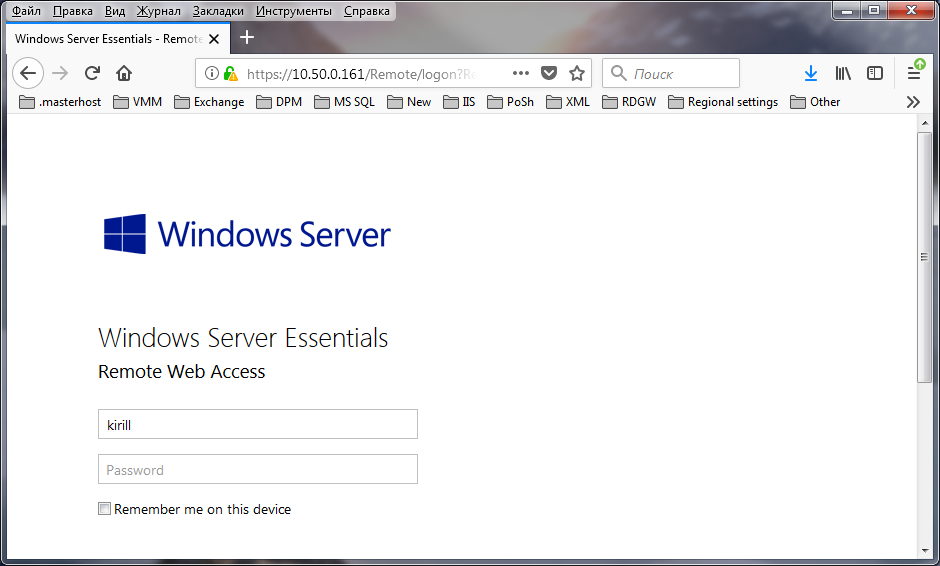
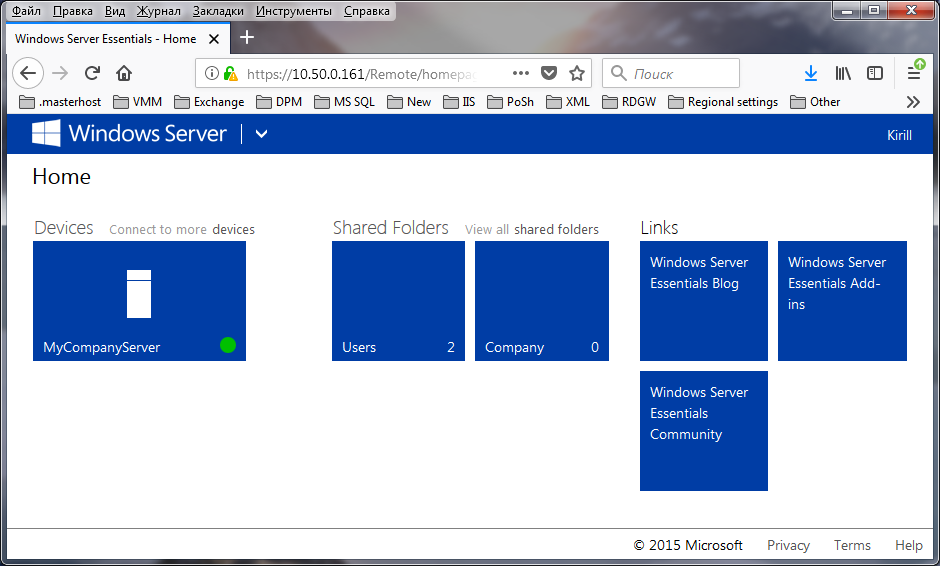
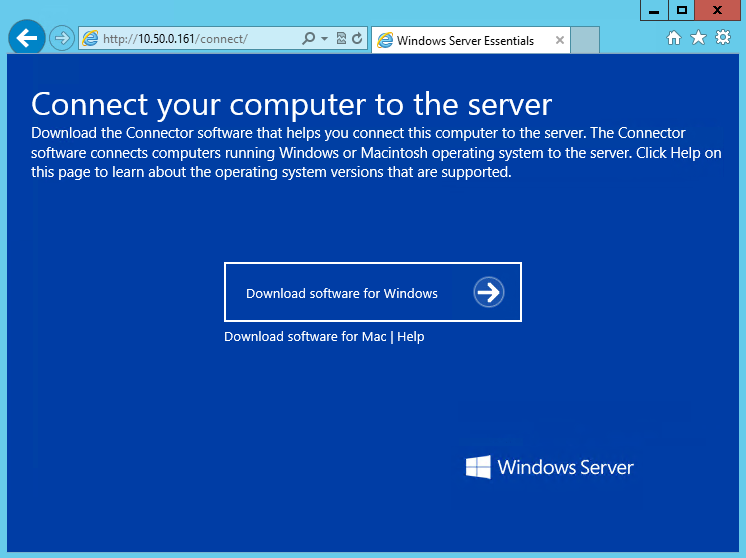
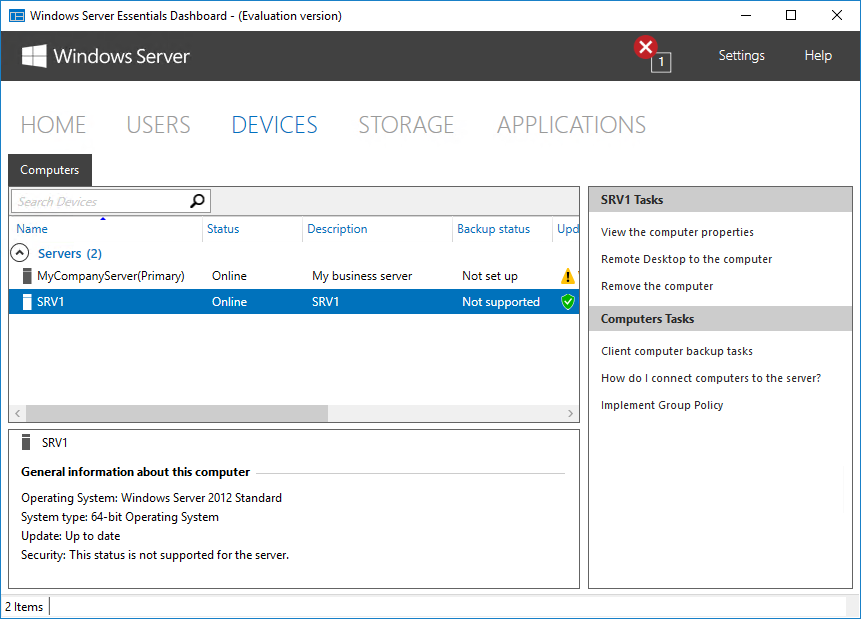
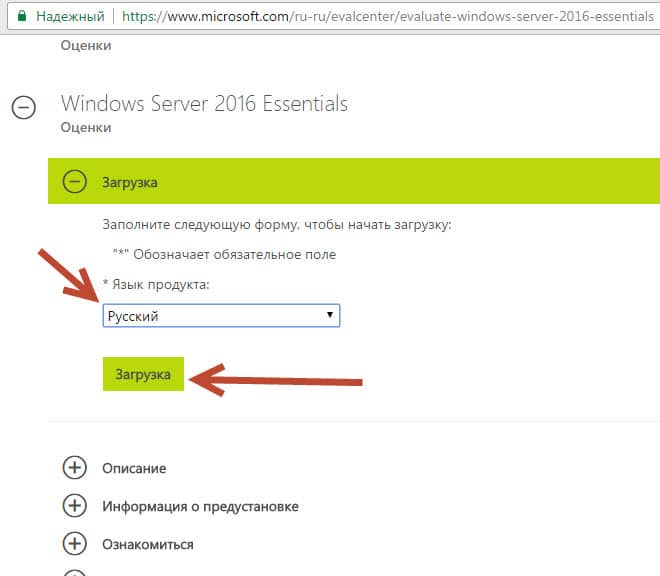
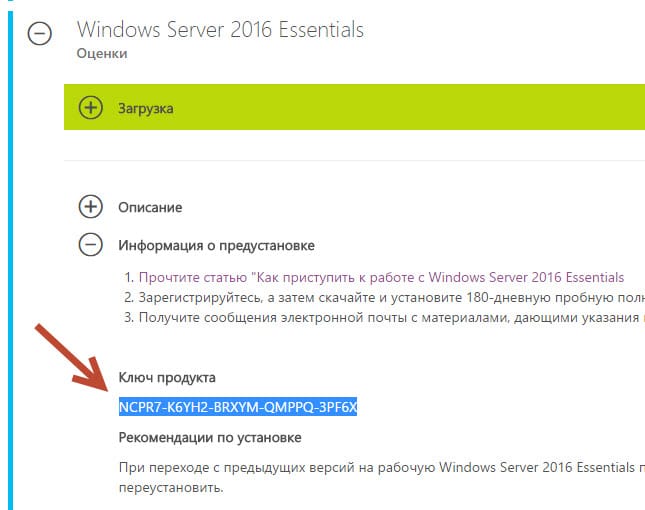
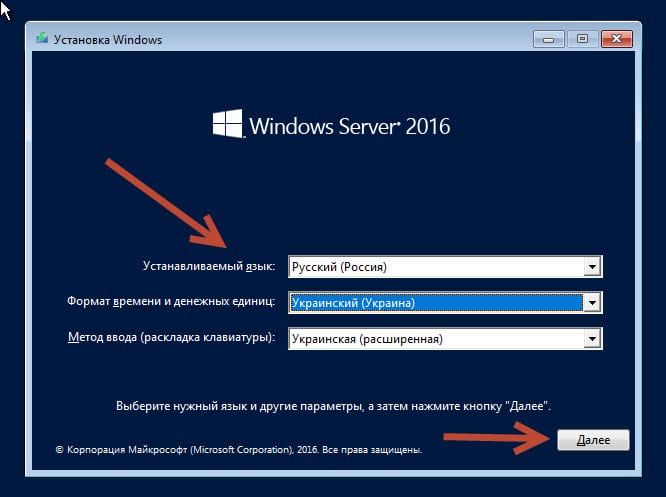
На днях мне в руки попал экземпляр Windows Server 2016 Essentials. Для тех, кто не в курсе, Essentials — это редакция Windows Server, специально предназначенная для использования в небольших организациях. Она входит в линейку серверных операционных систем Microsoft, однако имеет некоторые особенности, о которых мы сегодня и поговорим.
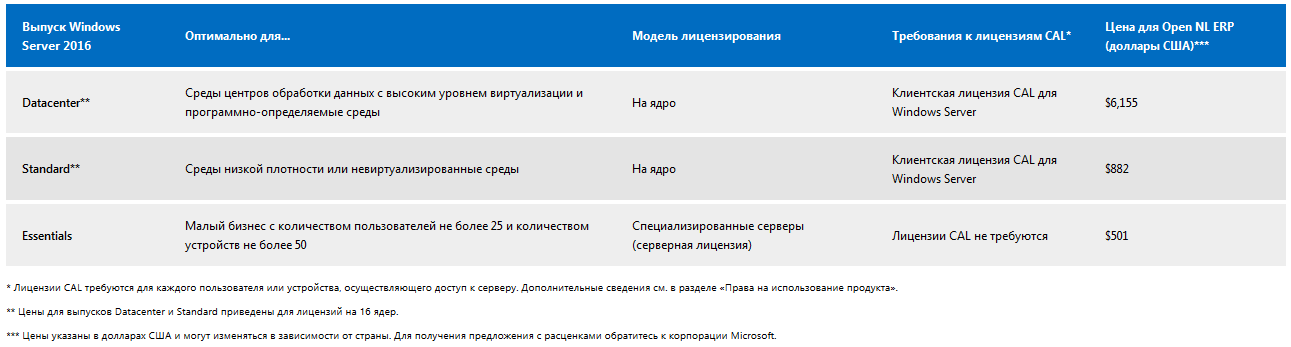
Для наглядности рассмотрим таблицу сравнения основных редакций Windows Server 2016, взятую с сайта Microsoft. Как видно из нее, ключевое отличие Essentials заключается в схеме лицензирования:
• Редакции Standard и Datacenter лицензируются по количеству физических ядер процессора, а для доступа к серверу требуются клиентские лицензии CAL;
• Редакция Essentials лицензируется на сервер и не требует наличия клиентских лицензий, а на количество подключений действует фиксированное ограничение в 25 пользователей50 устройств.
Есть несколько сценариев использования Windows Server Essentials. Предполагаемый по умолчанию — это первый (и единственный) сервер в небольшой организации. С него и начнем.
Установка в качестве первого сервера
Установка Essentials возможна как на физический сервер, так и в качестве виртуальной машины на Hyper-V. Независимо от варианта установки на сервере должно быть не более 2-х физических процессоров и максимум 64 Гб оперативной памяти.
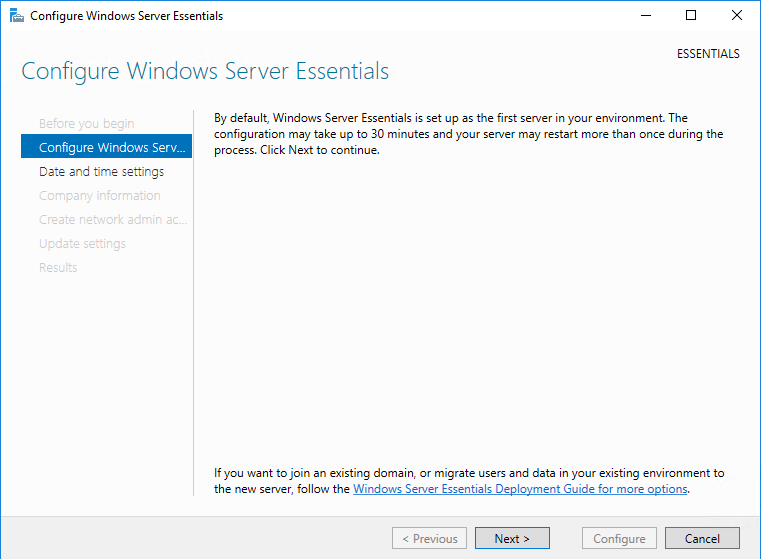
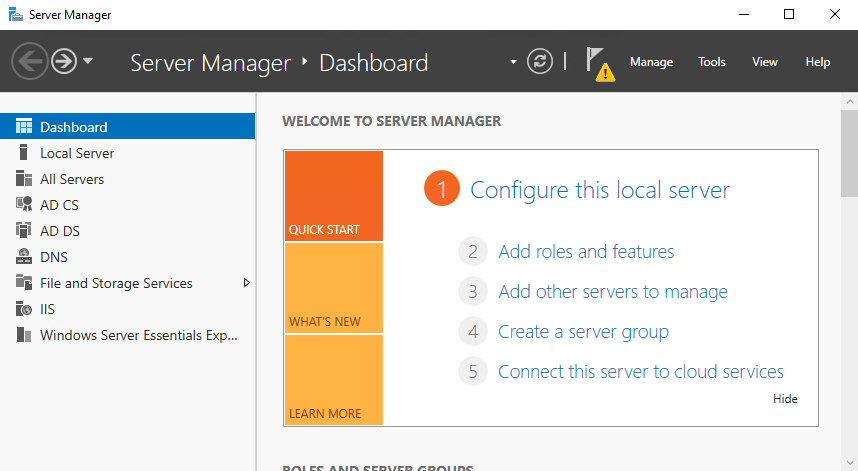
Сама процедура установки операционной системы ничем не отличается от обычной, все самое интересное начинается позднее. Сразу после установки автоматически запускается мастер настройки, с помощью которого и происходит превращение обычного сервера в Windows Server Essentials.
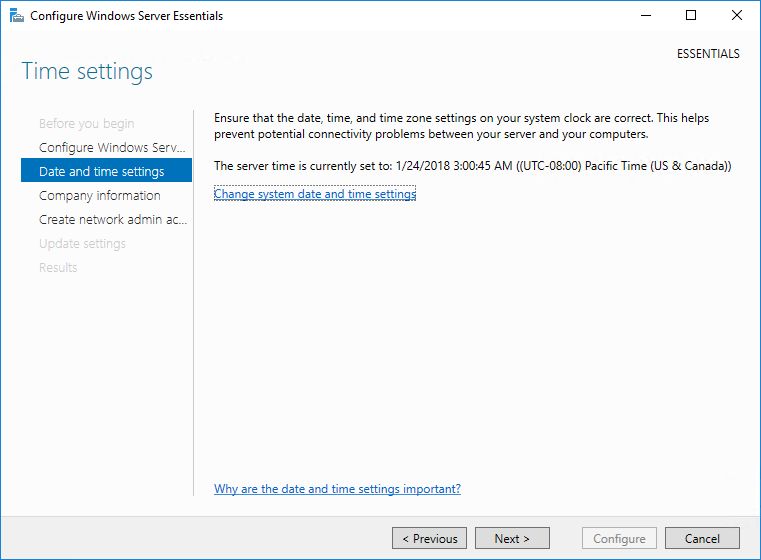
Первым делом мастер предлагает настроить дату, время и выбрать часовой пояс.
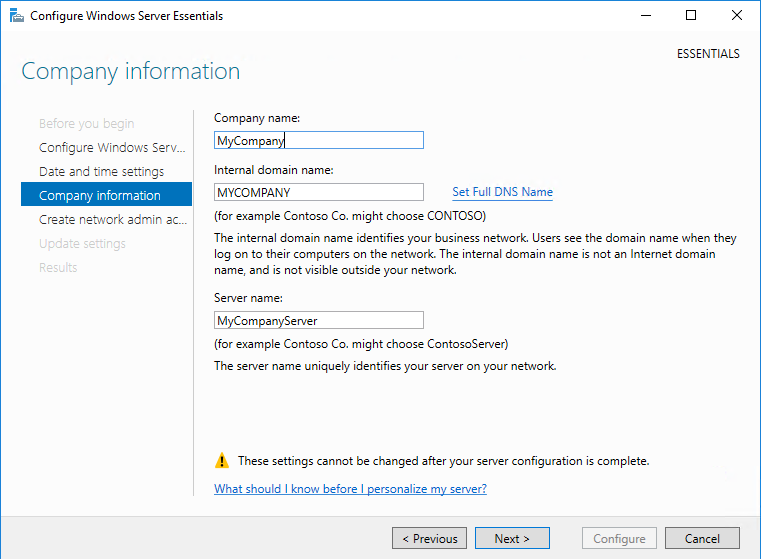
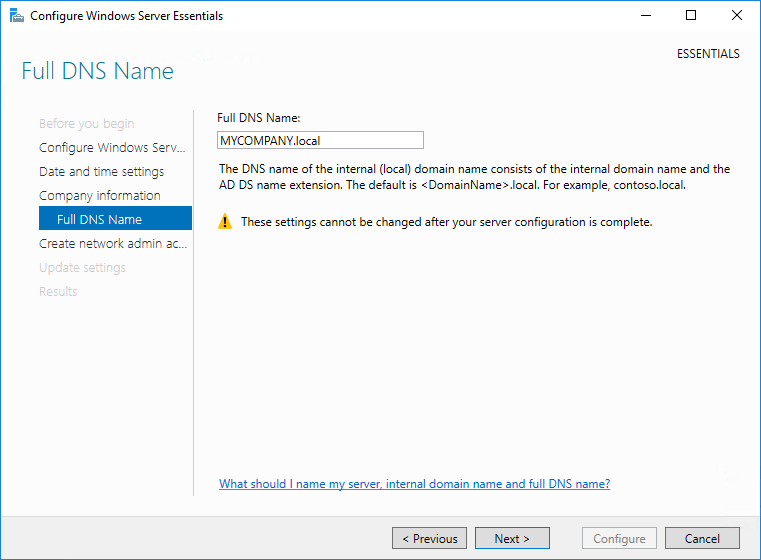
В следующем окне надо ввести информацию о компании. Этот этап очень важен, поскольку в процессе подготовки будет создан домен Active Directory, а указанное имя будет выбрано в качестве имени домена. Изменить эти настройки позже не получится, поэтому к выбору имени надо подходить серьезно.
Если нажать на ссылку «Set Full DNS Name», то появится дополнительное окно для указания полного доменного имени. По умолчанию используется имя DomainName.local.
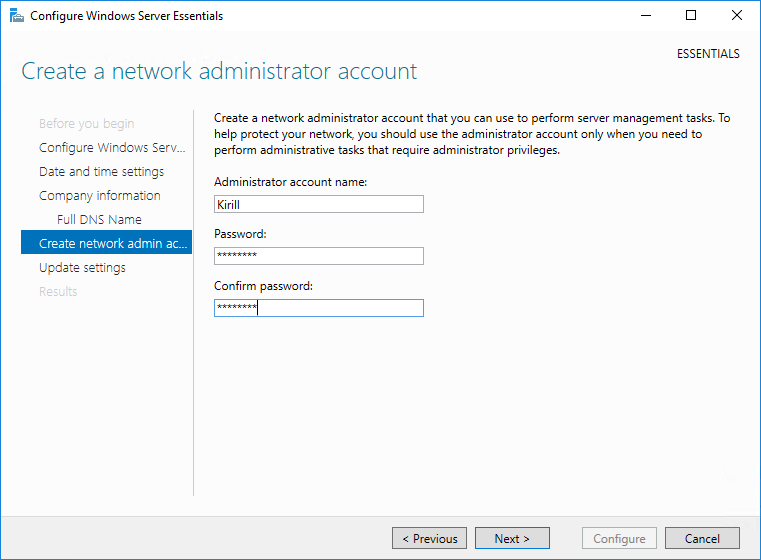
Затем надо задать учетные данные пользователя, который будет иметь административные права на сервере. Обратите внимание, что после окончания работы мастера все ранее созданные на сервере пользователи будут недоступны.
