В компьютере множество самых разных файлов самых разных форматов. Какими-то файлами из этих форматов мы пользуемся часто, с другими же работаем крайне редко или вообще никогда. Но есть в компьютере и те, знать и уметь пользоваться которыми просто необходимо. И один из них – doc файлы. Это самые разные документы, с работой над которыми начинают свою работу все пользователи, решившие освоить компьютер. Конечно, если Вы используете компьютер только для игр и общения в Интернете, то без Ворда можно спокойно обойтись. Но в этом случае вряд ли Вас можно назвать уверенным пользователем. Ведь уверенный пользователь – это тот, кто умеет выполнять на компьютере основные операции (создавать папку, копировать, удалять) и работать с популярными программами, в числе которых Word и Excel. В этом обзоре я как раз и расскажу, как пользоваться бесплатной программой WindowsWord для просмотра и редактирования файлов типа Doc.
Вот, как выглядит ссылка на программу на моем рабочем столе
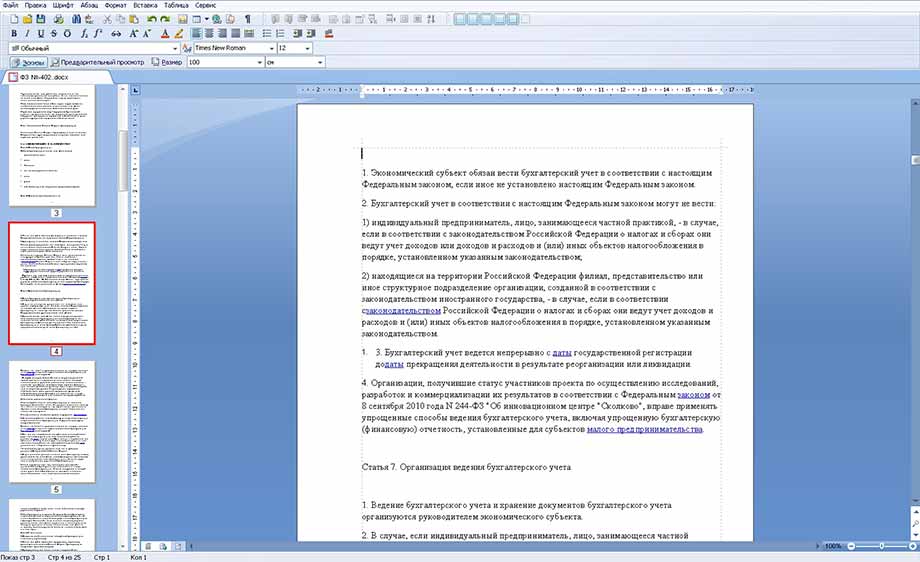
Открываем программу. Нам нужно открыть новый текстовый документ. Для этого нужно нажать файл, как показано на картинке
затем нажать кнопку открыть, как показано ниже
Получаем вот такой обычный в итоге файл
Сохранять файл, также очень просто. Нужно нажать кнопку с дискеткой и файл сохранится
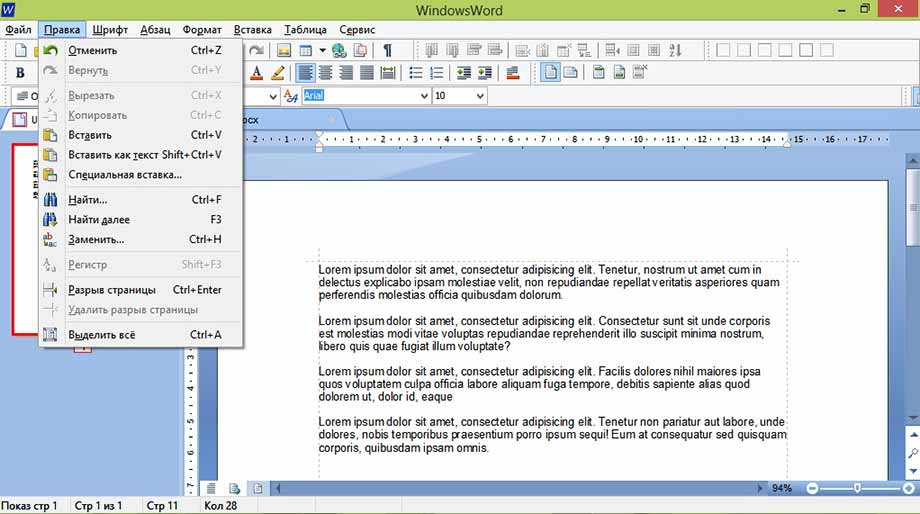
Теперь рассмотрим функцию поиска по документу. Ведь, если документ составляет не один десяток страниц, часто требуется поиск. Для этого на верхней панели инструментов находим вкладку правка и в ней поиск, как показано на рисунке или просто сочетанием клавиш Ctrl+F
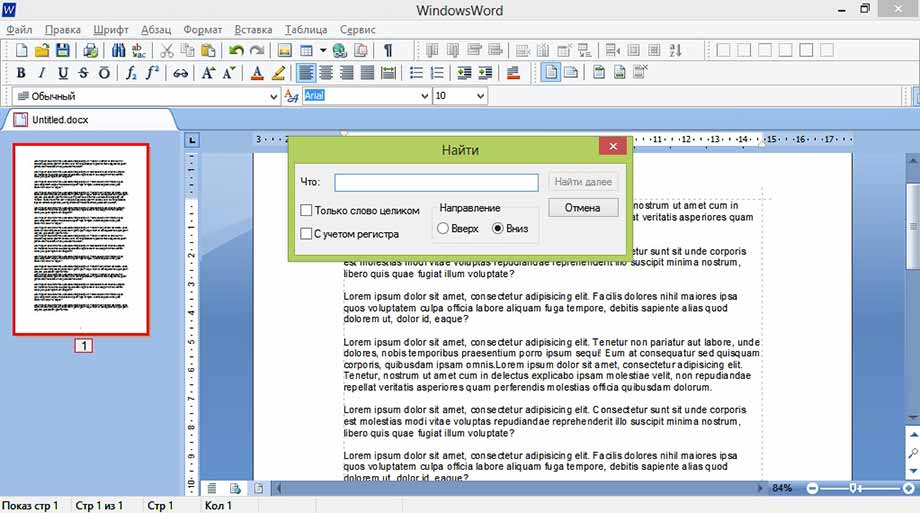
далее вы увидите окно поиска
нем и можно вводить искомые слова.
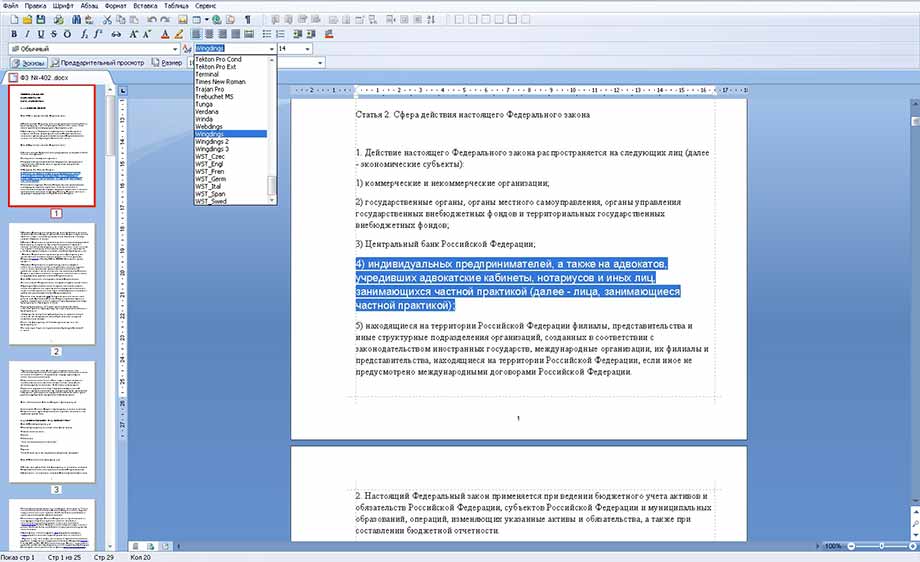
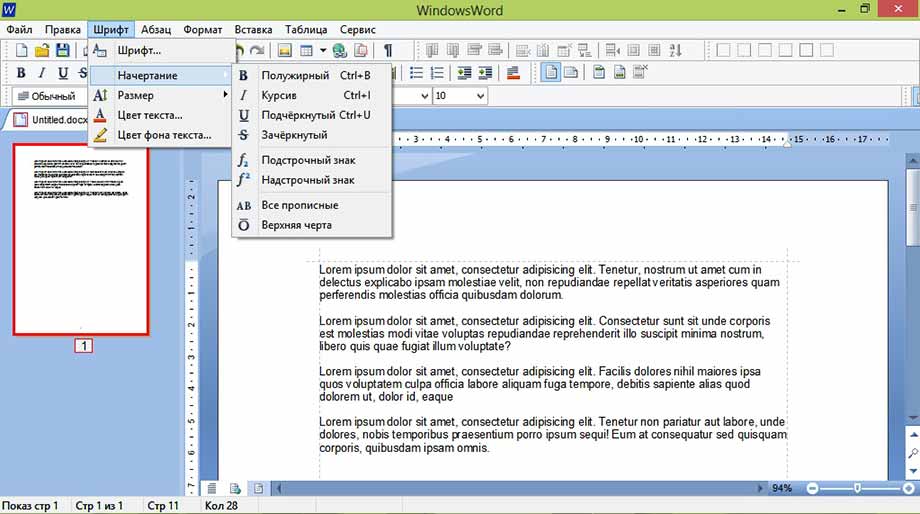
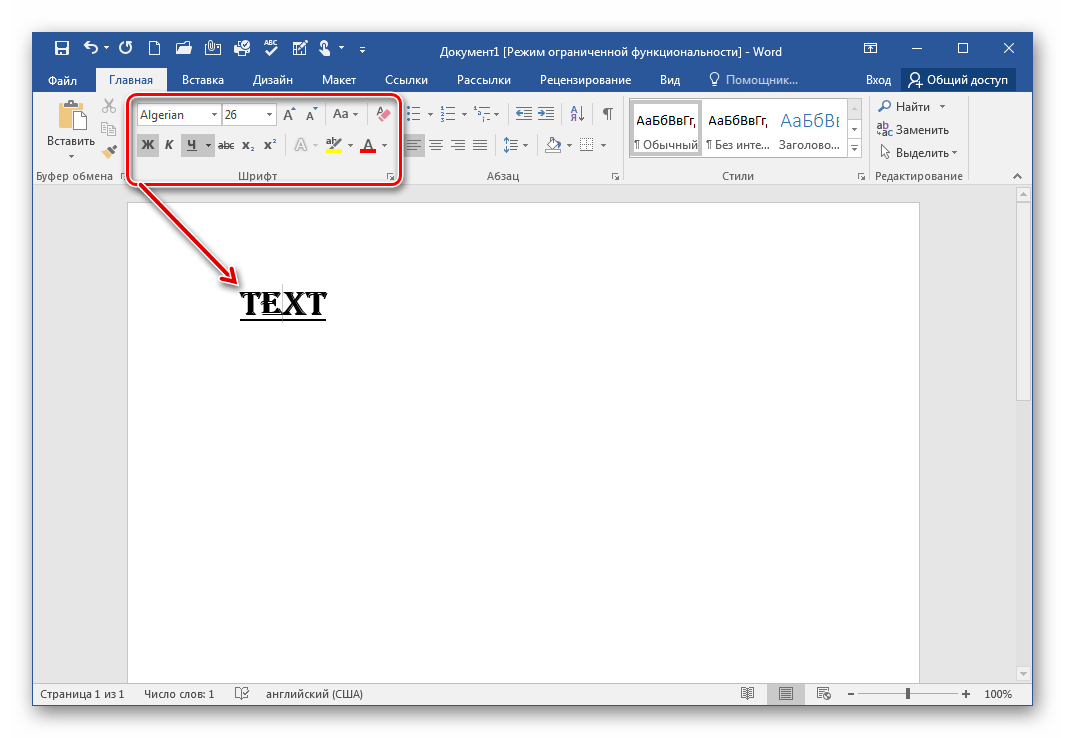
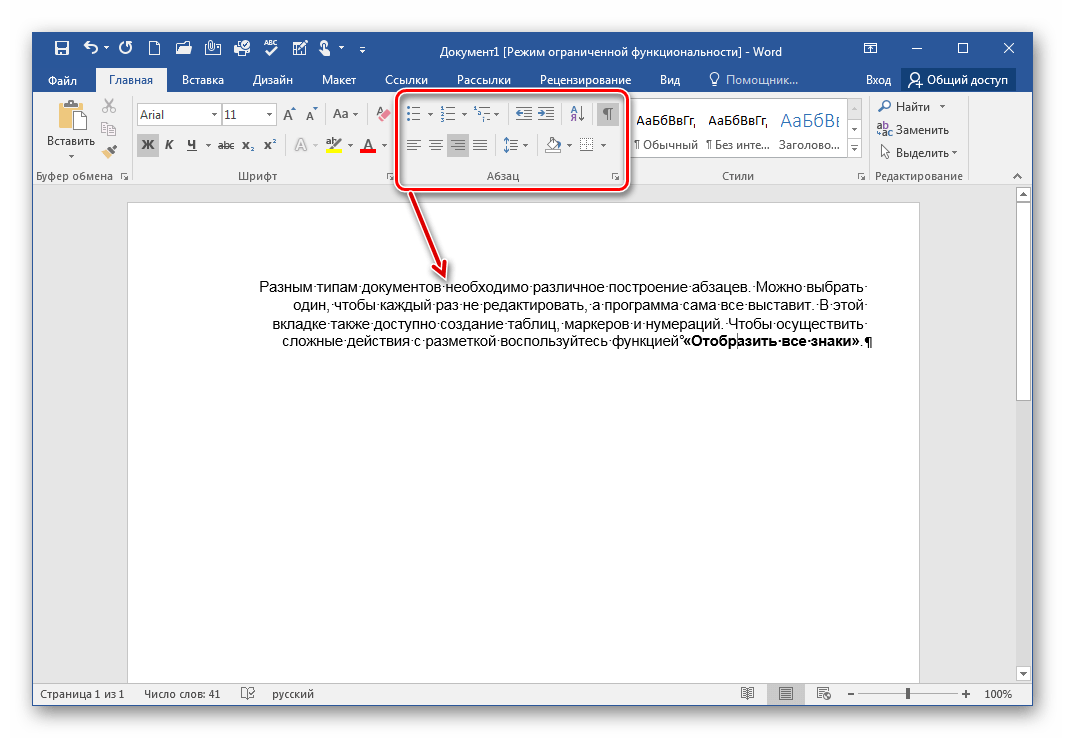
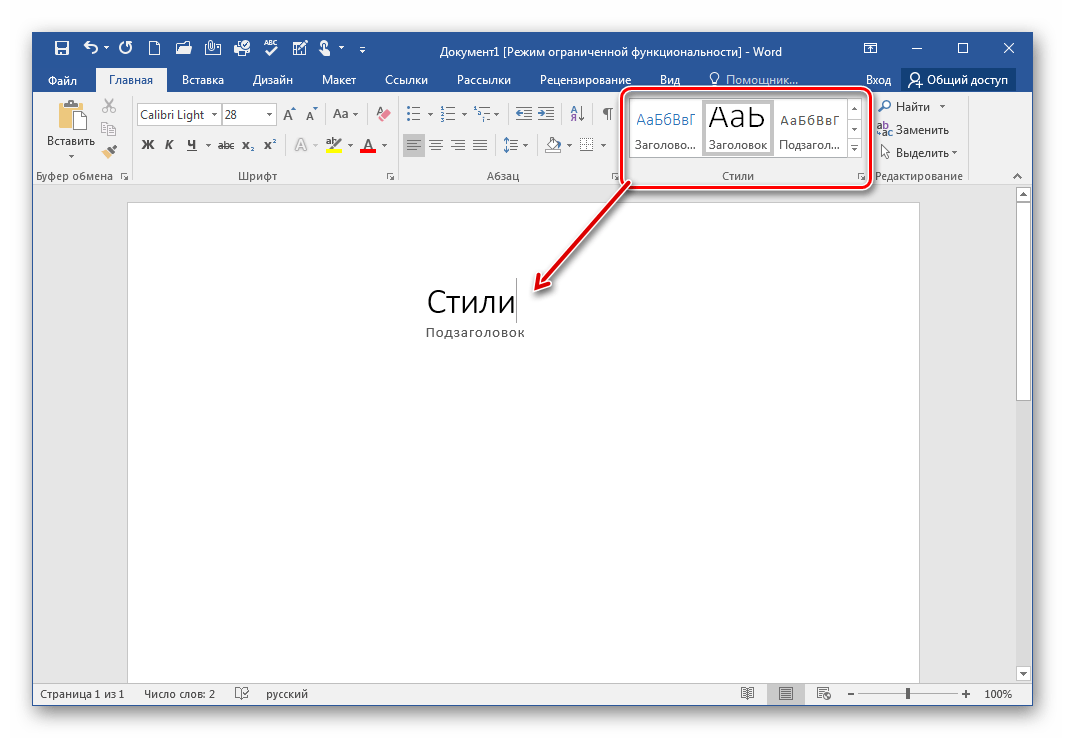
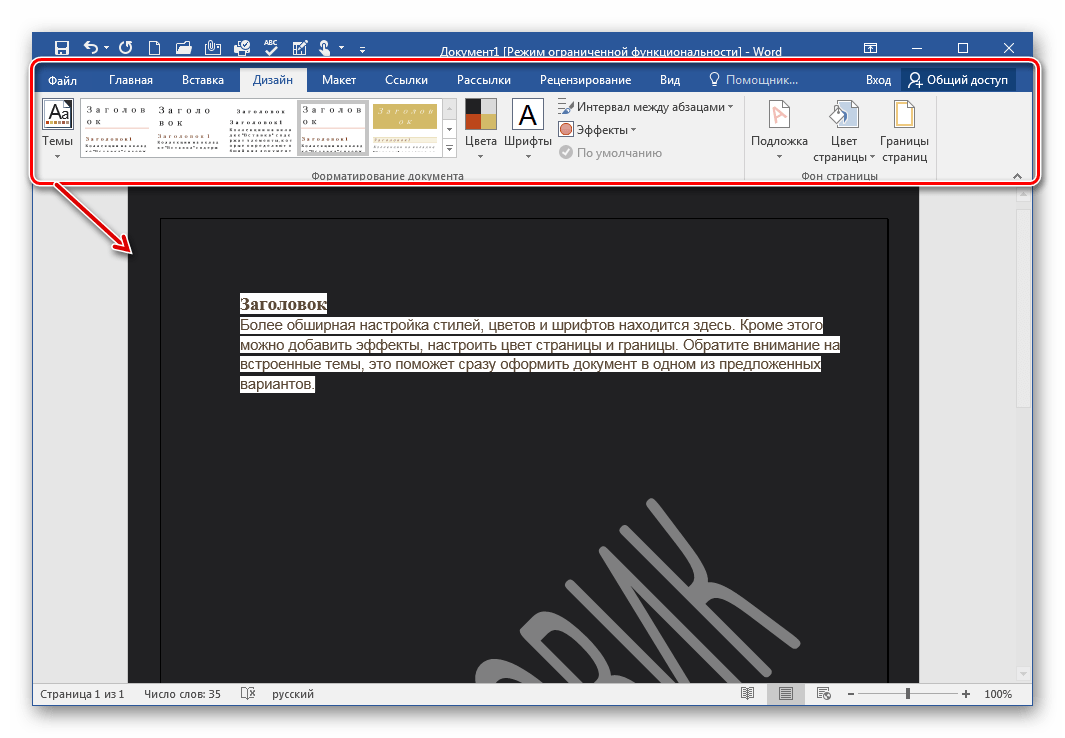
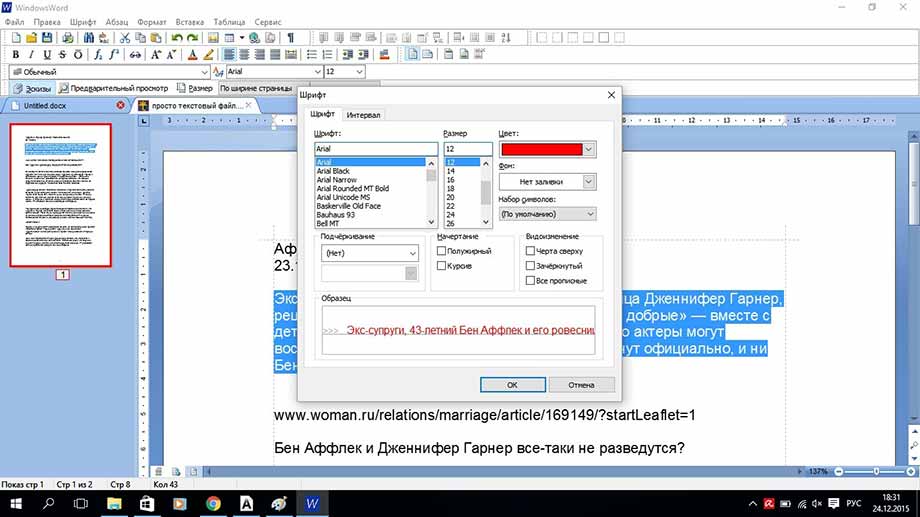
Но не будем забывать о том, что мы редактируем именно текст. Поэтому нам очень важно работать с шрифтом. В программе WindowsWord есть специальное окно Шрифт, которое можно открыть, кликнув на кнопку в верхней панели инструментов Шрифт. Здесь легко поменять шрифт, размер шрифта, стиль написания (жирный, полужирный, курсив, зачеркнутый), а также цвет шрифта и цвет фона шрифта. Вот так выглядит это окно
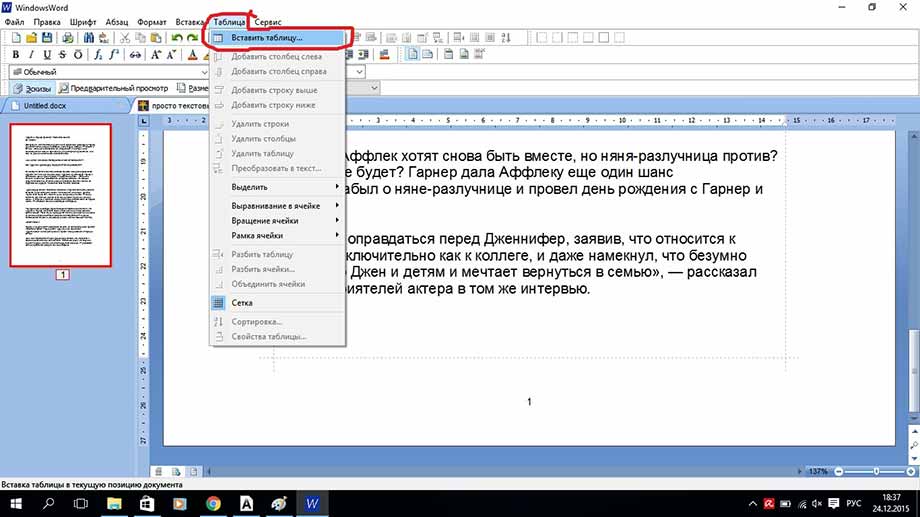
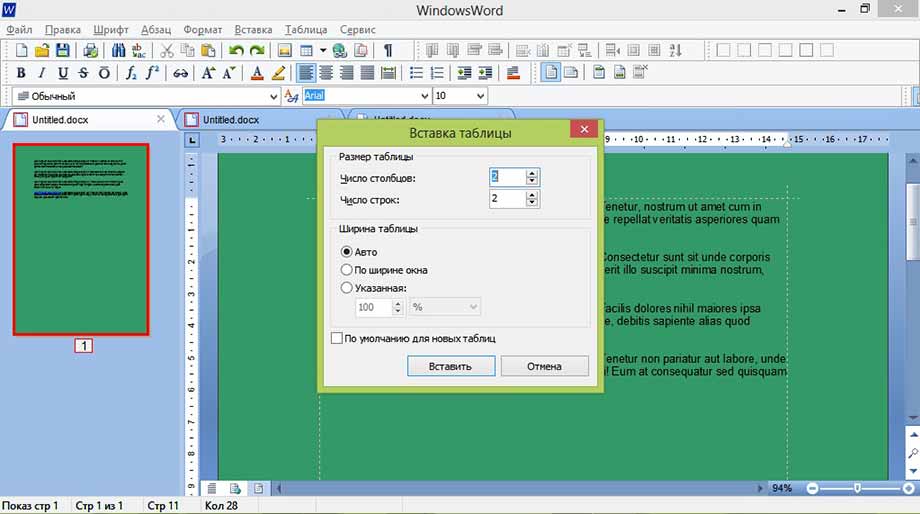
Теперь рассмотрим работу с таблицами. Здесь все очень просто для создания таблицы кликаем на вкладку таблица, создать таблицу, как показано ниже
В открывшемся окне выбираем число строк и столбцов, а также масштаб таблицы
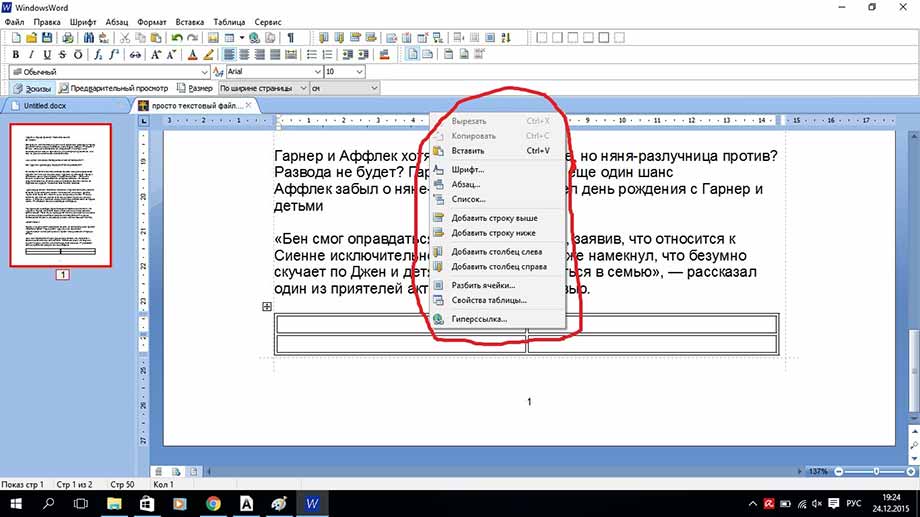
Если кликнуть по полю таблицы правой кнопкой мыши, в открывшемся меню можно выбрать: вырезать, копировать, вставить, изменение параметров шрифта, абзаца, списка, можно добавить строку выше или ниже, а также добавить столбец слева или справа, разбить ячейку и просмотреть свойства всей таблицы
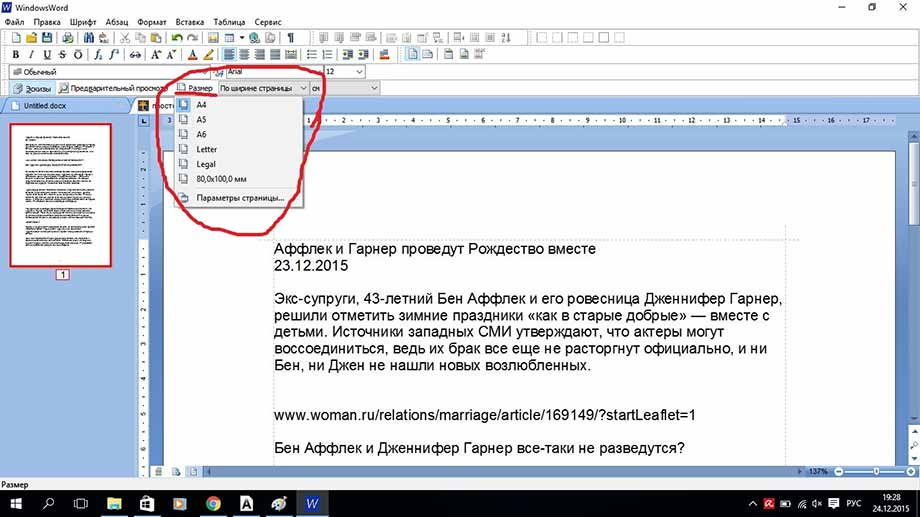
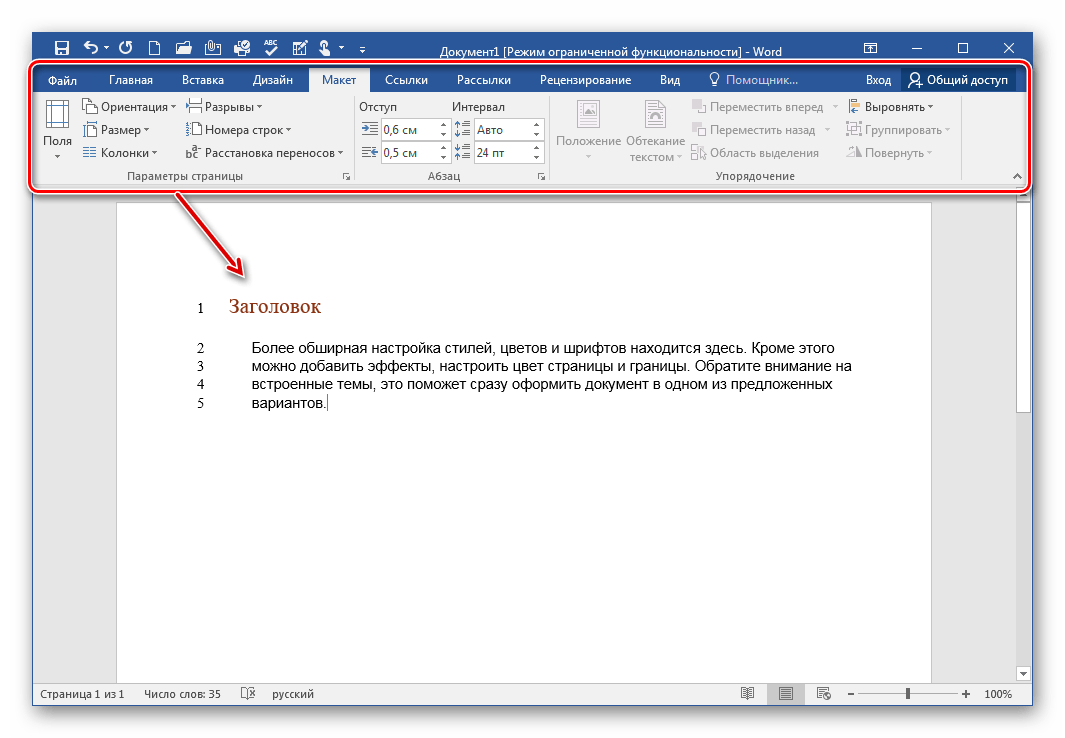
Также можно легко поменять размер документа из А4 в А5, А6 или вообще задать свой размер страницы. Кнопка размер находится в нижней части панели инструментов
На этом я закончу свой обзор основных функций нового бесплатного редактора WindowsWord.
В итоге, могу сказать, что пользоваться им очень просто, легче Microsoft Office на мой взгляд. И для новичков подходит больше, т.к. нет огромного числа кнопок, в которых новичку так просто запутаться. Для обычного редактирования подходит великолепно. Основные плюсы: простота использования и бесплатность данного текстового редактора.
Совсем недавно состоялся релиз новой программы, которая выполняет все функции офиса, но при этом не требует дополнительной активации и довольно проста в применении на практике. Именно об основах работы с ней мы и поговорим ниже.
