Windows Server 2016 was, at the time, the fastest and most advanced server that Microsoft ever produced. However, Server 2019 has improved performance over Server 2016 in multiple areas. Quite a few features have been added, a number have been improved upon, and some aspects have been removed. As luck would have it, all the new features are covered in our Windows Server training.
Because the previous version was so solid and the newest version has quite a few improvements and new features, many administrators are asking which is better: Server 2016 or Server 2019?
Windows Server 2016 vs Server 2019: What’s New?
Microsoft focused on a few critical areas in their most recent release. New features in Windows Server 2019 include improved security and better enabled hyper-convergence. Some of the major improvements Server 2019 has over 2016 are facilitating a hybrid platform that can easily work with on-prem resources and the cloud simultaneously, as well as improving the main areas comprising the application platform. These categories are some of the biggest Windows Server 2016 vs. Windows 2019 differences.
Storage Migration Service
One of the challenges Microsoft and consumers alike face is maintaining legacy systems that have far outlived their usefulness. This eats up resources while compromising overall security. However, upgrading to new systems can seem difficult and cost-prohibitive to many users.
Several years ago, administrators were really kicking the tires of Server 2019. A brief glance at IT discussion boards at that time shows the same question that’s being asked today about Server 2019 — is it worth it?
This year, Microsoft introduced Storage Migration Service, a tool that facilitates migration to Server 2019 from every version of Windows Server dating back to 2003. Although mechanisms that allow file copying and transfer have existed for years, administrators have never before had access to a tool that fully automated the process of migrating files, shares, permissions, and the identity of an old server onto a new one.
This corresponds with improvements in Storage Replica, a feature that facilitates replicating a storage logical unit number (LUN) between servers. Windows Server 2019 Standard Edition doesn’t require a Windows Server Datacenter license, allowing you to replicate storage volumes that contain up to 2TB of data at a time.
System Insights
Machine learning and artificial intelligence have come a long way in a short time, and Server 2019 enhances performance over Server 2016 with a System Insights module. It’s easy to review a system log of past events, and administrators have been able to view live occurrences for years. With this module, however, the server also looks to the future, analyzing the platform for issues before they happen. This limits downtime, reduces crashes, and can preclude potential security issues.
Systems Insights builds on the Windows Admin Center, where Server 2019 has improved over Server 2016. With 2019, you can check the status of latency, storage, cluster CPU, and IOPS in real-time, giving unprecedented visibility into your systems’ operating environment and health.
Azure Network Adapter
When the cloud was first introduced, it was met with an odd mixture of responses. Many believed that it would completely replace on-premises data centers, but server technology continued to be geared toward the latter. Over the past few years, the strengths and weaknesses of both cloud and on-prem resources have become more evident. There’s a cornerstone role for both, and neither is going anywhere.
This required a server designed around facilitating the seamless integration of both technologies, and Server 2019 is able to do that much more efficiently than Server 2016. The Azure Network Adapter automates the creation of a VPN tunnel between an on-prem Windows Server 2019 and a cloud-based Azure environment. Although administrators could do this manually before, it wasn’t the most natural process. Performance and security in Server 2016 were less optimal than what Server 2019 offers. This automated network adapter takes the hassle out of the entire situation, effortlessly incorporating the two for the highest security and performance levels.
Cluster Sets
With the combination of cloud and on-prem technology, drastically increased deployment of virtual machines, and the need to access massive data sets stored across numerous drives, clusters have become more and more critical. While Server 2016 heavily emphasized clusters, Server 2019 introduces the concept of Cluster Sets, which are essentially clusters of clusters.
This large-scale application of the cluster concept improves the availability of applications and data while emphasizing resiliency across the entire system, making Windows Server 2019 a much better choice than 2016. Cluster Sets are geared for high growth, providing an extremely efficient way to scale without compromising performance.
Persistent Memory
Drastically increased data storage is one thing, but the ability to rapidly access that data is another. Persistent Memory, or PMem, is Microsoft’s solution — and it’s impressive. At Microsoft Ignite 2018, the latest version of Windows Server demonstrated an astounding latency of fewer than 40 microseconds, even when performing as many as 13.8 million input/output operations per second (IOPS). Windows Server 2019 vs. 2016 performance is more than double the prior industry benchmark of 6.7 million IOPS, and it required a mere 12 server nodes.
In addition to its speed, one of PMem’s most notable features is its resiliency. This non-volatile RAM maintains its contents through both scheduled and unexpected power cycles, which is why it’s often referenced as «storage-class memory.»
Virtual Network Peering
While the cloud has drastically improved network flexibility and functionality, it has come at a cost. When dealing with a public cloud and multi-cloud world, the devices you’re using can continually shift between any number of racks, cages, or datacenters. You might even have reoccurring migrations between regions and hosting providers, which triggers a tremendous amount of effort by network administrators to address, readdress, and update device tables just to maintain a functioning network.
Depending on your setup, Vnet Peering functionality is somewhat limited to resources in the same cloud region or even datacenter. Even with these constraints, however, the consistency in virtual networks with Server 2019 represents a substantial improvement over Windows Server 2016.
Precision Time Protocol (PTP) with Leap Second
This is a specialized feature that isn’t necessary for the majority of users, but it’s a game changer for those who need it. Some industries and applications require absolute precision timekeeping, down to the microsecond. While Server 2016 was accurate, 2019 is much better. PTP is a protocol that permits network devices to compile the latency added by each network device into timing measurements, resulting in the most accurate time tracking possible.
Another new feature, Leap Second, tracks the rotation of the earth and adds leap seconds to compensate for any resulting changes.