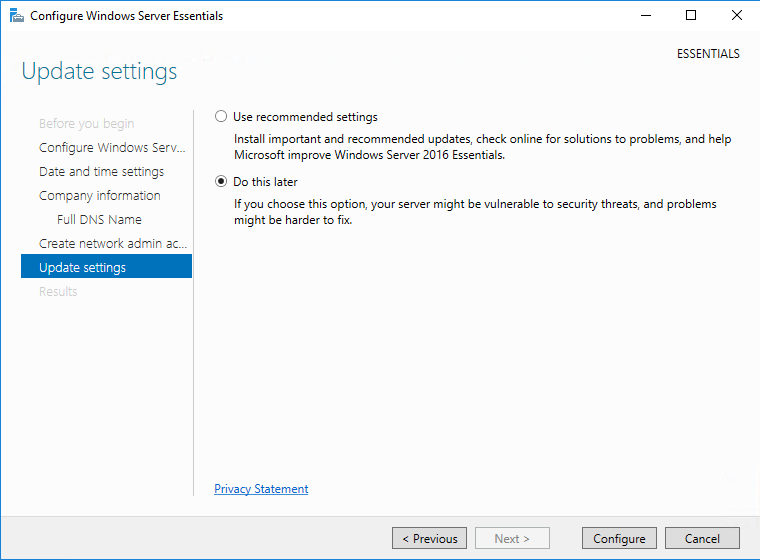
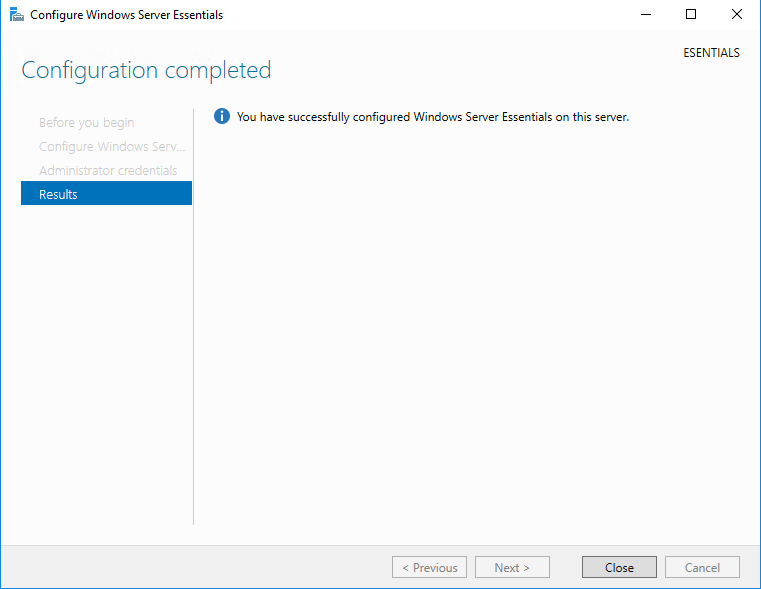
В завершение требуется выбрать настройки автоматического обновления. Здесь можно просто согласиться с рекомендованными параметрами или отложить настройку на потом. На этом этапе можно вернуться назад и поменять введенные настройки, например изменить имя домена или учетные данные администратора. Если же вы уверены в своих действиях, то надо нажать кнопку «Configure»
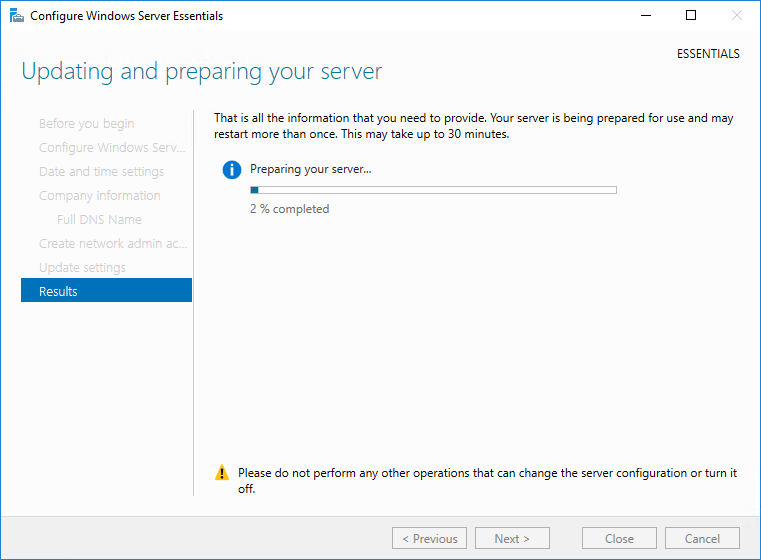
и дождаться окончания настройки. Процесс достаточно длительный и занимает от 10 до 30 минут, в зависимости от быстродействия сервера. В процессе сервер несколько раз перезагружается.
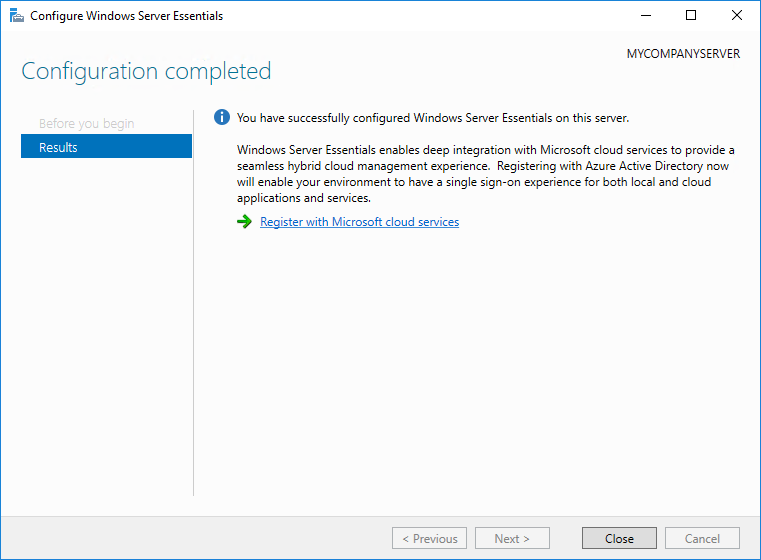
По окончании настройки можно сразу зарегистрировать сервер в облачных сервисах Microsoft.
Процедура настройки выглядит несерьезной, но это только на первый взгляд. На самом деле в процессе настройки на сервер устанавливаются роли доменного контроллера, сервера DNS, центра сертификации, файлового сервера, веб-сервера, роль Windows Server Essentials Experience и еще много всего по мелочи. Что примечательно, изменить набор устанавливаемых компонентов невозможно.
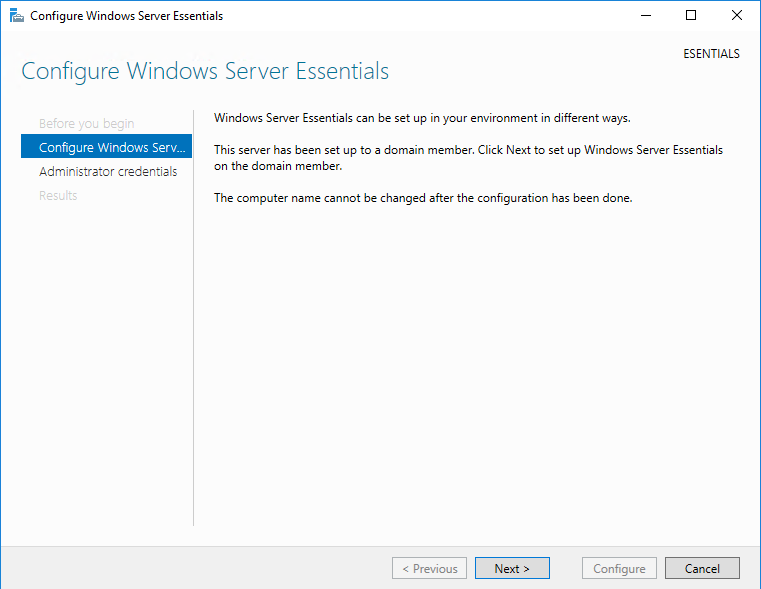
Установка в качестве рядового сервера в домене
Если у вас уже имеется домен Active Directory и вы зачем то хотите установить Windows Server Essentials в качестве рядового сервера, то сначала необходимо добавить сервер в домен и только после этого запускать мастер настройки. При этом процедура настройки сокращается до минимума.
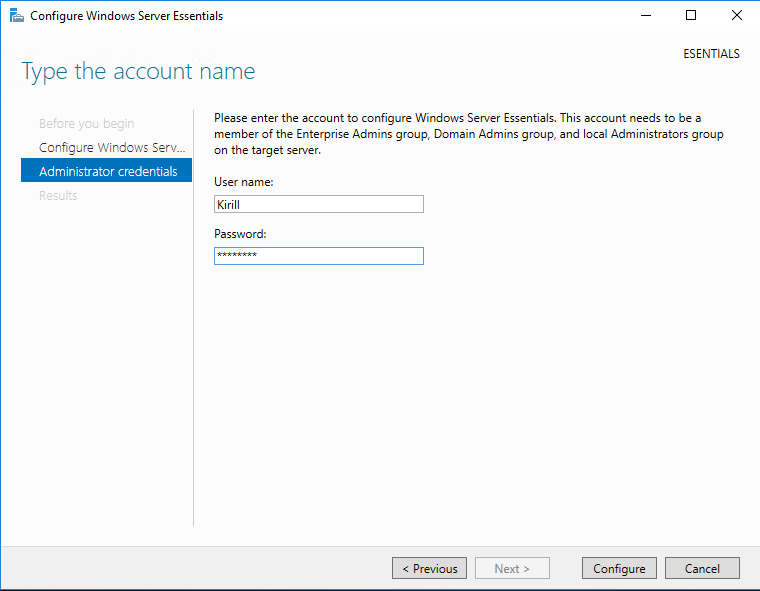
Надо только указать учетные данные пользователя для подключения к домену и запустить настройку. Обратите внимание, что указанный пользователь должен быть членом группы Enterprise Admins.
При таком варианте настройки на сервер устанавливаются все те-же компоненты, кроме роли доменного контроллера и DNS-сервера.
Панель управления
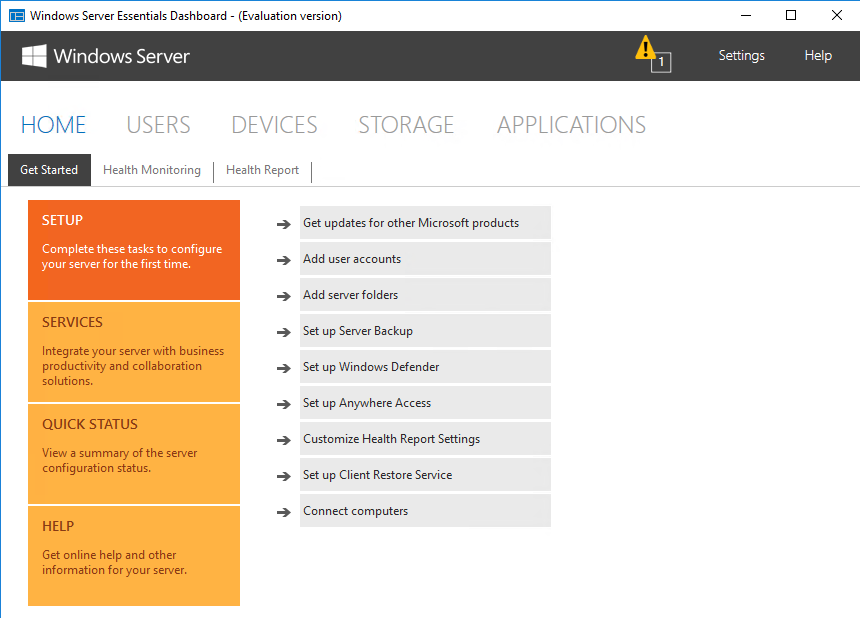
Кроме стандартных оснасток в Windows Server Essentials имеется специальная панель Windows Server Essentials Dashboard, которая становится доступной после завершения работы мастера. Эта панель предназначена для управления сервером и является отличительной чертой Essentials, поэтому рассмотрим ее поподробнее.
Внешне панель напоминает оснастку Server Manager, однако по своей сути кардинально от нее отличается. Предполагается, что редакция Essentials будет использоваться в небольших компаниях или филиалах, где зачастую отсутствуют квалифицированные системные администраторы, а управление сервером осуществляет сотрудник, более-менее знакомый с IT. Поэтому задача панели управления — предоставить максимально простой и быстрый доступ к наиболее важным функциям сервера.
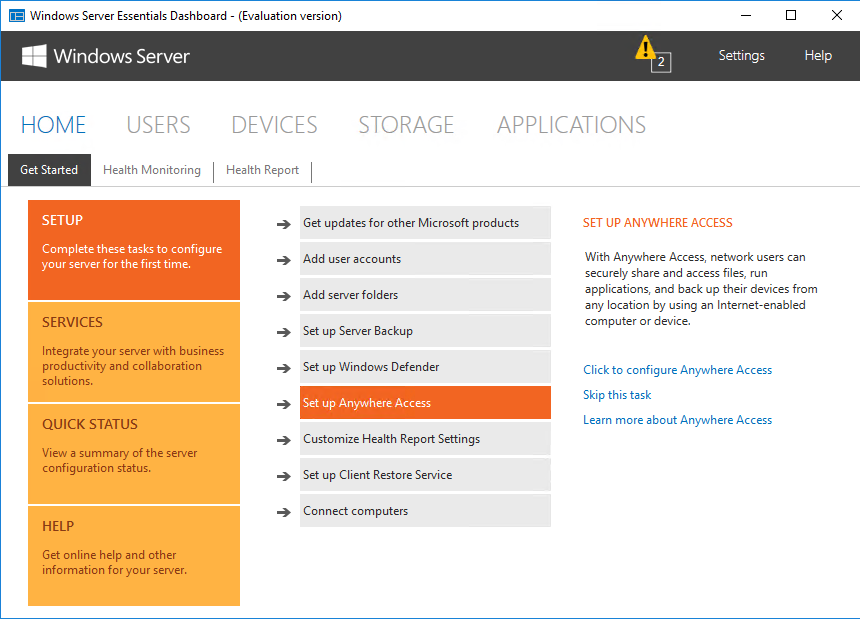
Панель состоит из нескольких основных разделов. Большинство разделов пересекаются между собой и ссылаются друг на друга. При запуски панели открывается домашний раздел, в котором имеется несколько вкладок. На вкладке «Setup» находятся ссылки на некоторые базовые настройки сервера. Все настройки производятся с помощью мастеров, достаточно только перейти на нужную вкладку и нажать на ссылку.
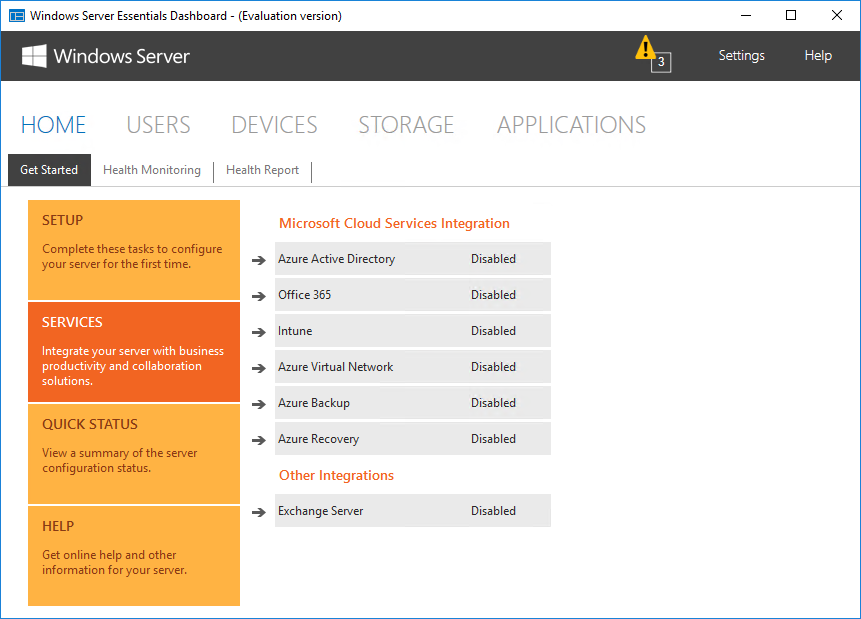
Windows Server 2016 Essentials можно интегрировать с облачными сервисами Microsoft, такими как Azure или Office 365. На вкладке «Services» показано состояние этих служб и отсюда же можно подключиться к нужной службе, при наличии активной подписки. После подключения службой можно управлять напрямую из консоли управления, это является особенностью Essentials.
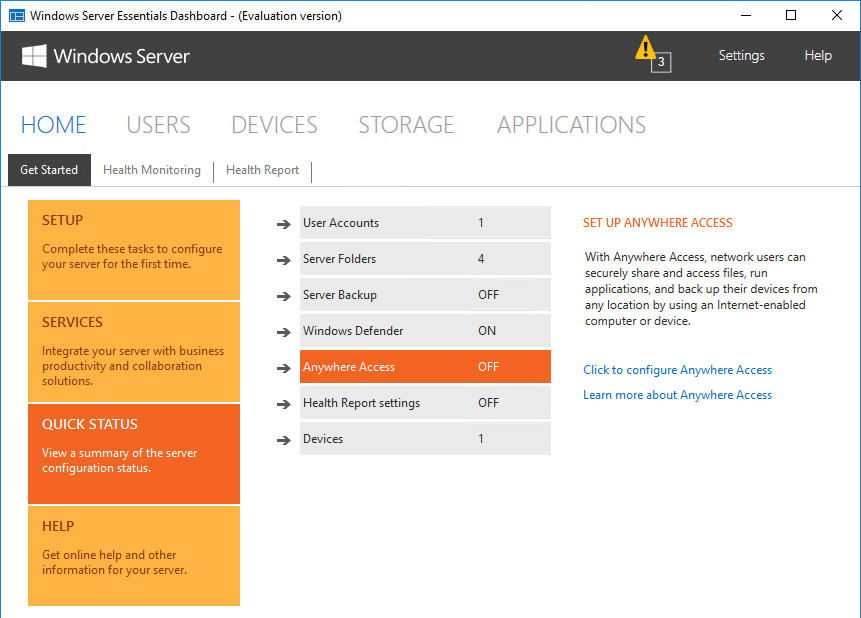
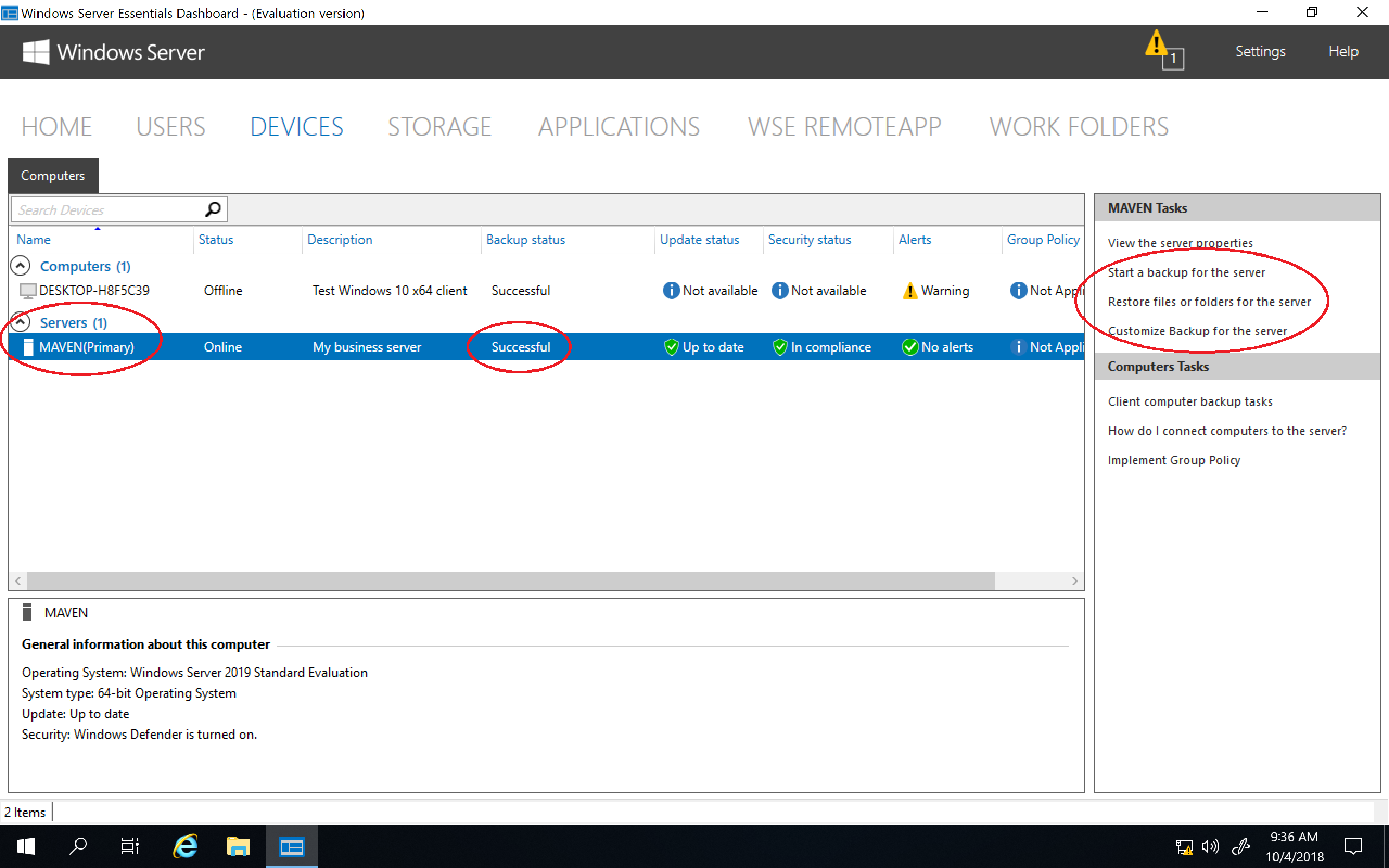
На вкладке «Quick Status» можно оперативно посмотреть текущее состояние сервера — количество пользователей и устройств, общие папки, состояние резервного копирования и т.п.
