Давайте сначала выясним, что есть и откуда пошла архитектура. X64 — это технология, разработанная AMD (AMD64), с целью незаметно и безболезненно для конечного пользователя перейти из 32-битного мира x86 (286-, 386-, 486-совместимые микропроцессоры) в новую 64-битную эру компьютерных вычислений. Intel в партнерстве с HP отказалась расширять древнюю платформу x86 и создала собственную 64 битную архитектуру Itanium IA-64. Так как Itanium был в корне отличным от предшественника, его возможности по эмуляции x86-приложений были, мягко говоря, слабыми. Intel надеялась, что рынок достаточно быстро адаптирует новую платформу, однако грамотного пути для миграции не нашлось. Поэтому Itanium не получил широкого распространения. AMD решила расширить уже отработанную архитектуру x86 новыми 64-битными возможностями, добавив в процессор 64-битные регистры. Такой вариант был принят рынком на ура. В итоге Intel скопировала архитектуру AMD64 (согласно договору AMD-Intel о кросс-лицензировании) и назвала ее EM64T. Обе x64-технологии в общем-то идентичны, за исключением мелких отличий в аппаратной реализации.
Microsoft выпустила 64-битную версию Windows XP и дала ей нехитрое название Windows XP 64-bit Edition. Эта ОС была создана для архитектуры IA-64 Itanium, была полностью 64-битной, но с помощью эмуляции поддерживала и 32-битные приложения. Более того, для IA-64 была и специальная версия Windows 2000 Server. Проблема заключалась в неторопливой адаптации IA-64, но когда AMD создала AMD64, а Intel ничего не оставалось, кроме того как последовать примеру, Microsoft разработала x64-версию Windows XP, а за ней и версию Windows Server 2003. 64-битные версии были гибридного типа, потому как могли исполнять и 32-битный и 64-битный код без необходимости программной эмуляции, хотя Windows XP x64 Edition для исполнения существующего 32-битного кода эта самая эмуляция оставалась обязательным условием.
Однако, с релизом Vista компания Microsoft одновременно выпустила обе версии: 32-битную x86 и 64-битную x64. Коробочные версии Vista Ultimate содержат обе редакции ОС, но OEM-версии могут содержать либо одну, либо другую — перед заказом необходимо определиться. Поэтому вопрос «Какую редакцию Windows Vista выбрать — 32 или 64-битную» приобрел особую актуальность.
Первое, что стоит сделать — проверить, что выбранный вами процессор поддерживает 64-битные инструкции. Если вы не знаете наверняка, то вот маленькая утилита
x64 detector, которая позволит проверить способности вашего CPU.
Но вот краткий итог:
• Почти все сервера AMD или Intel, проданные в течение последних двух лет обладают поддержкой x64
• Большинство настольных процессоров класса high-end как от AMD, так и от Intel, выпущенные в течение прошлого года, имеют x64-возможности
• Более дорогие модели процессоров Sempron имеют поддержку x64; более дешевые — нет
• Процессоры AMD Durons не поддерживают x64
• Все процессоры AMD Opteron имеют поддержку x64
• Все процессоры AMD X2, FX и Athlon64 имеют поддержку x64
• Все процессоры Intel Pentium D и Celeron D имеют поддержку x64
• Мобильные процессоры AMD Turion имеют поддержку x64
• Процессоры Intel Core 2 (мобильные, настольные и серверные) имеют поддержку x64
• Мобильные процессоры Intel Core Duo не поддерживают x64
• Мобильные процессоры Intel Pentium M не поддерживают x64.
Слабое место x64 — драйвера
Второе, на что стоит обратить внимание — проверить, все ли имеющиеся устройства имеют качественные x64-драйвера, причем неважно, включены ли они в состав ОС или их можно скачать с сайта производителя устройства. С этой точки зрения многие из материнских плат имеют проблемы со звуковыми и сетевыми драйверами. Поэтому посетите сайт производителя используемого вами чипсета. Драйвера, к примеру, для сетевых карт Gigabit LAN и аудиодрайвера с поддержкой звука 5.1 можно найти тут. NVIDIA тоже выпустила новые драйвера. ATI (теперь AMD) не отстает от конкурента — здесь можно найти последнюю версию драйверов . Буквально на днях Creative, наконец-то, выпустила 64-битную версию своих драйверов. Благо, многие производители уже выпустили драйвера для основных компонентов компьютера, но совершенно отсутствуют драйвера для периферийных устройств. Так что о вебкамерах, принтерах, сканерах и других устройствах можно забыть. По крайней мере, на время.
С драйверами (прим. имеются ввиду периферийные устройства) для 32-битной Windows Vista проблем, скорее всего, не возникнет. А вот когда дело коснется x64, то тут появляются проблемы. С этой точки зрения x64-версии очень непрактичны, потому многие из привычных устройств попросту не будут работать. Заставить работать основные компоненты системы относительно легко, но всегда есть одно-два устройства, которые намертво стопорят все попытки пользователя заставить их работать. По этой причине мало кто из производителей компьютеров решатся предустановить 64-битную версию Windows Vista, потому как в текущей ситуации поддержка 64-битных систем — сущий ад и ночной кошмар для производителей.
Серверам, с другой стороны, не требуются периферийные устройства и они, как правило, работают с ограниченным набором устройств, с которыми сервер продается. Каждый уважающий себя производитель серверного аппаратного обеспечения, предлагающий, к примеру, адаптеры HBA Fiber Channel или iSCSI, должны обеспечить полную поддержку x64. Microsoft Exchange Server 2007, например, доступен исключительно в 64-битном варианте, а в ближайшее время многие компании-производители ПО намерены выпустить 64-битные версии своих программных продуктов.
Профессиональные рабочие станции — еще один кандидат для 64-битных операционных систем, потому как именно x64 обеспечивает максимальную производительность и скорость работы. К примеру, бесплатные утилиты для редактирования образов оптимизированы для мультиядерных систем, да и к тому же полностью x64-совместимы. А вот Adobe даже не собирается выпускать 64-битную версию грядущего Photoshop CS3. Это не значит, что вы не сможете запустить 32-битную версию Photoshop; на самом деле, в Windows x64 приложение, скорее всего, будет чуть быстрее, потому как в x64 доступно больше 4Гб оперативной памяти. Пускай Adobe будет стыдно, потому что приложение Paint.NET в своей 64-битной реинкарнации показывает огромный прирост производительности — от 50 до 100%. Adobe стоило бы обеспечить поддержку x64 пару лет назад, однако, компания не намерена сделать это и в будущем году.
Вывод таков, что перед выполнением миграции вы должны внимательно оценить аппаратные ограничения своего компьютера. Если все из имеющихся у вас устройств корректно работают в Vista x64, то вперед — 64-битные вычисления откроют вам новые горизонты.
Источник:
thevista.ru
Перевод: deeper2k
Оцените статью: Голосов
- Минимальные
- Рекомендуемые
Минимальные системные требования Vista Home Basic
- Разрядность: x86 (32-bit) или x64 (64-bit)
- ЦП [CPU]: 800 MHz
- Видеоадаптер [GPU]: Встроенная или дискретная с поддержкой 3D
- Видеопамять [VRAM]: 32 Mb
- Винчестер [HDD]: 20 Gb
- Оперативная память [RAM]: 512 Mb
- Аудиокарта [AUDIO]: С поддержкой DirectX
- Контроллер: Клавиатура, Мышь
- Интернет: Широкополосное соединение
- DirectX: 9
- Разрешение экрана: VGA 640×480
- Дополнительно: DVD/CD привод или USB
Системные требования Home Premium, Vista Business, Vista Enterprise, Vista Ultimate
- Разрядность: x86 (32-bit) или x64 (64-bit)
- ЦП [CPU]: 1 GHz
- Видеоадаптер [GPU]: 3D адаптер
- Видеопамять [VRAM]: 128 Mb
- Винчестер [HDD]: 40 Gb
- Оперативная память [RAM]: 1 Gb
- Аудиокарта [AUDIO]: Совместимая с DirectX 9.0
- Контроллер: Клавиатура, Мышь Microsoft Mouse
- Интернет: Широкополосный доступ
- DirectX: 9.0c
- Разрешение экрана: SVGA 800×600
- Дополнительно: DVD/CD привод или USB
Примечание
Графическая плата с поддержкой драйвера WDDM, Pixel Shader 2.0 и 32 bit на пиксель
Для того, чтобы ОС Виндовс Виста нормально работала на вашем компьютере, его характеристики должны соответствовать следующим условиям: Процессор должен являться 32-bit (x86) или 64-bit (x64), с тактовой частотой 1 ГГц. Оперативной памяти оптимальным объемом будет 1 Гб, это позволит вам работать за персональным компьютером. Свободное место вашего жёсткого диска должно быть как минимум 20 гигабайт. GPU с памятью 128 МГц гигабайт с DX от 9.
Комментарии магазина.
Уважаемые пользователи, для связи с администрацией магазина можете воспользоваться формой контакта в правом нижнем углу окна.
А так же, если Вы приобрели наш товар и активировали ключ, оставьте пожалуйста комментарий, это помогает развитию магазина. Спасибо, что воспользовались нашими услугами!
Если Вы оставляете отзыв через личный кабинет, который у Вас появляется после покупки, то на сайте в отзывах он отображается от имени «Анонима». При написании отзыва непосредственно со страницы с товаром в поле ниже — пункты «Имя» и «Почта» обязательны, Ваш Email публично не публикуется, он нужен нам только для обратной связи.
Уважаемые пользователи, для связи с администрацией магазина можете воспользоваться формой контакта в правом нижнем углу окна.
А так же, если Вы приобрели наш товар и активировали ключ, оставьте пожалуйста комментарий, это помогает развитию магазина. Спасибо, что воспользовались нашими услугами!
Если Вы оставляете отзыв через личный кабинет, который у Вас появляется после покупки, то на сайте в отзывах он отображается от имени «Анонима». При написании отзыва непосредственно со страницы с товаром в поле ниже — пункты «Имя» и «Почта» обязательны, Ваш Email публично не публикуется, он нужен нам только для обратной связи.
Процент максимальной скидки, который Вы можете получить при покупке товаров в нашем магазине. Скидка считается по Вашему e-mail адресу, Вы можете совершать покупки разными кошельками, но использовать один электронный адрес почты, и тогда скидка будет всегда при Вас!
| Сумма покупок | Размер скидки |
|---|---|
| 1200$ | 8% |
| 800$ | 6% |
| 600$ | 4% |
| 350$ | 2% |
| 50$ | 1% |
- Размер: 4.32 GB
- Категория: виндовс / windows vista
- Загрузок: 67 456
- Комментарии: 16
- Дата обновления:09.10.2011
полный обзор Microsoft Windows Vista
Стадия разработки : Release
Год/Дата Выпуска: 2010
Версия: 6.0.6002.18005.090410-1830
Разработчик: Microsoft
Сайт разработчика: http://microsoft.ru
Автор сборки: m0nkrus
Разрядность: 32bit+64bit
Язык интерфейса: Английский + Русский
Таблэтка: Не требуется
Системные требования:
* 32-разрядный (x86) или 64-разрядный (х64) процессор с тактовой частотой 1 ГГц.
* 1 ГБ оперативной памяти.
* Поддержка интерфейса DirectX 9 с драйвером WDDM, не менее 128 МБ видеопамяти, функция Pixel Shader 2.0 и цветность 32 бит/пиксел.
* Жесткий диск емкостью 40 Гб с 15 Гб свободного дискового пространства.
* Дисковод для DVD-дисков.
* Возможность вывода аудиосигнала.
* Доступ в Интернет.
Описание:
Данная сборка является обновленной версией себя же, но от 06.05.2009. Накопилось достаточно интересных нововведений, чтобы появился смысл обновить данный продукт. Сборка включает в себя 4 модификации русской и английской версий Windows Vista Ultimate SP2 для 32-битного (x86) и для 64-битного (x64) ядра:
— Windows Vista Ultimate SP2 x86 Russian
— Windows Vista Ultimate SP2 x86 English
— Windows Vista Ultimate SP2 x64 Russian
— Windows Vista Ultimate SP2 x64 English
Работоспособность сборки тщательно проверена.
По окончании установки вы получаете полностью зарегистрированную и активированную версию Windows Vista Ultimate SP2 выбранной вами модификации. Кроме того, вы будете иметь возможность изменять язык интерфейса с английского на русский и обратно стандартными средствами Windows Vista Ultimate SP2 сразу по окончании установки.
ВНИМАНИЕ! Данная сборка предоставлена вам исключительно в ознакомительных целях. Все права на конкретные продукты принадлежат их правообладателям. Если вы воспользовались программными продуктами данной сборки, то подразумевается, что вы являетесь обладателем лицензии или же удалите данные продукты по истечении ознакомительного периода использования. За правонарушения, связанные с нелицензированным использованием, представленной на диске продукции, автор сборки ответственности не несет.
MD5: 0c0eba522424c30844a6d6aac7c0a652
SHA-1: d9d2d6f82b752e095027c53a6f3792a30a97310f
CRC32: F84C3125
Что нового
Что нового по сравнению с одноименной сборкой от 06.05.2009:
На самом раннем этапе установки теперь имеется предзагрузочное меню, в котором можно выбрать разрядность первичной оболочки, то есть какой загрузчик будет использован для установки, x86 или x64. Благодаря этому нововведению теперь можно не беспокоиться, что 64-битная версия ОС может не встать на RAID, и что пользователи 64-битной ОС окажутся без службы восстановления системы.
Используемая в сборке методика активации доработана. Теперь в случае, если вы устанавливаете систему на компьютер, имеющий в БИОС’е SLIC-таблицу версии 2.0 или 2.1, активатор не будет использован вообще — будут задействованы стандартные законные (почти) средства активации, разработанные Майкрософт для таких компьютеров.
Скриншоты:
![Microsoft Windows Vista Ultimate SP2 RUS-ENG x86-x64 -4in1- Activated (AIO) [29.11.2010] Скачать торрент Microsoft Windows Vista Ultimate SP2 RUS-ENG x86-x64 -4in1- Activated (AIO) [29.11.2010] Скачать торрент](https://torrent-wind.net/windows/windows_vista/2012-05/22/gzvw7c4fbtseunhkno4w1xaw2.jpg)
![Microsoft Windows Vista Ultimate SP2 RUS-ENG x86-x64 -4in1- Activated (AIO) [29.11.2010] Скачать торрент Microsoft Windows Vista Ultimate SP2 RUS-ENG x86-x64 -4in1- Activated (AIO) [29.11.2010] Скачать торрент](https://torrent-wind.net/windows/windows_vista/2012-05/22/re5fiecjx4uiu3of0b3g7xhua.jpg)
Скачать торрент:
с нашего сервера
Релиз проверен Администрацией! Можно качать, На этой странице доступно для скачивания Microsoft Windows Vista Ultimate SP2 RUS-ENG x86-x64 -4in1- Activated (AIO) [29.11.2010] Скачать торрент
оставайтесь на раздаче, оставляйте комментарии и помогите другим оценить качество сборки windows и программы
| Version of the Windows NT operating system | |
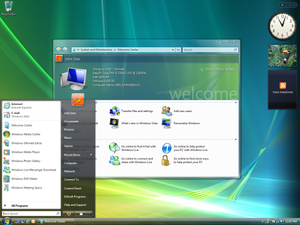
Screenshot of Windows Vista Ultimate, showing its desktop, taskbar, start menu, Windows Sidebar, Welcome Center, and glass effects of Windows Aero |
|
| Developer | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| Source model |
|
| Released to manufacturing |
November 8, 2006; 16 years ago[2] |
| General availability |
January 30, 2007; 16 years ago[3] |
| Final release | Service Pack 2 with security update rollup (6.0.6002)[4] / October 18, 2016; 6 years ago[5] |
| Update method |
|
| Platforms | IA-32 and x86-64 |
| Kernel type | Hybrid (NT) |
| Userland | Windows API, NTVDM, SUA |
| License | Proprietary commercial software |
| Preceded by | Windows XP (2001) |
| Succeeded by | Windows 7 (2009) |
| Official website | Windows Vista (archived at Wayback Machine) |
| Support status | |
| Mainstream support ended on April 10, 2012. Extended support ended on April 11, 2017.[6] Installing a service pack is required for users to receive updates and support after April 13, 2010. |
Windows Vista is a major release of the Windows NT operating system developed by Microsoft. It was the direct successor to Windows XP, which was released five years earlier, at the time being the longest time span between successive releases of Microsoft’s Windows desktop operating systems. Development was completed on November 8, 2006, and over the following three months, it was released in stages to computer hardware and software manufacturers, business customers, and retail channels. On January 30, 2007, it was released internationally and made available for purchase and download from the Windows Marketplace; this is the first release of Windows to be made available through a digital distribution platform.[7]
New features of Windows Vista include an updated graphical user interface and visual style dubbed «Aero,» a new search component called «Windows Search,» redesigned networking, audio, print, and display sub-systems, and new multimedia tools such as Windows DVD Maker. Windows Vista aimed to increase the level of communication between machines on a home network, using peer-to-peer technology to simplify sharing files and media between computers and devices. Windows Vista included version 3.0 of the .NET Framework, allowing software developers to write applications without traditional Windows APIs. Windows Vista removed support for devices without ACPI.
While these new features and security improvements garnered positive reviews, Windows Vista was also the target of much criticism and negative press. Criticism of Windows Vista includes its high system requirements, more restrictive licensing terms, lack of compatibility, longer boot time, and excessive authorization prompts from User Account Control. As a result of these and other issues, Windows Vista saw lower initial adoption and satisfaction rates than Windows XP. However, Windows Vista usage had surpassed Microsoft’s pre-launch two-year-out expectations of achieving 200 million users, with an estimated 330 million Internet users in January 2009. On October 22, 2010, Microsoft ceased sales of retail copies of Windows Vista, and the original equipment manufacturer’s sales for Windows Vista ceased a year later.[8] The market share of Windows Vista fell below 1% by the end of 2021, coinciding with the release of Windows 11.[9]
Mainstream support for Windows Vista ended on April 10, 2012, and extended support ended on April 11, 2017[10] Windows Vista was succeeded by Windows 7. As of February 2022, 0.18% of PCs run Windows Vista.[9]
Development[edit]
Microsoft began work on Windows Vista, known at the time by its codename «Longhorn», in May 2001,[11] five months before the release of Windows XP. It was originally expected to ship in October 2003 as a minor step between Windows XP and «Blackcomb», which was planned to be the company’s next major operating system release. Gradually, «Longhorn» assimilated many of the important new features and technologies slated for Blackcomb, resulting in the release date being pushed back several times in three years. In some builds of Longhorn, their license agreement said «For the Microsoft product codenamed ‘Whistler'». Many of Microsoft’s developers were also re-tasked to build updates to Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 to strengthen security. Faced with ongoing delays and concerns about feature creep, Microsoft announced on August 27, 2004, that it had revised its plans. For this reason, Longhorn was reset to start work on componentizing the Windows Server 2003 Service Pack 1 codebase, and over time re-incorporating the features that would be intended for an actual operating system release. However, some previously announced features such as WinFS were dropped or postponed, and a new software development methodology called the Security Development Lifecycle was incorporated to address concerns with the security of the Windows codebase, which is programmed in C, C++ and assembly. Longhorn became known as Vista in 2005.[12][13]
Longhorn[edit]
The early development stages of Longhorn were generally characterized by incremental improvements and updates to Windows XP. During this period, Microsoft was fairly quiet about what was being worked on, as their marketing and public relations efforts were more strongly focused on Windows XP, and Windows Server 2003, which was released in April 2003. Occasional builds of Longhorn were leaked onto popular file sharing networks such as IRC, BitTorrent, eDonkey and various newsgroups, and so most of what is known about builds before the first sanctioned development release of Longhorn in May 2003 is derived from these builds.
After several months of relatively little news or activity from Microsoft with Longhorn, Microsoft released Build 4008, which had made an appearance on the Internet around February 28, 2003.[14] It was also privately handed out to a select group of software developers. As an evolutionary release over build 3683, it contained several small improvements, including a modified blue «Plex» theme and a new, simplified Windows Image-based installer that operates in graphical mode from the outset, and completed an install of the operating system in approximately one third the time of Windows XP on the same hardware. An optional «new taskbar» was introduced that was thinner than the previous build and displayed the time differently.
The most notable visual and functional difference, however, came with Windows Explorer. The incorporation of the Plex theme made blue the dominant color of the entire application. The Windows XP-style task pane was almost completely replaced with a large horizontal pane that appeared under the toolbars. A new search interface allowed for filtering of results, searching for Windows help, and natural-language queries that would be used to integrate with WinFS. The animated search characters were also removed. The «view modes» were also replaced with a single slider that would resize the icons in real-time, in the list, thumbnail, or details mode, depending on where the slider was. File metadata was also made more visible and more easily editable, with more active encouragement to fill out missing pieces of information. Also of note was the conversion of Windows Explorer to being a .NET application.
Most builds of Longhorn and Vista were identified by a label that was always displayed in the bottom-right corner of the desktop. A typical build label would look like «Longhorn Build 3683.Lab06_N.020923-1821». Higher build numbers did not automatically mean that the latest features from every development team at Microsoft was included. Typically, a team working on a certain feature or subsystem would generate their working builds which developers would test with, and when the code was deemed stable, all the changes would be incorporated back into the main development tree at once. At Microsoft, several «Build labs» exist where the compilation of the entirety of Windows can be performed by a team. The name of the lab in which any given build originated is shown as part of the build label, and the date and time of the build follow that. Some builds (such as Beta 1 and Beta 2) only display the build label in the version information dialog (Winver). The icons used in these builds are from Windows XP.
At the Windows Hardware Engineering Conference (WinHEC) in May 2003, Microsoft gave their first public demonstrations of the new Desktop Window Manager and Aero. The demonstrations were done on a revised build 4015 which was never released. Several sessions for developers and hardware engineers at the conference focused on these new features, as well as the Next-Generation Secure Computing Base (previously known as «Palladium»), which at the time was Microsoft’s proposed solution for creating a secure computing environment whereby any given component of the system could be deemed «trusted». Also at this conference, Microsoft reiterated their roadmap for delivering Longhorn, pointing to an «early 2005» release date.[15]
Development reset[edit]
By 2004, it had become obvious to the Windows team at Microsoft that they were losing sight of what needed to be done to complete the next version of Windows and ship it to customers. Internally, some Microsoft employees were describing the Longhorn project as «another Cairo» or «Cairo.NET», referring to the Cairo development project that the company embarked on through the first half of the 1990s, which never resulted in a shipping operating system (though nearly all the technologies developed in that time did end up in Windows 95 and Windows NT[16]). Microsoft was shocked in 2005 by Apple’s release of Mac OS X Tiger. It offered only a limited subset of features planned for Longhorn, in particular fast file searching and integrated graphics and sound processing, but appeared to have impressive reliability and performance compared to contemporary Longhorn builds.[17] Most Longhorn builds had major Windows Explorer system leaks which prevented the OS from performing well, and added more confusion to the development teams in later builds with more and more code being developed which failed to reach stability.
In a September 23, 2005 front-page article in The Wall Street Journal,[18] Microsoft co-president Jim Allchin, who had overall responsibility for the development and delivery of Windows, explained how development of Longhorn had been «crashing into the ground» due in large part to the haphazard methods by which features were introduced and integrated into the core of the operating system, without a clear focus on an end-product. Allchin went on to explain how in December 2003, he enlisted the help of two other senior executives, Brian Valentine and Amitabh Srivastava, the former being experienced with shipping software at Microsoft, most notably Windows Server 2003,[19] and the latter having spent his career at Microsoft researching and developing methods of producing high-quality testing systems.[20] Srivastava employed a team of core architects to visually map out the entirety of the Windows operating system, and to proactively work towards a development process that would enforce high levels of code quality, reduce interdependencies between components, and in general, «not make things worse with Vista».[21] Since Microsoft decided that Longhorn needed to be further componentized, work started on builds (known as the Omega-13 builds) that would componentize existing Windows Server 2003 source code, and over time add back functionality as development progressed. Future Longhorn builds would start from Windows Server 2003 Service Pack 1 and continue from there.
This change, announced internally to Microsoft employees on August 26, 2004, began in earnest in September, though it would take several more months before the new development process and build methodology would be used by all of the development teams. A number of complaints came from individual developers, and Bill Gates himself, that the new development process was going to be prohibitively difficult to work within.
As Windows Vista[edit]
By approximately November 2004, the company had considered several names for the final release, ranging from simple to fanciful and inventive. In the end, Microsoft chose Windows Vista as confirmed on July 22, 2005, believing it to be a «wonderful intersection of what the product really does, what Windows stands for, and what resonates with customers, and their needs». Group Project Manager Greg Sullivan told Paul Thurrott «You want the PC to adapt to you and help you cut through the clutter to focus on what’s important to you. That’s what Windows Vista is all about: «bringing clarity to your world» (a reference to the three marketing points of Vista—Clear, Connected, Confident), so you can focus on what matters to you».[22] Microsoft co-president Jim Allchin also loved the name, saying that «Vista creates the right imagery for the new product capabilities and inspires the imagination with all the possibilities of what can be done with Windows—making people’s passions come alive.»[23]
After Longhorn was named Windows Vista in July 2005, an unprecedented beta-test program was started, involving hundreds of thousands of volunteers and companies. In September of that year, Microsoft started releasing regular Community Technology Previews (CTP) to beta testers from July 2005 to February 2006. The first of these was distributed at the 2005 Microsoft Professional Developers Conference, and was subsequently released to beta testers and Microsoft Developer Network subscribers. The builds that followed incorporated most of the planned features for the final product, as well as a number of changes to the user interface, based largely on feedback from beta testers. Windows Vista was deemed feature-complete with the release of the «February CTP», released on February 22, 2006, and much of the remainder of the work between that build and the final release of the product focused on stability, performance, application and driver compatibility, and documentation. Beta 2, released in late May, was the first build to be made available to the general public through Microsoft’s Customer Preview Program. It was downloaded over 5 million times. Two release candidates followed in September and October, both of which were made available to a large number of users.[24]
At the Intel Developer Forum on March 9, 2006, Microsoft announced a change in their plans to support EFI in Windows Vista. The UEFI 2.0 specification (which replaced EFI 1.10) was not completed until early 2006, and at the time of Microsoft’s announcement, no firmware manufacturers had completed a production implementation which could be used for testing. As a result, the decision was made to postpone the introduction of UEFI support to Windows; support for UEFI on 64-bit platforms was postponed until Vista Service Pack 1 and Windows Server 2008 and 32-bit UEFI would not be supported, as Microsoft did not expect many such systems to be built because the market was quickly moving to 64-bit processors.[25][26]
While Microsoft had originally hoped to have the consumer versions of the operating system available worldwide in time for the 2006 holiday shopping season, it announced in March 2006 that the release date would be pushed back to January 2007 in order to give the company—and the hardware and software companies that Microsoft depends on for providing device drivers—additional time to prepare. Because a release to manufacturing (RTM) build is the final version of code shipped to retailers and other distributors, the purpose of a pre-RTM build is to eliminate any last «show-stopper» bugs that may prevent the code from responsibly being shipped to customers, as well as anything else that consumers may find annoying. Thus, it is unlikely that any major new features would be introduced; instead, work would focus on Vista’s fit and finish. In just a few days, developers had managed to drop Vista’s bug count from over 2470 on September 22 to just over 1400 by the time RC2 shipped in early October. However, they still had a way to go before Vista was ready to RTM. Microsoft’s internal processes required Vista’s bug count to drop to 500 or fewer before the product could go into escrow for RTM.[27] For most of the pre-RTM builds, those 32-bit editions are only released.
On June 14, 2006, Windows developer Philip Su posted a blog entry which decried the development process of Windows Vista, stating that «The code is way too complicated, and that the pace of coding has been tremendously slowed down by overbearing process.»[28] The same post also described Windows Vista as having approximately 50 million lines of code, with about 2,000 developers working on the product. During a demonstration of the speech recognition feature new to Windows Vista at Microsoft’s Financial Analyst Meeting on July 27, 2006, the software recognized the phrase «Dear mom» as «Dear aunt». After several failed attempts to correct the error, the sentence eventually became «Dear aunt, let’s set so double the killer delete select all«.[29] A developer with Vista’s speech recognition team later explained that there was a bug with the build of Vista that was causing the microphone gain level to be set very high, resulting in the audio being received by the speech recognition software being «incredibly distorted».
Windows Vista build 5824 (October 17, 2006) was supposed to be the RTM release, but a bug, where the OOBE hangs at the start of the WinSAT Assessment (if upgraded from Windows XP), requiring the user to terminate the msoobe.exe by pressing Shift+F10 to open Command Prompt using either command-line tools or Task Manager prevented this, damaging development and lowering the chance that it would hit its January 2007 deadline.[31]
Development of Windows Vista came to an end when Microsoft announced that it had been finalized on November 8, 2006, and was concluded by co-president of Windows development, Jim Allchin.[32] The RTM’s build number had also jumped to 6000 to reflect Vista’s internal version number, NT 6.0.[33] Jumping RTM build numbers is common practice among consumer-oriented Windows versions, like Windows 98 (build 1998), Windows 98 SE (build 2222), Windows Me (build 3000) or Windows XP (build 2600), as compared to the business-oriented versions like Windows 2000 (build 2195) or Server 2003 (build 3790). On November 16, 2006, Microsoft made the final build available to MSDN and Technet Plus subscribers.[34] A business-oriented Enterprise edition was made available to volume license customers on November 30, 2006.[35] Windows Vista was launched for general customer availability on January 30, 2007.[3]
New or changed features[edit]
Windows Vista introduced several features and functionality not present in its predecessors.
End-user[edit]
- Windows Aero: The new graphical user interface is named Windows Aero, which Jim Allchin stated is an acronym for Authentic, Energetic, Reflective, and Open.[36] Microsoft intended the new interface to be cleaner and more aesthetically pleasing than those of previous Windows versions, featuring new transparencies, live thumbnails, live icons, and animations, thus providing a new level of eye candy. Laptop users report, however, that enabling Aero shortens battery life[37][38] and reduces performance.
- Windows shell: The new Windows shell offers a new range of organization, navigation, and search capabilities: Task panes in Windows Explorer are removed, integrating the relevant task options into the toolbar. A «Favorite links» pane has been added, enabling one-click access to common directories. A search box appears in every Explorer window. The address bar has been replaced with a breadcrumb navigation bar. Icons of certain file types in Windows Explorer are «live» and can be scaled in size up to 256 × 256 pixels. The preview pane allows users to see thumbnails of various files and view the contents of documents. The details pane shows information such as file size and type, and allows viewing and editing of embedded tags in supported file formats. The Start menu has changed as well; incorporating an instant search box, and the All Programs list uses a horizontal scroll bar instead of the cascading flyout menu seen in Windows XP. The word «Start» itself has been removed in favor of a blue orb that bears the Windows logo.
- Windows Search: A new search component of Windows Vista, it features instant search (also known as search as you type), which provides instant search results, thus finding files more quickly than the search features found in previous versions of Windows and can search the contents of recognized file types.[39] Users can search for certain metadata such as name, extension, size, date or attributes.
- Windows Sidebar: A transparent panel, anchored to the right side of the screen, wherein a user can place Desktop Gadgets, which are small applets designed for a specialized purpose (such as displaying the weather or sports scores). Gadgets can also be placed on the desktop.[40]
- Windows Internet Explorer 7: New user interface, tabbed browsing, RSS, a search box, improved printing,[41] Page Zoom, Quick Tabs (thumbnails of all open tabs), Anti-Phishing filter, several new security protection features, Internationalized Domain Name support (IDN), and improved web standards support. IE7 in Windows Vista runs in isolation from other applications in the operating system (protected mode); exploits and malicious software are restricted from writing to any location beyond Temporary Internet Files without explicit user consent.
- Windows Media Player 11, a major revamp of Microsoft’s program for playing and organizing music and video. New features in this version include word wheeling (incremental search or «search as you type»), a new GUI for the media library, photo display and organization, the ability to share music libraries over a network with other Windows Vista machines, Xbox 360 integration, and support for other Media Center Extenders.
- Windows Defender: An antispyware program with several real-time protection agents. It includes a software explorer feature, which provides access to startup programs, and allows one to view currently running software, network-connected applications, and Winsock providers (Winsock LSPs).
- Backup and Restore Center: Includes a backup and restore application that gives users the ability to schedule periodic backups of files on their computer, as well as recovery from previous backups. Backups are incremental, storing only the changes made each time, minimizing disk usage. It also features Complete PC Backup (available only in the Ultimate, Business, and Enterprise editions), which backs up an entire computer as an image onto a hard disk or DVD. Complete PC Backup can automatically recreate a machine setup onto new hardware or hard disk in case of any hardware failures. Complete PC Restore can be initiated from within Windows Vista or from the Windows Vista installation CD if a PC is so corrupt that it cannot start normally from the hard disk.
- Windows Mail: A replacement for Outlook Express that includes a new mail store that improves stability,[42] and features integrated instant search. It has a Phishing Filter like Internet Explorer 7 and Junk mail filtering that is enhanced through regular updates via Windows Update.[43]
- Windows Calendar is a new calendar and task application that integrates with Windows Contacts and Windows Mail. It is compatible with various calendar file types, such as the popular iCalendar.
- Windows Photo Gallery, a photo and movie library management application. It can import from digital cameras, tag and rate individual items, adjust colors and exposure, create and display slideshows (with pan and fade effects) through Direct3D and burn slideshows to a DVD.
- Windows DVD Maker, a companion program to Windows Movie Maker that provides the ability to create video DVDs based on a user’s content. Users can design a DVD with title, menus, video, soundtrack, pan and zoom motion effects on pictures or slides.
- Windows Media Center, which was previously exclusively bundled in a separate edition of Windows XP, known as Windows XP Media Center Edition, has been incorporated into the Home Premium and Ultimate editions of Windows Vista.
- Games: Most of the standard computer games included in previous versions of Windows have been redesigned to showcase Vista’s new graphical capabilities. New games available in Windows Vista are Chess Titans (3D Chess game), Mahjong Titans (3D Mahjong game), and Purble Place (a small collection of games, oriented towards younger children, including a matching game, a cake-creator game, and a dress-up puzzle game). Purble Place is the only one of the new games available in the Windows Vista Home Basic edition. InkBall is available for Home Premium (or better) users.
- Games Explorer: A new special folder called «Games» exposes installed video games and information about them. These metadata may be updated from the Internet.[44]
- Windows Mobility Center is a control panel that centralizes the most relevant information related to mobile computing (brightness, sound, battery level/power scheme selection, wireless network, screen orientation, presentation settings, etc.).
- Windows Fax and Scan Allows computers with fax modems to send and receive fax documents, as well as scan documents. It is not available in the Home editions of Windows Vista, but is available in the Business, Enterprise, and Ultimate editions.
- Windows Meeting Space replaces NetMeeting. Users can share applications (or their entire desktop) with other users on the local network, or over the Internet using peer-to-peer technology (higher editions than Starter and Home Basic can take advantage of hosting capabilities, Starter and Home Basic editions are limited to «join» mode only)
