| Version of the Windows NT operating system | |
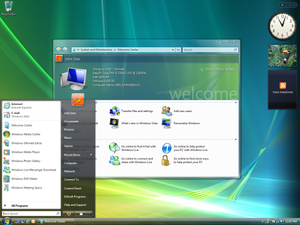
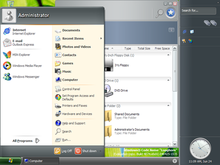
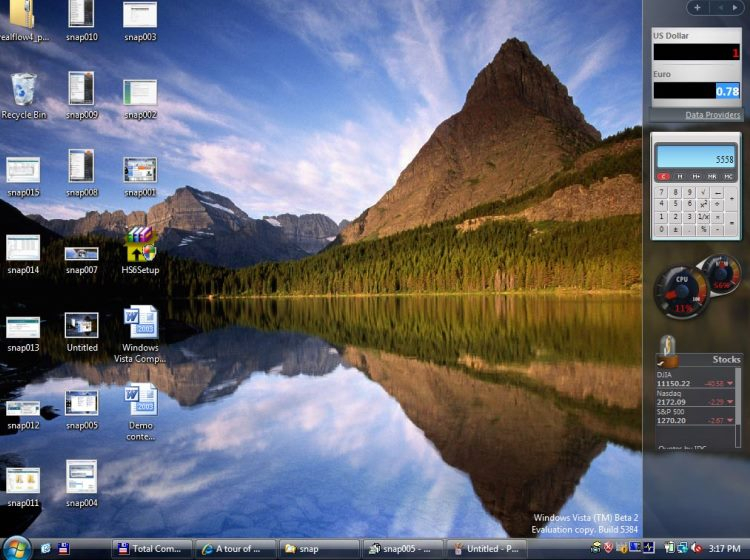
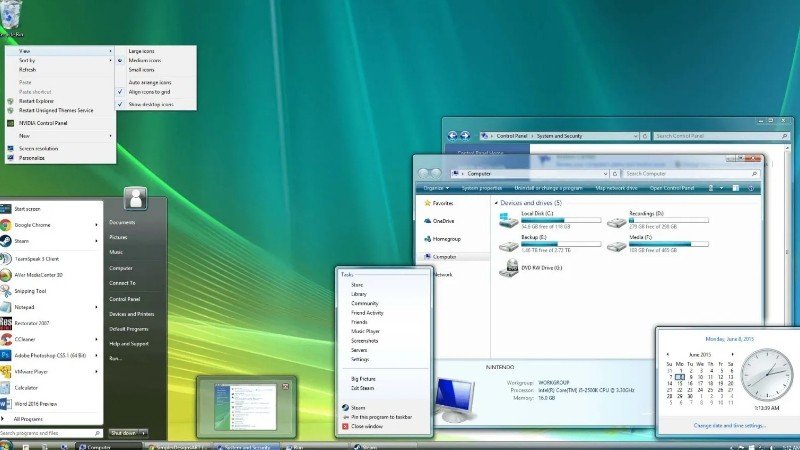
Screenshot of Windows Vista Ultimate, showing its desktop, taskbar, start menu, Windows Sidebar, Welcome Center, and glass effects of Windows Aero |
|
| Developer | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| Source model |
|
| Released to manufacturing |
November 8, 2006; 16 years ago[2] |
| General availability |
January 30, 2007; 16 years ago[3] |
| Final release | Service Pack 2 with security update rollup (6.0.6002)[4] / October 18, 2016; 6 years ago[5] |
| Update method |
|
| Platforms | IA-32 and x86-64 |
| Kernel type | Hybrid (NT) |
| Userland | Windows API, NTVDM, SUA |
| License | Proprietary commercial software |
| Preceded by | Windows XP (2001) |
| Succeeded by | Windows 7 (2009) |
| Official website | Windows Vista (archived at Wayback Machine) |
| Support status | |
| Mainstream support ended on April 10, 2012. Extended support ended on April 11, 2017.[6] Installing a service pack is required for users to receive updates and support after April 13, 2010. |
Windows Vista is a major release of the Windows NT operating system developed by Microsoft. It was the direct successor to Windows XP, which was released five years earlier, at the time being the longest time span between successive releases of Microsoft’s Windows desktop operating systems. Development was completed on November 8, 2006, and over the following three months, it was released in stages to computer hardware and software manufacturers, business customers, and retail channels. On January 30, 2007, it was released internationally and made available for purchase and download from the Windows Marketplace; this is the first release of Windows to be made available through a digital distribution platform.[7]
New features of Windows Vista include an updated graphical user interface and visual style dubbed «Aero,» a new search component called «Windows Search,» redesigned networking, audio, print, and display sub-systems, and new multimedia tools such as Windows DVD Maker. Windows Vista aimed to increase the level of communication between machines on a home network, using peer-to-peer technology to simplify sharing files and media between computers and devices. Windows Vista included version 3.0 of the .NET Framework, allowing software developers to write applications without traditional Windows APIs. Windows Vista removed support for devices without ACPI.
While these new features and security improvements garnered positive reviews, Windows Vista was also the target of much criticism and negative press. Criticism of Windows Vista includes its high system requirements, more restrictive licensing terms, lack of compatibility, longer boot time, and excessive authorization prompts from User Account Control. As a result of these and other issues, Windows Vista saw lower initial adoption and satisfaction rates than Windows XP. However, Windows Vista usage had surpassed Microsoft’s pre-launch two-year-out expectations of achieving 200 million users, with an estimated 330 million Internet users in January 2009. On October 22, 2010, Microsoft ceased sales of retail copies of Windows Vista, and the original equipment manufacturer’s sales for Windows Vista ceased a year later.[8] The market share of Windows Vista fell below 1% by the end of 2021, coinciding with the release of Windows 11.[9]
Mainstream support for Windows Vista ended on April 10, 2012, and extended support ended on April 11, 2017[10] Windows Vista was succeeded by Windows 7. As of February 2022, 0.18% of PCs run Windows Vista.[9]
Development[edit]
Microsoft began work on Windows Vista, known at the time by its codename «Longhorn», in May 2001,[11] five months before the release of Windows XP. It was originally expected to ship in October 2003 as a minor step between Windows XP and «Blackcomb», which was planned to be the company’s next major operating system release. Gradually, «Longhorn» assimilated many of the important new features and technologies slated for Blackcomb, resulting in the release date being pushed back several times in three years. In some builds of Longhorn, their license agreement said «For the Microsoft product codenamed ‘Whistler'». Many of Microsoft’s developers were also re-tasked to build updates to Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 to strengthen security. Faced with ongoing delays and concerns about feature creep, Microsoft announced on August 27, 2004, that it had revised its plans. For this reason, Longhorn was reset to start work on componentizing the Windows Server 2003 Service Pack 1 codebase, and over time re-incorporating the features that would be intended for an actual operating system release. However, some previously announced features such as WinFS were dropped or postponed, and a new software development methodology called the Security Development Lifecycle was incorporated to address concerns with the security of the Windows codebase, which is programmed in C, C++ and assembly. Longhorn became known as Vista in 2005.[12][13]
Longhorn[edit]
The early development stages of Longhorn were generally characterized by incremental improvements and updates to Windows XP. During this period, Microsoft was fairly quiet about what was being worked on, as their marketing and public relations efforts were more strongly focused on Windows XP, and Windows Server 2003, which was released in April 2003. Occasional builds of Longhorn were leaked onto popular file sharing networks such as IRC, BitTorrent, eDonkey and various newsgroups, and so most of what is known about builds before the first sanctioned development release of Longhorn in May 2003 is derived from these builds.
After several months of relatively little news or activity from Microsoft with Longhorn, Microsoft released Build 4008, which had made an appearance on the Internet around February 28, 2003.[14] It was also privately handed out to a select group of software developers. As an evolutionary release over build 3683, it contained several small improvements, including a modified blue «Plex» theme and a new, simplified Windows Image-based installer that operates in graphical mode from the outset, and completed an install of the operating system in approximately one third the time of Windows XP on the same hardware. An optional «new taskbar» was introduced that was thinner than the previous build and displayed the time differently.
The most notable visual and functional difference, however, came with Windows Explorer. The incorporation of the Plex theme made blue the dominant color of the entire application. The Windows XP-style task pane was almost completely replaced with a large horizontal pane that appeared under the toolbars. A new search interface allowed for filtering of results, searching for Windows help, and natural-language queries that would be used to integrate with WinFS. The animated search characters were also removed. The «view modes» were also replaced with a single slider that would resize the icons in real-time, in the list, thumbnail, or details mode, depending on where the slider was. File metadata was also made more visible and more easily editable, with more active encouragement to fill out missing pieces of information. Also of note was the conversion of Windows Explorer to being a .NET application.
Most builds of Longhorn and Vista were identified by a label that was always displayed in the bottom-right corner of the desktop. A typical build label would look like «Longhorn Build 3683.Lab06_N.020923-1821». Higher build numbers did not automatically mean that the latest features from every development team at Microsoft was included. Typically, a team working on a certain feature or subsystem would generate their working builds which developers would test with, and when the code was deemed stable, all the changes would be incorporated back into the main development tree at once. At Microsoft, several «Build labs» exist where the compilation of the entirety of Windows can be performed by a team. The name of the lab in which any given build originated is shown as part of the build label, and the date and time of the build follow that. Some builds (such as Beta 1 and Beta 2) only display the build label in the version information dialog (Winver). The icons used in these builds are from Windows XP.
At the Windows Hardware Engineering Conference (WinHEC) in May 2003, Microsoft gave their first public demonstrations of the new Desktop Window Manager and Aero. The demonstrations were done on a revised build 4015 which was never released. Several sessions for developers and hardware engineers at the conference focused on these new features, as well as the Next-Generation Secure Computing Base (previously known as «Palladium»), which at the time was Microsoft’s proposed solution for creating a secure computing environment whereby any given component of the system could be deemed «trusted». Also at this conference, Microsoft reiterated their roadmap for delivering Longhorn, pointing to an «early 2005» release date.[15]
Development reset[edit]
By 2004, it had become obvious to the Windows team at Microsoft that they were losing sight of what needed to be done to complete the next version of Windows and ship it to customers. Internally, some Microsoft employees were describing the Longhorn project as «another Cairo» or «Cairo.NET», referring to the Cairo development project that the company embarked on through the first half of the 1990s, which never resulted in a shipping operating system (though nearly all the technologies developed in that time did end up in Windows 95 and Windows NT[16]). Microsoft was shocked in 2005 by Apple’s release of Mac OS X Tiger. It offered only a limited subset of features planned for Longhorn, in particular fast file searching and integrated graphics and sound processing, but appeared to have impressive reliability and performance compared to contemporary Longhorn builds.[17] Most Longhorn builds had major Windows Explorer system leaks which prevented the OS from performing well, and added more confusion to the development teams in later builds with more and more code being developed which failed to reach stability.
In a September 23, 2005 front-page article in The Wall Street Journal,[18] Microsoft co-president Jim Allchin, who had overall responsibility for the development and delivery of Windows, explained how development of Longhorn had been «crashing into the ground» due in large part to the haphazard methods by which features were introduced and integrated into the core of the operating system, without a clear focus on an end-product. Allchin went on to explain how in December 2003, he enlisted the help of two other senior executives, Brian Valentine and Amitabh Srivastava, the former being experienced with shipping software at Microsoft, most notably Windows Server 2003,[19] and the latter having spent his career at Microsoft researching and developing methods of producing high-quality testing systems.[20] Srivastava employed a team of core architects to visually map out the entirety of the Windows operating system, and to proactively work towards a development process that would enforce high levels of code quality, reduce interdependencies between components, and in general, «not make things worse with Vista».[21] Since Microsoft decided that Longhorn needed to be further componentized, work started on builds (known as the Omega-13 builds) that would componentize existing Windows Server 2003 source code, and over time add back functionality as development progressed. Future Longhorn builds would start from Windows Server 2003 Service Pack 1 and continue from there.
This change, announced internally to Microsoft employees on August 26, 2004, began in earnest in September, though it would take several more months before the new development process and build methodology would be used by all of the development teams. A number of complaints came from individual developers, and Bill Gates himself, that the new development process was going to be prohibitively difficult to work within.
As Windows Vista[edit]
By approximately November 2004, the company had considered several names for the final release, ranging from simple to fanciful and inventive. In the end, Microsoft chose Windows Vista as confirmed on July 22, 2005, believing it to be a «wonderful intersection of what the product really does, what Windows stands for, and what resonates with customers, and their needs». Group Project Manager Greg Sullivan told Paul Thurrott «You want the PC to adapt to you and help you cut through the clutter to focus on what’s important to you. That’s what Windows Vista is all about: «bringing clarity to your world» (a reference to the three marketing points of Vista—Clear, Connected, Confident), so you can focus on what matters to you».[22] Microsoft co-president Jim Allchin also loved the name, saying that «Vista creates the right imagery for the new product capabilities and inspires the imagination with all the possibilities of what can be done with Windows—making people’s passions come alive.»[23]
After Longhorn was named Windows Vista in July 2005, an unprecedented beta-test program was started, involving hundreds of thousands of volunteers and companies. In September of that year, Microsoft started releasing regular Community Technology Previews (CTP) to beta testers from July 2005 to February 2006. The first of these was distributed at the 2005 Microsoft Professional Developers Conference, and was subsequently released to beta testers and Microsoft Developer Network subscribers. The builds that followed incorporated most of the planned features for the final product, as well as a number of changes to the user interface, based largely on feedback from beta testers. Windows Vista was deemed feature-complete with the release of the «February CTP», released on February 22, 2006, and much of the remainder of the work between that build and the final release of the product focused on stability, performance, application and driver compatibility, and documentation. Beta 2, released in late May, was the first build to be made available to the general public through Microsoft’s Customer Preview Program. It was downloaded over 5 million times. Two release candidates followed in September and October, both of which were made available to a large number of users.[24]
At the Intel Developer Forum on March 9, 2006, Microsoft announced a change in their plans to support EFI in Windows Vista. The UEFI 2.0 specification (which replaced EFI 1.10) was not completed until early 2006, and at the time of Microsoft’s announcement, no firmware manufacturers had completed a production implementation which could be used for testing. As a result, the decision was made to postpone the introduction of UEFI support to Windows; support for UEFI on 64-bit platforms was postponed until Vista Service Pack 1 and Windows Server 2008 and 32-bit UEFI would not be supported, as Microsoft did not expect many such systems to be built because the market was quickly moving to 64-bit processors.[25][26]
While Microsoft had originally hoped to have the consumer versions of the operating system available worldwide in time for the 2006 holiday shopping season, it announced in March 2006 that the release date would be pushed back to January 2007 in order to give the company—and the hardware and software companies that Microsoft depends on for providing device drivers—additional time to prepare. Because a release to manufacturing (RTM) build is the final version of code shipped to retailers and other distributors, the purpose of a pre-RTM build is to eliminate any last «show-stopper» bugs that may prevent the code from responsibly being shipped to customers, as well as anything else that consumers may find annoying. Thus, it is unlikely that any major new features would be introduced; instead, work would focus on Vista’s fit and finish. In just a few days, developers had managed to drop Vista’s bug count from over 2470 on September 22 to just over 1400 by the time RC2 shipped in early October. However, they still had a way to go before Vista was ready to RTM. Microsoft’s internal processes required Vista’s bug count to drop to 500 or fewer before the product could go into escrow for RTM.[27] For most of the pre-RTM builds, those 32-bit editions are only released.
On June 14, 2006, Windows developer Philip Su posted a blog entry which decried the development process of Windows Vista, stating that «The code is way too complicated, and that the pace of coding has been tremendously slowed down by overbearing process.»[28] The same post also described Windows Vista as having approximately 50 million lines of code, with about 2,000 developers working on the product. During a demonstration of the speech recognition feature new to Windows Vista at Microsoft’s Financial Analyst Meeting on July 27, 2006, the software recognized the phrase «Dear mom» as «Dear aunt». After several failed attempts to correct the error, the sentence eventually became «Dear aunt, let’s set so double the killer delete select all«.[29] A developer with Vista’s speech recognition team later explained that there was a bug with the build of Vista that was causing the microphone gain level to be set very high, resulting in the audio being received by the speech recognition software being «incredibly distorted».
Windows Vista build 5824 (October 17, 2006) was supposed to be the RTM release, but a bug, where the OOBE hangs at the start of the WinSAT Assessment (if upgraded from Windows XP), requiring the user to terminate the msoobe.exe by pressing Shift+F10 to open Command Prompt using either command-line tools or Task Manager prevented this, damaging development and lowering the chance that it would hit its January 2007 deadline.[31]
Development of Windows Vista came to an end when Microsoft announced that it had been finalized on November 8, 2006, and was concluded by co-president of Windows development, Jim Allchin.[32] The RTM’s build number had also jumped to 6000 to reflect Vista’s internal version number, NT 6.0.[33] Jumping RTM build numbers is common practice among consumer-oriented Windows versions, like Windows 98 (build 1998), Windows 98 SE (build 2222), Windows Me (build 3000) or Windows XP (build 2600), as compared to the business-oriented versions like Windows 2000 (build 2195) or Server 2003 (build 3790). On November 16, 2006, Microsoft made the final build available to MSDN and Technet Plus subscribers.[34] A business-oriented Enterprise edition was made available to volume license customers on November 30, 2006.[35] Windows Vista was launched for general customer availability on January 30, 2007.[3]
New or changed features[edit]
Windows Vista introduced several features and functionality not present in its predecessors.
End-user[edit]
- Windows Aero: The new graphical user interface is named Windows Aero, which Jim Allchin stated is an acronym for Authentic, Energetic, Reflective, and Open.[36] Microsoft intended the new interface to be cleaner and more aesthetically pleasing than those of previous Windows versions, featuring new transparencies, live thumbnails, live icons, and animations, thus providing a new level of eye candy. Laptop users report, however, that enabling Aero shortens battery life[37][38] and reduces performance.
- Windows shell: The new Windows shell offers a new range of organization, navigation, and search capabilities: Task panes in Windows Explorer are removed, integrating the relevant task options into the toolbar. A «Favorite links» pane has been added, enabling one-click access to common directories. A search box appears in every Explorer window. The address bar has been replaced with a breadcrumb navigation bar. Icons of certain file types in Windows Explorer are «live» and can be scaled in size up to 256 × 256 pixels. The preview pane allows users to see thumbnails of various files and view the contents of documents. The details pane shows information such as file size and type, and allows viewing and editing of embedded tags in supported file formats. The Start menu has changed as well; incorporating an instant search box, and the All Programs list uses a horizontal scroll bar instead of the cascading flyout menu seen in Windows XP. The word «Start» itself has been removed in favor of a blue orb that bears the Windows logo.
- Windows Search: A new search component of Windows Vista, it features instant search (also known as search as you type), which provides instant search results, thus finding files more quickly than the search features found in previous versions of Windows and can search the contents of recognized file types.[39] Users can search for certain metadata such as name, extension, size, date or attributes.
- Windows Sidebar: A transparent panel, anchored to the right side of the screen, wherein a user can place Desktop Gadgets, which are small applets designed for a specialized purpose (such as displaying the weather or sports scores). Gadgets can also be placed on the desktop.[40]
- Windows Internet Explorer 7: New user interface, tabbed browsing, RSS, a search box, improved printing,[41] Page Zoom, Quick Tabs (thumbnails of all open tabs), Anti-Phishing filter, several new security protection features, Internationalized Domain Name support (IDN), and improved web standards support. IE7 in Windows Vista runs in isolation from other applications in the operating system (protected mode); exploits and malicious software are restricted from writing to any location beyond Temporary Internet Files without explicit user consent.
- Windows Media Player 11, a major revamp of Microsoft’s program for playing and organizing music and video. New features in this version include word wheeling (incremental search or «search as you type»), a new GUI for the media library, photo display and organization, the ability to share music libraries over a network with other Windows Vista machines, Xbox 360 integration, and support for other Media Center Extenders.
- Windows Defender: An antispyware program with several real-time protection agents. It includes a software explorer feature, which provides access to startup programs, and allows one to view currently running software, network-connected applications, and Winsock providers (Winsock LSPs).
- Backup and Restore Center: Includes a backup and restore application that gives users the ability to schedule periodic backups of files on their computer, as well as recovery from previous backups. Backups are incremental, storing only the changes made each time, minimizing disk usage. It also features Complete PC Backup (available only in the Ultimate, Business, and Enterprise editions), which backs up an entire computer as an image onto a hard disk or DVD. Complete PC Backup can automatically recreate a machine setup onto new hardware or hard disk in case of any hardware failures. Complete PC Restore can be initiated from within Windows Vista or from the Windows Vista installation CD if a PC is so corrupt that it cannot start normally from the hard disk.
- Windows Mail: A replacement for Outlook Express that includes a new mail store that improves stability,[42] and features integrated instant search. It has a Phishing Filter like Internet Explorer 7 and Junk mail filtering that is enhanced through regular updates via Windows Update.[43]
- Windows Calendar is a new calendar and task application that integrates with Windows Contacts and Windows Mail. It is compatible with various calendar file types, such as the popular iCalendar.
- Windows Photo Gallery, a photo and movie library management application. It can import from digital cameras, tag and rate individual items, adjust colors and exposure, create and display slideshows (with pan and fade effects) through Direct3D and burn slideshows to a DVD.
- Windows DVD Maker, a companion program to Windows Movie Maker that provides the ability to create video DVDs based on a user’s content. Users can design a DVD with title, menus, video, soundtrack, pan and zoom motion effects on pictures or slides.
- Windows Media Center, which was previously exclusively bundled in a separate edition of Windows XP, known as Windows XP Media Center Edition, has been incorporated into the Home Premium and Ultimate editions of Windows Vista.
- Games: Most of the standard computer games included in previous versions of Windows have been redesigned to showcase Vista’s new graphical capabilities. New games available in Windows Vista are Chess Titans (3D Chess game), Mahjong Titans (3D Mahjong game), and Purble Place (a small collection of games, oriented towards younger children, including a matching game, a cake-creator game, and a dress-up puzzle game). Purble Place is the only one of the new games available in the Windows Vista Home Basic edition. InkBall is available for Home Premium (or better) users.
- Games Explorer: A new special folder called «Games» exposes installed video games and information about them. These metadata may be updated from the Internet.[44]
- Windows Mobility Center is a control panel that centralizes the most relevant information related to mobile computing (brightness, sound, battery level/power scheme selection, wireless network, screen orientation, presentation settings, etc.).
- Windows Fax and Scan Allows computers with fax modems to send and receive fax documents, as well as scan documents. It is not available in the Home editions of Windows Vista, but is available in the Business, Enterprise, and Ultimate editions.
- Windows Meeting Space replaces NetMeeting. Users can share applications (or their entire desktop) with other users on the local network, or over the Internet using peer-to-peer technology (higher editions than Starter and Home Basic can take advantage of hosting capabilities, Starter and Home Basic editions are limited to «join» mode only)
- Windows HotStart enables compatible computers to start applications directly from operating system startup or resume by the press of a button—this enables what Microsoft has described as appliance-like availability, which allows computers to function in a manner similar to a consumer electronics device such as a DVD player;[45] the feature was also designed to provide the instant-on feature availability that is traditionally associated with mobile devices.[46] While Microsoft has emphasized multimedia scenarios with Windows HotStart,[47] a user can configure this feature so that a button launches a preferred application.[48]
- Shadow Copy automatically creates daily backup copies of files and folders. Users can also create «shadow copies» by setting a System Protection Point using the System Protection tab in the System control panel. The user can view multiple versions of a file throughout a limited history and be allowed to restore, delete, or copy those versions. This feature is available only in the Business, Enterprise, and Ultimate editions of Windows Vista and is inherited from Windows Server 2003.[49]
- Windows Update: Software and security updates have been simplified,[50] now operating solely via a control panel instead of as a web application. Windows Mail’s spam filter and Windows Defender’s definitions are updated automatically via Windows Update. Users who choose the recommended setting for Automatic Updates will have the latest drivers installed and available when they add a new device.
- Parental controls: Allows administrators to monitor and restrict user activity, as well as control which websites, programs, and games each Standard user can use and install. This feature is not included in the Business or Enterprise editions of Vista.
- Windows SideShow: Enables the auxiliary displays on newer laptops or supported Windows Mobile devices. It is meant to be used to display device gadgets while the computer is on or off.
- Speech recognition is integrated into Vista.[51] It features a redesigned user interface and configurable command-and-control commands. Unlike the Office 2003 version, which works only in Office and WordPad, Speech Recognition in Windows Vista works for any accessible application. In addition, it currently supports several languages: British and American English, Spanish, French, German, Chinese (Traditional and Simplified), and Japanese.
- New fonts, including several designed for screen reading, and improved Chinese (Yahei, JhengHei), Japanese (Meiryo), and Korean (Mulgan) fonts. ClearType has also been enhanced and enabled by default.
- Improved audio controls allow the system-wide volume or volume of individual audio devices and even individual applications to be controlled separately. New audio functionalities such as room correction, bass management, speaker fill, and headphone virtualization have also been incorporated.
- Problem Reports and Solutions, a feature that allows users to check for solutions to problems or view previously sent problems for any solutions or additional information, if available.Windows System Assessment Tool is a tool used to benchmark system performance. Software such as games can retrieve this rating and modify its own behavior at runtime to improve performance. The benchmark tests CPU, RAM, 2-D and 3-D graphics acceleration, graphics memory and hard disk space.[52][53]
- Windows Ultimate Extras: The Ultimate edition of Windows Vista provides, via Windows Update, access to some additional features. These are a collection of additional MUI language packs, Texas Hold ‘Em (a Poker game) and Microsoft Tinker (a strategy game where the character is a robot), BitLocker and EFS enhancements that allow users to back up their encryption key online in a Digital Locker, and Windows Dreamscene, which enables the use of videos in MPEG and WMV formats as the desktop background. On April 21, 2008, Microsoft launched two more Ultimate Extras; three new Windows sound schemes, and a content pack for Dreamscene. Various DreamScene Content Packs have been released since the final version of DreamScene was released.
- Reliability and Performance Monitor includes various tools for tuning and monitoring system performance and resources activities of CPU, disks, network, memory and other resources. It shows the operations on files, the opened connections, etc.[54]
- Disk Management: The Logical Disk Manager in Windows Vista supports shrinking and expanding volumes on-the-fly.[55]
- Windows Anytime Upgrade: is a program that allows a user to upgrade their computer running Vista to a higher edition. For example, a computer running Windows Vista Home Basic can be upgraded to Home Premium or better. Anytime Upgrade permits users to upgrade without having their programs and data erased, and is cheaper than replacing the existing installation of Windows. Anytime Upgrade is no longer available for Vista.[56]
- Digital Locker Assistant: A program that facilitated access to downloads and purchases from the Windows Marketplace distribution platform.[57] Apps purchased from Windows Marketplace are managed by Microsoft Account credentials, which are used to access a user’s digital locker that stores the app and its associated information (e.g., licenses) off-site.[58]
Core[edit]
Vista includes technologies such as ReadyBoost[59] and ReadyDrive, which employ fast flash memory (located on USB flash drives and hybrid hard disk drives) to improve system performance by caching commonly used programs and data. This manifests itself in improved battery life on notebook computers as well, since a hybrid drive can be spun down when not in use.[60] Another new technology called SuperFetch utilizes machine learning techniques to analyze usage patterns to allow Windows Vista to make intelligent decisions about what content should be present in system memory at any given time. It uses almost all the extra RAM as disk cache.[61] In conjunction with SuperFetch, an automatic built-in Windows Disk Defragmenter makes sure that those applications are strategically positioned on the hard disk where they can be loaded into memory very quickly with the least physical movement of the hard disk’s read-write heads.[62]
As part of the redesign of the networking architecture, IPv6 has been fully incorporated into the operating system[63] and a number of performance improvements have been introduced, such as TCP window scaling.[64] Earlier versions of Windows typically needed third-party wireless networking software to work properly, but this is not the case with Vista, which includes more comprehensive wireless networking support.[65]
For graphics, Vista introduces a new Windows Display Driver Model[66] and a major revision to Direct3D. The new driver model facilitates the new Desktop Window Manager, which provides the tearing-free desktop and special effects that are the cornerstones of Windows Aero. Direct3D 10, developed in conjunction with major graphics card manufacturers, is a new architecture with more advanced shader support, and allows the graphics processing unit to render more complex scenes without assistance from the CPU. It features improved load balancing between CPU and GPU and also optimizes data transfer between them.[67] WDDM also provides video content playback that rivals typical consumer electronics devices. It does this by making it easy to connect to external monitors, providing for protected HD video playback, and increasing overall video playback quality. For the first time in Windows, graphics processing unit (GPU) multitasking is possible, enabling users to run more than one GPU-intensive application simultaneously.[68]
At the core of the operating system, many improvements have been made to the memory manager, process scheduler and I/O scheduler. The Heap Manager implements additional features such as integrity checking in order to improve robustness and defend against buffer overflow security exploits, although this comes at the price of breaking backward compatibility with some legacy applications.[69] A Kernel Transaction Manager has been implemented that enables applications to work with the file system and Registry using atomic transaction operations.[70]
[edit]
Improved security was a primary design goal for Vista.[71] Microsoft’s Trustworthy Computing initiative, which aims to improve public trust in its products, has had a direct effect on its development. This effort has resulted in a number of new security and safety features and an Evaluation Assurance Level rating of 4+.[72][73]
User Account Control, or UAC is perhaps the most significant and visible of these changes. UAC is a security technology that makes it possible for users to use their computer with fewer privileges by default, to stop malware from making unauthorized changes to the system. This was often difficult in previous versions of Windows, as the previous «limited» user accounts proved too restrictive and incompatible with a large proportion of application software, and even prevented some basic operations such as looking at the calendar from the notification tray. In Windows Vista, when an action is performed that requires administrative rights (such as installing/uninstalling software or making system-wide configuration changes), the user is first prompted for an administrator name and password; in cases where the user is already an administrator, the user is still prompted to confirm the pending privileged action. Regular use of the computer such as running programs, printing, or surfing the Internet does not trigger UAC prompts. User Account Control asks for credentials in a Secure Desktop mode, in which the entire screen is dimmed, and only the authorization window is active and highlighted. The intent is to stop a malicious program from misleading the user by interfering with the authorization window, and to hint to the user about the importance of the prompt.[74]
Testing by Symantec Corporation has proven the effectiveness of UAC. Symantec used over 2,000 active malware samples, consisting of backdoors, keyloggers, rootkits, mass mailers, trojan horses, spyware, adware, and various other samples. Each was executed on a default Windows Vista installation within a standard user account. UAC effectively blocked over 50 percent of each threat, excluding rootkits. 5 percent or less of the malware that evaded UAC survived a reboot.[75][76]
Internet Explorer 7’s new security and safety features include a phishing filter, IDN with anti-spoofing capabilities, and integration with system-wide parental controls. For added security, ActiveX controls are disabled by default. Also, Internet Explorer operates in a protected mode, which operates with lower permissions than the user and runs in isolation from other applications in the operating system, preventing it from accessing or modifying anything besides the Temporary Internet Files directory.[77] Microsoft’s anti-spyware product, Windows Defender, has been incorporated into Windows, protecting against malware and other threats. Changes to various system configuration settings (such as new auto-starting applications) are blocked unless the user gives consent.
Whereas prior releases of Windows supported per-file encryption using Encrypting File System, the Enterprise and Ultimate editions of Vista include BitLocker Drive Encryption, which can protect entire volumes, notably the operating system volume. However, BitLocker requires approximately a 1.5-gigabyte partition to be permanently not encrypted and to contain system files for Windows to boot. In normal circumstances, the only time this partition is accessed is when the computer is booting, or when there is a Windows update that changes files in this area, which is a legitimate reason to access this section of the drive. The area can be a potential security issue, because a hexadecimal editor (such as dskprobe.exe), or malicious software running with administrator and/or kernel level privileges would be able to write to this «Ghost Partition» and allow a piece of malicious software to compromise the system, or disable the encryption. BitLocker can work in conjunction with a Trusted Platform Module (TPM) cryptoprocessor (version 1.2) embedded in a computer’s motherboard, or with a USB key.[78] However, as with other full disk encryption technologies, BitLocker is vulnerable to a cold boot attack, especially where TPM is used as a key protector without a boot PIN being required too.[79]
A variety of other privilege-restriction techniques are also built into Vista. An example is the concept of «integrity levels» in user processes, whereby a process with a lower integrity level cannot interact with processes of a higher integrity level and cannot perform DLL–injection to processes of a higher integrity level. The security restrictions of Windows services are more fine-grained, so that services (especially those listening on the network) cannot interact with parts of the operating system they do not need to. Obfuscation techniques such as address space layout randomization are used to increase the amount of effort required of malware before successful infiltration of a system. Code integrity verifies that system binaries have not been tampered with by malicious code.
As part of the redesign of the network stack, Windows Firewall has been upgraded, with new support for filtering both incoming and outgoing traffic. Advanced packet filter rules can be created that can grant or deny communications to specific services.
The 64-bit versions of Vista require that all device drivers be digitally signed, so that the creator of the driver can be identified.[80]
System management[edit]
While much of the focus of Vista’s new capabilities highlighted the new user interface,[81] security technologies, and improvements to the core operating system, Microsoft also adding new deployment and maintenance features:
- The Windows Imaging Format (WIM) provides the cornerstone of Microsoft’s new deployment and packaging system. WIM files, which contain a HAL-independent image of Windows Vista, can be maintained and patched without having to rebuild new images. Windows Images can be delivered via Systems Management Server or Business Desktop Deployment technologies. Images can be customized and configured with applications then deployed to corporate client personal computers using little to no touch by a system administrator. ImageX is the Microsoft tool used to create and customize images.
- Windows Deployment Services replaces Remote Installation Services for deploying Vista and prior versions of Windows.
- Approximately 700 new Group Policy settings have been added, covering most aspects of the new features in the operating system, as well as significantly expanding the configurability of wireless networks, removable storage devices, and user desktop experience. Vista also introduced an XML-based format (ADMX) to display registry-based policy settings, making it easier to manage networks that span geographic locations and different languages.[82]
- Services for UNIX, renamed as «Subsystem for UNIX-based Applications», comes with the Enterprise and Ultimate editions of Vista. Network File System (NFS) client support is also included.
- Multilingual User Interface–Unlike previous versions of Windows (which required the loading of language packs to provide local-language support), Windows Vista Ultimate and Enterprise editions support the ability to dynamically change languages based on the logged-on user’s preference.
- Wireless Projector support
Developer[edit]
Windows Vista includes a large number of new application programming interfaces. Chief among them is the inclusion of version 3.0 of the .NET Framework, which consists of a class library and Common Language Runtime. Version 3.0 includes four new major components:[83]
- Windows Presentation Foundation is a user interface subsystem and framework based vector graphics, which makes use of 3D computer graphics hardware and Direct3D technologies. It provides the foundation for building applications and blending application UI, documents, and media content. It is the successor to Windows Forms.
- Windows Communication Foundation is a service-oriented messaging subsystem that enables applications and systems to interoperate locally or remotely using Web services.
- Windows Workflow Foundation provides task automation and integrated transactions using workflows. It is the programming model, engine, and tools for building workflow-enabled applications on Windows.
- Windows CardSpace is a component that securely stores digital identities of a person, and provides a unified interface for choosing the identity for a particular transaction, such as logging into a website.[84]
These technologies are also available for Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 to facilitate their introduction to and usage by developers and end-users.
There are also significant new development APIs in the core of the operating system, notably the completely re-designed audio, networking, print, and video interfaces, major changes to the security infrastructure, improvements to the deployment and installation of applications («ClickOnce» and Windows Installer 4.0), new device driver development model («Windows Driver Foundation»), Transactional NTFS, mobile computing API advancements (power management, Tablet PC Ink support, SideShow) and major updates to (or complete replacements of) many core subsystems such as Winlogon and CAPI.
There are some issues for software developers using some of the graphics APIs in Vista. Games or programs built solely on the Windows Vista-exclusive version of DirectX, version 10, cannot work on prior versions of Windows, as DirectX 10 is not available for previous Windows versions. Also, games that require the features of D3D9Ex, the updated implementation of DirectX 9 in Windows Vista are also incompatible with previous Windows versions.[85] According to a Microsoft blog, there are three choices for OpenGL implementation on Vista. An application can use the default implementation, which translates OpenGL calls into the Direct3D API and is frozen at OpenGL version 1.4, or an application can use an Installable Client Driver (ICD), which comes in two flavors: legacy and Vista-compatible. A legacy ICD disables the Desktop Window Manager, a Vista-compatible ICD takes advantage of a new API, and is fully compatible with the Desktop Window Manager.[86] At least two primary vendors, ATI and NVIDIA provided full Vista-compatible ICDs.[87] However, hardware overlay is not supported, because it is considered as an obsolete feature in Vista. ATI and NVIDIA strongly recommend using compositing desktop/Framebuffer Objects for same functionality.[88]
Installation[edit]
Windows Vista is the first Microsoft operating system:
- To use DVD-ROM media for installation[89]
- That can be installed only on a partition formatted with the NTFS file system[90]
- That provides support for loading drivers for SCSI, SATA and RAID controllers from any source in addition to floppy disks prior to its installation[91]
- That can be installed on and booted from systems with GPT disks and UEFI firmware[a][93]
Unification of OEM and retail installation[edit]
Windows Vista unifies the previously separate OEM and retail distributions of Microsoft Windows; a license for the edition purchased determines which version of Windows Vista is eligible for installation, regardless of its originating source. OEM and retail versions of Windows before Windows Vista were maintained separately on optical media—users with a manufacturer-supplied disc could not use a retail license during installation, and users with a retail disc could not use an OEM license during installation.[94]
Removed features[edit]
Some notable Windows XP features and components have been replaced or removed in Windows Vista, including several shell and Windows Explorer features, multimedia features, networking related functionality, Windows Messenger, NTBackup, the network Windows Messenger service, HyperTerminal, MSN Explorer, Active Desktop, and the replacement of NetMeeting with Windows Meeting Space. As a result, BOOTMGR in Windows Vista and later versions replaces the functions performed by NTLDR in all Windows NT versions up to Windows XP and directly executes winload.exe, the system loader used to continue the Windows boot process. Windows Vista also does not include the Windows XP «Luna» visual theme, or most of the classic color schemes that have been part of Windows since the Windows 3.x era. The «Hardware profiles» startup feature has also been removed, along with support for older motherboard technologies like the EISA bus, APM and game port support (though on the 32-bit version game port support can be enabled by applying an older driver).[95] IP over FireWire (TCP/IP over IEEE 1394) has been removed as well.[96] The IPX/SPX protocol has also been removed, although it can be enabled by a third-party plug-in.[97]
Support lifecycle[edit]
Support for the original release of Windows Vista (without a service pack) ended on April 13, 2010.[98] Service Pack 1 reached end of support on July 12, 2011, over three years after its general availability.[99]
Mainstream support for Windows Vista officially ended on April 10, 2012.[6] The «Extended Support» phase would last for the next 5 years, until April 11, 2017.[6] Microsoft is no longer offering no-charge incident support, warranty claims, or design fixes for the operating system. For IT pros or users who needed to make specific fixes to the commercial Windows code, Microsoft required an extended hotfix agreement, which provided an additional 90 days from April 10, 2012.
As part of the Extended Support phase, Vista users were still able to get security updates, and could still pay for support per incident, per-hour, or in other ways. Microsoft also made Windows Vista product information available through its online Knowledge Base. On April 11, 2017, support for Windows Vista ended.