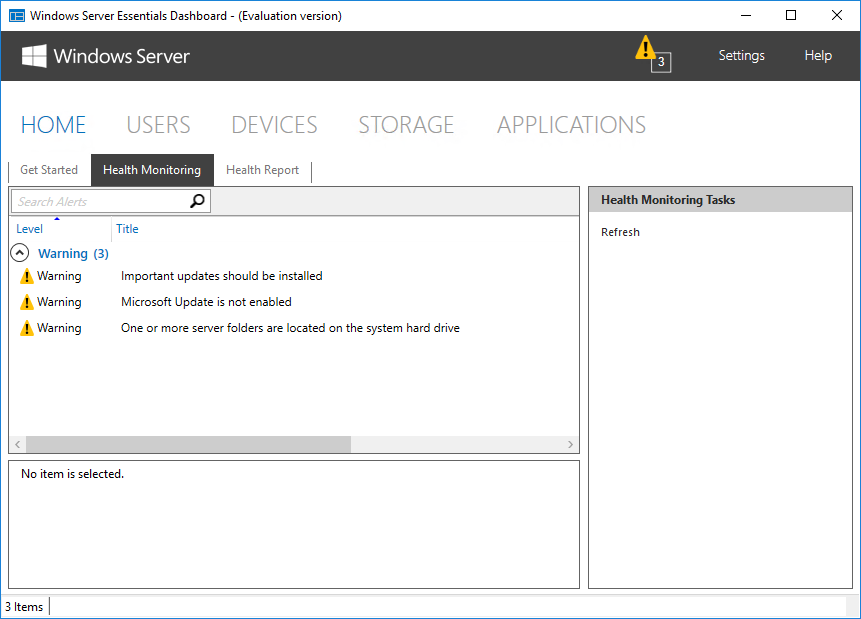
В подразделе «Health Monitoring» показаны сообщения системы о наличии проблем в работе сервера.
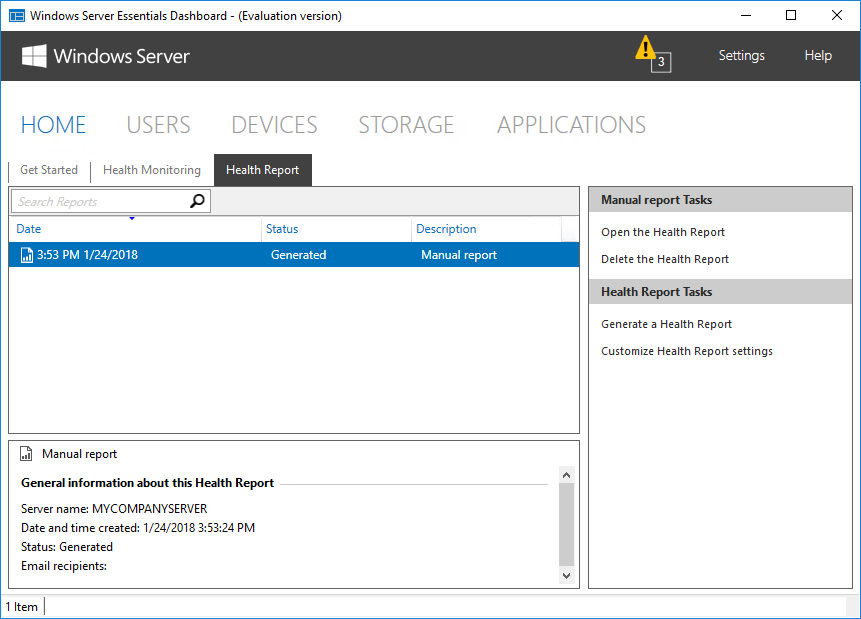
А в подразделе «Health Report» есть возможность получить отчет о состоянии сервера. В отчет входят в основном сообщения из предыдущего раздела, но с более подробным описанием. Отчет можно сгенерировать вручную или настроить создание по расписанию. Также при необходимости готовый отчет может отправляться на указанные адреса e-mail.
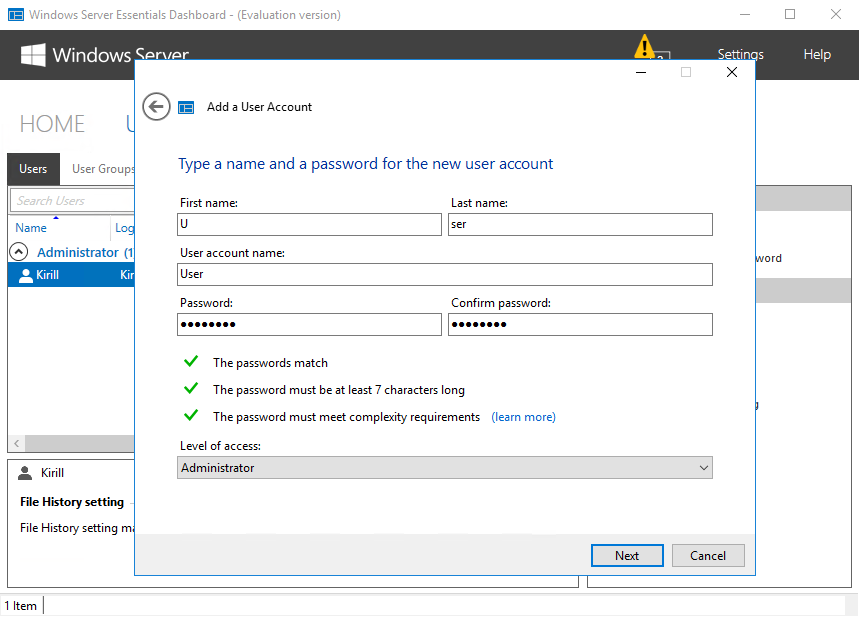
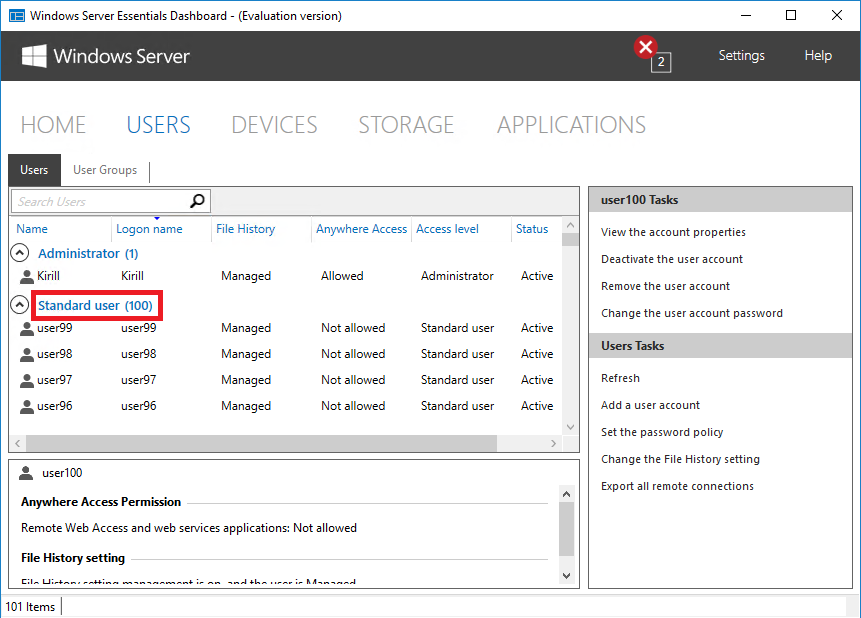
Переходим к следующему разделу «Users». Из этого раздела можно управлять пользователями и группами (создавать, удалять и т.п.) а также настраивать политику паролей (длина, сложность и т.п.).
Надо сказать, что поскольку интерфейс управления рассчитан на ″неискушенного″ пользователя и сильно упрощен, некоторые важные моменты в нем просто отсутствуют. К примеру при создании нового пользователя доступно только два уровня доступа — Standard User и Administrator. При этом Administrator означает, что пользователь будет добавлен не куда нибудь, а в группу администраторов домена.
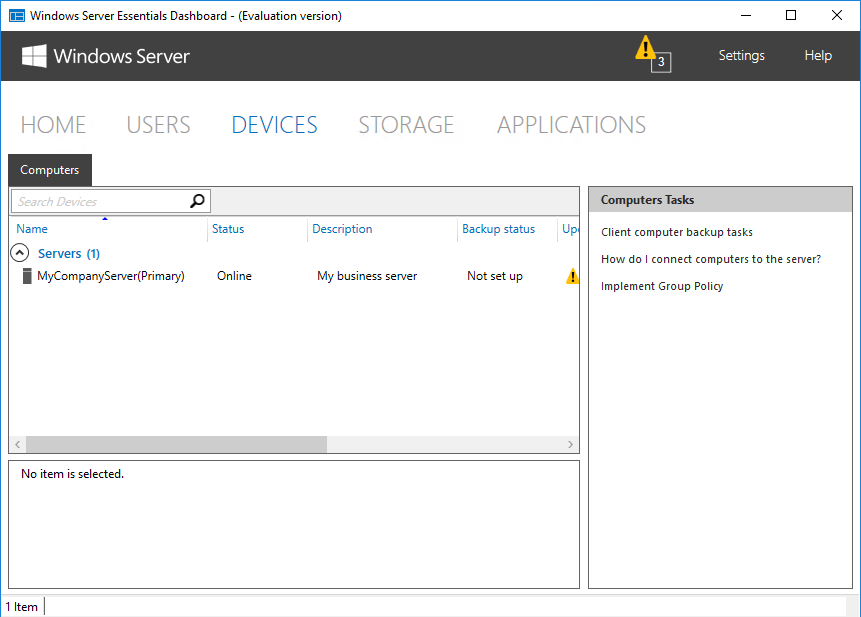
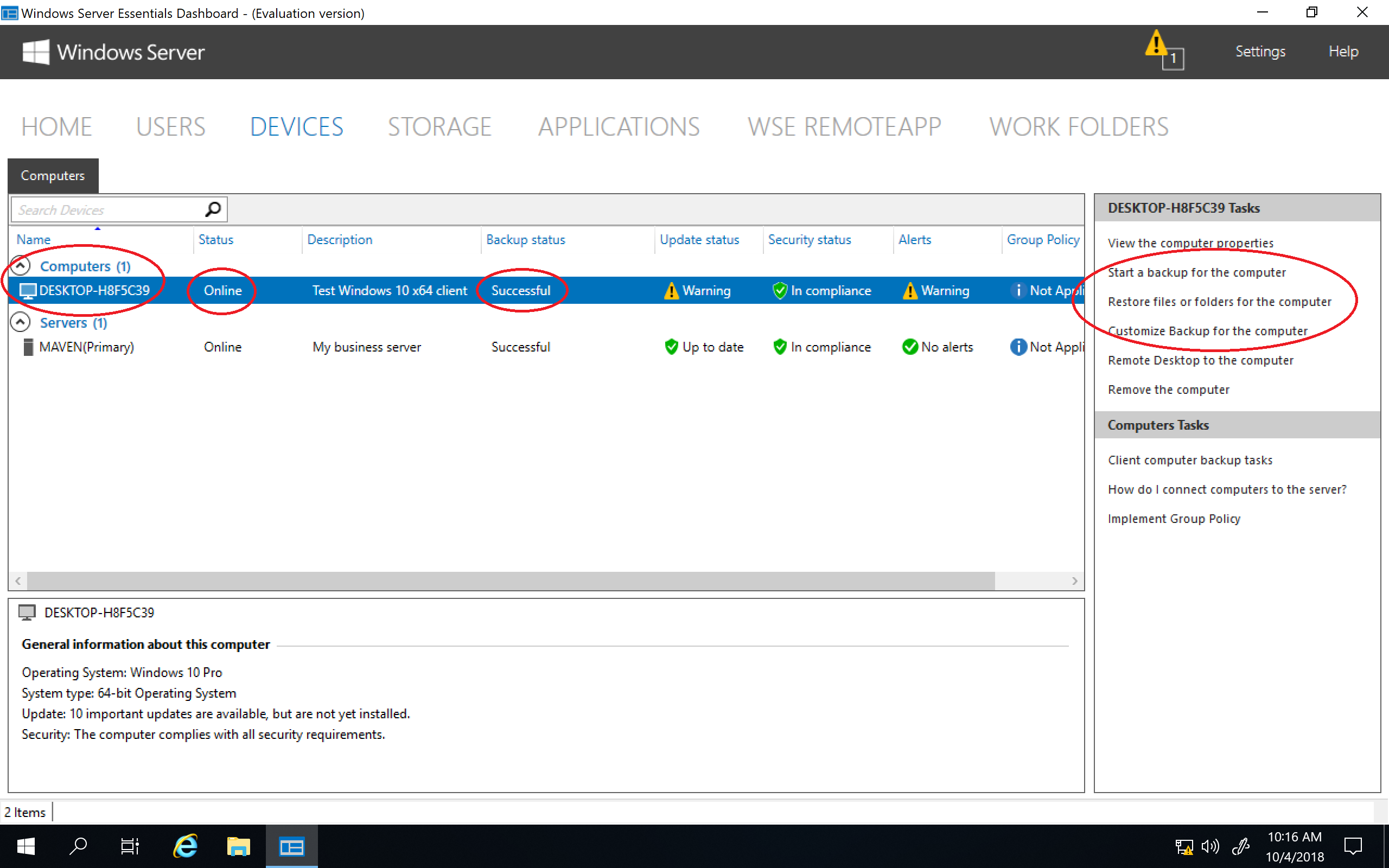
В разделе «Devices» отображаются компьютеры, подключенные к данному серверу. Чуть позже я расскажу о том, что представляет из себя процедура подключения.
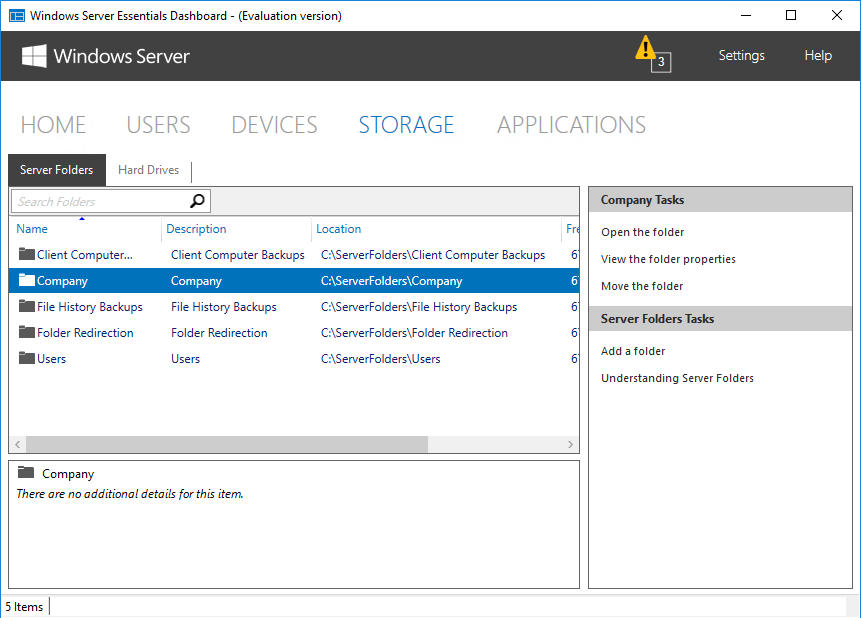
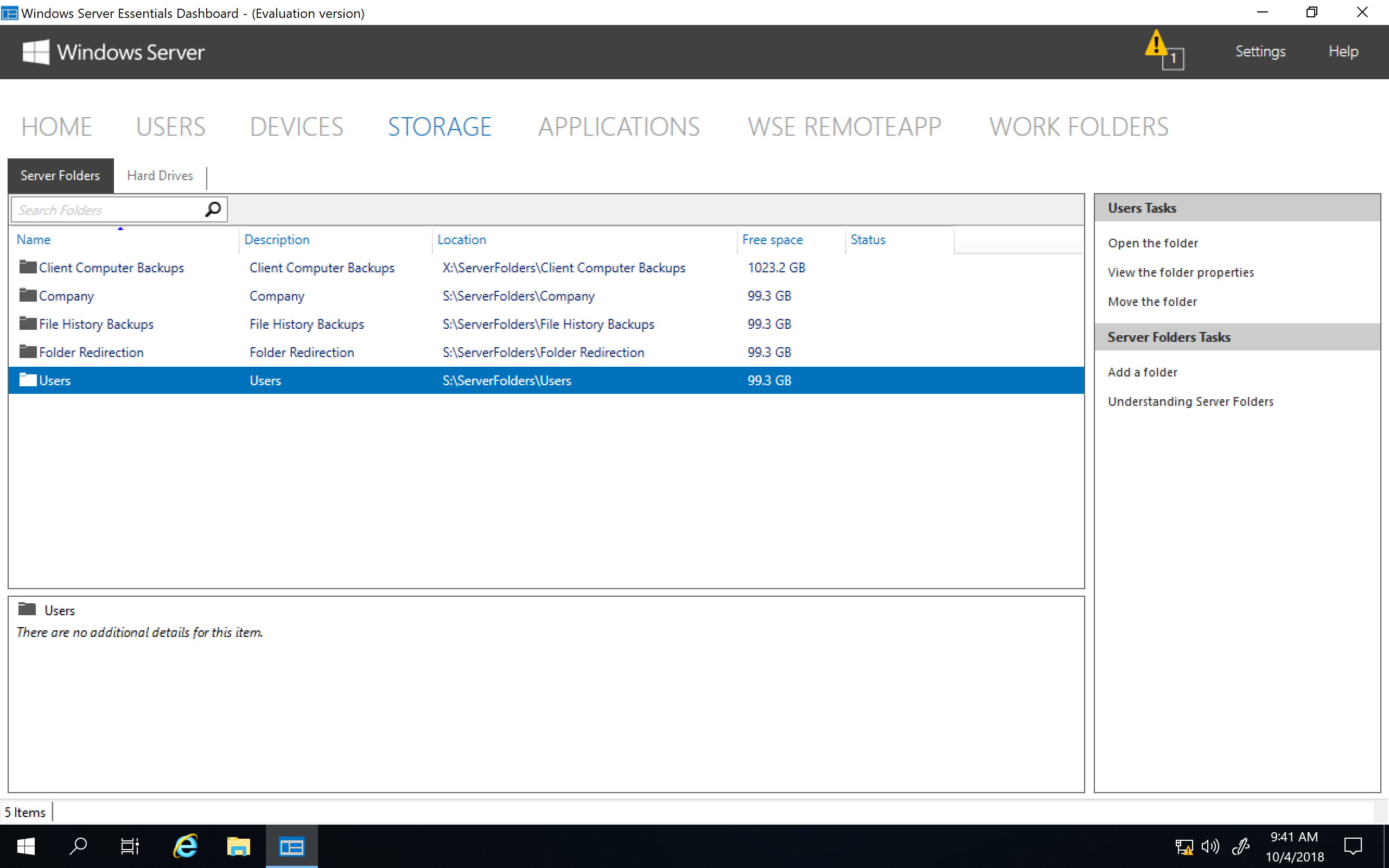
В разделе «Storage» показаны общие папки и жесткие диски, имеющиеся на сервере. Поддерживается технология Storage Spaces и при наличии на сервере нескольких физических дисков на базе Windows Server Essentials можно собрать отказоустойчивое файловое хранилище.