- Windows HotStart enables compatible computers to start applications directly from operating system startup or resume by the press of a button—this enables what Microsoft has described as appliance-like availability, which allows computers to function in a manner similar to a consumer electronics device such as a DVD player;[45] the feature was also designed to provide the instant-on feature availability that is traditionally associated with mobile devices.[46] While Microsoft has emphasized multimedia scenarios with Windows HotStart,[47] a user can configure this feature so that a button launches a preferred application.[48]
- Shadow Copy automatically creates daily backup copies of files and folders. Users can also create «shadow copies» by setting a System Protection Point using the System Protection tab in the System control panel. The user can view multiple versions of a file throughout a limited history and be allowed to restore, delete, or copy those versions. This feature is available only in the Business, Enterprise, and Ultimate editions of Windows Vista and is inherited from Windows Server 2003.[49]
- Windows Update: Software and security updates have been simplified,[50] now operating solely via a control panel instead of as a web application. Windows Mail’s spam filter and Windows Defender’s definitions are updated automatically via Windows Update. Users who choose the recommended setting for Automatic Updates will have the latest drivers installed and available when they add a new device.
- Parental controls: Allows administrators to monitor and restrict user activity, as well as control which websites, programs, and games each Standard user can use and install. This feature is not included in the Business or Enterprise editions of Vista.
- Windows SideShow: Enables the auxiliary displays on newer laptops or supported Windows Mobile devices. It is meant to be used to display device gadgets while the computer is on or off.
- Speech recognition is integrated into Vista.[51] It features a redesigned user interface and configurable command-and-control commands. Unlike the Office 2003 version, which works only in Office and WordPad, Speech Recognition in Windows Vista works for any accessible application. In addition, it currently supports several languages: British and American English, Spanish, French, German, Chinese (Traditional and Simplified), and Japanese.
- New fonts, including several designed for screen reading, and improved Chinese (Yahei, JhengHei), Japanese (Meiryo), and Korean (Mulgan) fonts. ClearType has also been enhanced and enabled by default.
- Improved audio controls allow the system-wide volume or volume of individual audio devices and even individual applications to be controlled separately. New audio functionalities such as room correction, bass management, speaker fill, and headphone virtualization have also been incorporated.
- Problem Reports and Solutions, a feature that allows users to check for solutions to problems or view previously sent problems for any solutions or additional information, if available.Windows System Assessment Tool is a tool used to benchmark system performance. Software such as games can retrieve this rating and modify its own behavior at runtime to improve performance. The benchmark tests CPU, RAM, 2-D and 3-D graphics acceleration, graphics memory and hard disk space.[52][53]
- Windows Ultimate Extras: The Ultimate edition of Windows Vista provides, via Windows Update, access to some additional features. These are a collection of additional MUI language packs, Texas Hold ‘Em (a Poker game) and Microsoft Tinker (a strategy game where the character is a robot), BitLocker and EFS enhancements that allow users to back up their encryption key online in a Digital Locker, and Windows Dreamscene, which enables the use of videos in MPEG and WMV formats as the desktop background. On April 21, 2008, Microsoft launched two more Ultimate Extras; three new Windows sound schemes, and a content pack for Dreamscene. Various DreamScene Content Packs have been released since the final version of DreamScene was released.
- Reliability and Performance Monitor includes various tools for tuning and monitoring system performance and resources activities of CPU, disks, network, memory and other resources. It shows the operations on files, the opened connections, etc.[54]
- Disk Management: The Logical Disk Manager in Windows Vista supports shrinking and expanding volumes on-the-fly.[55]
- Windows Anytime Upgrade: is a program that allows a user to upgrade their computer running Vista to a higher edition. For example, a computer running Windows Vista Home Basic can be upgraded to Home Premium or better. Anytime Upgrade permits users to upgrade without having their programs and data erased, and is cheaper than replacing the existing installation of Windows. Anytime Upgrade is no longer available for Vista.[56]
- Digital Locker Assistant: A program that facilitated access to downloads and purchases from the Windows Marketplace distribution platform.[57] Apps purchased from Windows Marketplace are managed by Microsoft Account credentials, which are used to access a user’s digital locker that stores the app and its associated information (e.g., licenses) off-site.[58]
Core[edit]
Vista includes technologies such as ReadyBoost[59] and ReadyDrive, which employ fast flash memory (located on USB flash drives and hybrid hard disk drives) to improve system performance by caching commonly used programs and data. This manifests itself in improved battery life on notebook computers as well, since a hybrid drive can be spun down when not in use.[60] Another new technology called SuperFetch utilizes machine learning techniques to analyze usage patterns to allow Windows Vista to make intelligent decisions about what content should be present in system memory at any given time. It uses almost all the extra RAM as disk cache.[61] In conjunction with SuperFetch, an automatic built-in Windows Disk Defragmenter makes sure that those applications are strategically positioned on the hard disk where they can be loaded into memory very quickly with the least physical movement of the hard disk’s read-write heads.[62]
As part of the redesign of the networking architecture, IPv6 has been fully incorporated into the operating system[63] and a number of performance improvements have been introduced, such as TCP window scaling.[64] Earlier versions of Windows typically needed third-party wireless networking software to work properly, but this is not the case with Vista, which includes more comprehensive wireless networking support.[65]
For graphics, Vista introduces a new Windows Display Driver Model[66] and a major revision to Direct3D. The new driver model facilitates the new Desktop Window Manager, which provides the tearing-free desktop and special effects that are the cornerstones of Windows Aero. Direct3D 10, developed in conjunction with major graphics card manufacturers, is a new architecture with more advanced shader support, and allows the graphics processing unit to render more complex scenes without assistance from the CPU. It features improved load balancing between CPU and GPU and also optimizes data transfer between them.[67] WDDM also provides video content playback that rivals typical consumer electronics devices. It does this by making it easy to connect to external monitors, providing for protected HD video playback, and increasing overall video playback quality. For the first time in Windows, graphics processing unit (GPU) multitasking is possible, enabling users to run more than one GPU-intensive application simultaneously.[68]
At the core of the operating system, many improvements have been made to the memory manager, process scheduler and I/O scheduler. The Heap Manager implements additional features such as integrity checking in order to improve robustness and defend against buffer overflow security exploits, although this comes at the price of breaking backward compatibility with some legacy applications.[69] A Kernel Transaction Manager has been implemented that enables applications to work with the file system and Registry using atomic transaction operations.[70]
[edit]
Improved security was a primary design goal for Vista.[71] Microsoft’s Trustworthy Computing initiative, which aims to improve public trust in its products, has had a direct effect on its development. This effort has resulted in a number of new security and safety features and an Evaluation Assurance Level rating of 4+.[72][73]
User Account Control, or UAC is perhaps the most significant and visible of these changes. UAC is a security technology that makes it possible for users to use their computer with fewer privileges by default, to stop malware from making unauthorized changes to the system. This was often difficult in previous versions of Windows, as the previous «limited» user accounts proved too restrictive and incompatible with a large proportion of application software, and even prevented some basic operations such as looking at the calendar from the notification tray. In Windows Vista, when an action is performed that requires administrative rights (such as installing/uninstalling software or making system-wide configuration changes), the user is first prompted for an administrator name and password; in cases where the user is already an administrator, the user is still prompted to confirm the pending privileged action. Regular use of the computer such as running programs, printing, or surfing the Internet does not trigger UAC prompts. User Account Control asks for credentials in a Secure Desktop mode, in which the entire screen is dimmed, and only the authorization window is active and highlighted. The intent is to stop a malicious program from misleading the user by interfering with the authorization window, and to hint to the user about the importance of the prompt.[74]
Testing by Symantec Corporation has proven the effectiveness of UAC. Symantec used over 2,000 active malware samples, consisting of backdoors, keyloggers, rootkits, mass mailers, trojan horses, spyware, adware, and various other samples. Each was executed on a default Windows Vista installation within a standard user account. UAC effectively blocked over 50 percent of each threat, excluding rootkits. 5 percent or less of the malware that evaded UAC survived a reboot.[75][76]
Internet Explorer 7’s new security and safety features include a phishing filter, IDN with anti-spoofing capabilities, and integration with system-wide parental controls. For added security, ActiveX controls are disabled by default. Also, Internet Explorer operates in a protected mode, which operates with lower permissions than the user and runs in isolation from other applications in the operating system, preventing it from accessing or modifying anything besides the Temporary Internet Files directory.[77] Microsoft’s anti-spyware product, Windows Defender, has been incorporated into Windows, protecting against malware and other threats. Changes to various system configuration settings (such as new auto-starting applications) are blocked unless the user gives consent.
Whereas prior releases of Windows supported per-file encryption using Encrypting File System, the Enterprise and Ultimate editions of Vista include BitLocker Drive Encryption, which can protect entire volumes, notably the operating system volume. However, BitLocker requires approximately a 1.5-gigabyte partition to be permanently not encrypted and to contain system files for Windows to boot. In normal circumstances, the only time this partition is accessed is when the computer is booting, or when there is a Windows update that changes files in this area, which is a legitimate reason to access this section of the drive. The area can be a potential security issue, because a hexadecimal editor (such as dskprobe.exe), or malicious software running with administrator and/or kernel level privileges would be able to write to this «Ghost Partition» and allow a piece of malicious software to compromise the system, or disable the encryption. BitLocker can work in conjunction with a Trusted Platform Module (TPM) cryptoprocessor (version 1.2) embedded in a computer’s motherboard, or with a USB key.[78] However, as with other full disk encryption technologies, BitLocker is vulnerable to a cold boot attack, especially where TPM is used as a key protector without a boot PIN being required too.[79]
A variety of other privilege-restriction techniques are also built into Vista. An example is the concept of «integrity levels» in user processes, whereby a process with a lower integrity level cannot interact with processes of a higher integrity level and cannot perform DLL–injection to processes of a higher integrity level. The security restrictions of Windows services are more fine-grained, so that services (especially those listening on the network) cannot interact with parts of the operating system they do not need to. Obfuscation techniques such as address space layout randomization are used to increase the amount of effort required of malware before successful infiltration of a system. Code integrity verifies that system binaries have not been tampered with by malicious code.
As part of the redesign of the network stack, Windows Firewall has been upgraded, with new support for filtering both incoming and outgoing traffic. Advanced packet filter rules can be created that can grant or deny communications to specific services.
The 64-bit versions of Vista require that all device drivers be digitally signed, so that the creator of the driver can be identified.[80]
System management[edit]
While much of the focus of Vista’s new capabilities highlighted the new user interface,[81] security technologies, and improvements to the core operating system, Microsoft also adding new deployment and maintenance features:
- The Windows Imaging Format (WIM) provides the cornerstone of Microsoft’s new deployment and packaging system. WIM files, which contain a HAL-independent image of Windows Vista, can be maintained and patched without having to rebuild new images. Windows Images can be delivered via Systems Management Server or Business Desktop Deployment technologies. Images can be customized and configured with applications then deployed to corporate client personal computers using little to no touch by a system administrator. ImageX is the Microsoft tool used to create and customize images.
- Windows Deployment Services replaces Remote Installation Services for deploying Vista and prior versions of Windows.
- Approximately 700 new Group Policy settings have been added, covering most aspects of the new features in the operating system, as well as significantly expanding the configurability of wireless networks, removable storage devices, and user desktop experience. Vista also introduced an XML-based format (ADMX) to display registry-based policy settings, making it easier to manage networks that span geographic locations and different languages.[82]
- Services for UNIX, renamed as «Subsystem for UNIX-based Applications», comes with the Enterprise and Ultimate editions of Vista. Network File System (NFS) client support is also included.
- Multilingual User Interface–Unlike previous versions of Windows (which required the loading of language packs to provide local-language support), Windows Vista Ultimate and Enterprise editions support the ability to dynamically change languages based on the logged-on user’s preference.
- Wireless Projector support
Developer[edit]
Windows Vista includes a large number of new application programming interfaces. Chief among them is the inclusion of version 3.0 of the .NET Framework, which consists of a class library and Common Language Runtime. Version 3.0 includes four new major components:[83]
- Windows Presentation Foundation is a user interface subsystem and framework based vector graphics, which makes use of 3D computer graphics hardware and Direct3D technologies. It provides the foundation for building applications and blending application UI, documents, and media content. It is the successor to Windows Forms.
- Windows Communication Foundation is a service-oriented messaging subsystem that enables applications and systems to interoperate locally or remotely using Web services.
- Windows Workflow Foundation provides task automation and integrated transactions using workflows. It is the programming model, engine, and tools for building workflow-enabled applications on Windows.
- Windows CardSpace is a component that securely stores digital identities of a person, and provides a unified interface for choosing the identity for a particular transaction, such as logging into a website.[84]
These technologies are also available for Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 to facilitate their introduction to and usage by developers and end-users.
There are also significant new development APIs in the core of the operating system, notably the completely re-designed audio, networking, print, and video interfaces, major changes to the security infrastructure, improvements to the deployment and installation of applications («ClickOnce» and Windows Installer 4.0), new device driver development model («Windows Driver Foundation»), Transactional NTFS, mobile computing API advancements (power management, Tablet PC Ink support, SideShow) and major updates to (or complete replacements of) many core subsystems such as Winlogon and CAPI.
There are some issues for software developers using some of the graphics APIs in Vista. Games or programs built solely on the Windows Vista-exclusive version of DirectX, version 10, cannot work on prior versions of Windows, as DirectX 10 is not available for previous Windows versions. Also, games that require the features of D3D9Ex, the updated implementation of DirectX 9 in Windows Vista are also incompatible with previous Windows versions.[85] According to a Microsoft blog, there are three choices for OpenGL implementation on Vista. An application can use the default implementation, which translates OpenGL calls into the Direct3D API and is frozen at OpenGL version 1.4, or an application can use an Installable Client Driver (ICD), which comes in two flavors: legacy and Vista-compatible. A legacy ICD disables the Desktop Window Manager, a Vista-compatible ICD takes advantage of a new API, and is fully compatible with the Desktop Window Manager.[86] At least two primary vendors, ATI and NVIDIA provided full Vista-compatible ICDs.[87] However, hardware overlay is not supported, because it is considered as an obsolete feature in Vista. ATI and NVIDIA strongly recommend using compositing desktop/Framebuffer Objects for same functionality.[88]
Installation[edit]
Windows Vista is the first Microsoft operating system:
- To use DVD-ROM media for installation[89]
- That can be installed only on a partition formatted with the NTFS file system[90]
- That provides support for loading drivers for SCSI, SATA and RAID controllers from any source in addition to floppy disks prior to its installation[91]
- That can be installed on and booted from systems with GPT disks and UEFI firmware[a][93]
Unification of OEM and retail installation[edit]
Windows Vista unifies the previously separate OEM and retail distributions of Microsoft Windows; a license for the edition purchased determines which version of Windows Vista is eligible for installation, regardless of its originating source. OEM and retail versions of Windows before Windows Vista were maintained separately on optical media—users with a manufacturer-supplied disc could not use a retail license during installation, and users with a retail disc could not use an OEM license during installation.[94]
Removed features[edit]
Some notable Windows XP features and components have been replaced or removed in Windows Vista, including several shell and Windows Explorer features, multimedia features, networking related functionality, Windows Messenger, NTBackup, the network Windows Messenger service, HyperTerminal, MSN Explorer, Active Desktop, and the replacement of NetMeeting with Windows Meeting Space. As a result, BOOTMGR in Windows Vista and later versions replaces the functions performed by NTLDR in all Windows NT versions up to Windows XP and directly executes winload.exe, the system loader used to continue the Windows boot process. Windows Vista also does not include the Windows XP «Luna» visual theme, or most of the classic color schemes that have been part of Windows since the Windows 3.x era. The «Hardware profiles» startup feature has also been removed, along with support for older motherboard technologies like the EISA bus, APM and game port support (though on the 32-bit version game port support can be enabled by applying an older driver).[95] IP over FireWire (TCP/IP over IEEE 1394) has been removed as well.[96] The IPX/SPX protocol has also been removed, although it can be enabled by a third-party plug-in.[97]
Support lifecycle[edit]
Support for the original release of Windows Vista (without a service pack) ended on April 13, 2010.[98] Service Pack 1 reached end of support on July 12, 2011, over three years after its general availability.[99]
Mainstream support for Windows Vista officially ended on April 10, 2012.[6] The «Extended Support» phase would last for the next 5 years, until April 11, 2017.[6] Microsoft is no longer offering no-charge incident support, warranty claims, or design fixes for the operating system. For IT pros or users who needed to make specific fixes to the commercial Windows code, Microsoft required an extended hotfix agreement, which provided an additional 90 days from April 10, 2012.
As part of the Extended Support phase, Vista users were still able to get security updates, and could still pay for support per incident, per-hour, or in other ways. Microsoft also made Windows Vista product information available through its online Knowledge Base. On April 11, 2017, support for Windows Vista ended.
Editions[edit]
Windows Vista shipped in six different editions.[100] These are roughly divided into two target markets, consumer and business, with editions varying to cater to specific sub-markets. For consumers, there are three editions, with two available for economically more developed countries. Windows Vista Starter edition is aimed at low-powered computers with availability only in emerging markets. Windows Vista Home Basic is intended for budget users. Windows Vista Home Premium covers the majority of the consumer market and contains applications for creating and using multimedia. The home editions cannot join a Windows Server domain. For businesses, there are three editions as well. Windows Vista Business is specifically designed for small and medium-sized enterprises,[101] while Windows Vista Enterprise[102] is only available to customers participating in Microsoft’s Software Assurance program. Windows Vista Ultimate contains the complete feature-set of both the Home and Business (combination of both Home Premium and Enterprise) editions, as well as a set of Windows Ultimate Extras, and is aimed at enthusiasts.
All editions except Windows Vista Starter support both 32-bit (x86) and 64-bit (x64) processor architectures.
In the European Union, Home Basic N and Business N variants are also available. These come without Windows Media Player, due to EU sanctions brought against Microsoft for violating anti-trust laws. Similar sanctions exist in South Korea.
Visual styles[edit]
A comparison of the four visual styles included in Windows Vista
Windows Vista has four distinct visual styles.[103][104]
- Windows Aero
- Vista’s default visual style, Windows Aero, is built on a desktop composition engine called Desktop Window Manager. Windows Aero introduces support for translucency effects (Glass), window thumbnails on the taskbar, window animations, and other visual effects (for example Windows Flip 3D), and is intended for mainstream and high-end video cards. To enable these features, the contents of every open window are stored in video memory to facilitate tearing-free movement of windows. As such, Windows Aero has significantly higher hardware requirements than its predecessors: systems running Vista must have video card drivers compatible with the Windows Display Driver Model (WDDM), and the minimum graphics memory required is 128 MB, depending on the resolution used.[105]
Windows Aero is not included in the Starter and Home Basic editions. A variant of Windows Aero, dubbed Windows Vista Standard, lacking the glass effects, window animations, and other advanced graphical effects, is included in Home Basic.[106]
- Windows Vista Basic
- This visual style does not employ the Desktop Window Manager; as such, it does not feature transparency or translucency, window animation, Windows Flip 3D or any of the functions provided by the DWM. It is the default visual style on Windows Vista Starter and on systems without WDDM-compatible display drivers, and has similar video card requirements to Windows XP. Before Service Pack 1, a machine that failed Windows Genuine Advantage validation would also default to this visual style.[107]
- Windows Standard
- The Windows Standard and Windows Classic visual styles reprise the user interface of Windows 9x, Windows 2000 and Microsoft’s Windows Server line of operating systems. As with previous versions of Windows, this visual style supports custom color schemes, which are collections of color settings. Windows Vista includes four high-contrast color schemes and the default color schemes from Windows 98 (titled «Windows Classic») and Windows 2000/Windows Me (titled «Windows Standard»).[106]
Hardware requirements[edit]
Computers with a «Certified for Windows Vista» sticker met WHQL Testing requirements and supported new features such as Windows Aero.
Computers capable of running Windows Vista are classified as Vista Capable and Vista Premium Ready.[108] A Vista Capable or equivalent PC is capable of running all editions of Windows Vista although some of the special features and high-end graphics options may require additional or more advanced hardware. A Vista Premium Ready PC can take advantage of Vista’s high-end features.[109]
Windows Vista’s Basic and Classic interfaces work with virtually any graphics hardware that supports Windows XP or 2000; accordingly, most discussion around Vista’s graphics requirements centers on those for the Windows Aero interface. As of Windows Vista Beta 2, the NVIDIA GeForce 6 series and later, the ATI Radeon 9500 and later, Intel’s GMA 950 and later integrated graphics, and a handful of VIA chipsets and S3 Graphics discrete chips are supported. Although originally supported, the GeForce FX 5 series has been dropped from newer drivers from NVIDIA. The last driver from NVIDIA to support the GeForce FX series on Vista was 96.85.[110][111] Microsoft offered a tool called the Windows Vista Upgrade Advisor[109] to assist Windows XP and Vista users in determining what versions of Windows their machine is capable of running. The required server connections for this utility are no longer available. Although the installation media included in retail packages is a 32-bit DVD, customers needing a CD-ROM or customers who wish for a 64-bit install media can acquire this media through the Windows Vista Alternate Media program.[112] The Ultimate edition includes both 32-bit and 64-bit media.[113] The digitally downloaded version of Ultimate includes only one version, either 32-bit or 64-bit, from Windows Marketplace.
| Component of PC | Minimum required | Recommended |
|---|---|---|
| Processor | 800 MHz | 1 GHz |
| Memory | 512 MB (384 MB for Starter edition) |
1 GB |
| Graphics card | Super VGA | WDDM 1.0-compliant 32 bits per pixel DirectX 9.0 support Pixel Shader 2.0 support |
| Graphics memory | — | 128 MB |
| Total HDD capacity | 20 GB | 40 GB |
| Free HDD space | 15 GB | 15 GB |
| Optical drives | CD-ROM drive | DVD-ROM drive |
| Others | — | TV tuner card (Premium, Ultimate) Touchscreen (Premium, Business, Ultimate) USB flash drive (Ultimate) Trusted Platform Module (Ultimate) |
Physical memory limits[edit]
The maximum amount of RAM that Windows Vista can support varies, depending on both its edition and its processor architecture, as shown in the table.[116]
| Edition | Processor architecture | |
|---|---|---|
| IA-32 | x64 | |
| Ultimate | 4 GB | 128 GB |
| Enterprise | ||
| Business | ||
| Home Premium | 16 GB | |
| Home Basic | 8 GB | |
| Starter | 1 GB | — |
Processor limits[edit]
The maximum number of logical processors[117] in a PC that Windows Vista supports is: 32[118] for 32-bit; 64[119] for 64-bit.[120]
The maximum number of physical processors in a PC that Windows Vista supports is: 2 for Business, Enterprise, and Ultimate, and 1 for Starter, Home Basic, and Home Premium.[121]
Updates[edit]
Microsoft occasionally releases updates such as service packs for its Windows operating systems to fix bugs, improve performance and add new features.
Service Pack 1[edit]
Windows Vista Service Pack 1 (SP1) was released on February 4, 2008, alongside Windows Server 2008 to OEM partners, after a five-month beta test period. The initial deployment of the service pack caused a number of machines to continually reboot, rendering the machines unusable.[122] This temporarily caused Microsoft to suspend automatic deployment of the service pack until the problem was resolved. The synchronized release date of the two operating systems reflected the merging of the workstation and server kernels back into a single code base for the first time since Windows 2000. MSDN subscribers were able to download SP1 on February 15, 2008. SP1 became available to current Windows Vista users on Windows Update and the Download Center on March 18, 2008.[123][124][125] Initially, the service pack only supported five languages – English, French, Spanish, German and Japanese. Support for the remaining 31 languages was released on April 14, 2008.[126]
A white paper, published by Microsoft on August 29, 2007, outlined the scope and intent of the service pack, identifying three major areas of improvement: reliability and performance, administration experience, and support for newer hardware and standards.[127]
One area of particular note is performance. Areas of improvement include file copy operations, hibernation, logging off on domain-joined machines, JavaScript parsing in Internet Explorer, network file share browsing,[124] Windows Explorer ZIP file handling,[128] and Windows Disk Defragmenter.[129] The ability to choose individual drives to defragment is being reintroduced as well.[124]
Service Pack 1 introduced support for some new hardware and software standards, notably the exFAT file system,[124] 802.11n wireless networking, IPv6 over VPN connections, and the Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol.[130]
Booting a system using Extensible Firmware Interface on x64 systems was also introduced;[124] this feature had originally been slated for the initial release of Vista but was delayed due to a lack of compatible hardware at the time. Booting from a GUID Partition Table–based hard drive greater than 2.19 TB is supported (x64 only).[131][132]
Two areas have seen changes in SP1 that have come as the result of concerns from software vendors. One of these is desktop search; users will be able to change the default desktop search program to one provided by a third party instead of the Microsoft desktop search program that comes with Windows Vista, and desktop search programs will be able to seamlessly tie in their services into the operating system.[125] These changes come in part due to complaints from Google, whose Google Desktop Search application was hindered by the presence of Vista’s built-in desktop search. In June 2007, Google claimed that the changes being introduced for SP1 «are a step in the right direction, but they should be improved further to give consumers greater access to alternate desktop search providers».[133] The other area of note is a set of new security APIs being introduced for the benefit of antivirus software that currently relies on the unsupported practice of patching the kernel (see Kernel Patch Protection).[134][135]
An update to DirectX 10, named DirectX 10.1,[124] marked mandatory several features that were previously optional in Direct3D 10 hardware. Graphics cards will be required to support DirectX 10.1.[136] SP1 includes a kernel (6001.18000) that matches the version shipped with Windows Server 2008.[137]
The Group Policy Management Console (GPMC) was replaced by the Group Policy Object Editor. An updated downloadable version of the Group Policy Management Console was released soon after the service pack.
SP1 enables support for hotpatching, a reboot-reduction servicing technology designed to maximize uptime. It works by allowing Windows components to be updated (or «patched») while they are still in use by a running process. Hotpatch-enabled update packages are installed via the same methods as traditional update packages, and will not trigger a system reboot.[138]
Service Pack 2[edit]
Service Pack 2 for Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008 was released through different channels between April[139] and June 2009, one year after the release of Windows Vista SP1, and four months before the release of Windows 7.[5] In addition to a number of security and other fixes, a number of new features have been added. However, it did not include Internet Explorer 8, but instead was included in Windows 7, which was released four months after Vista SP2.[140][141]
- Windows Search 4 (available for SP1 systems as a standalone update)
- Feature Pack for Wireless adds support for Bluetooth 2.1
- Windows Feature Pack for Storage enables the data recording onto Blu-ray media
- Windows Connect Now (WCN) to simplify Wi-Fi configuration
- Improved support for resuming with active Wi-Fi connections
- Improved support for eSATA drives
- The limit of 10 half-open, outgoing TCP connections introduced in Windows XP SP2 was removed
- Enables the exFAT file system to support UTC timestamps, which allows correct file synchronization across time zones
- Support for ICCD/CCID smart cards
- Support for VIA 64-bit CPUs
- Improved performance and responsiveness with the RSS feeds sidebar
- Improves audio and video performance for streaming high-definition content
- Improves Windows Media Center (WMC) in content protection for TV[142]
- Provides an improved power management policy that is approximately 10% more efficient than the original with the default policies[143]
Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008 share a single service pack binary, reflecting the fact that their code bases were joined with the release of Server 2008.[140] Service Pack 2 is not a cumulative update meaning that Service Pack 1 must be installed first.
Platform Update[edit]
The Platform Update for Windows Vista was released on October 27, 2009. It includes major new components that shipped with Windows 7, as well as updated runtime libraries.[144][145] It requires Service Pack 2 of Windows Vista or Windows Server 2008 and is listed on Windows Update as a Recommended download.
The Platform Update allows application developers to target both Windows Vista and Windows 7. It consists of the following components:
- Windows Graphics runtime: Direct2D, DirectWrite, Direct3D 11, DXGI 1.1, and WARP
- Updates to Windows Imaging Component
- Updates to XPS Print API, XPS Document API and XPS Rasterization Service
- Windows Automation API (updates to MSAA and UI Automation)
- Windows Portable Devices Platform (adds support for MTP over Bluetooth and MTP Device Services)
- Windows Ribbon API
- Windows Animation Manager library
Some updates are available as separate releases for both Windows XP and Windows Vista:
- Windows Management Framework: Windows PowerShell 2.0, Windows Remote Management 2.0, BITS 4.0
- Remote Desktop Connection 7.0 (RDP7) client
Although extensive, the Platform Update does not bring Windows Vista to the level of features and performance offered by Windows 7.[146] For example, even though Direct3D 11 runtime will be able to run on D3D9-class hardware and WDDM drivers using «feature levels» first introduced in Direct3D 10.1, Desktop Window Manager has not been updated to use Direct3D 10.1.[146]
In July 2011, Microsoft released the Platform Update Supplement for Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008, which contains several bug fixes and performance improvements.[147]
Out-of-band patches[edit]
BlueKeep patch[edit]
Microsoft has released an update for Windows Vista SP2 to resolve the BlueKeep security vulnerability (CVE-2019-0708), which affects the Remote Desktop Protocol in older Windows versions.[148] Subsequent related flaws, CVE-2019-1181, CVE-2019-1182, CVE-2019-1222 and CVE-2019-1226 (collectively known as DejaBlue) do not affect Windows Vista or earlier versions of Windows.[149] The installation of this patch changed the build number of Windows Vista from 6002 to 6003.[b]
Text Services Framework patch[edit]
The Text Services Framework was compromised by a privilege escalation vulnerability (CVE-2019-1162) that could allow attackers to use the framework to perform privileged operations, run software, or send messages to privileged processes from unprivileged processes—bypassing security features such as sandboxes or User Account Control. Microsoft remediated issues related to this vulnerability with the release of a patch in August 2019 for Windows Vista SP2, Windows Server 2008 SP2, and later versions of Windows.[152]
Malware Protection Engine patch[edit]
A vulnerability related to Windows Defender that affected the way the Malware Protection Engine operates (CVE-2017-0290) was reported in May 2017. If Windows Defender scanned a specially crafted file, it would lead to memory corruption, potentially allowing an attacker to control the affected machine or perform arbitrary code execution in the context of LocalSystem; the vulnerability was exacerbated by the default real-time protection settings of Windows Defender, which were configured to automatically initiate malware scans at regular intervals. The first version of the Protection Engine affected by the vulnerability is Version 1.1.13701.0—subsequent versions of the engine are unaffected. Microsoft released a patch to address the issue.[153]
Marketing campaign[edit]
The Mojave Experiment[edit]
In July 2008, Microsoft introduced a web-based advertising campaign called the «Mojave Experiment», which depicts a group of people who are asked to evaluate the newest operating system from Microsoft, calling it Windows ‘Mojave’. Participants are first asked about Vista, if they have used it, and their overall satisfaction with Vista on a scale of 1 to 10. They are then shown a demo of some of the new operating system’s features, and asked their opinion and satisfaction with it on the same 1 to 10 scale. After respondents rate «Mojave», they are then told that they were shown a demo of Windows Vista. The object was to test «A theory: If people could see Windows Vista firsthand, they would like it.» According to Microsoft, the initial sample of respondents rated Vista an average of 4.4 out of 10, and Mojave received an average of 8.5, with no respondents rating Mojave lower than they originally rated Windows Vista before the demo.[154][155] The «experiment» has been criticized for deliberate selection of positive statements and not addressing all aspects of Vista.[156] During the launch of Vista, Microsoft also made a lime flavored sparkling water available to campus visitors and developers.[157]
Reception[edit]
Windows Vista received mixed to negative reviews at the time of its release and throughout its lifespan, mainly for its much higher hardware requirements and perceived slowness compared to Windows XP.[158][159]
It received generally positive reviews from PC gamers who praised the advantages brought by DirectX 10, which allowed for better gaming performance and more realistic graphics, as well as support for many new capabilities featured in new GPUs.[160] However, many DirectX 9 games initially ran with lower frame rates compared to when they were run on Windows XP. In mid-2008, benchmarks suggested that the SP1 update improved performance to be on par with (or better than) Windows XP in terms of game performance.[161]