Low Extra Delay Background Transfer (LEDBAT)
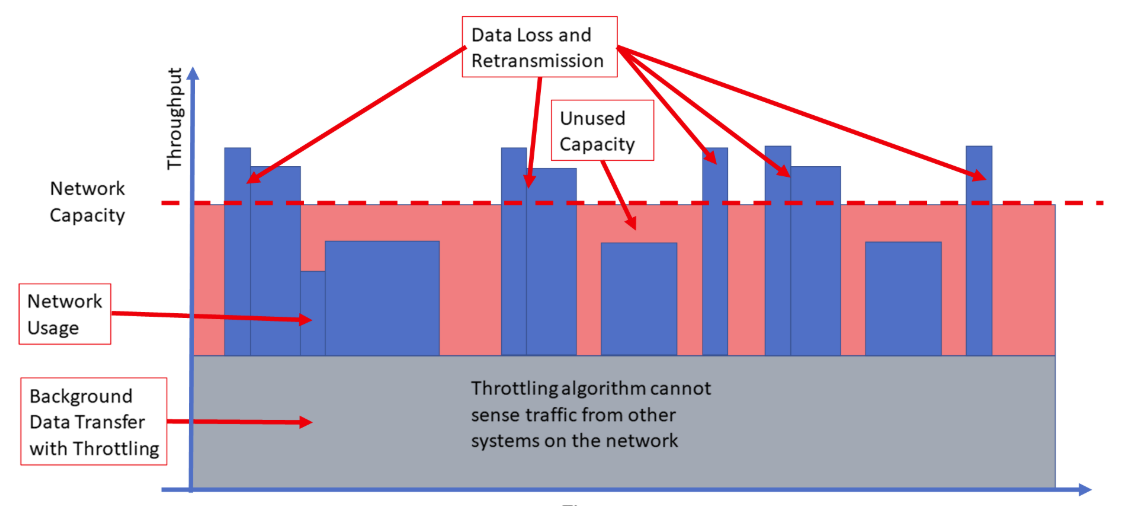
Managing bandwidth and minimizing network congestion isn’t a new battle for network administrators, but current tools have substantial limitations. For example, throttling outlines the maximum bandwidth permitted for a specific purpose, and those limits can’t be exceeded even when the entire bandwidth is unused and available. Background Intelligent Transfer Service (BITS) employs Adaptive Bit Rates (ABRs) to decide what level of bandwidth is available to lower priority traffic. Although useful, it can take quite a few adjustments to dial in the settings correctly, and each change introduces a delay.
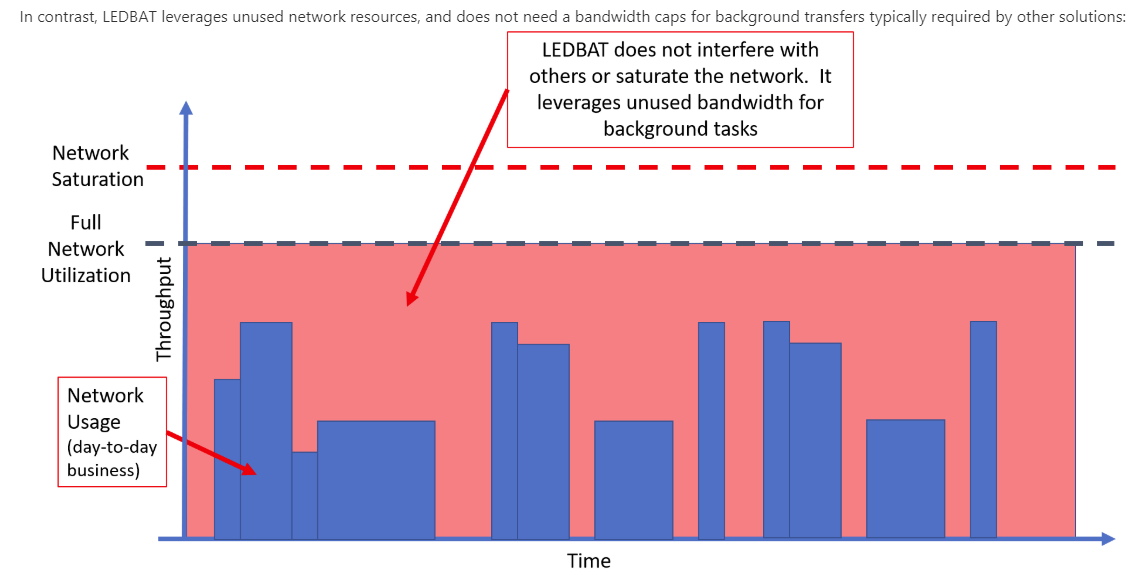
LEDBAT is a network congestion controller that manages available bandwidth for users and applications in real-time, then consumes the entire bandwidth when a network isn’t in use. It’s referred to as a scavenger protocol because it actively searches for any available bandwidth on the network and puts it to use.
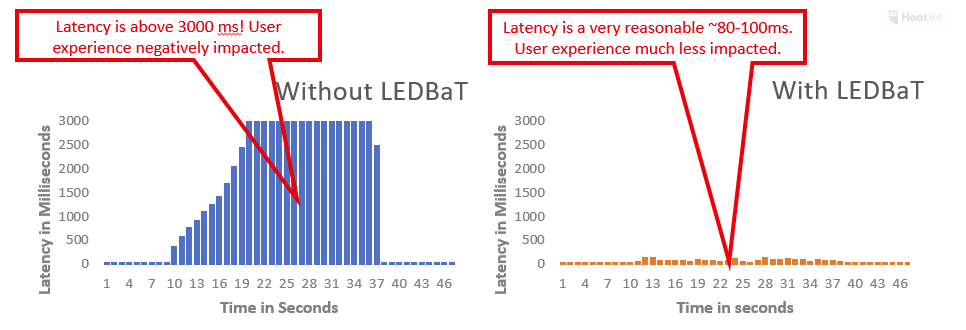
Latency is a critical concept in user satisfaction, and LEDBAT makes a remarkable difference. In the tables below, the same network traffic is shown with and without LEDBAT optimization in place. As you can see, the user experience is night and day.
Shielded Virtual Machines: Linux Expansion and HGS Offline Mode
Until now, shielded VMs were only available for Windows. With Windows Server 2019 Hyper-V technology, expanded support is now available for shielded VMs to Linux. This drastically expands network flexibility if you have Linux VMs, permitting secure data without loss of performance for both operating systems on the same network.
