Мы рассмотрим как настроить NTP сервер в сети предприятия, где компьютеры пользователей получают точное время от DC с ролью эмулятора PDC (главный контроллер домена – Primary Domain Controller), в свою очередь DC синхронизирует свое время с внешним источником времени. В данном примере мы будем получать время с серверов pool.ntp.org.
Начиная с Windows 2000 все операционные системы Windows включают в себя службу времени W32Time. Эта служба предназначена для синхронизации времени в пределах организации и отвечает за работу как клиентской, так и серверной части, причем один и тот же компьютер может быть одновременно и клиентом и сервером NTP (Network Time Protocol). По умолчанию клиенты в домене синхронизируют время с помощью службы времени Windows (Windows Time), а не с помощью протокола NTP.
Настройка сервера времени под Hyper-V
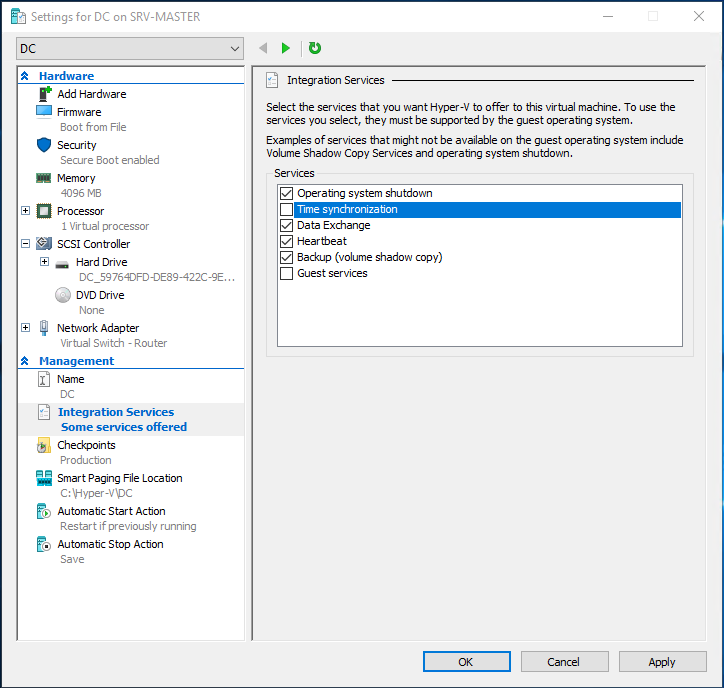
Для тех у кого контролер домена виртуализирован и поднят на Hyper-V, прежде необходимо отключить Time Synchronization, иначе виртуальная машина будет синхронизирована с Hyper-V сервером.
# Выключение синхронизации для VMware 5
Свойства машины - Options -> VMware Tools -> Synchronize guest time with host
# Выключение синхронизации для VMware 6
VMware Tools -> Time -> Synchronize guest time with host
Создание GPO для контроллера домена с ролью эмулятора PDC (главный контроллер домена – Primary Domain Controller)
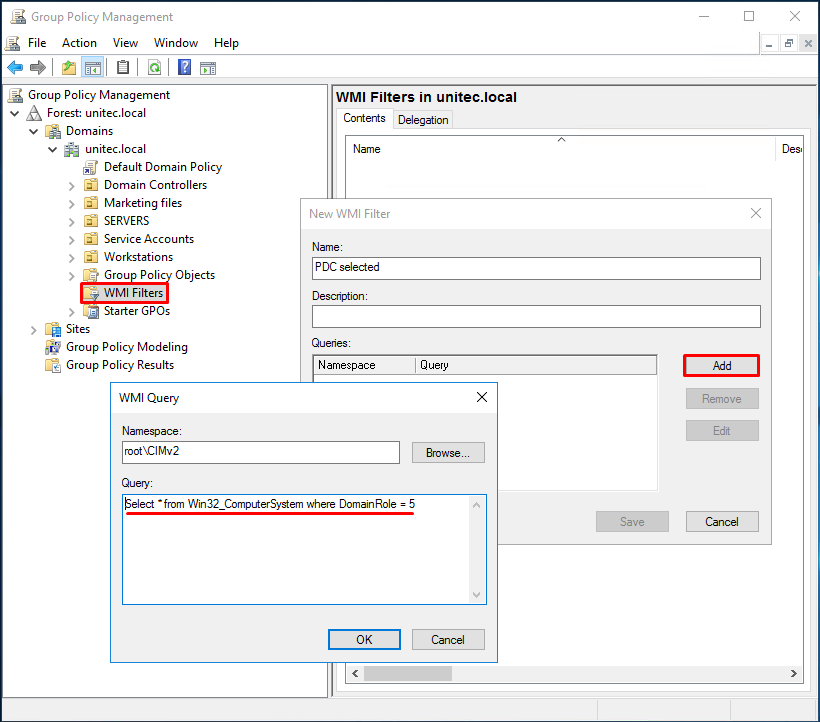
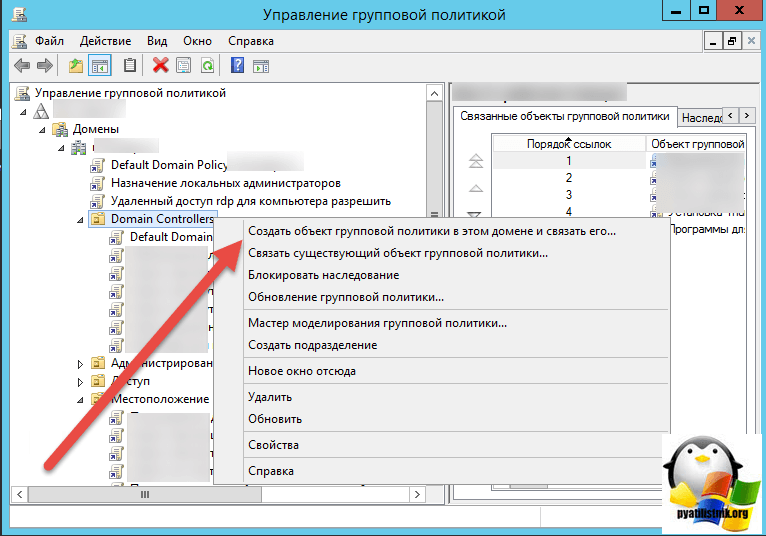
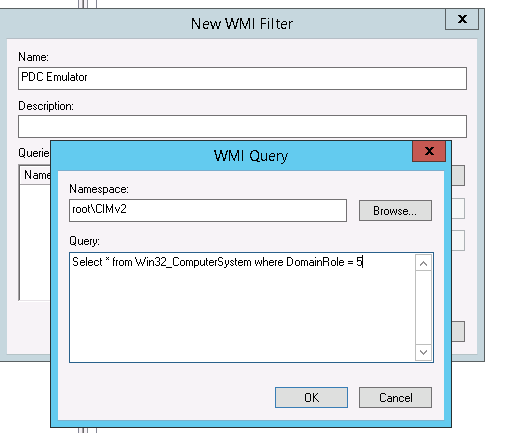
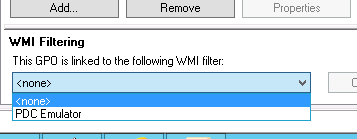
1 . Создание фильтра WMI
Нам необходимо настроить групповую политику для синхронизации NTP для контролера домена PDC, в связи с тем что роль PDC может перемещаться между контроллерами домена, нам необходимо применить политику к текущему владельцу роли PDC. Для этого мы создадим WMI фильтр, чтобы политика была применена для сервера с ролью PDC.
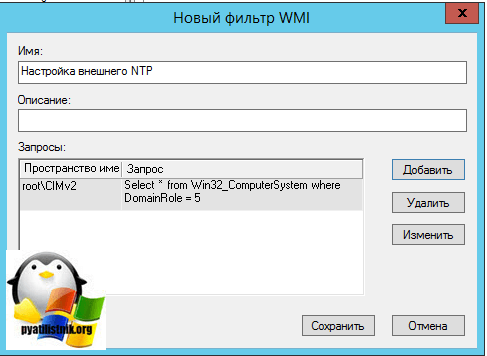
Для этого в консоли управления Group Policy Management Console (GPMC.msc), в разделе WMI Filters создадим новый WMI фильтр с именем PDC selected и запросом: Select * from Win32_ComputerSystem where DomainRole = 5
Select * from Win32_ComputerSystem where DomainRole = 5
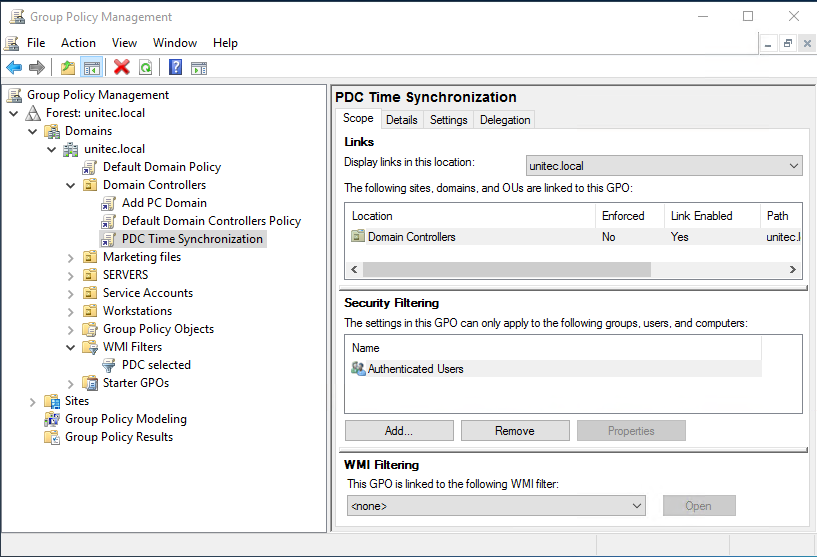
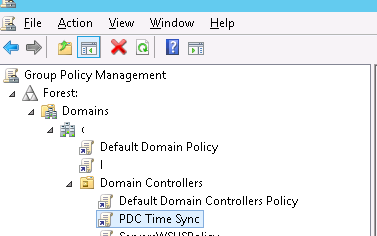
2 . Создаем и редактируем новую GPO
2.1 Для контейнера Domain Controllers создаем групповую политику, в нашем случае это PDC Time Synchronization.