Peter Bright of Ars Technica wrote that, despite its delays and feature cuts, Windows Vista was «a huge evolution in the history of the NT platform […] The fundamental changes to the platform are of a scale not seen since the release of NT [3.1; the first version].»[162] In a continuation of his previous assessment, Bright stated that «Vista is not simply XP with a new skin; core parts of the OS have been radically overhauled, and virtually every area has seen significant refinement. In terms of the magnitude and extent of these changes, Vista represents probably the biggest leap that the NT platform has ever seen. Never before have significant subsystems been gutted and replaced in the way they are in Vista.»[163] Many others in the tech industry echoed these sentiments at the time, directing praise towards the massive amount of technical features new to Windows Vista.[164]
Windows Vista received the «Best of CES» award at the Consumer Electronics Show in 2007.[165][166]
In its first year of availability, PC World rated it as the biggest tech disappointment of 2007,[167] and it was rated by InfoWorld as No. 2 of Tech’s all-time 25 flops.[168] Microsoft’s then much smaller competitor Apple noted that, despite Vista’s far greater sales, its own operating system did not seem to have suffered after its release, and would later invest in advertising mocking Vista’s unpopularity with users.[169][170]
Computer manufacturers such as Dell, Lenovo, and Hewlett-Packard released their newest computers with Windows Vista pre-installed; however, after the negative reception of the operating system, they also began selling their computers with Windows XP CDs included because of a drop in sales.[171]
Sales[edit]
A Gartner research report predicted that Vista business adoption in 2008 would overtake that of XP during the same time frame (21.3% vs. 16.9%)[172] while IDC had indicated that the launch of Windows Server 2008 served as a catalyst for the stronger adoption rates.[173][174] As of January 2009, Forrester Research had indicated that almost one third of North American and European corporations had started deploying Vista.[175] At a May 2009 conference, a Microsoft Vice President said «Adoption and deployment of Windows Vista has been slightly ahead of where we had been with XP» for big businesses.[176][177]
Within its first month, 20 million copies of Vista were sold, double the amount of Windows XP sales within its first month in October 2001, five years earlier.[178] Shortly after however, due to Vista’s relatively low adoption rates and continued demand for Windows XP, Microsoft decided to sell Windows XP until June 30, 2008, instead of the previously planned date of January 31, 2008.[179] There were reports of Vista users «downgrading» their operating systems back to XP, as well as reports of businesses planning to skip Vista.[180] A study conducted by ChangeWave in March 2008 showed that the percentage of corporate users who were «very satisfied» with Vista was dramatically lower than other operating systems, with Vista at 8%, compared to the 40% who said they were «very satisfied» with Windows XP.[181]
The internet-usage market share for Windows Vista after two years of availability, in January 2009, was 20.61%. This figure combined with World Internet Users and Population Stats yielded a user base of roughly 330 million,[182] which exceeded Microsoft’s two-year post launch expectations by 130 million.[183] The internet user base reached before the release of its successor (Windows 7) was roughly 400 million according to the same statistical sources.[citation needed]
Criticism[edit]
Windows Vista received mixed reviews. Criticism targets include protracted development time (5–6 years), more restrictive licensing terms, the inclusion of several technologies aimed at restricting the copying of protected digital media,[184] and the usability of the new User Account Control security technology. Moreover, some concerns have been raised about many PCs meeting «Vista Premium Ready» hardware requirements and Vista’s pricing.
Hardware requirements[edit]
While in 2005 Microsoft claimed «nearly all PCs on the market today will run Windows Vista»,[185] the higher requirements of some of the «premium» features, such as the Aero interface, affected many upgraders. According to the UK newspaper The Times in May 2006, the full set of features «would be available to less than 5 percent of Britain’s PC market»; however, this prediction was made several months before Vista was released.[186] This continuing lack of clarity eventually led to a class action against Microsoft as people found themselves with new computers that were unable to use the new software to its full potential despite the assurance of «Vista Capable» designations.[187] The court case has made public internal Microsoft communications that indicate that senior executives have also had difficulty with this issue. For example, Mike Nash (Corporate Vice President, Windows Product Management) commented, «I now have a $2,100 e-mail machine» because of his laptop’s lack of an appropriate graphics chip so hobbled Vista.[188]
Licensing[edit]
Criticism of upgrade licenses pertaining to Windows Vista Starter through Home Premium was expressed by Ars Technica‘s Ken Fisher, who noted that the new requirement of having a prior operating system already installed was going to irritate users who reinstall Windows regularly.[189]
It has been revealed that an Upgrade copy of Windows Vista can be installed clean without first installing a previous version of Windows. On the first install, Windows will refuse to activate. The user must then reinstall that same copy of Vista. Vista will then activate on the reinstall, thus allowing a user to install an Upgrade of Windows Vista without owning a previous operating system.[190] As with Windows XP, separate rules still apply to OEM versions of Vista installed on new PCs: Microsoft asserts that these versions are not legally transferable (although whether this conflicts with the right of first sale has yet to be clearly decided legally).[191]
Cost[edit]
Initially, the cost of Windows Vista was also a source of concern and commentary. A majority of users in a poll said that the prices of various Windows Vista editions posted on the Microsoft Canada website in August 2006 make the product too expensive.[192] A BBC News report on the day of Vista’s release suggested that, «there may be a backlash from consumers over its pricing plans—with the cost of Vista versions in the US roughly half the price of equivalent versions in the UK.»[193]
Since the release of Vista in 2006, Microsoft has reduced the retail, and upgraded the price point of Vista. Originally, Vista Ultimate was priced at $399, and Home Premium Vista at $239. These prices have since been reduced to $319 and $199 respectively.[194]
Digital rights management[edit]
Windows Vista supports additional forms of DRM restrictions. One aspect of this is the Protected Video Path, which is designed so that «premium content» from HD DVD or Blu-ray Discs may mandate that the connections between PC components be encrypted. Depending on what the content demands, the devices may not pass premium content over non-encrypted outputs, or they must artificially degrade the quality of the signal on such outputs or not display it at all. Drivers for such hardware must be approved by Microsoft; a revocation mechanism is also included, which allows Microsoft to disable drivers of devices in end-user PCs over the Internet.[195] Peter Gutmann, security researcher and author of the open source cryptlib library, claims that these mechanisms violate fundamental rights of the user (such as fair use), unnecessarily increase the cost of hardware, and make systems less reliable (the «tilt bit» being a particular worry; if triggered, the entire graphic subsystem performs a reset) and vulnerable to denial-of-service attacks.[196] However, despite several requests[197] for evidence supporting such claims Peter Gutmann has never supported his claims with any researched evidence. Proponents have claimed that Microsoft had no choice but to follow the demands of the movie studios, and that the technology will not actually be enabled until after 2010;[198][199] Microsoft also noted that content protection mechanisms have existed in Windows as far back as Windows ME, and that the new protections will not apply to any existing content, only future content.[200]
User Account Control[edit]
Although User Account Control (UAC) is an important part of Vista’s security infrastructure as it blocks software from silently gaining administrator privileges without the user’s knowledge, it has been widely criticized for generating too many prompts.[201] This has led many Vista UAC users to consider it troublesome, with some consequently either turning the feature off or (for Windows Vista Enterprise or Windows Vista Ultimate users) putting it in auto-approval mode.[202] Responding to this criticism, Microsoft altered the implementation to reduce the number of prompts with SP1.[138] Though the changes resulted in some improvement, it did not alleviate the concerns completely.[203]
Downgrade rights[edit]
End-users of licenses of Windows 7 acquired through OEM or volume licensing may downgrade to the equivalent edition of Windows Vista. Downgrade rights are not offered for Starter, Home Basic or Home Premium editions of Windows 7.[204] For Windows 8 licenses acquired through an OEM, a user may also downgrade to the equivalent edition of Windows Vista. Customers licensed for use of Windows 8 Enterprise are generally licensed for Windows 8 Pro, which may be downgraded to Windows Vista Business.
See also[edit]
- BlueKeep (security vulnerability)
- Comparison of Windows Vista and Windows XP
- Microsoft Security Essentials
Notes[edit]
- ^ 64-bit editions of Windows Vista only. Requires Service Pack 1.[92]
- ^ Installing the preview rollup package released for Windows Server 2008 on March 19, 2019, or any later released rollup package, will update the operating system kernel’s build number from version 6.0.6002 to 6.0.6003. This change was made so Microsoft could continue to service the operating system while avoiding “version-related issues”.[150] This same phenomenon would occur when a user installs the BlueKeep Patch (KB4499180)[151] onto Windows Vista as the patch was released in May 2019, two months after the change was initiated.
References[edit]
- ^ «Windows Licensing Programs». Microsoft. June 2011. Archived from the original on December 16, 2008. Retrieved September 21, 2008.
- ^ White, Nick (November 8, 2006). «Windows Vista releases to manufacturing». Windows Vista Team Blog. Microsoft. Archived from the original on August 9, 2005. Retrieved January 2, 2017.
- ^ a b «Microsoft Launches Windows Vista and the 2007 Office System to Consumers». News Center. Microsoft. January 29, 2007. Retrieved January 2, 2017.
- ^ «Windows Version Numbers — Version and build numbers of Microsoft Windows». www.gaijin.at.
- ^ a b Oiaga, Marius (May 26, 2009). «Download Windows Vista Service Pack 2 (SP2) RTM». Softpedia. SoftNews.
- ^ a b c «Windows Vista Lifecycle Policy». Microsoft. Retrieved January 2, 2017.
- ^ «Microsoft Unveils New Ways for Consumers to Get Windows Vista». News Center. Microsoft. January 17, 2007. Retrieved January 2, 2017.
- ^ Oiaga, Marius (December 3, 2010). «Slow Death for Windows Vista — Packaged Software End of Sales Reached in October». softpedia.
- ^ a b «Desktop Windows Version Market Share Worldwide». StatCounter Global Stats. Retrieved February 2, 2020.
- ^ «Microsoft Support Lifecycle». Support. Microsoft. Retrieved May 11, 2012.
- ^ Gallii, Peter (July 30, 2001). «Pushing Forward». eWeek. Retrieved July 7, 2006.
- ^ Microsoft Windows System Overview. Microsoft.com. Retrieved on October 14, 2011. Archived March 16, 2011, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Lipner, Steve; Howard, Michael (March 2005). «The Trustworthy Computing Security Development Lifecycle». Microsoft Developer Network. Microsoft. Retrieved August 9, 2006.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (March 1, 2003). «Longhorn Alpha Preview 2: Build 4008». Windows SuperSite. Archived from the original on January 17, 2007. Retrieved March 30, 2006.
- ^ «WinHEC 2003 Session Presentations». Microsoft. August 1, 2003. Archived from the original on December 16, 2005. Retrieved March 31, 2006.
- ^ Kaplan, Michael (October 16, 2005). «A reset does not mean everything was thrown away». Sorting It All Out. Retrieved April 2, 2006.
- ^ Keizer, Gregg (January 29, 2007). «Microsoft’s Vista Had Major Mac Envy, Company E-Mails Reveal». InformationWeek. UBM plc. Archived from the original on January 27, 2014. Retrieved February 28, 2013.
- ^ Guth, Robert (September 23, 2005). «Battling Google, Microsoft Changes How It Builds Software». The Wall Street Journal. pp. A1, ??. (viewable online here [1] Archived January 12, 2016, at the Wayback Machine)
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (April 16, 2003). «Brian Valentine talks Windows Server 2003». SuperSite for Windows. Archived from the original on June 14, 2006. Retrieved April 2, 2006.
- ^ Murphy, Victoria (May 26, 2003). «The Exterminator». Forbes Magazine. Archived from the original on January 2, 2004.
- ^ Torre, Charles; Scoble, Robert (December 23, 2005). «Rob Short (and kernel team) — Going deep inside Windows Vista’s kernel architecture». Channel 9. Microsoft.
- ^ Ricciuti, Mike (July 22, 2005). «Longhorn’s new name: Windows Vista». CNET. CBS Interactive. Retrieved March 15, 2016.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (November 1, 2006). «Road to Gold: The Long Road to Windows Vista Part 4: January — July 2005». Archived from the original on November 9, 2006. Retrieved November 2, 2006.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (November 5, 2006). «Paul Thurrott’s SuperSite for Windows: Road to Gold: The Long Road to Windows Vista Part 7: July 2006 – present». SuperSite for Windows. Penton. Archived from the original on November 9, 2006. Retrieved December 25, 2007.
- ^ Spooner, John (March 14, 2006). «Microsoft Shuts Windows on New PC Firmware». eWeek. Retrieved December 26, 2006.[permanent dead link]
- ^ «EFI and Windows Vista». WHDC. Microsoft. April 20, 2006. Archived from the original on February 5, 2008. Retrieved December 26, 2006.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (October 23, 2006). «Exclusive: Here Comes Windows Vista RC2». IT Pro. Archived from the original on October 11, 2006. Retrieved May 30, 2022.
- ^ «Broken Windows Theory». The World As Best As I Remember It. MSDN Blogs. June 14, 2006. Retrieved June 24, 2006.
- ^ «Glitch in voice-recognition software foils Microsoft demo». USA Today. Gannett Co. Inc. Associated Press. July 28, 2006.
- ^ Malone, Steve (October 27, 2006). «Windows Vista RTM code delayed». Digitimes/alphr. Retrieved August 20, 2015.
- ^ White, Nick (November 8, 2006). «Windows Vista releases to manufacturing». Windows Vista team blog. Archived from the original on April 7, 2014. Retrieved November 8, 2006. Windows Vista cost Microsoft six billion dollars to develop.«Vista – a $6 Billion Dollars Operating System – The best billions Bill Gates has ever spent». Softpedia. SoftNews. January 10, 2007. Retrieved October 2, 2008.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (October 27, 2006). «WinInfo Short Takes». WinInfo blog. WindowsITPro. Archived from the original on November 3, 2006. Retrieved October 27, 2006.
- ^ «MSDN Subscriptions». Microsoft. Retrieved October 27, 2006.
- ^ «Microsoft Business Value». Microsoft. Archived from the original on December 5, 2006. Retrieved November 30, 2006.
- ^ Allchin, Jim (November 9, 2006). «The Sounds of Windows Vista». Windows Vista Team Blog. Microsoft. Archived from the original on November 10, 2006. Retrieved April 25, 2015.
- ^ Murph, Darren (May 3, 2007). «Vista’s Aero interface blamed for truncated battery life». Engadget.
- ^ «Vista Battery Fix?». Microsoft. May 6, 2007. Archived from the original on March 13, 2008. Retrieved March 18, 2008.
- ^ «A Closer Look at Windows Vista Part II: Enhanced Search». ni.com. National Instruments. September 17, 2009. Archived from the original on September 29, 2011.
- ^ Durham, Joel Jr. (March 21, 2007). «Ten Must-Have Gadgets for Windows Vista Sidebar». PC Magazine. Ziff Davis. Retrieved March 19, 2016.
- ^ Windows Internet Explorer, Printing Advances Printing in IE7 Archived April 17, 2008, at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ Windows Mail Features Explained, See Reliability Section Windows Mail Archived April 30, 2008, at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ Windows Mail was demonstrated by the development team in this Channel 9 video Archived May 10, 2008, at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ Adams, Dan (December 7, 2006). «Vista and Games for Windows update». IGN. Ziff Davis. Retrieved March 18, 2016.
- ^ Suokko, Matti (2004). «Windows For Mobile PCs And Tablet PCs — CY05 And Beyond». Microsoft. Archived from the original (PPT) on December 14, 2005. Retrieved July 15, 2015.
- ^ Parker, Burt (2005). «Building a «Longhorn»-Ready Mobile PC». Microsoft. Archived from the original (PPT) on September 7, 2015. Retrieved August 4, 2015.
- ^ «Windows Longhorn ACPI and Power Management — Part 1». Microsoft. 2004. Archived from the original (PPT) on February 19, 2006. Retrieved August 4, 2015.
- ^ «Configuring Windows HotStart» (DOCX). Microsoft. March 19, 2010. Retrieved April 18, 2015.
- ^ «Selected Scenarios for Maintaining Data Integrity with Windows Vista». Microsoft. 2006. Archived from the original on August 20, 2006. Retrieved August 24, 2006.
- ^ Windows Update, Easier and Less Disruptive Windows Update in Windows Vista Archived May 22, 2008, at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ Windows Vista, SAPI Talking Windows Archived March 23, 2007, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Russell, Richard G. (May 6, 2005). «System Performance Assessment Tools for Windows Longhorn». Microsoft. Archived from the original (PPT) on November 18, 2012. Retrieved December 27, 2012.
- ^ «Introducing the Windows System Assessment Tool». Microsoft TechNet. Archived from the original on January 16, 2007.
- ^ Hruska, Joel (June 29, 2007). «Vista’s Reliability Monitor provides detailed information on OS uptime». Ars Technica. Condé Nast. Retrieved March 16, 2016.
- ^ O’Reilly, Dennis (May 22, 2007). «Partitioning a Hard Drive in Vista». PC World. IDG. Retrieved March 15, 2016.
- ^ «Upgrade to another edition of Windows Vista». Windows.microsoft.com. Retrieved February 4, 2012.
- ^ LeBlanc, Brandon (May 2, 2007). «Digital Locker Assistant helps manage purchased Apps». Windows Blogs. Microsoft. Retrieved December 26, 2016.
- ^ «Digital Locker». Windows Marketplace. Microsoft. 2007. Archived from the original on February 2, 2007. Retrieved December 26, 2016.
- ^ Shultz, Greg (April 13, 2006). «Windows Vista: ReadyBoost, ReadyDrive, and SuperFetch, oh my!». TechRepublic.
- ^ «Windows Vista: Ready for ReadyDrive — Charles — Channel 9». Channel 9. Microsoft.
- ^ «SuperFetch: How it Works & Myths – OSnews». www.osnews.com.
- ^ Shultz, Greg (July 9, 2008). «Understand how SuperFetch uses RAM to enhance system performance». TechRepublic. Retrieved October 2, 2008.
- ^ «Microsoft Leverages IPv6 With Vista». InformationWeek. UBM plc. January 24, 2006. Archived from the original on February 27, 2013.
- ^ «MSDN Blogs». msdn.com. Microsoft.
- ^ «Windows Vista: Enterprise Networking with Windows Vista». microsoft.com. Microsoft.
- ^ «Windows Vista: Creating a 3-D Desktop — How Windows Vista Works». HowStuffWorks. December 5, 2006.
- ^ White, Nick (August 16, 2006). «DirectX10: The Next Generation in Gaming». Windows Vista Team Blog. Archived from the original on November 18, 2008. Retrieved January 25, 2007.
- ^ «Windows Vista Display Driver Model». MSDN Library.
- ^ «Kernel Enhancements for Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008» (DOC). Microsoft. May 2006. Retrieved April 2, 2011.
- ^ «Inside the Windows Vista Kernel». microsoft.com. Microsoft.
- ^ Ricadela, Aaron (February 14, 2006). «Gates Says Security Is Job One For Vista». InformationWeek. UBM plc. Retrieved January 2, 2017.
- ^ Myers, Tim. «Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008 are Common Criteria Certified at EAL4+». Microsoft. Retrieved May 15, 2013.
- ^ «National Information Assurance Partnership Common Criteria Evaluation and Validation Scheme» (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on October 5, 2012. Retrieved May 15, 2013.
- ^ Stanek, William; Marquardt, Paul (February 6, 2007). «Understanding Windows Vista’s User Account Control». windowsdevcenter.com.
- ^ «Malware Removal Guide» (PDF). October 9, 2010. Archived from the original (PDF) on October 9, 2010. Retrieved March 26, 2021.
- ^ NortonLive Team (February 2010). Malware Removal Guide. Symantec. p. 41.
- ^ Protected Mode IE has been described in detail at the Internet Explorer team blog: Protected Mode in Vista IE7 Archived January 23, 2010, at the Wayback Machine and More details on Protected Mode IE in Windows Vista Archived January 27, 2006, at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ «BitLocker Drive Encryption: Executive Overview». Microsoft. April 5, 2006. Retrieved June 19, 2007.
- ^ Halderman, J. Alex; Schoen, Seth D.; Heninger, Nadia; Clarkson, William; Paul, William; Calandrino, Joseph A.; Feldman, Ariel J.; Appelbaum, Jacob; Felten, Edward W. (February 21, 2008). «Lest We Remember: Cold Boot Attacks on Encryption Keys». Princeton University. Retrieved February 22, 2008.
- ^ Windows Vista Feature Focus: 64-Bit (x64) Support. Winsupersite.com. Retrieved on October 14, 2011. Archived July 30, 2008, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ «What is Windows Aero?». windows.microsoft.com. Microsoft.
- ^ «What’s New in Group Policy in Windows Vista and Windows Server «Longhorn»«. TechNet. Microsoft. Archived from the original on May 8, 2006. Retrieved May 18, 2006.
- ^ .NET Framework 3.0 Technologies, Microsoft Archived July 18, 2006, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Vascellaro, Jessica E. (August 3, 2006). «New Ways to Prove You Are Who You Say You Are Online». The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved March 16, 2016.
- ^ Booker, Logan (15 September 2005). «DirectX 10: More harm than good for graphics?». Maximum Power Computing Atomic. Archived from the original on 27 June 2006. Retrieved 28 May 2006.
- ^ VedBrat, Kam (February 22, 2006). «more comments…» MSDN Blogs. Retrieved May 28, 2006.
- ^ Trevett, Neil (2006). «OpenGL on Vista». Khronos Group. Retrieved November 9, 2006.
- ^ Nguyen, Tuan. «OpenGL Now Natively Supported in Windows Vista». Archived from the original on May 21, 2008. Retrieved January 25, 2007.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (October 6, 2010). «Windows Vista Installation Super Guide, Part 3: Clean Install Windows Vista». SuperSite for Windows. Penton. Archived from the original on April 30, 2016. Retrieved April 26, 2016.
- ^ «You cannot select the Upgrade option when you try to install Windows Vista, and you receive the following message: ‘Upgrade has been disabled’«. How-to. Microsoft. Archived from the original on September 13, 2016. Retrieved April 26, 2016.
Windows Vista requires that the hard disk partition (disk volume) you are installing Vista into is formatted by using the NTFS file system.
- ^ Mueller, Scott (2015). Upgrading and Repairing PCs. Que Publishing. p. 295. ISBN 978-0-13-405769-9. Retrieved May 1, 2016.
- ^ «Notable Changes in Vista Service Pack 1». Microsoft. 2008. Archived from the original on May 3, 2008. Retrieved January 6, 2021.
- ^ «Windows and GPT FAQ». Microsoft. June 6, 2017. Archived from the original on February 10, 2019. Retrieved January 7, 2021.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (October 6, 2010). «Windows Vista Installation Super Guide, Part 3: Clean Install Windows Vista». SuperSite for Windows. Penton. Archived from the original on April 30, 2016. Retrieved May 30, 2015.
- ^ «Enable Game port on vista». Creative. December 8, 2004. Retrieved June 22, 2007.
- ^ «Discontinued Support for IP over 1394». Microsoft. December 8, 2004. Archived from the original on May 15, 2007. Retrieved June 22, 2007.
- ^ «IPX/SPX Protocol in Vista (32bit)». Starbase.com. May 5, 2008. Retrieved May 5, 2008.[permanent dead link]
- ^ «End of support for Windows XP SP2 and Windows Vista RTM». GB Technology. Retrieved May 14, 2010.
- ^ «Microsoft’s Windows Vista SP1 support ends July 12». Computerworld. July 12, 2011. Retrieved August 2, 2012.
- ^ «Microsoft Unveils Windows Vista Product Lineup». PressPass (Press release). Microsoft. February 26, 2006. Archived from the original on November 16, 2006. Retrieved October 31, 2006.
- ^ «Windows Vista Business». Microsoft.
- ^ «Windows Vista Enterprise». Microsoft.
- ^ VedBrat, Kam. «Desktop And Presentation Impact On Hardware Design» (PPT). Microsoft. Retrieved September 1, 2006.
- ^ Oiaga, Marius (December 12, 2006). «Windows Vista Graphical User Interface(s) – Aero, Standard, Basic and Classic». Softpedia. Retrieved April 28, 2009.
- ^ «Windows Vista Enterprise Hardware Planning Guidance». TechNet. Microsoft. 2006. Retrieved October 26, 2006.
- ^ a b Thurrott, Paul (August 25, 2008). «Windows Vista Feature Focus: Windows Vista Standard User Interface». SuperSite for Windows. Penton. Archived from the original on May 22, 2010. Retrieved April 28, 2009.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (August 25, 2008). «Windows Vista Feature Focus: Windows Vista Basic User Interface». SuperSite for Windows. Penton. Archived from the original on February 22, 2009. Retrieved April 28, 2009.
- ^ «Microsoft and PC Manufacturers Make It Easier for Customers to Get Ready for Windows Vista». PressPass. Microsoft. May 18, 2006. Retrieved May 18, 2006.
- ^ a b «Windows Vista Upgrade Advisor». Microsoft. Retrieved June 25, 2006.
- ^ «ForceWare Release 95». Nvidia.com. Retrieved October 2, 2008.
- ^ «MsBetas’ List of Vista Ready GPUs». Archived from the original on March 13, 2007. Retrieved July 30, 2007.
- ^ «Windows Vista Alternate Media». Microsoft. Retrieved August 20, 2007.
- ^ Windows Vista 64-bit Editions Archived July 24, 2008, at the Wayback Machine. Microsoft.com. Retrieved on October 14, 2011.
- ^ «Windows Vista: Recommended System Requirements». Microsoft. Archived from the original on January 1, 2008. Retrieved March 13, 2008.
- ^ Ashley, Mitchell (January 31, 2008). «Vista Starter — The Easy Button For Vista». Network World (International Data Group). Retrieved June 3, 2019.
- ^ «What is the maximum amount of RAM that Windows Vista can handle?». Microsoft. Retrieved April 18, 2014.
- ^ A logical processor is either: 1) One of the two handlers of the thread of instructions of one of the numbers of cores of one of the number of physical processors with support for HyperThreading; or 2) One of the numbers of cores of one of the numbers of physical processors without support for HyperThreading.
- ^ 32 cores without support for HyperThreading, 16 cores with support for HyperThreading.
- ^ 64 cores without support for HyperThreading, 32 cores with support for HyperThreading.
- ^ Logical processor limits for Windows Vista Archived January 27, 2011, at the Wayback Machine. Msdn.microsoft.com. Retrieved on October 14, 2011.
- ^ Physical processor limits for Windows Vista Archived July 14, 2012, at archive.today. Social.answers.microsoft.com (October 24, 2010). Retrieved on October 14, 2011.
- ^ «No update from Microsoft on Vista SP1, Media Center problems». Zdnet. February 18, 2008. Archived from the original on December 16, 2008. Retrieved October 8, 2008.
- ^ «Announcing the RTM of Windows Vista SP1». Microsoft. 4 February 2008. Archived from the original on 5 February 2008. Retrieved 4 February 2008.
- ^ a b c d e f «Windows Vista Service Pack 1 Beta White Paper». Microsoft. August 29, 2007. p. 1. Retrieved August 29, 2007.
- ^ a b «Feb. Launch Now Set for Windows Vista SP1». PC World Magazine. January 31, 2008. Archived from the original on February 6, 2008. Retrieved January 31, 2008.
- ^ Download Details: Windows Vista SP1 All Language Standalone (KB936330) Archived September 4, 2010, at the Wayback Machine. Microsoft.com (April 14, 2008). Retrieved on October 14, 2011.
- ^ Veneziani, Vince (August 30, 2007). «Windows Vista SP1 Gets Officially Announced». TechCrunch. AOL. Retrieved March 16, 2016.
- ^ Russinovich, Mark (August 7, 2007). «The Case of the Failed File Compression». Mark’s Blog. MSDN Blogs. Archived from the original on December 30, 2007. Retrieved October 20, 2007.
- ^ «Don’t judge a book by its cover–why Windows Vista Defrag is cool». The Filing Cabinet. MSDN Blogs. January 26, 2007. Archived from the original on April 28, 2010. Retrieved April 6, 2007.
- ^ «Overview of Windows Vista Service Pack 1». TechNet. Microsoft. February 5, 2008. Retrieved March 17, 2016.
- ^ «Windows and GPT FAQ». MSDN. Microsoft. June 15, 2011. Retrieved February 4, 2012.
- ^ It is possible only when installing from installation DVD of Windows Vista x64 with its service pack 1 integrated.
- ^ Fisher, Ken (June 21, 2007). «Google says Vista search changes not enough». Ars Technica. Retrieved October 20, 2007.
- ^ Fulton, Scott M., III (October 19, 2006). «Vista SP1 to Include Common Security APIs for Partners». BetaNews. Retrieved June 12, 2007.
- ^ «Kernel Patch Protection Criteria Evaluation Document». Microsoft. December 19, 2006. Retrieved June 12, 2007.
- ^ Hruska, Joel (August 9, 2007). «Microsoft releases information on upcoming D3D 10.1 update». Retrieved August 10, 2008.
- ^ Lowe, Scott (January 13, 2010). «An updated guide to common Microsoft software versions». TechRepublic. CBS Interactive. Retrieved March 17, 2016.
- ^ a b «Notable Changes in Vista Service Pack 1». Microsoft. Archived from the original on 3 May 2008. Retrieved 2 May 2008.
- ^ LeBlanc, Brandon (April 28, 2009). «Windows Vista SP2 RTM + Windows Vista SP1 Blocker Tool Removed». Windows Vista Team Blog. Archived from the original on May 18, 2014.
- ^ a b Nash, Mike (October 25, 2008). «Windows Vista Team Blog : Windows Vista Service Pack 2 Beta». Archived from the original on May 9, 2013. Retrieved October 25, 2008.
- ^ «Information about Windows Server 2008 Service Pack 2 and Windows Vista Service Pack 2». Microsoft. October 2, 2008. Retrieved October 17, 2008.
- ^ «What’s New In Windows Vista SP2?». February 6, 2009. Archived from the original on February 12, 2009. Retrieved February 6, 2009.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (February 24, 2009). «Windows Vista SP2: What to Expect». IT Pro. Penton. Retrieved May 30, 2022.
- ^ «Description of the Platform Update for Windows Server 2008 and the Platform Update for Windows Vista». Microsoft Support. October 27, 2009.
- ^ «The Platform Update for Windows Vista». DirectX Developer Blog. September 10, 2009. Archived from the original on April 8, 2014.
- ^ a b Lawrence, Mark (25 November 2009). «Internet Explorer announces to use DirectWrite & Direct2D (comment from Microsoft official)». Archived from the original on 8 April 2014.
- ^ «Platform Update Supplement for Windows Vista and for Windows Server 2008». Microsoft Support (4.0 ed.). Microsoft. February 8, 2011. Archived from the original on December 28, 2011. Retrieved June 28, 2019.
- ^ «Customer guidance for CVE-2019-0708». Microsoft. Retrieved September 16, 2019.
- ^ Greenberg, Andy (August 13, 2019). «DejaBlue: New BlueKeep-Style Bugs Renew The Risk Of A Windows worm». wired. Retrieved August 15, 2019.
- ^ «Build number changing to 6003 in Windows Server 2008».
- ^ «May 14, 2019—KB4499180 (Security-only update)». Microsoft Support. Retrieved January 14, 2022.
- ^ «CVE-2019-1162 — Security Update Guide — Microsoft Windows ALPC Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability». Customer Guidance Security Update Guide. Microsoft. August 13, 2019. Retrieved December 22, 2020.
- ^ «Microsoft Security Advisory 4022344». Microsoft. Retrieved December 23, 2020.
- ^ «The Mojave Experiment». Mojaveexperiment.com. Retrieved October 2, 2008.
- ^ «The Mojave Experiment: Microsoft Windows Vista». Microsoft.
- ^ «Blog Posts Poke Holes in ‘Taste Test’ by Microsoft». The New York Times. August 4, 2008. Retrieved April 8, 2009.
- ^ Oiaga, Marius (November 2, 2007). «Windows Vista Tastes Like Bubbles…» softpedia. Retrieved February 23, 2022.
- ^ ssinchak (June 27, 2007). «Hacking Windows Vista: Speeding Up the System Boot». Extremetech. Retrieved July 30, 2022.
- ^ Anderson, Tim (December 6, 2007). «Is Windows Vista slower than Windows XP?». The Guardian. Retrieved July 30, 2022.
- ^ DirectX 10: The Future of PC Gaming, Tim Smalley, 30 November 2006 Archived April 23, 2008, at the Wayback Machine. Bit-tech.net (November 30, 2006). Retrieved on October 14, 2011.
- ^ Durham, Joel (May 12, 2008). «Gaming Performance: Windows Vista SP1 vs. XP SP3». ExtremeTech. Ziff Davis. Archived from the original on June 7, 2011. Retrieved July 29, 2008.
- ^ Bright, Peter (March 19, 2007). «Windows Vista: more than just a pretty face». ArsTechnica. Condé Nast. Retrieved July 15, 2015.
- ^ Bright, Peter (June 7, 2007). «Windows Vista: Under the Hood». ArsTechnica. Condé Nast. Retrieved July 15, 2015.
- ^ «Paul Thurrott’s SuperSite for Windows: Windows Vista Review, Part 1: Introduction». August 19, 2007. Archived from the original on August 19, 2007. Retrieved December 31, 2019.
- ^ «Windows Vista Named «Best of CES» at the 2007 International Consumer Electronics Show». News Center. Microsoft. January 10, 2007. Retrieved May 25, 2015.
- ^ «Best of CES 2007 awards Consumer Electronics Show, January 8 to 11». CNET. CBS Interactive. 2007. Archived from the original on January 22, 2007. Retrieved May 25, 2015.
- ^ Tynan, Dan (December 16, 2007). «The 15 Biggest Tech Disappointments of 2007». PC World. IDG. Archived from the original on December 18, 2007. Retrieved December 18, 2007.: listed as No. 1 of «The 15 Biggest Tech Disappointments of 2007»
- ^ McAllister, Neil (January 21, 2008). «Tech’s all-time top 25 flops». InfoWorld. IDG. Retrieved January 27, 2008.
- ^ Flynn, Laurie (April 26, 2007). «Apple Zooms Past Rivals, With 88% Profit Growth». The New York Times. Retrieved December 2, 2015.
- ^ Prague, Liam (February 1, 2022). «Happy birthday, Windows Vista: Troubled teen hits 15». www.theregister.com. Retrieved July 29, 2022.
- ^ Horowitz, Michael (April 23, 2008). «Who’s selling Windows XP in July?». CNET. CBS Interactive. Retrieved March 14, 2016.
- ^ Hoover, J. Nicholas (May 8, 2008). «Microsoft’s Windows Vista Spin Merits Second Look». InformationWeek. UBM plc. Retrieved February 16, 2009.
- ^ Gillen, Al; Waldman, Brett (March 2008). «Document at a Glance – 211087». IDC. Archived from the original on December 16, 2008. Retrieved February 16, 2009.
- ^ O’Neill, Shane (October 30, 2008). «Vista Fights for Relevancy Against Poor Sales, XP, Windows 7». PC World. IDG. Retrieved February 16, 2009.
- ^ Lai, Eric (February 7, 2009). «Vista Makes Converts of Gamers, Enterprises». PC World. Retrieved February 9, 2009.
- ^ Lai, Eric (28 May 2009). «Microsoft: Vista’s enterprise momentum will ‘accrue’ for Windows 7». Computerworld. Archived from the original on 2 March 2007. Retrieved 2 June 2009.
- ^ Reller, Tami (May 28, 2009). «Cowen and Company Technology Media & Telecom Conference». Microsoft. Archived from the original (DOC) on June 16, 2009.
- ^ Microsoft: First Month Vista Sales Double XP, article by Nate Mook Archived December 24, 2007, at the Wayback Machine. Betanews.com (March 26, 2007). Retrieved on October 14, 2011.
- ^ Fried, Ina (September 27, 2007). «Microsoft extends Windows XP’s stay». CNET.
- ^ Windows XP vs. Vista: An Explosion of Opinion Archived February 12, 2022, at the Wayback Machine. Abcnews.go.com (March 20, 2008). Retrieved on October 14, 2011.
- ^ «Leopard drubs Vista in corporate satisfaction survey». March 26, 2008. Archived from the original on November 9, 2019. Retrieved May 30, 2022.
- ^ «AMD 50×15—World Internet Usage». AMD. February 2, 2009. Archived from the original on February 24, 2008. Retrieved November 1, 2009.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (September 16, 2006). «Allchin: 200 Million Windows Vista Users in 24 Months». IT Pro. Penton. Archived from the original on November 9, 2019. Retrieved May 30, 2022.
- ^ Sullivan, John (March 6, 2007). «What’s wrong with Microsoft Windows Vista?». Free Software Foundation. Retrieved March 24, 2007.
- ^ Spooner, John G.; Foley, Mary Jo (August 5, 2005). «Will Your PC Run Windows Vista?». eWeek. QuinStreet. Retrieved August 15, 2006.[permanent dead link]
- ^ Judge, Elizabeth (May 20, 2006). «Windows revamp ‘too advanced for most PCs’«. The Times. London. Retrieved August 15, 2006.
- ^ Gregg Keizer (November 26, 2007).Lawyers: Even Microsoft Confused Over Vista Marketing Archived November 28, 2007, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ «They Criticized Vista. And They Should Know.» Archived April 13, 2019, at the Wayback Machine, The New York Times, March 9, 2008.
- ^ Fisher, Ken (January 28, 2007). «Vista «upgrade» drops compliance checking, requires the old OS to install». Ars Technica. Retrieved January 28, 2007.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (February 3, 2007). «How to Clean Install Windows Vista with Upgrade Media». Supersite for Windows. Penton. Archived from the original on February 5, 2007. Retrieved February 5, 2007.
- ^ Fried, Ina (October 17, 2006). «Microsoft limits Vista transfers». CNET. CBS Interactive.
- ^
Beer, Stan (August 30, 2006). «Windows Vista too expensive says, users». ITWire.com. Archived from the original on September 9, 2006. Retrieved October 19, 2006. - ^ «Microsoft starts Vista hard sell». Technology. BBC News. January 30, 2007. Retrieved January 30, 2007.
- ^ Protalinski, Emil (June 25, 2009). «Windows 7 pricing announced: cheaper than Vista (Updated)». Retrieved October 4, 2009.
- ^ «Output Content Protection and Windows Vista». WHDC. Microsoft. April 27, 2005. Archived from the original on November 16, 2006. Retrieved January 8, 2007.
- ^ Gutmann, Peter (January 27, 2007). «A Cost Analysis of Windows Vista Content Protection». Retrieved January 27, 2007. Also available: PDF version Archived May 11, 2011, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Bott and Ou call out Gutmann’s Vista FUD Archived August 31, 2007, at the Wayback Machine. Blogs.guardian.co.uk. Retrieved on October 14, 2011.
- ^ Smith, Paul (December 31, 2006). «Windows Vista DRM nonsense». Retrieved January 3, 2007.
- ^ Fisher, Ken (May 21, 2006). «Hollywood reportedly in agreement to delay forced quality downgrades for Blu-ray, HD DVD». Ars Technica. Retrieved January 21, 2007.
- ^ Marsh, Dave (January 20, 2007). «Windows Vista Content Protection—Twenty Questions (and Answers)». Windows Vista team blog. Microsoft. Archived from the original on January 21, 2013. Retrieved January 20, 2007.
- ^ «User Account Control: yes, you can turn it off. Is this a good or a bad thing?». Ars Technica. September 10, 2006.
- ^ «Don’t Shut Off Vista UAC, There’s A Better Way». InformationWeek. June 11, 2007. Retrieved October 14, 2011.
- ^ Torode, Christina (April 2, 2008). «Minasi says Vista SP1 solves problems, adds new ones». SearchWinIT.com.
- ^ «Downgrade rights for owners of licensed Windows 8 and Windows 7» (PDF). microsoft.com.
External links[edit]
- Windows Vista End of Support
- Windows Vista Service Pack 2 (SP2) Update
| Version of the Windows NT operating system | |