One of the most noticeable Server 2016 vs. 2019 differences is that Server 2019 introduces the capability to host virtual machines offline, allowing you to shield them as long as the Hyper-V host’s security hasn’t changed.
Enhanced Windows Defender Advanced Threat Protection
When it comes to security, Server 2019 vs. 2016 isn’t even a contest. The newest security set included with Windows Server 2019 provides an array of intrusion prevention capabilities, such as attack detection, zero-day exploits, and preventative protection. Expect Breach is one feature that constantly monitors areas that have been identified as vulnerable to detect a breach instantly if one occurs.
Data Plane Development Kit (DPDK)
The demand for increased media resolution has driven the evolution from high-definition to 4K, and the industry is already preparing for the next leap into 8K resolution. Real-time multiplayer gaming and augmented reality/virtual reality (AR/VR) will only drive the demand for resolution higher. Cisco estimates that IP video traffic will comprise an astounding 82 percent of all consumer internet traffic by 2021.
Facilitating this while maintaining an operational network requires high bandwidth and low latency, necessitating a modified approach to network architecture. This need is met by mating DPDK libraries with Windows Server, which bypasses the host networking stack and emphasizes fast packet processing capabilities by user-mode applications. Until now, DPDK was exclusively available on Linux, but Windows 2019 vs. 2016 Server provides a tremendous boost in flexibility.
Server 2019 Improvements Over Server 2016
When you’re looking at Windows Server 2016 vs. 2019 differences, the benefits aren’t limited to new features. Although Server 2019 introduces an impressive array of new capabilities, the improvements on existing functionalities is equally remarkable.
Container Networking with Kubernetes
In recent years, application modernization using containers has become increasingly popular. As applications are moved from virtual machines to containers, being able to exercise network management agility takes on critical importance. Windows Server utilizes Kubernetes to orchestrate this via an open-source, standardized framework, and Server 2019 noticeably increases usability over Server 2016 in two ways.
First, enhanced platform network resiliency is a cornerstone concept in 2019 and positively impacts container employment. Second, the support of container networking plugins has been increased, providing greater flexibility than 2016 had across a variety of user requirements.
Improved Storage Spaces Direct (S2D)
Virtual machines have continued to grow in popularity and utility, requiring servers to evolve in ways that continue to support this technology. S2D is the primary software-defined solution Microsoft uses for hyper-converged infrastructure (HCI) deployments. It sets aside local storage space in each individual server, then aggregates that space in a distributed storage system to facilitate the employment of virtual machines.
Critical upgrades for Server 2019 include 64TB of space per volume and an astounding 4PB of space per storage pool. Microsoft has also streamlined the ability to monitor and manage S2D through the Windows Admin Center, enabling the functionality to increase simultaneously with storage upgrades.
Resilient File System (ReFS)
The amount of data we digitize and constantly reference has increased exponentially, and so has the way we handle it. Limited storage space on single drives has evolved into massive storage distributed among sizeable arrays of disks. Microsoft previously utilized NTFS to manage files, but by Server 2012, this system had become outdated, leading to the inaugural version of the Resilient File System.
ReFS was designed to be self-repairing and facilitate virtualization between physical disks and logical volumes. The earliest versions offered some improvement over NTFS but were slower in many respects. Server 2016 addressed these issues, implementing ReFS in a highly improved and fully functional approach to file storage. Server 2019 built on that foundation to emphasize two crucial improvements: deduplication and compression. Although Server 2016 was functional, Server 2019 fully supports both processes and eliminates a few persistent bugs 2016 had.
Cloud Witness
This high availability feature employs failover clusters stored in the Azure cloud platform to ensure continued operation if a site outage occurs. In Server 2016, Cloud Witness required a cluster name object (CNO) with an Active Directory account to access this feature. Server 2019 is an improvement over 2016 Cloud Witness functionality, eliminating this requirement and permitting a local user account on the Windows Server to employ failover clusters.
Software-Defined Networking (SDN) Gateways
Although SDN has been around for a while, its importance is only increasing. Software-defined networking frees a network from its physical constraints by abstracting it, overlaying an SDN on top of the underlying physical cable, VLANs, and gateway addresses. This allows for rapid design, deployment, and adjustment of the network without requiring any material change, drastically improving network deployment speed, security features, and various automation capabilities.
Server 2019’s gateways boast substantial speed improvements over Windows Server 2016 that can be as much as three times faster, depending on your application. Microsoft’s most recent release also supports IPv6 and dual-stack IPv4/IPv6 addressing, permitting encryption for all traffic on your virtual network.
Virtual Network (Vnet) Encryption
Traffic encryption has typically been done at the application layer, but Server 2019 expands 2016’s ability to encrypt traffic between virtual machines. It’s now built into the operating system as a foundation of server, application, and hypervisor communications. Network administrators can protect all subnet communications between host servers, automatically encrypting all network traffic that occurs under that umbrella.
This provides increased efficiency and performance when more web frontend and backend databases need to be added because they join the same encrypted communication stream that’s already been established. Securing comms at the network level rather than the application level is a substantial improvement in encrypted network performance.
Dynamic Virtual Machine Multi-Queue (d.VMMQ)
VMs need the highest level of throughput possible. As network interface cards have gotten faster, the level of processing required to facilitate low-latency network traffic began to exceed what a single CPU could facilitate. Server 2019 introduces Virtual Machine Multi-Queue, which is an improvement over Server 2016’s Virtual Machine Queue, so traffic can be processed by multiple processors.
Although the capability for this technically existed previously, it was a labor-intensive manual effort that required quite a bit of planning, monitoring, establishing baselines, and constant tuning to achieve the optimal effect. With d.VMMQ, that entire process is automated and is designed to autotune to the existing workload. After a supporting driver has been installed, no further setup is required.
What’s Gone with Windows Server 2019?
Along with the tremendous number of new and improved features, Server 2019 has removed several aspects of Server 2016. Although these are reasonable adjustments, if you’re migrating from Server 2016 and your infrastructure employs any of the below features, it’s good to know they won’t be available before you begin updating your server.