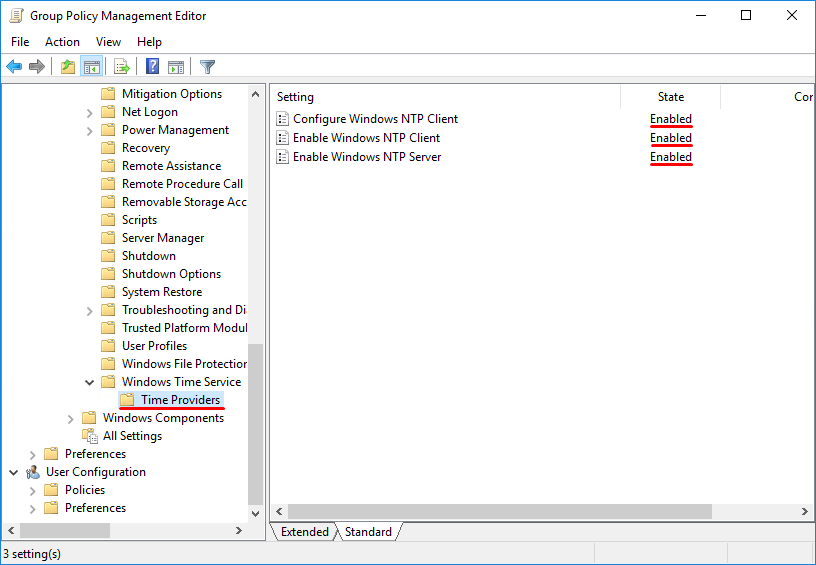
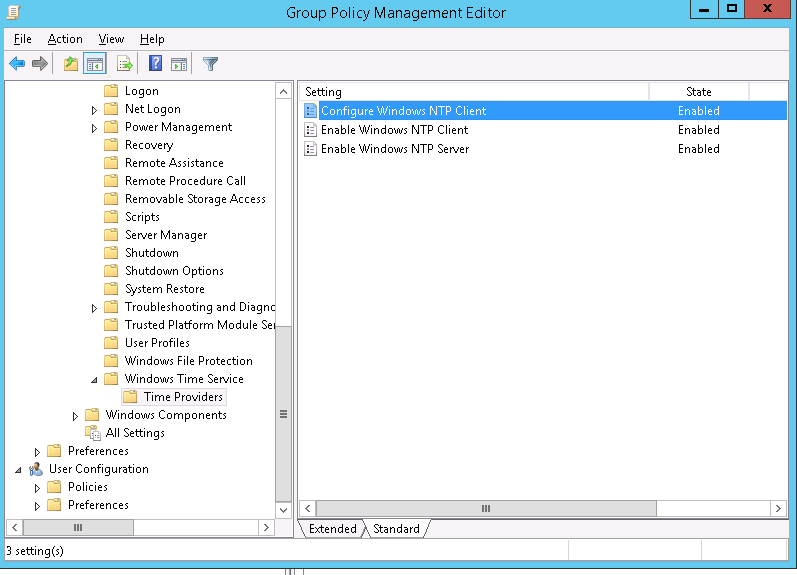
2.2 Редактируем политику PDC Time Synchronization, разворачиваем Computer Configuration -> Policies -> Administrative Templates -> System -> Windows Time Service -> Time Providers и включаем следующие политики:
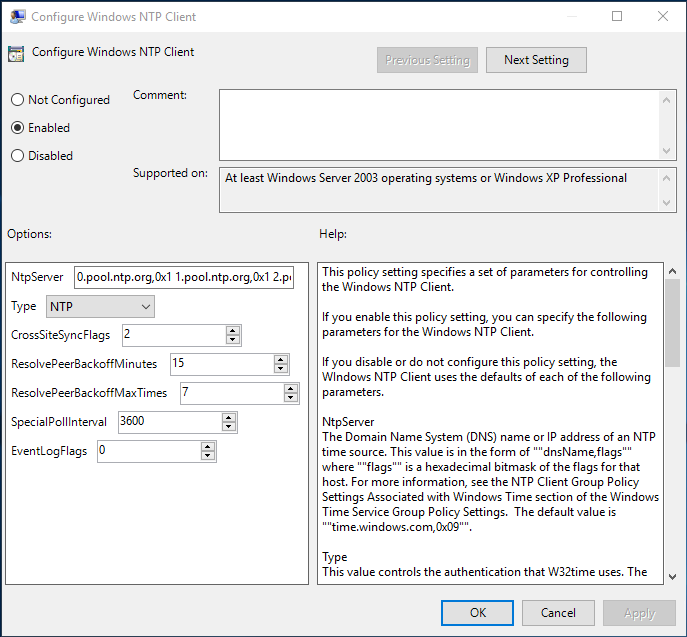
Configure Windows NTP Client: Enabled Enable Windows NTP Client: Enabled Enable Windows NTP Server: Enabled
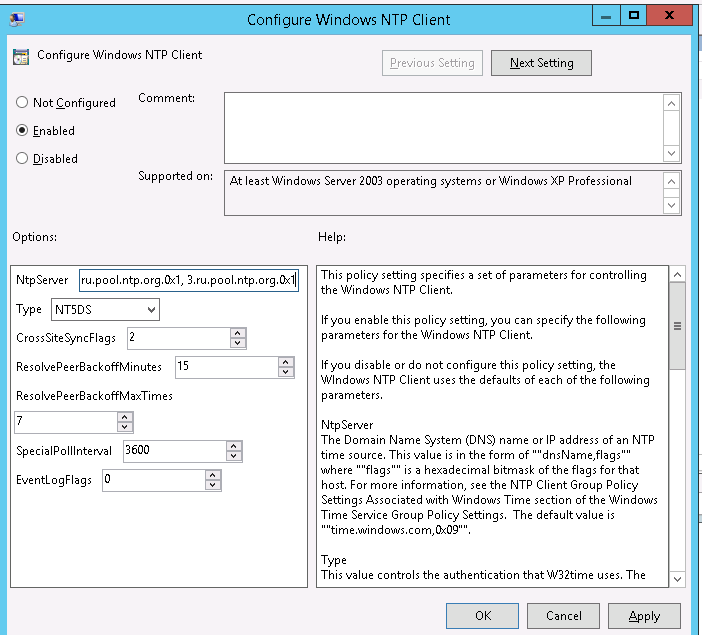
2.3 В настройках политики Enable Windows NTP Server, задаем:
NtpServer: 0.pool.ntp.org,0x1 1.pool.ntp.org,0x1 2.pool.ntp.org,0x1 Type: NTP CrossSiteSyncFlags: 2 ResolvePeerBackoffMinutes: 15 Resolve Peer BAckoffMaxTimes: 7 SpecilalPoolInterval: 3600 EventLogFlags: 0
Дополнительные опции политики
Enable Windows NTP Server
NoSync — NTP-сервер не синхронизируется с внешним источником времени. Используются встроенные часы в микросхему CMOS самого сервера; NTP — NTP-сервер синхронизируется серверами указаными в параметре NtpServer; NT5DS — NTP-сервер производит синхронизацию согласно доменной иерархии; AllSync — NTP-сервер использует для синхронизации все доступные источники.
Выбрать сервер для синхронизации вы можете по ссылке NTPPoolServers
Параметр NtpServer задает NTP-сервера, с которыми будем синхронизировать время. По умолчанию там задан NTP-сервер Microsoft (time.windows.com,0x1), дополнительные сервера можно добавит через пробел. В конце каждого имени сервера можно добавлять флаг (сервер,0x1) который определяет режим для синхронизации с сервером времени.
Допускаются следующие значения:
0x1 – SpecialInterval, использование специального интервала опроса; 0x2 – режим UseAsFallbackOnly; 0x4 – SymmetricActive, симметричный активный режим; 0x8 – Client, отправка запроса в клиентском режиме.
Проверяем ответ NTP сервера
w32tm /stripchart /computer:192.168.1.100 /dataonly /samples:5В этой статье показано, как настроить службу времени Windows (NTP) в Windows Server 2016, чтобы она действовала как NTP-сервер для клиентских компьютеров домена.

Содержание
- Немного теории
- Проверяем откуда сервер берет время
- Быстрая настройка NTP на Windows Server 2016
- Расширенная настройка NTP на Windows Server 2016
- Проверка работы NTP сервера (Живой ли внешний NTP сервер с которого мы берем время)
- Список команд w32tm
- Также хотел бы поделится комментарием найденным на форуме
Немного теории
Синхронизация времени — важный и во многом достаточно критичный аспект работы Active Directory, особенно сегодня, когда широко используется взаимодействие с внешними системами и работа с сотрудниками, которые могут находиться в различных часовых поясах. Применение систем виртуализации вносит дополнительные особенности, которые также следует учитывать. Поэтому данный вопрос может оказаться не столь простым, как кажется, а синхронизация с внешним источником точного времени становится одной из актуальных задач.
Прежде всего вспомним, как происходит синхронизация времени в Active Directory. В качестве эталона времени выступает контроллер, владеющий ролью эмулятора PDC. Это FSMO-роль и эмулятором PDC может являться только один контроллер в каждом домене. С ним синхронизируют время остальные контроллеры домена. Доменные ПК и рядовые серверы сверяют часы с ближайшим контроллером домена.
Сам эмулятор PDC в качестве источника точного времени может использовать либо аппаратные часы материнской платы, либо внешний источник точного времени, при нахождении в виртуальной среде также может быть использовано время хоста виртуализации.
О последней поговорим более подробно. Раньше все было довольно просто, источником времени в домене обычно служили аппаратные часы эмулятора PDC, ну отстали или убежали на пару минут, в конце концов можно и подвести. Когда добавилось требование взаимодействия с внешними системами критичными к точному времени (например, использующих криптографию), то в качестве источника времени стал выступать внешний сервер. От него получал время эмулятор PDC, с ним синхронизировались контроллеры, а от них точное время расходилось на остальных участников домена.

С приходом виртуализации все изменилось, появился еще один источник времени — время хоста виртуализации. Многие гипервизоры по умолчанию имеют включенной настройку синхронизации времени гостевых систем и при попадании в виртуальную среду контроллера может возникнуть следующая коллизия: контроллер синхронизирует время с хостом, но сам хост, являясь членом домена, в свою очередь синхронизируется с контроллером.
Еще хуже, если в виртуальную среду попадает эмулятор PDC, в силу особенностей таймера виртуальных машин, время внутри может достаточно сильно плавать, поэтому виртуальный эмулятор PDC всегда должен синхронизировать время с внешним источником, а синхронизация времени с хостом должна быть отключена, последнее касается и всех остальных виртуальных членов домена.
Проверяем откуда сервер берет время
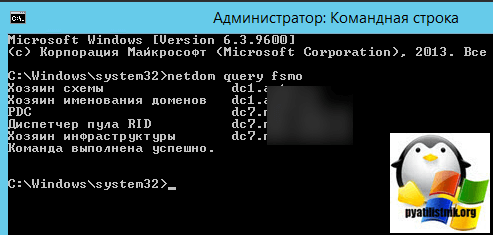
Давайте перейдем от теории к практике. Начнем с того, что выясним кто из контроллеров является эмулятором PDC и эталоном времени для домена. Это можно сделать на любом контроллере домена командой:
netdom query fsmoВ выводе будут показаны все хозяева операций, нас интересует только эмулятор PDC.

Затем перейдем на указанный контроллер и узнаем источник времени для него, для этого выполните команду:
w32tm /query /source
Если в выводе вы увидите:
Local CMOS Clock
Free-Running System Clockто источником времени являются аппаратные часы. А если там будет:
VM IC Time Synchronization Provider
то вы имеете дело с виртуальной машиной, которая синхронизирует время с хостом.