Screenshot of Windows Vista Ultimate, showing its desktop, taskbar, start menu, Windows Sidebar, Welcome Center, and glass effects of Windows Aero |
|
| Developer | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| Source model |
|
| Released to manufacturing |
November 8, 2006; 16 years ago[2] |
| General availability |
January 30, 2007; 16 years ago[3] |
| Final release | Service Pack 2 with security update rollup (6.0.6002)[4] / October 18, 2016; 6 years ago[5] |
| Update method |
|
| Platforms | IA-32 and x86-64 |
| Kernel type | Hybrid (NT) |
| Userland | Windows API, NTVDM, SUA |
| License | Proprietary commercial software |
| Preceded by | Windows XP (2001) |
| Succeeded by | Windows 7 (2009) |
| Official website | Windows Vista (archived at Wayback Machine) |
| Support status | |
| Mainstream support ended on April 10, 2012. Extended support ended on April 11, 2017.[6] Installing a service pack is required for users to receive updates and support after April 13, 2010. |
Windows Vista is a major release of the Windows NT operating system developed by Microsoft. It was the direct successor to Windows XP, which was released five years earlier, at the time being the longest time span between successive releases of Microsoft’s Windows desktop operating systems. Development was completed on November 8, 2006, and over the following three months, it was released in stages to computer hardware and software manufacturers, business customers, and retail channels. On January 30, 2007, it was released internationally and made available for purchase and download from the Windows Marketplace; this is the first release of Windows to be made available through a digital distribution platform.[7]
New features of Windows Vista include an updated graphical user interface and visual style dubbed «Aero,» a new search component called «Windows Search,» redesigned networking, audio, print, and display sub-systems, and new multimedia tools such as Windows DVD Maker. Windows Vista aimed to increase the level of communication between machines on a home network, using peer-to-peer technology to simplify sharing files and media between computers and devices. Windows Vista included version 3.0 of the .NET Framework, allowing software developers to write applications without traditional Windows APIs. Windows Vista removed support for devices without ACPI.
While these new features and security improvements garnered positive reviews, Windows Vista was also the target of much criticism and negative press. Criticism of Windows Vista includes its high system requirements, more restrictive licensing terms, lack of compatibility, longer boot time, and excessive authorization prompts from User Account Control. As a result of these and other issues, Windows Vista saw lower initial adoption and satisfaction rates than Windows XP. However, Windows Vista usage had surpassed Microsoft’s pre-launch two-year-out expectations of achieving 200 million users, with an estimated 330 million Internet users in January 2009. On October 22, 2010, Microsoft ceased sales of retail copies of Windows Vista, and the original equipment manufacturer’s sales for Windows Vista ceased a year later.[8] The market share of Windows Vista fell below 1% by the end of 2021, coinciding with the release of Windows 11.[9]
Mainstream support for Windows Vista ended on April 10, 2012, and extended support ended on April 11, 2017[10] Windows Vista was succeeded by Windows 7. As of February 2022, 0.18% of PCs run Windows Vista.[9]
Development[edit]
Microsoft began work on Windows Vista, known at the time by its codename «Longhorn», in May 2001,[11] five months before the release of Windows XP. It was originally expected to ship in October 2003 as a minor step between Windows XP and «Blackcomb», which was planned to be the company’s next major operating system release. Gradually, «Longhorn» assimilated many of the important new features and technologies slated for Blackcomb, resulting in the release date being pushed back several times in three years. In some builds of Longhorn, their license agreement said «For the Microsoft product codenamed ‘Whistler'». Many of Microsoft’s developers were also re-tasked to build updates to Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 to strengthen security. Faced with ongoing delays and concerns about feature creep, Microsoft announced on August 27, 2004, that it had revised its plans. For this reason, Longhorn was reset to start work on componentizing the Windows Server 2003 Service Pack 1 codebase, and over time re-incorporating the features that would be intended for an actual operating system release. However, some previously announced features such as WinFS were dropped or postponed, and a new software development methodology called the Security Development Lifecycle was incorporated to address concerns with the security of the Windows codebase, which is programmed in C, C++ and assembly. Longhorn became known as Vista in 2005.[12][13]
Longhorn[edit]
The early development stages of Longhorn were generally characterized by incremental improvements and updates to Windows XP. During this period, Microsoft was fairly quiet about what was being worked on, as their marketing and public relations efforts were more strongly focused on Windows XP, and Windows Server 2003, which was released in April 2003. Occasional builds of Longhorn were leaked onto popular file sharing networks such as IRC, BitTorrent, eDonkey and various newsgroups, and so most of what is known about builds before the first sanctioned development release of Longhorn in May 2003 is derived from these builds.
After several months of relatively little news or activity from Microsoft with Longhorn, Microsoft released Build 4008, which had made an appearance on the Internet around February 28, 2003.[14] It was also privately handed out to a select group of software developers. As an evolutionary release over build 3683, it contained several small improvements, including a modified blue «Plex» theme and a new, simplified Windows Image-based installer that operates in graphical mode from the outset, and completed an install of the operating system in approximately one third the time of Windows XP on the same hardware. An optional «new taskbar» was introduced that was thinner than the previous build and displayed the time differently.
The most notable visual and functional difference, however, came with Windows Explorer. The incorporation of the Plex theme made blue the dominant color of the entire application. The Windows XP-style task pane was almost completely replaced with a large horizontal pane that appeared under the toolbars. A new search interface allowed for filtering of results, searching for Windows help, and natural-language queries that would be used to integrate with WinFS. The animated search characters were also removed. The «view modes» were also replaced with a single slider that would resize the icons in real-time, in the list, thumbnail, or details mode, depending on where the slider was. File metadata was also made more visible and more easily editable, with more active encouragement to fill out missing pieces of information. Also of note was the conversion of Windows Explorer to being a .NET application.
Most builds of Longhorn and Vista were identified by a label that was always displayed in the bottom-right corner of the desktop. A typical build label would look like «Longhorn Build 3683.Lab06_N.020923-1821». Higher build numbers did not automatically mean that the latest features from every development team at Microsoft was included. Typically, a team working on a certain feature or subsystem would generate their working builds which developers would test with, and when the code was deemed stable, all the changes would be incorporated back into the main development tree at once. At Microsoft, several «Build labs» exist where the compilation of the entirety of Windows can be performed by a team. The name of the lab in which any given build originated is shown as part of the build label, and the date and time of the build follow that. Some builds (such as Beta 1 and Beta 2) only display the build label in the version information dialog (Winver). The icons used in these builds are from Windows XP.
At the Windows Hardware Engineering Conference (WinHEC) in May 2003, Microsoft gave their first public demonstrations of the new Desktop Window Manager and Aero. The demonstrations were done on a revised build 4015 which was never released. Several sessions for developers and hardware engineers at the conference focused on these new features, as well as the Next-Generation Secure Computing Base (previously known as «Palladium»), which at the time was Microsoft’s proposed solution for creating a secure computing environment whereby any given component of the system could be deemed «trusted». Also at this conference, Microsoft reiterated their roadmap for delivering Longhorn, pointing to an «early 2005» release date.[15]
Development reset[edit]
By 2004, it had become obvious to the Windows team at Microsoft that they were losing sight of what needed to be done to complete the next version of Windows and ship it to customers. Internally, some Microsoft employees were describing the Longhorn project as «another Cairo» or «Cairo.NET», referring to the Cairo development project that the company embarked on through the first half of the 1990s, which never resulted in a shipping operating system (though nearly all the technologies developed in that time did end up in Windows 95 and Windows NT[16]). Microsoft was shocked in 2005 by Apple’s release of Mac OS X Tiger. It offered only a limited subset of features planned for Longhorn, in particular fast file searching and integrated graphics and sound processing, but appeared to have impressive reliability and performance compared to contemporary Longhorn builds.[17] Most Longhorn builds had major Windows Explorer system leaks which prevented the OS from performing well, and added more confusion to the development teams in later builds with more and more code being developed which failed to reach stability.
In a September 23, 2005 front-page article in The Wall Street Journal,[18] Microsoft co-president Jim Allchin, who had overall responsibility for the development and delivery of Windows, explained how development of Longhorn had been «crashing into the ground» due in large part to the haphazard methods by which features were introduced and integrated into the core of the operating system, without a clear focus on an end-product. Allchin went on to explain how in December 2003, he enlisted the help of two other senior executives, Brian Valentine and Amitabh Srivastava, the former being experienced with shipping software at Microsoft, most notably Windows Server 2003,[19] and the latter having spent his career at Microsoft researching and developing methods of producing high-quality testing systems.[20] Srivastava employed a team of core architects to visually map out the entirety of the Windows operating system, and to proactively work towards a development process that would enforce high levels of code quality, reduce interdependencies between components, and in general, «not make things worse with Vista».[21] Since Microsoft decided that Longhorn needed to be further componentized, work started on builds (known as the Omega-13 builds) that would componentize existing Windows Server 2003 source code, and over time add back functionality as development progressed. Future Longhorn builds would start from Windows Server 2003 Service Pack 1 and continue from there.
This change, announced internally to Microsoft employees on August 26, 2004, began in earnest in September, though it would take several more months before the new development process and build methodology would be used by all of the development teams. A number of complaints came from individual developers, and Bill Gates himself, that the new development process was going to be prohibitively difficult to work within.
As Windows Vista[edit]
By approximately November 2004, the company had considered several names for the final release, ranging from simple to fanciful and inventive. In the end, Microsoft chose Windows Vista as confirmed on July 22, 2005, believing it to be a «wonderful intersection of what the product really does, what Windows stands for, and what resonates with customers, and their needs». Group Project Manager Greg Sullivan told Paul Thurrott «You want the PC to adapt to you and help you cut through the clutter to focus on what’s important to you. That’s what Windows Vista is all about: «bringing clarity to your world» (a reference to the three marketing points of Vista—Clear, Connected, Confident), so you can focus on what matters to you».[22] Microsoft co-president Jim Allchin also loved the name, saying that «Vista creates the right imagery for the new product capabilities and inspires the imagination with all the possibilities of what can be done with Windows—making people’s passions come alive.»[23]
After Longhorn was named Windows Vista in July 2005, an unprecedented beta-test program was started, involving hundreds of thousands of volunteers and companies. In September of that year, Microsoft started releasing regular Community Technology Previews (CTP) to beta testers from July 2005 to February 2006. The first of these was distributed at the 2005 Microsoft Professional Developers Conference, and was subsequently released to beta testers and Microsoft Developer Network subscribers. The builds that followed incorporated most of the planned features for the final product, as well as a number of changes to the user interface, based largely on feedback from beta testers. Windows Vista was deemed feature-complete with the release of the «February CTP», released on February 22, 2006, and much of the remainder of the work between that build and the final release of the product focused on stability, performance, application and driver compatibility, and documentation. Beta 2, released in late May, was the first build to be made available to the general public through Microsoft’s Customer Preview Program. It was downloaded over 5 million times. Two release candidates followed in September and October, both of which were made available to a large number of users.[24]
At the Intel Developer Forum on March 9, 2006, Microsoft announced a change in their plans to support EFI in Windows Vista. The UEFI 2.0 specification (which replaced EFI 1.10) was not completed until early 2006, and at the time of Microsoft’s announcement, no firmware manufacturers had completed a production implementation which could be used for testing. As a result, the decision was made to postpone the introduction of UEFI support to Windows; support for UEFI on 64-bit platforms was postponed until Vista Service Pack 1 and Windows Server 2008 and 32-bit UEFI would not be supported, as Microsoft did not expect many such systems to be built because the market was quickly moving to 64-bit processors.[25][26]
While Microsoft had originally hoped to have the consumer versions of the operating system available worldwide in time for the 2006 holiday shopping season, it announced in March 2006 that the release date would be pushed back to January 2007 in order to give the company—and the hardware and software companies that Microsoft depends on for providing device drivers—additional time to prepare. Because a release to manufacturing (RTM) build is the final version of code shipped to retailers and other distributors, the purpose of a pre-RTM build is to eliminate any last «show-stopper» bugs that may prevent the code from responsibly being shipped to customers, as well as anything else that consumers may find annoying. Thus, it is unlikely that any major new features would be introduced; instead, work would focus on Vista’s fit and finish. In just a few days, developers had managed to drop Vista’s bug count from over 2470 on September 22 to just over 1400 by the time RC2 shipped in early October. However, they still had a way to go before Vista was ready to RTM. Microsoft’s internal processes required Vista’s bug count to drop to 500 or fewer before the product could go into escrow for RTM.[27] For most of the pre-RTM builds, those 32-bit editions are only released.
On June 14, 2006, Windows developer Philip Su posted a blog entry which decried the development process of Windows Vista, stating that «The code is way too complicated, and that the pace of coding has been tremendously slowed down by overbearing process.»[28] The same post also described Windows Vista as having approximately 50 million lines of code, with about 2,000 developers working on the product. During a demonstration of the speech recognition feature new to Windows Vista at Microsoft’s Financial Analyst Meeting on July 27, 2006, the software recognized the phrase «Dear mom» as «Dear aunt». After several failed attempts to correct the error, the sentence eventually became «Dear aunt, let’s set so double the killer delete select all«.[29] A developer with Vista’s speech recognition team later explained that there was a bug with the build of Vista that was causing the microphone gain level to be set very high, resulting in the audio being received by the speech recognition software being «incredibly distorted».
Windows Vista build 5824 (October 17, 2006) was supposed to be the RTM release, but a bug, where the OOBE hangs at the start of the WinSAT Assessment (if upgraded from Windows XP), requiring the user to terminate the msoobe.exe by pressing Shift+F10 to open Command Prompt using either command-line tools or Task Manager prevented this, damaging development and lowering the chance that it would hit its January 2007 deadline.[31]
Development of Windows Vista came to an end when Microsoft announced that it had been finalized on November 8, 2006, and was concluded by co-president of Windows development, Jim Allchin.[32] The RTM’s build number had also jumped to 6000 to reflect Vista’s internal version number, NT 6.0.[33] Jumping RTM build numbers is common practice among consumer-oriented Windows versions, like Windows 98 (build 1998), Windows 98 SE (build 2222), Windows Me (build 3000) or Windows XP (build 2600), as compared to the business-oriented versions like Windows 2000 (build 2195) or Server 2003 (build 3790). On November 16, 2006, Microsoft made the final build available to MSDN and Technet Plus subscribers.[34] A business-oriented Enterprise edition was made available to volume license customers on November 30, 2006.[35] Windows Vista was launched for general customer availability on January 30, 2007.[3]
New or changed features[edit]
Windows Vista introduced several features and functionality not present in its predecessors.
End-user[edit]
- Windows Aero: The new graphical user interface is named Windows Aero, which Jim Allchin stated is an acronym for Authentic, Energetic, Reflective, and Open.[36] Microsoft intended the new interface to be cleaner and more aesthetically pleasing than those of previous Windows versions, featuring new transparencies, live thumbnails, live icons, and animations, thus providing a new level of eye candy. Laptop users report, however, that enabling Aero shortens battery life[37][38] and reduces performance.
- Windows shell: The new Windows shell offers a new range of organization, navigation, and search capabilities: Task panes in Windows Explorer are removed, integrating the relevant task options into the toolbar. A «Favorite links» pane has been added, enabling one-click access to common directories. A search box appears in every Explorer window. The address bar has been replaced with a breadcrumb navigation bar. Icons of certain file types in Windows Explorer are «live» and can be scaled in size up to 256 × 256 pixels. The preview pane allows users to see thumbnails of various files and view the contents of documents. The details pane shows information such as file size and type, and allows viewing and editing of embedded tags in supported file formats. The Start menu has changed as well; incorporating an instant search box, and the All Programs list uses a horizontal scroll bar instead of the cascading flyout menu seen in Windows XP. The word «Start» itself has been removed in favor of a blue orb that bears the Windows logo.
- Windows Search: A new search component of Windows Vista, it features instant search (also known as search as you type), which provides instant search results, thus finding files more quickly than the search features found in previous versions of Windows and can search the contents of recognized file types.[39] Users can search for certain metadata such as name, extension, size, date or attributes.
- Windows Sidebar: A transparent panel, anchored to the right side of the screen, wherein a user can place Desktop Gadgets, which are small applets designed for a specialized purpose (such as displaying the weather or sports scores). Gadgets can also be placed on the desktop.[40]
- Windows Internet Explorer 7: New user interface, tabbed browsing, RSS, a search box, improved printing,[41] Page Zoom, Quick Tabs (thumbnails of all open tabs), Anti-Phishing filter, several new security protection features, Internationalized Domain Name support (IDN), and improved web standards support. IE7 in Windows Vista runs in isolation from other applications in the operating system (protected mode); exploits and malicious software are restricted from writing to any location beyond Temporary Internet Files without explicit user consent.
- Windows Media Player 11, a major revamp of Microsoft’s program for playing and organizing music and video. New features in this version include word wheeling (incremental search or «search as you type»), a new GUI for the media library, photo display and organization, the ability to share music libraries over a network with other Windows Vista machines, Xbox 360 integration, and support for other Media Center Extenders.
- Windows Defender: An antispyware program with several real-time protection agents. It includes a software explorer feature, which provides access to startup programs, and allows one to view currently running software, network-connected applications, and Winsock providers (Winsock LSPs).
- Backup and Restore Center: Includes a backup and restore application that gives users the ability to schedule periodic backups of files on their computer, as well as recovery from previous backups. Backups are incremental, storing only the changes made each time, minimizing disk usage. It also features Complete PC Backup (available only in the Ultimate, Business, and Enterprise editions), which backs up an entire computer as an image onto a hard disk or DVD. Complete PC Backup can automatically recreate a machine setup onto new hardware or hard disk in case of any hardware failures. Complete PC Restore can be initiated from within Windows Vista or from the Windows Vista installation CD if a PC is so corrupt that it cannot start normally from the hard disk.
- Windows Mail: A replacement for Outlook Express that includes a new mail store that improves stability,[42] and features integrated instant search. It has a Phishing Filter like Internet Explorer 7 and Junk mail filtering that is enhanced through regular updates via Windows Update.[43]
- Windows Calendar is a new calendar and task application that integrates with Windows Contacts and Windows Mail. It is compatible with various calendar file types, such as the popular iCalendar.
- Windows Photo Gallery, a photo and movie library management application. It can import from digital cameras, tag and rate individual items, adjust colors and exposure, create and display slideshows (with pan and fade effects) through Direct3D and burn slideshows to a DVD.
- Windows DVD Maker, a companion program to Windows Movie Maker that provides the ability to create video DVDs based on a user’s content. Users can design a DVD with title, menus, video, soundtrack, pan and zoom motion effects on pictures or slides.
- Windows Media Center, which was previously exclusively bundled in a separate edition of Windows XP, known as Windows XP Media Center Edition, has been incorporated into the Home Premium and Ultimate editions of Windows Vista.
- Games: Most of the standard computer games included in previous versions of Windows have been redesigned to showcase Vista’s new graphical capabilities. New games available in Windows Vista are Chess Titans (3D Chess game), Mahjong Titans (3D Mahjong game), and Purble Place (a small collection of games, oriented towards younger children, including a matching game, a cake-creator game, and a dress-up puzzle game). Purble Place is the only one of the new games available in the Windows Vista Home Basic edition. InkBall is available for Home Premium (or better) users.
- Games Explorer: A new special folder called «Games» exposes installed video games and information about them. These metadata may be updated from the Internet.[44]
- Windows Mobility Center is a control panel that centralizes the most relevant information related to mobile computing (brightness, sound, battery level/power scheme selection, wireless network, screen orientation, presentation settings, etc.).
- Windows Fax and Scan Allows computers with fax modems to send and receive fax documents, as well as scan documents. It is not available in the Home editions of Windows Vista, but is available in the Business, Enterprise, and Ultimate editions.
- Windows Meeting Space replaces NetMeeting. Users can share applications (or their entire desktop) with other users on the local network, or over the Internet using peer-to-peer technology (higher editions than Starter and Home Basic can take advantage of hosting capabilities, Starter and Home Basic editions are limited to «join» mode only)
- Windows HotStart enables compatible computers to start applications directly from operating system startup or resume by the press of a button—this enables what Microsoft has described as appliance-like availability, which allows computers to function in a manner similar to a consumer electronics device such as a DVD player;[45] the feature was also designed to provide the instant-on feature availability that is traditionally associated with mobile devices.[46] While Microsoft has emphasized multimedia scenarios with Windows HotStart,[47] a user can configure this feature so that a button launches a preferred application.[48]
- Shadow Copy automatically creates daily backup copies of files and folders. Users can also create «shadow copies» by setting a System Protection Point using the System Protection tab in the System control panel. The user can view multiple versions of a file throughout a limited history and be allowed to restore, delete, or copy those versions. This feature is available only in the Business, Enterprise, and Ultimate editions of Windows Vista and is inherited from Windows Server 2003.[49]
- Windows Update: Software and security updates have been simplified,[50] now operating solely via a control panel instead of as a web application. Windows Mail’s spam filter and Windows Defender’s definitions are updated automatically via Windows Update. Users who choose the recommended setting for Automatic Updates will have the latest drivers installed and available when they add a new device.
- Parental controls: Allows administrators to monitor and restrict user activity, as well as control which websites, programs, and games each Standard user can use and install. This feature is not included in the Business or Enterprise editions of Vista.
- Windows SideShow: Enables the auxiliary displays on newer laptops or supported Windows Mobile devices. It is meant to be used to display device gadgets while the computer is on or off.
- Speech recognition is integrated into Vista.[51] It features a redesigned user interface and configurable command-and-control commands. Unlike the Office 2003 version, which works only in Office and WordPad, Speech Recognition in Windows Vista works for any accessible application. In addition, it currently supports several languages: British and American English, Spanish, French, German, Chinese (Traditional and Simplified), and Japanese.
- New fonts, including several designed for screen reading, and improved Chinese (Yahei, JhengHei), Japanese (Meiryo), and Korean (Mulgan) fonts. ClearType has also been enhanced and enabled by default.
- Improved audio controls allow the system-wide volume or volume of individual audio devices and even individual applications to be controlled separately. New audio functionalities such as room correction, bass management, speaker fill, and headphone virtualization have also been incorporated.
- Problem Reports and Solutions, a feature that allows users to check for solutions to problems or view previously sent problems for any solutions or additional information, if available.Windows System Assessment Tool is a tool used to benchmark system performance. Software such as games can retrieve this rating and modify its own behavior at runtime to improve performance. The benchmark tests CPU, RAM, 2-D and 3-D graphics acceleration, graphics memory and hard disk space.[52][53]
- Windows Ultimate Extras: The Ultimate edition of Windows Vista provides, via Windows Update, access to some additional features. These are a collection of additional MUI language packs, Texas Hold ‘Em (a Poker game) and Microsoft Tinker (a strategy game where the character is a robot), BitLocker and EFS enhancements that allow users to back up their encryption key online in a Digital Locker, and Windows Dreamscene, which enables the use of videos in MPEG and WMV formats as the desktop background. On April 21, 2008, Microsoft launched two more Ultimate Extras; three new Windows sound schemes, and a content pack for Dreamscene. Various DreamScene Content Packs have been released since the final version of DreamScene was released.
- Reliability and Performance Monitor includes various tools for tuning and monitoring system performance and resources activities of CPU, disks, network, memory and other resources. It shows the operations on files, the opened connections, etc.[54]
- Disk Management: The Logical Disk Manager in Windows Vista supports shrinking and expanding volumes on-the-fly.[55]
- Windows Anytime Upgrade: is a program that allows a user to upgrade their computer running Vista to a higher edition. For example, a computer running Windows Vista Home Basic can be upgraded to Home Premium or better. Anytime Upgrade permits users to upgrade without having their programs and data erased, and is cheaper than replacing the existing installation of Windows. Anytime Upgrade is no longer available for Vista.[56]
- Digital Locker Assistant: A program that facilitated access to downloads and purchases from the Windows Marketplace distribution platform.[57] Apps purchased from Windows Marketplace are managed by Microsoft Account credentials, which are used to access a user’s digital locker that stores the app and its associated information (e.g., licenses) off-site.[58]
Core[edit]
Vista includes technologies such as ReadyBoost[59] and ReadyDrive, which employ fast flash memory (located on USB flash drives and hybrid hard disk drives) to improve system performance by caching commonly used programs and data. This manifests itself in improved battery life on notebook computers as well, since a hybrid drive can be spun down when not in use.[60] Another new technology called SuperFetch utilizes machine learning techniques to analyze usage patterns to allow Windows Vista to make intelligent decisions about what content should be present in system memory at any given time. It uses almost all the extra RAM as disk cache.[61] In conjunction with SuperFetch, an automatic built-in Windows Disk Defragmenter makes sure that those applications are strategically positioned on the hard disk where they can be loaded into memory very quickly with the least physical movement of the hard disk’s read-write heads.[62]
As part of the redesign of the networking architecture, IPv6 has been fully incorporated into the operating system[63] and a number of performance improvements have been introduced, such as TCP window scaling.[64] Earlier versions of Windows typically needed third-party wireless networking software to work properly, but this is not the case with Vista, which includes more comprehensive wireless networking support.[65]
For graphics, Vista introduces a new Windows Display Driver Model[66] and a major revision to Direct3D. The new driver model facilitates the new Desktop Window Manager, which provides the tearing-free desktop and special effects that are the cornerstones of Windows Aero. Direct3D 10, developed in conjunction with major graphics card manufacturers, is a new architecture with more advanced shader support, and allows the graphics processing unit to render more complex scenes without assistance from the CPU. It features improved load balancing between CPU and GPU and also optimizes data transfer between them.[67] WDDM also provides video content playback that rivals typical consumer electronics devices. It does this by making it easy to connect to external monitors, providing for protected HD video playback, and increasing overall video playback quality. For the first time in Windows, graphics processing unit (GPU) multitasking is possible, enabling users to run more than one GPU-intensive application simultaneously.[68]
At the core of the operating system, many improvements have been made to the memory manager, process scheduler and I/O scheduler. The Heap Manager implements additional features such as integrity checking in order to improve robustness and defend against buffer overflow security exploits, although this comes at the price of breaking backward compatibility with some legacy applications.[69] A Kernel Transaction Manager has been implemented that enables applications to work with the file system and Registry using atomic transaction operations.[70]
[edit]
Improved security was a primary design goal for Vista.[71] Microsoft’s Trustworthy Computing initiative, which aims to improve public trust in its products, has had a direct effect on its development. This effort has resulted in a number of new security and safety features and an Evaluation Assurance Level rating of 4+.[72][73]
User Account Control, or UAC is perhaps the most significant and visible of these changes. UAC is a security technology that makes it possible for users to use their computer with fewer privileges by default, to stop malware from making unauthorized changes to the system. This was often difficult in previous versions of Windows, as the previous «limited» user accounts proved too restrictive and incompatible with a large proportion of application software, and even prevented some basic operations such as looking at the calendar from the notification tray. In Windows Vista, when an action is performed that requires administrative rights (such as installing/uninstalling software or making system-wide configuration changes), the user is first prompted for an administrator name and password; in cases where the user is already an administrator, the user is still prompted to confirm the pending privileged action. Regular use of the computer such as running programs, printing, or surfing the Internet does not trigger UAC prompts. User Account Control asks for credentials in a Secure Desktop mode, in which the entire screen is dimmed, and only the authorization window is active and highlighted. The intent is to stop a malicious program from misleading the user by interfering with the authorization window, and to hint to the user about the importance of the prompt.[74]
