagefile:{путь к новому файлу wim} /compress:max - Подключить следующий образ из оригинального wim-файла в точку монтирования
dism /mount-wim /wimfile:"D:WS2012R2ISOsourcesinstall.wim" /Index:2 /mountdir:{директория для монтированния образа} - Добавить в новый файл следующий образ методом «захвата»
dism /append-image /imagefile:{путь к новому файлу wim} /captureDir:{директория с смонтированным образом} /name:{оригинальное имя} /description:{оригинальное описание} - Размонтировать образ, повторить итерацию добавления для каждого дополнительного образа
dism /unmount-WIM /MountDir:{директория с смонтированным образом} /Discard
Автоматизируем скриптом:
dism /export-image /sourceimagefile:D:WS2012R2ISOsourcesinstall.wim /sourceindex:1 /destinationimagefile:D:WS2012R2ISOsourcesinstall1.wim /compress:max
dism /mount-wim /wimfile:"D:WS2012R2ISOsourcesinstall.wim" /Index:2 /mountdir:D:WS2012R2MOUNT
dism /append-image /imagefile:D:WS2012R2ISOsourcesinstall1.wim /captureDir:mount /name:"Windows Server 2012 R2 SERVERSTANDARD" /description:"Windows Server 2012 R2 SERVERSTANDARD"
dism /unmount-WIM /MountDir:D:WS2012R2MOUNT /discard
dism /mount-wim /wimfile:"D:WS2012R2ISOsourcesinstall.wim" /Index:3 /mountdir:D:WS2012R2MOUNT
dism /append-image /imagefile:D:WS2012R2ISOsourcesinstall1.wim /captureDir:mount /name:"Windows Server 2012 R2 SERVERDATACENTERCORE" /description:"Windows Server 2012 R2 SERVERDATACENTERCORE"
dism /unmount-WIM /MountDir:D:WS2012R2MOUNT /discard
dism /mount-wim /wimfile:"D:WS2012R2ISOsourcesinstall.wim" /Index:4 /mountdir:D:WS2012R2MOUNT
dism /append-image /imagefile:D:WS2012R2ISOsourcesinstall1.wim /captureDir:mount /name:"Windows Server 2012 R2 SERVERDATACENTER" /description:"Windows Server 2012 R2 SERVERDATACENTER"
dism /unmount-WIM /MountDir:D:WS2012R2MOUNT /discard
Удалите оригинальный install.wim, а сформированный install1.wim переименуйте в install.wim
Создание компактного образа install.esd
По совету D1abloRUS, если вы хотите получить инсталляционный диск минимального размера умещающийся на DVD5, можно экспортировать один (и только один) из образов в esd файл. Например, для экспорта Windows Server 2012 R2 Standard, используйте команду
dism /export-image /sourceimagefile:D:WS2012R2ISOsourcesinstall.wim /sourceindex:2 /destinationimagefile:D:WS2012R2ISOsourcesinstall.esd /compress:recovery
Оригинальный install.wim можно удалить.
Сборка ISO-файла
Для сборки нам потребуется утилита oscdimg.exe из комплекта Windows ADK. Если у вас ее не оказалось, можно просто скачать утилиту по ссылке (не используйте из этого комплекта ничего, кроме самой утилиты).
Tip & Trick #3. Для того, чтобы не было проблем с загрузкой из образа, следует расположить загрузочные файлы в пределах первых 4 гигабайт образа. Для этого используем файл bootorder.txt
bootbcd
bootboot.sdi
bootbootfix.bin
bootbootsect.exe
bootetfsboot.com
bootmemtest.exe
booten-usbootsect.exe.mui
bootfontschs_boot.ttf
bootfontscht_boot.ttf
bootfontsjpn_boot.ttf
bootfontskor_boot.ttf
bootfontswgl4_boot.ttf
sourcesboot.wim
Пути в этом файле указываются относительно корневой директории с образом, поэтому подстраивать пути на ваши фактические не требуется.
Tip & Trick #4. Если install.wim имеет размер больше 4700Mb, то инсталлятор вылетит с ошибкой «Windows cannot open the required file D:sourcesinstall.wim. Error code: 0x8007000D».
Нас учили что жизнь — это бой, поэтому разделим исходный install.wim на два командой
dism /split-Image /imagefile:D:WS2012R2ISOsourcesinstall.wim /swmfile:D:WS2012R2ISOsourcesinstall.swm /filesize:4096
Оригинальный файл install.wim можно удалить.
Tip & Trick #5. Вообще Microsoft говорит, что
пить
так делать нельзя.
In Windows 8.1 and Windows 8, Windows Setup does not support installing a split .wim file.
Мы говорим, что будем! Инсталлятор прекрасно подхватывает swm-файл. Проблем с установкой не будет.