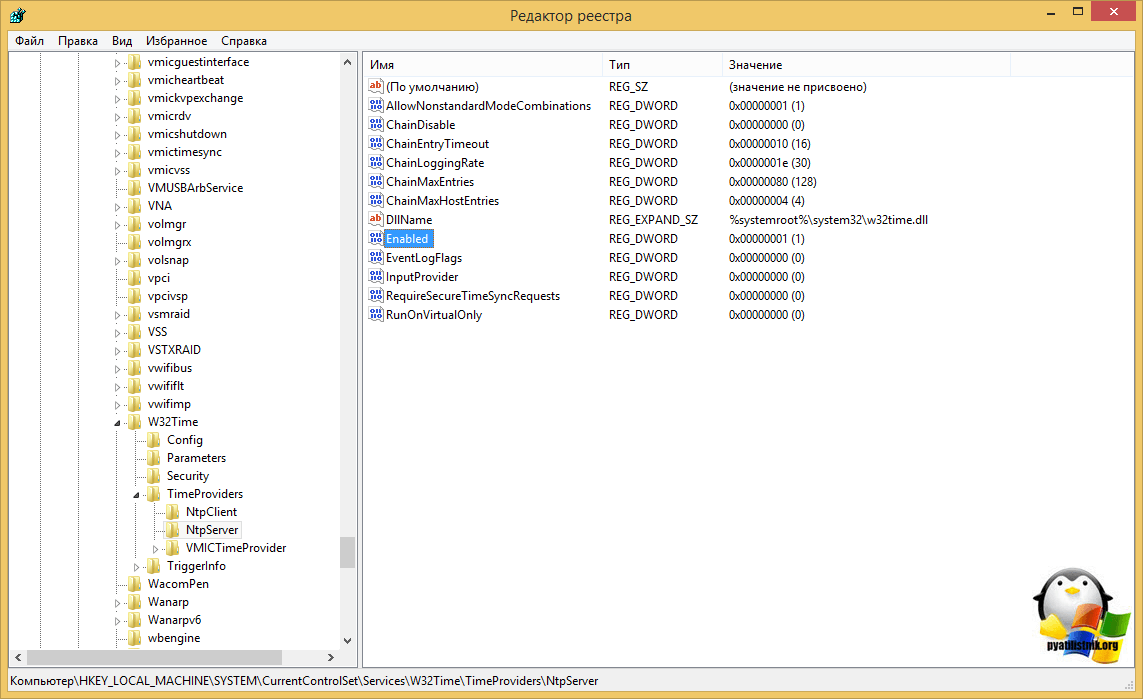
Данную настройку следует исправить, это можно сделать в настройках виртуальной машины, отключив синхронизацию времени с хостом, либо в самой системе, для этого откройте ветвь реестра:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesW32TimeTimeProvidersVMICTimeProviderи установите для параметра Enabled значение 0.
После данного изменения следует перезапустить Службу времени Windows как показано ниже или перезагрузить компьютер.
net stop w32time
net start w32timeДалее будет показана быстрая настройка NTP клиента на сервере и более расширенная.
Быстрая настройка NTP на Windows Server 2016
На вашем Windows Server 2016 нажмите кнопку Windows и введите: PowerShell, щелкните правой кнопкой мыши и выберите «Запуск от имени администратора».
Введите следующие команды
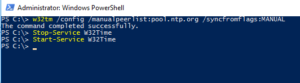
w32tm /config /manualpeerlist:ntp1.stratum2.ru /syncfromflags:manual /reliable:yes /update
reliable:(YES|NO) — определяет, является ли этот компьютер надежным источником времени
Stop-Service w32time
Start-Service w32timeКонечно, вы можете взять любой NTP-сервер, какой захотите. Я брал отсюда
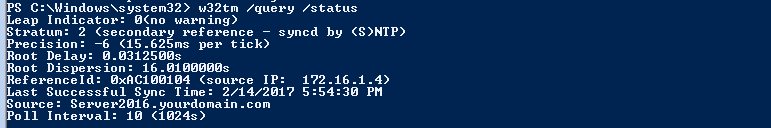
Теперь проверьте, правильно ли настроен сервер времени на вашем сервере Server 2016, набрав:
w32tm /query /status
Расширенная настройка NTP на Windows Server 2016
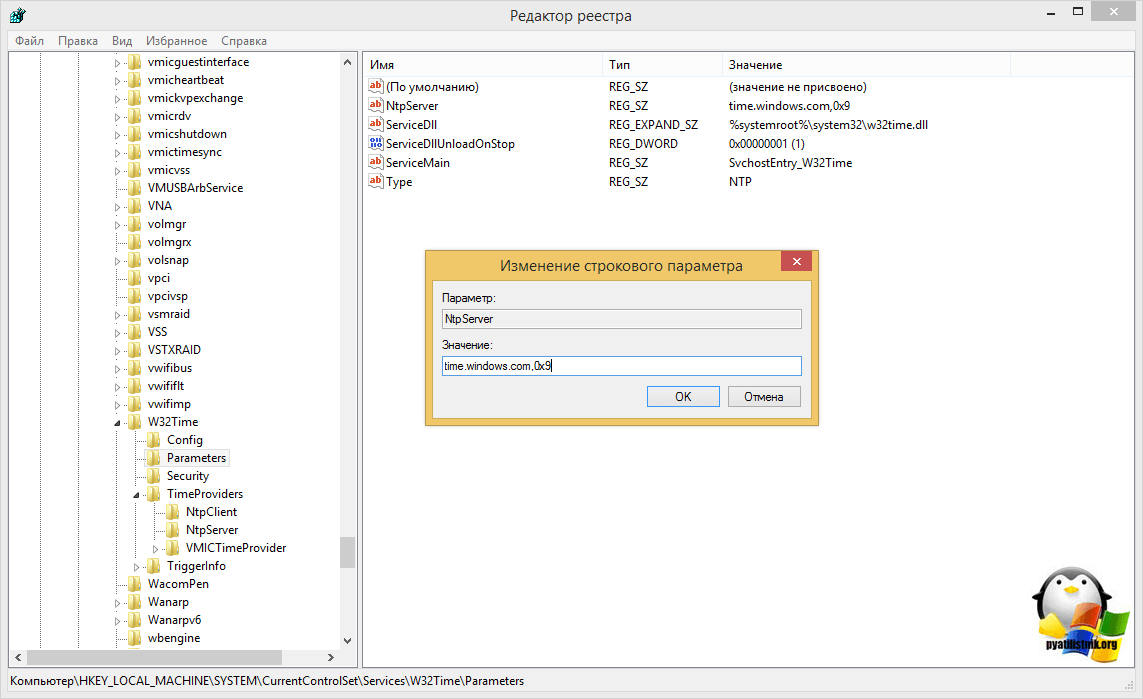
Расширенная настройка нашего эмулятора PDC на работу с внешними источниками точного времени. Все изменения также будут вноситься через реестр. Прежде всего изменим тип сервера на NTP, для этого откроем ветку
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesW32TimeParameters
и для параметра Type укажем строковое значение NTP. А для параметра NtpServer зададим адреса серверов точного времени, после каждого из которых, через запятую укажем 0x8, если мы хотим работать как стандартный NTP-клиент или 0x1 если будем использовать собственные параметры, например:
ntp1.stratum2.ru,0x1 ntp2.stratum2.ru,0x1 ntp4.stratum2.ru,0x1
После чего в
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesW32TimeTimeProvidersNtpServer
Параметр Enabled установим в значение 1.

Затем перейдем в
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesW32TimeConfig
и установим для параметра AnnounceFlags значение A.
Значение «AnnounceFlags» может составлять сумму его флагов, например:
10=2+8 — NTP-сервер заявляет о себе как о надежном источнике времени при условии, что сам получает время из надежного источника либо является PDC корневого домена. Флаг 10 задается по умолчанию как для членов домена, так и для отдельно стоящих серверов.
5=1+4 — NTP-сервер всегда заявляет о себе как о надежном источнике времени. Например, чтобы заявить рядовой сервер (не контроллер домена) как надежный источник времени, нужен флаг 5;

Следующие параметры будут работать, только если мы при указании серверов добавили 0x1, иначе будут использоваться настройки, предлагаемые сервером. Чтобы задать период синхронизации откройте ветку
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesW32TimeTimeProvidersNtpClient
и для параметра SpecialPollInterval укажите десятичное значение в секундах.

Вернемся в
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesW32TimeConfig
И зададим максимальное время опережения и отставания часов, после которых синхронизация производиться не будет. Для этого используются параметры MaxPosPhaseCorrection (опережение) и MaxNegPhaseCorrection (отставание) для которых также следует задать десятичное значение в секундах. По умолчанию стоит 48 часов. Это значит, что если время на эмуляторе PDC уйдет от точного источника более чем на 48 часов в любую сторону, то синхронизация производиться не будет.

Если вы хотите, чтобы время синхронизировалось всегда, то установите в оба параметра шестнадцатеричное значение FFFFFFFF.
Выполнив настройки перезапустите Службу времени Windows, это также можно сделать в командной строке:
net stop w32time
net start w32timeПосле чего еще раз выполним команду чтобы показать источники времени и их состояние
w32tm /query /peers
выполняем еще команду
w32tm /query /source
и убедимся, что источником времени для эмулятора PDC является внешний сервер.
Затем выполним данную команду на рядовых контроллерах домена, в качестве источника времени там должен быть указан эмулятор PDC, и на обычных ПК, где в выводе будет присутствовать любой из контроллеров домена. Обязательно выполните контроль для виртуальных машин, чтобы быть уверенным, что они используют время домена, а не хоста виртуализации.
Проверка работы NTP сервера (Живой ли внешний NTP сервер с которого мы берем время)
В Windows, нужно открыть командную строку и выполнить команду w32tm со специальными параметрами. Где ntp1.stratum2.ru — это NTP сервер
w32tm /stripchart /computer:ntp1.stratum2.ru /dataonly /samples:3Ответ будет содержать локальное время, и разницу со временем на указанном NTP сервере. Например:
w32tm /stripchart /computer:ntp1.stratum2.ru /dataonly /samples:3
Tracking ntp1.stratum2.ru [88.147.254.230:123].
Collecting 3 samples.
The current time is 8/1/2022 3:48:56 PM.
15:48:56, +00.0098812s
15:48:58, -00.0036452s
15:49:00, +00.0005137s
PS C:UsersAdministrator>На данном выводе видно что погрешность синхронизации составяляет +00.0098812s
Список команд w32tm
Основные команды конфигурации w32tm
- w32tm /register — Регистрация и включение службы со стандартными параметрами.
- w32tm /unregister — Отключение службы и удаление параметров конфигурации.
- w32tm /monitor — Просмотр информации по домену.
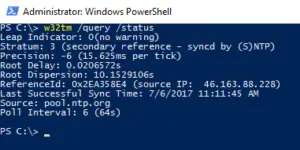
- w32tm /resync — Команда принудительной синхронизации с заданным в конфигурации источником.
- w32tm /config /update — Применить и сохранить конфигурацию.
- w32tm /config /syncfromflags:domhier /update – Задаем настройку синхронизации с контроллером домена.
- w32tm /config /syncfromflags:manual /manualpeerlist:time.windows.com – задать конкретные источники синхронизации времени по протоколу NTP.
Просмотр параметров (/query)
- w32tm /query /computer:<target> — Информация о стутусе синхронизации определенной станции (если имя не указано — используется локальный компьютер).
- w32tm /query /Source – Показать источник времени.
- w32tm /query /Configuration — Вывод всех настроек службы времени Windows.
- w32tm /query /Peers – Показать источники времени и их состояние.