Testing by Symantec Corporation has proven the effectiveness of UAC. Symantec used over 2,000 active malware samples, consisting of backdoors, keyloggers, rootkits, mass mailers, trojan horses, spyware, adware, and various other samples. Each was executed on a default Windows Vista installation within a standard user account. UAC effectively blocked over 50 percent of each threat, excluding rootkits. 5 percent or less of the malware that evaded UAC survived a reboot.[75][76]
Internet Explorer 7’s new security and safety features include a phishing filter, IDN with anti-spoofing capabilities, and integration with system-wide parental controls. For added security, ActiveX controls are disabled by default. Also, Internet Explorer operates in a protected mode, which operates with lower permissions than the user and runs in isolation from other applications in the operating system, preventing it from accessing or modifying anything besides the Temporary Internet Files directory.[77] Microsoft’s anti-spyware product, Windows Defender, has been incorporated into Windows, protecting against malware and other threats. Changes to various system configuration settings (such as new auto-starting applications) are blocked unless the user gives consent.
Whereas prior releases of Windows supported per-file encryption using Encrypting File System, the Enterprise and Ultimate editions of Vista include BitLocker Drive Encryption, which can protect entire volumes, notably the operating system volume. However, BitLocker requires approximately a 1.5-gigabyte partition to be permanently not encrypted and to contain system files for Windows to boot. In normal circumstances, the only time this partition is accessed is when the computer is booting, or when there is a Windows update that changes files in this area, which is a legitimate reason to access this section of the drive. The area can be a potential security issue, because a hexadecimal editor (such as dskprobe.exe), or malicious software running with administrator and/or kernel level privileges would be able to write to this «Ghost Partition» and allow a piece of malicious software to compromise the system, or disable the encryption. BitLocker can work in conjunction with a Trusted Platform Module (TPM) cryptoprocessor (version 1.2) embedded in a computer’s motherboard, or with a USB key.[78] However, as with other full disk encryption technologies, BitLocker is vulnerable to a cold boot attack, especially where TPM is used as a key protector without a boot PIN being required too.[79]
A variety of other privilege-restriction techniques are also built into Vista. An example is the concept of «integrity levels» in user processes, whereby a process with a lower integrity level cannot interact with processes of a higher integrity level and cannot perform DLL–injection to processes of a higher integrity level. The security restrictions of Windows services are more fine-grained, so that services (especially those listening on the network) cannot interact with parts of the operating system they do not need to. Obfuscation techniques such as address space layout randomization are used to increase the amount of effort required of malware before successful infiltration of a system. Code integrity verifies that system binaries have not been tampered with by malicious code.
As part of the redesign of the network stack, Windows Firewall has been upgraded, with new support for filtering both incoming and outgoing traffic. Advanced packet filter rules can be created that can grant or deny communications to specific services.
The 64-bit versions of Vista require that all device drivers be digitally signed, so that the creator of the driver can be identified.[80]
System management[edit]
While much of the focus of Vista’s new capabilities highlighted the new user interface,[81] security technologies, and improvements to the core operating system, Microsoft also adding new deployment and maintenance features:
- The Windows Imaging Format (WIM) provides the cornerstone of Microsoft’s new deployment and packaging system. WIM files, which contain a HAL-independent image of Windows Vista, can be maintained and patched without having to rebuild new images. Windows Images can be delivered via Systems Management Server or Business Desktop Deployment technologies. Images can be customized and configured with applications then deployed to corporate client personal computers using little to no touch by a system administrator. ImageX is the Microsoft tool used to create and customize images.
- Windows Deployment Services replaces Remote Installation Services for deploying Vista and prior versions of Windows.
- Approximately 700 new Group Policy settings have been added, covering most aspects of the new features in the operating system, as well as significantly expanding the configurability of wireless networks, removable storage devices, and user desktop experience. Vista also introduced an XML-based format (ADMX) to display registry-based policy settings, making it easier to manage networks that span geographic locations and different languages.[82]
- Services for UNIX, renamed as «Subsystem for UNIX-based Applications», comes with the Enterprise and Ultimate editions of Vista. Network File System (NFS) client support is also included.
- Multilingual User Interface–Unlike previous versions of Windows (which required the loading of language packs to provide local-language support), Windows Vista Ultimate and Enterprise editions support the ability to dynamically change languages based on the logged-on user’s preference.
- Wireless Projector support
Developer[edit]
Windows Vista includes a large number of new application programming interfaces. Chief among them is the inclusion of version 3.0 of the .NET Framework, which consists of a class library and Common Language Runtime. Version 3.0 includes four new major components:[83]
- Windows Presentation Foundation is a user interface subsystem and framework based vector graphics, which makes use of 3D computer graphics hardware and Direct3D technologies. It provides the foundation for building applications and blending application UI, documents, and media content. It is the successor to Windows Forms.
- Windows Communication Foundation is a service-oriented messaging subsystem that enables applications and systems to interoperate locally or remotely using Web services.
- Windows Workflow Foundation provides task automation and integrated transactions using workflows. It is the programming model, engine, and tools for building workflow-enabled applications on Windows.
- Windows CardSpace is a component that securely stores digital identities of a person, and provides a unified interface for choosing the identity for a particular transaction, such as logging into a website.[84]
These technologies are also available for Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 to facilitate their introduction to and usage by developers and end-users.
There are also significant new development APIs in the core of the operating system, notably the completely re-designed audio, networking, print, and video interfaces, major changes to the security infrastructure, improvements to the deployment and installation of applications («ClickOnce» and Windows Installer 4.0), new device driver development model («Windows Driver Foundation»), Transactional NTFS, mobile computing API advancements (power management, Tablet PC Ink support, SideShow) and major updates to (or complete replacements of) many core subsystems such as Winlogon and CAPI.
There are some issues for software developers using some of the graphics APIs in Vista. Games or programs built solely on the Windows Vista-exclusive version of DirectX, version 10, cannot work on prior versions of Windows, as DirectX 10 is not available for previous Windows versions. Also, games that require the features of D3D9Ex, the updated implementation of DirectX 9 in Windows Vista are also incompatible with previous Windows versions.[85] According to a Microsoft blog, there are three choices for OpenGL implementation on Vista. An application can use the default implementation, which translates OpenGL calls into the Direct3D API and is frozen at OpenGL version 1.4, or an application can use an Installable Client Driver (ICD), which comes in two flavors: legacy and Vista-compatible. A legacy ICD disables the Desktop Window Manager, a Vista-compatible ICD takes advantage of a new API, and is fully compatible with the Desktop Window Manager.[86] At least two primary vendors, ATI and NVIDIA provided full Vista-compatible ICDs.[87] However, hardware overlay is not supported, because it is considered as an obsolete feature in Vista. ATI and NVIDIA strongly recommend using compositing desktop/Framebuffer Objects for same functionality.[88]
Installation[edit]
Windows Vista is the first Microsoft operating system:
- To use DVD-ROM media for installation[89]
- That can be installed only on a partition formatted with the NTFS file system[90]
- That provides support for loading drivers for SCSI, SATA and RAID controllers from any source in addition to floppy disks prior to its installation[91]
- That can be installed on and booted from systems with GPT disks and UEFI firmware[a][93]
Unification of OEM and retail installation[edit]
Windows Vista unifies the previously separate OEM and retail distributions of Microsoft Windows; a license for the edition purchased determines which version of Windows Vista is eligible for installation, regardless of its originating source. OEM and retail versions of Windows before Windows Vista were maintained separately on optical media—users with a manufacturer-supplied disc could not use a retail license during installation, and users with a retail disc could not use an OEM license during installation.[94]
Removed features[edit]
Some notable Windows XP features and components have been replaced or removed in Windows Vista, including several shell and Windows Explorer features, multimedia features, networking related functionality, Windows Messenger, NTBackup, the network Windows Messenger service, HyperTerminal, MSN Explorer, Active Desktop, and the replacement of NetMeeting with Windows Meeting Space. As a result, BOOTMGR in Windows Vista and later versions replaces the functions performed by NTLDR in all Windows NT versions up to Windows XP and directly executes winload.exe, the system loader used to continue the Windows boot process. Windows Vista also does not include the Windows XP «Luna» visual theme, or most of the classic color schemes that have been part of Windows since the Windows 3.x era. The «Hardware profiles» startup feature has also been removed, along with support for older motherboard technologies like the EISA bus, APM and game port support (though on the 32-bit version game port support can be enabled by applying an older driver).[95] IP over FireWire (TCP/IP over IEEE 1394) has been removed as well.[96] The IPX/SPX protocol has also been removed, although it can be enabled by a third-party plug-in.[97]
Support lifecycle[edit]
Support for the original release of Windows Vista (without a service pack) ended on April 13, 2010.[98] Service Pack 1 reached end of support on July 12, 2011, over three years after its general availability.[99]
Mainstream support for Windows Vista officially ended on April 10, 2012.[6] The «Extended Support» phase would last for the next 5 years, until April 11, 2017.[6] Microsoft is no longer offering no-charge incident support, warranty claims, or design fixes for the operating system. For IT pros or users who needed to make specific fixes to the commercial Windows code, Microsoft required an extended hotfix agreement, which provided an additional 90 days from April 10, 2012.
As part of the Extended Support phase, Vista users were still able to get security updates, and could still pay for support per incident, per-hour, or in other ways. Microsoft also made Windows Vista product information available through its online Knowledge Base. On April 11, 2017, support for Windows Vista ended.
Editions[edit]
Windows Vista shipped in six different editions.[100] These are roughly divided into two target markets, consumer and business, with editions varying to cater to specific sub-markets. For consumers, there are three editions, with two available for economically more developed countries. Windows Vista Starter edition is aimed at low-powered computers with availability only in emerging markets. Windows Vista Home Basic is intended for budget users. Windows Vista Home Premium covers the majority of the consumer market and contains applications for creating and using multimedia. The home editions cannot join a Windows Server domain. For businesses, there are three editions as well. Windows Vista Business is specifically designed for small and medium-sized enterprises,[101] while Windows Vista Enterprise[102] is only available to customers participating in Microsoft’s Software Assurance program. Windows Vista Ultimate contains the complete feature-set of both the Home and Business (combination of both Home Premium and Enterprise) editions, as well as a set of Windows Ultimate Extras, and is aimed at enthusiasts.
All editions except Windows Vista Starter support both 32-bit (x86) and 64-bit (x64) processor architectures.
In the European Union, Home Basic N and Business N variants are also available. These come without Windows Media Player, due to EU sanctions brought against Microsoft for violating anti-trust laws. Similar sanctions exist in South Korea.
Visual styles[edit]
A comparison of the four visual styles included in Windows Vista
Windows Vista has four distinct visual styles.[103][104]
- Windows Aero
- Vista’s default visual style, Windows Aero, is built on a desktop composition engine called Desktop Window Manager. Windows Aero introduces support for translucency effects (Glass), window thumbnails on the taskbar, window animations, and other visual effects (for example Windows Flip 3D), and is intended for mainstream and high-end video cards. To enable these features, the contents of every open window are stored in video memory to facilitate tearing-free movement of windows. As such, Windows Aero has significantly higher hardware requirements than its predecessors: systems running Vista must have video card drivers compatible with the Windows Display Driver Model (WDDM), and the minimum graphics memory required is 128 MB, depending on the resolution used.[105]
Windows Aero is not included in the Starter and Home Basic editions. A variant of Windows Aero, dubbed Windows Vista Standard, lacking the glass effects, window animations, and other advanced graphical effects, is included in Home Basic.[106]
- Windows Vista Basic
- This visual style does not employ the Desktop Window Manager; as such, it does not feature transparency or translucency, window animation, Windows Flip 3D or any of the functions provided by the DWM. It is the default visual style on Windows Vista Starter and on systems without WDDM-compatible display drivers, and has similar video card requirements to Windows XP. Before Service Pack 1, a machine that failed Windows Genuine Advantage validation would also default to this visual style.[107]
- Windows Standard
- The Windows Standard and Windows Classic visual styles reprise the user interface of Windows 9x, Windows 2000 and Microsoft’s Windows Server line of operating systems. As with previous versions of Windows, this visual style supports custom color schemes, which are collections of color settings. Windows Vista includes four high-contrast color schemes and the default color schemes from Windows 98 (titled «Windows Classic») and Windows 2000/Windows Me (titled «Windows Standard»).[106]
Hardware requirements[edit]
Computers with a «Certified for Windows Vista» sticker met WHQL Testing requirements and supported new features such as Windows Aero.
Computers capable of running Windows Vista are classified as Vista Capable and Vista Premium Ready.[108] A Vista Capable or equivalent PC is capable of running all editions of Windows Vista although some of the special features and high-end graphics options may require additional or more advanced hardware. A Vista Premium Ready PC can take advantage of Vista’s high-end features.[109]
Windows Vista’s Basic and Classic interfaces work with virtually any graphics hardware that supports Windows XP or 2000; accordingly, most discussion around Vista’s graphics requirements centers on those for the Windows Aero interface. As of Windows Vista Beta 2, the NVIDIA GeForce 6 series and later, the ATI Radeon 9500 and later, Intel’s GMA 950 and later integrated graphics, and a handful of VIA chipsets and S3 Graphics discrete chips are supported. Although originally supported, the GeForce FX 5 series has been dropped from newer drivers from NVIDIA. The last driver from NVIDIA to support the GeForce FX series on Vista was 96.85.[110][111] Microsoft offered a tool called the Windows Vista Upgrade Advisor[109] to assist Windows XP and Vista users in determining what versions of Windows their machine is capable of running. The required server connections for this utility are no longer available. Although the installation media included in retail packages is a 32-bit DVD, customers needing a CD-ROM or customers who wish for a 64-bit install media can acquire this media through the Windows Vista Alternate Media program.[112] The Ultimate edition includes both 32-bit and 64-bit media.[113] The digitally downloaded version of Ultimate includes only one version, either 32-bit or 64-bit, from Windows Marketplace.
| Component of PC | Minimum required | Recommended |
|---|---|---|
| Processor | 800 MHz | 1 GHz |
| Memory | 512 MB (384 MB for Starter edition) |
1 GB |
| Graphics card | Super VGA | WDDM 1.0-compliant 32 bits per pixel DirectX 9.0 support Pixel Shader 2.0 support |
| Graphics memory | — | 128 MB |
| Total HDD capacity | 20 GB | 40 GB |
| Free HDD space | 15 GB | 15 GB |
| Optical drives | CD-ROM drive | DVD-ROM drive |
| Others | — | TV tuner card (Premium, Ultimate) Touchscreen (Premium, Business, Ultimate) USB flash drive (Ultimate) Trusted Platform Module (Ultimate) |
Physical memory limits[edit]
The maximum amount of RAM that Windows Vista can support varies, depending on both its edition and its processor architecture, as shown in the table.[116]
| Edition | Processor architecture | |
|---|---|---|
| IA-32 | x64 | |
| Ultimate | 4 GB | 128 GB |
| Enterprise | ||
| Business | ||
| Home Premium | 16 GB | |
| Home Basic | 8 GB | |
| Starter | 1 GB | — |
Processor limits[edit]
The maximum number of logical processors[117] in a PC that Windows Vista supports is: 32[118] for 32-bit; 64[119] for 64-bit.[120]
The maximum number of physical processors in a PC that Windows Vista supports is: 2 for Business, Enterprise, and Ultimate, and 1 for Starter, Home Basic, and Home Premium.[121]
Updates[edit]
Microsoft occasionally releases updates such as service packs for its Windows operating systems to fix bugs, improve performance and add new features.
Service Pack 1[edit]
Windows Vista Service Pack 1 (SP1) was released on February 4, 2008, alongside Windows Server 2008 to OEM partners, after a five-month beta test period. The initial deployment of the service pack caused a number of machines to continually reboot, rendering the machines unusable.[122] This temporarily caused Microsoft to suspend automatic deployment of the service pack until the problem was resolved. The synchronized release date of the two operating systems reflected the merging of the workstation and server kernels back into a single code base for the first time since Windows 2000. MSDN subscribers were able to download SP1 on February 15, 2008. SP1 became available to current Windows Vista users on Windows Update and the Download Center on March 18, 2008.[123][124][125] Initially, the service pack only supported five languages – English, French, Spanish, German and Japanese. Support for the remaining 31 languages was released on April 14, 2008.[126]
A white paper, published by Microsoft on August 29, 2007, outlined the scope and intent of the service pack, identifying three major areas of improvement: reliability and performance, administration experience, and support for newer hardware and standards.[127]
One area of particular note is performance. Areas of improvement include file copy operations, hibernation, logging off on domain-joined machines, JavaScript parsing in Internet Explorer, network file share browsing,[124] Windows Explorer ZIP file handling,[128] and Windows Disk Defragmenter.[129] The ability to choose individual drives to defragment is being reintroduced as well.[124]
Service Pack 1 introduced support for some new hardware and software standards, notably the exFAT file system,[124] 802.11n wireless networking, IPv6 over VPN connections, and the Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol.[130]
Booting a system using Extensible Firmware Interface on x64 systems was also introduced;[124] this feature had originally been slated for the initial release of Vista but was delayed due to a lack of compatible hardware at the time. Booting from a GUID Partition Table–based hard drive greater than 2.19 TB is supported (x64 only).[131][132]
Two areas have seen changes in SP1 that have come as the result of concerns from software vendors. One of these is desktop search; users will be able to change the default desktop search program to one provided by a third party instead of the Microsoft desktop search program that comes with Windows Vista, and desktop search programs will be able to seamlessly tie in their services into the operating system.[125] These changes come in part due to complaints from Google, whose Google Desktop Search application was hindered by the presence of Vista’s built-in desktop search. In June 2007, Google claimed that the changes being introduced for SP1 «are a step in the right direction, but they should be improved further to give consumers greater access to alternate desktop search providers».[133] The other area of note is a set of new security APIs being introduced for the benefit of antivirus software that currently relies on the unsupported practice of patching the kernel (see Kernel Patch Protection).[134][135]
An update to DirectX 10, named DirectX 10.1,[124] marked mandatory several features that were previously optional in Direct3D 10 hardware. Graphics cards will be required to support DirectX 10.1.[136] SP1 includes a kernel (6001.18000) that matches the version shipped with Windows Server 2008.[137]
The Group Policy Management Console (GPMC) was replaced by the Group Policy Object Editor. An updated downloadable version of the Group Policy Management Console was released soon after the service pack.
SP1 enables support for hotpatching, a reboot-reduction servicing technology designed to maximize uptime. It works by allowing Windows components to be updated (or «patched») while they are still in use by a running process. Hotpatch-enabled update packages are installed via the same methods as traditional update packages, and will not trigger a system reboot.[138]
Service Pack 2[edit]
Service Pack 2 for Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008 was released through different channels between April[139] and June 2009, one year after the release of Windows Vista SP1, and four months before the release of Windows 7.[5] In addition to a number of security and other fixes, a number of new features have been added. However, it did not include Internet Explorer 8, but instead was included in Windows 7, which was released four months after Vista SP2.[140][141]
- Windows Search 4 (available for SP1 systems as a standalone update)
- Feature Pack for Wireless adds support for Bluetooth 2.1
- Windows Feature Pack for Storage enables the data recording onto Blu-ray media
- Windows Connect Now (WCN) to simplify Wi-Fi configuration
- Improved support for resuming with active Wi-Fi connections
- Improved support for eSATA drives
- The limit of 10 half-open, outgoing TCP connections introduced in Windows XP SP2 was removed
- Enables the exFAT file system to support UTC timestamps, which allows correct file synchronization across time zones
- Support for ICCD/CCID smart cards
- Support for VIA 64-bit CPUs
- Improved performance and responsiveness with the RSS feeds sidebar
- Improves audio and video performance for streaming high-definition content
- Improves Windows Media Center (WMC) in content protection for TV[142]
- Provides an improved power management policy that is approximately 10% more efficient than the original with the default policies[143]
Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008 share a single service pack binary, reflecting the fact that their code bases were joined with the release of Server 2008.[140] Service Pack 2 is not a cumulative update meaning that Service Pack 1 must be installed first.
Platform Update[edit]
The Platform Update for Windows Vista was released on October 27, 2009. It includes major new components that shipped with Windows 7, as well as updated runtime libraries.[144][145] It requires Service Pack 2 of Windows Vista or Windows Server 2008 and is listed on Windows Update as a Recommended download.
The Platform Update allows application developers to target both Windows Vista and Windows 7. It consists of the following components:
- Windows Graphics runtime: Direct2D, DirectWrite, Direct3D 11, DXGI 1.1, and WARP
- Updates to Windows Imaging Component
- Updates to XPS Print API, XPS Document API and XPS Rasterization Service
- Windows Automation API (updates to MSAA and UI Automation)
- Windows Portable Devices Platform (adds support for MTP over Bluetooth and MTP Device Services)
- Windows Ribbon API
- Windows Animation Manager library
Some updates are available as separate releases for both Windows XP and Windows Vista:
- Windows Management Framework: Windows PowerShell 2.0, Windows Remote Management 2.0, BITS 4.0
- Remote Desktop Connection 7.0 (RDP7) client
Although extensive, the Platform Update does not bring Windows Vista to the level of features and performance offered by Windows 7.[146] For example, even though Direct3D 11 runtime will be able to run on D3D9-class hardware and WDDM drivers using «feature levels» first introduced in Direct3D 10.1, Desktop Window Manager has not been updated to use Direct3D 10.1.[146]
In July 2011, Microsoft released the Platform Update Supplement for Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008, which contains several bug fixes and performance improvements.[147]
Out-of-band patches[edit]
BlueKeep patch[edit]
Microsoft has released an update for Windows Vista SP2 to resolve the BlueKeep security vulnerability (CVE-2019-0708), which affects the Remote Desktop Protocol in older Windows versions.[148] Subsequent related flaws, CVE-2019-1181, CVE-2019-1182, CVE-2019-1222 and CVE-2019-1226 (collectively known as DejaBlue) do not affect Windows Vista or earlier versions of Windows.[149] The installation of this patch changed the build number of Windows Vista from 6002 to 6003.[b]
Text Services Framework patch[edit]
The Text Services Framework was compromised by a privilege escalation vulnerability (CVE-2019-1162) that could allow attackers to use the framework to perform privileged operations, run software, or send messages to privileged processes from unprivileged processes—bypassing security features such as sandboxes or User Account Control. Microsoft remediated issues related to this vulnerability with the release of a patch in August 2019 for Windows Vista SP2, Windows Server 2008 SP2, and later versions of Windows.[152]
Malware Protection Engine patch[edit]
A vulnerability related to Windows Defender that affected the way the Malware Protection Engine operates (CVE-2017-0290) was reported in May 2017. If Windows Defender scanned a specially crafted file, it would lead to memory corruption, potentially allowing an attacker to control the affected machine or perform arbitrary code execution in the context of LocalSystem; the vulnerability was exacerbated by the default real-time protection settings of Windows Defender, which were configured to automatically initiate malware scans at regular intervals. The first version of the Protection Engine affected by the vulnerability is Version 1.1.13701.0—subsequent versions of the engine are unaffected. Microsoft released a patch to address the issue.[153]
Marketing campaign[edit]
The Mojave Experiment[edit]
In July 2008, Microsoft introduced a web-based advertising campaign called the «Mojave Experiment», which depicts a group of people who are asked to evaluate the newest operating system from Microsoft, calling it Windows ‘Mojave’. Participants are first asked about Vista, if they have used it, and their overall satisfaction with Vista on a scale of 1 to 10. They are then shown a demo of some of the new operating system’s features, and asked their opinion and satisfaction with it on the same 1 to 10 scale. After respondents rate «Mojave», they are then told that they were shown a demo of Windows Vista. The object was to test «A theory: If people could see Windows Vista firsthand, they would like it.» According to Microsoft, the initial sample of respondents rated Vista an average of 4.4 out of 10, and Mojave received an average of 8.5, with no respondents rating Mojave lower than they originally rated Windows Vista before the demo.[154][155] The «experiment» has been criticized for deliberate selection of positive statements and not addressing all aspects of Vista.[156] During the launch of Vista, Microsoft also made a lime flavored sparkling water available to campus visitors and developers.[157]
Reception[edit]
Windows Vista received mixed to negative reviews at the time of its release and throughout its lifespan, mainly for its much higher hardware requirements and perceived slowness compared to Windows XP.[158][159]
It received generally positive reviews from PC gamers who praised the advantages brought by DirectX 10, which allowed for better gaming performance and more realistic graphics, as well as support for many new capabilities featured in new GPUs.[160] However, many DirectX 9 games initially ran with lower frame rates compared to when they were run on Windows XP. In mid-2008, benchmarks suggested that the SP1 update improved performance to be on par with (or better than) Windows XP in terms of game performance.[161]
Peter Bright of Ars Technica wrote that, despite its delays and feature cuts, Windows Vista was «a huge evolution in the history of the NT platform […] The fundamental changes to the platform are of a scale not seen since the release of NT [3.1; the first version].»[162] In a continuation of his previous assessment, Bright stated that «Vista is not simply XP with a new skin; core parts of the OS have been radically overhauled, and virtually every area has seen significant refinement. In terms of the magnitude and extent of these changes, Vista represents probably the biggest leap that the NT platform has ever seen. Never before have significant subsystems been gutted and replaced in the way they are in Vista.»[163] Many others in the tech industry echoed these sentiments at the time, directing praise towards the massive amount of technical features new to Windows Vista.[164]
Windows Vista received the «Best of CES» award at the Consumer Electronics Show in 2007.[165][166]
In its first year of availability, PC World rated it as the biggest tech disappointment of 2007,[167] and it was rated by InfoWorld as No. 2 of Tech’s all-time 25 flops.[168] Microsoft’s then much smaller competitor Apple noted that, despite Vista’s far greater sales, its own operating system did not seem to have suffered after its release, and would later invest in advertising mocking Vista’s unpopularity with users.[169][170]
Computer manufacturers such as Dell, Lenovo, and Hewlett-Packard released their newest computers with Windows Vista pre-installed; however, after the negative reception of the operating system, they also began selling their computers with Windows XP CDs included because of a drop in sales.[171]
Sales[edit]
A Gartner research report predicted that Vista business adoption in 2008 would overtake that of XP during the same time frame (21.3% vs. 16.9%)[172] while IDC had indicated that the launch of Windows Server 2008 served as a catalyst for the stronger adoption rates.[173][174] As of January 2009, Forrester Research had indicated that almost one third of North American and European corporations had started deploying Vista.[175] At a May 2009 conference, a Microsoft Vice President said «Adoption and deployment of Windows Vista has been slightly ahead of where we had been with XP» for big businesses.[176][177]
Within its first month, 20 million copies of Vista were sold, double the amount of Windows XP sales within its first month in October 2001, five years earlier.[178] Shortly after however, due to Vista’s relatively low adoption rates and continued demand for Windows XP, Microsoft decided to sell Windows XP until June 30, 2008, instead of the previously planned date of January 31, 2008.[179] There were reports of Vista users «downgrading» their operating systems back to XP, as well as reports of businesses planning to skip Vista.[180] A study conducted by ChangeWave in March 2008 showed that the percentage of corporate users who were «very satisfied» with Vista was dramatically lower than other operating systems, with Vista at 8%, compared to the 40% who said they were «very satisfied» with Windows XP.[181]
The internet-usage market share for Windows Vista after two years of availability, in January 2009, was 20.61%. This figure combined with World Internet Users and Population Stats yielded a user base of roughly 330 million,[182] which exceeded Microsoft’s two-year post launch expectations by 130 million.[183] The internet user base reached before the release of its successor (Windows 7) was roughly 400 million according to the same statistical sources.[citation needed]
Criticism[edit]
Windows Vista received mixed reviews. Criticism targets include protracted development time (5–6 years), more restrictive licensing terms, the inclusion of several technologies aimed at restricting the copying of protected digital media,[184] and the usability of the new User Account Control security technology. Moreover, some concerns have been raised about many PCs meeting «Vista Premium Ready» hardware requirements and Vista’s pricing.
Hardware requirements[edit]