Первые шаги
Итак, вы установили программу, ее пошаговая установка описана в предыдущей статье. Что дальше? Нажимаем двойным кликом на значок на рабочем столе, который выглядит вот так
Перед нами открывается окно программы. Оно довольно непримечательное, не отличается от тех, что, возможно, вы видели ранее, но интерфейс ее удобен и все необходимое и часто используемое расположено перед глазами, что помогает легко сориентироваться.
Сверху перед нами расположена панель инструментов, чуть ниже белое поле, которое является аналогом чистого листа бумаги и на котором собственно нужно набирать и редактировать текст, а слева можно просмотреть количество страниц и их миниатюрное изображение.
Панель инструментов
Примерно так панель инструментов выглядит целиком:
Как видим, ее самая верхняя часть имеет такие вкладки:
-
Файл;
-
Правка;
-
Шрифт;
-
Абзац;
-
Формат;
-
Вставка;
-
Таблица;
-
Сервис.
При нажатии на любую из них выскакивает контекстное меню, состоящее из различных инструментов, которые помогают при работе с текстом. Так можно нажать каждую вкладку, чтоб зрительно ознакомиться с интерфейсом.
Далее представлены значки самых часто применяемых функций, которые используются в работе с текстовыми документами. Они органично рассортированы по разделам, что помогает легко сориентироваться даже неопытному пользователю.
Перечислять их все мы не будем, так как их довольно много, а разберемся с основными задачами.
Сохранение
Первое о чем нужно постоянно помнить при работе с документами – это сохранение, без этой функции вся ваша работа будет проделана зря. На панели инструментов она выглядит так 
Настройка
После более детального ознакомления всех функций панель инструментов (или панель быстрого доступа) можно настроить исходя из частоты использования необходимых функций, которые нужны всегда под рукой. Это организует вашу работу и сделает ее еще более оперативной.
Редактирование документов
Программа наличествует в себе все стандартные функции редактирования:
-
размер и формат шрифта
-
вставить, копировать, вырезать
-
вперед, назад
-
начертание текста
-
расположение текста
-
масштабирование
.
Еще много полезного можно найти в программе WindowsWord, но главная ее особенность – это простота использования и понятность интерфейса. Вдохновения вам!
В редакторе Windows word присутствует набор всех необходимых функций для создания/редактирования текста.
Для быстрого редактирования документа, полезно пользоваться панелью быстрого доступа в верхней правой части экрана. Все важные действия : «Создать»,» Открыть», «Сохранить»,»Печать», «Вставить», «Отменить/Вернуть», «Маркеры», «Нумерация», «Отступы», редактирование текста в документе, а также стили шрифта, варианты начертания и масштабирование всегда находятся под рукой.
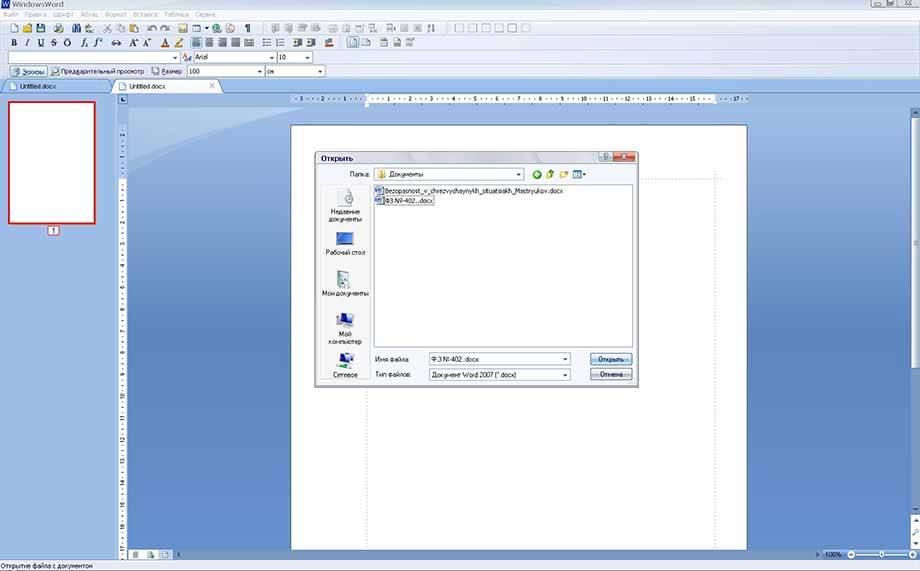
Для создания нового документа нужно нажать в верхнем правом углу на панели быстрого доступа кнопку «Создать», или выполнить действие: «Файл» -> «Создать». Чтобы редактирования уже существующий документ необходимо нажать на кнопку «Открыть», либо действие «Файл -> «Открыть», а затем выбрать нужный файл и подтвердить свой выбор.
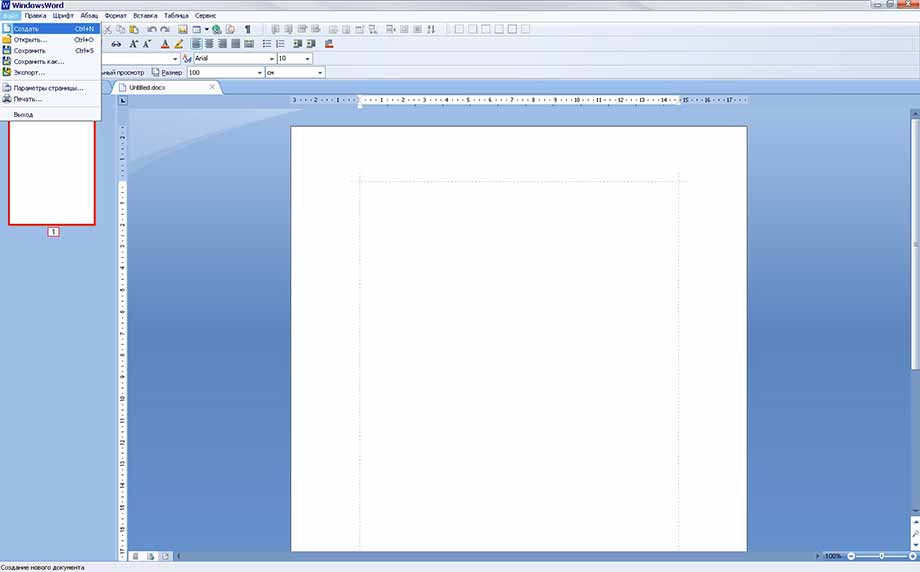
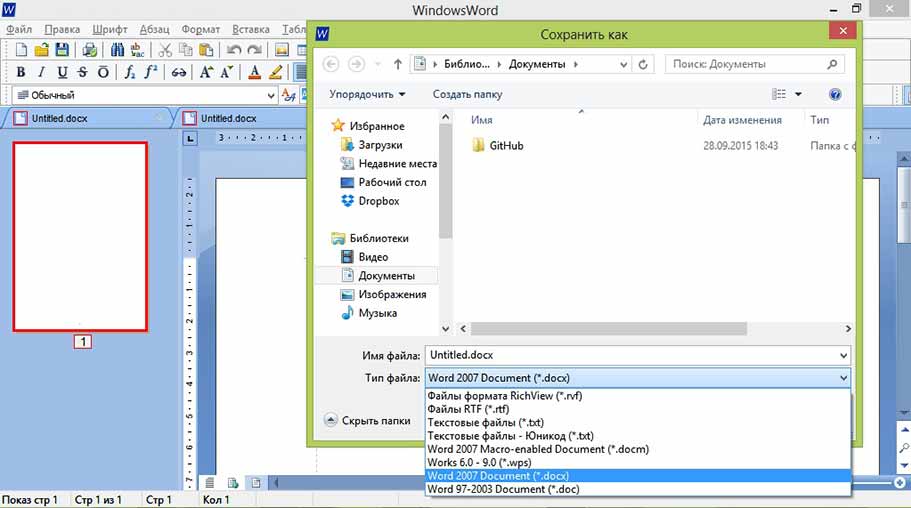
Сохранить документ можно щелчком по иконке с дискетой на панели быстрого доступа, или действием: «Файл» -> «Сохранить». Для сохранения документа в разных форматах, требуется зайти: «Файл» -> «Сохранить как…» и выбрать нужный формат.
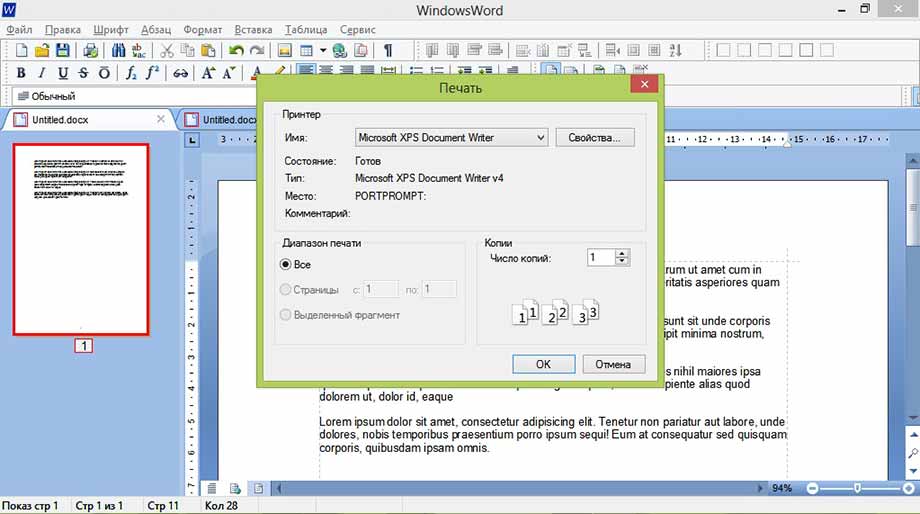
Можно распечатать весь документ, либо определенную страницу нажав кнопку «Печать» в виде иконки принтера на панели, либо через «Файл» -> «Печать…». Будет предложено выбрать принтер, диапазон печати и число копий.
Если потребуется найти в тексте определенное слово или предложение, можно воспользоваться кнопкой «Найти…» на панели быстрого доступа, или зайти: «Правка»- Найти».
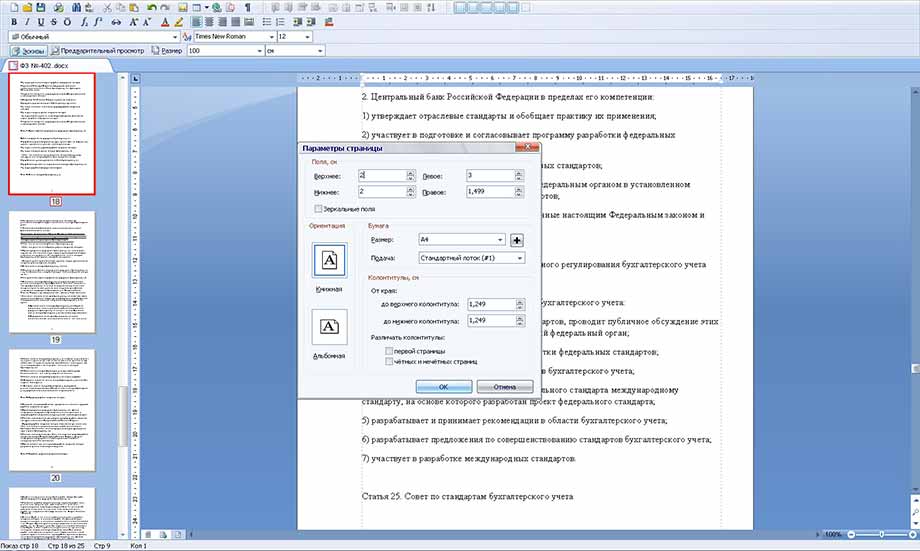
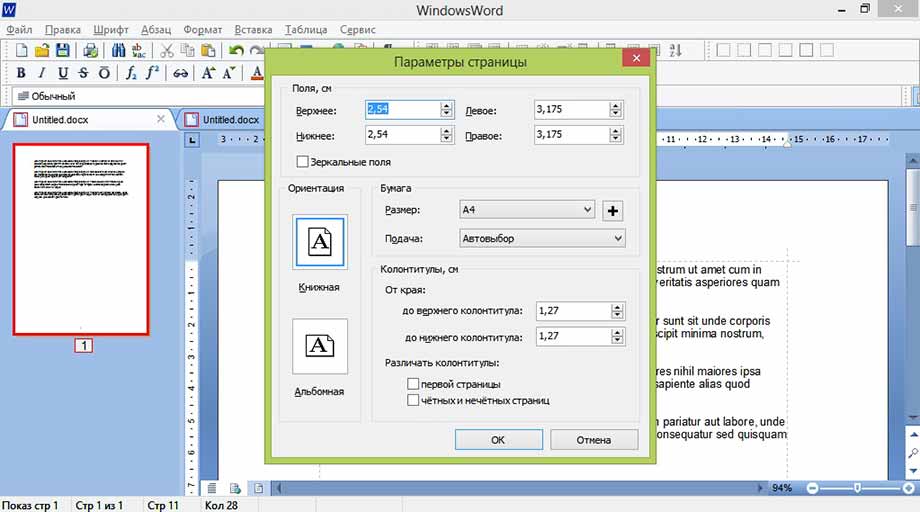
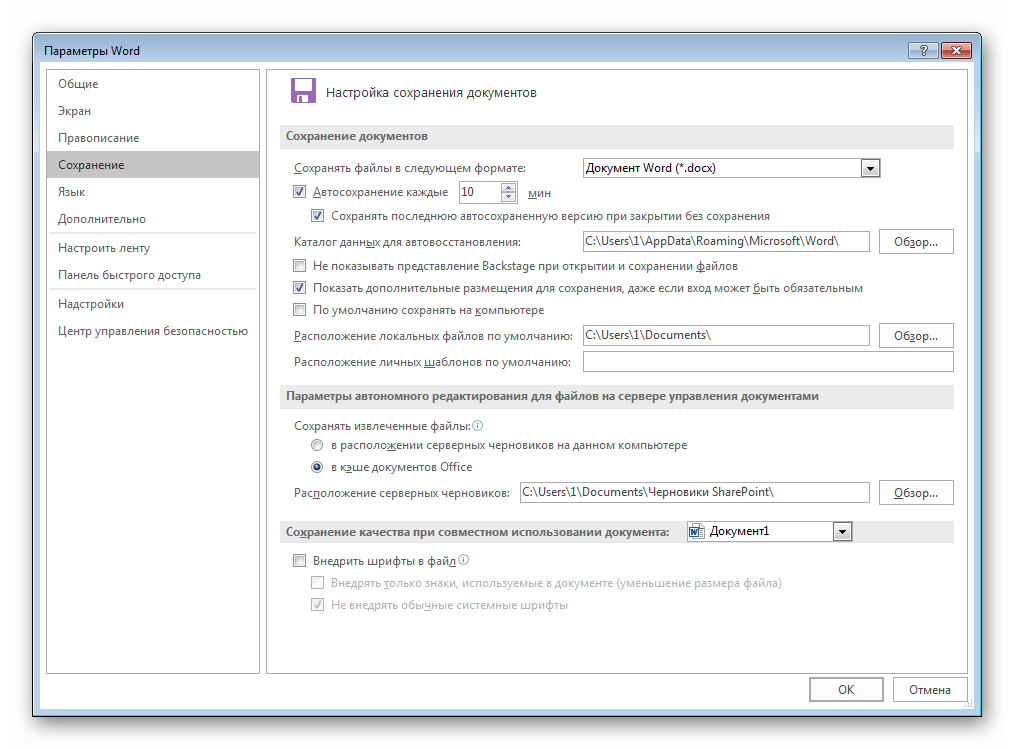
Настройку параметров страницы, полей, колонтитулов и параметров бумаги можно найти, выполнив действие: «Файл» -> «Параметры страницы», и в появившемся окошке выставить нужное значение. Далее подтвердить щелчком «Ok».
Часто при редактировании возникает необходимость отмены совершенного действия или его возврата. Для такого случая предусмотрены кнопки «Отменить» и «Вернуть» на панели и во вкладке «Правка».
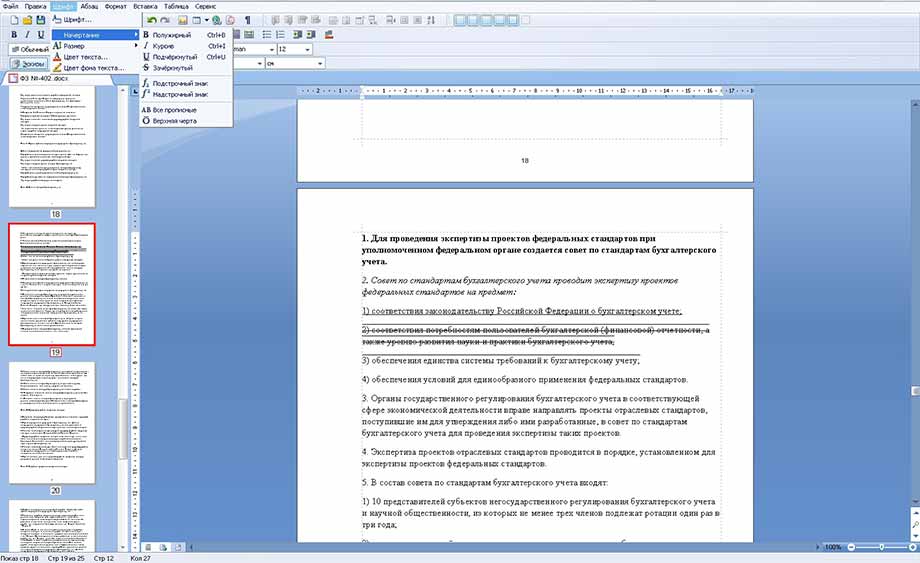
Изменение стиля шрифта, начертание, размер, цвет и фон текста возможно во вкладках «Шрифт» и «Формат». Для оперативного изменения предусмотрены колонки стилей и кегля текста на панели быстрого доступа.
Для выделения в тексте важных моментов обычно используются начертания: полужирный, курсив, подчеркнутый, зачеркнутый, которые находятся во вкладке «Шрифт»
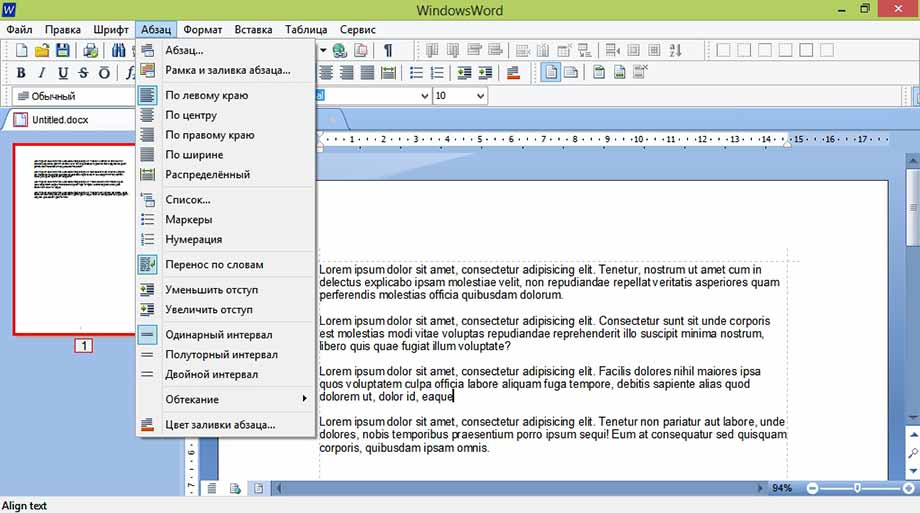
Работая с абзацами, можно редактировать текст по краям, ширине, центру, распределить по длине, если пользоваться вкладкой «Абзац»
При необходимости создать маркированный/нумерованный список, можно воспользоваться вкладкой «Абзац»- > «Список».
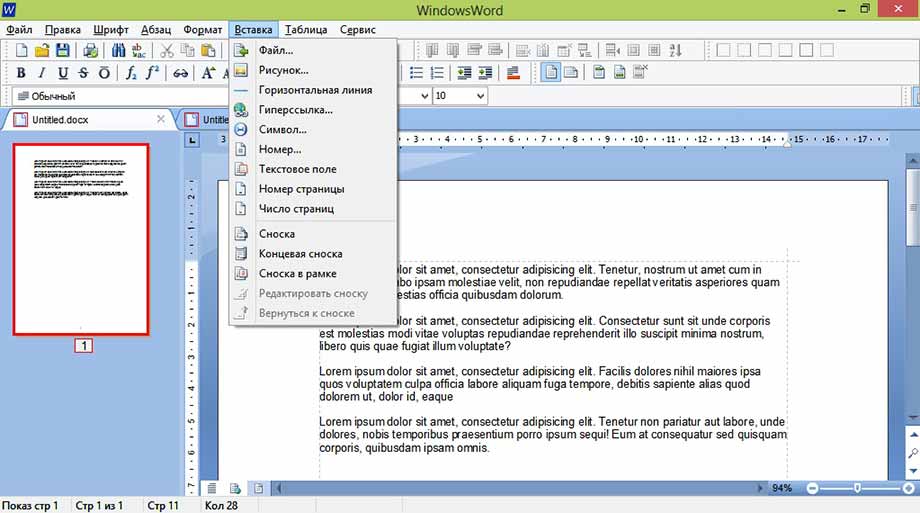
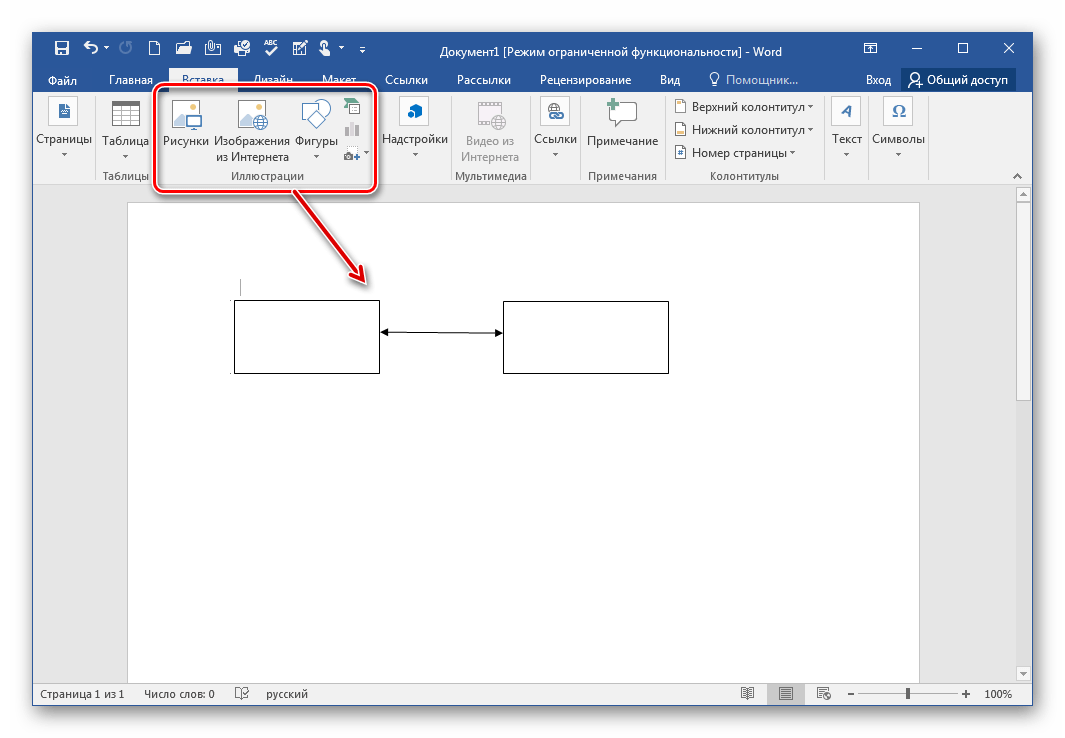
Вкладка «Вставка» позволит вставить в документ: файл, рисунок, горизонтальные линии, гиперссылку, номер страницы, текстовое поле, число страниц и разного вида сноски.
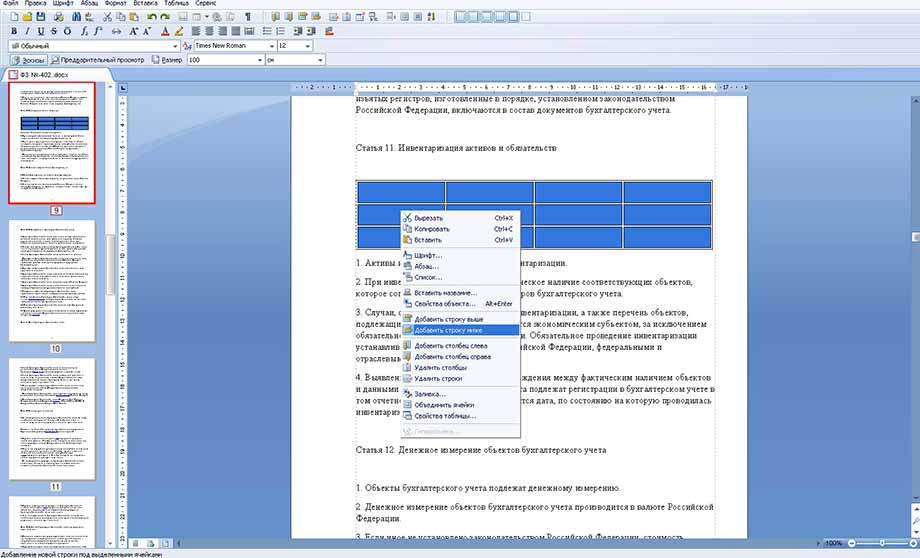
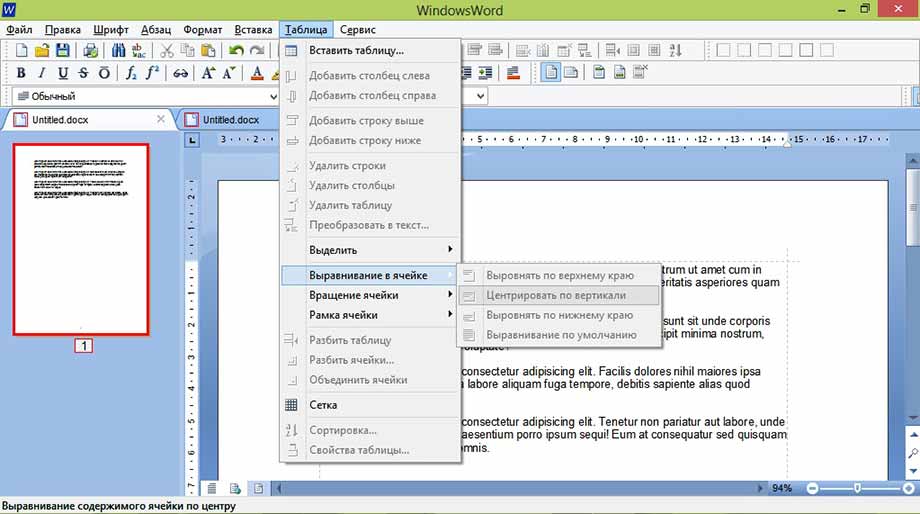
При работе с таблицами необходимо использовать вкладку «Таблица», либо иконку таблицы на панели для быстрого размещения с выбранным количеством ячеек. Даже после размещения таблицы, можно дополнять её столбцами и строками с любой стороны, а также удалять, объединять и разбивать ячейки. Для этого нужно выделить таблицу и щелкнуть правой кнопкой мышки, а в появившемся окошке выбрать нужное действие.
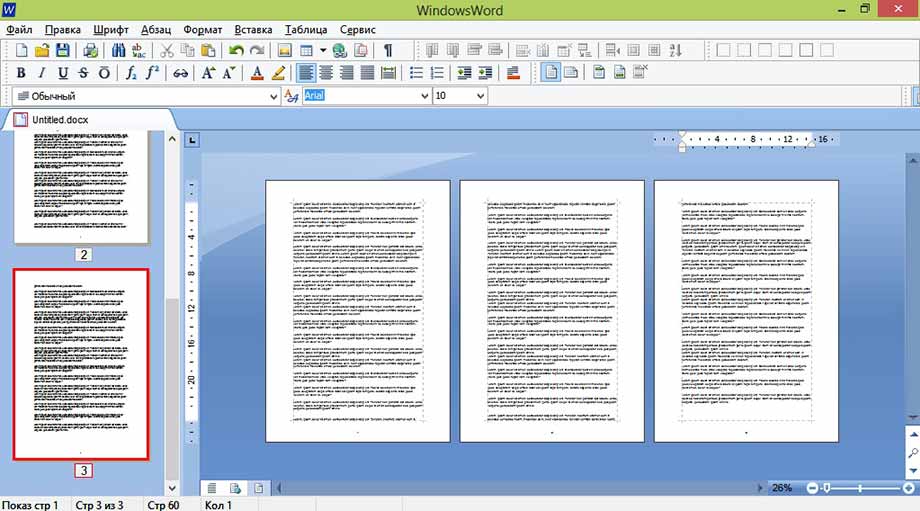
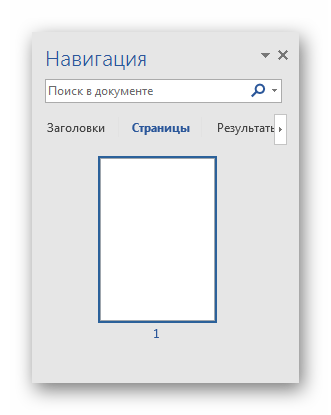
При работе с большим объемом текста, для быстрого перемещения по страницам можно использовать «Эскизы» в левой части экрана. Красной рамкой выделяется текущая страница и её номер.
Как пользоваться редактором WindowsWord
Текстовый редактор WindowsWord – незаменимая программа в офисе и дома. Она проста в использовании и выполняет полный набор необходимых функций по созданию и редактированию текстовых файлов.
Главное окно программы состоит из нескольких частей:
-
Панель управления в верхней части окна,
-
Панель навигации слева,
-
Само поле для текста в виде белого листа,
-
В нижней части панель со статистикой документа и выбором масштаба отображения.
Главный экран
Меню Файл
В верхней части панели управления расположены выпадающие меню с разнообразными функциями.
Создать
После запуска программы перед вами откроется пустой лист, который можно редактировать – это новый документ. Для создания другого нового документа в меню «Файл» кликните на пункт «Создать» — откроется новый пустой файл.
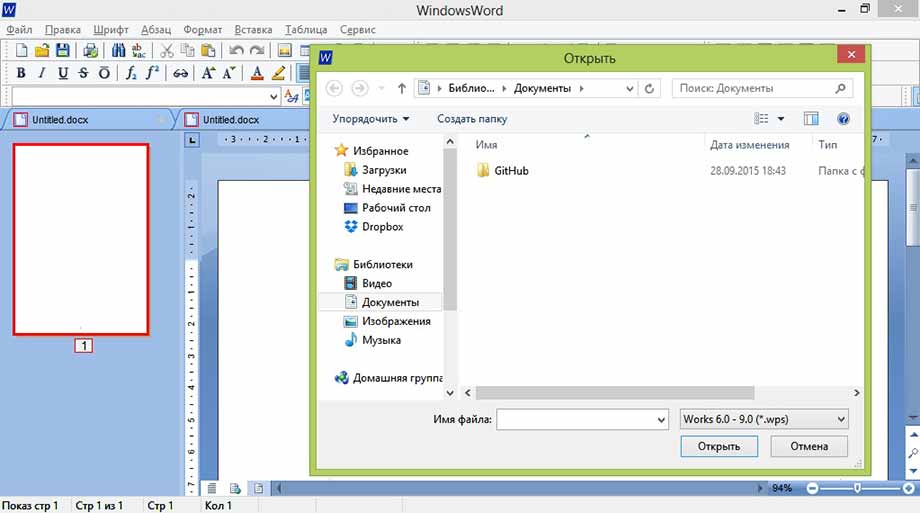
Чтобы открыть существующий документ, выберите первый пункт «Открыть» в меню «Файл», после этого откроется диалоговое окно, предлагающее перейти в определённую директорию (папку) и выбрать нужный документ. К тому же вы можете выбрать в этом же окне тип документов, который будет отображаться: doc, docx, rtf и т.д.