Собираем образ командой:
oscdimg -m -n -yoD:WS2012R2bootorder.txt -bD:WS2012R2ISOBOOTetfsboot.com -lIR5_SSS_X64FREV_EN-US_DV9 D:WS2012R2ISO en_windows_server_2012R2_August_2016.iso
Уважаемый ildarz подсказывает, что для создания образа, одинаково хорошо работающего с BIOS и EFI, следует руководствоваться KB947024 и создавать образ так:
oscdimg -m -u2 -udfver102 -yoD:WS2012R2bootorder.txt -bootdata:2#p0,e,bD:WS2012R2ISOBOOTEtfsboot.com#pEF,e,bD:WS2012R2ISOEFImicrosoftBOOTefisys.bin -lIR5_SSS_X64FREV_EN-US_DV9 D:WS2012R2ISO en_windows_server_2012R2_August_2016.iso
Работоспособность проверена в ESXi с любым типом загрузки (BIOS/EFI).
Все получилось? Поздравляю!
Но решена ли проблема полностью? Для идеала необходимо интегрировать еще сотню «опциональных» и «рекомендованных» обновлений, но с этим не будем торопиться. Дадим Microsoft шанс самим разобраться в том бардаке, который они устроили с обновлениями.
PS. Зачем мы все это делали? Для того, чтобы освежить память, сделать работу чуть удобнее и получить несколько простых командных файлов, при помощи которых в дальнейшем можно практически автоматизированно интегрировать обновления в серверный дистрибутив, экономя время ввода сервера в эксплуатацию. Тем более есть надежда, что начиная с октября интегрировать обновления станет гораздо проще.
Точно так же вы сможете интегрировать Windows 7 convenience rollup и не наступить на грабли распаковки обновлений, невозможности загрузки из образа, превышения размера install.wim.
Спасибо за внимание и до новых встреч, друзья.
Если есть возможность поделиться опытом — жду вас в комментариях.
Windows Server 2012 R2, codenamed «Windows Server Blue», is the seventh version of the Windows Server operating system by Microsoft, as part of the Windows NT family of operating systems. It was unveiled on June 3, 2013 at TechEd North America,[5] and released on October 18 of the same year.[2] It is the successor to Windows Server 2012, and is based on the Windows 8.1 codebase.
| Version of the Windows NT operating system | |

Screenshot of Windows Server 2012 R2, showing the Server Manager application which is automatically opened when an administrator logs on, start button, taskbar, and the blue color of Aero Lite |
|
| Developer | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| OS family | Microsoft Windows |
| Working state | Current |
| Source model | Closed source / Shared source |
| Released to manufacturing |
August 27, 2013; 9 years ago[1] |
| General availability |
October 18, 2013; 9 years ago[2] |
| Latest release | 6.3 (Build 9600) / October 11, 2022; 3 months ago[3] |
| Marketing target | Business |
| Update method | Windows Update, Windows Server Update Services, SCCM |
| Platforms | x86-64 |
| Kernel type | Hybrid (Windows NT kernel) |
| Default user interface |
Windows shell (GUI) |
| License | Trialware |
| Preceded by | Windows Server 2012 |
| Succeeded by | Windows Server 2016 |
| Official website | www.microsoft.com/en-us/server-cloud/windows-server/default.aspx |
| Support status | |
|
A further update, formally designated Windows Server 2012 R2 Update, was released in April 2014.[6] It is a cumulative set of security, critical and other updates.[7] Windows Server 2012 R2 is derived from the Windows 8.1 codebase, and runs only on 64-bit processors.
Windows Server 2012 R2 was succeeded by Windows Server 2016, which is derived from the Windows 10 codebase.
FeaturesEdit
The following features are introduced in Windows Server 2012 R2:
- Automated Tiering: Storage Spaces stores most frequently accessed files on fastest physical media[8]
- Deduplication for VHD: Reduces the storage space for VHD files with largely similar contents by storing the similar contents only once[8]
- Windows PowerShell v4, which now includes a Desired State Configuration (DSC) feature
- Integrated Office 365 support (Essentials edition)
- User interface changes reflecting Windows 8.1, including visible Start button.[9]
- UEFI-based virtual machines
- Upgrades from driver emulators to synthetic hardware drivers to minimize legacy support
- Faster VM deployment (approximately half the time)[10]
- Internet Information Services 8.5: Support for logging to Event Tracing for Windows and the ability to log any request/response headers. To improve scalability, if IIS is configured with 100 or more web sites, by default it will not automatically start any of them. Alongside this, a new «Idle Worker Process Page-Out» configuration option has been added to application pools to instruct Windows to page-out the process if it has been idle for the idle time-out period (by default, 20 minutes).[11]
- Server Message Block: Performance and event logging quality improvements, support for Hyper-V Live Migration over SMB, bandwidth prioritization management, and the ability to remove SMB 1.0 support[12]
- Windows Deployment Services: Support for managing WDS via PowerShell.[13]
- Windows Defender is available in a Server Core installation, and is installed and enabled by default.[14][dubious – discuss]
- IP Address Management (IPAM): Extended to support role-based access control, allowing for fine-grained control over which users can view or change configurations for DHCP reservations, scopes, IP address blocks, DNS resource records, etc. Additionally, IPAM can integrate with System Center Virtual Machine Manager 2012 R2 to have coordinated IP policy across both physical and virtual environments. The IPAM database can be stored in a SQL Server instance instead of Windows Internal Database.[15]
- Group Policy has a new «Policy Cache» setting which allows domain-joined machines to store a copy of the group policy settings on the client machine and, depending on the speed of access to the domain controller, use those at startup time instead of waiting for the policy settings to download. This can improve startup times on machines that are disconnected from the company network.[16] New Group Policy settings have been added to cover new features in Windows 8.1 and Internet Explorer 11, such as enabling/disabling SPDY/3 support, configuring start screen layouts, and detecting phone numbers in web pages.[17]
- TLS support is extended to support RFC 5077, «Transport Layer Security (TLS) Session Resumption without Server-Side State», which improves performance of long-running TLS-secured connections that need to reconnect due to session expiration.