While in 2005 Microsoft claimed «nearly all PCs on the market today will run Windows Vista»,[185] the higher requirements of some of the «premium» features, such as the Aero interface, affected many upgraders. According to the UK newspaper The Times in May 2006, the full set of features «would be available to less than 5 percent of Britain’s PC market»; however, this prediction was made several months before Vista was released.[186] This continuing lack of clarity eventually led to a class action against Microsoft as people found themselves with new computers that were unable to use the new software to its full potential despite the assurance of «Vista Capable» designations.[187] The court case has made public internal Microsoft communications that indicate that senior executives have also had difficulty with this issue. For example, Mike Nash (Corporate Vice President, Windows Product Management) commented, «I now have a $2,100 e-mail machine» because of his laptop’s lack of an appropriate graphics chip so hobbled Vista.[188]
Licensing[edit]
Criticism of upgrade licenses pertaining to Windows Vista Starter through Home Premium was expressed by Ars Technica‘s Ken Fisher, who noted that the new requirement of having a prior operating system already installed was going to irritate users who reinstall Windows regularly.[189]
It has been revealed that an Upgrade copy of Windows Vista can be installed clean without first installing a previous version of Windows. On the first install, Windows will refuse to activate. The user must then reinstall that same copy of Vista. Vista will then activate on the reinstall, thus allowing a user to install an Upgrade of Windows Vista without owning a previous operating system.[190] As with Windows XP, separate rules still apply to OEM versions of Vista installed on new PCs: Microsoft asserts that these versions are not legally transferable (although whether this conflicts with the right of first sale has yet to be clearly decided legally).[191]
Cost[edit]
Initially, the cost of Windows Vista was also a source of concern and commentary. A majority of users in a poll said that the prices of various Windows Vista editions posted on the Microsoft Canada website in August 2006 make the product too expensive.[192] A BBC News report on the day of Vista’s release suggested that, «there may be a backlash from consumers over its pricing plans—with the cost of Vista versions in the US roughly half the price of equivalent versions in the UK.»[193]
Since the release of Vista in 2006, Microsoft has reduced the retail, and upgraded the price point of Vista. Originally, Vista Ultimate was priced at $399, and Home Premium Vista at $239. These prices have since been reduced to $319 and $199 respectively.[194]
Digital rights management[edit]
Windows Vista supports additional forms of DRM restrictions. One aspect of this is the Protected Video Path, which is designed so that «premium content» from HD DVD or Blu-ray Discs may mandate that the connections between PC components be encrypted. Depending on what the content demands, the devices may not pass premium content over non-encrypted outputs, or they must artificially degrade the quality of the signal on such outputs or not display it at all. Drivers for such hardware must be approved by Microsoft; a revocation mechanism is also included, which allows Microsoft to disable drivers of devices in end-user PCs over the Internet.[195] Peter Gutmann, security researcher and author of the open source cryptlib library, claims that these mechanisms violate fundamental rights of the user (such as fair use), unnecessarily increase the cost of hardware, and make systems less reliable (the «tilt bit» being a particular worry; if triggered, the entire graphic subsystem performs a reset) and vulnerable to denial-of-service attacks.[196] However, despite several requests[197] for evidence supporting such claims Peter Gutmann has never supported his claims with any researched evidence. Proponents have claimed that Microsoft had no choice but to follow the demands of the movie studios, and that the technology will not actually be enabled until after 2010;[198][199] Microsoft also noted that content protection mechanisms have existed in Windows as far back as Windows ME, and that the new protections will not apply to any existing content, only future content.[200]
User Account Control[edit]
Although User Account Control (UAC) is an important part of Vista’s security infrastructure as it blocks software from silently gaining administrator privileges without the user’s knowledge, it has been widely criticized for generating too many prompts.[201] This has led many Vista UAC users to consider it troublesome, with some consequently either turning the feature off or (for Windows Vista Enterprise or Windows Vista Ultimate users) putting it in auto-approval mode.[202] Responding to this criticism, Microsoft altered the implementation to reduce the number of prompts with SP1.[138] Though the changes resulted in some improvement, it did not alleviate the concerns completely.[203]
Downgrade rights[edit]
End-users of licenses of Windows 7 acquired through OEM or volume licensing may downgrade to the equivalent edition of Windows Vista. Downgrade rights are not offered for Starter, Home Basic or Home Premium editions of Windows 7.[204] For Windows 8 licenses acquired through an OEM, a user may also downgrade to the equivalent edition of Windows Vista. Customers licensed for use of Windows 8 Enterprise are generally licensed for Windows 8 Pro, which may be downgraded to Windows Vista Business.
See also[edit]
- BlueKeep (security vulnerability)
- Comparison of Windows Vista and Windows XP
- Microsoft Security Essentials
Notes[edit]
- ^ 64-bit editions of Windows Vista only. Requires Service Pack 1.[92]
- ^ Installing the preview rollup package released for Windows Server 2008 on March 19, 2019, or any later released rollup package, will update the operating system kernel’s build number from version 6.0.6002 to 6.0.6003. This change was made so Microsoft could continue to service the operating system while avoiding “version-related issues”.[150] This same phenomenon would occur when a user installs the BlueKeep Patch (KB4499180)[151] onto Windows Vista as the patch was released in May 2019, two months after the change was initiated.
References[edit]
- ^ «Windows Licensing Programs». Microsoft. June 2011. Archived from the original on December 16, 2008. Retrieved September 21, 2008.
- ^ White, Nick (November 8, 2006). «Windows Vista releases to manufacturing». Windows Vista Team Blog. Microsoft. Archived from the original on August 9, 2005. Retrieved January 2, 2017.
- ^ a b «Microsoft Launches Windows Vista and the 2007 Office System to Consumers». News Center. Microsoft. January 29, 2007. Retrieved January 2, 2017.
- ^ «Windows Version Numbers — Version and build numbers of Microsoft Windows». www.gaijin.at.
- ^ a b Oiaga, Marius (May 26, 2009). «Download Windows Vista Service Pack 2 (SP2) RTM». Softpedia. SoftNews.
- ^ a b c «Windows Vista Lifecycle Policy». Microsoft. Retrieved January 2, 2017.
- ^ «Microsoft Unveils New Ways for Consumers to Get Windows Vista». News Center. Microsoft. January 17, 2007. Retrieved January 2, 2017.
- ^ Oiaga, Marius (December 3, 2010). «Slow Death for Windows Vista — Packaged Software End of Sales Reached in October». softpedia.
- ^ a b «Desktop Windows Version Market Share Worldwide». StatCounter Global Stats. Retrieved February 2, 2020.
- ^ «Microsoft Support Lifecycle». Support. Microsoft. Retrieved May 11, 2012.
- ^ Gallii, Peter (July 30, 2001). «Pushing Forward». eWeek. Retrieved July 7, 2006.
- ^ Microsoft Windows System Overview. Microsoft.com. Retrieved on October 14, 2011. Archived March 16, 2011, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Lipner, Steve; Howard, Michael (March 2005). «The Trustworthy Computing Security Development Lifecycle». Microsoft Developer Network. Microsoft. Retrieved August 9, 2006.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (March 1, 2003). «Longhorn Alpha Preview 2: Build 4008». Windows SuperSite. Archived from the original on January 17, 2007. Retrieved March 30, 2006.
- ^ «WinHEC 2003 Session Presentations». Microsoft. August 1, 2003. Archived from the original on December 16, 2005. Retrieved March 31, 2006.
- ^ Kaplan, Michael (October 16, 2005). «A reset does not mean everything was thrown away». Sorting It All Out. Retrieved April 2, 2006.
- ^ Keizer, Gregg (January 29, 2007). «Microsoft’s Vista Had Major Mac Envy, Company E-Mails Reveal». InformationWeek. UBM plc. Archived from the original on January 27, 2014. Retrieved February 28, 2013.
- ^ Guth, Robert (September 23, 2005). «Battling Google, Microsoft Changes How It Builds Software». The Wall Street Journal. pp. A1, ??. (viewable online here [1] Archived January 12, 2016, at the Wayback Machine)
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (April 16, 2003). «Brian Valentine talks Windows Server 2003». SuperSite for Windows. Archived from the original on June 14, 2006. Retrieved April 2, 2006.
- ^ Murphy, Victoria (May 26, 2003). «The Exterminator». Forbes Magazine. Archived from the original on January 2, 2004.
- ^ Torre, Charles; Scoble, Robert (December 23, 2005). «Rob Short (and kernel team) — Going deep inside Windows Vista’s kernel architecture». Channel 9. Microsoft.
- ^ Ricciuti, Mike (July 22, 2005). «Longhorn’s new name: Windows Vista». CNET. CBS Interactive. Retrieved March 15, 2016.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (November 1, 2006). «Road to Gold: The Long Road to Windows Vista Part 4: January — July 2005». Archived from the original on November 9, 2006. Retrieved November 2, 2006.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (November 5, 2006). «Paul Thurrott’s SuperSite for Windows: Road to Gold: The Long Road to Windows Vista Part 7: July 2006 – present». SuperSite for Windows. Penton. Archived from the original on November 9, 2006. Retrieved December 25, 2007.
- ^ Spooner, John (March 14, 2006). «Microsoft Shuts Windows on New PC Firmware». eWeek. Retrieved December 26, 2006.[permanent dead link]
- ^ «EFI and Windows Vista». WHDC. Microsoft. April 20, 2006. Archived from the original on February 5, 2008. Retrieved December 26, 2006.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (October 23, 2006). «Exclusive: Here Comes Windows Vista RC2». IT Pro. Archived from the original on October 11, 2006. Retrieved May 30, 2022.
- ^ «Broken Windows Theory». The World As Best As I Remember It. MSDN Blogs. June 14, 2006. Retrieved June 24, 2006.
- ^ «Glitch in voice-recognition software foils Microsoft demo». USA Today. Gannett Co. Inc. Associated Press. July 28, 2006.
- ^ Malone, Steve (October 27, 2006). «Windows Vista RTM code delayed». Digitimes/alphr. Retrieved August 20, 2015.
- ^ White, Nick (November 8, 2006). «Windows Vista releases to manufacturing». Windows Vista team blog. Archived from the original on April 7, 2014. Retrieved November 8, 2006. Windows Vista cost Microsoft six billion dollars to develop.«Vista – a $6 Billion Dollars Operating System – The best billions Bill Gates has ever spent». Softpedia. SoftNews. January 10, 2007. Retrieved October 2, 2008.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (October 27, 2006). «WinInfo Short Takes». WinInfo blog. WindowsITPro. Archived from the original on November 3, 2006. Retrieved October 27, 2006.
- ^ «MSDN Subscriptions». Microsoft. Retrieved October 27, 2006.
- ^ «Microsoft Business Value». Microsoft. Archived from the original on December 5, 2006. Retrieved November 30, 2006.
- ^ Allchin, Jim (November 9, 2006). «The Sounds of Windows Vista». Windows Vista Team Blog. Microsoft. Archived from the original on November 10, 2006. Retrieved April 25, 2015.
- ^ Murph, Darren (May 3, 2007). «Vista’s Aero interface blamed for truncated battery life». Engadget.
- ^ «Vista Battery Fix?». Microsoft. May 6, 2007. Archived from the original on March 13, 2008. Retrieved March 18, 2008.
- ^ «A Closer Look at Windows Vista Part II: Enhanced Search». ni.com. National Instruments. September 17, 2009. Archived from the original on September 29, 2011.
- ^ Durham, Joel Jr. (March 21, 2007). «Ten Must-Have Gadgets for Windows Vista Sidebar». PC Magazine. Ziff Davis. Retrieved March 19, 2016.
- ^ Windows Internet Explorer, Printing Advances Printing in IE7 Archived April 17, 2008, at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ Windows Mail Features Explained, See Reliability Section Windows Mail Archived April 30, 2008, at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ Windows Mail was demonstrated by the development team in this Channel 9 video Archived May 10, 2008, at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ Adams, Dan (December 7, 2006). «Vista and Games for Windows update». IGN. Ziff Davis. Retrieved March 18, 2016.
- ^ Suokko, Matti (2004). «Windows For Mobile PCs And Tablet PCs — CY05 And Beyond». Microsoft. Archived from the original (PPT) on December 14, 2005. Retrieved July 15, 2015.
- ^ Parker, Burt (2005). «Building a «Longhorn»-Ready Mobile PC». Microsoft. Archived from the original (PPT) on September 7, 2015. Retrieved August 4, 2015.
- ^ «Windows Longhorn ACPI and Power Management — Part 1». Microsoft. 2004. Archived from the original (PPT) on February 19, 2006. Retrieved August 4, 2015.
- ^ «Configuring Windows HotStart» (DOCX). Microsoft. March 19, 2010. Retrieved April 18, 2015.
- ^ «Selected Scenarios for Maintaining Data Integrity with Windows Vista». Microsoft. 2006. Archived from the original on August 20, 2006. Retrieved August 24, 2006.
- ^ Windows Update, Easier and Less Disruptive Windows Update in Windows Vista Archived May 22, 2008, at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ Windows Vista, SAPI Talking Windows Archived March 23, 2007, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Russell, Richard G. (May 6, 2005). «System Performance Assessment Tools for Windows Longhorn». Microsoft. Archived from the original (PPT) on November 18, 2012. Retrieved December 27, 2012.
- ^ «Introducing the Windows System Assessment Tool». Microsoft TechNet. Archived from the original on January 16, 2007.
- ^ Hruska, Joel (June 29, 2007). «Vista’s Reliability Monitor provides detailed information on OS uptime». Ars Technica. Condé Nast. Retrieved March 16, 2016.
- ^ O’Reilly, Dennis (May 22, 2007). «Partitioning a Hard Drive in Vista». PC World. IDG. Retrieved March 15, 2016.
- ^ «Upgrade to another edition of Windows Vista». Windows.microsoft.com. Retrieved February 4, 2012.
- ^ LeBlanc, Brandon (May 2, 2007). «Digital Locker Assistant helps manage purchased Apps». Windows Blogs. Microsoft. Retrieved December 26, 2016.
- ^ «Digital Locker». Windows Marketplace. Microsoft. 2007. Archived from the original on February 2, 2007. Retrieved December 26, 2016.
- ^ Shultz, Greg (April 13, 2006). «Windows Vista: ReadyBoost, ReadyDrive, and SuperFetch, oh my!». TechRepublic.
- ^ «Windows Vista: Ready for ReadyDrive — Charles — Channel 9». Channel 9. Microsoft.
- ^ «SuperFetch: How it Works & Myths – OSnews». www.osnews.com.
- ^ Shultz, Greg (July 9, 2008). «Understand how SuperFetch uses RAM to enhance system performance». TechRepublic. Retrieved October 2, 2008.
- ^ «Microsoft Leverages IPv6 With Vista». InformationWeek. UBM plc. January 24, 2006. Archived from the original on February 27, 2013.
- ^ «MSDN Blogs». msdn.com. Microsoft.
- ^ «Windows Vista: Enterprise Networking with Windows Vista». microsoft.com. Microsoft.
- ^ «Windows Vista: Creating a 3-D Desktop — How Windows Vista Works». HowStuffWorks. December 5, 2006.
- ^ White, Nick (August 16, 2006). «DirectX10: The Next Generation in Gaming». Windows Vista Team Blog. Archived from the original on November 18, 2008. Retrieved January 25, 2007.
- ^ «Windows Vista Display Driver Model». MSDN Library.
- ^ «Kernel Enhancements for Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008» (DOC). Microsoft. May 2006. Retrieved April 2, 2011.
- ^ «Inside the Windows Vista Kernel». microsoft.com. Microsoft.
- ^ Ricadela, Aaron (February 14, 2006). «Gates Says Security Is Job One For Vista». InformationWeek. UBM plc. Retrieved January 2, 2017.
- ^ Myers, Tim. «Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008 are Common Criteria Certified at EAL4+». Microsoft. Retrieved May 15, 2013.
- ^ «National Information Assurance Partnership Common Criteria Evaluation and Validation Scheme» (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on October 5, 2012. Retrieved May 15, 2013.
- ^ Stanek, William; Marquardt, Paul (February 6, 2007). «Understanding Windows Vista’s User Account Control». windowsdevcenter.com.
- ^ «Malware Removal Guide» (PDF). October 9, 2010. Archived from the original (PDF) on October 9, 2010. Retrieved March 26, 2021.
- ^ NortonLive Team (February 2010). Malware Removal Guide. Symantec. p. 41.
- ^ Protected Mode IE has been described in detail at the Internet Explorer team blog: Protected Mode in Vista IE7 Archived January 23, 2010, at the Wayback Machine and More details on Protected Mode IE in Windows Vista Archived January 27, 2006, at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ «BitLocker Drive Encryption: Executive Overview». Microsoft. April 5, 2006. Retrieved June 19, 2007.
- ^ Halderman, J. Alex; Schoen, Seth D.; Heninger, Nadia; Clarkson, William; Paul, William; Calandrino, Joseph A.; Feldman, Ariel J.; Appelbaum, Jacob; Felten, Edward W. (February 21, 2008). «Lest We Remember: Cold Boot Attacks on Encryption Keys». Princeton University. Retrieved February 22, 2008.
- ^ Windows Vista Feature Focus: 64-Bit (x64) Support. Winsupersite.com. Retrieved on October 14, 2011. Archived July 30, 2008, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ «What is Windows Aero?». windows.microsoft.com. Microsoft.
- ^ «What’s New in Group Policy in Windows Vista and Windows Server «Longhorn»«. TechNet. Microsoft. Archived from the original on May 8, 2006. Retrieved May 18, 2006.
- ^ .NET Framework 3.0 Technologies, Microsoft Archived July 18, 2006, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Vascellaro, Jessica E. (August 3, 2006). «New Ways to Prove You Are Who You Say You Are Online». The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved March 16, 2016.
- ^ Booker, Logan (15 September 2005). «DirectX 10: More harm than good for graphics?». Maximum Power Computing Atomic. Archived from the original on 27 June 2006. Retrieved 28 May 2006.
- ^ VedBrat, Kam (February 22, 2006). «more comments…» MSDN Blogs. Retrieved May 28, 2006.
- ^ Trevett, Neil (2006). «OpenGL on Vista». Khronos Group. Retrieved November 9, 2006.
- ^ Nguyen, Tuan. «OpenGL Now Natively Supported in Windows Vista». Archived from the original on May 21, 2008. Retrieved January 25, 2007.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (October 6, 2010). «Windows Vista Installation Super Guide, Part 3: Clean Install Windows Vista». SuperSite for Windows. Penton. Archived from the original on April 30, 2016. Retrieved April 26, 2016.
- ^ «You cannot select the Upgrade option when you try to install Windows Vista, and you receive the following message: ‘Upgrade has been disabled’«. How-to. Microsoft. Archived from the original on September 13, 2016. Retrieved April 26, 2016.
Windows Vista requires that the hard disk partition (disk volume) you are installing Vista into is formatted by using the NTFS file system.
- ^ Mueller, Scott (2015). Upgrading and Repairing PCs. Que Publishing. p. 295. ISBN 978-0-13-405769-9. Retrieved May 1, 2016.
- ^ «Notable Changes in Vista Service Pack 1». Microsoft. 2008. Archived from the original on May 3, 2008. Retrieved January 6, 2021.
- ^ «Windows and GPT FAQ». Microsoft. June 6, 2017. Archived from the original on February 10, 2019. Retrieved January 7, 2021.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (October 6, 2010). «Windows Vista Installation Super Guide, Part 3: Clean Install Windows Vista». SuperSite for Windows. Penton. Archived from the original on April 30, 2016. Retrieved May 30, 2015.
- ^ «Enable Game port on vista». Creative. December 8, 2004. Retrieved June 22, 2007.
- ^ «Discontinued Support for IP over 1394». Microsoft. December 8, 2004. Archived from the original on May 15, 2007. Retrieved June 22, 2007.
- ^ «IPX/SPX Protocol in Vista (32bit)». Starbase.com. May 5, 2008. Retrieved May 5, 2008.[permanent dead link]
- ^ «End of support for Windows XP SP2 and Windows Vista RTM». GB Technology. Retrieved May 14, 2010.
- ^ «Microsoft’s Windows Vista SP1 support ends July 12». Computerworld. July 12, 2011. Retrieved August 2, 2012.
- ^ «Microsoft Unveils Windows Vista Product Lineup». PressPass (Press release). Microsoft. February 26, 2006. Archived from the original on November 16, 2006. Retrieved October 31, 2006.
- ^ «Windows Vista Business». Microsoft.
- ^ «Windows Vista Enterprise». Microsoft.
- ^ VedBrat, Kam. «Desktop And Presentation Impact On Hardware Design» (PPT). Microsoft. Retrieved September 1, 2006.
- ^ Oiaga, Marius (December 12, 2006). «Windows Vista Graphical User Interface(s) – Aero, Standard, Basic and Classic». Softpedia. Retrieved April 28, 2009.
- ^ «Windows Vista Enterprise Hardware Planning Guidance». TechNet. Microsoft. 2006. Retrieved October 26, 2006.
- ^ a b Thurrott, Paul (August 25, 2008). «Windows Vista Feature Focus: Windows Vista Standard User Interface». SuperSite for Windows. Penton. Archived from the original on May 22, 2010. Retrieved April 28, 2009.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (August 25, 2008). «Windows Vista Feature Focus: Windows Vista Basic User Interface». SuperSite for Windows. Penton. Archived from the original on February 22, 2009. Retrieved April 28, 2009.
- ^ «Microsoft and PC Manufacturers Make It Easier for Customers to Get Ready for Windows Vista». PressPass. Microsoft. May 18, 2006. Retrieved May 18, 2006.
- ^ a b «Windows Vista Upgrade Advisor». Microsoft. Retrieved June 25, 2006.
- ^ «ForceWare Release 95». Nvidia.com. Retrieved October 2, 2008.
- ^ «MsBetas’ List of Vista Ready GPUs». Archived from the original on March 13, 2007. Retrieved July 30, 2007.
- ^ «Windows Vista Alternate Media». Microsoft. Retrieved August 20, 2007.
- ^ Windows Vista 64-bit Editions Archived July 24, 2008, at the Wayback Machine. Microsoft.com. Retrieved on October 14, 2011.
- ^ «Windows Vista: Recommended System Requirements». Microsoft. Archived from the original on January 1, 2008. Retrieved March 13, 2008.
- ^ Ashley, Mitchell (January 31, 2008). «Vista Starter — The Easy Button For Vista». Network World (International Data Group). Retrieved June 3, 2019.
- ^ «What is the maximum amount of RAM that Windows Vista can handle?». Microsoft. Retrieved April 18, 2014.
- ^ A logical processor is either: 1) One of the two handlers of the thread of instructions of one of the numbers of cores of one of the number of physical processors with support for HyperThreading; or 2) One of the numbers of cores of one of the numbers of physical processors without support for HyperThreading.
- ^ 32 cores without support for HyperThreading, 16 cores with support for HyperThreading.
- ^ 64 cores without support for HyperThreading, 32 cores with support for HyperThreading.
- ^ Logical processor limits for Windows Vista Archived January 27, 2011, at the Wayback Machine. Msdn.microsoft.com. Retrieved on October 14, 2011.
- ^ Physical processor limits for Windows Vista Archived July 14, 2012, at archive.today. Social.answers.microsoft.com (October 24, 2010). Retrieved on October 14, 2011.
- ^ «No update from Microsoft on Vista SP1, Media Center problems». Zdnet. February 18, 2008. Archived from the original on December 16, 2008. Retrieved October 8, 2008.
- ^ «Announcing the RTM of Windows Vista SP1». Microsoft. 4 February 2008. Archived from the original on 5 February 2008. Retrieved 4 February 2008.
- ^ a b c d e f «Windows Vista Service Pack 1 Beta White Paper». Microsoft. August 29, 2007. p. 1. Retrieved August 29, 2007.
- ^ a b «Feb. Launch Now Set for Windows Vista SP1». PC World Magazine. January 31, 2008. Archived from the original on February 6, 2008. Retrieved January 31, 2008.
- ^ Download Details: Windows Vista SP1 All Language Standalone (KB936330) Archived September 4, 2010, at the Wayback Machine. Microsoft.com (April 14, 2008). Retrieved on October 14, 2011.
- ^ Veneziani, Vince (August 30, 2007). «Windows Vista SP1 Gets Officially Announced». TechCrunch. AOL. Retrieved March 16, 2016.
- ^ Russinovich, Mark (August 7, 2007). «The Case of the Failed File Compression». Mark’s Blog. MSDN Blogs. Archived from the original on December 30, 2007. Retrieved October 20, 2007.
- ^ «Don’t judge a book by its cover–why Windows Vista Defrag is cool». The Filing Cabinet. MSDN Blogs. January 26, 2007. Archived from the original on April 28, 2010. Retrieved April 6, 2007.
- ^ «Overview of Windows Vista Service Pack 1». TechNet. Microsoft. February 5, 2008. Retrieved March 17, 2016.
- ^ «Windows and GPT FAQ». MSDN. Microsoft. June 15, 2011. Retrieved February 4, 2012.
- ^ It is possible only when installing from installation DVD of Windows Vista x64 with its service pack 1 integrated.
- ^ Fisher, Ken (June 21, 2007). «Google says Vista search changes not enough». Ars Technica. Retrieved October 20, 2007.
- ^ Fulton, Scott M., III (October 19, 2006). «Vista SP1 to Include Common Security APIs for Partners». BetaNews. Retrieved June 12, 2007.
- ^ «Kernel Patch Protection Criteria Evaluation Document». Microsoft. December 19, 2006. Retrieved June 12, 2007.
- ^ Hruska, Joel (August 9, 2007). «Microsoft releases information on upcoming D3D 10.1 update». Retrieved August 10, 2008.
- ^ Lowe, Scott (January 13, 2010). «An updated guide to common Microsoft software versions». TechRepublic. CBS Interactive. Retrieved March 17, 2016.
- ^ a b «Notable Changes in Vista Service Pack 1». Microsoft. Archived from the original on 3 May 2008. Retrieved 2 May 2008.
- ^ LeBlanc, Brandon (April 28, 2009). «Windows Vista SP2 RTM + Windows Vista SP1 Blocker Tool Removed». Windows Vista Team Blog. Archived from the original on May 18, 2014.
- ^ a b Nash, Mike (October 25, 2008). «Windows Vista Team Blog : Windows Vista Service Pack 2 Beta». Archived from the original on May 9, 2013. Retrieved October 25, 2008.
- ^ «Information about Windows Server 2008 Service Pack 2 and Windows Vista Service Pack 2». Microsoft. October 2, 2008. Retrieved October 17, 2008.
- ^ «What’s New In Windows Vista SP2?». February 6, 2009. Archived from the original on February 12, 2009. Retrieved February 6, 2009.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (February 24, 2009). «Windows Vista SP2: What to Expect». IT Pro. Penton. Retrieved May 30, 2022.
- ^ «Description of the Platform Update for Windows Server 2008 and the Platform Update for Windows Vista». Microsoft Support. October 27, 2009.
- ^ «The Platform Update for Windows Vista». DirectX Developer Blog. September 10, 2009. Archived from the original on April 8, 2014.
- ^ a b Lawrence, Mark (25 November 2009). «Internet Explorer announces to use DirectWrite & Direct2D (comment from Microsoft official)». Archived from the original on 8 April 2014.
- ^ «Platform Update Supplement for Windows Vista and for Windows Server 2008». Microsoft Support (4.0 ed.). Microsoft. February 8, 2011. Archived from the original on December 28, 2011. Retrieved June 28, 2019.
- ^ «Customer guidance for CVE-2019-0708». Microsoft. Retrieved September 16, 2019.
- ^ Greenberg, Andy (August 13, 2019). «DejaBlue: New BlueKeep-Style Bugs Renew The Risk Of A Windows worm». wired. Retrieved August 15, 2019.
- ^ «Build number changing to 6003 in Windows Server 2008».
- ^ «May 14, 2019—KB4499180 (Security-only update)». Microsoft Support. Retrieved January 14, 2022.
- ^ «CVE-2019-1162 — Security Update Guide — Microsoft Windows ALPC Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability». Customer Guidance Security Update Guide. Microsoft. August 13, 2019. Retrieved December 22, 2020.
- ^ «Microsoft Security Advisory 4022344». Microsoft. Retrieved December 23, 2020.
- ^ «The Mojave Experiment». Mojaveexperiment.com. Retrieved October 2, 2008.
- ^ «The Mojave Experiment: Microsoft Windows Vista». Microsoft.
- ^ «Blog Posts Poke Holes in ‘Taste Test’ by Microsoft». The New York Times. August 4, 2008. Retrieved April 8, 2009.
- ^ Oiaga, Marius (November 2, 2007). «Windows Vista Tastes Like Bubbles…» softpedia. Retrieved February 23, 2022.
- ^ ssinchak (June 27, 2007). «Hacking Windows Vista: Speeding Up the System Boot». Extremetech. Retrieved July 30, 2022.
- ^ Anderson, Tim (December 6, 2007). «Is Windows Vista slower than Windows XP?». The Guardian. Retrieved July 30, 2022.
- ^ DirectX 10: The Future of PC Gaming, Tim Smalley, 30 November 2006 Archived April 23, 2008, at the Wayback Machine. Bit-tech.net (November 30, 2006). Retrieved on October 14, 2011.
- ^ Durham, Joel (May 12, 2008). «Gaming Performance: Windows Vista SP1 vs. XP SP3». ExtremeTech. Ziff Davis. Archived from the original on June 7, 2011. Retrieved July 29, 2008.
- ^ Bright, Peter (March 19, 2007). «Windows Vista: more than just a pretty face». ArsTechnica. Condé Nast. Retrieved July 15, 2015.
- ^ Bright, Peter (June 7, 2007). «Windows Vista: Under the Hood». ArsTechnica. Condé Nast. Retrieved July 15, 2015.
- ^ «Paul Thurrott’s SuperSite for Windows: Windows Vista Review, Part 1: Introduction». August 19, 2007. Archived from the original on August 19, 2007. Retrieved December 31, 2019.
- ^ «Windows Vista Named «Best of CES» at the 2007 International Consumer Electronics Show». News Center. Microsoft. January 10, 2007. Retrieved May 25, 2015.
- ^ «Best of CES 2007 awards Consumer Electronics Show, January 8 to 11». CNET. CBS Interactive. 2007. Archived from the original on January 22, 2007. Retrieved May 25, 2015.
- ^ Tynan, Dan (December 16, 2007). «The 15 Biggest Tech Disappointments of 2007». PC World. IDG. Archived from the original on December 18, 2007. Retrieved December 18, 2007.: listed as No. 1 of «The 15 Biggest Tech Disappointments of 2007»
- ^ McAllister, Neil (January 21, 2008). «Tech’s all-time top 25 flops». InfoWorld. IDG. Retrieved January 27, 2008.
- ^ Flynn, Laurie (April 26, 2007). «Apple Zooms Past Rivals, With 88% Profit Growth». The New York Times. Retrieved December 2, 2015.
- ^ Prague, Liam (February 1, 2022). «Happy birthday, Windows Vista: Troubled teen hits 15». www.theregister.com. Retrieved July 29, 2022.
- ^ Horowitz, Michael (April 23, 2008). «Who’s selling Windows XP in July?». CNET. CBS Interactive. Retrieved March 14, 2016.
- ^ Hoover, J. Nicholas (May 8, 2008). «Microsoft’s Windows Vista Spin Merits Second Look». InformationWeek. UBM plc. Retrieved February 16, 2009.
- ^ Gillen, Al; Waldman, Brett (March 2008). «Document at a Glance – 211087». IDC. Archived from the original on December 16, 2008. Retrieved February 16, 2009.
- ^ O’Neill, Shane (October 30, 2008). «Vista Fights for Relevancy Against Poor Sales, XP, Windows 7». PC World. IDG. Retrieved February 16, 2009.
- ^ Lai, Eric (February 7, 2009). «Vista Makes Converts of Gamers, Enterprises». PC World. Retrieved February 9, 2009.
- ^ Lai, Eric (28 May 2009). «Microsoft: Vista’s enterprise momentum will ‘accrue’ for Windows 7». Computerworld. Archived from the original on 2 March 2007. Retrieved 2 June 2009.
- ^ Reller, Tami (May 28, 2009). «Cowen and Company Technology Media & Telecom Conference». Microsoft. Archived from the original (DOC) on June 16, 2009.
- ^ Microsoft: First Month Vista Sales Double XP, article by Nate Mook Archived December 24, 2007, at the Wayback Machine. Betanews.com (March 26, 2007). Retrieved on October 14, 2011.
- ^ Fried, Ina (September 27, 2007). «Microsoft extends Windows XP’s stay». CNET.
- ^ Windows XP vs. Vista: An Explosion of Opinion Archived February 12, 2022, at the Wayback Machine. Abcnews.go.com (March 20, 2008). Retrieved on October 14, 2011.
- ^ «Leopard drubs Vista in corporate satisfaction survey». March 26, 2008. Archived from the original on November 9, 2019. Retrieved May 30, 2022.
- ^ «AMD 50×15—World Internet Usage». AMD. February 2, 2009. Archived from the original on February 24, 2008. Retrieved November 1, 2009.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (September 16, 2006). «Allchin: 200 Million Windows Vista Users in 24 Months». IT Pro. Penton. Archived from the original on November 9, 2019. Retrieved May 30, 2022.
- ^ Sullivan, John (March 6, 2007). «What’s wrong with Microsoft Windows Vista?». Free Software Foundation. Retrieved March 24, 2007.
- ^ Spooner, John G.; Foley, Mary Jo (August 5, 2005). «Will Your PC Run Windows Vista?». eWeek. QuinStreet. Retrieved August 15, 2006.[permanent dead link]
- ^ Judge, Elizabeth (May 20, 2006). «Windows revamp ‘too advanced for most PCs’«. The Times. London. Retrieved August 15, 2006.
- ^ Gregg Keizer (November 26, 2007).Lawyers: Even Microsoft Confused Over Vista Marketing Archived November 28, 2007, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ «They Criticized Vista. And They Should Know.» Archived April 13, 2019, at the Wayback Machine, The New York Times, March 9, 2008.
- ^ Fisher, Ken (January 28, 2007). «Vista «upgrade» drops compliance checking, requires the old OS to install». Ars Technica. Retrieved January 28, 2007.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (February 3, 2007). «How to Clean Install Windows Vista with Upgrade Media». Supersite for Windows. Penton. Archived from the original on February 5, 2007. Retrieved February 5, 2007.
- ^ Fried, Ina (October 17, 2006). «Microsoft limits Vista transfers». CNET. CBS Interactive.
- ^
Beer, Stan (August 30, 2006). «Windows Vista too expensive says, users». ITWire.com. Archived from the original on September 9, 2006. Retrieved October 19, 2006. - ^ «Microsoft starts Vista hard sell». Technology. BBC News. January 30, 2007. Retrieved January 30, 2007.
- ^ Protalinski, Emil (June 25, 2009). «Windows 7 pricing announced: cheaper than Vista (Updated)». Retrieved October 4, 2009.
- ^ «Output Content Protection and Windows Vista». WHDC. Microsoft. April 27, 2005. Archived from the original on November 16, 2006. Retrieved January 8, 2007.
- ^ Gutmann, Peter (January 27, 2007). «A Cost Analysis of Windows Vista Content Protection». Retrieved January 27, 2007. Also available: PDF version Archived May 11, 2011, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Bott and Ou call out Gutmann’s Vista FUD Archived August 31, 2007, at the Wayback Machine. Blogs.guardian.co.uk. Retrieved on October 14, 2011.
- ^ Smith, Paul (December 31, 2006). «Windows Vista DRM nonsense». Retrieved January 3, 2007.
- ^ Fisher, Ken (May 21, 2006). «Hollywood reportedly in agreement to delay forced quality downgrades for Blu-ray, HD DVD». Ars Technica. Retrieved January 21, 2007.
- ^ Marsh, Dave (January 20, 2007). «Windows Vista Content Protection—Twenty Questions (and Answers)». Windows Vista team blog. Microsoft. Archived from the original on January 21, 2013. Retrieved January 20, 2007.
- ^ «User Account Control: yes, you can turn it off. Is this a good or a bad thing?». Ars Technica. September 10, 2006.
- ^ «Don’t Shut Off Vista UAC, There’s A Better Way». InformationWeek. June 11, 2007. Retrieved October 14, 2011.
- ^ Torode, Christina (April 2, 2008). «Minasi says Vista SP1 solves problems, adds new ones». SearchWinIT.com.
- ^ «Downgrade rights for owners of licensed Windows 8 and Windows 7» (PDF). microsoft.com.
External links[edit]
- Windows Vista End of Support
- Windows Vista Service Pack 2 (SP2) Update
#1