- w32tm /query /Status – Статус службы времени.
- w32tm /query /Verbose – Подробный вывод всей информации о работе службы.
Также хотел бы поделится комментарием найденным на форуме
За настройку NTP через политики надо больно бить по рукам. 1. В доменной среде ничего не надо делать, контроллеры берут время с PDC, клиенты с контроллера. 2. Точности времени секунда в секунду не добьетесь. Больная тема для меня. Предыдущие админы нахреначили синхронизацию чуть ли не в 10 разных политиках, до сих пор натыкаюсь и с матами удаляю. Есть проблема с синхронизацией времени? На всех контроллерах: 1. Убиваем службу w32time 2. Грохаем ветку реестра HKLMSystemCurrentControlSetservicesW32Time 3. Регистрируем службу заново 4. Проверяем, что параметр TYPE в HKLMSystemCurrentControlSetservicesW32TimeParameters равен NT5DS Конфигурация NTP-сервера Задаем тип синхронизации внутренних часов, на использование внешнего источника. NoSync — NTP-сервер не синхронизируется с каким либо внешним источником времени. Используются системные часы, встроенные в микросхему CMOS самого сервера. NTP — NTP-сервер синхронизируется с внешними серверами времени, которые указаны в параметре реестра NtpServer. NT5DS — NTP-сервер производит синхронизацию согласно доменной иерархии. AllSync — NTP-сервер использует для синхронизации все доступные источники. На PDC настраиваем синхронизацию с внешним поставщиком времени 5. И ничего б*ть не трогаем!=) Через какое-то время время стабилизируется. Для понимания — время не импортируется, оно сверяется и подгоняется под эталон. Не забываем, что для керберос разница в 5 минут не критична. Хитрожопых кадровиков и безопасников, желающих снихронить свои убогие СКУДы с виндовыми тачками слать надолго и подальше. Всё, я кончил =) ===
Полностью согласен. Время домена — не повод для торговли. Оно должно быть правильным, но в разумных пределах, плюс-минус несколько минут не являются критичными для общения. Хотя встречал домен, где для хождения кербероса админы сделали максимальную погрешность часов сутки. Всякое бывает, но «правильный» админ всегда найдет решение… или костыль… ===
ПК не знает и никак не узнает, что PDC сменился. Так что политика обязательно должна быть! === А ему не надо знать. Он кричит в сеть «PDC!!!», а те сами знают, кому из них отозваться. У них DNS для этого есть.
Обновлено 12.11.2019
Добрый день уважаемые читатели и гости блога pyatilistnik.org, как много люди говорят о времени, что оно быстро или медленно бежит, и все понимают, что оно бесценно и важно. Так и в инфраструктуре Active Directory, она является одним из важнейших факторов, правильного функционирования домена. В домене все друг другу доверяют, и один раз авторизовавшись и получив все тикеты от Kerberos, пользователь ходит куда угодно, ограничиваясь лишь своими доступными правами. Так вот если у вас не будет точного времени на ваших рабочих станциях к контроллеру домена, то можете считать, что у вас начинаются серьезные проблемы, о которых мы поговорим ниже и рассмотрим как их устранить с помощью настройки NTP сервера в Windows.
Синхронизация времени в Active Directory
Среди компьютеров, участвующих в Active Directory работает следующая схема синхронизация времени.
- Контроллер корневого домена в лесу AD, которому принадлежит FSMО-роль эмулятора PDC (назовем его корневым PDC), является источником времени для всех остальных контроллеров этого домена.
- Контроллеры дочерних доменов синхронизируют время с вышестоящих по топологии AD контроллеров домена.
- Рядовые члены домена (сервера и рабочие станции) синхронизируют свое время с ближайшим к ним доступным контроллером домена, соблюдая топологию AD.
Корневой PDC может синхронизировать свое время как со внешним источником, так и с самим собой, последнее задано конфигурацией по умолчанию и является абсурдом, о чем периодически намекают ошибки в системном журнале.
Синхронизация клиентов корневого PDC может осуществятся как с его внутренних часов, так и с внешнего источника. В первом случае сервер времени корневого PDC объявляет себя как «надежный» (reliable).
Далее я приведу оптимальную с моей точки зрения конфигурацию сервера времени корневого PDC, при которой сам корневой PDC периодически синхронизирует свое время от достоверного источника в интернете, а время обращающихся к нему клиентов синхронизирует со своими внутренними часами.
Для того, чтобы понять кто у вас в сети является NTP сервером из контроллеров домена, прочитайте вот эту статью, многие вопросы отпадут сами собой
Вводим netdom query fsmo. В моем примере, роль PDC и NTP сервера, принадлежит контроллеру dc7
Конфигурация NTP-сервера на корневом PDC
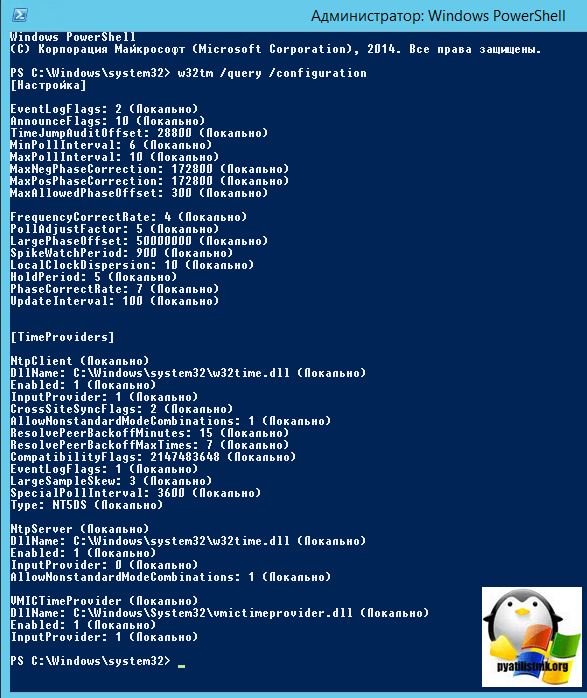
Конфигурирование сервера времени в Windows (NTP-сервера) может осуществляться как с помощью утилиты командной строки w32tm, так и через реестр. Где возможно, я приведу оба варианта. Но в начале посмотрите полностью ваши настройки на компьютере, делается это командой:
w32tm /query /configuration
EventLogFlags: 2 (Локально)
AnnounceFlags: 10 (Локально)
TimeJumpAuditOffset: 28800 (Локально)
MinPollInterval: 6 (Локально)
MaxPollInterval: 10 (Локально)
MaxNegPhaseCorrection: 172800 (Локально)
MaxPosPhaseCorrection: 172800 (Локально)
MaxAllowedPhaseOffset: 300 (Локально)FrequencyCorrectRate: 4 (Локально)
PollAdjustFactor: 5 (Локально)
LargePhaseOffset: 50000000 (Локально)
SpikeWatchPeriod: 900 (Локально)
LocalClockDispersion: 10 (Локально)
HoldPeriod: 5 (Локально)
PhaseCorrectRate: 7 (Локально)
UpdateInterval: 100 (Локально)[TimeProviders]
NtpClient (Локально)
DllName: C:Windowssystem32w32time.dll (Локально)
Enabled: 1 (Локально)
InputProvider: 1 (Локально)
CrossSiteSyncFlags: 2 (Локально)
AllowNonstandardModeCombinations: 1 (Локально)
ResolvePeerBackoffMinutes: 15 (Локально)
ResolvePeerBackoffMaxTimes: 7 (Локально)
CompatibilityFlags: 2147483648 (Локально)
EventLogFlags: 1 (Локально)
LargeSampleSkew: 3 (Локально)
SpecialPollInterval: 3600 (Локально)
Type: NT5DS (Локально)NtpServer (Локально)
DllName: C:Windowssystem32w32time.dll (Локально)
Enabled: 1 (Локально)
InputProvider: 0 (Локально)
AllowNonstandardModeCombinations: 1 (Локально)VMICTimeProvider (Локально)
DllName: C:WindowsSystem32vmictimeprovider.dll (Локально)
Enabled: 1 (Локально)
InputProvider: 1 (Локально)
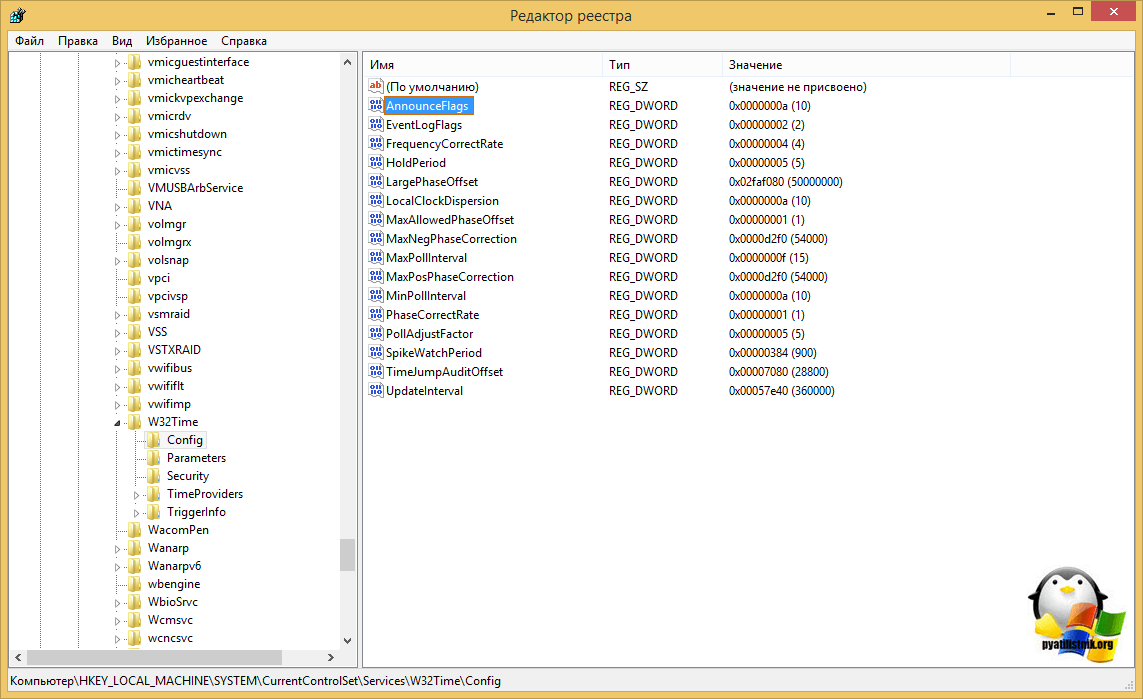
Включение синхронизации внутренних часов с внешним источником
Объявление NTP-сервера в качестве надежного
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesW32TimeConfig]
"AnnounceFlags"=dword:0000000aw32tm /config /reliable:yes
Включение NTP-сервера
NTP-сервер по умолчанию включен на всех контроллерах домена, однако его можно включить и на рядовых серверах.