- Hyper-V role and Hyper-V management console are added to the Essentials edition.[18]
- Windows Server Update Services was made available for Windows Server 2012 R2 Essentials edition.[19]
- ReFS gained support for alternate data streams and automatic error-correction on parity spaces.[20]
EditionsEdit
According to the Windows Server 2012 R2 datasheet published on May 31, 2013, there are four editions of this operating system: Foundation, Essentials, Standard and Datacenter.[21] As with Windows Server 2012, the Datacenter and Standard editions are feature-identical, varying only based on licensing (particularly licensing of virtual instances). The Essentials edition has the same features as the Datacenter and Standard products, with some restrictions.[22]
See alsoEdit
- Microsoft Servers
- Comparison of Microsoft Windows versions
- History of Microsoft Windows
- Comparison of operating systems
- List of operating systems
ReferencesEdit
- ^ Anderson, Brad (27 August 2013). «Today is the RTM for Windows Server 2012 R2!». Enterprise Mobility and Security Blog. Microsoft.
- ^ a b Jeff Meisner (August 14, 2013). «Save the date: Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows System Center 2012 R2 and Windows Intune update coming Oct. 18 — The Official Microsoft Blog — Site Home — TechNet Blogs». TechNet Blogs. Retrieved February 10, 2014.
- ^ «October 11, 2022—KB5018474 (Monthly Rollup)». support.microsoft.com. October 11, 2022.
- ^ «Search product lifecycle – Windows Server 2012 R2». Microsoft.com. Retrieved December 27, 2018.
- ^ Damien Caro (June 10, 2013). «Windows Server 2012 R2–First look — Damien Caro’s Blog — Site Home — TechNet Blogs». Blogs.technet.com. Retrieved June 25, 2013.
- ^ «August updates for Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2 — Windows Experience BlogWindows Experience Blog». blogs.windows.com.
- ^ «Windows Server 2012 R2 Update (KB2919355)». Microsoft Download Center.
- ^ a b Jackson, Joab (June 5, 2013). «Windows Server 2012 R2 bulks up on storage and networking». PC World. IDG. Retrieved September 20, 2013.
- ^ Sams, Brad (June 25, 2013). «Windows 8.1 Start button revealed in Windows Server 2012 R2». Neowin.net. Neowin LLC. Retrieved September 20, 2013.
- ^ Tulloch, Mitch (2013). Introducing Windows Server 2012 R2 (PDF) (Preview Release ed.). Redmond, Washington: Microsoft Press. ISBN 978-0-7356-8293-1. Retrieved September 19, 2013.
- ^ «What’s New in IIS 8.5?». Microsoft.
- ^ «What’s New for SMB in Windows Server 2012 R2».
- ^ «What’s New for Windows Deployment Services in Windows Server 2012 R2».
- ^ «What’s Changed in Security Technologies in Windows 8.1».
- ^ «What’s New in IPAM in Windows Server 2012 R2».
- ^ «What’s New in Group Policy in Windows Server 2012 R2». Microsoft.
- ^ «What’s new in Group Policy in Windows Server 2012 R2». Group Policy Central. 25 June 2013.
- ^ Fabritius, David (3 September 2013). «Understanding Licensing for Windows Server 2012 R2 Essentials and the Windows Server Essentials Experience role». The Windows Server Essentials and Small Business Server Blog.
- ^ «Windows Server 2012 R2 Products and Editions Comparison». Download Center. Microsoft. 7 February 2014. Retrieved 30 June 2016.
- ^ «Resilient File System Overview». TechNet Library. Microsoft. 29 February 2012. Retrieved 25 December 2013.
- ^ «Cloud Optimize Your Business» (PDF). Microsoft. Retrieved August 2, 2013.
- ^ Mackie, Kurt (June 20, 2013). «Microsoft Enhancing Windows Server 2012 R2 Essentials for SMBs». Redmondmag.com. Retrieved June 25, 2013.
Further readingEdit
- Mackie, Kurt (June 20, 2013). «Microsoft Profiles Hyper-V Improvements in Windows Server 2012 R2». Redmondmag.com. Retrieved September 20, 2013.
- «Best of TechEd 2013 – What’s New in Hyper-V in Windows Server 2012 R2 — IT Pros ROCK! at Microsoft — Site Home — TechNet Blogs». Blogs.technet.com. June 10, 2013. Retrieved September 20, 2013.
- «Top Windows Server 2012 R2 Hyper-V Virtualization Features». Petri.co.il. June 3, 2013. Retrieved September 20, 2013.
- Savill, John (June 3, 2013). «New Features Windows Server 2012 R2 | Windows Server 2012 content from». Windows IT Pro. Retrieved September 20, 2013.