Отправлено 10 Июль 2008 — 15:50
eXPert9504
-
- Участники
-
- 85 сообщений
Advanced Member
Скачал Vistу. Но там 8 версий 4 из которых х64. Помогите с выбором. Стоит ли ставить х64 без необходимости 4гб оперативки?
Нужна помощь в поиске программы, кряка, драйверов? Пишите в личку))).
Наверх
#2

j.a.g.u.a.r
Отправлено 10 Июль 2008 — 16:27
j.a.g.u.a.r
-
- Участники
-
- 20 сообщений
Участник
Скачал Vistу. Но там 8 версий 4 из которых х64. Помогите с выбором. Стоит ли ставить х64 без необходимости 4гб оперативки?
Для начала полную конфигурацию ПК в студию, потом я тебе дам четкий ответ, какую именно тебе лучше ставить
Наверх
#3

eXPert9504
Отправлено 10 Июль 2008 — 16:56
eXPert9504
-
- Участники
-
- 85 сообщений
Advanced Member
Компьютер
Тип компьютера ACPI компьютер на базе x86
Операционная система Microsoft Windows Vista Ultimate
Пакет обновления ОС —
Internet Explorer 7.0.6000.16386 (IE 7.0 — Vista)
DirectX DirectX 10.0
Имя компьютера EXPERT-ПК
Имя пользователя eXPert
Вход в домен eXPert-ПК
Дата / Время 2008-07-10 / 19:56
Системная плата
Тип ЦП DualCore Intel Core 2 Duo E4400, 2000 MHz (10 x 200)
Системная плата Gigabyte GA-945PLM-S2 v1 (3 PCI, 1 PCI-E x16, 2 DDR2 DIMM, Audio, Gigabit LAN)
Чипсет системной платы Intel Lakeport i945PL
Системная память 1024 Мб (DDR2-667 DDR2 SDRAM)
DIMM1: Kingston 9905316-105.A00LF 1 Гб DDR2-667 DDR2 SDRAM (5-5-5-15 @ 333 МГц) (4-4-4-12 @ 266 МГц) (3-3-3-9 @ 200 МГц)
Тип BIOS Award Modular (04/26/07)
Коммуникационный порт Последовательный порт (COM1)
Коммуникационный порт Последовательный порт (COM2)
Коммуникационный порт Порт принтера (LPT1)
Дисплей
Видеоадаптер NVIDIA GeForce 8600 GT (256 Мб)
Видеоадаптер NVIDIA GeForce 8600 GT (256 Мб)
3D-акселератор nVIDIA GeForce 8600 GT
Монитор Acer AL1716 [17″ LCD] (L460C260404E)
Мультимедиа
Звуковой адаптер Realtek ALC883 @ Intel 82801GB ICH7 — High Definition Audio Controller [A-1]
Хранение данных
Контроллер IDE Контроллер Intel® 82801GB/GR/GH (семейство ICH7) Serial ATA Storage — 27C0
Контроллер хранения данных Microsoft iSCSI инициатор
Флоппи-накопитель Дисковод
Дисковый накопитель ST3250410AS ATA Device (250 Гб, 7200 RPM, SATA-II)
Оптический накопитель HL-DT-ST DVDRAM GSA-H44N ATA Device (DVD+R9:10x, DVD-R9:10x, DVD+RW:18x/8x, DVD-RW:18x/6x, DVD-RAM:12x, DVD-ROM:16x, CD:48x/32x/48x DVD+RW/DVD-RW/DVD-RAM)
Статус SMART жёстких дисков OK
Разделы
C: (NTFS) 61498 Мб (51364 Мб свободно)
D: (NTFS) 176971 Мб (140019 Мб свободно)
Общий объём 232.9 Гб (186.9 Гб свободно)
Ввод
Клавиатура Стандартная (101/102 клавиши) или клавиатура PS/2 Microsoft Natural
Мышь PS/2-совместимая мышь
Периферийные устройства
Принтер Fax
Принтер Microsoft XPS Document Writer
Контроллер USB1 Intel 82801GB ICH7 — USB Universal Host Controller [A-1]
Контроллер USB1 Intel 82801GB ICH7 — USB Universal Host Controller [A-1]
Контроллер USB1 Intel 82801GB ICH7 — USB Universal Host Controller [A-1]
Контроллер USB1 Intel 82801GB ICH7 — USB Universal Host Controller [A-1]
Контроллер USB2 Intel 82801GB ICH7 — Enhanced USB2 Controller [A-1]
DMI
DMI поставщик BIOS Award Software International, Inc.
DMI версия BIOS F5
DMI производитель системы
DMI система
DMI системная версия
DMI системный серийный номер
DMI системный UUID 00000000-00000000-00000016-E68B1240
DMI производитель системной платы Gigabyte Technology Co., Ltd.
DMI системная плата 945PLM-S2
DMI версия системной платы x.x
DMI серийный номер системной платы
DMI производитель шасси
DMI версия шасси
DMI серийный номер шасси
DMI Asset-тэг шасси
DMI тип шасси Desktop Case
DMI всего / свободных сокетов памяти 4 / 3
Сообщение отредактировал eXPert9504: 10 Июль 2008 — 16:57
Нужна помощь в поиске программы, кряка, драйверов? Пишите в личку))).
Наверх
#4