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesW32TimeTimeProvidersNtpServer]
"Enabled"=dword:00000001
Задание списка внешних источников для синхронизации
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesW32TimeParameters]
"NtpServer"="time.nist.gov,0x8 ntp1.imvp.ru,0x8 ntp2.imvp.ru,0x8 time.windows.com,0x8 ru.pool.ntp.org,0x8"w32tm /config /manualpeerlist:"time.nist.gov,0x8 ntp1.imvp.ru,0x8 ntp2.imvp.ru,0x8 time.windows.com,0x8 ru.pool.ntp.org,0x8"
Флаг 0×8 на конце означает, что синхронизация должна происходить в режиме клиента NTP, через предложенные этим сервером интервалы времени. Для того, чтобы задать свой интервал синхронизации, необходимо использовать флаг 0×1.
Задание интервала синхронизации с внешним источником
Время в секундах между опросами источника синхронизации, по умолчанию 900с = 15мин. Работает только для источников, помеченных флагом 0×1.
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesW32TimeTimeProvidersNtpClient]
"SpecialPollInterval"=dword:00000384
Установка минимальной положительной и отрицательной коррекции
Максимальная положительная и отрицательная коррекция времени (разница между внутренними часами и источником синхронизации) в секундах, при превышении которой синхронизация не происходит. Рекомендую значение 0xFFFFFFFF, при котором коррекция сможет производиться всегда.
[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesW32TimeConfig]
"MaxPosPhaseCorrection"=dword:FFFFFFFF
"MaxNegPhaseCorrection"=dword:FFFFFFFF
Все необходимое одной строкой
w32tm.exe /config /manualpeerlist:"time.nist.gov,0x8 ntp1.imvp.ru,0x8 ntp2.imvp.ru,0x8 time.windows.com,0x8 pool.ntp.org,0x8" /syncfromflags:manual /reliable:yes /update
Полезные команды
- Применение внесенных в конфигурацию службы времени изменений
w32tm /config /update - Принудительная синхронизация от источника
w32tm /resync /rediscover - Отображение состояния синхронизации контроллеров домена в домене
w32tm /monitor - Отображение текущих источников синхронизации и их статуса
w32tm /query /peers
Настройка NTP сервера и клиента групповой политикой
Раз уж у нас с вами домен Active Directory, то глупо не использовать групповые политики, для массовой настройки серверов и рабочих станций, я покажу как настроить ваш NTP сервер в windows и клиента. Открываем оснастку «Редактор групповых политик». Перед тем как настроить наш NTP сервер в Windows, нам необходимо создать WMI фильтр, который будет применять политику, только к серверу мастера PDC.
Вводим имя запроса, пространство имен, будет иметь значение «rootCIMv2» и запрос «Select * from Win32_ComputerSystem where DomainRole = 5». Сохраняем его.
Затем вы создаете политику на контейнере Domain Controllers.
В самом низу политики применяете ваш созданный WMI фильтр.
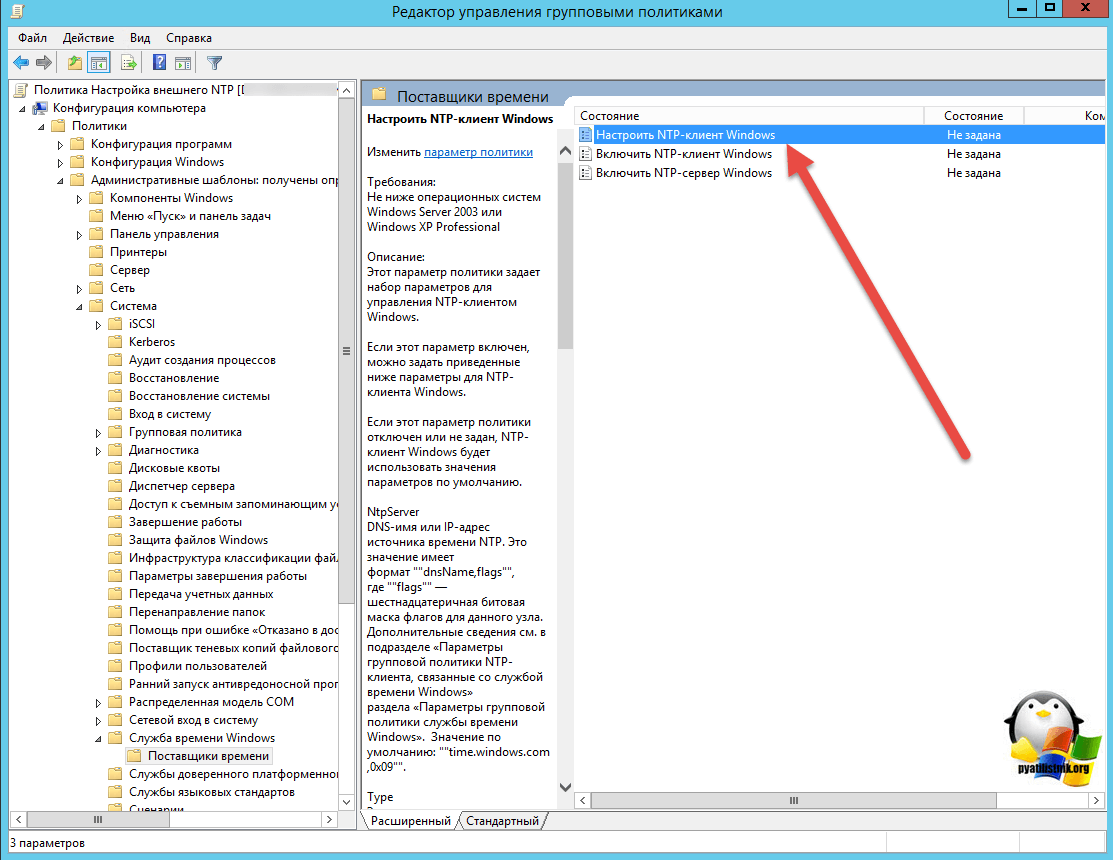
Переходим в ветку: Конфигурация компьютера > Политики > Административные шаблоны > Система > Служба времени Windows > Поставщики времени.
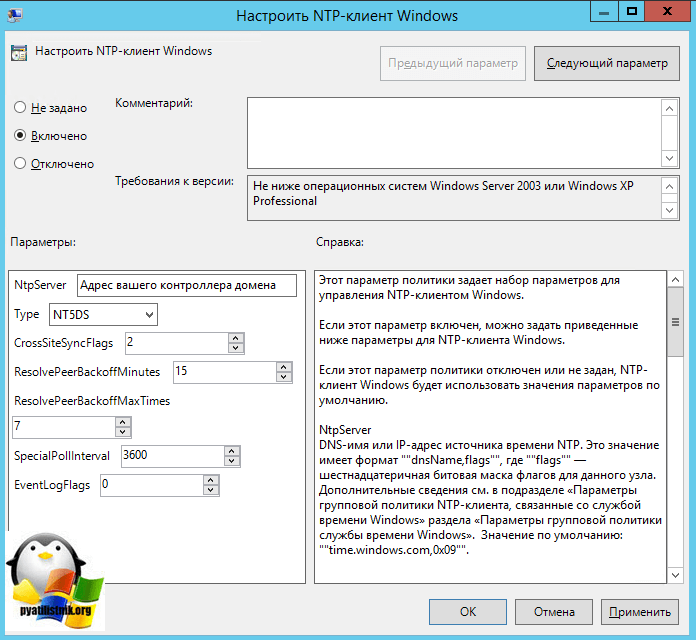
Тут открываем политику «Настроить NTP-клиент Windows». Задаем параметры
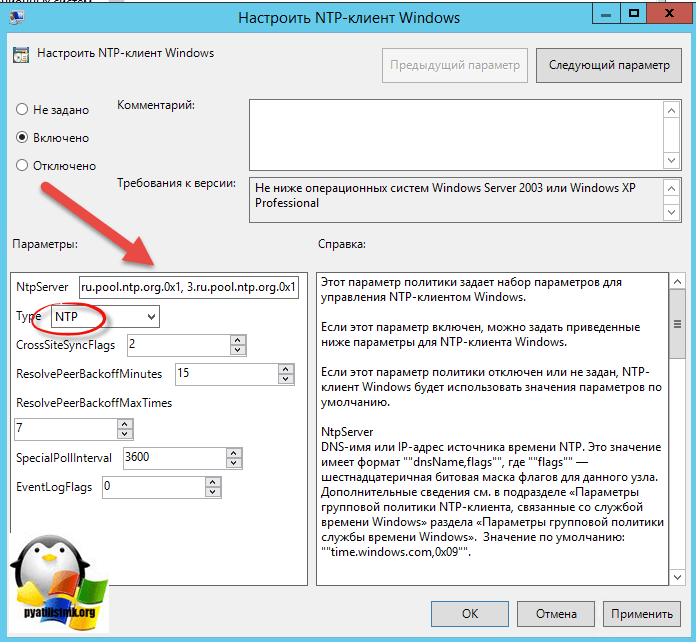
- NtpServer: 0.ru.pool.ntp.org,0x1 1.ru.pool.ntp.org,0x1 2.ru.pool.ntp.org,0x1 3.ru.pool.ntp.org,0x1
- Type: NTP
- CrossSiteSyncFlags: 2. Двойка означает, если этот параметр равен 2 (Все), можно использовать любого участника синхронизации. Это значение игнорируется, если не задано значение NT5DS. Значение по умолчанию: 2 (десятичное) (0x02 (шестнадцатеричное))
- ResolvePeerBackoffMinutes: 15. Это значение, выраженное в минутах, определяет интервал ожидания службы W32time перед попыткой разрешения DNS-имени в случае неудачи. Значение по умолчанию: 15 минут
- Resolve Peer BAckoffMaxTimes: 7. Это значение определяет число попыток разрешения DNS-имени, предпринимаемых службой W32time перед перезапуском процесса обнаружения. При каждом неудачном разрешении DNS-имени интервал ожидания перед следующей попыткой удваивается. Значение по умолчанию: семь попыток.
- SpecilalPoolInterval: 3600. Это значение параметра NTP-клиента, выраженное в секундах, определяет частоту опроса настроенного вручную источника времени, который использует особый интервал опроса. Если для параметра NTPServer установлен флаг SpecialInterval, клиент использует значение, заданное как SpecialPollInterval, вместо значений MinPollInterval и MaxPollInterval, чтобы определить частоту опроса источника времени. Значение по умолчанию: 3600 секунд (1 час).
- EventLogFlags: 0
Делаем отдельную групповую политику для клиентских рабочих машин, вот с такими параметрами.
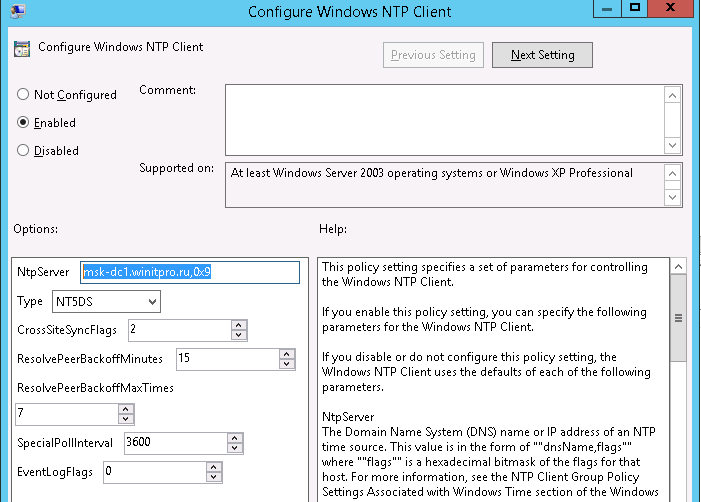
- NtpServer: Адрес вашего контроллера домена с ролью PDC.
