Open firewall ports in Windows 10
- Navigate to Control Panel, System and Security and Windows Firewall.
- Select Advanced settings and highlight Inbound Rules in the left pane.
- Right click Inbound Rules and select New Rule.
- Add the port you need to open and click Next.
- Add the protocol (TCP or UDP) and the port number into the next window and click Next.
How do I enable port 22 on Windows?
Configure the Windows Firewall
- Click on Start –> Control Panel –> Windows Firewall –> Exceptions Tab.
- Click the Add Port button.
- Name: SSH.
- Port Number: 22.
- TCP.
- Click OK to add the SSH exception to the firewall.
- Click OK to close the Windows Firewall screen.
How do I open a port on Windows Server 2016?
To open a port in the firewall using the GUI in Windows Server 2008/2012 R2 and Windows Server 2016, follow the below steps:
- Log in using an administrator account.
- Click Start > Administrative Tools > Windows Firewall with Advanced Security.
How do I open the ports on my router?
Open the web browser and type the IP address of the router (default is 192.168.1.1) into the address bar and then Press Enter. Type the username and password in the login page, the default username and password both are admin. Click Forwarding->Virtual Servers on the left side, and then click Add New… button.
How do I open port 8080?
This means the port is opened:
- To open the port, open Windows Firewall:
- In Advanced Settings in the left-hand pane, click Inbound Rules.
- In the wizard, select Port and click Next:
- Check TCP, check Specific local ports, enter 8080, and click Next:
- Click Allow the connection and click Next:
- Check your networks.
How do you check if a port is blocked in Windows?
Checking Windows Firewall for blocked ports
- Launch Command Prompt.
- Run netstat -a -n.
- Check to see if the specific port is listed. If it is, then it means that the server is listening on that port.
How do you check if a port is open in Windows?
Type “netstat -a” in the Command Prompt window, and press “Enter.” The computer displays a list of all open TCP and UDP ports. Look for any port number that displays the word “LISTENING” under the “State” column. If you need to ping through a port to a specific IP use telnet.
How do I check if a port is open on a Windows server?
How to Find Open Ports on a Server
- Open the Command Prompt by clicking on “Start” then “All Programs” then “Accessories” then “Command Prompt.”
- Listen for open ports by typing ‘netstat -an. | find /i “listening”‘ in the command prompt. Hit the “Enter” key on your keyboard and wait for all of the ports to show up on the screen.
How do I open a port on a Windows server?
Open firewall ports in Windows 10
- Navigate to Control Panel, System and Security and Windows Firewall.
- Select Advanced settings and highlight Inbound Rules in the left pane.
- Right click Inbound Rules and select New Rule.
- Add the port you need to open and click Next.
- Add the protocol (TCP or UDP) and the port number into the next window and click Next.
How do you check if a port is open on a remote server?
Telnet: You should also test the connection using telnet as this allows you to specify the TCP port.
- Open a command prompt.
- Type in “telnet <IP ADDRESS OF SERVER PC> <PORT>” and press enter.
- If a blank screen appears then the port is open, and the test is successful.
- If you receive a connecting
How do I open port 8000 on my router?
To enable a port range in advance
- Click Advanced settings in the left column of the Windows Firewall window.
- Click Inbound Rules in the left column.
- Click New Rules in the right column.
- Select Port and click next.
- Select TCP and enter 8000, 8001, 8002, 8003, 9000, 80, 443 in the Specific local ports field.
- Click Next.
How do I open a port in Windows 7 with CMD?
You can identify open ports on a Windows 7 machine by running a single command with the correct switches from the command prompt. Run the “netstat” command to quickly identify open ports. Click the Windows “Start” button to show the Search input box. Type “cmd” into the Search box.
How do I find my IP address and port number?
The port number is “tacked on” to the end of the IP address, for example, “192.168.1.67:80” shows both the IP address and port number. When data arrives at a device, the network software looks at the port number and sends it to the right program. To find a port address, review an app’s technical documentation.
How do I kill a port in Windows?
Kill the process at a certain port in Windows 7
- Type netstat -a -o -n and it will bring up a network list, look at the PID (e.g. 8080).
- To find out what PID 8080 was (hopefully not a trojan) I typed tasklist /FI “PID eq 8080″
- To kill it type taskkill /F /PID 2600.
How do you check which ports are open in Windows?
- Open a command prompt window (as Administrator) From “StartSearch box” Enter “cmd” then right-click on “cmd.exe” and select “Run as Administrator”
- Enter the following text then hit Enter. netstat -abno.
