В прошлом нашем посте мы рассказали как готовим стандартные клиентские виртуальные машины и показали на примере нашего нового тарифа с Ultralight windows vds за 99 рублей, как мы создавали стандартный образ Windows Server 2019 Core.
В службу поддержки стали поступать заявки как работать с Server 2019 Core без привычной графической оболочки. Мы решили показать работу с Windows Server 2019 Core и как установить на него GUI.
Не повторяйте это на рабочих машинах, не используйте Server Core как рабочий стол, отключите RDP, обезопасьте свою информационную систему, именно безопасность — это главная фишка «Core» инсталляции.
В одной из следующих наших статей мы рассмотрим таблицу совместимости программ с Windows Server Core. В этой статье мы затронем то, как установить оболочку.
Оболочка сторонними средствами
1. Сложный, но наиболее экономичный способ
В Server Core из коробки нет привычного нам explorer.exe, чтобы облегчить нам жизнь, мы скачаем explorer++. Он заменяет все, что умеет оригинальный explorer. Рассматривался только explorer++, но подойдет почти любой файловый менеджер, в том числе Total Commander, FAR Manager и другие.
Скачиваем файлы.
Сначала нам нужно скачать файл на сервер. Это можно сделать через SMB (общую папку), Windows Admin Center и Invoke-WebRequest, он работает с параметром -UseBasicParsing.
Invoke-WebRequest -UseBasicParsing -Uri 'https://website.com/file.exe' -OutFile C:UsersAdministratorDownloadsfile.exeГде -uri это URL файла, а -OutFile полный путь куда его скачивать, указывая расширение файла и
C помощью Powershell:
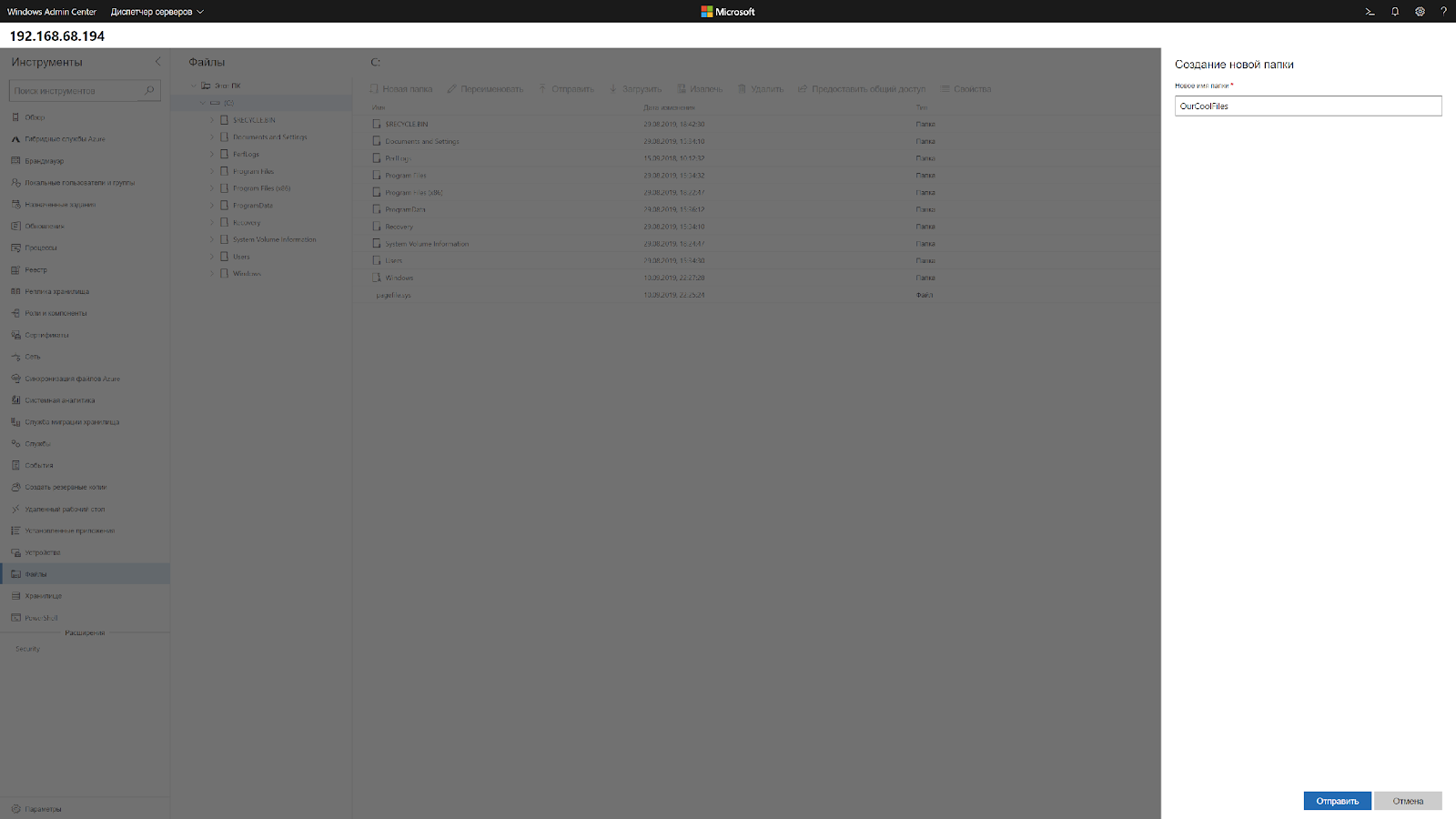
На сервере создаём новую папку:
New-Item -Path 'C:OurCoolFiles' -ItemType DirectoryРасшариваем общую папку:
New-SmbShare -Path 'C:OurCoolFiles' -FullAccess Administrator
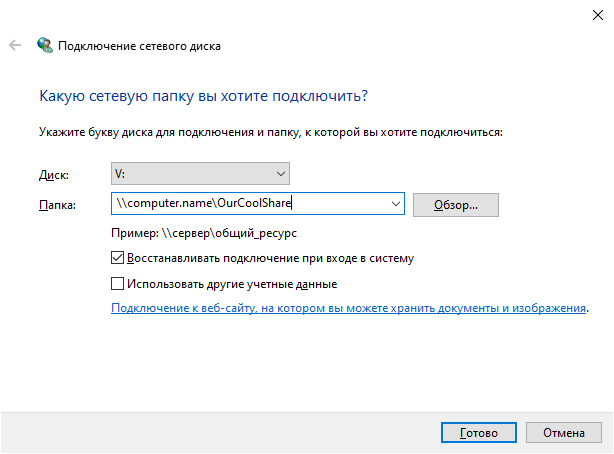
-Name OurCoolShareНа вашем ПК папка подключается как сетевой диск.
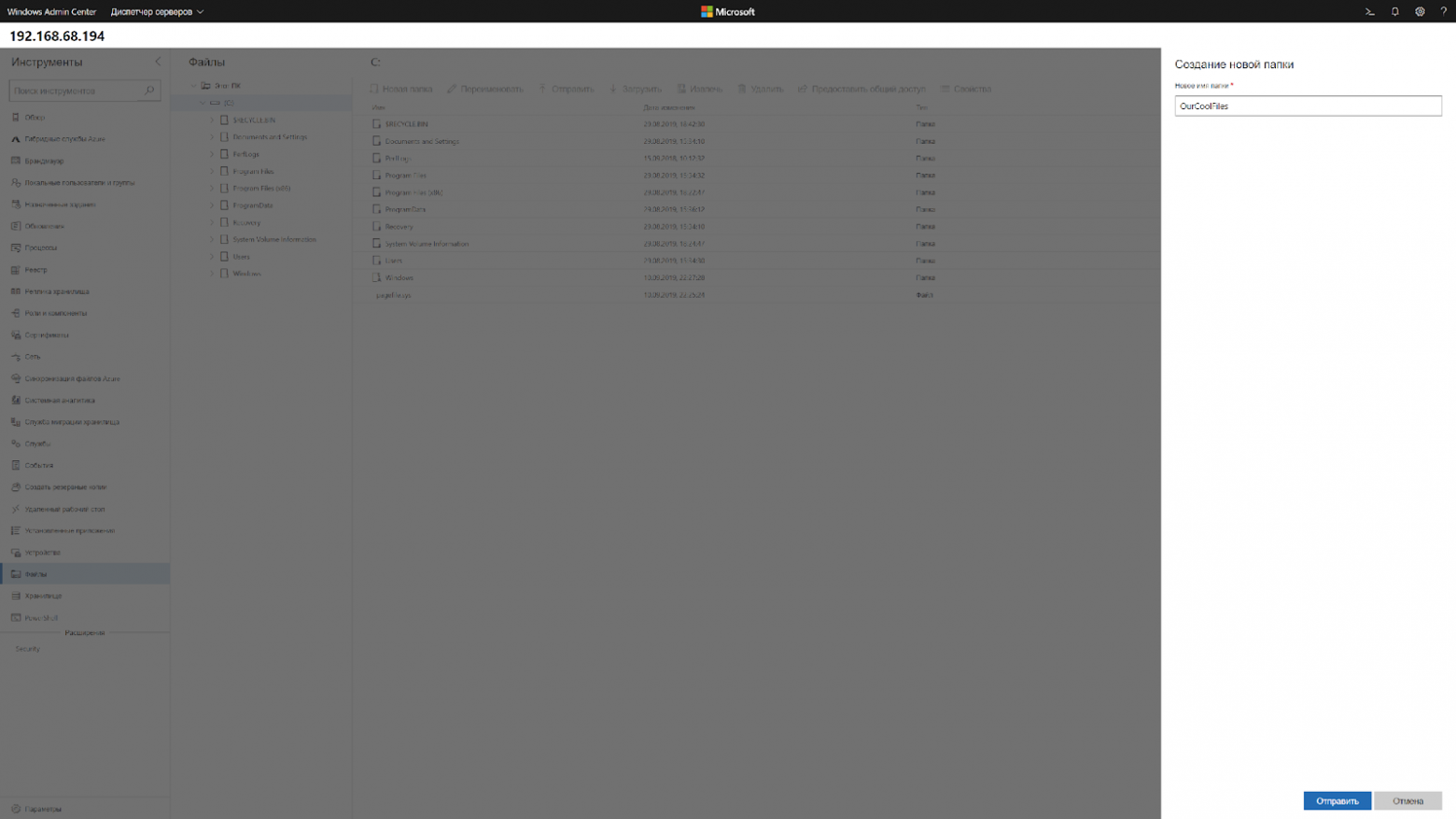