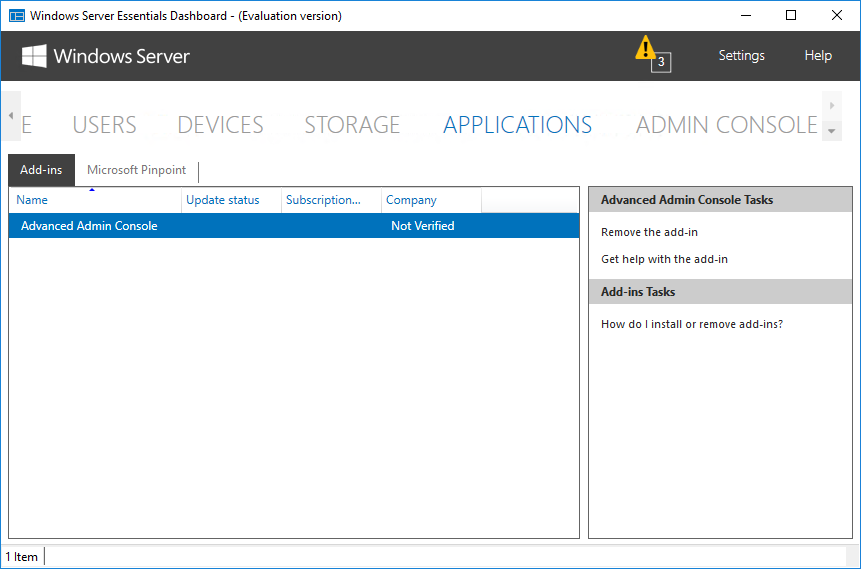
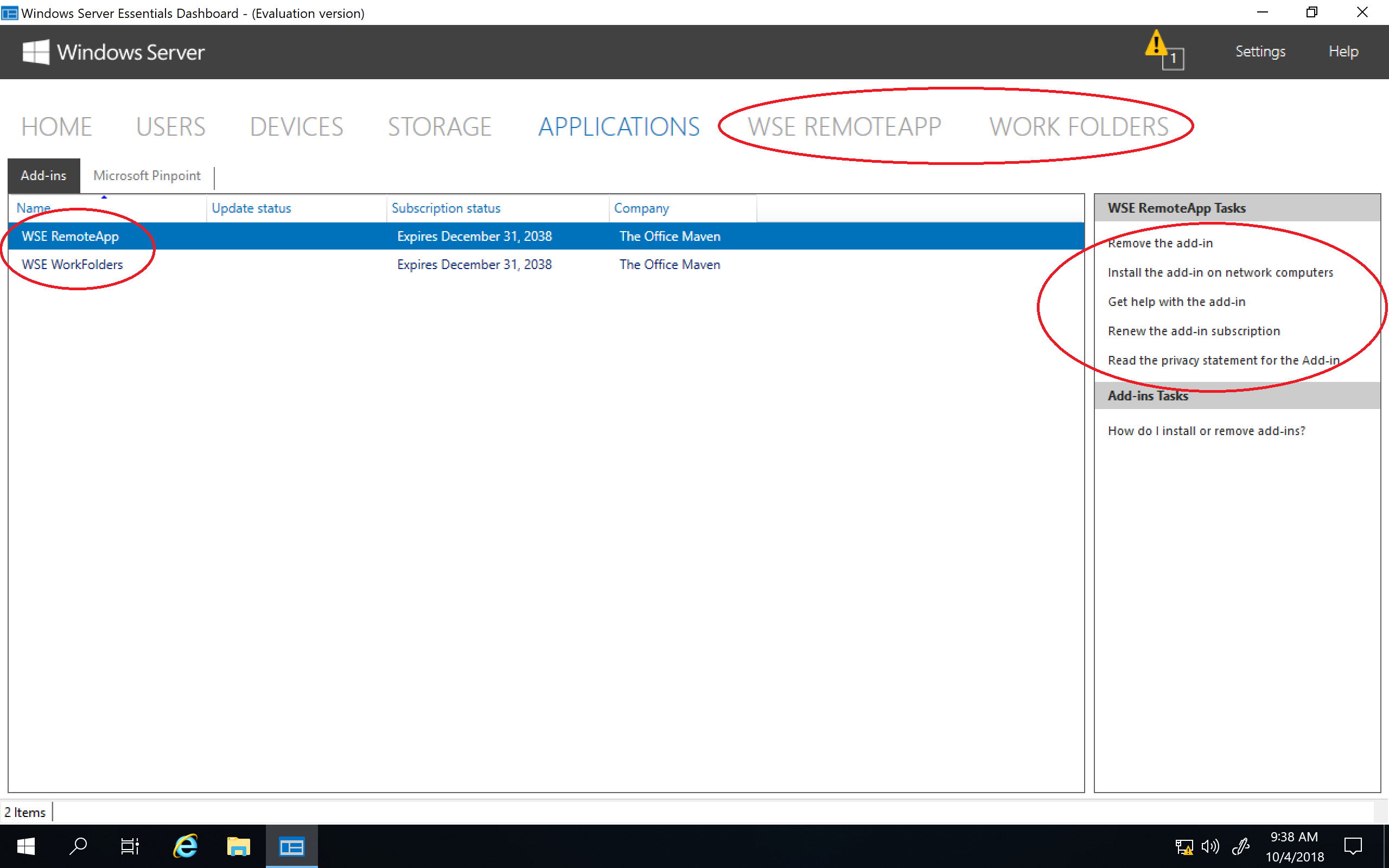
В разделе «Applications» должны отображаться специальные приложения, установленные на сервере.
Приложения эти представляют из себя дополнения для стандартного функционала для Windows Server Essentials. Их можно найти в Центре партнеров Microsoft (бывший Microsoft Pinpoint), на сайтах разработчиков либо написать самому, с помощью Windows Server Essentials SDK.
В качестве примера я установил приложение Advanced Admin Console, предназначенное для администрирования сервера. Как видите, приложения интегрируются в консоль управления и расширяют ее функциональность.
Удаленный доступ
Одна из интересных возможностей Windows Server Essentials является функция под ″скромным″ названием повсеместный доступ (Anywhere Access). Эта функция обеспечивает удаленный доступ к данным и приложениям с помощью веб-браузера. По умолчанию Anywhere Access не включен и перед тем, как его использовать, необходимо произвести настройку. Настройка осуществляется с помощью мастера, который запускается по ссылке на вкладке «Setup».
Примечание. Для настройки Anywhere Access в обязательном порядке требуется наличие SSL-сертификата.
Подключение снаружи осуществляется по адресу https://DomainName/Remote, а при подключении внутри локальной сети https://ServerName/Remote.
Надо сказать, что веб-консоль не особо функциональна, в основном ее можно использовать для управления файлами и папками, находящимися на сервере. Однако большим плюсом консоли является то, что доступ к файлам можно осуществить практически с любого устройства, на котором имеется подключение к сети и веб-браузер.
Подключение компьютера
Подключение компьютера — одна из эксклюзивных функций Essentials. Подключить можно клиентские и серверные ОС Windows, а также MacOS. Для подключения необходимо зайти по адресу http://ServerName/connect, загрузить коннектор и установить его на подключаемый компьютер.
После установки и настройки коннектора подключенный компьютер появляется в панели управления и мы можем посмотреть его свойства и состояние некоторых компонентов. Также для каждого подключенного устройства автоматически настраивается резервное копирование. Ну и еще можно подключиться к выбранному компьютеру по RDP прямо из панели управления.
А теперь рассмотрим некоторые интересные моменты, которые отсутствуют в официальной документации.
Без настройки
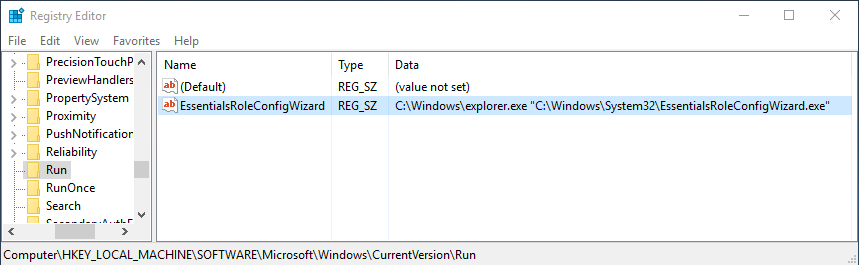
Первый вопрос, который возник у меня — можно ли использовать Windows Server Essentials как обычный сервер? Технически можно, для этого достаточно отменить процедуру настройки. Мастер настройки представляет собой обычный исполняемый файл с именем EssentialsRoleConfigurationVizard.exe, находящийся в папке C:WindowsSystem32. Автоматический запуск мастера обеспечивается с помощью ключа реестра EssentialsRoleConfigurationVizard в разделе HKLMSoftwareMicrosoftWindowsCurrentVersionRun и для отмены запуска достаточно удалить этот ключ.
После этого сервером вполне можно пользоваться, но без настройки не запустится панель управления и, соответственно, все эксклюзивные возможности Windows Server Essentials будут недоступны. Кроме того возможно, что подобное поведение нарушает лицензионное соглашение.
Ограничения
Редакция Essentials отличается от остальных редакций Windows наличием некоторых ограничений. Это очень важный момент, поэтому рассмотрим эти ограничения поподробнее.
Приложения
Windows Server Essentials никак не ограничена в установке приложений и на данную редакцию вполне можно устанавливать такие серверные приложения как Exchange, SQL Server и т.п. Однако при этом необходимо помнить, что редакция Essentials поддерживает не более 2-х физических процессоров и максимум 64 Гб оперативной памяти. Если лимит на процессоры не особо ограничивает сервер по производительности, то с памятью все гораздо хуже. 64 Гб ОЗУ для сервера это крайне мало, поэтому на базе Essentials не получится создать более-менее производительное решение. Обойти это ограничение невозможно, сколько бы памяти не было установлено в сервере, доступно системе будет не более 64Гб.
Роли сервера
В Windows Server 2016 Essentials доступен весь базовый функционал Windows Server. Отсутствуют все новые фичи виртуализации, такие как контейнеры или нано-сервер, но роль Hyper-V установить можно. Хотя при ограничении на количество памяти использование Essentials как сервер виртуализации не имеет особого смысла.
Отдельно стоит упомянуть о ролях RDS (Remote Desktop Services). Эти роли доступны для выбора и их все можно установить на сервер. Однако редакция Essentials ограничена всего 2 подключениями по RDP и это ограничение никак нельзя обойти. Даже если установить на сервер роль RDP-сервера и навесить на него терминальные лицензии, количество возможных подключений не увеличится.
Дело в том, что для подключения по RDP необходимо наличие клиентских лицензий (CAL), а Essentials не использует клиентские лицензии. Это обстоятельство исключает возможность использования Windows Server Essentials в качестве сервера RDS.
Пользователи и устройства
Редакция Essentials отличается наличием ограничения на 25 пользователей50 устройств. Но что именно означают эти ограничения и можно ли их обойти?
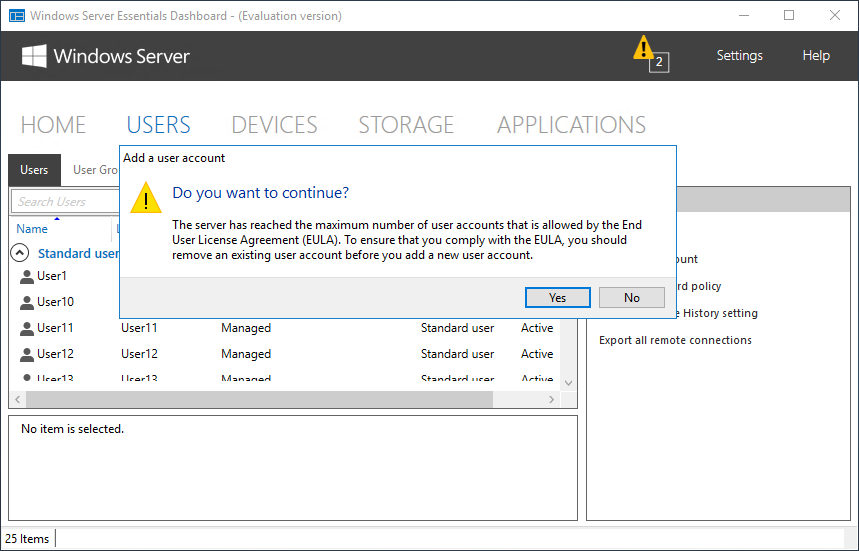
Для примера возьмем ограничение в 25 пользователей и попробуем его превысить. И действительно, при попытке создать пользователя сверх лимита будет выдано сообщение о нарушении лицензионного соглашения, а сам процесс создания завершится ошибкой. Но это только при создании пользователя из панели управления.
Используя оснастку ADUC или PowerShell можно без проблем создать любое количество пользователей. Т.е. ограничение не техническое и при необходимости его можно легко обойти, хотя это и будет нарушением лицензионного соглашения.
Что касается 50 устройств, то тут ограничение работает, но только на количество подключенных устройств. Т.е. количество учетных записей компьютеров в Active Directory не ограничено и их также можно создавать в любом количестве.
Смена редакции
При выборе Windows Server Essentials необходимо четко понимать все ограничения этой операционной системы и быть уверенным в том, что они не станут препятствием для роста компании в будущем. Однако если это уже произошло, то отчаиваться не стоит. Конечно, изменить лимиты невозможно, но можно изменить саму редакцию операционной системы.
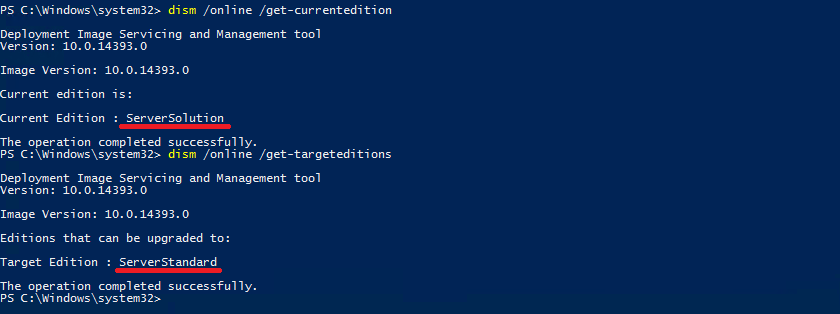
Сделать это можно с помощью утилиты dism. Например так можно посмотреть текущую редакцию:
Dism /Online /Get-CurrentEdition
А так — определить редакцию, на которую можно перейти:
Dism /Online /Get-TargetEditions
Как видите, с Essentials можно перейти на редакцию Standard. Для этого достаточно выполнить такую команду:
Dism /Online /Set-Edition:ServerStandard /AcceptEula /ProductKey:xxxxx-xxxxx-xxxxx-xxxxx-xxxxx
Что примечательно, после апгрейда настройки и установленные роли сервера остаются неизменными, при этом снимаются все ограничения редакции Essentials. Конечно после этой операции потребуется раскошелится на клиентские лицензии, а также пересчитать количество серверных лицензий в соответствии с ядрами процессора.
Заключение
В заключение рассмотрим плюсы и минусы Windows Server Essentials. К плюсам можно отнести:
+ Экономия на покупке клиентских и серверных лицензий;
+ Простота настройки и использования;
+ Интеграция с облачными службами;
+ Возможность без особых потерь перейти на полноценную редакцию Windows Server.
Ну и минусы, как же без них:
– Лимит на количество пользователейустройств;
– Ограничение на количество процессоров и максимальный размер памяти;
– Невозможность использования в качестве сервера удаленных рабочих столов;
– Непрозрачная процедура настройки, не позволяющая выбрать только необходимый функционал;
– Очень грубые и примитивные (на мой взгляд) настройки в консоли управления.
Минусов получилось больше, хотя в целом Windows Server Essentials неплохая система, вполне подходящая для своих целей. Главное при выборе четко понимать все ее особенности и быть уверенным в своем выборе.
11 февраля 2020

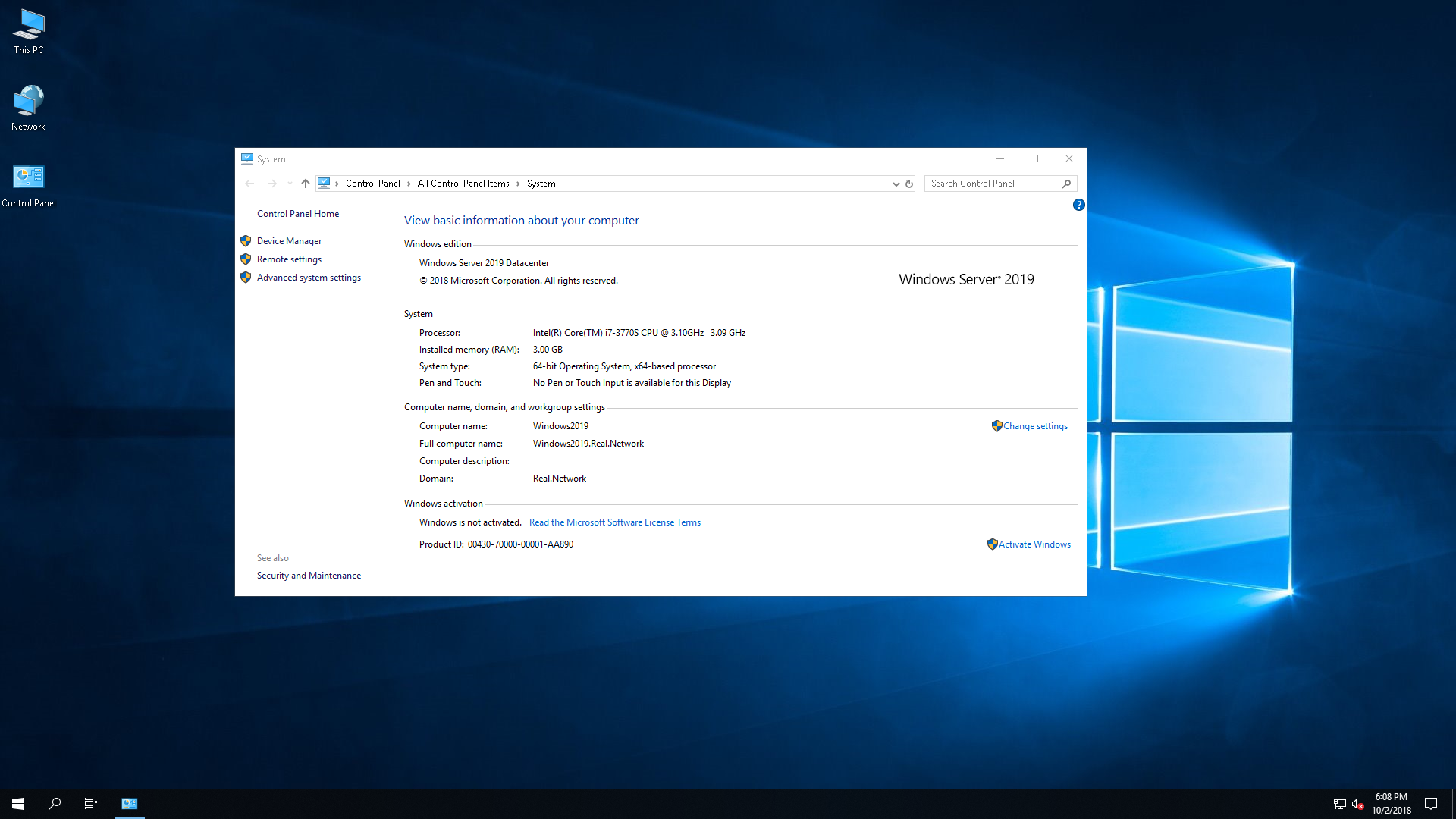
Недавно было анонсировано семейство Microsoft Windows Server 2019, и несмотря на общедоступность информации в интернете, поиск точных данных обо всех выпусках, опция и версиях может быть довольно затруднительным. Возможно, даже сложнее чем может показаться изначально.
Может быть не понятно, какие выпуски или версии Windows Server 2019 существуют, чем они отличаются друг от друга. Например, чем Hyper-V Server 2019 (бесплатный продукт) отличается в виртуализации от Windows Server 2019 Datacenter с Hyper-V? Они используют точно такой же гипервизор? И обеспечивает ли Windows Server 2019 Essentials гипервизор вообще?
По мере того, как находятся ответы, могут возникать все новые и новые вопросы:
-
Можно ли установить недавно анонсированные функции Windows Server On Demand на Windows Server 2019 с интерфейсом рабочего стола (GUI)? (Нет)
-
Можно ли преобразовать Windows Server 2019 Server Core в Desktop Experience и наоборот? (Нет)
-
Может ли Windows Server 2019 Datacenter быть преобразован в Стандартный и наоборот? (Да)
-
Могу ли я активировать ознакомительную версию в конце 180-дневного ознакомительного периода (или возможно, продлить ее)? (Да)
-
Могу ли я использовать “Центр администрирования Windows” в браузере Opera или в Windows 7 для удаленного управления Windows Server 2019 Server Core или другими серверами? (Да)
-
А как насчет Windows Storage Server 2019 Workgroup? (нет такого понятия)
Поиск ответов на некоторые вопросы приводит к большему количеству задаваемых вопросов. Все это закончилось проведением небольшого исследования. Теперь можно подтвердить: не всегда легко понять, какие продукты существуют, как они отличаются друг от друга, каковы их функции, какой продукт подходит и на что он способен? Зачем обновляться до Windows Server 2019 (Datacenter или Standard, Essentials или Hyper-V)? Или, возможно, лучше придерживаться старых добрых версий, которыми используются сейчас, например Windows Server 2016 или Windows Server 2012 R2 или даже 2008 R2?
Что нового в Windows Server 2019?
Компания Microsoft, концентрирует свои маркетинговые усилия, на продвижении инноваций и новых возможностей в 4 категориях: гибридные возможности с Azure, HCI (гиперконвергентная инфраструктура), безопасность и «быстрые инновации для приложений». Хотя больше, все привыкли к незначительным обновлениям Windows. Windows 2019 предлагает больше, чем просто пакет обновления. Например, в области безопасности появился Advanced Threat Protection (ATP), который ранее был независимым продуктом.
Windows Server 2019 Datacenter and Standard
- Основными продуктами семейства Windows Server 2019 являются Windows Server 2019 Standard и Datacenter. Любой из них может быть установлен в режиме Server Core или Desktop Experience (GUI). Сначала рассмотрим различия между выпусками Standard и Datacenter, а затем обсудим их подопции Server Core и Desktop Experience.
- Windows Server 2019 Datacenter является наиболее полным выпуском семейства продуктов Microsoft Server и, вместе с тем, самым дорогим, по оценкам Microsoft. Это отражает увеличение цены по сравнению с MSRP аналогичного сервера, версии 2016 года. Стоимость лицензии рассчитывается на основе ядра / клиентской лицензии.