Открыть файл
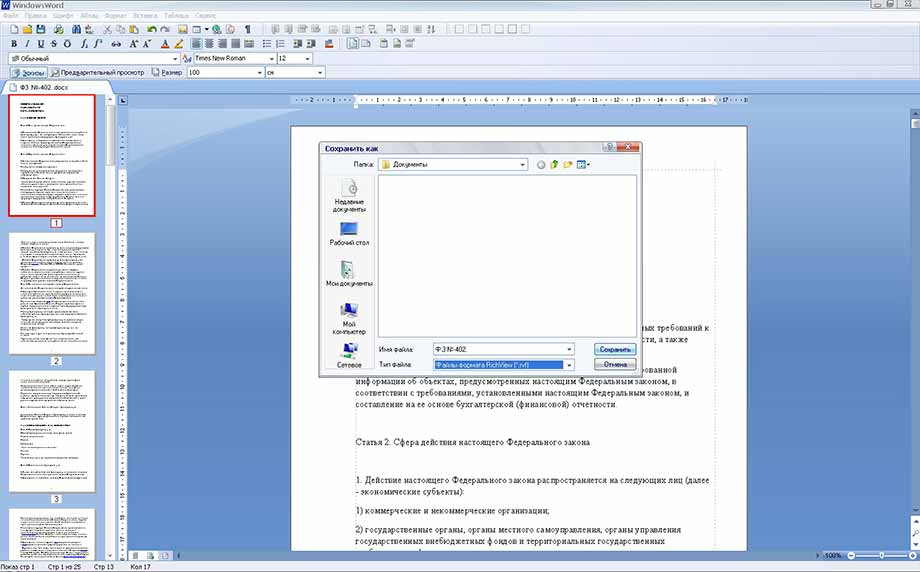
После окончения редактирования документа сохраните его с помощью пункта «Сохранить как» в меню «Файл» или нажмите комбинацию клавиш Ctrl+s. В появившемся окне выберите папку, имя для файла и его формат.
Сохранить как
Параметры страницы
Если нужно создать свой файл на листе, отличном от А4 по умолчанию, перейдите в меню Файл, пункт Параметры страницы. Там можно изменить размер, ориентацию, поля и колонтитулы листа.
Печать
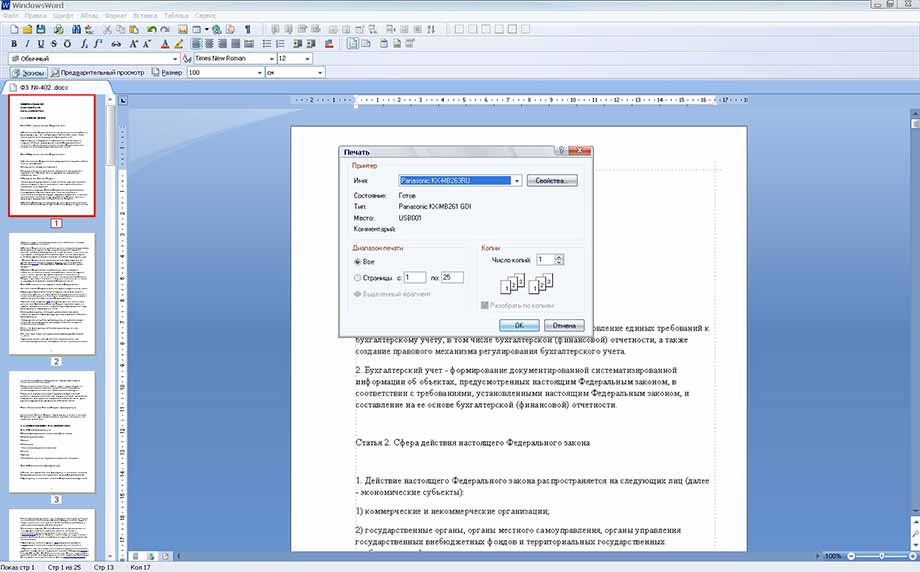
Пункт «Печать» в меню «Файл» предоставляет возможность распечатать готовый документ, выбрав принтер, нужные страницы документа (диапазон печати) и число копий.
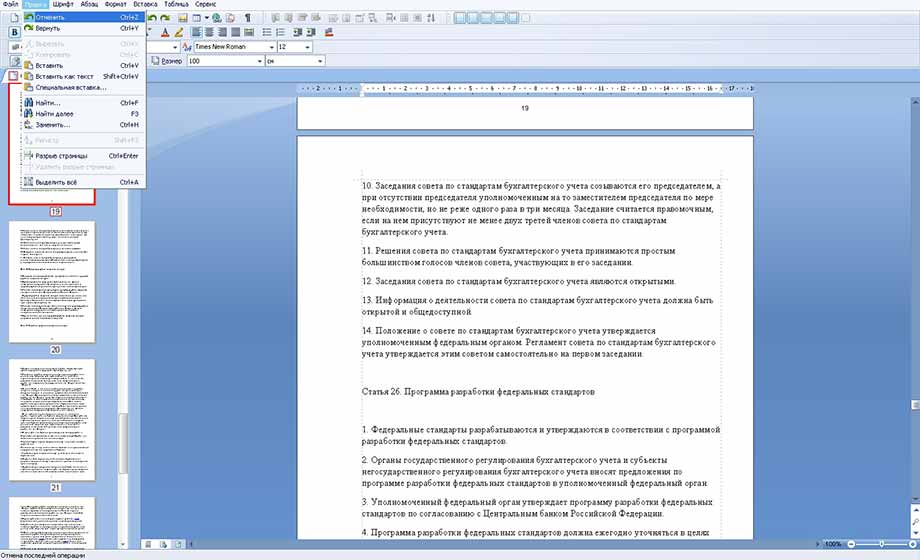
Следующее выпадающее меню программы – это «Правка». Пункты этого меню снабжены значками, которые помогут разобраться в функциях меню.
В первой части расположены «Отменить» и «Вернуть» — то есть каждое ваше действие в текущем документе можно отменить или, если оно всё же необходимо, вернуть как было. Удобно для этого пользоваться горячими клавишами Ctrl+z и Ctrl+y соответственно.
Вторая часть содержит функции «Вырезать», «Копировать», «Вставить» — это действия с текстом и изображениями, которые делаются над выделенными элементами. Это помогает работать не только с текстом и изображениями одного документа, но и копировать, вырезать и вставлять из другого файла или браузера
Меню Правка
Найти
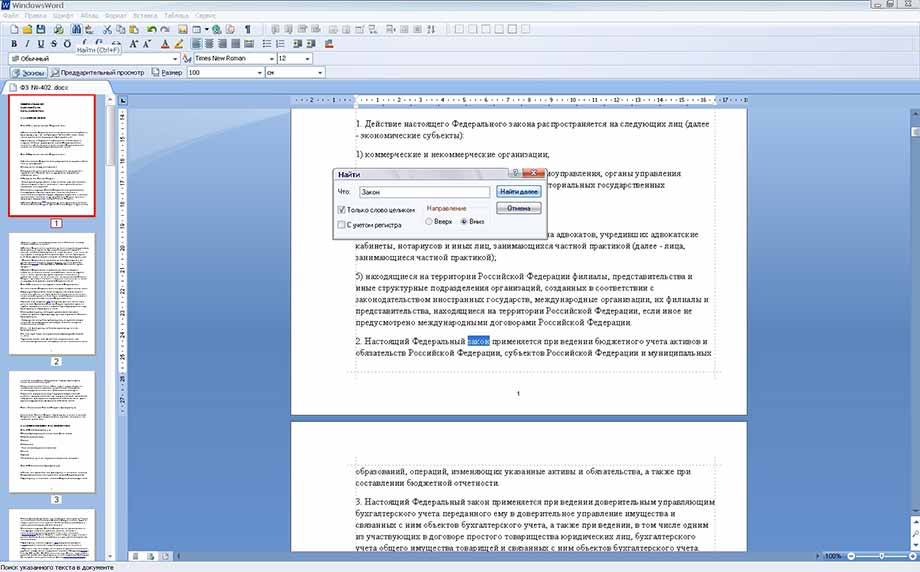
Найти и заменить фразу или слово в тексте можно с помощью соответствующего пункта в меню «Правка».
Заменить
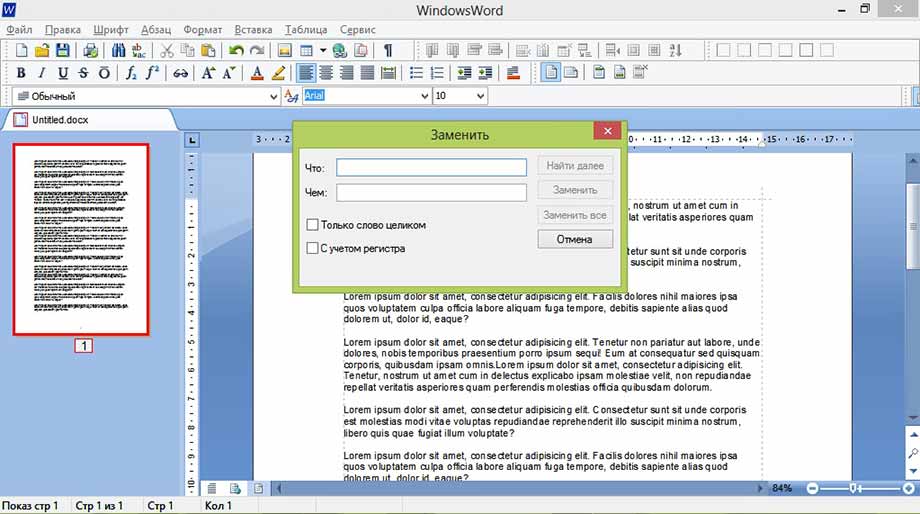
Меню Шрифт
Работа с внешним видом шрифта текста осуществляется в меню «Шрифт». Здесь можно изменить цвет, начертание, шрифт, размер и фон выделенного фрагмента текста.
Меню Абзац
Меню абзац для редактирования общего вида документа.
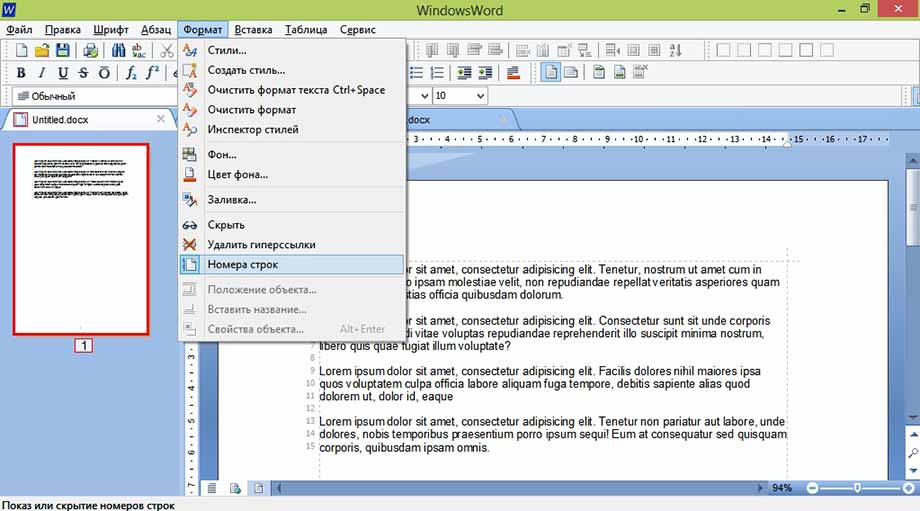
Меню Формат
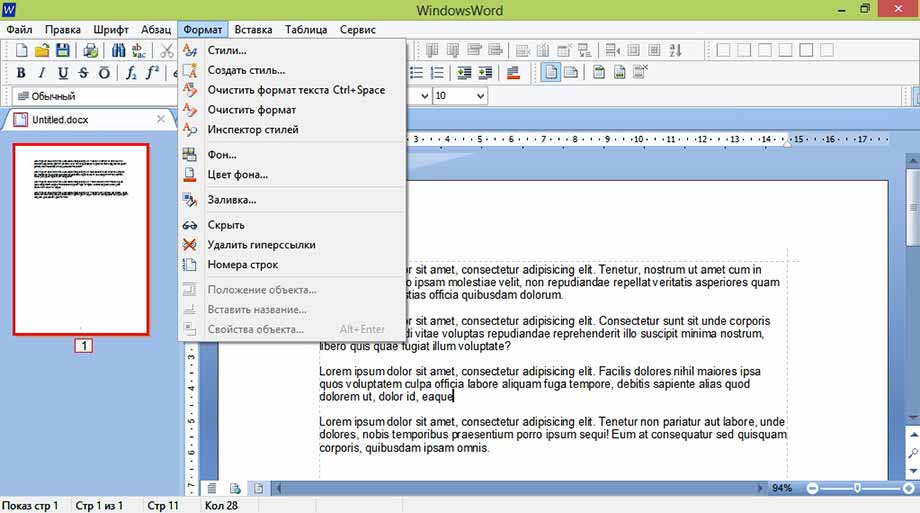
Фон (окно)
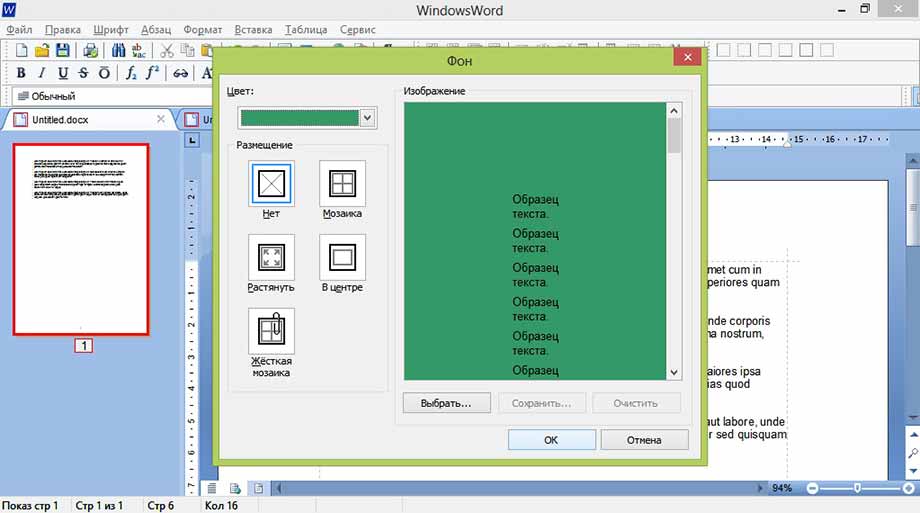
(эффект)
Номера строк
Добавление элементов осуществляется через меню «Вставка». Картинку можно добавить через диалоговое окно пункта «Рисунок».
Меню Вставка
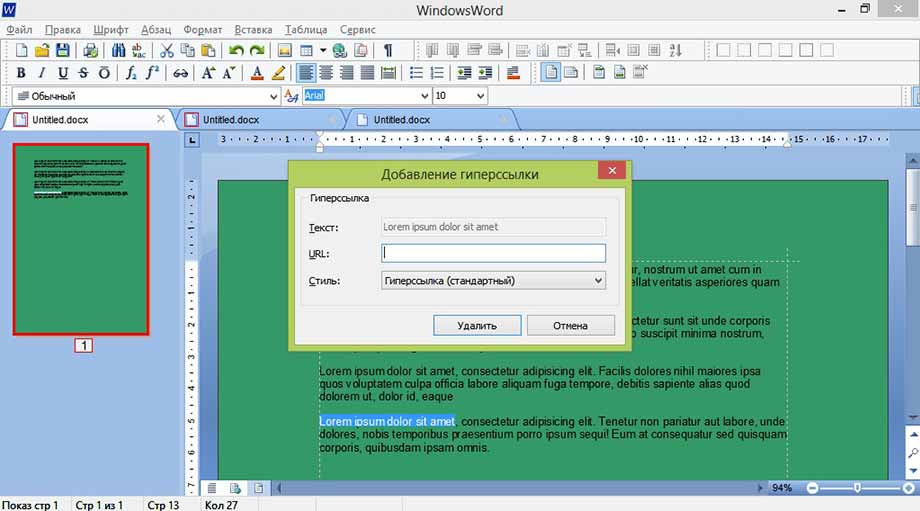
Гиперссылка
Для создания ссылки на сайт выделите часть текста, который должен быть ссылкой, и в открывшемся окне вставьте нужный адрес.
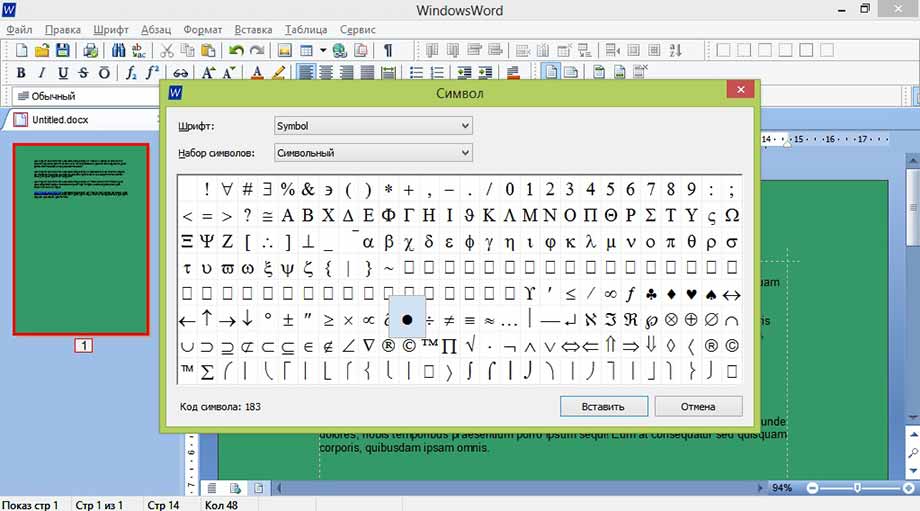
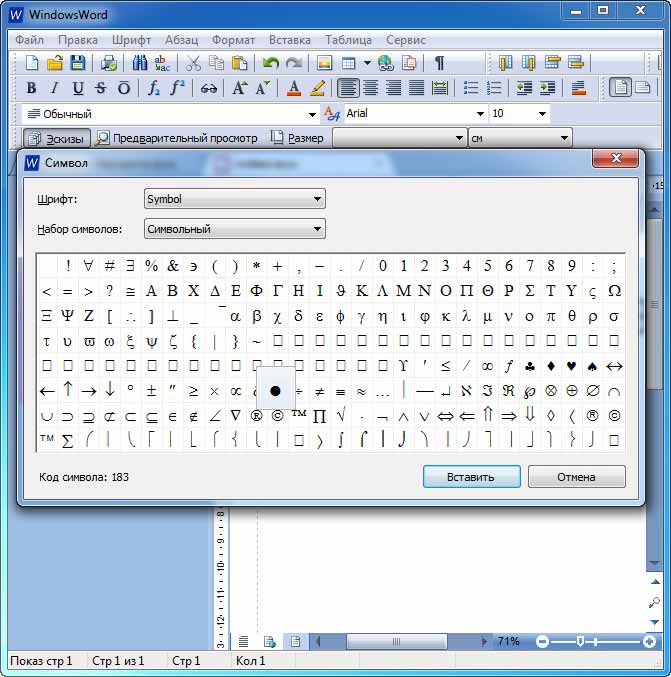
Символ
Символы математических формул и другие символы, которых нет на клавиатуре добавь с помощью пункта «Символы».
Добавить таблицу и изменять её параметры можно через меню «Таблица», где присутствуют все необходимые функции
Меню Таблица
Вставить таблицу
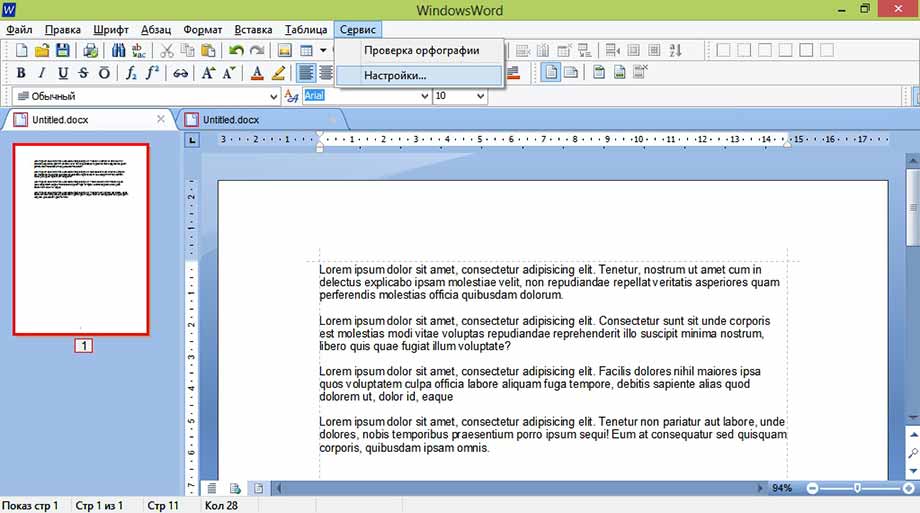
Меню Сервис
В выпадающем меню «Сервис» присутствуют всего два пункта «Проверка орфографии» и «Настройки».
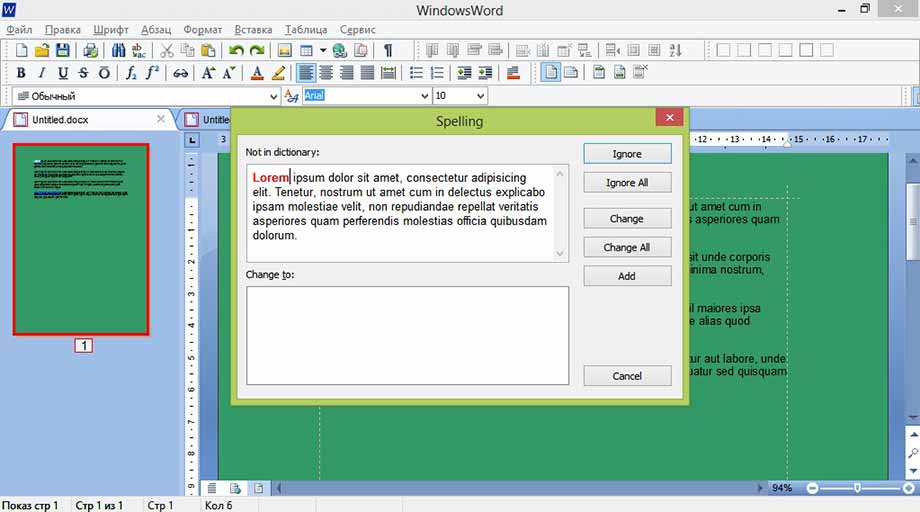
Проверка орфографии
Пункт «Проверка орфографии» помогает избежать орфографических, пунктуационных и других ошибок в тексте документа, просто указывая на них или предлагая варианты исправления.
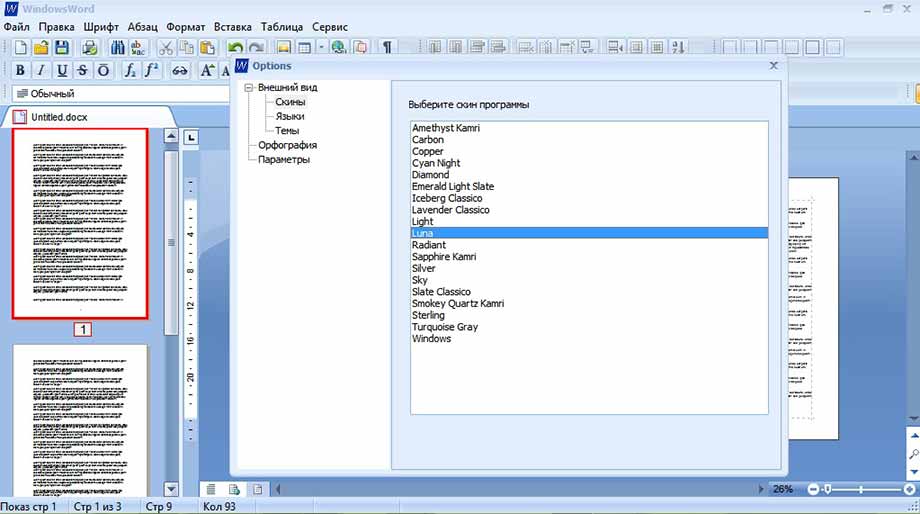
Настройки
Настроить программу, поменять оформление, выбрать язык и нюансы орфографии поможет пункт «Настройки». Например, выбрав «Внешний вид — Скины» пользователь может выбрать тему оформления самой программы на свой вкус. По умолчанию стоит Windows.
Сохранив все изменения закрыть программу можно тремя способами:
-
Выбрав пункт «Выход» меню «Файл»,
-
Нажав на пиктограмму крестика в правом верхнем углу окна,
-
Воспользовавшись комбинацией клавиш Alt+F4.
Масштабирование
Чтобы увидеть весь документ целиком или приблизить его фрагмент, воспользуйтесь правой частью нижней панели окна реактора. Для изменения масштаба отображения документа передвиньте ползунок или нажмите на «+» или «-».
Windows Word – это новый удобный редактор текстовых файлов, доступный для бесплатного скачивания. Программа подойдет для создания и редактирования файлов с текстовой информацией, чтения книг и тому подобного. Выглядит редактор следующим образом:
Запустив приложение, вы можете начать создание нового документа, после чего воспользоваться функцией его сохранения. Она предельно проста и аналогична такой же функции в любых других приложениях Windows: Файл -> Сохранить, либо Файл -> Сохранить как…
Либо вы можете открыть уже имеющийся файл, дабы ознакомиться с его содержимым и/или отредактировать содержащуюся в нем информацию. Это также осуществляется стандартным образом: Файл -> Открыть -> Имя искомого файла.
Как и любой солидный редактор, Windows Word, помимо всего прочего, имеет функцию быстрого поиска слов или фрагментов текста по открытому файлу. Для того, чтобы вызвать окно поиска, можно нажать комбинацию клавиш Ctrl + F, либо кнопку с изображением бинокля. В открывшемся окне необходимо ввести слово или фразу, которую вы хотите найти в тексте. Также можно выбрать функции поиска: учитывать либо не учитывать регистр, искать только совпадения слова целиком, вести поиск ниже текущего положения курсора или выше него. После этого нужно нажать на кнопку «Найти далее», и совпадения в тексте выделятся синим цветом.
Редактирование текстовой информации в Windows Word подчиняется тем же правилам, что и работа с текстами в любом другом редакторе. Помимо непосредственного редактирования текстов, с помощью этого редактора вы сможете добавить в файл гиперссылки, рисунки, таблицы. Это можно сделать как через меню «Вставка» и «Таблица», так и с помощью соответствующих кнопок на панели. С помощью последовательности действий Вставка -> Символ можно вставить в документ символы греческого алфавита, математических формул и многие другие.
Конечно же, в Windows Word предусмотрено также большое количество возможностей для изменения стиля текста. Вы можете выбрать шрифт, цвет текста и фона, сделать шрифт полужирным, курсивным, подчеркнутым или перечеркнутым, подстрочным или надстрочным. Все это можно сделать как через меню «Шрифт» («Начертание», «Размер», «Цвет текста», «Цвет фона текста»), так и с использованием соответствующих кнопок.
В редакторе Windows Word также имеется удобный пункт меню «Абзац», с помощью которого можно отформатировать текст: выбрать распределение строк по левому, правому краю, по ширине или по центру. Также через этот пункт меню можно добавить нумерацию, маркеры, изменить отступы и интервалы. То же самое можно сделать при помощи кнопок на панели, а также посредством перетягивания соответствующих слайдеров на основном рабочем поле.
Документ, открытый в Windows Word, также можно отправить на печать. Это можно сделать либо через меню Файл –> Печать, либо при помощи кнопки с изображением принтера. Имеется и возможность осуществить предварительный просмотр открытого документа перед печатью, чтобы получить более полное представление о том, как он будет выглядеть на бумаге.
Программа Word
В этом уроке я расскажу о программе Microsoft Word (ворд). Что это за приложение, как его открыть на компьютере. Как пользоваться программой: печатать текст и работать с документами.
Что такое Word
Microsoft Word – это программа для печати. В ней можно набрать текст любого типа: статью, документ, реферат, курсовую, диплом и даже книгу. Также в Ворде можно оформить текст: изменить шрифт, размер букв, добавить таблицу, фотографию и многое другое. И вывести на бумагу – распечатать на принтере.
Программа представляет собой белый лист бумаги, на котором, используя клавиатуру, печатают текст. Также на нем располагают другие элементы: таблицы, картинки и прочее.
Если нужно напечатать много текста и на один лист он не поместится, программа автоматически добавит еще страницы.
Набранный текст можно отредактировать: изменить размер букв, шрифт, начертание и многое другое. Для этого в Ворде есть специальная панель в верхней части. На ней находятся кнопки редактирования.
Но это не все кнопки. Остальные расположены на других вкладках.
Как открыть программу
Приложение Word запускается через вот такую иконку на Рабочем столе компьютера:
Если значка нет, ищите его среди всех программ в Пуске.
На заметку. Чтобы вынести иконку на экран, зажмите ее левой кнопкой мыши и перетяните на Рабочий стол. Или щелкните по ней правой кнопкой мыши, выберите «Отправить» – «Рабочий стол (создать ярлык)».
Вот как выглядит приложение Microsoft Word 2016-2019. Для начала работы нажмите на пункт «Новый документ».
Откроется пустой лист. Он как будто обрезан, но это из-за того, что страница не поместилась на экран. Чтобы ее увидеть целиком, покрутите колесико на мышке или подвиньте ползунок с правой стороны.
На сегодняшний день это последняя версия программы. Есть более ранняя 2010-2013 года — выглядит она примерно так же. Еще часто можно встретить версию 2007 года. Она выглядит немного иначе, но имеет все необходимые инструменты.
На некоторых старых компьютерах можно встретить и версию 2003 года. У нее другой дизайн, меньше функций. Но с основными задачами программа справляется.
Основы работы в Ворде
Печать текста
Рабочая область приложения – белый лист, на котором мигает палочка. Этим мигающим курсором отмечено то место, где будет набираться текст.
По умолчанию он установлен в начале листа, в левом верхнем углу. Но не в самом верху страницы, так как у нее есть поля – пустые области с каждой стороны.
Без полей с документом работать неудобно, да и при распечатке часть слов обрежется. Поэтому пустое поле должно быть с каждой стороны: сверху, снизу, слева и справа.
Изменить масштаб страницы, то есть приблизить или отдалить ее, можно через ползунок в правом нижнем углу. Но учтите, что таким образом поменяется только отображение листа, но не него реальный размер.