Через Windows Admin Center создаем новую папку выбрав пункт в меню.
Переходим в общую папку и жмем кнопку отправить, выбираем файл.
Добавляем оболочку в планировщик.
Если вы не хотите запускать оболочку вручную при каждом входе в систему, то нужно добавить её в планировщик задач.
$A = New-ScheduledTaskAction -Execute "C:OurCoolFilesexplorer++.exe"
$T = New-ScheduledTaskTrigger -AtLogon
$P = New-ScheduledTaskPrincipal "localAdministrator"
$S = New-ScheduledTaskSettingsSet
$D = New-ScheduledTask -Action $A -Principal $P -Trigger $T -Settings $S
Register-ScheduledTask StartExplorer -InputObject $DБез планировщика можно запустить через CMD:
CD C:OurCoolFilesExplorer++.exeСпособ 2. Запускаем родной Explorer
Remember, no GUI
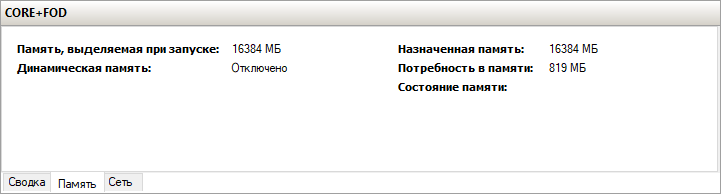
Server Core App Compatibility Feature on Demand (FOD), вернет в систему: MMC, Eventvwr, PerfMon, Resmon, Explorer.exe и даже Powershell ISE. Подробнее можете ознакомиться на MSDN. Существующий набор ролей и компонентов он не расширяет.