Internet Storage Name Service (iSNS)
Interaction between iSNS servers and clients has traditionally used this feature, but Server Message Block has replaced it. SMB was initially introduced in Server 2012, and its functionality has increased to the point where it can do everything iSNS could and more.
Print Components for Server Core
In nearly all previous versions of Windows Server, these print components were disabled by default. In Server 2016, Microsoft changed the default settings to enabled. This didn’t prove to be useful, so one of Server 2019’s differences over 2016 was reverting to a default disablement. If you need these components, however, you can run a commandlet to enable them.
Business Scanning/Distributed Scan Management
This feature was introduced in Server 2012 and required that scanners support it. The tech is now outdated, and no scanners currently support it, so it has been removed.
Remote Desktop Connection Broker and Virtualization Host in Server Core Installation
Microsoft found that these features weren’t useful in most server configurations. As a result, they’re not included by default in any version except Windows Server with Desktop Experience, but can be installed if you need them for your Remote Desktop infrastructure.
Which is Better: Server 2016 or Server 2019?
Windows Server 2019 has been widely praised within the IT community as a substantial improvement over Server 2016. Increased security, decreased latency, and a vastly improved suite of tools to facilitate hybrid platforms are phenomenally useful assets. All in all, this is definitely a win for information technology.
Беспрецедентная гиперконвергентная инфраструктура
Развивайте инфраструктуру своего центра обработки данных, чтобы обеспечить высокую эффективность и безопасность.
|
Описание компонента |
Windows Server 2008 R2 |
Windows Server 2012 R2 |
Windows Server 2016 |
Windows Server 2019 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Объединенное управление в Центре администрирования Windows — это удобный браузерный интерфейс для удаленного управления HCI, который включает программно-определяемую сетевую конфигурацию и мониторинг. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Дисковые пространства защищают ваши данные от дисковых сбоев и со временем расширяют хранилище по мере того, как вы добавляете диски на серверы. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Расширенные локальные дисковые пространства позволяют создавать программно-определяемое хранилище, используя соответствующие отраслевым стандартам серверы с локальным хранилищем, которое может масштабироваться до 1 ПБ на пул носителей в Windows Server 2016 и 4 ПБ на пул носителей и 64 ТБ на том в Windows Server 2019. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Четность с зеркалированием позволяет создавать тома, которые частично являются зеркалированными и частично четными для двукратного повышения производительности в развертываниях локальных дисковых пространств. Сначала записи оказываются в зеркалированной части и постепенно перемещаются в четную часть. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Вложенная четность с зеркалированием обеспечивает сохраняемость состоящих из двух узлов кластеров на периферии после нескольких одновременных сбоев. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Память класса хранилища поддерживает новое поколение серверного оборудования, включая память класса хранилища, которая существенно повышает производительность серверных приложений. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Флэш-накопитель USB (в качестве свидетеля кластера). Поддержка использования флэш-накопителя USB в качестве свидетеля кластера позволяет создавать истинные развертывания HCI из двух узлов без дополнительных зависимостей. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Репликация хранилищ обеспечивает возможность синхронной и асинхронной репликации между серверами на уровне блоков независимо от используемых хранилищ в целях аварийного восстановления; кроме того, эта технология позволяет расширять кластеры отработки отказа для обеспечения высокой доступности. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Качество обслуживания для хранилища (QoS) использует политики для определения и мониторинга минимальных и максимальных значений на входе и выходе хранилища, обеспечивая стабильную производительность виртуальных машин. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Дедупликация данных позволяет экономить до 90 % томов благодаря однократному сохранению дублирующихся файлов в томе с помощью логических указателей. В Windows Server 2019 добавлена поддержка дедупликации посредством томов ReFS. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Дедупликация ReFS поддерживается в ReFS, чтобы оптимизировать свободное пространство тома путем исследования данных в дублирующихся частях. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Устойчивость хранилищ виртуальных машин обеспечивает интеллектуальные средства для сохранения состояний сеансов виртуальных машин, чтобы уменьшить негативные последствия незначительных нарушений в работе хранилищ. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Облако-свидетель позволяет использовать хранилище BLOB-объектов Azure в качестве свидетеля в кворуме для расширенного кластера. Кроме того, в Windows Server 2019 можно создать свидетеля общей папки, который использует не объект имени кластера (CNO), а просто учетную запись локального пользователя на сервере, к которому подключен FSW. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Мониторинг работоспособности хранилища позволяет осуществлять непрерывный мониторинг, составлять отчетность и обслуживать хранилища напрямую. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Мониторинг на уровне кластера позволяет наблюдать за использованием памяти и ресурсов ЦП, объемом хранилища, количеством операций ввода-вывода в секунду, пропускной способностью и задержкой в режиме реального времени и отправляет четкие оповещения, если какой-то параметр отклоняется от нормы. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Наборы кластеров позволяют создавать большие масштабируемые кластеры, которые отличаются значительной гибкостью с точки зрения развертывания и вывода из эксплуатации, без ущерба для устойчивости системы. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Последовательное обновление ОС кластера позволяет администратору без проблем обновить операционную систему узлов в отказоустойчивом кластере с Windows Server 2012 R2 и Windows Server 2016 до Windows Server 2019. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Кластер в режиме смешанных ОС позволяет узлам кластера Windows Server 2012 R2 взаимодействовать с узлами Windows Server 2016. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Отказоустойчивые кластеры с поддержкой сайта группируют узлы в расширенные кластеры в зависимости от физического местоположения и расширяют возможность выполнения ключевых операций в течение жизненного цикла кластера, таких как отработка отказа, политики размещения, обмен периодическими сигналами между узлами и поведение кворума. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Энергонезависимая память. Поддержка технологии энергонезависимой памяти обеспечивает доступ на уровне байтов к энергонезависимым носителям и значительно уменьшает задержку при сохранении и извлечении данных. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Рабочие нагрузки Linux и FreeBSD обеспечивают работу большинства программно-определяемых функций ЦОД Windows Server для гостевых систем Linux и FreeBSD, выполняемых в Hyper-V, повышая функциональность, производительность и управляемость. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Оперативное добавление и удаление дисков, памяти и сетей позволяет добавлять и удалять сетевые адаптеры и регулировать выделенный объем памяти, не прерывая работу виртуальной машины. Функция регулировки памяти работает, даже если для узла Hyper-V включена динамическая память. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Сетевой контроллер предоставляет централизованную программируемую точку автоматизации для настройки, мониторинга, диагностики и устранения неполадок виртуальной сетевой инфраструктуры в вашем ЦОД, а также для управления ею. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Виртуальные сети помогают создавать сетевые слои поверх общей физической структуры, используемой несколькими клиентами. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Программный балансировщик нагрузки. Балансировщик нагрузки 3 и 4 уровней с поддержкой облачных технологий, обеспечивающий балансировку нагрузки «Север — Юг» и «Восток — Запад». |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Пиринг виртуальных сетей обеспечивает высокоскоростное подключение между двумя виртуальными сетями. Трафик между виртуальными сетями проходит через базовую структурную сеть без шлюза. Обе виртуальные сети должны являться частью одной и той же метки центра обработки данных. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Распределенный брандмауэр и микросегментирование динамически сегментируют сети с учетом меняющихся потребностей приложений и требований безопасности; для этого используются брандмауэр с сохранением состояния и сетевые группы безопасности. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Гибридные шлюзы SDN. Это высокодоступные шлюзы с несколькими клиентами, которые подключают виртуальные сети клиента к Azure, другим облакам на базе Windows Server, высокоскоростным глобальным сетям и локальным невиртуальным ресурсам. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Усовершенствованный шлюз SDN. Туннели GRE и VPN-подключения «сеть-сеть» IPSec начинают работать до 3 раз быстрее. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Конвергентный RDM. Трафик хранилища и клиентский трафик Ethernet с одной базовой NIC объединяются с целью значительной экономии затрат, обеспечения нужной пропускной способности и качества услуг. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Протокол PTP позволяет сетевым устройствам добавлять задержку, вызванную каждым сетевым устройством, в измерения времени, тем самым создавая гораздо более точный образец времени, чем протокол NTP. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Корректировочная секунда. Поддержка периодического добавления 1 секунды к отсчету времени UTC с целью корректировки из-за замедления вращения Земли гарантирует точность, отслеживаемость и выполнение требований. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
HTTP/2. Поддержка HTTP/2 (RFC 7540) на встроенном сервере HTTP. Теперь Windows Server 2019 гарантирует высокую производительность и безопасность развертываемых вами сайтов с помощью HTTP/2. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Фоновая передача с оптимизацией задержки (LEDBAT) в Windows Server 2019 обеспечивает возможность фоновой передачи с низкой дополнительной задержкой (LEDBAT) и контролирует перегрузку в сети. LEDBAT предназначена для автоматического предоставления пропускной способности пользователям и приложениям. Если сеть не используется, потребляется вся пропускная способность. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Управление IP-адресами (IPAM) и DNS. Поддерживается комплексное управление DNS и DHCP с контролем доступа на основе ролей в разных лесах AD. DNS обеспечивает управление трафиком, балансировку нагрузки, развертывания с разделением вычислительных мощностей и профилактику атак типа «Усиление DNS». |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Брокер подключения RDS высокой доступности помогает создать отказоустойчивый брокер подключений для сценариев со службами удаленных рабочих столов (RDS). |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
Программно-конфигурируемая сеть (SDN) с IPv4/IPv6 предоставляет возможность централизованного конфигурирования физических и виртуальных сетевых устройств и управления ими. Кроме того, Windows Server 2019 теперь поддерживает IPv6 и двойную адресацию стека IPv4/IPv6. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Windows Server is Microsoft’s operating system that was first released into the market back in 2003. Since its initial release, several versions of this operating system have been developed. Each version builds on the flaws of its predecessor, or new opportunities prompt developers to incorporate new features.
The different versions of Microsoft Windows Server compare differently against each other based on the features each has. However, they all serve the same purpose; they are all windows operating systems. Here are the features that each of the above versions portrays that create a distinction between each other:
Microsoft Windows Server 2019
This is the most recent and most advanced version of Microsoft Windows Server. It was released into the market on the 2nd of October, 2018. It comes with the following impressive features:
Storage
- Some intense changes have been made in the Microsoft Windows Server storage for a better experience. For instance, you are bound to experience the following:
Storage Migration Service
- This feature allows you to quickly move servers to a new version of Microsoft Windows Server. It ensures you do not have to make any changes whenever you move to a new server. A graphic tool configures your data on your server, retains its identity, and then transfers it to the new server.
Storage Spaces Direct
You will encounter the following new storage space direct system features:
- Native support for persistence memory
- Two-server clusters with a USB flash witness
- Windows admin center support
- Performance history
- 2x faster mirror-accelerated parity
- Drive latency outlier detection
- Two-node hyper-converged infrastructure at the edge
- You can scale up to 4 PB per cluster
- Manually delimit the allocation of volume to step up fault tolerance.
Storage Replica
- This comes with a test failover feature that allows mounting of destination storage to validate replication or data backup. Storage Replica log performance has also been massively boosted while the Windows Admin Support Center is readily at your disposal.
System Insights
- The system insight feature gives Windows Server 2019 to make the local predictive analysis. Such will give you insight into the functional status of your server. The system runs diagnostics on your servers and detects flaws early enough before they are problematic.
Hybrid Cloud
- A new Server Core App Compatibility Feature on Demand (FOD) comes in handy to improve the app compatibility of the Windows Server Core Installation. As such, you can now enjoy a graphical environment that serves to increase the functionality and compatibility of Server Core yet keeping lean.