Для печати текста установите нужную раскладку (язык) на панели задач – в правом нижнем углу экрана. Это можно сделать мышкой или через сочетание клавиш Shift и Alt.
- Для печати большой буквы нажмите Shift и, не отпуская, кнопку с буквой.
- Для печати знака в верхнем ряду клавиш (там, где цифры) также зажимайте Shift.
- Для удаления используйте клавишу Backspace. Обычно она находится после кнопки = в верхнем ряду и на ней нарисована стрелка влево.
- Для перехода на новую строку используйте клавишу Enter. А для удаления строки – Backspace.
- Промежутки между словами делайте пробелом – самой длинной кнопкой в нижней части. Между словами должен быть только один пробел (ни два, ни три).
- Точка в русской раскладке находится в нижнем ряду клавиш – после буквы Ю.
- Запятая в русской раскладке – это так же кнопка, что и точка, но нажимать ее нужно вместе с Shift.
О значении каждой клавиши на клавиатуре и их сочетаниях читайте в этом уроке.
Сохранение
Набранный текст не будет зафиксирован до тех пор, пока вы его не сохраните. Можно набрать хоть сто страниц, но они не останутся в компьютере.
Для сохранения используйте кнопку с изображением дискеты в верхнем левом углу программы. Или «Файл» — «Сохранить как…».
Если документ еще ни разу не записывался, то появится окно с выбором места, куда его отправить. Нажмите «Обзор».
Выскочит окошко сохранения. Перейдите через него в нужную папку, напечатайте название и нажмите «Сохранить». Документ запишется в файл. Найти его можно будет в указанном при сохранении месте.
А если документ уже был записан, то при нажатии на иконку дискеты окошко не появится. Новый документ автоматически перезапишется вместо старого файла (обновится).
Чтобы узнать, куда именно он был записан, нажмите «Файл» — «Сохранить как…». Появится окошко записи, где будет указана папка, в которой находится этот файл.
Редактирование текста
Для изменения внешнего вида текста используйте вкладку «Главная» на панели инструментов вверху. Здесь можно настроить шрифт, выравнивание, начертание и другие параметры.
Если необходимо изменить уже напечатанный текст, то сначала его нужно выделить. Для этого поставить курсор в самое начало (перед первой буквой), зажать левую кнопку мыши и обвести текст. Он обозначится другим цветом.
Затем выбрать нужные параметры во вкладке «Главная» в верхней части. Все изменения затронут только выделенную часть.
Для отмены используйте кнопку со стрелкой в верхнем левом углу программы.
Основные инструменты редактирования текста:
При наведении курсора на любую из кнопок на панели инструментов, появится всплывающая подсказка с описанием.
Оформление
Если составляете документ исключительно для себя, то оформляйте его так, как вам удобнее. Но если нужно отправить файл другим людям, лучше следовать определенным правилам:
- В начале предложения первая буква печатается прописной (большой), остальные – строчными (маленькими).
- Заголовок набирается с большой буквы. После него точка не ставится.
- После знаков препинания ставится один пробел. Перед ними пробел не ставится. Например, цвет: белый, синий, красный.
- После кавычек и скобок пробел не ставится. Например, «Преступление и наказание».
- Тире отделяется пробелами с двух сторон. Дефис не отделяется ни одним пробелом.
- Текст должен быть структурированным: разбит на абзацы, иметь заголовки разных уровней. Желательно использовать маркированные и нумерованные списки.
Что касается требований к шрифту, они зависят от типа документа. Если речь идет о реферате, курсовой или дипломной работе, то обычно требования указываются отдельно. А официальные документы должны быть оформлены по ГОСТу.
Универсальные правила оформления:
- Вид шрифта: Times New Roman или Arial.
- Размер шрифта: основной текст – 12 или 14, заголовки – 16, подзаголовки – 14, таблицы – 10 или 12.
- Выравнивание: основной текст – по ширине, заголовки – по центру.
- Междустрочный интервал – 1,5.
- Поля: левое — не менее 30 мм, правое — не менее 10 мм, верхнее и нижнее — не менее 20 мм.
Другие возможности программы Word
Добавить таблицу, изображение, фигуру. Делается это через вкладку «Вставка». Еще через нее можно вставить символ, диаграмму, титульный лист, сделать разрыв. А также добавить номера страниц.
Настроить поля, размер страниц, ориентацию. Эти инструменты находятся во вкладке «Макет». Также здесь можно настроить отступы и интервалы, выполнить автоматическую расстановку переносов.
Линейка и масштаб. Через вкладку «Вид» можно показать или скрыть линейку, настроить масштаб и визуальное представление страниц.
Вывод на печать. Для распечатки на принтере нажмите на «Файл» и выберите «Печать». Сделайте необходимые настройки и нажмите на кнопку «Печать».
В версии 2016-2021 для возврата к редактированию документа, щелкните по кнопке со стрелкой в верхнем левом углу.
 |
|

Microsoft Office 365 version of Microsoft Word, with the new redesign applied |
|
| Developer(s) | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| Initial release | October 25, 1983; 39 years ago (as Multi-Tool Word) |
| Stable release |
2209 (16.0.15629.20208) |
| Repository | none |
| Written in | C++ (back-end)[2] |
| Operating system |
|
| Platform | IA-32, x64, ARM, ARM64 |
| Type | Word processor |
| License | Trialware |
| Website | products.office.com/word |

Word for Mac running on macOS Ventura (13.2) |
|
| Developer(s) | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| Stable release |
16.64 (Build 22081401) |
| Repository | none |
| Written in | C++ (back-end), Objective-C (API/UI)[2] |
| Operating system | macOS |
| Type | Word processor |
| License | Proprietary software plus services |
| Website | products.office.com/word |

Screenshot of Microsoft Word for Android 13 |
|
| Original author(s) | Microsoft Corporation |
|---|---|
| Developer(s) | Microsoft Corporation |
| Initial release | January 29, 2015; 8 years ago[5] |
| Stable release |
16.0.15427.20090 |
| Repository | none |
| Operating system | Android Pie and later |
| License | Proprietary commercial software |
| Website | products.office.com/word |
| Developer(s) | Microsoft Corporation |
|---|---|
| Initial release | March 27, 2014; 8 years ago[7] |
| Stable release |
2.63.2 |
| Repository | none |
| Operating system | iOS 14 or later IPadOS 14 or later |
| License | Proprietary commercial software |
| Website | products.office.com/word |
| Developer(s) | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| Repository | none |
| Operating system | Windows 10 and later, Windows 10 Mobile |
| Type | Word processor |
| License | Freemium |
| Website | www.microsoft.com/store/productId/9WZDNCRFJB9S |
Microsoft Word is a word processing software developed by Microsoft. It was first released on October 25, 1983,[9] under the name Multi-Tool Word for Xenix systems.[10][11][12] Subsequent versions were later written for several other platforms including: IBM PCs running DOS (1983), Apple Macintosh running the Classic Mac OS (1985), AT&T UNIX PC (1985), Atari ST (1988), OS/2 (1989), Microsoft Windows (1989), SCO Unix (1990), macOS (2001), Web browsers (2010), iOS (2014) and Android (2015). Using Wine, versions of Microsoft Word before 2013 can be run on Linux.
Commercial versions of Word are licensed as a standalone product or as a component of Microsoft Office suite of software, which can be purchased either with a perpetual license or as part of a Microsoft 365 subscription.
History[edit]
Origins[edit]
In 1981, Microsoft hired Charles Simonyi, the primary developer of Bravo, the first GUI word processor, which was developed at Xerox PARC.[13] Simonyi started work on a word processor called Multi-Tool Word and soon hired Richard Brodie, a former Xerox intern, who became the primary software engineer.[13][14][15]
Microsoft announced Multi-Tool Word for Xenix[13] and MS-DOS in 1983.[16] Its name was soon simplified to Microsoft Word.[10] Free demonstration copies of the application were bundled with the November 1983 issue of PC World, making it the first to be distributed on-disk with a magazine.[10][17] That year Microsoft demonstrated Word running on Windows.[18]
Unlike most MS-DOS programs at the time, Microsoft Word was designed to be used with a mouse.[16] Advertisements depicted the Microsoft Mouse and described Word as a WYSIWYG, windowed word processor with the ability to undo and display bold, italic, and underlined text,[19] although it could not render fonts.[10] It was not initially popular, since its user interface was different from the leading word processor at the time, WordStar.[20] However, Microsoft steadily improved the product, releasing versions 2.0 through 5.0 over the next six years. In 1985, Microsoft ported Word to the classic Mac OS (known as Macintosh System Software at the time). This was made easier by Word for DOS having been designed for use with high-resolution displays and laser printers, even though none were yet available to the general public.[21] It was also notable for its very fast cut-and-paste function and unlimited number of undo operations, which are due to its usage of the piece table data structure.[22]
Following the precedents of LisaWrite and MacWrite, Word for Mac OS added true WYSIWYG features. It fulfilled a need for a word processor that was more capable than MacWrite.[23] After its release, Word for Mac OS’s sales were higher than its MS-DOS counterpart for at least four years.[13]
The second release of Word for Mac OS, shipped in 1987, was named Word 3.0 to synchronize its version number with Word for DOS; this was Microsoft’s first attempt to synchronize version numbers across platforms. Word 3.0 included numerous internal enhancements and new features, including the first implementation of the Rich Text Format (RTF) specification, but was plagued with bugs. Within a few months, Word 3.0 was superseded by a more stable Word 3.01, which was mailed free to all registered users of 3.0.[21] After MacWrite Pro was discontinued in the mid-1990s, Word for Mac OS never had any serious rivals. Word 5.1 for Mac OS, released in 1992, was a very popular word processor owing to its elegance, relative ease of use, and feature set. Many users say it is the best version of Word for Mac OS ever created.[21][24]
In 1986, an agreement between Atari and Microsoft brought Word to the Atari ST[25] under the name Microsoft Write. The Atari ST version was a port of Word 1.05 for the Mac OS[26][27] and was never updated.
The first version of Word for Windows was released in 1989. With the release of Windows 3.0 the following year, sales began to pick up and Microsoft soon became the market leader for word processors for IBM PC-compatible computers.[13] In 1991, Microsoft capitalized on Word for Windows’ increasing popularity by releasing a version of Word for DOS, version 5.5, that replaced its unique user interface with an interface similar to a Windows application.[28][29] When Microsoft became aware of the Year 2000 problem, it made Microsoft Word 5.5 for DOS available for free downloads. As of February 2021, it is still available for download from Microsoft’s website.[30]
In 1991, Microsoft embarked on a project code-named Pyramid to completely rewrite Microsoft Word from the ground up. Both the Windows and Mac OS versions would start from the same code base. It was abandoned when it was determined that it would take the development team too long to rewrite and then catch up with all the new capabilities that could have been added at the same time without a rewrite. Instead, the next versions of Word for Windows and Mac OS, dubbed version 6.0, both started from the code base of Word for Windows 2.0.[24]
With the release of Word 6.0 in 1993, Microsoft again attempted to synchronize the version numbers and coordinate product naming across platforms, this time across DOS, Mac OS, and Windows (this was the last version of Word for DOS). It introduced AutoCorrect, which automatically fixed certain typing errors, and AutoFormat, which could reformat many parts of a document at once. While the Windows version received favorable reviews (e.g., from InfoWorld[31]), the Mac OS version was widely derided. Many accused it of being slow, clumsy, and memory intensive, and its user interface differed significantly from Word 5.1.[24] In response to user requests, Microsoft offered Word 5 again, after it had been discontinued.[32] Subsequent versions of Word for macOS are no longer direct ports of Word for Windows, instead featuring a mixture of ported code and native code.
Word for Windows[edit]
Word for Windows is available stand-alone or as part of the Microsoft Office suite. Word contains rudimentary desktop publishing capabilities and is the most widely used word processing program on the market. Word files are commonly used as the format for sending text documents via e-mail because almost every user with a computer can read a Word document by using the Word application, a Word viewer or a word processor that imports the Word format (see Microsoft Word Viewer).
Word 6 for Windows NT was the first 32-bit version of the product,[33] released with Microsoft Office for Windows NT around the same time as Windows 95. It was a straightforward port of Word 6.0. Starting with Word 95, each release of Word was named after the year of its release, instead of its version number.[34]
Word 2007 introduced a redesigned user interface that emphasized the most common controls, dividing them into tabs, and adding specific options depending on the context, such as selecting an image or editing a table.[35] This user interface, called Ribbon, was included in Excel, PowerPoint and Access 2007, and would be later introduced to other Office applications with Office 2010 and Windows applications such as Paint and WordPad with Windows 7, respectively.[36]
The redesigned interface also includes a toolbar that appears when selecting text, with options for formatting included.[37]
Word 2007 also included the option to save documents as Adobe Acrobat or XPS files,[37] and upload Word documents like blog posts on services such as WordPress.
Word 2010 allows the customization of the Ribbon,[38] adds a Backstage view for file management,[39] has improved document navigation, allows creation and embedding of screenshots,[40] and integrates with online services such as Microsoft OneDrive.[41]
Word 2019 added a dictation function.
Word 2021 added co-authoring, a visual refresh on the start experience and tabs, automatic cloud saving, dark mode, line focus, an updated draw tab, and support for ODF 1.3.
Word for Mac[edit]
The Mac was introduced on January 24, 1984, and Microsoft introduced Word 1.0 for Mac a year later, on January 18, 1985. The DOS, Mac, and Windows versions are quite different from each other. Only the Mac version was WYSIWYG and used a graphical user interface, far ahead of the other platforms. Each platform restarted its version numbering at «1.0».[42] There was no version 2 on the Mac, but version 3 came out on January 31, 1987, as described above. Word 4.0 came out on November 6, 1990, and added automatic linking with Excel, the ability to flow text around graphics, and a WYSIWYG page view editing mode. Word 5.1 for Mac, released in 1992 ran on the original 68000 CPU and was the last to be specifically designed as a Macintosh application. The later Word 6 was a Windows port and poorly received. Word 5.1 continued to run well until the last Classic MacOS. Many people continue to run Word 5.1 to this day under an emulated Mac classic system for some of its excellent features, such as document generation and renumbering, or to access their old files.
Microsoft Word 2011 running on OS X
In 1997, Microsoft formed the Macintosh Business Unit as an independent group within Microsoft focused on writing software for Mac OS. Its first version of Word, Word 98, was released with Office 98 Macintosh Edition. Document compatibility reached parity with Word 97,[32] and it included features from Word 97 for Windows, including spell and grammar checking with squiggles.[43] Users could choose the menus and keyboard shortcuts to be similar to either Word 97 for Windows or Word 5 for Mac OS.
Word 2001, released in 2000, added a few new features, including the Office Clipboard, which allowed users to copy and paste multiple items.[44] It was the last version to run on classic Mac OS and, on Mac OS X, it could only run within the Classic Environment. Word X, released in 2001, was the first version to run natively on, and required, Mac OS X,[43] and introduced non-contiguous text selection.[45]
Word 2004 was released in May 2004. It included a new Notebook Layout view for taking notes either by typing or by voice.[46] Other features, such as tracking changes, were made more similar with Office for Windows.[47]
Word 2008, released on January 15, 2008, included a Ribbon-like feature, called the Elements Gallery, that can be used to select page layouts and insert custom diagrams and images. It also included a new view focused on publishing layout, integrated bibliography management,[48] and native support for the new Office Open XML format. It was the first version to run natively on Intel-based Macs.[49]
Word 2011, released in October 2010, replaced the Elements Gallery in favor of a Ribbon user interface that is much more similar to Office for Windows,[50] and includes a full-screen mode that allows users to focus on reading and writing documents, and support for Office Web Apps.[51]
Word 2021 added real-time co-authoring, automatic cloud saving, dark mode, immersive reader enhancements, line focus, a visual refresh, the ability to save pictures in SVG format, and a new Sketched style outline.
File formats[edit]
| DOC | Legacy Word document |
|---|---|
| DOT | Legacy Word templates |
| WBK | Legacy Word document backup |
| DOCX | XML Word document |
| DOCM | XML Word macro-enabled document |
| DOTX | XML Word template |
| DOTM | XML Word macro-enabled template |
| DOCB | XML Word binary document |
Filename extensions[edit]
Microsoft Word’s native file formats are denoted either by a .doc or .docx filename extension.
Although the .doc extension has been used in many different versions of Word, it actually encompasses four distinct file formats:
- Word for DOS
- Word for Windows 1 and 2; Word 3 and 4 for Mac OS
- Word 6 and Word 95 for Windows; Word 6 for Mac OS
- Word 97 and later for Windows; Word 98 and later for Mac OS
(The classic Mac OS of the era did not use filename extensions.)[52]
The newer .docx extension signifies the Office Open XML international standard for Office documents and is used by default by Word 2007 and later for Windows as well as Word 2008 and later for macOS.[53]
Binary formats (Word 97–2007)[edit]
During the late 1990s and early 2000s, the default Word document format (.DOC) became a de facto standard of document file formats for Microsoft Office users.[citation needed] There are different versions of «Word Document Format» used by default in Word 97–2007.[54] Each binary word file is a Compound File,[55] a hierarchical file system within a file. According to Joel Spolsky, Word Binary File Format is extremely complex mainly because its developers had to accommodate an overwhelming number of features and prioritize performance over anything else.
As with all OLE Compound Files, Word Binary Format consists of «storages», which are analogous to computer folders and «streams», which are similar to computer files. Each storage may contain streams or other storage. Each Word Binary File must contain a stream called the «WordDocument» stream and this stream must start with a File Information Block (FIB).[57] FIB serves as the first point of reference for locating everything else, such as where the text in a Word document starts, ends, what version of Word created the document and other attributes.
Word 2007 and later continue to support the DOC file format, although it is no longer the default.
XML Document (Word 2003)[edit]
The .docx XML format introduced in Word 2003[58] was a simple, XML-based format called WordProcessingML or WordML.
The Microsoft Office XML formats are XML-based document formats (or XML schemas) introduced in versions of Microsoft Office prior to Office 2007. Microsoft Office XP introduced a new XML format for storing Excel spreadsheets and Office 2003 added an XML-based format for Word documents.
These formats were succeeded by Office Open XML (ECMA-376) in Microsoft Office 2007.
Cross-version compatibility[edit]
Opening a Word Document file in a version of Word other than the one with which it was created can cause an incorrect display of the document. The document formats of the various versions change in subtle and not-so-subtle ways (such as changing the font or the handling of more complex tasks like footnotes). Formatting created in newer versions does not always survive when viewed in older versions of the program, nearly always because that capability does not exist in the previous version.[59] Rich Text Format (RTF), an early effort to create a format for interchanging formatted text between applications, is an optional format for Word that retains most formatting and all content of the original document.
Third-party formats[edit]
Plugins permitting the Windows versions of Word to read and write formats it does not natively support, such as international standard OpenDocument format (ODF) (ISO/IEC 26300:2006), are available. Up until the release of Service Pack 2 (SP2) for Office 2007, Word did not natively support reading or writing ODF documents without a plugin, namely the SUN ODF Plugin or the OpenXML/ODF Translator. With SP2 installed, ODF format 1.1 documents can be read and saved like any other supported format in addition to those already available in Word 2007.[59][60][61][62][63] The implementation faces substantial criticism, and the ODF Alliance and others have claimed that the third-party plugins provide better support.[64] Microsoft later declared that the ODF support has some limitations.[65]
In October 2005, one year before the Microsoft Office 2007 suite was released, Microsoft declared that there was insufficient demand from Microsoft customers for the international standard OpenDocument format support and that therefore it would not be included in Microsoft Office 2007. This statement was repeated in the following months.[66][67][68][69] As an answer, on October 20, 2005, an online petition was created to demand ODF support from Microsoft.[70]
In May 2006, the ODF plugin for Microsoft Office was released by the OpenDocument Foundation.[71] Microsoft declared that it had no relationship with the developers of the plugin.[72]
In July 2006, Microsoft announced the creation of the Open XML Translator project – tools to build a technical bridge between the Microsoft Office Open XML Formats and the OpenDocument Format (ODF). This work was started in response to government requests for interoperability with ODF. The goal of the project was not to add ODF support to Microsoft Office, but only to create a plugin and an external toolset.[73][74] In February 2007, this project released a first version of the ODF plugin for Microsoft Word.[75]
In February 2007, Sun released an initial version of its ODF plugin for Microsoft Office.[76] Version 1.0 was released in July 2007.[77]
Microsoft Word 2007 (Service Pack 1) supports (for output only) PDF and XPS formats, but only after manual installation of the Microsoft ‘Save as PDF or XPS’ add-on.[78][79] On later releases, this was offered by default.
Features and flaws[edit]
Among its features, Word includes a built-in spell checker, a thesaurus, a dictionary, and utilities for manipulating and editing text. The following are some aspects of its feature set.
Templates[edit]
Several later versions of Word include the ability for users to create their formatting templates, allowing them to define a file in which: the title, heading, paragraph, and other element designs differ from the standard Word templates.[80] Users can find how to do this under the Help section located near the top right corner (Word 2013 on Windows 8).
For example, Normal.dotm is the master template from which all Word documents are created. It determines the margin defaults as well as the layout of the text and font defaults. Although Normal.dotm is already set with certain defaults, the user can change it to new defaults. This will change other documents which were created using the template.[81] It was previously Normal.dot.[82]
Image formats[edit]
Word can import and display images in common bitmap formats such as JPG and GIF. It can also be used to create and display simple line art. Microsoft Word added support[83] for the common SVG vector image format in 2017 for Office 365 ProPlus subscribers and this functionality was also included in the Office 2019 release.
WordArt[edit]
An example image created with WordArt
WordArt enables drawing text in a Microsoft Word document such as a title, watermark, or other text, with graphical effects such as skewing, shadowing, rotating, stretching in a variety of shapes and colors, and even including three-dimensional effects. Users can apply formatting effects such as shadow, bevel, glow, and reflection to their document text as easily as applying bold or underline. Users can also spell-check text that uses visual effects and add text effects to paragraph styles.
Macros[edit]
A Macro is a rule of pattern that specifies how a certain input sequence (often a sequence of characters) should be mapped to an output sequence according to a defined process. Frequently used or repetitive sequences of keystrokes and mouse movements can be automated. Like other Microsoft Office documents, Word files can include advanced macros and even embedded programs. The language was originally WordBasic, but changed to Visual Basic for Applications as of Word 97.
This extensive functionality can also be used to run and propagate viruses in documents. The tendency for people to exchange Word documents via email, USB flash drives, and floppy disks made this an especially attractive vector in 1999. A prominent example was the Melissa virus, but countless others have existed.
These macro viruses were the only known cross-platform threats between Windows and Macintosh computers and they were the only infection vectors to affect any macOS system up until the advent of video codec trojans in 2007.[citation needed] Microsoft released patches for Word X and Word 2004 that effectively eliminated the macro problem on the Mac by 2006.
Word’s macro security setting, which regulates when macros may execute, can be adjusted by the user, but in the most recent versions of Word, it is set to HIGH by default, generally reducing the risk from macro-based viruses, which have become uncommon.
Layout issues[edit]
Before Word 2010 (Word 14) for Windows, the program was unable to correctly handle ligatures defined in OpenType fonts.[84] Those ligature glyphs with Unicode codepoints may be inserted manually, but are not recognized by Word for what they are, breaking spell checking, while custom ligatures present in the font are not accessible at all. Since Word 2010, the program now has advanced typesetting features which can be enabled,[85] OpenType ligatures,[86] kerning and hyphenation (previous versions already had the latter two features). Other layout deficiencies of Word include the inability to set crop marks or thin spaces. Various third-party workaround utilities have been developed.[87]
In Word 2004 for Mac OS X, support of complex scripts was inferior even to Word 97[88] and Word 2004 did not support Apple Advanced Typography features like ligatures or glyph variants.[89]
Issues with technical documents[edit]
Microsoft Word is only awkwardly suitable for some kinds of technical writing, specifically, that which requires mathematical equations,[90] figure placement, table placement and cross-references to any of these items.[citation needed] The usual workaround for equations is to use a third-party equation typesetter.[citation needed] Figures and tables must be placed manually; there is an anchor mechanism but it is not designed for fully automatic figure placement and editing text after placing figures and tables often requires re-placing those items by moving the anchor point and even then the placement options are limited.[citation needed] This problem is deeply baked into Word’s structure since 1985 as it does not know where page breaks will occur until the document is printed.[citation needed]
Bullets and numbering[edit]
Microsoft Word supports bullet lists and numbered lists. It also features a numbering system that helps add correct numbers to pages, chapters, headers, footnotes, and entries of tables of content; these numbers automatically change to correct ones as new items are added or existing items are deleted. Bullets and numbering can be applied directly to paragraphs and converted to lists.[91] Word 97 through 2003, however, had problems adding correct numbers to numbered lists. In particular, a second irrelevant numbered list might have not started with number one but instead resumed numbering after the last numbered list. Although Word 97 supported a hidden marker that said the list numbering must restart afterward, the command to insert this marker (Restart Numbering command) was only added in Word 2003. However, if one were to cut the first item of the listed and paste it as another item (e.g. fifth), then the restart marker would have moved with it and the list would have restarted in the middle instead of at the top.[92]
Users can also create tables in Word. Depending on the version, Word can perform simple calculations – along with support for formulas and equations as well.
Word continues to default to non-Unicode characters and non-hierarchical bulleting, despite user preference for Powerpoint-style symbol hierarchies (e.g., filled circle/emdash/filled square/endash/emptied circle) and universal compatibility.
AutoSummarize[edit]
Available in certain versions of Word (e.g., Word 2007), AutoSummarize highlights passages or phrases that it considers valuable and can be a quick way of generating a crude abstract or an executive summary.[93] The amount of text to be retained can be specified by the user as a percentage of the current amount of text.
According to Ron Fein of the Word 97 team, AutoSummarize cuts wordy copy to the bone by counting words and ranking sentences. First, AutoSummarize identifies the most common words in the document (barring «a» and «the» and the like) and assigns a «score» to each word – the more frequently a word is used, the higher the score. Then, it «averages» each sentence by adding the scores of its words and dividing the sum by the number of words in the sentence – the higher the average, the higher the rank of the sentence. «It’s like the ratio of wheat to chaff,» explains Fein.[94]
AutoSummarize was removed from Microsoft Word for Mac OS X 2011, although it was present in Word for Mac 2008. AutoSummarize was removed from the Office 2010 release version (14) as well.[95]
Other platforms[edit]
Word for mobile[edit]
Word Mobile is a word processor that allows creating and editing documents. It supports basic formatting, such as bolding, changing font size, and changing colors (from red, yellow, or green). It can add comments, but can’t edit documents with tracked changes. It can’t open password-protected documents; change the typeface, text alignment, or style (normal, heading 1); create bulleted lists; insert pictures; or undo.[96][97][98] Word Mobile is neither able to display nor insert footnotes, endnotes, page headers, page footers, page breaks, certain indentation of lists, and certain fonts while working on a document, but retains them if the original document has them.[99] In addition to the features of the 2013 version, the 2007 version on Windows Mobile also has the ability to save documents in the Rich Text Format and open legacy PSW (Pocket Word).[99] Furthermore, it includes a spell checker, word count tool, and a «Find and Replace» command. In 2015, Word Mobile became available for Windows 10 and Windows 10 Mobile on Windows Store.[100]
Word for the web[edit]
Word for the web is a free lightweight version of Microsoft Word available as part of Office on the web, which also includes web versions of Microsoft Excel and Microsoft PowerPoint.
Word for the web lacks some Ribbon tabs, such as Design and Mailings. Mailings allows users to print envelopes and labels and manage mail merge printing of Word documents.[101][102] Word for the web is not able to edit certain objects, such as: equations, shapes, text boxes or drawings, but a placeholder may be present in the document. Certain advanced features like table sorting or columns will not be displayed but are preserved as they were in the document. Other views available in the Word desktop app (Outline, Draft, Web Layout, and Full-Screen Reading) are not available, nor are side-by-side viewing, split windows, and the ruler.[103]
Password protection[edit]
Three password types can be set in Microsoft Word,
- Password to open a document[104]
- Password to modify a document[104]
- Password restricting formatting and editing[105]
The second and third password types were developed by Microsoft for convenient shared use of documents rather than for their protection. There is no encryption of documents that are protected by such passwords and the Microsoft Office protection system saves a hash sum of a password in a document’s header where it can be easily accessed and removed by the specialized software. Password to open a document offers much tougher protection that had been steadily enhanced in the subsequent editions of Microsoft Office.
Word 95 and all the preceding editions had the weakest protection that utilized a conversion of a password to a 16-bit key.
Key length in Word 97 and 2000 was strengthened up to 40 bit. However, modern cracking software allows removing such a password very quickly – a persistent cracking process takes one week at most. Use of rainbow tables reduces password removal time to several seconds. Some password recovery software can not only remove a password but also find an actual password that was used by a user to encrypt the document using the brute-force attack approach. Statistically, the possibility of recovering the password depends on the password strength.
Word’s 2003/XP version default protection remained the same but an option that allowed advanced users to choose a Cryptographic Service Provider was added.[106] If a strong CSP is chosen, guaranteed document decryption becomes unavailable and, therefore, a password can’t be removed from the document. Nonetheless, a password can be fairly quickly picked with a brute-force attack, because its speed is still high regardless of the CSP selected. Moreover, since the CSPs are not active by default, their use is limited to advanced users only.
Word 2007 offers significantly more secure document protection which utilizes the modern Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) that converts a password to a 128-bit key using a SHA-1 hash function 50,000 times. It makes password removal impossible (as of today, no computer that can pick the key in a reasonable amount of time exists) and drastically slows the brute-force attack speed down to several hundreds of passwords per second.
Word’s 2010 protection algorithm was not changed apart from the increasing number of SHA-1 conversions up to 100,000 times and consequently, the brute-force attack speed decreased two times more.