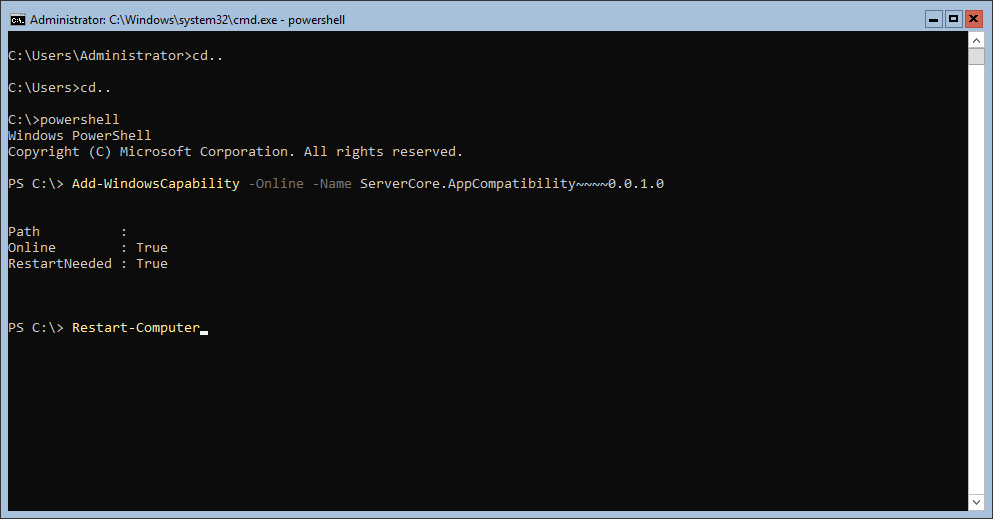
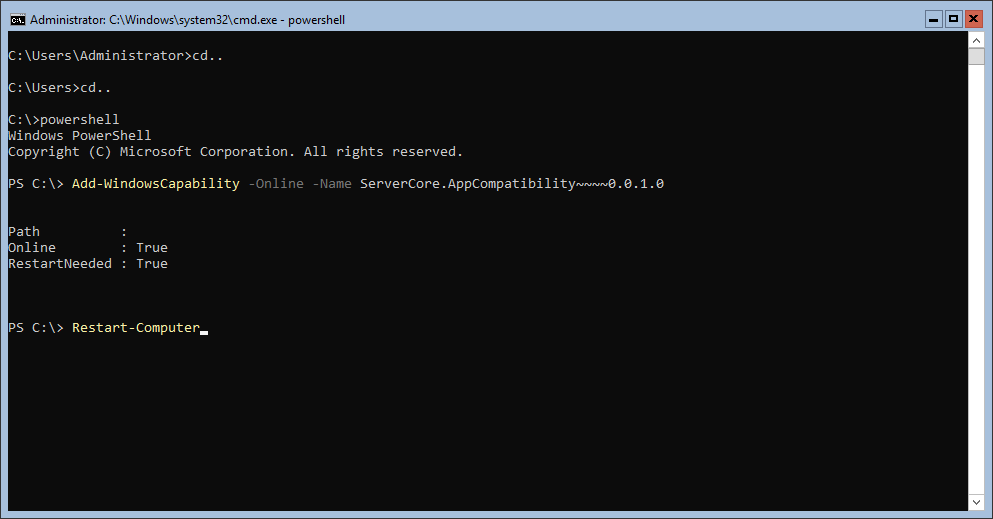
Запустите Powershell и введите следующую команду:
Add-WindowsCapability -Online -Name ServerCore.AppCompatibility~~~~0.0.1.0Затем перезагрузите сервер:
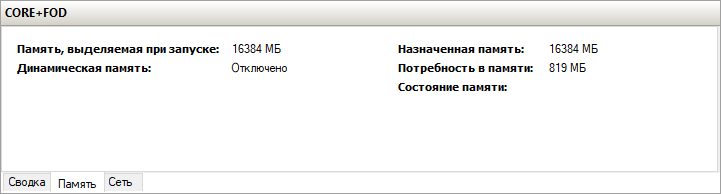
Restart-ComputerПосле этого вы сможете запускать даже Microsoft Office, но потеряете примерно 200 мегабайт ОЗУ навсегда, даже если в системе нет активных пользователей.
Windows Server 2019 c установленным Features on Demand
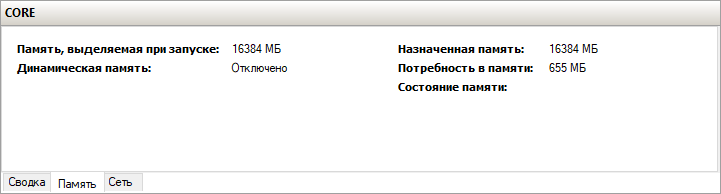
Windows Server 2019 CORE
На этом всё. В следующей статье мы рассмотрим таблицу совместимости программ с Windows Server Core.