- Type: NT5DS
- CrossSiteSyncFlags: 2
- ResolvePeerBackoffMinutes: 15
- Resolve Peer BAckoffMaxTimes: 7
- SpecilalPoolInterval: 3600
- EventLogFlags: 0
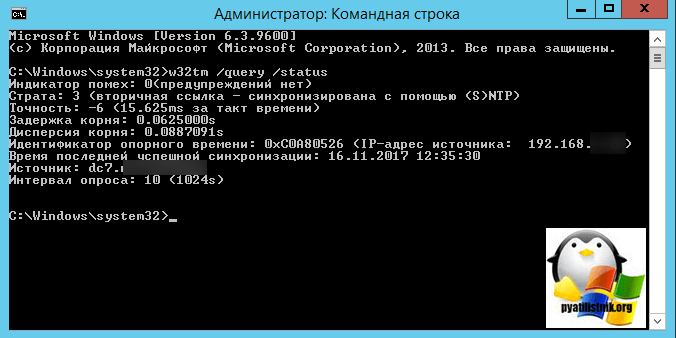
Далее идем на клиента и обновляем групповые политики gpupdate /force и вводим команду w32tm /query /status
Особенности виртуализированных контроллеров домена
Контроллеры домена, работающие в виртуализированной среде, требуют к себе особенного отношения.
- Средства синхронизации времени виртуальной машины и хостовой ОС должны быть выключены. Во всех адекватных системах виртуализации (Microsoft, vmWare и т. д.) присутствуют компоненты интеграции гостевой ОС с хостовой, которые значительно повышают производительность и управляемость гостевой системой. Среди этих компонентов всегда есть средство синхронизации времени гостевой ОС с хостовой, которое очень полезно для рядовых машин, но противопоказано для контроллеров домена. Потому как в этом случае весьма вероятен цикл, при котором контроллер домена и хостовая ОС будут синхронизировать друг друга. Последствия печальны.
- Для корневого PDC синхронизация с внешним источником должна быть настроена всегда. В виртуальной среде часы не настолько точны как в физической, потому как виртуальная машина работает с виртуальным процессором и прерываниями, для которых характерно как замедление, так и ускорение относительно «обычной» частоты. Если не настроить синхронизацию виртуализированного корневого PDC с внешним источником, время на всех компьютерах предприятия может убегать/отставать на пару часов в сутки. Не трудно представить неприятности, которые может принести такое поведение.
Служба времени Windows, несмотря на кажущуюся простоту, является одной из основ, необходимых для нормального функционирования домена Active Directory. В правильно настроенной среде AD служба времени работает следующим образом: компьютеры пользователей получают точное время от ближайшего контроллера домена, на котором они зарегистрировались. Все контроллеры домена в свою очередь получают точное время от DC с FSMO ролью «Эмулятор PDC», а контролер PDC синхронизирует свое время с неким внешним источником времени. В качестве внешнего источника времени может выступать один или несколько NTP серверов, например time.windows.com или NTP сервер вашего Интернет-провайдера. Также нужно отметить, что по умолчанию клиенты в домене синхронизируют время с помощью службы времени Windows (Windows Time), а не с помощью протокола NTP.
Если вы столкнулись с ситуацией, когда время на клиентах и контроллерах домена различается, возможно, в вашем домене есть проблемы с синхронизацией времени и эта статья будет вам полезна.
В первую очередь выберите подходящий NTP сервер, который вы могли бы использовать. Список общедоступных NTP серверов доступен на сайте http://ntp.org. В нашем примере мы будем использовать NTP сервера из пула ru.pool.ntp.org:
- 0.ru.pool.ntp.org
- 1.ru.pool.ntp.org
- 2.ru.pool.ntp.org
- 3.ru.pool.ntp.org
Настройка синхронизации времени в домене с помощью групповых политик состоит из двух шагов:
1) Создание GPO для контроллера домена с ролью PDC
2) Создание GPO для клиентов (опционально)
Настройка политики синхронизации NTP на контролере домена PDC
Этот шаг предполагает настройку контроллера домена с ролью эмулятора PDC на синхронизацию времени с внешним NTP сервером. Т.к. теоретически роль эмулятора PDC может перемещаться между контроллерами домена, нам нужно сделать политику, которая применялась бы только к текущему владельцу роли PDC. Для этого в консоли управления Group Policy Management Console (GPMC.msc), создадим новый WMI фильтр групповых политик. Для этого в разделе WMI Filters создадим фильтр и именем PDC Emulator и WMI запросом:
Select * from Win32_ComputerSystem where DomainRole = 5
Затем создайте новую GPO и назначьте ее на контейнер Domain Controllers.
Перейдите в режим редактирования политики и разверните следующий раздел политик: Computer Configuration->Administrative Templates->System->Windows Time Service->Time Providers
Нас интересуют три политики:
- Configure Windows NTP Client: Enabled (настройки политики описаны ниже)
- Enable Windows NTP Client: Enabled
- Enable Windows NTP Server: Enabled
В настройках политики Configure Windows NTP Client укажите следующие параметры:
- NtpServer: 0.ru.pool.ntp.org,0x1 1.ru.pool.ntp.org,0x1 2.ru.pool.ntp.org,0x1 3.ru.pool.ntp.org,0x1
- Type: NTP
- CrossSiteSyncFlags: 2
- ResolvePeerBackoffMinutes: 15
- Resolve Peer BAckoffMaxTimes: 7
- SpecilalPoolInterval: 3600
- EventLogFlags: 0
Совет. Не забудьте настроить межсетевой экран таким образом, чтобы сервер PDC мог получить доступ к внешним NTP серверам по протоколу NTP (UDP порт 123).
Примечание. Обратите внимание на синтаксис в поле NtpServer. Формат указания нескольких NTP серверов такой:ntsrv1.org,0x1 ntpsrv2.org,0x1 (разделитель пробел). На скриншоте указаны ошибочные данные!
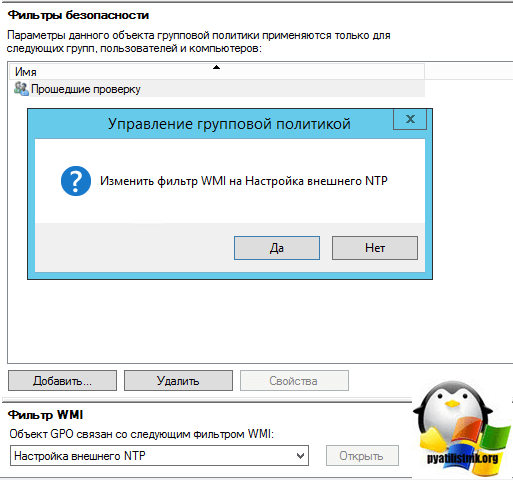
Примените созданный ранее фильтр PDC Emulator к данной политике.
Совет. Найти имя сервера с ролью PDC можно с помощью команды:
netdom query fsmo
Осталось обновить политики на контроллере PDC:
gpupdate /force
Вручную запустите синхронизацию времени:
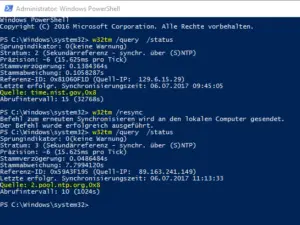
w32tm /resync
Проверьте текущие настройки NTP:
w32tm /query /status
Совет. В том случае, если время не синхронизировалось, перезапустите службу времени Windows и сбросьте текущие настройки:
net stop w32time
w32tm.exe /unregister
w32tm.exe /register
net start w32time
Настройка синхронизации времени на клиентах домена
В среде Active Directory по умолчанию клиенты домена синхронизируют свое время с контролерами домена (опция Nt5DS – синхронизировать время согласно иерархии домена). Как правило, эта схема работает и не требует перенастройки. Однако при наличии проблем с синхронизацией времени на клиентах домена, можно попробовать принудительно назначить сервер времени для клиентов с помощью GPO.
Для этого создайте новую GPO и назначьте ее на контейнеры (OU) с компьютерами. В редакторе GPO перейдите в раздел Computer Configuration -> Administrative Templates -> System -> Windows Time Service -> Time Providers и включите политику Configure Windows NTP Client.
В качестве сервера NTP укажите имя или ip адрес PDC, например msk-dc1.winitpro.ru,0x9, а в качестве типа синхронизации — NT5DS
Обновите настройки групповых политик на клиентах и проверьте, что клиенты успешно синхронизировали свое время с PDC.
Совет. Указанная схема применима только к небольшим доменам. Для больших распределенных доменов с большим количеством DC и сайтов придется создать отдельную политику для каждого сайта, чтобы клиенты синхронизировали свое время с DC в сайте.
This article shows how to configure Windows Time Service (NTP) on Windows Server 2016 so that it acts as an NTP server for domain client computers.
Configure Windows Time Service (NTP)
A prerequisite to having the correct time on the Windows clients, we must have a correct time on the Windows 2016 server. So the first step is to sync server time with pool.ntp.org. Type the following commands on PowerShell:
w32tm /config /manualpeerlist:pool.ntp.org /syncfromflags:MANUAL
Then apply the changes, this is done by restarting the time service. First, we stop the service and then we start it again.
Stop-Service w32time
Start-Service w32time
Now the Windows Server 2016 is an NTP client of pool.ntp.org and its time/clock is synced with the NTP pool servers (The server is at the same time the NTP server for other domain client systems).
Optional: Server is in a Hyper-V VM
If your Windows Server 2016 machine is a VM inside Hyper-V, you have to disable time sync. Go to:
M settings-> Management-> Integration Services
and uncheck:
Time Synchronization.
Otherwise, Windows Server 2016 time/clock will be synced with the Host time/clock.
Configure Windows Clients
Then go to the client machines and run the following command on PowerShell to force them to sync their time/clock with the domain controller on the Windows Server 2016.
w32tm /resync
You can check the time synchronization status using the following command.
w32tm /query /status
In this article, I will show you how to configure NTP Server on Windows Server 2016 in just a few steps.
We will use PowerShell to change the NTP Server and we will validate if it worked afterward.
Configure the NTP Server on Windows Server 2016
On your Windows Server, 2016 hit the Windows Button and type: PowerShell and right-click it and select Run as Administrator
Type the following commands
w32tm /config /manualpeerlist:pool.ntp.org /syncfromflags:MANUAL Stop-Service w32time Start-Service w32time
Of course, you can take any NTP Server that you want.
Now verify if the time-server was set correctly on your Server 2016 by typing:
w32tm /query /status
You should get a reply like this:
Now we will go ahead and verify if our clients sync properly.
Verifying if the Time Server was correctly set on our Clients
On a client computer open a PowerShell with right-click and Run as Administrator….
Type:
w32tm /query /status
Check the time-server and type:
w32tm /resync w32tm /query /status
Then you are able to see that the time-server actually changed like in the example below.
And that’s it! Easy, right?
Always make sure that you use the same time-server in your network and that all your clients are syncing with it. If you have time differences inside of your Active Directory Domain you will run into major issues.