- Find the Port that you are listening on under “Local Address”
- Look at the process name directly under that.
How can I check if port 80 is open?
6 Answers. Start->Accessories right click on “Command prompt”, in menu click “Run as Administrator” (on Windows XP you can just run it as usual), run netstat -anb then look through output for your program. BTW, Skype by default tries to use ports 80 and 443 for incoming connections.
How do I check if a port is free in Windows?
If this check fails, another application is using port 80.
- From the Windows Start menu, select Run.
- In the Run dialog box, enter: cmd .
- Click OK.
- In the command window, enter: netstat -ano.
- A list of active connections is displayed.
- Start Windows Task Manager and select the Processes tab.
How can I tell if port 22 is open?
Check port 25 in Windows
- Open “Control Panel“.
- Go to “Programs“.
- Select “Turn Windows features on or off ”.
- Check the “Telnet Client” box.
- Click “OK“. A new box saying “Searching for required files“ will appear on your screen. When the process is completed, telnet should be fully functional.
How do I check if port 3389 is open?
Click either TCP or UDP, and then click OK. Repeat steps 1 through 9 for each port to open. To find open ports on a computer, use netstat command line. To display all open ports, open DOS command, type netstat and press Enter.
Which port is my application using Windows?
Checking which application is using a port:
- Open the command prompt – start » run » cmd or start » All Programs » Accessories » Command Prompt.
- Type netstat -aon.
- If the port is being used by any application, then that application’s detail will be shown.
- Type tasklist.
How can I check which ports are open?
How to find open ports on a computer
- To display all open ports, open DOS command, type netstat and press Enter.
- To list all listening ports, use netstat -an.
- To see what ports your computer actually communicates with, use netstat -an |find /i “established”
- To find specified open port, use find switch.
How do I scan a port to open CMD?
Type “netstat -a” in the Command Prompt window, and press “Enter.” The computer displays a list of all open TCP and UDP ports.
How do I check if a port 1433 is open?
Open the 1433 port in your firewall.
- In the SQL Server Configuration Manager, right-click TCP/IP and select Properties.
- Select the IP Addresses tab and make sure the TCP Port for IP1 is 1433 .
How do I open a port on Windows Server 2012?
In order to open an inbound port, go to “Inbound Rules” under the “Windows Firewall with Advanced Security on Local Computer”, and click “New Rule” in the sidebar. Choose “Port” as the kind of rule you want to create. This will allow you to create rules for inbound connections to both TCP and UDP ports.
How do I open a port in Windows Firewall?
Windows Firewall
- To open a port, navigate to Start > Control Panel > System and Security.
- Click Check firewall status. The Windows Firewall window appears.
- Click Advanced settings.
- Click Inbound Rules.
- Click New Rule.
- Click Port.
- Click Next.
- Click TCP or UDP depending on the desired port.
How do I check if a port is open Linux?
How to check the listening ports and applications on Linux:
- Open a terminal application i.e. shell prompt.
- Run any one of the following command: sudo lsof -i -P -n | grep LISTEN. sudo netstat -tulpn | grep LISTEN. sudo nmap -sTU -O IP-address-Here.
What port is Telnet?
Typically, this protocol is used to establish a connection to Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) port number 23, where a Telnet server application (telnetd) is listening. Telnet, however, predates TCP/IP and was originally run over Network Control Program (NCP) protocols.
Can I ping a port?
Because ping doesn’t operate over a protocol with port numbers, you cannot ping a particular port on a machine. However, you can use other tools to open a connection to a particular IP and port and obtain the same information you would get if you could ping an IP and port.
Is port 80 blocked?
The most commonly blocked ports are port 80 and port 25. With blocked port 80 you will need to run your web server on a non-standard port.
How do I find out what application is using port 80?
To check what’s using Port 80:
- Open Command Line and use netstat -aon | findstr :80. -a Displays all active connections and the TCP and UDP ports on which the computer is.
- Then, to find which programs are using it, take the PID number and put them in tasklist /svc /FI “PID eq [PID Number]”
- Closing programs should resolve.
How can I tell if port 21 is open?
How to check if port 21 is blocked?
- On Windows OS. go to the Start Menu on the bottom left corner; click Run and type cmd;
- On MAC OS. go to Applications directory; choose Utilities and this will open you a command line; type telnet.mydomain.com 21.
- On Linux. open your terminal emulator; type telnet.mydomain.com 21.