Editions[edit]
Windows Vista shipped in six different editions.[100] These are roughly divided into two target markets, consumer and business, with editions varying to cater to specific sub-markets. For consumers, there are three editions, with two available for economically more developed countries. Windows Vista Starter edition is aimed at low-powered computers with availability only in emerging markets. Windows Vista Home Basic is intended for budget users. Windows Vista Home Premium covers the majority of the consumer market and contains applications for creating and using multimedia. The home editions cannot join a Windows Server domain. For businesses, there are three editions as well. Windows Vista Business is specifically designed for small and medium-sized enterprises,[101] while Windows Vista Enterprise[102] is only available to customers participating in Microsoft’s Software Assurance program. Windows Vista Ultimate contains the complete feature-set of both the Home and Business (combination of both Home Premium and Enterprise) editions, as well as a set of Windows Ultimate Extras, and is aimed at enthusiasts.
All editions except Windows Vista Starter support both 32-bit (x86) and 64-bit (x64) processor architectures.
In the European Union, Home Basic N and Business N variants are also available. These come without Windows Media Player, due to EU sanctions brought against Microsoft for violating anti-trust laws. Similar sanctions exist in South Korea.
Visual styles[edit]
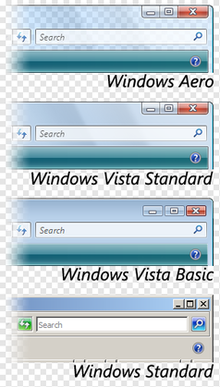
A comparison of the four visual styles included in Windows Vista
Windows Vista has four distinct visual styles.[103][104]
- Windows Aero
- Vista’s default visual style, Windows Aero, is built on a desktop composition engine called Desktop Window Manager. Windows Aero introduces support for translucency effects (Glass), window thumbnails on the taskbar, window animations, and other visual effects (for example Windows Flip 3D), and is intended for mainstream and high-end video cards. To enable these features, the contents of every open window are stored in video memory to facilitate tearing-free movement of windows. As such, Windows Aero has significantly higher hardware requirements than its predecessors: systems running Vista must have video card drivers compatible with the Windows Display Driver Model (WDDM), and the minimum graphics memory required is 128 MB, depending on the resolution used.[105]
Windows Aero is not included in the Starter and Home Basic editions. A variant of Windows Aero, dubbed Windows Vista Standard, lacking the glass effects, window animations, and other advanced graphical effects, is included in Home Basic.[106]
- Windows Vista Basic
- This visual style does not employ the Desktop Window Manager; as such, it does not feature transparency or translucency, window animation, Windows Flip 3D or any of the functions provided by the DWM. It is the default visual style on Windows Vista Starter and on systems without WDDM-compatible display drivers, and has similar video card requirements to Windows XP. Before Service Pack 1, a machine that failed Windows Genuine Advantage validation would also default to this visual style.[107]
- Windows Standard
- The Windows Standard and Windows Classic visual styles reprise the user interface of Windows 9x, Windows 2000 and Microsoft’s Windows Server line of operating systems. As with previous versions of Windows, this visual style supports custom color schemes, which are collections of color settings. Windows Vista includes four high-contrast color schemes and the default color schemes from Windows 98 (titled «Windows Classic») and Windows 2000/Windows Me (titled «Windows Standard»).[106]
Hardware requirements[edit]
Computers with a «Certified for Windows Vista» sticker met WHQL Testing requirements and supported new features such as Windows Aero.
Computers capable of running Windows Vista are classified as Vista Capable and Vista Premium Ready.[108] A Vista Capable or equivalent PC is capable of running all editions of Windows Vista although some of the special features and high-end graphics options may require additional or more advanced hardware. A Vista Premium Ready PC can take advantage of Vista’s high-end features.[109]
Windows Vista’s Basic and Classic interfaces work with virtually any graphics hardware that supports Windows XP or 2000; accordingly, most discussion around Vista’s graphics requirements centers on those for the Windows Aero interface. As of Windows Vista Beta 2, the NVIDIA GeForce 6 series and later, the ATI Radeon 9500 and later, Intel’s GMA 950 and later integrated graphics, and a handful of VIA chipsets and S3 Graphics discrete chips are supported. Although originally supported, the GeForce FX 5 series has been dropped from newer drivers from NVIDIA. The last driver from NVIDIA to support the GeForce FX series on Vista was 96.85.[110][111] Microsoft offered a tool called the Windows Vista Upgrade Advisor[109] to assist Windows XP and Vista users in determining what versions of Windows their machine is capable of running. The required server connections for this utility are no longer available. Although the installation media included in retail packages is a 32-bit DVD, customers needing a CD-ROM or customers who wish for a 64-bit install media can acquire this media through the Windows Vista Alternate Media program.[112] The Ultimate edition includes both 32-bit and 64-bit media.[113] The digitally downloaded version of Ultimate includes only one version, either 32-bit or 64-bit, from Windows Marketplace.
| Component of PC | Minimum required | Recommended |
|---|---|---|
| Processor | 800 MHz | 1 GHz |
| Memory | 512 MB (384 MB for Starter edition) |
1 GB |
| Graphics card | Super VGA | WDDM 1.0-compliant 32 bits per pixel DirectX 9.0 support Pixel Shader 2.0 support |
| Graphics memory | — | 128 MB |
| Total HDD capacity | 20 GB | 40 GB |
| Free HDD space | 15 GB | 15 GB |
| Optical drives | CD-ROM drive | DVD-ROM drive |
| Others | — | TV tuner card (Premium, Ultimate) Touchscreen (Premium, Business, Ultimate) USB flash drive (Ultimate) Trusted Platform Module (Ultimate) |
Physical memory limits[edit]
The maximum amount of RAM that Windows Vista can support varies, depending on both its edition and its processor architecture, as shown in the table.[116]
| Edition | Processor architecture | |
|---|---|---|
| IA-32 | x64 | |
| Ultimate | 4 GB | 128 GB |
| Enterprise | ||
| Business | ||
| Home Premium | 16 GB | |
| Home Basic | 8 GB | |
| Starter | 1 GB | — |
Processor limits[edit]
The maximum number of logical processors[117] in a PC that Windows Vista supports is: 32[118] for 32-bit; 64[119] for 64-bit.[120]
The maximum number of physical processors in a PC that Windows Vista supports is: 2 for Business, Enterprise, and Ultimate, and 1 for Starter, Home Basic, and Home Premium.[121]
Updates[edit]
Microsoft occasionally releases updates such as service packs for its Windows operating systems to fix bugs, improve performance and add new features.
Service Pack 1[edit]
Windows Vista Service Pack 1 (SP1) was released on February 4, 2008, alongside Windows Server 2008 to OEM partners, after a five-month beta test period. The initial deployment of the service pack caused a number of machines to continually reboot, rendering the machines unusable.[122] This temporarily caused Microsoft to suspend automatic deployment of the service pack until the problem was resolved. The synchronized release date of the two operating systems reflected the merging of the workstation and server kernels back into a single code base for the first time since Windows 2000. MSDN subscribers were able to download SP1 on February 15, 2008. SP1 became available to current Windows Vista users on Windows Update and the Download Center on March 18, 2008.[123][124][125] Initially, the service pack only supported five languages – English, French, Spanish, German and Japanese. Support for the remaining 31 languages was released on April 14, 2008.[126]
A white paper, published by Microsoft on August 29, 2007, outlined the scope and intent of the service pack, identifying three major areas of improvement: reliability and performance, administration experience, and support for newer hardware and standards.[127]
One area of particular note is performance. Areas of improvement include file copy operations, hibernation, logging off on domain-joined machines, JavaScript parsing in Internet Explorer, network file share browsing,[124] Windows Explorer ZIP file handling,[128] and Windows Disk Defragmenter.[129] The ability to choose individual drives to defragment is being reintroduced as well.[124]
Service Pack 1 introduced support for some new hardware and software standards, notably the exFAT file system,[124] 802.11n wireless networking, IPv6 over VPN connections, and the Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol.[130]
Booting a system using Extensible Firmware Interface on x64 systems was also introduced;[124] this feature had originally been slated for the initial release of Vista but was delayed due to a lack of compatible hardware at the time. Booting from a GUID Partition Table–based hard drive greater than 2.19 TB is supported (x64 only).[131][132]
Two areas have seen changes in SP1 that have come as the result of concerns from software vendors. One of these is desktop search; users will be able to change the default desktop search program to one provided by a third party instead of the Microsoft desktop search program that comes with Windows Vista, and desktop search programs will be able to seamlessly tie in their services into the operating system.[125] These changes come in part due to complaints from Google, whose Google Desktop Search application was hindered by the presence of Vista’s built-in desktop search. In June 2007, Google claimed that the changes being introduced for SP1 «are a step in the right direction, but they should be improved further to give consumers greater access to alternate desktop search providers».[133] The other area of note is a set of new security APIs being introduced for the benefit of antivirus software that currently relies on the unsupported practice of patching the kernel (see Kernel Patch Protection).[134][135]
An update to DirectX 10, named DirectX 10.1,[124] marked mandatory several features that were previously optional in Direct3D 10 hardware. Graphics cards will be required to support DirectX 10.1.[136] SP1 includes a kernel (6001.18000) that matches the version shipped with Windows Server 2008.[137]
The Group Policy Management Console (GPMC) was replaced by the Group Policy Object Editor. An updated downloadable version of the Group Policy Management Console was released soon after the service pack.
SP1 enables support for hotpatching, a reboot-reduction servicing technology designed to maximize uptime. It works by allowing Windows components to be updated (or «patched») while they are still in use by a running process. Hotpatch-enabled update packages are installed via the same methods as traditional update packages, and will not trigger a system reboot.[138]
Service Pack 2[edit]
Service Pack 2 for Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008 was released through different channels between April[139] and June 2009, one year after the release of Windows Vista SP1, and four months before the release of Windows 7.[5] In addition to a number of security and other fixes, a number of new features have been added. However, it did not include Internet Explorer 8, but instead was included in Windows 7, which was released four months after Vista SP2.[140][141]
- Windows Search 4 (available for SP1 systems as a standalone update)
- Feature Pack for Wireless adds support for Bluetooth 2.1
- Windows Feature Pack for Storage enables the data recording onto Blu-ray media
- Windows Connect Now (WCN) to simplify Wi-Fi configuration
- Improved support for resuming with active Wi-Fi connections
- Improved support for eSATA drives
- The limit of 10 half-open, outgoing TCP connections introduced in Windows XP SP2 was removed
- Enables the exFAT file system to support UTC timestamps, which allows correct file synchronization across time zones
- Support for ICCD/CCID smart cards
- Support for VIA 64-bit CPUs
- Improved performance and responsiveness with the RSS feeds sidebar
- Improves audio and video performance for streaming high-definition content
- Improves Windows Media Center (WMC) in content protection for TV[142]
- Provides an improved power management policy that is approximately 10% more efficient than the original with the default policies[143]
Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008 share a single service pack binary, reflecting the fact that their code bases were joined with the release of Server 2008.[140] Service Pack 2 is not a cumulative update meaning that Service Pack 1 must be installed first.
Platform Update[edit]
The Platform Update for Windows Vista was released on October 27, 2009. It includes major new components that shipped with Windows 7, as well as updated runtime libraries.[144][145] It requires Service Pack 2 of Windows Vista or Windows Server 2008 and is listed on Windows Update as a Recommended download.
The Platform Update allows application developers to target both Windows Vista and Windows 7. It consists of the following components:
- Windows Graphics runtime: Direct2D, DirectWrite, Direct3D 11, DXGI 1.1, and WARP
- Updates to Windows Imaging Component
- Updates to XPS Print API, XPS Document API and XPS Rasterization Service
- Windows Automation API (updates to MSAA and UI Automation)
- Windows Portable Devices Platform (adds support for MTP over Bluetooth and MTP Device Services)
- Windows Ribbon API
- Windows Animation Manager library
Some updates are available as separate releases for both Windows XP and Windows Vista:
- Windows Management Framework: Windows PowerShell 2.0, Windows Remote Management 2.0, BITS 4.0
- Remote Desktop Connection 7.0 (RDP7) client
Although extensive, the Platform Update does not bring Windows Vista to the level of features and performance offered by Windows 7.[146] For example, even though Direct3D 11 runtime will be able to run on D3D9-class hardware and WDDM drivers using «feature levels» first introduced in Direct3D 10.1, Desktop Window Manager has not been updated to use Direct3D 10.1.[146]
In July 2011, Microsoft released the Platform Update Supplement for Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008, which contains several bug fixes and performance improvements.[147]
Out-of-band patches[edit]
BlueKeep patch[edit]
Microsoft has released an update for Windows Vista SP2 to resolve the BlueKeep security vulnerability (CVE-2019-0708), which affects the Remote Desktop Protocol in older Windows versions.[148] Subsequent related flaws, CVE-2019-1181, CVE-2019-1182, CVE-2019-1222 and CVE-2019-1226 (collectively known as DejaBlue) do not affect Windows Vista or earlier versions of Windows.[149] The installation of this patch changed the build number of Windows Vista from 6002 to 6003.[b]
Text Services Framework patch[edit]
The Text Services Framework was compromised by a privilege escalation vulnerability (CVE-2019-1162) that could allow attackers to use the framework to perform privileged operations, run software, or send messages to privileged processes from unprivileged processes—bypassing security features such as sandboxes or User Account Control. Microsoft remediated issues related to this vulnerability with the release of a patch in August 2019 for Windows Vista SP2, Windows Server 2008 SP2, and later versions of Windows.[152]
Malware Protection Engine patch[edit]
A vulnerability related to Windows Defender that affected the way the Malware Protection Engine operates (CVE-2017-0290) was reported in May 2017. If Windows Defender scanned a specially crafted file, it would lead to memory corruption, potentially allowing an attacker to control the affected machine or perform arbitrary code execution in the context of LocalSystem; the vulnerability was exacerbated by the default real-time protection settings of Windows Defender, which were configured to automatically initiate malware scans at regular intervals. The first version of the Protection Engine affected by the vulnerability is Version 1.1.13701.0—subsequent versions of the engine are unaffected. Microsoft released a patch to address the issue.[153]
Marketing campaign[edit]
The Mojave Experiment[edit]
In July 2008, Microsoft introduced a web-based advertising campaign called the «Mojave Experiment», which depicts a group of people who are asked to evaluate the newest operating system from Microsoft, calling it Windows ‘Mojave’. Participants are first asked about Vista, if they have used it, and their overall satisfaction with Vista on a scale of 1 to 10. They are then shown a demo of some of the new operating system’s features, and asked their opinion and satisfaction with it on the same 1 to 10 scale. After respondents rate «Mojave», they are then told that they were shown a demo of Windows Vista. The object was to test «A theory: If people could see Windows Vista firsthand, they would like it.» According to Microsoft, the initial sample of respondents rated Vista an average of 4.4 out of 10, and Mojave received an average of 8.5, with no respondents rating Mojave lower than they originally rated Windows Vista before the demo.[154][155] The «experiment» has been criticized for deliberate selection of positive statements and not addressing all aspects of Vista.[156] During the launch of Vista, Microsoft also made a lime flavored sparkling water available to campus visitors and developers.[157]
Reception[edit]
Windows Vista received mixed to negative reviews at the time of its release and throughout its lifespan, mainly for its much higher hardware requirements and perceived slowness compared to Windows XP.[158][159]
It received generally positive reviews from PC gamers who praised the advantages brought by DirectX 10, which allowed for better gaming performance and more realistic graphics, as well as support for many new capabilities featured in new GPUs.[160] However, many DirectX 9 games initially ran with lower frame rates compared to when they were run on Windows XP. In mid-2008, benchmarks suggested that the SP1 update improved performance to be on par with (or better than) Windows XP in terms of game performance.[161]
Peter Bright of Ars Technica wrote that, despite its delays and feature cuts, Windows Vista was «a huge evolution in the history of the NT platform […] The fundamental changes to the platform are of a scale not seen since the release of NT [3.1; the first version].»[162] In a continuation of his previous assessment, Bright stated that «Vista is not simply XP with a new skin; core parts of the OS have been radically overhauled, and virtually every area has seen significant refinement. In terms of the magnitude and extent of these changes, Vista represents probably the biggest leap that the NT platform has ever seen. Never before have significant subsystems been gutted and replaced in the way they are in Vista.»[163] Many others in the tech industry echoed these sentiments at the time, directing praise towards the massive amount of technical features new to Windows Vista.[164]
Windows Vista received the «Best of CES» award at the Consumer Electronics Show in 2007.[165][166]
In its first year of availability, PC World rated it as the biggest tech disappointment of 2007,[167] and it was rated by InfoWorld as No. 2 of Tech’s all-time 25 flops.[168] Microsoft’s then much smaller competitor Apple noted that, despite Vista’s far greater sales, its own operating system did not seem to have suffered after its release, and would later invest in advertising mocking Vista’s unpopularity with users.[169][170]
Computer manufacturers such as Dell, Lenovo, and Hewlett-Packard released their newest computers with Windows Vista pre-installed; however, after the negative reception of the operating system, they also began selling their computers with Windows XP CDs included because of a drop in sales.[171]
Sales[edit]
A Gartner research report predicted that Vista business adoption in 2008 would overtake that of XP during the same time frame (21.3% vs. 16.9%)[172] while IDC had indicated that the launch of Windows Server 2008 served as a catalyst for the stronger adoption rates.[173][174] As of January 2009, Forrester Research had indicated that almost one third of North American and European corporations had started deploying Vista.[175] At a May 2009 conference, a Microsoft Vice President said «Adoption and deployment of Windows Vista has been slightly ahead of where we had been with XP» for big businesses.[176][177]
Within its first month, 20 million copies of Vista were sold, double the amount of Windows XP sales within its first month in October 2001, five years earlier.[178] Shortly after however, due to Vista’s relatively low adoption rates and continued demand for Windows XP, Microsoft decided to sell Windows XP until June 30, 2008, instead of the previously planned date of January 31, 2008.[179] There were reports of Vista users «downgrading» their operating systems back to XP, as well as reports of businesses planning to skip Vista.[180] A study conducted by ChangeWave in March 2008 showed that the percentage of corporate users who were «very satisfied» with Vista was dramatically lower than other operating systems, with Vista at 8%, compared to the 40% who said they were «very satisfied» with Windows XP.[181]
The internet-usage market share for Windows Vista after two years of availability, in January 2009, was 20.61%. This figure combined with World Internet Users and Population Stats yielded a user base of roughly 330 million,[182] which exceeded Microsoft’s two-year post launch expectations by 130 million.[183] The internet user base reached before the release of its successor (Windows 7) was roughly 400 million according to the same statistical sources.[citation needed]
Criticism[edit]
Windows Vista received mixed reviews. Criticism targets include protracted development time (5–6 years), more restrictive licensing terms, the inclusion of several technologies aimed at restricting the copying of protected digital media,[184] and the usability of the new User Account Control security technology. Moreover, some concerns have been raised about many PCs meeting «Vista Premium Ready» hardware requirements and Vista’s pricing.
Hardware requirements[edit]
While in 2005 Microsoft claimed «nearly all PCs on the market today will run Windows Vista»,[185] the higher requirements of some of the «premium» features, such as the Aero interface, affected many upgraders. According to the UK newspaper The Times in May 2006, the full set of features «would be available to less than 5 percent of Britain’s PC market»; however, this prediction was made several months before Vista was released.[186] This continuing lack of clarity eventually led to a class action against Microsoft as people found themselves with new computers that were unable to use the new software to its full potential despite the assurance of «Vista Capable» designations.[187] The court case has made public internal Microsoft communications that indicate that senior executives have also had difficulty with this issue. For example, Mike Nash (Corporate Vice President, Windows Product Management) commented, «I now have a $2,100 e-mail machine» because of his laptop’s lack of an appropriate graphics chip so hobbled Vista.[188]
Licensing[edit]
Criticism of upgrade licenses pertaining to Windows Vista Starter through Home Premium was expressed by Ars Technica‘s Ken Fisher, who noted that the new requirement of having a prior operating system already installed was going to irritate users who reinstall Windows regularly.[189]
It has been revealed that an Upgrade copy of Windows Vista can be installed clean without first installing a previous version of Windows. On the first install, Windows will refuse to activate. The user must then reinstall that same copy of Vista. Vista will then activate on the reinstall, thus allowing a user to install an Upgrade of Windows Vista without owning a previous operating system.[190] As with Windows XP, separate rules still apply to OEM versions of Vista installed on new PCs: Microsoft asserts that these versions are not legally transferable (although whether this conflicts with the right of first sale has yet to be clearly decided legally).[191]
Cost[edit]
Initially, the cost of Windows Vista was also a source of concern and commentary. A majority of users in a poll said that the prices of various Windows Vista editions posted on the Microsoft Canada website in August 2006 make the product too expensive.[192] A BBC News report on the day of Vista’s release suggested that, «there may be a backlash from consumers over its pricing plans—with the cost of Vista versions in the US roughly half the price of equivalent versions in the UK.»[193]
Since the release of Vista in 2006, Microsoft has reduced the retail, and upgraded the price point of Vista. Originally, Vista Ultimate was priced at $399, and Home Premium Vista at $239. These prices have since been reduced to $319 and $199 respectively.[194]
Digital rights management[edit]
Windows Vista supports additional forms of DRM restrictions. One aspect of this is the Protected Video Path, which is designed so that «premium content» from HD DVD or Blu-ray Discs may mandate that the connections between PC components be encrypted. Depending on what the content demands, the devices may not pass premium content over non-encrypted outputs, or they must artificially degrade the quality of the signal on such outputs or not display it at all. Drivers for such hardware must be approved by Microsoft; a revocation mechanism is also included, which allows Microsoft to disable drivers of devices in end-user PCs over the Internet.[195] Peter Gutmann, security researcher and author of the open source cryptlib library, claims that these mechanisms violate fundamental rights of the user (such as fair use), unnecessarily increase the cost of hardware, and make systems less reliable (the «tilt bit» being a particular worry; if triggered, the entire graphic subsystem performs a reset) and vulnerable to denial-of-service attacks.[196] However, despite several requests[197] for evidence supporting such claims Peter Gutmann has never supported his claims with any researched evidence. Proponents have claimed that Microsoft had no choice but to follow the demands of the movie studios, and that the technology will not actually be enabled until after 2010;[198][199] Microsoft also noted that content protection mechanisms have existed in Windows as far back as Windows ME, and that the new protections will not apply to any existing content, only future content.[200]
User Account Control[edit]
Although User Account Control (UAC) is an important part of Vista’s security infrastructure as it blocks software from silently gaining administrator privileges without the user’s knowledge, it has been widely criticized for generating too many prompts.[201] This has led many Vista UAC users to consider it troublesome, with some consequently either turning the feature off or (for Windows Vista Enterprise or Windows Vista Ultimate users) putting it in auto-approval mode.[202] Responding to this criticism, Microsoft altered the implementation to reduce the number of prompts with SP1.[138] Though the changes resulted in some improvement, it did not alleviate the concerns completely.[203]
Downgrade rights[edit]
End-users of licenses of Windows 7 acquired through OEM or volume licensing may downgrade to the equivalent edition of Windows Vista. Downgrade rights are not offered for Starter, Home Basic or Home Premium editions of Windows 7.[204] For Windows 8 licenses acquired through an OEM, a user may also downgrade to the equivalent edition of Windows Vista. Customers licensed for use of Windows 8 Enterprise are generally licensed for Windows 8 Pro, which may be downgraded to Windows Vista Business.
See also[edit]
- BlueKeep (security vulnerability)
- Comparison of Windows Vista and Windows XP
- Microsoft Security Essentials
Notes[edit]
- ^ 64-bit editions of Windows Vista only. Requires Service Pack 1.[92]
- ^ Installing the preview rollup package released for Windows Server 2008 on March 19, 2019, or any later released rollup package, will update the operating system kernel’s build number from version 6.0.6002 to 6.0.6003. This change was made so Microsoft could continue to service the operating system while avoiding “version-related issues”.[150] This same phenomenon would occur when a user installs the BlueKeep Patch (KB4499180)[151] onto Windows Vista as the patch was released in May 2019, two months after the change was initiated.
References[edit]
- ^ «Windows Licensing Programs». Microsoft. June 2011. Archived from the original on December 16, 2008. Retrieved September 21, 2008.
- ^ White, Nick (November 8, 2006). «Windows Vista releases to manufacturing». Windows Vista Team Blog. Microsoft. Archived from the original on August 9, 2005. Retrieved January 2, 2017.
- ^ a b «Microsoft Launches Windows Vista and the 2007 Office System to Consumers». News Center. Microsoft. January 29, 2007. Retrieved January 2, 2017.
- ^ «Windows Version Numbers — Version and build numbers of Microsoft Windows». www.gaijin.at.
- ^ a b Oiaga, Marius (May 26, 2009). «Download Windows Vista Service Pack 2 (SP2) RTM». Softpedia. SoftNews.
- ^ a b c «Windows Vista Lifecycle Policy». Microsoft. Retrieved January 2, 2017.
- ^ «Microsoft Unveils New Ways for Consumers to Get Windows Vista». News Center. Microsoft. January 17, 2007. Retrieved January 2, 2017.
- ^ Oiaga, Marius (December 3, 2010). «Slow Death for Windows Vista — Packaged Software End of Sales Reached in October». softpedia.
- ^ a b «Desktop Windows Version Market Share Worldwide». StatCounter Global Stats. Retrieved February 2, 2020.
- ^ «Microsoft Support Lifecycle». Support. Microsoft. Retrieved May 11, 2012.
- ^ Gallii, Peter (July 30, 2001). «Pushing Forward». eWeek. Retrieved July 7, 2006.
- ^ Microsoft Windows System Overview. Microsoft.com. Retrieved on October 14, 2011. Archived March 16, 2011, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Lipner, Steve; Howard, Michael (March 2005). «The Trustworthy Computing Security Development Lifecycle». Microsoft Developer Network. Microsoft. Retrieved August 9, 2006.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (March 1, 2003). «Longhorn Alpha Preview 2: Build 4008». Windows SuperSite. Archived from the original on January 17, 2007. Retrieved March 30, 2006.
- ^ «WinHEC 2003 Session Presentations». Microsoft. August 1, 2003. Archived from the original on December 16, 2005. Retrieved March 31, 2006.
- ^ Kaplan, Michael (October 16, 2005). «A reset does not mean everything was thrown away». Sorting It All Out. Retrieved April 2, 2006.
- ^ Keizer, Gregg (January 29, 2007). «Microsoft’s Vista Had Major Mac Envy, Company E-Mails Reveal». InformationWeek. UBM plc. Archived from the original on January 27, 2014. Retrieved February 28, 2013.
- ^ Guth, Robert (September 23, 2005). «Battling Google, Microsoft Changes How It Builds Software». The Wall Street Journal. pp. A1, ??. (viewable online here [1] Archived January 12, 2016, at the Wayback Machine)
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (April 16, 2003). «Brian Valentine talks Windows Server 2003». SuperSite for Windows. Archived from the original on June 14, 2006. Retrieved April 2, 2006.
- ^ Murphy, Victoria (May 26, 2003). «The Exterminator». Forbes Magazine. Archived from the original on January 2, 2004.
- ^ Torre, Charles; Scoble, Robert (December 23, 2005). «Rob Short (and kernel team) — Going deep inside Windows Vista’s kernel architecture». Channel 9. Microsoft.
- ^ Ricciuti, Mike (July 22, 2005). «Longhorn’s new name: Windows Vista». CNET. CBS Interactive. Retrieved March 15, 2016.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (November 1, 2006). «Road to Gold: The Long Road to Windows Vista Part 4: January — July 2005». Archived from the original on November 9, 2006. Retrieved November 2, 2006.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (November 5, 2006). «Paul Thurrott’s SuperSite for Windows: Road to Gold: The Long Road to Windows Vista Part 7: July 2006 – present». SuperSite for Windows. Penton. Archived from the original on November 9, 2006. Retrieved December 25, 2007.
- ^ Spooner, John (March 14, 2006). «Microsoft Shuts Windows on New PC Firmware». eWeek. Retrieved December 26, 2006.[permanent dead link]
- ^ «EFI and Windows Vista». WHDC. Microsoft. April 20, 2006. Archived from the original on February 5, 2008. Retrieved December 26, 2006.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (October 23, 2006). «Exclusive: Here Comes Windows Vista RC2». IT Pro. Archived from the original on October 11, 2006. Retrieved May 30, 2022.
- ^ «Broken Windows Theory». The World As Best As I Remember It. MSDN Blogs. June 14, 2006. Retrieved June 24, 2006.
- ^ «Glitch in voice-recognition software foils Microsoft demo». USA Today. Gannett Co. Inc. Associated Press. July 28, 2006.
- ^ Malone, Steve (October 27, 2006). «Windows Vista RTM code delayed». Digitimes/alphr. Retrieved August 20, 2015.
- ^ White, Nick (November 8, 2006). «Windows Vista releases to manufacturing». Windows Vista team blog. Archived from the original on April 7, 2014. Retrieved November 8, 2006. Windows Vista cost Microsoft six billion dollars to develop.«Vista – a $6 Billion Dollars Operating System – The best billions Bill Gates has ever spent». Softpedia. SoftNews. January 10, 2007. Retrieved October 2, 2008.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (October 27, 2006). «WinInfo Short Takes». WinInfo blog. WindowsITPro. Archived from the original on November 3, 2006. Retrieved October 27, 2006.
- ^ «MSDN Subscriptions». Microsoft. Retrieved October 27, 2006.
- ^ «Microsoft Business Value». Microsoft. Archived from the original on December 5, 2006. Retrieved November 30, 2006.
- ^ Allchin, Jim (November 9, 2006). «The Sounds of Windows Vista». Windows Vista Team Blog. Microsoft. Archived from the original on November 10, 2006. Retrieved April 25, 2015.
- ^ Murph, Darren (May 3, 2007). «Vista’s Aero interface blamed for truncated battery life». Engadget.
- ^ «Vista Battery Fix?». Microsoft. May 6, 2007. Archived from the original on March 13, 2008. Retrieved March 18, 2008.
- ^ «A Closer Look at Windows Vista Part II: Enhanced Search». ni.com. National Instruments. September 17, 2009. Archived from the original on September 29, 2011.
- ^ Durham, Joel Jr. (March 21, 2007). «Ten Must-Have Gadgets for Windows Vista Sidebar». PC Magazine. Ziff Davis. Retrieved March 19, 2016.
- ^ Windows Internet Explorer, Printing Advances Printing in IE7 Archived April 17, 2008, at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ Windows Mail Features Explained, See Reliability Section Windows Mail Archived April 30, 2008, at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ Windows Mail was demonstrated by the development team in this Channel 9 video Archived May 10, 2008, at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ Adams, Dan (December 7, 2006). «Vista and Games for Windows update». IGN. Ziff Davis. Retrieved March 18, 2016.
- ^ Suokko, Matti (2004). «Windows For Mobile PCs And Tablet PCs — CY05 And Beyond». Microsoft. Archived from the original (PPT) on December 14, 2005. Retrieved July 15, 2015.
- ^ Parker, Burt (2005). «Building a «Longhorn»-Ready Mobile PC». Microsoft. Archived from the original (PPT) on September 7, 2015. Retrieved August 4, 2015.
- ^ «Windows Longhorn ACPI and Power Management — Part 1». Microsoft. 2004. Archived from the original (PPT) on February 19, 2006. Retrieved August 4, 2015.
- ^ «Configuring Windows HotStart» (DOCX). Microsoft. March 19, 2010. Retrieved April 18, 2015.
- ^ «Selected Scenarios for Maintaining Data Integrity with Windows Vista». Microsoft. 2006. Archived from the original on August 20, 2006. Retrieved August 24, 2006.
- ^ Windows Update, Easier and Less Disruptive Windows Update in Windows Vista Archived May 22, 2008, at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ Windows Vista, SAPI Talking Windows Archived March 23, 2007, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Russell, Richard G. (May 6, 2005). «System Performance Assessment Tools for Windows Longhorn». Microsoft. Archived from the original (PPT) on November 18, 2012. Retrieved December 27, 2012.
- ^ «Introducing the Windows System Assessment Tool». Microsoft TechNet. Archived from the original on January 16, 2007.
- ^ Hruska, Joel (June 29, 2007). «Vista’s Reliability Monitor provides detailed information on OS uptime». Ars Technica. Condé Nast. Retrieved March 16, 2016.
- ^ O’Reilly, Dennis (May 22, 2007). «Partitioning a Hard Drive in Vista». PC World. IDG. Retrieved March 15, 2016.
- ^ «Upgrade to another edition of Windows Vista». Windows.microsoft.com. Retrieved February 4, 2012.
- ^ LeBlanc, Brandon (May 2, 2007). «Digital Locker Assistant helps manage purchased Apps». Windows Blogs. Microsoft. Retrieved December 26, 2016.
- ^ «Digital Locker». Windows Marketplace. Microsoft. 2007. Archived from the original on February 2, 2007. Retrieved December 26, 2016.
- ^ Shultz, Greg (April 13, 2006). «Windows Vista: ReadyBoost, ReadyDrive, and SuperFetch, oh my!». TechRepublic.
- ^ «Windows Vista: Ready for ReadyDrive — Charles — Channel 9». Channel 9. Microsoft.
- ^ «SuperFetch: How it Works & Myths – OSnews». www.osnews.com.
- ^ Shultz, Greg (July 9, 2008). «Understand how SuperFetch uses RAM to enhance system performance». TechRepublic. Retrieved October 2, 2008.
- ^ «Microsoft Leverages IPv6 With Vista». InformationWeek. UBM plc. January 24, 2006. Archived from the original on February 27, 2013.
- ^ «MSDN Blogs». msdn.com. Microsoft.
- ^ «Windows Vista: Enterprise Networking with Windows Vista». microsoft.com. Microsoft.
- ^ «Windows Vista: Creating a 3-D Desktop — How Windows Vista Works». HowStuffWorks. December 5, 2006.
- ^ White, Nick (August 16, 2006). «DirectX10: The Next Generation in Gaming». Windows Vista Team Blog. Archived from the original on November 18, 2008. Retrieved January 25, 2007.
- ^ «Windows Vista Display Driver Model». MSDN Library.
- ^ «Kernel Enhancements for Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008» (DOC). Microsoft. May 2006. Retrieved April 2, 2011.
- ^ «Inside the Windows Vista Kernel». microsoft.com. Microsoft.
- ^ Ricadela, Aaron (February 14, 2006). «Gates Says Security Is Job One For Vista». InformationWeek. UBM plc. Retrieved January 2, 2017.
- ^ Myers, Tim. «Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008 are Common Criteria Certified at EAL4+». Microsoft. Retrieved May 15, 2013.
- ^ «National Information Assurance Partnership Common Criteria Evaluation and Validation Scheme» (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on October 5, 2012. Retrieved May 15, 2013.
- ^ Stanek, William; Marquardt, Paul (February 6, 2007). «Understanding Windows Vista’s User Account Control». windowsdevcenter.com.
- ^ «Malware Removal Guide» (PDF). October 9, 2010. Archived from the original (PDF) on October 9, 2010. Retrieved March 26, 2021.
- ^ NortonLive Team (February 2010). Malware Removal Guide. Symantec. p. 41.
- ^ Protected Mode IE has been described in detail at the Internet Explorer team blog: Protected Mode in Vista IE7 Archived January 23, 2010, at the Wayback Machine and More details on Protected Mode IE in Windows Vista Archived January 27, 2006, at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ «BitLocker Drive Encryption: Executive Overview». Microsoft. April 5, 2006. Retrieved June 19, 2007.
- ^ Halderman, J. Alex; Schoen, Seth D.; Heninger, Nadia; Clarkson, William; Paul, William; Calandrino, Joseph A.; Feldman, Ariel J.; Appelbaum, Jacob; Felten, Edward W. (February 21, 2008). «Lest We Remember: Cold Boot Attacks on Encryption Keys». Princeton University. Retrieved February 22, 2008.
- ^ Windows Vista Feature Focus: 64-Bit (x64) Support. Winsupersite.com. Retrieved on October 14, 2011. Archived July 30, 2008, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ «What is Windows Aero?». windows.microsoft.com. Microsoft.
- ^ «What’s New in Group Policy in Windows Vista and Windows Server «Longhorn»«. TechNet. Microsoft. Archived from the original on May 8, 2006. Retrieved May 18, 2006.
- ^ .NET Framework 3.0 Technologies, Microsoft Archived July 18, 2006, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Vascellaro, Jessica E. (August 3, 2006). «New Ways to Prove You Are Who You Say You Are Online». The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved March 16, 2016.
- ^ Booker, Logan (15 September 2005). «DirectX 10: More harm than good for graphics?». Maximum Power Computing Atomic. Archived from the original on 27 June 2006. Retrieved 28 May 2006.
- ^ VedBrat, Kam (February 22, 2006). «more comments…» MSDN Blogs. Retrieved May 28, 2006.
- ^ Trevett, Neil (2006). «OpenGL on Vista». Khronos Group. Retrieved November 9, 2006.
- ^ Nguyen, Tuan. «OpenGL Now Natively Supported in Windows Vista». Archived from the original on May 21, 2008. Retrieved January 25, 2007.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (October 6, 2010). «Windows Vista Installation Super Guide, Part 3: Clean Install Windows Vista». SuperSite for Windows. Penton. Archived from the original on April 30, 2016. Retrieved April 26, 2016.
- ^ «You cannot select the Upgrade option when you try to install Windows Vista, and you receive the following message: ‘Upgrade has been disabled’«. How-to. Microsoft. Archived from the original on September 13, 2016. Retrieved April 26, 2016.
Windows Vista requires that the hard disk partition (disk volume) you are installing Vista into is formatted by using the NTFS file system.
- ^ Mueller, Scott (2015). Upgrading and Repairing PCs. Que Publishing. p. 295. ISBN 978-0-13-405769-9. Retrieved May 1, 2016.
- ^ «Notable Changes in Vista Service Pack 1». Microsoft. 2008. Archived from the original on May 3, 2008. Retrieved January 6, 2021.
- ^ «Windows and GPT FAQ». Microsoft. June 6, 2017. Archived from the original on February 10, 2019. Retrieved January 7, 2021.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (October 6, 2010). «Windows Vista Installation Super Guide, Part 3: Clean Install Windows Vista». SuperSite for Windows. Penton. Archived from the original on April 30, 2016. Retrieved May 30, 2015.
- ^ «Enable Game port on vista». Creative. December 8, 2004. Retrieved June 22, 2007.
- ^ «Discontinued Support for IP over 1394». Microsoft. December 8, 2004. Archived from the original on May 15, 2007. Retrieved June 22, 2007.
- ^ «IPX/SPX Protocol in Vista (32bit)». Starbase.com. May 5, 2008. Retrieved May 5, 2008.[permanent dead link]
- ^ «End of support for Windows XP SP2 and Windows Vista RTM». GB Technology. Retrieved May 14, 2010.
- ^ «Microsoft’s Windows Vista SP1 support ends July 12». Computerworld. July 12, 2011. Retrieved August 2, 2012.
- ^ «Microsoft Unveils Windows Vista Product Lineup». PressPass (Press release). Microsoft. February 26, 2006. Archived from the original on November 16, 2006. Retrieved October 31, 2006.
- ^ «Windows Vista Business». Microsoft.
- ^ «Windows Vista Enterprise». Microsoft.
- ^ VedBrat, Kam. «Desktop And Presentation Impact On Hardware Design» (PPT). Microsoft. Retrieved September 1, 2006.
- ^ Oiaga, Marius (December 12, 2006). «Windows Vista Graphical User Interface(s) – Aero, Standard, Basic and Classic». Softpedia. Retrieved April 28, 2009.
- ^ «Windows Vista Enterprise Hardware Planning Guidance». TechNet. Microsoft. 2006. Retrieved October 26, 2006.