Security
Windows Defender Advanced Threat Protection (ATP)
This defense mechanism senses and responds to any memory and kernel-level attacks. It suppresses malicious files and cuts short malicious processes. The system works by initiating the following operations:
- Attack surface reduction, blocks malware from getting into the machine by blocking any suspicious and insecure files.
- Network protection
- Controlled folder access
- Exploit protection it seeks vulnerabilities in systems and alerts you accordingly.
Security with Software Defined Networking (SDN)
- SDN seeks to secure your data files, either on-premises or in your cloud. You and your clients have confidence in the security of your data.
Shielded Virtual Machines Improvement
- Branch office improvement, you can run shielded virtual machines on machines with connectivity to the Host Guardian Service by using the new fallback HGS and other offline mode features. Such allow you to configure a second-party set of URLs for Hyper-V to see if it won’t reach your primary server.
- Offline modes give you the capabilities to launch your shielded VMs even in the absence of HGS.
Troubleshooting improvement
- Should you lose your connectivity to your VMs, new tools have been incorporated to detect any connectivity issues.
- Even better, the tools need not be configured since they become available automatically. You place your VM on a Hyper-V host that is running on Window Server version 1803 or later.
Linux support
Windows Server 2019 can comfortably run in a mixed OS environment. It can support Ubuntu, Red Hat Enterprise Linux, and SUSE Linux Enterprise Server inside the virtual machines.
- HTTP/2 for a faster and safer Web
- You will not have to worry about security issues when you are surfing on your internet on account of:
- Coalescing of connections, to prevent interrupted and unencrypted browsing experience
- Upgraded HTTP/2’S server cipher suite comes in handy for efficient mitigation of faulty connections and ease of deployment.
- New TCP congestion provider to Cubic, such will give you more throughputs.
Upgrade Windows Admin Centre
A readily available windows admin center is at your beck and call and comes with no additional costs. This will enable you to manage your windows server, hyper-converged resources, and Windows 10 PCs.
Microsoft Windows Server 2016
Lots of features were incorporated into the Microsoft Windows Server 2016, but the following make the app stand out from the rest of the servers:
Nano Server
This flaunts a 92% smaller installation footprint than a typical Windows Server Graphic User Interface (GUI). It further comes along with an array of good qualities:
- Fewer updates and reboots since it is a bare-metal OS.
- It has a much-reduced attack surface than GUI. Any server roles are injected from other sources; hence, a little window of opportunity for malware.
- Small in size hence readily portable across servers, physical sites, and data centers.
- It can easily host a standard Windows Server workload such as a Hyper-V host.
Containers
Containers allow you to isolate apps and services in an agile and administrative way. Microsoft Windows Server 2016 flaunts two containers:
- Windows Server Container. Such aims to handle lower workloads that can comfortably share the same resources.i
- Hyper-V Container. This is appropriate for high-trust workloads.
Linux Secure Boot
- Linux Secure Boot protects the server’s launch environment against attacks from rootkits and other boot-time malware. With this version, you can deploy Linux VMs without having to disable the otherwise stellar Secure Boot feature as you would with the windows server.
ReFS
- The new Resilient File System (ReFS) helps in Storage Spaces Direct and Hyper-V workloads. This system is much more stable and stronger than in preceding versions to optimize these functions.
Storage Spaces Direct
- If you want to create redundant and flexible disk storage in an affordable environment, this feature comes in handy. The feature stretches storage spaces to allow failover cluster nodes to use their local storage inside this cluster, avoiding shared storage fabric.
Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS v4)
- Here is another excellent feature that seeks to support claims (token)-based identity. Claims-based identity is essential on account of the need for a single-sign-on (SSO) between on-premises Active Directory and various cloud services.
- The feature will also support OpenID Connect-based authentication, hybrid conditional access, and Multi-factor authentication (MFA). Hybrid conditional access enables ADFS to respond to issues that could be attributed to security policy compliance.
Nested Virtualization
- This is the ability of a virtual machine to host another virtual machine. A useful application of this feature is when a business wants to deploy additional Hyper-V hosts and requires stepping down hardware costs.
Hyper-V Hot-Add Virtual Hardware
- With this feature, you can add virtual hardware or adjust the allocated Ram to a virtual machine. This was an impossible feat in the past, but Microsoft Windows Server 2016 has made it possible. Even more exciting, you can add this virtual hardware while the VMs are up and running.
PowerShell Direct
- You can now send PowerShell directly to the Hyper-V host’s VMs with Microsoft Windows Server 2016.
Microsoft Windows Server 2012
The highlight of this version is the effort to make it cloud-ready. Moreover, the addition of the following features makes it a worthy bargain.
Server Manager
- The Microsoft Windows Server 2012 flaunts a new server manager with a new look and feel in the user interface. You can now group many servers on your network and manage them from a focal point in one window. Such will save you time that you used in past versions jumping from one window to another to work on your servers.
Windows PowerShell 3.0
- PowerShell seeks to stretch more control of Windows servers. This tool works hand-in-hand with the GUI to executive your commands. However, it is the dominant force of the two; hence, fewer crashes and issues are likely to happen. PowerShell is a revolutionary feature that will make the administration of windows servers more efficient.
Hyper-V 3.0
- This virtualization platform will allow you to run multiple virtual machines on a single windows server. When used with Microsoft System Centre, the experience is even better.
Storage
- Storage space has also been massively boosted in Microsoft Server 2012. The different available pools of storage are divided into different spaces. Furthermore, in the pools, you can add up any physical disk as well as configure mirroring. This ability to add up more space as you please is quite an impressive feature.
Data Deduplication
- This is a data compression technique that will help you eliminate duplicates of repetitive data. Large chunks are analyzed, and if any matches up, the extra copy is replaced with a reference that directs to the stored piece.
Server Message Block (SMB) 3.0
- SMB file sharing protocol comes with a set of beneficial features such as; hot pluggable interfaces, multichannel, encryption, deduplication, Volume Shadow Copy Services (VSS), among others.
Dynamic Access Control (DAC)
- DAC manages how files and folders are accessed. It classifies data files in order of device claims and resource claims.