There is no question about it, having accurate time in your environment set in critical infrastructure systems is a must. Many business-critical applications and infrastructure systems rely on accurate time synchronized between them to ensure the system functions as expected. Time skew can cause all kinds of weirdness when it is misconfigured or out of sync between different servers/systems. This is especially true in a Windows Server Active Directory domain. Having accurate time between a client computer and domain controllers is essential. Let’s take a look at how to set ntp server Windows 2016 or Windows 2019 to see how this can be easily carried out.
What is NTP?
Wen it comes to synchronizing time in most enviornments, Network Time Protocol (NTP) is the protocol that is used to ensure accurate time across your environent. In most environments, NTP servers, special time servers, are configured that provide an external time source for which your internal servers can synchronize with.
There are several widely known NTP IP addresses on the Internet that provide reliable time sources for your network. The NTP.org servers are one such set of time servers that provide an NTP source for configuration.
There are a few NTP values to be aware of:
- NTP Server – This is a specialized server that is able to detremine the precise time from an external timing reference such as GPS and passes these precise time values on to your network
- Offset – This is the difference in time between the external time server and the time on a local client computer. The larger the offset, the more inaccurate the timing source is.
- Delay – This is the value of the round-trip time (latency) of the timing message between the client to the server and back again.
How Time is synchronized in a Windows Server domain
In a Windows domain, Microsoft has default configuration in place that takes care of a good portion of the NTP configuration. Starting with Windows 2000 Server, Windows clients are configured as NTP Clients. When configured as an NTP client, Windows computers only attempt to contact the domain controller for NTP synchronization or a manually specified NTP server.

Microsoft has made the domain controller the default in a Windows domain since it makes sense that clients already have a secure channel established with DCs for other types of communications. Additionally, accurate and synchronized time between domain controllers and clients is especially important for all kinds of things such as logins, group policy synchronization and other tasks/operations.
The order of operations or hierarchy in a Windows domain is as follows:
- Domain members attempt to synchronize time with any domain controller located in the domain
- Domain controllers synchronize with a more authoritative domain controller
- The first domain controller that is installed in the environment is automatically configured to be a reliable time source.
- Other than the first domain controller installed, the PDC emulator (if role has been moved from the first DC installed) generally holds the position of best time source.
An important point to consider and that comes into play when thinking about why we set ntp server in Windows 2016 or Windows 2019 is the authoritative domain controller must have a reliable source to synchronize with as well. This is generally an external time server outside of the domain hierarchy.
Now that we know how the domain hierarchy for time is configured, how is the external time source configured on your domain controller that is configured as the reliable source of time?
Configuring Windows Time Service with W32tm.exe
When it comes to Windows Server environments like Windows Server 2016 or Windows Server 2019, there is a special Windows service that controls the time synchronization of your Windows hosts. This is the Windows Time Service.
Microsoft provides a command line tool to interact with the Windows Time Service called W32tm.exe. This has been included in Windows operating systems since Windows XP/Windows 2003 and later. It can be used to configure Windows Time service parameters as well as diagnose time service problems. This is generally the tool of choice when it comes to configuring, monitoring, and administering Windows Time.
Using the W32tm.exe utility is fairly straightforward. It can be used from a normal command prompt as well as from a PowerShell prompt. There are several command parameters included that allow not only configuring the NTP servers you want to query, but also parameters that allow viewing the low level registry configuration as well as the synchronization status.
You can read the official Microsoft KB on the Windows Time service and the W32tm.exe utility here:
- https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server/networking/windows-time-service/windows-time-service-tools-and-settings
However, there are a few commands I would like to show you for the purposes of configuring your Domain controller that is to be the reliable time source (PDC Emulator) for your domain.
The first command is the command line entry to specify your NTP servers, which in this case I am using the NTP.org servers to set as the source of my NTP synchronization.
w32tm /config /syncfromflags:manual /manualpeerlist:"0.us.pool.ntp.org 1.us.pool.ntp.org 2.us.pool.ntp.org 3.us.pool.ntp.org" /update Stop-Service w32time Start-Service w32time
If you want to view the status of the NTP synchronization on your server after you have configured the values and restarted the w32time service, you can use the following command:
w32tm /query /status
You can also check the values configured in your registry key hkey local machine system currentcontrolset services w32time config using the commands below. You can drill into the configuration parameters using the /dumpreg /subkey command.
w32tm /dumpreg w32tm /dumpreg /subkey:parameters
Final Thoughts
As shown, you can easily set NTP Server Windows 2016 or Windows 2019 using the w32tm command utility that allows interacting with the time service in Windows Server.
In a Windows domain, you want to configure your authoritative time source domain controller, which by default is the PDC Emulator, to pull time information from an authoritative source like NTP.org or some other reliable NTP time server.
After configuring the time source, the other domain controllers will synchronize with this server and then the Windows clients joined to the domain will synchronize with the domain controllers that have the corrected time from the authoritative server.
How to sync the time to a public time server using NTP
You need to use the w32tm command.
First check the current settings :
What about the 0x1 parameter ?
https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/help/875424/time-synchronization-may-not-succeed-when-you-try-to-synchronize-with
- 0x01 – Use special poll interval Special Interval
- 0x02 – Use As Fall back Only
- 0x04 – Send request as Symmetric Active mode
- 0x08 – Send request as Client mode
To set a new External Time Server like pool.ntp.org use this command :
net stop w32time w32tm /config /manualpeerlist:pool.ntp.org /syncfromflags:MANUAL net start w32time w32tm /resync
This is the configuration :
w32tm /query /configuration
These are all the command line switches :
w32tm [/? | /register | /unregister ]
? – this help screen.
register – register to run as a service and add default
configuration to the registry.
unregister – unregister service and remove all configuration
information from the registry.
w32tm /monitor [/domain:<domain name>]
[/computers:<name>[,<name>[,<name>…]]]
[/threads:<num>] [/ipprotocol:<4|6>] [/nowarn]
domain – specifies which domain to monitor. If no domain name
is given, or neither the domain nor computers option is
specified, the default domain is used. This option may be
used more than once.
computers – monitors the given list of computers. Computer
names are separated by commas, with no spaces. If a name is
prefixed with a ‘*’, it is treated as an AD PDC. This option
may be used more than once.
threads – how many computers to analyze simultaneously. The
default value is 3. Allowed range is 1-50.
ipprotocol – specify the IP protocol to use. The default is
to use whatever is available.
nowarn – skip warning message.
w32tm /ntte <NT time epoch>
Convert a NT system time, in (10^-7)s intervals from 0h 1-Jan 1601,
into a readable format.
w32tm /ntpte <NTP time epoch>
Convert an NTP time, in (2^-32)s intervals from 0h 1-Jan 1900, into
a readable format.
w32tm /resync [/computer:<computer>] [/nowait] [/rediscover] [/soft]
Tell a computer that it should resynchronize its clock as soon
as possible, throwing out all accumulated error statistics.
computer:<computer> – computer that should resync. If not
specified, the local computer will resync.
nowait – do not wait for the resync to occur;
return immediately. Otherwise, wait for the resync to
complete before returning.
rediscover – redetect the network configuration and rediscover
network sources, then resynchronize.
soft – resync utilizing existing error statistics. Not useful,
provided for compatibility.
w32tm /stripchart /computer:<target> [/period:<refresh>]
[/dataonly] [/samples:<count>] [/packetinfo] [/ipprotocol:<4|6>]
Display a strip chart of the offset between this computer and
another computer.
computer:<target> – the computer to measure the offset against.
period:<refresh> – the time between samples, in seconds. The
default is 2s
dataonly – display only the data, no graphics.
samples:<count> – collect <count> samples, then stop. If not
specified, samples will be collected until Ctrl-C is pressed.
packetinfo – print out NTP packet response message.
ipprotocol – specify the IP protocol to use. The default is
to use whatever is available.
w32tm /config [/computer:<target>] [/update]
[/manualpeerlist:<peers>] [/syncfromflags:<source>]
[/LocalClockDispersion:<seconds>]
[/reliable:(YES|NO)]
[/largephaseoffset:<milliseconds>]
computer:<target> – adjusts the configuration of <target>. If not
specified, the default is the local computer.
update – notifies the time service that the configuration has
changed, causing the changes to take effect.
manualpeerlist:<peers> – sets the manual peer list to <peers>,
which is a space-delimited list of DNS and/or IP addresses.
When specifying multiple peers, this switch must be enclosed in
quotes.
syncfromflags:<source> – sets what sources the NTP client should
sync from. <source> should be a comma separated list of
these keywords (not case sensitive):
MANUAL – sync from peers in the manual peer list
DOMHIER – sync from an AD DC in the domain hierarchy
NO – sync from none
ALL – sync from both manual and domain peers
LocalClockDispersion:<seconds> – configures the accuracy of the
internal clock that w32time will assume when it can’t acquire
time from its configured sources.
reliable:(YES|NO) – set whether this machine is a reliable time source.
This setting is only meaningful on domain controllers.
YES – this machine is a reliable time service
NO – this machine is not a reliable time service
largephaseoffset:<milliseconds> – sets the time difference between
local and network time which w32time will consider a spike.
w32tm /tz
Display the current time zone settings.
w32tm /dumpreg [/subkey:<key>] [/computer:<target>]
Display the values associated with a given registry key.
The default key is HKLMSystemCurrentControlSetServicesW32Time
(the root key for the time service).
subkey:<key> – displays the values associated with subkey <key>
of the default key.
computer:<target> – queries registry settings for computer <target>.
w32tm /query [/computer:<target>]
{/source | /configuration | /peers | /status}
[/verbose]
Display a computer’s windows time service information.
computer:<target> – query the information of <target>. If not
specified, the default is the local computer.
source: display the time source.
configuration: display the configuration of run-time and where
the setting comes from. In verbose mode, display the undefined
or unused setting too.
peers: display a list of peers and their status.
status: display windows time service status.
verbose: set the verbose mode to display more information.
w32tm /debug {/disable | {/enable /file:<name> /size:<bytes> /entries:<value>
[/truncate]}}
Enable or disable local computer windows time service private log.
disable: disable the private log.
enable: enable the private log.
file:<name> – specify the absolute filename.
size:<bytes> – specify the maximum size for circular logging.
entries:<value> – contains a list of flags, specified by number and
separated by commas, that specify the types of information that
should be logged. Valid numbers are 0 to 300. A range of numbers
is valid, in addition to single numbers, such as 0-100,103,106.
Value 0-300 is for logging all information.
truncate: truncate the file if it exists.
Now that you set the server to properly sync you can use this one as internal NTP server for other devices.
TIP :
Keep in mind to set the firewall UDP 123 rules to accept.
More info see here
Enjoy !
This entry was posted on Wednesday, October 30th, 2019 at 4:18 pm and is filed under Server, Windows. You can follow any responses to this entry through the RSS 2.0 feed.
You can leave a response, or trackback from your own site.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Network Time Protocol (NTP)
- Active Directory Time Synchronization Architecture
- How to check the configuration from client side
- External Time Source
- Stratum Value
- Configure a reliable external time source for the Forest Root Domain PDC Emulator
- Remove the reliable external time source settings from the old PDC Emulator (If you are changing the PDC emulator)
- Post configuration checking
- A Note on Registry keys
- Designing a Time Service Policy
- How can we ensure that our systems are maintaining accurate time?