- ^ a b Thurrott, Paul (August 25, 2008). «Windows Vista Feature Focus: Windows Vista Standard User Interface». SuperSite for Windows. Penton. Archived from the original on May 22, 2010. Retrieved April 28, 2009.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (August 25, 2008). «Windows Vista Feature Focus: Windows Vista Basic User Interface». SuperSite for Windows. Penton. Archived from the original on February 22, 2009. Retrieved April 28, 2009.
- ^ «Microsoft and PC Manufacturers Make It Easier for Customers to Get Ready for Windows Vista». PressPass. Microsoft. May 18, 2006. Retrieved May 18, 2006.
- ^ a b «Windows Vista Upgrade Advisor». Microsoft. Retrieved June 25, 2006.
- ^ «ForceWare Release 95». Nvidia.com. Retrieved October 2, 2008.
- ^ «MsBetas’ List of Vista Ready GPUs». Archived from the original on March 13, 2007. Retrieved July 30, 2007.
- ^ «Windows Vista Alternate Media». Microsoft. Retrieved August 20, 2007.
- ^ Windows Vista 64-bit Editions Archived July 24, 2008, at the Wayback Machine. Microsoft.com. Retrieved on October 14, 2011.
- ^ «Windows Vista: Recommended System Requirements». Microsoft. Archived from the original on January 1, 2008. Retrieved March 13, 2008.
- ^ Ashley, Mitchell (January 31, 2008). «Vista Starter — The Easy Button For Vista». Network World (International Data Group). Retrieved June 3, 2019.
- ^ «What is the maximum amount of RAM that Windows Vista can handle?». Microsoft. Retrieved April 18, 2014.
- ^ A logical processor is either: 1) One of the two handlers of the thread of instructions of one of the numbers of cores of one of the number of physical processors with support for HyperThreading; or 2) One of the numbers of cores of one of the numbers of physical processors without support for HyperThreading.
- ^ 32 cores without support for HyperThreading, 16 cores with support for HyperThreading.
- ^ 64 cores without support for HyperThreading, 32 cores with support for HyperThreading.
- ^ Logical processor limits for Windows Vista Archived January 27, 2011, at the Wayback Machine. Msdn.microsoft.com. Retrieved on October 14, 2011.
- ^ Physical processor limits for Windows Vista Archived July 14, 2012, at archive.today. Social.answers.microsoft.com (October 24, 2010). Retrieved on October 14, 2011.
- ^ «No update from Microsoft on Vista SP1, Media Center problems». Zdnet. February 18, 2008. Archived from the original on December 16, 2008. Retrieved October 8, 2008.
- ^ «Announcing the RTM of Windows Vista SP1». Microsoft. 4 February 2008. Archived from the original on 5 February 2008. Retrieved 4 February 2008.
- ^ a b c d e f «Windows Vista Service Pack 1 Beta White Paper». Microsoft. August 29, 2007. p. 1. Retrieved August 29, 2007.
- ^ a b «Feb. Launch Now Set for Windows Vista SP1». PC World Magazine. January 31, 2008. Archived from the original on February 6, 2008. Retrieved January 31, 2008.
- ^ Download Details: Windows Vista SP1 All Language Standalone (KB936330) Archived September 4, 2010, at the Wayback Machine. Microsoft.com (April 14, 2008). Retrieved on October 14, 2011.
- ^ Veneziani, Vince (August 30, 2007). «Windows Vista SP1 Gets Officially Announced». TechCrunch. AOL. Retrieved March 16, 2016.
- ^ Russinovich, Mark (August 7, 2007). «The Case of the Failed File Compression». Mark’s Blog. MSDN Blogs. Archived from the original on December 30, 2007. Retrieved October 20, 2007.
- ^ «Don’t judge a book by its cover–why Windows Vista Defrag is cool». The Filing Cabinet. MSDN Blogs. January 26, 2007. Archived from the original on April 28, 2010. Retrieved April 6, 2007.
- ^ «Overview of Windows Vista Service Pack 1». TechNet. Microsoft. February 5, 2008. Retrieved March 17, 2016.
- ^ «Windows and GPT FAQ». MSDN. Microsoft. June 15, 2011. Retrieved February 4, 2012.
- ^ It is possible only when installing from installation DVD of Windows Vista x64 with its service pack 1 integrated.
- ^ Fisher, Ken (June 21, 2007). «Google says Vista search changes not enough». Ars Technica. Retrieved October 20, 2007.
- ^ Fulton, Scott M., III (October 19, 2006). «Vista SP1 to Include Common Security APIs for Partners». BetaNews. Retrieved June 12, 2007.
- ^ «Kernel Patch Protection Criteria Evaluation Document». Microsoft. December 19, 2006. Retrieved June 12, 2007.
- ^ Hruska, Joel (August 9, 2007). «Microsoft releases information on upcoming D3D 10.1 update». Retrieved August 10, 2008.
- ^ Lowe, Scott (January 13, 2010). «An updated guide to common Microsoft software versions». TechRepublic. CBS Interactive. Retrieved March 17, 2016.
- ^ a b «Notable Changes in Vista Service Pack 1». Microsoft. Archived from the original on 3 May 2008. Retrieved 2 May 2008.
- ^ LeBlanc, Brandon (April 28, 2009). «Windows Vista SP2 RTM + Windows Vista SP1 Blocker Tool Removed». Windows Vista Team Blog. Archived from the original on May 18, 2014.
- ^ a b Nash, Mike (October 25, 2008). «Windows Vista Team Blog : Windows Vista Service Pack 2 Beta». Archived from the original on May 9, 2013. Retrieved October 25, 2008.
- ^ «Information about Windows Server 2008 Service Pack 2 and Windows Vista Service Pack 2». Microsoft. October 2, 2008. Retrieved October 17, 2008.
- ^ «What’s New In Windows Vista SP2?». February 6, 2009. Archived from the original on February 12, 2009. Retrieved February 6, 2009.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (February 24, 2009). «Windows Vista SP2: What to Expect». IT Pro. Penton. Retrieved May 30, 2022.
- ^ «Description of the Platform Update for Windows Server 2008 and the Platform Update for Windows Vista». Microsoft Support. October 27, 2009.
- ^ «The Platform Update for Windows Vista». DirectX Developer Blog. September 10, 2009. Archived from the original on April 8, 2014.
- ^ a b Lawrence, Mark (25 November 2009). «Internet Explorer announces to use DirectWrite & Direct2D (comment from Microsoft official)». Archived from the original on 8 April 2014.
- ^ «Platform Update Supplement for Windows Vista and for Windows Server 2008». Microsoft Support (4.0 ed.). Microsoft. February 8, 2011. Archived from the original on December 28, 2011. Retrieved June 28, 2019.
- ^ «Customer guidance for CVE-2019-0708». Microsoft. Retrieved September 16, 2019.
- ^ Greenberg, Andy (August 13, 2019). «DejaBlue: New BlueKeep-Style Bugs Renew The Risk Of A Windows worm». wired. Retrieved August 15, 2019.
- ^ «Build number changing to 6003 in Windows Server 2008».
- ^ «May 14, 2019—KB4499180 (Security-only update)». Microsoft Support. Retrieved January 14, 2022.
- ^ «CVE-2019-1162 — Security Update Guide — Microsoft Windows ALPC Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability». Customer Guidance Security Update Guide. Microsoft. August 13, 2019. Retrieved December 22, 2020.
- ^ «Microsoft Security Advisory 4022344». Microsoft. Retrieved December 23, 2020.
- ^ «The Mojave Experiment». Mojaveexperiment.com. Retrieved October 2, 2008.
- ^ «The Mojave Experiment: Microsoft Windows Vista». Microsoft.
- ^ «Blog Posts Poke Holes in ‘Taste Test’ by Microsoft». The New York Times. August 4, 2008. Retrieved April 8, 2009.
- ^ Oiaga, Marius (November 2, 2007). «Windows Vista Tastes Like Bubbles…» softpedia. Retrieved February 23, 2022.
- ^ ssinchak (June 27, 2007). «Hacking Windows Vista: Speeding Up the System Boot». Extremetech. Retrieved July 30, 2022.
- ^ Anderson, Tim (December 6, 2007). «Is Windows Vista slower than Windows XP?». The Guardian. Retrieved July 30, 2022.
- ^ DirectX 10: The Future of PC Gaming, Tim Smalley, 30 November 2006 Archived April 23, 2008, at the Wayback Machine. Bit-tech.net (November 30, 2006). Retrieved on October 14, 2011.
- ^ Durham, Joel (May 12, 2008). «Gaming Performance: Windows Vista SP1 vs. XP SP3». ExtremeTech. Ziff Davis. Archived from the original on June 7, 2011. Retrieved July 29, 2008.
- ^ Bright, Peter (March 19, 2007). «Windows Vista: more than just a pretty face». ArsTechnica. Condé Nast. Retrieved July 15, 2015.
- ^ Bright, Peter (June 7, 2007). «Windows Vista: Under the Hood». ArsTechnica. Condé Nast. Retrieved July 15, 2015.
- ^ «Paul Thurrott’s SuperSite for Windows: Windows Vista Review, Part 1: Introduction». August 19, 2007. Archived from the original on August 19, 2007. Retrieved December 31, 2019.
- ^ «Windows Vista Named «Best of CES» at the 2007 International Consumer Electronics Show». News Center. Microsoft. January 10, 2007. Retrieved May 25, 2015.
- ^ «Best of CES 2007 awards Consumer Electronics Show, January 8 to 11». CNET. CBS Interactive. 2007. Archived from the original on January 22, 2007. Retrieved May 25, 2015.
- ^ Tynan, Dan (December 16, 2007). «The 15 Biggest Tech Disappointments of 2007». PC World. IDG. Archived from the original on December 18, 2007. Retrieved December 18, 2007.: listed as No. 1 of «The 15 Biggest Tech Disappointments of 2007»
- ^ McAllister, Neil (January 21, 2008). «Tech’s all-time top 25 flops». InfoWorld. IDG. Retrieved January 27, 2008.
- ^ Flynn, Laurie (April 26, 2007). «Apple Zooms Past Rivals, With 88% Profit Growth». The New York Times. Retrieved December 2, 2015.
- ^ Prague, Liam (February 1, 2022). «Happy birthday, Windows Vista: Troubled teen hits 15». www.theregister.com. Retrieved July 29, 2022.
- ^ Horowitz, Michael (April 23, 2008). «Who’s selling Windows XP in July?». CNET. CBS Interactive. Retrieved March 14, 2016.
- ^ Hoover, J. Nicholas (May 8, 2008). «Microsoft’s Windows Vista Spin Merits Second Look». InformationWeek. UBM plc. Retrieved February 16, 2009.
- ^ Gillen, Al; Waldman, Brett (March 2008). «Document at a Glance – 211087». IDC. Archived from the original on December 16, 2008. Retrieved February 16, 2009.
- ^ O’Neill, Shane (October 30, 2008). «Vista Fights for Relevancy Against Poor Sales, XP, Windows 7». PC World. IDG. Retrieved February 16, 2009.
- ^ Lai, Eric (February 7, 2009). «Vista Makes Converts of Gamers, Enterprises». PC World. Retrieved February 9, 2009.
- ^ Lai, Eric (28 May 2009). «Microsoft: Vista’s enterprise momentum will ‘accrue’ for Windows 7». Computerworld. Archived from the original on 2 March 2007. Retrieved 2 June 2009.
- ^ Reller, Tami (May 28, 2009). «Cowen and Company Technology Media & Telecom Conference». Microsoft. Archived from the original (DOC) on June 16, 2009.
- ^ Microsoft: First Month Vista Sales Double XP, article by Nate Mook Archived December 24, 2007, at the Wayback Machine. Betanews.com (March 26, 2007). Retrieved on October 14, 2011.
- ^ Fried, Ina (September 27, 2007). «Microsoft extends Windows XP’s stay». CNET.
- ^ Windows XP vs. Vista: An Explosion of Opinion Archived February 12, 2022, at the Wayback Machine. Abcnews.go.com (March 20, 2008). Retrieved on October 14, 2011.
- ^ «Leopard drubs Vista in corporate satisfaction survey». March 26, 2008. Archived from the original on November 9, 2019. Retrieved May 30, 2022.
- ^ «AMD 50×15—World Internet Usage». AMD. February 2, 2009. Archived from the original on February 24, 2008. Retrieved November 1, 2009.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (September 16, 2006). «Allchin: 200 Million Windows Vista Users in 24 Months». IT Pro. Penton. Archived from the original on November 9, 2019. Retrieved May 30, 2022.
- ^ Sullivan, John (March 6, 2007). «What’s wrong with Microsoft Windows Vista?». Free Software Foundation. Retrieved March 24, 2007.
- ^ Spooner, John G.; Foley, Mary Jo (August 5, 2005). «Will Your PC Run Windows Vista?». eWeek. QuinStreet. Retrieved August 15, 2006.[permanent dead link]
- ^ Judge, Elizabeth (May 20, 2006). «Windows revamp ‘too advanced for most PCs’«. The Times. London. Retrieved August 15, 2006.
- ^ Gregg Keizer (November 26, 2007).Lawyers: Even Microsoft Confused Over Vista Marketing Archived November 28, 2007, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ «They Criticized Vista. And They Should Know.» Archived April 13, 2019, at the Wayback Machine, The New York Times, March 9, 2008.
- ^ Fisher, Ken (January 28, 2007). «Vista «upgrade» drops compliance checking, requires the old OS to install». Ars Technica. Retrieved January 28, 2007.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (February 3, 2007). «How to Clean Install Windows Vista with Upgrade Media». Supersite for Windows. Penton. Archived from the original on February 5, 2007. Retrieved February 5, 2007.
- ^ Fried, Ina (October 17, 2006). «Microsoft limits Vista transfers». CNET. CBS Interactive.
- ^
Beer, Stan (August 30, 2006). «Windows Vista too expensive says, users». ITWire.com. Archived from the original on September 9, 2006. Retrieved October 19, 2006. - ^ «Microsoft starts Vista hard sell». Technology. BBC News. January 30, 2007. Retrieved January 30, 2007.
- ^ Protalinski, Emil (June 25, 2009). «Windows 7 pricing announced: cheaper than Vista (Updated)». Retrieved October 4, 2009.
- ^ «Output Content Protection and Windows Vista». WHDC. Microsoft. April 27, 2005. Archived from the original on November 16, 2006. Retrieved January 8, 2007.
- ^ Gutmann, Peter (January 27, 2007). «A Cost Analysis of Windows Vista Content Protection». Retrieved January 27, 2007. Also available: PDF version Archived May 11, 2011, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Bott and Ou call out Gutmann’s Vista FUD Archived August 31, 2007, at the Wayback Machine. Blogs.guardian.co.uk. Retrieved on October 14, 2011.
- ^ Smith, Paul (December 31, 2006). «Windows Vista DRM nonsense». Retrieved January 3, 2007.
- ^ Fisher, Ken (May 21, 2006). «Hollywood reportedly in agreement to delay forced quality downgrades for Blu-ray, HD DVD». Ars Technica. Retrieved January 21, 2007.
- ^ Marsh, Dave (January 20, 2007). «Windows Vista Content Protection—Twenty Questions (and Answers)». Windows Vista team blog. Microsoft. Archived from the original on January 21, 2013. Retrieved January 20, 2007.
- ^ «User Account Control: yes, you can turn it off. Is this a good or a bad thing?». Ars Technica. September 10, 2006.
- ^ «Don’t Shut Off Vista UAC, There’s A Better Way». InformationWeek. June 11, 2007. Retrieved October 14, 2011.
- ^ Torode, Christina (April 2, 2008). «Minasi says Vista SP1 solves problems, adds new ones». SearchWinIT.com.
- ^ «Downgrade rights for owners of licensed Windows 8 and Windows 7» (PDF). microsoft.com.
External links[edit]
- Windows Vista End of Support
- Windows Vista Service Pack 2 (SP2) Update
| Version of the Windows NT operating system | |

Screenshot of Windows Vista Ultimate, showing its desktop, taskbar, start menu, Windows Sidebar, Welcome Center, and glass effects of Windows Aero |
|
| Developer | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| Source model |
|
| Released to manufacturing |
November 8, 2006; 16 years ago[2] |
| General availability |
January 30, 2007; 16 years ago[3] |
| Final release | Service Pack 2 with security update rollup (6.0.6002)[4] / October 18, 2016; 6 years ago[5] |
| Update method |
|
| Platforms | IA-32 and x86-64 |
| Kernel type | Hybrid (NT) |
| Userland | Windows API, NTVDM, SUA |
| License | Proprietary commercial software |
| Preceded by | Windows XP (2001) |
| Succeeded by | Windows 7 (2009) |
| Official website | Windows Vista (archived at Wayback Machine) |
| Support status | |
| Mainstream support ended on April 10, 2012. Extended support ended on April 11, 2017.[6] Installing a service pack is required for users to receive updates and support after April 13, 2010. |
Windows Vista is a major release of the Windows NT operating system developed by Microsoft. It was the direct successor to Windows XP, which was released five years earlier, at the time being the longest time span between successive releases of Microsoft’s Windows desktop operating systems. Development was completed on November 8, 2006, and over the following three months, it was released in stages to computer hardware and software manufacturers, business customers, and retail channels. On January 30, 2007, it was released internationally and made available for purchase and download from the Windows Marketplace; this is the first release of Windows to be made available through a digital distribution platform.[7]
New features of Windows Vista include an updated graphical user interface and visual style dubbed «Aero,» a new search component called «Windows Search,» redesigned networking, audio, print, and display sub-systems, and new multimedia tools such as Windows DVD Maker. Windows Vista aimed to increase the level of communication between machines on a home network, using peer-to-peer technology to simplify sharing files and media between computers and devices. Windows Vista included version 3.0 of the .NET Framework, allowing software developers to write applications without traditional Windows APIs. Windows Vista removed support for devices without ACPI.
While these new features and security improvements garnered positive reviews, Windows Vista was also the target of much criticism and negative press. Criticism of Windows Vista includes its high system requirements, more restrictive licensing terms, lack of compatibility, longer boot time, and excessive authorization prompts from User Account Control. As a result of these and other issues, Windows Vista saw lower initial adoption and satisfaction rates than Windows XP. However, Windows Vista usage had surpassed Microsoft’s pre-launch two-year-out expectations of achieving 200 million users, with an estimated 330 million Internet users in January 2009. On October 22, 2010, Microsoft ceased sales of retail copies of Windows Vista, and the original equipment manufacturer’s sales for Windows Vista ceased a year later.[8] The market share of Windows Vista fell below 1% by the end of 2021, coinciding with the release of Windows 11.[9]
Mainstream support for Windows Vista ended on April 10, 2012, and extended support ended on April 11, 2017[10] Windows Vista was succeeded by Windows 7. As of February 2022, 0.18% of PCs run Windows Vista.[9]
Development[edit]
Microsoft began work on Windows Vista, known at the time by its codename «Longhorn», in May 2001,[11] five months before the release of Windows XP. It was originally expected to ship in October 2003 as a minor step between Windows XP and «Blackcomb», which was planned to be the company’s next major operating system release. Gradually, «Longhorn» assimilated many of the important new features and technologies slated for Blackcomb, resulting in the release date being pushed back several times in three years. In some builds of Longhorn, their license agreement said «For the Microsoft product codenamed ‘Whistler'». Many of Microsoft’s developers were also re-tasked to build updates to Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 to strengthen security. Faced with ongoing delays and concerns about feature creep, Microsoft announced on August 27, 2004, that it had revised its plans. For this reason, Longhorn was reset to start work on componentizing the Windows Server 2003 Service Pack 1 codebase, and over time re-incorporating the features that would be intended for an actual operating system release. However, some previously announced features such as WinFS were dropped or postponed, and a new software development methodology called the Security Development Lifecycle was incorporated to address concerns with the security of the Windows codebase, which is programmed in C, C++ and assembly. Longhorn became known as Vista in 2005.[12][13]
Longhorn[edit]
The early development stages of Longhorn were generally characterized by incremental improvements and updates to Windows XP. During this period, Microsoft was fairly quiet about what was being worked on, as their marketing and public relations efforts were more strongly focused on Windows XP, and Windows Server 2003, which was released in April 2003. Occasional builds of Longhorn were leaked onto popular file sharing networks such as IRC, BitTorrent, eDonkey and various newsgroups, and so most of what is known about builds before the first sanctioned development release of Longhorn in May 2003 is derived from these builds.
After several months of relatively little news or activity from Microsoft with Longhorn, Microsoft released Build 4008, which had made an appearance on the Internet around February 28, 2003.[14] It was also privately handed out to a select group of software developers. As an evolutionary release over build 3683, it contained several small improvements, including a modified blue «Plex» theme and a new, simplified Windows Image-based installer that operates in graphical mode from the outset, and completed an install of the operating system in approximately one third the time of Windows XP on the same hardware. An optional «new taskbar» was introduced that was thinner than the previous build and displayed the time differently.
The most notable visual and functional difference, however, came with Windows Explorer. The incorporation of the Plex theme made blue the dominant color of the entire application. The Windows XP-style task pane was almost completely replaced with a large horizontal pane that appeared under the toolbars. A new search interface allowed for filtering of results, searching for Windows help, and natural-language queries that would be used to integrate with WinFS. The animated search characters were also removed. The «view modes» were also replaced with a single slider that would resize the icons in real-time, in the list, thumbnail, or details mode, depending on where the slider was. File metadata was also made more visible and more easily editable, with more active encouragement to fill out missing pieces of information. Also of note was the conversion of Windows Explorer to being a .NET application.
Most builds of Longhorn and Vista were identified by a label that was always displayed in the bottom-right corner of the desktop. A typical build label would look like «Longhorn Build 3683.Lab06_N.020923-1821». Higher build numbers did not automatically mean that the latest features from every development team at Microsoft was included. Typically, a team working on a certain feature or subsystem would generate their working builds which developers would test with, and when the code was deemed stable, all the changes would be incorporated back into the main development tree at once. At Microsoft, several «Build labs» exist where the compilation of the entirety of Windows can be performed by a team. The name of the lab in which any given build originated is shown as part of the build label, and the date and time of the build follow that. Some builds (such as Beta 1 and Beta 2) only display the build label in the version information dialog (Winver). The icons used in these builds are from Windows XP.
At the Windows Hardware Engineering Conference (WinHEC) in May 2003, Microsoft gave their first public demonstrations of the new Desktop Window Manager and Aero. The demonstrations were done on a revised build 4015 which was never released. Several sessions for developers and hardware engineers at the conference focused on these new features, as well as the Next-Generation Secure Computing Base (previously known as «Palladium»), which at the time was Microsoft’s proposed solution for creating a secure computing environment whereby any given component of the system could be deemed «trusted». Also at this conference, Microsoft reiterated their roadmap for delivering Longhorn, pointing to an «early 2005» release date.[15]
Development reset[edit]
By 2004, it had become obvious to the Windows team at Microsoft that they were losing sight of what needed to be done to complete the next version of Windows and ship it to customers. Internally, some Microsoft employees were describing the Longhorn project as «another Cairo» or «Cairo.NET», referring to the Cairo development project that the company embarked on through the first half of the 1990s, which never resulted in a shipping operating system (though nearly all the technologies developed in that time did end up in Windows 95 and Windows NT[16]). Microsoft was shocked in 2005 by Apple’s release of Mac OS X Tiger. It offered only a limited subset of features planned for Longhorn, in particular fast file searching and integrated graphics and sound processing, but appeared to have impressive reliability and performance compared to contemporary Longhorn builds.[17] Most Longhorn builds had major Windows Explorer system leaks which prevented the OS from performing well, and added more confusion to the development teams in later builds with more and more code being developed which failed to reach stability.
In a September 23, 2005 front-page article in The Wall Street Journal,[18] Microsoft co-president Jim Allchin, who had overall responsibility for the development and delivery of Windows, explained how development of Longhorn had been «crashing into the ground» due in large part to the haphazard methods by which features were introduced and integrated into the core of the operating system, without a clear focus on an end-product. Allchin went on to explain how in December 2003, he enlisted the help of two other senior executives, Brian Valentine and Amitabh Srivastava, the former being experienced with shipping software at Microsoft, most notably Windows Server 2003,[19] and the latter having spent his career at Microsoft researching and developing methods of producing high-quality testing systems.[20] Srivastava employed a team of core architects to visually map out the entirety of the Windows operating system, and to proactively work towards a development process that would enforce high levels of code quality, reduce interdependencies between components, and in general, «not make things worse with Vista».[21] Since Microsoft decided that Longhorn needed to be further componentized, work started on builds (known as the Omega-13 builds) that would componentize existing Windows Server 2003 source code, and over time add back functionality as development progressed. Future Longhorn builds would start from Windows Server 2003 Service Pack 1 and continue from there.
This change, announced internally to Microsoft employees on August 26, 2004, began in earnest in September, though it would take several more months before the new development process and build methodology would be used by all of the development teams. A number of complaints came from individual developers, and Bill Gates himself, that the new development process was going to be prohibitively difficult to work within.
As Windows Vista[edit]
By approximately November 2004, the company had considered several names for the final release, ranging from simple to fanciful and inventive. In the end, Microsoft chose Windows Vista as confirmed on July 22, 2005, believing it to be a «wonderful intersection of what the product really does, what Windows stands for, and what resonates with customers, and their needs». Group Project Manager Greg Sullivan told Paul Thurrott «You want the PC to adapt to you and help you cut through the clutter to focus on what’s important to you. That’s what Windows Vista is all about: «bringing clarity to your world» (a reference to the three marketing points of Vista—Clear, Connected, Confident), so you can focus on what matters to you».[22] Microsoft co-president Jim Allchin also loved the name, saying that «Vista creates the right imagery for the new product capabilities and inspires the imagination with all the possibilities of what can be done with Windows—making people’s passions come alive.»[23]
After Longhorn was named Windows Vista in July 2005, an unprecedented beta-test program was started, involving hundreds of thousands of volunteers and companies. In September of that year, Microsoft started releasing regular Community Technology Previews (CTP) to beta testers from July 2005 to February 2006. The first of these was distributed at the 2005 Microsoft Professional Developers Conference, and was subsequently released to beta testers and Microsoft Developer Network subscribers. The builds that followed incorporated most of the planned features for the final product, as well as a number of changes to the user interface, based largely on feedback from beta testers. Windows Vista was deemed feature-complete with the release of the «February CTP», released on February 22, 2006, and much of the remainder of the work between that build and the final release of the product focused on stability, performance, application and driver compatibility, and documentation. Beta 2, released in late May, was the first build to be made available to the general public through Microsoft’s Customer Preview Program. It was downloaded over 5 million times. Two release candidates followed in September and October, both of which were made available to a large number of users.[24]
At the Intel Developer Forum on March 9, 2006, Microsoft announced a change in their plans to support EFI in Windows Vista. The UEFI 2.0 specification (which replaced EFI 1.10) was not completed until early 2006, and at the time of Microsoft’s announcement, no firmware manufacturers had completed a production implementation which could be used for testing. As a result, the decision was made to postpone the introduction of UEFI support to Windows; support for UEFI on 64-bit platforms was postponed until Vista Service Pack 1 and Windows Server 2008 and 32-bit UEFI would not be supported, as Microsoft did not expect many such systems to be built because the market was quickly moving to 64-bit processors.[25][26]
While Microsoft had originally hoped to have the consumer versions of the operating system available worldwide in time for the 2006 holiday shopping season, it announced in March 2006 that the release date would be pushed back to January 2007 in order to give the company—and the hardware and software companies that Microsoft depends on for providing device drivers—additional time to prepare. Because a release to manufacturing (RTM) build is the final version of code shipped to retailers and other distributors, the purpose of a pre-RTM build is to eliminate any last «show-stopper» bugs that may prevent the code from responsibly being shipped to customers, as well as anything else that consumers may find annoying. Thus, it is unlikely that any major new features would be introduced; instead, work would focus on Vista’s fit and finish. In just a few days, developers had managed to drop Vista’s bug count from over 2470 on September 22 to just over 1400 by the time RC2 shipped in early October. However, they still had a way to go before Vista was ready to RTM. Microsoft’s internal processes required Vista’s bug count to drop to 500 or fewer before the product could go into escrow for RTM.[27] For most of the pre-RTM builds, those 32-bit editions are only released.
On June 14, 2006, Windows developer Philip Su posted a blog entry which decried the development process of Windows Vista, stating that «The code is way too complicated, and that the pace of coding has been tremendously slowed down by overbearing process.»[28] The same post also described Windows Vista as having approximately 50 million lines of code, with about 2,000 developers working on the product. During a demonstration of the speech recognition feature new to Windows Vista at Microsoft’s Financial Analyst Meeting on July 27, 2006, the software recognized the phrase «Dear mom» as «Dear aunt». After several failed attempts to correct the error, the sentence eventually became «Dear aunt, let’s set so double the killer delete select all«.[29] A developer with Vista’s speech recognition team later explained that there was a bug with the build of Vista that was causing the microphone gain level to be set very high, resulting in the audio being received by the speech recognition software being «incredibly distorted».
Windows Vista build 5824 (October 17, 2006) was supposed to be the RTM release, but a bug, where the OOBE hangs at the start of the WinSAT Assessment (if upgraded from Windows XP), requiring the user to terminate the msoobe.exe by pressing Shift+F10 to open Command Prompt using either command-line tools or Task Manager prevented this, damaging development and lowering the chance that it would hit its January 2007 deadline.[31]
Development of Windows Vista came to an end when Microsoft announced that it had been finalized on November 8, 2006, and was concluded by co-president of Windows development, Jim Allchin.[32] The RTM’s build number had also jumped to 6000 to reflect Vista’s internal version number, NT 6.0.[33] Jumping RTM build numbers is common practice among consumer-oriented Windows versions, like Windows 98 (build 1998), Windows 98 SE (build 2222), Windows Me (build 3000) or Windows XP (build 2600), as compared to the business-oriented versions like Windows 2000 (build 2195) or Server 2003 (build 3790). On November 16, 2006, Microsoft made the final build available to MSDN and Technet Plus subscribers.[34] A business-oriented Enterprise edition was made available to volume license customers on November 30, 2006.[35] Windows Vista was launched for general customer availability on January 30, 2007.[3]
New or changed features[edit]
Windows Vista introduced several features and functionality not present in its predecessors.
End-user[edit]
- Windows Aero: The new graphical user interface is named Windows Aero, which Jim Allchin stated is an acronym for Authentic, Energetic, Reflective, and Open.[36] Microsoft intended the new interface to be cleaner and more aesthetically pleasing than those of previous Windows versions, featuring new transparencies, live thumbnails, live icons, and animations, thus providing a new level of eye candy. Laptop users report, however, that enabling Aero shortens battery life[37][38] and reduces performance.
- Windows shell: The new Windows shell offers a new range of organization, navigation, and search capabilities: Task panes in Windows Explorer are removed, integrating the relevant task options into the toolbar. A «Favorite links» pane has been added, enabling one-click access to common directories. A search box appears in every Explorer window. The address bar has been replaced with a breadcrumb navigation bar. Icons of certain file types in Windows Explorer are «live» and can be scaled in size up to 256 × 256 pixels. The preview pane allows users to see thumbnails of various files and view the contents of documents. The details pane shows information such as file size and type, and allows viewing and editing of embedded tags in supported file formats. The Start menu has changed as well; incorporating an instant search box, and the All Programs list uses a horizontal scroll bar instead of the cascading flyout menu seen in Windows XP. The word «Start» itself has been removed in favor of a blue orb that bears the Windows logo.
- Windows Search: A new search component of Windows Vista, it features instant search (also known as search as you type), which provides instant search results, thus finding files more quickly than the search features found in previous versions of Windows and can search the contents of recognized file types.[39] Users can search for certain metadata such as name, extension, size, date or attributes.
- Windows Sidebar: A transparent panel, anchored to the right side of the screen, wherein a user can place Desktop Gadgets, which are small applets designed for a specialized purpose (such as displaying the weather or sports scores). Gadgets can also be placed on the desktop.[40]
- Windows Internet Explorer 7: New user interface, tabbed browsing, RSS, a search box, improved printing,[41] Page Zoom, Quick Tabs (thumbnails of all open tabs), Anti-Phishing filter, several new security protection features, Internationalized Domain Name support (IDN), and improved web standards support. IE7 in Windows Vista runs in isolation from other applications in the operating system (protected mode); exploits and malicious software are restricted from writing to any location beyond Temporary Internet Files without explicit user consent.
- Windows Media Player 11, a major revamp of Microsoft’s program for playing and organizing music and video. New features in this version include word wheeling (incremental search or «search as you type»), a new GUI for the media library, photo display and organization, the ability to share music libraries over a network with other Windows Vista machines, Xbox 360 integration, and support for other Media Center Extenders.
- Windows Defender: An antispyware program with several real-time protection agents. It includes a software explorer feature, which provides access to startup programs, and allows one to view currently running software, network-connected applications, and Winsock providers (Winsock LSPs).
- Backup and Restore Center: Includes a backup and restore application that gives users the ability to schedule periodic backups of files on their computer, as well as recovery from previous backups. Backups are incremental, storing only the changes made each time, minimizing disk usage. It also features Complete PC Backup (available only in the Ultimate, Business, and Enterprise editions), which backs up an entire computer as an image onto a hard disk or DVD. Complete PC Backup can automatically recreate a machine setup onto new hardware or hard disk in case of any hardware failures. Complete PC Restore can be initiated from within Windows Vista or from the Windows Vista installation CD if a PC is so corrupt that it cannot start normally from the hard disk.
- Windows Mail: A replacement for Outlook Express that includes a new mail store that improves stability,[42] and features integrated instant search. It has a Phishing Filter like Internet Explorer 7 and Junk mail filtering that is enhanced through regular updates via Windows Update.[43]
- Windows Calendar is a new calendar and task application that integrates with Windows Contacts and Windows Mail. It is compatible with various calendar file types, such as the popular iCalendar.
- Windows Photo Gallery, a photo and movie library management application. It can import from digital cameras, tag and rate individual items, adjust colors and exposure, create and display slideshows (with pan and fade effects) through Direct3D and burn slideshows to a DVD.
- Windows DVD Maker, a companion program to Windows Movie Maker that provides the ability to create video DVDs based on a user’s content. Users can design a DVD with title, menus, video, soundtrack, pan and zoom motion effects on pictures or slides.
- Windows Media Center, which was previously exclusively bundled in a separate edition of Windows XP, known as Windows XP Media Center Edition, has been incorporated into the Home Premium and Ultimate editions of Windows Vista.
- Games: Most of the standard computer games included in previous versions of Windows have been redesigned to showcase Vista’s new graphical capabilities. New games available in Windows Vista are Chess Titans (3D Chess game), Mahjong Titans (3D Mahjong game), and Purble Place (a small collection of games, oriented towards younger children, including a matching game, a cake-creator game, and a dress-up puzzle game). Purble Place is the only one of the new games available in the Windows Vista Home Basic edition. InkBall is available for Home Premium (or better) users.
- Games Explorer: A new special folder called «Games» exposes installed video games and information about them. These metadata may be updated from the Internet.[44]
- Windows Mobility Center is a control panel that centralizes the most relevant information related to mobile computing (brightness, sound, battery level/power scheme selection, wireless network, screen orientation, presentation settings, etc.).
- Windows Fax and Scan Allows computers with fax modems to send and receive fax documents, as well as scan documents. It is not available in the Home editions of Windows Vista, but is available in the Business, Enterprise, and Ultimate editions.
- Windows Meeting Space replaces NetMeeting. Users can share applications (or their entire desktop) with other users on the local network, or over the Internet using peer-to-peer technology (higher editions than Starter and Home Basic can take advantage of hosting capabilities, Starter and Home Basic editions are limited to «join» mode only)
- Windows HotStart enables compatible computers to start applications directly from operating system startup or resume by the press of a button—this enables what Microsoft has described as appliance-like availability, which allows computers to function in a manner similar to a consumer electronics device such as a DVD player;[45] the feature was also designed to provide the instant-on feature availability that is traditionally associated with mobile devices.[46] While Microsoft has emphasized multimedia scenarios with Windows HotStart,[47] a user can configure this feature so that a button launches a preferred application.[48]
- Shadow Copy automatically creates daily backup copies of files and folders. Users can also create «shadow copies» by setting a System Protection Point using the System Protection tab in the System control panel. The user can view multiple versions of a file throughout a limited history and be allowed to restore, delete, or copy those versions. This feature is available only in the Business, Enterprise, and Ultimate editions of Windows Vista and is inherited from Windows Server 2003.[49]
- Windows Update: Software and security updates have been simplified,[50] now operating solely via a control panel instead of as a web application. Windows Mail’s spam filter and Windows Defender’s definitions are updated automatically via Windows Update. Users who choose the recommended setting for Automatic Updates will have the latest drivers installed and available when they add a new device.
- Parental controls: Allows administrators to monitor and restrict user activity, as well as control which websites, programs, and games each Standard user can use and install. This feature is not included in the Business or Enterprise editions of Vista.
- Windows SideShow: Enables the auxiliary displays on newer laptops or supported Windows Mobile devices. It is meant to be used to display device gadgets while the computer is on or off.
- Speech recognition is integrated into Vista.[51] It features a redesigned user interface and configurable command-and-control commands. Unlike the Office 2003 version, which works only in Office and WordPad, Speech Recognition in Windows Vista works for any accessible application. In addition, it currently supports several languages: British and American English, Spanish, French, German, Chinese (Traditional and Simplified), and Japanese.
- New fonts, including several designed for screen reading, and improved Chinese (Yahei, JhengHei), Japanese (Meiryo), and Korean (Mulgan) fonts. ClearType has also been enhanced and enabled by default.
- Improved audio controls allow the system-wide volume or volume of individual audio devices and even individual applications to be controlled separately. New audio functionalities such as room correction, bass management, speaker fill, and headphone virtualization have also been incorporated.
- Problem Reports and Solutions, a feature that allows users to check for solutions to problems or view previously sent problems for any solutions or additional information, if available.Windows System Assessment Tool is a tool used to benchmark system performance. Software such as games can retrieve this rating and modify its own behavior at runtime to improve performance. The benchmark tests CPU, RAM, 2-D and 3-D graphics acceleration, graphics memory and hard disk space.[52][53]
- Windows Ultimate Extras: The Ultimate edition of Windows Vista provides, via Windows Update, access to some additional features. These are a collection of additional MUI language packs, Texas Hold ‘Em (a Poker game) and Microsoft Tinker (a strategy game where the character is a robot), BitLocker and EFS enhancements that allow users to back up their encryption key online in a Digital Locker, and Windows Dreamscene, which enables the use of videos in MPEG and WMV formats as the desktop background. On April 21, 2008, Microsoft launched two more Ultimate Extras; three new Windows sound schemes, and a content pack for Dreamscene. Various DreamScene Content Packs have been released since the final version of DreamScene was released.