Photo in the article by “Wikimedia Commons” https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:An_open_stained-glass_window_in_the_Port_Elizabeth_Main_Library,_South_Africa.jpg
You can configure network port forwarding in all Windows versions without using third-party tools. Using a port forwarding rule, you can redirect an incoming TCP connection (IPv4 or IPv6) from a local TCP port to any other port number, or even to a port on a remote computer. Windows port forwarding is most commonly used to bypass firewalls or to hide an internal host or service from the external network (NAT/PAT).
In the Linux world, port forwarding is configured quite simply using iptables or firewalld rules. On Windows Server hosts, the Routing and Remote Access Service (RRAS) is typically used to configure port redirections. However, there is an easier way to enable port forwarding using netsh portproxy mode, which works on all versions of Windows from Win XP to current builds of Windows 11 and Windows Server 2022.
Contents:
- How to Enable Port Forwarding on Windows with Netsh Portproxy?
- Configuring Firewall Rules for Port Forwarding Mode in Windows
- Managing Netsh Port Forwarding Rules in Windows
- Port Forwarding with NAT Rules on Hyper-V Virtual Switch
How to Enable Port Forwarding on Windows with Netsh Portproxy?
You can configure port forwarding in Windows using the Portproxy mode of the Netsh command.
The command syntax is as follows:
netsh interface portproxy add v4tov4 listenaddress=localaddress listenport=localport connectaddress=destaddress connectport=destport
where
- listenaddress –is a local IP address to listen for incoming connection (useful if you have multiple NICs in different subnets/VLANs or multiple IP addresses on one interface);
- listenport – a local TCP port number to listen on (the connection is waiting on);
- connectaddress – is a local or remote IP address (or DNS name) to which you want to redirect the incoming connection;
- connectport – is a TCP port to which the connection from
listenportis forwarded to.
Using the netsh interface portproxy add v4tov6/v6tov4/v6tov6 options, you can create port forwarding rules between IPv4 and IPv6 addresses.
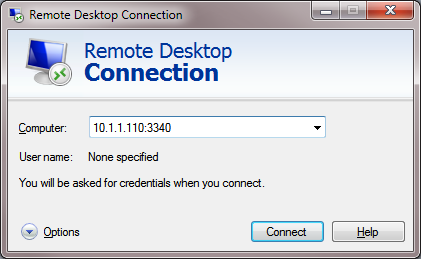
Let’s suppose your task is to make the RDP service respond on a non-standard port, for example 3340 (of course, this port number can be changed in the Windows settings, but we are using RDP to make it easier to demonstrate the port forwarding technique). To do this, we need to redirect incoming traffic from TCP port 3340 to another local port 3389 (this is the default RDP port number).
Please note that the local port number that you specified in listenport should not be listened (used) by another service or process. Check that the port number is not used:
netstat -na|find "3340"
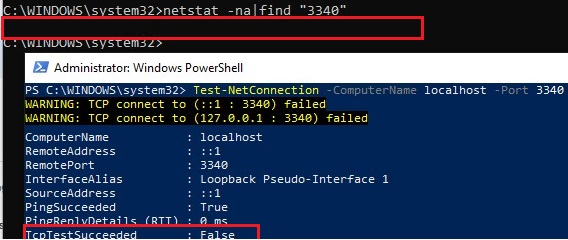
Alternatively, you can check that the port is not listening locally using the PowerShell cmdlet Test-NetConnection:
Test-NetConnection -ComputerName localhost -Port 3340
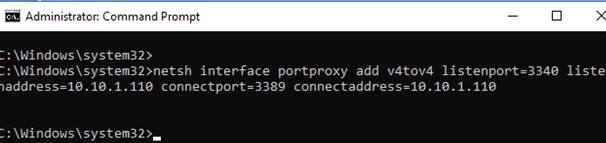
To create a port forwarding rule on Windows, open a command prompt as an administrator and run the following command:
netsh interface portproxy add v4tov4 listenport=3340 listenaddress=10.1.1.110 connectport=3389 connectaddress=10.1.1.110
Where 10.10.1.110 – the current IP address of your computer on which port forwarding is configured.
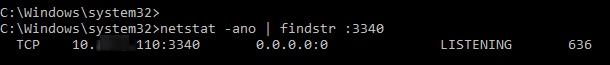
Now, use the netstat tool to check that Windows is now listening on local port 3340:
netstat -ano | findstr :3340
Note. If this command returns nothing and port forwarding through the netsh interface portproxy doesn’t work, make sure that you have the iphlpsvc (IP Helper) service running on your Windows device.