Предлагаем обновлённый тариф UltraLite Windows VDS за 99 рублей с установленной Windows Server 2019 Core.
В прошлом нашем посте мы рассказали как готовим стандартные клиентские виртуальные машины и показали на примере нашего нового тарифа Ultralight за 120 рублей, как мы создавали стандартный образ Windows Server 2019 Core.
В службу поддержки стали поступать заявки как работать с Server 2019 Core без привычной графической оболочки. Мы решили показать работу с Windows Server 2019 Core и как установить на него GUI.
Не повторяйте это на рабочих машинах, не используйте Server Core как рабочий стол, отключите RDP, обезопасьте свою информационную систему, именно безопасность — это главная фишка «Core» инсталляции.
В одной из следующих наших статей мы рассмотрим таблицу совместимости программ с Windows Server Core. В этой статье мы затронем то, как установить оболочку.
Оболочка сторонними средствами
1. Сложный, но наиболее экономичный способ
В Server Core из коробки нет привычного нам explorer.exe, чтобы облегчить нам жизнь, мы скачаем explorer++. Он заменяет все, что умеет оригинальный explorer. Рассматривался только explorer++, но подойдет почти любой файловый менеджер, в том числе Total Commander, FAR Manager и другие.
Скачиваем файлы.
Сначала нам нужно скачать файл на сервер. Это можно сделать через SMB (общую папку) и Windows Admin Center. Invoke-WebRequest на Windows Server Core не работает из-за отсутствия Internet Explorer’a.
C помощью Powershell:
На сервере создаём новую папку:
New-Item -Path 'C:OurCoolFiles' -ItemType DirectoryРасшариваем общую папку:
New-SmbShare -Path 'C:OurCoolFiles' -FullAccess Administrator
-Name OurCoolShareНа вашем ПК папка подключается как сетевой диск.
Через Windows Admin Center создаем новую папку выбрав пункт в меню.
Переходим в общую папку и жмем кнопку отправить, выбираем файл.
Добавляем оболочку в планировщик.
Если вы не хотите запускать оболочку вручную при каждом входе в систему, то нужно добавить её в планировщик задач.
$A = New-ScheduledTaskAction -Execute "C:OurCoolFilesexplorer++.exe"
$T = New-ScheduledTaskTrigger -AtLogon
$P = New-ScheduledTaskPrincipal "localAdministrator"
$S = New-ScheduledTaskSettingsSet
$D = New-ScheduledTask -Action $A -Principal $P -Trigger $T -Settings $S
Register-ScheduledTask StartExplorer -InputObject $DБез планировщика можно запустить через CMD:
CD C:OurCoolFilesExplorer++.exeСпособ 2. Запускаем родной Explorer
Remember, no GUI
Server Core App Compatibility Feature on Demand (FOD), вернет в систему: MMC, Eventvwr, PerfMon, Resmon, Explorer.exe и даже Powershell ISE. Подробнее можете ознакомиться на MSDN. Существующий набор ролей и компонентов он не расширяет.
Запустите Powershell и введите следующую команду:
Add-WindowsCapability -Online -Name ServerCore.AppCompatibility~~~~0.0.1.0Затем перезагрузите сервер:
Restart-ComputerПосле этого вы сможете запускать даже Microsoft Office, но потеряете примерно 200 мегабайт ОЗУ навсегда, даже если в системе нет активных пользователей.
Windows Server 2019 c установленным Features on Demand
Windows Server 2019 CORE
На этом всё. В следующей статье мы рассмотрим таблицу совместимости программ с Windows Server Core.
Let’s block ads! (Why?)
Hello World,
Today, it will be a quick post. We will basically perform a basic installation of Windows 2019 Server. This type of post is probably all around internet but we needed to test and check by ourselves if any major changes occurred. As you can guess, the installation nowadays is quite straight forward. The most difficult decision to take is which flavor/version of Windows 2019 Server to install. We will quickly go through some of the basics about Windows 2019 and then we will move on the installation part….
So,let’s start this !