- Reliability and Performance Monitor includes various tools for tuning and monitoring system performance and resources activities of CPU, disks, network, memory and other resources. It shows the operations on files, the opened connections, etc.[54]
- Disk Management: The Logical Disk Manager in Windows Vista supports shrinking and expanding volumes on-the-fly.[55]
- Windows Anytime Upgrade: is a program that allows a user to upgrade their computer running Vista to a higher edition. For example, a computer running Windows Vista Home Basic can be upgraded to Home Premium or better. Anytime Upgrade permits users to upgrade without having their programs and data erased, and is cheaper than replacing the existing installation of Windows. Anytime Upgrade is no longer available for Vista.[56]
- Digital Locker Assistant: A program that facilitated access to downloads and purchases from the Windows Marketplace distribution platform.[57] Apps purchased from Windows Marketplace are managed by Microsoft Account credentials, which are used to access a user’s digital locker that stores the app and its associated information (e.g., licenses) off-site.[58]
Core[edit]
Vista includes technologies such as ReadyBoost[59] and ReadyDrive, which employ fast flash memory (located on USB flash drives and hybrid hard disk drives) to improve system performance by caching commonly used programs and data. This manifests itself in improved battery life on notebook computers as well, since a hybrid drive can be spun down when not in use.[60] Another new technology called SuperFetch utilizes machine learning techniques to analyze usage patterns to allow Windows Vista to make intelligent decisions about what content should be present in system memory at any given time. It uses almost all the extra RAM as disk cache.[61] In conjunction with SuperFetch, an automatic built-in Windows Disk Defragmenter makes sure that those applications are strategically positioned on the hard disk where they can be loaded into memory very quickly with the least physical movement of the hard disk’s read-write heads.[62]
As part of the redesign of the networking architecture, IPv6 has been fully incorporated into the operating system[63] and a number of performance improvements have been introduced, such as TCP window scaling.[64] Earlier versions of Windows typically needed third-party wireless networking software to work properly, but this is not the case with Vista, which includes more comprehensive wireless networking support.[65]
For graphics, Vista introduces a new Windows Display Driver Model[66] and a major revision to Direct3D. The new driver model facilitates the new Desktop Window Manager, which provides the tearing-free desktop and special effects that are the cornerstones of Windows Aero. Direct3D 10, developed in conjunction with major graphics card manufacturers, is a new architecture with more advanced shader support, and allows the graphics processing unit to render more complex scenes without assistance from the CPU. It features improved load balancing between CPU and GPU and also optimizes data transfer between them.[67] WDDM also provides video content playback that rivals typical consumer electronics devices. It does this by making it easy to connect to external monitors, providing for protected HD video playback, and increasing overall video playback quality. For the first time in Windows, graphics processing unit (GPU) multitasking is possible, enabling users to run more than one GPU-intensive application simultaneously.[68]
At the core of the operating system, many improvements have been made to the memory manager, process scheduler and I/O scheduler. The Heap Manager implements additional features such as integrity checking in order to improve robustness and defend against buffer overflow security exploits, although this comes at the price of breaking backward compatibility with some legacy applications.[69] A Kernel Transaction Manager has been implemented that enables applications to work with the file system and Registry using atomic transaction operations.[70]
[edit]
Improved security was a primary design goal for Vista.[71] Microsoft’s Trustworthy Computing initiative, which aims to improve public trust in its products, has had a direct effect on its development. This effort has resulted in a number of new security and safety features and an Evaluation Assurance Level rating of 4+.[72][73]
User Account Control, or UAC is perhaps the most significant and visible of these changes. UAC is a security technology that makes it possible for users to use their computer with fewer privileges by default, to stop malware from making unauthorized changes to the system. This was often difficult in previous versions of Windows, as the previous «limited» user accounts proved too restrictive and incompatible with a large proportion of application software, and even prevented some basic operations such as looking at the calendar from the notification tray. In Windows Vista, when an action is performed that requires administrative rights (such as installing/uninstalling software or making system-wide configuration changes), the user is first prompted for an administrator name and password; in cases where the user is already an administrator, the user is still prompted to confirm the pending privileged action. Regular use of the computer such as running programs, printing, or surfing the Internet does not trigger UAC prompts. User Account Control asks for credentials in a Secure Desktop mode, in which the entire screen is dimmed, and only the authorization window is active and highlighted. The intent is to stop a malicious program from misleading the user by interfering with the authorization window, and to hint to the user about the importance of the prompt.[74]
Testing by Symantec Corporation has proven the effectiveness of UAC. Symantec used over 2,000 active malware samples, consisting of backdoors, keyloggers, rootkits, mass mailers, trojan horses, spyware, adware, and various other samples. Each was executed on a default Windows Vista installation within a standard user account. UAC effectively blocked over 50 percent of each threat, excluding rootkits. 5 percent or less of the malware that evaded UAC survived a reboot.[75][76]
Internet Explorer 7’s new security and safety features include a phishing filter, IDN with anti-spoofing capabilities, and integration with system-wide parental controls. For added security, ActiveX controls are disabled by default. Also, Internet Explorer operates in a protected mode, which operates with lower permissions than the user and runs in isolation from other applications in the operating system, preventing it from accessing or modifying anything besides the Temporary Internet Files directory.[77] Microsoft’s anti-spyware product, Windows Defender, has been incorporated into Windows, protecting against malware and other threats. Changes to various system configuration settings (such as new auto-starting applications) are blocked unless the user gives consent.
Whereas prior releases of Windows supported per-file encryption using Encrypting File System, the Enterprise and Ultimate editions of Vista include BitLocker Drive Encryption, which can protect entire volumes, notably the operating system volume. However, BitLocker requires approximately a 1.5-gigabyte partition to be permanently not encrypted and to contain system files for Windows to boot. In normal circumstances, the only time this partition is accessed is when the computer is booting, or when there is a Windows update that changes files in this area, which is a legitimate reason to access this section of the drive. The area can be a potential security issue, because a hexadecimal editor (such as dskprobe.exe), or malicious software running with administrator and/or kernel level privileges would be able to write to this «Ghost Partition» and allow a piece of malicious software to compromise the system, or disable the encryption. BitLocker can work in conjunction with a Trusted Platform Module (TPM) cryptoprocessor (version 1.2) embedded in a computer’s motherboard, or with a USB key.[78] However, as with other full disk encryption technologies, BitLocker is vulnerable to a cold boot attack, especially where TPM is used as a key protector without a boot PIN being required too.[79]
A variety of other privilege-restriction techniques are also built into Vista. An example is the concept of «integrity levels» in user processes, whereby a process with a lower integrity level cannot interact with processes of a higher integrity level and cannot perform DLL–injection to processes of a higher integrity level. The security restrictions of Windows services are more fine-grained, so that services (especially those listening on the network) cannot interact with parts of the operating system they do not need to. Obfuscation techniques such as address space layout randomization are used to increase the amount of effort required of malware before successful infiltration of a system. Code integrity verifies that system binaries have not been tampered with by malicious code.
As part of the redesign of the network stack, Windows Firewall has been upgraded, with new support for filtering both incoming and outgoing traffic. Advanced packet filter rules can be created that can grant or deny communications to specific services.
The 64-bit versions of Vista require that all device drivers be digitally signed, so that the creator of the driver can be identified.[80]
System management[edit]
While much of the focus of Vista’s new capabilities highlighted the new user interface,[81] security technologies, and improvements to the core operating system, Microsoft also adding new deployment and maintenance features:
- The Windows Imaging Format (WIM) provides the cornerstone of Microsoft’s new deployment and packaging system. WIM files, which contain a HAL-independent image of Windows Vista, can be maintained and patched without having to rebuild new images. Windows Images can be delivered via Systems Management Server or Business Desktop Deployment technologies. Images can be customized and configured with applications then deployed to corporate client personal computers using little to no touch by a system administrator. ImageX is the Microsoft tool used to create and customize images.
- Windows Deployment Services replaces Remote Installation Services for deploying Vista and prior versions of Windows.
- Approximately 700 new Group Policy settings have been added, covering most aspects of the new features in the operating system, as well as significantly expanding the configurability of wireless networks, removable storage devices, and user desktop experience. Vista also introduced an XML-based format (ADMX) to display registry-based policy settings, making it easier to manage networks that span geographic locations and different languages.[82]
- Services for UNIX, renamed as «Subsystem for UNIX-based Applications», comes with the Enterprise and Ultimate editions of Vista. Network File System (NFS) client support is also included.
- Multilingual User Interface–Unlike previous versions of Windows (which required the loading of language packs to provide local-language support), Windows Vista Ultimate and Enterprise editions support the ability to dynamically change languages based on the logged-on user’s preference.
- Wireless Projector support
Developer[edit]
Windows Vista includes a large number of new application programming interfaces. Chief among them is the inclusion of version 3.0 of the .NET Framework, which consists of a class library and Common Language Runtime. Version 3.0 includes four new major components:[83]
- Windows Presentation Foundation is a user interface subsystem and framework based vector graphics, which makes use of 3D computer graphics hardware and Direct3D technologies. It provides the foundation for building applications and blending application UI, documents, and media content. It is the successor to Windows Forms.
- Windows Communication Foundation is a service-oriented messaging subsystem that enables applications and systems to interoperate locally or remotely using Web services.
- Windows Workflow Foundation provides task automation and integrated transactions using workflows. It is the programming model, engine, and tools for building workflow-enabled applications on Windows.
- Windows CardSpace is a component that securely stores digital identities of a person, and provides a unified interface for choosing the identity for a particular transaction, such as logging into a website.[84]
These technologies are also available for Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 to facilitate their introduction to and usage by developers and end-users.
There are also significant new development APIs in the core of the operating system, notably the completely re-designed audio, networking, print, and video interfaces, major changes to the security infrastructure, improvements to the deployment and installation of applications («ClickOnce» and Windows Installer 4.0), new device driver development model («Windows Driver Foundation»), Transactional NTFS, mobile computing API advancements (power management, Tablet PC Ink support, SideShow) and major updates to (or complete replacements of) many core subsystems such as Winlogon and CAPI.
There are some issues for software developers using some of the graphics APIs in Vista. Games or programs built solely on the Windows Vista-exclusive version of DirectX, version 10, cannot work on prior versions of Windows, as DirectX 10 is not available for previous Windows versions. Also, games that require the features of D3D9Ex, the updated implementation of DirectX 9 in Windows Vista are also incompatible with previous Windows versions.[85] According to a Microsoft blog, there are three choices for OpenGL implementation on Vista. An application can use the default implementation, which translates OpenGL calls into the Direct3D API and is frozen at OpenGL version 1.4, or an application can use an Installable Client Driver (ICD), which comes in two flavors: legacy and Vista-compatible. A legacy ICD disables the Desktop Window Manager, a Vista-compatible ICD takes advantage of a new API, and is fully compatible with the Desktop Window Manager.[86] At least two primary vendors, ATI and NVIDIA provided full Vista-compatible ICDs.[87] However, hardware overlay is not supported, because it is considered as an obsolete feature in Vista. ATI and NVIDIA strongly recommend using compositing desktop/Framebuffer Objects for same functionality.[88]
Installation[edit]
Windows Vista is the first Microsoft operating system:
- To use DVD-ROM media for installation[89]
- That can be installed only on a partition formatted with the NTFS file system[90]
- That provides support for loading drivers for SCSI, SATA and RAID controllers from any source in addition to floppy disks prior to its installation[91]
- That can be installed on and booted from systems with GPT disks and UEFI firmware[a][93]
Unification of OEM and retail installation[edit]
Windows Vista unifies the previously separate OEM and retail distributions of Microsoft Windows; a license for the edition purchased determines which version of Windows Vista is eligible for installation, regardless of its originating source. OEM and retail versions of Windows before Windows Vista were maintained separately on optical media—users with a manufacturer-supplied disc could not use a retail license during installation, and users with a retail disc could not use an OEM license during installation.[94]
Removed features[edit]
Some notable Windows XP features and components have been replaced or removed in Windows Vista, including several shell and Windows Explorer features, multimedia features, networking related functionality, Windows Messenger, NTBackup, the network Windows Messenger service, HyperTerminal, MSN Explorer, Active Desktop, and the replacement of NetMeeting with Windows Meeting Space. As a result, BOOTMGR in Windows Vista and later versions replaces the functions performed by NTLDR in all Windows NT versions up to Windows XP and directly executes winload.exe, the system loader used to continue the Windows boot process. Windows Vista also does not include the Windows XP «Luna» visual theme, or most of the classic color schemes that have been part of Windows since the Windows 3.x era. The «Hardware profiles» startup feature has also been removed, along with support for older motherboard technologies like the EISA bus, APM and game port support (though on the 32-bit version game port support can be enabled by applying an older driver).[95] IP over FireWire (TCP/IP over IEEE 1394) has been removed as well.[96] The IPX/SPX protocol has also been removed, although it can be enabled by a third-party plug-in.[97]
Support lifecycle[edit]
Support for the original release of Windows Vista (without a service pack) ended on April 13, 2010.[98] Service Pack 1 reached end of support on July 12, 2011, over three years after its general availability.[99]
Mainstream support for Windows Vista officially ended on April 10, 2012.[6] The «Extended Support» phase would last for the next 5 years, until April 11, 2017.[6] Microsoft is no longer offering no-charge incident support, warranty claims, or design fixes for the operating system. For IT pros or users who needed to make specific fixes to the commercial Windows code, Microsoft required an extended hotfix agreement, which provided an additional 90 days from April 10, 2012.
As part of the Extended Support phase, Vista users were still able to get security updates, and could still pay for support per incident, per-hour, or in other ways. Microsoft also made Windows Vista product information available through its online Knowledge Base. On April 11, 2017, support for Windows Vista ended.
Editions[edit]
Windows Vista shipped in six different editions.[100] These are roughly divided into two target markets, consumer and business, with editions varying to cater to specific sub-markets. For consumers, there are three editions, with two available for economically more developed countries. Windows Vista Starter edition is aimed at low-powered computers with availability only in emerging markets. Windows Vista Home Basic is intended for budget users. Windows Vista Home Premium covers the majority of the consumer market and contains applications for creating and using multimedia. The home editions cannot join a Windows Server domain. For businesses, there are three editions as well. Windows Vista Business is specifically designed for small and medium-sized enterprises,[101] while Windows Vista Enterprise[102] is only available to customers participating in Microsoft’s Software Assurance program. Windows Vista Ultimate contains the complete feature-set of both the Home and Business (combination of both Home Premium and Enterprise) editions, as well as a set of Windows Ultimate Extras, and is aimed at enthusiasts.
All editions except Windows Vista Starter support both 32-bit (x86) and 64-bit (x64) processor architectures.
In the European Union, Home Basic N and Business N variants are also available. These come without Windows Media Player, due to EU sanctions brought against Microsoft for violating anti-trust laws. Similar sanctions exist in South Korea.
Visual styles[edit]
A comparison of the four visual styles included in Windows Vista
Windows Vista has four distinct visual styles.[103][104]
- Windows Aero
- Vista’s default visual style, Windows Aero, is built on a desktop composition engine called Desktop Window Manager. Windows Aero introduces support for translucency effects (Glass), window thumbnails on the taskbar, window animations, and other visual effects (for example Windows Flip 3D), and is intended for mainstream and high-end video cards. To enable these features, the contents of every open window are stored in video memory to facilitate tearing-free movement of windows. As such, Windows Aero has significantly higher hardware requirements than its predecessors: systems running Vista must have video card drivers compatible with the Windows Display Driver Model (WDDM), and the minimum graphics memory required is 128 MB, depending on the resolution used.[105]
Windows Aero is not included in the Starter and Home Basic editions. A variant of Windows Aero, dubbed Windows Vista Standard, lacking the glass effects, window animations, and other advanced graphical effects, is included in Home Basic.[106]
- Windows Vista Basic
- This visual style does not employ the Desktop Window Manager; as such, it does not feature transparency or translucency, window animation, Windows Flip 3D or any of the functions provided by the DWM. It is the default visual style on Windows Vista Starter and on systems without WDDM-compatible display drivers, and has similar video card requirements to Windows XP. Before Service Pack 1, a machine that failed Windows Genuine Advantage validation would also default to this visual style.[107]
- Windows Standard
- The Windows Standard and Windows Classic visual styles reprise the user interface of Windows 9x, Windows 2000 and Microsoft’s Windows Server line of operating systems. As with previous versions of Windows, this visual style supports custom color schemes, which are collections of color settings. Windows Vista includes four high-contrast color schemes and the default color schemes from Windows 98 (titled «Windows Classic») and Windows 2000/Windows Me (titled «Windows Standard»).[106]
Hardware requirements[edit]
Computers with a «Certified for Windows Vista» sticker met WHQL Testing requirements and supported new features such as Windows Aero.
Computers capable of running Windows Vista are classified as Vista Capable and Vista Premium Ready.[108] A Vista Capable or equivalent PC is capable of running all editions of Windows Vista although some of the special features and high-end graphics options may require additional or more advanced hardware. A Vista Premium Ready PC can take advantage of Vista’s high-end features.[109]
Windows Vista’s Basic and Classic interfaces work with virtually any graphics hardware that supports Windows XP or 2000; accordingly, most discussion around Vista’s graphics requirements centers on those for the Windows Aero interface. As of Windows Vista Beta 2, the NVIDIA GeForce 6 series and later, the ATI Radeon 9500 and later, Intel’s GMA 950 and later integrated graphics, and a handful of VIA chipsets and S3 Graphics discrete chips are supported. Although originally supported, the GeForce FX 5 series has been dropped from newer drivers from NVIDIA. The last driver from NVIDIA to support the GeForce FX series on Vista was 96.85.[110][111] Microsoft offered a tool called the Windows Vista Upgrade Advisor[109] to assist Windows XP and Vista users in determining what versions of Windows their machine is capable of running. The required server connections for this utility are no longer available. Although the installation media included in retail packages is a 32-bit DVD, customers needing a CD-ROM or customers who wish for a 64-bit install media can acquire this media through the Windows Vista Alternate Media program.[112] The Ultimate edition includes both 32-bit and 64-bit media.[113] The digitally downloaded version of Ultimate includes only one version, either 32-bit or 64-bit, from Windows Marketplace.
| Component of PC | Minimum required | Recommended |
|---|---|---|
| Processor | 800 MHz | 1 GHz |
| Memory | 512 MB (384 MB for Starter edition) |
1 GB |
| Graphics card | Super VGA | WDDM 1.0-compliant 32 bits per pixel DirectX 9.0 support Pixel Shader 2.0 support |
| Graphics memory | — | 128 MB |
| Total HDD capacity | 20 GB | 40 GB |
| Free HDD space | 15 GB | 15 GB |
| Optical drives | CD-ROM drive | DVD-ROM drive |
| Others | — | TV tuner card (Premium, Ultimate) Touchscreen (Premium, Business, Ultimate) USB flash drive (Ultimate) Trusted Platform Module (Ultimate) |
Physical memory limits[edit]
The maximum amount of RAM that Windows Vista can support varies, depending on both its edition and its processor architecture, as shown in the table.[116]
| Edition | Processor architecture | |
|---|---|---|
| IA-32 | x64 | |
| Ultimate | 4 GB | 128 GB |
| Enterprise | ||
| Business | ||
| Home Premium | 16 GB | |
| Home Basic | 8 GB | |
| Starter | 1 GB | — |
Processor limits[edit]
The maximum number of logical processors[117] in a PC that Windows Vista supports is: 32[118] for 32-bit; 64[119] for 64-bit.[120]
The maximum number of physical processors in a PC that Windows Vista supports is: 2 for Business, Enterprise, and Ultimate, and 1 for Starter, Home Basic, and Home Premium.[121]
Updates[edit]
Microsoft occasionally releases updates such as service packs for its Windows operating systems to fix bugs, improve performance and add new features.
Service Pack 1[edit]
Windows Vista Service Pack 1 (SP1) was released on February 4, 2008, alongside Windows Server 2008 to OEM partners, after a five-month beta test period. The initial deployment of the service pack caused a number of machines to continually reboot, rendering the machines unusable.[122] This temporarily caused Microsoft to suspend automatic deployment of the service pack until the problem was resolved. The synchronized release date of the two operating systems reflected the merging of the workstation and server kernels back into a single code base for the first time since Windows 2000. MSDN subscribers were able to download SP1 on February 15, 2008. SP1 became available to current Windows Vista users on Windows Update and the Download Center on March 18, 2008.[123][124][125] Initially, the service pack only supported five languages – English, French, Spanish, German and Japanese. Support for the remaining 31 languages was released on April 14, 2008.[126]
A white paper, published by Microsoft on August 29, 2007, outlined the scope and intent of the service pack, identifying three major areas of improvement: reliability and performance, administration experience, and support for newer hardware and standards.[127]
One area of particular note is performance. Areas of improvement include file copy operations, hibernation, logging off on domain-joined machines, JavaScript parsing in Internet Explorer, network file share browsing,[124] Windows Explorer ZIP file handling,[128] and Windows Disk Defragmenter.[129] The ability to choose individual drives to defragment is being reintroduced as well.[124]
Service Pack 1 introduced support for some new hardware and software standards, notably the exFAT file system,[124] 802.11n wireless networking, IPv6 over VPN connections, and the Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol.[130]
Booting a system using Extensible Firmware Interface on x64 systems was also introduced;[124] this feature had originally been slated for the initial release of Vista but was delayed due to a lack of compatible hardware at the time. Booting from a GUID Partition Table–based hard drive greater than 2.19 TB is supported (x64 only).[131][132]
Two areas have seen changes in SP1 that have come as the result of concerns from software vendors. One of these is desktop search; users will be able to change the default desktop search program to one provided by a third party instead of the Microsoft desktop search program that comes with Windows Vista, and desktop search programs will be able to seamlessly tie in their services into the operating system.[125] These changes come in part due to complaints from Google, whose Google Desktop Search application was hindered by the presence of Vista’s built-in desktop search. In June 2007, Google claimed that the changes being introduced for SP1 «are a step in the right direction, but they should be improved further to give consumers greater access to alternate desktop search providers».[133] The other area of note is a set of new security APIs being introduced for the benefit of antivirus software that currently relies on the unsupported practice of patching the kernel (see Kernel Patch Protection).[134][135]
An update to DirectX 10, named DirectX 10.1,[124] marked mandatory several features that were previously optional in Direct3D 10 hardware. Graphics cards will be required to support DirectX 10.1.[136] SP1 includes a kernel (6001.18000) that matches the version shipped with Windows Server 2008.[137]
The Group Policy Management Console (GPMC) was replaced by the Group Policy Object Editor. An updated downloadable version of the Group Policy Management Console was released soon after the service pack.
SP1 enables support for hotpatching, a reboot-reduction servicing technology designed to maximize uptime. It works by allowing Windows components to be updated (or «patched») while they are still in use by a running process. Hotpatch-enabled update packages are installed via the same methods as traditional update packages, and will not trigger a system reboot.[138]
Service Pack 2[edit]
Service Pack 2 for Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008 was released through different channels between April[139] and June 2009, one year after the release of Windows Vista SP1, and four months before the release of Windows 7.[5] In addition to a number of security and other fixes, a number of new features have been added. However, it did not include Internet Explorer 8, but instead was included in Windows 7, which was released four months after Vista SP2.[140][141]
- Windows Search 4 (available for SP1 systems as a standalone update)
- Feature Pack for Wireless adds support for Bluetooth 2.1
- Windows Feature Pack for Storage enables the data recording onto Blu-ray media
- Windows Connect Now (WCN) to simplify Wi-Fi configuration
- Improved support for resuming with active Wi-Fi connections
- Improved support for eSATA drives
- The limit of 10 half-open, outgoing TCP connections introduced in Windows XP SP2 was removed
- Enables the exFAT file system to support UTC timestamps, which allows correct file synchronization across time zones
- Support for ICCD/CCID smart cards
- Support for VIA 64-bit CPUs
- Improved performance and responsiveness with the RSS feeds sidebar
- Improves audio and video performance for streaming high-definition content
- Improves Windows Media Center (WMC) in content protection for TV[142]
- Provides an improved power management policy that is approximately 10% more efficient than the original with the default policies[143]
Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008 share a single service pack binary, reflecting the fact that their code bases were joined with the release of Server 2008.[140] Service Pack 2 is not a cumulative update meaning that Service Pack 1 must be installed first.
Platform Update[edit]
The Platform Update for Windows Vista was released on October 27, 2009. It includes major new components that shipped with Windows 7, as well as updated runtime libraries.[144][145] It requires Service Pack 2 of Windows Vista or Windows Server 2008 and is listed on Windows Update as a Recommended download.
The Platform Update allows application developers to target both Windows Vista and Windows 7. It consists of the following components:
- Windows Graphics runtime: Direct2D, DirectWrite, Direct3D 11, DXGI 1.1, and WARP
- Updates to Windows Imaging Component
- Updates to XPS Print API, XPS Document API and XPS Rasterization Service
- Windows Automation API (updates to MSAA and UI Automation)
- Windows Portable Devices Platform (adds support for MTP over Bluetooth and MTP Device Services)
- Windows Ribbon API
- Windows Animation Manager library
Some updates are available as separate releases for both Windows XP and Windows Vista:
- Windows Management Framework: Windows PowerShell 2.0, Windows Remote Management 2.0, BITS 4.0
- Remote Desktop Connection 7.0 (RDP7) client
Although extensive, the Platform Update does not bring Windows Vista to the level of features and performance offered by Windows 7.[146] For example, even though Direct3D 11 runtime will be able to run on D3D9-class hardware and WDDM drivers using «feature levels» first introduced in Direct3D 10.1, Desktop Window Manager has not been updated to use Direct3D 10.1.[146]
In July 2011, Microsoft released the Platform Update Supplement for Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008, which contains several bug fixes and performance improvements.[147]
Out-of-band patches[edit]
BlueKeep patch[edit]
Microsoft has released an update for Windows Vista SP2 to resolve the BlueKeep security vulnerability (CVE-2019-0708), which affects the Remote Desktop Protocol in older Windows versions.[148] Subsequent related flaws, CVE-2019-1181, CVE-2019-1182, CVE-2019-1222 and CVE-2019-1226 (collectively known as DejaBlue) do not affect Windows Vista or earlier versions of Windows.[149] The installation of this patch changed the build number of Windows Vista from 6002 to 6003.[b]
Text Services Framework patch[edit]
The Text Services Framework was compromised by a privilege escalation vulnerability (CVE-2019-1162) that could allow attackers to use the framework to perform privileged operations, run software, or send messages to privileged processes from unprivileged processes—bypassing security features such as sandboxes or User Account Control. Microsoft remediated issues related to this vulnerability with the release of a patch in August 2019 for Windows Vista SP2, Windows Server 2008 SP2, and later versions of Windows.[152]
Malware Protection Engine patch[edit]
A vulnerability related to Windows Defender that affected the way the Malware Protection Engine operates (CVE-2017-0290) was reported in May 2017. If Windows Defender scanned a specially crafted file, it would lead to memory corruption, potentially allowing an attacker to control the affected machine or perform arbitrary code execution in the context of LocalSystem; the vulnerability was exacerbated by the default real-time protection settings of Windows Defender, which were configured to automatically initiate malware scans at regular intervals. The first version of the Protection Engine affected by the vulnerability is Version 1.1.13701.0—subsequent versions of the engine are unaffected. Microsoft released a patch to address the issue.[153]
Marketing campaign[edit]
The Mojave Experiment[edit]
In July 2008, Microsoft introduced a web-based advertising campaign called the «Mojave Experiment», which depicts a group of people who are asked to evaluate the newest operating system from Microsoft, calling it Windows ‘Mojave’. Participants are first asked about Vista, if they have used it, and their overall satisfaction with Vista on a scale of 1 to 10. They are then shown a demo of some of the new operating system’s features, and asked their opinion and satisfaction with it on the same 1 to 10 scale. After respondents rate «Mojave», they are then told that they were shown a demo of Windows Vista. The object was to test «A theory: If people could see Windows Vista firsthand, they would like it.» According to Microsoft, the initial sample of respondents rated Vista an average of 4.4 out of 10, and Mojave received an average of 8.5, with no respondents rating Mojave lower than they originally rated Windows Vista before the demo.[154][155] The «experiment» has been criticized for deliberate selection of positive statements and not addressing all aspects of Vista.[156] During the launch of Vista, Microsoft also made a lime flavored sparkling water available to campus visitors and developers.[157]
Reception[edit]
Windows Vista received mixed to negative reviews at the time of its release and throughout its lifespan, mainly for its much higher hardware requirements and perceived slowness compared to Windows XP.[158][159]
It received generally positive reviews from PC gamers who praised the advantages brought by DirectX 10, which allowed for better gaming performance and more realistic graphics, as well as support for many new capabilities featured in new GPUs.[160] However, many DirectX 9 games initially ran with lower frame rates compared to when they were run on Windows XP. In mid-2008, benchmarks suggested that the SP1 update improved performance to be on par with (or better than) Windows XP in terms of game performance.[161]
Peter Bright of Ars Technica wrote that, despite its delays and feature cuts, Windows Vista was «a huge evolution in the history of the NT platform […] The fundamental changes to the platform are of a scale not seen since the release of NT [3.1; the first version].»[162] In a continuation of his previous assessment, Bright stated that «Vista is not simply XP with a new skin; core parts of the OS have been radically overhauled, and virtually every area has seen significant refinement. In terms of the magnitude and extent of these changes, Vista represents probably the biggest leap that the NT platform has ever seen. Never before have significant subsystems been gutted and replaced in the way they are in Vista.»[163] Many others in the tech industry echoed these sentiments at the time, directing praise towards the massive amount of technical features new to Windows Vista.[164]
Windows Vista received the «Best of CES» award at the Consumer Electronics Show in 2007.[165][166]
In its first year of availability, PC World rated it as the biggest tech disappointment of 2007,[167] and it was rated by InfoWorld as No. 2 of Tech’s all-time 25 flops.[168] Microsoft’s then much smaller competitor Apple noted that, despite Vista’s far greater sales, its own operating system did not seem to have suffered after its release, and would later invest in advertising mocking Vista’s unpopularity with users.[169][170]
Computer manufacturers such as Dell, Lenovo, and Hewlett-Packard released their newest computers with Windows Vista pre-installed; however, after the negative reception of the operating system, they also began selling their computers with Windows XP CDs included because of a drop in sales.[171]
Sales[edit]
A Gartner research report predicted that Vista business adoption in 2008 would overtake that of XP during the same time frame (21.3% vs. 16.9%)[172] while IDC had indicated that the launch of Windows Server 2008 served as a catalyst for the stronger adoption rates.[173][174] As of January 2009, Forrester Research had indicated that almost one third of North American and European corporations had started deploying Vista.[175] At a May 2009 conference, a Microsoft Vice President said «Adoption and deployment of Windows Vista has been slightly ahead of where we had been with XP» for big businesses.[176][177]
Within its first month, 20 million copies of Vista were sold, double the amount of Windows XP sales within its first month in October 2001, five years earlier.[178] Shortly after however, due to Vista’s relatively low adoption rates and continued demand for Windows XP, Microsoft decided to sell Windows XP until June 30, 2008, instead of the previously planned date of January 31, 2008.[179] There were reports of Vista users «downgrading» their operating systems back to XP, as well as reports of businesses planning to skip Vista.[180] A study conducted by ChangeWave in March 2008 showed that the percentage of corporate users who were «very satisfied» with Vista was dramatically lower than other operating systems, with Vista at 8%, compared to the 40% who said they were «very satisfied» with Windows XP.[181]
The internet-usage market share for Windows Vista after two years of availability, in January 2009, was 20.61%. This figure combined with World Internet Users and Population Stats yielded a user base of roughly 330 million,[182] which exceeded Microsoft’s two-year post launch expectations by 130 million.[183] The internet user base reached before the release of its successor (Windows 7) was roughly 400 million according to the same statistical sources.[citation needed]
Criticism[edit]
Windows Vista received mixed reviews. Criticism targets include protracted development time (5–6 years), more restrictive licensing terms, the inclusion of several technologies aimed at restricting the copying of protected digital media,[184] and the usability of the new User Account Control security technology. Moreover, some concerns have been raised about many PCs meeting «Vista Premium Ready» hardware requirements and Vista’s pricing.
Hardware requirements[edit]
While in 2005 Microsoft claimed «nearly all PCs on the market today will run Windows Vista»,[185] the higher requirements of some of the «premium» features, such as the Aero interface, affected many upgraders. According to the UK newspaper The Times in May 2006, the full set of features «would be available to less than 5 percent of Britain’s PC market»; however, this prediction was made several months before Vista was released.[186] This continuing lack of clarity eventually led to a class action against Microsoft as people found themselves with new computers that were unable to use the new software to its full potential despite the assurance of «Vista Capable» designations.[187] The court case has made public internal Microsoft communications that indicate that senior executives have also had difficulty with this issue. For example, Mike Nash (Corporate Vice President, Windows Product Management) commented, «I now have a $2,100 e-mail machine» because of his laptop’s lack of an appropriate graphics chip so hobbled Vista.[188]
Licensing[edit]
Criticism of upgrade licenses pertaining to Windows Vista Starter through Home Premium was expressed by Ars Technica‘s Ken Fisher, who noted that the new requirement of having a prior operating system already installed was going to irritate users who reinstall Windows regularly.[189]
It has been revealed that an Upgrade copy of Windows Vista can be installed clean without first installing a previous version of Windows. On the first install, Windows will refuse to activate. The user must then reinstall that same copy of Vista. Vista will then activate on the reinstall, thus allowing a user to install an Upgrade of Windows Vista without owning a previous operating system.[190] As with Windows XP, separate rules still apply to OEM versions of Vista installed on new PCs: Microsoft asserts that these versions are not legally transferable (although whether this conflicts with the right of first sale has yet to be clearly decided legally).[191]
Cost[edit]
Initially, the cost of Windows Vista was also a source of concern and commentary. A majority of users in a poll said that the prices of various Windows Vista editions posted on the Microsoft Canada website in August 2006 make the product too expensive.[192] A BBC News report on the day of Vista’s release suggested that, «there may be a backlash from consumers over its pricing plans—with the cost of Vista versions in the US roughly half the price of equivalent versions in the UK.»[193]
Since the release of Vista in 2006, Microsoft has reduced the retail, and upgraded the price point of Vista. Originally, Vista Ultimate was priced at $399, and Home Premium Vista at $239. These prices have since been reduced to $319 and $199 respectively.[194]
Digital rights management[edit]
Windows Vista supports additional forms of DRM restrictions. One aspect of this is the Protected Video Path, which is designed so that «premium content» from HD DVD or Blu-ray Discs may mandate that the connections between PC components be encrypted. Depending on what the content demands, the devices may not pass premium content over non-encrypted outputs, or they must artificially degrade the quality of the signal on such outputs or not display it at all. Drivers for such hardware must be approved by Microsoft; a revocation mechanism is also included, which allows Microsoft to disable drivers of devices in end-user PCs over the Internet.[195] Peter Gutmann, security researcher and author of the open source cryptlib library, claims that these mechanisms violate fundamental rights of the user (such as fair use), unnecessarily increase the cost of hardware, and make systems less reliable (the «tilt bit» being a particular worry; if triggered, the entire graphic subsystem performs a reset) and vulnerable to denial-of-service attacks.[196] However, despite several requests[197] for evidence supporting such claims Peter Gutmann has never supported his claims with any researched evidence. Proponents have claimed that Microsoft had no choice but to follow the demands of the movie studios, and that the technology will not actually be enabled until after 2010;[198][199] Microsoft also noted that content protection mechanisms have existed in Windows as far back as Windows ME, and that the new protections will not apply to any existing content, only future content.[200]
User Account Control[edit]
Although User Account Control (UAC) is an important part of Vista’s security infrastructure as it blocks software from silently gaining administrator privileges without the user’s knowledge, it has been widely criticized for generating too many prompts.[201] This has led many Vista UAC users to consider it troublesome, with some consequently either turning the feature off or (for Windows Vista Enterprise or Windows Vista Ultimate users) putting it in auto-approval mode.[202] Responding to this criticism, Microsoft altered the implementation to reduce the number of prompts with SP1.[138] Though the changes resulted in some improvement, it did not alleviate the concerns completely.[203]
Downgrade rights[edit]
End-users of licenses of Windows 7 acquired through OEM or volume licensing may downgrade to the equivalent edition of Windows Vista. Downgrade rights are not offered for Starter, Home Basic or Home Premium editions of Windows 7.[204] For Windows 8 licenses acquired through an OEM, a user may also downgrade to the equivalent edition of Windows Vista. Customers licensed for use of Windows 8 Enterprise are generally licensed for Windows 8 Pro, which may be downgraded to Windows Vista Business.
See also[edit]
- BlueKeep (security vulnerability)
- Comparison of Windows Vista and Windows XP
- Microsoft Security Essentials
Notes[edit]
- ^ 64-bit editions of Windows Vista only. Requires Service Pack 1.[92]
- ^ Installing the preview rollup package released for Windows Server 2008 on March 19, 2019, or any later released rollup package, will update the operating system kernel’s build number from version 6.0.6002 to 6.0.6003. This change was made so Microsoft could continue to service the operating system while avoiding “version-related issues”.[150] This same phenomenon would occur when a user installs the BlueKeep Patch (KB4499180)[151] onto Windows Vista as the patch was released in May 2019, two months after the change was initiated.
References[edit]
- ^ «Windows Licensing Programs». Microsoft. June 2011. Archived from the original on December 16, 2008. Retrieved September 21, 2008.
- ^ White, Nick (November 8, 2006). «Windows Vista releases to manufacturing». Windows Vista Team Blog. Microsoft. Archived from the original on August 9, 2005. Retrieved January 2, 2017.
- ^ a b «Microsoft Launches Windows Vista and the 2007 Office System to Consumers». News Center. Microsoft. January 29, 2007. Retrieved January 2, 2017.
- ^ «Windows Version Numbers — Version and build numbers of Microsoft Windows». www.gaijin.at.
- ^ a b Oiaga, Marius (May 26, 2009). «Download Windows Vista Service Pack 2 (SP2) RTM». Softpedia. SoftNews.
- ^ a b c «Windows Vista Lifecycle Policy». Microsoft. Retrieved January 2, 2017.
- ^ «Microsoft Unveils New Ways for Consumers to Get Windows Vista». News Center. Microsoft. January 17, 2007. Retrieved January 2, 2017.
- ^ Oiaga, Marius (December 3, 2010). «Slow Death for Windows Vista — Packaged Software End of Sales Reached in October». softpedia.
- ^ a b «Desktop Windows Version Market Share Worldwide». StatCounter Global Stats. Retrieved February 2, 2020.
- ^ «Microsoft Support Lifecycle». Support. Microsoft. Retrieved May 11, 2012.
- ^ Gallii, Peter (July 30, 2001). «Pushing Forward». eWeek. Retrieved July 7, 2006.
- ^ Microsoft Windows System Overview. Microsoft.com. Retrieved on October 14, 2011. Archived March 16, 2011, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Lipner, Steve; Howard, Michael (March 2005). «The Trustworthy Computing Security Development Lifecycle». Microsoft Developer Network. Microsoft. Retrieved August 9, 2006.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (March 1, 2003). «Longhorn Alpha Preview 2: Build 4008». Windows SuperSite. Archived from the original on January 17, 2007. Retrieved March 30, 2006.
- ^ «WinHEC 2003 Session Presentations». Microsoft. August 1, 2003. Archived from the original on December 16, 2005. Retrieved March 31, 2006.
- ^ Kaplan, Michael (October 16, 2005). «A reset does not mean everything was thrown away». Sorting It All Out. Retrieved April 2, 2006.
- ^ Keizer, Gregg (January 29, 2007). «Microsoft’s Vista Had Major Mac Envy, Company E-Mails Reveal». InformationWeek. UBM plc. Archived from the original on January 27, 2014. Retrieved February 28, 2013.
- ^ Guth, Robert (September 23, 2005). «Battling Google, Microsoft Changes How It Builds Software». The Wall Street Journal. pp. A1, ??. (viewable online here [1] Archived January 12, 2016, at the Wayback Machine)
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (April 16, 2003). «Brian Valentine talks Windows Server 2003». SuperSite for Windows. Archived from the original on June 14, 2006. Retrieved April 2, 2006.
- ^ Murphy, Victoria (May 26, 2003). «The Exterminator». Forbes Magazine. Archived from the original on January 2, 2004.
- ^ Torre, Charles; Scoble, Robert (December 23, 2005). «Rob Short (and kernel team) — Going deep inside Windows Vista’s kernel architecture». Channel 9. Microsoft.