Check the status of the service in the services.msc console or using the PowerShell command:
Get-Service iphlpsvc
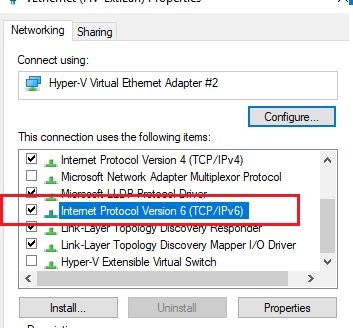
IPv6 support must be enabled on the network interface for which the port forwarding rule is being created.
These are the prerequisites for the correct operation of port forwarding in Windows. Without the IP Helper service and without IPv6 support enabled, the port redirection won’t work.
To make port forwarding work on Windows Server 2003/XP, you must additionally set the IPEnableRouter parameter to 1 under the registry key HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE SystemCurrentControlSetservicesTcpipParameter.
Set-ItemProperty -Path HKLM:systemCurrentControlSetservicesTcpipParameters -Name IpEnableRouter -Value 1
This option also allows you to enable routing between different subnets in Hyper-V.
You can identify the process that is listening on the specified port by its PID (in our example, the PID is 636):
tasklist | findstr 636
Now try to connect to the new port from a remote computer using any RDP client. You need to specify 3340 as the RDP port number. It is specified after the colon following the RDP host address. For example, 10.10.1.110:3340
In this example, port TCP/3340 must first be opened in Windows Defender Firewall (see the next section of the article).
The RDP connection should be established successfully.
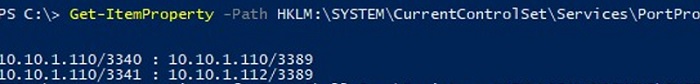
Portproxy port forwarding rules are permanent and are not cleared when you restart Windows. These rules are stored in the registry. You can list the netsh forwarding rules in the registry using PowerShell:
Get-ItemProperty -Path HKLM:SYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesPortProxyv4tov4tcp
If you want to forward an incoming TCP connection to a remote computer, use the following command:
netsh interface portproxy add v4tov4 listenport=3389 listenaddress=0.0.0.0 connectport=3389 connectaddress=192.168.100.101
This rule will redirect all incoming RDP traffic (from local TCP port 3389) from this computer to a remote host with an IP address 192.168.1.100.
Note that the portproxy mode in Windows doesn’t support saving the source IP in a forwarded network packet. Those, if you forward port 443 port from a Windows device to an internal web server, then all incoming connections will appear on the target server as coming from the same IP address (from your Windows host with netsh portproxy enabled). If you need to use source IP forwarding, you need to use NAT on an external firewall or on Hyper-V (described below).
Also, you can use the SSH tunnels in Windows to forward the local port to a remote server.
Configuring Firewall Rules for Port Forwarding Mode in Windows
Ensure that your firewall (Microsoft Windows Defender or a third-party firewall, which is often part of the anti-virus software) allows incoming connections to the new port. You can add a new allow rule to Windows Defender Firewall with the command:
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name="forwarded_RDPport_3340" protocol=TCP dir=in localip=10.1.1.110 localport=3340 action=allow
Or using the New-NetFirewallRule PowerShell cmdlet:
New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName "forwarder_RDP_3340" -Direction Inbound -Protocol TCP –LocalPort 3340 -Action Allow
When creating an inbound firewall rule for TCP/3340 port via Windows Defender Firewall graphical interface, you don’t need to associate a program or process with the rule. This port is only listened on by the network driver.
If you disable the portproxy rule, be sure to remove the remaining firewall rule as follows:
netsh advfirewall firewall del rule name="RDP_3340"
or remove firewall rule with PowerShell:
Remove-NetFirewallRule -Name RDP_3340
Managing Netsh Port Forwarding Rules in Windows
You can create any number of port forwarding rules in Windows. All netsh interface portproxy rules are persistent and remain after a Windows restart.
Several times I encountered cases when in Windows Server 2012 R2 the port forwarding rules were reset after the server was rebooted. In this case, you need to check whether there is a periodic disconnection on the network interface and whether the IP address changes when the OS boots (it is better to use a static IP instead of dynamic DHCP). As a workaround, I had to add a batch script with the netsh interface portproxy rules to the Windows Task Scheduler that run on the system startup.