Overview Windows 2019 Server
Windows Editions
As mentioned in our previous post, Windows 2019 server ship in 3 Editions
- Windows 2019 Essentials
- Windows 2019 Standard
- Windows 2019 Datacenter
When working on projects, most of the time the Windows 2019 Datacenter edition is used because there is no feature limitations and because it’s also a good choice when using it in highly virtualized environment. When using a Windows 2019 Standard edition, the licensing includes the right to run 2 additional Virtual machines while Datacenter allows you to run an unlimited of virtual machines without paying extra costs.
Windows Datacenter offers more features that the standard edition. Storage Replica, Storage Direct spaces, shielded virtual machines, software defined network… for example are not included in the Standard Edition.
Windows Servicing Channel Models
Another important element to take into account is the Windows servicing Channel a company want to use. As briefly explained in our previous post, a user can choose between two type of releases when working with Windows Server Operating system. You can choose between
- Long Term Service Channel (LTSC)
- Semi-Annual Channel (SAC)
This choice is important because it will define if a desktop interface can be used or not on top of your Server installation. Long Term service Channel (LTSC) would be the way forward if you need a desktop interface on your server and if you need to have a stable and predictable release cycle. Choosing LTSC release ensure that Desktop experience feature is available and you would benefit from a mainstream support for 5 years and extra 5 years for extended support.
Semi-annual Channel (SAC) release are made available twice a year and they will be supported for 18 months. The SAC release does not ship with any desktop interface and no option to install any. So, if you need a desktop interface (for example, you want to use Remote Desktop services), you should stick to the LTSC. SAC releases will probably include latest technology and features but no all companies can move to this aggressive cycle release
Step by Step installation
Assumptions
To perform this installation,
- we have downloaded the Windows 2019 Evaluation Edition which ships with Desktop Experience option.
- We have installed Windows 2019 and Hyper-v role on a physical machine (this is not explained on this post)
- We have created a virtual machine and installation will be performed on top of it
- We will install the Datacenter edition with Desktop experience in this guide
Quick Step by Step Guide
Step 1 – Your virtual machine is powered off
Step 2 – Open your virtual machine settings and mount the iso file, change the boot order if needed.
Step 3 – Boot your virtual machine
Step 4 – the windows installer will show up and will prompt you to Select your regional settings (Language and Keyboard layout)
click on picture for better resolution
Step 5 – The Wizard start and you can see the Install now button. click on it to proceed with the installation.
click on picture for better resolution
The setup wizard initialize and will prepare the next steps
click on picture for better resolution
Step 6 – in the selection dialog box, you can choose which Windows 2019 edition you want to use and with or without desktop interface. We have selected Datacenter + Desktop Experience option
click on picture for better resolution
Step 7 – In the license agreement page, accept it and proceed
click on picture for better resolution
Step 8 – In the installation page, select the option custom.
click on picture for better resolution
Step 9 – In the Disk page, accept default and proceed. The wizard will create all the necessary partition needed
click on picture for better resolution
Step 10 – In the Installing Windows step, you can relax and wait for the machine to reboot
click on picture for better resolution
click on picture for better resolution
Step 11 – The system will reboot perform some post actions
click on picture for better resolution
Step 12 – You will be presented with the Customize page where you basically need to provide password for the local admin account to be used
click on picture for better resolution
Step 13 – When done, you will be presented with the login page with the familiar background image used in Windows 2016 and Windows 10
click on picture for better resolution
Step 14 – You can login and start customize your installation by providing computer name, join the machine to a domain, set network settings, install roles and anything you would need to do have a functional server that meets your requirements. When you open server manager (or when started automatically), you will see a popup messaging inviting you to test the Windows Admin Center.
click on picture for better resolution
We are planning to install and play around with the new web interface that will provide another set of tool that can be used to manage remotely a server box. We might share our findings in a future post….
Final notes
As you can see, the process has not changed much. Installation process is quite straight forward and seems even simplify as almost no questions or customization settings are shown during the installation. Now that the installation has been performed, we will need to dig a little bit to see what has been changed and/or improved in this release. This might be the subject of a future post as well.
Till next time
See ya
Hyper-V Server 2019 GUI Installation Guide
Introduction
Hyper-V Server does not include much in the way of graphical tools, but third-party alternatives can be installed.
I found a disturbing lack of basic instructions for using Hyper-V Server 2019, so it is my hope that this guide is useful to somebody.
Before starting this guide, enable Remote Desktop support in Hyper-V Server using the built-in configuration menu. If you connect to the Hyper-V Server with Remote Desktop, it will make it easy to copy and paste text (and later, files) from a normal Windows desktop machine.