Microsoft Server 2012 R2
Microsoft Server 2012 R2 was a significant improvement on Microsoft Server 2012. Some of the improvements made include:
File Services and Storage
- Work folders. You can make corporate data available to your users since your users’ devices do not have to be domain-connected.
- SMB. This feature was introduced in the server 2012 but made better in this version. Better performance, automatic rebalancing of Scale-Out File Server clients, and support for multiple SMB instances are some of the improvements.
- DFS Namespace and DFS Replication. You can now recover any corrupt databases or files that are hidden in DFSR private folders.
- Storage spaces have also been significantly extended to accommodate more data.
Health Report
- A readily available health report is one of the highlights of this version. Furthermore, you can customize it according to your needs for it to display what you want to monitor.
BranchCashe
- BranchCashe is a Wide Area Network (WAN) bandwidth optimization technology that may come with Windows software. If you want to access an offsite server, you can use this feature to boost data access.
Remote Web Access
- You can remotely access your servers online with many Microsoft servers, but with this version, this feature is boosted extensively. It is further with HTML5 support.
Pre-configured Auto-VPN Dialing
- A client VPN comes in handy if you need to access an on-site network resource.
Server Deployment
- With this version, you can install Microsoft Server 2012 as a member server in a domain of any size. Furthermore, as you install as a member server, you can have multiple servers running Essential on your domain.
All the above Microsoft Servers are built upon each other; the more recent versions are built on the flaws of their predecessors. As such, the later the release, the better features you are bound to enjoy.
If you’re looking for a software company you can trust for its integrity and honest business practices, look no further than SoftwareKeep. We are a Microsoft Certified Partner and a BBB Accredited Business that cares about bringing our customers a reliable, satisfying experience on the software products they need. We will be with you before, during, and after all the sales.
That’s our 360 Degree SoftwareKeep Guarantee. So, what are you waiting for? Call us Today on +1 877 315 1713 or email sales@softwarekeep.com. As well, you can reach us via Live Chat.
Windows Server is Microsoft’s operating system that was first released into the market back in 2003. Since its initial release, several versions of this operating system have been developed. Each version builds on the flaws of its predecessor, or new opportunities prompt developers to incorporate new features.
The different versions of Microsoft Windows Server compare differently against each other based on the features each has. However, they all serve the same purpose; they are all windows operating systems. Here are the features that each of the above versions portrays that create a distinction between each other:
Microsoft Windows Server 2019
This is the most recent and most advanced version of Microsoft Windows Server. It was released into the market on the 2nd of October, 2018. It comes with the following impressive features:
Storage
- Some intense changes have been made in the Microsoft Windows Server storage for a better experience. For instance, you are bound to experience the following:
Storage Migration Service
- This feature allows you to quickly move servers to a new version of Microsoft Windows Server. It ensures you do not have to make any changes whenever you move to a new server. A graphic tool configures your data on your server, retains its identity, and then transfers it to the new server.
Storage Spaces Direct
You will encounter the following new storage space direct system features:
- Native support for persistence memory
- Two-server clusters with a USB flash witness
- Windows admin center support
- Performance history
- 2x faster mirror-accelerated parity
- Drive latency outlier detection
- Two-node hyper-converged infrastructure at the edge
- You can scale up to 4 PB per cluster
- Manually delimit the allocation of volume to step up fault tolerance.
Storage Replica
- This comes with a test failover feature that allows mounting of destination storage to validate replication or data backup. Storage Replica log performance has also been massively boosted while the Windows Admin Support Center is readily at your disposal.
System Insights
- The system insight feature gives Windows Server 2019 to make the local predictive analysis. Such will give you insight into the functional status of your server. The system runs diagnostics on your servers and detects flaws early enough before they are problematic.
Hybrid Cloud
- A new Server Core App Compatibility Feature on Demand (FOD) comes in handy to improve the app compatibility of the Windows Server Core Installation. As such, you can now enjoy a graphical environment that serves to increase the functionality and compatibility of Server Core yet keeping lean.
Security
Windows Defender Advanced Threat Protection (ATP)
This defense mechanism senses and responds to any memory and kernel-level attacks. It suppresses malicious files and cuts short malicious processes. The system works by initiating the following operations:
- Attack surface reduction, blocks malware from getting into the machine by blocking any suspicious and insecure files.
- Network protection
- Controlled folder access
- Exploit protection it seeks vulnerabilities in systems and alerts you accordingly.
Security with Software Defined Networking (SDN)
- SDN seeks to secure your data files, either on-premises or in your cloud. You and your clients have confidence in the security of your data.
Shielded Virtual Machines Improvement
- Branch office improvement, you can run shielded virtual machines on machines with connectivity to the Host Guardian Service by using the new fallback HGS and other offline mode features. Such allow you to configure a second-party set of URLs for Hyper-V to see if it won’t reach your primary server.
- Offline modes give you the capabilities to launch your shielded VMs even in the absence of HGS.
Troubleshooting improvement
- Should you lose your connectivity to your VMs, new tools have been incorporated to detect any connectivity issues.
- Even better, the tools need not be configured since they become available automatically. You place your VM on a Hyper-V host that is running on Window Server version 1803 or later.
Linux support
Windows Server 2019 can comfortably run in a mixed OS environment. It can support Ubuntu, Red Hat Enterprise Linux, and SUSE Linux Enterprise Server inside the virtual machines.
- HTTP/2 for a faster and safer Web
- You will not have to worry about security issues when you are surfing on your internet on account of:
- Coalescing of connections, to prevent interrupted and unencrypted browsing experience
- Upgraded HTTP/2’S server cipher suite comes in handy for efficient mitigation of faulty connections and ease of deployment.
- New TCP congestion provider to Cubic, such will give you more throughputs.
Upgrade Windows Admin Centre
A readily available windows admin center is at your beck and call and comes with no additional costs. This will enable you to manage your windows server, hyper-converged resources, and Windows 10 PCs.