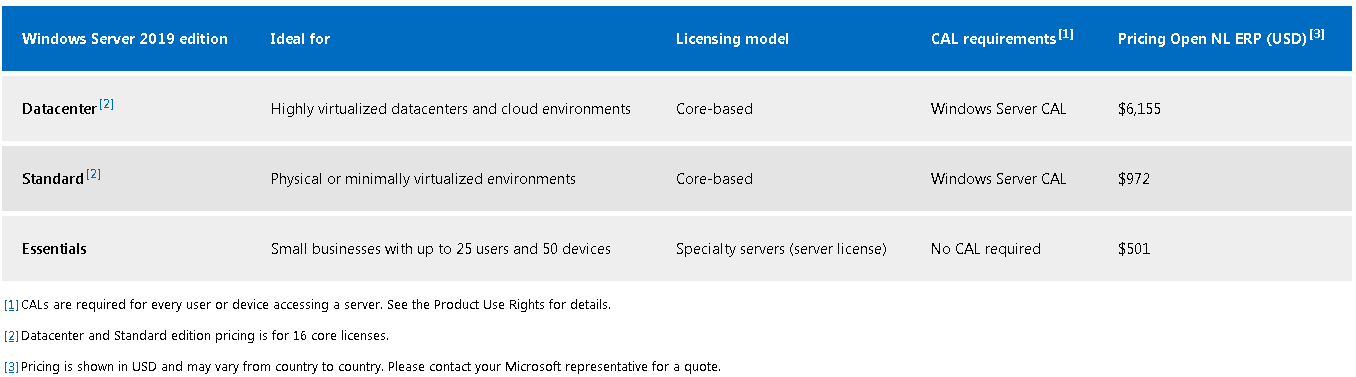
- Лицензия Datacenter предоставляет самый широкий набор функций и возможностей с наименьшим количеством лицензионных ограничений среди всех выпусков Server. Например, все серверы, которые виртуализированы на сервере Datacenter, лицензируются автоматически их хостом Datacenter, учитывая, что хост-сервер и гостевые серверы имеют одинаковую версию. Такие гости также могут быть автоматически активированы с помощью активации виртуальной машины (AVMA).
- В Windows Server 2016 была представлена защищенная виртуальная машина — новая функция, доступная только в выпуске Datacenter. В отличие от этого, Host Guardian Service был доступен только в выпуске Datacenter Windows Server 2016, хотя в выпуске Windows Server 2019 служба Host Guardian стала доступна также и в Standard версии. Хотя такое и происходит время от времени, это не правило, а скорее исключение. В итоге: новые возможности представлены в новых выпусках Windows Server, в то время как другие функции отключены. Некоторые функции являются эксклюзивными для выпуска Datacenter, тогда как иногда такие функции становятся доступными для более дешевых вариантов лицензирования.
- Вот список функций, которые были удалены из Windows Server 1803, а также список функций, которые больше не поддерживаются. Стоит учесть, что это только частичный список по сравнению с, гораздо более длинным списком в семействе продуктов Windows Server 2019. Это связано с двумя основными причинами: 1. Windows Server 2019 является обновлением с 2019 года, тогда как версия 1803 является обновлением с 1709. Вполне вероятно, что больше функций было отклонено как в версии 1709, так и в 1809; 2. Windows Server 2019 состоит из целого семейства продуктов (включая Essentials, где Essentials Experience только что снята с производства).
- В качестве дополнения, можно заметить, что Windows Server 1809 является эквивалентом Windows Server 2019 Server Core. Server 2019 относится к каналу долгосрочного обслуживания (LTSC), тогда как сервер 1809 доступен только в качестве серверного ядра и является частью Semi-Annual Channel.
- Datacenter Exclusive Capabilities. Назовем несколько возможностей, которые поддерживаются только в Windows Server 2019 Datacenter, а не в Standard (или в Essentials): роль сетевого контроллера; Программно-определяемая сеть (SDN); Программно-определяемое хранилище (SDS), дедупликация, доступ к памяти; Storage Spaces / Direct (S2D); Репликация хранилища (частичная доступность в стандарте); Автоматическая активация виртуальной машины (AVMA); Лицензионное ограничение для 2 операционных сред / контейнеров Hyper-V (VM) в стандартной версии и неограниченное в Datacenter.
- Вот подробное сравнение Microsoft со сравнением функций Windows Server 2019 Datacenter и Standard. На самом деле, это не сравнение, а список возможностей. Сравнение подчеркивает различия, тогда как это «сравнение» на самом деле затрудняет выявление различий, превращая его в список функций.
- Microsoft, определяет Windows Server 2019 Datacenter как «идеальный для высоко виртуализированных центров обработки данных и облачных сред». Стандартная версия описывается как «идеальная для физических или минимально виртуализированных сред». В отличие от этого, “сводный брат” Hyper-V Server 2019, кажется, не идеален ни для чего.
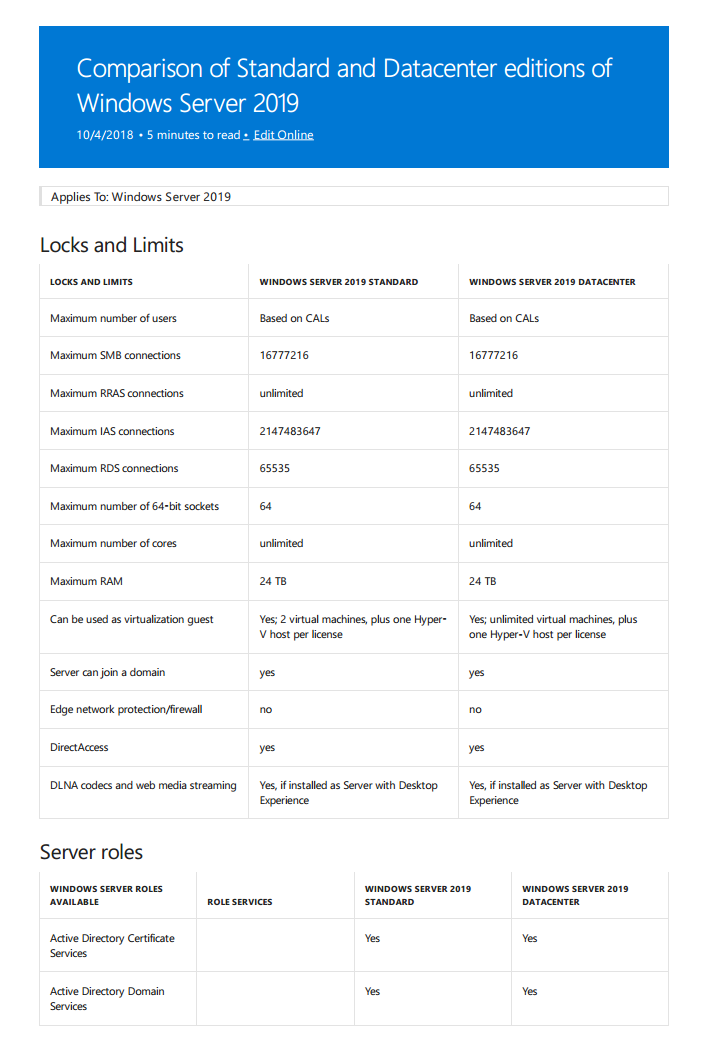
Windows Server 2019: Server Core против Desktop Experience (GUI)
- Как и в предыдущих версиях Windows Server, также в версии 2019, Standard или Datacenter поставляются с двумя вариантами установки: для установки в форме Server Core или Desktop Experience (GUI).
- Server Core был впервые представлен в Windows 2008. Теоретически, им можно управлять локально только через командную строку или Powershell, поскольку он не включает локальный графический интерфейс (GUI). Однако это не так. Некоторые инструменты с графическим интерфейсом по умолчанию были в Server Core, например: диспетчер задач, редактор реестра и др.
- Вот список программ с графическим интерфейсом, которые поддерживаются в Server Core версии 2019 и могут выполняться при установке Windows 2019: control.exe intl.cpl (выбор региона); control.exe timedate.cpl (настройка даты и времени); regedit (редактор реестра); notepad (текстовый редактор); msinfo32.exe (системная информация); taskmgr.exe (диспетчер задач); msiexec.exe (установщик Windows); cmd.exe и powershell.exe.
- Кроме этого, Microsoft предоставляет еще некоторые решения с GUI. Такие приложения включают в себя множество утилит Sysinternals, а также приложения, которые можно установить с помощью команды Powershell Install-Windows Feature.
- Вот список программ с графическим интерфейсом, которые доступны в Sysinternals и поддерживаются Windows 2019 Server Core: adexplorer.exe (проводник активного каталога); procxp.exe (проводник процессов); procmon.exe (монитор процесса); tcpview.exe; vmmap.exe; remmap 1.50; protqueryui.exe 1.0.
- Кроме того, что предоставляет Microsoft, существуют сторонние инструменты, которые могут быть установлены на Server Core для обеспечения дополнительного функционала. Например, можно установить WinRar на Core.
- И чтобы сделать Server Core полнофункциональной рабочей станцией с графическим интерфейсом, можно установить несколько сторонних инструментов, в том числе: файловый менеджер, диспетчер Hyper-V и даже приложение для имитации работы рабочего стола в Windows. Чтобы сделать его еще более похожим, можно добавить фоновое изображение Windows по умолчанию. Итого, это Windows Server 2019 Core с возможностью выполнения нескольких задач с помощью приложений с графическим интерфейсом (большинство из которых бесплатные).
- Это не означает, что серверное ядро должно быть преобразовано в рабочий стол. Но да, его можно использовать для управления машинами Hyper-V; Управление файлами может стать проще с WinRar или Explorer++. Ядро сервера можно немного расширить, чтобы найти золотую середину между Powershell и полноценным опытом с привычным графическим интерфейсом.
- То же самое относится и к бесплатному Hyper-V Server 2019. Это может быть еще более значимым в случае сервера Hyper-V, поскольку такой параметр позволяет управлять виртуальными машинами изнутри сервера Hyper-V, а не зависеть от другой лицензии Windows и компьютера. Таким образом, снижается сложность и стоимость.
- Независимо от возможностей графического интерфейса и аналогично другим серверам, Server Core предназначен для удаленного управления либо с помощью PowerShell, либо с помощью специализированных инструментов удаленного управления, таких как средства удаленного администрирования сервера (RSAT), диспетчер серверов, оснастка MMC, службы удаленных рабочих столов. и последнее, но не менее важное: Центр администрирования Windows (WAC).
- Преимущества версии Server Core включают меньшую занимаемую площадь (более низкое потребление ресурсов процессора, оперативной памяти и дискового пространства), меньшую уязвимость и большую устойчивость к кибератакам, поскольку она содержит меньшую поверхность для атаки, меньше обновлений и исправлений и меньше перезагрузок.
- Естественно, с каждым установленным приложением теряются некоторые из преимуществ. Многие приложения сегодня доступны в portable версии, то есть они не изменяют системные параметры и, следовательно, снижают нагрузку на систему, вызывая меньшее влияние на производительность и снижая риск уязвимости. Это не имеет место в 100% случаев, но дано, как правило.
Server with Desktop Experience — это классическая и хорошо известная форма Windows Server, которая была со времен культовой Windows NT. Desktop Experience, содержит графический интерфейс, облегчающий управление. Графический интерфейс Windows Server 2019 аналогичен Windows 10 версии 1809, хотя параметры конфигурации Windows Server по умолчанию, как правило, более безопасны, в отличие от Windows 10.
- В прошлом, Microsoft позволяла выбирать между Server Core и Desktop Experience. Однако это больше не поддерживается в версии 2019.
- Server Core Limitations, Unsupported Capabilities. Вообще говоря, Server with Desktop Experience может делать все, что может Server Core, хотя ожидается, что Server Core будет работать лучше. Однако это не так. В Server Core отсутствует совместимость с различными приложениями и функциями, поэтому он не может полностью заменить Server Desktop Experience. В основном он не совместим с приложениями, которым требуется графический интерфейс.
- Для примера, следующие приложения и возможности, несовместимы с ядром сервера: диспетчер виртуальных машин Microsoft Server 2019 (SCVMM), SCDPM 2019, Sharepoint Server 2019, Project Server 2019, Windows Tiff IFilter, клиент печати через Интернет, комплект RAS Connection Manager, Simple TCP / IP-сервисы, TFTP-клиент, служба поиска Windows, программа просмотра XPS и многое другое.
Преобразование Datacenter в Standard Edition и наоборот
- Windows Server 2019 Standard и Datacenter — это, по сути, один и тот же продукт, отличающийся друг от друга по функциям только благодаря лицензированию. Таким образом, выпуски Datacenter и Standard могут быть преобразованы друг в друга после установки. Это можно сделать после активации, введя ключ активации, который затем определяет и при необходимости преобразует Windows в соответствующую редакцию. Вкратце: Windows Server 2019 Datacenter может быть активирован в Standard и наоборот.
- Чтобы активировать ознакомительную версию Windows Server, ее необходимо сначала преобразовать в Retail. После этого, ее можно активировать. Так что да, это возможно, просто требуется дополнительный шаг.
Windows Server 2019 Essentials
- Windows Server 2019 Essentials предназначен для небольших предприятий. Ранее он назывался Small Business Server (SBS) или Microsoft BackOffice Server. Редакция Essentials ограничена в возможностях и вариантах лицензирования и, соответственно, самая дешевая среди семейства. По словам Microsoft, издание Essentials «идеально подходит для малых предприятий с количеством пользователей до 25 и 50 устройствами». В Essentials отсутствуют «расширенные» функции, такие как поддержка службы миграции хранилищ (SMS), которые доступны в выпусках Standard и Datacenter. Essentials также ограничен во многих аспектах. Например, это должен быть единственный контроллер домена, то есть он не может находиться вместе с другим сервером Essentials в том же домене.
- Поддерживает ли Windows Server Essentials роль Hyper-V. Некоторые тестирования показывают, что Windows Server Essentials может быть размещен в качестве гостя Hyper-V или гипервизора, на котором размещены другие виртуальные машины. Эти роли могут быть настроены параллельно.
- Традиционно, Windows Server Essentials предустановлен и предварительно настроен с несколькими ролями сервера: доменные службы Active Directory (ADDS), DNS-сервер и веб-сервер (IIS). Предполагается, что это также относится к версии 2019 в соответствии с документацией, которая доступна в сети, где также можно найти информацию о том, что роль Essentials Experience больше не поддерживается. Вполне возможно, что 2019 Essentials был стандартизирован, чтобы выглядеть и работать как обычный сервер. Таким образом, он ограничен в функциях из-за лицензирования.
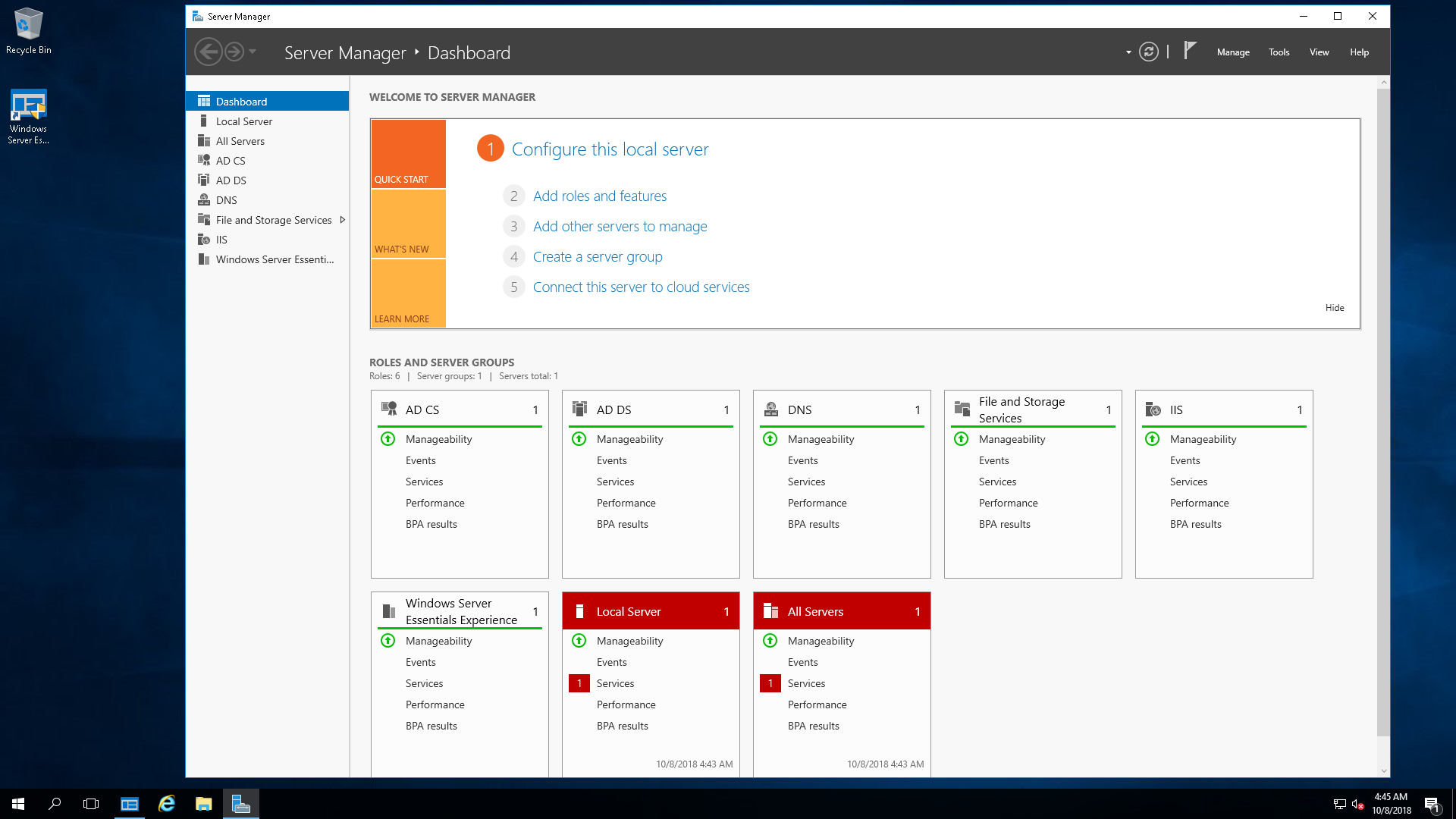
- Исторически, Essentials поставляется с несколько упрощенным графическим интерфейсом, называющийся Essentials Dashboard, который автоматически выполняет комплексные задачи по настройке. Предварительная конфигурация, предоставленная ролью Essentials Experience, предполагает упрощение управления Essentials. В какой-то степени это все, что нужно: проще управлять сервером.
- Однако в мае прошлого года, Microsoft объявила, что Windows Server 2019 Essentials не будет более существовать, поскольку выпуск Essentials устарел. Несмотря на это, позднее, Microsoft вернула Essentials, и на сегодняшний день она жива с новой версией: Windows Server 2019 Essentials.
- К сожалению, роль Essentials Experience исключена из Windows Server 2019 Essentials. И очень жаль, поскольку некоторые пользователи Essentials зависят от этой роли, поскольку они не знакомы со «стандартными» панелями управления или инструментами сервера. Вместо панели инструментов Essentials, Microsoft рекомендует использовать альтернативные варианты управления, направляя своих клиентов к широко распространенному инструменту: Центру администрирования Windows.
- Essentials поставляется с новыми функциями семейства Server 2019, включая Storage Migration Services, System Insights, а также с возможностями безопасности Windows ATP (ранее Aorato).
- Как заявлено Microsoft, в настоящее время не планируется выпускать будущие версии Server Essentials, цитата: «Существует большая вероятность того, что это может быть последним выпуском Windows Server Essentials».
- Как заявляет Microsoft, здесь, в настоящее время Microsoft планирует не выпускать будущие версии выпуска Server Essentials, цитата: «Существует большая вероятность того, что это (то есть Essentials 2019) может быть последним выпуском Windows Server Essentials».
Microsoft Hyper-V Server
Microsoft Hyper-V Server — это родной брат семейства Windows Server. Он предназначен для достижения только одной цели: гипервизировать виртуальные машины, то есть быть хостом и запускать виртуальные машины. Несмотря на это, Hyper-V Server может выполнять другие функции, такие как запуск файловых служб или IIS. С учетом сказанного, просто тот факт, что это технически возможно, не означает, что он имеет право, так как лицензия может не разрешать это. Стоит обратить внимание, что несмотря на то, что это бесплатный продукт, лицензионное соглашение Hyper-V Server должно быть согласовано во время установки.
Настройка сервера Hyper-V проста и понятна. Ключ активации не требуется, и есть меньше вариантов выбора, так как Hyper-V Server не предоставляет никаких опций для графического интерфейса. Скорее, он установлен по умолчанию в качестве серверного ядра, которое нельзя изменить позже. Следовательно, после установки Hyper-V Server 2019, нет приятного графического интерфейса для работы. Скорее, пользователю предлагается управлять своими виртуальными машинами удаленно (или локально через командную строку / powershell). При загрузке Hyper-V он автоматически загружает синюю оболочку sconfig (sconfig.cmd), как показано ниже. Это позволяет инициализировать машину через базовую конфигурацию.