- Thurrott, Paul (June 7, 2013). «Windows Server 2012 Essentials R2 Preview | Windows Server 2012 content from Paul Thurrott’s SuperSite for Windows». Winsupersite.com. Retrieved September 20, 2013.
- «Microsoft Announces Windows Server 2012 R2 at TechEd 2013 North America — Canadian IT Professionals — Site Home — TechNet Blogs». Blogs.technet.com. June 3, 2013. Retrieved September 20, 2013.
Содержание
- Просмотр всех установленных обновлений Windows
- Просмотр журнала обновлений WindowsUpdate.log в Windows 10 / Windows Server 2016
- Как посмотреть установленные обновления windows server
- Как посмотреть установленные обновления на вашем ПК с Windows 10, 8.1 или серверной ОС, например Windows 2012 и 2012 R2
- Как проверить установленный Центр обновления Windows в Windows 10
- Несколько недостатков этого метода
- Лучший способ проверить установленные обновления в Windows 10/2012 R2 / 2016/2019
- Поиск установленных обновлений из командной строки
- Get-WmiObject
- Get-SilWindowsUpdate
- Microsoft Update Client Install History
Просмотр всех установленных обновлений Windows
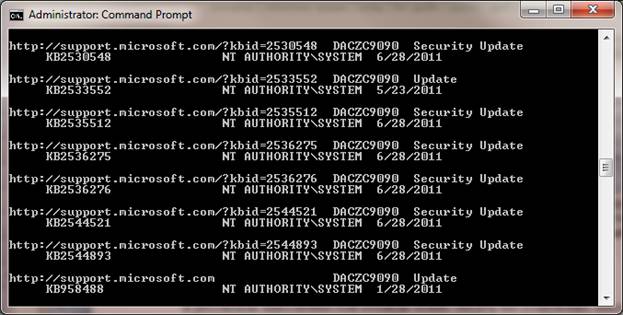
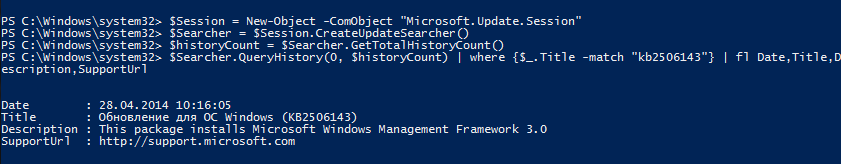
Как узнать какие обновления ОС Windows установлены на вашем ПК или сервере? Конечно, можно открыть «Панель управления->Установка/удаление программ», либо элемент Update History в Windows 7/2008 и просмотреть список установленных обновлений, однако с помощью графического интерфейса нельзя ни выгрузить этот список, ни осуществить поиск по нему. В таком случае, необходимо прибегнуть к помощи командной строки. С помощью следующей команды можно вывести подробный список всех обновлений, которые установлены на данной системе Windows:
В результатах выполнения этой команды можно увидеть что установлено, кем и когда, кроме того, выводится ссылка на статью в базе знания Microsoft (KB). Для того, чтобы получить список установленных обновлений в текстовом виде, можно просто перенаправить вывод этой команды в текстовый файл, а затем открыть его в любимом текстовом редакторе:
Текстовый файл с именем updatelist.txt создастся в каталоге C:WindowsSystem32.
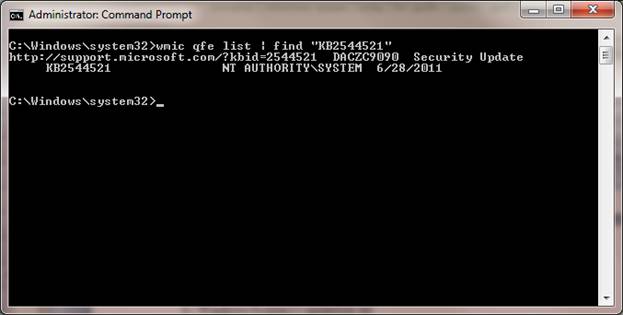
Если нужно узнать установлено ли конкретное обновление Windows на данной системе (например, KB2544521), можно воспользоваться командой find, перенаправив вывод в нее:
Как вы видите, обновление KB2544521 уже установлено.
Еще один способ просмотра установленных обновлений в Windows – использование утилиты “systeminfo”. Данная команда в отличии от предыдущей выведет лишь список номеров KB (в дополнении к системной информации). В данном случае также можно перенаправить вывод этой команды в текстовый файл:
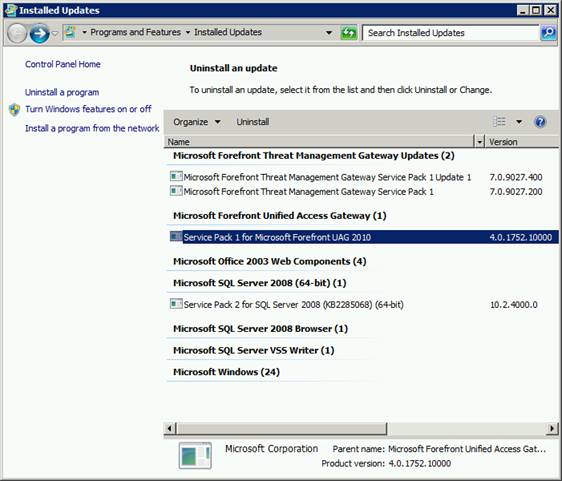
Однако будьте внимательными, все эти команды отображают лишь установленные обновления и хотфиксы для самой ОС Windows, информации об обновлениях любых других продуктов Microsoft (таких как, UAG, Office, TMG, SQL или Exchange) здесь отсутствует. Для просмотра установленных обновлений на эти продукты, необходимо в меню пуск набрать: “View Installed Updates”, после чего откроется стандартное окно, доступное из панели управления.