To display a list of all enabled TCP port forwarding rules on Windows, run the command:
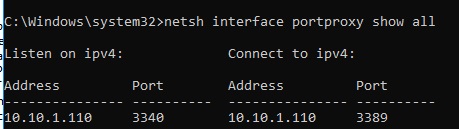
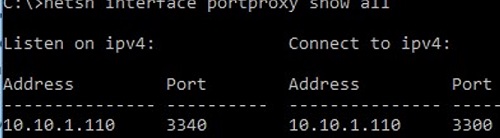
netsh interface portproxy show all
In our case, there is only one forwarding rule from local port 3340 to 3389:
Listen on ipv4: Connect to ipv4: Address Port Address Port --------------- ---------- --------------- ---------- 10.1.1.110 3340 10.1.1.110 3389
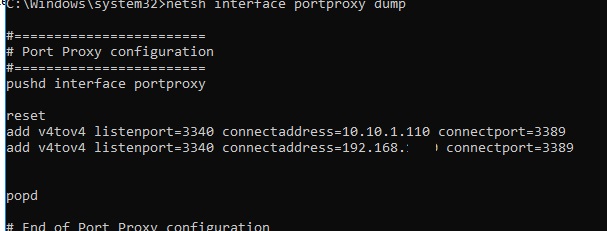
Tip. You can also list all port forwarding rules in portproxy as follows:
netsh interface portproxy dump
#======================== # Port Proxy configuration #======================== pushd interface portproxy reset add v4tov4 listenport=3340 connectaddress=10.1.1.110 connectport=3389 popd # End of Port Proxy configuration
If you need to change the settings of an existing portproxy rule, use the following command:
netsh interface portproxy set v4tov4 listenport=3340 listenaddress=10.10.1.110 connectport=3300 connectaddress=10.10.1.110
In this example, we have changed the portproxy target port number to 3300.
To remove a specific port forwarding rule:
netsh interface portproxy delete v4tov4 listenport=3340 listenaddress=10.1.1.110
To remove all existing port mapping rules and completely clear the port forwarding rules table:
netsh interface portproxy reset
Important. This port forwarding scheme works only for TCP ports. You won’t be able to forward UDP ports this way. Also, you can’t use the loopback interface 127.0.0.1 (localhost) as the connectaddress.
You can use Windows Server with the RRAS (Routing and Remote Access Service and NAT) role installed to enable port forwarding for UDP traffic. You can configure port forwarding between server network interfaces using the graphical snap-in (rrasmgmt.msc) or with the command:
netsh routing ip nat add portmapping Ethernet1 udp 0.0.0.0 53 192.168.100.100 53
The list of NAT port forwarding rules in Windows Server can be listed as follows:
netsh routing ip nat show interface
If you have WSL (Windows Subsystem for Linux) installed on your computer, you can create a simple PowerShell script to create a port forwarding rule to the WSL 2 virtual machine (a WSL2 VM has its own virtual ethernet adapter with a unique IP address):
wsl --shutdown;
netsh interface portproxy reset;
$wsl_ipaddr = wsl -d Ubuntu-20.04 hostname -I;
netsh interface portproxy add v4tov4 listenport=443 listenaddress=0.0.0.0 connectport=443 connectaddress=$wsl_ipaddr ;
netsh interface portproxy show all;
exit;
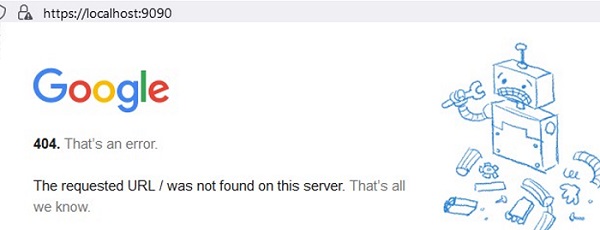
Another implicit feature of portproxy is the ability to make any remote network service look like it runs locally. For example, you want to forward the connections from local port 9090 to a remote HTTPS server (google.com:443)
netsh interface portproxy add v4tov4 listenport=9090 connectport=443 connectaddress=google.com protocol=tcp
Now, the Google search page will open if you go to http://localhost:9090/ in your browser (you need to ignore SSL_ERROR_BAD_CERT_DOMAIN errors). So despite the browser accessing the local computer address, it opens a page from an external web server.
Windows cannot forward a range of TCP ports. If you need to forward multiple ports, you will have to manually create multiple portproxy redirecting rules.
Port forwarding rules can also be used to redirect a port from the external IP address of a physical NIC to a port of a virtual machine running on the same host. In Hyper-V, you can configure port forwarding on a Virtual Switch level (see below).