Reception[edit]
|
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (December 2021) |
Initial releases of Word were met with criticism. Byte in 1984 criticized the documentation for Word 1.1 and 2.0 for DOS, calling it «a complete farce». It called the software «clever, put together well and performs some extraordinary feats», but concluded that «especially when operated with the mouse, has many more limitations than benefits … extremely frustrating to learn and operate efficiently».[107] PC Magazine‘s review was very mixed, stating: «I’ve run into weird word processors before, but this is the first time one’s nearly knocked me down for the count» but acknowledging that Word’s innovations were the first that caused the reviewer to consider abandoning WordStar. While the review cited an excellent WYSIWYG display, sophisticated print formatting, windows, and footnoting as merits, it criticized many small flaws, very slow performance, and «documentation produced by Madame Sadie’s Pain Palace». It concluded that Word was «two releases away from potential greatness».[108]
Compute!’s Apple Applications in 1987 stated that «despite a certain awkwardness», Word 3.01 «will likely become the major Macintosh word processor» with «far too many features to list here». While criticizing the lack of true WYSIWYG, the magazine concluded that «Word is marvelous. It’s like a Mozart or Edison, whose occasional gaucherie we excuse because of his great gifts».[109]
Compute! in 1989 stated that Word 5.0’s integration of text and graphics made it «a solid engine for basic desktop publishing». The magazine approved of improvements to text mode, described the $75 price for upgrading from an earlier version as «the deal of the decade» and concluded that «as a high-octane word processor, Word is worth a look».[110]
During the first quarter of 1996, Microsoft Word accounted for 80% of the worldwide word processing market.[111]
Release history[edit]
| Legend: | Old version, not maintained | Older version, still maintained | Current stable version |
|---|
Microsoft Word 2010 running on Windows 7
| Year released | Name | Version | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1989 | Word for Windows 1.0 | 1.0 | Code-named Opus[112] |
| 1990 | Word for Windows 1.1 | 1.1 | For Windows 3.0.[113] Code-named Bill the Cat[citation needed] |
| 1990 | Word for Windows 1.1a | 1.1a | On March 25, 2014, Microsoft made the source code to Word for Windows 1.1a available to the public via the Computer History Museum.[114][115] |
| 1991 | Word for Windows 2.0 | 2.0 | Included in Office 3.0. |
| 1993 | Word for Windows 6.0 | 6.0 | Version numbers 3, 4, and 5 were skipped, to bring Windows version numbering in line with that of DOS, Mac OS, and WordPerfect (the main competing word processor at the time). Also, a 32-bit version for Windows NT only. Included in Office 4.0, 4.2, and 4.3. |
| 1995 | Word for Windows 95 | 7.0 | Included in Office 95 |
| 1997 | Word 97 | 8.0 | Included in Office 97 |
| 1998 | Word 98 | 8.5 | Included in Office 97 |
| 1999 | Word 2000 | 9.0 | Included in Office 2000 |
| 2001 | Word 2002 | 10.0 | Included in Office XP |
| 2003 | Microsoft Word 2003 | 11.0 | Included in Office 2003 |
| 2006 | Microsoft Word 2007 | 12.0 | Included in Office 2007; released to businesses on November 30, 2006, released worldwide to consumers on January 30, 2007. Extended support until October 10, 2017. |
| 2010 | Word 2010 | 14.0 | Included in Office 2010; skipped 13.0 due to triskaidekaphobia.[116] |
| 2013 | Word 2013 | 15.0 | Included in Office 2013 |
| 2016 | Word 2016 | 16.0 | Included in Office 2016 |
| 2019 | Word 2019 | 16.0 | Included in Office 2019 |
| 2021 | Word 2021 | 16.0 | Included in Office 2021 |
| Year released | Name | Version | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1985 | Word 1 | 1.0 | |
| 1987 | Word 3 | 3.0 | |
| 1989 | Word 4 | 4.0 | Part of Office 1.0 and 1.5 |
| 1991 | Word 5 | 5.0 |
|
| 1992 | Word 5.1 | 5.1 |
|
| 1993 | Word 6 | 6.0 |
|
| 1998 | Word 98 | 8.5 |
|
| 2000 | Word 2001 | 9.0 |
|
| 2001 | Word v. X | 10.0 |
|
| 2004 | Word 2004 | 11.0 | Part of Office 2004 |
| 2008 | Word 2008 | 12.0 | Part of Office 2008 |
| 2010 | Word 2011 | 14.0 | Part of Office 2011; skipped 13.0 due to triskaidekaphobia.[116] |
| 2015 | Word 2016 | 16.0 | Part of Office 2016; skipped 15.0 |
| 2019 | Word 2019 | 16.0 | Part of Office 2019 |
| 2021 | Word 2021 | 16.0 | Included in Office 2021 |
| Year released | Name | Version | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1983 | Word 1 | 1.0 | Initial version of Word |
| 1985 | Word 2 | 2.0 | |
| 1986 | Word 3 | 3.0 | |
| 1987 | Word 4 | 4.0 | |
| 1989 | Word 5 | 5.0 | |
| 1991 | Word 5.1 | 5.1 | |
| 1991 | Word 5.5 | 5.5 | First DOS version to use a Windows-like user interface |
| 1993 | Word 6 | 6.0 | Last DOS version. |
| Platform | Year released | Name | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| Atari ST | 1988 | Microsoft Write | Based on Microsoft Word 1.05 for Mac OS |
| OS/2 | 1989 | Microsoft Word 5.0 | Word 5.0 ran both under DOS and OS/2 dual-mode as a native OS/2 application |
| OS/2 | 1991 | Microsoft Word 5.5 | Word 5.5 ran both under DOS and OS/2 dual-mode as a native OS/2 application |
| OS/2 | 1990 | Microsoft Word for OS/2 Presentation Manager version 1.1 | |
| OS/2 | 1991 | Microsoft Word for OS/2 Presentation Manager version 1.2[citation needed] | |
| SCO Unix | 1990 | Microsoft Word for Unix version 5.0[117] | |
| SCO Unix | 1991 | Microsoft Word for Unix version 5.1[118] |
References[edit]
- ^ «Update history for Microsoft Office 2019». Microsoft Docs. Retrieved April 13, 2021.
- ^ a b «C++ in MS Office». cppcon. July 17, 2014. Archived from the original on November 7, 2019. Retrieved June 25, 2019.
- ^ «System requirements for Office». Office.com. Microsoft. Retrieved March 30, 2019.
- ^ «Update history for Office for Mac». Microsoft Docs.
- ^ Lardinois, Frederic (January 29, 2015). «Microsoft’s Office For Android Tablets Comes Out Of Preview». TechCrunch. Retrieved January 28, 2023.
- ^ «Microsoft Word: Write, Edit & Share Docs on the Go APKs». APKMirror.
- ^ Cunningham, Andrew (March 27, 2014). «Microsoft brings Office to iPad, makes iPhone version free to all». Ars Technica. Retrieved January 27, 2023.
- ^ «Microsoft Word». App Store.
- ^ «Version 1.0 of today’s most popular applications, a visual tour – Pingdom Royal». Pingdom. June 17, 2009. Archived from the original on August 13, 2018. Retrieved April 12, 2016.
- ^ a b c d A. Allen, Roy (October 2001). «Chapter 12: Microsoft in the 1980s» (PDF). A History of the Personal Computer: The People and the Technology (1st ed.). Allan Publishing. pp. 12/25–12/26. ISBN 978-0-9689108-0-1. Retrieved November 7, 2010.
- ^ «Microsoft Office online, Getting to know you…again: The Ribbon». Archived from the original on May 11, 2011.
- ^ «The history of branding, Microsoft history». Archived from the original on May 28, 2009.
- ^ a b c d e Edwards, Benj (October 22, 2008). «Microsoft Word Turns 25». PC World. Archived from the original on July 4, 2012. Retrieved November 7, 2010.
- ^ Tsang, Cheryl (1999). Microsoft First Generation. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-0-471-33206-0.
- ^ Schaut, Rick (May 19, 2004). «Anatomy of a Software Bug». MSDN Blogs. Archived from the original on February 1, 2010. Retrieved December 2, 2006.
- ^ a b Markoff, John (May 30, 1983). «Mouse and new WP program join Microsoft product lineup». InfoWorld. p. 10. Retrieved November 7, 2010.
- ^ Pollack, Andrew (August 25, 1983). «Computerizing Magazines». The New York Times. Retrieved April 24, 2013.
- ^ Lemmons, Phil (December 1983). «Microsoft Windows». BYTE. p. 48. Retrieved October 20, 2013.
- ^ Advertisement (December 1983). «Undo. Windows. Mouse. Finally». BYTE. pp. 88–89. Retrieved October 20, 2013.
- ^ Peterson, W.E. Pete (1994). Almost Perfect: How a Bunch of Regular Guys Built Wordperfect Corporation. Prima Publishing. ISBN 0-7881-9991-9.
- ^ a b c d e f Knight, Dan (May 22, 2008). «Microsoft Word for Mac History». Low End Mac. Retrieved November 7, 2010.
- ^ «The Piece Table».
- ^ Brand, Stewart (1989). Whole Earth Software Catalog. ISBN 9780385233019.
For a year, I waited for a heavier-duty word processor than MACWRITE. I finally got it— WORD.
- ^ a b c Schaut, Rick (February 26, 2004). «Mac Word 6.0». Buggin’ My Life Away. MSDN Blogs. Archived from the original on May 14, 2004. Retrieved June 21, 2010.
- ^ «Atari announces agreement with Microsoft». Atarimagazines.com. April 25, 2008. Retrieved June 21, 2010.
- ^ «Feature Review: Microsoft Write». Atarimagazines.com. April 25, 2008. Retrieved June 21, 2010.
- ^ «Today’s Atari Corp.: A close up look inside». Atarimagazines.com. April 25, 2008. Retrieved June 21, 2010.
- ^ Miller, Michael J. (November 12, 1990). «First Look: Microsoft Updates Look of And Adds Pull-Down Menus to Character-Based Word 5.5». InfoWorld. p. 151. Retrieved November 7, 2010.
- ^ Needleman, Raphael (November 19, 1990). «Microsoft Word 5.5: Should You Fight or Switch?». InfoWorld. p. 106. Retrieved November 7, 2010.
- ^ «Microsoft Word 5.5 for MS-DOS (EXE format)». Microsoft Download Center. Retrieved August 19, 2011.
- ^ «War of the Words». InfoWorld. February 7, 1994. pp. 66–79. Retrieved November 7, 2010.
- ^ a b Lockman, James T.W. (May 15, 1998). «UGeek Software Review: Microsoft Office 98 Gold for Macintosh». Archived from the original on December 3, 2010. Retrieved November 7, 2010.
- ^ Rose, Daniel. «Microsoft Office for Windows NT». DanielSays.com – Daniel’s Legacy Computer Collections. Archived from the original on January 27, 2015. Retrieved May 15, 2015.
- ^ Ericson, Richard (October 11, 2006). «Final Review: The Lowdown on Office 2007». Computerworld. Retrieved November 8, 2010.
- ^ Lowe, Scott (December 11, 2006). «An introduction to the Microsoft Office 2007 ribbon interface». TechRepublic. Retrieved December 14, 2021.
- ^ Shultz, Greg (February 25, 2009). «Be ready for new and improved applets in Windows 7». TechRepublic. Archived from the original on December 14, 2021. Retrieved December 14, 2021.
- ^ a b Lowe, Scott (January 26, 2007). «Explore what is new and different in Microsoft Word 2007». TechRepublic. Retrieved December 14, 2021.
- ^ Mendelson, Edward (May 11, 2010). «Microsoft Office 2010». PC Magazine. Retrieved November 8, 2010.
- ^ Mendelson, Edward (May 11, 2010). «Microsoft Office 2010: Office 2010’s Backstage View». PC Magazine. Archived from the original on December 2, 2010. Retrieved November 8, 2010.
- ^ Mendelson, Edward (May 11, 2010). «Microsoft Office 2010: Lots of Graphics Options». PC Magazine. Archived from the original on April 24, 2010. Retrieved December 14, 2021.
- ^ «Introduction to Word Web App». Microsoft. Retrieved November 8, 2010.
- ^ «Microsoft Word 1.x (Mac)». WinWorld. Retrieved December 22, 2021.
- ^ a b McLean, Prince (November 12, 2007). «Road to Mac Office 2008: an introduction (Page 3)». AppleInsider. Archived from the original on July 7, 2011. Retrieved November 7, 2010.
- ^ Tetrault, Gregory (January 2001). «Review: Microsoft Office 2001». ATPM: About This Particular Macintosh. Retrieved November 7, 2010.
- ^ Negrino, Tom (February 1, 2002). «Review: Microsoft Office v. X». MacWorld. Archived from the original on August 18, 2010. Retrieved November 7, 2010.
- ^ Lunsford, Kelly; Michaels, Philip; Snell, Jason (March 3, 2004). «Office 2004: First Look». MacWorld. Archived from the original on June 25, 2010. Retrieved November 7, 2010.
- ^ Friedberg, Steve (May 25, 2004). «Review: Microsoft Office». MacNN. Archived from the original on April 5, 2010. Retrieved November 7, 2010.
- ^ McLean, Prince (November 14, 2007). «Road to Mac Office 2008: Word ’08 vs Pages 3.0». AppleInsider. Retrieved November 7, 2010.
- ^ McLean, Prince (November 12, 2007). «Road to Mac Office 2008: an introduction (Page 4)». AppleInsider. Archived from the original on July 7, 2011. Retrieved November 7, 2010.
- ^ McLean, Prince (March 29, 2010). «New Office 11 for Mac sports dense ribbons of buttons». AppleInsider. Retrieved November 7, 2010.
- ^ Dilger, Daniel Eran (October 25, 2010). «Review: Microsoft’s Office 2011 for Mac (Page 2)». Apple Insider. Archived from the original on October 28, 2010. Retrieved November 7, 2010.
- ^ Oakley, Howard (May 2, 2015). «.why .the .extensions? Quirks in the naming of files and folders». The Eclectic Light Company. Archived from the original on February 26, 2020. Retrieved February 26, 2020.
Macs used to be the only computers that did not need filename extensions…on classic Mac systems, you can name applications, documents, and most other files almost anything that you like, as the name is not linked in any way to the type of thing that file is.
- ^ «DOCX Transitional (Office Open XML), ISO 29500:2008-2016, ECMA-376, Editions 1-5». loc.gov. January 20, 2017. Retrieved July 9, 2019.
- ^ «5 Appendix A: Product Behavior» (PDF). [MS-DOC]: Word (.doc) Binary File Format (PDF). Redmond, WA: Microsoft. Archived from the original on January 10, 2015. Retrieved January 10, 2015.
- ^ «2.1 File Structure» (PDF). [MS-DOC]: Word (.doc) Binary File Format (PDF). Redmond, WA: Microsoft. Archived from the original on January 10, 2015. Retrieved January 10, 2015.
- ^ «2.1.1 WordDocument Stream» (PDF). [MS-DOC]: Word (.doc) Binary File Format (PDF). Redmond, WA: Microsoft. Archived from the original on January 10, 2015. Retrieved January 10, 2015.
- ^ «What You Can Do with Word XML [Word 2003 XML Reference]». MSDN. 2004.
- ^ a b Casson, Tony; Ryan, Patrick S. (May 1, 2006). «Open Standards, Open Source Adoption in the Public Sector, and Their Relationship to Microsoft’s Market Dominance». In Bolin, Sherrie (ed.). Standards Edge: Unifier or Divider?. Sheridan Books. p. 87. SSRN 1656616.
- ^ «Microsoft Expands List of Formats Supported in Microsoft Office, May 21, 2008». News Center. Microsoft. May 21, 2008. Retrieved April 24, 2013.
- ^ Fulton, Scott M. III (May 21, 2008). «Next Office 2007 service pack will include ODF, PDF support options». Betanews.
- ^ Andy Updegrove (May 21, 2008). «Microsoft Office 2007 to Support ODF – and not OOXML, May 21, 2008». Consortiuminfo.org. Retrieved June 21, 2010.
- ^ «Microsoft: Why we chose ODF support over OOXML, 23 May 2008». Software.silicon.com. Archived from the original on July 21, 2009. Retrieved June 21, 2010.
- ^ «Fact-sheet Microsoft ODF support» (PDF). odfalliance. Archived from the original (PDF) on June 11, 2009. Retrieved May 24, 2009.
Microsoft Excel 2007 will process ODF spreadsheet documents when loaded via the Sun Plug-In 3.0 for Microsoft Office or the SourceForge «OpenXML/ODF Translator Add-in for Office,» but will fail when using the «built-in» support provided by Office 2007 SP2.
- ^ Microsoft. «What happens when I save a Word 2007 document in the OpenDocument Text format?». Archived from the original on March 18, 2010. Retrieved April 5, 2010.
- ^ Goodwins, Rupert (October 3, 2005). «Office 12 to support PDF creation, 3 October 2005». News.zdnet.co.uk. Archived from the original on July 23, 2009. Retrieved June 21, 2010.
- ^ Marson, Ingrid (October 6, 2005). «Microsoft ‘must support OpenDocument’, 6 October 2005». News.zdnet.co.uk. Archived from the original on July 25, 2009. Retrieved June 21, 2010.
- ^ March 23, 2006, Gates: Office 2007 will enable a new class of application Mass. holding tight to OpenDocument – ZDNet Archived July 21, 2009, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ «May 08, 2006 – Microsoft Office to get a dose of OpenDocument». Zdnet.com.au. Archived from the original on July 22, 2009. Retrieved June 21, 2010.
- ^ OpenDocument Fellowship (October 20, 2005). «OpenDocument Support: Tell Microsoft You Want It!, 20 October 2005». Opendocumentfellowship.com. Archived from the original on March 23, 2008. Retrieved June 21, 2010.
- ^ «Coming soon: ODF for MS Office, May 04, 2006». Linux-watch.com. May 4, 2006. Retrieved June 21, 2010.
- ^ LaMonica, Martin (May 5, 2006). «Microsoft Office to get a dose of OpenDocument». CNET News. Retrieved June 21, 2010.
- ^ «Microsoft Expands Document Interoperability, July 5, 2006». Microsoft.com. July 5, 2006. Archived from the original on February 4, 2007. Retrieved June 21, 2010.
- ^ Jones, Brian; Rajabi, Zeyad (July 6, 2006). «Open XML Translator project announced (ODF support for Office)». Brian Jones: Office Solutions. Microsoft. Archived from the original on January 18, 2010. Retrieved April 24, 2013.
- ^ LaMonica, Martin (February 1, 2007). «Microsoft to release ODF document converter». CNet News. Retrieved April 24, 2013.
- ^ Lombardi, Candace (February 7, 2007). «Sun to release ODF translator for Microsoft Office». CNET. Retrieved June 21, 2010.
- ^ Paul, Ryan (July 7, 2007). «Sun releases ODF Plugin 1.0 for Microsoft Office, July 07, 2007». Arstechnica.com. Retrieved June 21, 2010.
- ^ «Download details: 2007 Microsoft Office Add-in: Microsoft Save as PDF or XPS». Microsoft.com. November 8, 2006. Retrieved June 21, 2010.
- ^ Microsoft to remove PDF support from Office 2007 in wake of Adobe dispute, Friday, June 2, 2006 Microsoft to remove PDF support from Office 2007 in wake of Adobe dispute | TG Daily Archived February 1, 2009, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Klein, Matt. «Word Formatting: Mastering Styles and Document Themes». How-To Geek. Retrieved July 9, 2019.
- ^ «Change the Normal template (Normal.dotm )». support.microsoft.com. Retrieved May 20, 2021.
- ^ in-depth explanation of Normal.dot Archived June 20, 2005, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ «Edit SVG images in Microsoft Office 365». Office Support. Microsoft. Retrieved February 4, 2019.
- ^ What’s new in Word 2010. Retrieved July 1, 2010.
- ^ Improving the look of papers written in Microsoft Word. Retrieved May 30, 2010.
- ^ How to Enable OpenType Ligatures in Word 2010, Oreszek Blog, May 17, 2009.
- ^ Such as «How to delete a blank page in Word». Sbarnhill.mvps.org. Archived from the original on May 5, 2010. Retrieved June 21, 2010.
- ^ Alan Wood. «Unicode and Multilingual Editors and Word Processors for Mac OS X».
- ^ Neuburg, Matt (May 19, 2004). «TidBITS : Word Up! Word 2004, That Is». Db.tidbits.com. Archived from the original on July 8, 2012. Retrieved June 21, 2010.
- ^ «Automatically numbering equations and other equation-related questions in Word for Mac 2011». Microsoft Community. February 6, 2013.
- ^ McGhie, John (March 26, 2011). «Word’s numbering explained». word.mvps.org.
- ^ Aldis, Margaret (March 26, 2011). «Methods for restarting list numbering». Word.mvps.org.
- ^ «How To Access Auto Summarize in Microsoft Word 2007». Sue’s Word Tips. December 14, 2011. Retrieved July 9, 2019.
- ^ Gore, Karenna (February 9, 1997). «Cognito Auto Sum». Slate. Retrieved June 21, 2010.
- ^ Changes in Word 2010 (for IT pros). Technet.microsoft.com (May 16, 2012). Retrieved July 17, 2013.
- ^ Ralph, Nate. «Office for Windows Phone 8: Your handy starter guide». TechHive. Archived from the original on October 15, 2014. Retrieved August 30, 2014.
- ^ Wollman, Dana. «Microsoft Office Mobile for iPhone hands-on». Engadget. Retrieved August 30, 2014.
- ^ Pogue, David (June 19, 2013). «Microsoft Adds Office for iPhone. Yawn». The New York Times. Retrieved August 30, 2014.
- ^ a b Unsupported Features in Word Mobile. Microsoft. Retrieved September 21, 2007.
- ^ Koenigsbauer, Kirk; Microsoft 365, Corporate Vice President for (July 29, 2015). «Office Mobile apps for Windows 10 are here!». Microsoft 365 Blog. Retrieved July 11, 2020.
- ^ Bradley, Tony (February 2, 2015). «Office Online vs. Office 365: What’s free, what’s not, and what you really need». PC World. Archived from the original on July 24, 2017. Retrieved July 16, 2020.
- ^ Ansaldo, Michael (September 28, 2017). «Microsoft Office Online review: Work with your favorite Office formats for free». PC World. Retrieved October 31, 2019.
- ^ «Differences between using a document in the browser and in Word». Office Support. Microsoft. Archived from the original on November 7, 2017. Retrieved November 1, 2017.
- ^ a b «Password protect documents, workbooks, and presentations». Microsoft Office website. Microsoft. Retrieved April 24, 2013.
- ^ «How to Restrict Editing in Word 2010/2007». Trickyways. June 22, 2010. Retrieved April 24, 2010.
- ^ «How safe is Word encryption. Is it secure?». Oraxcel.com. Archived from the original on April 17, 2013. Retrieved April 24, 2013.
- ^ Cameron, Janet (September 1984). «Word Processing Revisited». BYTE (review). p. 171. Retrieved October 23, 2013.
- ^ Manes, Stephen (February 21, 1984). «The Unfinished Word». PC Magazine. p. 192. Retrieved October 19, 2021.
- ^ McNeill, Dan (December 1987). «Macintosh: The Word Explosion». Compute!’s Apple Applications. pp. 54–60. Retrieved September 14, 2016.
- ^ Nimersheim, Jack (December 1989). «Compute! Specific: MS-DOS». Compute!. pp. 11–12.
- ^ «Data Stream». Next Generation. No. 21. Imagine Media. September 1996. p. 21.
- ^ Opus Development Postmortem
- ^ «Microsoft Word 1.x (Windows) – Stats, Downloads and Screenshots :: WinWorld». WinWorld. Retrieved July 3, 2016.
- ^ Shustek, Len (March 24, 2014). «Microsoft Word for Windows Version 1.1a Source Code». Retrieved March 29, 2014.
- ^ Levin, Roy (March 25, 2014). «Microsoft makes source code for MS-DOS and Word for Windows available to public». Official Microsoft Blog. Archived from the original on March 28, 2014. Retrieved March 29, 2014.
- ^ a b «Office 14». Office Watch. June 1, 2007.
For the sake of superstition the next version of Office won’t be called ’13’.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ Marshall, Martin (January 8, 1990). «SCO Begins Shipping Microsoft Word 5.0 for Unix and Xenix». InfoWorld. p. 6. Retrieved May 20, 2021.
- ^ «Microsoft Word: SCO announces Word for Unix Systems Version 5.1». EDGE: Work-Group Computing Report. March 11, 1991. p. 33. Retrieved May 20, 2021 – via Gale General OneFile.
Further reading[edit]
- Tsang, Cheryl. Microsoft: First Generation. New York: John Wiley & Sons, Inc. ISBN 978-0-471-33206-0.
- Liebowitz, Stan J. & Margolis, Stephen E. Winners, Losers & Microsoft: Competition and Antitrust in High Technology Oakland: Independent Institute. ISBN 978-0-945999-80-5.
External links[edit]
- Microsoft Word – official site
- Find and replace text by using regular expressions (Advanced) — archived official support website
 |
|

Microsoft Office 365 version of Microsoft Word, with the new redesign applied |
|
| Developer(s) | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| Initial release | October 25, 1983; 39 years ago (as Multi-Tool Word) |
| Stable release |
2209 (16.0.15629.20208) |
| Repository | none |
| Written in | C++ (back-end)[2] |
| Operating system |
|
| Platform | IA-32, x64, ARM, ARM64 |
| Type | Word processor |
| License | Trialware |
| Website | products.office.com/word |

Word for Mac running on macOS Ventura (13.2) |
|
| Developer(s) | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| Stable release |
16.64 (Build 22081401) |
| Repository | none |
| Written in | C++ (back-end), Objective-C (API/UI)[2] |
| Operating system | macOS |
| Type | Word processor |
| License | Proprietary software plus services |
| Website | products.office.com/word |

Screenshot of Microsoft Word for Android 13 |
|
| Original author(s) | Microsoft Corporation |
|---|---|
| Developer(s) | Microsoft Corporation |
| Initial release | January 29, 2015; 8 years ago[5] |
| Stable release |
16.0.15427.20090 |
| Repository | none |
| Operating system | Android Pie and later |
| License | Proprietary commercial software |
| Website | products.office.com/word |
| Developer(s) | Microsoft Corporation |
|---|---|
| Initial release | March 27, 2014; 8 years ago[7] |
| Stable release |
2.63.2 |
| Repository | none |
| Operating system | iOS 14 or later IPadOS 14 or later |
| License | Proprietary commercial software |
| Website | products.office.com/word |
| Developer(s) | Microsoft |
|---|---|
| Repository | none |
| Operating system | Windows 10 and later, Windows 10 Mobile |
| Type | Word processor |
| License | Freemium |
| Website | www.microsoft.com/store/productId/9WZDNCRFJB9S |
Microsoft Word is a word processing software developed by Microsoft. It was first released on October 25, 1983,[9] under the name Multi-Tool Word for Xenix systems.[10][11][12] Subsequent versions were later written for several other platforms including: IBM PCs running DOS (1983), Apple Macintosh running the Classic Mac OS (1985), AT&T UNIX PC (1985), Atari ST (1988), OS/2 (1989), Microsoft Windows (1989), SCO Unix (1990), macOS (2001), Web browsers (2010), iOS (2014) and Android (2015). Using Wine, versions of Microsoft Word before 2013 can be run on Linux.
Commercial versions of Word are licensed as a standalone product or as a component of Microsoft Office suite of software, which can be purchased either with a perpetual license or as part of a Microsoft 365 subscription.
History[edit]
Origins[edit]
In 1981, Microsoft hired Charles Simonyi, the primary developer of Bravo, the first GUI word processor, which was developed at Xerox PARC.[13] Simonyi started work on a word processor called Multi-Tool Word and soon hired Richard Brodie, a former Xerox intern, who became the primary software engineer.[13][14][15]
Microsoft announced Multi-Tool Word for Xenix[13] and MS-DOS in 1983.[16] Its name was soon simplified to Microsoft Word.[10] Free demonstration copies of the application were bundled with the November 1983 issue of PC World, making it the first to be distributed on-disk with a magazine.[10][17] That year Microsoft demonstrated Word running on Windows.[18]
Unlike most MS-DOS programs at the time, Microsoft Word was designed to be used with a mouse.[16] Advertisements depicted the Microsoft Mouse and described Word as a WYSIWYG, windowed word processor with the ability to undo and display bold, italic, and underlined text,[19] although it could not render fonts.[10] It was not initially popular, since its user interface was different from the leading word processor at the time, WordStar.[20] However, Microsoft steadily improved the product, releasing versions 2.0 through 5.0 over the next six years. In 1985, Microsoft ported Word to the classic Mac OS (known as Macintosh System Software at the time). This was made easier by Word for DOS having been designed for use with high-resolution displays and laser printers, even though none were yet available to the general public.[21] It was also notable for its very fast cut-and-paste function and unlimited number of undo operations, which are due to its usage of the piece table data structure.[22]
Following the precedents of LisaWrite and MacWrite, Word for Mac OS added true WYSIWYG features. It fulfilled a need for a word processor that was more capable than MacWrite.[23] After its release, Word for Mac OS’s sales were higher than its MS-DOS counterpart for at least four years.[13]
The second release of Word for Mac OS, shipped in 1987, was named Word 3.0 to synchronize its version number with Word for DOS; this was Microsoft’s first attempt to synchronize version numbers across platforms. Word 3.0 included numerous internal enhancements and new features, including the first implementation of the Rich Text Format (RTF) specification, but was plagued with bugs. Within a few months, Word 3.0 was superseded by a more stable Word 3.01, which was mailed free to all registered users of 3.0.[21] After MacWrite Pro was discontinued in the mid-1990s, Word for Mac OS never had any serious rivals. Word 5.1 for Mac OS, released in 1992, was a very popular word processor owing to its elegance, relative ease of use, and feature set. Many users say it is the best version of Word for Mac OS ever created.[21][24]
In 1986, an agreement between Atari and Microsoft brought Word to the Atari ST[25] under the name Microsoft Write. The Atari ST version was a port of Word 1.05 for the Mac OS[26][27] and was never updated.
The first version of Word for Windows was released in 1989. With the release of Windows 3.0 the following year, sales began to pick up and Microsoft soon became the market leader for word processors for IBM PC-compatible computers.[13] In 1991, Microsoft capitalized on Word for Windows’ increasing popularity by releasing a version of Word for DOS, version 5.5, that replaced its unique user interface with an interface similar to a Windows application.[28][29] When Microsoft became aware of the Year 2000 problem, it made Microsoft Word 5.5 for DOS available for free downloads. As of February 2021, it is still available for download from Microsoft’s website.[30]
In 1991, Microsoft embarked on a project code-named Pyramid to completely rewrite Microsoft Word from the ground up. Both the Windows and Mac OS versions would start from the same code base. It was abandoned when it was determined that it would take the development team too long to rewrite and then catch up with all the new capabilities that could have been added at the same time without a rewrite. Instead, the next versions of Word for Windows and Mac OS, dubbed version 6.0, both started from the code base of Word for Windows 2.0.[24]
With the release of Word 6.0 in 1993, Microsoft again attempted to synchronize the version numbers and coordinate product naming across platforms, this time across DOS, Mac OS, and Windows (this was the last version of Word for DOS). It introduced AutoCorrect, which automatically fixed certain typing errors, and AutoFormat, which could reformat many parts of a document at once. While the Windows version received favorable reviews (e.g., from InfoWorld[31]), the Mac OS version was widely derided. Many accused it of being slow, clumsy, and memory intensive, and its user interface differed significantly from Word 5.1.[24] In response to user requests, Microsoft offered Word 5 again, after it had been discontinued.[32] Subsequent versions of Word for macOS are no longer direct ports of Word for Windows, instead featuring a mixture of ported code and native code.
Word for Windows[edit]
Word for Windows is available stand-alone or as part of the Microsoft Office suite. Word contains rudimentary desktop publishing capabilities and is the most widely used word processing program on the market. Word files are commonly used as the format for sending text documents via e-mail because almost every user with a computer can read a Word document by using the Word application, a Word viewer or a word processor that imports the Word format (see Microsoft Word Viewer).
Word 6 for Windows NT was the first 32-bit version of the product,[33] released with Microsoft Office for Windows NT around the same time as Windows 95. It was a straightforward port of Word 6.0. Starting with Word 95, each release of Word was named after the year of its release, instead of its version number.[34]
Word 2007 introduced a redesigned user interface that emphasized the most common controls, dividing them into tabs, and adding specific options depending on the context, such as selecting an image or editing a table.[35] This user interface, called Ribbon, was included in Excel, PowerPoint and Access 2007, and would be later introduced to other Office applications with Office 2010 and Windows applications such as Paint and WordPad with Windows 7, respectively.[36]
The redesigned interface also includes a toolbar that appears when selecting text, with options for formatting included.[37]
Word 2007 also included the option to save documents as Adobe Acrobat or XPS files,[37] and upload Word documents like blog posts on services such as WordPress.
Word 2010 allows the customization of the Ribbon,[38] adds a Backstage view for file management,[39] has improved document navigation, allows creation and embedding of screenshots,[40] and integrates with online services such as Microsoft OneDrive.[41]
Word 2019 added a dictation function.
Word 2021 added co-authoring, a visual refresh on the start experience and tabs, automatic cloud saving, dark mode, line focus, an updated draw tab, and support for ODF 1.3.