Для поиска конкретного обновления можно в окне поиска (в правом верхнем углу) набрать KB и номер апдейта, однако поиск выполняется не очень корректно, поэтому иногда проще найти нужное обновление простым просмотром списка.
Также при установке обновлений не стоит забывать, что они требуют перезагрузки системы. В Windows 7 после установки обновлений она перезагружается автоматически, что достаточно неудобно. К счастью, можно отключить автоматическую перезагрузку Windows после установки обновлений.
Источник
Просмотр журнала обновлений WindowsUpdate.log в Windows 10 / Windows Server 2016
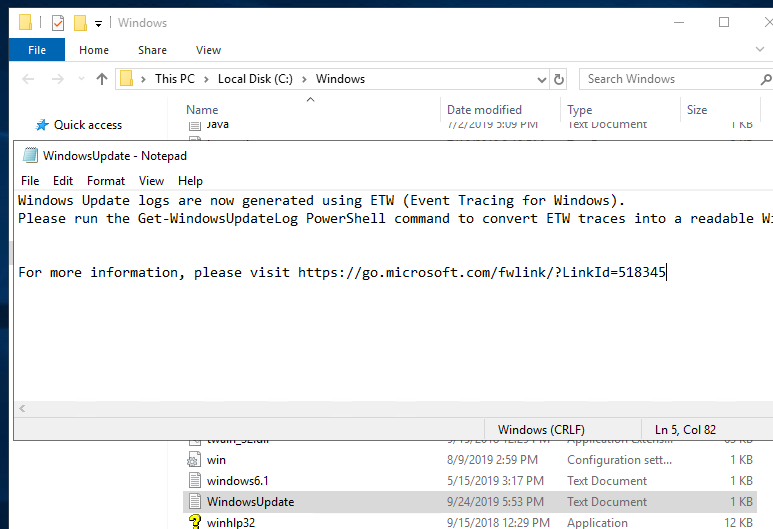
Исторически для анализа работы агента и службы обновления Windows используется текстовый файл WindowsUpdate.log. Однако в Windows 10 (Windows Server 2016/2019) вместо привычного текстового файла логи Windows Update ведутся в формате Event Tracing for Windows (ETW). За счет этого увеличивается быстродействие подсистемы записи логов и экономится место на диске.
Таким образом, события Windows Update теперь больше не записываются в реальном времени в файл %windir%WindowsUpdate.log. И хотя сам файл все еще присутствует в корне папки Windows, в нем лишь указано, что для сбора логов теперь применяется формат ETW.
Главное неудобство для администраторов – теперь вы не можете быстро проанализировать текстовый файл WindowsUpdate.log, найти ошибки в службе агента обновлений Windows (см. полный список ошибок Windows Update), проверить настройки WSUS и проанализировать историю установки обновлений.
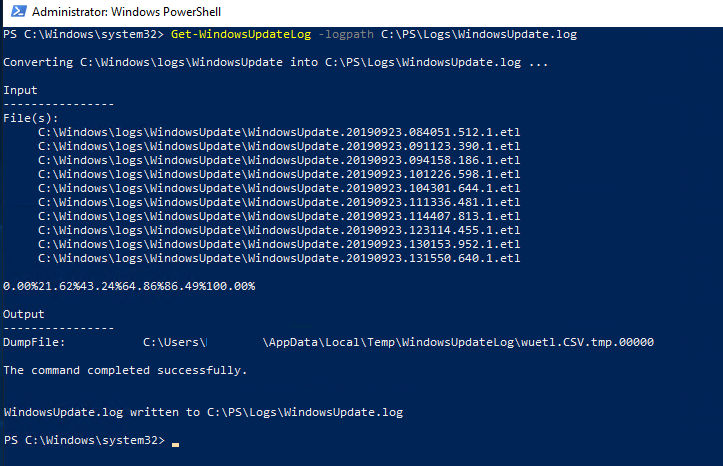
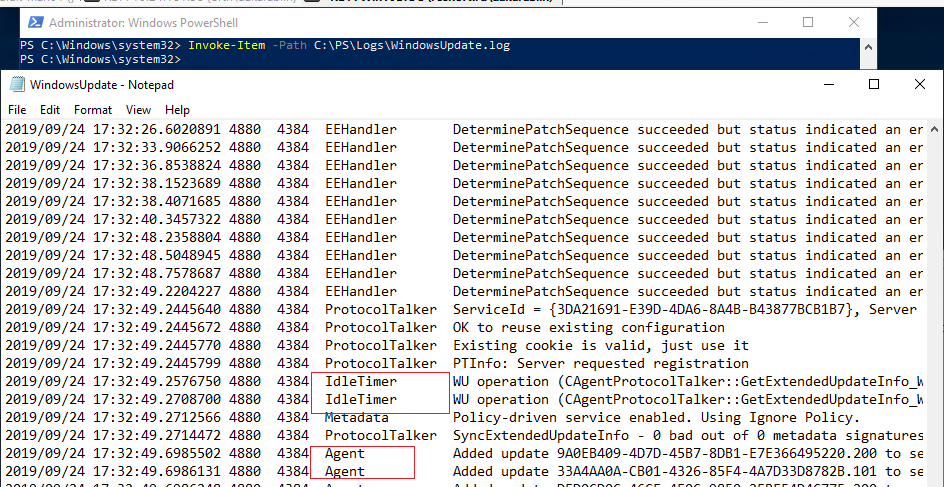
Вы можете сконвертировать события ETW в привычный текстовый формат WindowsUpdate.log для более удобного анализа событий службы обновлений. Для этого используется командлет PowerShell — Get-WindowsUpdateLog. Данный командлет позволяет собрать информацию со всех .etl файлов (хранятся в каталоге C:WINDOWSLogsWindowsUpdate) и сформировать один файл WindowsUpdate.log.