- ^ Ricciuti, Mike (July 22, 2005). «Longhorn’s new name: Windows Vista». CNET. CBS Interactive. Retrieved March 15, 2016.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (November 1, 2006). «Road to Gold: The Long Road to Windows Vista Part 4: January — July 2005». Archived from the original on November 9, 2006. Retrieved November 2, 2006.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (November 5, 2006). «Paul Thurrott’s SuperSite for Windows: Road to Gold: The Long Road to Windows Vista Part 7: July 2006 – present». SuperSite for Windows. Penton. Archived from the original on November 9, 2006. Retrieved December 25, 2007.
- ^ Spooner, John (March 14, 2006). «Microsoft Shuts Windows on New PC Firmware». eWeek. Retrieved December 26, 2006.[permanent dead link]
- ^ «EFI and Windows Vista». WHDC. Microsoft. April 20, 2006. Archived from the original on February 5, 2008. Retrieved December 26, 2006.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (October 23, 2006). «Exclusive: Here Comes Windows Vista RC2». IT Pro. Archived from the original on October 11, 2006. Retrieved May 30, 2022.
- ^ «Broken Windows Theory». The World As Best As I Remember It. MSDN Blogs. June 14, 2006. Retrieved June 24, 2006.
- ^ «Glitch in voice-recognition software foils Microsoft demo». USA Today. Gannett Co. Inc. Associated Press. July 28, 2006.
- ^ Malone, Steve (October 27, 2006). «Windows Vista RTM code delayed». Digitimes/alphr. Retrieved August 20, 2015.
- ^ White, Nick (November 8, 2006). «Windows Vista releases to manufacturing». Windows Vista team blog. Archived from the original on April 7, 2014. Retrieved November 8, 2006. Windows Vista cost Microsoft six billion dollars to develop.«Vista – a $6 Billion Dollars Operating System – The best billions Bill Gates has ever spent». Softpedia. SoftNews. January 10, 2007. Retrieved October 2, 2008.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (October 27, 2006). «WinInfo Short Takes». WinInfo blog. WindowsITPro. Archived from the original on November 3, 2006. Retrieved October 27, 2006.
- ^ «MSDN Subscriptions». Microsoft. Retrieved October 27, 2006.
- ^ «Microsoft Business Value». Microsoft. Archived from the original on December 5, 2006. Retrieved November 30, 2006.
- ^ Allchin, Jim (November 9, 2006). «The Sounds of Windows Vista». Windows Vista Team Blog. Microsoft. Archived from the original on November 10, 2006. Retrieved April 25, 2015.
- ^ Murph, Darren (May 3, 2007). «Vista’s Aero interface blamed for truncated battery life». Engadget.
- ^ «Vista Battery Fix?». Microsoft. May 6, 2007. Archived from the original on March 13, 2008. Retrieved March 18, 2008.
- ^ «A Closer Look at Windows Vista Part II: Enhanced Search». ni.com. National Instruments. September 17, 2009. Archived from the original on September 29, 2011.
- ^ Durham, Joel Jr. (March 21, 2007). «Ten Must-Have Gadgets for Windows Vista Sidebar». PC Magazine. Ziff Davis. Retrieved March 19, 2016.
- ^ Windows Internet Explorer, Printing Advances Printing in IE7 Archived April 17, 2008, at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ Windows Mail Features Explained, See Reliability Section Windows Mail Archived April 30, 2008, at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ Windows Mail was demonstrated by the development team in this Channel 9 video Archived May 10, 2008, at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ Adams, Dan (December 7, 2006). «Vista and Games for Windows update». IGN. Ziff Davis. Retrieved March 18, 2016.
- ^ Suokko, Matti (2004). «Windows For Mobile PCs And Tablet PCs — CY05 And Beyond». Microsoft. Archived from the original (PPT) on December 14, 2005. Retrieved July 15, 2015.
- ^ Parker, Burt (2005). «Building a «Longhorn»-Ready Mobile PC». Microsoft. Archived from the original (PPT) on September 7, 2015. Retrieved August 4, 2015.
- ^ «Windows Longhorn ACPI and Power Management — Part 1». Microsoft. 2004. Archived from the original (PPT) on February 19, 2006. Retrieved August 4, 2015.
- ^ «Configuring Windows HotStart» (DOCX). Microsoft. March 19, 2010. Retrieved April 18, 2015.
- ^ «Selected Scenarios for Maintaining Data Integrity with Windows Vista». Microsoft. 2006. Archived from the original on August 20, 2006. Retrieved August 24, 2006.
- ^ Windows Update, Easier and Less Disruptive Windows Update in Windows Vista Archived May 22, 2008, at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ Windows Vista, SAPI Talking Windows Archived March 23, 2007, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Russell, Richard G. (May 6, 2005). «System Performance Assessment Tools for Windows Longhorn». Microsoft. Archived from the original (PPT) on November 18, 2012. Retrieved December 27, 2012.
- ^ «Introducing the Windows System Assessment Tool». Microsoft TechNet. Archived from the original on January 16, 2007.
- ^ Hruska, Joel (June 29, 2007). «Vista’s Reliability Monitor provides detailed information on OS uptime». Ars Technica. Condé Nast. Retrieved March 16, 2016.
- ^ O’Reilly, Dennis (May 22, 2007). «Partitioning a Hard Drive in Vista». PC World. IDG. Retrieved March 15, 2016.
- ^ «Upgrade to another edition of Windows Vista». Windows.microsoft.com. Retrieved February 4, 2012.
- ^ LeBlanc, Brandon (May 2, 2007). «Digital Locker Assistant helps manage purchased Apps». Windows Blogs. Microsoft. Retrieved December 26, 2016.
- ^ «Digital Locker». Windows Marketplace. Microsoft. 2007. Archived from the original on February 2, 2007. Retrieved December 26, 2016.
- ^ Shultz, Greg (April 13, 2006). «Windows Vista: ReadyBoost, ReadyDrive, and SuperFetch, oh my!». TechRepublic.
- ^ «Windows Vista: Ready for ReadyDrive — Charles — Channel 9». Channel 9. Microsoft.
- ^ «SuperFetch: How it Works & Myths – OSnews». www.osnews.com.
- ^ Shultz, Greg (July 9, 2008). «Understand how SuperFetch uses RAM to enhance system performance». TechRepublic. Retrieved October 2, 2008.
- ^ «Microsoft Leverages IPv6 With Vista». InformationWeek. UBM plc. January 24, 2006. Archived from the original on February 27, 2013.
- ^ «MSDN Blogs». msdn.com. Microsoft.
- ^ «Windows Vista: Enterprise Networking with Windows Vista». microsoft.com. Microsoft.
- ^ «Windows Vista: Creating a 3-D Desktop — How Windows Vista Works». HowStuffWorks. December 5, 2006.
- ^ White, Nick (August 16, 2006). «DirectX10: The Next Generation in Gaming». Windows Vista Team Blog. Archived from the original on November 18, 2008. Retrieved January 25, 2007.
- ^ «Windows Vista Display Driver Model». MSDN Library.
- ^ «Kernel Enhancements for Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008» (DOC). Microsoft. May 2006. Retrieved April 2, 2011.
- ^ «Inside the Windows Vista Kernel». microsoft.com. Microsoft.
- ^ Ricadela, Aaron (February 14, 2006). «Gates Says Security Is Job One For Vista». InformationWeek. UBM plc. Retrieved January 2, 2017.
- ^ Myers, Tim. «Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008 are Common Criteria Certified at EAL4+». Microsoft. Retrieved May 15, 2013.
- ^ «National Information Assurance Partnership Common Criteria Evaluation and Validation Scheme» (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on October 5, 2012. Retrieved May 15, 2013.
- ^ Stanek, William; Marquardt, Paul (February 6, 2007). «Understanding Windows Vista’s User Account Control». windowsdevcenter.com.
- ^ «Malware Removal Guide» (PDF). October 9, 2010. Archived from the original (PDF) on October 9, 2010. Retrieved March 26, 2021.
- ^ NortonLive Team (February 2010). Malware Removal Guide. Symantec. p. 41.
- ^ Protected Mode IE has been described in detail at the Internet Explorer team blog: Protected Mode in Vista IE7 Archived January 23, 2010, at the Wayback Machine and More details on Protected Mode IE in Windows Vista Archived January 27, 2006, at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ «BitLocker Drive Encryption: Executive Overview». Microsoft. April 5, 2006. Retrieved June 19, 2007.
- ^ Halderman, J. Alex; Schoen, Seth D.; Heninger, Nadia; Clarkson, William; Paul, William; Calandrino, Joseph A.; Feldman, Ariel J.; Appelbaum, Jacob; Felten, Edward W. (February 21, 2008). «Lest We Remember: Cold Boot Attacks on Encryption Keys». Princeton University. Retrieved February 22, 2008.
- ^ Windows Vista Feature Focus: 64-Bit (x64) Support. Winsupersite.com. Retrieved on October 14, 2011. Archived July 30, 2008, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ «What is Windows Aero?». windows.microsoft.com. Microsoft.
- ^ «What’s New in Group Policy in Windows Vista and Windows Server «Longhorn»«. TechNet. Microsoft. Archived from the original on May 8, 2006. Retrieved May 18, 2006.
- ^ .NET Framework 3.0 Technologies, Microsoft Archived July 18, 2006, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Vascellaro, Jessica E. (August 3, 2006). «New Ways to Prove You Are Who You Say You Are Online». The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved March 16, 2016.
- ^ Booker, Logan (15 September 2005). «DirectX 10: More harm than good for graphics?». Maximum Power Computing Atomic. Archived from the original on 27 June 2006. Retrieved 28 May 2006.
- ^ VedBrat, Kam (February 22, 2006). «more comments…» MSDN Blogs. Retrieved May 28, 2006.
- ^ Trevett, Neil (2006). «OpenGL on Vista». Khronos Group. Retrieved November 9, 2006.
- ^ Nguyen, Tuan. «OpenGL Now Natively Supported in Windows Vista». Archived from the original on May 21, 2008. Retrieved January 25, 2007.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (October 6, 2010). «Windows Vista Installation Super Guide, Part 3: Clean Install Windows Vista». SuperSite for Windows. Penton. Archived from the original on April 30, 2016. Retrieved April 26, 2016.
- ^ «You cannot select the Upgrade option when you try to install Windows Vista, and you receive the following message: ‘Upgrade has been disabled’«. How-to. Microsoft. Archived from the original on September 13, 2016. Retrieved April 26, 2016.
Windows Vista requires that the hard disk partition (disk volume) you are installing Vista into is formatted by using the NTFS file system.
- ^ Mueller, Scott (2015). Upgrading and Repairing PCs. Que Publishing. p. 295. ISBN 978-0-13-405769-9. Retrieved May 1, 2016.
- ^ «Notable Changes in Vista Service Pack 1». Microsoft. 2008. Archived from the original on May 3, 2008. Retrieved January 6, 2021.
- ^ «Windows and GPT FAQ». Microsoft. June 6, 2017. Archived from the original on February 10, 2019. Retrieved January 7, 2021.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (October 6, 2010). «Windows Vista Installation Super Guide, Part 3: Clean Install Windows Vista». SuperSite for Windows. Penton. Archived from the original on April 30, 2016. Retrieved May 30, 2015.
- ^ «Enable Game port on vista». Creative. December 8, 2004. Retrieved June 22, 2007.
- ^ «Discontinued Support for IP over 1394». Microsoft. December 8, 2004. Archived from the original on May 15, 2007. Retrieved June 22, 2007.
- ^ «IPX/SPX Protocol in Vista (32bit)». Starbase.com. May 5, 2008. Retrieved May 5, 2008.[permanent dead link]
- ^ «End of support for Windows XP SP2 and Windows Vista RTM». GB Technology. Retrieved May 14, 2010.
- ^ «Microsoft’s Windows Vista SP1 support ends July 12». Computerworld. July 12, 2011. Retrieved August 2, 2012.
- ^ «Microsoft Unveils Windows Vista Product Lineup». PressPass (Press release). Microsoft. February 26, 2006. Archived from the original on November 16, 2006. Retrieved October 31, 2006.
- ^ «Windows Vista Business». Microsoft.
- ^ «Windows Vista Enterprise». Microsoft.
- ^ VedBrat, Kam. «Desktop And Presentation Impact On Hardware Design» (PPT). Microsoft. Retrieved September 1, 2006.
- ^ Oiaga, Marius (December 12, 2006). «Windows Vista Graphical User Interface(s) – Aero, Standard, Basic and Classic». Softpedia. Retrieved April 28, 2009.
- ^ «Windows Vista Enterprise Hardware Planning Guidance». TechNet. Microsoft. 2006. Retrieved October 26, 2006.
- ^ a b Thurrott, Paul (August 25, 2008). «Windows Vista Feature Focus: Windows Vista Standard User Interface». SuperSite for Windows. Penton. Archived from the original on May 22, 2010. Retrieved April 28, 2009.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (August 25, 2008). «Windows Vista Feature Focus: Windows Vista Basic User Interface». SuperSite for Windows. Penton. Archived from the original on February 22, 2009. Retrieved April 28, 2009.
- ^ «Microsoft and PC Manufacturers Make It Easier for Customers to Get Ready for Windows Vista». PressPass. Microsoft. May 18, 2006. Retrieved May 18, 2006.
- ^ a b «Windows Vista Upgrade Advisor». Microsoft. Retrieved June 25, 2006.
- ^ «ForceWare Release 95». Nvidia.com. Retrieved October 2, 2008.
- ^ «MsBetas’ List of Vista Ready GPUs». Archived from the original on March 13, 2007. Retrieved July 30, 2007.
- ^ «Windows Vista Alternate Media». Microsoft. Retrieved August 20, 2007.
- ^ Windows Vista 64-bit Editions Archived July 24, 2008, at the Wayback Machine. Microsoft.com. Retrieved on October 14, 2011.
- ^ «Windows Vista: Recommended System Requirements». Microsoft. Archived from the original on January 1, 2008. Retrieved March 13, 2008.
- ^ Ashley, Mitchell (January 31, 2008). «Vista Starter — The Easy Button For Vista». Network World (International Data Group). Retrieved June 3, 2019.
- ^ «What is the maximum amount of RAM that Windows Vista can handle?». Microsoft. Retrieved April 18, 2014.
- ^ A logical processor is either: 1) One of the two handlers of the thread of instructions of one of the numbers of cores of one of the number of physical processors with support for HyperThreading; or 2) One of the numbers of cores of one of the numbers of physical processors without support for HyperThreading.
- ^ 32 cores without support for HyperThreading, 16 cores with support for HyperThreading.
- ^ 64 cores without support for HyperThreading, 32 cores with support for HyperThreading.
- ^ Logical processor limits for Windows Vista Archived January 27, 2011, at the Wayback Machine. Msdn.microsoft.com. Retrieved on October 14, 2011.
- ^ Physical processor limits for Windows Vista Archived July 14, 2012, at archive.today. Social.answers.microsoft.com (October 24, 2010). Retrieved on October 14, 2011.
- ^ «No update from Microsoft on Vista SP1, Media Center problems». Zdnet. February 18, 2008. Archived from the original on December 16, 2008. Retrieved October 8, 2008.
- ^ «Announcing the RTM of Windows Vista SP1». Microsoft. 4 February 2008. Archived from the original on 5 February 2008. Retrieved 4 February 2008.
- ^ a b c d e f «Windows Vista Service Pack 1 Beta White Paper». Microsoft. August 29, 2007. p. 1. Retrieved August 29, 2007.
- ^ a b «Feb. Launch Now Set for Windows Vista SP1». PC World Magazine. January 31, 2008. Archived from the original on February 6, 2008. Retrieved January 31, 2008.
- ^ Download Details: Windows Vista SP1 All Language Standalone (KB936330) Archived September 4, 2010, at the Wayback Machine. Microsoft.com (April 14, 2008). Retrieved on October 14, 2011.
- ^ Veneziani, Vince (August 30, 2007). «Windows Vista SP1 Gets Officially Announced». TechCrunch. AOL. Retrieved March 16, 2016.
- ^ Russinovich, Mark (August 7, 2007). «The Case of the Failed File Compression». Mark’s Blog. MSDN Blogs. Archived from the original on December 30, 2007. Retrieved October 20, 2007.
- ^ «Don’t judge a book by its cover–why Windows Vista Defrag is cool». The Filing Cabinet. MSDN Blogs. January 26, 2007. Archived from the original on April 28, 2010. Retrieved April 6, 2007.
- ^ «Overview of Windows Vista Service Pack 1». TechNet. Microsoft. February 5, 2008. Retrieved March 17, 2016.
- ^ «Windows and GPT FAQ». MSDN. Microsoft. June 15, 2011. Retrieved February 4, 2012.
- ^ It is possible only when installing from installation DVD of Windows Vista x64 with its service pack 1 integrated.
- ^ Fisher, Ken (June 21, 2007). «Google says Vista search changes not enough». Ars Technica. Retrieved October 20, 2007.
- ^ Fulton, Scott M., III (October 19, 2006). «Vista SP1 to Include Common Security APIs for Partners». BetaNews. Retrieved June 12, 2007.
- ^ «Kernel Patch Protection Criteria Evaluation Document». Microsoft. December 19, 2006. Retrieved June 12, 2007.
- ^ Hruska, Joel (August 9, 2007). «Microsoft releases information on upcoming D3D 10.1 update». Retrieved August 10, 2008.
- ^ Lowe, Scott (January 13, 2010). «An updated guide to common Microsoft software versions». TechRepublic. CBS Interactive. Retrieved March 17, 2016.
- ^ a b «Notable Changes in Vista Service Pack 1». Microsoft. Archived from the original on 3 May 2008. Retrieved 2 May 2008.
- ^ LeBlanc, Brandon (April 28, 2009). «Windows Vista SP2 RTM + Windows Vista SP1 Blocker Tool Removed». Windows Vista Team Blog. Archived from the original on May 18, 2014.
- ^ a b Nash, Mike (October 25, 2008). «Windows Vista Team Blog : Windows Vista Service Pack 2 Beta». Archived from the original on May 9, 2013. Retrieved October 25, 2008.
- ^ «Information about Windows Server 2008 Service Pack 2 and Windows Vista Service Pack 2». Microsoft. October 2, 2008. Retrieved October 17, 2008.
- ^ «What’s New In Windows Vista SP2?». February 6, 2009. Archived from the original on February 12, 2009. Retrieved February 6, 2009.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (February 24, 2009). «Windows Vista SP2: What to Expect». IT Pro. Penton. Retrieved May 30, 2022.
- ^ «Description of the Platform Update for Windows Server 2008 and the Platform Update for Windows Vista». Microsoft Support. October 27, 2009.
- ^ «The Platform Update for Windows Vista». DirectX Developer Blog. September 10, 2009. Archived from the original on April 8, 2014.
- ^ a b Lawrence, Mark (25 November 2009). «Internet Explorer announces to use DirectWrite & Direct2D (comment from Microsoft official)». Archived from the original on 8 April 2014.
- ^ «Platform Update Supplement for Windows Vista and for Windows Server 2008». Microsoft Support (4.0 ed.). Microsoft. February 8, 2011. Archived from the original on December 28, 2011. Retrieved June 28, 2019.
- ^ «Customer guidance for CVE-2019-0708». Microsoft. Retrieved September 16, 2019.
- ^ Greenberg, Andy (August 13, 2019). «DejaBlue: New BlueKeep-Style Bugs Renew The Risk Of A Windows worm». wired. Retrieved August 15, 2019.
- ^ «Build number changing to 6003 in Windows Server 2008».
- ^ «May 14, 2019—KB4499180 (Security-only update)». Microsoft Support. Retrieved January 14, 2022.
- ^ «CVE-2019-1162 — Security Update Guide — Microsoft Windows ALPC Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability». Customer Guidance Security Update Guide. Microsoft. August 13, 2019. Retrieved December 22, 2020.
- ^ «Microsoft Security Advisory 4022344». Microsoft. Retrieved December 23, 2020.
- ^ «The Mojave Experiment». Mojaveexperiment.com. Retrieved October 2, 2008.
- ^ «The Mojave Experiment: Microsoft Windows Vista». Microsoft.
- ^ «Blog Posts Poke Holes in ‘Taste Test’ by Microsoft». The New York Times. August 4, 2008. Retrieved April 8, 2009.
- ^ Oiaga, Marius (November 2, 2007). «Windows Vista Tastes Like Bubbles…» softpedia. Retrieved February 23, 2022.
- ^ ssinchak (June 27, 2007). «Hacking Windows Vista: Speeding Up the System Boot». Extremetech. Retrieved July 30, 2022.
- ^ Anderson, Tim (December 6, 2007). «Is Windows Vista slower than Windows XP?». The Guardian. Retrieved July 30, 2022.
- ^ DirectX 10: The Future of PC Gaming, Tim Smalley, 30 November 2006 Archived April 23, 2008, at the Wayback Machine. Bit-tech.net (November 30, 2006). Retrieved on October 14, 2011.
- ^ Durham, Joel (May 12, 2008). «Gaming Performance: Windows Vista SP1 vs. XP SP3». ExtremeTech. Ziff Davis. Archived from the original on June 7, 2011. Retrieved July 29, 2008.
- ^ Bright, Peter (March 19, 2007). «Windows Vista: more than just a pretty face». ArsTechnica. Condé Nast. Retrieved July 15, 2015.
- ^ Bright, Peter (June 7, 2007). «Windows Vista: Under the Hood». ArsTechnica. Condé Nast. Retrieved July 15, 2015.
- ^ «Paul Thurrott’s SuperSite for Windows: Windows Vista Review, Part 1: Introduction». August 19, 2007. Archived from the original on August 19, 2007. Retrieved December 31, 2019.
- ^ «Windows Vista Named «Best of CES» at the 2007 International Consumer Electronics Show». News Center. Microsoft. January 10, 2007. Retrieved May 25, 2015.
- ^ «Best of CES 2007 awards Consumer Electronics Show, January 8 to 11». CNET. CBS Interactive. 2007. Archived from the original on January 22, 2007. Retrieved May 25, 2015.
- ^ Tynan, Dan (December 16, 2007). «The 15 Biggest Tech Disappointments of 2007». PC World. IDG. Archived from the original on December 18, 2007. Retrieved December 18, 2007.: listed as No. 1 of «The 15 Biggest Tech Disappointments of 2007»
- ^ McAllister, Neil (January 21, 2008). «Tech’s all-time top 25 flops». InfoWorld. IDG. Retrieved January 27, 2008.
- ^ Flynn, Laurie (April 26, 2007). «Apple Zooms Past Rivals, With 88% Profit Growth». The New York Times. Retrieved December 2, 2015.
- ^ Prague, Liam (February 1, 2022). «Happy birthday, Windows Vista: Troubled teen hits 15». www.theregister.com. Retrieved July 29, 2022.
- ^ Horowitz, Michael (April 23, 2008). «Who’s selling Windows XP in July?». CNET. CBS Interactive. Retrieved March 14, 2016.
- ^ Hoover, J. Nicholas (May 8, 2008). «Microsoft’s Windows Vista Spin Merits Second Look». InformationWeek. UBM plc. Retrieved February 16, 2009.
- ^ Gillen, Al; Waldman, Brett (March 2008). «Document at a Glance – 211087». IDC. Archived from the original on December 16, 2008. Retrieved February 16, 2009.
- ^ O’Neill, Shane (October 30, 2008). «Vista Fights for Relevancy Against Poor Sales, XP, Windows 7». PC World. IDG. Retrieved February 16, 2009.
- ^ Lai, Eric (February 7, 2009). «Vista Makes Converts of Gamers, Enterprises». PC World. Retrieved February 9, 2009.
- ^ Lai, Eric (28 May 2009). «Microsoft: Vista’s enterprise momentum will ‘accrue’ for Windows 7». Computerworld. Archived from the original on 2 March 2007. Retrieved 2 June 2009.
- ^ Reller, Tami (May 28, 2009). «Cowen and Company Technology Media & Telecom Conference». Microsoft. Archived from the original (DOC) on June 16, 2009.
- ^ Microsoft: First Month Vista Sales Double XP, article by Nate Mook Archived December 24, 2007, at the Wayback Machine. Betanews.com (March 26, 2007). Retrieved on October 14, 2011.
- ^ Fried, Ina (September 27, 2007). «Microsoft extends Windows XP’s stay». CNET.
- ^ Windows XP vs. Vista: An Explosion of Opinion Archived February 12, 2022, at the Wayback Machine. Abcnews.go.com (March 20, 2008). Retrieved on October 14, 2011.
- ^ «Leopard drubs Vista in corporate satisfaction survey». March 26, 2008. Archived from the original on November 9, 2019. Retrieved May 30, 2022.
- ^ «AMD 50×15—World Internet Usage». AMD. February 2, 2009. Archived from the original on February 24, 2008. Retrieved November 1, 2009.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (September 16, 2006). «Allchin: 200 Million Windows Vista Users in 24 Months». IT Pro. Penton. Archived from the original on November 9, 2019. Retrieved May 30, 2022.
- ^ Sullivan, John (March 6, 2007). «What’s wrong with Microsoft Windows Vista?». Free Software Foundation. Retrieved March 24, 2007.
- ^ Spooner, John G.; Foley, Mary Jo (August 5, 2005). «Will Your PC Run Windows Vista?». eWeek. QuinStreet. Retrieved August 15, 2006.[permanent dead link]
- ^ Judge, Elizabeth (May 20, 2006). «Windows revamp ‘too advanced for most PCs’«. The Times. London. Retrieved August 15, 2006.
- ^ Gregg Keizer (November 26, 2007).Lawyers: Even Microsoft Confused Over Vista Marketing Archived November 28, 2007, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ «They Criticized Vista. And They Should Know.» Archived April 13, 2019, at the Wayback Machine, The New York Times, March 9, 2008.
- ^ Fisher, Ken (January 28, 2007). «Vista «upgrade» drops compliance checking, requires the old OS to install». Ars Technica. Retrieved January 28, 2007.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (February 3, 2007). «How to Clean Install Windows Vista with Upgrade Media». Supersite for Windows. Penton. Archived from the original on February 5, 2007. Retrieved February 5, 2007.
- ^ Fried, Ina (October 17, 2006). «Microsoft limits Vista transfers». CNET. CBS Interactive.
- ^
Beer, Stan (August 30, 2006). «Windows Vista too expensive says, users». ITWire.com. Archived from the original on September 9, 2006. Retrieved October 19, 2006. - ^ «Microsoft starts Vista hard sell». Technology. BBC News. January 30, 2007. Retrieved January 30, 2007.
- ^ Protalinski, Emil (June 25, 2009). «Windows 7 pricing announced: cheaper than Vista (Updated)». Retrieved October 4, 2009.
- ^ «Output Content Protection and Windows Vista». WHDC. Microsoft. April 27, 2005. Archived from the original on November 16, 2006. Retrieved January 8, 2007.
- ^ Gutmann, Peter (January 27, 2007). «A Cost Analysis of Windows Vista Content Protection». Retrieved January 27, 2007. Also available: PDF version Archived May 11, 2011, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Bott and Ou call out Gutmann’s Vista FUD Archived August 31, 2007, at the Wayback Machine. Blogs.guardian.co.uk. Retrieved on October 14, 2011.
- ^ Smith, Paul (December 31, 2006). «Windows Vista DRM nonsense». Retrieved January 3, 2007.
- ^ Fisher, Ken (May 21, 2006). «Hollywood reportedly in agreement to delay forced quality downgrades for Blu-ray, HD DVD». Ars Technica. Retrieved January 21, 2007.
- ^ Marsh, Dave (January 20, 2007). «Windows Vista Content Protection—Twenty Questions (and Answers)». Windows Vista team blog. Microsoft. Archived from the original on January 21, 2013. Retrieved January 20, 2007.
- ^ «User Account Control: yes, you can turn it off. Is this a good or a bad thing?». Ars Technica. September 10, 2006.
- ^ «Don’t Shut Off Vista UAC, There’s A Better Way». InformationWeek. June 11, 2007. Retrieved October 14, 2011.
- ^ Torode, Christina (April 2, 2008). «Minasi says Vista SP1 solves problems, adds new ones». SearchWinIT.com.
- ^ «Downgrade rights for owners of licensed Windows 8 and Windows 7» (PDF). microsoft.com.
External links[edit]
- Windows Vista End of Support
- Windows Vista Service Pack 2 (SP2) Update
| Windows Vista | |
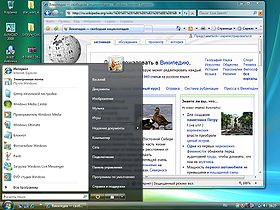 Вид рабочего стола Windows Vista |
|
| Разработчик |
Microsoft Corporation |
|---|---|
| Семейство ОС |
Windows NT |
| Первый выпуск |
30 ноября 2006 (для корпоративных клиентов) |
| Последняя версия |
6.0 (Build 6002.18005.090410-1830) Service Pack 2 (SP2) RTM — 25 мая 2009 |
| Тип ядра |
Гибридное ядро |
| Интерфейс |
Windows Aero |
| Лицензия |
Microsoft EULA |
| Состояние |
Общая поддержка:
Расширенная поддержка:
|
| Веб-сайт |
Windows Vista — Домашняя страница |
Windows Vista (МФА: [ˈwɪn.doʊz ˈvɪstə]) — операционная система семейства Microsoft Windows NT, предназначенная для пользовательских персональных компьютеров. В стадии разработки данная операционная система имела кодовое название «Longhorn».
В линейке продуктов Windows NT Windows Vista носит номер версии 6.0 (Windows 2000 — 5.0, Windows XP — 5.1, Windows Server 2003 — 5.2). Для обозначения «Windows Vista» иногда используют аббревиатуру «WinVI», которая объединяет название «Vista» и номер версии, записанный римскими цифрами.
Windows Vista, как и Windows XP, — исключительно клиентская система. Microsoft также выпустила серверную версию Windows Vista — Windows Server 2008.
30 ноября 2006 года Microsoft официально выпустила Windows Vista и Office 2007 для корпоративных клиентов. 30 января 2007 года начались продажи системы в СНГ для обычных пользователей.[3]
По данным веб-аналитики от W3Schools, по состоянию на октябрь 2012 года, доля рынка Windows Vista равна ▼ 3,0 %; это значение достигало максимума в 18,6 % в октябре 2009 года[4].
Содержание
- 1 История
- 2 Обзор
- 3 Выпуски Windows Vista
- 3.1 Основные
- 3.2 Связанные с требованиями законодательства определённых стран
- 4 Стили оформления
- 5 Аппаратные требования
- 6 Особенности Windows Vista
- 6.1 Новые или улучшенные возможности
- 6.1.1 Улучшения безопасности
- 6.1 Новые или улучшенные возможности
- 7 Пакеты обновления и поддержка
- 7.1 Пакет обновления 1
- 7.2 Пакет обновления 2
- 8 Разработка Windows Vista
- 9 Критика Windows Vista
- 10 Рыночный провал Windows Vista
- 11 См. также
- 12 Примечания
- 13 Литература
- 14 Ссылки
- 14.1 Microsoft
- 14.2 Критика
История
На раннем этапе разработки система была известна под кодовым именем Longhorn (по имени бара Longhorn Saloon вблизи лыжного курорта Вистлер в Британской Колумбии). Название «Vista» было объявлено 22 июля 2005 года. Спустя несколько месяцев Microsoft также переименовали Windows Longhorn Server в Windows Server 2008. С 8 ноября 2006 года полноценная версия Windows Vista доступна для производителей оборудования. Публичный релиз для конечных пользователей состоялся 30 января 2007 года.
Стоит заметить, что многие функции, намечавшиеся в Windows Vista, были опущены Microsoft из-за возмущения общественности. Например, предполагалось, что OpenGL будет реализован как надстройка над Direct3D. Это привело бы к серьёзному падению производительности OpenGL по сравнению с Direct3D и к фиксации версии OpenGL. Опасения не оправдались, поддержка OpenGL в Windows Vista осталась[5]. Не вошла в Windows Vista и файловая система WinFS — на сей раз из-за проблем с производительностью.
Обзор
В Windows Vista обновлена подсистема управления памятью и вводом-выводом. Новой функциональностью также является «Гибридный спящий режим» или режим «гибернации», при использовании которого содержимое оперативной памяти дополнительно записывается на HDD, но и из памяти также не удаляется. В результате если подача энергии не прекращалась, то компьютер восстанавливает свою работу, пользуясь информацией из ОЗУ. Если питание компьютера выключалось, операционная система использует сохранённую на HDD копию ОЗУ и загружает информацию с неё (аналог спящего режима). Режим реализован благодаря так называемым «файлам гибернации», которые занимают объём на жёстком диске, равный объёму установленной на компьютере оперативной памяти. Возможно пользовательское удаление этих файлов с утратой функции гибернации. При этом, восстановление этих файлов без особых затруднений возможно путём вызова специальных команд из командной строки.
С 28 июля 2005 года разработчикам и ИТ-профессионалам была разослана первая бета-версия. В неё были включены все разработанные на тот день технические возможности и наглядно представлены основы новой архитектуры системы. Первая бета-версия была выпущена для того, чтобы у ИТ-аудитории сложилось первое впечатление о новой операционной системе, и для обнаружения ошибок в новой системе ещё до её официального выпуска. По результатам первого этапа бета-тестирования были доработаны пользовательские функции системы, которые затем были представлены во второй бета-версии. Финальная версия Windows Vista представлена в вариантах для 32- и для 64-разрядных процессоров.
Windows Vista имеет также новый логотип. По мнению дизайнеров компании, этот логотип иллюстрирует изменения в пользовательском интерфейсе новой операционной системы (который из-за внешнего вида называют «стеклянным»).
Выпуски Windows Vista
Основные
- Starter: распространяется Microsoft только на некоторых развивающихся рынках в бедных странах (а также в виде предустановленной ОС на некоторых моделях нетбуков); имеет символическую цену и множество функциональных ограничений. К примеру, максимально допустимое дисковое пространство ограничено 250 Гб, память — 1 гигабайтом, а процессор — одним ядром (32 bit) без технологии Hyper-threading.
- Home Basic: поддержка не более 2-х процессоров (с неограниченным количеством ядер) с 8 гигабайтами максимального объёма оперативной памяти для платформы amd64 (64х-битная) и 3,4 гигабайтами для платформы x86 (32х-битная), read-only версия MeetingSpace, 5 подключений по SMB, нет интерфейса Windows Aero, отсутствуют возможность присоединения к домену, а также редактор групповых и локальных политик, нет поддержки EFS.
- Home Premium: поддержка до 2-х процессоров с 16 гигабайтами максимального объёма оперативной памяти, HDTV, запись видео-DVD, 10 подключений по SMB, поддержка сенсорных экранов, автоматическое резервное копирование, интерфейс Windows Aero, отсутствует возможность присоединения к домену, редактор групповых и локальных политик, нет поддержки EFS, поддержка Microsoft Anna — функции, позволяющей компьютеру автоматически читать заданную текстовую информацию (на английском языке, аналогичной версии для чтения русских текстов пока нет).
- Business: нет родительского контроля, поддержка до 2 процессоров, урезана мультимедийная часть и убраны развлекательные приложения. Данная версия Vista поддерживает работу в домене, политики и шифрованную файловую систему EFS.
- Enterprise: многоязычный интерфейс, сервисы Microsoft Windows для UNIX, корпоративные многопользовательские лицензии, шифровальщик дисков BitLocker, урезана мультимедийная часть.
- Ultimate: включает все возможности Enterprise и Home Premuim, плюс дополнительные Ultimate Extras, хорошо развита мультимедийная часть, поддержка анимированных обоев рабочего стола, а поддержка мультиязычного пользовательского интерфейса позволяет менять по желанию язык пользовательского интерфейса операционной системы.
- Ultimate Upgrade Limited Numbered Signature Edition[6]: каждый экземпляр имеет порядковый номер и подпись Билла Гейтса. Выпускается ограниченным тиражом — 20000 экземпляров.
Связанные с требованиями законодательства определённых стран
- …N: для Европы, без Windows Media Player.
- …K: для Кореи. Содержат ссылки на ПО, альтернативное Windows Messenger и Windows Media Player. Версия …KN вообще не будет иметь этих программ.
Стили оформления
Windows Vista поддерживает четыре варианта оформления пользовательского интерфейса:
- Windows Aero — это оригинальный стиль оформления с прозрачными многоцветными рамками окон, применяемый по умолчанию для компьютеров с более чем 512 Mb ОЗУ и соответствующим спецификации «Vista Ready» видеоадаптером (обязательна поддержка DirectX-9c, желательно DirectX-10). Доступна на Windows Vista Home Premium, Windows Vista Business и более старших редакциях.
- Windows Vista — упрощённый стиль — это оригинальный стиль оформления, применяемый по умолчанию для компьютеров, которые по каким-либо причинам не готовы к запуску Windows Aero. Этот стиль также применяется при запуске приложений в режиме совместимости.
- Windows Vista Standard — Windows Aero с некоторыми отключенными возможностями (например, прозрачность окон и Windows Flip 3D). Требования к системе — такие же, как и у Windows Aero. Доступна на Windows Vista Home Basic.
- Windows Standard — минимальные требования к системе, оформление окон в стиле «классической» темы Windows XP. Доступны различные цветовые схемы, в частности, подобные схемам Windows 98; пользователь может создавать свои цветовые схемы.
- Пользовательские темы оформления — пользователи, недовольные интерфейсом Windows Vista могут разработать и применить собственный стиль оформления. Для этого необходимо установить неофициальный патч нарушив при этом EULA, позволяющий применять неподписанные Microsoft темы и визуальные стили оформления системы.
Аппаратные требования
Согласно информации от Microsoft, компьютеры, на которых можно запускать Windows Vista, классифицируются как Vista Capable (удовлетворяющие минимальным параметрам) и Vista Premium Ready (удовлетворяющие рекомендуемым параметрам)[7] [8].
| Минимальные требования | Рекомендуемые требования | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 800 МГц | 1 ГГц |
| ОЗУ | 512 МБ | 1 ГБ (Для лучшей производительности требуется 2 ГБ и более). |
| Видеоадаптер | DirectX 9 | DirectX 9 совместимый с поддержкой технологий
Hardware Pixel Shader v2.0 и WDDM |
| Видеопамять | 32 МБ (для выпуска Home Basic) | 128 МБ |
| Жёсткий диск | 20 ГБ | 40 ГБ |
| Свободное место на жестком диске | 15 ГБ | 20 ГБ |
| Другие приводы | CD-ROM | DVD-ROM |
Особенности Windows Vista
Новые или улучшенные возможности
- По утверждению самой Microsoft, время загрузки системы меньше, чем в Windows XP и на большинстве компьютеров составляет меньше минуты.[9] Уменьшено время входа и выхода из спящего режима до 6 секунд.[9]. Но с появлением пользовательского интерфейса приходится ждать значительно дольше, чтобы начать полноценную работу, пока пройдут фоновые процессы, сильно затрудняющие работу сторонних программ.[10][11]
- Благодаря технологии «Windows ReadyBoost» стало возможно использование ёмкости внешних USB флеш накопителей для своппинга, что в некоторых случаях увеличивает производительность на 40 %.[9]
- По информации Microsoft, за 180 дней доступности в Windows Vista было найдено меньше уязвимостей, чем в Windows XP. Вероятность попадания в систему вирусов, червей и руткитов на 35 % меньше, чем в Windows XP SP3, на 60 % меньше, чем в Windows XP SP2 и на 90 % — чем в Windows XP без сервиспака.[12]
- Windows Shell: новый Windows Shell значительно отличается от оболочки в Windows XP, предлагая новый диапазон организации, навигации и поиска. Панель предварительного просмотра позволяет пользователям просматривать миниатюры различных файлов и просмотр содержимого документа.