Сервер Hyper-V — это выделенный сервер с урезанной функциональностью. Как таковой, он потребляет наименьшее количество ресурсов и является наименее уязвимым для атак. Большинство функций Windows здесь недоступны, а большая часть ресурсов оставлена для пользователя. Следовательно, есть много мнений в сети, предполагающих, что это может быть идеальным решением для предприятия. Тем более, что Hyper-V поставляется с той же технологией гипервизора семейства Windows Server (то есть, что и в Windows Server 2019 Datacenter). Сервер Hyper-V позволяет знакомиться и работать с миром виртуализации.
Поскольку сервер Hyper-V не предоставляет никаких лицензий для продуктов Windows, в идеале его можно использовать для запуска уже лицензированных компьютеров под управлением Windows. Такие машины могут быть перенесены с физического на виртуальный, так называемый P2V или с других гипервизоров. Сервер Hyper-V также может использоваться для запуска рабочих нагрузок Linux или VDI.
Сравнение возможностей Windows Server 2008 R2–2019
Microsoft недавно выпустила 11-страничное сравнение функций Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2016 и Windows Server 2019. Несмотря на то, что компания игнорирует Windows Server 2019 в сравнительном сравнении на своей веб-странице, сравнение загружаемых функций в прикрепленном PDF, является всеобъемлющим и включает в себя также и Windows Server 2019.
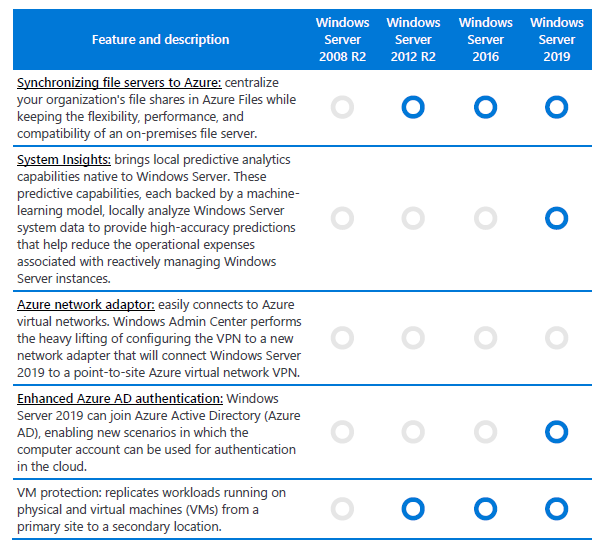
Доступный на официальном сайте PDF, с 11 страницами, сравнивает функции версий Windows Server 2008 R2 — 2019 в нескольких областях: гибридные возможности с Azure, HCI (гиперконвергентная инфраструктура), безопасность и «быстрые инновации для приложений». Все это области, которые Microsoft в настоящее время продвигает, и где внедряется самый высокий уровень инноваций по сравнению с предыдущими версиями.
Мы рассмотрели различия и уникальности основных выпусков и опций семейства продуктов Windows Server 2019: Standard против Datacenter, Server Core против Server with Desktop Experience (GUI), Essentials и Hyper-V Server против Server with Hyper-V role. Надеемся, этой статьей, пользователям стало хоть немного проще ориентироваться в сложном, на первый взгляд, разнообразии семейства Microsoft.
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia

Windows Server 2019 Essentials displaying the Windows Server Essentials Server Manager |
|
| Developer(s) | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| Final release |
2019 |
| Type | Operating system |
| License | Commercial proprietary software |
| Website | microsoft.com/windows-server/ |
Windows Server Essentials (formerly Small Business Server or SBS)[2] is an integrated server suite from Microsoft for businesses with no more than 25 users or 50 devices. It includes Windows Server, Exchange Server, Windows SharePoint Services, and Microsoft Outlook. Application server technologies are tightly integrated to provide and offer management benefits such as integrated setup, enhanced monitoring, Remote Web Workplace, a unified management console, and remote access.
Windows Server Essentials 2019 was the last release of this product. Microsoft has since discontinued this suite in favor of Microsoft 365 and Microsoft Azure. Those holding an «Essentials» license receive an activation key for Windows Server 2022 instead.
History[edit]
As Small Business Server[edit]
Initially, Microsoft marketed the Small Business Server (SBS) an edition of Microsoft BackOffice Server. With the release of Windows 2000, however, Microsoft spun off Small Business Server 2000 as a separate offering. Until this point, the Premium editions of SBS included SQL Server, ISA Server, and FrontPage. SBS 2003 and later all bear the «Windows» brand and are editions of Windows Server.
SBS 2008 came with an edition of Windows Server 2008 bears the name Windows Server 2008 for Windows Essential Server Solutions («WinWESS»), also known as Windows Server 2008 Standard FE.[3] This edition of Windows Server 2008 is available outside the product suite, supporting a maximum of 15 Client Access Licenses.[4] SBS 2008 Premium edition does not include ISA Server but includes SQL Server 2008. Those upgrading to SBS 2008 Premium edition via Software Assurance were compensated with a free license for the latest version of ISA Server.[5] In December 2008, Microsoft also introduced a Windows Essential Business Server product aimed at medium-sized businesses, but this was discontinued in June 2010 due to low demand.
SBS 2011 was available in Essentials, Standard, and Premium editions. The Essentials edition is a scaled down version for 1 to 25 users; the other editions are based on the Windows Server codebase and include Exchange Server, Windows SharePoint Services, and Microsoft Outlook in addition to what comes with Window Server.
As Windows Server Essentials[edit]
Starting with Windows Server 2012, Microsoft renamed SBS to Windows Server Essentials. Four versions of Windows Server Essentials were released along with their Windows Server siblings: 2012, 2012 R2,[6] 2016, and 2019.[7] Windows Server 2019 Essentials removed many features found in previous versions of Windows Server Essentials because the «Windows Server Essentials Experience» role was not included in any of the Windows Server 2019 SKUs. This includes Essentials Connector, Client PC Backup, Office 365 integration, Remote Web Access, and the Windows Server Essentials Dashboard.[8][9]
Discontinuation[edit]
In September 2018, the Windows Server hinted that Windows Server Essentials 2019 might be the last version of this product.[10] Following the release of Windows Server 2022, Microsoft announced that their Windows Server Essentials 2022 offering is merely a customized licensing scheme for the Standard edition of Windows Server 2022.[11]
At the time of discontinuation, Microsoft offered the same software as part of its Microsoft 365 and Microsoft Azure plans.
Versions[edit]
- October 22, 1997 – BackOffice Small Business Server 4.0
- Consists of Windows NT Server 4.0 SP3 and includes Exchange Server 5.0 SP1, Internet Information Services 3.0, SQL Server 6.5 SP3, Proxy Server 1.0, Internet Explorer 3.02 or 4.01, and Outlook 97; allows 25 client licenses.
- May 24, 1999 – BackOffice Small Business Server 4.5
- Consists of Windows NT Server 4.0 SP4 and includes Exchange Server 5.5 SP2, IIS 4.0, SQL Server 7.0, Proxy Server 2.0, Internet Explorer 5.0, Outlook 2000, and FrontPage 2000; allows 50 client licenses.
- February 21, 2001 – Microsoft Small Business Server 2000
- Consists of Windows 2000 Server (including Internet Explorer 5.0 and IIS 5.0) and includes Exchange 2000 Server, SQL Server 2000 Standard Edition, Internet Security & Acceleration Server 2000, Outlook 2000 and FrontPage 2000; allows 50 client licenses.
- October 9, 2003 – Windows Small Business Server 2003 (codenamed Bobcat)
- Consists of Windows Server 2003 and includes Microsoft Exchange Server 2003, Microsoft Outlook 2003, Windows SharePoint Services 2.0, and optionally Microsoft SQL Server 2000, ISA Server 2000 (upgrade to ISA Server 2004 in Small Business Server Premium SP1), and Microsoft FrontPage 2003 in Premium edition; allows 75 client licenses. Service Pack 1 for Windows Small Business Server 2003 was released on July 25, 2005.[12]
- July 29, 2006 – Windows Small Business Server 2003 R2
- Consists of Windows Server 2003 and includes Microsoft Exchange Server 2003, Microsoft Outlook 2003, Windows SharePoint Services 2.0, and optionally Microsoft SQL Server 2005 Workgroup Edition, ISA Server 2004, and Microsoft FrontPage 2003 in Premium edition; allows 75 client licenses. A major addition is a built-in patch management tool optimized for small businesses, based on Microsoft Windows Server Update Services. Exchange database size limit is set to 18 GB by default but can be expanded to 75 GB using a registry key.
- August 21, 2008[13] – Windows Small Business Server 2008 (codenamed Cougar)
- Consists of Windows Server 2008 and includes Microsoft Exchange Server 2007, Windows SharePoint Services 3.0 and 120-day trial subscriptions of new security products from Microsoft, namely, Forefront Security for Exchange and Windows Live OneCare for Server.[14][15] The standard edition of SBS 2008 will be a single server product for small businesses. The premium edition will contain a license for Windows Server 2008 and SQL Server 2008 Standard Edition, with the option to run SQL Server on either the main SBS server, or a second server. The premium edition will therefore be targeted at dual-server scenarios such as terminal services application sharing, line of business applications, edge security, secondary domain controllers, and virtualization.[16] In addition to features present in previous versions, new features include:
- A streamlined administration and management console that is designed around tasks to be accomplished rather than underlying technologies[17]
- Built-in support for registering and configuring domain name and DNS records via multiple registrars
- Monitoring reports that gather data from both servers and clients on the network, including Security Center status (anti-virus, spyware, and client firewall) from all the clients
- New features in the Remote Web Workplace, such as the ability to define default and allowed PCs for each user
- Office Live Small Business integration for and configuring a public web site or extranet
- New server backup features, based on the incremental block-based backup technology in Windows Server 2008 (tape backup no longer supported via native tools, but continues to be supported via third parties)
- SBS 2008 requires installation behind a separate network firewall device. In contrast with SBS 2003, it does not support being installed directly on the edge of the network, ISA Server is no longer bundled and a dual-NIC configuration is not possible.[18]
- Migration of 32-bit SBS 2003 versions to 64-bit SBS 2008 and SBS2011 has no in place upgrade and can be problematic.[19][20][21] Inability to upgrade Sharepoint[22] (WSS 2.0) by WSS 3.0 or SharePoint 2010 Foundation.
- SBS 2008 was released to manufacturing on August 21, 2008[23] and was launched on November 12, 2008.[24] Windows Small Business Server 2008 supports organizations with up to 75 users or devices.[15] A notable change from SBS 2003 is that CALs are not enforced electronically.[25]
- December 13, 2010 – Windows Small Business Server 2011
- Microsoft announced two successors to the SBS series during WPC 2010, both based on Windows Server 2008 R2. One successor (code name «Aurora») supports a maximum of 25 users, does not include Exchange, SharePoint and Windows Server Update Services (WSUS), and is oriented to attach cloud services. The other successor (code name «SBS 7») is the more direct successor of SBS 2008, and continues to support a maximum of 75 users, and includes Exchange, SharePoint and WSUS.
- Late in 2010, Microsoft announced the official branding for the 2011 wave: SBS «7» became «Windows Small Business Server 2011 Standard,» and «Aurora» was christened «Windows Small Business Server 2011 Essentials.» Whereas formerly, the premium edition of SBS was packaged as a superset of the standard edition, in the 2011 wave, it was be available as an add-on, containing standalone copies of SQL Server 2008 R2 and Windows Server 2008 R2. It could be added to either SBS 2011 Essentials or Standard.
- In mid-December, Microsoft released SBS 2011 Standard to TechNet and MSDN subscribers for evaluation. Microsoft released SBS 2011 Standard to volume licensing customers in early January and as a trial in mid-January. SBS 2011 requires an Internet connection.
- October 10, 2012 – Windows Server 2012 Essentials
- In July 2012, Microsoft announced that there would not be another SBS product. Rather, Windows Server 2012 Essentials succeeded SBS Essentials.[26] Windows Server 2012 Essentials does not include Microsoft Exchange Server, which is used for messaging and collaboration, including the ability to host email. Windows Server Essentials and its successors were designed for small businesses with up to 25 users and 50 devices.
- September 9, 2013 – Windows Server 2012 R2 Essentials
- October 12, 2016 – Windows Server 2016 Essentials
- November 13, 2018 – Windows Server 2019 Essentials
- Windows Server 2019 Essentials removed many features found in previous versions of Windows Server Essentials, including Remote Web Access, Essentials Connector, Client PC Backup, Office 365 integration and the Windows Server Essentials Dashboard.[8][9] It is the last version of Windows Server Essentials.
Licensing[edit]
Normally, Microsoft licenses its on-premises server products on a per-seat or per-user basis, i.e., the licensing cost depends on how many users or computers use these products. Businesses that install them require to obtain client access licenses (CALs). Windows Server 2012 Essentials and later do not need any CALs. However, this has not always been the case. Earlier versions – Windows Small Business Server (SBS) – had their own types of CAL, and included the user CALs for Windows Server, Exchange Server, and eventually SQL Server. The SBS CALs cost more than the Windows Server CALs, but less than the sum of separate access licenses for the two or three servers.
Windows Small Business Server has the following design restrictions:[27]
- Only one computer in the domain can run SBS. The domain supports multiple servers (including additional domain controllers) running any other operating system, such as Windows Server, but only one SBS.
- SBS must be the root of the Active Directory forest.
- SBS cannot establish a trust relationship with any other domains or have sub-domains.
- SBS is limited to 75 users or devices depending on the type of CAL.
- SBS 2003 and earlier are limited to no more than 4 GB of RAM. SBS 2008 supports a maximum of 32GB. It requires a minimum of 4GB for installation, but needs more for performance.
- SBS 2003 R2 and earlier are only available for the IA-32 (32-bit) architecture.
- SBS 2008 is only available for the x86-64 architecture.
- The SQL Server that comes with SBS 2008 is «SQL Server 2008 Standard Edition for Small Business.».[28][29] It cannot be installed outside a network that has a domain controller, and must have fewer than 75 PCs or users (depending on the CAL.)
- Remote Desktop Services on SBS is restricted to two simultaneous sessions. (Change from SBS 2000 policy)[30] Terminal Services in application sharing mode needs to be run on a second server running a separately obtained copy of Windows Server.
To remove these restrictions and upgrade to regular editions of Windows Server, Exchange Server, SQL Server and ISA Server, there was a Windows Small Business Server 2003 R2 Transition Pack.[31]
References[edit]
- ^ «What’s New in Windows Server 2019 Essentials». Windows Server Essentials documentations. Microsoft – via Microsoft Docs.
- ^ «Frequently Asked Questions» (PDF). Windows Server Essentials portal. Microsoft. October 5, 2012. p. 1. Retrieved July 11, 2013.
Q: Why did Microsoft change the name of Windows Small Business Server Essentials to Windows Server Essentials? A: […]
- ^ «Windows Small Business Server 2008 Technical FAQ». Microsoft Technet. Microsoft Corporation. Retrieved June 9, 2010.
Windows Server 2008 Standard FE is the shortened name for Windows Server 2008 for Windows Essential Server Solutions. When you run the Winver tool you will see this reference.
- ^ «Managing Licenses in Windows Server 2008 for Windows Essential Server Solutions». Technet.microsoft.com. March 10, 2009. Retrieved August 30, 2012.
- ^ «SBS 2008 RC1 and EBS 2008 RC1 finalised». Geekzone.co.nz. Retrieved August 30, 2012.
- ^ «Windows Server Essentials». Microsoft Technet. Microsoft. Retrieved February 10, 2013.
- ^ «Update on Windows Server 2019 availability». Windows Server Blog. Microsoft. November 13, 2018.
- ^ a b eross-msft. «What’s New in Windows Server 2019 Essentials». docs.microsoft.com. Retrieved December 17, 2020.
- ^ a b «Windows Server 2019 — end of an era». The Office Maven. September 7, 2018.
- ^ Pivovarova, Irina; Apolinario, Vinicius (September 5, 2018). «Windows Server 2019 Essentials update». Microsoft Windows Server Blog. Microsoft.
All of this led to our decision to offer yet another version of on-premises server for small businesses – Windows Server 2019 Essentials. This edition will be released along with the other editions of Windows Server 2019 later this year. There is a strong possibility that this could be the last edition of Windows Server Essentials.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ «Get started with Windows Server Essentials». Windows Server Essentials documentations. Microsoft. September 3, 2021.
With Windows Server 2022, the Essentials edition is available to purchase from OEMs only, however there is no specific installation media. Instead, an Essentials edition product key is used to activate the Standard edition of Windows Server 2022 and means you get all the same features.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ «Windows Small Business Server 2003 Service Pack 1». Download Center. Microsoft. August 18, 2012.
- ^ Paron, Dean (October 21, 2008). «SBS 2008: Released to Manufacturing!». The Windows Server Essentials and Small Business Server Blog. Microsoft – via Blog Archive.
- ^ «SBS 2008 editions». microsoft.com. Microsoft. Archived from the original on February 25, 2008.
- ^ a b «Introducing the Windows Essential Server Solutions Family of Products». Blogs.technet.com. February 20, 2008. Retrieved August 30, 2012.
- ^ SBS Server #1 is required to be 64-bit; SBS Server #2 will provide the option to run as either 32-bit or 64-bit. Microsoft unveils new Small Business Server
- ^ «Windows SBS Console». Microsoft. August 17, 2008. Archived from the original on August 17, 2008. Retrieved March 26, 2021.
- ^ «Preparing your Network for Small Business Server 2008». Sbs.seandaniel.com. May 1, 2008. Retrieved August 30, 2012.
- ^ «Migrate to Windows Small Business Server 2008 from Windows Small Business Server 2003». Technet.microsoft.com. Retrieved August 30, 2012.
- ^ «Migrate to Windows Small Business Server 2011 Standard from Windows Small Business Server 2003». Technet.microsoft.com. Retrieved August 30, 2012.
- ^ e.g. Migration Tool has increased default 7 day Active Directory coexistence period to 21 days to address this
- ^ «Installing Windows SharePoint Services 3.0 on a Server Running Windows Small Business Server 2003». Technet.microsoft.com. April 27, 2009. Retrieved August 30, 2012.
- ^ «Small Business Server 2008 (SBS 2008) Released to Manufacturing». Geekzone.co.nz. Retrieved August 30, 2012.
- ^ «Microsoft SMB Community Blog». Blogs.msdn.com. Retrieved August 30, 2012.
- ^ «SBS 2008 and the usage of CAL’s». Social.technet.microsoft.com. Retrieved August 30, 2012.
- ^ Windows Small Business Server Essentials becomes Windows Server 2012 Essentials
- ^ «Windows Small Business Server 2003 R2: Frequently Asked Questions». Microsoft. July 11, 2006. Retrieved September 2, 2006.
- ^ «Microsoft SQL Server Editions | The Cloud Ready Information Platform». Microsoft.com. Retrieved August 30, 2012.
- ^ «Microsoft Windows Small Business Server (SBS) Features». Microsoft.com. Retrieved August 30, 2012.
- ^ «Licensing – Windows Small Business Server 2003 R2: Frequently Asked Questions». Microsoft. Retrieved September 2, 2006.
- ^ «Windows Small Business Server 2003 R2 Transition Pack». Microsoft.com. Retrieved August 30, 2012.
External links[edit]
- The Windows Server Essentials and Small Business Server Blog in Microsoft Blog Archive
- SBSFaq.com, an independent blog
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia

Windows Server 2019 Essentials displaying the Windows Server Essentials Server Manager |
|
| Developer(s) | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| Final release |
2019 |
| Type | Operating system |
| License | Commercial proprietary software |
| Website | microsoft.com/windows-server/ |
Windows Server Essentials (formerly Small Business Server or SBS)[2] is an integrated server suite from Microsoft for businesses with no more than 25 users or 50 devices. It includes Windows Server, Exchange Server, Windows SharePoint Services, and Microsoft Outlook. Application server technologies are tightly integrated to provide and offer management benefits such as integrated setup, enhanced monitoring, Remote Web Workplace, a unified management console, and remote access.
Windows Server Essentials 2019 was the last release of this product. Microsoft has since discontinued this suite in favor of Microsoft 365 and Microsoft Azure. Those holding an «Essentials» license receive an activation key for Windows Server 2022 instead.
History[edit]
As Small Business Server[edit]
Initially, Microsoft marketed the Small Business Server (SBS) an edition of Microsoft BackOffice Server. With the release of Windows 2000, however, Microsoft spun off Small Business Server 2000 as a separate offering. Until this point, the Premium editions of SBS included SQL Server, ISA Server, and FrontPage. SBS 2003 and later all bear the «Windows» brand and are editions of Windows Server.
SBS 2008 came with an edition of Windows Server 2008 bears the name Windows Server 2008 for Windows Essential Server Solutions («WinWESS»), also known as Windows Server 2008 Standard FE.[3] This edition of Windows Server 2008 is available outside the product suite, supporting a maximum of 15 Client Access Licenses.[4] SBS 2008 Premium edition does not include ISA Server but includes SQL Server 2008. Those upgrading to SBS 2008 Premium edition via Software Assurance were compensated with a free license for the latest version of ISA Server.[5] In December 2008, Microsoft also introduced a Windows Essential Business Server product aimed at medium-sized businesses, but this was discontinued in June 2010 due to low demand.
SBS 2011 was available in Essentials, Standard, and Premium editions. The Essentials edition is a scaled down version for 1 to 25 users; the other editions are based on the Windows Server codebase and include Exchange Server, Windows SharePoint Services, and Microsoft Outlook in addition to what comes with Window Server.