Чтобы сформировать файл WindowsUpdate.log и поместить его в каталог C:PSLogs, выполните следующую команду в консоли PowerShell:
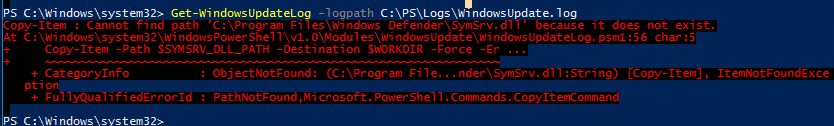
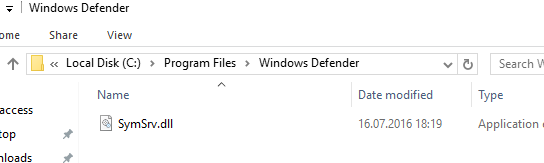
Файл “C:Program FilesWindows DefenderSymSrv.dll” обычно отсутствует, если на сервере не установлен антивирус Windows Defender.
Чтобы исправить ошибку, вы можете установить Defender, скопировать файл SymSrv.dll с другого Windows Server 2016/ Windows 10 или поиском найти его в каталоге “C:WindowsWinSxS” (у меня каталог назывался C:WindowsWinSxSamd64_windows-defender-service-cloudclean_…) и скопировать его в папку C:Program FilesWindows Defender.
В старых версиях Windows 10 при первом запуске командлет Get-WindowsUpdateLog скачает и установит сервер символов Microsoft (Microsoft Internet Symbol Store). В последних версиях Windows 10 выполняется онлайн доступ к серверу символов Microsoft в Azure. Затем командлет:
Это значит, что у вас не установлен сервер символов Windows Symbol (сейчас нельзя скачать отдельную программу установки Windows symbols, т.к. они автоматически загружаются из хранилища символов в Azure). Для изолированных сред вы можете использовать офлайн версию сервера символов согласно статье Offline Symbols for Windows Update.
Откройте файл журнала с помощью такой команды PowerShell:
Анализировать получившийся файл WindowsUpdate.log довольно сложно, т.к. в нем собираются данные из множества источников:
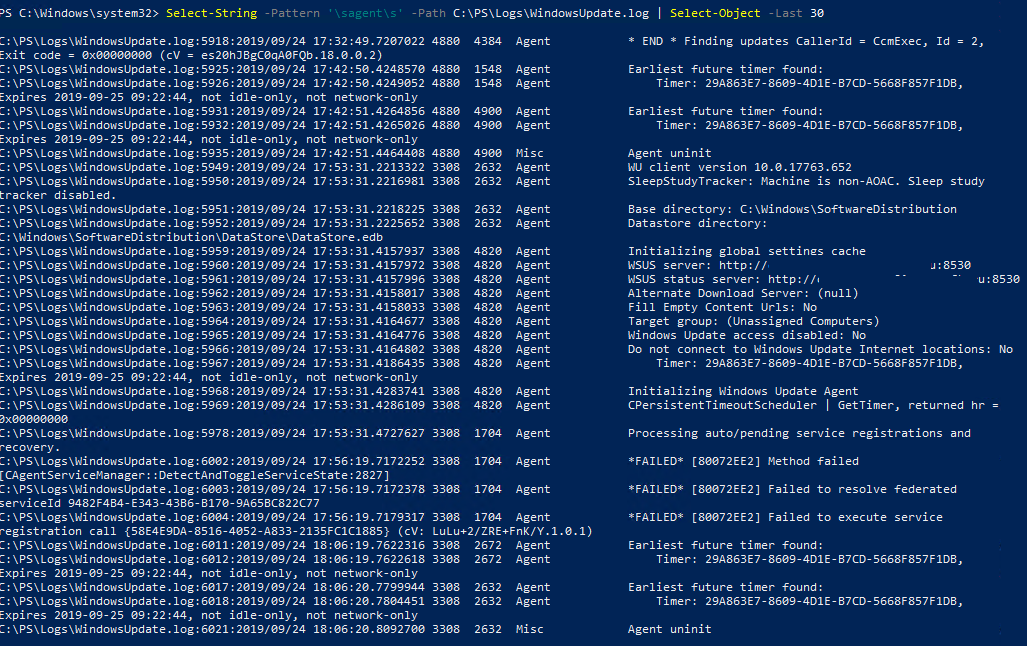
Вы можете выбрать последние 30 событий от агента обновления Windows (agent) с помощью простого регулярного выражения:
Можно отфильтровать события в логе по нескольким источникам:
Аналогично вы можете искать события по номеру KB, ошибка (строки FAILED, Exit Code, FATAL).