Word for Mac[edit]
The Mac was introduced on January 24, 1984, and Microsoft introduced Word 1.0 for Mac a year later, on January 18, 1985. The DOS, Mac, and Windows versions are quite different from each other. Only the Mac version was WYSIWYG and used a graphical user interface, far ahead of the other platforms. Each platform restarted its version numbering at «1.0».[42] There was no version 2 on the Mac, but version 3 came out on January 31, 1987, as described above. Word 4.0 came out on November 6, 1990, and added automatic linking with Excel, the ability to flow text around graphics, and a WYSIWYG page view editing mode. Word 5.1 for Mac, released in 1992 ran on the original 68000 CPU and was the last to be specifically designed as a Macintosh application. The later Word 6 was a Windows port and poorly received. Word 5.1 continued to run well until the last Classic MacOS. Many people continue to run Word 5.1 to this day under an emulated Mac classic system for some of its excellent features, such as document generation and renumbering, or to access their old files.
Microsoft Word 2011 running on OS X
In 1997, Microsoft formed the Macintosh Business Unit as an independent group within Microsoft focused on writing software for Mac OS. Its first version of Word, Word 98, was released with Office 98 Macintosh Edition. Document compatibility reached parity with Word 97,[32] and it included features from Word 97 for Windows, including spell and grammar checking with squiggles.[43] Users could choose the menus and keyboard shortcuts to be similar to either Word 97 for Windows or Word 5 for Mac OS.
Word 2001, released in 2000, added a few new features, including the Office Clipboard, which allowed users to copy and paste multiple items.[44] It was the last version to run on classic Mac OS and, on Mac OS X, it could only run within the Classic Environment. Word X, released in 2001, was the first version to run natively on, and required, Mac OS X,[43] and introduced non-contiguous text selection.[45]
Word 2004 was released in May 2004. It included a new Notebook Layout view for taking notes either by typing or by voice.[46] Other features, such as tracking changes, were made more similar with Office for Windows.[47]
Word 2008, released on January 15, 2008, included a Ribbon-like feature, called the Elements Gallery, that can be used to select page layouts and insert custom diagrams and images. It also included a new view focused on publishing layout, integrated bibliography management,[48] and native support for the new Office Open XML format. It was the first version to run natively on Intel-based Macs.[49]
Word 2011, released in October 2010, replaced the Elements Gallery in favor of a Ribbon user interface that is much more similar to Office for Windows,[50] and includes a full-screen mode that allows users to focus on reading and writing documents, and support for Office Web Apps.[51]
Word 2021 added real-time co-authoring, automatic cloud saving, dark mode, immersive reader enhancements, line focus, a visual refresh, the ability to save pictures in SVG format, and a new Sketched style outline.
File formats[edit]
| DOC | Legacy Word document |
|---|---|
| DOT | Legacy Word templates |
| WBK | Legacy Word document backup |
| DOCX | XML Word document |
| DOCM | XML Word macro-enabled document |
| DOTX | XML Word template |
| DOTM | XML Word macro-enabled template |
| DOCB | XML Word binary document |
Filename extensions[edit]
Microsoft Word’s native file formats are denoted either by a .doc or .docx filename extension.
Although the .doc extension has been used in many different versions of Word, it actually encompasses four distinct file formats:
- Word for DOS
- Word for Windows 1 and 2; Word 3 and 4 for Mac OS
- Word 6 and Word 95 for Windows; Word 6 for Mac OS
- Word 97 and later for Windows; Word 98 and later for Mac OS
(The classic Mac OS of the era did not use filename extensions.)[52]
The newer .docx extension signifies the Office Open XML international standard for Office documents and is used by default by Word 2007 and later for Windows as well as Word 2008 and later for macOS.[53]
Binary formats (Word 97–2007)[edit]
During the late 1990s and early 2000s, the default Word document format (.DOC) became a de facto standard of document file formats for Microsoft Office users.[citation needed] There are different versions of «Word Document Format» used by default in Word 97–2007.[54] Each binary word file is a Compound File,[55] a hierarchical file system within a file. According to Joel Spolsky, Word Binary File Format is extremely complex mainly because its developers had to accommodate an overwhelming number of features and prioritize performance over anything else.
As with all OLE Compound Files, Word Binary Format consists of «storages», which are analogous to computer folders and «streams», which are similar to computer files. Each storage may contain streams or other storage. Each Word Binary File must contain a stream called the «WordDocument» stream and this stream must start with a File Information Block (FIB).[57] FIB serves as the first point of reference for locating everything else, such as where the text in a Word document starts, ends, what version of Word created the document and other attributes.
Word 2007 and later continue to support the DOC file format, although it is no longer the default.
XML Document (Word 2003)[edit]
The .docx XML format introduced in Word 2003[58] was a simple, XML-based format called WordProcessingML or WordML.
The Microsoft Office XML formats are XML-based document formats (or XML schemas) introduced in versions of Microsoft Office prior to Office 2007. Microsoft Office XP introduced a new XML format for storing Excel spreadsheets and Office 2003 added an XML-based format for Word documents.
These formats were succeeded by Office Open XML (ECMA-376) in Microsoft Office 2007.
Cross-version compatibility[edit]
Opening a Word Document file in a version of Word other than the one with which it was created can cause an incorrect display of the document. The document formats of the various versions change in subtle and not-so-subtle ways (such as changing the font or the handling of more complex tasks like footnotes). Formatting created in newer versions does not always survive when viewed in older versions of the program, nearly always because that capability does not exist in the previous version.[59] Rich Text Format (RTF), an early effort to create a format for interchanging formatted text between applications, is an optional format for Word that retains most formatting and all content of the original document.
Third-party formats[edit]
Plugins permitting the Windows versions of Word to read and write formats it does not natively support, such as international standard OpenDocument format (ODF) (ISO/IEC 26300:2006), are available. Up until the release of Service Pack 2 (SP2) for Office 2007, Word did not natively support reading or writing ODF documents without a plugin, namely the SUN ODF Plugin or the OpenXML/ODF Translator. With SP2 installed, ODF format 1.1 documents can be read and saved like any other supported format in addition to those already available in Word 2007.[59][60][61][62][63] The implementation faces substantial criticism, and the ODF Alliance and others have claimed that the third-party plugins provide better support.[64] Microsoft later declared that the ODF support has some limitations.[65]
In October 2005, one year before the Microsoft Office 2007 suite was released, Microsoft declared that there was insufficient demand from Microsoft customers for the international standard OpenDocument format support and that therefore it would not be included in Microsoft Office 2007. This statement was repeated in the following months.[66][67][68][69] As an answer, on October 20, 2005, an online petition was created to demand ODF support from Microsoft.[70]
In May 2006, the ODF plugin for Microsoft Office was released by the OpenDocument Foundation.[71] Microsoft declared that it had no relationship with the developers of the plugin.[72]
In July 2006, Microsoft announced the creation of the Open XML Translator project – tools to build a technical bridge between the Microsoft Office Open XML Formats and the OpenDocument Format (ODF). This work was started in response to government requests for interoperability with ODF. The goal of the project was not to add ODF support to Microsoft Office, but only to create a plugin and an external toolset.[73][74] In February 2007, this project released a first version of the ODF plugin for Microsoft Word.[75]
In February 2007, Sun released an initial version of its ODF plugin for Microsoft Office.[76] Version 1.0 was released in July 2007.[77]
Microsoft Word 2007 (Service Pack 1) supports (for output only) PDF and XPS formats, but only after manual installation of the Microsoft ‘Save as PDF or XPS’ add-on.[78][79] On later releases, this was offered by default.
Features and flaws[edit]
Among its features, Word includes a built-in spell checker, a thesaurus, a dictionary, and utilities for manipulating and editing text. The following are some aspects of its feature set.
Templates[edit]
Several later versions of Word include the ability for users to create their formatting templates, allowing them to define a file in which: the title, heading, paragraph, and other element designs differ from the standard Word templates.[80] Users can find how to do this under the Help section located near the top right corner (Word 2013 on Windows 8).
For example, Normal.dotm is the master template from which all Word documents are created. It determines the margin defaults as well as the layout of the text and font defaults. Although Normal.dotm is already set with certain defaults, the user can change it to new defaults. This will change other documents which were created using the template.[81] It was previously Normal.dot.[82]
Image formats[edit]
Word can import and display images in common bitmap formats such as JPG and GIF. It can also be used to create and display simple line art. Microsoft Word added support[83] for the common SVG vector image format in 2017 for Office 365 ProPlus subscribers and this functionality was also included in the Office 2019 release.
WordArt[edit]
An example image created with WordArt
WordArt enables drawing text in a Microsoft Word document such as a title, watermark, or other text, with graphical effects such as skewing, shadowing, rotating, stretching in a variety of shapes and colors, and even including three-dimensional effects. Users can apply formatting effects such as shadow, bevel, glow, and reflection to their document text as easily as applying bold or underline. Users can also spell-check text that uses visual effects and add text effects to paragraph styles.
Macros[edit]
A Macro is a rule of pattern that specifies how a certain input sequence (often a sequence of characters) should be mapped to an output sequence according to a defined process. Frequently used or repetitive sequences of keystrokes and mouse movements can be automated. Like other Microsoft Office documents, Word files can include advanced macros and even embedded programs. The language was originally WordBasic, but changed to Visual Basic for Applications as of Word 97.
This extensive functionality can also be used to run and propagate viruses in documents. The tendency for people to exchange Word documents via email, USB flash drives, and floppy disks made this an especially attractive vector in 1999. A prominent example was the Melissa virus, but countless others have existed.
These macro viruses were the only known cross-platform threats between Windows and Macintosh computers and they were the only infection vectors to affect any macOS system up until the advent of video codec trojans in 2007.[citation needed] Microsoft released patches for Word X and Word 2004 that effectively eliminated the macro problem on the Mac by 2006.
Word’s macro security setting, which regulates when macros may execute, can be adjusted by the user, but in the most recent versions of Word, it is set to HIGH by default, generally reducing the risk from macro-based viruses, which have become uncommon.
Layout issues[edit]
Before Word 2010 (Word 14) for Windows, the program was unable to correctly handle ligatures defined in OpenType fonts.[84] Those ligature glyphs with Unicode codepoints may be inserted manually, but are not recognized by Word for what they are, breaking spell checking, while custom ligatures present in the font are not accessible at all. Since Word 2010, the program now has advanced typesetting features which can be enabled,[85] OpenType ligatures,[86] kerning and hyphenation (previous versions already had the latter two features). Other layout deficiencies of Word include the inability to set crop marks or thin spaces. Various third-party workaround utilities have been developed.[87]
In Word 2004 for Mac OS X, support of complex scripts was inferior even to Word 97[88] and Word 2004 did not support Apple Advanced Typography features like ligatures or glyph variants.[89]
Issues with technical documents[edit]
Microsoft Word is only awkwardly suitable for some kinds of technical writing, specifically, that which requires mathematical equations,[90] figure placement, table placement and cross-references to any of these items.[citation needed] The usual workaround for equations is to use a third-party equation typesetter.[citation needed] Figures and tables must be placed manually; there is an anchor mechanism but it is not designed for fully automatic figure placement and editing text after placing figures and tables often requires re-placing those items by moving the anchor point and even then the placement options are limited.[citation needed] This problem is deeply baked into Word’s structure since 1985 as it does not know where page breaks will occur until the document is printed.[citation needed]
Bullets and numbering[edit]
Microsoft Word supports bullet lists and numbered lists. It also features a numbering system that helps add correct numbers to pages, chapters, headers, footnotes, and entries of tables of content; these numbers automatically change to correct ones as new items are added or existing items are deleted. Bullets and numbering can be applied directly to paragraphs and converted to lists.[91] Word 97 through 2003, however, had problems adding correct numbers to numbered lists. In particular, a second irrelevant numbered list might have not started with number one but instead resumed numbering after the last numbered list. Although Word 97 supported a hidden marker that said the list numbering must restart afterward, the command to insert this marker (Restart Numbering command) was only added in Word 2003. However, if one were to cut the first item of the listed and paste it as another item (e.g. fifth), then the restart marker would have moved with it and the list would have restarted in the middle instead of at the top.[92]
Users can also create tables in Word. Depending on the version, Word can perform simple calculations – along with support for formulas and equations as well.
Word continues to default to non-Unicode characters and non-hierarchical bulleting, despite user preference for Powerpoint-style symbol hierarchies (e.g., filled circle/emdash/filled square/endash/emptied circle) and universal compatibility.
AutoSummarize[edit]
Available in certain versions of Word (e.g., Word 2007), AutoSummarize highlights passages or phrases that it considers valuable and can be a quick way of generating a crude abstract or an executive summary.[93] The amount of text to be retained can be specified by the user as a percentage of the current amount of text.
According to Ron Fein of the Word 97 team, AutoSummarize cuts wordy copy to the bone by counting words and ranking sentences. First, AutoSummarize identifies the most common words in the document (barring «a» and «the» and the like) and assigns a «score» to each word – the more frequently a word is used, the higher the score. Then, it «averages» each sentence by adding the scores of its words and dividing the sum by the number of words in the sentence – the higher the average, the higher the rank of the sentence. «It’s like the ratio of wheat to chaff,» explains Fein.[94]
AutoSummarize was removed from Microsoft Word for Mac OS X 2011, although it was present in Word for Mac 2008. AutoSummarize was removed from the Office 2010 release version (14) as well.[95]
Other platforms[edit]
Word for mobile[edit]
Word Mobile is a word processor that allows creating and editing documents. It supports basic formatting, such as bolding, changing font size, and changing colors (from red, yellow, or green). It can add comments, but can’t edit documents with tracked changes. It can’t open password-protected documents; change the typeface, text alignment, or style (normal, heading 1); create bulleted lists; insert pictures; or undo.[96][97][98] Word Mobile is neither able to display nor insert footnotes, endnotes, page headers, page footers, page breaks, certain indentation of lists, and certain fonts while working on a document, but retains them if the original document has them.[99] In addition to the features of the 2013 version, the 2007 version on Windows Mobile also has the ability to save documents in the Rich Text Format and open legacy PSW (Pocket Word).[99] Furthermore, it includes a spell checker, word count tool, and a «Find and Replace» command. In 2015, Word Mobile became available for Windows 10 and Windows 10 Mobile on Windows Store.[100]
Word for the web[edit]
Word for the web is a free lightweight version of Microsoft Word available as part of Office on the web, which also includes web versions of Microsoft Excel and Microsoft PowerPoint.
Word for the web lacks some Ribbon tabs, such as Design and Mailings. Mailings allows users to print envelopes and labels and manage mail merge printing of Word documents.[101][102] Word for the web is not able to edit certain objects, such as: equations, shapes, text boxes or drawings, but a placeholder may be present in the document. Certain advanced features like table sorting or columns will not be displayed but are preserved as they were in the document. Other views available in the Word desktop app (Outline, Draft, Web Layout, and Full-Screen Reading) are not available, nor are side-by-side viewing, split windows, and the ruler.[103]
Password protection[edit]
Three password types can be set in Microsoft Word,
- Password to open a document[104]
- Password to modify a document[104]
- Password restricting formatting and editing[105]
The second and third password types were developed by Microsoft for convenient shared use of documents rather than for their protection. There is no encryption of documents that are protected by such passwords and the Microsoft Office protection system saves a hash sum of a password in a document’s header where it can be easily accessed and removed by the specialized software. Password to open a document offers much tougher protection that had been steadily enhanced in the subsequent editions of Microsoft Office.
Word 95 and all the preceding editions had the weakest protection that utilized a conversion of a password to a 16-bit key.
Key length in Word 97 and 2000 was strengthened up to 40 bit. However, modern cracking software allows removing such a password very quickly – a persistent cracking process takes one week at most. Use of rainbow tables reduces password removal time to several seconds. Some password recovery software can not only remove a password but also find an actual password that was used by a user to encrypt the document using the brute-force attack approach. Statistically, the possibility of recovering the password depends on the password strength.
Word’s 2003/XP version default protection remained the same but an option that allowed advanced users to choose a Cryptographic Service Provider was added.[106] If a strong CSP is chosen, guaranteed document decryption becomes unavailable and, therefore, a password can’t be removed from the document. Nonetheless, a password can be fairly quickly picked with a brute-force attack, because its speed is still high regardless of the CSP selected. Moreover, since the CSPs are not active by default, their use is limited to advanced users only.
Word 2007 offers significantly more secure document protection which utilizes the modern Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) that converts a password to a 128-bit key using a SHA-1 hash function 50,000 times. It makes password removal impossible (as of today, no computer that can pick the key in a reasonable amount of time exists) and drastically slows the brute-force attack speed down to several hundreds of passwords per second.
Word’s 2010 protection algorithm was not changed apart from the increasing number of SHA-1 conversions up to 100,000 times and consequently, the brute-force attack speed decreased two times more.
Reception[edit]
|
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (December 2021) |
Initial releases of Word were met with criticism. Byte in 1984 criticized the documentation for Word 1.1 and 2.0 for DOS, calling it «a complete farce». It called the software «clever, put together well and performs some extraordinary feats», but concluded that «especially when operated with the mouse, has many more limitations than benefits … extremely frustrating to learn and operate efficiently».[107] PC Magazine‘s review was very mixed, stating: «I’ve run into weird word processors before, but this is the first time one’s nearly knocked me down for the count» but acknowledging that Word’s innovations were the first that caused the reviewer to consider abandoning WordStar. While the review cited an excellent WYSIWYG display, sophisticated print formatting, windows, and footnoting as merits, it criticized many small flaws, very slow performance, and «documentation produced by Madame Sadie’s Pain Palace». It concluded that Word was «two releases away from potential greatness».[108]
Compute!’s Apple Applications in 1987 stated that «despite a certain awkwardness», Word 3.01 «will likely become the major Macintosh word processor» with «far too many features to list here». While criticizing the lack of true WYSIWYG, the magazine concluded that «Word is marvelous. It’s like a Mozart or Edison, whose occasional gaucherie we excuse because of his great gifts».[109]
Compute! in 1989 stated that Word 5.0’s integration of text and graphics made it «a solid engine for basic desktop publishing». The magazine approved of improvements to text mode, described the $75 price for upgrading from an earlier version as «the deal of the decade» and concluded that «as a high-octane word processor, Word is worth a look».[110]
During the first quarter of 1996, Microsoft Word accounted for 80% of the worldwide word processing market.[111]
Release history[edit]
| Legend: | Old version, not maintained | Older version, still maintained | Current stable version |
|---|
Microsoft Word 2010 running on Windows 7
| Year released | Name | Version | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1989 | Word for Windows 1.0 | 1.0 | Code-named Opus[112] |
| 1990 | Word for Windows 1.1 | 1.1 | For Windows 3.0.[113] Code-named Bill the Cat[citation needed] |
| 1990 | Word for Windows 1.1a | 1.1a | On March 25, 2014, Microsoft made the source code to Word for Windows 1.1a available to the public via the Computer History Museum.[114][115] |
| 1991 | Word for Windows 2.0 | 2.0 | Included in Office 3.0. |
| 1993 | Word for Windows 6.0 | 6.0 | Version numbers 3, 4, and 5 were skipped, to bring Windows version numbering in line with that of DOS, Mac OS, and WordPerfect (the main competing word processor at the time). Also, a 32-bit version for Windows NT only. Included in Office 4.0, 4.2, and 4.3. |
| 1995 | Word for Windows 95 | 7.0 | Included in Office 95 |
| 1997 | Word 97 | 8.0 | Included in Office 97 |
| 1998 | Word 98 | 8.5 | Included in Office 97 |
| 1999 | Word 2000 | 9.0 | Included in Office 2000 |
| 2001 | Word 2002 | 10.0 | Included in Office XP |
| 2003 | Microsoft Word 2003 | 11.0 | Included in Office 2003 |
| 2006 | Microsoft Word 2007 | 12.0 | Included in Office 2007; released to businesses on November 30, 2006, released worldwide to consumers on January 30, 2007. Extended support until October 10, 2017. |
| 2010 | Word 2010 | 14.0 | Included in Office 2010; skipped 13.0 due to triskaidekaphobia.[116] |
| 2013 | Word 2013 | 15.0 | Included in Office 2013 |
| 2016 | Word 2016 | 16.0 | Included in Office 2016 |
| 2019 | Word 2019 | 16.0 | Included in Office 2019 |
| 2021 | Word 2021 | 16.0 | Included in Office 2021 |
| Year released | Name | Version | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1985 | Word 1 | 1.0 | |
| 1987 | Word 3 | 3.0 | |
| 1989 | Word 4 | 4.0 | Part of Office 1.0 and 1.5 |
| 1991 | Word 5 | 5.0 |
|
| 1992 | Word 5.1 | 5.1 |
|
| 1993 | Word 6 | 6.0 |
|
| 1998 | Word 98 | 8.5 |
|
| 2000 | Word 2001 | 9.0 |
|
| 2001 | Word v. X | 10.0 |
|
| 2004 | Word 2004 | 11.0 | Part of Office 2004 |
| 2008 | Word 2008 | 12.0 | Part of Office 2008 |
| 2010 | Word 2011 | 14.0 | Part of Office 2011; skipped 13.0 due to triskaidekaphobia.[116] |
| 2015 | Word 2016 | 16.0 | Part of Office 2016; skipped 15.0 |
| 2019 | Word 2019 | 16.0 | Part of Office 2019 |
| 2021 | Word 2021 | 16.0 | Included in Office 2021 |
| Year released | Name | Version | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1983 | Word 1 | 1.0 | Initial version of Word |
| 1985 | Word 2 | 2.0 | |
| 1986 | Word 3 | 3.0 | |
| 1987 | Word 4 | 4.0 | |
| 1989 | Word 5 | 5.0 | |
| 1991 | Word 5.1 | 5.1 | |
| 1991 | Word 5.5 | 5.5 | First DOS version to use a Windows-like user interface |
| 1993 | Word 6 | 6.0 | Last DOS version. |
| Platform | Year released | Name | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| Atari ST | 1988 | Microsoft Write | Based on Microsoft Word 1.05 for Mac OS |
| OS/2 | 1989 | Microsoft Word 5.0 | Word 5.0 ran both under DOS and OS/2 dual-mode as a native OS/2 application |
| OS/2 | 1991 | Microsoft Word 5.5 | Word 5.5 ran both under DOS and OS/2 dual-mode as a native OS/2 application |
| OS/2 | 1990 | Microsoft Word for OS/2 Presentation Manager version 1.1 | |
| OS/2 | 1991 | Microsoft Word for OS/2 Presentation Manager version 1.2[citation needed] | |
| SCO Unix | 1990 | Microsoft Word for Unix version 5.0[117] | |
| SCO Unix | 1991 | Microsoft Word for Unix version 5.1[118] |
References[edit]
- ^ «Update history for Microsoft Office 2019». Microsoft Docs. Retrieved April 13, 2021.
- ^ a b «C++ in MS Office». cppcon. July 17, 2014. Archived from the original on November 7, 2019. Retrieved June 25, 2019.
- ^ «System requirements for Office». Office.com. Microsoft. Retrieved March 30, 2019.
- ^ «Update history for Office for Mac». Microsoft Docs.
- ^ Lardinois, Frederic (January 29, 2015). «Microsoft’s Office For Android Tablets Comes Out Of Preview». TechCrunch. Retrieved January 28, 2023.
- ^ «Microsoft Word: Write, Edit & Share Docs on the Go APKs». APKMirror.
- ^ Cunningham, Andrew (March 27, 2014). «Microsoft brings Office to iPad, makes iPhone version free to all». Ars Technica. Retrieved January 27, 2023.
- ^ «Microsoft Word». App Store.
- ^ «Version 1.0 of today’s most popular applications, a visual tour – Pingdom Royal». Pingdom. June 17, 2009. Archived from the original on August 13, 2018. Retrieved April 12, 2016.
- ^ a b c d A. Allen, Roy (October 2001). «Chapter 12: Microsoft in the 1980s» (PDF). A History of the Personal Computer: The People and the Technology (1st ed.). Allan Publishing. pp. 12/25–12/26. ISBN 978-0-9689108-0-1. Retrieved November 7, 2010.
- ^ «Microsoft Office online, Getting to know you…again: The Ribbon». Archived from the original on May 11, 2011.
- ^ «The history of branding, Microsoft history». Archived from the original on May 28, 2009.
- ^ a b c d e Edwards, Benj (October 22, 2008). «Microsoft Word Turns 25». PC World. Archived from the original on July 4, 2012. Retrieved November 7, 2010.
- ^ Tsang, Cheryl (1999). Microsoft First Generation. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-0-471-33206-0.
- ^ Schaut, Rick (May 19, 2004). «Anatomy of a Software Bug». MSDN Blogs. Archived from the original on February 1, 2010. Retrieved December 2, 2006.
- ^ a b Markoff, John (May 30, 1983). «Mouse and new WP program join Microsoft product lineup». InfoWorld. p. 10. Retrieved November 7, 2010.
- ^ Pollack, Andrew (August 25, 1983). «Computerizing Magazines». The New York Times. Retrieved April 24, 2013.
- ^ Lemmons, Phil (December 1983). «Microsoft Windows». BYTE. p. 48. Retrieved October 20, 2013.
- ^ Advertisement (December 1983). «Undo. Windows. Mouse. Finally». BYTE. pp. 88–89. Retrieved October 20, 2013.
- ^ Peterson, W.E. Pete (1994). Almost Perfect: How a Bunch of Regular Guys Built Wordperfect Corporation. Prima Publishing. ISBN 0-7881-9991-9.
- ^ a b c d e f Knight, Dan (May 22, 2008). «Microsoft Word for Mac History». Low End Mac. Retrieved November 7, 2010.
- ^ «The Piece Table».
- ^ Brand, Stewart (1989). Whole Earth Software Catalog. ISBN 9780385233019.
For a year, I waited for a heavier-duty word processor than MACWRITE. I finally got it— WORD.
- ^ a b c Schaut, Rick (February 26, 2004). «Mac Word 6.0». Buggin’ My Life Away. MSDN Blogs. Archived from the original on May 14, 2004. Retrieved June 21, 2010.
- ^ «Atari announces agreement with Microsoft». Atarimagazines.com. April 25, 2008. Retrieved June 21, 2010.
- ^ «Feature Review: Microsoft Write». Atarimagazines.com. April 25, 2008. Retrieved June 21, 2010.
- ^ «Today’s Atari Corp.: A close up look inside». Atarimagazines.com. April 25, 2008. Retrieved June 21, 2010.
- ^ Miller, Michael J. (November 12, 1990). «First Look: Microsoft Updates Look of And Adds Pull-Down Menus to Character-Based Word 5.5». InfoWorld. p. 151. Retrieved November 7, 2010.
- ^ Needleman, Raphael (November 19, 1990). «Microsoft Word 5.5: Should You Fight or Switch?». InfoWorld. p. 106. Retrieved November 7, 2010.
- ^ «Microsoft Word 5.5 for MS-DOS (EXE format)». Microsoft Download Center. Retrieved August 19, 2011.
- ^ «War of the Words». InfoWorld. February 7, 1994. pp. 66–79. Retrieved November 7, 2010.
- ^ a b Lockman, James T.W. (May 15, 1998). «UGeek Software Review: Microsoft Office 98 Gold for Macintosh». Archived from the original on December 3, 2010. Retrieved November 7, 2010.
- ^ Rose, Daniel. «Microsoft Office for Windows NT». DanielSays.com – Daniel’s Legacy Computer Collections. Archived from the original on January 27, 2015. Retrieved May 15, 2015.
- ^ Ericson, Richard (October 11, 2006). «Final Review: The Lowdown on Office 2007». Computerworld. Retrieved November 8, 2010.
- ^ Lowe, Scott (December 11, 2006). «An introduction to the Microsoft Office 2007 ribbon interface». TechRepublic. Retrieved December 14, 2021.
- ^ Shultz, Greg (February 25, 2009). «Be ready for new and improved applets in Windows 7». TechRepublic. Archived from the original on December 14, 2021. Retrieved December 14, 2021.
- ^ a b Lowe, Scott (January 26, 2007). «Explore what is new and different in Microsoft Word 2007». TechRepublic. Retrieved December 14, 2021.
- ^ Mendelson, Edward (May 11, 2010). «Microsoft Office 2010». PC Magazine. Retrieved November 8, 2010.
- ^ Mendelson, Edward (May 11, 2010). «Microsoft Office 2010: Office 2010’s Backstage View». PC Magazine. Archived from the original on December 2, 2010. Retrieved November 8, 2010.
- ^ Mendelson, Edward (May 11, 2010). «Microsoft Office 2010: Lots of Graphics Options». PC Magazine. Archived from the original on April 24, 2010. Retrieved December 14, 2021.
- ^ «Introduction to Word Web App». Microsoft. Retrieved November 8, 2010.
- ^ «Microsoft Word 1.x (Mac)». WinWorld. Retrieved December 22, 2021.
- ^ a b McLean, Prince (November 12, 2007). «Road to Mac Office 2008: an introduction (Page 3)». AppleInsider. Archived from the original on July 7, 2011. Retrieved November 7, 2010.
- ^ Tetrault, Gregory (January 2001). «Review: Microsoft Office 2001». ATPM: About This Particular Macintosh. Retrieved November 7, 2010.
- ^ Negrino, Tom (February 1, 2002). «Review: Microsoft Office v. X». MacWorld. Archived from the original on August 18, 2010. Retrieved November 7, 2010.
- ^ Lunsford, Kelly; Michaels, Philip; Snell, Jason (March 3, 2004). «Office 2004: First Look». MacWorld. Archived from the original on June 25, 2010. Retrieved November 7, 2010.
- ^ Friedberg, Steve (May 25, 2004). «Review: Microsoft Office». MacNN. Archived from the original on April 5, 2010. Retrieved November 7, 2010.
- ^ McLean, Prince (November 14, 2007). «Road to Mac Office 2008: Word ’08 vs Pages 3.0». AppleInsider. Retrieved November 7, 2010.
- ^ McLean, Prince (November 12, 2007). «Road to Mac Office 2008: an introduction (Page 4)». AppleInsider. Archived from the original on July 7, 2011. Retrieved November 7, 2010.
- ^ McLean, Prince (March 29, 2010). «New Office 11 for Mac sports dense ribbons of buttons». AppleInsider. Retrieved November 7, 2010.
- ^ Dilger, Daniel Eran (October 25, 2010). «Review: Microsoft’s Office 2011 for Mac (Page 2)». Apple Insider. Archived from the original on October 28, 2010. Retrieved November 7, 2010.
- ^ Oakley, Howard (May 2, 2015). «.why .the .extensions? Quirks in the naming of files and folders». The Eclectic Light Company. Archived from the original on February 26, 2020. Retrieved February 26, 2020.
Macs used to be the only computers that did not need filename extensions…on classic Mac systems, you can name applications, documents, and most other files almost anything that you like, as the name is not linked in any way to the type of thing that file is.
- ^ «DOCX Transitional (Office Open XML), ISO 29500:2008-2016, ECMA-376, Editions 1-5». loc.gov. January 20, 2017. Retrieved July 9, 2019.
- ^ «5 Appendix A: Product Behavior» (PDF). [MS-DOC]: Word (.doc) Binary File Format (PDF). Redmond, WA: Microsoft. Archived from the original on January 10, 2015. Retrieved January 10, 2015.
- ^ «2.1 File Structure» (PDF). [MS-DOC]: Word (.doc) Binary File Format (PDF). Redmond, WA: Microsoft. Archived from the original on January 10, 2015. Retrieved January 10, 2015.
- ^ «2.1.1 WordDocument Stream» (PDF). [MS-DOC]: Word (.doc) Binary File Format (PDF). Redmond, WA: Microsoft. Archived from the original on January 10, 2015. Retrieved January 10, 2015.