As Windows Server Essentials[edit]
Starting with Windows Server 2012, Microsoft renamed SBS to Windows Server Essentials. Four versions of Windows Server Essentials were released along with their Windows Server siblings: 2012, 2012 R2,[6] 2016, and 2019.[7] Windows Server 2019 Essentials removed many features found in previous versions of Windows Server Essentials because the «Windows Server Essentials Experience» role was not included in any of the Windows Server 2019 SKUs. This includes Essentials Connector, Client PC Backup, Office 365 integration, Remote Web Access, and the Windows Server Essentials Dashboard.[8][9]
Discontinuation[edit]
In September 2018, the Windows Server hinted that Windows Server Essentials 2019 might be the last version of this product.[10] Following the release of Windows Server 2022, Microsoft announced that their Windows Server Essentials 2022 offering is merely a customized licensing scheme for the Standard edition of Windows Server 2022.[11]
At the time of discontinuation, Microsoft offered the same software as part of its Microsoft 365 and Microsoft Azure plans.
Versions[edit]
- October 22, 1997 – BackOffice Small Business Server 4.0
- Consists of Windows NT Server 4.0 SP3 and includes Exchange Server 5.0 SP1, Internet Information Services 3.0, SQL Server 6.5 SP3, Proxy Server 1.0, Internet Explorer 3.02 or 4.01, and Outlook 97; allows 25 client licenses.
- May 24, 1999 – BackOffice Small Business Server 4.5
- Consists of Windows NT Server 4.0 SP4 and includes Exchange Server 5.5 SP2, IIS 4.0, SQL Server 7.0, Proxy Server 2.0, Internet Explorer 5.0, Outlook 2000, and FrontPage 2000; allows 50 client licenses.
- February 21, 2001 – Microsoft Small Business Server 2000
- Consists of Windows 2000 Server (including Internet Explorer 5.0 and IIS 5.0) and includes Exchange 2000 Server, SQL Server 2000 Standard Edition, Internet Security & Acceleration Server 2000, Outlook 2000 and FrontPage 2000; allows 50 client licenses.
- October 9, 2003 – Windows Small Business Server 2003 (codenamed Bobcat)
- Consists of Windows Server 2003 and includes Microsoft Exchange Server 2003, Microsoft Outlook 2003, Windows SharePoint Services 2.0, and optionally Microsoft SQL Server 2000, ISA Server 2000 (upgrade to ISA Server 2004 in Small Business Server Premium SP1), and Microsoft FrontPage 2003 in Premium edition; allows 75 client licenses. Service Pack 1 for Windows Small Business Server 2003 was released on July 25, 2005.[12]
- July 29, 2006 – Windows Small Business Server 2003 R2
- Consists of Windows Server 2003 and includes Microsoft Exchange Server 2003, Microsoft Outlook 2003, Windows SharePoint Services 2.0, and optionally Microsoft SQL Server 2005 Workgroup Edition, ISA Server 2004, and Microsoft FrontPage 2003 in Premium edition; allows 75 client licenses. A major addition is a built-in patch management tool optimized for small businesses, based on Microsoft Windows Server Update Services. Exchange database size limit is set to 18 GB by default but can be expanded to 75 GB using a registry key.
- August 21, 2008[13] – Windows Small Business Server 2008 (codenamed Cougar)
- Consists of Windows Server 2008 and includes Microsoft Exchange Server 2007, Windows SharePoint Services 3.0 and 120-day trial subscriptions of new security products from Microsoft, namely, Forefront Security for Exchange and Windows Live OneCare for Server.[14][15] The standard edition of SBS 2008 will be a single server product for small businesses. The premium edition will contain a license for Windows Server 2008 and SQL Server 2008 Standard Edition, with the option to run SQL Server on either the main SBS server, or a second server. The premium edition will therefore be targeted at dual-server scenarios such as terminal services application sharing, line of business applications, edge security, secondary domain controllers, and virtualization.[16] In addition to features present in previous versions, new features include:
- A streamlined administration and management console that is designed around tasks to be accomplished rather than underlying technologies[17]
- Built-in support for registering and configuring domain name and DNS records via multiple registrars
- Monitoring reports that gather data from both servers and clients on the network, including Security Center status (anti-virus, spyware, and client firewall) from all the clients
- New features in the Remote Web Workplace, such as the ability to define default and allowed PCs for each user
- Office Live Small Business integration for and configuring a public web site or extranet
- New server backup features, based on the incremental block-based backup technology in Windows Server 2008 (tape backup no longer supported via native tools, but continues to be supported via third parties)
- SBS 2008 requires installation behind a separate network firewall device. In contrast with SBS 2003, it does not support being installed directly on the edge of the network, ISA Server is no longer bundled and a dual-NIC configuration is not possible.[18]
- Migration of 32-bit SBS 2003 versions to 64-bit SBS 2008 and SBS2011 has no in place upgrade and can be problematic.[19][20][21] Inability to upgrade Sharepoint[22] (WSS 2.0) by WSS 3.0 or SharePoint 2010 Foundation.
- SBS 2008 was released to manufacturing on August 21, 2008[23] and was launched on November 12, 2008.[24] Windows Small Business Server 2008 supports organizations with up to 75 users or devices.[15] A notable change from SBS 2003 is that CALs are not enforced electronically.[25]
- December 13, 2010 – Windows Small Business Server 2011
- Microsoft announced two successors to the SBS series during WPC 2010, both based on Windows Server 2008 R2. One successor (code name «Aurora») supports a maximum of 25 users, does not include Exchange, SharePoint and Windows Server Update Services (WSUS), and is oriented to attach cloud services. The other successor (code name «SBS 7») is the more direct successor of SBS 2008, and continues to support a maximum of 75 users, and includes Exchange, SharePoint and WSUS.
- Late in 2010, Microsoft announced the official branding for the 2011 wave: SBS «7» became «Windows Small Business Server 2011 Standard,» and «Aurora» was christened «Windows Small Business Server 2011 Essentials.» Whereas formerly, the premium edition of SBS was packaged as a superset of the standard edition, in the 2011 wave, it was be available as an add-on, containing standalone copies of SQL Server 2008 R2 and Windows Server 2008 R2. It could be added to either SBS 2011 Essentials or Standard.
- In mid-December, Microsoft released SBS 2011 Standard to TechNet and MSDN subscribers for evaluation. Microsoft released SBS 2011 Standard to volume licensing customers in early January and as a trial in mid-January. SBS 2011 requires an Internet connection.
- October 10, 2012 – Windows Server 2012 Essentials
- In July 2012, Microsoft announced that there would not be another SBS product. Rather, Windows Server 2012 Essentials succeeded SBS Essentials.[26] Windows Server 2012 Essentials does not include Microsoft Exchange Server, which is used for messaging and collaboration, including the ability to host email. Windows Server Essentials and its successors were designed for small businesses with up to 25 users and 50 devices.
- September 9, 2013 – Windows Server 2012 R2 Essentials
- October 12, 2016 – Windows Server 2016 Essentials
- November 13, 2018 – Windows Server 2019 Essentials
- Windows Server 2019 Essentials removed many features found in previous versions of Windows Server Essentials, including Remote Web Access, Essentials Connector, Client PC Backup, Office 365 integration and the Windows Server Essentials Dashboard.[8][9] It is the last version of Windows Server Essentials.
Licensing[edit]
Normally, Microsoft licenses its on-premises server products on a per-seat or per-user basis, i.e., the licensing cost depends on how many users or computers use these products. Businesses that install them require to obtain client access licenses (CALs). Windows Server 2012 Essentials and later do not need any CALs. However, this has not always been the case. Earlier versions – Windows Small Business Server (SBS) – had their own types of CAL, and included the user CALs for Windows Server, Exchange Server, and eventually SQL Server. The SBS CALs cost more than the Windows Server CALs, but less than the sum of separate access licenses for the two or three servers.
Windows Small Business Server has the following design restrictions:[27]
- Only one computer in the domain can run SBS. The domain supports multiple servers (including additional domain controllers) running any other operating system, such as Windows Server, but only one SBS.
- SBS must be the root of the Active Directory forest.
- SBS cannot establish a trust relationship with any other domains or have sub-domains.
- SBS is limited to 75 users or devices depending on the type of CAL.
- SBS 2003 and earlier are limited to no more than 4 GB of RAM. SBS 2008 supports a maximum of 32GB. It requires a minimum of 4GB for installation, but needs more for performance.
- SBS 2003 R2 and earlier are only available for the IA-32 (32-bit) architecture.
- SBS 2008 is only available for the x86-64 architecture.
- The SQL Server that comes with SBS 2008 is «SQL Server 2008 Standard Edition for Small Business.».[28][29] It cannot be installed outside a network that has a domain controller, and must have fewer than 75 PCs or users (depending on the CAL.)
- Remote Desktop Services on SBS is restricted to two simultaneous sessions. (Change from SBS 2000 policy)[30] Terminal Services in application sharing mode needs to be run on a second server running a separately obtained copy of Windows Server.
To remove these restrictions and upgrade to regular editions of Windows Server, Exchange Server, SQL Server and ISA Server, there was a Windows Small Business Server 2003 R2 Transition Pack.[31]
References[edit]
- ^ «What’s New in Windows Server 2019 Essentials». Windows Server Essentials documentations. Microsoft – via Microsoft Docs.
- ^ «Frequently Asked Questions» (PDF). Windows Server Essentials portal. Microsoft. October 5, 2012. p. 1. Retrieved July 11, 2013.
Q: Why did Microsoft change the name of Windows Small Business Server Essentials to Windows Server Essentials? A: […]
- ^ «Windows Small Business Server 2008 Technical FAQ». Microsoft Technet. Microsoft Corporation. Retrieved June 9, 2010.
Windows Server 2008 Standard FE is the shortened name for Windows Server 2008 for Windows Essential Server Solutions. When you run the Winver tool you will see this reference.
- ^ «Managing Licenses in Windows Server 2008 for Windows Essential Server Solutions». Technet.microsoft.com. March 10, 2009. Retrieved August 30, 2012.
- ^ «SBS 2008 RC1 and EBS 2008 RC1 finalised». Geekzone.co.nz. Retrieved August 30, 2012.
- ^ «Windows Server Essentials». Microsoft Technet. Microsoft. Retrieved February 10, 2013.
- ^ «Update on Windows Server 2019 availability». Windows Server Blog. Microsoft. November 13, 2018.
- ^ a b eross-msft. «What’s New in Windows Server 2019 Essentials». docs.microsoft.com. Retrieved December 17, 2020.
- ^ a b «Windows Server 2019 — end of an era». The Office Maven. September 7, 2018.
- ^ Pivovarova, Irina; Apolinario, Vinicius (September 5, 2018). «Windows Server 2019 Essentials update». Microsoft Windows Server Blog. Microsoft.
All of this led to our decision to offer yet another version of on-premises server for small businesses – Windows Server 2019 Essentials. This edition will be released along with the other editions of Windows Server 2019 later this year. There is a strong possibility that this could be the last edition of Windows Server Essentials.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ «Get started with Windows Server Essentials». Windows Server Essentials documentations. Microsoft. September 3, 2021.
With Windows Server 2022, the Essentials edition is available to purchase from OEMs only, however there is no specific installation media. Instead, an Essentials edition product key is used to activate the Standard edition of Windows Server 2022 and means you get all the same features.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ «Windows Small Business Server 2003 Service Pack 1». Download Center. Microsoft. August 18, 2012.
- ^ Paron, Dean (October 21, 2008). «SBS 2008: Released to Manufacturing!». The Windows Server Essentials and Small Business Server Blog. Microsoft – via Blog Archive.
- ^ «SBS 2008 editions». microsoft.com. Microsoft. Archived from the original on February 25, 2008.
- ^ a b «Introducing the Windows Essential Server Solutions Family of Products». Blogs.technet.com. February 20, 2008. Retrieved August 30, 2012.
- ^ SBS Server #1 is required to be 64-bit; SBS Server #2 will provide the option to run as either 32-bit or 64-bit. Microsoft unveils new Small Business Server
- ^ «Windows SBS Console». Microsoft. August 17, 2008. Archived from the original on August 17, 2008. Retrieved March 26, 2021.
- ^ «Preparing your Network for Small Business Server 2008». Sbs.seandaniel.com. May 1, 2008. Retrieved August 30, 2012.
- ^ «Migrate to Windows Small Business Server 2008 from Windows Small Business Server 2003». Technet.microsoft.com. Retrieved August 30, 2012.
- ^ «Migrate to Windows Small Business Server 2011 Standard from Windows Small Business Server 2003». Technet.microsoft.com. Retrieved August 30, 2012.
- ^ e.g. Migration Tool has increased default 7 day Active Directory coexistence period to 21 days to address this
- ^ «Installing Windows SharePoint Services 3.0 on a Server Running Windows Small Business Server 2003». Technet.microsoft.com. April 27, 2009. Retrieved August 30, 2012.
- ^ «Small Business Server 2008 (SBS 2008) Released to Manufacturing». Geekzone.co.nz. Retrieved August 30, 2012.
- ^ «Microsoft SMB Community Blog». Blogs.msdn.com. Retrieved August 30, 2012.
- ^ «SBS 2008 and the usage of CAL’s». Social.technet.microsoft.com. Retrieved August 30, 2012.
- ^ Windows Small Business Server Essentials becomes Windows Server 2012 Essentials
- ^ «Windows Small Business Server 2003 R2: Frequently Asked Questions». Microsoft. July 11, 2006. Retrieved September 2, 2006.
- ^ «Microsoft SQL Server Editions | The Cloud Ready Information Platform». Microsoft.com. Retrieved August 30, 2012.
- ^ «Microsoft Windows Small Business Server (SBS) Features». Microsoft.com. Retrieved August 30, 2012.
- ^ «Licensing – Windows Small Business Server 2003 R2: Frequently Asked Questions». Microsoft. Retrieved September 2, 2006.
- ^ «Windows Small Business Server 2003 R2 Transition Pack». Microsoft.com. Retrieved August 30, 2012.
External links[edit]
- The Windows Server Essentials and Small Business Server Blog in Microsoft Blog Archive
- SBSFaq.com, an independent blog
На чтение 8 мин Просмотров 2.6к. Опубликовано 27.03.2020
Недавно мир увидело свет новое семейство Microsoft Windows Server 2019. Данные об этом присутствуют в интернете, но все они имеют достаточно общий характер. И часто это является причиной того, что узнать более подробно о выпусках, версиях и опциях может оказаться сложнее, чем это некоторым кажется на первый взгляд.
Не для всех очевидно, какие выпуски в настоящий момент уже присутствуют на рынке, и чем они могут отличаться. К примеру, что за конкретные особенности присутствуют у не требующего оплаты продукта Hyper-V Server 2019 и чем они отличают его от Windows Server 2019 Standard? Какой в этом случае используется гипервизор? А есть ли он вообще?
Информация многим столь интересна, что постоянно возникают все новые вопросы, на которые специалисты могут дать утвердительные или отрицательные ответы. Некоторые из них прозвучат так:
- Windows Server 2019 Server Core не преобразуется в Desktop Experience и наоборот;
- Windows Server 2019 Datacenter преобразуется в Стандартный;
- ознакомительная версия свободно продлевается после «пробных» 3 месяцев;
- для удаленного управления Windows Server 2019 Server Core можно использовать «Центр администрирования Windows», предлагаемый браузером Opera.
Но это далеко не все, что интересует пользователей, поэтому нам показалось целесообразным проведение небольшого исследования. Цель – выяснить, какие же продукты существуют в настоящий момент, в чем их коренные отличия? Не лучше ли продолжать использовать «старые добрые версии», широко использующиеся сегодня?
Что новенького?
Специалисты Microsoft пытаются сосредоточить свои усилия на работе в нескольких категориях:
- гибридные варианты с Azure;
- меры по обеспечению безопасности;
- HCI;
- так называемая «быстрая инновация», касающаяся приложений.
Конечно, все больше привыкли к небольшим, лишенным таких масштабов обновлением операционной системы. Windows 19 – это больше, чем очередные изменения. Ярким примером тому становится ATP (Advanced Threat Protection) – прежде он являлся независимым, отдельным продуктом.
Datacenter и Standart
Основными предлагаемыми вариантами новой системы становятся Standart, и, конечно, Datacenter. И тот, и другой может устанавливаться в Desktop Experience или Server Core. Необходимо рассмотреть коренные отличия между данными выпусками, параллельно обсудив подопции.
Datacenter становится наиболее полным вариантом продуктов семейства, но и наиболее дорогостоящим (согласно оценкам Microsoft). Цена, если сравнивать с аналогичным продуктом 2016 года, действительно, несколько выросла.
Приобретенная лицензия Datacenter предлагает достаточный набор функций и минимальное число лицензионных ограничений из всех вариантов. К примеру, виртуализированные на Datacenter могут автоматически лицензироваться на хосте при учете, что и хостинг, и гостевые варианты будут иметь ту же версию. Подобные «гости» активируются с использованием виртуальной системы (AVMA) в автоматическом режиме.
В Windows Server 2019 заинтересованным лицам представляется определенная система, имеющая средства защиты – это революционная особенность, являющаяся доступной, правда, лишь в Datacenter. Host Gurdian Service ранее присутствовала только в версии 2016 г., а в последнем выпуске доступна уже в версии «Стандарт». Но это является не правилом, а, можно сказать, исключением. В результате хочется сделать некий предварительный вывод: в Windows Server пользователям представлен ряд новых опций тогда как другие часто попросту отключаются. Ряд обретенных функций являются эксклюзивными и предлагаются только для Datacenter, другие становятся доступными и при приобретении более дешевых версий лицензии.
Некоторые функции, к которым привыкли потребители, из Windows Server 1803 удалены – предлагается даже список тех опций, что более не поддерживаются. Необходимо учесть, что приведенный вариант далеко не полон и это, прежде всего, связывается с такими причинами как:
- Windows Server 2019 — последнее обновление 2019 г, а версия 1803 – с варианта 1709. Возможно, в данном варианте было отклонено большее количество функций;
- Windows Server 2019 – это целое, и весьма обширное, семейство предлагаемых пользователю продуктов.
Можно также отметить, что Windows Server 1809 выступает достойной альтернативой Windows Server 2019 Server Core. Server 2019 предстает в качестве канала длительного обслуживания, а вариант 1807 доступен разве что в виде ядра сервера.
Exclusive Capabilities (Datacenter). В наличии имеется ряд способных заинтересовать пользователя возможностей, выгодно отличающих версию 2019 г. (речь идет о Datacenter):
- использование в качестве контроллера сети;
- выявление сети с использованием специальных программ;
- осуществление репликации хранилищ;
- программное выявление хранилищ;
- дедубликация;
- ограничения для использования более одной операционной среды.
Сравним Microsoft и тем, что предлагает новая система. Данное сравнение, скорее, станет перечнем опций, поскольку различия найти сложно – скорее, это дополнение.
Разработчики характеризуют Datacenter как оптимальный вариант для облачных сред и центров, где осуществляется обработка данных. Похоже выглядит описание и стандартного варианта. «Близкий родственник» систем – Hyper-V Server 2019, видимо, удовлетворяющим потребности во всех отношениях пользователем тоже не признается.
Server Core
Вне зависимости от того что предлагает интерфейс, и по аналогии с рядом иных серверов SC предоставляет возможности удаленного администрирования с использованием специализированных инструментов. Среди них – диспетчер серверов, использование удаленного рабочего стола, RSAT и, конечно WAC, который представляет собой центр администрирования.
Среди несомненных плюсов Server Core – меньшая площадь, которую занимает версия, сниженное потребление ресурсов, сниженная уязвимость и проявляемая стойкость к гиператакам. Система представляет меньшую поверхность, возможную для атак, ей требуется незначительное число обновлений и исправлений, а также перезагрузок.
С любым установленным приложением могут быть утеряны какие-то из указанных плюсов. Некоторые доступны уже если речь дет о версии portable и никак не отражаются на работе системы, а значит, способны снизить нагрузку и минимально отразиться на производительности, повлияв на саму возможность уязвимости. Но такой подход не может считаться обязательным в 100% ситуаций.
Desktop Experience – это «классика», являющаяся востребованной еще с эпохи NT. Версия облегчает администрирование благодаря удобному графическому интерфейсу. У представленной системы он аналогичен Windows, но особенности конфигурации гарантируют значительно более высокий уровень безопасности.
Microsoft ранее была предоставлена возможность выбора меж Server Core и Desktop Experience. В актуальном варианте 2019 данная возможность уже не присутствует.
Server Core Limitations и Unsupported Capabilities. В Server Core нет совместимости с некоторыми приложениями и рядом функций, а потому назвать его полноценной заменой Desktop Experience нельзя. В основном, вариант не работает с приложениями, где присутствует графический интерфейс.
Данные о версии Essentias
Вариант признан оптимальным для компаний с небольшим числом сотрудников. Ранее версия Windows Server 2019 Essentials(подробнее по ссылке) носила название Small Business Server (SBS) (Microsoft BackOffice Server). Новая редакция существенно ограничивает возможности, а также варианты получения лицензии, а значит, является самой дешевой в семействе. Согласно утверждениям разработчика, вариант подходит для использования компаниями с количеством сотрудников от 25 до 50 человек. Расширенных функций попросту нет, поскольку такие опции как поддержка миграции хранилищ является доступной в выпусках Datacenter и Standart.
То есть Essentias имеет массу ограничений и это должен понимать пользователь. К примеру, данный вариант может выступать только в качестве единственного контроллера домена, то есть не может присутствовать там вместе с еще одним сервером.
Как правило, Windows Server Essentias предустанавливается, выполняя несколько ролей:
- в качестве доменных служб;
- в качестве DNS-сервера;
- в качестве веб-сервера.
Считается, что все это также можно отнести к варианту 2019 согласно документам, присутствующим в сети. Достаточно просто найти данные, свидетельствующие, что именно более не поддерживается. Вероятно, в 2019 году Essentias стандартизируется и сможет организовать работу в качестве обычного сервера. Данный факт говорит о том, что версия является весьма ограниченной из-за особенностей лицензирования.