- Мгновенный поиск: Мгновенный поиск в Windows Vista представляет собой новый способ мгновенного поиска, который значительно быстрее и более глубокий.
- Боковая панель Windows: прозрачная панель сбоку экрана, где пользователь может разместить Гаджеты.
Улучшения безопасности
- User Account Control (UAC) — система контроля учётных записей пользователей, которая требует явного разрешения пользователя при выполнении любого действия, требующего административных полномочий, вне зависимости от прав текущего аккаунта пользователя. Если пользователь не является администратором, будет выводиться запрос, в котором можно выбрать административную учётную запись и выполнить операцию с её правами, введя пароль — это позволяет производить конфигурирование системы и установку приложений из учётной записи ограниченного пользователя, не используя явно механизм runas и без необходимости переключения в другую учётную запись (что требовалось в XP, например, в случае изменения параметров TCP/IP). Если пользователь входит в группу «Администраторы», то ему потребуется (при настройках по умолчанию) подтвердить использования прав, ответив на запрос системы. UAC запрашивает данные в режиме Secure Desktop, с помощью которого осуществляется защита от перехвата данных и контроля за окном ввода со стороны сторонних программ (примерно такой же режим был использован при входе в домен NT с требованием двукратного нажатия Ctrl-Alt-Del). UAC можно отключить для отдельных категорий учётных записей и переконфигурировать, используя локальную (или групповую при использовании в домене) политику безопасности: например, можно задать обязательное введение пароля для использования административных полномочий всеми пользователями (включая администраторов), запретить эти действия пользователям ограниченных учётных записей и т. д.[13][14][15]
- Технологии, предотвращающие использование эксплойтов[16][17] — операционная система Windows Vista обладает некоторыми преимуществами, препятствующими использованию обнаруженных уязвимостей в программном обеспечении, но полностью реализуемыми только в 64-битных версиях и с программами, написанными с учётом этих возможностей:
- Data Execution Prevention
- Vista использует технологию Address Space Layout Randomization (ASLR), для загрузки кода системы в случайным образом выбранные участки памяти. По умолчанию все системные файлы загружаются в один из 256 случайно выбранных участков памяти. Другие исполняемые файлы могут использовать особый бит в заголовке PE-формата, чтобы система запускала их код с использованием ASLR. Для таких приложений случайным образом будут также определены области стека и кучи.[18]
- Изменение в формате исполняемых файлов.
- Шифрование диска Bitlocker — Предоставляет возможность шифрования системного диска, используя интерфейс командной строки и другие разделы. При этом используется USB-ключ или Trusted Platform Module для хранения ключей шифрования. Для шифрования разделов, по умолчанию, используется алгоритм AES с длиной ключа 128 бит в режиме шифрования CBC. Данная возможность присутствует в версиях Vista Enterprise или Ultimate.[19][20][21]
- Система шифрования файлов EFS. Эта система, появившаяся впервые в Windows 2000, работает в версиях Vista Business, Enterprise или Ultimate и даёт возможность «прозрачного» шифрования файлов на уровне файловой системы алгоритмами AES (с 256-битным ключом) или 3-DES. Для каждого файла случайным образом генерируется ключ шифрования, который, в свою очередь, шифруется открытым ключом пользователям (по умолчанию 2048 бит). В Vista с помощью политик появилась возможность задавать разную длину открытого ключа пользователя (1024, 2048, 4096,…), сохранять ключ на смарт-картах (по умолчанию, ключ хранится локально, защищённый паролем пользователя) и шифровать файл подкачки, а также требовать обязательного шифрования пользовательской папки с документами.[22][23]
- Предотвращение заражения вирусами с извлекаемых носителей. По умолчанию в Windows Vista отключён автозапуск программ с флеш-карт и устройств USB. Это удерживает компьютер от самозаражения вирусами, переносчиками которых могут являться и флеш-карты. Так же имеются политики управляющие доступом к внешним носителям (включая USB), что также способствует защите конфиденциальных данных.
- Блокировка прямой записи на диск. Windows Vista запрещает прямую запись на диск (\.PhysicalDriveX), если с диска смонтирована файловая система. Подробнее — см. http://support.microsoft.com/kb/942448/
- Защитник Windows. В Windows Vista появилась встроенная программа, которая служит для борьбы со шпионским программным обеспечением.
- Родительский контроль. В составе домашних изданий Windows имеется функция родительского контроля, которая помогает ограничить использование компьютера детьми. Например, можно настроить веб-фильтр для блокировки нежелательных сайтов, запретить использовать компьютерные игры, не предназначенные для их возраста. Также с помощью родительского контроля можно запретить использовать конкретную программу, установить временное ограничение и просматривать отчет о работе родительского контроля. Не секрет, что в Windows XP и более ранних операционных системах приходилось тратить много сил и времени, чтобы застраховаться от последствий неосторожного использования компьютера детьми.
- Internet Explorer 9. У Windows Vista есть возможность загрузить браузер Internet Explorer 9.
- Предотвращение выполнения данных (DEP) в Windows Vista изменился тем, что теперь он включен по умолчанию. И теперь эта ОС может включать программную реализацию защиты, даже если процессор не поддерживает DEP. Однако могут происходить ложные срабатывания и некоторые несовместимые устаревшие и даже некоторые новые программы могут не запуститься, хотя их можно поставить в список исключений или на крайний случай отключить DEP с помощью утилиты командной строки «bcdedit».
Пакеты обновления и поддержка
Microsoft регулярно выпускает пакеты обновлений своих операционных систем, устраняющие выявленные проблемы и добавляющие новые возможности.
C 15 января 2008 года в России начал издаваться журнал «Windows Vista».
Пакет обновления 1
Пакет обновления 1 (SP1) для ОС Windows Vista выпущен 4 февраля 2008 года.[24]
- По заявлениям Microsoft, после инсталляции SP1 копирование файлов на локальных накопителях будет осуществляться на 25 % быстрее.
- Решена проблема, приводившая к появлению сообщений об ошибках при копировании больших файлов через локальную сеть. Windows Vista с установленным пакетом обновлений также будет более оперативно обрабатывать изображения высокого разрешения.
- В сервис-пак включены дополнения, улучшающие совместимость операционной системы с новыми видеоадаптерами, некоторыми типами мониторов и принтеров.
- В состав пакета обновлений также входят исправления, уменьшающие время вывода компьютера из спящего режима, повышающие производительность браузера Internet Explorer 7 и улучшающие схему управления питанием ноутбуков. Традиционно в сервис-пак включены все ранее выпущенные обновления и исправления.
Первоначально пакет обновления был доступен на пяти языках — английском, немецком, французском, испанском и японском. В середине апреля 2008 года Microsoft опубликовала версии пакета обновлений на других языках. Между тем, пока остаются нерешёнными проблемы совместимости SP1 с некоторыми драйверами устройств.[25] Перед установкой SP1 система Windows Update проверяет компьютер на предмет наличия проблемных компонентов, и в случае их обнаружения откладывает инсталляцию.
Перед установкой Пакета обновления 1 необходимо предварительно деинсталлировать его тестовую версию.
Пакет обновления 2
Пакет обновления 2 доступен к загрузке с сайта Microsoft. В Service Pack 2 присутствует :
- Windows Search 4
- поддержка Bluetooth 2.1/3.0 (для версии Bluetooth 3.0 доступен лишь beta-драйвер)
- поддержка 64-разрядных процессоров VIA
- возможность записи оптических дисков формата Blu-ray
- мастер Windows Connect Now (WCN) для упрощения настройки беспроводных сетей Wi-Fi
- файловая система exFAT, с поддержкой записи в файлы дат в международном формате, по Гринвичу, что позволит безошибочно синхронизировать файлы между различными часовыми поясами
- поддержка смарт-карт формата ICCD/CCID
- улучшенная защита ТВ-контента в Windows Media Center (WMC)
- улучшена работа Wi-Fi после выхода из спящего режима
- внесены исправления в DirectX
- обновлён компонент RSS в боковой панели
- увеличена производительность при воспроизведении HD-видео[26]
- Снято ограничение на количество полуоткрытых соединений
- Добавлена совместимость с Windows 7
- Устанавливается DirectX 11
- Обновлён Device Stage
В отличие от Service Pack для предыдущих версий Windows, SP2 нельзя установить без предварительной установки SP1. Это сделано с целью объединить SP для двух платформ — Windows Vista и Windows Server 2008.
25 мая 2009[27] единый Service Pack 2 для Windows Vista и Windows Server 2008 стал доступен для публичного скачивания с сайта Microsoft на английском, немецком, испанском, французском и японском языках.
1 июля 2009 Пакет обновления 2 для Windows Vista на русском языке стал доступен для автоматической установки через Центр обновления Windows.
22 июня 2009 Пакет обновления 2 (SP2) для Windows Server 2008 и пакет обновления 2 (SP2) для Windows Vista — отдельная версия для всех языков (KB948465) (475 MB][28][29]
Компания Microsoft собиралась выпустить Пакет обновления 3 (SP3) для Windows Vista и Windows Server 2008 в 2010 году.[60] Но вскоре стало известно, что выход пакета обновления был отменён.
12 июля 2011 официально прекращена поддержка Windows Vista SP1 — об этом пишет neowin.net. Это означает, что Microsoft прекратила выпускать обновления безопасности для этой операционной системы, что делает её с каждым днем все менее защищенной.
Прекращение поддержки не затронет операционные системы Vista с установленным обновлением SP2, поэтому всем пользователям, которые все ещё не установили это обновление, рекомендуется это сделать в ближайшее время. Поддержка Windows Vista SP2 продлится до 11 апреля 2017.
Разработка Windows Vista
Разработка Windows Vista (под кодовым названием «Longhorn») началась в мае 2001 года, за пять месяцев до выхода Windows XP и продолжалась до ноября 2006 года. Первоначально Microsoft ожидала завершить версию в конце 2003 года и представить как незначительный шаг между Windows XP (под кодовым названием «Whistler») и Windows 7 (под кодовым названием «Blackcomb» и «Vienna»). Концепция Longhorn была намеком на тот план. Первоначально Longhorn разрабатывался на основе Windows XP, но с 2004 года Microsoft «перезагрузила» проект, то есть начала с нуля разрабатывать, но уже на основе Windows 2003. В связи с этим, некоторые особенности, такие как WinFX и NGSCB, были исключены или понижены. В середине 2005 года «Longhorn» был переименован в Windows Vista.
Критика Windows Vista
Windows Vista критикуется по таким статьям:
- Некоторые действия, выполнявшиеся на XP мгновенно, на Vista производятся с небольшой задержкой. Это показывают тесты Tom’s Hardware[30] — лишь некоторые программы (скорее всего, многопоточные) на Vista работают быстрее. По сообщению того же сайта, были также обнаружены ошибки в оболочке WV[31].
- Была выброшена часть проверенного кода и написан новый. По утверждениям Symantec и McAfee, это должно привести к уязвимостям — как минимум, первое время[32][33].
- Windows иногда упрекают в ущемлении свободы, связанные с защитой «премиум-контента» от копирования (Protected Media Path)[34]. А именно:
- Установка неподписанных драйверов на 64-битную версию Vista возможна исключительно обходными путями[35][36] и полностью отключает проигрывание премиум-контента. В Windows XP цифровая подпись означала «проверенность» и «стабильность» драйвера — пользователи могли ставить и неподписанные, а производители подписывали лишь важнейшие версии. В Vista же подпись — необходимое условие работы (по крайней мере будет таковым, когда премиум-контент станет широко распространённым).
- Microsoft оставляет за собой право отозвать драйвер в любой момент, если в нём будет найдена уязвимость[37]. Если устройство старое, есть шансы, что производитель (или его правопреемник) не будет переписывать драйверы, и проигрывание будет недоступно (остальные функции не страдают)[38]. Пострадают от этого только рядовые пользователи, а никак не организованные незаконные распространители объектов АП — найдя подходящую аппаратно-программную конфигурацию, они могут свободно расшифровывать видео на отключённом от Интернета компьютере.
- Чтобы защита работала, все устройства, связанные с проигрыванием, должны быть допущены Microsoft. Часть требований: прежде чем быть допущенным к проигрыванию, устройство должно пройти особый тест на работоспособность (Hardware Functionality Scan)[39][40], расшифровка должна происходить на самих устройствах, а не на незащищённых каналах (DVI без HDCP, VGA, S/P-DIF) на звук и видео должны накладываться помехи[41].
- В некоторых ситуациях пользователям протокола BitTorrent требуется большое количество полуоткрытых исходящих соединений. На это в Windows стоит ограничение, которое было введено компанией Microsoft в попытке замедлить распространение вирусов с зараженного компьютера, а также ограничить возможности участия компьютера в DoS-атаках. Однако, с выходом Service Pack 2 данная проблема устранена самой компанией Microsoft — после установки SP2 число полуоткрытых соединений становится неограниченным.
- Есть старое программное обеспечение, которое несовместимо с Windows Vista[42], а также драйверы и устройства. Более того, в Vista была переделана поддержка USB в сторону более строгого контроля соблюдения стандарта, что сделало некоторые не совсем совместимые со стандартом (но работающие в XP и Linux) USB устройства принципиально несовместимыми с Vista (переписывание драйвера — не спасает).
- Интерфейс Aero, по мнению Пола Таррота, имеет недостаток в виде сложноотличимого текущего окна от всех остальных (активное окно заметно отличается от остальных лишь подсветкой кнопки закрытия окна)[43]
- User Account Control часто раздражает пользователей, задавая даже в рутинных операциях много вопросов[44], однако при необходимости его может отключить опытный пользователь или администратор. Кроме того, Symantec выпустил утилиту Norton UAC Tool, которая заметно уменьшает количество запросов, используя механизм белого списка.[45]
- В домашней версии Vista остался старый механизм инсталляции обновлений. Процесс полной инсталляции обновлений занимает довольно продолжительное время (в зависимости от объёма обновлений и вычислительной мощности компьютера — от 20 мин до 1-1,5 часа) и на Vista разделяется на автоматически протекающие собственно установку и последующую настройку установленных обновлений. Отличием домашних версий является то, что второй процесс — настройка установленных обновлений — не запускается операционной системой автоматически — пользователю приходится запускать его вручную, включением компьютера.
- для соблюдения неоднократно сорванных сроков выхода на рынок в релизе Vista были убраны те возможности, которые были ранее обещаны и даже появлялись в бета-версиях. Это вызвало огромное недовольство в мире крупных корпораций.
- реальные аппаратные требования Windows Vista куда превосходили возможности широко распространенных компьютеров тех лет, и были намного выше, чем заявленные. Также на публику утек скандал между «отделом дружбы с Intel» и отделом разработки Windows внутри Microsoft, поднявшийся до уровня вице-президента. Отдел разработки настаивал на том, что смягчать официально заявленные требования к оборудованию нельзя, однако же Intel настаивал на их смягчении для того, чтобы продержать в производстве ещё какое-то время устаревший, но на тот момент очень популярный чипсет (который не удовлетворял не-смягченным требованиям, и был бы немедленно убит как рыночный продукт в случае релиза Vista с не-смягченными требованиями). Дружба с Intel победила, требования смягчили, при том, что Vista работала неудовлетворительно медленно на данном чипсете.
Рыночный провал Windows Vista
Существует мнение, что Windows Vista является худшей операционной системой, выпущенной Microsoft[46][47]. Также Windows Vista заняла первое место в конкурсе «Провал года»[48], проводимого сайтом Pwnie award, созданным в 2007 году. Более того, по предположению сайта The Inquirer.net, по ряду беспрецедентных промоакций, связанных с продвижением WV на рынке, можно сделать вывод о том, что руководство Microsoft признало Windows Vista провалом[49].
Огромное количество пользователей по всему миру удаляли легальную Windows Vista с ноутбуков и устанавливали взамен Windows XP, часто нелицензионную. Причина тут только в неудовлетворительной работе Vista на данной аппаратуре, ибо ни одна предыдущая версия Windows никогда не вызывала такой реакции (то есть это невозможно объяснить консерватизмом пользователей), не вызывает её и Windows 7.
После выхода Windows 7 (по сути, улучшенной версии Windows Vista с оптимизациями производительности и исправлениями ошибок) Windows Vista практически немедленно вымерла (что не относится к её серверной версии). Так как стандартной практикой разработчиков настольных приложений в наше время является их тестирование на двух ОС — Windows XP и Windows 7. И то, по состоянию на май 2012 года, Windows XP стремительно теряет свои владения, уступая их Windows 7.
Срок поддержки ОС Windows XP продлен производителем до беспрецедентного в истории компьютерной техники (за исключением крайне дорогих серверов масштаба предприятия) срока в 13 лет. Кроме того, MS не удалось отказаться от продаж Windows XP до выхода Windows 7, хотя такой отказ есть стандартная практика этой компании (как и любой другой).
См. также
- Windows Vista Starter
- Windows XP
- Windows 7
- Windows 8
Примечания
- ↑ It’s the end of mainstream support for Windows Vista
- ↑ Сегодня заканчивается бесплатная фаза поддержки Windows Vista и Office 2007
- ↑ Microsoft Launches Windows Vista and the 2007 Office System to Consumers. PressCentre. Microsoft New Zealand (30 января 2007). Архивировано из первоисточника 23 августа 2011. Проверено 9 ноября 2009.
- ↑ По состоянию на июль 2012 года, W3schools.
- ↑ Windows Vista обзавелась нативной поддержкой OpenGL.
- ↑ Vista: теперь с подписью Билла Гейтса — Цифровик.ру
- ↑ Microsoft и производители компьютеров улучшают систему перехода на Windows Vista для покупателей (англ.). PressPass. Microsoft (May 18 2006). Архивировано из первоисточника 23 августа 2011. Проверено 15 июля 2006.
- ↑ Windows Vista Enterprise Hardware Planning Guidance — Путеводитель по запланированным аппаратным требованиям Windows Vista (англ.). Microsoft. Архивировано из первоисточника 23 августа 2011. Проверено 15 июля 2006.
- ↑ 1 2 3 http://www.microsoft.com/windows/products/windowsvista/facts.mspx страница из архива
- ↑ Уменьшение времени загрузки Windows Vista
- ↑ Microsoft’s hidden diagnostic tool unlocks Vista startup secrets
- ↑ Microsoft Security Intelligence Report, Key Findings Summary. (Jan-June 2007.) The full report.
- ↑ TheVista.ru:User Account Control
- ↑ The Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008 Developer Story: Windows Vista Application Development Requirements for User Account Control (UAC). The Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008 Developer Story Series. Microsoft (April 2007). Архивировано из первоисточника 23 августа 2011. Проверено 8 октября 2007.
- ↑ User Account Control Overview. Technet. Архивировано из первоисточника 23 августа 2011.
- ↑ Технологии защиты приложений в Windows Vista и Windows Server 2008
- ↑ Об уникальных средствах обеспечения безопасности 64-разрядных версий Windows Vista
- ↑ Address Space Layout Randomization in Windows Vista
- ↑ Windows BitLocker Drive Encryption Frequently Asked Questions. Microsoft. Архивировано из первоисточника 23 августа 2011. Проверено 5 сентября 2007.
- ↑ Niels Fergusson (August 2006). «AES-CBC + Elephant Diffuser: A Disk Encryption Algorithm for Windows Vista» (Microsoft). Проверено 2008-02-22.
- ↑ Защита данных с помощью шифрования диска BitLocke
- ↑ New Security Features in Windows Vista(technet.microsoft.com)
- ↑ Обновленная EFS в Vista и Longhorn (oszone.net)
- ↑ Windows Vista Service Pack 1 (SP1)
- ↑ Список драйверов, несовместимых с Windows Vista в SP1
- ↑ МИР NVIDIA / Новости / сегодня, 1 июля
- ↑ Download details: Windows Server 2008 Service Pack 2 and Windows Vista Service Pack 2 — Five Language Standalone for x64-based systems (KB948465)
- ↑ Пакет обновления 2 (SP2) для Windows Server 2008 и пакет обновления 2 (SP2) для Windows Vista — отдельная версия для всех языков (KB948465)
- ↑ Получение последнего пакета обновления для Windows Vista
- ↑ Windows Vista: тесты | THG.RU
- ↑ У фотографов проблемы с Windows Vista | THG.RU
- ↑ Symantec sees an Achilles’ heel in Vista (англ.)
- ↑ Microstft increasing security risk with Vista (англ.)
- ↑ Microsoft: архитектура защиты премиум-контента от копирования (англ.), слайды 3—7
- ↑ Microsoft: Kernel mede code signing walkthrough (англ.)
- ↑ Driver Signature Enforcement Overrider 1.3b (англ.)
- ↑ Microsoft blocks 64-bit driver (англ.)
- ↑ Windows Vista Content Protection: 20 questions and Answers (англ.)
- ↑ Microsoft: архитектура защиты премиум-контента от копирования (англ.), слайд 9
- ↑ Заявка на патент: Сканирование функциональности аппаратного обеспечения (англ.)
- ↑ Microsoft: архитектура защиты премиум-контента от копирования (англ.), слайд 13; это названо «resolution constriction».
- ↑ Six months on, Vista users still griping
- ↑ Windows Vista February 2006 CTP (Build 5308/5342) Review, Part 5: Where Vista Fails
- ↑ Microsoft: «механизм управления учётными записями пользователей (UAC) раздражает пользователей»
- ↑ Norton Labs
- ↑ POINT.RU: Большой провал Microsoft . Vista признана худшей технологией
- ↑ Windows становится опасным, а Vista — худшая из всех версий Винды. — Форум сторонников КПРФ : KPRF.ORG : Политический форум
- ↑ Pwnie Awards 2010
- ↑ Microsoft признает провал Windows Vista
Литература
- Пол Мак-Федрис. Microsoft Windows Vista. Полное руководство = Microsoft Windows Vista Unleashed. — М.: «Вильямс», 2007. — С. 864. — ISBN 978-5-8459-1302-9
- Брайан Ливингстон, Пол Таррот. Секреты Microsoft Windows Vista = Windows Vista Secrets. — М.: «Диалектика», 2007. — С. 456. — ISBN 0-7645-7704-2
Ссылки
| Windows Vista в Викиновостях? |
Microsoft
- Домашняя страница Windows Vista (рус.)
- Microsoft Windows Vista homepage (англ.)
- Техцентр Windows Vista
- Доклад о ключевых изменениях в ядре Windows Vista SP1
- Страница загрузки пакета обновлений Windows Vista SP1
- Страница загрузки пакета обновлений Windows Vista SP2
- Список совместимости приложений Windows Vista для ИТ-специалистов
Критика
- Infuture.ru: Microsoft: «механизм управления учетными записями пользователей (UAC) раздражает пользователей»
- CNET Hollywood, Microsoft align on new Windows’ (англ.)
- BadVista.org (англ.)
- Technology Review ‘Will Windows Upgrade Hand Power To Big Media?’ (англ.)
- PC Stats ‘Windows Vista, HDCP and Digital Rights Management’ (англ.)
- Yahoo News ‘Ten Reasons to Buy Windows Vista (and «five things that will give you pause»)’ (англ.)
- Paul Thurrott ‘Where Vista Fails’ (англ.)
- A Cost Analysis of Windows Vista Content Protection (англ.)
- Windows Vista Content Protection (англ.)
- Как вернуть деньги за OEM-Windows, 3dnews.ru, 28 сентября 2009 г
| |
||
|---|---|---|
|
Оболочки над MS-DOS: 1.0 • 2.x • 3.x • Windows 9x: 95 • 98 • ME • Windows NT: NT 3.1 • NT 3.5 • NT 3.51 • NT 4.0 • 2000 • XP • Vista • 7 • 8 |
||
| Windows Server |
2003 • Home (2011) • 2008 (HPC 2008 • R2) • Essential Business • MultiPoint • Small Business • 2012 |
 |
| Специализированные |
Embedded (Automotive • POSReady) • PE • FLP |
|
| Мобильные |
Windows CE (1.0 • 2.0 • 3.0 • 4.0 • 5.0 • 6.0 • 7.0) • Mobile • Phone • RT |
|
| Другие проекты |
Xenix • OS/2 • Singularity • Midori • Закрытые: Neptune • Nashville • Odyssey • Cairo |
|
| Альтернативные реализации |
ReactOS • Wine |
Windows Vista [ˈwɪn.doʊz ˈvɪstə]’ — операционная система семейства Windows NT производства корпорации Microsoft. На стадии разработки имела кодовое имя «Longhorn». Построена на основе гибридного ядра NT версии 6.0. В качестве сокращенного имени иногда используется акроним «WinVI», объединяющий первые три буквы названия и версию ядра в римской записи. Предназначена исключительно для рабочих станций и персональных компьютеров; её ориентированная на серверы «сестра» — Windows Server 2008.
30 ноября 2006 года Microsoft официально выпустила Windows Vista и Office 2007 для корпоративных клиентов. 30 января 2007 года начались продажи системы в СНГ для обычных пользователей[3]. Vista получила обновлённый дизайн пользовательского интерфейса по сравнению с Windows XP. По данным веб-аналитики W3Schools, по состоянию на октябрь 2015 года доля рынка Windows Vista составляет ▼0,5%; это значение достигало максимума в 25,02% в октябре 2009 года, после чего начало снижаться, в том числе из-за выхода Windows 7.
По информации NetMarketShare, на 2019 год WIndows Vista используется всего на 0,14% персональных компьютеров.
История[]
На раннем этапе разработки система была известна под кодовым именем Longhorn (по имени бара Longhorn Saloon вблизи лыжного курорта Whistler (рус. Вистлер) в Британской Колумбии). Название Vista было объявлено 22 июля 2005 года. Спустя несколько месяцев Microsoft также переименовала Windows Longhorn Server в Windows Server 2008. С 8 ноября 2006 года полноценная версия Windows Vista доступна для производителей оборудования. Релиз для конечных пользователей состоялся 30 января 2007 года.
Стоит заметить, что выпуск многих функций, анонсированных в Windows Vista, был отменен Microsoft из-за недовольства общественности. Например, предполагалось, что OpenGL будет реализован как надстройка над Direct3D. Это привело бы к серьёзному падению производительности OpenGL по сравнению с Direct3D и к фиксации версии OpenGL. Опасения не оправдались, поддержка OpenGL в Windows Vista осталась. Не вошла в Windows Vista и файловая система WinFS — на сей раз из-за проблем с производительностью.
Обзор[]
В Windows Vista обновлена подсистема управления памятью и вводом-выводом (I/O). Новой функциональностью также является «Гибридный спящий режим», при использовании которого содержимое оперативной памяти дополнительно записывается на HDD, но и из памяти также не удаляется. В результате, если питание не выключалось, компьютер восстанавливает работу, пользуясь информацией из ОЗУ. Если же подача энергии прекратилась, операционная система использует сохранённую на HDD копию ОЗУ и загружает информацию из неё (аналог спящего режима). Режим реализован благодаря так называемым «файлам гибернации», которые занимают объём на жёстком диске, равный объёму установленной на компьютере оперативной памяти. Пользователь может удалить эти файлы (утратив функцию гибернации). При этом восстановление данных файлов возможно путём вызова специальных команд из командной строки.
С 28 июля 2005 года разработчикам и IT-профессионалам рассылалась первая бета-версия. В ней были представлены основы новой архитектуры системы и все разработанные на тот день технические возможности. Первая бета-версия была выпущена для того, чтобы у аудитории сложилось первое впечатление о новой ОС, а также для обнаружения ошибок в новой системе до её официального выпуска. По результатам первого этапа бета-тестирования были доработаны пользовательские функции системы, которые затем были представлены во второй бета-версии. Финальная версия Windows Vista представлена в вариантах для 32- и 64-разрядных процессоров.
Windows Vista имеет также новый логотип. По мнению дизайнеров компании, этот логотип иллюстрирует изменения в пользовательском интерфейсе новой операционной системы (который получил название Aero из-за применения эффекта прозрачности).
Редакции Windows Vista[]
- Основная статья: Редакции Windows Vista
Операционная система была доступна в шести разных вариациях (Starter, Home Basic, Home Premium, Business, Enterprise, и Ultimate). Все они отличались друг от друга функционалом и стоимостью. Все редакции (кроме Starter) поддерживают 64-битную архитектуру и могут работать более чем с 4 ГБ оперативной памяти.
Стили оформления[]
Windows Vista поддерживает четыре варианта оформления пользовательского интерфейса:
- Windows Aero — это оригинальный стиль оформления с полупрозрачными многоцветными рамками окон, применяемый по умолчанию для компьютеров с более чем 512 МБ ОЗУ и соответствующим спецификации «Vista Ready» видеоадаптером (обязательна поддержка DirectX 9c, желательно DirectX 10). Доступна в выпусках Home Premium, Business, Enterprise и Ultimate).
- Упрощённый стиль — это оригинальный стиль оформления, применяемый по умолчанию для компьютеров, которые по каким-либо причинам не готовы к запуску Windows Aero. Этот стиль также применяется при запуске приложений в режиме совместимости.
- Стандартная — Windows Aero с некоторыми отключенными возможностями (например, прозрачность окон и Windows Flip 3D). Требования к системе — такие же, как и у Windows Aero. Доступна на Windows Vista Home Basic.
- Классическая — минимальные требования к системе, оформление окон в стиле «классической» темы Windows XP. Доступны различные цветовые схемы, в частности, подобные схемам Windows 98; пользователь может создавать свои цветовые схемы.
- Пользовательские темы оформления — неофициальный способ настройки интерфейса, который заключается в модификации ОС и разрешении установки неподписанных тем (данные действия нарушают EULA).
 Стиль «Windows Aero». |
 Стиль «Windows Vista — упрощённый стиль». |
 Стиль «Windows Standard» и «Windows Classic». |
 Стиль «Windows Vista Standard». |
Аппаратные требования[]
Согласно информации Microsoft, компьютеры, на которых можно запускать Windows Vista, классифицируются как Vista Capable (удовлетворяющие минимальным параметрам для Windows Vista Home Basic (За это позже посудили Microsoft, за заблуждение пользователя)) и Vista Premium Ready (удовлетворяющие рекомендуемым параметрам).
{| class=»wikitable»
!
!Минимальные требования
!Рекомендуемые требования
|-
|Процессор
|800 МГц
|1 ГГц
|-
|ОЗУ
|512 МБ
|1 ГБ (Для лучшей производительности требуется 2 ГБ и более).
|-
|Видеоадаптер
|DirectX 9
|DirectX 9 совместимый с поддержкой технологий
Hardware Pixel Shader v2.0 и WDDM
|-
|Видеопамять
|32 МБ (для выпуска Home Basic)
|128 МБ
|-
|Жёсткий диск
|20 ГБ
|40 ГБ
|-
|Свободное место на жестком диске
|15 ГБ
|20 ГБ
|-
|Другие приводы
|CD-ROM
|DVD-ROM
|}
Особенности Windows Vista[]
Новые или улучшенные возможности[]
- По утверждению Microsoft, время загрузки системы меньше, чем в Windows XP, и на большинстве компьютеров составляет меньше минуты. Уменьшено время выхода из спящего режима до 6 секунд. Однако реальные показатели менее впечатляющие, так как пользователю приходится ждать завершения фоновых процессов, сильно затрудняющих работу прикладных программ.
- Благодаря технологии Windows ReadyBoost стало возможно использование ёмкости внешних USB флеш накопителей для своппинга, что в некоторых случаях увеличивает производительность на 40 %[9].
- По информации Microsoft, за 180 дней доступности в Windows Vista было найдено меньше уязвимостей, чем в Windows XP. Вероятность попадания в систему вирусов, червей и руткитов на 35 % меньше, чем в Windows XP SP3, на 60 % меньше, чем в Windows XP SP2 и на 90 % — чем в Windows XP без сервиспака[12].
- Windows Shell: новый Windows Shell значительно отличается от оболочки в Windows XP, предлагая новый диапазон организации, навигации и поиска. Панель предварительного просмотра позволяет пользователям просматривать миниатюры различных файлов и просмотр содержимого документа.
- Мгновенный поиск: Мгновенный поиск в Windows Vista представляет собой новый способ мгновенного поиска, который значительно быстрее и более глубокий.
- Боковая панель Windows: прозрачная панель сбоку экрана, где пользователь может разместить мини-приложения (гаджеты).
Улучшения безопасности[]
- User Account Control (UAC) — система контроля учётных записей пользователей, которая требует явного разрешения пользователя при выполнении любого действия, требующего административных полномочий, вне зависимости от прав текущего аккаунта пользователя. Если пользователь не является администратором, будет выводиться запрос, в котором можно выбрать административную учётную запись и выполнить операцию с её правами, введя пароль, — это позволяет производить конфигурирование системы и установку приложений из учётной записи ограниченного пользователя, не используя явно механизм runas и без необходимости переключения в другую учётную запись (что требовалось в XP, например, в случае изменения параметров TCP/IP). Если пользователь входит в группу «Администраторы», то ему потребуется (при настройках по умолчанию) подтвердить использования прав, ответив на запрос системы. UAC запрашивает данные в режиме Secure Desktop, с помощью которого осуществляется защита от перехвата данных и контроля за окном ввода со стороны сторонних программ (примерно такой же режим был использован при входе в домен NT с требованием двукратного нажатия Ctrl-Alt-Del). UAC можно отключить для отдельных категорий учётных записей и переконфигурировать, используя локальную (или групповую при использовании в домене) политику безопасности: например, можно задать обязательное введение пароля для использования административных полномочий всеми пользователями (включая администраторов), запретить эти действия пользователям ограниченных учётных записей и т. д.[13][14][15]
- Технологии, предотвращающие использование эксплойтов[16][17] — операционная система Windows Vista обладает некоторыми преимуществами, препятствующими использованию обнаруженных уязвимостей в программном обеспечении, но полностью реализуемыми только в 64-битных версиях и с программами, написанными с учётом этих возможностей:
- Data Execution Prevention
- Vista использует технологию Address Space Layout Randomization (ASLR), для загрузки кода системы в случайным образом выбранные участки памяти. По умолчанию все системные файлы загружаются в один из 256 случайно выбранных участков памяти. Другие исполняемые файлы могут использовать особый бит в заголовке PE-формата, чтобы система запускала их код с использованием ASLR. Для таких приложений случайным образом будут также определены области стека и кучи[18].
- Изменение в формате исполняемых файлов.
- Шифрование диска Bitlocker — Предоставляет возможность шифрования системного диска, используя интерфейс командной строки и другие разделы. При этом используется USB-ключ или Trusted Platform Module для хранения ключей шифрования. Для шифрования разделов, по умолчанию, используется алгоритм AES с длиной ключа 128 бит в режиме шифрования CBC. Данная возможность присутствует в версиях Vista Enterprise или Ultimate[19][20][21].
- Система шифрования файлов EFS. Эта система, появившаяся впервые в Windows 2000, работает в версиях Vista Business, Enterprise или Ultimate и даёт возможность «прозрачного» шифрования файлов на уровне файловой системы алгоритмами AES (с 256-битным ключом) или 3-DES. Для каждого файла случайным образом генерируется ключ шифрования, который, в свою очередь, шифруется открытым ключом пользователям (по умолчанию 2048 бит). В Vista с помощью политик появилась возможность задавать разную длину открытого ключа пользователя (1024, 2048, 4096,…), сохранять ключ на смарт-картах (по умолчанию, ключ хранится локально, защищённый паролем пользователя) и шифровать файл подкачки, а также требовать обязательного шифрования пользовательской папки с документами[22][23].
- Предотвращение заражения вирусами с извлекаемых носителей. По умолчанию в Windows Vista отключён автозапуск программ с флеш-карт и устройств USB. Это предотвращает заражение компьютера вирусами, переносчиками которых могут являться и флеш-карты. Имеются политики управления доступом к внешним носителям (включая USB), что также способствует защите конфиденциальных данных.
- Блокировка прямой записи на диск. Windows Vista запрещает прямую запись на диск (\.PhysicalDriveX), если с диска смонтирована файловая система[24].
- Защитник Windows (Windows Defender). В Windows Vista появилась встроенная программа, которая служит для борьбы со шпионским программным обеспечением.
- Родительский контроль. В составе домашних изданий Windows имеется функция родительского контроля, которая помогает ограничить использование компьютера детьми. Например, можно настроить веб-фильтр для блокировки нежелательных сайтов, запретить использовать компьютерные игры, не предназначенные для их возраста. Также с помощью родительского контроля можно запретить использовать конкретную программу, установить временное ограничение и просматривать отчёт о работе родительского контроля.
- Предотвращение выполнения данных (DEP) включено по умолчанию в Windows Vista. И эта ОС может включать программную реализацию защиты, даже если процессор не поддерживает DEP. Однако могут происходить ложные срабатывания и некоторые несовместимые устаревшие и даже некоторые новые программы могут не запуститься, хотя их можно поставить в список исключений или на крайний случай отключить DEP с помощью утилиты командной строки «bcdedit».
Пакеты обновления и поддержка[]
Microsoft регулярно выпускает пакеты обновлений своих операционных систем, устраняющие выявленные проблемы и добавляющие новые возможности.
Пакет обновлений 1[]
Пакет обновлений 1 (SP1) для ОС Windows Vista выпущен 4 февраля 2008 года[25].
- По заявлениям Microsoft, после установки SP1 копирование файлов на локальных накопителях будет осуществляться на 25 % быстрее.
- Решена проблема, приводившая к появлению сообщений об ошибках при копировании больших файлов через локальную сеть. Windows Vista с установленным пакетом обновлений также будет более оперативно обрабатывать изображения высокого разрешения.
- В пакет обновления включены дополнения, улучшающие совместимость операционной системы с новыми видеоадаптерами, некоторыми типамимониторов и принтеров.
- В состав пакета обновлений также входят исправления, уменьшающие время вывода компьютера из спящего режима, повышающие производительность браузера Internet Explorer 7 и улучшающие схему управления питанием ноутбуков. Традиционно в пакет обновления включены все ранее выпущенные обновления и исправления.
Первоначально пакет обновления был доступен на пяти языках — английском, немецком, французском, испанском и японском. В середине апреля 2008 года Microsoft опубликовала версии пакета обновлений на других языках. Между тем, пока остаются нерешёнными проблемы совместимости SP1 с некоторыми драйверами устройств[26]. Перед установкой SP1 система Windows Update проверяет компьютер на предмет наличия проблемных компонентов, и в случае их обнаружения откладывает установку.
Перед установкой пакета обновления 1 необходимо предварительно удалить его тестовую версию (если она была установлена).
Пакет обновлений 2[]
В пакете обновлений 2 присутствуют:
- Windows Search 4.0;
- поддержка Bluetooth 2.1/3.0 (для версии Bluetooth 3.0 доступен лишь beta-драйвер);
- поддержка 64-разрядных процессоров VIA;
- возможность записи оптических дисков формата Blu-ray;
- мастер Windows Connect Now (WCN) для упрощения настройки беспроводных сетей Wi-Fi;
- файловая система exFAT, с поддержкой записи в файлы дат в международном формате, по Гринвичу, что позволит безошибочно синхронизировать файлы между различными часовыми поясами;
- поддержка смарт-карт формата ICCD/CCID;
- улучшенная защита ТВ-контента в Windows Media Center;
- улучшена работа Wi-Fi после выхода из спящего режима;
- внесены исправления в DirectX;
- обновлён компонент RSS в боковой панели;
- увеличена производительность при воспроизведении HD-видео[27];
- Снято ограничение на количество полуоткрытых соединений;
- Добавлена совместимость с Windows 7;
- Обновлён Device Stage.
В отличие от Service Pack для предыдущих версий Windows, SP2 нельзя установить без предварительной установки SP1. Это сделано с целью объединить пакеты обновлений для двух платформ — Windows Vista и Windows Server 2008
Компания Microsoft собиралась выпустить Пакет обновлений 3 (SP3) для Windows Vista и Windows Server 2008 в 2010 году.[60] Но вскоре стало известно, что выход пакета обновлений был отменён.