Microsoft Windows Server 2016
Lots of features were incorporated into the Microsoft Windows Server 2016, but the following make the app stand out from the rest of the servers:
Nano Server
This flaunts a 92% smaller installation footprint than a typical Windows Server Graphic User Interface (GUI). It further comes along with an array of good qualities:
- Fewer updates and reboots since it is a bare-metal OS.
- It has a much-reduced attack surface than GUI. Any server roles are injected from other sources; hence, a little window of opportunity for malware.
- Small in size hence readily portable across servers, physical sites, and data centers.
- It can easily host a standard Windows Server workload such as a Hyper-V host.
Containers
Containers allow you to isolate apps and services in an agile and administrative way. Microsoft Windows Server 2016 flaunts two containers:
- Windows Server Container. Such aims to handle lower workloads that can comfortably share the same resources.i
- Hyper-V Container. This is appropriate for high-trust workloads.
Linux Secure Boot
- Linux Secure Boot protects the server’s launch environment against attacks from rootkits and other boot-time malware. With this version, you can deploy Linux VMs without having to disable the otherwise stellar Secure Boot feature as you would with the windows server.
ReFS
- The new Resilient File System (ReFS) helps in Storage Spaces Direct and Hyper-V workloads. This system is much more stable and stronger than in preceding versions to optimize these functions.
Storage Spaces Direct
- If you want to create redundant and flexible disk storage in an affordable environment, this feature comes in handy. The feature stretches storage spaces to allow failover cluster nodes to use their local storage inside this cluster, avoiding shared storage fabric.
Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS v4)
- Here is another excellent feature that seeks to support claims (token)-based identity. Claims-based identity is essential on account of the need for a single-sign-on (SSO) between on-premises Active Directory and various cloud services.
- The feature will also support OpenID Connect-based authentication, hybrid conditional access, and Multi-factor authentication (MFA). Hybrid conditional access enables ADFS to respond to issues that could be attributed to security policy compliance.
Nested Virtualization
- This is the ability of a virtual machine to host another virtual machine. A useful application of this feature is when a business wants to deploy additional Hyper-V hosts and requires stepping down hardware costs.
Hyper-V Hot-Add Virtual Hardware
- With this feature, you can add virtual hardware or adjust the allocated Ram to a virtual machine. This was an impossible feat in the past, but Microsoft Windows Server 2016 has made it possible. Even more exciting, you can add this virtual hardware while the VMs are up and running.
PowerShell Direct
- You can now send PowerShell directly to the Hyper-V host’s VMs with Microsoft Windows Server 2016.
Microsoft Windows Server 2012
The highlight of this version is the effort to make it cloud-ready. Moreover, the addition of the following features makes it a worthy bargain.
Server Manager
- The Microsoft Windows Server 2012 flaunts a new server manager with a new look and feel in the user interface. You can now group many servers on your network and manage them from a focal point in one window. Such will save you time that you used in past versions jumping from one window to another to work on your servers.
Windows PowerShell 3.0
- PowerShell seeks to stretch more control of Windows servers. This tool works hand-in-hand with the GUI to executive your commands. However, it is the dominant force of the two; hence, fewer crashes and issues are likely to happen. PowerShell is a revolutionary feature that will make the administration of windows servers more efficient.
Hyper-V 3.0
- This virtualization platform will allow you to run multiple virtual machines on a single windows server. When used with Microsoft System Centre, the experience is even better.
Storage
- Storage space has also been massively boosted in Microsoft Server 2012. The different available pools of storage are divided into different spaces. Furthermore, in the pools, you can add up any physical disk as well as configure mirroring. This ability to add up more space as you please is quite an impressive feature.
Data Deduplication
- This is a data compression technique that will help you eliminate duplicates of repetitive data. Large chunks are analyzed, and if any matches up, the extra copy is replaced with a reference that directs to the stored piece.
Server Message Block (SMB) 3.0
- SMB file sharing protocol comes with a set of beneficial features such as; hot pluggable interfaces, multichannel, encryption, deduplication, Volume Shadow Copy Services (VSS), among others.
Dynamic Access Control (DAC)
- DAC manages how files and folders are accessed. It classifies data files in order of device claims and resource claims.
Microsoft Server 2012 R2
Microsoft Server 2012 R2 was a significant improvement on Microsoft Server 2012. Some of the improvements made include:
File Services and Storage
- Work folders. You can make corporate data available to your users since your users’ devices do not have to be domain-connected.
- SMB. This feature was introduced in the server 2012 but made better in this version. Better performance, automatic rebalancing of Scale-Out File Server clients, and support for multiple SMB instances are some of the improvements.
- DFS Namespace and DFS Replication. You can now recover any corrupt databases or files that are hidden in DFSR private folders.
- Storage spaces have also been significantly extended to accommodate more data.
Health Report
- A readily available health report is one of the highlights of this version. Furthermore, you can customize it according to your needs for it to display what you want to monitor.
BranchCashe
- BranchCashe is a Wide Area Network (WAN) bandwidth optimization technology that may come with Windows software. If you want to access an offsite server, you can use this feature to boost data access.
Remote Web Access
- You can remotely access your servers online with many Microsoft servers, but with this version, this feature is boosted extensively. It is further with HTML5 support.
Pre-configured Auto-VPN Dialing
- A client VPN comes in handy if you need to access an on-site network resource.
Server Deployment
- With this version, you can install Microsoft Server 2012 as a member server in a domain of any size. Furthermore, as you install as a member server, you can have multiple servers running Essential on your domain.
All the above Microsoft Servers are built upon each other; the more recent versions are built on the flaws of their predecessors. As such, the later the release, the better features you are bound to enjoy.
If you’re looking for a software company you can trust for its integrity and honest business practices, look no further than SoftwareKeep. We are a Microsoft Certified Partner and a BBB Accredited Business that cares about bringing our customers a reliable, satisfying experience on the software products they need. We will be with you before, during, and after all the sales.
That’s our 360 Degree SoftwareKeep Guarantee. So, what are you waiting for? Call us Today on +1 877 315 1713 or email sales@softwarekeep.com. As well, you can reach us via Live Chat.