j.a.g.u.a.r
Отправлено 10 Июль 2008 — 17:20
j.a.g.u.a.r
-
- Участники
-
- 20 сообщений
Участник
Windows Vista Home Premium SP1 X86 rus
Наверх
#5

eXPert9504
Отправлено 11 Июль 2008 — 08:31
eXPert9504
-
- Участники
-
- 85 сообщений
Advanced Member
х64 быстрее работает чем х86?
Нужна помощь в поиске программы, кряка, драйверов? Пишите в личку))).
Наверх
#6

kalyambus
Отправлено 23 Июль 2008 — 22:47
kalyambus
-
- Участники
-
- 26 сообщений
Участник
по своему опыту, советую поставить х86, и лучше Ultimate. С х64 больше напряга. Самый примитивный — две директории програм файлз. к тому же не все 32-разрядные проги смогут корректно стать на х64.
К тому же для того что б почувствовать реальную производительность 64-разр. системы нужно минимум 4 гига оперативки на висте!!!
Наверх
#7

mace
Отправлено 24 Июль 2008 — 01:24
mace
-
- Участники
-
- 5 сообщений
Читатель
по своему опыту, советую поставить х86, и лучше Ultimate. С х64 больше напряга. Самый примитивный — две директории програм файлз. к тому же не все 32-разрядные проги смогут корректно стать на х64.
К тому же для того что б почувствовать реальную производительность 64-разр. системы нужно минимум 4 гига оперативки на висте!!!
слушай посоветуй и мне тогда, у меня стоит х64 Виста, но мне почему то кажеться, что она изредка мне инет подлагивает, мож есть где-нить хороший ФАК, как избавится от служб ненужных, ненужных вопросов, и где можно взяти Хорошую (если можна так назвать) Висту
конфиг компа
QuadCore Intel Core 2 Quad Q6600, 2400 MHz (9 x 267)
Системная плата Asus P5KPL-E (3 PCI, 2 PCI-E x1, 1 PCI-E x16, 4 DDR2 DIMM, Audio, Video, Gigabit LAN)
Чипсет системной платы Intel Bearlake G31
Системная память 4096 Мб (DDR2-800 DDR2 SDRAM)
DIMM2: Corsair XMS2 CM2X2048-6400C5DHX 2 Гб DDR2-800 DDR2 SDRAM (5-5-5-18 @ 400 МГц) (4-4-4-13 @ 270 МГц)
DIMM4: Corsair XMS2 CM2X2048-6400C5DHX 2 Гб DDR2-800 DDR2 SDRAM (5-5-5-18 @ 400 МГц) (4-4-4-13 @ 270 МГц)
Видеоадаптер NVIDIA GeForce 8600 GT (1024 Мб)
интересует можно ли грубо говоря увеличить скорость потока (интернет).
Спасибо за помощь.
Наверх
#8

VERWOLF999
Отправлено 24 Июль 2008 — 02:55
VERWOLF999
-
- Участники
-
- 130 сообщений
Advanced Member
Что значит инет подлагивает?
На 64 инет идет лучше, чем на 32! Даже под диал-ап…
Просто, наверное, 64-битный ишак хреново настроен (да, он периодически глючит, имеется в виду исключительно русская версия…). Воспользуйся 32-битным (в опциях есть).
С твоими параметрами железа я бы только видяшку поменял для полного счастья.
А по поводу 32 или 64… Нормально работают 32-битные приложения под 64 (если, конечно, стоит СП1), а железо у тебя именно поддерживающее 64!
Кстати, у меня 64 ультима на 2-х гигах ОЗУ-хи. После настроек и периодическом дефраге жестяка (планировку отключил) летает (увы, старые игрухи подтормаживают). Используется исключительно для работы (ноут, система баребоне COMPAL IFL90, параметры уже на форуме приводил).
А по поводу напряга с двумя директориями програмс файлз, интересно, для чего туда вообще лезть, поискать экзешники??? Тупизм!!! 64 если засунет при инталяции прогу не в ту директорию сразу об этом сообщит и самостоятельно переинсталирует в нужную без протери производительности.
Наверх
#9

mace
Отправлено 24 Июль 2008 — 12:01
mace
-
- Участники
-
- 5 сообщений
Читатель
Что значит инет подлагивает?
На 64 инет идет лучше, чем на 32! Даже под диал-ап…
Просто, наверное, 64-битный ишак хреново настроен (да, он периодически глючит, имеется в виду исключительно русская версия…). Воспользуйся 32-битным (в опциях есть).
С твоими параметрами железа я бы только видяшку поменял для полного счастья.
А по поводу 32 или 64… Нормально работают 32-битные приложения под 64 (если, конечно, стоит СП1), а железо у тебя именно поддерживающее 64!
Кстати, у меня 64 ультима на 2-х гигах ОЗУ-хи. После настроек и периодическом дефраге жестяка (планировку отключил) летает (увы, старые игрухи подтормаживают). Используется исключительно для работы (ноут, система баребоне COMPAL IFL90, параметры уже на форуме приводил).
А по поводу напряга с двумя директориями програмс файлз, интересно, для чего туда вообще лезть, поискать экзешники??? Тупизм!!! 64 если засунет при инталяции прогу не в ту директорию сразу об этом сообщит и самостоятельно переинсталирует в нужную без протери производительности.
та я изначально не хотел брать 8800, просто в игры мя как-то не прёт уже гамать) разве что в WoWку изредка, а ей сильная видюха не нужна)
Т.е. ты предлагаешь поставить себе англ. ультим? А как там с подержкой, укр/рус. шрифтов?
_http://torrents.ru/forum/viewtopic.php?t=783124 вот эта сборка, подойдет?
Наверх
#10

kalyambus
Отправлено 24 Июль 2008 — 16:27
kalyambus
-
- Участники
-
- 26 сообщений
Участник
слушай посоветуй и мне тогда, у меня стоит х64 Виста, но мне почему то кажеться, что она изредка мне инет подлагивает, ……
Попробуйте вто самое время когда «инет подлагивает» открыт монитор ресурсов (правой кнопкой на панели задач-диспетчер задач-вкладка быстродествие-монитор ресурсов). Там имеется 4 графика, описывающие работу системы . Щелкнув на графике Сеть можно подробно увидеть количество пакетов, отправляемых и получаемых с интернета.
Возможно в этот момет работает центр обновления или загружаются обновления на другие программы.
И еще советую периодически чистить историю (журнал) просмотров в интернет броузере. (напр в IE7: сервис-удалить журнал обозревателя-журнал/удалить историю)
Наверх
#11

mace
Отправлено 24 Июль 2008 — 17:33
mace
-
- Участники
-
- 5 сообщений
Читатель
Попробуйте вто самое время когда «инет подлагивает» открыт монитор ресурсов (правой кнопкой на панели задач-диспетчер задач-вкладка быстродествие-монитор ресурсов). Там имеется 4 графика, описывающие работу системы . Щелкнув на графике Сеть можно подробно увидеть количество пакетов, отправляемых и получаемых с интернета.
Возможно в этот момет работает центр обновления или загружаются обновления на другие программы.И еще советую периодически чистить историю (журнал) просмотров в интернет броузере. (напр в IE7: сервис-удалить журнал обозревателя-журнал/удалить историю)
мммм хорошо гляну
та я IE не юзаю, я по опере, и кеш по мере тоже чищу.
Спасибо большое за советы
Наверх
#12

alex1x
Отправлено 25 Июль 2008 — 17:36
alex1x
-
- Участники
-
- 175 сообщений
Advanced Member
Т.е. ты предлагаешь поставить себе англ. ультим? А как там с подержкой, укр/рус. шрифтов?
_http://torrents.ru/forum/viewtopic.php?t=783124 вот эта сборка, подойдет?
англ ультим. имеет поддержку всех щрифтов и языков, включая японский.
плюс меняется язык интерфейса в 3 клика (полностью)
Люди стали умирать, когда они поверили в то, что они смертны.
Наверх
#13

samirhung
Отправлено 25 Июль 2008 — 19:18
samirhung
-
- Участники
-
- 19 сообщений
Читатель
плюс меняется язык интерфейса в 3 клика (полностью)
а с этого места по подробней пожайлуста. просто у самого такая проблема. опишите эту процедуру.
Наверх
#14

kalyambus
Отправлено 25 Июль 2008 — 19:35
kalyambus
-
- Участники
-
- 26 сообщений
Участник
а с этого места по подробней пожайлуста. просто у самого такая проблема. опишите эту процедуру.
Эта процедура доступна только после установки языковых пакетов. Установить их можна с помощью центра обновлений (все), Русский языковый пакет есть гдето на форуме.
Есле проблема касается отображения шрифта с украинской раскладки, смотрим тут _https://philka.ru/forum/index.php?showtopic=14581&st=0&p=92147&#entry92147
Сообщение отредактировал kalyambus: 25 Июль 2008 — 19:36
Наверх
#15

mace
Отправлено 26 Июль 2008 — 18:54
mace
-
- Участники
-
- 5 сообщений
Читатель
Эта процедура доступна только после установки языковых пакетов. Установить их можна с помощью центра обновлений (все), Русский языковый пакет есть гдето на форуме.
Есле проблема касается отображения шрифта с украинской раскладки, смотрим тут _https://philka.ru/forum/index.php?showtopic=14581&st=0&p=92147&#entry92147
спасибо огромное) помог после установки новой винды)
Наверх
#16

The MEk
Отправлено 31 Июль 2008 — 12:36
The MEk
-
- Участники
-
- 4 сообщений
Читатель
2 месяца юзаю висту х64 (сначала на 2 гигах оперативы, теперь на 4) пробовал х32, дык х64 работает порезвее, в частности игрули шустрее грузятся/бегають
Наверх
#17

igro70
Отправлено 04 Август 2008 — 14:03
igro70
-
- Участники
-
- 6 сообщений
Читатель
Проблема 64 висты.Невозможно установить WED-камеру.При установке дров пишет отказ установки т.к дрова без подписи.
Танцы с бубном не помогают.
Имею две камеры обе не работают в 64 Висте это Jenius Messenger 310 и Defender C-011.Хотя первая имет сертификат Висты а вторая даже вроде как подерку дров судя по паспорту.
В Висте 32 обе работают отлично.
Пробовал даже так
1При перезагрузке F8 дальше установить дрова без подписи.
2 Запускаем строку bcdedit /set testsigning off
Максиму что удавалось это работа камеры до перезагрузки потом снова пишет драйвер отключен обр. к поставщику.
Друзья может у кого есть решение этой проблемы!!!!!!!!!!
Сообщение отредактировал igro70: 04 Август 2008 — 14:04
Наверх
Недавно Microsoft огласила системные требования и рекомендации, касающиеся Windows Vista. Надо сказать, что предоставленные компанией сведения удивят многих.
Основные системные требования
Минимальные требования для основной версии — Vista Home Basic — звучат
Недавно Microsoft огласила системные требования и рекомендации, касающиеся Windows Vista. Надо сказать, что предоставленные компанией сведения удивят многих.
Основные системные требования
Минимальные требования для основной версии — Vista Home Basic — звучат как заявления продавцов компьютеров шестилетней давности: 32-разрядный (платформа x86) или 64-разрядный (платформа x64) микропроцессор с частотой не менее 800 МГц, 512 Мбайт оперативной памяти, жесткий диск 20 Гбайт (не менее 15 Гбайт свободного дискового пространства) и привод CD-ROM.
Важно понимать, что обеспечивает такая конфигурация аппаратной части. Vista Home Basic и Vista Home Basic N (версия для Европейского союза, ЕС) не поддерживают превосходный интерфейс Windows Aero (ранее известный как Aero Glass). Минимальные требования не оговаривают тип видеокарты, необходимый для работы интерфейса Aero. Vista Home Basic поддерживает интерфейсы Windows Classic и Vista Basic, работающие практически с любой видеокартой, и интерфейс Vista Standard, визуально напоминающий интерфейс Windows Basic, но включающий композиции для настольных систем нижнего уровня, разработанных Microsoft для Aero. На настольном компьютере интерфейс Windows Vista Standard функционирует более надежно и эффективно, чем интерфейс Windows Vista Basic, но требует 3D-видеокарты c поддержкой стандарта Microsoft DirectX 9.0. Этот стандарт поддерживают большинство видеокарт, существующих сегодня на рынке, включая многие встроенные микросхемы.
Для версий Vista Home Premium, Vista Business (и версию Vista Business N для ЕС), Vista Enterprise и Vista Ultimate требуется процессор 1 ГГц, 1 Гбайт оперативной памяти, видеокарта, подходящая для Aero (т. е. видеокарта или встроенная микросхема с поддержкой стандарта Microsoft DirectX 9.0), жесткий диск 40 Гбайт (не менее 15 Гбайт свободного дискового пространства) и DVD-дисковод.
Рекомендации Microsoft по повышению производительности
Для достижения наилучшей производительности системы Vista Microsoft рекомендует использовать специальную графическую плату с поддержкой Pixel Shader 2.0 (новая технология, ориентированная на поддержку игр и анимации) и новый драйвер Windows Display Driver Model (WDDM). Напомним, что эти технологии поддерживаются большинством существующих на сегодня 3D-видеокарт от крупных производителей, таких как ATI и nVIDIA. Существует даже комплект интегральных графических микросхем Intel Graphics Media Accelerator (GMA) 950 с полной поддержкой интерфейса Vista Aero, что позволяет получать поразительные результаты даже на ноутбуках и планшетных компьютерах низшего класса. Microsoft также рекомендует установку совместимой звуковой карты, предпочтительно с многоканальным звуковым выходом.
Реальные минимальные требования
Заявленные Microsoft рекомендации для системы Vista представляются неадекватными. Попытки запуска Vista на компьютере с процессором 800 МГц и 512 Мбайт оперативной памяти едва ли дадут положительные результаты. Многие корпорации пожелают перейти на Vista на базе существующей аппаратной платформы, но наилучшее и, вероятно, наиболее экономичное решение — это приобретение новых аппаратных средств. Самые перспективные решения включают 64-разрядные многоядерные процессоры AMD или Intel. Сегодня более эффективны и имеют более высокую производительность модели AMD. Это означает, что для настольного компьютера целесообразно приобрести двухъядерный процессор AMD Athlon 64 X2 for Desktop или процессор Intel Pentium класса D, а для ноутбука или планшетного ПК — процессор AMD Turion 64 X2 Mobile Technology. Также хорошо работают и, как правило, имеют продолжительное время работы от батарей микросхемы Core Duo и Core 2 Duo от Intel, однако эти технологии бывают только 32-разрядные.
Что касается оперативной памяти, то не следует рассматривать варианты менее 1 Гбайт, особенно для компьютеров с интегральной графикой, «отбирающей» у системы оперативную память. Для Windows XP чем больше оперативной памяти, тем лучше: Vista также использует все предоставленные ресурсы, динамически меняя объем занимаемой памяти в соответствии с возможностями системы. Создателям контента, инженерам и другим квалифицированным пользователям тоже понадобится больше оперативной памяти. Если беспокоит предельный уровень в 4 Гбайт, налагаемый 32-разрядными компьютерами, можно рассмотреть один из вариантов Vista x64 (доступный для всех пользователей версий Vista Home Basic, Vista Home Premium, Vista Business, Vista Enterprise и Vista Ultimate). В зависимости от версии, эти 64-разрядные системы могут использовать до 128 Гбайт оперативной памяти; для Vista Home Basic возможен доступ к 8 Гбайт оперативной памяти; Vista Home Premium поддерживает 16 Гбайт оперативной памяти.
Какую графическую карту лучше купить? Если только не используется ПК с интегральной графической микросхемой GMA 950 от Intel, целесообразно приобрести специальную графическую карту c выделенной оперативной памятью не менее 64 Мбайт и поддержкой интерфейса Aero. Объем необходимой видеопамяти зависит от разрешения экрана дисплея. Для дисплеев с разрешением 1024 x 768 требуется 64 Мбайт видеопамяти, для 1920 x 1200 — 128 Мбайт, а для дисплеев с еще большим разрешением — не менее 256 Мбайт. Эти цифры не должны пугать: большинство современных графических карт предусматривают не менее 128 Мбайт специализированной памяти. Если предполагается использовать возможности Vista для полнодискового шифрования BitLocker и Boot Integrity, для реализации наиболее защищенного варианта требуется микросхема Trusted Platform Module (TPM) 1.2 на материнской плате. Кстати, функция BitLocker доступна только для версии Vista Enterprise, обслуживаемой в рамках лицензионного соглашения Software Assurance, и для приобретаемой в розницу версии Vista Ultimate.
Рекомендации
Сегодня, учитывая широкую доступность Vista Beta 2, самое время приступить к оценке системы. Необходимые пользователям функции и характер эксплуатации систем — факторы, определяющие конфигурацию аппаратной части, обеспечивающей наибольшую эффективность Vista. Переход на Vista станет революционной модернизацией в силу многих новых возможностей и изменений, реализованных в этой технологии, поэтому никогда не рано начать планирование. Поможет в этом знание требований к аппаратной части.
Поль Тюрро — редактор новостей в Windows IT Pro. Готовит еженедельные выпуски Windows IT Pro UPDATE, а также ежедневные выпуски новостей WinInfo.
С ним можно связаться по адресу: thurott@win2000mag.com


![Microsoft Windows Vista Ultimate SP2 RUS-ENG x86-x64 -4in1- Activated (AIO) [29.11.2010] Скачать торрент](https://torrent-wind.net/uploads/posts/2011-10/1318153822_315d4e491b6c6176793dc0cee628b023.png)
![Microsoft Windows Vista Ultimate SP2 RUS-ENG x86-x64 -4in1- Activated (AIO) [29.11.2010] Скачать торрент Microsoft Windows Vista Ultimate SP2 RUS-ENG x86-x64 -4in1- Activated (AIO) [29.11.2010] Скачать торрент](https://torrent-wind.net/windows/windows_vista/2012-05/22/6zlfjxaukqhmd064e8ytngogj.jpg)
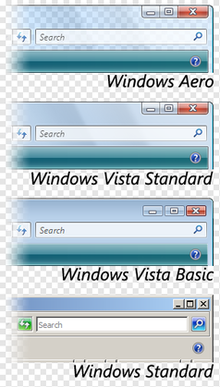



 Наверх
Наверх