12 июля 2011 была официально прекращена поддержка Windows Vista SP1.
Прекращение поддержки не затронет операционные системы Vista с установленным обновлением SP2, поэтому всем пользователям, которые все ещё не установили это обновление, рекомендуется это сделать в ближайшее время.
Поддержка Windows Vista SP2 продлится до 11 апреля 2017 года.
Разработка Windows Vista[]
Основные статьи: Разработка Windows Vista, Windows Longhorn, Windows Longhorn Server
Разработка Windows Vista началась в мае 2001 года, за пять месяцев до выхода Windows XP и продолжалась до ноября 2006 года. Первоначально Microsoft ожидала завершить версию в конце 2003 года и представить как незначительный шаг между Windows XP (с кодовым названием Whistler) и Windows 7 (с кодовыми названиями Blackcomb и Vienna). Концепция Longhorn была намеком на тот план. Первоначально Longhorn разрабатывалась на основе Windows XP, но с 2004 года Microsoft «перезагрузила» проект, то есть начала разрабатывать ОС с нуля, взяв за основу Windows Server 2003. В связи с этим, некоторые особенности, такие как WinFS и NGSCB, были исключены. В середине 2005 года Longhorn была переименована в Windows Vista.
Критика Windows Vista[]
Windows Vista критикуется по таким статьям:
- Некоторые действия, выполнявшиеся на XP мгновенно, на Vista производятся с небольшой задержкой. Это показывают тесты Tom’s Hardware[28] — лишь некоторые программы (скорее всего, многопоточные) в Vista работают быстрее. По сообщению того же сайта, были также обнаружены ошибки в оболочке ОС[29].
- Системные требования на момент выпуска ОС, показались многим пользователям завышенными по сравнению с Windows XP.
- Windows иногда упрекают в ущемлении свободы, связанные с защитой «премиум-контента» от копирования (Protected Media Path)[30]. А именно:
- Установка неподписанных драйверов на 64-битную версию Vista возможна исключительно обходными путями[31][32] и полностью отключает проигрывание премиум-контента. В Windows XP цифровая подпись означала «проверенность» и «стабильность» драйвера — пользователи могли ставить и неподписанные, а производители подписывали лишь важнейшие версии. В Vista же подпись — необходимое условие работы (по крайней мере будет таковым, когда премиум-контент станет широко распространённым).
- Microsoft оставляет за собой право отозвать драйвер в любой момент, если в нём будет найдена уязвимость[33]. Если устройство старое, есть шансы, что производитель (или его правопреемник) не будет переписывать драйверы, и проигрывание будет недоступно (остальные функции не страдают)[34]. Пострадают от этого только рядовые пользователи, а никак не пираты — найдя подходящую аппаратно-программную конфигурацию, они могут свободно расшифровывать видео на отключённом от Интернета компьютере.
- Чтобы защита работала, все устройства, связанные с проигрыванием, должны быть допущены Microsoft. Часть требований: прежде чем быть допущенным к проигрыванию, устройство должно пройти особый тест на работоспособность (Hardware Functionality Scan)[35][36], расшифровка должна происходить на самих устройствах, а не на незащищённых каналах (DVI без HDCP, VGA, S/P-DIF) на звук и видео должны накладываться помехи[37].
- В некоторых ситуациях пользователям протокола BitTorrent требуется большое количество полуоткрытых исходящих соединений. На это в Windows стоит ограничение, которое было введено компанией Microsoft в попытке замедлить распространение вирусов с зараженного компьютера, а также ограничить возможности участия компьютера в DoS-атаках. Однако, с выходом Service Pack 2 данная проблема устранена самой компанией Microsoft — после установки SP2 число полуоткрытых соединений становится неограниченным.
- Есть старое программное обеспечение, которое несовместимо с Windows Vista[38], а также драйверы и устройства. Более того, в Vista была переделана поддержка USB в сторону более строгого контроля соблюдения стандарта, что сделало некоторые не совсем совместимые со стандартом (но работающие в Windows XP и Linux) USB-устройства принципиально несовместимыми с Vista (в том числе с обновлёнными драйверами).
- Интерфейс Aero, по мнению Пола Таррота, имеет недостаток в виде сложноотличимого текущего окна от всех остальных (активное окно заметно отличается от остальных лишь подсветкой кнопки закрытия окна)[39]
- User Account Control часто раздражает пользователей, задавая даже в рутинных операциях много вопросов[40], однако при необходимости его может отключить опытный пользователь или администратор. Кроме того, Symantec выпустил утилиту Norton UAC Tool, которая заметно уменьшает количество запросов, используя механизм белого списка[41].
- В домашней версии Vista остался старый механизм инсталляции обновлений. Процесс полной инсталляции обновлений занимает довольно продолжительное время (в зависимости от объёма обновлений и вычислительной мощности компьютера — от 20 мин до 1,5 часов) и на Vista разделяется на автоматически протекающие собственно установку и последующую настройку установленных обновлений. Отличием домашних версий является то, что второй процесс — настройка установленных обновлений — не запускается операционной системой автоматически — пользователю приходится запускать его вручную, включением компьютера.
- Для соблюдения неоднократно сорванных сроков выхода на рынок, из релизной версии Vista были исключены многие обещанные и даже предоставлены в бета-версиях возможности. Это вызвало огромное недовольство среди пользователей.
- Реальные аппаратные требования Windows Vista превосходили возможности широко распространённых компьютеров тех лет, и были намного выше, чем заявленные. Также на публику утек скандал между «отделом дружбы с Intel» и отделом разработки Windows внутри Microsoft, поднявшийся до уровня вице-президента. Отдел разработки настаивал на том, что смягчать официально заявленные требования к оборудованию нельзя, однако же Intel настаивала на их смягчении для того, чтобы продержать в производстве ещё какое-то время устаревший, но на тот момент очень популярный чипсет (который не удовлетворял несмягченным требованиям, и был бы немедленно «убит» как рыночный продукт в случае релиза Vista с несмягченными требованиями). Дружба с Intel победила, требования смягчили, при том, что Vista работала неудовлетворительно медленно на данном чипсете.
Рыночный провал Windows Vista[]
Существует мнение, что Windows Vista является худшей операционной системой Microsoft[42][43]. Также Windows Vista заняла первое место в конкурсе «Провал года»[44], проводимом сайтом Pwnie award, созданным в 2007 году. Пользователи очень долго ждали «Висту» и слишком привыкли к Windows XP. Более того, по предположению The Inquirer.net, по ряду беспрецедентных промоакций, связанных с продвижением Vista на рынке, можно сделать вывод о том, что руководство Microsoft признало ОС провалом[45].
Огромное количество пользователей по всему миру удаляли легальную Windows Vista с ноутбуков и устанавливали взамен Windows XP, часто нелицензионную. Причина кроется в неудовлетворённости системой, так как ни одна предыдущая версия Windows не вызывала такой реакции пользователей, не вызывает её и Windows 7.
После выхода Windows 7 (по сути, улучшенной версии Windows Vista с оптимизациями производительности и исправлениями ошибок) Windows Vista практически немедленно вымерла и популярность данной системы также практически немедленно снизилась (что не относится к её серверной версии).
Наступило 30 января, день, который будет вписан в компьютерные хроники рядом с датами 24 августа 1995 года и 24 октября 2001 года. В продажу поступает очередная версия Windows — Windows Vista. C момента выхода предыдущей версии — Windows XP — прошло более пяти лет: ситуация, совсем недавно совершенно немыслимая, ведь за 12 лет с 1990-го по 2001-й год увидело свет 13 версий Windows.
Как это было уже много раз с предыдущими версиями, в ожидании выхода Windows Vista сообщество пользователей и специалистов разделилось на несколько групп. Одна часть радостно встречает новую ОС, потому что она новая, красивее выглядит и предоставляет новые возможности и удобства. Другая часть (таких людей меньше, чем в любой другой группе) ждет новую ОС, потому что хорошо представляет себе ее преимущества, в том числе в удобстве и безопасности работы. Третья активно возмущается количеством «рюшечек» и «бантиков», только которыми, якобы, новая система и отличается от предыдущей версии, «неимоверным» количеством ошибок и сыростью этой новой ОС. И громогласно заявляет, что до выхода пакета исправлений, а еще лучше — второго пакета исправлений, Windows Vista появится на их компьютерах только через трупы владельцев оных. При этом в большинстве случаев те, кто относятся к третьей группе, и пальцем не ударят ради того, чтобы узнать, а какие, собственно, существуют различия между системами помимо интерфейса. Наконец, четвертая и самая многочисленная знает, что существует Windows, а детали ее не интересуют — какая есть на компьютере, такая и есть. Хотя, конечно, чем красивее, тем лучше.
Впрочем, как уже сказано, ничего странного в этом нет — подобная ситуация повторяется уже много лет с каждой очередной версией Windows. Наоборот, было бы странно, если бы что-то изменилось.
Пять лет — срок долгий, было опробовано, обдумано и отброшено множество вариантов интерфейса. Одной только кнопки «Пуск» было сделано несколько сотен. А что вы скажете о варианте интерфейса, при котором меню «Пуск», появляясь на экране, не перекрывает рабочий стол, который как бы откидывается назад и вправо?

Произошла смена концепций разработки, вызванная тем, что взаимосвязи между отдельными модулями, составляющими систему, стали чрезмерно сложными и с трудом отслеживаемыми.
В этот же период вместилась и задержка из-за отвлечения сил и ресурсов на разработку Windows XP SP2. Между прочим, в Microsoft считают, что ее можно было бы назвать новой версией операционной системы, а не просто очередным набором исправлений, и в чем-то они правы. Тем более что пример систем, практически идентичных по интерфейсу, но достаточно сильно различающихся по внутреннему устройству, уже был — это Windows 3.1, Windows 3.11 для рабочих групп и Windows NT 3.1.
Но все это теперь в прошлом, и «Ух ты», или как предпочитает говорить молодежь, «Вау», уже началось (рекламная кампания Windows Vista проходит под девизом The «Wow» starts now).
С чего начинается Vista? Конечно, с покупки дистрибутива. А прежде, чем купить, нужно выбрать редакцию системы (ситуацию, когда используется диск «Весь софт на одном DVD» рассматривать не будем, знатоки подобных ситуаций сами могут внести коррективы в этот рассказ). Таких редакций шесть. Пять из них показаны на рисунке, шестую, Starter Edition, самую дешевую и малофункциональную, здесь рассматривать не будем.
Три редакции предназначены для домашнего использования, две — для деловых применений. Самая старшая система, Ultimate, в отличие от Windows XP относится к классу домашних и предназначена в первую очередь для тех, кто пользуется одним и тем же компьютером и дома, и на работе (это, между прочим, до некоторой степени объясняет и установленную для нее цену, о которой ниже). Vista Home Basic — самая простая, и предназначена преимущественно для тех случаев, когда компьютер недостаточно мощный, чтобы в полной мере реализовать возможности Vista. Основной системой для дома должна стать Vista Home Premium. Она несколько дороже Home Basic, но содержит в себе практически весь функционал. Что касается версий для деловых применений… да ну их, это забота системных администраторов.
Вкратце остановимся на различиях между версиями. Отказавшись от Home Premium и выбрав Home Basic, вы теряете: возможность пользоваться новым интерфейсом Aero («аэро», о нем ниже), возможность записи DVD средствами системы, без привлечения сторонних программ, функциональность медиацентра (если установлен ТВ-тюнер, можно смотреть программы, записывать их по расписанию, получать программу телепередач через Интернет и пр. — см. статью о Windows XP MCE, опубликованную на ixbt).
Windows Vista Ultimate содержит больше возможностей, нежели Home Premium, но они, как правило, бесполезны для домашнего пользователя — это возможность включения системы в домен (кто знает — тот поймет, а для обычного пользователя «эта роль ругательная и я прошу её ко мне не применять»), поддержка шифрования диска (BitLocker) и возможность переключения языка интерфейса (MUI).
Изменение языка интерфейса возможно и в остальных версиях установкой языковых пакетов (LIP), но если MUI дает возможность оперативно изменять язык, то при использовании LIP язык интерфейса можно изменить только установкой пакета или его удалением. То есть, дело это достаточно хлопотное.
Еще одной заманчивой возможностью Vista Ultimate являются так называемые дополнительные возможности Windows Ultimate (Windows Ultimate Extras). Это дополнительные программные компоненты, загружаемые с сайта Windows Update и доступные только пользователям этой редакции. Полный их состав пока не объявлен, но уже продемонстрированы: рабочий стол с воспроизводимым на нем видеоизображением и средство обработки фотографий. Будет среди дополнений и возможность запуска виртуальных машин.
Подробное описание функциональности версий было размещено на сайте ранее.
Замечание для владельцев ТВ-тюнеров. Не думайте, что Vista всеядна и будет работать с любой, даже самой дешевой железякой, в которую втыкается телеантенна, вовсе нет. Ничто не мешает вам использовать тюнер в Vista точно так же, как вы используете его в ХР, то есть, запуская программу, входившую в комплект поставки или добытую иными путями. Но Vista более разборчива. Она признает тюнер своим только в том случае, если в тюнере имеется аппаратное кодирование MPEG-2. Некоторые разработчики, правда, сумели обойти это ограничение, добавив функцию кодирования в драйверы устройства. Но такое решение не устраняет причины, из-за которой требование аппаратного кодирования и было введено.
Если вы были или являетесь владельцем ТВ-тюнера из нижнего ценового диапазона, то наверняка видели в документации требования к процессору. И эти требования были тем выше, чем выше качество изображения. Ведь кодирование видеосигнала требует достаточно большой вычислительной мощности. А Windows Vista может одновременно записывать сразу две передачи, если установлено два тюнера. К тому же запись по расписанию может включиться в тот момент, когда компьютер занят какой-либо ресурсоемкой задачей, игрой, например. И что тогда, делать три дела сразу и все три — кое-как? Чтобы фоновая запись телепередач и работа оказывали как можно меньшее влияние друг на друга и было введено требование аппаратного кодирования.
После того, как нужная редакция выбрана, можно идти в магазин за коробкой, но перед этим нужно проверить содержимое кошелька. Поскольку Microsoft не продает свои продукты конечным пользователям, она указывает только рекомендуемую цену, а фактическая цена покупки может довольно заметно отличаться и в меньшую, и в большую стороны. Рекомендованная цена Home Basic — 199 долларов, Home Premium — 239, Ultimate — аж 399! Русские версии дешевле процентов на 20. Можно сэкономить немалую сумму, если у вас уже есть легальная копия Windows XP или Windows 2000. Обновление обойдется примерно вдвое дешевле покупки полной версии. Еще меньше стоят ОЕМ версии, которыми можно воспользоваться, если вы решите собирать компьютер сами.
Если вы купите коробку (полную или обновление), то обнаружите в ней два диска, один с 32-разрядной версией системы, второй — с 64-разрядной. Какую именно ставить — выбор за вами. А нужная редакция будет выбрана непосредственно при установке в зависимости от того, какой ключ вы введете.
Системными требованиями можно особенно голову не забивать — Vista будет работать практически на любом более-менее современном компьютере, лишь бы у него было не меньше 512 мегабайт памяти. Впрочем, рекомендуется иметь хотя бы гигабайт. Так что приступайте к установке.
При первом взгляде на Windows Vista сразу привлекает внимание новый интерфейс и его трехмерная разновидность — «аэро» (в Home Basic, как уже упоминалось, отсутствует). Если видеоадаптер в вашем компьютере относительно новый, то есть модель (а не конкретный экземпляр) выпущена не больше двух-трех лет назад, то края окошек оказываются прозрачными. При наведении указателя мыши на кнопку панели задач всплывает экранчик, в реальном времени показывающий содержимое данного окна, даже если оно свернуто или закрыто другими окнами, а при нажатии клавиш Win+Tab окошки выстраиваются друг за дружкой, причем, опять же, каждое из них отображается в реальном времени, а не статичной картинкой.
Если Aero отсутствует, хотя система его требованиям соответствует, то… нет, не буду нарушать плавное течение мысли «умственными» словами о реестре, параметры и пр. Если возникнут вопросы — задайте их в форуме «ОС и системное ПО».
Сразу заметно, что внешний вид системы существенно изменился по сравнению с XP — и это закономерно. Компьютер превращается из некоего высокотехнологического устройства, с которым может справиться только специалист, в обычное бытовое устройство наподобие телевизора, видеомагнитофона или микроволновой печи. Значит, и внешний вид его должен измениться — прибор из научной лаборатории, серый «кирпич» девяностых годов все больше и больше вытесняется разноцветными корпусами, способными украсить интерьер жилого дома.
Изображение на экране тоже должно радовать глаз обладателя компьютера, и что бы там ни говорили поборники аскетического интерфейса, реалии рынка берут свое — надо угодить требованиям основной массы покупателей.
Впрочем, суровая простота тоже не забыта — можно сменить оформление интерфейса на классическое. На большей части функциональности это не скажется, но о преимуществах «аэро» придется забыть. Еще одна потеря, парадоксальная на первый взгляд и вполне закономерная на деле, — некоторое снижение скорости работы. Казалось бы, снизив количество работы по прорисовке интерфейса, мы должны получить выигрыш. На самом деле, получается проигрыш, поскольку, снизив суммарное количество работы, мы перекладываем ее всю на плечи центрального процессора.
Чтобы было понятнее, можно привести такой пример — в какой-нибудь из современных игрушек включим программный рендеринг. Удастся ли получить выигрыш, даже если учесть, что множество видеоэффектов при этом окажутся отключенными? Точно так же и в Vista режим «аэро» вовсю использует графический ускоритель, что приводит к разгрузке ЦП и высвобождению его времени для рабочих программ. А выбор классического оформления (и даже оформления Aero Basic) переводит систему в обычный режим программного формирования элементов интерфейса.
Но вернемся к нашему экрану. Следующее изменение — в функциональности меню. Список программ не разворачивается вправо, занимая порой львиную долю экрана, а показывается иерархическим списком здесь же, над кнопкой.
Впрочем, лазить по меню вовсе не обязательно. Можно набрать в нижнем окошке несколько букв из названия программы или команды, система «прошерстит» список и оставит в нем лишь команды, соответствующие запросу (аналогичный механизм реализован в проводнике и в панели управления).
Сразу после установки быстро найти можно лишь пункты меню. Но через некоторое время в списке окажутся и файлы, и закладки из избранного, и другие объекты.
Встроенный в систему механизм поиска индексирует диски и помогает быстро найти нужный объект. Первоначальная индексация, сопровождаемая интенсивным морганием индикатора работы жесткого диска, может занять довольно много времени, но она весьма желательна. В конце концов, лучше один раз «прошерстить» жесткий диск и в дальнейшем пользоваться результатами, чем просматривать его при каждом поиске.
Внешний вид окон проводника и его функциональность заметно изменились. Сразу после открытия окна в строке адреса бежит зеленая полоска — это система собирает информацию о содержимом папки. Если индексирование данного объекта уже выполнено, полоска бежит быстро или проскакивает незаметно, если оно не делалось — медленно.
Режимов отображения содержимого папки и возможностей управления этими режимами способами стало больше: окна папок теперь масштабируемые. Раньше каждый из режимов (список, таблица, крупные и мелкие значки и др.) был, как бы обособлен друг от друга: из одного режима можно было перейти в другой, но различия между ними были выражены достаточно резко. В Vista режимы стали всего лишь разными масштабами отображения. Каждый из режимов получил несколько вариантов, отличающихся размером изображений.
При изменении масштаба (самый простой способ — нажать клавишу Ctrl и крутить колесико мыши) происходит постепенное изменение размеров изображения, затем режим изменяется на другой, размеры элементов продолжают изменяться, режим меняется снова и так до тех пор, пока не будет достигнуто максимальное увеличение — значки размером 256х256 точек (или максимальное уменьшение). При увеличении значки объектов, содержимое которых можно отобразить графически, показывают, что находится в данном объекте.
Впрочем, об изменениях в интерфейсе и о новой функциональности можно говорить очень долго, поэтому последуем совету Козьмы Пруткова, заткнем фонтан и перейдем к другим сторонам Vista.
Раньше при выборе программ (особенно игр) приходилось тщательно изучать их системные требования и сравнивать их с характеристиками компьютера. Иначе был риск потратить деньги на то, что окажется невозможным использовать. Если для технически подкованных пользователей это было не слишком сложной задачей, то для людей, покупающих «пентиум и жифорс», выбор становился делом не совсем тривиальным. Windows Vista предоставляет новый способ решения этой задачи. Она вычисляет рейтинг компьютера.
Оцениваются пять характеристик компьютера — скорость процессора, объем оперативной памяти, производительность видеоадаптера при работе с интерфейсом, она же — в играх, а также ёмкость жесткого диска. Затем берется минимальная из этих оценок и присваивается компьютеру. Идея состоит в том, что разработчики игр будут помечать игры таким же рейтингом, и выбор программ, способных хорошо или хотя бы приемлемо работать на данном компьютере, сильно упростится. Посмотрел рейтинг компьютера, сравнил с рейтингом программы — и все стало ясно.
Конечно, этот рейтинг — не аптекарские весы, а довольно приблизительная оценка, но основу для выбора программ она дает. А технически подкованным пользователям никто не мешает и дальше сравнивать характеристики компьютера с требованиями программы.
Стоит обратить внимание, что числа в рейтинге — условные, их величины эмпирическим путем подобраны так, чтобы более-менее соответствовать друг другу при сопоставлении характеристик компьютера и требований ПО. Рейтинг не имеет каких-либо жестких границ (например, от единицы до шести), по мере совершенствования оборудования он будет расти и расти. Не исключено, что в дальнейшем оценки будут пересматриваться.
От оценок можно перейти к достаточно животрепещущему вопросу: а насколько медленнее будет работать Vista по сравнению с ХР.
Ответ простой — не медленнее, по крайней мере, на компьютерах с гигабайтом памяти. Microsoft заказала специальное исследование, подробный отчет о котором можете изучить сами: VistaXPBusResp.pdf.
«Ага, знаем мы эти заказные отчёты», — подумаете вы. Но, ей-же-ей, полученные результаты, если бы они были заказанными, могли бы выглядеть и лучше.
А результаты не удивительны. Ведь в Vista, на самом деле, есть довольно много внутренних усовершенствований, в том числе в диспетчеризации процессов, в управлении вводом-выводом… Признайтесь, у вас наверняка хотя бы раз был случай, когда окно проводника зависало из-за того, что система упорно пыталась вытащить информацию с плохо читающегося компакт-диска и прервать этот процесс можно было только вытащив диск? А в Vista можно нажать Ctrl+C — и мучительный процесс будет прерван.
Также вы наверняка не раз ждали, когда неиспользовавшаяся некоторое время задача подгрузится с диска, который при этом издавал непрерывное журчание. В Vista можно уменьшить время реакции в подобных случаях, воспользовавшись функцией ReadyBoost. Если воткнуть достаточно быструю флеш-память и согласиться на использование ее для ускорения работы системы, то на нее будут скопированы файлы самой системы и прикладных программ, и когда они потребуются, то загрузка пойдет параллельно с флеш-памяти и жесткого диска и закончится гораздо быстрее.
Следует отметить, что об ускорении собственно работы компьютера в данном случае речи не идет, только об ускорении запуска программ и переключения между ними. Но ваша работа пойдет быстрее, а может, и раздражительность уменьшится. Ведь эффект может оказаться весьма заметным, особенно если на компьютере недостаточно памяти, а увеличить ее объем сложно или вообще невозможно (например, в ноутбуке).
Безопасность… это тема для отдельной статьи, слишком много нужно рассказать.
В общем, если высказаться вкратце, Vista — это та вещь, которую стоит попробовать.

Новости
3DNews Новости Software Операционные системы В этом месяце операционной системе Windo…
Самое интересное в обзорах
Операционная система Windows Vista отпраздновала своё 15-летие в этом месяце. Стабильная версия программной платформы стала доступна потребителям 30 января 2007 года. Корпоративные клиенты Microsoft получили к ней доступ немногим раньше, 8 ноября 2006 года. На этом завершился этап разработки ОС, которая должна была стать заменой чрезвычайно удачной Windows XP, вышедшей в массы в октябре 2001 года.
Источник изображения: Heise
Любопытно, что процесс создания Vista (на этапе разработки ОС носила имя Longhorn) был запущен ещё в мае 2001 года, за пять месяцев до официального запуска Windows XP. Предполагалось, что она выйдет на рынок в 2003 году, но затянувшийся процесс разработки не позволил сделать этого. Причиной задержки стали проблемы с реализацией ряда функций, которые изначально планировались для более поздних версий Windows (Blackcomb), но были перенесены в Vista.
Только после проведённой в 2004 году реорганизации и отказа от реализации некоторых функций, таких как платформа управления данными и метаданными WinFS, разработку Vista удалось завершить в «разумные сроки». По оценкам делового издания BusinessWeek, в течение пяти лет в разработке платформы Longhorn участвовало около 10 тыс. сотрудников Microsoft. Любопытно, что журнал оценил разработку ОС в $10 млрд, тогда как официальные данные софтверного гиганта указывают, что создание программной платформы обошлось в $6 млрд.
Источник изображения: 3DNews
Одна из любопытных особенностей Vista заключается в том, что потребителям были доступны сразу семь редакций ОС, чего раньше ещё не было. В потребительском сегменте были представлены версии от Vista Starter для развивающихся стран и Vista Home Basic для растущих рынков и новых нетбуков, до Vista Home Premium. В бизнес-сегменте были представлены Vista Business для малых и средних предприятий и Vista Enterprise для крупных клиентов. Отдельного упоминания заслуживает Vista Ultimate, которая объединила в себе функции других версий ОС.
В Vista разработчики впервые представили функцию контроля учётных записей (UAC), которая запрашивает подтверждение действий, для выполнения которых требуются права администратора. Несмотря на кажущуюся полезность, функция была раскритикована из-за того, что система слишком часто выдавала запросы на подтверждение тех или иных действий. Позднее в Windows 7 частота срабатываний UAC была существенно снижена.
Стоит также отметить, что Vista была первой ОС Microsoft, которая вышла в версиях для 32- и 64-разрядных процессоров, хотя многие версии были 32-разрядными и для их использования также требовалось не менее 1 Гбайт оперативной памяти и от 40 до 80 Гбайт дискового пространства. Частью Vista также стали DirectX 10.0 и Aero Glass. В некоторых потребительских версиях появился Windows Media Center, предназначенный для воспроизведения мультимедийного контента. Кроме того, Microsoft представила в Vista боковую панель с мини-приложениями для рабочего стола, которая исчезла с выходом Windows 7. В версиях Vista Enterprise и Vista Ultimate появилось приложение Virtual PC Express, предназначенное для запуска программных решений в виртуальной среде.
Источник изображения: 3DNews
Ещё одно нововведение касается обновлений, которые с выходом Vista впервые стали выпускаться ежемесячно и были доступны через «Центр обновлений Windows». В феврале 2008 года разработчики выпустили пакет обновлений Service Pack 1, а уже в апреле 2009-го — Service Pack 2. Официальная поддержка Windows Vista завершилась 11 апреля 2017 года.
Конечно, ОС Vista трудно назвать популярной среди потребителей, но именно эта версия платформы заложила основу для Windows 7, которая оказалась очень успешной. ОС Windows 7 была выпущена в октябре 2009 года и до сих пор продолжает пользоваться популярностью, несмотря на то, что её поддержка завершилась 14 января 2020 года. На данный момент Microsoft выпускает обновления для корпоративных версий Windows 7 в рамках программы расширенных обновлений безопасности.
Если вы заметили ошибку — выделите ее мышью и нажмите CTRL+ENTER.
Самые обсуждаемые публикации


Данная статья представляет краткий обзор всех версий операционной системы Windows.
Версия Вашей системы: Windows 7
Версии для настольных компьютеров
| Логотип | Версия | Год | Статус |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
Windows 1 | 1985 | Не поддерживается Не используется |
 |
Windows 2 | 1987 | |
 |
Windows 3 | 1990 | |
 |
Windows NT 3.1 | 1993 | |
 |
Windows NT 3.5 Workstation | 1994 | |
 |
Windows NT 3.51 | 1995 | |
 |
Windows 95 | 1995 | |
 |
Windows NT 4.0 | 1996 | |
 |
Windows 98 | 1998 | |
 |
Windows Millenium | 2000 | |
 |
Windows 2000 (NT 5.0) | 2000 | |
 |
Windows XP (NT 5.1) | 2001 | Не поддерживается Встречается редко |
 |
Windows Vista (NT 6.0) | 2006 | Не поддерживается Почти, не используется |
 |
Windows 7 (NT 6.1) | 2009 | Не поддерживается Пока используется |
 |
Windows 8 (NT 6.2) | 2012 | Не поддерживается Почти, не используется |
 |
Windows 8.1 (NT 6.3) | 2013 | Поддерживается Почти, не используется |
 |
Windows 10 (NT 10) | 2015 | Поддерживается Активно используется |
 |
Windows 11 (NT 10) | 2021 | Поддерживается Начинает применяться |
Серверные Windows
| Логотип | Версия | Год | Статус |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
Windows NT 3.1 Advanced Server | 1993 | Не поддерживается Как правило, не используется |
 |
Windows NT 3.5 Server | 1994 | |
 |
Windows NT 3.51 Server | 1995 | |
 |
Windows NT 4.0 Server | 1996 | |
 |
Windows 2000 Server | 2000 | |
 |
Windows Server 2003 | 2003 | |
 |
Windows Server 2003 R2 | 2005 | |
 |
Windows Server 2008 | 2008 | |
 |
Windows Server 2008 R2 | 2009 | Не поддерживается Пока еще используется |
 |
Windows Server 2012 | 2012 | Поддерживается Активно используется |
 |
Windows Server 2012 R2 | 2013 | |
 |
Windows Server 2016 | 2016 | |
 |
Windows Server 2019 | 2018 | |
 |
Windows Server 2022 | 2021 | Начало использования |
Все версии Windows по линейкам + хронология
| Линейка | Годы | Перечисление версий |
|---|---|---|
| 16 бит | 1985 — 1995 | Windows 1 / 2 / 3 |
| 32 бита (9x) |
1995 — 2001 | Windows 95 / 98 / ME |
| NT (32 и 64 бита) |
с 1993 | Windows NT 3.1 / NT 3.5 / NT 3.51 / NT 4.0 Workstation / 2000 / XP / Vista / 7 / 8 / 8.1 / 10 |
| NT Servers (32 и 64 бита) |
с 1993 | Windows NT 3.1 / NT 3.5 / NT 3.51 / NT 4.0 Server / 2000 Server / 2003 / 2003 R2 / 2008 / 2008 R2 / 2012 / 2012 R2 / 2016 / 2019 / 2022 |
История успеха
Данная история успеха отражает частоту использования системы; количество глюков, с которыми столкнулись пользователи; отзывы.
 |
Windows 1 | Неудача |
 |
Windows 2 | Нейтрально |
 |
Windows 3 | Успех |
 |
Windows 95 | Неудача |
 |
Windows 98 | Успех |
 |
Windows Millenium | Провал |
 |
Windows 2000 | Нейтрально |
 |
Windows XP | Большой успех |
 |
Windows Vista | Провал |
 |
Windows 7 | Успех |
 |
Windows 8 | Провал |
 |
Windows 8.1 | Неудача |
 |
Windows 10 | Успех |
 |
Windows 11 | Нейтрально |
* несмотря на провал некоторых версий операционной системы, они несли новые функции, которые перешли в уже успешные версии. Например, в миллениум появились красивые иконки и окна, которые перешли в Windows 2000. Поэтому провал не стоит оценивать, как неудачную работу.
 Windows 1
Windows 1
Годы поддержки: 1985 — 2001. Ветка: 16 бит.
Издания: —
Что нового
До Windows 1 был MS-DOS, поэтому самое главное новшество — графический интерфейс и возможность управления при помощи мыши.
Системные требования
| Процессор | 8088 |
|---|---|
| Оперативная память | 256 Кбайт |
| Объем жесткого диска | 3 Мб |
 Windows 2
Windows 2
Годы поддержки: 1989 — 2001. Ветка: 16 бит.
Издания: —
Что нового
- Возможность использования сочетания клавиш.
- Появились перекрывающиеся окна.
- Возможность увеличить и уменьшить окно.
Системные требования
| Процессор | 8088 |
|---|---|
| Оперативная память | 256 Кбайт |
| Объем жесткого диска | 3 Мб |
 Windows 3
Windows 3
Годы поддержки: 1990 — 2008. Ветка: 16 бит.
Издания: —
Что нового
- Первый (от Microsoft) удобный для пользователя интерфейс.
- Появление диспетчера программ.
- Появление мультимедийных возможностей.
- Поддержка сети (с 3.1).
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 8086/8088 | 80486DX 33 МГц |
| Оперативная память | 640 Кбайт | 4 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 6,5 Мб | 60 Мб |
 Windows NT 3.1
Windows NT 3.1
Годы поддержки: 1993 — 2001. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 16, 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: —
Что нового
- Первая система на базе ядра NT.
- Поддержка файловой системы NTFS.
Системные требования
| Процессор | Intel 80386 |
|---|---|
| Оперативная память | 2 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 8 Мб |
 Windows NT 3.5 Workstation
Windows NT 3.5 Workstation
Годы поддержки: 1994 — 2001. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 16, 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: —
Что нового
- Встроенная поддержка Winsock и TCP/IP.
- Появление сервера и клиента DHCP и WINS.
- Предоставление общего доступа к файлам и принтерам.
- Поддержка VFAT.
Системные требования
| Процессор | 33 МГц |
|---|---|
| Оперативная память | 12 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 70 Мб |
 Windows NT 3.51 Workstation
Windows NT 3.51 Workstation
Годы поддержки: 1995 — 2001. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 16, 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: —
Системные требования
| Процессор | 33 МГц |
|---|---|
| Оперативная память | 12 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 70 Мб |
 Windows 95
Windows 95
Годы поддержки: 1995 — 2001. Ветка: 9x (32 бита).
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 80386 DX | Pentium |
| Оперативная память | 4 Мб | 8 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 50 Мб | 100 Мб |
 Windows NT 4.0 Workstation
Windows NT 4.0 Workstation
Годы поддержки: 1996 — 2004. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: —
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 486/25 | 486DX2/50 |
| Оперативная память | 12 Мб | 24 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 128 Мб | 1 Гб |
 Windows 98
Windows 98
Годы поддержки: 1998 — 2006. Ветка: 9x (32 бита).
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 486DX 66 МГц | Pentium |
| Оперативная память | 16 Мб | 24 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 200 Мб | 500 Мб |
 Windows Millenium
Windows Millenium
Годы поддержки: 2000 — 2006. Ветка: 9x (32 бита).
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 150 МГц | 300 МГц |
| Оперативная память | 32 Мб | 128 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 200 Мб | 500 Мб |
 Windows 2000
Windows 2000
Годы поддержки: 2000 — 2010. Ветка: NT.
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 133 МГц | 1 ГГц |
| Оперативная память | 32 Мб | 128 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 2 Гб | 20 Гб |
 Windows XP
Windows XP
Годы поддержки: 2000 — 2010. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Редакции: XP, XP Professional
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 233 МГц | 300 МГц |
| Оперативная память | 64 Мб | 128 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 1,5 Гб | от 1,5 Гб |
 Windows Vista
Windows Vista
Годы поддержки: 2006 — 2017. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: Начальная (Starter), Домашняя базовая (Basic), Домашняя расширенная (Premium), Бизнес (Business), Корпоративная (Enterprise), Максимальная (Ultimate)
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 800 МГц | 1 ГГц |
| Оперативная память | 512 Мб | 1 Гб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 20 Гб | 40 Гб |
 Windows 7
Windows 7
Годы поддержки: 2009 — 2020. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: Начальная (Starter), Домашняя базовая (Home Basic), Домашняя расширенная (Home Premium), Профессиональная (Professional), Корпоративная (Enterprise), Максимальная (Ultimate)
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Архитектура | 32-бит | 64-бит | 32-бит | 64-бит |
| Процессор | 1 ГГц | |||
| Оперативная память | 1 Гб | 2 Гб | 4 Гб | |
| Объем жесткого диска | 16 Гб | 20 Гб | 16 Гб | 20 Гб |
 Windows 8
Windows 8
Годы поддержки: 2012 — 2016. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: 8, 8 Профессиональная (Pro), 8 Корпоративная (Enterprise)
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Архитектура | 32-бит | 64-бит | 32-бит | 64-бит |
| Процессор | 1 ГГц | |||
| Оперативная память | 1 Гб | 2 Гб | 4 Гб | |
| Объем жесткого диска | 16 Гб | 20 Гб | 16 Гб | 20 Гб |
 Windows 8.1
Windows 8.1
Годы поддержки: 2013 — 2023. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: 8, 8 Профессиональная (Pro), 8 Корпоративная (Enterprise)
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Архитектура | 32-бит | 64-бит | 32-бит | 64-бит |
| Процессор | 1 ГГц | |||
| Оперативная память | 1 Гб | 2 Гб | 4 Гб | |
| Объем жесткого диска | 16 Гб | 20 Гб | 16 Гб | 20 Гб |
 Windows 10
Windows 10
Годы поддержки: 2015 — 2025. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Издания
- Домашняя (Home). Для большинства домашних компьютеров. Нет возможности настроить удаленный рабочий стол для того, чтобы к систему можно было подключиться удаленно; нет возможности использования групповых политик и присоединения к домену.
- Профессиональная (Pro). Содержит все функции домашней версии + возможность присоединения к домену, использования групповых политик, возможность подключения к компьютеру с использованием удаленного рабочего стола.
- Корпоративная (Enterprise). Урезаны некоторые функции домашней версии. Есть все дополнительные функции версии Pro + DirectAccess, AppLocker.
- S. Является урезанной версией; предустановлена на некоторые устройства. Не поддерживает стандартную установку приложений — возможна установка только из магазина Windows.
Что нового
Windows 10 претерпевает сильные изменения с выходом новых билдов. Поэтому нововведения будем рассматривать исходя из этого.
Билд 1507 (ноябрь 2015):
- Улучшенная производительность.
- Новый встроенный браузер Microsoft Edge.
- Автоматическое сжимание соседнего окна, при прижимании активного окна в одной из сторон рабочего стола.
- «Все приложения» в «Пуск» поддерживают отображение в 2048 элементов (раньше только 512).
- Принудительная установка обновлений.
- Использование виртуального голосового помощника Кортана.
- Обновленный меню пуск — представляет из себя гибрид предыдущих версий и Windows 8 (вернулся старый вариант раскрытия, а в правой части появились плитки).
- Возможность создания нескольких рабочих столов.
- Отказ от плиточной системы Windows 8.
1607 (август 2016):
- Возможность рукописного ввода (Windows Ink).
- Идентификация с помощью веб-камеры.
- Синхронизация с мобильного устройства уведомлений.
- Изменение меню параметров системы.
1703 (апрель 2017):
- Встроенная поддержка шлемов виртуальной реальности.
- Игровой режим
- По умолчанию предлагается командная строка в Powershell.
- Доступ к классической панели управления скрыт из контекстного меню. Теперь его можно вызвать командой control.
- Улучшение работы встроенного антивируса.
- Идентификация с помощью веб-камеры для Active Directory.
- Возможность создавать скриншот с выделением области с помощью сочетания клавиш Win + Shaft + S.
- Поддержка шрифта Брайля.
- Увеличенное время работы от батареи.
1709 (октябрь 2017):
- Возможность работы Cortana на одном устройстве и окончание работы на другом.