Также вы можете сформировать файл WindowsUpdate.log для удаленного компьютера/сервера:
Источник
Как посмотреть установленные обновления windows server
Как узнать какие обновления операционной системы Windows установлены на Ваш компьютер или сервер? Можно открыть Панель управления затем Установка/удаление программ, либо элемент Update History в Windows 7/2008 и просмотреть список установленных обновлений, однако с помощью графического интерфейса нельзя ни выгрузить этот список, ни осуществить поиск по нему.
В этом случае будет полезна командная строка. С помощью команды wmic qfe list можно вывести подробный список всех обновлений, которые установлены на данной системе Windows.
wmic qfe list
В результатах выполнения этой команды можно видеть, что установлено, каким пользователем и когда, кроме того, выводится ссылка на статью в базе знания Microsoft (KB). Для того, чтобы получить список установленных обновлений в текстовом виде, можно просто перенаправить вывод этой команды в текстовый файл, а затем открыть его в любимом текстовом редакторе:
wmic qfe list > updatelist.txt && updatelist.txt
Текстовый файл с именем updatelist.txt создастся в каталоге C:WindowsSystem32.
Если нужно узнать установлено ли конкретное обновление Windows на данной системе (например, KB2536275), можно воспользоваться командой find, перенаправив вывод в нее:
wmic qfe list | find » KB2536275″
Из указанного выше примера видно, что обновление KB2536275 установлено.
Еще один способ просмотра установленных обновлений в Windows – использование утилиты “systeminfo”. Данная команда в отличии от предыдущей выведет лишь список номеров KB (в дополнении к системной информации). В данном случае также можно перенаправить вывод этой команды в текстовый файл:
systeminfo > sysinfo.txt && sysinfo.txt
Однако будьте внимательными, все эти команды отображают лишь установленные обновления и hotfix * для самой ОС Windows, информации об обновлениях любых других продуктов Microsoft (таких как, UAG, Office, TMG, SQL или Exchange) здесь отсутствует. Для просмотра, установленных обновлений на эти продукты, необходимо в меню пуск набрать: Просмотр установленных обновлений, после чего откроется стандартное окно, доступное из панели управления.
Для поиска конкретного обновления можно в окне поиска, в правом верхнем углу набрать KB и номер апдейта, однако поиск выполняется не очень корректно, поэтому иногда проще найти нужное обновление простым просмотром списка.
Также при установке обновлений не стоит забывать, что они требуют перезагрузки системы.
Источник
Как посмотреть установленные обновления на вашем ПК с Windows 10, 8.1 или серверной ОС, например Windows 2012 и 2012 R2
Хотя цель обновления Windows — повысить производительность системы, увеличить скорость и исправить ошибки безопасности, иногда это может повредить и вашему компьютеру. Очень важно определить, какие обновления были установлены недавно, если у вас возникли проблемы с ОС Windows или приложениями на вашем компьютере. Когда вы работаете в серверной среде, вы должны проявлять особую осторожность при установке обновлений Windows. Некоторые обновления могут вызвать проблемы с установленными приложениями или настройкой сервера с клиентами. В этом руководстве объясняется, где и как просмотреть установленные обновления на вашем ПК с Windows 10 и Windows 2012 R2 (и на последних серверах).
Проверка установленного обновления Windows — не сложная задача, но вы можете пропустить или запутать место, которое вы должны проверить, поскольку каждый интерфейс в каждой операционной системе Windows отличается.
Как проверить установленный Центр обновления Windows в Windows 10
Это можно проверить в панели управления. Это покажет подробную информацию об обновлениях с номером базы знаний и датой установки.
1) Чтобы перейти к настройкам «Центра обновления Windows», введите в поиске «Обновление». Вы попадете в приложение настроек в Windows 10. Нажмите «Настройки Центра обновления Windows», как показано ниже.
2) На следующем экране нажмите «Дополнительные параметры», чтобы просмотреть историю установленных обновлений.
3) Нажмите «Просмотреть историю обновлений».
Здесь будут показаны установленные обновления на вашем настольном или портативном компьютере с Windows 10.
Несколько недостатков этого метода
Лучший способ проверить установленные обновления в Windows 10/2012 R2 / 2016/2019
Перейдите в классическую (мы называем ее «нормальной») панель управления и нажмите «Программы и компоненты».
Здесь вы можете просмотреть установленные обновления в серверной или клиентской операционной системе с указанием даты установки. Легко выбрать отдельные установленные обновления и удалить их (если вы считаете, что именно это обновление вызывает проблему на вашем компьютере или сервере).
Мы надеемся, что это небольшое руководство будет полезно для поиска установленных обновлений Windows на серверных компьютерах с Windows 10 или 2012 R2.