- Summary
- References
Introduction
In an Active Directory domain, it is very important for all clocks to be within 5 minutes of each other (by default) due to the implementation of the Kerberos protocol for authentication.
Also, Active Directory uses multi-master replication model between Domain Controllers. So it is important that changes made at a later actual time on one DC don’t get overwritten by similar changes on another DC, whose time is
set wrong thus making it look like the most recent change.
In this article, we would discuss the AD Time Synchronization architecture, how to configure an external time source and various other aspects of the Windows Time Service.
We also recommend checking this TechNet article, which gives a very good insight of the Windows Time Service:
https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc773013(WS.10).aspx
Network Time Protocol (NTP)
Network Time Protocol (NTP) is the default time synchronization protocol used by the Windows Time Service (WTS) in Windows servers and workstations.
NTP is implemented via UDP over port 123 and can operate in broadcast and multicast modes, or by direct queries.
Active Directory Time Synchronization Architecture
In Active Directory deployment, the only computer configured with a time server explicitly should be computer holding the PDC Emulator FSMO role in the forest root domain.
This is because the Forest root domain PDC emulator is the one and only one-time source for all the Domain Controllers, member servers and windows based workstations for the entire forest.
It is possible to override this configuration and bypass PDC emulator, but the default (and recommend) configuration is that all domain members should sync time with forest PDC emulator, directly or indirectly.
- All domain controllers in the forest root domain synchronize time with the PDC Emulator FSMO role-holder.
- All Domain Controllers in child Domains synchronize time with any Domain Controller with Parent Domain or with PDC Emulator of its own Domain.
- All PDC Emulator FSMO role-holders in child domains synchronize their time with domain controllers in their parent domain (including, potentially, the PDC Emulator FSMO role-holder in the forest root domain).
- All domain member computers (Servers / Workstations/ any other devices) synchronize time with domain controller computers in their respective domains.
Diagram Source: Microsoft
How to check the configuration from client side
To determine if a domain member is configured for domain time sync, examine the REG_SZ value at HKLMSystemCurrentControlSetServicesW32TimeParametersType.
- If it is set to «Nt5DS» then the computer is synchronizing time with the Active Directory time hierarchy.
- If it’s configured with the value «NTP» then the computer is synchronizing time with the NTP server specified in the NtpServer REG_SZ value in the same registry key.
External Time Source
Since PDC Emulator of the forest root domain is the main time source of the entire forest, it is important that the system clock of this computer is accurate.
To maintain the accuracy, the forest root domain PDC emulator must be configured to synchronize its time with an external time source which is reliable. Example: Windows Time Server or Google Time Server.
Stratum Value
The degree to which a computer’s time is accurate is called a
stratum.
- The most accurate time source on a network (such as a hardware clock) occupies the lowest stratum level, or stratum one.
This accurate time source is called a reference clock.
- An NTP server that acquires its time directly from a reference clock occupies a stratum that is one level higher than that of the reference clock.
- Resources that acquire time from the NTP server are two steps away from the reference clock, and therefore occupy a stratum that is two higher than the most accurate time source, and so on.
As a computer’s stratum number increases, the time on its system clock may become less accurate.
Therefore, the stratum level of any computer is an indicator of how closely that computer is synchronized with the most accurate time source.
So when you configure a new PDC emulator or move existing PDC emulator role to a different domain controller, please follow below steps for external time source configuration.
Old PDC Emulator: DC1.subhro.com
New PDC Emulator: DC2.subhro.com
External Time Sources: 1) time.windows.com 2) time.google.com
Configure a reliable external time source for the Forest Root Domain PDC Emulator
Note: If Forest PDC Emulator is a VM, make sure it is
not configured to Sync time with its host.
1. On the PDC Emulator, run the following command from command prompt (Admin Mode)
w32tm /config /manualpeerlist:»0.time.windows.com,0x1 1. time.google.com ,0X1″ /syncfromflags:manual /reliable:yes /update
2. Check and confirm the below registry value:
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesW32TimeParametersType has “NTP” as the value
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesW32TimeParametersNtpServer
has the value «0.time.windows.com,0x1 1. time.google.com ,0X1»
Please note: Make sure the time server names are resolvable. Otherwise, please use IP address.
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesW32TimeConfigAnnounceFlags
has the value 0x5. This value indicates that this system is configured to sync with an external time source. If the value is 0XA, it means this system will not sync with any external time source but would sync with itself.
3. Configure poll interval with external time source by modifying below registry key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesW32TimeTimeProvidersNtpClientSpecialPollInterval
Put the value in seconds. For example, if you want to set the poll interval to 1 hour, put 3600 here.
4. Run the following commands in sequential order :
net stop w32time
net start w32time
5. If required, restart the new PDC emulator.
Remove the reliable external time source settings from the old PDC Emulator (If you are changing the PDC emulator)
1. Run the following command from command prompt of the old PDC Emulator :
w32tm /config /syncfromflags:domhier /reliable:no /update
2. Check and confirm the registry key
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesW32TimeParametersType has “NT5DS” as the value
3. Run the following commands in sequential order :
net stop w32time
net start w32time
2. If required, restart the server.
Post configuration checking
1. Check the time configuration by running the command
w32tm /query /configuration
2. Check the time synchronization report by running the command
Click here to get the Powershell script, which will automate the Time Skew report for your domain, and will send the result in an email.
3. To compare the time synchronization of a server with an external time source use the following command
w32tm /stripchart /computer: time.windows.com
d: Internal delay (time difference between the UDP package received and UDP package sent on the server side.
O: Actual offset between the local time and the server time.
4. To check the time source of a server run this command
w32tm /query /status
5. To manually sync the time with time source, run this command
w32tm /resync
Few points to observe from the above output:
-
Root dispersion is the maximum clock time difference that was ever observed between the local clock and the root clock. As you can see, this value has been reduced to milliseconds after synchronization.
- Since the primary time source (time.windows.com) is not reachable, it has automatically switched to secondary time source (time.google.com).
- Stratum value was earlier 1, indicating that no external time source was configured and this PDC emulator was the root time source (which is not the recommended configuration, as explained earlier)
After running the first sync, the server detected the newly configured external time source and marked it as root (Stratum value 1). Therefore, the new value of the PDC emulator has been changed to one level up, which is 2.
A Note on Registry keys
There is an article on Technet which explains these registry values which we have used here.
https://blogs.msdn.microsoft.com/w32time/2008/02/26/configuring-the-time-service-ntpserver-and-specialpollinterval/
Excerpts from that article
It is important to note that W32Time will only actively synchronize with one time source at a time, even though you are able to list more than one time source. The reason for this is simple: If your favorite time source goes down,
it would be good to have a backup, or possibly a list of backups.
W32Time configures the list of time sources through the following key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesW32TimeParametersNtpServer
The NtpServer key is a space-delimited list of time servers, either as DNS address or as IP addresses. Each server in the list can optionally have a set of flags, which are denoted as a hex value at the end of the address, separated
by a comma.
Now let’s take a look at the flags. We have 4 possible flags:
• 0x01 SpecialInterval
• 0x02 UseAsFallbackOnly
• 0x04 SymmatricActive
• 0x08 Client
For 99% of cases, we only care about the first two options, so that is where we will focus. If you use the SpecialInterval flag, then you need to also set the «SpecialPollInterval» key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetServicesW32TimeTimeProviders
NtpClientSpecialPollInterval
Normally, W32Time will poll (make a time request) on a floating interval, based on the quality of the time samples being returned by the time source. You can, however, specify a static interval that the time service will synchronize
on. This value is in seconds. For example, if you set an of 3600, the time service will synchronize every hour (60 minutes * 60 seconds).
The second flag is the UseAsFallbackOnly option. Setting this flag will tell the time service that you want to try every other time server specified before trying this one.
Designing a Time Service Policy
Configuring PDC Emulator and external time source is only one part of the time service configuration. There are still many other points which we need to consider. Some of the important points are described below.
1.
Force all windows systems to use Domain Controller as their time source
By default in Active Directory domain environment clients synchronize their time with domain controllers (option Nt5DS — synchronize time to domain hierarchy).
Typically, this behavior does not need to be reconfigured. However, if you want to ensure that the default behavior would not be overridden by someone on the client side, you can force a Group Policy to push the configuration.
a) Navigate to Computer Configuration->Policies->Administrative Templates->System->Windows Time Service->Time Providers. In the right pane, double-click “Enable Windows NTP Client”. Set it to “Enabled” and click OK.
b) Next, double-click “Configure Windows NTP Client”. Configure the options then append, 0x1 to the NtpServer field so that it reads yourdc.yourdomain.com,0x1)
2.
Disable Virtual Machine Time Sync from host
All modern hypervisors have the ability to provide time synchronization to guest machines through that hypervisor’s integration tools. If enabled, guest machines will draw time from the physical host they are running on.
In an Active Directory environment, it is recommended to disable Virtual Machine time sync with a host, to avoid potential conflict.
3. Enable DHCP Scope Option
If you would like to push NTP server settings to a non-windows device (Like IP Phone), use DHCP scope option 042. Do not use DHCP scope option 004 unless it is specifically mentioned in any documentation.
4.
Allow UDP Port 123 through Firewall
UDP port 123 should be unblocked by the firewalls, in both directions.
Also, remember NTP client sends UDP request from random port >1023 to port 123 on NTP server. It waits for a response on the same originating port. The firewall should be able to keep open originating port for UDP traffic from
NTP server.
5.
Configure Static Devices
There are few static devices (like few SAN, NAS devices) which do not support NTP server configuration over Group Policy or DHCP. For such devices, you need to configure the time sources statically, from the device console.
The downside is, if NTP server name would be changed, you have to change these settings manually.
How can we ensure that our systems are maintaining accurate time?
We recommend to follow below steps to ensure that all systems in an AD environment are maintaining accurate time.
a) Forest Root Domain PDC Emulator should sync its time with external NTP server on a regular basis.
To ensure that, follow these steps
1. Execute w32tm /query /status from the forest root domain PDC emulator. Validate the NTP server, last sync time, root desperation.
2. Compare the PDC emulator clock time with any world clock time and observe the difference in seconds. One such site is https://www.timeanddate.com/ , where you can view world clock with second value and can compare with your
PDC.
b) All other Domain Controllers should sync time with Forest Root Domain PDC emulator on a regular basis. The time difference between Domain Controllers should be less than 1 second in an entire forest.
To ensure that, configure a scheduled task, which would generate the Time Skew Report for all Domain Controllers and send it to your mailbox.
Click here for the script, which I have prepared for this purpose.
c) All other computers and workstations should sync with Domain Controllers at a regular interval.
Summary
In this article, we have gone through the time service architecture within an Active Directory Forest. We have also discussed how to configure external time source for Forest PDC Emulator, and how to ensure client systems will
follow the Active Directory Time Architecture.
Additionally, we have covered some best practices related to Time Service Configuration of virtual machines, Firewall Port Configuration and configuring non windows devices.
References
1. https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc773013(WS.10).aspx
2. https://blogs.msdn.microsoft.com/w32time/2008/02/26/configuring-the-time-service-ntpserver-and-specialpollinterval/