Step 1) Install Chrome
In the command prompt on the Hyper-V server, run this command:
Powershell
This loads Powershell which gives us many additional capabilities, including the ability to download files.
Find a current Chrome setup URL by downloading it in the web browser on a «normal» computer, and looking in your browser’s download history. Then, back on the Hyper-V server, run this command, replacing YOUR_CHROME_SETUP_URL with the URL you found.
(New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadFile("YOUR_CHROME_SETUP_URL", "ChromeSetup.exe")
(hint: to paste text in a command/powershell window, right-click)
Now exit Powershell
exit
Run ChromeSetup.exe
ChromeSetup.exe
Complete the installation using the setup GUI.
Run Chrome
"C:Program Files (x86)GoogleChromeApplicationchrome.exe"
Step 2) Install Cairo (3rd-party desktop environment)
In Chrome, open https://cairoshell.com/, and download the latest 64 bit Cairo installer from GitHub. When the download completes, use Chrome to launch the Cairo setup executable. I don’t know if it matters, but in Cairo setup, I checked the box to Replace Explorer.
Proceed through Cairo’s welcome tour. When it asks which apps you want to include in the Programs menu, make sure you add Chrome and PowerShell.
Re-launching Cairo
If you ever find that the Cairo shell isn’t running when you log in, you can launch it with the command:
"C:Program FilesCairo ShellCairoDesktop.exe"
Step 3) Install 7-Zip
In Chrome, open https://www.7-zip.org, then download and install 7-Zip 64-bit. I used the .exe installer.
Back in Cairo, click your Programs menu, and choose App Grabber. Add 7-Zip to your programs menu.
Run 7-Zip from the Programs menu, and in 7-Zip‘s options, click the plus button to associate 7-Zip with all supported file types.
Close 7-Zip.
Step 4) Install Explorer++ (3rd-party file explorer)
In Chrome, open https://explorerplusplus.com/
Download the 64 bit version.
In 7-Zip, extract Explorer++.exe to C:Explorer++Explorer++.exe.
In Cairo Settings (Menu button in upper-left corner), Advanced, set the File manager path to C:Explorer++Explorer++.exe.
Add Explorer++ to Cairo’s Programs menu, similar to how you added 7-Zip earlier. You’ll notice that Explorer++ does not appear as an installed application in App Grabber. Instead, you must click the Browse… button to locate Explorer++ where you extracted it.
Step 5) Install Windows Admin Center (WAC)
In Chrome, open https://aka.ms/windowsadmincenter
Download the latest stable release (I wouldn’t recommend a preview version unless you have a specific reason).
Run the installer.
When you get to the part about SSL and a certificate, you can either use the self-signed option or add your own. I prefer to add my own so I can have my desktop PC trust it and no longer get browser warnings when accessing the interface via HTTPS. Add your own certificate or not, then complete the installation.
How I added my own certificate
To generate certificates, I used this tool to create a HyperV1.pfx file with my server’s host name HyperV1 in the list of domain names. Then I copied and pasted the pfx file from my normal workstation, through remote desktop, to the C:UsersAdministratorDocuments folder on the Hyper-V server.
Next, I opened a PowerShell window on the Hyper-V Server, and navigated to the Documents folder.
cd "C:UsersAdministratorDocuments"
Then I used Import-PfxCertificate to import the certificate into the server’s certificate store.
Import-PfxCertificate -FilePath HyperV1.pfx -CertStoreLocation Cert:LocalMachineMy
The output conveniently includes the certificate’s Thumbprint, which you can copy by selecting the thumbprint with the mouse and pressing enter. Back in the Windows Admin Center installer, I pasted this thumbprint in the appropriate text box, and proceeded with installation
Remote Management
Now that Windows Admin Center is installed, you can use it for most remote management tasks by navigating to your server’s IP or host name in a web browser. To authenticate, enter the user name Administrator and the password you used when you first set up the server.
For more-advanced management, such as to pass through a physical device to a VM, it may be necessary to install Hyper-V Manager on another Windows system and connect remotely to the Hyper-V Server, which of course is a pain in the ass. https://timothygruber.com/hyper-v-2/remotely-managing-hyper-v-server-in-a-workgroup-or-non-domain/