Источник
Поиск установленных обновлений из командной строки
Иногда требуется проверить установленные в системе обновления. Конечно, можно просмотреть журнал обновлений, однако выискивать нужное обновление в длинном списке достаточно сложно и долго. Поэтому гораздо проще воспользоваться командной строкой, которая предоставляет для этого несколько способов.
Быстрее и проще всего отыскать нужный апдейт с помощью утилиты командной строки wmic.exe. Так следующая команда выведет полный список установленных обновлений:
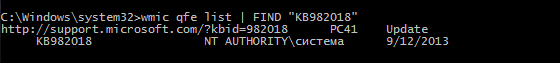
А так мы найдем найдем нужное:
wmic qfe list | find ″KB982018″
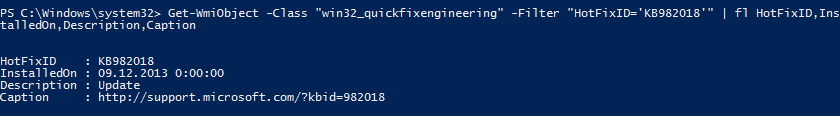
Get-WmiObject
PowerShell также позволяет просмотреть установленные обновления. Сделать это можно с помощью командлета Get-WmiObject, например:
Как видите, команда несколько сложнее и требуется дополнительно отформатировать вывод, однако результат такой же, как и у утилиты wmic. Что неудивительно, так как в обоих случаях данные получаются путем обращения к WMI классу win32_quickfixengineering. Обратите внимание, что он содержит данные только об обновлениях операционной системы и ее компонентов. Получить информацию об обновлениях для других продуктов MS (Office, Exchange и т.п) таким образом не получится.
Get-SilWindowsUpdate
В Windows Server 2012 R2 имеется модуль SoftwareInventoryLogging, предназначенный для инвентаризации установленного ПО. В состав этого модуля входит командлет Get-SilWindowsUpdate, с помощью которого также можно посмотреть установленные обновления. Например:
Этот командлет также использует WMI запрос к классу MsftSil_WindowsUpdate. Get-SilWindowsUpdate очень прост и удобен в использовании, но к сожалению доступен он далеко не везде. Модуль SoftwareInventoryLogging присутствует только в серверных ОС начиная с Windows Server 2012 R2 с установленным обновлением KB3000850.
Microsoft Update Client Install History
Еще один вариант поиска обновлений — просмотр истории клиента обновления. Например:
Способ (в отличие от предыдущих) достаточно громоздкий, однако позволяет найти информацию об всех обновлениях обновления (как самой ОС, так и доп. приложений). Таким образом можно найти обновления, которые были установлены с помощью системы автоматического обновления. Если обновления были загружены и установлены вручную (или с помощью каких либо пользовательских сценариев), то таким образом найти их не удастся.
Источник
| Version of Microsoft Windows | |
 |
|
| OS family | Windows NT |
|---|---|
| Version | 6.3 |
| Codename | Server Blue |
| Architecture | x64 |
| Latest build | 6.3.9600.17415 |
| Release date | 2013-10-18 |
| Support end | 2023-10-10 2026-10-13 (with Extended Security Updates) |
| Client counterpart | |
| Windows 8.1 | |
| Replaces | |
| Windows Server 2012 | |
| Replaced by | |
| Windows Server 2016 | |
Windows Server 2012 R2 is the server counterpart of Windows 8.1. It reached RTM on 27 August 2013 and was released on 18 October of that year. It replaces Windows Server 2012 and was replaced by Windows Server 2016.
This is the first version of Windows Server to drop support for processors without the CMPXCHG16b, PrefetchW and LAHF/SAHF instructions. It is the last version to support upgrade paths to Windows Server 2016 and also the last version to support upgrade paths from Windows Server 2008 R2.
Editions[edit | edit source]
There are four editions of this operating system: Essentials, Foundation, Standard and Datacenter. As with Windows Server 2012, the Datacenter and Standard editions are feature identical, varying only based on licensing (particularly licensing of Hyper-V VMs). The Essentials edition has the same features as the Datacenter and Standard products, with some restrictions.
Changes[edit | edit source]
- Automated Tiering: Storage Spaces stores most frequently accessed files on fastest physical media.
- Deduplication for VHD: Reduces the storage space for VHD files with largely similar contents by storing the similar contents only once.
- Windows PowerShell v4, which now includes a Desired State Configuration (DSC) feature.
- Web Application Reverse Proxy.
- Integrated Office 365 support.
- The return of the Start button.
Hardware compatibility[edit | edit source]
Windows Server 2012 R2 is officially compatible with Intel processors up to Skylake (6th Generation). On Kaby Lake (7th Generation) up to Coffee Lake (8th/9th Generation), Server 2012 R2 is not supported due to a lack of Windows Update and Intel Graphics, however, hacks have been made to get both working. For Ice Lake (10th Generation) up to Alder Lake (12th Generation), no known hacks have appeared for Intel Graphics, but the chipset drivers for Ice Lake, Tiger Lake (11th Generation), and Alder Lake have been confirmed to install without any issues.
List of known builds[edit | edit source]
Build list legend
Available build
Confirmed build
Unconfirmed build
Fake build
Existing page
Non-existent page