Port Forwarding with NAT Rules on Hyper-V Virtual Switch
When using the Hyper-V role on your computer (it can be installed on both Windows 10/11 and Windows Server, or as a free Hyper-V Server), you can configure DNAT port forwarding rules using PowerShell. Suppose you want to redirect all HTTPS traffic that your Hyper-V host receives to the IP address of the virtual machine running on the host. To do this, use the Hyper-V StaticMapping commands.
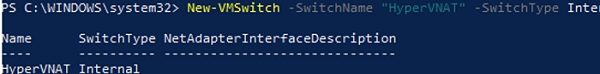
Create a Hyper-V virtual switch:
New-VMSwitch -SwitchName NAT_Switch -SwitchType Internal
Set the IP address for the new virtual switch:
New-NetIPAddress -IPAddress 192.168.100.1 -PrefixLength 24 -InterfaceAlias "vEthernet (NAT_Switch)"
Enable NAT for this network:
New-NetNat -Name NATNetwork -InternalIPInterfaceAddressPrefix 192.168.100.0/24
Connect the VM to your NAT_Switch and assign it a static IP address (for example, 192.168.10.80). Set the Hyper-V virtual switch IP address (192.168.100.1 in this case) as the default gateway for the virtual machine’s network connection.
You can now enable port forwarding from the Hyper-V host to the virtual machine:
Add-NetNatStaticMapping -NatName NATNetwork443 -Protocol TCP -ExternalIPAddress 0.0.0.0/24 -ExternalPort 443 -InternalIPAddress 192.168.10.80 -InternalPort 443
After executing these PowerShell commands, all HTTPS traffic that comes to the TCP/443 port of the Hyper-V host will be forwarded to the private IP address of the virtual machine.
If you want to create a port forwarding rule for a non-standard port, don’t forget to open it in Windows Firewall:
New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName "HyperV_Nat_444" -Direction Inbound -LocalPort 444 -Protocol TCP -Action Allow -Enabled True
You can display a complete list of NAT/PAT port forwarding rules on a Hyper-V host like this:
Get-NetNat
Windows — Open a port on the Firewall using the command-line
Windows — Open a port on the Firewall using the command-line
Would you like to learn how to open a TCP port on the Windows Firewall using the command-line? In this tutorial, we are going to show you how to use the command-line to create a firewall rule to open a port on Windows.
• Windows 2012 R2
• Windows 2016
• Windows 2019
• Windows 10
• Windows 7
Equipment list
The following section presents the list of equipment used to create this tutorial.
As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
Windows Related Tutorial:
On this page, we offer quick access to a list of tutorials related to Windows.
Tutorial Firewall — Open a TCP port using the command-line
As an Administrator, start an elevated command-line.
Create a firewall rule to open a TCP port.
Verify the created firewall rule.
Here is the command output:
In our example, we created a firewall rule to allow the input on the TCP port 80 using the command-line.
Create a firewall rule to allow the input to multiple TCP ports.
Verify the created firewall rule.
Here is the command output:
In our example, we created a firewall rule to open multiple TCP ports using the command-line.
Congratulations! You are able to create a firewall rule to open a TCP port using the command-line on Windows.
VirtualCoin CISSP, PMP, CCNP, MCSE, LPIC22021-05-26T13:01:07-03:00
Related Posts
Page load link
Join Our Newsletter

Ok
I have very little experience working with AWS. So I read through all question on Stackoverflow but couldn’t find the answer, hence I am asking this question.
I have setup an EC2 instance (Windows Server 2016). While setting up the instance at Configure Security Group the settings that I used are as follows:
For RDP I think I should put my IP, so that only I can access the Windows Server from my IP. Kindly correct me if I am wrong.
In my Windows Server 2016, I have installed Tomcat which runs on port 8080 and in firewall settings I have created an inbound rule for port 8080 as well. Therefore as shown in above screenshot I have kept port 8080 open for all. Is this correct? I am not sure what I should put as Source for port 8080.
Finally when things are setup correctly, I am able to access my tomcat homepage from Windows Server 2016 (localhost:8080) and also from external machine i.e. (EC2 public IP :8080)
The crux of the problem is when I leave these settings as is, somehow my Windows Server 2016 gets infected by Viruses and Trojans. I have to run Windows Defender to get rid of them but despite that every 2-3 days I still see viruses on my Windows Server 2016.
How can I secure my EC2 Instance Windows Server 2016 so that it does not get infected by viruses? Any help is much appreciated.