- ^ «What You Can Do with Word XML [Word 2003 XML Reference]». MSDN. 2004.
- ^ a b Casson, Tony; Ryan, Patrick S. (May 1, 2006). «Open Standards, Open Source Adoption in the Public Sector, and Their Relationship to Microsoft’s Market Dominance». In Bolin, Sherrie (ed.). Standards Edge: Unifier or Divider?. Sheridan Books. p. 87. SSRN 1656616.
- ^ «Microsoft Expands List of Formats Supported in Microsoft Office, May 21, 2008». News Center. Microsoft. May 21, 2008. Retrieved April 24, 2013.
- ^ Fulton, Scott M. III (May 21, 2008). «Next Office 2007 service pack will include ODF, PDF support options». Betanews.
- ^ Andy Updegrove (May 21, 2008). «Microsoft Office 2007 to Support ODF – and not OOXML, May 21, 2008». Consortiuminfo.org. Retrieved June 21, 2010.
- ^ «Microsoft: Why we chose ODF support over OOXML, 23 May 2008». Software.silicon.com. Archived from the original on July 21, 2009. Retrieved June 21, 2010.
- ^ «Fact-sheet Microsoft ODF support» (PDF). odfalliance. Archived from the original (PDF) on June 11, 2009. Retrieved May 24, 2009.
Microsoft Excel 2007 will process ODF spreadsheet documents when loaded via the Sun Plug-In 3.0 for Microsoft Office or the SourceForge «OpenXML/ODF Translator Add-in for Office,» but will fail when using the «built-in» support provided by Office 2007 SP2.
- ^ Microsoft. «What happens when I save a Word 2007 document in the OpenDocument Text format?». Archived from the original on March 18, 2010. Retrieved April 5, 2010.
- ^ Goodwins, Rupert (October 3, 2005). «Office 12 to support PDF creation, 3 October 2005». News.zdnet.co.uk. Archived from the original on July 23, 2009. Retrieved June 21, 2010.
- ^ Marson, Ingrid (October 6, 2005). «Microsoft ‘must support OpenDocument’, 6 October 2005». News.zdnet.co.uk. Archived from the original on July 25, 2009. Retrieved June 21, 2010.
- ^ March 23, 2006, Gates: Office 2007 will enable a new class of application Mass. holding tight to OpenDocument – ZDNet Archived July 21, 2009, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ «May 08, 2006 – Microsoft Office to get a dose of OpenDocument». Zdnet.com.au. Archived from the original on July 22, 2009. Retrieved June 21, 2010.
- ^ OpenDocument Fellowship (October 20, 2005). «OpenDocument Support: Tell Microsoft You Want It!, 20 October 2005». Opendocumentfellowship.com. Archived from the original on March 23, 2008. Retrieved June 21, 2010.
- ^ «Coming soon: ODF for MS Office, May 04, 2006». Linux-watch.com. May 4, 2006. Retrieved June 21, 2010.
- ^ LaMonica, Martin (May 5, 2006). «Microsoft Office to get a dose of OpenDocument». CNET News. Retrieved June 21, 2010.
- ^ «Microsoft Expands Document Interoperability, July 5, 2006». Microsoft.com. July 5, 2006. Archived from the original on February 4, 2007. Retrieved June 21, 2010.
- ^ Jones, Brian; Rajabi, Zeyad (July 6, 2006). «Open XML Translator project announced (ODF support for Office)». Brian Jones: Office Solutions. Microsoft. Archived from the original on January 18, 2010. Retrieved April 24, 2013.
- ^ LaMonica, Martin (February 1, 2007). «Microsoft to release ODF document converter». CNet News. Retrieved April 24, 2013.
- ^ Lombardi, Candace (February 7, 2007). «Sun to release ODF translator for Microsoft Office». CNET. Retrieved June 21, 2010.
- ^ Paul, Ryan (July 7, 2007). «Sun releases ODF Plugin 1.0 for Microsoft Office, July 07, 2007». Arstechnica.com. Retrieved June 21, 2010.
- ^ «Download details: 2007 Microsoft Office Add-in: Microsoft Save as PDF or XPS». Microsoft.com. November 8, 2006. Retrieved June 21, 2010.
- ^ Microsoft to remove PDF support from Office 2007 in wake of Adobe dispute, Friday, June 2, 2006 Microsoft to remove PDF support from Office 2007 in wake of Adobe dispute | TG Daily Archived February 1, 2009, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Klein, Matt. «Word Formatting: Mastering Styles and Document Themes». How-To Geek. Retrieved July 9, 2019.
- ^ «Change the Normal template (Normal.dotm )». support.microsoft.com. Retrieved May 20, 2021.
- ^ in-depth explanation of Normal.dot Archived June 20, 2005, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ «Edit SVG images in Microsoft Office 365». Office Support. Microsoft. Retrieved February 4, 2019.
- ^ What’s new in Word 2010. Retrieved July 1, 2010.
- ^ Improving the look of papers written in Microsoft Word. Retrieved May 30, 2010.
- ^ How to Enable OpenType Ligatures in Word 2010, Oreszek Blog, May 17, 2009.
- ^ Such as «How to delete a blank page in Word». Sbarnhill.mvps.org. Archived from the original on May 5, 2010. Retrieved June 21, 2010.
- ^ Alan Wood. «Unicode and Multilingual Editors and Word Processors for Mac OS X».
- ^ Neuburg, Matt (May 19, 2004). «TidBITS : Word Up! Word 2004, That Is». Db.tidbits.com. Archived from the original on July 8, 2012. Retrieved June 21, 2010.
- ^ «Automatically numbering equations and other equation-related questions in Word for Mac 2011». Microsoft Community. February 6, 2013.
- ^ McGhie, John (March 26, 2011). «Word’s numbering explained». word.mvps.org.
- ^ Aldis, Margaret (March 26, 2011). «Methods for restarting list numbering». Word.mvps.org.
- ^ «How To Access Auto Summarize in Microsoft Word 2007». Sue’s Word Tips. December 14, 2011. Retrieved July 9, 2019.
- ^ Gore, Karenna (February 9, 1997). «Cognito Auto Sum». Slate. Retrieved June 21, 2010.
- ^ Changes in Word 2010 (for IT pros). Technet.microsoft.com (May 16, 2012). Retrieved July 17, 2013.
- ^ Ralph, Nate. «Office for Windows Phone 8: Your handy starter guide». TechHive. Archived from the original on October 15, 2014. Retrieved August 30, 2014.
- ^ Wollman, Dana. «Microsoft Office Mobile for iPhone hands-on». Engadget. Retrieved August 30, 2014.
- ^ Pogue, David (June 19, 2013). «Microsoft Adds Office for iPhone. Yawn». The New York Times. Retrieved August 30, 2014.
- ^ a b Unsupported Features in Word Mobile. Microsoft. Retrieved September 21, 2007.
- ^ Koenigsbauer, Kirk; Microsoft 365, Corporate Vice President for (July 29, 2015). «Office Mobile apps for Windows 10 are here!». Microsoft 365 Blog. Retrieved July 11, 2020.
- ^ Bradley, Tony (February 2, 2015). «Office Online vs. Office 365: What’s free, what’s not, and what you really need». PC World. Archived from the original on July 24, 2017. Retrieved July 16, 2020.
- ^ Ansaldo, Michael (September 28, 2017). «Microsoft Office Online review: Work with your favorite Office formats for free». PC World. Retrieved October 31, 2019.
- ^ «Differences between using a document in the browser and in Word». Office Support. Microsoft. Archived from the original on November 7, 2017. Retrieved November 1, 2017.
- ^ a b «Password protect documents, workbooks, and presentations». Microsoft Office website. Microsoft. Retrieved April 24, 2013.
- ^ «How to Restrict Editing in Word 2010/2007». Trickyways. June 22, 2010. Retrieved April 24, 2010.
- ^ «How safe is Word encryption. Is it secure?». Oraxcel.com. Archived from the original on April 17, 2013. Retrieved April 24, 2013.
- ^ Cameron, Janet (September 1984). «Word Processing Revisited». BYTE (review). p. 171. Retrieved October 23, 2013.
- ^ Manes, Stephen (February 21, 1984). «The Unfinished Word». PC Magazine. p. 192. Retrieved October 19, 2021.
- ^ McNeill, Dan (December 1987). «Macintosh: The Word Explosion». Compute!’s Apple Applications. pp. 54–60. Retrieved September 14, 2016.
- ^ Nimersheim, Jack (December 1989). «Compute! Specific: MS-DOS». Compute!. pp. 11–12.
- ^ «Data Stream». Next Generation. No. 21. Imagine Media. September 1996. p. 21.
- ^ Opus Development Postmortem
- ^ «Microsoft Word 1.x (Windows) – Stats, Downloads and Screenshots :: WinWorld». WinWorld. Retrieved July 3, 2016.
- ^ Shustek, Len (March 24, 2014). «Microsoft Word for Windows Version 1.1a Source Code». Retrieved March 29, 2014.
- ^ Levin, Roy (March 25, 2014). «Microsoft makes source code for MS-DOS and Word for Windows available to public». Official Microsoft Blog. Archived from the original on March 28, 2014. Retrieved March 29, 2014.
- ^ a b «Office 14». Office Watch. June 1, 2007.
For the sake of superstition the next version of Office won’t be called ’13’.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ Marshall, Martin (January 8, 1990). «SCO Begins Shipping Microsoft Word 5.0 for Unix and Xenix». InfoWorld. p. 6. Retrieved May 20, 2021.
- ^ «Microsoft Word: SCO announces Word for Unix Systems Version 5.1». EDGE: Work-Group Computing Report. March 11, 1991. p. 33. Retrieved May 20, 2021 – via Gale General OneFile.
Further reading[edit]
- Tsang, Cheryl. Microsoft: First Generation. New York: John Wiley & Sons, Inc. ISBN 978-0-471-33206-0.
- Liebowitz, Stan J. & Margolis, Stephen E. Winners, Losers & Microsoft: Competition and Antitrust in High Technology Oakland: Independent Institute. ISBN 978-0-945999-80-5.
External links[edit]
- Microsoft Word – official site
- Find and replace text by using regular expressions (Advanced) — archived official support website
 ворд |
|
| Тип | Текстовый процессор |
|---|---|
| Разработчик | Microsoft |
| Операционная система | Microsoft Windows |
| Последняя версия | 15.0.4745.1001 (11 августа 2015 год) |
| Читаемые форматы файлов | DOC |
| Создаваемые форматы файлов | DOC |
| Лицензия | Проприетарное программное обеспечение |
| Сайт | office.microsoft.com/ru-ru/word |
Microsoft Word (часто — MS Word, WinWord или просто Word) — текстовый процессор, предназначенный для создания, просмотра и редактирования текстовых документов, с локальным применением простейших формтаблично-матричных алгоритмов. Выпускается корпорацией Microsoft в составе пакета Microsoft Office. Первая версия была написана Ричардом Броди (Richard Brodie) для IBM PC, использующих DOS, в 1983 году. Позднее выпускались версии для Apple Macintosh (1984), SCO UNIX и Microsoft Windows (1989). Текущей версией является Microsoft Office Word 2016 для Windows и Microsoft Office Word 2011 для Mac.
 |
|
| Тип | Текстовый процессор |
|---|---|
| Разработчик | Microsoft |
| Операционная система | Mac OS X |
| Последняя версия | OS X: 2011,
Windows: 2013 |
| Читаемые форматы файлов | DOC |
| Создаваемые форматы файлов | DOC |
| Лицензия | Проприетарное программное обеспечение |
| Сайт | microsoft.com/rus/mac/word |
Начало[]
Microsoft Word многим обязан Bravo — текстовому процессору с оригинальным графическим интерфейсом, разработанному в исследовательском центре «Xerox PARC». Создатель Bravo Чарльз Симони (Charles Simonyi) покинул PARC в 1981 году. Тем же летом Симони переманил Броди, с которым вместе работал над Bravo.
Первый выпуск Word для MS-DOS состоялся в конце 1983 года. Он был плохо принят рынком, продажи снижало наличие конкурирующего продукта — WordPerfect.
Однако версия для «макинтоша», выпущенная в 1985 году, получила широкое распространение. Через два года «Word 3.01 для Macintosh» усилил позиции (версия 3.0 изобиловала ошибками и быстро была заменена). Как и прочее программное обеспечение для «макинтоша», Word был полностью WYSIWYG-редактором (принцип «What You See Is What You Get» — «получаю то, что вижу»).
Хотя MS-DOS и являлась текстовой операционной системой, лишённой графической оболочки, Word для DOS был первым текстовым процессором для IBM PC, который был способен отображать разметку текста, например, полужирный или курсивный текст в процессе редактирования. Однако он всё же не являлся в полном смысле WYSIWYG-редактором. Другие же текстовые процессоры, такие как WordStar и WordPerfect, использовали простой текстовый экран с кодами разметки, иногда текст был цветным.
Однако, поскольку в большинстве программного обеспечения под DOS применялись собственные труднозапоминаемые комбинации «горячих клавиш» для каждой команды (например, в Word’е для DOS сохранение файла выполнялось по комбинации ESC-T-S) и большинство секретарей умели пользоваться только WordPerfect, компании-пользователи WordPerfect весьма неохотно переходили на конкурирующие с ним продукты, имеющие сравнительно небольшие преимущества.
1990—1995 годы[]
Первая версия Word для Windows, выпущенная в 1989 году, продавалась по цене $500. Она демонстрировала выбранный компанией «Майкрософт» путь развития: как и сама Windows, она многое взяла от Macintosh и использовала стандартные клавиатурные сокращения (например, Ctrl+S для сохранения файла). После выпуска в следующем году Windows 3.0 продажи поползли вверх (Word 1.0 гораздо лучше работал с Windows 3.0, чем с более старыми версиями Windows x386 и Windows x286), главный конкурент — WordPerfect — не смог выпустить рабочую версию под Windows, что оказалось для него смертельной ошибкой. Версия 2.0 утвердила WinWord на позиции лидера рынка.
Последовавшие версии добавляли возможности, выходящие за рамки простого текстового процессора. Инструменты рисования позволяли выполнять примитивные операции вёрстки, такие, как добавление графики в документ, хотя, естественно, специализированные программы для вёрстки лучше справляются с этими задачами. Внедрение объектов, сравнение версий документа, мультиязычная поддержка и многие другие возможности были добавлены за последовавшие несколько лет.
Настоящее время[]
Microsoft Word является наиболее популярным из используемых в данный момент текстовых процессоров, что сделало его бинарный формат документастандартом де-факто, и многие конкурирующие программы имеют поддержку совместимости с данным форматом. Расширение «.doc» на платформе IBM PC стало синонимом двоичного формата Word 97—2000. Фильтры экспорта и импорта в данный формат присутствуют в большинстве текстовых процессоров. Формат документа разных версий Word меняется, различия бывают довольно тонкими. Форматирование, нормально выглядящее в последней версии, может не отображаться в старых версиях программы, однако есть ограниченная возможность сохранения документа с потерей части форматирования для открытия в старых версиях продукта. Последняя версия MS Word 2007 «использует по умолчанию» формат, основанный на XML, — Microsoft Office Open XML. Спецификации форматов файлов Word 97-2007 были опубликованы Microsoft в 2008 году[1][2]. Ранее большая часть информации, нужной для работы с данным форматом, добывалась посредством обратного инжиниринга, поскольку основная её часть отсутствовала в открытом доступе или была доступна лишь ограниченному числу партнёров и контролирующих организаций.
- Как и прочие приложения из Microsoft Office, Word может расширять свои возможности посредством использования встроенного макроязыка (сначала использовался WordBasic, с версии Word 97 применяется VBA — Visual Basic для приложений). Однако это предоставляет широкие возможности для написания встраиваемых в документы вирусов (так называемые «макровирусы»). Наиболее ярким примером была эпидемия червя Melissa. В связи с этим многие считают разумной рекомендацию всегда выставлять наивыск3424324324
ший уровень настроек безопасности при использовании Word (Меню: «Tools>Macro>Security», «Сервис>Макрос>Безопасность…» в локализованных русских версиях). Также нелишним будет использовать антивирусное программное обеспечение. Первым вирусом, заражавшим документы Microsoft Word, был DMV, созданный в декабре 1994 года Дж. Мак-Намарой для демонстрации возможности создания макровирусов. Первым же вирусом, попавшим в «дикую природу» и вызвавшим первую в мире эпидемию макровирусов (это произошло в июле-августе 1995 года), был Concept.
12 августа 2009 года суд штата Техас запретил продажу программы Word на территории США, в связи с тем, что Microsoft незаконно использует метод чтения XML-файлов, патент на который принадлежит канадской компании i4i.
История версий[]
Версии для MS-DOS:
- 1983, ноябрь Word 1
- 1985 Word 2
- 1986 Word 3
- 1987 Word 4, также известный как Microsoft Word 4.0 для PC
- 1989 Word 5
- 1991 Word 5.5
Версии для Apple Macintosh:
- 1985, январь Word 1 для Macintosh
- 1987 Word 3
- 1989 Word 4
- 1991 Word 5le
- 1993 Word 6
- 1998 Word 98
- 2000 Word 2001, последняя из версий, совместимых с Mac OS 9
- 2001 Word v.X, первая версия исключительно для Mac OS X
- 2004 Word 2004
- 2008 Word 2008
- 2011 Word 2011
Версии для Apple iOS:
- 2014 Word for iPad
Версии для Microsoft Windows:
- 1989, ноябрь Word для Windows
- 1991 Word 2 для Windows
- 1993 Word 6 для Windows (номер «6» был введён для продолжения линейки номеров DOS-версий, единой нумерации с Mac-версиями и с WordPerfect, лидером рынка среди текстовых процессоров на тот момент)
- 1995 Word 95 (Word 7)
- 1997 Word 97 (Word
- 1999 Word 2000 (Word 9)
- 2001 Word 2002 (Word 10)
- 2003 Word 2003 (также известный как Word 11, однако официально именуемый Microsoft Office Word 2003)
- 2007 Word 2007 (революционная смена интерфейса, поддержка формата OOXML — *.docx)
- 2010 Word 2010
- 2012 Word 2013
- 2015 Word 2016
Версии для SCO UNIX:
- Microsoft Word для UNIX Systems, Release 5.1
Парольная защита документов MS Word[]
На документ Microsoft Word могут быть установлены 3 типа паролей:
- Пароль для открытия документа[3]
- Пароль для изменения документа[4]
- Пароль на внесение примечаний и исправлений (для версий 2003 и ниже). В новых версиях MS Word 20072010 этот тип пароля называется «Пароль для Ограничения форматирования и редактирования»[5]
Вне зависимости от версий MS Word, в которой был создан документ, «пароль разрешения записи» и «пароль на внесение примечаний и исправлений»можно удалить из документа мгновенно[6]. Эти типы паролей служат не столь для защиты документа, как для обеспечения коллективной работы над документом. А основную защиту документа от несанкционированного доступа обеспечивает «пароль для открытия документа».
В документах ранних версиях MS Word (до MS Office 2003 включительно) пароль для открытия файла может быть без проблем взломан.
В последних версия MS Office 2007 2010 компания Microsoft использует стойкий алгоритм шифрования AES с 128-битным ключом. Формирование ключа происходит путем 50000 100000 кратного применения SHA-1 хэш функции, что делает перебор паролей крайне медленным, и при использовании стойкого пароля шансы его подобрать близки к нулю[7].
Критика[]
Чаще всего Microsoft Word подвергается критике за низкую безопасность, закрытый исходный код, отсутствие полноценной кроссплатформенности[8]. Ранее Word критиковали также за закрытый формат файлов (открытая документация на бинарные форматы появилась только в начале 2008 года). Это побудило отдельные организации перейти к использованию других текстовых процессоров, таких как OpenOffice Writer, входящего в офисный пакетOpenOffice.org. Инструментов Microsoft Word недостаточно для создания качественного полиграфического продукта[9].
Недокументированные возможности и курьёзы[]
Следующие функции вводятся в любом месте документа с начала строки. Замена их на определённый текст осуществляется при нажатии клавиши Enter.
Функция rand()[]
=rand(x,y)
В редакторе версии младше 2007 строка с командой будет заменена матрицей из панграмм:
Съешь ещё этих мягких французских булок, да выпей чаю.
Параметр x задаёт количество столбцов матрицы, y — количество строк. Параметры можно не указывать.
В редакторе Word 2007 строка с данной функцией будет заменена на отрывок из текста справки, параметр x задаёт количество абзацев, y — количество предложений в каждом абзаце. Функция =rand.old(x, y) работает как =rand(x, y) в более ранних версиях редактора.
Функция lorem()[]
=lorem()
В редакторах Word 2007 и 2010 строка с данной функцией будет заменена на отрывок из текста Lorem ipsum.
Курьёзные ошибки в модуле проверки русской орфографии версии 2003 года[]
Модуль проверки русской орфографии, поставляемый с русифицированными версиями Microsoft Word за исключением MS Word 2013, является упрощенной версией системы Орфо, производимой российской компанией ООО «Информатик».
- Набор фразы Правоспособность-способность иметь права и нести гражданские обязанности вызывает (иногда после нажатия Enter), если включена автоматическая проверка орфографии, незамедлительное закрытие приложения без сохранения изменений. Данную ошибку эксплуатирует троян «Trojan.WordCrash» (по классификации антивирусной лаборатории Dr.Web), который добавляет данную фразу во все документы с расширением *.doc и *.rtf.
- При наборе в MS Word 97—2010 фразы «Хочу избежать службу в армии» модуль проверки грамматики в качестве одного из вариантов исправлений предлагает текст «Ошибка в управлении. Глагол „избежать“ требует дополнения в родительном падеже. Например: „Никому не удалось избежать службы в армии“.» Проверка грамматики реагирует на словосочетание «избежать что-либо» (при правильном «избежать чего-либо»).
- Word 2003 не знает цвет «голубой». Более ранние версии Word этот цвет знали.
Почти все недоработки были исправлены в Microsoft Word 2003 SP3 и последующих версиях продукта.
Как работать в Word для чайников
Автор:
Обновлено: 29.04.2018
Microsoft Word — это текстовой редактор, который может быть частью пакета Microsoft Office или программой, установленной на вашем компьютере отдельно. Программа может использоваться для записи писем и различных типов документов, которые могут включать в себя графику и изображения. В этом руководстве объясняется, как открыть Microsoft Word, запустить, создать и сохранить новый документ с использованием операционной системы Windows 7.
Не стоит бояться, что что-то может не получиться или пойти не так. Эта программа создавалась для пользователей, и она продумана до мелочей, чтобы вам было максимально удобно использовать ее. И конечно же в каждом деле главное тренировка, не бойтесь делать ошибок. Если вы случайно нажали не туда, в левом верхнем углу всегда есть изогнутая стрелка, которая позволяет отменить последнее действие. Сделать это можно также используя сочетание клавиш Ctrl и Z.
Как работать в Word для чайников
Последний совет перед началом подробных инструкций по использованию текстового редактора от Windows — не забывайте сохранять файл. Это особенно важно при работе с объемными текстами или серьезной документацией. Бывает всякое: могут отключить электричество, ноутбук может разрядиться и выключиться, да и от поломок никто не застрахован. Терять важные файлы и потом тратить часы на их восстановление — не самое приятное занятие. Все, что вам нужно — время от времени нажимать на дискету в левом верхнем углу.
Содержание
- Как создать документ
- Навигация по программе
- Как выбрать (выделить) текст
- Меняем размер и шрифт
- Выравнивание текста
- Как выделить текст жирным шрифтом, курсивом или подчеркиванием
- Копируем и вставляем
- Как создать нумерованный или маркированный список
- Вставляем таблицу
- Видео — Word для начинающих
Как создать документ
Программу можно найти в меню «Пуск» в разделе «Microsoft Office». Следуйте этим пошаговым инструкциям, чтобы запустить документ в Microsoft Word.
- Шаг 1. На рабочем столе или в меню «Пуск» откройте Microsoft Word.
Открываем Microsoft Word
- Шаг 2. Microsoft Word откроется и предложит вам выбрать шаблон документа или пустой документ.
Выбираем шаблон
- Шаг 3. Если вы не хотите использовать какой-либо из отображаемых шаблонов, щелкните пустой документ.
Щелкаем пустой документ
- Шаг 4. Новый пустой документ откроется для вас, чтобы начать вводить текст.
Навигация по программе
- Шаг 1. Мигающий курсор (указатель мыши) в документе сообщает вам, где вы печатаете. Где бы ни находился мигающий курсор, буквы, которые вы вводите, будут вставлены в эту точку. Когда вы начинаете пустой документ, мигающий курсор будет в начале вашего документа, это значит, что он готов для начала ввода.
Мигающий курсор
- Шаг 2. По мере ввода курсор также перемещается с каждой буквой. Это показывает вам, где находится фокус для ввода.
Где находится фокус для ввода
- Шаг 3. Переместите указатель мышью туда, где вы хотите изменить или добавить текст. Щелкните мышью. Мигающий курсор будет перемещен в то место, где вы нажали, для редактирования или вставки текста.
- Шаг 4. Перемещаться по документу можно с помощью стрелок. Нажатие этих клавиш со стрелками перемещает мигающий курсор вверх, вниз по строкам текста, и направо/налево по одному символу.
Перемещаться по документу можно с помощью стрелок
Как выбрать (выделить) текст
Выбор или выделение текста позволяет вам изменять выделенный фрагмент с точки зрения стиля, шрифта и/или цвета и даже заменять слова, если это необходимо. Следуйте этим пошаговым инструкциям, чтобы выбрать текст в документе.
Шаг 1. Для выбора текста используется мышь. При перемещении указатель будет меняться.
Шаг 2. Переместите указатель на начало необходимого фрагмента. Нажмите и удерживайте левую кнопку мыши. Выполняя это, переместите указатель туда, где необходимо остановить выбор. При перемещении мыши текст будет выделяться. Когда вы закончите свой выбор, отпустите левую кнопку мыши.
Выделение текста с помощью мыши
Выбранный текст теперь может быть отформатирован или изменен.
Скопировать текст можно с помощью клавиш Ctrl+C. Удалить текст — Backspace.
Backspace
Меняем размер и шрифт
Следующие действия могут помочь сделать ваш текст более интересным и привлекательным. Текст может быть изменен по-разному.
- Шаг 1. Для начала фрагмент текста нужно выделить, вы уже умеете это делать.
- Шаг 2. Чтобы поменять вид шрифта, щелкните на стрелку рядом со стилем шрифта в панели инструментов.
Меняем вид шрифта
- Шаг 3. Выберите стиль шрифта из раскрывающегося списка.
Выбираем стиль шрифта
- Шаг 4. Рядом с полем стиля шрифта находится поле, содержащее число и стрелку. Оно изменяет размер шрифта. Нажмите на стрелку. Выберите размер так же как и стиль из раскрывающегося списка опций. Итак, выбрав шрифт Bad Scrit и размер — 16, мы получим следующее.
Пример шрифта Bad Scrit и размера -16
Выравнивание текста
Иногда создаваемый документ может требовать разное расположение абзацев. По умолчанию текст выравнивается по левому краю. Однако текст может выравниваться и по правому краю и по центру.
Выравнивание текста по левому краю
На заметку! Выделить весь текст Ctrl + A.
- Шаг 1. Чтобы изменить макет вашего текста, выделите текст, любым удобным для вас способом.
- Шаг 2. Чтобы выровнять его по центру, щелкните значок «Выровнять по центру» на ленте форматирования в верхней части документа.
Выравнивание текста по центру
- Шаг 3. Чтобы выровнять выделенный текст по правому краю, щелкните следующий значок в этом ряду.
- Шаг 4. Чтобы «обосновать» текст так, чтобы он был выровнен как справа, так и слева, щелкните значок «Выравнивание по ширине».
Изменить выбранный текст можно, используя комбинацию сочетаний клавиш, что иногда бывает проще:
- По центру — выделите текст, нажмите клавишу Ctrl + E.
- По правому краю — Ctrl + R.
- По ширине — Ctrl + J.
- По левому краю — Ctrl + L.
Горячие клавиши word
Как выделить текст жирным шрифтом, курсивом или подчеркиванием
Возможность изменить стиль шрифта может сделать ваш документ более интересным. Различные стили текста, такие как полужирный или курсив, могут выделять его. Подчеркивание может быть полезно для заголовков.
- Шаг 1. Как обычно, выделите необходимый вам фрагмент текста.
- Шаг 2. Чтобы изменить выделенный шрифт на полужирный, нажмите «Ж» на панели форматирования.
Чтобы изменить выделенный шрифт на полужирный, нажмите «Ж»
- Шаг 3. Чтобы изменить выделенный шрифт на курсив, нажмите «К» в ленте форматирования.
- Шаг 4. Чтобы изменить выделенный текст так, чтобы он был подчеркнут, нажмите «Ч» на ленте форматирования.
Чтобы текст был подчеркнут, нажмите Ч
- Шаг 5. Также можно изменить выделенный текст, используя сочетания клавиш:
- полужирный — Ctrl + B;
- курсив — Ctrl + I;
- подчеркивание — Ctrl + U.
Копируем и вставляем
Говорить о важности этих двух функций не приходится. Они значительно экономят наше время, позволяют вставлять текст из сторонних источников, не перепечатывая его, как это было во времена печатных машинок.
- Шаг 1. Выделите нужный вам фрагмент.
- Шаг 2. Щелкните по значку копирования в левой части ленты форматирования. Текст тут же скопируется в буфер обмена вашего компьютера.
Кнопка копирования
- Шаг 3. Переместите курсор и нажмите «Вставить».
Сделать это можно и с помощью горячих клавиш. Все как и в прошлый раз: нажмите одновременно Ctrl и С, чтобы скопировать текст, и Ctrl и V, чтобы вставить.
Как создать нумерованный или маркированный список
Использование нумерованных или маркированных списков может помочь выделить элементы или показать важные шаги, иерархию или последовательность чего-либо.
- Шаг 1. Чтобы создать нумерованный список, щелкните значок нумерации.
Создаем нумерованный список
- Шаг 2. В тексте появится первый пункт.
Первый пункт
- Шаг 3. Начните вводить свой текст. По окончании ввода нажмите на кнопку «Ввод» на вашей клавиатуре. Появится второй пункт. И так далее.
Второй пункт
Чтобы остановить добавление новых элементов и вернуться к стандартному тексту, щелкните значок нумерации еще раз в верхней части документа.
Маркированный список создается по такому же принципу, единственное отличие заключается в 1 шаге. Вместо кнопки «Нумерация» нажмите на кнопку «Маркеры», она расположена правее.
Есть еще один способ создания списка. Сначала пользователем вводятся все пункты списка, каждый обязательно с новой строки. Когда все пункты набраны выделите их все и нажмите либо на нумерацию, либо на маркеры, в зависимости от того какой именно список вам нужен.
Создание нумерованного списка с помощью выделения
У вас получится тот же результат. Это разные способы и здесь нет правильного или неправильного, главное, что цель достигнута. Используйте удобный вам способ.
Пример нумерованного списка
Вставляем таблицу
Таблицы помогают структурировать информацию, подавать ее в более презентабельном виде. Без этого навыка не обойтись.
- Шаг 1. В верхней панели инструментов перейдите на вкладку «Вставка».
- Шаг 2. Нажмите на значок таблицы. Перед вами откроется окно, в котором нужно выбрать количество ячеек. Сделать это можно и вписав цифры вручную. Для этого на появившейся панели нажмите на область «Нарисовать таблицу».