Essentias предоставляется с простым интерфейсом (Dashboard). Он очевидно не способствует выполнению ряда комплексных задач в области настроек. Предоставляется упрощенная конфигурация, которая существенно облегчает работу. В принципе, предлагается все, что требуется: комфорт управления сервером.
Но недавно в Microsoft объявлено, что Essentias признается нерабочим — якобы вариант устарел морально. Правда, вскоре решение вернули, и сегодня им дополняется новая версия.
Увы, Essentias Eхperience разработчиками из операционной системы исключается. Это вызывает, скорее, негативные эмоции, поскольку ряд пользователей не знакомы с другими панелями управления и инструментами сервера. Помимо панели инструментов Essentias, Microsoft рекомендуется использование других вариантов управления при направлении клиентов в инструменту, используемому достаточно широко, а именно Центру администрирования.
Анализ возможностей, предоставляемых Windows Server R2-2019
Не так давно Microsoft было выпущено подробное сравнение основных функций ряда систем. Оно включает 11 страниц и, несомненно, будет интересно пользователям. Даже если оставить без внимания то, что компания проигнорировала в данном обзоре Windows Server 2019, оставив его без внимания при публикации на собственной веб-странице, исследование все же является достаточно полным. Оно затрагивает массу нюансов.
Как уже сказано выше, информация присутствует в доступе на официальном сайте, версии сравниваются по ряду критериев:
- гибридные варианты с Azure;
- уровень безопасности;
- HCI;
- использование для приложений «быстрых инноваций.
Все эти сферы в настоящий момент активно продвигаются, внедряются инновации на высоком уровне.
Мы проанализировали различия и уникальные черты приложений Windows Server 2019. Надеемся, что благодаря данному материалу пользователи с легкостью сориентируются в разнообразии продуктов Windows.
As mentioned in my previous post, Microsoft has completely removed the Windows Server Essentials Experience (WSEE) server role from Windows Server 2019. However, since the entire Windows Server Essentials Experience is basically just an elaborate .NET application that is installed on top of the Windows Server operating system (and not some tightly integrated component of the OS itself), it can quite readily be installed on Windows Server 2019 (and beyond).
Background Information And Proof Of Concept
Windows Server 2016 is built upon the Windows 10 version 1607 platform, and so it stands to reason that any .NET application that runs on it “should” run equally well on Windows Server 2019 (which is built upon the similar, but newer, Windows 10 version 1809 platform). This certainly holds true for the Windows Server Essentials Experience .NET application seeing as it runs exactly the same under Windows Server 2019 as it does under Windows Server 2016.
To install Windows Server Essentials Experience on Windows Server 2019, all that needs to be done is for you to copy its required files and registry entries from Windows Server 2016 over to Windows Server 2019, add its prerequisite server roles and features, create its required services, and then complete its setup process by running the Configure Windows Server Essentials wizard. No file modifications, complicated system changes, or so-called “hacks” are required whatsoever (it’s 100% plug-n-play). And, as you can see from the following screenshots, everything works quite nicely once it has been properly installed and configured.
• The “Configure Windows Server Essentials” wizard works perfectly when performing the initial configuration of Windows Server Essentials on Windows Server 2019:
• The configuration wizard even works when Windows Server 2019 is joined to an existing domain (i.e. when it is running as a member server, rather than acting as the primary domain controller):
After Windows Server Essentials has been successfully configured, you can then simply open up the server Dashboard (as usual) and start enjoying all the features of Windows Server Essentials Experience on Windows Server 2019…
• Client Connect and Client Backup works:
• Server Backup works:
• Storage (Server Folders, Storage Spaces, etc.) works:
• Anywhere Access / Remote Web Access works:
• Add-ins work (including our very own WSE RemoteApp 2016 and WSE WorkFolders 2016):
Everything works exactly as it does under Windows Server 2016!
Obviously, doing this will never be sanctioned nor supported by Microsoft, and so you may be asking yourself why not just stick with using Windows Server 2016 seeing as it will be fully supported by Microsoft for many years to come? While you certainly can (and should) do that, probably the best answer I can give you here is… Because you can! That being said, it would also be good for me to mention that since Windows Server 2019 has now reached general availability (A.K.A. RTM), there will come a time in the not too distant future, when Microsoft will stop selling Windows Server 2016 licenses. And so being able to do this will allow those folks who wish to set up a new server with Windows Server Essentials Experience to continue to be able to do so once those Windows Server 2016 licenses become hard (if not impossible) to find. It will also allow those folks who would like to enjoy the added security, and other benefits, that come along with using Windows Server 2019 to be able to continue using Windows Server Essentials Experience (client computer backup, Remote Web Access, etc.) on their Small Office / Home Office (SOHO) servers.
How To Get Started
The installation can be performed by grabbing the install.wim file from a Windows Server 2016 Essentials installation disc (or from a mounted ISO image), and then mounting and extracting it using the Deployment Image Servicing and Management (DISM) command-line tool by following the steps Microsoft provides here. After doing that, grab all of the required files (including the ones in the GAC), extract the required registry entries, and copy them over to Windows Server 2019. Then use Server Manager to add the prerequisite server roles and features, create the required services, and use PowerShell to start the initial configuration of Windows Server Essentials. That should be enough information to get you started, and well on your way to, installing Windows Server Essentials Experience from Windows Server 2016 on Windows Server 2019. If you happen to run into any snags along the way, or just need a pointer or two, you can ask your question(s) over on our Questions & Answers (Q&A) forum, and I’ll do my best to try and help you out.
UPDATE: See this comment for a list of steps that can be used to manually install Windows Server Essentials Experience onto Windows Server 2019 (NO LONGER RECOMMENDED!).
💡 ALTERNATIVELY (and MUCH BETTER), if you happen to own a license for one of our software products, then you can contact us with the User Name from the license of your purchased product, and we’ll be more than happy to share (at no additional charge) a password that you can enter below in order to download the WSEE Installer package (i.e. MSI file) that we’ve built for our own use in installing (and uninstalling) Windows Server Essentials Experience on Windows Server 2019 and beyond:
The WSEE Installer makes installing Windows Server Essentials Experience (WSEE) on Windows Server 2019 / 2022 / vNext super simple! All that needs to be done is for you to install Windows Server 2019 / 2022 / vNext (Standard or Datacenter; the Windows Server 2019 Essentials SKU is supported, but NOT recommended), with the Desktop Experience GUI in the language of your choice, onto your server and then run the WSEE Installer package’s MSI file directly from the server’s desktop. The WSEE Installer will handle installing all required files, registry entries, prerequisite server roles/features, services, permissions, etc., and then launch the “Configure Windows Server Essentials” wizard in order to walk you through configuring Windows Server Essentials on your server (as shown in the images above). The WSEE Installer will even monitor your installation and alert you whenever updates become available (via a health alert that gets displayed within the server Dashboard, and optionally emailed to you via the Windows Server Essentials server’s built-in Health Report Add-In feature). Available updates can then be, quickly and easily, installed via our WSEE Updater program. 😎
➡ INFO: The WSEE Installer does so much more for you than can ever be achieved with a manual installation of WSEE, that we no longer recommend folks attempt to install WSEE manually. Using the WSEE Installer will net you a MUCH MORE complete / proper / secure (and hassle free) installation of WSEE (including alerts whenever updates become available, and a simple/easy means of installing the updates via our WSEE Updater program), and so we now STRONGLY RECOMMEND that everyone use it instead.
NOTE: We DO NOT SELL the WSEE Installer (so please don’t bother asking us to). It is ONLY made available to our existing customers. If you do not want to purchase one of our products, then you will need to manually install WSEE on Windows Server 2019 by following the list of steps that have been provided below (NO LONGER RECOMMENDED!).
NOTE: You may use the WSEE Installer to install WSEE on a single server only (i.e. it’s one WSEE installation per purchased product). If you wish to use the WSEE Installer to install WSEE on multiple servers (for testing or migration purposes, for other clients, family members, friends, etc.), then each server installation MUST be associated with a unique licensee (i.e. User Name) from one of our software products. For additional info see: WSEE Installer policy
INFO: The WSEE Installer was built using Windows Server 2016 Standard OS Build 14393.4169 as the source. It is available in Dutch, English, French, German, Italian, Spanish, etc. Be sure to specify your language preference when requesting download access. The language of the WSEE Installer you use should match the language of the installation media used to install Windows Server onto your server (i.e. don’t mismatch the languages).
💡 UPDATE (1/26/2023): The WSEE Installer Version 10.0.14393.4169 (Revision 20) is available for download now (by entering a password below). Click here to see what’s new!
❗ NOTE: If you’ve installed WSEE on your server via any prior version of the WSEE Installer, use the WSEE Updater to bring your existing WSEE installation up-to-date.
Enter Password to Download:
Enter Password to Download:
Enter Password to Download:
Enter Password to Download:
Enter Password to Download:
Enter Password to Download:
Enter Password to Download:
Enter Password to Download:
Enter Password to Download:
Enter Password to Download:
INFO: Our WSE RemoteApp 2016 and WSE WorkFolders 2016 products run splendidly on Windows Server 2019 / 2022 / vNext with WSEE installed. Your existing, or newly purchased, license covers the use of the product on Windows Server 2016, 2019, 2022, or vNext.
Suggestions, Limitations, and Known Issues
• While in-place upgrades and domain migrations from earlier versions of Windows Server (Essentials) work just fine, I myself highly recommend that you start off with a brand new/clean (out-of-the-box) instance of Windows Server 2019 / 2022 / vNext Standard or Datacenter (with the Desktop Experience GUI in the language of your choice), that has all of the latest Windows Updates installed. The server may be natively joined to a domain if desired, but make sure that no other server roles, features or applications have been installed.
• You should NOT attempt to install Windows Server Essentials Experience on the Windows Server 2019 Essentials SKU (which, despite its name, has absolutely nothing whatsoever to do with “Essentials” as we currently know it). This is because Microsoft has removed all of the Remote Desktop Services roles from the SKU, and so the required Remote Desktop Gateway role will not be available for use by the Anywhere Access / Remote Web Access feature of Windows Server Essentials. Save yourself the time and hassle, and just use Windows Server 2019 Standard or Datacenter instead (and don’t fret about silly CALs). If needed, you can convert Windows Server 2019 Essentials into Standard or Datacenter by running one of the DISM commands shown below.
NOTE: You can download an evaluation version of Windows Server 2019 (Standard or Datacenter), in ISO format, from the Microsoft Evaluation Center here. Or, you can download an evaluation version of Windows Server 2022 (Standard or Datacenter), in ISO format, from the Microsoft Evaluation Center here.
INFO: You can evaluate the product for up to 180 days, and you can extend the trial period for another full 180 days (up to six times for a grand total of 3 years) by running the following command from an elevated command prompt:
slmgr -rearm
INFO: You can run one of the following commands, from an elevated command prompt, in order to convert the evaluation version into a regular retail version (Standard or Datacenter) using a purchased Product Key:
DISM /online /Set-edition:ServerStandard /ProductKey:XXXXX-XXXXX-XXXXX-XXXXX-XXXXX /AcceptEula
DISM /online /Set-edition:ServerDatacenter /ProductKey:XXXXX-XXXXX-XXXXX-XXXXX-XXXXX /AcceptEula
💡 HINT: You can run one of the following commands, from an elevated command prompt, in order to convert the evaluation version into a volume-licensed version (Standard or Datacenter) using a KMS Client Setup Key:
Windows Server 2019:
DISM /online /Set-edition:ServerStandard /ProductKey:N69G4-B89J2-4G8F4-WWYCC-J464C /AcceptEula
DISM /online /Set-edition:ServerDatacenter /ProductKey:WMDGN-G9PQG-XVVXX-R3X43-63DFG /AcceptEula
Windows Server 2022:
DISM /online /Set-edition:ServerStandard /ProductKey:VDYBN-27WPP-V4HQT-9VMD4-VMK7H /AcceptEula
DISM /online /Set-edition:ServerDatacenter /ProductKey:WX4NM-KYWYW-QJJR4-XV3QB-6VM33 /AcceptEula
You can then automate activation of the volume-licensed version using abbodi’s KMS_VL_ALL script that sets up a local KMS server emulator on the server. 😎
• (8/25/2019): After configuring Windows Server Essentials, you may notice that the Network icon down in the notification area of the server’s taskbar complains that there is no Internet connection (when there actually is), and/or you may receive a health alert stating that your “Active Directory domain names can’t be resolved.“. If so, then change the adapter settings/options for the network connection on your Essentials server so that its preferred IPv4 DNS server address is set to the default 127.0.0.1 localhost/loopback address, and its alternate IPv4 DNS server address is set to the IP address of your network router (e.g. 192.168.1.1) or other DNS server (e.g. 8.8.8.8). You should also verify that the preferred IPv6 DNS server address is set to its default ::1 value.
NOTE: In addition, you should also change the adapter settings/options for the network connection on ALL of your client computers so that their preferred IPv4 DNS server address is set to the static IP address of your Essentials server, and their alternate IPv4 DNS server address is set to the IP address of your network router (e.g. 192.168.1.1) or other DNS server (e.g. 8.8.8.8). Doing so will allow the client-side Windows Server Essentials Connector software’s installer (which you can download from each of your client computers by browsing to http://<ServerName>/connect, where <ServerName> is the name of your Essentials server) to be able to successfully locate and connect the client computer to your Essentials server.
➡ INFO: If you do not want to join your connected client computers to the Windows Server Essentials domain, then you can use Microsoft’s SkipDomainJoin connection method instead.
• During (and after) the configuration of Anywhere Access / Remote Web Access, you may see a benign error about your firewall settings (i.e. “There is an error in your firewall settings – Your firewall may be blocking Anywhere Access to your server and the problem cannot be repaired automatically.“). You can safely ignore this error seeing as it is just a false-positive that is being caused by an issue where the localized names of the required firewall rules are not being properly read from their resource files.
NOTE: The accompanying health alert will automatically be disabled for you when using our WSEE Installer (but the error will still appear within the Configure/Repair Anywhere Access Wizard itself).
• While this one is actually a long-standing issue in Essentials (going all the way back to the days of Windows Home Server 2011 and Windows Small Business Server 2011 Essentials), I’ve never personally experienced it until installing Windows Server Essentials Experience on Windows Server 2019… During (and after) the configuration of Anywhere Access / Remote Web Access, you may see a benign error about your Remote Desktop Services settings (i.e. “There is an error in your Remote Desktop Services settings – There is an issue with your Remote Desktop Services settings that cannot be automatically repaired. Please contact Product Support.“). You can correct this issue by following the steps listed under the “Configure the RDP Gateway SSL” heading here.
NOTE: Our WSE RemoteApp 2016 and WSE WorkFolders 2016 add-ins will automatically repair this issue for you (in the background) when they are installed.
• (3/8/2021): The Microsoft Online Integration Services (such as Office 365 and Azure Active Directory) will work as designed when WSEE has been installed using our WSEE Installer (Version 10.0.14393.4169 (Revision 3) or greater).
NOTE: The online integration services in Windows Server Essentials are NOT compatible with multi-factor authentication (MFA) being enabled on your Office 365 / Azure Active Directory user accounts. Therefore, you should make sure that MFA is disabled by signing in to the Microsoft 365 admin center, clicking on Users → Active users, clicking on your admin user, and then clicking on the Manage multifactor authentication link located on the Account tab.
Microsoft has also implemented something called security defaults in Azure Active Directory, and since enforcing the enabling of MFA on all of your user accounts (within 14 days) is part of this security feature, you will need to disable it as follows:
• Sign in to the Azure portal as an administrator.
• Browse to Manage Azure Active Directory → Properties.
• Select Manage security defaults.
• Set the Enable security defaults toggle to No.
• Select Save.
• (3/15/2021): Use of the Windows Server Essentials Best Practice Analyzer (BPA) tool is supported when WSEE has been installed using our WSEE Installer (Version 10.0.14393.4169 (Revision 4) or greater).
NOTE: To run the Windows Server Essentials Best Practice Analyzer (BPA) tool:
• Log on to the Essentials server as an administrator, and then open the Configure Windows Server Essentials wizard (click Start → type EssentialsRoleConfigWizard.exe).
• Close the configuration wizard after confirming that Windows Server Essentials has been successfully configured on the server.
• Open Server Manager, and then click the Windows Server Essentials Experience tab.
• In the details pane, scroll down to the BEST PRACTICES ANALYZER.
• If a filter is applied, click Clear All.
• Click TASKS, and then click Start BPA Scan.
• Review each BPA message, and follow the instructions to resolve issues, if necessary.
SEE: Rules used by the Windows Server Essentials Best Practices Analyzer (BPA) Tool
Closing Remarks
We’ve tested all of this quite extensively, and it consistently works great for us here. However, your results may vary. Please don’t blame us (nor Microsoft) if you can’t get it to work, or if something goes wrong on your server. None of this is officially supported by Microsoft (nor by us!), and so you should proceed at your own risk. You fully assume all risk, responsibility, and liability associated with the installation. And as always, make sure that you have a working backup of your server, and all of your data, before proceeding.
That being said, it works so well for us here, that we have now switched all of our SOHO servers over to running Windows Server 2019 / 2022 / vNext with Windows Server Essentials Experience installed.
That’s it! Enjoy using Windows Server Essentials Experience on Windows Server 2019 / 2022 / vNext.
— MIKE (The Office Maven)
EDIT (6/26/2019): As the months keep flying on by, we’re finding that the longer we use Windows Server Essentials Experience on Windows Server 2019, the more we’re coming to realize just how much better Windows Server 2019 is than Windows Server 2016. While the “Essentials” bits themselves are of course identical (seeing as they’re just being brought straight over, untouched, from 2016), they run MUCH BETTER under 2019. Windows Server 2019 is leaps-and-bounds faster than Windows Server 2016 is (it boots up faster, and everything, including the server Dashboard, etc., just runs faster/better under it). Lots of bugs that plague 2016 are fixed under 2019. Overall, we’re finding that using WSEE on 2019 is an all-around much better experience.
EDIT (9/1/2021): The Windows Server Essentials Experience also installs, and runs wonderfully, on Microsoft’s GA/RTM release of Windows Server 2022. Enjoy! 😎
EDIT (1/26/2023): The Windows Server Essentials Experience also installs, and runs wonderfully, on Microsoft’s preview release of Windows Server Preview Build 25284 (i.e. the next version of Windows Server with the new Windows 11 style Graphical User Interface!). Enjoy! 😎
Решил написать подробную инструкцию по установке и настройке нового Windows server 2016 Essentials, а заодно и сделать небольшой обзор новых возможностей этой серверной «оси».
Почему собственно Essentials ?
Многие малые компании начинают свою работу с покупки Windows server standard.
И зря тратят деньги!
Ведь если в вашей компании, например, планируется работа до 25 пользователей в 1С Предприятии, тогда Вам идеально подойдет именно Essentials!
Минус, на мой взгляд, здесь только один:
Нет, возможность поднять службу терминалов для удаленной работы пользователей на этом сервере в 1С (Использовать обычный всем нам знакомый удаленный рабочий стол).
Эта версия лицензируется по количеству процессоров на сервере и главное не требует CAL лицензий! (клиентские лицензии на подключение).
Но большинству малых предприятий с уверенностью можно рекомендовать редакцию Essentials.
Экономия здесь очевидна:
Например, редакция —
Microsoft Windows Server 2012 R2 Standard Edition x64 Russian 2CPU/2VM DVD ОЕМ —
Обойдется примерно в ~ 43 000 руб. + CAL на каждого пользователя еще примерно ~1500 руб.
(20 пользователей = 30 000 руб).
Итого: ~ 73 000 руб.
Тогда как Microsoft Windows Server Essentials 2016 Single Multilanguage
Обойдется нам примерно в ~ 26 000 руб!
Если сравнивать редакции Essentials и Standard, на предмет функционала, то с уверенностью можно казать что Essentials почти не уступает Standard, все нужные основные компоненты и роли там также доступны, а сама операционная система идеально подойдет начинающим системным администраторам, так как многие функции, можно реализовать двумя, тремя кликами мышкой.
Много нового появилось в этой версии, и действительно есть, что рассказать, но об этом позже, пока скачаем дистрибутив Windows server 2016 Essentials и установим его.
Скачать бесплатно пакет установки рекомендую на сайте Microsoft.
Установка и настройка Windows server 2016 Essentials
Там же бесплатно получим ключик на 180 дней. За этот период мы успеем его хорошо протестировать и связаться с партнерами Microsoft для получения лицензии.
Установка и настройка Windows server 2016 Essentials
Итак, если образ *ISO скачали (его размер около 4500 Mb).
Запишем его на диск или сделаем «загрузочную флешку» здесь кому как удобно и приступаем к установке.
Сама установка довольно простая, и некоторые трудности могут быть лишь при настройке (первичной) редакции Essentials.
Установка и настройка Windows server 2016 Essentials
Установка и настройка Windows server 2016 Essentials
Укажем «Формат времени и денежных единиц» Ваша страна.
И выберем из списка «Метод ввода (раскладка клавиатуры)», затем клик «Далее».
Установка и настройка Windows server 2016 Essentials
Клик по кнопке «Установить». Затем в следующем окне введем «Ключ продукта» (Тот который мы получили еще на сайте Microsoft когда качали установочный пакет). Так Essentials будет активирован в тестовом периоде на 180 дней.
Если Вы хотите больше узнать о технической стороне 1С, тогда регистрируйтесь на первый бесплатный модуль курса: Администратор 1С >>>