- Отключение протокола SMBv1. Включить можно вручную.
- Появление панели «Люди».
- Информация о GPU в диспетчере задач.
- Полноэкранный режим Microsoft Edge
- Увеличенное время работы от батареи (функция Power Throttling).
- Появление панели эмодзи.
- Выборочная синхронизация OneDrive.
- Исправление проблемы торможения в играх.
1803 (апрель 2018):
- Возможность восстановить пароль с помощью контрольных вопросов.
1809 (октябрь 2018):
- Темная тема для проводника.
- Возможность получения доступа к сообщениям с телефона (функция «Ваш телефон»).
1903 (май 2019):
- Изолированный рабочий стол для безопасного запуска приложений.
1909 (ноябрь 2019):
- Универсальный поиск в Проводнике.
- Улучшение производительности.
2004 (май 2020):
- Функция «Загрузка из облака» для переустановки Windows 10.
- Регулирование пропускной способности для обновлений Windows.
- Отображение температуры видеоядра в Диспетчере задач.
- Возможность удаления Блокнот, Paint, WordPad.
- Возможность использование Windows без пароля.
* данный список содержит часть нововведений. Полный список на странице в Википедии.
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Архитектура | 32-бит | 64-бит | 32-бит | 64-бит |
| Процессор | 1 ГГц | |||
| Оперативная память | 1 Гб | 2 Гб | 4 Гб | |
| Объем жесткого диска | 16 Гб | 20 Гб | 16 Гб | 20 Гб |
 Windows 11 (последняя для настольных компьютеров)
Windows 11 (последняя для настольных компьютеров)
Годы поддержки: 2021 — 2031. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: только 64 бита.
Основные издания: Домашняя (Home), Профессиональная (Pro), 8 Корпоративная (Enterprise).
Дополнительные издания: для обучения (Education), для облаков (Cloud).
Системные требования
| Процессор | 2 ядра, 1 ГГц |
|---|---|
| Оперативная память | 4 Гб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 64 Гб |
| БИОС (прошивка) | UEFI |
| Видеоадаптер | Совместимый с DirectX 12 / WDDM 2.x |
| Интернет | Для Home необходим вход под учетной записью Microsoft. |
 Windows NT 3.1 Advanced Server
Windows NT 3.1 Advanced Server
Годы поддержки: 1993 — 2001. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 16, 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: —
Системные требования
| Процессор | Intel 80386 |
|---|---|
| Оперативная память | 2 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 8 Мб |
 Windows NT 3.5 Server
Windows NT 3.5 Server
Годы поддержки: 1994 — 2001. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 16, 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: —
Что нового
- Встроенная поддержка Winsock и TCP/IP.
- Появление сервера DHCP и WINS.
- Предоставление общего доступа к файлам и принтерам.
- Поддержка VFAT.
Системные требования
| Процессор | 33 МГц |
|---|---|
| Оперативная память | 16 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 70 Мб |
 Windows NT 3.51 Server
Windows NT 3.51 Server
Годы поддержки: 1995 — 2001. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 16, 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: —
Системные требования
| Процессор | 33 МГц |
|---|---|
| Оперативная память | 16 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 70 Мб |
 Windows NT 4.0 Server
Windows NT 4.0 Server
Годы поддержки: 1996 — 2004. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: Server, Enterprise Edition, Terminal Server
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 486/25 | 486DX2/50 |
| Оперативная память | 16 Мб | 24 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 128 Мб | 1 Гб |
 Windows 2000 Server
Windows 2000 Server
Годы поддержки: 2000 — 2010. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: Server, Advanced Server и Datacenter Server
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 133 МГц | 1 ГГц |
| Оперативная память | 32 Мб | 128 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 2 Гб | 20 Гб |
 Windows Server 2003
Windows Server 2003
Годы поддержки: 2003 — 2015. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: Web, Standard, Enterprise, Datacenter
Системные требования
Web, Standard, Enterprise:
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 133 МГц | 550 МГц |
| Оперативная память | 128 Мб | 256 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 1,5 Гб | 2 Гб |
Datacenter Edition:
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 400 МГц | 733 МГц |
| Оперативная память | 512 Мб | 1 Гб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 1,5 Гб | 2 Гб |
 Windows Server 2003 R2
Windows Server 2003 R2
Годы поддержки: 2005 — 2015. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: Standard, Enterprise, Datacenter
Системные требования
Standard, Enterprise:
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 133 МГц | 550 МГц |
| Оперативная память | 128 Мб | 256 Мб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 1,2 Гб | 2 Гб |
Datacenter Edition:
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 400 МГц | 733 МГц |
| Оперативная память | 512 Мб | 1 Гб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 1,2 Гб | 2 Гб |
 Windows Server 2008
Windows Server 2008
Годы поддержки: 2008 — 2020. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 32 и 64 бита.
Издания: Web, Standard, Enterprise, Datacenter, HPC, Storage, Itanium
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Архитектура | 32-бит | 64-бит | 32-бит | 64-бит |
| Процессор | 1 ГГц | 1.4 ГГц | 2 ГГц | |
| Оперативная память | 512 Мб | 2 Гб | ||
| Объем жесткого диска | 10 Гб | 40 Гб |
 Windows Server 2008 R2
Windows Server 2008 R2
Годы поддержки: 2009 — 2020. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 64 бита.
Издания: Foundation, Small Business, Web, Standard, Enterprise, Datacenter, HPC, Itanium
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 1.4 ГГц | 2 ГГц |
| Оперативная память | 512 Мб | 2 Гб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 10 Гб | 40 Гб |
 Windows Server 2012
Windows Server 2012
Годы поддержки: 2012 — 2023. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 64 бита.
Издания: Foundation, Essentials, Standard, Datacenter
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 1.4 ГГц | 2 ГГц |
| Оперативная память | 2 Гб | 4 Гб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 32 Гб | 60 Гб |
 Windows Server 2012 R2
Windows Server 2012 R2
Годы поддержки: 2013 — 2023. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 64 бита.
Издания: Foundation, Essentials, Standard, Datacenter
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 1.4 ГГц | 2 ГГц |
| Оперативная память | 2 Гб | 4 Гб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 32 Гб | 60 Гб |
 Windows Server 2016
Windows Server 2016
Годы поддержки: 2016 — 2026. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 64 бита.
Издания: Essentials, Standard, Datacenter
Что нового
- Лицензирование на физические ядра процессора (минимум 16).
- Новый режим установки — Nano.
- Появление контейнерной виртуализации.
- OpenGL и OpenCL для RDP.
- Шифрование виртуальных машин и внутреннего сетевого трафика.
- Блочная репликация файловых хранилищ.
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 1.4 ГГц | 3.1 ГГц |
| Оперативная память | 2 Гб | 4 Гб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 32 Гб | 60 Гб |
Более подробно в обзоре Windows Server 2016.
 Windows Server 2019
Windows Server 2019
Годы поддержки: 2018 — 2029. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 64 бита.
Издания: Standard, Datacenter
Что нового
- Улучшенная безопасность — встроенные технологии Defender ATP и Defender Exploit Guard.
- Windows Subsystem Linux (WSL) — контейнеры для поддержки приложений Linux.
- Для построения кластера с четным количеством узлов в качестве диска-свидетеля может выступать USB-диск.
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 1.4 ГГц | 3.1 ГГц |
| Оперативная память | 512 Мб (Nano) 2 Гб (GUI) |
4 Гб |
| Объем жесткого диска | 32 Гб | 60 Гб |
 Windows Server 2022 (последняя для серверов)
Windows Server 2022 (последняя для серверов)
Годы поддержки: 2021 — 2031. Ветка: NT. Разрядность: 64 бита.
Издания: Standard, Datacenter
Что нового
- Улучшенная безопасность.
- Больше возможностей для работы с облаками, особенно, Microsoft Azure.
Системные требования
| Минимальные | Рекомендуемые | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 1.4 ГГц | 3.1 ГГц |
| Оперативная память | 512 Мб (Nano) 2 Гб (GUI) Поддержка ECC |
4 Гб
Поддержка ECC |
| Объем жесткого диска | 32 Гб | 60 Гб |
| Сетевой адаптер | 1 гигабит в секунду |
Windows 7 была выпущена Microsoft 22 октября 2009 года как последняя из линейки операционных систем Windows 25-летней давности и как преемница Windows Vista. Windows 7 была выпущена вместе с Windows Server 2008 R2, серверным аналогом Windows 7.
Windows 7 это последняя версия Windows. Выпущенная в 2009 году Windows 7 получила всеобщее признание за то, что она намного лучше, чем Windows Vista, которая была подвергнута резкой критике как пользователями, так и критиками.
…
Сравнительная таблица.
| Windows 7 | Windows Vista | |
|---|---|---|
| Выпущено в производство | 22 июля 2009 г .; 10 лет назад | 8 ноября 2006 г .; 13 лет назад |
Что было до Windows 7?
Версии для персональных компьютеров
| Имя и фамилия | Кодовое имя | Версия |
|---|---|---|
| Windows Vista | Longhorn | NT 6.0 |
| Windows 7 | Windows 7 | NT 6.1 |
| Windows 8 | Windows 8 | NT 6.2 |
| Windows 8.1 | Синии | NT 6.3 |
Vista или Windows 7 старше?
Последняя версия Windows должна быть выпущена в октябре 2009 года. Это всего через два года после выпуска Windows Vista, что означает, что это не серьезное обновление.
Могу ли я по-прежнему использовать Windows Vista в 2020 году?
Microsoft прекратила поддержку Windows Vista. Это означает, что больше не будет никаких дополнительных исправлений безопасности или исправлений ошибок для Vista, а также технической помощи. Операционные системы, которые больше не поддерживаются, более уязвимы для злонамеренных атак, чем более новые операционные системы.
Можно ли обновить Windows Vista?
Краткий ответ: Да, вы можете обновить Vista до Windows 7 или до последней версии Windows 10.
Что пошло не так с Vista?
В связи с новыми функциями Vista, возникла критика в отношении использования аккумулятор в ноутбуках работает под управлением Vista, которая может разряжать аккумулятор намного быстрее, чем Windows XP, сокращая время автономной работы. С отключенными визуальными эффектами Windows Aero время автономной работы равно или лучше, чем у систем Windows XP.
Как долго просуществовала Vista?
В мае 2010 года рыночная доля Windows Vista оценивалась в диапазоне от 15% до 26%.
…
Windows Vista.
| Успешно | Windows 7 (2009) |
| Официальный веб-сайт | Windows Vista |
| Статус поддержки | |
|---|---|
| Основная поддержка закончилась 10 апреля 2012 г. Расширенная поддержка закончилась 11 апреля 2017 г. |
Windows Vista 32-битная?
С выпуском Vista Microsoft одновременно запустила 32-битный x86 и 64-битные версии x64. Розничные версии содержат как x86, так и x64 версии, в то время как OEM-версии содержат одну или другую, и вы должны решить перед заказом.
Какое старое название Windows?
Microsoft Windows, также называемая Windows и Операционная система Windows, компьютерная операционная система (ОС), разработанная корпорацией Microsoft для работы на персональных компьютерах (ПК). Оснащенная первым графическим пользовательским интерфейсом (GUI) для IBM-совместимых ПК, ОС Windows вскоре стала доминировать на рынке ПК.
Почему не было Windows 9?
Оказывается, что Microsoft могла пропустить Windows 9 и сразу перешел к 10 по причине, которая восходит к эпохе 2 года. … По сути, существует давний сокращенный код, предназначенный для различения Windows 95 и 98, который не понимает, что теперь существует Windows 9.
Когда вышла Windows 11?
Видео: Microsoft показывает Windows 11
И многие изображения в прессе для Windows 11 укажите дату 20 октября на панели задач, отметили в The Verge.
Есть ли в Windows Vista Windows 10?
Microsoft не поддерживает обновление с Vista до Windows 10. … Однако большинство предприятий по-прежнему используют Windows 7, и я ожидаю, что большинство поставщиков браузеров и антивирусного программного обеспечения продолжат поддерживать ее после окончания поддержки Microsoft.
Почему заканчивается Windows 7?
Поддержка Windows 7 закончилась 14 января 2020. Если вы все еще используете Windows 7, ваш компьютер может стать более уязвимым для угроз безопасности.

Операционной системе Windows уже более трех десятилетий, и именно в этом году самая известная ОС в ноябре будет отмечать 35 летие. За это время было много версий системы, которые компания Microsoft разрабатывала и предлагала пользователям.
В настоящее время последней версией операционной системы Microsoft является Windows 10. Версия, которая для многих, несомненно, является лучшей в истории, с современным интерфейсом и множеством параметров конфигурации. В нашей статье мы предлагаем посмотреть, как со временем система совершенствовалась и адаптировалась к потребностям пользователей.
Windows 1.0
Хотя до появления Windows 1.0 уже говорили о существовании первой версии Windows, правда заключается в том, что до 20 ноября 1985 года эта первая версия системы не была официально анонсирована. Версия, которая предлагала мало функциональных возможностей и не была полной операционной системой, поскольку это было скорее графическое расширение MS-DOS.
Windows 1.0 поддерживалась до 31 декабря 2001 года, несмотря на то, что версия почти не обладала функциональностью, Redmond предлагал поддержку чуть более 16 лет.
Windows 2.0
Между тем, всего через два года, в ноябре 1987 года, появилась Windows 2.0. Эта версия была быстро обновлена до v2.03, которая уже включала известные всем окна. Не говоря уже о том, что в неё уже были включены определенные утилиты, которые, можно сказать, должны были стать источником нынешних средств автоматизации делопроизводства.
Эта версия Windows поддерживалась до той же даты, что и предыдущая версия. То есть до 31 декабря 2001 года, когда Microsoft решила прекратить поддержку Windows 1.0 и 2.0.
Windows 3.0
22 мая 1990 года была выпущена операционная система Windows 3.0 с графическим интерфейсом. Это была первая коммерчески успешная версия, продавшая до двух миллионов копий всего за несколько месяцев с момента ее запуска.
С обновлением до версии 3.1 система получила знаменитую игру Minesweeper, которая на протяжении многих лет радовала пользователей. Кроме того, мы также должны выделить наличие файлов и менеджера программ. Данную версию компания поддерживала до 31 декабря 2001 года. Та же дата, что и у двух предыдущих ОС.
Windows 95
24 августа 1995 года – важная дата в жизни операционной системы Windows, поскольку это день, когда была выпущена знаменитая версия Windows 95. Эта версия предлагает значительно улучшенный интерфейс и в ней уже появляется «Панель задач» и меню «Пуск», два очень важных элемента, которые до сих пор являются частью операционной системы Windows. Также стоит отметить, что Windows 95 включала в себя Internet Explorer, веб-браузер, который сопровождал систему в течение многих лет и, следовательно, поддержку Интернета.
Эта версия, предназначенная для потребительского рынка и с которой переходили от 16-разрядной многозадачной архитектуры к 32-разрядной соответствующей архитектуре, а также многозадачности. Стандартная поддержка для Windows 95 продолжалась до 31 декабря 2000 года, а расширенная до 31 декабря 2001 года.
Windows 98
Хотя до появления Windows 98 мы должны упомянуть, что была версия Windows NT, которая была ориентирована на бизнес-клиентов. Однако 25 июня 1998 года Microsoft выпустила новую версию своей операционной системы. Как и предыдущая, она получила в качестве своего имени последние две цифры года своего запуска, и это была версия, которая шла с файловой системой FAT32 и пыталась расширить доступ к сети. Кроме того, она включала в себя поддержку DVD и USB.
Однако большая сложность системы привела к значительному снижению производительности, что делает ее одной из наиболее критикуемых версий Windows за ее медлительность и ненадежность по сравнению с Windows 95. Несмотря на это, Windows 98 имела стандартную поддержку до 30 июня 2002 года и расширенную поддержку, которая закончилась 11 июля 2006 года.
Windows 2000
29 марта 1999 года была запущена операционная система Windows NT 5.0 EUR Edition, которая представляла собой не что иное, как немецкую версию Windows NET 5.0 и впоследствии называлась Windows 2000.
Windows 2000 включала новые опции для лучшей защиты файлов и даже имела собственную домашнюю версию, Windows 2000 Millennium Edition (ME), которая включала новые инструменты и опции мультимедиа. Стандартная поддержка для этого выпуска закончилась 30 июня 2005 г., а расширенная поддержка – 13 июля 2010 г.
Windows XP
Еще один большой скачок в развитии операционной системы Microsoft произошел 25 октября 2001 года, когда была запущена Windows XP. Это был большой успех, поскольку это действительно был высококачественный продукт. Версия, которая была построена из ядра Windows NT и выпускалась в двух разных редакциях: Home и Professional.
В визуальном аспекте необходимо выделить значительные улучшения в пользовательском интерфейсе с новыми значками, меню и параметрами, которые позволили пользователям углубляться и контролировать все виды задач в системе. Но Windows XP не только предлагала графические улучшения, но и значительно увеличила скорость и маневренность.
В Windows XP встроены такие функции, как шифрование системных файлов, поддержка сетей WiFi, удаленная помощь и 64-разрядная версия, что вызвало взрыв на рынке операционных систем. Эта версия имела стандартную поддержку от Microsoft до 14 апреля 2009 года, в то время как расширенная поддержка продолжалась до 8 апреля 2014 года.
Windows Vista
Windows Vista, выпущенная Microsoft 30 января 2007 года и включающая в себя бесчисленное количество новых функций, переработанную оболочку и интерфейс с серьезными изменениями, нацеленные на повышение безопасности, однако не понравилась подавляющему большинству пользователей.
С Windows Vista мы смогли увидеть интерфейс Aero UI, который, несомненно, предлагал отличную визуальную привлекательность, но оказался слишком проблематичным на менее мощных компьютерах. Множество обстоятельств сделало Windows Vista провалом в истории операционных систем, несмотря на большие ожидания компании.
Постоянные проблемы, медлительность и перегрузки затмили все графические новинки. Эта версия получала стандартную поддержку от компании до 10 апреля 2012 года, а расширенная поддержка была продлена до 11 апреля 2017 года.
Windows 7
22 октября 2009 года Microsoft объявила о выпуске Windows 7 в качестве замены Windows Vista и стала одной из самых важных версий ОС компании.
В данную систему была добавлена поддержка мультитач, переработанная оболочка Windows, новая панель задач, сетевая система, улучшения производительности и скорости, а также сокращение потребления ресурсов. Кроме того, Windows 7 представила новый дизайн панели задач, сделав ее более широкой, и систему с большими значками. Стандартная поддержка Windows 7 продолжалась до 13 января 2015 года, а расширенная поддержка до 14 января 2020 года.
Windows 8
Почти три года спустя, 26 октября 2012 г., была выпущена Windows 8. Версия, в которой была добавлена поддержка микропроцессоров ARM. Интерфейс в новой системе был изменен, чтобы сделать ее более удобной для устройств с сенсорными экранами. Также в системе было удалено меню «Пуск», что не нравилось подавляющему большинству пользователей.
Плохие отзывы пользователей о новом интерфейсе Metro заставили Microsoft запустить Windows 8.1, чтобы добавить некоторые улучшения. Стандартная и расширенная поддержка для Windows 8 закончилась 12 января 2016 года, тогда как для Windows 8.1 стандартная поддержка продолжалась до 9 января 2018 года, а расширенная поддержка все еще действует до 10 января 2023 года.
Windows 10
29 июля 2015 года Microsoft выпустила последнюю и ожидаемую версию своей операционной системы Windows 10. Версия, которая имеет большой набор приложений и современный интерфейс с отличной производительностью. Кросс-платформенность новой системы позволяет использовать ее на компьютерах и мобильных устройствах.
Но это не единственные новинки, поскольку также стоит отметить универсальные приложения: новый браузер Edge, помощник Cortana, новая страница конфигурации системы, TimeLine и возвращение меню «Пуск», которое жаждали подавляющее большинство пользователей. Одним словом – это лучшая версия системы на сегодняшний день и продукт, отвечающий потребностям пользователей.
Windows 10 имеет стандартную поддержку, действующую до 9 января 2024 года, в то время как расширенная поддержка продлится до 9 января 2029 года.
Поделиться
Материал из Национальной библиотеки им. Н. Э. Баумана
Последнее изменение этой страницы: 13:45, 16 ноября 2016.
 |
|
| Разработчик | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| Линейка ОС | Windows NT |
| Дата выхода на производство |
11 ноября 2006 (RTM) 30 января 2007 (для обычных пользователей) |
| Последний релиз | 6.0 (Build 6002.18005.090410-1830) Service Pack 2 (SP2) RTM (25 мая 2009) |
| Ядро (тип) | Гибридное ядро |
| По умолчанию пользовательский интерфейс |
Windows Aero |
| Лицензия | Microsoft EULA |
| Предшественник | Windows XP |
| Преемник | Windows 7 |
| Официальный веб-сайт | web.archive.org/web/20060414151446/http://www.microsoft.com/rus/windowsvista/ |
Microsoft Windows Vista — операционная система семейства Windows NT корпорации Microsoft. Была выпущена 30 января 2007 года. На стадии разработки имела кодовое имя «Longhorn». Построена на основе гибридного ядра NT версии 6.0. В качестве сокращенного имени иногда используется акроним «WinVI», объединяющий две первые буквы названия и версию ядра в римской записи. Предназначена исключительно для рабочих станций и персональных компьютеров; её ориентированная на серверы «сестра» — Windows Server 2008. Следующее за выходом Windows XP и предшественником Windows 7 .
30 ноября 2006 года Microsoft официально выпустила Windows Vista и Office 2007 для корпоративных клиентов. 30 января 2007 года начались продажи системы в СНГ для обычных пользователей. Vista получила обновлённый дизайн пользовательского интерфейса по сравнению с Windows XP. По данным веб-аналитики W3Schools, по состоянию на сентябрь 2016 года доля рынка Windows Vista составляет ▼ 0,2%; это значение достигало максимума в 18,6% в октябре 2009 года, после чего начало снижаться, в том числе из-за выхода Windows 7.[1]
Содержание
- 1 История
- 2 Обзор
- 3 Особенности
- 4 Издания
- 5 Обновления
- 5.1 Service pack 1
- 5.2 Service pack 2
- 6 Критика
- 7 Системные требования
- 7.1 Vista Capable
- 7.2 Vista Premium Ready
- 7.3 Установка
- 8 Рыночный провал Windows Vista
- 9 Примечания
История
На раннем этапе разработки система была известна под кодовым именем Longhorn (по имени бара Longhorn Saloon вблизи лыжного курорта Вистлер в Британской Колумбии). Название Vista было объявлено 22 июля 2005 года. Спустя несколько месяцев Microsoft также переименовала Windows Longhorn Server в Windows Server 2008. С 8 ноября 2006 года полноценная версия Windows Vista доступна для производителей оборудования. Релиз выпуска для конечных пользователей состоялся 30 января 2007 года.
Стоит заметить, что выпуск многих функций, анонсированных в Windows Vista, был отменен Microsoft из-за недовольства общественности. Например, предполагалось, что OpenGL будет реализован как надстройка над Direct3D. Это привело бы к серьёзному падению производительности OpenGL по сравнению с Direct3D и к фиксации версии OpenGL. Опасения не оправдались, поддержка OpenGL в Windows Vista осталась. Не вошла в Windows Vista и файловая система WinFS — на сей раз из-за проблем с производительностью.
Обзор
В Windows Vista обновлена подсистема управления памятью и вводом-выводом (I/O). Новой функциональностью также является «Гибридный спящий режим», при использовании которого содержимое оперативной памяти дополнительно записывается на HDD, но и из памяти также не удаляется. В результате, если питание не выключалось, компьютер восстанавливает работу, пользуясь информацией из ОЗУ. Если же подача энергии прекратилась, операционная система использует сохранённую на HDD копию ОЗУ и загружает информацию из неё (аналог спящего режима). Режим реализован благодаря так называемым «файлам гибернации», которые занимают объём на жёстком диске, равный объёму установленной на компьютере оперативной памяти. Пользователь может удалить эти файлы (утратив функцию гибернации). При этом, восстановление данных файлов возможно путём вызова специальных команд из командной строки.
С 28 июля 2005 года разработчикам и IT-профессионалам была разослана первая бета-версия. В ней были представлены основы новой архитектуры системы и все разработанные на тот день технические возможности. Первая бета-версия была выпущена для того, чтобы у аудитории сложилось первое впечатление о новой ОС, а также для обнаружения ошибок в новой системе до её официального выпуска. По результатам первого этапа бета-тестирования были доработаны пользовательские функции системы, которые затем были представлены во второй бета-версии. Финальная версия Windows Vista представлена в вариантах для 32- и 64-разрядных процессоров.
Windows Vista имеет также новый логотип. По мнению дизайнеров компании, этот логотип иллюстрирует изменения в пользовательском интерфейсе новой операционной системы (который получил название Aero из-за применения эффекта прозрачности).
| Минимальные требования | Рекомендуемые требования | |
|---|---|---|
| Процессор | 800 МГц | 1 ГГц (Для лучшей производительности рекомендуется двухъядерный процессор с 2 ГГц и более) |
| ОЗУ | 512 МБ | 1 ГБ (Для лучшей производительности требуется 2 ГБ и более). |
| Видеоадаптер | DirectX 9 | DirectX 9 совместимый с поддержкой технологий Hardware Pixel Shader v2.0 и WDDM |
| Видеопамять | 32 МБ (для выпуска Home Basic) | 128 МБ |
| Жёсткий диск | 20 ГБ | 40 ГБ |
| Свободное место на жестком диске | 15 ГБ | 20 ГБ |
| Другие приводы | CD-ROM | DVD-ROM |
Особенности
- Новый интерфейс Windows Aero. Windows Vista предлагает различные пользовательские интерфейсы, начиная с интерфейса Basic (напоминает интерфейс Windows XP) и заканчивая насыщенным различными эффектами высококачественным графическим интерфейсом, получившим название Windows Aero. Новый интерфейс Windows Aero отличается красивой графикой, полупрозрачными окнами, 3-мерными перспективами, богатыми текстурами и анимационными картинками.
- Боковая панель (Sidebar). В боковую панель можно установить некоторые специальные мини-приложения. Это могут быть часы, слайд-шоу с фотографиями, ленты новостей, адресная книга или панель быстрых заметок. Также можно вывести прогноз погоды, курс валют и др.
- Новый Windows Explorer. Новый Explorer сохранил структуру меню Windows XP и добавил ещё одну панель. Она позволяет изменить организацию окна Explorer, а также отображение значков файлов и папок. В зависимости от содержимого в панели выводятся различные опции.
- Обновленная система поиска. В Windows Vista интегрирован движок индексного поиска. Поиск проводится сразу же, по мере набора нужнго слова. При вводе каждой следующей буквы Vista сужает результат поиска. Если необходимо запустить программу, то достаточно ввести часть имени ярлыка или исполняемого файла.
- Технология ReadyBoost. Предназначенная для компьютеров с небольшим объёмом оперативной памяти, технология ReadyBoost позволяет использовать ёмкость флэш-накопителя для дополнения оперативной памяти.
- Встроенные средства диагностики. Средства диагностики аппаратного обеспечения способны обнаружить ошибки и либо устранить неполадку самостоятельно, либо помочь пользователю осуществить восстановление.
- Функции энергосбережения и питания. Управление электропитанием Vista было существенно улучшено по сравнению с XP, теперь оно использует так называемые «планы электропитания». Microsoft поддерживает три плана: «сбалансированный», «экономичный» и «производительный».
- Режим гибернации. Гибернация — это режим энергоснабжения, при котором все открытые документы и приложения сохраняются на жесткий диск, и только после этого питание компьютера отключается. Когда пользователь хочет вернуться к работе, компьютер выходит из режима гибернации и восстанавливает ранее сохраненные документы и приложения.
- User Account Control (UAC) — система контроля учетных записей пользователей, которая требует явного разрешения пользователя при выполнении любого действия, требующего административных полномочий, вне зависимости от прав текущего аккаунта пользователя. User Account Control, например, предупреждает пользователя перед установкой новой программы, а также при запуске исполняемых файлов. Подобный способ предотвращает автоматическую установку вредоносных и шпионских программ, поскольку все другие окна будут заблокированы, пока пользователь не даст ответ в окне подтверждения UAC.
- Windows Defender призван защитить систему от вредоносных и шпионских программ.
- Шифрование дисков BitLocker. BitLocker выполняет две взаимодополняющие, но различные функции. Во-первых, он обеспечивает шифрование всего тома операционной системы Windows. Во-вторых, на компьютерах с совместимым доверенным платформенным модулем (TPM) он позволяет проверить целостность загрузочных компонентов до запуска Windows Vista.
- Функция восстановления. Windows Vista, как и Windows XP, поддерживает точки восстановления. Однако, в Windows Vista эта функция более мощная, она позволяет восстанавливать предыдущее состояние отдельных файлов или папок.
- Система шифрования файлов EFS. EFS предназначена для шифрования файлов и папок на пользовательском уровне. Если на одном компьютере работает несколько пользователей, то, благодаря EFS, каждый из них может зашифровать свои данные.
- Улучшенные сетевые функции. С целью повышения безопасности большинство сетевых функций в Windows Vista были усовершенствованны. Теперь стек TCP/IP стал поддерживать двухуровневую архитектуру протокола IP, в которой протоколы IPv4 и IPv6 стали совместно использовать транспортный уровень и уровень кадрирования. Кроме того, начиная с этой версии Windows, протокол IPv6 стал включенным по умолчанию. Новая версия стека TCP/IP обладает многими возможностями. Среди них — возможность автоматической настройки. Кроме того, в Vista создана собственная архитектура беспроводных сетей под названием Native Wi-Fi, которая является частью сетевого стека. Она дает много преимуществ, среди которых:
- Улучшенная возможность обнаружения и создания беспроводных сетей;
- Быстрое подключение к беспроводной сети с помощью Центра управления сетями;
- Служба единого входа в беспроводные сети, проверяющая доступность сети перед тем, как пользователь проходит проверку подлинности в Active Directory;
- Поддержка современных протоколов безопасности (WPA, WPA2, EAP, PEAP-TLS, WEP);
- Защита от большинства типов атак на беспроводные сети;
- Средства диагностики, которые позволяют выявить проблемы с сетью и автоматически их устранить.
- Конференц-зал – встроенная программа, которая помогает работать группам от двух до десяти пользователей вместе. Конференц-зал подойдет для демонстрации презентаций PowerPoint или при редактировании документов. Также конференц-зал позволит упростить работу по раздаче файлов.
- Windows CardSpace — новая технология от Microsoft, созданная для сокращения количества используемых паролей. При посещении web-сайта, поддерживающего эту технологию, вместо ввода пароля можно будет использовать информационную карту. Все данные, необходимые для аутентификации пользователя, хранятся на ней в зашифрованном виде, что обеспечивает дополнительную безопасность.[2]
Издания
- Windows Vista Starter – издание предназначенное для семейного использования и пользователей начального уровня на развивающихся рынках. Особенности: 32-разрядная операционная система, специально разработанная для недорогих компьютеров, упрощенный интерфейс Windows Vista, различные функциональные ограничения.
- Windows Vista Home Basic — издание для домашних пользователей, которым требуются основные возможности компьютера. В этом издании отсутствует интерфейс Windows Aero, нет поддержки шифрованной файловой системы EFS.
- Windows Vista Home Premium — издание для домашних настольных и переносных компьютеров, содержит Windows Media Center, интерфейс пользователя Windows Aero, DVD-студию Windows, функции архивации по расписанию и архивации по сети, поддержку сенсорных устройств. Также как и в Home Basic нет поддержки шифрованной файловой системы EFS.
- Windows Vista Business — основной выпуск Windows Vista для настольных и мобильных ПК в организациях. Данное предложение предназначено для сегментов малых, средних и крупных предприятий. Windows Vista Business содержит все функции Windows Vista Home Basic (за исключением некоторых развлекательных функций), а также имеет следующие отличительные особенности: интерфейс Windows Aero, функциональные возможности системы Windows Tablet PC, функции архивации и восстановления (средство архивации CompletePC, автоматическое восстановление файлов и теневое копирование), возможность подключения к домену, поддержка групповой политики и шифрованной файловой системы, а также специальные возможности для малых предприятий, включая поддержку факсов, сканеров и ресурсы для малого бизнеса.
- Windows Vista Enterprise — это расширенный выпуск Windows Vista для настольных и мобильных ПК, используемых в организациях. Данное предложение действительно только для клиентов, заключивших соглашение Microsoft Software Assurance. В дополнение ко всем особенностям Windows Vista Business в данный выпуск включены следующие возможности: шифрование диска BitLocker, поддержка всех существующих языков интерфейса, лицензионные права на четыре виртуальные операционные системы, подсистема для приложений на основе UNIX (SUA).
- Windows Vista Ultimate является наиболее полным выпуском Windows Vista для настольных и мобильных ПК и предназначен для домашних пользователей и малых предприятий. Этот выпуск обладает всеми возможностями Windows Vista Home Premium и Windows Vista Enterprise, а так же располагает расширенными средствами работы с мультимедиа.
- Windows Vista Ultimate Limited Numbered Signature Edition – ограниченная версия (20 тыс. экземпляров) с подписью Билла Гейтса.
Обновления
Service pack 1
Пакет SP1 содержит полный набор обновлений для Windows Vista, которые корпорация Microsoft выпустила в течение последнего года, а также новые возможности. В частности, повышена скорость копирования файлов, улучшен процесс обновления программного обеспечения, добавлена поддержка Direct3D 10.1, улучшена совместимость с MPEG-2, устранены ошибки, возникающие в приложениях Windows Calendar и Windows Media Player, улучшены производительность и энергопотребление системы.
Благодаря обновлению SP1 в Windows Vista появилась поддержка большинства существующего, на момент выхода пакета, аппаратного и программного обеспечения — это около 80 тыс. устройств и компонентов. Также с выходом Windows Vista SP1 добавилась совместимость с основными бизнес-приложениями таких производителей, как Adobe, Cisco, Citrix, IBM, Nortel, Oracle, SAP, Sun и Symantec.
Первая общедоступная версия Windows Vista SP1 RC была выложена в декабре 2007 года. 18 марта 2008 года пакет обновлений появился на английском, французском, испанском, немецком и японском языках. В апреле этого же года вышла русская версия первого пакета обновлений.
Service pack 2
Второй пакет обновлений для операционной системы Windows Vista, на данный момент, находится в стадии бета-тестирования. Как ожидается, финальная версия пакета принесет с собой поддержку 64-разрядных процессоров VIA, поддержку файловой системы exFAT, возможность записи Blu-ray дисков, поддержку последней технологии Bluetooth 2.1, конфигурационный инструмент Windows Connect Now (WCN) Wi-Fi и последнюю версию настольного поискового движка Windows Search 4. Кроме того, SP2 должен будет улучшить производительность Wi-Fi при выходе Vista из режима сна, снизить использование гаджетами ресурсов и выполнить некоторую общую настройку системы.
Критика
Обширной критике подвергались системные требования, предъявленные Microsoft, к оборудованию на котором может работать Windows Vista. Как известно, Microsoft разделила системные требования на две категории: «Vista Capable» и «Vista Premium Ready». Знак «Vista Capable» означал, что компьютер может запускать Vista со всеми основными функциями. Однако, как оказалось, на компьютере с параметрами удовлетворяющих критерию «Vista Capable» нельзя воспользоваться всеми графическими нововведениями новой операционной системы.[3]
Также критике подвергалась система контроля учетных записей пользователей (UAC). По словам представителей Лаборатории Касперского (ЛК), средство управления пользовательскими привилегиями и учетными записями User Account Control (UAC), встроенное в Windows Vista, представляет собой настолько докучающий пользователям элемент безопасности, что многие просто отключают его. Наталья Касперская, будучи руководителем ЛК, отметила, что без UAC Windows Vista менее безопасна, чем Winows XP SP2. Кроме того, в ЛК заявили, что аналитики компании обнаружили пять способов обхода UAC, а создатели злонамеренного ПО обнаружат их еще больше.[4]
Системные требования
Microsoft разделяет системные требования на две категории: «Vista Capable» и «Vista Premium Ready». «Vista Capable» означает, что система может запускать Vista со всеми основными функциями.[5]
Vista Capable
- Процессор с тактовой частотой 800 МГц;
- 512 мегабайт оперативной памяти;
- Видеокарта поддерживающая DirectX 9
Уровень «Vista Capable» лишь гарантирует, что Vista будет работать. Перечисленные выше требования соответствуют лишь удовлетворительному уровню работы.
По заявлению Microsoft, маркировка «Premium Ready» гарантирует, что ПК будет поддерживать максимум функций Windows Vista, включая интерфейс Windows Aero.
Vista Premium Ready
- Процессор с тактовой частотой от 1 ГГц (32-разрядный (x86) или 64-разрядный (x64);
- 1 гигабайт оперативной памяти;
- Видеокарта совместимая с DirectX 9, с 128 МБ памяти и поддержкой технологий Hardware Pixel Shader v2.0 и WDDM;
- DVD-ROM;
- Жесткий диск объемом 40 ГБ, из которых свободны должны быть как минимум 15;
- Возможность воспроизведения звука;
- Наличие доступа в интернет.
Установка
Как скачать и установить Windows Vista.
Рыночный провал Windows Vista
Существует мнение, что Windows Vista является худшей операционной системой Microsoft.[6]
Также Windows Vista заняла первое место в конкурсе «Провал года», проводимом сайтом Pwnie award, созданным в 2007 году. Пользователи очень долго ждали Windows Vista и слишком привыкли к Windows XP.
Более того, по предположению The Inquirer.net, по ряду беспрецедентных промоакций, связанных с продвижением Windows Vista на рынке, можно сделать вывод о том, что руководство Microsoft признало ОС провалом. В настоящее время Windows Vista имеет очень низкую популярность.[7]
Огромное количество пользователей по всему миру удаляли легальную Windows Vista с ноутбуков и устанавливали взамен Windows XP, часто нелицензионную. Причина кроется в неудовлетворённости системой, так как ни одна предыдущая версия Windows не вызывала такой реакции пользователей.
После выхода Windows 7 (по сути, улучшенной версии Windows Vista с оптимизациями производительности и исправлениями ошибок) количество установленных на компьютеры копий Windows Vista резко упало, популярность данной системы также практически немедленно снизилась (что не относится к её серверной версии).[8]
Примечания
- ↑ Windows Vista [Электронный ресурс] : Материал из Википедии — свободной энциклопедии: — Режим доступа:https://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/Windows_Vista
- ↑ Windows Vista [Электронный ресурс] : Материал из http://www.tadviser.ru/: — Режим доступа: http://www.tadviser.ru/index.php/%D0%9F%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B4%D1%83%D0%BA%D1%82:Windows_Vista#.D0.98.D0.B7.D0.B4.D0.B0.D0.BD.D0.B8.D1.8F
- ↑ Windows Vista [Электронный ресурс] : Материал из https://www.heise.de/: — Режим доступа: https://www.heise.de/security/
- ↑ Windows Vista [Электронный ресурс] : Материал из http://labs.norton.com/
- ↑ Windows Vista [Электронный ресурс] : Материал из http://www.thg.ru/: — Режим доступа: http://www.thg.ru/howto/windows_vista/windows_vista-05.html
- ↑ Windows Vista [Электронный ресурс] : Материал из http://www.point.ru/: — Режим доступа: http://www.point.ru/news/stories/19316/
- ↑ Windows Vista [Электронный ресурс] : Материал из http://www.kprf.org/: — Режим доступа: http://www.kprf.org/showthread-t_2285.html
- ↑ Windows Vista [Электронный ресурс] : Материал из http://www.softodrom.ru/: — Режим доступа: http://news.softodrom.ru/ap/b1754.shtml