Вставляем таблицу
Вам останется лишь заполнить поля. Если вам вдруг понадобятся дополнительные строки или колонки, вам не придется переделывать ее целиком. Щелкните левой кнопкой мыши в области таблицы. В появившемся меню нажмите «Вставить» и выберите подходящий вариант.
Добавление необходимых столбцов в таблицу
Эти основные знания должны сформировать у вас основные принципы работы с текстом. Выделим основные:
- Текст вводится туда, где находится мигающий курсор и никуда больше.
- Чтобы изменить символ, слово, строку, абзац или весь текст, его в первую очередь нужно выделить. Необходимо, чтобы компьютер понимал над чем именно он должен производить действия.
- Выделив текст с ним можно делать все что угодно. Вы можете потренироваться, выделить фрагмент и поочередно нажимать на кнопки, которые расположены на вкладке «Главная». Вы заметите, какие функции могут использоваться совместно, а какие являются взаимоисключающими.
- Не забывайте сохранять изменения, так вы обезопасите себя.
- Используйте те способы решения стоящей перед вами задачи, которые удобны именно вам.
Видео — Word для начинающих
Рекомендуем похожие статьи
Содержание
- Набор шаблонов для быстрого оформления документа
- Рабочая область
- Настройка шрифта
- Инструменты форматирования абзаца
- Готовые стили для подзаголовков
- Вставка объектов в текст
- Выбор дизайна и темы документа
- Настройка макета
- Добавление ссылок с дополнительными сведениями
- Массовая рассылка документа
- Настраиваемая панель быстрого доступа
- Автоматическое сохранение файла
- Навигация по документу
- Запись макросов
- Достоинства
- Недостатки
- Скачать пробную версию Microsoft Word
- Вопросы и ответы
Microsoft Word – самый популярный текстовый редактор, и практический каждый пользователь если не работал в нем, то точно слышал об этой программе. Основной функционал и возможности мы подробно разберем в данной статье.
Набор шаблонов для быстрого оформления документа
Стартовая страница сделана удобно. Слева находится создание нового проекта, а также открытие документов, которые редактировались недавно. Справа расположен список заготовленных шаблонов. С их помощью пользователь может быстро подобрать подходящий тип документа и полностью подстроить его под свои нужды. Здесь находятся: резюме, грамоты, открытки, приглашения и многое другое.
Рабочая область
Текст набирается на белом листе, который занимает почти все место в главном окне. Снизу можно изменить масштаб листа или его ориентацию. Большинство инструментов находится сверху в отведенных вкладках, что помогает быстрее найти нужную функцию, поскольку все они рассортированы.
Настройка шрифта
Пользователь может набирать текст любым шрифтом, установленным на компьютере. Кроме этого есть переключатели, задающие верхний либо нижний регистр, таким же образом меняются и числа под буквами, что обычно требуется для математических формул, специфических названий. Доступно изменение цвета и выбор стиля, например, полужирный, курсив или подчеркнутый.
Переход к дополнительным настройкам шрифта осуществляется через этот же раздел, нажатием на стрелку справа от «Шрифт». Открывается новое окно, в котором выбирается межзнаковый интервал, смещение, масштаб и настраиваются OpenType знаки.
Инструменты форматирования абзаца
Разным типам документов необходимо различное построение абзацев. Можно выбрать один вариант расположения текста, а в дальнейшем программа автоматически будет применять эти настройки. Здесь также доступно создание таблиц, маркеров и нумераций. Чтобы осуществить сложные действия с разметкой, воспользуйтесь функцией «Отобразить все знаки».
Готовые стили для подзаголовков
Выделения, заголовки и прочие стили выбираются в отведенном для этого меню. Там присутствует несколько вариантов каждого типа, что поможет при формировании вида документа, а также доступно создание вручную, через специальное окно.
Вставка объектов в текст
Перейдем в другую вкладку, где находится вставка различных элементов в документ, изображений, фигур, видео или таблиц. Обратите внимание, если есть подключение к интернету, то можно загрузить оттуда картинку и вставить на лист, это же касается и видеозаписей.
Стоит обратить внимание на примечания. Выделите определенный участок текста, зажав левую кнопку мыши, и нажмите на «Вставить примечание». Такая функция будет полезной для выделения какой-либо информации либо объяснения строки — это пригодится, если документ будет передан другому пользователю.
Выбор дизайна и темы документа
Более обширная настройка стилей, цветов и шрифтов находится здесь. Кроме этого можно добавить эффекты, настроить цвет страницы и границы. Обратите внимание на встроенные темы — они помогут сразу оформить документ в одном из предложенных вариантов.
Настройка макета
Воспользуйтесь этой вкладкой, дабы обозначить границы, разрыв страниц или интервал. Просто настройте один раз, и данные параметры будут применяться ко всем листам в проекте. Чтобы получить больше возможностей редактирования, нужно раскрыть определенный элемент, после чего появится новое окно со всеми пунктами.
Добавление ссылок с дополнительными сведениями
Отсюда осуществляется добавление оглавлений, сносок, списка литературы, названий и предметных указателей. Благодаря данным функциям оформление рефератов и других подобных документов происходит быстрее.
Массовая рассылка документа
Word позволяет создать одну копию файла и рассылать ее множеству пользователей. Специально под это выведена отдельная вкладка. Вы самостоятельно указываете получателей, используя существующий список, или выбираете из контактов Outlook.
Настраиваемая панель быстрого доступа
Если вы часто используете определенные функции, то логично будет вывести их на эту панель, чтобы они всегда были на виду. В настройках таких команд несколько десятков, нужно просто выбрать необходимые и добавить.
Все активированные команды отображаются сверху в главном окне, что позволяет моментально воспользоваться одной из них. Кроме этого не стоит забывать, что есть еще и различные сочетания клавиш, они отобразятся, если навести на определенный элемент курсор.
Автоматическое сохранение файла
Иногда неожиданно выключается электричество или зависает компьютер. В таком случае вы можете утратить несохраненный набранный текст. Чтобы такого не произошло, воспользуйтесь специальной функцией, благодаря которой документ будет автоматически сохраняться каждый промежуток времени. Пользователь сам настраивает этот период и выбирает место сохранения.
Навигация по документу
Воспользуйтесь данным инструментом для поиска в документе. Здесь отображаются заголовки и страницы, а строка сверху позволяет найти любой фрагмент, это также поможет, если необходимо отыскать рисунок или видео.
Запись макросов
Чтобы не выполнять один и тот же процесс несколько раз, можно настроить макрос. Данная функция помогает объединить несколько действий в одно, а затем запускать его с помощью горячих клавиш либо кнопки на панели быстрого доступа. Сохранение макроса для всех документов осуществляется через организатор.
Достоинства
- Программа полностью на русском языке;
- Поддерживает множество языков ввода;
- Простой и удобный интерфейс;
- В наличии десятки полезных функций и инструментов.
Недостатки
- Программа распространяется платно.
Давайте подведем итоги по Microsoft Word – отличный текстовый редактор, который установлен на компьютере у миллионов пользователей по всему миру, а это говорит о его удобности и качестве. Даже начинающий пользователь легко и быстро освоит данную программу.
Загрузить последнюю версию программы с официального сайта
Похожие программы и статьи:
Microsoft Word
Рейтинг:
3.69 из 5
(32 голосов)
Система: Windows 7, 8, 8.1, 10, XP, Vista
Категория: Текстовые редакторы для Windows
Размер: 5400 MB
Язык: Русский
Версия: 2016
Microsoft Word — популярный во всем мире текстовый редактор. Оснащен всеми необходимыми инструментами и функциями для комфортной работы. Используется миллионами пользователей ежедневно.
 |
|
 Microsoft Word 2010 |
|
| Тип |
Текстовый процессор |
|---|---|
| Разработчик |
Microsoft |
| Операционная система |
Microsoft Windows |
| Последняя версия |
14.0.6112.5000 (27 июня 2011 года) |
| Лицензия |
Проприетарное |
| Сайт |
Домашняя страница Microsoft Office Word |
 Microsoft Word 2008 в Mac OS X 10.5 |
|
| Тип |
Текстовый процессор |
|---|---|
| Разработчик |
Майкрософт |
| Операционная система |
Mac OS X |
| Последняя версия |
14.1.0 Build 110310 (2011 SP1) (12 апреля 2011 года) |
| Лицензия |
Проприетарное программное обеспечение |
| Сайт |
Microsoft Word 2011 for Mac |
Microsoft Word (часто — MS Word, WinWord или просто Word) — текстовый процессор, предназначенный для создания, просмотра и редактирования текстовых документов, с локальным применением простейших форм таблично-матричных алгоритмов. Выпускается корпорацией Microsoft в составе пакета Microsoft Office. Первая версия была написана Ричардом Броди (Richard Brodie) для IBM PC, использующих DOS, в 1983 году. Позднее выпускались версии для Apple Macintosh (1984), SCO UNIX и Microsoft Windows (1989). Текущей версией является Microsoft Office Word 2010 для Windows и Microsoft Office Word 2011 для Mac.
Содержание
- 1 Начало
- 2 1990—1995 годы
- 3 Настоящее время
- 4 История версий
- 5 Парольная защита документов MS Word
- 6 Критика
- 7 Недокументированные возможности и курьёзы
- 7.1 Функция rand()
- 7.2 Функция lorem()
- 7.3 Курьёзные ошибки в модуле проверки русской орфографии версии 2003 года
- 8 Примечания
- 9 Литература
- 10 Ссылки
Начало
Microsoft Word многим обязан Bravo — текстовому процессору с оригинальным графическим интерфейсом, разработанному в исследовательском центре «Xerox PARC». Создатель Bravo Чарльз Симони (Charles Simonyi) покинул PARC в 1981 году. Тем же летом Симони переманил Броди, с которым вместе работал над Bravo.
Первый выпуск Word для MS-DOS состоялся в конце 1983 года. Он был плохо принят рынком, продажи снижало наличие конкурирующего продукта — WordPerfect.
Однако версия для «макинтоша», выпущенная в 1985 году, получила широкое распространение. Через два года «Word 3.01 для Macintosh» усилил позиции (версия 3.0 изобиловала ошибками и быстро была заменена). Как и прочее программное обеспечение для «макинтоша», Word был полностью WYSIWYG-редактором (принцип «What You See Is What You Get» — «получаю то, что вижу»).
Хотя MS-DOS и являлась текстовой операционной системой, лишённой графической оболочки, Word для DOS был первым текстовым процессором для IBM PC, который был способен отображать разметку текста, например, полужирный или курсивный текст в процессе редактирования. Однако он всё же не являлся в полном смысле WYSIWYG-редактором. Другие же текстовые процессоры, такие как WordStar и WordPerfect, использовали простой текстовый экран с кодами разметки, иногда текст был цветным.
Однако, поскольку в большинстве программного обеспечения под DOS применялись собственные труднозапоминаемые комбинации «горячих клавиш» для каждой команды (например, в Word’е для DOS сохранение файла выполнялось по комбинации ESC-T-S) и большинство секретарей умели пользоваться только WordPerfect, компании-пользователи WordPerfect весьма неохотно переходили на конкурирующие с ним продукты, имеющие сравнительно небольшие преимущества.
1990—1995 годы
Первая версия Word для Windows, выпущенная в 1989 году, продавалась по цене 500 долларов США. Она демонстрировала выбранный компанией «Майкрософт» путь развития: как и сама Windows, она многое взяла от Macintosh и использовала стандартные клавиатурные сокращения (например, CTRL-S для сохранения файла). После выпуска в следующем году Windows 3.0 продажи поползли вверх (Word 1.0 гораздо лучше работал с Windows 3.0, чем с более старыми версиями Windows x386 и Windows x286), главный конкурент — WordPerfect — не смог выпустить рабочую версию под Windows, что оказалось для него смертельной ошибкой. Версия 2.0 утвердила WinWord на позиции лидера рынка.
У Word для Macintosh никогда не было серьёзных конкурентов, даже несмотря на наличие программ вроде Nisus, предоставлявшей возможность выделения нескольких несвязных кусков текста (появившуюся только в Word 2002 из Office XP), и несмотря на мнение многих пользователей об отсутствии кардинальных различий между версиями 3.01, выпущенной в 1987 году, и 5.0, выпущенной в 1991-м. Однако версия 6.0 для Macintosh, вышедшая в 1994 году, была многими воспринята довольно скептически. Это была первая версия без значительных отличий в коде ядра между версиями под Windows и под Mac. Версия под Windows, следовавшая за 2.0, была пронумерована как 6.0 для координации названия версий под разные платформы.
Последовавшие версии добавляли возможности, выходящие за рамки простого текстового процессора. Инструменты рисования позволяли выполнять примитивные операции вёрстки, такие как добавление графики в документ, хотя, естественно, специализированные программы для вёрстки лучше справляются с этими задачами. Внедрение объектов, сравнение версий документа, мультиязычная поддержка и многие другие возможности были добавлены за последовавшие несколько лет.
Настоящее время
Microsoft Word является наиболее популярным из используемых в данный момент текстовых процессоров, что сделало его бинарный формат документа стандартом де-факто, и многие конкурирующие программы имеют поддержку совместимости с данным форматом. Расширение «.doc» на платформе IBM PC стало синонимом двоичного формата Word 97—2000. Фильтры экспорта и импорта в данный формат присутствуют в большинстве текстовых процессоров. Формат документа разных версий Word меняется, различия бывают довольно тонкими. Форматирование, нормально выглядящее в последней версии, может не отображаться в старых версиях программы, однако есть ограниченная возможность сохранения документа с потерей части форматирования для открытия в старых версиях продукта. Последняя версия MS Word 2007 «использует по умолчанию» формат, основанный на XML, — Microsoft Office Open XML. Спецификации форматов файлов Word 97-2007 были опубликованы Microsoft в 2008 году.[1][2] Ранее большая часть информации, нужной для работы с данным форматом, добывалась посредством обратного инжиниринга, поскольку основная её часть отсутствовала в открытом доступе или была доступна лишь ограниченному числу партнёров и контролирующих организаций.
Как и прочие приложения из Microsoft Office, Word может расширять свои возможности посредством использования встроенного макроязыка (сначала использовался WordBasic, с версии Word 97 применяется VBA — Visual Basic для приложений). Однако это предоставляет широкие возможности для написания встраиваемых в документы вирусов (так называемые «макровирусы»). Наиболее ярким примером была эпидемия червя Melissa. В связи с этим, многие считают разумной рекомендацию всегда выставлять наивысший уровень настроек безопасности при использовании Word (Меню: «Tools>Macro>Security», «Сервис>Макрос>Безопасность…» в локализованных русских версиях). Также нелишним будет использовать антивирусное программное обеспечение. Первым вирусом, заражавшим документы Microsoft Word, был DMV, созданный в декабре 1994 года Дж. Мак-Намарой для демонстрации возможности создания макровирусов. Первым же вирусом, попавшим в «дикую природу» и вызвавшим первую в мире эпидемию макровирусов (это произошло в июле-августе 1995 года), был Concept.
12 августа 2009 года суд штата Техас запретил продажу программы Word на территории США, в связи с тем, что Microsoft незаконно использует метод чтения XML-файлов, патент на который принадлежит канадской компании i4i[3]
История версий
Версии для MS-DOS:
- 1983, ноябрь Word 1
- 1985 Word 2
- 1986 Word 3
- 1987 Word 4, также известный как Microsoft Word 4.0 для PC
- 1989 Word 5
- 1991 Word 5.5
Версии для Apple Macintosh:
- 1985, январь Word 1 для Macintosh
- 1987 Word 3
- 1989 Word 4
- 1991 Word 5le
- 1993 Word 6
- 1998 Word 98
- 2000 Word 2001, последняя из версий, совместимых с Mac OS 9
- 2001 Word v.X, первая версия исключительно для Mac OS X
- 2004 Word 2004
- 2008 Word 2008
- 2011 Word 2011
Версии для Microsoft Windows:
- 1989, ноябрь Word для Windows
- 1991 Word 2 для Windows
- 1993 Word 6 для Windows (номер «6» был введён для продолжения линейки номеров DOS-версий, единой нумерации с Mac-версиями и с WordPerfect, лидером рынка среди текстовых процессоров на тот момент)
- 1995 Word 95 (Word 7)
- 1997 Word 97 (Word
- 1999 Word 2000 (Word 9)
- 2001 Word 2002 (Word 10)
- 2001 Word XP, см. выше
- 2003 Word 2003 (также известный как Word 11, однако официально именуемый Microsoft Office Word 2003)
- 2007 Word 2007 (революционная смена интерфейса, поддержка формата OOXML — *.docx)
- 2010 Word 2010
Версии для SCO UNIX:
- Microsoft Word для UNIX Systems, Release 5.1
Парольная защита документов MS Word
На документ Microsoft Word могут быть установлены 3 типа паролей:
- Пароль для открытия документа[4]
- Пароль для изменения документа[5]
- Пароль на внесение примечаний и исправлений (для версий 2003 и ниже). В новых версиях MS Word 20072010 этот тип пароля называется «Пароль для Ограничения форматирования и редактирования»[6]
Вне зависимости от версий MS Word в которой был создан документ, «пароль разрешения записи» и «пароль на внесение примечаний и исправлений» можно удалить из документа мгновенно[7]. Эти типы паролей служат не столь для защиты документа, как для обеспечения коллективной работы над документом. А основную защиту документа от несанкционированного доступа обеспечивает «пароль для открытия документа».
В документах ранних версиях MS Word (до MS Office 2003 включительно) пароль для открытия файла может быть без проблем взломан.
В последних версия MS Office 2007 2010 комания Microsoft использует стойкий алгоритм шифрования AES с 128-битным ключом. Формирование ключа происходит путем 50000 100000 кратного применения SHA-1 хэш функции, что делает перебор паролей крайне медленным, и при использовании стойкого пароля шансы его подобрать близки к нулю[8]
Критика
Чаще всего Microsoft Word подвергается критике за низкую безопасность, закрытый исходный код, отсутствие полноценной кроссплатформенности[9]. Ранее Word критиковали также за закрытый формат файлов (открытая документация на бинарные форматы появилась только в начале 2008 года). Это побудило отдельные организации перейти к использованию других текстовых процессоров, таких как OpenOffice Writer, входящего в офисный пакет OpenOffice.org.
Недокументированные возможности и курьёзы
Следующие функции вводятся в любом месте документа с начала строки. Замена их на определённый текст осуществляется при нажатии клавиши Enter.
Функция rand()
=rand(x,y)
В редакторе версии младше 2007 строка с командой будет заменена матрицей из панграмм:
Съешь ещё этих мягких французских булок, да выпей чаю.
Параметр x задаёт количество столбцов матрицы, y — количество строк. Параметры можно не указывать.
В редакторе Word 2007 строка с данной функцией будет заменена на отрывок из текста справки, параметр x задаёт количество абзацев, y — количество предложений в каждом абзаце. Функция =rand.old(x, y) работает как =rand(x, y) в более ранних версиях редактора.
Функция lorem()
=lorem()
В редакторе Word 2007 строка с данной функцией будет заменена на отрывок из текста Lorem ipsum.
Курьёзные ошибки в модуле проверки русской орфографии версии 2003 года
- Набор фразы Правоспособность-способность иметь права и нести гражданские обязанности вызывает (иногда после нажатия Enter), если включена автоматическая проверка орфографии, незамедлительное закрытие приложения без сохранения изменений. Данную ошибку эксплуатирует троян «Trojan.WordCrash» (по классификации антивирусной лаборатории Dr.Web), который добавляет данную фразу во все документы с расширением *.doc и *.rtf.
- При наборе в MS Word 97—2010 фразы «Хочу избежать службу в армии» модуль проверки грамматики в качестве одного из вариантов исправлений предлагает текст «Ошибка в управлении. Глагол „избежать“ требует дополнения в родительном падеже. Например: „Никому не удалось избежать службы в армии“.» Проверка грамматики реагирует на словосочетание «избежать что-либо» (при правильном «избежать чего-либо»).
- При проверке орфографии буквы Ё и Е не различаются, вследствие чего словосочетание «Бёлый Снёг» Word считает верным.
- При наборе в MS Word 95-97 фразы «мультиканальный модуль», проверка орфографии выдает ошибку (считает, что пропущен пробел) и в качестве правильного варианта исправлений предлагает текст Мультик анальный. Аналогичные исправления были предложены для других слов: шестик|анальный, ель|цинизма, зад|обреет, заруб|ежом, кол|басит, культ|урологии, отмель|кала, стриптиз|ершей…
Почти все недоработки были исправлены в Microsoft Word 2003 SP3 и последующих версиях продукта.
Примечания
- ↑ Microsoft Office Binary (doc, xls, ppt) File Formats. Microsoft (February 15 2008). Архивировано из первоисточника 24 августа 2011. Проверено 21 февраля 2008.
- ↑ Standard ECMA-376 — Office Open XML File Formats. Ecma International (December 2006). Архивировано из первоисточника 24 августа 2011. Проверено 21 февраля 2008.
- ↑ Суд запретил Microsoft продавать Word в США
- ↑ Шифрование документа и задание пароля для его открытия. Справка Microsoft Office
- ↑ Задание пароля для изменения документа. Справка Microsoft Office
- ↑ Ограничение на внесение изменений в файлы Word и Excel. Справка Microsoft Office
- ↑ Парольная защита документов Microsoft Office. Андрей Малышев. Журнал «Компьютер пресс»
- ↑ Office 2007: новый формат и новая защита. Андрей Малышев. Журнал «Компьютер пресс»
- ↑ Почему форматы Microsoft Office такие сложные? (Джоэл Спольски)
Литература
- Tsang, Cheryl. Microsoft: First Generation. New York: John Wiley & Sons, Inc. ISBN 0-471-33206-2.
- Дэн Гукин Word 2010 для чайников = Word 2010 for Dummies. — М.: «Диалектика», 2010. — С. 352. — ISBN 978-5-8459-1681-5
Ссылки
- Спецификация формата Microsoft Word 97-2007 (англ.)
- MS-Word НЕ является форматом обмена документов (англ.)
| |
||
|---|---|---|
| Клиентские приложения | Accounting · Access · Lync · Entourage · Excel · Groove · InfoPath · InterConnect · MapPoint · OneNote · Outlook · PowerPoint · Project · Publisher · SharePoint Designer · Visio · Word |  |
| Серверные приложения | Communications · Forms · Groove · PerformancePoint · Project · Project Portfolio · SharePoint | |
| Устаревшие приложения | Binder · Data Analyzer · FrontPage · Liquid Motion · Mail · Office Assistants · PhotoDraw · Photo Editor · Schedule+ · Vizact · Web Components | |
| Онлайн-службы | Office Online · Office 365 · Office Live Meeting · SkyDrive | |
| Версии для Windows | 3.0 · 4.0 · 4.3 · 95 · 97 · 2000 · XP · 2003 · 2007 · 2010 · 2013 | |
| Версии для Mac OS | 98 · 2001 · X · 2004 · 2008 · 2011 | |
| Технологии | Object Linking and Embedding · Office Open XML · Visual Studio Tools for Office · Visual Basic for Applications | |
| Категория |
| |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Свободные | AbiWord · Bean · Calligra Words · GNU TeXmacs · KWord · LibreOffice · LyX · NeoOffice · OpenOffice.org Writer · Ted | ||||||
| Freeware |
Adobe Buzzword · Atlantis Nova · Google Docs · IBM Lotus Symphony · Jarte (standard) · TextMaker (2008) |
||||||
| Retail |
|
||||||
| Категория • Сравнение • Список |

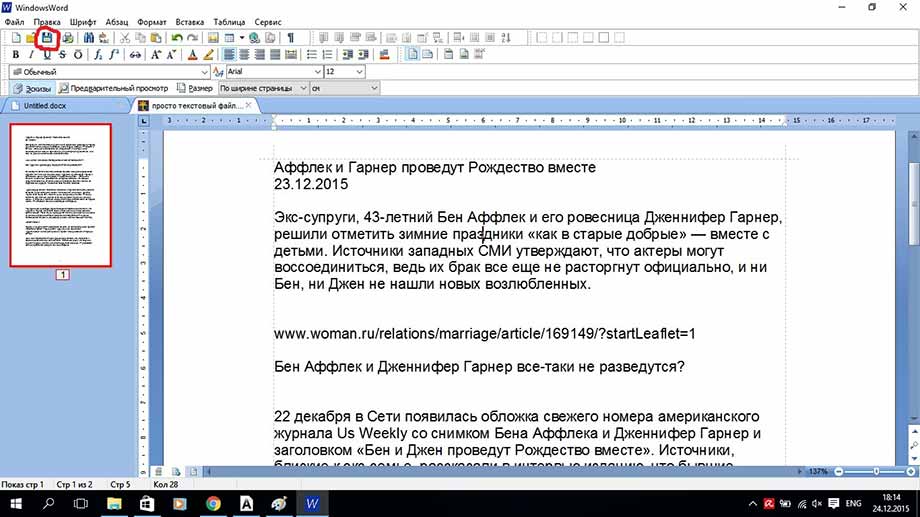
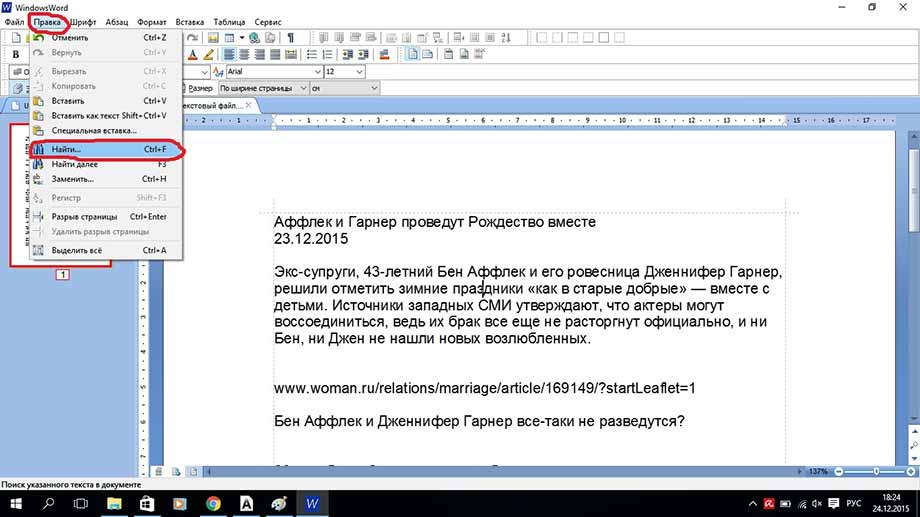
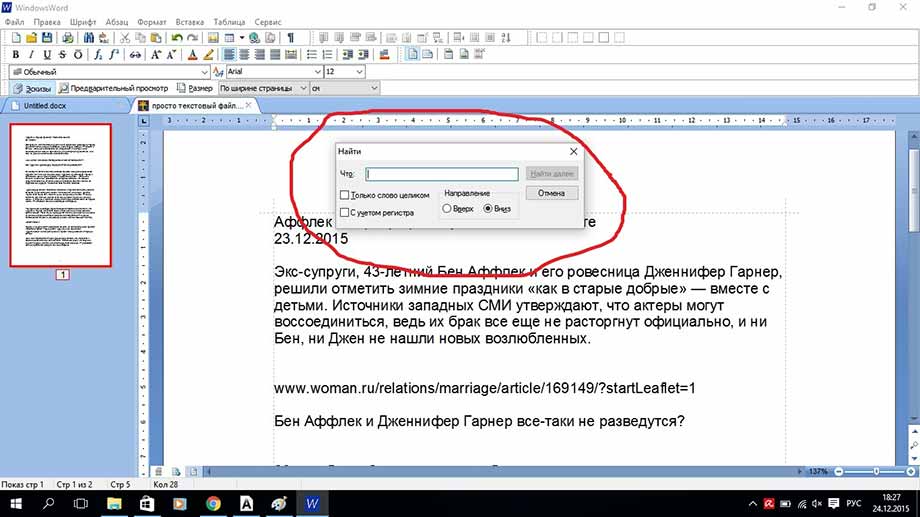
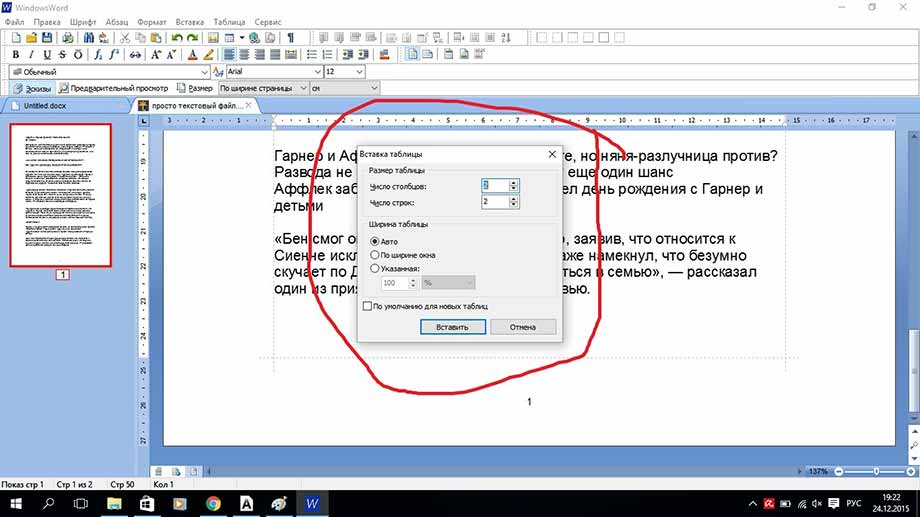


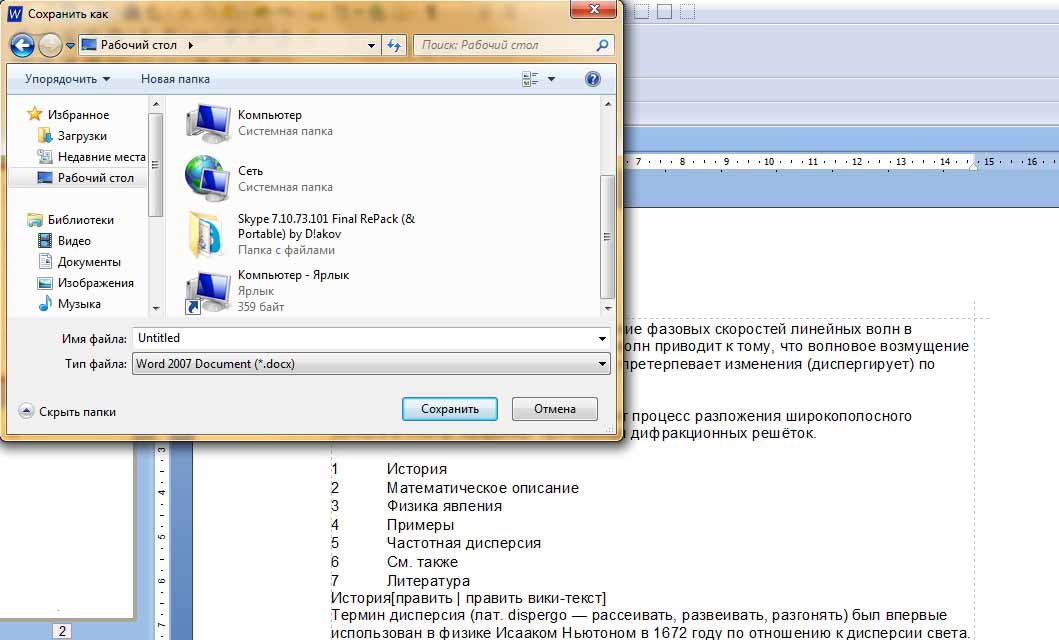





 .
.